Page 1
QuickSpecs
Overview
System Logic
System Logic
System LogicSystem Logic
Cabinet 2
Cabinet 2
Cabinet 2Cabinet 2
System Logic
System Logic
System LogicSystem Logic
Cabinet 2
Cabinet 2
Cabinet 2Cabinet 2
System Logic
System Logic
System LogicSystem Logic
Cabinet 1
Cabinet 1
Cabinet 1Cabinet 1
Front View
Front View
Front ViewFront View
System Logic
System Logic
System LogicSystem Logic
Cabinet 1
Cabinet 1
Cabinet 1Cabinet 1
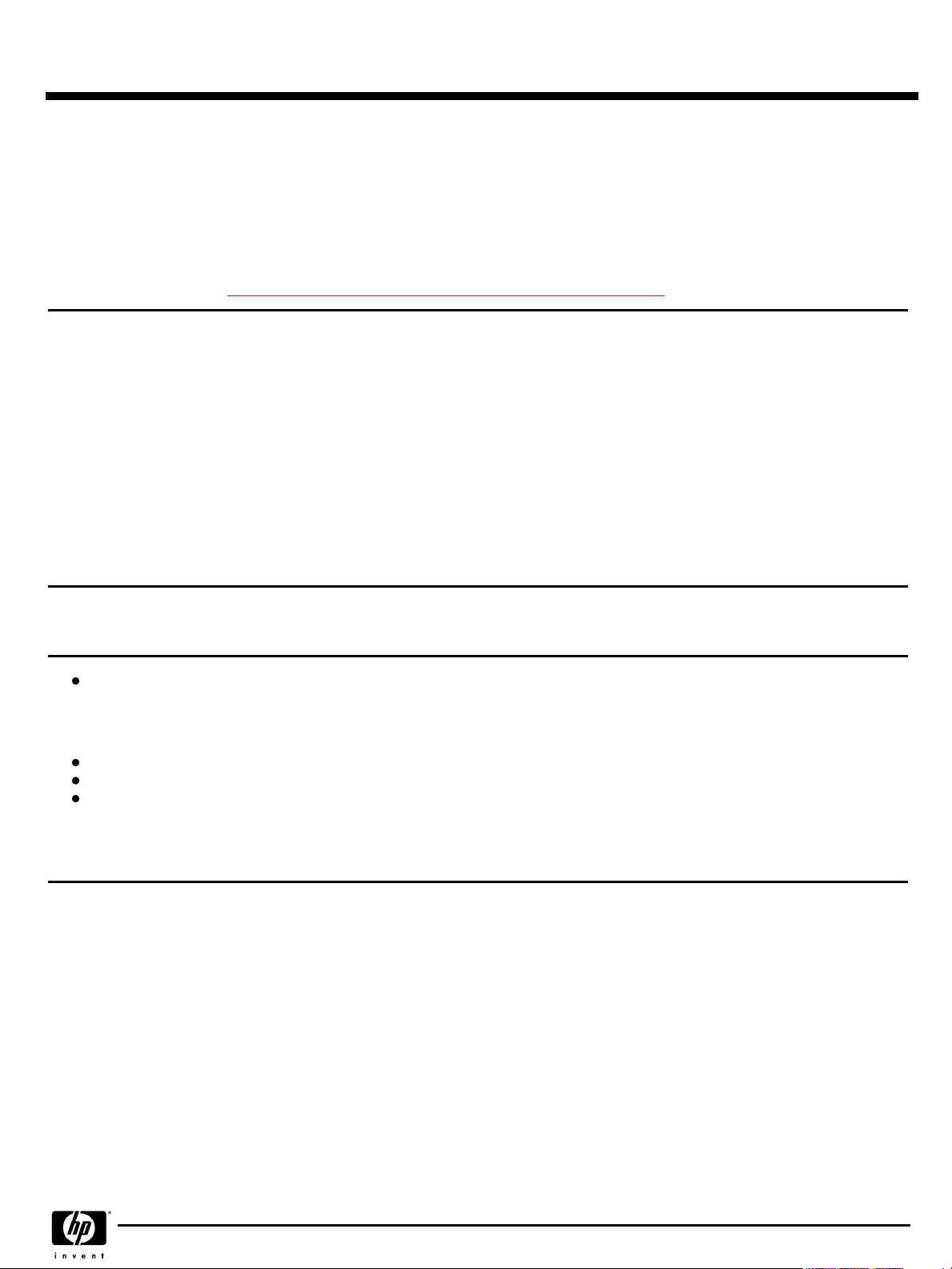
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
System Power
System Power
System PowerSystem Power
Cabinet
Cabinet
CabinetCabinet
System Power
System Power
System PowerSystem Power
Cabinet
Cabinet
CabinetCabinet
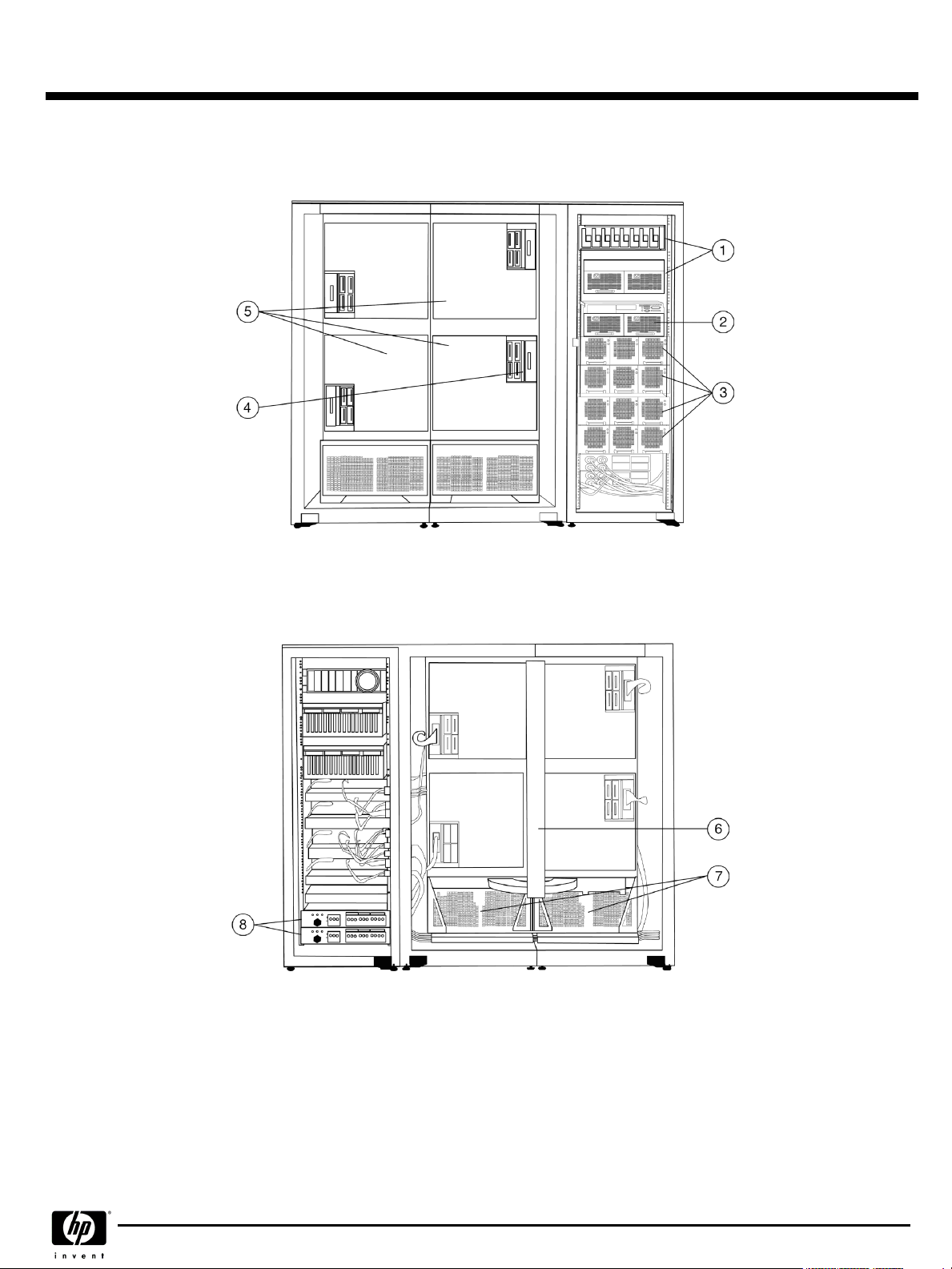
1.
Optional PCI or StorageWorks drawers
2.
Standard 14-slot PCI I/O Master drawer
3.
48-volt DC power shelves, 2 power supplies per shelf, plus optional lN+1
(Model 24 includes 3 shelves, Model 32 includes 4 shelves)
4.
Connections for PCI drawers
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Rear View
Rear View
Rear ViewRear View
5.
6.
7.
8.
System boxes each with 2 QBB's (Model 24 includes 3 system boxes, 6
QBB's, Model 32 includes 4 system boxes, 8 QBB's)
Global switch
Cooling blowers
Two AC input controllers
Page 1
Page 2

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Overview
At A Glance
At A Glance
At A GlanceAt A Glance
AlphaServer GS320 systems include:
One 1224-MHz CPU module; up to 32 1224-MHz Alpha 21264 processors are supported
Optional HP Capacity on Demand (CoD) SMP processors for non-disruptive performance growth
16-MB on-board cache per processor
Advanced crossbar switch with 7-GB memory bandwidth per building block; up to 57-GB memory bandwidth per system
Choice of memory: up to 256-GB memory supported
PCI I/O master drawer with 12 configurable PCI slots; up to 224 64-bit PCI slots supported
Up to 64 64-bit PCI buses with 12.8-GB aggregate I/O bandwidth
PCI 10/100 Mbit Ethernet adapter
18.2-GB SCSI disk drive
600-MB CD-ROM drive
Enhanced reliability with ECC-protected memory, processor cache, and system data paths
Security of RAID storage and online add and removal of CPUs
Optional redundant power supplies with N+1 power option
Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS factory installed software (FIS); optional high availability support with Tru64 UNIX and OpenVMS cluster solutions
Product warranty, one-year hardware, on-site next business day
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 2
Page 3

QuickSpecs
Standard Features
Processor
Processor
ProcessorProcessor
Cache Memory
Cache Memory
Cache MemoryCache Memory
Architecture
Architecture
ArchitectureArchitecture
CPUs, Memory, and I/O
CPUs, Memory, and I/O
CPUs, Memory, and I/OCPUs, Memory, and I/O
Slots
Slots
SlotsSlots
Up to 32 Alpha 21264 6/1224-MHz CPUs (one CPU per module)
64K I and D caches on-chip; 16-MB ECC on-board cache per CPU
AlphaServer GS320 utilizes two-level crossbar switch structure
Quad building blocks (QBBs) support up to four CPUs, four memory modules, and eight PCI buses on a 7-GB non-blocking
crossbar switch backplane
Up to eight QBBs are connected by a second level non-blocking switch with 14-GB of bandwidth
Base systems contain one CPU and one master PCI I/O drawer
Maximum CPUs supported
Maximum memory supported
Maximum PCI slots supported
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
System capacities shown are available with both Tru64 UNIX and OpenVMS operating systems.
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Model 24
Model 24 Model 32
Model 24Model 24
24 32
192 GB (24 modules) 256 GB (32 modules)
168 224
Model 24 and Model 32 base systems include 12 configurable PCI slots.
Model 32
Model 32Model 32
Network and I/O
Network and I/O
Network and I/ONetwork and I/O
Controllers
Controllers
ControllersControllers
Boot/Diagnostic Devices
Boot/Diagnostic Devices
Boot/Diagnostic DevicesBoot/Diagnostic Devices
Internal Disk Expansion
Internal Disk Expansion
Internal Disk ExpansionInternal Disk Expansion
Power Supplies
Power Supplies
Power SuppliesPower Supplies
Ethernet
Console ports
Boot/diagnostic devices included in master PCI shelf box
CD-ROM or DVD-ROM
Hard Drives
Total Drive Bays
3-phase power subsystem with power cords; optional redundant 48 VDC hot swap power supplies
PCI Dual 10/100 Mbit Fast Ethernet Adapter (DE602) included in master PCI shelf box;
additional Ethernet adapters available as options
One bi-directional parallel port with 25-pin D-subminiature connector
Two EIA-232 full duplex asynchronous modem control serial ports, 9-pin D-subminiature
connectors
One PS/2 compatible keyboard port; one PS/2 compatible mouse port
One 5.25-inch half height 600-MB CD-ROM drive or 16X DVD-ROM
One 18.2-GB 10,000 rpm SCSI disk drive
Up to 14 146-GB drives (2,044 GB) may be mounted in optional storage shelves in the
system power cabinet
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 3
Page 4

QuickSpecs
Standard Features
OS Support
OS Support
OS SupportOS Support
Service and Support
Service and Support
Service and SupportService and Support
Tru64 UNIX systems include pre-installed software, Base license, Unlimited User license, Server Extension license, Internet
Express, and Secure Web Server
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
http://www.hp.com/alphaserver/products/options.html
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
OpenVMS systems include pre-installed software, Base license and Enterprise Integration Server License Package Revision
V3.0A
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
http://www.hp.com/alphaserver/products/options.html
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Support for up to eight total instances of Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS, or a combination of both, in hardware partitions on a
single GS320 hardware platform (up to six instances supported on Model 24 systems, up to eight instances supported on
Model 32 systems)
Protected by HP Services including a one-year on-site hardware warranty training, consulting, network integration, software
support, comprehensive system maintenance and guaranteed uptime services are also available for customers requiring
higher levels of service and support.
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Tru64 UNIX refers to versions 4.0G, 5.1, 5.1A, or later. Refer to the "Supported Options List"–
– for any unique limitations based on OS version.
This Web site is available in English only.
OpenVMS refers to versions 7.2-1H1, 7.2-2, 7.3, or later. Refer to the "Supported Options List" –
– for any unique limitations based on OS version.
This Web site is available in English only.
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 4
Page 5
QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Systems
Important note before you begin
Important note before you begin
Important note before you beginImportant note before you begin
Systems may be configured with more than 16 CPUs per partition, only when used with Tru64 UNIX V5.1 or OpenVMS V7.2-1H1 with Update #5. System
components, such as master PCI drawers and numbers of PCI options supported must be consistent with this requirement.
Step 1 - Assess Application Requirements
Step 1 - Assess Application Requirements
Step 1 - Assess Application RequirementsStep 1 - Assess Application Requirements
Selection of system components must be made in the context of total application requirements. Although the configuration of system components
must be done in steps (for example, base packages, CPUs, memories, etc.), these steps cannot be done in isolation.
The order in which requirements are assessed is also important, since one requirement may impact others. Before proceeding, it would be useful to
assess the total application requirements in the following order:
What level of availability is required?
If no single points of failure are allowed, then the solution should be configured as a multi-system cluster.
If access to specific devices must be assured, consider redundant adapters - RAID, N+1 power, redundant PCI drawers, and redundant consoles.
If software redundancy is required, consider clusters and/or hardware partitioning. The choice of hardware partitioning will generate a need for
multiple master PCI drawers, multiple consoles, and I/O adapters.
If the "CPU On-Line Add and Remove" feature is required, refer to document EK-GSHPG-RM for configuration and operational requirements.
What level of hardware partitioning is required for optimal system management?
What overall capacities are required in terms of processor performance, memory capacity, and disk storage?
How should the system be configured to optimize performance?
In most cases, optimum performance is achieved if the system resources (CPUs, memory, and I/O adapters) are balanced across the quad building
blocks in the system.
Memory should be configured according to application guidelines listed in Step 4.
What are the near-term system expansion needs?
How will system cabinets be physically arranged? This will determine if expansion cabinets are required and what cable lengths are required.
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
application requirements.
System Ordering Requirements:
System Ordering Requirements:
System Ordering Requirements:System Ordering Requirements:
Certain system components or services are either required for normal operation or are recommended for best system performance and/or operation. This
document uses the following definitions to specify these options:
Most configuration steps require that these data be considered in whole or in part. Be sure to execute each step in the context of the total
Mandatory purchase
Mandatory purchase
Mandatory purchaseMandatory purchase
Required to function
Required to function
Required to functionRequired to function
available onsite.
Recommended
Recommended
RecommendedRecommended
: The system cannot function without this option or service - the option or service must be ordered with the system.
: This option or service is needed to support a working system - the option or service must be ordered with the system or be
: System performance or function will be enhanced if this option or service is ordered.
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 5
Page 6
QuickSpecs
Systems
Step 2 - Select base system
Step 2 - Select base system
Step 2 - Select base systemStep 2 - Select base system
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
AlphaServer GS320 systems require selection of the following items:
Mandatory Purchases:
Mandatory Purchases:
Mandatory Purchases:Mandatory Purchases:
Base system with operating system license (either OpenVMS or Tru64 UNIX), which includes one 1224-MHz CPU module
Minimum of one memory module
Required Options and Services:
Required Options and Services:
Required Options and Services:Required Options and Services:
Software media and documentation for first system onsite
Installation and/or startup services
System management console or device and software with equivalent functionality
Recommended Services:
Recommended Services:
Recommended Services:Recommended Services:
HP Care Pack Service Package
VIS Services
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
anticipated near-term system growth.
The base system should be selected in the context of the number of hardware partitions required, the total capacity required, and the
AlphaServer GS320 (1224-MHz) Base Systems
AlphaServer GS320 (1224-MHz) Base Systems
AlphaServer GS320 (1224-MHz) Base SystemsAlphaServer GS320 (1224-MHz) Base Systems
Model
Model
ModelModel
Model 24
Model 24
Model 24
Model 24
Model 32
Model 32
Model 32
Model 32
OS
OS
OSOS
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIX
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIX
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
System Boxes/
System Boxes/
System Boxes/System Boxes/
QBBs Included
QBBs Included
QBBs IncludedQBBs Included
3/6
3/6
3/6
3/6
4/8
4/8
4/8
4/8
Total CPUs
Total CPUs
Total CPUsTotal CPUs
Supported
Supported
SupportedSupported
24
24
24
24
32
32
32
32
Input Power
Input Power
Input PowerInput Power
120/208V
380-415V
120/208V
380-415V
120/208V
380-415V
120/208V
380-415V
Order Number
Order Number
Order NumberOrder Number
DA-320DG-AA
DA-320DG-AB
DY-320DG-AA
DY-320DG-AB
DA-320EG-AA
DA-320EG-AB
DY-320EG-AA
DY-320EG-AB
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 6
Page 7

