Page 1

3PAR GeoCluster
1.0.0.14 for Windows
User’s Guide
3PAR Inc.
4209 Technology Drive
Fremont, CA 94538 U.S.A.
320-200263 November 2010
Page 2

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Revision Notice
This is the first release of this manual. A complete revision history is provided at the end of this manual.
Changes
The material in this document is for information only and is subject to change without notice. While reasonable
efforts have been made in the preparation of this document to assure its accuracy, 3PAR Inc. assumes no liability
resulting from errors or omissions in this document or from the use of the information contained herein.
3PAR reserves the right to make changes in the product design without reservation and without notification to its
users.
Updates to the Documentation at 3PAR Central
Any updates to this document or other 3PAR technical documents, can be found by logging into 3PAR Central’s
Document Control System from 3PAR’s Support page, at: http://www.3PAR.com/support/index.html.
3PAR Technical Support and Services
Contact your local service provider for technical support and services.
Sales and Ordering Information
For sales and ordering information, contact
3PAR Inc.
4209 Technology Drive
Fremont, CA 94538 U.S.A.
Telephone: 510-413-5999
Fax: 510-413-5699
E-mail: salesinfo@3PAR.com
Reader Comments and Suggestions
E-mail your comments and suggestions about this document to: ReaderComments@3PAR.com
Copyright
Printed Material
Copyright © 2010 3PAR Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or
otherwise, without the prior written consent of 3PAR Inc., 4209 Technology Drive, Fremont, CA 94538. By way of
exception to the foregoing, the user may print one copy of electronic material for personal use only.
Trademarks
3PAR, InServ, InForm, InSpire and Serving Information are registered trademarks of 3PAR Inc.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are owned by their respective owners.
320-200263 Page 2
Page 3
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Table of Contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Audience
1.2 Related Documents
1.3 Organization
1.4 Typographical Conventions
1.5 Advisories
2 Overview
2.1 What is 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows?
2.1.1 Microsoft Cluster Server
2.1.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows and Remote Copy
2.1.3 Cluster Resources
2.1.4 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
2.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Failover Algorithm
2.2.1 Failover Sequence from an MSCS Perspective
2.2.2 Failover Sequence from a Remote Copy Perspective
2.2.3 Failover Outcome
2.3 Practical Considerations and Best Practices
3 Installation and Configuration
3.1 Pre-Installation Requirements
3.2 Installation
3.3 Configuration
3.3.1 Integrating the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource in a Services and
Applications Group
3.3.2 Configuring 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource’s Parameters
3.4 Configuration Best Practices
3.4.1 Cluster Design and Configuration
3.4.2 Resources Configuration
3.4.3 Remote Copy Groups Configuration
3.4.4 SSH
4 Using 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
320-200263 Page 3
Page 4

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
4.1 Recovering from a Failover
4.1.1 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Decision Matrix
4.1.1.1 Remote Copy is Fully Functional
4.1.1.2 Remote Copy’s Function is Altered
4.1.1.3 Remote Copy is Disrupted
4.1.2 Failover Scenarios and Recovery Operations
4.1.2.1 Failover to a Local Site Node
4.1.2.2 Failover to a Remote Site Node, with no Remote Copy Interruption
4.1.2.3 Failover to a Remote Site Node, with Remote Copy Interrupted
4.2 Uninstalling 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
4.3 Other Useful Operations
4.3.1 CLI commands
4.3.1.1 Checking Remote Copy Groups Status
4.3.1.2 Checking Remote Copy Links
4.3.1.3 Checking Latency on Remote Copy Links
5 Troubleshooting
5.1 Cluster.log Report
5.1.1 Extracting the Cluster.log Report
5.1.1.1 Useful Switches
5.1.2 Reading the Cluster.log
5.1.2.1 Reading Cluster.log events
5.1.2.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Specific Events
5.1.2.3 Troubleshooting a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Failure
5.2 Known Issues
5.2.1 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Deletion
5.3 Event Catalog
5.3.1 Online and Online Thread Events
5.3.2 Offline Events
5.3.3 Open and Close Events
5.3.4 Terminate Events
5.3.5 Health Check Events and Other Events
6 Revision history
320-200263 Page 4
Page 5
1
Introduction
In this chapter
1.1 Audience 1
1.2 Related Documents 2
1.3 Organization 2
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
1.4 Typographical conventions 3
1.5 Advisories 3
This user’s guide provides the information needed to install, configure and use
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
1.1 Audience
This user guide is intended for system administrators in charge of the installation and
management of Windows Clusters and SAN storage administrators.
320-200263 Page 5
Page 6

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
For Information About…
Read the…
CLI commands and their usage
3PAR InForm OS Command Line
Interface Reference
Identifying storage server
components and
detailed alert information
3PAR InForm OS Messages and
Operator’s Guide
Using the Command Line Interface
(CLI) to configure and manage
InServ Storage Servers
3PAR InForm OS CLI
Administrator’s
Manual
Using the InForm Graphical User
Interface (GUI) to configure and
administer InServ Storage Servers
3PAR InForm OS Management
Console Online Help
Using 3PAR Remote Copy
3PAR Remote Copy User’s Guide
1.2 Related Documents
The following documents also provide information related to the InServ Storage Server:
1.3 Organization
This document is organized as follows:
This chapter provides an overview of this guide, including intended audience, related
documentation, typographical conventions and advisories.
Chapter 2, Overview, provides an overview of 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows, including
how it interfaces with Microsoft Cluster Server (MSCS), 3PAR InServ and 3PAR Remote
Copy.
Chapter 3, Installation and Configuration, describes how to install and configure 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows.
Chapter 4, Using, describes how to operate 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
Chapter 5, Troubleshooting, describes how to assess errors and provides a list of
known issues.
This guide also contains a revision history and index for reference.
320-200263 Page 6
Page 7
Typeface
Meaning
Example
ABCDabcd
Used for dialog box
elements such as titles and
button labels.
Enter your system name in the
Value box and click OK
ABCDabcd
Used for file names, paths
and screen output and for
text you are to enter.
Found < 12 > 73G disks.
Enter cli at the Windows
command prompt.
<ABCDabcd>
Used for variables in file
names, paths and screen
output and variables in
user input.
[root@(<systemIDnodeID>)root]
To continue Enter your
system name ==>
<systemname>
NOTE: Notes are reminders, tips or suggestions that supplement the
procedures included in this guide.
CAUTION: Cautions alert you to actions that can cause damage to
equipment, software or data.
WARNING: Warnings alert you to actions that can cause injury to people
or irreversible damage to data or the operating system.
1.4 Typographical conventions
The following typographical conventions are used in this guide:
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
1.5 Advisories
To avoid injury to people or damage to data and equipment, be sure to observe the
cautions and warnings in this guide. Always be careful when handling any electrical
equipment.
320-200263 Page 7
Page 8

