Page 1

HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch
User Guide
Part number: 331399-004
Fourth edition: February 2006
Page 2

Legal notices
© 2004, 2006 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft®, Windows®, and Windows NT® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netscape Navigator is a U.S. trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation.
Cisco® is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries.
Printed in the US
Part number: 331399-004
Fourth edition: February 2006
2
Page 3

Contents
Introduction
Overview................................................................................................................................................ 5
Additional references ............................................................................................................................... 5
Features.................................................................................................................................................. 6
Enterprise class performance ................................................................................................................ 6
GbE2 Interconnect Switch redundancy................................................................................................... 8
Configuration and management............................................................................................................ 8
Diagnostic tools .................................................................................................................................. 8
GbE2 Interconnect Switch architecture...................................................................................................... 10
HP Ethernet Connectivity Mapper utility (hpecm).................................................................................... 12
GbE2 Interconnect Switches ............................................................................................................... 12
Redundant crosslinks ......................................................................................................................... 12
Redundant paths to server bays .......................................................................................................... 12
Supported technologies .......................................................................................................................... 12
Layer 2 switching.............................................................................................................................. 12
IEEE 802.1Q-based Virtual Local Area Network ................................................................................... 13
Spanning Tree Protocol...................................................................................................................... 13
Simple Network Management Protocol ................................................................................................ 13
Port mirroring ................................................................................................................................... 13
Port trunking and load balancing ........................................................................................................ 13
Trivial File Transfer Protocol support..................................................................................................... 13
Store and forward switching scheme ................................................................................................... 14
Bootstrap Protocol............................................................................................................................. 14
Network Time Protocol....................................................................................................................... 14
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) .............................................................................14
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+).........................................................14
Secure Shell and Secure Copy............................................................................................................ 15
XModem.......................................................................................................................................... 15
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping ......................................................................... 15
Jumbo frames ................................................................................................................................... 15
Auto-MDI/MDIX................................................................................................................................ 15
Auto-negotiation of duplex mode and speed......................................................................................... 15
Redundant images in firmware............................................................................................................ 16
External components .............................................................................................................................. 16
GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel .................................................................................................. 16
QuadT2 Interconnect Module panel .................................................................................................... 18
QuadSX Interconnect Module panel .................................................................................................... 19