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Systems
Step 3 - Additional SMP CPUs
Step 3 - Additional SMP CPUs
Step 3 - Additional SMP CPUsStep 3 - Additional SMP CPUs
AlphaServer GS320 base systems contain one CPU module. Additional SMP CPUs may be added, up to the limits shown in above table. SMP CPU
options include an operating system SMP license.
HP Capacity on Demand
HP Capacity on Demand
HP Capacity on DemandHP Capacity on Demand
(CoD) CPUs
GS160/320 SMP upgrade CPU, 6/1224-MHz with 16-MB on-board cache, Tru64 UNIX
GS160/320 SMP upgrade CPU, 6/1224-MHz with 16-MB on-board cache, OpenVMS
AlphaServer GS320 base systems can be configured with optional HP Capacity on Demand
(CoD) CPUs for non-disruptive future capacity expansion. The CPUs will be field installed as
part of the system installation. The total number of CPUs - base CPU, SMP CPUs, and CoD
CPUs - must adhere to the limits shown in the above table. Refer to the HP Capacity on
Demand Program described in the "Upgrades"section.
GS160/320 CoD SMP CPU, includes one 6/1224-MHz CPU module with 16-MB on-board cache,
Tru64 UNIX SMP license, and CoD program license
GS160/320 CoD SMP CPU, includes one 6/1224-MHz CPU module with 16-MB on-board cache,
OpenVMS SMP license, and CoD program license
3X-KN8AC-AD
3X-KN8AC-AE
3X-KN8CC-AD
3X-KN8CC-AE
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 7
Page 8

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Step 4 - Select Memory Options
Step 4 - Select Memory Options
Step 4 - Select Memory OptionsStep 4 - Select Memory Options
Memory options are engineered specifically for use with this series and include additional required components that are integral to the system
architecture.
Memory options consist of a series of base modules that contain one memory array. A second array (called
"upgrades" in the table) may be added to a base module in the factory or in the field.
Memory Configuration Guidelines
Memory Configuration Guidelines
Memory Configuration GuidelinesMemory Configuration Guidelines
Memory options should be selected in the context of the application's sensitivity to memory bandwidth and memory capacity, and the number of hardware
partitions. This will determine the number of memory base modules and upgrades needed. The total capacity required will determine the size of the arrays to
be chosen.
0.5-GB GS80/160/320 base memory module
0.5-GB GS80/160/320 memory DIMM upgrade
1-GB GS80/160/320 base memory module
1-GB GS80/160/320 memory DIMM upgrade
2-GB GS80/160/320 base memory module
2-GB GS80/160/320 memory DIMM upgrade
4-GB GS80/160/320 base memory module
4-GB GS80/160/320 memory DIMM upgrade
3X-MS8AA-AB
3X-MS8AA-AU
3X-MS8AA-BB
3X-MS8AA-BU
3X-MS8AA-CB
3X-MS8AA-CU
3X-MS8AA-DB
3X-MS8AA-DU
The configuration of memory may influence the performance of applications, and there are numerous ways to configure the choices of memory base modules
and upgrade DIMMs. The following general guidelines can lead to several configuration choices. Application-specific guidelines will help narrow down the
choices.
Configuring for capacity: The highest capacity is achieved when the 3X-MS8AA-DB/DU combination is used.
Configuring for performance: Interleaved operations reduce the average latency and increase the memory throughput over non-interleaved
operations. Each memory base module is capable of 4-way interleaving with one array (no upgrades added) or 8-way interleaving with two arrays
(base module plus one upgrade). A QBB configured with eight arrays (four base modules plus four array upgrades) provides 32-way interleaving and
has the maximum potential memory bandwidth. Refer to "Memory Applications Examples" below to determine which applications gain the most
benefit from this bandwidth.
Memory modules should be configured in powers of 2: that is, 0, 1, 2, or 4 base modules in a QBB. Upgrades should also be installed in powers of 2:
0, 1, 2, or 4 base modules in a QBB.
Although mixed-capacity memory modules may be configured, the highest bandwidth is achieved when a QBB is populated with eight identical arrays:
four base modules and four upgrades. The next-highest bandwidth would be four base modules (four arrays).
If it is not possible to match the capacities of all the arrays, the next best choice is to configure pairs of identical base modules, or base
module/upgrade combinations. For example, a configuration of two 2-GB base modules (3X-MS8AA-CB), each with a 1-GB upgrade (3X-MS8AABU), is a better choice than a configuration of three 2-GB modules (3X-MS8AA-CB).
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 8
Page 9
QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Memory Application Examples
Memory Application Examples
Memory Application ExamplesMemory Application Examples
Configuring memory is a compromise between cost, total memory capacity, and memory bandwidth requirements. The behavior of the application must be
used to define the most-desired configuration. Some applications are sensitive to memory capacity, some are sensitive to memory bandwidth, some are
sensitive to neither. If actual application measurements are not available, the following may be used as guidelines:
Large memory (VLM) applications, in which large amounts of memory can substantially reduce I/O, may be optimized for total memory capacity and
future capacity growth. In VLM applications, the right balance might be one memory base module, with upgrade, for every two CPUs. This would
result in one memory array per CPU.
Typical commercial applications, such as transaction processing (OLTP) and multi-user timesharing, usually operate efficiently from cache and may not
be materially affected by memory bandwidth. Memory configuration is a balance between memory bandwidth and future capacity growth. It is
advisable to match the number of arrays to the number of CPUs.
Data mining can benefit from additional memory bandwidth. It is best to match the number of memory base modules to the number of CPUs.
The most demanding high-performance technical applications (HPTC) achieve a performance level that is directly proportional to memory bandwidth.
In these cases, configure one memory base module, with upgrade, per CPU. This results in two memory arrays per CPU.
The following table represents how 8 GB could be configured in a 4-CPU QBB in each of the four referenced applications. The numbers under each
application represent how many of each memory option would be ordered.
Memory Configuration Examples
Memory Configuration Examples
Memory Configuration ExamplesMemory Configuration Examples
1-GB base module
1-GB upgrade
2-GB base module
2-GB upgrade
The following additional configuration options utilizing the 4-GB base module are available:
4-GB base module
4-GB upgrade
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Step 5 - Evaluate Configuration Requirements to Support Optional Partitioning
Step 5 - Evaluate Configuration Requirements to Support Optional Partitioning
Step 5 - Evaluate Configuration Requirements to Support Optional PartitioningStep 5 - Evaluate Configuration Requirements to Support Optional Partitioning
Configuration Requirements for Partitions
Configuration Requirements for Partitions
Configuration Requirements for PartitionsConfiguration Requirements for Partitions
Configuring partitions requires some attention to detail with respect to minimum requirements for option selection, population, and option placement.
Minimum Hardware Required per AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition
Minimum Hardware Required per AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition
Minimum Hardware Required per AlphaServer GS320 Hardware PartitionMinimum Hardware Required per AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition
N/R = Not recommended - For these applications, configure either four or eight like-sized memory options rather than one or two.
A single AlphaServer GS320 can be divided into logical hardware partitions, each running an instance of Tru64 UNIX or an instance of OpenVMS.
Each partition is allocated its own dedicated "shared-nothing" set of hardware resources: QBB(s), CPU module(s), memory module(s), and I/O.
Multiple-QBB hard partitions within a GS server do not provide complete hardware failure isolation across hard partitions. Single hard partitioned
QBBs within the server do provide hardware failure isolation.
Each hardware partition is viewed as a unique node, from a system point-of-view, with its own instance of Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS operating system
and application software, independent system console, and error log.
Hardware partitions are defined on QBB boundaries; each partition is an integer multiple of QBBs.
Up to six hardware partitions are supported on GS320 Model 24 systems; up to eight hardware partitions are supported on Model 32 systems
One system management console (3X-DS8BA-xx or 3X-DS8DA-xx) and one console hub (3X-DS8AA-AA) are recommended per system.
Supported option rules apply for maximum configurations of each AlphaServer GS320 system partition. Care must be exercised to ensure that any
planned reconfiguration of hardware partitions will not violate option support rules.
(3X-MS8AA-BB)
(3X-MS8AA-BU)
(3X-MS8AA-CB)
(3X-MS8AA-CU)
(3X-MS8AA-DB)
(3X-MS8AA-DU)
– Configuring a QBB with a total of 8 GB for specific applications
Application
Application
ApplicationApplication
VLM
- - -
- - 2 2 4
2 2
2 2
- -
OLTP, Timesharing
Data Mining
HPTC
4
4
-
- -
N/R N/R
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 9
Page 10

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Each hardware partition requires a minimum of one QBB, however, multiple QBBs are allowed within a single hardware partition. The first QBB in a hardware
partition must be configured with the minimum hardware listed below. This, and other QBBs in the partition, can be configured with additional hardware once
this minimum requirement is met.
One Alpha 21264 6/1224-MHz CPU module
One 3X-MS8AA-BB/CB/DB memory module (1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB)
One 3X-KFWHA-AA system I/O module and one 3X-DWWPA-AA master PCI drawer. Depending upon configuration, this may require the use of a
3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF expansion cabinet
AlphaServer GS320 systems are normally configured according to standard module placement rules, and are shipped with one copy of the operating
system installed at the factory (Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS). However, systems with hardware partitions offer hardware and software configuration
flexibility. Factory integration services (VIS) are recommended to enable custom module configuration and factory installation of multiple copies of
the operating system on hardware partitioned systems.
Optimizing System Resources
Optimizing System Resources
Optimizing System ResourcesOptimizing System Resources
The following configuration guidelines can be used to improve performance in systems or in each partition of a hardware-partitioned system.
Balance the resources in the system (or hardware partition) based upon the available backplane space and the proposed option populations:
Sparsely configured systems, those using half or less than half of their available capacity for CPUs, memory, and PCI drawers, should be configured
with the options concentrated in as few QBBs as possible. For example, a GS320 Model 32 with 16 CPUs, 16 memory modules, and four PCI
drawers would usually be configured in the first four QBBs. The first four QBBs would be "active" and the 5th through 8th QBBs would be available for
expansion.
Densely populated systems, those using more than half of their available capacity for CPUs, memory, and PCI drawers, should be configured with the
options spread out across all QBBs.
Configure active QBBs symmetrically, each with CPUs, memory, and PCI drawers.
Configure the I/O adapters so that each active QBB has direct access to the most frequently accessed data.
System Software Required for AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition Support
System Software Required for AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition Support
System Software Required for AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition SupportSystem Software Required for AlphaServer GS320 Hardware Partition Support
Software Licensing for Hardware Partitions
Software Licensing for Hardware Partitions
Software Licensing for Hardware PartitionsSoftware Licensing for Hardware Partitions
Base systems include operating system license (Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS) that licenses hardware partitions up to the physical limit of the base system
package: six hardware partitions for Model 24 systems, eight partitions for Model 32 systems.
User and capacity-based licensing is unaffected by hardware partitions. Examples:
If a product is licensed for 200 concurrent users, these users can be split among the partitions, but cannot exceed 200 total users.
If users have an enterprise capacity license for a product, that license can be loaded into the license databases on each of the hardware partitions.
Licensing Partitioned AlphaServer GS320 Systems for Both OpenVMS and Tru64 UNIX
Licensing Partitioned AlphaServer GS320 Systems for Both OpenVMS and Tru64 UNIX
Licensing Partitioned AlphaServer GS320 Systems for Both OpenVMS and Tru64 UNIXLicensing Partitioned AlphaServer GS320 Systems for Both OpenVMS and Tru64 UNIX
If the system requires both OpenVMS and Tru64 UNIX operating systems be licensed, one operating system license is included in the base system
and the second is added as a line item. The second operating system license upgrade, which includes the license for only one CPU, would be added
to the order using the following part numbers. Order appropriate media and documentation kits from Step 13.
Only those SMP processors intended for use with the second operating system must be similarly licensed. Use the following license-only part numbers
to add an SMP license for any CPUs intended for use with the second operating system:
The order of licensing is not important, but the following examples are similarly constructed for clarity. The configuration starts with a Tru64 UNIX base
system part number and the addition of OpenVMS licenses.
Example 1: 32-CPU GS320 system in which all processors are licensed for both OpenVMS and Tru64 UNIX:
Base system order would include: DA-320EE-Ax and 31 3X-KN8AB-AD SMP upgrade CPUs
Add one QB-63PAQ-AG OpenVMS software upgrade and 31 QL-MT1A9-6R OpenVMS Alpha SMP licenses
Example 2: 32-CPU GS320 system in which all processors are licensed for Tru64 UNIX and 16 processors are also licensed for OpenVMS:
Base system order would include: DA-320EE-Ax and 31 3X-KN8AB-AD SMP upgrade CPUs
Add one QB-63PAQ-AG OpenVMS software upgrade and 15 QL-MT1A9-6R OpenVMS Alpha SMP licenses
User and capacity-based licenses would be added for the second operating system environment as though it were a standalone system.
OpenVMS software upgrade for GS160/GS320
Tru64 UNIX software upgrade for GS160/GS320
OpenVMS Alpha SMP license for GS160/GS320
Tru64 UNIX Alpha SMP license for GS160/GS320
QB-63PAQ-AG
QB-595AN-AA
QL-MT1A9-6R
QL-MT4A9-6R
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 10
Page 11
QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Step 6 - Configure Packaging Options
Step 6 - Configure Packaging Options
Step 6 - Configure Packaging OptionsStep 6 - Configure Packaging Options
Step 6a - Redundant (N+1) Power Supplies
Step 6a - Redundant (N+1) Power Supplies
Step 6a - Redundant (N+1) Power SuppliesStep 6a - Redundant (N+1) Power Supplies
Power supplies included with Model 24 and Model 32 systems can support all combinations of CPUs, memory, and I/O that can be configured
within the system boxes.
Additional 48V power regulators can be ordered to provide N+ 1 power redundancy.
For Model 24 systems, order three power supplies to achieve N+ 1 capability; for Model 32 systems, order four power supplies to achieve N+1
capability.
Step 6b - Internal System Expansion
Step 6b - Internal System Expansion
Step 6b - Internal System ExpansionStep 6b - Internal System Expansion
AlphaServer GS320 Model 24 and Model 32 systems support two additional shelves in the power cabinet
Available choices are:
2000W 48V power supply
H7506-BA
One additional PCI drawer (master or expansion)
One additional PCI drawer (master or expansion) and one DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelf, or
One or two StorageWorks DS-SL13R-xx shelves
Mixed configurations of BA36R and DS-SL13R-xx shelves are supported
Internal StorageWorks
Internal StorageWorks
Internal StorageWorksInternal StorageWorks
Expansion
Expansion
ExpansionExpansion
Configuring
Configuring
ConfiguringConfiguring
DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 (LVD)
DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 (LVD)
DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 (LVD)DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 (LVD)
Shelves
Shelves
ShelvesShelves
System power cabinet provides space for up to two forward facing storage shelves.
Up to two DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 SCSI (LVD) shelves; each shelf supports a maximum of 14
Ultra3 disk drives
Each single-bus Ultra3 shelf requires a 3X-KZPCA-AA Ultra2 (LVD) SCSI adapter or DS-KZPCCxx RAID controller and a SCSI cable to connect controller to shelf
Each split-bus Ultra3 shelf requires two 3X-KZPCA-AA Ultra2 (LVD) SCSI adapters, at least one
dual-channel 3X-KZPEA-DB Ultra3 (LVD) SCSI adapter, or DS-KZPCC-xx RAID controllers and
SCSI cables to connect controller to shelf
Ultra3 shelves connected to 3X-KZPCA-AA adapters in the power cabinet require BN38C-02
2-meter cables; DS-KZPCC-xx RAID controllers require BN37A-02 2-meter cables.
Ultra3 shelves connected to 3X-KZPCA-AA adapters in an attached expander cabinet require
BN38C-10 10-meter cables; DS-KZPCC-xx RAID controllers require BN37A-10 10-meter
cables.
Ultra3 shelves connected to 3X-KZPCA-AA adapters in a remote expander cabinet require 10
20-meter BN38C-xx cables, depending upon physical cabinet location; DS-KZPCC-xx RAID
controllers require BN37A-xx cables.
Ultra3 Universal drives are listed in a subsequent section
StorageWorks Model 4314R Ultra3 SCSI (LVD) single-bus Universal drive rackmount shelf,
International except Japan
StorageWorks Model 4314R Ultra3 SCSI (LVD) single-bus Universal drive rackmount shelf, Japan
StorageWorks Model 4354R Ultra3 SCSI (LVD) split-bus Universal drive rackmount shelf, International
except Japan
StorageWorks Model 4354R Ultra3 SCSI (LVD) split-bus Universal drive rackmount shelf, Japan
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Model 4314 shelf with DS-KZPCC-CE RAID controller does not support a disk drive in the last slot.
DS-SL13R-AA
DS-SL13R-AJ
DS-SL13R-BA
DS-SL13R-BJ
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 11
Page 12
QuickSpecs
Options
Power Option for
Power Option for
Power Option forPower Option for
DS-SL13R-xx Shelves
DS-SL13R-xx Shelves
DS-SL13R-xx ShelvesDS-SL13R-xx Shelves
System I/O Expansion
System I/O Expansion
System I/O ExpansionSystem I/O Expansion
Redundant power supply for 4314R Ultra3 (LVD) StorageWorks shelf, North America
Redundant power supply for 4314R Ultra3 (LVD) StorageWorks shelf, International
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Additional power supply provides N+ 1 power for 4314R Ultra3 (LVD) StorageWorks shelves;
power supply uses a dedicated location in the shelf.
Not required for 4354R shelves.
Model 24 systems support up to 12 PCI drawers; Model 32 systems support up to 16 PCI
drawers. One PCI drawer included in Model 24 and Model 32 base systems.
Model 24 and Model 32 power cabinets provide space for one additional PCI drawer if no
more than one internal storage shelf is configured.
Additional PCI drawers and storage shelves can be configured in 3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF I/O
expansion cabinets, described in a subsequent section.
All PCI drawers contain 14 PCI slots configured into four PCI buses. Two of the buses have
four slots each; the other two buses have three slots each.
There are two types of PCI drawers: expansion drawers and master drawers. Base systems
include one PCI master drawer with 12 configurable PCI slots.
Expansion drawers contain 14 PCI slots and an N+1 redundant power system; expansion
drawers are used for most PCI expansion applications.
Optional master drawers contain 13 configurable PCI slots, N+1 redundant power system,
plus the console ports and storage devices required for use as a system console. (These devices
are listed on page 2. Note that the Fast Ethernet adapter is not included with optional master
PCI drawers.) Optional master drawers have two applications:
As redundant console sub-systems
As consoles for individual partitions in hardware partitioned systems
PCI drawers are connected to a QBB utilizing a 3X-KFWHA-AA system I/O module that
connects to the PCI drawer using two BN39B cables.
DS-SE2UP-AA
DS-SE2UP-AI
PCI Drawer Expansion
PCI Drawer Expansion
PCI Drawer ExpansionPCI Drawer Expansion
PCI drawers are connected to a QBB utilizing a 3X-KFWHA-AA system I/O module that
connects to the PCI drawer using two BN39B cables.
Maximum one additional drawer in system power cabinet; see "External Expansion Cabinets"
for more details.
PCI drawers can be split between multiple QBBs as long as all QBBs are contained within the
same hardware partition.
PCI drawers mounted in a common H9A20 Expansion Cabinet can server multiple systems.
Master PCI shelf mount box for system and I/O expansion cabinets with standard I/O PCI module
and 13 PCI expansion slots. (The 1st master comes standard with all systems and includes a standard
Ethernet network card and the system module and cable pair for connection to the QBB.)
Expansion PCI shelf mount box for system and I/O expansion cabinets with 14 PCI expansion slots
System I/O module for connecting to master or expansion PCI shelves
I/O module cable for connection between I/O module and master or expansion PCI shelves mounted
in system power cabinet; two are mandatory per system I/O module
3X-DWWPA-AA
3X-DWWPA-BA
3X-KFWHA-AA
BN39B-04
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 12
Page 13