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
2
Overview
In This Chapter
2.1 What is 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows? ........................................................................................... 8
2.1.1 Microsoft Cluster Server ............................................................................................................. 9
2.1.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows and Remote Copy ................................................................... 10
2.1.3 Cluster Resources ..................................................................................................................... 11
2.1.4 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows ................................................................................................. 12
2.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Failover Algorithm ......................................................................... 13
2.2.1 Failover Sequence from an Microsoft Cluster Server Perspective ........................................... 13
2.2.2 Failover Sequence from a Remote Copy Perspective .............................................................. 13
2.2.3 Failover Outcome ..................................................................................................................... 14
2.1 What is 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows?
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows is an add-on to Microsoft Cluster Server. It manages the
hosting of Microsoft Cluster Server nodes on 3PAR InServ storage arrays in synergy with
3PAR Remote Copy, allowing the nodes to be located in geographically remote sites and
replicated in real-time. It ensures continuity of service in most cases of site failure and an
enhanced Recovery Time Objective in case continuity of service has been disrupted.
320-200263 Page 8
Page 9

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
2.1.1 Microsoft Cluster Server
Microsoft Cluster Server revolves around the active/passive clustering of several Windows
servers, called nodes. The cluster structure allows single resources to be shared by all the
nodes, with typically only one node, the owner node being able to access these at a given
time. Clustering also allows failover capability, which ensures continuity of service in case
one or more nodes experience problems by making sure the owner role is transferred to a
functional node.
MSCS avoids split-brain scenarios, where, in case of communication failure, each node is
likely to conclude being the active one, resulting in simultaneous resource access and data
corruption, using specific methods. Among those methods, 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
supports the following:
Majority Node Set, which, in order to be ideally configured, requires an odd number
of servers. In case of failure, the new owner node can only be selected from nodes
able to perceive at least 50% of the total number of nodes, plus themselves. Nodes
not meeting this requirement at any time will exclude themselves from the cluster.
The odd node can be located remotely from all the other nodes and is traditionally
named “Quorum”.
Majority Node Set with File Share, which instead of the odd node configuration
makes a shared storage space that hosts a file called the file share witness accessible
to all the nodes.
Locating nodes on sites geographically remote from each other further ensures continuity
of service by protecting the cluster against site failure. However, the implementation of
remote sites has its own specific constraints. This design is called metropolitan clusters or
geographically dispersed clusters.
320-200263 Page 9
Page 10
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
2.1.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows and Remote Copy
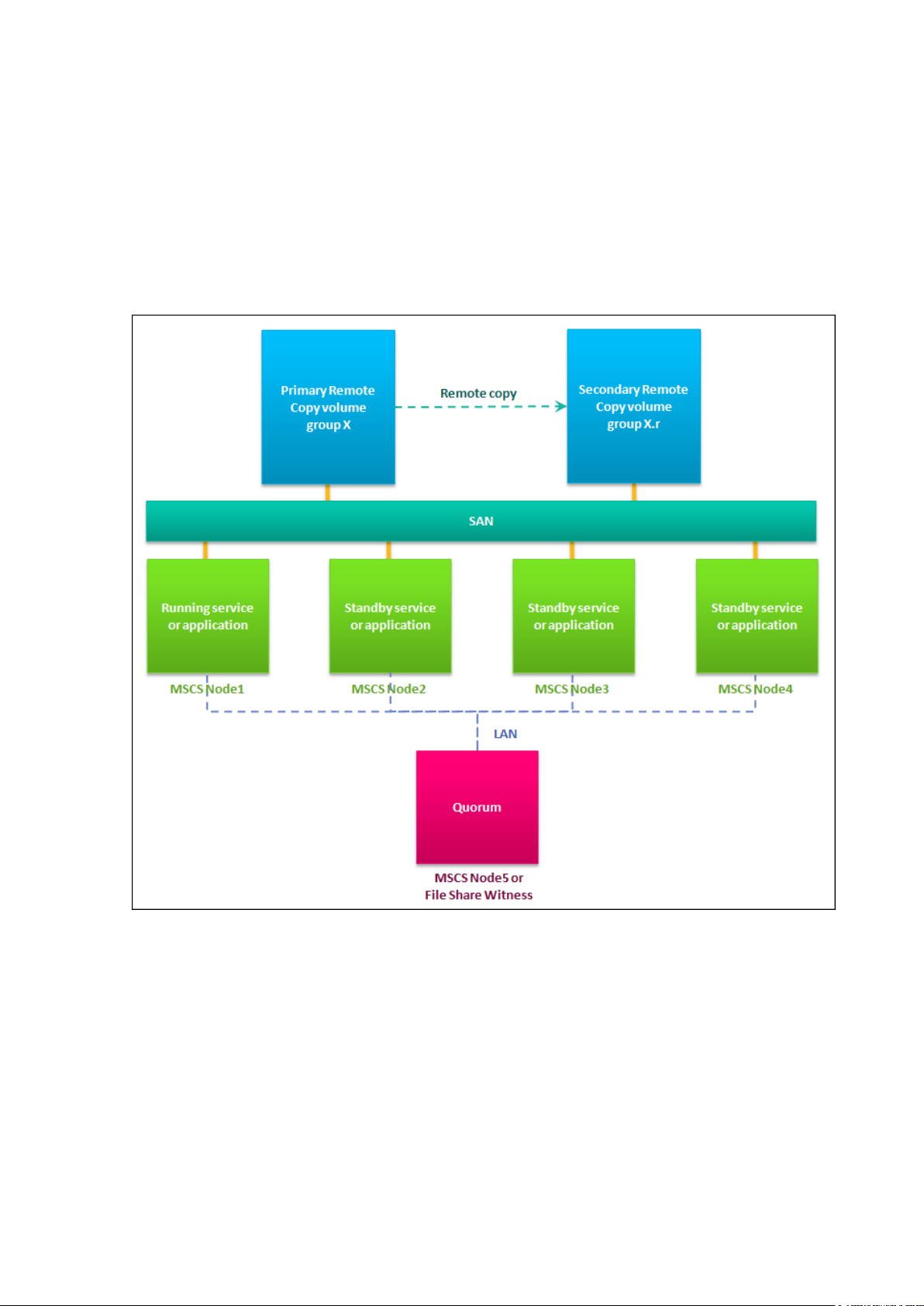
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows allows cluster resources to be hosted on an InServ storage
array and replicated on a remote site via 3PAR Remote Copy. This way, the safety of critical
production data is ensured. Moreover, in case of a site failure and the ensuing cluster
failover to the remote site, 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows manages the failover of Remote
Copy, reversing the source and target Remote Copy groups, in a timeframe transparent to
hosted applications tolerant to Microsoft Cluster Server failover.
320-200263 Page 10
Figure 2-1: Typical 4-nodes configuration.
Page 11
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: Each 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource corresponds to a
single Remote Copy group. Though a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
resource may manage several disk resources, all these disk resources have
to be located on VVs in the same Remote Copy group (see diagram below).
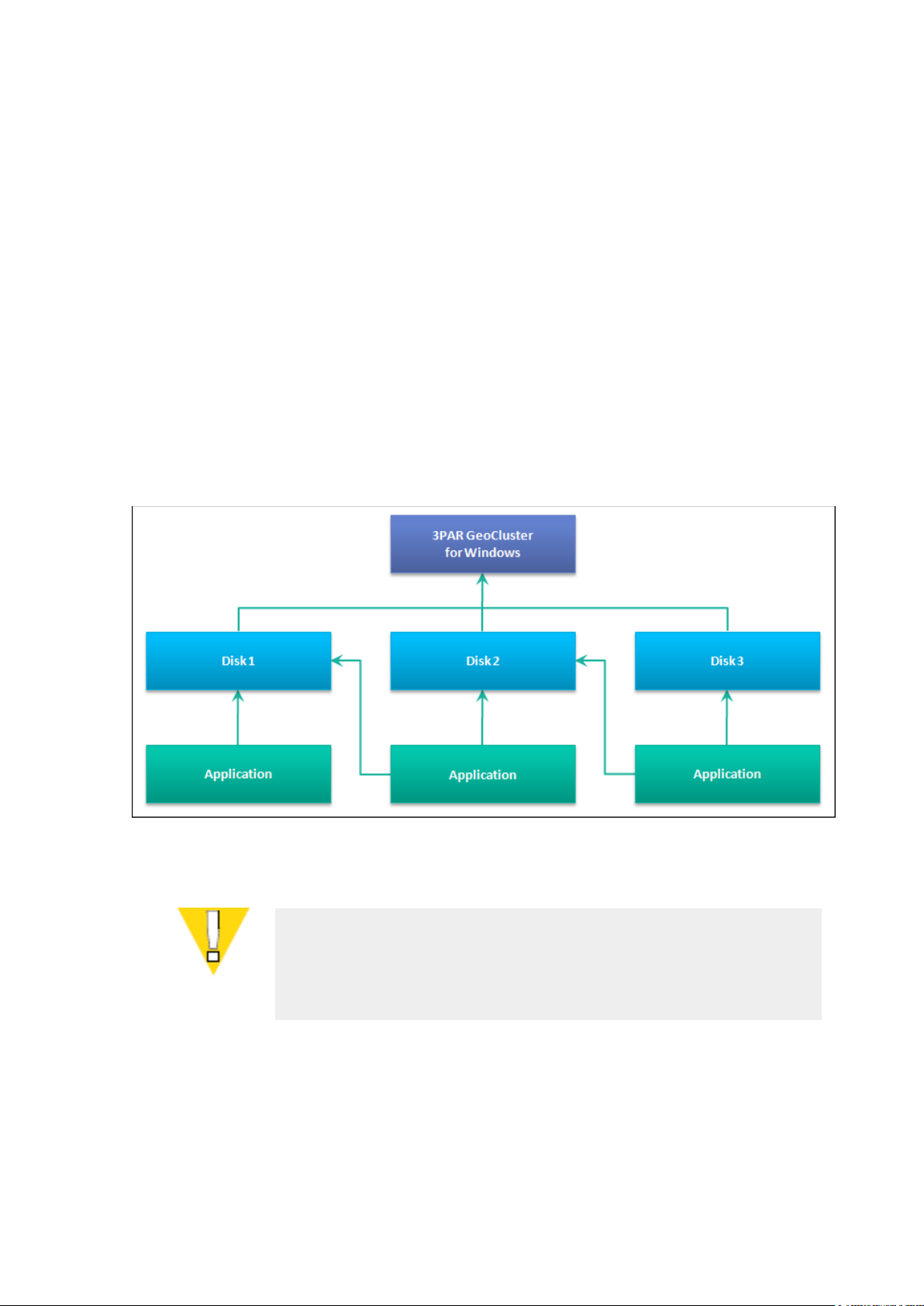
2.1.3 Cluster Resources
Cluster resources are grouped into Services and Applications groups. Several resources
grouped together can be organized via dependencies which ensures that a single resource
cannot be brought online (to a functional status) if any resource higher in the hierarchy is
itself not online--whether because it has been turned off or is dysfunctional.
In a typical 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows configuration, three following resources can be
found:
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource, on which the disk resources depend.
The disk storage resources, which correspond to Virtual Volumes located on InServ
storage arrays. They depend on the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource and any
application resource depends on a disk storage resource.
The application resources, which are hosted on the disk resources on which they
depend.
Figure 2-2: Example of resources dependencies
320-200263 Page 11
Page 12