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. 21
Installing the GbE2 Interconnect Switches and Interconnect Modules............................................................. 21
HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit option.................................................................. 21
Installation guidelines ........................................................................................................................ 21
Installing a new GbE2 Interconnect Switch for a new deployment............................................................ 21
Replacing an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch ................................................................................... 22
Upgrading from an existing GbE Interconnect Switch............................................................................. 23
Upgrading from an RJ-45 Patch Panel or RJ-45 Patch Panel 2 ................................................................. 24
Planning the GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration.................................................................................. 24
Default settings ................................................................................................................................. 24
GbE2 Interconnect Switch security....................................................................................................... 25
Manually configuring a GbE2 Interconnect Switch ................................................................................ 26
Configuring multiple GbE2 Interconnect Switches.................................................................................. 26
Cabling the GbE2 Interconnect Switch...................................................................................................... 26
Powering up the GbE2 Interconnect Switch ............................................................................................... 27
Contents 3
Page 4

Accessing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch...................................................................................................27
Logging on and configuring the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.......................................................................... 28
Supporting software and special considerations......................................................................................... 29
HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices
Class A equipment................................................................................................................................. 30
Modifications ........................................................................................................................................ 30
Cables ................................................................................................................................................. 30
Canadian Notice (Avis Canadien) ........................................................................................................... 30
Class A equipment ............................................................................................................................ 30
European Union Regulatory Notice .......................................................................................................... 31
BSMI Notice.......................................................................................................................................... 32
Japanese Notice.................................................................................................................................... 32
Korean Notice....................................................................................................................................... 32
HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices
Class A equipment................................................................................................................................. 33
Modifications ........................................................................................................................................ 33
Cables ................................................................................................................................................. 33
Canadian Notice (Avis Canadien) ........................................................................................................... 33
Class A equipment ............................................................................................................................ 33
European Union Regulatory Notice .......................................................................................................... 34
BSMI Notice.......................................................................................................................................... 35
Japanese Notice.................................................................................................................................... 35
Korean Notice....................................................................................................................................... 35
Laser compliance ................................................................................................................................... 35
Technical specifications
Runtime switching software default settings
Switch A and Switch B: general default settings ......................................................................................... 39