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Step 6c - External Expansion Cabinets
Step 6c - External Expansion Cabinets
Step 6c - External Expansion CabinetsStep 6c - External Expansion Cabinets
Additional PCI drawers and storage shelves can be installed in optional 3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF expansion cabinets. Up to four 3X-H9A20AD/AE/AF cabinets are supported.
3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF I/O expansion cabinet can be configured to hold all disk BA36R StorageWorks shelves or
DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 StorageWorks shelves or combination of StorageWorks shelves and PCI drawers.
If no PCI drawers are configured, cabinet supports up to eight BA36R or five DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelves.
If one PCI drawer is configured, cabinet supports up to five BA36R or four DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelves.
If two PCI drawers are configured, cabinet supports up to four BA36R or three DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelves.
If three PCI drawers are configured, cabinet supports up to two BA36R or two DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelves.
If four PCI drawers are configured, cabinet supports one BA36R or DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelf.
BA36R and DS-SL13R-xx StorageWorks shelves can be combined in the same expansion cabinet.
If large quantities of disks are required, the use of StorageWorks Storage Array cabinets and components is highly recommended.
Systems installed in the US and Canada may use the 3X-H9A20-AD when 120V input power is required. In all other cases, the 3X-H9A20-AF is
preferred because of the ability to support dual AC input.
3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF cabinets may be joined to GS320 systems. PCI drawers placed in these cabinets require 7-meter I/O cables.
3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF cabinets may be placed up to 6 meters from the system cabinet. Multiple expander cabinets may be connected to one
another or placed separately. Each group of free-standing H9A20 cabinets requires an end-panel trim kit (CK-H9A20-AB).
PCI drawers placed in remote cabinets require 10-meter I/O cables.
Black I/O expansion cabinet for use with GS320 systems, includes two 120V single-phase power
controllers and cords for use in US and Canada - Does not support dual AC input configurations
Black I/O expansion cabinet for use with GS320 systems, includes two 220-240V single phase
power controllers and cords for use in Europe – Supports dual AC input configurations
Black I/O expansion cabinet for use with GS320 systems, includes two 200-240V single phase
power controllers and cords for use in US, Canada, and Japan – Supports dual AC input configurations
Black end-panel trim kit for remote 3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF cabinets
I/O module cables for connection between I/O module and master or expansion PCI drawers
mounted in 3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF expansion cabinet adjacent to the system; two cables (BN39B-07
or BN39B-10) are mandatory per PCI drawer.
I/O module cables for connection between I/O module and master or expansion PCI drawers
mounted in a second expansion cabinet or in remote 3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF expansion cabinets; two
cables (BN39B-07 or BN39B-10) are mandatory per PCI drawer.
3X-H9A20-AD
3X-H9A20-AE
3X-H9A20-AF
CK-H9A20-AB
BN39B-07
BN39B-10
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 13
Page 14
QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Step 7 - Storage
Step 7 - Storage
Step 7 - StorageStep 7 - Storage
Step 7a - Storage Adapters and Controllers
Step 7a - Storage Adapters and Controllers
Step 7a - Storage Adapters and ControllersStep 7a - Storage Adapters and Controllers
Tru64 UNIX supports a maximum of 64 total SCSI controllers per operating system instance (hardware partition). OpenVMS supports a maximum of
26 total SCSI controllers per operating system instance. Total SCSI controllers (all types) in the system must be within these limits regardless of the
maximum per system I/O adapter limitations. Refer to the "Supported Options List" for specific configuration rules.
Each master PCI drawer contains embedded SCSI controllers (a FIS disk and a CD), which is included in the overall count of SCSI controllers
configured in the system (or partition). Tru64 UNIX counts FIS disk and CD-ROM as an embedded SCSI device. OpenVMS counts the FIS disk only as
an embedded SCSI device. Therefore, one (OpenVMS) or two (Tru64 UNIX) SCSI controllers per master PCI drawer must be included in the total
count of SCSI devices in the system.
Calculating the total number of SCSI controllers in the system (or partition) is done by adding all the devices in the system that the operating system
categorizes as a SCSI device. Tru64 UNIX includes the following devices in this count: KZPBA-CA, KZPBA-CB, 3X-KZPBA-CC, 3X-KZPCA-AA, DSKZPCC-CE, DS-KGPSA-CA., DS-KGPSA-DA Fibre Channel, and two embedded master PCI components per master PCI drawer. OpenVMS includes
the following devices in this count: KZPBA-CA, KZPBA-CB, 3X-KZPBA-CC, 3X-KZPCA-AA, 3X-KZPEA-DB, DS-KZPCC-AC, and one embedded master
PCI component per master PCI drawer.
For cluster configurations, use Y cable (BN39A-0G).
Manufacturing may substitute correct cable lengths depending on configuration.
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
PCI drawers must be included in this calculation.
"Per System" quantities apply to systems or to each hardware partition. The SCSI adapters included in the base system or in 3x-DWWPA-AA master
PCI Fibre Channel adapter (uses one PCI slot); requires Fibre Channel with SC
connector for adapter
2-GB PCI Fibre Channel adapter, (uses one PCI slot); requires Fibre Channel
cable with LC connector for adapter
2-GB PCI-X Fibre Channel adapter
Fibre Channel SC-SC cable (BNGBX-xx),
xx=02, 03, 05, 10, 15, 30, 50 meters
Fibre Channel SC-LC cable, 2-meter (2976), 5-meter (2977), 15-meter
(2978), 30-meter (3458), 50-meter (3459)
Fibre Channel LC-LC cable, 2-meter (2979), 5-meter (2980), 15-meter
(2981), 30-meter (3454), 50-meter (3455)
PCI 1-port UltraSCSI single-ended host adapter (uses one PCI slot)
PCI 1-port UltraSCSI differential host adapter* (uses one PCI slot); requires
BN38C-xx cable
VHDCI male-to-68-pin HD male UltraSCSI cable
xx=02, 03, 05, 10, 20 meters (use -02 for connecting SCSI adapter to
SCSI devices when both the PCI shelf and StorageWorks shelf are in the
system cabinet or in an adjacent expansion cabinet; use -05, -10, and -20 for
connecting SCSI adapter to SCSI devices when the PCI shelf and
StorageWorks shelf are in two different cabinets)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
per partition.
* = Tru64 UNIX V5.1 is required to support 62 adapters per partition and 13 adapters per PCI drawer. Tru64 UNIX 4.0G supports 24 adapters
Maximum # Supported
Maximum # Supported
Maximum # SupportedMaximum # Supported
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIXTru64 UNIX
Per
System
26/62*26/26*
62 26 13 26 26 4
8 8 8 8
8 8 8 8 8 8
24/62*24/26*12/13*
Per
QBB
Per PCI
Drawer
13 26 26 13
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMSOpenVMS
Per
System
Per
QBB
24 24 12
Per PCI
Drawer
DS-KGPSA-CA
DS-KGPSA-DA
DS-KGPSA-EA
BNGBX-xx
3R-Axxxx-AA
3R-Axxxx-AA
KZPBA-CA
3X-KZPBA-CC
BN38C-xx
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 14
Page 15

QuickSpecs
Options
PCI 2-channel Ultra3 (LVD) SCSI adapter, 64-bit/66-MHz (uses one PCI slot);
includes internal 68-pin HD and external 68-pin VHDCI connectors; requires 3XBC56J-xx cable to connect adapter to DS-SL13R-Bx/ DS-SSL14-xx Ultra3 shelf.
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
is required, maximum cable length is 12 meters.
68-pin VHDCI male-to-VHDCI male UltraSCSI cable;
xx=02, 03, 04, for 6, 12, and 24 meters respectively
PCI 1-port Ultra2 (LVD) SCSI adapter, 32-bit, single-channel (uses one PCI slot);
includes external 68-pin HD connectors; requires BN38C-xx cable to connect
adapter to Ultra2 or Ultra3 shelf; HSZxx RAID controllers not supported.
68-pin HD male-to-VHDCI male UltraSCSI cable; xx=02, 03, 05, 10, 20
meters
PCI 1-channel Ultra2 (LVD) SCSI RAID controller**, 16-MB cache, (uses one
PCI slot); supports 14 disks per channel with DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 shelves;
requires BN37A-xx cable to connect adapter to DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 shelf.
PCI 3-channel Ultra2 (LVD) SCSI RAID controller**, 64-MB cache, (uses one
PCI slot); supports 14 disks per channel with DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 shelves;
requires BN37A-xx cable to connect adapter to DS-SL13R-xx Ultra3 shelf.
68-pin VHDCI male-to-VHDCI male UltraSCSI cable;
xx=02, 03, 05, 10, 20 meters
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
NOTES
NOTES
NOTESNOTES
OpenVMS 7.2-2, or later, is required; Tru64 UNIX 5.1B PK4, or later
** = Requires a Graphics Adapter or Graphical Display Station for its configuration utility (other than the base system console.)
:
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
4 4 4 4 4 4
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 8
8 8 8
- - -
- - -
3X-KZPEA-DB
3X-BC56J-xx
3X-KZPCA-AA
BN38C-xx
DS-KZPCC-AC
DS-KZPCC-CE
BN37A-xx
Use 2-meter cable to connect adapters, controllers, and shelves within the GS320 power cabinet.
Use 10-meter cable to connect adapters, controllers to shelves in attached H9A20 expander cabinets.
Use 10- to 25-meter cables to connect adapters, controllers to shelves in remote expander cabinets.
HVD to LVD Converters
HVD to LVD Converters
HVD to LVD ConvertersHVD to LVD Converters
HVD (High Voltage Differential) adapters and LVD (Low Voltage Differential) devices are normally
incompatible due to their different signaling voltage levels. This incompatibility does not allow direct
communication between the different technologies. The HVD to LVD converter allows connectivity
between legacy HVD Host Bus Adapters and today's LVD devices. The converter provides:
Connectivity in direct attach or shared configurations of all currently available LVD devices,
including disks, tapes, libraries, and shelves (4314 or 4354) when used with the KZPBA-CB
and 3X-KZPBA-CC HVD adapters. With the retirement of StorageWorks 1 disks and HVD
shelves (BA36R), converters are desirable where upgrades to LVD HBAs, or upgrades to
current operating system versions are not possible.
Shared and direct attach configurations are interconnected much the same as those previously
configured with homogeneous HVD solutions, except that the HVD output is now passed
through the converter before proceeding to the LVD device. Where required, Y cables
(BN21W-0B), terminators (H879-AA), cables (BN38C-10, BN37A-20), one or two HVD/LVD
converters (one-port, two-port), Memory Channel adapters (CCMAB), one Memory Channel
cable
(BN39B-10), are used in conjunction with the LVD device of choice.
HVD to LVD one-port converter
HVD to LVD two-port converter
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 15
Page 16

QuickSpecs
Options
CI Adapters
CI Adapters
CI AdaptersCI Adapters
(OpenVMS only)
Step 7b - Internal Storage
Step 7b - Internal Storage
Step 7b - Internal StorageStep 7b - Internal Storage
Ultra3 SCSI
Ultra3 SCSI
Ultra3 SCSIUltra3 SCSI
Devices
Devices
DevicesDevices
SL13R-xx Shelves)
Ultra2 SCSI
Ultra2 SCSI
Ultra2 SCSIUltra2 SCSI
Devices
Devices
DevicesDevices
SL13R-xx Shelves)
(LVD)
Storage
Storage
StorageStorage
(for use with DS-
(LVD)
Tape
Tape
TapeTape
(for use with DS-
PCI CI adapter, maximum 26 per system or hardware partition (12 per QBB,
six per PCI); requires two PCI slots
Computer interconnect cable set, connects CIPCA to star coupler;
select length xx=10, 20, 45 meters
18.2-GB Ultra3 SCSI 15,000 rpm Universal 1-inch disk drive
36.4-GB Ultra3 SCSI 10,000 rpm Universal 1-inch disk drive
36.4-GB Ultra3 SCSI 15,000 rpm Universal 1-inch disk drive
72.8-GB Ultra3 SCSI 10,000 rpm Universal 1-inch disk drive
72.8-GB Ultra3 SCSI 15,000 rpm Universal 1-inch disk drive
146-GB Ultra3 SCSI 10,000 rpm Universal 1-inch disk drive
AIT-351B, 35-GB tape drive embedded in hot-plug Universal carrier
AIT-50, 50-GB tape drive embedded in hot-plug Universal carrier
SDT-10,000, 20/40-GB DAT tape drive embedded in hot-plug Universal carrier
AIT-100, 2000-GB tape drive embedded in hot-plug Universal carrier
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
CIPCA-BA
BNCIA-xx
3R-A3848-AA
3R-A3838-AA
3R-A3849-AA
3R-A3839-AA
3R-A3851-AA
3R-A3841-AA
3R-A2396-AA
3R-A2779-AA
3R-A2780-AA
3R-A3621-AA
Step 7c - Tape Devices
Step 7c - Tape Devices
Step 7c - Tape DevicesStep 7c - Tape Devices
3U Rackmount Tape Drive
3U Rackmount Tape Drive
3U Rackmount Tape Drive3U Rackmount Tape Drive
Enclosure
Enclosure
EnclosureEnclosure
Tape Drives for Use in 3U
Tape Drives for Use in 3U
Tape Drives for Use in 3UTape Drives for Use in 3U
Rackmount Tape Drive
Rackmount Tape Drive
Rackmount Tape DriveRackmount Tape Drive
Enclosure
Enclosure
EnclosureEnclosure
(Requires 3X-KZPCA-AA or 3XKZPEA-DB LVD Adapter)
Preconfigured
Preconfigured
PreconfiguredPreconfigured
Configurations
Configurations
ConfigurationsConfigurations
3U LVD Rackmount Tape Drive Enclosure for use in H9Axx Series Cabinets, 0 drives, carbon black
Rackmount kit for H9Axx Series Cabinet, carbon black – required for mounting 3U Rackmount Tape
Drive Enclosure in H9Axx cabinets
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
to two full height devices. Select up to four AIT or DAT devices, or two DLT/SDLT devices with 3U
Rackmount Tape Drive Enclosure
(274338-B21), or select preconfigured configurations listed below.
AIT 35/70-GB 3U internal tape drive, carbon black
AIT 50/100-GB 3U internal tape drive, carbon black (157766-B22)
DAT 20/40-GB 3U internal tape drive, carbon black (157769-B22)
DLT8000 40/80-GB internal tape drive, carbon black
SDLT 110/220-GB internal tape drive, carbon black
SDLT 160/320-GB internal tape drive, carbon black
AIT 50-GB, 3U rackmount kit, carbon black
DLT 40/80-GB, 3U rackmount kit, carbon black
DLT 40/80-GB, dual-drive, 3U rackmount kit, carbon black
SDLT 110/220-GB, single drive, 3U rackmount kit, carbon black
SDLT 110/220-GB, dual-drive, 3U rackmount kit, carbon black
The 3U Tape Drive Enclosure supports up to four internal half-height removable devices, or up
274338-B21
3R-A3804-AA
216884-B21
3R-A3753-AA
3R-A3752-AA
146196-B22
192106-B25
257319-B21
274333-B21
274332-B21
274335-B21
274331-B21
274334-B21
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 16
Page 17