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Figure 2-3: Example of correspondence between Cluster resources and InServ elements
2.1.4 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows is packaged into a Microsoft Installer, which, once executed,
installs two .dll files to the relevant folders:
InServ ClRes.dll, which handles core operations.
InServ AdmExt.dll , which handles configuration.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows is fully integrated into the MSCS architecture. The
configuration interface is integrated into the MSCS interface, in the corresponding resource
property window.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows communicates with InServ Storage Arrays via an SSH
connection to the InForm OS.
320-200263 Page 12
Page 13
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: See section 3.4 Best Practices for considerations related to the
use of SSH.
2.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Failover Algorithm
This section describes the method 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows follows in order to handle
failovers.
2.2.1 Failover Sequence from a Microsoft Cluster Server Perspective
Failover occurs from one of the following:
An administrator's action results in an active node becoming unavailable.
One of the nodes’ cluster resources goes offline.
You can set whether a cluster resource failure will trigger a failover in its properties.
When a failover is triggered, it causes MSCS to bring the whole resource group offline and
search for a functional node to bring the resource group online. If the dependencies are set
correctly, MSCS will attempt to bring the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource online.
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource will perform a decision algorithm, taking into
account conditions such as whether it is on the primary or secondary site and whether the
Remote Copy links are up.
Depending on the outcome of the decision process, that particular node may be able to
bring its 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource online. If online, the cluster will move to
the next node and so on, until it is able to find a node able to start its 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource and the resources that depend on it or until it fails.
2.2.2 Failover Sequence from a Remote Copy Perspective
In a normal working situation, the InServ storage arrays and the Remote Copy groups they
host are considered by the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource to have one of the
following roles:
Primary - This array is considered to be the replication’s source, when the cluster is in
normal working order.
Secondary - This array is considered to be the replication’s destination, when the
cluster is in normal working order.
If the Remote Copy replication fails, whether due to a failure or administrator action, and
MSCS has a node try to take hold of the replication VVs on the secondary InServ , then the
320-200263 Page 13
Page 14
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: In the latter scenario, the primary InServ will not automatically
switch to the secondary-rev role and will continue to identify itself as the
primary server. This scenario requires careful administrator consideration,
as it can result in data loss. For more information, see section 4.1.
secondary InServ will become Primary-rev (Primary in a reversed replication situation). The
VVs included in the Remote Copy groups will change from read-only to read-write status.
The Secondary-rev status can be set manually in certain scenarios. This implies that the
primary InServ has been set to be the replication destination while the secondary InServ
has become the primary-rev due to a failure.
2.2.3 Failover Outcome
Depending upon the site on which that owner node ends up being located, the failover will
do one of the followings:
The owner node stays on the local site – There is no consequence for the status of
the InServ storage arrays hosting the Remote Copy groups.
The owner node ends up being located on the remote site, with no disruption to the
replication - The primary and secondary InServs see their roles reversed with no
further notable effect. This scenario is typical of a manually initiated failover or a disk
or application resource failure.
The owner node ends up being located on the remote site, with the secondary InServ
becoming primary-rev because of a replication failure - While the disruption to
continuity of service will be limited, the restoration of the cluster to its original
situation will require additional manual operations, which are described in section
4.1.
320-200263 Page 14
Page 15