Switch A and Switch B: port names, VLANs, STP, trunking default settings..................................................... 45
Performing a serial download
Introduction........................................................................................................................................... 47
Serial upgrade of boot code firmware image procedure ............................................................................. 47
Serial upgrade of operating system firmware procedure ............................................................................. 49
SNMP MIBs support
Introduction........................................................................................................................................... 52
SNMP manager software........................................................................................................................ 52
Supported MIBs ..................................................................................................................................... 52
Supported traps..................................................................................................................................... 53
Safe Mode configuration
Introduction........................................................................................................................................... 55
User account information ........................................................................................................................ 55
Safe Mode............................................................................................................................................ 55
GbE2 Interconnect Switch replacement scenario using a Safe Mode configuration ......................................... 56
Safe Mode configuration file templates ..................................................................................................... 56
Safe Mode configuration file template modification ...............................................................................56
Applying the Safe Mode template configuration file............................................................................... 56
Electrostatic discharge
Overview.............................................................................................................................................. 58
Grounding methods ............................................................................................................................... 58
RJ-45 pin specification
Troubleshooting
Index
Contents 4
Page 5
Introduction
Overview
This user guide provides installation and reference information for the following kits:
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit
Additional references
Once the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is installed, you are ready to configure it. Detailed information about how to
configure the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is available in the reference guides listed below. To obtain these guides, go
to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Application Guide
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Command Reference Guide
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Browser-based Interface Reference Guide
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Quick Setup Instructions
• HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Quick Setup Instructions
• HP BladeSystem p-Class SAN Connectivity Kit Quick Setup Instructions
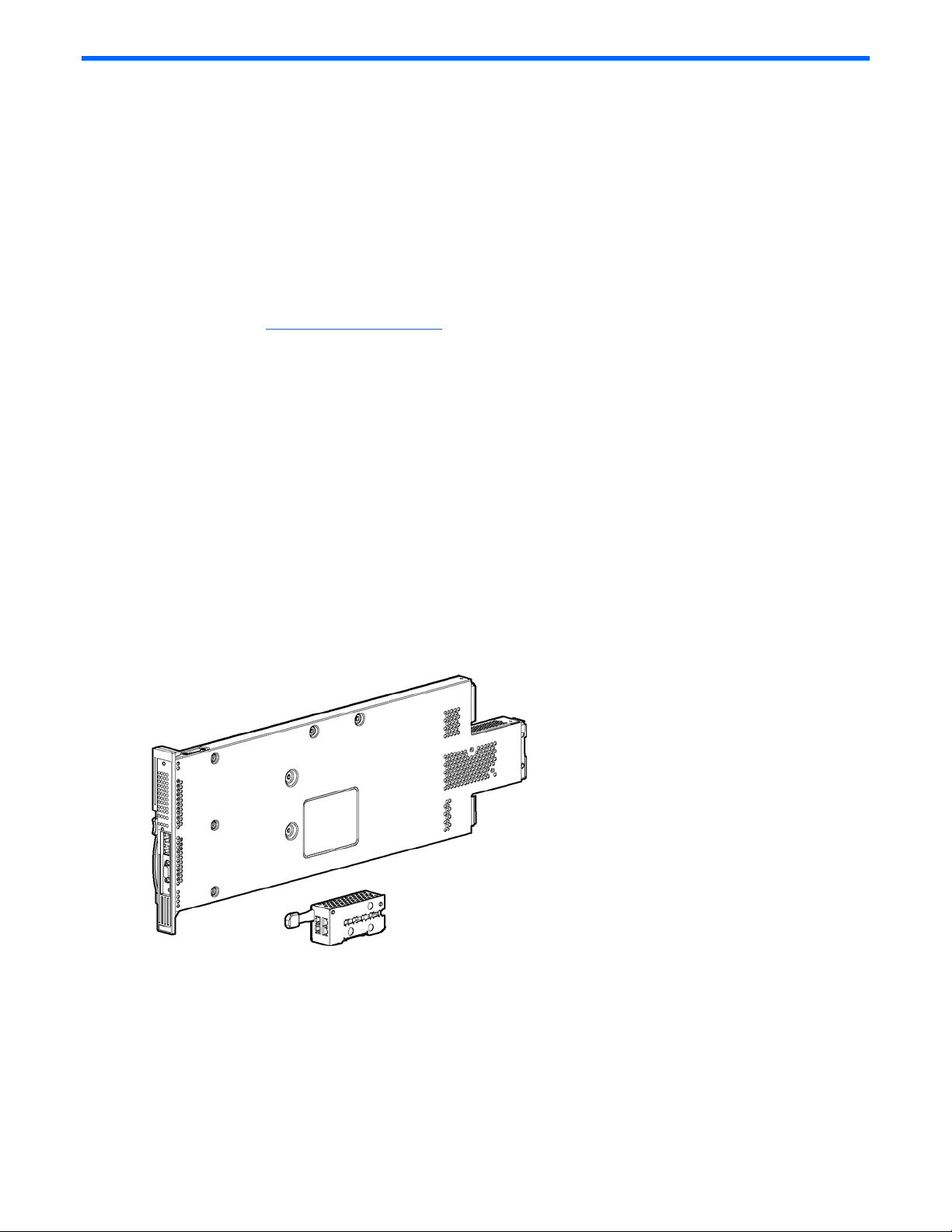
The HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit contains two HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switches
and two QuadT2 Interconnect Modules.
The HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switches and QuadT2 Interconnect Modules use 10Base-T/100BaseTX/1000Base-T Gigabit Layer 2 switching technology to provide between 32-to-1 (blocking) to 32-to-12 (blocking)
reduction in the number of networking cables per BL p-Class server blade enclosure.
), and search for GbE2.
Each HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch and QuadT2 Interconnect Module reduces sixteen 10BaseT/100Base-TX/1000Base-T server networking ports to one to four RJ-45 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T ports
(located on the removable interconnect module) and one to two RJ-45 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T ports
(located on the front of the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch).
Figure 1 HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch and QuadT2 Interconnect Module
The HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit contains two HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switches
and two QuadSX Interconnect Modules.
The HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switches and QuadSX Interconnect Modules use 10Base-T/100BaseTX/1000Base-T and 1000Base-SX Gigabit Layer 2 switching technology to provide between 32-to-1 (blocking) to 32to-12 (blocking) reduction in the number of networking cables per BL p-Class server blade enclosure.
Each HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch and QuadSX Interconnect Module reduces sixteen 10BaseT/100Base-TX/1000Base-T server networking ports to one to four LC 1000Base-SX ports (located on the removable
interconnect module) and one to two RJ-45 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T ports (located on the front of the HP
ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch).