QuickSpecs
Options
5U Rackmount Tape Drive
5U Rackmount Tape Drive
5U Rackmount Tape Drive5U Rackmount Tape Drive
Enclosure
Enclosure
EnclosureEnclosure
AA or 3X-KZPEA-DB LVD
Adapter)
Tape Drives for Use in 5U
Tape Drives for Use in 5U
Tape Drives for Use in 5UTape Drives for Use in 5U
Tape Drive Enclosure
Tape Drive Enclosure
Tape Drive EnclosureTape Drive Enclosure
Preconfigured
Preconfigured
PreconfiguredPreconfigured
Configurations
Configurations
ConfigurationsConfigurations
AIT Tabletop Tape Drives
AIT Tabletop Tape Drives
AIT Tabletop Tape DrivesAIT Tabletop Tape Drives
(Requires 3X-KZPCA-
5U Rackmount Tape Drive Enclosure (Requires 3X-KZPCA-AA or 3X-KZPEA-DB LVD Adapter)
Rackmount Kit for H9Axx Series Cabinet, carbon black – required for mounting 5U Rackmount Tape
Drive Enclosure in H9Axx cabinets
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
DLT or SDLT devices with 274339-B21, or select preconfigured configurations listed below.
DLT8000 40/80-GB tape drive, carbon black
SDLT 110/220-GB tape drive, carbon black
SDLT 160/320-GB tape drive, carbon black
SDLT 110/220-GB Tape Array III, 5U rackmount kit, carbon black
DLT 40/80-GB Tape Array III, 5U rackmount kit, carbon black
DLT Tape Array III Model 0 enclosure, U.S.
Same as above, International
Same as above, Japan
AIT 35/70-GB 8-mm LVD tabletop tape drive, North America carbon black; requires LVD adapter
Same as above, International
Same as above, Japan
AIT 50/100-GB 8-mm SCSI tabletop tape drive with 120V North America power cord, carbon
black; requires Ultra2 (LVD) adapter
Same as above, International
Same as above, Japan
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
The 5U Rackmount Tape Drive Enclosure supports four full-height devices; select up to four
274339-B21
254795-001
146196-B22
192106-B25
257319-B21
274336-B21
274337-B21
168047-001
168047-B31
168047-291
216885-001
216885-B31
216885-291
157767-002
157767-B32
155767-292
AIT Hot-plug Tape Drives
AIT Hot-plug Tape Drives
AIT Hot-plug Tape DrivesAIT Hot-plug Tape Drives
AIT Autoloaders
AIT Autoloaders
AIT AutoloadersAIT Autoloaders
AIT Tape Libraries
AIT Tape Libraries
AIT Tape LibrariesAIT Tape Libraries
DAT Tabletop Tape Drives
DAT Tabletop Tape Drives
DAT Tabletop Tape DrivesDAT Tabletop Tape Drives
AIT 35/70-GB hot-plug LVD Universal tape drive, uses two slots in 43xxx shelves
AIT 50/100-GB hot-plug LVD Universal tape drive, uses two slots in or 43xxx shelves
AIT-100, 2000-GB tape drive embedded in hot-plug Universal carrier
AIT 35-GB tabletop autoloader, 8 cartridge, U.S.
Same as above, International
AIT 35-GB rackmount autoloader, 8 cartridge, U.S.
Same as above, International
AIT Rail kit for rackmount autoloader
SSL2020 AIT tabletop library with one AIT 50-GB drive and 20 slots, LVD
SSL2020 AIT tabletop library with two AIT 50-GB drives and 20 slots, LVD
SSL2020 AIT rackmount library with one AIT 50-GB drive and 20 slots, LVD
SSL2020 AIT rackmount library with two AIT 50-GB drives and 20 slots, LVD
DAT 12/24-GB 4-mm narrow single-ended tabletop SCSI tape drive with 120V North American
power cord; requires BN31W-xx SCSI cable
DAT 20/40-GB 4-mm Wide Ultra2 (LVD) tabletop SCSI tape drive with 120V North American power
cord, carbon black; requires Ultra2 (LVD) adapter
Same as above, International
Same as above, Japan
3R-A2396-AA
3R-A2779-AA
3R-A3621-AA
292355-001
292355-B31
280349-001
280349-B31
284930-001
175195-B21
175195-B22
175196-B21
175196-B22
DS-TLZ10-DB
157770-002
157770-B32
157770-292
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 17
Page 18

QuickSpecs
Options
DAT Hot-plug Tape Drive
DAT Hot-plug Tape Drive
DAT Hot-plug Tape DriveDAT Hot-plug Tape Drive
DAT Autoloaders
DAT Autoloaders
DAT AutoloadersDAT Autoloaders
DLT/SDLT Tabletop Tape
DLT/SDLT Tabletop Tape
DLT/SDLT Tabletop TapeDLT/SDLT Tabletop Tape
Drives
Drives
(Requires 3X-KZPCA-AA
DrivesDrives
or
3X-KZPEA-DB LVD Adapter)
Library Rackmount Kit for
Library Rackmount Kit for
Library Rackmount Kit forLibrary Rackmount Kit for
MSL5xxx Tape Libraries in
MSL5xxx Tape Libraries in
MSL5xxx Tape Libraries inMSL5xxx Tape Libraries in
H9Axx Cabinet Series
H9Axx Cabinet Series
H9Axx Cabinet SeriesH9Axx Cabinet Series
DAT 20/40-GB DDS4 hot-plug LVD Universal tape drive, uses two slots in 43xxx shelves
DAT 20/40-GB auto loader external; requires BN31W-xx SCSI cable and 3X-KZPCA-AA, 3X-KZPEADB, or 3X-DEPVZ-AA adapter, North America
Same as above, International
Same as above, Japan
DLT8000 tabletop 40/80-GB DLT external tape drive, carbon black - U.S.
Same as above – Japan
SDLT tabletop 110/220-GB external tape drive, carbon black- U.S.
Same as above – International
Same as above – Japan
SDLT tabletop 160/320-GB external tape drive, carbon black - U.S.
Same as above - International
Same as above - Japan
Rackmount kit for H9Axx Series cabinets – required for mounting MSL5000 series in H9Axx cabinets
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
3R-A2780-AA
166505-001
166505-B31
166505-291
146197-B23
146197-292
192103-002
192103-B32
192103-292
257319-001
257319-B31
257319-291
254795-001
SDLT Tape Libraries
SDLT Tape Libraries
SDLT Tape LibrariesSDLT Tape Libraries
StorageWorks
StorageWorks
StorageWorksStorageWorks
MSL5026SL SDLT
MSL5026SL SDLT
MSL5026SL SDLTMSL5026SL SDLT
110/220-GB Tape Library
110/220-GB Tape Library
110/220-GB Tape Library110/220-GB Tape Library
StorageWorks
StorageWorks
StorageWorksStorageWorks
MSL5026S2 SDLT
MSL5026S2 SDLT
MSL5026S2 SDLTMSL5026S2 SDLT
160/320-GB Tape Library
160/320-GB Tape Library
160/320-GB Tape Library160/320-GB Tape Library
SDLT Tape Libraries require the use of either a 3X-KZPCA-AA or 3X-KZPEA-DB adapter; Tru64 UNIX
5.1B requires a minimum level of PK4
MSL5026SL, SDLT tabletop library with one 110/220-GB SDLT tape drive, LVD; graphite
MSL5026SL, SDLT tabletop library with two 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, LVD; graphite
MSL5026SL, SDLT rackmount library with one 110/220-GB SDLT tape drive, LVD; graphite – requires
rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5026SL, SDLT rackmount library with two 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, LVD; graphite –
requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5026S2, SDLT rackmount library with 0 drives, LVD; graphite – requires rackmount kit (254795-
001)
MSL5026S2, SDLT rackmount library with one 160/320-GB SDLT tape drive, LVD; graphite –
requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5026S2, SDLT rackmount library with one 160/320-GB SDLT tape drive, LVD; graphite –
requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5026S2, SDLT rackmount library with one 160/320-GB SDLT tape drive, Fibre Channel
Interface; graphite – requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5026S2, SDLT rackmount library with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, Fibre Channel
Interface; graphite – requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5026S2, SDLT tabletop library with one 160/320-GB SDLT tape drive, LVD; graphite
MSL5026S2, SDLT tabletop library with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, LVD; graphite
MSL5000 SDLT2 upgrade drive, all
302511-B21
302511-B22
302512-B21
302512-B22
293472-B21
293472-B22
293472-B23
293472-B24
293472-B25
293473-B21
293473-B21
293475-B21
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 18
Page 19

QuickSpecs
Options
StorageWorks
StorageWorks
StorageWorksStorageWorks
MSL5052SL SDLT
MSL5052SL SDLT
MSL5052SL SDLTMSL5052SL SDLT
110/220-GB Tape Library
110/220-GB Tape Library
110/220-GB Tape Library110/220-GB Tape Library
StorageWorks
StorageWorks
StorageWorksStorageWorks
MSL5052S2 SDLT
MSL5052S2 SDLT
MSL5052S2 SDLTMSL5052S2 SDLT
160/320-GB Tape Library
160/320-GB Tape Library
160/320-GB Tape Library160/320-GB Tape Library
StorageWorks
StorageWorks
StorageWorksStorageWorks
ESL9322S2 SDLT
ESL9322S2 SDLT
ESL9322S2 SDLTESL9322S2 SDLT
160/320-GB
160/320-GB
160/320-GB160/320-GB
Tape Library
Tape Library
Tape LibraryTape Library
MSL5052, 0 drives, LVD, rackmount
MSL5052SL SDLT tabletop library with two 110/220-GB tape drives, LVD
MSL5052SL SDLT rackmount library with two 110/220-GB tape drives, LVD – requires rackmount kit
(254795-001)
MSL5052SL SDLT 110/220-GB drive field upgrade, LVD
MSL5052S2, SDLT rackmount library with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, LVD; graphite –
requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5052S2, SDLT rackmount library with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, Fibre Channel
Interface; graphite – requires rackmount kit (254795-001)
MSL5052S2, SDLT tabletop library with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, LVD; graphite
ESL9322S2 SDLT tape library, with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, 222 slots
ESL9322S2 SDLT tape library, with eight 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, 222 slots
ESL9322S2 SDLT tape library, with two 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, 322 slots
ESL9322S2 SDLT tape library, with eight 160/320-GB SDLT tape drives, 322 slots
ESL9000 SDLT2 LVD upgrade drive
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
255102-B21
249490-B21
249491-B21
231823-B22
293474-B21
293474-B24
293476-B21
293409-B22
293409-B28
293410-B22
293410-B28
293414-B21
StorageWorks ESL9595SL
StorageWorks ESL9595SL
StorageWorks ESL9595SLStorageWorks ESL9595SL
SDLT 110/220-GB Tape
SDLT 110/220-GB Tape
SDLT 110/220-GB TapeSDLT 110/220-GB Tape
Library
Library
LibraryLibrary
StorageWorks
StorageWorks
StorageWorksStorageWorks
ESL9595S2 SDLT
ESL9595S2 SDLT
ESL9595S2 SDLTESL9595S2 SDLT
160/320-GB Tape Library
160/320-GB Tape Library
160/320-GB Tape Library160/320-GB Tape Library
Step 7d – External Storage
Step 7d – External Storage
Step 7d – External StorageStep 7d – External Storage
External Storage Arrays
External Storage Arrays
External Storage ArraysExternal Storage Arrays
ESA 10000 Storage is supported on Tru64 UNIX and OpenVMS systems.
SW800 CI Storage Arrays (HSJ5x product set) are supported on OpenVMS systems.
Complete ordering and configuring information is available at
(Only Tru64 UNIX and OpenVMS operating systems options are supported.) NOTE: This website is available in English only.
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library, 0 drives, 400 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library, two 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, 400 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library with 16 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, 400 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library with 0 drives, 500 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library with two 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, 500 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library with 16 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, 500 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library, 0 drives, 595 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library with two 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, 595 slots
ESL9595SL SDLT tape library with 16 drives 110/220-GB SDLT tape drives, 595 slots
ESL9595S2 SDLT2 tape library, two 160/320-GB tape drives, 400 slots
ESL9595S2 SDLT2 tape library with 16 160/320-GB tape drives, 400 slots
ESL9595S2 SDLT2 tape library with two 160/320-GB tape drives, 500 slots
ESL9595S2 SDLT2 tape library with 16 160/320-GB tape drives, 500 slots
ESL9595S2 SDLT2 tape library with two 160/320-GB tape drives, 595 slots
ESL9595S2 SDLT2 tape library with 16 160/320-GB tape drives, 595 slots
ESL9000 SDLT2 LVD upgrade drive
http://www.hp.com/products/StorageWorks/
274672-B21
274672-B22
274672-B28
281627-B21
281627-B22
281627-B28
281628-B21
281628-B22
281628-B28
293411-B22
293411-B28
293412-B22
293412-B28
293413-B22
293413-B28
293414-B21
Storage Array Controllers
Storage Array Controllers
Storage Array ControllersStorage Array Controllers
The following controllers are used in StorageWorks array packaging:
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 19
Page 20