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
3
Installation and Configuration
In this Chapter
3.1 Pre-Installation Considerations 2
3.1.1 Support Considerations 2
3.1.2 Pre-Installation Requirements 2
3.2 Installation 3
3.3 Configuration 3
3.3.1 Integrating 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource in a Services and
Applications Group 3
3.3.2 Configuring 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource’s parameters 4
3.4 Configuration Best Practices 7
3.4.1 Cluster Design and Configuration 7
3.4.2 Resource Configuration 8
3.4.3 Remote Copy Groups Configuration 10
3.4.5 SSH 11
320-200263 Page 15
Page 16

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
3.1 Pre-Installation Considerations
3.1.1 Support Considerations
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows comes as an installer package for installation. The installers
are different if you are running an x86 or an X64 operating system.
Supported platforms for 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows are Windows Server 2008 Enterprise,
Windows Server 2008 Datacenter, Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise and Windows Server
2008 R2 Datacenter. Both x86 and X64 versions of the OS are supported.
Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 libraries will be installed as part of the installer package.
InServ T Class Systems, F Class Systems and S Class Systems are supported.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows supports InServ InFormOS 2.2.4 and 2.3.1 and all associated
MUs.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows is supported with Volume Groups in Synchronous mode only.
The maximum number of nodes in the cluster is limited by Microsoft Cluster Server.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows supports both IP and FC on the transport layer for Remote
Copy.
3.1.2 Pre-Installation Requirements
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows assumes all the requirements from MSCS are met. The cluster
in which it will be installed should pass the Validate a Configuration Wizard from MSCS
before the installation of the software.
The Remote Copy license must be installed on both InServs that constitute the Remote Copy
pair.
The 3PAR InServs running the Remote Copy should be in a healthy state prior to the
installation of 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
The Remote Copy Links between the Remote copy pairs should be “Up”. The Remote Copy
Volume Groups should be in a “Started” state and virtual volumes should be “Synced”.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows must be installed on each cluster node.
320-200263 Page 16
Page 17

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
NOTE: In order to install 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows, you must be logged
in as domain administrator or have domain administrator rights.
3.2 Installation
In order to install 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows, perform the following steps:
1. Copy the installer package to the cluster node you which you wish to install 3PAR GeoCluster
for Windows.
2. Double-click the installer package to execute it.
3. Click Next.
4. Click Install.
5. Click Finish, to complete the installation.
3.3 Configuration
3.3.1 Integrating 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource in a
Services and Applications Group
The following steps can be performed on any node of the cluster, in the Cluster Failover
Manager interface, in the relevant Services and Application group. The Failover Cluster
Manager can be accessed via Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > Failover Cluster
Manager.
320-200263 Page 17
Page 18

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
1. Click Add a resource > More resources > Add 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
2. When prompted, click Yes to validate the resource creation.
A New 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource will appear under other resources in an
offline status.
3.3.2 Configuring 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource’s
parameters
In order for 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource to manage the different nodes and
InServ storage arrays, 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows cluster resource needs to be
configured as follows:
320-200263 Page 18
Page 19

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
In order to configure 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows, perform the following steps:
1 Right-click the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource.
2 Right-click Properties.
3 Right-click the Parameters tab.
Set the Advanced Policies tab as follows:
1 In the Basic resource health check interval group box, select Use this time period (mm:ss)
and set the time period to 00:05.
2 In the Thorough resource health check interval group box, select Use this time period
(mm:ss) and set the time period to 05:00.
320-200263 Page 19
Page 20

NOTE: Validating the changes made to the resource’s parameters will
initiate verifications on the node owning the resource at the time of the
validation, against the InServ storage array located on the same site. The IP
address, the Remote Copy group and the login and password will be
checked. If any of these do not pass verification, 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource cannot be brought online.
Click the Parameters tab
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Set the Parameters tab as follows:
1 Distribute the nodes between the Site A and Site B fields, to reflect where they are physically
located.
2 In the Site A group box, enter the IP address of the InServ storage array present on the local
site, the name of the Remote Copy Group it hosts and the login and password required to
access its CLI.
3 In the Site B group box, enter the IP address of the InServ storage array present on the
remote site, the name of the Remote Copy Group it hosts and the login and password
required to access its CLI.
4 Validate the changes by clicking OK.
320-200263 Page 20
Page 21

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
NOTE: Once the cluster is fully configured, it is advised to fail its
Applications and Services group over to a node on the remote site in order
to validate the configuration and then fail it back.
CAUTION: The parameters fields are case-sensitive.
3.4 Configuration Best Practices
3.4.1 Cluster Design and Configuration
When configuring a Majority Node Set cluster, you may wish to exclude the quorum node
from the possible owners list. This can be done in the Services and applications group’s
properties.
When adding additional nodes to an already configured non-File Share Witness Majority
Node Set cluster, ensure that the ultimate node count is an odd number. Also, ensure that
the new nodes have been correctly distributed between sites in the Parameters tab of 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows resource.
320-200263 Page 21
Page 22

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
By default, after a general reboot, a cluster will start the Services and applications group on
node 1. The possible owners list allows you to set the cluster for different behaviors.
In a geographically dispersed cluster design, it is strongly advised to have at least two nodes
installed on each site, for a total of four nodes. A two-node design, with one node at each
site, will cause inter-site failover in any failover scenario, from which it is considerably more
constraining to recover.
At any given time during the cluster creation process, the Validate a Configuration Wizard
feature of MSCS can be used to ensure the cluster is functional. It performs a check of basic
cluster functions and can be accessed in the right-click menu of the cluster > Validate this
Cluster. If the Validate a Configuration Wizard test fails, refer to the MSCS help resource to
determine the cause of the dysfunction.
3.4.2 Resource Configuration
While not compulsory, the dependencies configuration described below is strongly advised.
Dependencies can be set in the Dependencies tab of each resource. There, the user can indicate on
which other resource(s) this particular resource will depend. Other configurations for the
dependencies may cause dysfunctions of the failover process :
1 The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource should be at the top of the dependencies
hierarchy. There is no change to perform in its properties.
2 Set the properties of the disk resources corresponding to the Remote Copy group’s VVs
to have a dependency toward the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource.
320-200263 Page 22
Page 23

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
3 Finally, set the application resources to have a dependency on the disk resource(s)
hosting them.
In the Properties dialog box of the Services and applications group, it is important to ensure
that the Prevent Failback option is selected in the Failover tab.
320-200263 Page 23
Page 24