Introduction 5
Page 6
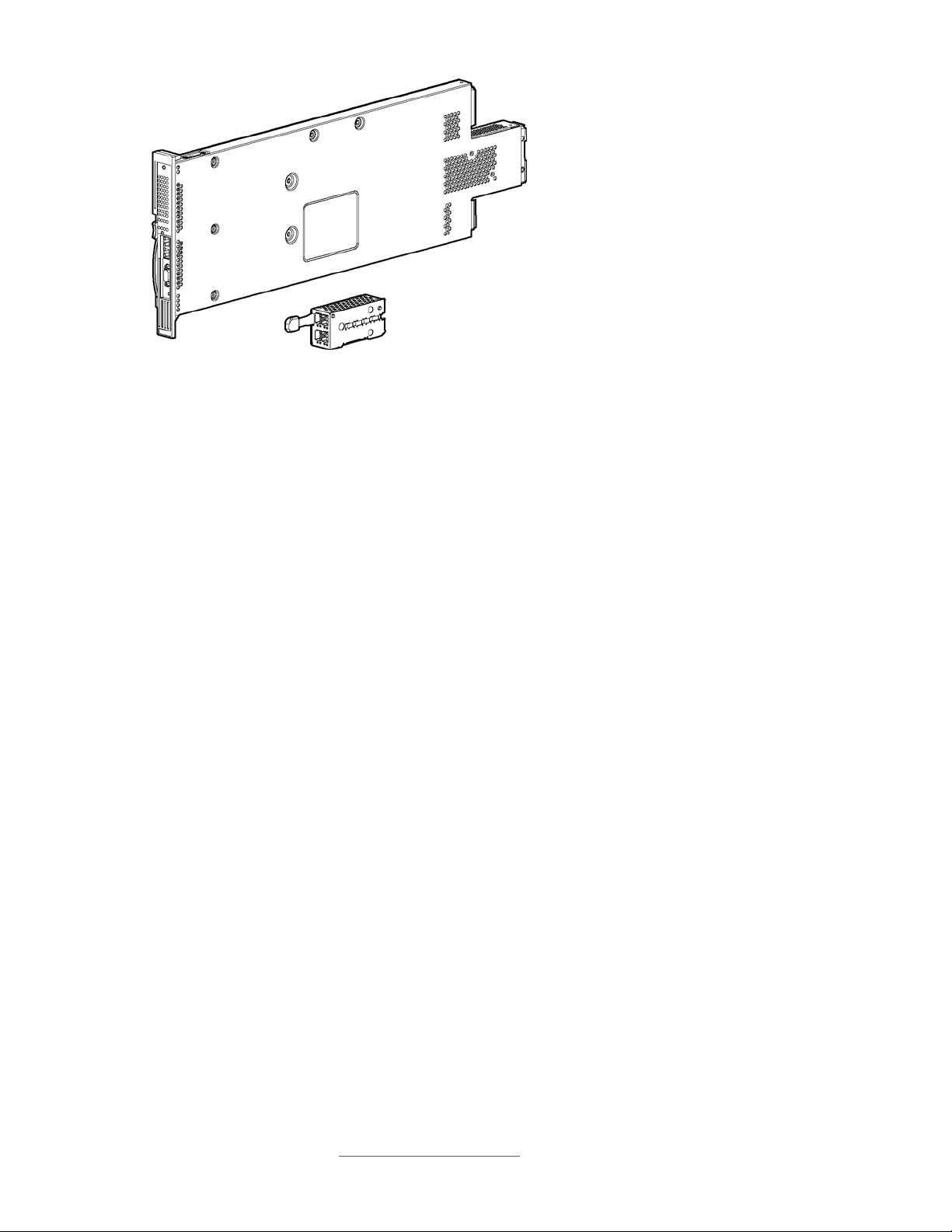
Figure 2 HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch and QuadSX Interconnect Module
Features
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch and interconnect modules are designed for easy installation and
high performance in an environment where traffic on the network and the number of users increases continually.