QuickSpecs
Options
HSV110 Enterprise Virtual
HSV110 Enterprise Virtual
HSV110 Enterprise VirtualHSV110 Enterprise Virtual
Storage Array 5000
Storage Array 5000
Storage Array 5000Storage Array 5000
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 2C6D-B 60-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, M3220
controller assembly with dual HSV110 controllers, six M5214 dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive
enclosures, four 12-port FC loop switches; requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283198-B21)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 2C6D-B 50-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, M3220
controller assembly with dual HSV110 controllers, six M5214 dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive
enclosures, four 12-port FC loop switches; requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283198-B22)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 2C12D-B 60-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, M3220
controller assembly with dual HSV110 controllers, 12 M5214 dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive
enclosures, four 12-port FC loop switches; requires DS-KGPSA-xx, (283199-B21)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 2C12D-B 50-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, M3220
controller assembly with dual HSV110 controllers, 12 M5214 dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive
enclosures, four 12-port FC loop switches; requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283199-B22)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 8C8D 60-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, four M3220
controller assembly with eight HSV110 controllers, eight M5214 dual FC loop 14-bay drive
enclosures; requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283263-B21)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 8C8D 50-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, four M3220
controller assembly, with eight HSV110 controllers, eight M5214 dual FC loop 14-bay drive
enclosures; requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283263-B22)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 0C6D-B 60-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, six M5214
dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive enclosures, 12 16.4-feet/5-meter interconnect cables (to
2C12D-B); requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283264-B21)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 0C6D-B 50-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, six M5214
dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive enclosures, 12 16.4-feet/5-meter interconnect cables (to
2C12D-B); requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283264-B22)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 0C12D-B 60-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, 12 M5214
dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive enclosures, 24 16.4-feet/5-meter interconnect cables (to two
2C12D-Bs); requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283265-B21)
Enterprise Virtual Array Model 0C12D-B 50-Hz, includes 41U graphite storage cabinet, 12 M5214
dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay drive enclosures, 24 16.4-feet/5-meter interconnect cables (to two
2C12D-Bs); requires DS-KGPSA-xx (283265-B22)
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
DS-SV110-JA
DS-SV110-JB
DS-SV110-KA
DS-SV110-KB
DS-SV110-LA
DS-SV110-LB
DS-SV110-MA
DS-SV110-MB
DS-SV110-NA
DS-SV110-NB
SAN Solutions Kits
SAN Solutions Kits
SAN Solutions KitsSAN Solutions Kits
Enterprise Virtual Array
Enterprise Virtual Array
Enterprise Virtual ArrayEnterprise Virtual Array
3000
3000
30003000
Tru64 UNIX SAN Solutions Kit for Enterprise Virtual Array V3.0 (333683-B21)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
NHD6
Tru64 UNIX V5.1B requires Patch Kit 2 (BL22): T64V51BB22AS002-20030415.tar
OpenVMS SAN Solutions Kit for Enterprise Virtual Array V3.0 (333684-B21)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
OpenVMS V7.3 requires TIMA Kit: DEC-AXPVMS-VMS73_FIBRE_SCSI_V0500
OpenVMS V7.3-1 requires TIMA Kit: DEC-AXPVMS-VMS731_UPDATE-V0100-4.PCS
Enterprise Virtual Array 3000, 60 Hz, includes one 3U controller assembly, two HSV100 controllers,
two M5114 dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay disk enclosures, 42U graphite storage cabinet
(321618-B21)
Enterprise Virtual Array 3000, 50 Hz, includes one 3U controller assembly, two HSV100 controllers,
two M5114 dual-redundant FC loop 14-bay disk enclosures, 42U graphite storage cabinet
(321619-B21)
Tru64 UNIX V5.1A requires Patch Kit 4 (BL21): T64V51AB21AS0004-20030206.tar,
OpenVMS V7.2-2 requires TIMA Kit: DEC-AXPVMS-VMS722_FIBRE_SCSI-V0400
I
QB-720AB-SA
QB-720AC-SA
DS-SWR20-AA
DS-SWR20-AB
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 20
Page 21
QuickSpecs
Options
EVA 3000 SAN Solution
EVA 3000 SAN Solution
EVA 3000 SAN SolutionEVA 3000 SAN Solution
Kits
Kits
KitsKits
Modular SAN Array 1000
Modular SAN Array 1000
Modular SAN Array 1000Modular SAN Array 1000
(msa 1000)
(msa 1000)
(msa 1000)(msa 1000)
StorageWorks Disk Array
StorageWorks Disk Array
StorageWorks Disk ArrayStorageWorks Disk Array
Family
Family
FamilyFamily
Tru64 UNIX SAN Solutions Kit for Enterprise Virtual Array 3000 V2.0 (250193-B22)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
NHD6
Tru64 UNIX V5.1B requires Patch Kit 2 (BL22): T64V51BB22AS0002-20030415.tar
OpenVMS SAN Solutions Kit for Enterprise Virtual Array 3000 V2.0 (250194-B22)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
OpenVMS V7.3 requires TIMA Kit: DEC-AXPVMS-VMS73_FIBRE_SCS-V0500
OpenVMS V7.3-1 requires TIMA Kit: DEC-AXPVMS-VMS731_UPDATE-V0100-4.PCSI
Modular SAN Array 1000, supported on Tru64 UNIX and two-node clusters (maximum); supported
with DS-KGPSA-CA and DS-KGPSA-DA adapters; requires connection via a switch - no direct connect;
no support for FC arbitrated loop
Tru64 UNIX V5.1A requires Patch Kit 4: T64V51AB21AS0004-20030206.tar
Tru64 UNIX V5.1B requires Patch Kit 1: T64V51BB03AS0001-20021229.tar
NOTE: The HP StorageWorks Disk Array Family, specifically the XP128 and XP1024, are supported on AlphaServer
GS160 systems. For product and ordering information, refer to the following Web pages:
http://www.hp.com/products1/storage/products/disk_arrays/highend/xp1024/index.html
http://www.hp.com/products1/storage/products/disk_arrays/highend/xp128/index.html
The following part numbers have been assigned for reference purposes only:
3R-A4417-AA
3R-A4418-AA
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Tru64 UNIX V5.1A requires Patch Kit 4 (BL21): T64V51AB21AS0004-20030206.tar,
OpenVMS V7.2-2 requires TIMA Kit: DEC-AXPVMS-VMS722_FIBRE_SCSI-V0400
A7876A
A7906A
XP128 Disk Array Control Frame
XP1024 Disk Array Control Frame
QB-6RPAB-SB
QB-6RPAC-SB
3R-A4328-AA
Step 7e – Fibre Channel Options
Step 7e – Fibre Channel Options
Step 7e – Fibre Channel OptionsStep 7e – Fibre Channel Options
Fibre Channel Disk Drives
Fibre Channel Disk Drives
Fibre Channel Disk DrivesFibre Channel Disk Drives
Fibre Channel Data
Fibre Channel Data
Fibre Channel DataFibre Channel Data
Routers
Routers
RoutersRouters
Fibre Channel
Fibre Channel
Fibre ChannelFibre Channel
Switches
Switches
SwitchesSwitches
The following hubs, data routers, switches, and cables are used in Fibre Channel configurations using
the DS-KGPSA-xx adapter.
36-GB 10K rpm dual-port 2-Gb/sec FC-AL 1-inch (25.4 mm) drive (238590-B21)
36-GB 15K rpm dual-port 2-Gb/sec FC-AL 1-inch (2.54 cm) drive (236205-B21)
72-GB 10K rpm dual-port 2-Gb/sec FC-AL 1-inch (2.54 cm) drive (238921-B21)
72-GB 15K rpm dual-port 2-Gb/sec FC-AL 1-inch (2.54 cm) drive (293568-B21)
146-GB 10K rpm dual-port 2-Gb/sec FC-AL 1-inch (25.4 mm) drive (293556-B21)
1 Fibre Channel x 2 HVD data router (163082-B21)
1 Fibre Channel x 2 LVD data router (163083-B21)
2 x 4 LVD Fiber Channel to SCSI Network Storage Router (262653-B21)
2 x 4 HVD Fiber Channel to SCSI Network Storage Router (262654-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 8-port SAN switch (Base) (322120-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 8-port SAN switch (Power pack) (322121-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 16-port SAN switch (Base)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 16-port SAN switch (Power pack) (322119-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 32-port SAN switch (Base) (240603-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 32-port SAN switch (Power pack) (333764-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 64-port core switch (Base) (332177-B21)
Fibre Channel 2-Gb 64-port core switch (Power pack) (332178-B21)
3R-A3239-AA
3R-A3210-AA
3R-A3260-AA
3R-A3971-AA
3R-A3975-AA
3R-A2673-AA
3R-A2774-AA
3R-A3740-AA
3R-A3741-AA
DS-DSGGD-BC
DS-DSGGD-CC
DS-DSGGD-CA
DS-DSGGD-CB
DS-DSGGD-AB
DS-DSGGD-DB
DS-DSGGE-BA
DS-DSGGE-CA
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 21
Page 22
QuickSpecs
Options
McData 64-port Fibre
McData 64-port Fibre
McData 64-port FibreMcData 64-port Fibre
Channel SAN Director
Channel SAN Director
Channel SAN DirectorChannel SAN Director
Class Switches
Class Switches
Class SwitchesClass Switches
Fibre Channel Cables
Fibre Channel Cables
Fibre Channel CablesFibre Channel Cables
SAN Director 64 (2 Gb) 32 ports, base model
SAN Director 140 (2 Gb) 140 ports
SAN Edge Switch 2 Gb, 24 ports
SAN Edge Switch 2 Gb, 32 ports
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Refer to the Switches, Hubs, and Interconnects QuickSpecs at:
http://www.compaq.com/products/quickspecs/North_America/10490.html
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
2-meter LC-SC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221691-B21)
5-meter LC-SC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221691-B22)
15-meter LC-SC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221691-B23)
30-meter LC-SC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221691-B26)
50-meter LC-SC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221691-B27)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
2-meter LC-LC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221692-B21)
5-meter LC-LC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221692-B22)
15-meter LC-LC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221692-B23)
30-meter LC-LC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221692-B26)
50-meter LC-LC multi-mode Fibre Channel cable (221692-B27)
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Connection for, or between, 1-Gb and/or 2-Gb SAN switches requires different cables.
The following LC-SC connector cables support connectivity between 1-Gb and 2-Gb devices.
The following LC-LC connector cables support connectivity between 2-Gb and 2-Gb devices.
DS-DMGGD-BA
DS-DMGGD-CA
DS-DMGGE-BD
DS-DMGGE-BC
3R-A2976-AA
3R-A2977-AA
3R-A2978-AA
3R-A3458-AA
3R-A3459-AA
3R-A2979-AA
3R-A2980-AA
3R-A2981-AA
3R-A3454-AA
3R-A3455-AA
Step 8 - Networks and Communications
Step 8 - Networks and Communications
Step 8 - Networks and CommunicationsStep 8 - Networks and Communications
One Fast Ethernet adapter included in base systems. Connection of system to Ethernet requires twisted-pair cable.
PCI LAN Communications Controllers
PCI LAN Communications Controllers
PCI LAN Communications ControllersPCI LAN Communications Controllers
Requires 3X-DWWPA-AA /BA PCI shelf mount box
Each adapter/controller uses one PCI slot
A maximum of 16 network adapters - 3X-DE602-xx, DEGPA-xx, 3X-DEFPA-xx - are supported per system or hardware partition.
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
calculations. Operating System limitations may further limit the maximum number of configurable options.
"Per System" quantities apply to systems or to each hardware partition. The 3X-DE602-xx included in base system must be included in these
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 22
Page 23
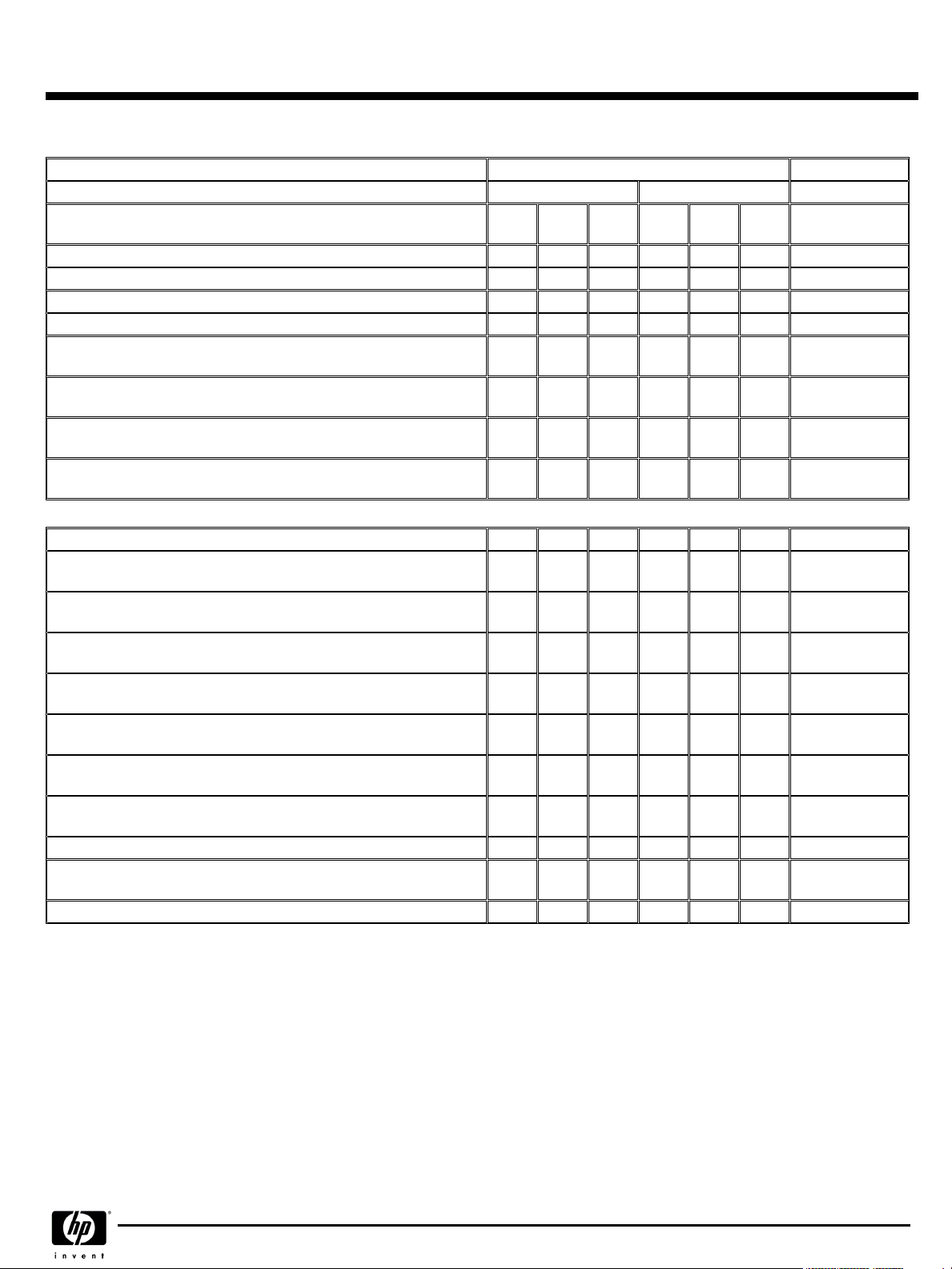
QuickSpecs
Options
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
10/100-Mbit Fast Ethernet Adapter
10/100-Mbit Fast Ethernet Adapter
10/100-Mbit Fast Ethernet Adapter10/100-Mbit Fast Ethernet Adapter
PCI Dual-port 10/100 UTP Fast Ethernet adapter and base module
PCI Dual-port Fast Ethernet "TX" add-on daughter card
Single-port multi-mode fiber (MMF) add-on daughter card
Category 5 cross-over cable for point-to-point, unshielded
xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1, 3, 4, 7, 0.5 meters
Category 5 cross-over cable for point-to-point, shielded
xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1, 3, 4, 7, 0.5 meters
Category 5 straight through for system to repeater or hub, unshielded, xx=01,
03, 04, 07, 0E, 0B for 1, 3, 4, 7, 0.5, 0.2 meters
Twisted pair, shielded cable, xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1, 3, 4, 7, 0.5
meters
FDDI Controllers
FDDI Controllers
FDDI ControllersFDDI Controllers
PCI FDDIcontroller, fiber, single-attachment station multimode fiber, requires
BN34x SC type connecting cable
PCI FDDIcontroller, fiber, dual-attachment station multimode fiber, requires
BN34x SC type connecting cable
Multimode fiber optic duplex cable, SC connector-to-ST connector,
xx=01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2E, 4E for 01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2.5, 4.5 meters
Multimode fiber optic duplex cable, SC connector-to-SC connector,
xx=01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2E, 4E for 01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2.5, 4.5 meters
Multimode fiber optic duplex cable, SC connector-to-MIC connector,
xx=01, 03, 10 for 01, 03, 10 meters
PCI FDDIcontroller, copper, dual-attachment station UTP, requires BN26x or
BN25H connecting cables
PCI FDDIcontroller, copper, single-attachment station UTP, requires BN26x or
BN25H connecting cables
8-pin MP-to-8-pin MP, screened, EIA/TIA category 5 cable
8-pin MP-to-8-pin MP, screened, crossover, EIA/TIA category 5 cable, 3
meters
3-meter unshielded twisted pair RJ45 connectors
Maximum # Supported
Maximum # Supported
Maximum # SupportedMaximum # Supported
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIXTru64 UNIX
Per
System
Per
Per PCI
QBB
Drawer
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 4 8 8 6
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 8 8 8 8
Per
System
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMSOpenVMS
Per
QBB
Per PCI
Drawer
3X-DE602-BB
3X-DE602-TA
3X-DE602-FA
BN24Q-xx
BN28Q-xx
BN25G-xx
BN26M-xx
3X-DEFPA-AC
3X-DEFPA-DC
BN34A-xx
BN34B-xx
BN34D-xx
3X-DEFPA-MC
3X-DEFPA-UC
BN26M-xx
BN26S-03
BN25H-03
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 23
Page 24
QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Gigabit Ethernet Adapter
Gigabit Ethernet Adapter
Gigabit Ethernet AdapterGigabit Ethernet Adapter
For maximum performance, HP recommends configuring two DEGPA-SA adapters (or less) per PCI drawer, however, eight adapters per PCI drawer may be
configured to achieve maximum connectivity.
PCI Gigabit Ethernet adapter, does not support network boot (BN34B)
PCI-to-Gigabit Ethernet UTP adapter (32-/64-bit) does not support network
boot uses BN 24Q, BN28Q, BN25Q, BN26M cables
Multimode fiber optic duplex cable, SC connector-to-SC connector,
xx=01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2E, 4E for 01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2.5, 4.5 meters
Category 5 cross-over cable for point-to-point, unshielded
xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1,3,4, 7, 0.5 meters
Category 5 cross-over cable for point-to-point, shielded
xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1,3,4, 7, 0.5 meters
Category 5 straight through for system to repeater or hub, unshielded, xx=01,
03, 04, 07, 0E, 0B for 1,3,4, 7, 0.5, 0.2 meters
Twisted pair, shielded cable,
xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1,3,4, 7, 0.5 meters
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
* = Tru64 UNIX V5.1 is required to support 16 adapters per System/Drawer. Tru64 UNIX 4.0G supports eight adapters per system/QBB..
8/16* 8/16*
4 4 4 4 4 4
8 16 16 8
DEGPA-SA
(EOL 12/03)
3X-DEGXA-SA
DEGPA-TA
(EOL 12/03)
3X-DEGXA-TA
BN34B-xx
BN24Q-xx
BN28Q-xx
BN25G-xx
BN26M-xx
ATM Adapters
ATM Adapters
ATM AdaptersATM Adapters
For maximum performance, HP recommends configuring four 3X-DAPCA-FA adapters (or less) per PCI drawer; however, eight adapters per PCI drawer may
be configured to achieve maximum connectivity.
PCI-to-ATMworks 155-Mbit adapter, fiber, uses BN34B cable
PCI-to-ATMworks 155-Mbit adapter, UTP, uses BN25G and BN26M cables
Multimode fiber optic duplex cable, SC connector-to-SC connector,
xx=01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2E, 4E for 01, 03, 10, 20, 30, 2.5, 4.5 meters
Category 5 straight through for system to repeater or hub, unshielded, xx=01,
03, 04, 07, 0E, 0B for 1,3,4, 7, 0.5, 0.2 meters
Category 5 straight through for system to repeater of hub, shielded
xx=01, 03, 04, 07, 0E for 1,3,4, 7, 0.5 meters
8 8 8 8 8 8
8 8 8 8 8 8
3X-DAPBA-FA
3X-DAPBA-UA
BN34B-xx
BN25G-xx
BN26M-xx
Synchronous Controllers
Synchronous Controllers
Synchronous ControllersSynchronous Controllers
PCI 2-port intelligent synchronous controller (OpenVMS/Tru64 UNIX systems
require a WAN/X.25 Kit. Refer to the latest option QuickSpecs for further
information
PCI 4-port intelligent synchronous controller (OpenVMS/Tru64 UNIX systems
require a WAN/X.25 Kit. Refer to the latest option QuickSpecs for further
information.
DataFire SYNC 2000 EIA-530 single-port cable
DataFire SYNC 2000 V.11/x.21 single-port cable
DataFire SYNC 2000 V.35 single-port cable
DataFire SYNC 2000 V.24/EIA232 single-port cable
4 4 4 10 10 10
4 4 4 10 10 10
3X-PBXDD-AA
3X-PBXDD-AB
3X-BC34G-06
3X-BC34S-06
3X-BC34T-06
3X-BC34L-06
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 24
Page 25

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Step 9 - MEMORY CHANNEL
Step 9 - MEMORY CHANNEL
Step 9 - MEMORY CHANNELStep 9 - MEMORY CHANNEL
Up to two PCI System Area Network controllers supported on a G320 partition
Two-node clusters can be configured by ordering a CCMAB-AA for each node and one BN39B-04 or BN39B-10 cable; cable connects directly to
CCMAB-AA in each node.
For a two-node cluster that will not be rebooted when adding additional members, order one CCMAB-AA adapter and one BN39B-04 or BN39B10 cable for each node, and one CCMHB-AA hub for the cluster.
For three or four node clusters, order one CCMAB-AA adapter and one BN39B-04 or BN39B-10 cable for each node and one CCMHB-AA hub for
the cluster
CCMHB-AA includes four CCMLB-AA line cards and supports up to four nodes; expansion up to eight system nodes can be achieved by adding up to
four additional CCMLB-AA line cards
If two or more CCMAB-AA controllers are configured in each node (dual rail), a second CCMHB-AA hub is required
If using a MEMORY CHANNEL adapter module (54-24962-01) prior to revision D02, up to two MEMORY CHANNEL adapters can be placed on
a PCI bus, however, no additional PCI devices can be placed on the same PCI bus, and the remaining slots must be left empty
Tru64 UNIX Systems
Tru64 UNIX Systems
Tru64 UNIX SystemsTru64 UNIX Systems
(V5.1 and later)
in Clusters using MEMORY
in Clusters using MEMORY
in Clusters using MEMORYin Clusters using MEMORY
CHANNEL Interconnect
CHANNEL Interconnect
CHANNEL InterconnectCHANNEL Interconnect
Each system in the cluster requires a TruCluster Server software license
(QL-6BRAQ-AA)
Alternately a TruCluster Plus Software package including licenses for: TruCluster Server, Logical Storage
Manager, and AdvFS Utilities can be ordered (QP-6R9AQ-AA)
OpenVMS Systems in
OpenVMS Systems in
OpenVMS Systems inOpenVMS Systems in
Clusters using MEMORY
Clusters using MEMORY
Clusters using MEMORYClusters using MEMORY
CHANNEL Interconnect
CHANNEL Interconnect
CHANNEL InterconnectCHANNEL Interconnect
MEMORY CHANNEL
MEMORY CHANNEL
MEMORY CHANNELMEMORY CHANNEL
Fiber Optic Cable Option
Fiber Optic Cable Option
Fiber Optic Cable OptionFiber Optic Cable Option
Requires OpenVMS V7.2-1H1 or later and OpenVMS Cluster license (QL-MUZAQ-AA)
In cases where nodes must be separated by a longer distance than standard copper cables
allow, the CCMFB option converts the output of the standard CCMAB controller or CCMLB
line card to single-mode fiber optic cable. The fiber optic connection may be up to 2,000
meters long between two CCMAB controllers connected in virtual hub mode, or 3,000 meters
between a CCMAB controller and a CCMHB hub. (The connection from the CCMHB hub to
a second system may also be 3,000 meters). The CCMFB option requires a second PCI slot in
the system from which it draws power only. It is normally connected to the corresponding
CCMAB controller with the short BN39B-01 cable. The CCMFB is also used in the CCMHB
hub where it occupies a slot normally used by the CCMLB line card, limiting expansion to four
radial fiber optic connections.
The CCMHB-BA hub expansion box provides additional slots for up to eight fiber optic
connections. Two standard length, single-mode fiber optic cables are available (BN34R-10 and
BN34R-31); however, users normally provide this connection. Customers should reference the
TIA/EIA 568-A Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard, Section 12.3.4.
Fiber optic connectivity is completely transparent to the systems using it and has no
performance impact.
Up to two CCMHB-AA hubs may be mounted in a 3X-H9A20-AD expansion cabinet by
utilizing a 2T-MAVRK-AA rack-mounting kit for each hub. A second MEMORY CHANNEL Hub
(CCMHB-AA or CCMHM-BA) mounted in an expansion cabinet reduces the amount of
StorageWorks shelves by one.
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 25
Page 26