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
In the Policies tab of the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource, it is advised to set the
Pending timeout option to a value greater than 30 seconds. Depending on the context or the
cluster design, it might be advised to set it higher.
3.4.3 Remote Copy Groups Configuration
While the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource checks certain parameters on the local
InServ storage array (see Configuring 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource parameters), no
verifications are made on the remote site storage array. It is the administrator’s
responsibility to ensure the Remote Copy groups are properly configured.
A given Remote Copy group may only have one given 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
pointing to it.
A given 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource may point to only one Remote Copy group.
VVs should be present on cluster nodes on both sites and have the same LUN number set on
each node.
VSS Snapshots of volumes located in 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows-managed VVs, if created
on a different volume than their parent volume, should in any case be created within the VVs
of the Remote Copy group. Creating these snapshots outside the Remote Copy group will
result in data loss if an inter-site failover occurs.
Remote Copy groups should be set to “auto_recover” to allow Remote Copy groups to
start when Remote Copy links are brought up after an inter-site link failure.
320-200263 Page 24
Page 25

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: TCP/IP port 22 should be enabled on network firewalls between
MSCS nodes and InServs.
3.4.5 SSH
The number of SSH connections for a single instance of the InForm OS is limited to sixteen at
any given time. Each instance of 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource will use one SSH
connection (as will administrative SSH connections.). This must be taken into consideration
when designing a cluster relying on 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
Disruptions of the SSH communication between 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows and InServ
storage arrays, or of the Remote Copy link between InServ Storage Arrays, do not affect the
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource. This kind of disruption will not cause any resource
to be brought offline or failover to take place. The same applies to InServ node reboots and,
by extension, InServ node firmware upgrades. These modifications will not affect the cluster
function and should not cause any resource to be brought offline or a failover to take place.
320-200263 Page 25
Page 26

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
4
Using 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows
In this Chapter
4.1 Recovering from a Failover 1
4.1.1 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource Decision Matrix 1
4.1.1.1 Remote Copy is Fully Functional 1
4.1.1.2 Remote Copy’s Function is Altered 2
4.1.1.3 Remote Copy is Disrupted 2
4.1.2 Failover Scenarios and Recovery Operations 3
4.1.2.1 Failover to a Local Site Node 3
4.1.2.2 Failover to a Remote Site Node, with no Remote Copy Interruption 5
4.1.2.3 Failover to a Remote Site Node, with Remote Copy Interrupted 7
4.2 Uninstalling 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows 8
4.3 Other Useful Operations 12
4.3.1 CLI Commands 12
This chapter describes how to restore a cluster to its original situation after an inter-site
failover and other minor operations.
320-200263 Page 26
Page 27

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Local Remote Copy
Group Role
Remote Copy Group Role
Outcome
Primary
Secondary
Online
Primary
Other than Secondary
Failed
Primary-Rev
Secondary-Rev
Online
Secondary
Primary
Online after reverse*
Secondary-Rev
Any
Failed
NOTE: “Online after reverse” means that MSCS is bringing the 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows resource online on a cluster node located on the
remote site. As long as the replication is functional, this switch in roles
will cause the Remote Copy setup to reverse the replication process. The
secondary Remote Copy group will have its role changed to primary and
the primary Remote Copy group will become secondary. This is a specific
failover scenario, which is addressed later in this chapter.
4.1 Recovering from a Failover.
4.1.1 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource Decision Matrix
During the failover process, every time MSCS calls upon a Services and applications group
on a node, it will first trigger the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource, provided this
resource is at the top of the dependencies hierarchy. See section 3.4 Dependencies for
more information. The resource will then go through one of the following decision
matrices, in order to determine its status. Most decision outcomes will cause no noticeable
consequences, as they correspond to the expectable behavior of MSCS (simply put, if a
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource is not supposed to come online, it will expectably
not come online). Only two behaviors, described below, require administrator attention:
Online after reverse and Online after failover.
4.1.1.1 Remote Copy is fully functional.
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource will consider that Remote Copy is fully
functional if the following conditions are met:
Remote Copy System is started.
The Remote Copy group is started.
It will then consider the role of the Remote Copy group it is linked to on its local InServ
storage array and the role of the corresponding Remote Copy group located on the remote
site InServ storage array and decide whether to come online successfully, as follows:
320-200263 Page 27
Page 28

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Local Remote Copy Group Role
Remote Copy Group Role
Outcome
Primary
Secondary
Online
Primary
Secondary-Rev
Failed
Primary
Unknown
Failed
Primary-Rev
Any
Online
Secondary
Any
Failed
Secondary-Rev
Any
Failed
Local Remote Copy Group
Role
Remote Copy Group Role
Outcome
Primary
Any
Online
Secondary
Any
Online after failover*
Primary-Rev
Any
Online
Secondary-Rev
Any
Failed
CAUTION: The “Online after failover” case implies that MSCS is bringing the
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource online on a cluster node located on
the remote site, while the replication is interrupted. The secondary Remote
Copy group will have its role changed to primary-rev, while the primary
remote copy group will likely stay primary at the moment of the failure. This
is a specific failover scenario that will require the cluster administrator’s
attention; it is addressed later in this chapter.
4.1.1.2 Remote Copy’s Function is altered
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource will consider that Remote Copy is altered if the
following conditions are met:
Remote Copy is started.
The Remote Copy group is stopped.
It will then consider the role of the Remote Copy group it is linked to on its local InServ
storage array and the role of the corresponding Remote Copy group located on the remote
site InServ storage array and decide whether to come online successfully, as follows:
4.1.1.3 Remote Copy is disrupted.
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource will consider that Remote Copy is disrupted if
the following conditions are met:
Remote Copy System is stopped.
Remote Copy Group is stopped.
It will then consider the role of the Remote Copy group it is linked to on its local InServ
storage array and the role of the corresponding Remote Copy group located on the remote
site InServ storage array and decide whether to come online successfully, as follows:
320-200263 Page 28
Page 29

4.1.2 Failover Scenarios and Recovery Operations
When a failover occurs, the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource behavior can be
narrowed down to the following scenarios. For each of these scenarios, the context and
causes for the failover should be taken into careful consideration as they each imply very
different levels of criticality.
4.1.2.1 Failover to a Local Site Node
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Figure 4-1: Failover to local node.
A failover to a local site node could be initiated for the following reasons:
Hardware or software failure on the active node.
Administrator’s action in MSCS Failover Cluster Manager.
320-200263 Page 29
Page 30

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: Before attempting to restore the cluster to its original situation,
ensure that any failure on the original active node has been corrected.
Changes to Remote Copy
This scenario will not have any consequence for the Remote Copy roles, as the node taking
over the active role is located on the same site.
Recovery Operation
1. In Failover Cluster Manager, right-click on the Services or application group.
2. Select Move this service or application to another node.
3. Select the relevant node from the list.
320-200263 Page 30
Page 31

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
4.1.2.2 Failover to a Remote Site Node, with no Remote Copy
Interruption.
Figure 4-2: Failover to remote node.
A failover to a remote site node could be initiated for the following reasons:
Hardware or software failure on the local site, affecting all of the local site nodes, but not the
local site InServ or the Remote Copy system.
Administrator’s action in MSCS Failover Cluster Manager.
320-200263 Page 31
Page 32