Enterprise class performance
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch features include:
• Up to a 16-to-1 reduction in networking cables and connections, concentration of sixteen 10/100/1000
Ethernet networking ports down to as little as one Gigabit Ethernet port, or up to six Gigabit Ethernet ports for
additional bandwidth and redundant connections to the network backbone
• Multi-layer switching capability with Layer 3 support for routing and Internet Protocol (IP) load balancing content
delivery switching
• Pass-through ProLiant BL20p G2 Fibre Channel storage signals via the optional GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit
• Fully supported on the existing ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure and infrastructure compatible with any
combination of ProLiant server blades
• Ability to upgrade from an existing GbE Interconnect Switch or Patch Panel interconnect without having to
power down the server blades and the server blade enclosure
• Pre-configured for immediate use with the ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure
• System security including Secure Shell (SSH), Secure Copy (SCP), 255 port-based IEEE 802.1Q tagged Virtual
Local Area Networks (VLANs) per GbE2 Interconnect Switch, RADIUS user authentication and authorization, or
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+) Authentication, Authorization, and
Accounting (AAA)
• An extensive list of industry standard protocol support, compatible with widely-used networking components
• 9K jumbo frames that improve performance by increasing application throughput and decreasing server
processor utilization
• Robust configuration and management from any switch port using the included browser-based and scriptable
command line user interfaces
• Support for Telnet, Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), SCP and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
file transfer, human read/write configuration file, XModem, an extensive list of Management Information Base
objects (MIBs), and more, further enhance the management capabilities
• Fully end-to-end redundant architecture maximizing network availability
• Support for Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping for multicasting
• Support for Uplink Failure Detection (UFD) for network path resiliency. It works in conjunction with NIC teaming
functionality that is supported on the blade servers. This feature tracks the link state on uplink ports. When an
uplink port goes down or is in STP blocking state, this feature will enable the switch to auto-disable the
downlinks which are connected to the blade server NICs. This enables NIC teaming software to detect link
failure on the primary NIC port and fail over to the secondary NIC in the team. As a result, the secondary path
is enabled for continued blade server access.
When used in conjunction with UFD, NIC teams on the blade server must be configured for switch redundancy.
That is, the team will span ports on both Switch A and Switch B. Refer to the HP ProLiant Network Adapter
Teaming white paper on http://www.hp.com/support
for additional information.
Introduction 6
Page 7

• Remote Monitoring (RMON) feature, which allows network devices to exchange network monitoring data.
RMON performs the following major functions:
• Gathers cumulative statistics for Ethernet interfaces
• Tracks a history of statistics for Ethernet interfaces
• Creates and triggers alarms for user-defined events
• Quality of Service (QoS) feature, where the switch uses the Differentiated Services (RFCs 2474 and 2475)
architecture to provide QoS functions. QoS allocates guaranteed bandwidth to the critical applications and
limits bandwidth for less critical applications. QoS allows prioritization of network traffic, thereby providing
better service for selected applications.
• Access control lists that allow you to classify and segment traffic. This allows different levels of service to
different traffic types.
• Switch software supports RIP version 1 (RIPv1) and RIP version 2 (RIPv2) for exchanging TCP/IP route
information with other routers.
• An administrator can define end user accounts that permit limited access to the switch. The switch requires
username/password authentication for end users.
• Fast Uplink Convergence that enables the switch to quickly recover from the failure of the primary link or trunk
group in a Layer 2 network using Spanning Tree Protocol.
• Support for Secure Shell (SSH) version 2. SSH is a protocol that enables remote administrators to log securely
into the switch over a network to execute management commands.
• Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) allows the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to control and configure trunk
groups dynamically. The GbE2 supports the IEEE 802.3ad-2002 standard.
• Configurable Trunk Hash Algorithm feature, which allows you to configure the particular parameters for the
switch Trunk Hash algorithm, instead of relying on the default values. You can configure new default behavior
for L2 traffic and L3 traffic by selecting up to two of the following parameters to create your optimal
configuration:
• Source IP (SIP)
• Destination IP (DIP)
• Source MAC (SMAC)
• Destination MAC (DMAC)
• Switch software provides SNMP v1.0 and SNMP v3.0 support for access through any network management
software, such as HP-OpenView.
• Switch software provides user-level security for its ports using the IEEE 802.1x protocol,
which is a more secure alternative to other methods of port-based network access control. This feature provides
security to all ports of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
• Support for HTTP software upgrade using the Browser-Based Interface
(BBI). FTP or TFTP server is not required to perform a software upgrade.
• Port Fast Forwarding that allows a port that participates in Spanning Tree to bypass the Listening and Learning
states and enter directly into the Forwarding state.
• Switch software supports the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol. The GbE2 implementation
conforms to the OSPF version 2 specifications detailed in Internet RFC 1583.
• Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) enables redundant router configurations within a LAN, providing
alternate router paths for a host. VRRP eliminates single points-of-failure within a network.