QuickSpecs
Options
MEMORY CHANNEL
MEMORY CHANNEL
MEMORY CHANNELMEMORY CHANNEL
Controller
Controller
ControllerController
Country-specific Power
Country-specific Power
Country-specific PowerCountry-specific Power
Cords for Standalone
Cords for Standalone
Cords for StandaloneCords for Standalone
MEMORY CHANNEL
MEMORY CHANNEL
MEMORY CHANNELMEMORY CHANNEL
Hubs
Hubs
HubsHubs
PCI System Area Network controller, maximum two per system, two per node
System Area Network hub with four line cards; includes BN19P-2E power cord for Canada, Japan,
and U.S. operations; country-specific power cord for other regions is required
MEMORY CHANNEL hub expansion box with no line cards
MEMORY CHANNEL hub rack-mounting kit
Expansion line card for CCMHB hub
1-meter cable for CCMAB and CCMHB
4-meter cable for CCMAB and CCMHB
10-meter cable for CCMAB and CCMHB
Copper-to-single mode fiber optic converter
Australia, New Zealand
Central Europe
Denmark
Egypt, India
Ireland, United Kingdom
Israel
Italy
Switzerland
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
CCMAB-AA
CCMHB-AA
CCMHB-BA
2T-MAVRK-AA
CCMLB-AA
BN39B-01
BN39B-04
BN39B-10
CCMFB-AA
BN19H-2E
BN19C-2E
BN19K-2E
BN19S-2E
BN19A-2E
BN18L-2E
BN19M-2E
BN19E-2E
Power Cord for MEMORY
Power Cord for MEMORY
Power Cord for MEMORYPower Cord for MEMORY
CHANNEL Hubs
CHANNEL Hubs
CHANNEL HubsCHANNEL Hubs
Rackmounted in 3X-
Rackmounted in 3X-
Rackmounted in 3X-Rackmounted in 3XH9A20- ADAE/AF
H9A20- ADAE/AF
H9A20- ADAE/AFH9A20- ADAE/AF
Cabinets
Cabinets
CabinetsCabinets
IEC 320 power cord (one mandatory per hub)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
MEMORY CHANNEL hubs mounted in 3X-H9A20-AD cabinets do not require additional power cords.
BN35S-02
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 26
Page 27

QuickSpecs
Options
Step 10 - System Console Support
Step 10 - System Console Support
Step 10 - System Console SupportStep 10 - System Console Support
System Management
System Management
System ManagementSystem Management
Console
Console
ConsoleConsole
PC-based Windows 2000 system management console in tower package, includes network interface
cards and console software, U.S./Canada/Japan
PC-based Windows 2000 system management console in mini-tower package, includes network
interface cards and console software, Europe
PC-based Windows 2000 system management console in desktop package, includes network
interface cards and console software, U.S./Canada/Japan
PC-based Windows 2000 system management console in desktop package, includes network
interface cards and console software, Europe
Console hub for use with system management console, includes console concentrator, cables, and
universal power supply; mounts in system cabinet and communicates with the system management
console over Ethernet using the Telnet protocol.
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
AlphaServer GS320 systems require the ability to log console messages, provide remote access for service and
support, and, in some cases, manage multiple hardware partitions. The system management console is mandatory if
the customer has no other means to provide these capabilities.
PC-based system management console is required for system power-up, diagnostics, console partitioning, and console
display and logging for use with AlphaServer GS80/160/320 systems.
Includes network interface cards, universal modem, console software, 101-key keyboard, mouse, and console
documentation kit
A monitor is required for use with the system management console. Choose monitor listed in Step 12.
Systems configured with redundant consoles or employing hardware partitioning require the ability to connect
multiple consoles. A console hub is mandatory if the customer has no other means to provide these capabilities.
A console printer is recommended, but not required.
3X-DS8DA-AA
3X-DS8DA-AB
3X-DS8DA-BA
3X-DS8DA-BB
3X-DS8AA-AA
System Management
System Management
System ManagementSystem Management
Console - ConsoleWorks
Console - ConsoleWorks
Console - ConsoleWorksConsole - ConsoleWorks
Upgrade Licenses
Upgrade Licenses
Upgrade LicensesUpgrade Licenses
System management consoles include ConsoleWorks, which supports up to 8 partitions on a single system
Support for additional GS Series partitions on a second GS system require the purchase of an add on license for 2,
4, or 8 partitions on that system
Use of a single console for management of multiple GS systems requires use of a multiple port Ethernet Hub such as
HP Procurve Series
AlphaServer GS System Management, 2 Partition ConsoleWorks License from TECSys Development
LP
AlphaServer GS System Management, 2 Partition ConsoleWorks License from TECSys Development
LP
AlphaServer GS System Management, 8 Partitions ConsoleWorks License from TECSys Development
LP
QM-6K4AA-AB
QM-6K4AA-AC
QM-6K4AA-AD
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 27
Page 28

QuickSpecs
Options
System Management
System Management
System ManagementSystem Management
Console - Modem
Console - Modem
Console - ModemConsole - Modem
Localization Kits
Localization Kits
Localization KitsLocalization Kits
System management consoles include one adapter kit
In all other cases, the appropriate localization kit is required:
Australia
Austria
Belgium
China
Denmark
Finland, Norway
France
Germany
Greece
India
Italy
Netherlands
New Zealand
Sweden, Iceland
Switzerland
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
3X-DS8xA-AA/BA includes a localization kit for use in US, Canada, Japan, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Peru, and
Taiwan
3X-DS8xA-AB/BB includes a localization kit for use in Great Britain, Ireland, Hong Kong, Singapore, and Malaysia
3R-A1608-AA
3R-A1607-AA
3R-A1609-AA
3R-A1594-AA
3R-A1596-AA
3R-A1597-AA
3R-A1598-AA
3R-A1595-AA
3R-A1606-AA
3R-A1600-AA
3R-A1601-AA
3R-A1602-AA
3R-A1603-AA
3R-A1604-AA
3R-A1610-AA
System Management
System Management
System ManagementSystem Management
Console - Country-specific
Console - Country-specific
Console - Country-specificConsole - Country-specific
Power Cords
Power Cords
Power CordsPower Cords
Step 11 - Graphics Support
Step 11 - Graphics Support
Step 11 - Graphics SupportStep 11 - Graphics Support
Graphics support for an AlphaServer G320 can be provided through use of a graphics adapter
System management console includes a line cord for use in North America. Order a country-specific line cord if
required
Australia, New Zealand
Central Europe
Denmark
Egypt, India
Ireland, United Kingdom
Israel
Italy
Japan
North America
Switzerland
2D RADEON 7500 PCI graphics card, maximum one per system or hardware partition
BN19H-2E
BN19C-2E
BN19K-2E
BN19S-2E
BN19A-2E
BN18L-2E
BN19M-2E
3X-BN46F-02
BN26J-1K
BN19E-2E
3X-PBXGG-AA
(Q4 03)
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 28
Page 29

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Step 12 - Monitors, Keyboards, Mouse
Step 12 - Monitors, Keyboards, Mouse
Step 12 - Monitors, Keyboards, MouseStep 12 - Monitors, Keyboards, Mouse
Graphics monitors other than those listed below can be used if compatible with SVGA graphics ordered with system.
Selection of video extension cable and country-specific power cord is mandatory for all monitors; order power cord as appropriate.
Add or order appropriate keyboard and mouse
Monitors will ship with, but not be integrated with systems.
Keyboard or Mouse
Keyboard or Mouse
Keyboard or MouseKeyboard or Mouse
Extension Cable
Extension Cable
Extension CableExtension Cable
Video Extension Cable
Video Extension Cable
Video Extension CableVideo Extension Cable
Mouse
Mouse
MouseMouse
Carbon/Silver Monitors
Carbon/Silver Monitors
Carbon/Silver MonitorsCarbon/Silver Monitors
6-foot (1.8-meter) keyboard or mouse extension cable (order two cables to extend both keyboard
and mouse)
6-foot (1.8-meter) video extension cable
3-button mouse – carbon
V7550 17-inch (16-inch viewable image size) flat-faced shadow mask color monitor, two-tone
(carbon/silver), 0.25mm dot pitch, VGA to 1024 x 768 @85 Hz, MPRII/TCO99/Energy Star
compliant, Northern Hemisphere with North America power cord, VGA cable
Same as above, with Euro power cord
Same as above, APD, no power cord
Same as above, Southern Hemisphere, with Australia/New Zealand power cord
S7500 17-inch (16-inch viewable image size) FST multi-frequency color monitor,
2-tone (carbon/silver), 0.24-mm dot pitch, VGA to 1024 x 768 @ 85 Hz, MPRII/TCO 99/Energy
Star Compliant, Northern Hemisphere with PRC power cord CCIB, VGA cable
P930 19-inch (18-inch viewable image size) auto-scanning color monitor, Diamondtron NF, 0.24-mm
aperture grille pitch, VGA to 1600 x 1200 @85 Hz, MPRII/TCO 99/Energy Star Compliant,
Northern Hemisphere with North America power cord, VGA cable
Same as above, with Euro power cord
Same as above, Taiwan, with North America power cord
Same as above, Southern Hemisphere, 0.25 to 0.27 mm aperture grille pitch, with Australia/New
Zealand power cord
S9500 19-inch (18-inch viewable image size) FST multi-frequency color monitor,
2-tone (carbon/silver), 0.24-mm dot pitch, VGA to 1280 x 1024 @ 85 Hz, MPRII/TCO 99/Energy
Star Compliant, Northern Hemisphere with PRC power cord CCIB, VGA cable
P1130 21-inch (19.8-inch viewable image size) FD Trinitron auto-scanning color monitor, 0.24-mm
aperture grille pitch, VGA to 1792 x 1344 @85Hz, dual video input, USB Hub, MPRII/TCO
99/Energy Star Compliant, Northern Hemisphere with North America power cord, VGA cable
Same as above, with Euro power cord
Same as above, Taiwan, no power cord
Same as above, with PRC power cord, CCIB
Same as above, Southern Hemisphere, with Australia/New Zealand power cord
3X-BC34A-06
BN39C-02
3R-A3480-AA
3R-A4002-AA
3R-A4201-AA
3R-A4202-AA
3R-A4203-AA
3R-A4800-AA
3R-A4215-AA
3R-A4391-AA
3R-A4392-AA
3R-A4393-AA
3R-A4801-AA
3R-A4216-AA
3R-A4396-AA
3R-A4397-AA
3R-A4400-AA
3R-A4398-AA
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 29
Page 30

QuickSpecs
Options
Carbon/Silver Flat Panel
Carbon/Silver Flat Panel
Carbon/Silver Flat PanelCarbon/Silver Flat Panel
Monitors
Monitors
MonitorsMonitors
Monitor Power Cords
Monitor Power Cords
Monitor Power CordsMonitor Power Cords
Keyboards
Keyboards
KeyboardsKeyboards
TFT1825, 18-inch (18-inch viewable image size) TFT flat panel monitor, 0.28-mm pixel pitch, 1600 x
1200 @60 Hz, multi-mode support, MPRII/TCO99/Energy Star compliant, one VGA, one DVI-I input
connector, North America power cord, VGA, and DVI-I cables
TFT1520, 15-inch (15-inch viewable image size) TFT flat panel monitor, 0.297-mm pixel pitch, 1024
x 768 @75 Hz, multi-mode support, MPRII/TCO99/Energy Star compliant, two video input
connectors (one VGA and one DVI-I), North America power cord, VGA, and DVI-I cables
Australia, New Zealand
Central Europe
Denmark
Egypt, India
Ireland, United Kingdom
Italy
Japan
North America
Switzerland
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Select a keyboard and mouse
Select an opal OpenVMS keyboard for use with VT5xx text terminals
All keyboards listed may not be available in all geographies
3R-A4292-AA
3R-A4249-AA
BN19H-2E
BN19C-2E
BN19K-2E
BN19S-2E
BN19A-2E
BN19M-2E
3X-BN46F-02
BN26J-1K
BN19E-2E
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 30
Page 31

QuickSpecs
Options
Keyboard/Language
Keyboard/Language
Keyboard/LanguageKeyboard/Language
U.S./English keyboard
Arabic keyboard
Belgian keyboard
BHCSY keyboard
Canadian/English keyboard
Canadian/French keyboard
Cyrillic keyboard (Russian)
Czech keyboard
Danish keyboard
Dutch keyboard
Finnish keyboard
French keyboard
German keyboard
Greek keyboard
Hebrew keyboard
Hungarian keyboard
International keyboard
Italian keyboard
Japanese keyboard
Korean keyboard
Latin-American keyboard
Norwegian keyboard
Polish keyboard
Portuguese keyboard
Romanian keyboard
Simplified Chinese keyboard
Slovak keyboard
Spanish keyboard
Swedish keyboard
Swiss/French keyboard
Swiss/German keyboard
Traditional Chinese keyboard
Thai keyboard
Turkish Q keyboard
Turkish/F keyboard
UK keyboard
Yugoslavian keyboard
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMSOpenVMS
LK461-A2
LK461-AB
LK461-AQ
LK461-AC
LK461-BT
LK461-BV
LK461-AD
LK461-AH
LK461-AF
LK461-AP
LK461-AG
LK461-BH
LK461-AT
LK461-BQ
LK461-AI
-
-
LK461-AN
LK461-BP
LK461-AV
LK461-BL
LK461-CZ
LK461-AS
LK461-AM
LK461-AK
LK461-AL
-
LK461-BU
LK461-BW
LK461-BY
Opal
Opal
OpalOpal
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIXTru64 UNIX
3R-A4362-AA
3R-LKQ48-BR
3R-LKQ48-AB
3R-LKQ48-AX
3R-LKQ48-AC
3R-LKQ48-BT
3R-LKQ48-BV
3R-LKQ48-AD
3R-LKQ48-AH
3R-LKQ48-AF
3R-LKQ48-AP
3R-A4358-AA
3R-LKQ48-BH
3R-LKQ48-AT
3R-LKQ48-BQ
3R-A4362-AA
3R-A4363-AA
3R-LKQ48-AJ
3R-LKQ48-BK
3R-LKQ48-AR
3R-LKQ48-AN
3R-LKQ48-BP
3R-LKQ48-AV
3R-A4370-AA
3R-LKQ48-CZ
3R-A4372-AA
3R-LKQ48-AM
3R-A4374-AA
3R-LKQ48-BI
3R-LKQ48-CB
3R-LKQ48-BU
3R-A4378-AA
-
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Carbon
Carbon
CarbonCarbon
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMSOpenVMS
3X-LK462-A2
3X-LK462-AB
3X-LK462-AQ
3X-LK462-AC
3X-LK462-BT
3X-LK462-BV
3X-LK462-AD
3X-LK462-AH
3X-LK462-AF
3X-LK462-AP
3X-LK462-AG
3X-LK462-BH
3X-LK462-AT
3X-LK462-BQ
3X-LK462-AI
-
-
3X-LK462-AI
3X-LK462-BP
3X-LK462-AV
3X-LK462-BL
3X-LK462-CZ
3X-LK462-AS
3X-LK462-AM
3X-LK462-AK
3X-LK462-AL
-
3X-LK462-BU
3X-LK462-BW
3X-LK462-BY
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 31
Page 32