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: Before attempting to restore the cluster to its original situation,
ensure that any failure on the local site has been corrected.
Changes to Remote Copy
This scenario will cause the Remote Copy groups to reverse their roles as follows:
The secondary Remote Copy group, located on the remote site, will have its role changed to
primary.
The primary Remote Copy group, located on the local site, will have its role changed to
secondary.
Recovery Operation
1. In Failover Cluster Manager, right-click on the Services or Application group.
2. Select Move this service or application to another node.
3. Select the relevant node from the list.
320-200263 Page 32
Page 33
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
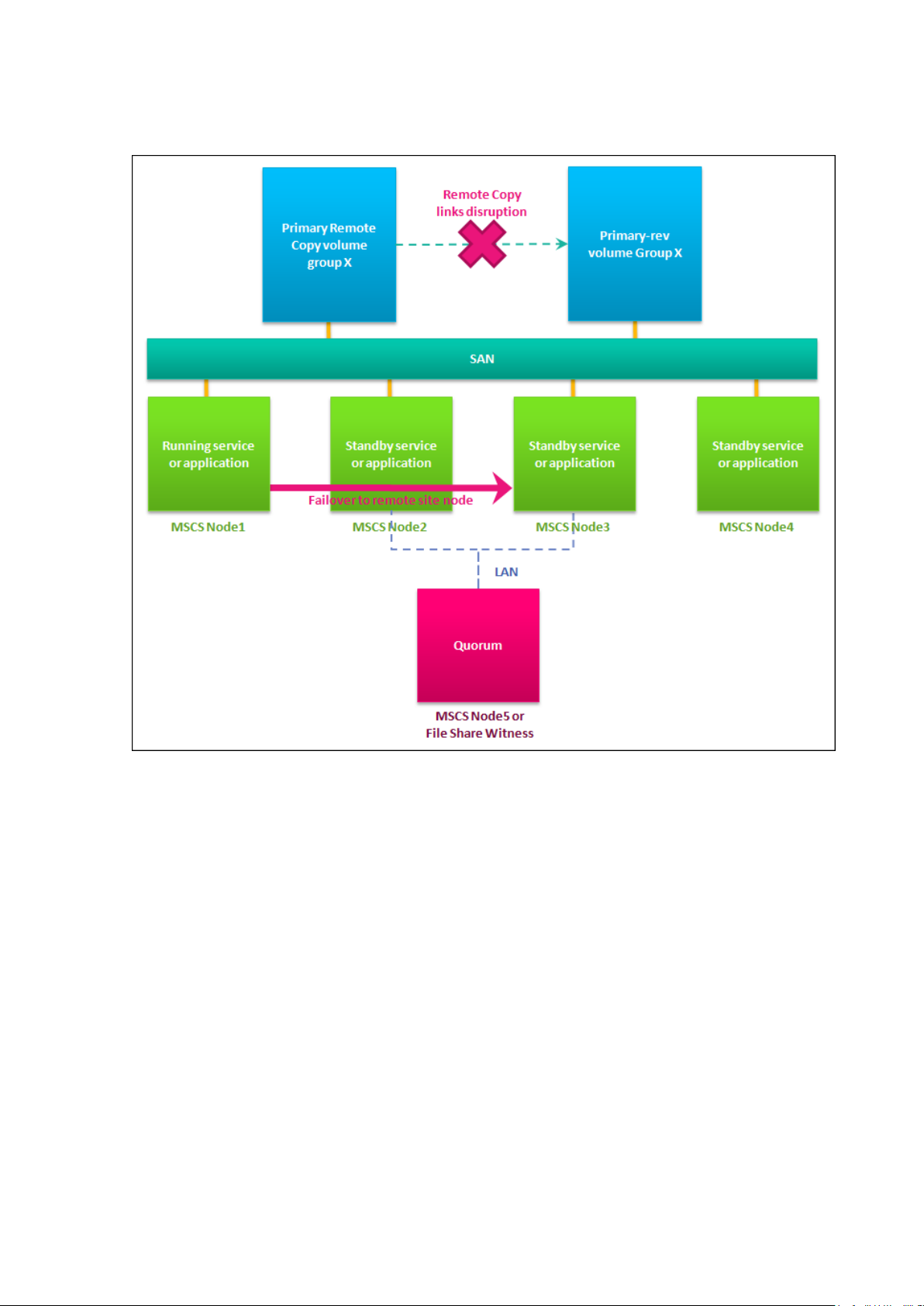
4.1.2.3 Failover to a Remote Site Node, with Remote Copy Interrupted.
Figure 4-3: Failover to remote node, with Remote Copy disrupted.
A failover to a remote site with Remote Copy disruption node can be initiated for the
following reasons:
Hardware or software failure on the local site affecting the Remote Copy System and all of
the local cluster nodes.
Failure on the local site InServ.
Changes to Remote Copy
This scenario will cause the following changes to the Remote Copy organization:
The secondary Remote Copy group, located on the remote site, will have its role changed to
primary-rev.
If the local InServ is still functional, the primary Remote Copy group, with no knowledge of
the Remote Copy group role change, will retain its role.
320-200263 Page 33
Page 34

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
CAUTION: The following operation requires the 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource and, consequently, any dependent resource to be
brought offline.
CAUTION: Before uninstalling 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows, ensure that
no 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource is owned by the cluster node on
which you wish to perform the uninstall.
CAUTION: Before uninstalling 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource,
ensure that no Failover Cluster Manager windows is open.
NOTE: Uninstalling 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource requires a
reboot in order to complete.
Recovery Operations
In this scenario, it is assumed that the only healthy set of data is the one hosted on the
remote site. The first step will be to reintegrate the local Remote Copy group in the
replication process, to ensure data safety. It is performed by setting its role to secondaryrev.
In order to do so, perform the following steps:
1. Ensure that the Remote Copy system is operational on both site’s InServ s.
2. On the remote InServ, using the CLI, issue the command setrcopygroup recover
<remote Remote Copy group’s name>.
Once this is done and the data is replicated, the data can be considered healthy on both
sites. The next step consists in reversing the replication to its original state, with the local
Remote Copy group reverting to the primary role and the remote Remote Copy group
reverting to the secondary role.
In order to do so, perform the following steps:
1. Ensure that the Remote Copy System is operational and the Remote Copy groups are fully
functional on both sites.
2. On the remote InServ, using the CLI interface, issue the command setrcopygroup
restore <remote Remote Copy group’s name>.
4.2 Uninstalling 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
320-200263 Page 34
Page 35

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
In order to uninstall 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource, perform the following steps:
1. Ensure that the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource installer package is present on
the node from which you wish to perform the uninstall.
2. Double-click the installer package and launch the installation wizard.
3. Click Next.
4. Select Remove and click Next.
5. Click Remove.
6. Click Ok.
7. If the node on which you are performing the uninstall is the last one that is installed in
the cluster, click Yes. Otherwise, click No.
8. Click Finish
9. Complete the uninstall by rebooting the server.
4.3 Other Useful Operations
4.3.1 CLI Commands
The following CLI commands may be useful to the administration of an MSCS cluster relying
on 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
4.3.1.1 Checking Remote Copy groups status
To check the status of the Remote Copy group, issue the command “showrcopy”.
4.3.1.2 Checking Remote Copy links
To check the state of the Remote Copy links, issue the command “showrcopy links”.
4.3.1.3 Checking Latency on Remote Copy Links
320-200263 Page 35
Page 36