• Allows secure browser access (HTTPS) to management functions
Introduction 7
Page 8

GbE2 Interconnect Switch redundancy
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch offers several redundancy and failover features. With these
features, the network configuration can be designed to allow for continued network access to each server blade in
case of a component or link failure. GbE2 Interconnect Switch redundancy and failover features include:
• Two separate GbE2 Interconnect Switches per one ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure
• Four Gigabit Ethernet uplink ports in the back and two Gigabit Ethernet uplink ports in the front, per GbE2
Interconnect Switch, for designing fully meshed uplink paths to the network backbone
• Server networking connections routed to each of the separate GbE2 Interconnect Switches for redundant paths
to tolerate a switch or port malfunction
• Redundant data path 10/100/1000 Ethernet cross connections between GbE2 Interconnect Switches
• STP support that eliminates potential problems caused by redundant networking paths and provides for failover
with a secondary path in case of primary path failure; supports IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol and is
compatible with Cisco® PVST+ and Cisco PVST, when the other device is configured as untagged or configured
to use 802.1q tagging. Release 2.0 also supports IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) and
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP).
• Redundant power supplies and redundant cooling fans within the server blade enclosure
• Redundant firmware images and configuration settings in memory
• Redundant, configurable Domain Name System (DNS) clients, syslog servers, gateways, and community strings
and SNMP trap manager hosts
Configuration and management
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch provides the following configuration and management interfaces
and tools:
• A scriptable command line interface (CLI) allows local, Telnet, or Secure Shell (SSH) access.
• A browser-based interface (BBI) allows remote access using a Web browser such as Microsoft® Internet
Explorer or Netscape Navigator.
• Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) manageability and monitoring are supported.
• The GbE2 Interconnect Switch functionality allows you to upload and download interconnect switch
configurations via Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) and Secure Copy Protocol (SCP), thus allowing the rapid
deployment of multiple server blade systems, and providing robust backup and restore capabilities.
• Network Time Protocol (NTP) is supported, allowing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to display and record the
accurate date and time as provided by an NTP server.
• Two firmware images, either of which can be selected to be the current runtime image, can be held in memory.
• Remote authentication dial-in user service (RADIUS) provides support for user authentication and authorization.
• TACACS+ provides support for Cisco TACACS+ server compatible authentication, authorization, and
accounting.
• The user interfaces provide multi-level password protected user accounts.
• The setup utility allows step-by-step tailored configuration.
• IP settings can be set manually or obtained automatically from a Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) server.
• A text-based, human read/write configuration file provides viewing, printing, and editing capabilities.
• A Domain Name System (DNS) client supports primary and secondary DNS servers.
• Any port may be enabled or disabled as desired.
• Any GbE2 Interconnect Switch port can be used to perform switch management and Preboot Execution
Environment (PXE).