QuickSpecs
Options
Step 13 - System Software
Step 13 - System Software
Step 13 - System SoftwareStep 13 - System Software
Media and documentation required for first system on site
Software Processor Code = Q
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIX
Tru64 UNIXTru64 UNIX
When using Tru64 UNIX
When using Tru64 UNIX
When using Tru64 UNIXWhen using Tru64 UNIX
V5.1 or later
V5.1 or later
V5.1 or laterV5.1 or later
Tru64 UNIX base systems include pre-installed software, Base license, Unlimited User license,
Server Extension license, Internet Express, and Secure Web Server
Tru64 UNIX media and online documentation on CD-ROM
Tru64 UNIX full hard copy documentation
TruCluster Plus Software Package with licenses for TruCluster Server, Logical Storage Manager, and
AdvFS Utilities
TruCluster Server license
Logical Storage Manager License
AdvFS Utilities License
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 25 client concurrent use license
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 50 client concurrent use license
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 100 client concurrent use license
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 250 client concurrent use license
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 500 client concurrent use license
Layered products media and documentation for Tru64 UNIX on CD-ROM
DECnet/OSI end-system license for Tru64 UNIX
DECnet/OSI extended function license for Tru64 UNIX
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
QA-6ADAA-H8
QA-6ADAA-GZ
QP-6R9AQ-AA
QL-6BRAQ-AA
QL-2GVAQ-AA
QL-0EGAQ-AA
QL-5U29M-3D
QL-5U29M-3E
QL-5U29M-3F
QL-5U29M-3G
QL-5U29M-3H
QA-054AA-H8
QL-MTJAQ-AA
QL-MTKAQ-AA
When using Tru64 UNIX
When using Tru64 UNIX
When using Tru64 UNIXWhen using Tru64 UNIX
V4.0G
V4.0G
V4.0GV4.0G
Tru64 UNIX media and online documentation on CD-ROM
Tru64 UNIX full hard copy documentation
StorageWorks software package with licenses for Logical Storage Manager and AdvFS Utilities
TruCluster Available Server license
TruCluster Production Server license
Tru64 UNIX Driver for MEMORY CHANNEL license
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 25 Client Concurrent License
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 50 Client Concurrent License
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 100 Client Concurrent License
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 250 Client Concurrent License
Advanced Server for Tru64 UNIX, 500 Client Concurrent License
Layered products media and documentation for Tru64 UNIX on CD-ROM
DECnet/OSI end-system license
DECnet/OSI extended function license
QA-MT4AA-H8
QA-MT4AA-GZ
QB-5RXAQ-AA
QL-05SAQ-AA
QB-3RLAQ-AA
QB-4ZCAQ-AA
QL-5U29M-3D
QL-5U29M-3E
QL-5U29M-3F
QL-5U29M-3G
QL-5U29M-3H
QA-054AA-H8
QL-MTJAQ-AA
QL-MTKAQ-AA
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 32
Page 33

QuickSpecs
Options
OpenVMS
OpenVMS
OpenVMSOpenVMS
Concurrent Use 1-user license
Concurrent Use 2-user license
Concurrent Use 4-user license
Concurrent Use 8-user license
Concurrent Use 16-user license
Concurrent Use 32-user license
Concurrent Use 64-user license
Concurrent Use 128-user license
Concurrent Use 256-user license
Traditional unlimited-user license
OpenVMS V7.2-1H1 media and online documentation on CD-ROM
OpenVMS media and documentation on CD-ROM
OpenVMS base hard copy documentation
Layered products media and documentation for OpenVMS on CD-ROM; includes HP Enterprise
Integration Server for OpenVMS media and documentation
DECnet/OSI end-system license
DECnet/OSI extended-function license
Cluster License for OpenVMS Alpha
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
OpenVMS system base packages include Base license and HP Enterprise Integration Server for OpenVMS License
Package Revision V3.0A
OpenVMS Concurrent Use licenses provide the right to interactively use the operating system by the specified
number of concurrent users on a designated OpenVMS system. OpenVMS Concurrent Use licenses can be moved
from one system to another at user discretion and can be shared in a mixed OpenVMS VAX and OpenVMS Alpha
cluster.
QL-MT3AA-3B
QL-MT3AA-3C
QL-MT3AA-3D
QL-MT3AA-3E
QL-MT3AA-3F
QL-MT3AA-3G
QL-MT3AA-3H
QL-MT3AA-3J
QL-MT3AA-3K
QL-MT2AQ-AA
QA-MT1AU-H8
QA-MT1AA-H8
QA-09SAA-GZ
QA-03XAA-H8
QL-MTFAQ-AA
QL-MTGAQ-AA
QL-MUZAQ-AA
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 33
Page 34
QuickSpecs
Options
OpenVMS Galaxy -
OpenVMS Galaxy -
OpenVMS Galaxy -OpenVMS Galaxy OpenVMS Galaxy
OpenVMS Galaxy
OpenVMS GalaxyOpenVMS Galaxy
Licensing Requirements
Licensing Requirements
Licensing RequirementsLicensing Requirements
For more details about OpenVMS Galaxy licensing requirements, refer to the Software Product
Description for the Galaxy Software Architecture on OpenVMS Alpha: SPD 70.44.xx
For more information about OpenVMS Galaxy requirements, configurations, and procedures, refer to
the OpenVMS Alpha Galaxy Guide. The latest version is always available at
http://www.openvms.hp.com/gsseries/index.html.
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Galaxy 1-CPU License
Galaxy 2-CPU License
Galaxy 4-CPU License
Galaxy 8-CPU License
Galaxy 16-CPU License
Example: 24-CPU GS320 system in which all processors are licensed for OpenVMS with two hard
partitions (one 8-CPU SMP and one 16-CPU Galaxy)
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
One SMP Extension License (included in the SMP CPU upgrade) is mandatory for each CPU
after the first CPU.
For each AlphaServer GS320 CPU in an OpenVMS Galaxy, one OpenVMS Galaxy License is
mandatory.
HP layered products are licensed as follows:
One capacity license per system
One user license per use
One capacity license per system
One user license per use
Up to eight instances of OpenVMS are supported in OpenVMS Galaxy configurations on
AlphaServer GS320 Model 32 systems, up to six instances on Model 24 systems.
One OpenVMS Base Operating System License (included in base system) is mandatory for
AlphaServer GS320 configured as an OpenVMS Galaxy system.
.
This website is available in English only.
QL-66XAA-3B
QL-66XAA-3C
QL-66XAA-3D
QL-66XAA-3E
QL-66XAA-3F
Base system order would include a DY-320DE-Ax and 23 3X-KN8AB-AE SMP upgrade CPUs
Add one QL-66XAA-3E Galaxy 8-CPU license and one QL-66XAA-3F Galaxy 16-CPU license
for a total of 16 Galaxy licenses for the 16-CPU hard partition with Galaxy.
No other licenses are required for OpenVMS on the SMP instance in the second hard partition
with eight CPUs.
Step 14 - Hardware and Software Support Services
Step 14 - Hardware and Software Support Services
Step 14 - Hardware and Software Support ServicesStep 14 - Hardware and Software Support Services
Installation or Installation and Startup is required for all AlphaServer GS320 systems.
Select one of the optional HP Care Pack Service Packages described below that best supports the customer's operational requirements for system
availability.
HP Care Pack Services
HP Care Pack Services
HP Care Pack ServicesHP Care Pack Services
HP Care Pack Services are available for AlphaServer systems running Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS operating systems.
HP Care Pack Services are designed for customers who require support beyond that provided by the hardware
product warranty with coverage for both Principal servers systems and SSPs (Subsequent System Packages) - that
meet a full range of customer support requirements.
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 34
Page 35
QuickSpecs
Options
Program Features – Principal Server
Program Features – Principal Server
Program Features – Principal ServerProgram Features – Principal Server
HP Support Plus
HP Support Plus
HP Support PlusHP Support Plus
HP Support Plus 24
HP Support Plus 24
HP Support Plus 24HP Support Plus 24
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
13 x 5 HW/SW support
4-hour response on-site hardware support
2-hour response for software support
License Subscription for HP O/S software and embedded L/P
(i.e., EIS for OpenVMS, unlimited users, and server extensions for Tru64 UNIX)
Consolidated Software Media Update Distribution for OpenVMS or Tru64 UNIX and their
layered products. (Some layered products on Consolidated Media Update Distribution can be
ordered separately.)
24 x 7 HW/SW support
Named HW engineer
4-hour response on-site hardware support
2-hour response for software support
License Subscription for HP O/S software and embedded L/P
(i.e., EIS for OpenVMS, unlimited users, and server extensions for Tru64 UNIX)
Consolidated Software Media Update Distribution for OpenVMS or Tru64 UNIX and their
layered products. (Some layered products on Consolidated Media Update Distribution can be
ordered separately.)
SSPs
SSPs
SSPsSSPs
(Subsequent System Packages)
Installation
Installation
InstallationInstallation
Installation & Startup HP
Installation & Startup HP
Installation & Startup HPInstallation & Startup HP
O/S
O/S
O/SO/S
Program Features – Additional Services
Program Features – Additional Services
Program Features – Additional ServicesProgram Features – Additional Services
For HP Care Pack Support Plus and Support Plus 24
HW Support at same level as corresponding package for Principal server
License Subscription: HP O/S (where applicable)
Telephone support through Principal server covered by full support package
Preinstallation review
Unpacking of equipment
Assemble and test
Basic product usage info
No software installation added
Preinstallation review
Unpacking of equipment
Assemble and test
Basic product usage info
Install operating systems
Product configuration
Print and network access
Orientation
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 35
Page 36
QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Model/HP
Model/HP
Model/HPModel/HP
Care Pack
Care Pack
Care PackCare Pack
Services
Services
ServicesServices
AlphaServer GS320 Model 24
AlphaServer GS320 Model 24
AlphaServer GS320 Model 24AlphaServer GS320 Model 24
HP Support Plus
HP Support Plus 24
Installation
Installation & Startup
AlphaServer GS320 Model 32
AlphaServer GS320 Model 32
AlphaServer GS320 Model 32AlphaServer GS320 Model 32
HP Support Plus
HP Support Plus 24
Installation
Installation & Startup
NOTES
NOTES
:
NOTESNOTES
AlphaServer GS320 systems include one-year hardware warranty with 5 x 9, on-site Next Business Day response.
HP Care Pack Services include support for new HP branded hardware options internal to the AlphaServer enclosure plus a monitor (17-inch or less
excluding flat panel models).
External storage devices/cabinets carry their own level of warranty and should be quoted separately for uplifted warranty services.
In addition to the HP Care Pack Services shown above, other service packages are available for separate hardware and software support.
For more information on Hardware and Software Upfront Services and other HP service options available for AlphaServers, consult your Sales
Account Manager, HP Services Principal, or visit
Software - Americas and
Software - Americas and
Software - Americas andSoftware - Americas and
Asia Pacific Only
Asia Pacific Only
Asia Pacific OnlyAsia Pacific Only
Principal Server
Principal Server
Principal ServerPrincipal Server
1 year
1 year
1 year1 year
FP-W0105-12 FP-W0105-36 FP-W2105-12 FP-W2105-36
FP-W0205-12 FP-W0205-36 FP-W2205-12 FP-W2205-36
FP-WINST-32 FP-WINST-32 FP-WINST-32 FP-WINST-32
FP-WSTAR-32 FP-WSTAR-32 FP-WSTAR-32 FP-WSTAR-32
FP-W0106-12 FP-W0106-36 FP-W2106-12 FP-W2106-36
FP-W0206-12 FP-W0206-36 FP-W2206-12 FP-W2206-36
FP-WINST-32 FP-WINST-32 FP-WINST-32 FP-WINST-32
FP-WSTAR-32 FP-WSTAR-32 FP-WSTAR-32 FP-WSTAR-32
Systems include 90-day Conformance to SPD; select optional Software Support Services if
required.
Software service for Tru64 UNIX include advisory and remedial software support with new
version license rights for Tru64 UNIX Base, unlimited users, and Server Extensions
Software service for OpenVMS include advisory and remedial software support with new
version license rights for OpenVMS Base and Enterprise Integration Package
Principal Server
Principal Server
Principal ServerPrincipal Server
3 years
3 years
3 years3 years
http://www.hp.com/services/
Subsequent Systems
Subsequent Systems
Subsequent SystemsSubsequent Systems
1 year
1 year
1 year1 year
--
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
This website is available in English only.
Subsequent Systems
Subsequent Systems
Subsequent SystemsSubsequent Systems
3 years
3 years
3 years3 years
Recommended Factory
Recommended Factory
Recommended FactoryRecommended Factory
Integration Services
Integration Services
Integration ServicesIntegration Services
Value-added Implementation Services (VIS) provides systems integration and delivery services. VIS
services, including system integration, extended burn-in, custom documentation, and on-site services can
be custom-quoted for the full range of AlphaServer configurations.These pre-packaged services are
offered for systems shipped to North America and Japan. For similar services in Europe, e-mail specific
requirements to:
Pre-packaged VIS services are recommended for popular AlphaServer GS160 system configurations
that include up to one storage array:
Basic Integration Service (YT-CSSIT-V1) System integration, testing, extended burn-in, custom
documentation, and installation of a single operating system instance
Partioning Service (YT-CSSIT-P1) Configuration of additional instances of an operating system
System integration, testing, extended burn-in, and custom documentation of hardwarepartitioned systems
customsystems.europe@hp.com
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 36
Page 37
QuickSpecs
Options
Basic Integration Service
Basic Integration Service
Basic Integration ServiceBasic Integration Service
Partitioning Service
Partitioning Service
Partitioning ServicePartitioning Service
Systems integration and delivery services related to the configuration of the first and/or only instance
of an operating system on a single AlphaServer GS320 platform. Includes the following:
Configuration of multiple, non-clustered instances of a second or subsequent operating system on a
single AlphaServer GS320 platform. This service is ordered along with the required YT-CSSIT-V1.
Order one (1) YT-CSSIT-P1 option for the second hardware partition and for each additional hardware
partition on an AlphaServer GS320 system. Includes the following:
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
YT-CSSIT-V1
Staging and Integration of the AlphaServer GS320
Software load of a single instance of an operating system and current revisions of firmware
Hardware configuration, custom placement, and integration of internal options of the server
per customer specifications
Installation of a single instance of either Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS Operating System
Configuration, exercise, and test of up to one intelligent RAID array controller and associated
disks per customer requirements
Testing of the system and its components for a full 100 hour burn-in
Mini-CCD (Custom Configuration Documentation) containing equipment listing, system
environmental information, and software version levels
YT-CSSIT-P1
Technical edit of order to guide component selection and option placement
Software load of an instance of an operating system on a hardware/software partition
Configuration and hardware integration (as described above) of the server partition per
specifications
Partition testing with the system and its components during the 100 hour burn-in
Extra RAID Pair Service
Extra RAID Pair Service
Extra RAID Pair ServiceExtra RAID Pair Service
Clustering Service
Clustering Service
Clustering ServiceClustering Service
Configuration of additional Intelligent RAID controller pairs beyond the internal and external RAID
controller pairs included within the scope of the prerequisite YT-CSSIT-V1 and/or optional YT-CSSIT-P1
services on the same single AlphaServer GS320 platform. The following services are included in the
optional YT-CSSIT-R1 Extra RAID Pair Service per each additional pair of Intelligent RAID controllers
configured:
Technical edit of order to guide component selection and option placement
Configuration of the disks of the additional controller pair per customer specifications
Hardware configuration verification
Custom disk placement and verification
Installation of current revisions of firmware
Configuration, exercise and testing of up to one pair of additional intelligent array controller
pair and associated disk drives for each YT-CSSIT-R1
Controller and disk testing with the system and its components during the 100 hour burn-in
Configuration of a single cluster instance for AlphaServer GS320 platforms. This is a per-cluster service
and is ordered along with the prerequisite YT-CSSIT-V1 services.
Technical edit of order to guide component selection and option placement
Configuration of a cluster per specifications
Hardware and software configuration verification
Installation of either Tru64 UNIX TruCluster software or OpenVMS cluster software and
configuration of node functions
Installation of current revisions of firmware
Cluster failover testing with the system and its components during the full 100 hour burn-in
YT-CSSIT-R1
YT-CSSIT-C1
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 37
Page 38

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Options
Full Custom
Full Custom
Full CustomFull Custom
Configurations
Configurations
ConfigurationsConfigurations
Step 15 - Recommended Online Power Protection/UPS Solutions for AlphaServer GS320
Step 15 - Recommended Online Power Protection/UPS Solutions for AlphaServer GS320
Step 15 - Recommended Online Power Protection/UPS Solutions for AlphaServer GS320Step 15 - Recommended Online Power Protection/UPS Solutions for AlphaServer GS320
A dual-AC power option provides the capability to connect to two separate synchronized AC feeds: a primary AC feed and a secondary AC feed.
The feeds can be direct from the power utility, or they can be a combination of utility feeds and UPS or generator feeds. The preferred (primary)
feed is chosen and set by the user. In the event of failure of the primary feed, the switch will automatically transfer the load to the secondary feed
without power interruption. The selected AC feed can also be switched manually.
The option cabinet must be positioned adjacent to the system power cabinet and it is bolted to it.
Power requirements for the dual AC power option are identical to the system to which it is connected.
The dual-AC switch option can be factory configured or installed as a field upgrade.
The primary and secondary 3-phase AC sources must be nominally of the same level, frequency and phase rotation. To ensure virtually uninterrupted
transfers between the two AC sources, the two input sources must be synchronized, typically within 5 to 15 electrical degrees. Questions regarding
the dual-AC option can be answered by an environmental specialist at 1-800-354-9000.
The primary and secondary 3-phase AC sources must have a THD of less than 10%.
The dual-AC power option consists of two component types:
One AC switch configured within an H9A20 cabinet (3X-H7512-AC/AD). The cabinet has dedicated mounting space for a second AC switch that is
not included.
A second electronic AC switch (3X-H7512-BA/BB) that mounts within the 3X-H7512-AC/AD cabinet.
AlphaServer GS320 Model 24 and Model 32 systems require both the 3X-H7512-AC/AD and the 3X-H7512-BA/BB
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
feeds.
3X-H9A20-AD/AE/AF expansion cabinets include N+1 power on separate power controllers and may be directly connected to two different AC
The Integration Service Packages address the most-common customer requirements. For a wider range
of configurations, customers can also choose additional customized services based upon a Statement
of Work agreement. This includes: cluster add-on nodes, larger storage configurations, custom option
support, custom system packaging, mixed operating system partitions, and configured multi-system
clusters. Contact your Custom Solutions provider or Sales Representative for these services.
Black dual AC transfer switch. Requires 3X-H7512-BA for use with AlphaServer GS320 Model 24
and Model 32 systems, for use in US/Canada, 120/208V
Black dual AC transfer switch. Requires 3X-H7512-BB for use with AlphaServer GS320 Model 24
and Model 32 systems, for use in Europe, 380-415V
Dual AC transfer switch upgrade for use with AlphaServer GS320 Model 24 and Model 32 systems;
requires 3X-H7512-AC, for use in US/Canada, 120/208V
Dual AC transfer switch upgrade for use with AlphaServer GS320 Model 24 and Model 32 systems;
requires 3X-H7512-AD, for use in Europe, 380-415V
3X-H7512-AC
3X-H7512-AD
3X-H7512-BA
3X-H7512-BB
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 38
Page 39