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
NOTE: This command may return surprisingly high latencies. It is normal
behavior and implies that no data is currently being copied.
To check the latency of Remote Copy, issue the command “statrcopy –hb”.
320-200263 Page 36
Page 37

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
5
Troubleshooting
In This Chapter
5.1 Cluster.log Report 1
5.1.1 Extracting the cluster.log Report 1
5.1.1.1 Useful Switches 2
5.1.2 Reading the cluster.log 2
5.1.2.1 Reading Cluster.log events 2
5.1.2.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Specific Events 3
5.1.2.3 Troubleshooting a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Failure 4
5.2 Known issues 4
5.2.1 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Deletion 4
5.3 Event Catalog 5
5.3.1 Online and OnlineThread Events 5
5.3.2 Offline Events 9
5.3.3 Open and Close Events 10
5.3.4 Terminate Events 11
5.3.5 Health Check Events and Other Events 11
320-200263 Page 37
Page 38

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
5.1 Cluster.log Report
5.1.1 Extracting the cluster.log Report
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource logs the traces of its activity in the
cluster.log report of Microsoft Cluster Server. In order to trace the activity of the
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource, this report first has to be extracted. This can be
achieved by entering the following command in a DOS prompt:
cluster /cluster:[cluster name] LOG /G
By default, the cluster.log report will then be extracted to the following location on each
functional node of the cluster:
C:\windows\cluster\reports\cluster.log
5.1.1.1 Useful Switches
To gather all of the cluster’s cluster.log file in a specific directory on the server the command
is run on , add the following switch:
/copy:<target directory>
When using the ”/copy” switch, the DOS prompt should show a path to the
parent directory of the subdirectory you have set as a destination for the cluster.log
extraction. For example, if you intend to extract the cluster.log report to
“c:\temp\report”, position the prompt under “c:\temp” and run
“cluster /cluster:[cluster name] LOG /G /copy:report”.
To specify how far in the past data should be collected, add the following switch:
/span:<minutes>
This switch allows controlling the size of the log file, by limiting the data collection to the
relevant timeframe.
320-200263 Page 38
Page 39

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
NOTE: RCM and RHS events may directly concern 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resources. When they do, the name of the resource will appear in
the event description.
5.1.2 Reading the cluster.log
5.1.2.1 Reading Cluster.log events
Cluster logs lines will display the following information:
1. PID and thread ID in hex format. This information is not described in this document.
2. Date and time of the event.
3. Entry type. It indicates the severity level of the message, which can be :
INFO: The event is informational.
WARN: The event implies a critical condition, while not being an error in itself.
ERR: This event indicates a dysfunction.
4. Source. There a limited number of possible sources:
RES: means the event has been logged by a specific resource DLL. The 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows will log its event with the RES source.
RCM: Resource Control Manager manages resources according to their
dependencies.
RHS: Resource Host Subsystem acts as an interface between RCM and resource dlls.
Other sources: NM (Network Manager), IM (Interface Manager), GUM (Global
Update Manager), while potentially useful, are not directly related to 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows.
Event description: Format and content may vary depending on the source and the
manufacturer, especially in the case of [RES] events.
320-200263 Page 39
Page 40

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
NOTE: The OnlineThread events will be an important source of information
when dealing with cluster dysfunctions.
5.1.2.2 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Specific Events
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows specific events show as follows in the cluster.log:
00001770.00000360::2010/09/30-17:53:52.239 INFO [RES] 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows <GeoCluster 4>: Online: request.
[RES] As a cluster resource, 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows events always have [RES] as a
source.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows marks all specific 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
events.
<GeoCluster 4> is the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource name as it appears in
Failover Cluster Manager.
Online: is the event category, as far as the 3PAR Cluster Extension Resource dll is
concerned. Event categories are addressed in the following subsection.
request. is the actual description of the event.
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource events can be categorized as follows:
Online and OnlineThread events relate to the process of bringing online the 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows resource.
Offline events relate to the process of bringing the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
offline.
Terminate events relate to the process of performing an immediate shutdown of the
resource.
Open and Close events relate to the processes of creating new resource instances and
removing them from the cluster.
IsAlive events relate to the thorough resource health checks function.
320-200263 Page 40
Page 41

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
NOTE: Deleting the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource might be
required for certain operations, such as its own version upgrade.
5.1.2.3 Troubleshooting a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Failure
The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource, upon which depend disk and application
resources, will perform a series of checks upon being brought online. If any of these checks
fail, it will in turn fail. Whether it is right after being installed and configured for the first
time, during a failover test or for an actual site failure, MSCS will attempt to bring the 3PAR
GeoCluster for Windows online on one to several cluster nodes in turn. Every time it
happens, the decision sequence followed by the resource will be logged in the cluster.log.
In order to find and analyze this event sequence, when browsing the relevant cluster.log
report, search for the following event:
OnlineThread: Error <Windows error code> bringing
resource online.
This event concludes any event sequence leading to a failure to bring the 3PAR GeoCluster
for Windows resource online. The events leading to this outcome should provide an explicit
story of why it happened. Any step of the resource decision matrix, whether successful or
failed, will be sanctioned by a cluster.log event. A list of all known 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows events is included in chapter 5.3.
In addition, any event with the mention of the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
name as it shows under Other Resource in Cluster Failover Manager will directly relates to
the resource and give hints as to how it was managed by MSCS central resources, such as
Resource Host Subsystem (RHS) or Resource Control Manager (RCM).
5.2 Known issues
5.2.1 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows Resource Deletion
Symptoms
Deleting the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource in Failover Cluster Manager can cause
other 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resources to fail, even if they are not part of the same
Service and Applications group.
320-200263 Page 41
Page 42

CAUTION: This workaround implies that the inter-site failover capabilities of
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows will be unavailable during the operation
requiring the deletion of the resource.
Workaround
In order to prevent this behavior from affecting production resources via the dependencies,
it is advised to remove dependencies toward the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
during any operation requiring the deletion of the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource.
The production resources will still be accessible.
5.3 Event Catalog
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
What follows is a list of all 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows events, by categories. For each of
them, the severity level and an explanation of the event is given. The mention <Windows
error code> means that something in relation with Windows inner workings has failed.
See the following webpage for more information http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-
us/library/ms681381(VS.85).aspx .
5.3.1 Online and OnlineThread Events
Online: request
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: A request has been made for the resource to be brought online.
Online: Unable to start thread. Error:<Windows error code>
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The thread necessary to the process of bringing the resource online could not
be created, for a reason related to the Windows error code specified.
Online: sanity check failed! resid = <resid>
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: A verification of the resource core functionalities has failed. This error implies
a major dysfunction of a software component such as MSCS or the 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource or corrupted memory.
320-200263 Page 42
Page 43