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Upgrades
AlphaServer GS320 System Hardware Expansion
AlphaServer GS320 System Hardware Expansion
AlphaServer GS320 System Hardware ExpansionAlphaServer GS320 System Hardware Expansion
An AlphaServer GS320 Model 24 can be internally upgraded to an AlphaServer GS320 Model 32 by adding two quad building blocks.
AlphaServer 320 731-MHz to 1224-MHz System Hardware Upgrades
AlphaServer 320 731-MHz to 1224-MHz System Hardware Upgrades
AlphaServer 320 731-MHz to 1224-MHz System Hardware UpgradesAlphaServer 320 731-MHz to 1224-MHz System Hardware Upgrades
AlphaServer 320 731-MHz or 1001-MHz systems are field upgradeable to 1224-MHz systems.
System Speed Hardware
System Speed Hardware
System Speed HardwareSystem Speed Hardware
System expansion hardware to upgrade an AlphaServer GS320 Model 24 to an AlphaServer GS320
Model 32. Includes two quad building blocks and associated power supplies and cabling.
Upgrades require the return of the replaced System Box and SMP Modules
System Upgrade Hardware to upgrade a 731-MHz or 1001-MHz Tru64 UNIX AlphaServer GS160
to 1224-MHz - includes a dual QBB system box upgrade to 16 MB of cache, eight 1224-MHz CPU
modules, and Tru64 UNIX Licenses.
System Upgrade Hardware to upgrade a 731-MHz or 1001-MHz OpenVMS AlphaServer GS160
to 1224-MHz - includes a dual QBB system box upgrade to 16 MB of cache, eight 1224-MHz CPU
modules, and OpenVMS Licenses.
DH-320EH-AX
DH-160CA-AU
DH-160CA-BU
FRU Level Upgrade
FRU Level Upgrade
FRU Level UpgradeFRU Level Upgrade
Global Clock Module
Global Clock Module
Global Clock ModuleGlobal Clock Module
Upgrade
Upgrade
UpgradeUpgrade
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
them with higher speed CPUs) must order the specified clock option.
AlphaServer 731-MHz
AlphaServer 731-MHz
AlphaServer 731-MHzAlphaServer 731-MHz
GS320 System Hardware
GS320 System Hardware
GS320 System HardwareGS320 System Hardware
Appearance Upgrades
Appearance Upgrades
Appearance UpgradesAppearance Upgrades
HP Capacity on Demand (CoD) Program
HP Capacity on Demand (CoD) Program
HP Capacity on Demand (CoD) ProgramHP Capacity on Demand (CoD) Program
AlphaServer GS320 customers can add additional CPU capacity on demand without waiting to purchase the resource when it is required and without re-
booting their system. The HP Capacity on Demand Program, outlined below, is a two-part process.
Part 1
Part 1
Part 1Part 1
When ordering an upgrade, blue cabinet users with 731-MHz EV67 CPUs, who are planning on discontinuing use of the 731-MHz CPUs (not mixing
Contact HP Services for detailed information
Contact HP Services for detailed information
Contact HP Services for detailed informationContact HP Services for detailed information
System Box Level Upgrade to upgrade existing 4-MB or 8-MB cache capable System Box to 16-MB
cache capable system Box
GS160/320 SMP upgrade CPU, 6/1224-MHz with 16-MB on-board cache, Tru64 UNIX
GS160/320 SMP upgrade CPU, 6/1224-MHz with 16-MB on-board cache, OpenVMS
GS160/320 Model M16 10-port Clock Module Upgrade - required for AlphaServer GS320 731MHz system upgrades.
AlphaServer trim panel can be ordered to change external top gun blue skins to carbon black
AlphaServer GS320 top gun blue to carbon black conversion skin kit
H9A20-AA/AB/AC Expansion Cabinet GS320 top gun blue to carbon black conversion skin kit
Customer purchases a system with Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS CoD SMP CPU(s) (3X-KN8CAAD or 3X-KN8CA-AE), or customer purchases Tru64 UNIX or OpenVMS CoD SMP CPU(s) for
field installation within an installed AlphaServer GS320 system.
When purchasing the CoD CPU(s), the customer signs a CoD program agreement to purchase
the CPU module(s) within 18 months or upon "first use" of the module(s).
A blank copy of the agreement is available through your local HP representative or call 1-800282-6672 -- Full program terms are outlined in this agreement.
3X-BA51A-GU
3X-KN8AC-AD
3X-KN8AC-AE
3X-WFCLK-CA
CK-GSBCK-AC
CK-GSBCK-AD
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 39
Page 40
QuickSpecs
Upgrades
Part 2
Part 2
Part 2Part 2
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
option price.
GS160/320 CoD SMP CPU, includes one 6/1224-MHz CPU module with 16-MB on-board cache
and Tru64 UNIX SMP license for use under the CoD program terms
GS160/320 CoD SMP CPU, includes: one 6/1224-MHz CPU module with 16-MB on-board cache
and OpenVMS SMP license for use under the CoD program terms
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
The customer will be invoiced for the CPU module(s) upon notification by the customer of "first
use" or expiration of the 18-month period.
CoD CPUs are field installed. Field installation on existing systems is not included in the CPU
3X-KN8CC-AD
3X-KN8CC-AE
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 40
Page 41

QuickSpecs
TechSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
Physical Characteristics
Physical Characteristics
Physical CharacteristicsPhysical Characteristics
Heat dissipation
Heat dissipation
Heat dissipationHeat dissipation
GS320 Model 24
GS320 Model 24 GS320 Model 32
GS320 Model 24GS320 Model 24
Dimensions
Dimensions
DimensionsDimensions
(H x W x D)
Shipping Dimensions
Shipping Dimensions
Shipping DimensionsShipping Dimensions
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
represent the largest of the cabinets
Weight Maximum
Weight Maximum
Weight MaximumWeight Maximum
Configuration
Configuration
ConfigurationConfiguration
Maximum Shipping
Maximum Shipping
Maximum ShippingMaximum Shipping
Weight
Weight
WeightWeight
Minimally configured
Minimally configured
Minimally configuredMinimally configured
system
system
systemsystem
(system and power cabinet)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
system I/O module, minimally configured PCI shelf, and one disk drive.
Fully configured system
Fully configured system
Fully configured systemFully configured system
(system and power cabinet)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
I/O modules, two PCI shelves, and a single storage shelf with six disk drives. Fully configured Model 32 systems include 12
power supplies, 32 CPU modules, 32 memory modules, 16 system I/O modules, two PCI shelves, and a single storage
shelf with six disk drives.
Fully configured system
Fully configured system
Fully configured systemFully configured system
(system cabinet with two I/O
expansion cabinets)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
expansion cabinets, each includes three PCI shelves, four StorageWorks shelves, and 24 disk drives.
The AlphaServer GS320 is shipped in three cabinets, which are joined in the field. The shipping dimensions shown
Minimally configured system contains six or eight power supplies, single CPU module, single memory module, single
Fully configured Model 24 systems include nine power supplies, 24 CPU modules, 24 memory modules, 12 system
"Fully configured system and two expansion cabinets" consist of the above "fully configured system" plus two
67 x 55.1 x 39.4 in
(170 x 140 x 100 cm)
76.5 x 44 x 48 in
(195 x 112 x 122 cm)
1,978 lb (897 kg) 2,168 lb (983 kg)
2,238 lb (1,014 kg)
5,000 W (17,100 Btu/hr) 6,400 W (21,900 Btu/hr)
9,300 W (31,800 Btu/hr)
14,000 W (47,800 Btu/hr) 16,400 W (56,000 Btu/hr)
GS320 Model 32
GS320 Model 32GS320 Model 32
67 x 55.1 x 39.4 in
(170 x 140 x 100 cm)
76.5 x 44 x 48 in
(195 x 112 x 122 cm)
2,428 lb (101 kg)
11,700 W (40,000 Btu/hr)
Clearances
Clearances
ClearancesClearances
Environmental
Environmental
EnvironmentalEnvironmental
Front
Front
FrontFront
Rear
Rear
RearRear
Left Side
Left Side
Left SideLeft Side
Right Side
Right Side
Right SideRight Side
Temperature
Temperature
TemperatureTemperature
Humidity
Humidity
HumidityHumidity
Altitude
Altitude
AltitudeAltitude
Vibration
Vibration
VibrationVibration
Operating
Operating
OperatingOperating
29.5 in (75 cm) 29.5 in (75 cm)
29.5 in (75 cm) 29.5 in (75 cm)
None None
None None
Operating
Operating
OperatingOperating
41° to 95° F (5° to 35° C)
10% to 90% 10% to 95%
0 to 10,000 ft (0 to 3 km)
5 to 500 Hz @ .1G maximum
Service
Service
ServiceService
Non-Operating
Non-Operating
Non-OperatingNon-Operating
–40° to 151° F (–40° to 66° C)
40,000 ft (12.2 km)
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 41
Page 42

QuickSpecs
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
TechSpecs
Regulatory
Regulatory
RegulatoryRegulatory
Power Requirements
Power Requirements
Power RequirementsPower Requirements
Nominal voltage(s)
Nominal voltage(s)
Nominal voltage(s)Nominal voltage(s)
Frequency range
Frequency range
Frequency rangeFrequency range
Phases
Phases
PhasesPhases
Maximum input
Maximum input
Maximum inputMaximum input
current/circuit
current/circuit
current/circuitcurrent/circuit
Rating
Rating
RatingRating
Surge current
Surge current
Surge currentSurge current
Total Volt-Amps
Total Volt-Amps
Total Volt-AmpsTotal Volt-Amps
Power cord length
Power cord length
Power cord lengthPower cord length
Power cap
Power cap
Power capPower cap
Receptacle
Receptacle
ReceptacleReceptacle
(industry equivalent)
Nominal voltage
Nominal voltage
Nominal voltageNominal voltage
Frequency range
Frequency range
Frequency rangeFrequency range
Phases
Phases
PhasesPhases
Maximum input
Maximum input
Maximum inputMaximum input
current/circuit
current/circuit
current/circuitcurrent/circuit
Rating
Rating
RatingRating
Surge current
Surge current
Surge currentSurge current
Total Volt-Amps
Total Volt-Amps
Total Volt-AmpsTotal Volt-Amps
Power cord length
Power cord length
Power cord lengthPower cord length
Power cap
Power cap
Power capPower cap
Receptacle
Receptacle
ReceptacleReceptacle
(industry equivalent)
(system)
(site)
(s)
(system)
(site)
Agency approvals
Agency approvals
Agency approvalsAgency approvals
Reviewed to
Reviewed to
Reviewed toReviewed to
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Power system provides near unity power factor that allows full utilization of the input line current (Watts = VA).
U.S./Canada
U.S./Canada
U.S./CanadaU.S./Canada
120/208V
50 to 60 Hz 50 to 60 Hz 50 to 60 Hz
3-phase star 3-phase star 3-phase star
3-wire+N+GND
170A peak 160A peak 170A peak
15 ft (4.5 m) 15 ft (4.5 m) 15 ft (4.5 m)
2 DEC 12-12314-00 2 DEC 12-12314-00 2 DEC 12-14379-06
2 DEC 12-12315-01 2 DEC 12-12315-01
2 NEMA L21-30R 2 NEMA L21-30R
U.S./Canada
U.S./Canada
U.S./CanadaU.S./Canada
120/208V
50 to 60 Hz 50 to 60 Hz 50 to 60 Hz
3-phase star 3-phase star 3-phase star
3-wire+N+GND
170A peak 160A peak 170A peak
15 ft/4.5 m 15 ft/4.5 m 15 ft/4.5 m
2 DEC 12-12314-00 2 DEC 12-12314-00 2 DEC 12-14379-06
2 DEC 12-12315-01 2 DEC 12-12315-01
2 NEMA L21-30R 2 NEMA L21-30R
UL Listed to UL1950
cUL Listed to CAN/C22.2 No. 950-M89
FCC Part 15 (Class A)
EN 60950 1922/A4:1997, European Norm
AS/NZS 3260:1993, Australian/New Zealand Standard
73/23/EEC, Low Voltage Directive
IEC950, 2nd Ed., 4th Amend.
GS320 Model 24
GS320 Model 24
GS320 Model 24GS320 Model 24
Japan
Japan
JapanJapan
202V
2 circuits 2 circuits 2 circuits
4-wire mid-GND or
21A 21A 13A
30A 30A 32A
9600VA 9600VA 9600VA
2 circuits 2 circuits 2 circuits
23A 24A 15A
30A 30A 32A
12000VA 12000VA 12000VA
3-wire junction GND
GS320 Model 32
GS320 Model 32
GS320 Model 32GS320 Model 32
Japan
Japan
JapanJapan
202V
4-wire mid-GND or
3-wire junction GND
Europe
Europe
EuropeEurope
380 to 415V
3-wire+N+GND
2 Hubbell 532R6W
2 IEC 309 (32A)
Europe
Europe
EuropeEurope
380 to 415V
3-wire+N+GND
2 Hubbell 532R6W
2 IEC 309 (32A)
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 42
Page 43

QuickSpecs
TechSpecs
H9A20 I/O Expander Cabinet
H9A20 I/O Expander Cabinet
H9A20 I/O Expander CabinetH9A20 I/O Expander Cabinet
Physical Characteristics
Physical Characteristics
Physical CharacteristicsPhysical Characteristics
Clearances
Clearances
ClearancesClearances
Dimensions
Dimensions
DimensionsDimensions
(H x W x D)
Shipping Dimensions
Shipping Dimensions
Shipping DimensionsShipping Dimensions
Weight Maximum
Weight Maximum
Weight MaximumWeight Maximum
Configuration
Configuration
ConfigurationConfiguration
Shipping Weight
Shipping Weight
Shipping WeightShipping Weight
Maximum Configuration
Maximum Configuration
Maximum ConfigurationMaximum Configuration
Front
Front
FrontFront
Rear
Rear
RearRear
Left Side
Left Side
Left SideLeft Side
Right Side
Right Side
Right SideRight Side
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
67 x 24 x 39.4 in (170 x 60 x 100 cm)
76.5 x 44 x 48 in (195 x 92 x 122 cm)
700 lb (320 kg)
830 lb (380 kg)
Operating
Operating
OperatingOperating
29.5 in (75 cm) 29.5 in (75 cm)
6.0 in (15 cm)
None None
None None
Service
Service
ServiceService
29.5 in (75 cm)
Environmental
Environmental
EnvironmentalEnvironmental
Heat dissipation
Heat dissipation
Heat dissipationHeat dissipation
Power Requirements
Power Requirements
Power RequirementsPower Requirements
Temperature
Temperature
TemperatureTemperature
Humidity
Humidity
HumidityHumidity
Altitude
Altitude
AltitudeAltitude
Vibration
Vibration
VibrationVibration
Minimally configured
Minimally configured
Minimally configuredMinimally configured
cabinet
cabinet
cabinetcabinet
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Fully configured cabinet
Fully configured cabinet
Fully configured cabinetFully configured cabinet
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
nominal input voltages of 200-240V.
Minimally configured expander cab contains a minimally configured PCI shelf and one disk drive
Fully configured expander cab contains three PCI shelves and 24 disk drives
The US/Canada model supports nominal input voltages of 115-117V. The Japan and Europe models support
Operating
Operating
OperatingOperating
41° to 95° F (5° to 35° C)
10% to 90% 10% to 95%
0 to 10,000 ft (0 to 3 km)
5 to 500 Hz @ .1G maximum
250 W/850 Btu/hr
2,400 W/8,200 Btu/hr
Non-Operating
Non-Operating
Non-OperatingNon-Operating
–40° to 151° F (–40° to 66° C)
40,000 ft (12.2 km)
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 43
Page 44

QuickSpecs
TechSpecs
Cabinet
Cabinet
CabinetCabinet
Nominal voltage(s)
Nominal voltage(s)
Nominal voltage(s)Nominal voltage(s)
Frequency range
Frequency range
Frequency rangeFrequency range
Phases
Phases
PhasesPhases
Dual AC source support
Dual AC source support
Dual AC source supportDual AC source support
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE: NOTE:
Maximum input
Maximum input
Maximum inputMaximum input
current/circuit
current/circuit
current/circuitcurrent/circuit
Rating
Rating
RatingRating
Surge current
Surge current
Surge currentSurge current
Total Volt-Amps
Total Volt-Amps
Total Volt-AmpsTotal Volt-Amps
Power cord length
Power cord length
Power cord lengthPower cord length
Power cap
Power cap
Power capPower cap
Receptacle
Receptacle
ReceptacleReceptacle
(industry equivalent)
3X-H9A20-AE/AF expansion cabinets are recommended for use with dual AC sources
(system)
(site)
HP AlphaServer GS320 (1224 MHz)
U.S./Canada
U.S./Canada
U.S./CanadaU.S./Canada
3X-H9A20-AD
120V
50 to 60 Hz 50 to 60 Hz 50 to 60 Hz
2 circuits 2 circuits 2 circuits
1-phase 1-phase 1-phase
2-wire+ GND 2-wire+ GND 2-wire+ GND
No
No
NoNo
22A 12A 11A
30A 30A 32A
150A peak 150A peak 170A peak
2600VA 2600VA 2600VA
15 ft (4.5 m) 15 ft (4.5 m) 15 ft (4.5 m)
2 DEC 12-11193-00 2 DEC 12-16886-00 2 DEC 12-14379-07
2 DEC 12-11194-00 2 DEC 12-19658-01
2 NEMA L5-30R 2 NEMA L6-30R
Japan
Japan
JapanJapan
3X-H9A20-AF
200 to 240V 220 to 240V
Yes
Yes Yes
YesYes
Europe
Europe
EuropeEurope
3X-H9A20-AE
Yes
YesYes
2 Hubbell 332R6W
2 IEC 309 (32A)
© Copyright 2003 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
UNIX is a registered trademark or trademark of The Open Group in the U.S. and/or other countries. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional
warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
DA - 11424 North America — Version 7 — August 19, 2003
Page 44
 Loading...
Loading...