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
OnlineThread: Unable to read properties, error:<Windows error
code>
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource parameters (set in the
Parameters tab of the resource in Failover Cluster Manager) could not be read. Typically, it
may have been left empty.
OnlineThread: Unable to find the synchronous remote copy group
\"<Remote Copy group name>" on the local InServ.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The Remote Copy group could not be accessed from the InServ located on
the same site as the node attempting to bring the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online.
OnlineThread: Unable to find the synchronous remote copy group
\"<Remote Copy group name>" on the remote InServ.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The Remote Copy group could not be accessed from the InServ located on
the site remote to the node attempting to bring the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online.
OnlineThread: Error <Windows error code> bringing resource
online.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: MSCS experiences an error bringing the resource online. This event will be
found at the end of any event sequence leading to a failure to bring the 3PAR GeoCluster
for Windows resource online.
OnlineThread: Everything is good, primary locally and started.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: This event indicates that the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource was
able to connect to the InServ located on the same site, was able to access the Remote Copy
group set in its parameters and found it to have the primary role and started.
OnlineThread: RC configuration not complete, remote copy group
\"<Remote Copy group name>" status is \"New\".
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: Remote Copy configuration was found incomplete during the process of
bringing the InServ Cluster Resource online, as the Remote Copy group status was “New”.
320-200263 Page 43
Page 44

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
OnlineThread: Unable to find the remote copy group \"<Remote
Copy group name>" target on the local InServ.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource was not able to find viable target
information in the Remote Copy group information. This event is unlikely to appear under
normal conditions and is indicative of discrepancies between the version of InForm OS and
3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
OnlineThread: Remote copy group \"<Remote Copy group name>"
role (<Remote Copy group role>) is invalid on the remote
InServ.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: During the process of bringing a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online, Remote Copy information is found to be inconsistent with what is expected. This
event is unlikely to appear under normal conditions and is indicative of discrepancies
between the version of InForm OS and 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
OnlineThread: Failover has occurred and we are on the wrong
site.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: Upon an attempting to be brought online, the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
resource found out that a failover was taking place and concluded that it was not itself
located on the site where a node is supposed to take over.
OnlineThread: Nothing to do, RC group is primary locally and
secondary on the remote InServ.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource finds no blocking condition to its
bringing online and finds out that it is located on the primary Remote Copy group site and
that the Remote Copy is stopped.
OnlineThread: RC is down, however we are on the good site so
there is nothing to do.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: Upon being brought online, the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
found out that Remote Copy was stopped, but did not consider it a blocking condition.
320-200263 Page 44
Page 45

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
OnlineThread: Remote copy group \"<Remote Copy group name>"
status (<Remote Copy group status>) is invalid on the local
InServ.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: During the process of bringing a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online, Remote Copy information is found to be inconsistent with what is expected. This
event is unlikely to appear under normal conditions and is indicative of discrepancies
between the version of InForm OS and 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
OnlineThread: Nothing to do, we are on the good site.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: Upon being brought online, the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
found out that its Remote Copy group had the Primary-rev role and is going along with the
process.
OnlineThread: The virtual volume named locally <VV name> is not
synced.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: During the process of bringing a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online, Virtual Volume information is found to be inconsistent with what is expected. This
event is unlikely to appear under normal conditions and is indicative of discrepancies
between the version of InForm OS and 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
OnlineThread: Remote copy group \"<Remote Copy group name>"
status is starting or started.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: During the process of bringing a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online, the relevant Virtual Volumes were found to be synced and therefore were not
considered a blocking condition to a failover.
OnlineThread: The remote copy group was stopped on purpose. No
failover will be initiated.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: During the process of bringing a 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
online, Remote Copy group information was found to be a blocking condition to failover.
Target was found ready, but the secondary Remote Copy group was found stopped. This
event implies the Remote Copy group was stopped manually.
320-200263 Page 45
Page 46

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
OnlineThread: Unable to find the periodic remote copy group
\"<Remote Copy group>" on the local InServ.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: Upon checking for the presence of a 3PAR Synchronous long distance
dedicated Remote Copy group, 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows found none. If a periodic
remote group were expected, then this is a problematic condition.
OnlineThread: There was a failover and we are on the wrong
site.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: Upon being brought online, the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource
found out that its Remote Copy group had the secondary-rev role and found it to be a
blocking condition.
OnlineThread: Unable to query the local InServ.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource was not able to establish an SSH
connection to the InServ located on the same site.
5.3.2 Offline Events
Offline: resource sanity check failed! resid = <resid>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: A verification of the resource core functionalities has failed. This error implies
a major dysfunction of a software component such as MSCS or the 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource or corrupted memory.
Offline: request.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: A request has been made for the resource to be brought offline.
Offline: Unable to start thread. Error: <Windows error code>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The thread necessary to the process of bringing the resource offline could
not be created, for a reason related to the Windows error code specified.
5.3.3 Open and Close Events
Close: request for resource <Resource name>.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: A request was made to close the specified resource instance.
320-200263 Page 46
Page 47

3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
Close: request for resource with resid <resid>.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: A request was made to close the specified resource instance.
Close: resource sanity check failed! resid = <resid>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: A verification of the resource core functionalities has failed. This error implies
a major dysfunction of a software component such as MSCS or the 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource or corrupted memory.
Open: failed with error <Windows error code>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The thread necessary to the process of creating a new resource instance
could not be created, for a reason related to the Windows error code specified.
Open: Unable to open the resource. Error: <Windows error code>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The process of creating a new resource instance failed, for a reason related
to the Windows error code specified.
Open: Unable to open the cluster. Error: <Windows error code>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource was not able to open a
connection to the cluster.
Open: Unable to allocate resource data structure. Error:
<Windows error code>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource could not be given the system
resources it needed. Typically, this event may indicate not enough RAM is available on the
server.
Open: Unable to open Parameters key. Error: <Windows error
code>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource experienced an error on a
specific internal operation.
320-200263 Page 47
Page 48

5.3.4 Terminate Events
Terminate resource sanity check failed! resid =<resid>.
Severity level: Error.
Explanation: A verification of the resource core functionalities has failed. This error implies
a major dysfunction of a software component such as MSCS or the 3PAR GeoCluster for
Windows resource or corrupted memory.
Terminate request.
Severity level: Informational.
Explanation: A request has been made for the resource to be terminated.
5.3.5 Health Check Events and Other Events
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
IsAlive: The Network link is down, unable to reach <IP
address>.
Severity level: Warning.
Explanation: The 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows resource was unable to reach the InServ
at the specified IP address during a thorough resource health check.
IsAlive: Remote copy group <Remote Copy group name> status
(<Remote Copy group status>) is invalid on local InServ.
Severity level: Warning.
Explanation: During a thorough resource health check the 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows
resource online, Remote Copy information is found to be inconsistent with what is
expected. This event is unlikely to appear under normal conditions and is indicative of
discrepancies between the version of InForm OS and 3PAR GeoCluster for Windows.
320-200263 Page 48
Page 49

Release level
Revision history
320-200263
October 2010
First release of this manual to support product release.
6
Revision History
3PAR GeoCluster 1.0.0.14 for Windows User’s Guide
320-200263 Page 49
 Loading...
Loading...