Diagnostic tools
The hardware, software, and firmware diagnostic tools that are available include:
• HP Systems Insight Manager automatic discovery and identification
• Power-on self-test (POST) built into the GbE2 Interconnect Switch boot process
• GbE2 Interconnect Switch port mirroring
• GbE2 Interconnect Switch LED panel displaying per port status and speed
• Interconnect module LEDs displaying per port status and speed
• System, management, and option compatibility status LEDs
• Front panel reset power switch, DB-9 port, and two Gigabit Ethernet ports
Introduction 8
Page 9

• Statistic monitoring including port utilization, data packets received/transmitted, port error packets, trunk
utilization, and so on
• Ping and trace route capability
• Remote syslog with support for primary and secondary syslog server
• Portable Diagnostic Station option to configure and diagnose a GbE2 Interconnect Switch and server blade
removed from the rack
• The ability to return the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to known good condition in case of firmware corruption
• State information dump for tuning and debugging switch performance
• Panic command for immediate state dump to flash memory and automatic switch boot
• Ability to set NVRAM diagnostic flags
Introduction 9
Page 10
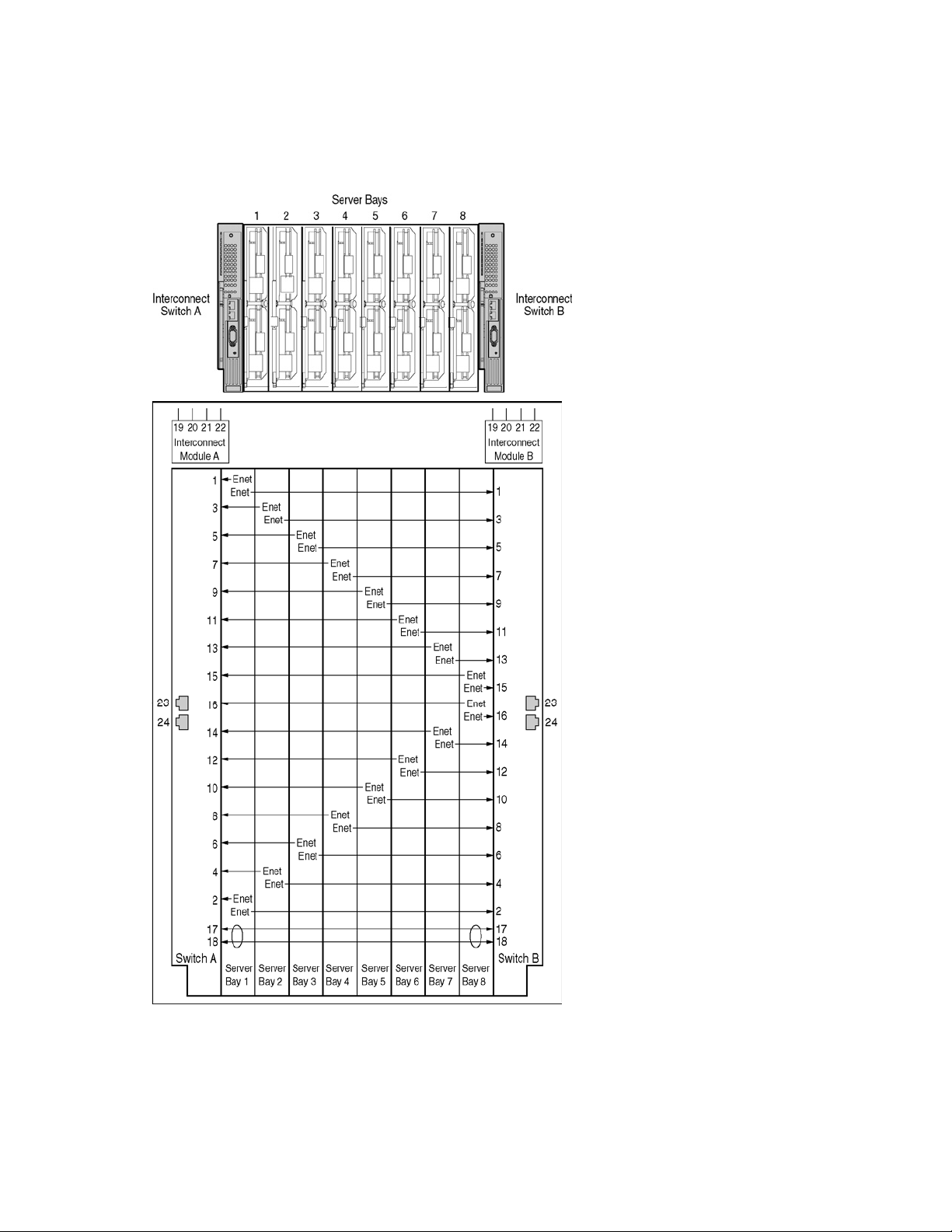
GbE2 Interconnect Switch architecture
The ProLiant BL p-Class system provides integrated switching technology for network cable reduction.
The following diagram illustrates the Ethernet signal connectivity between server bays and the interconnect bays
through the backplane for the p-Class server enclosure.
Figure 3 Ethernet signal connectivity via backplane
Introduction 10
Page 11
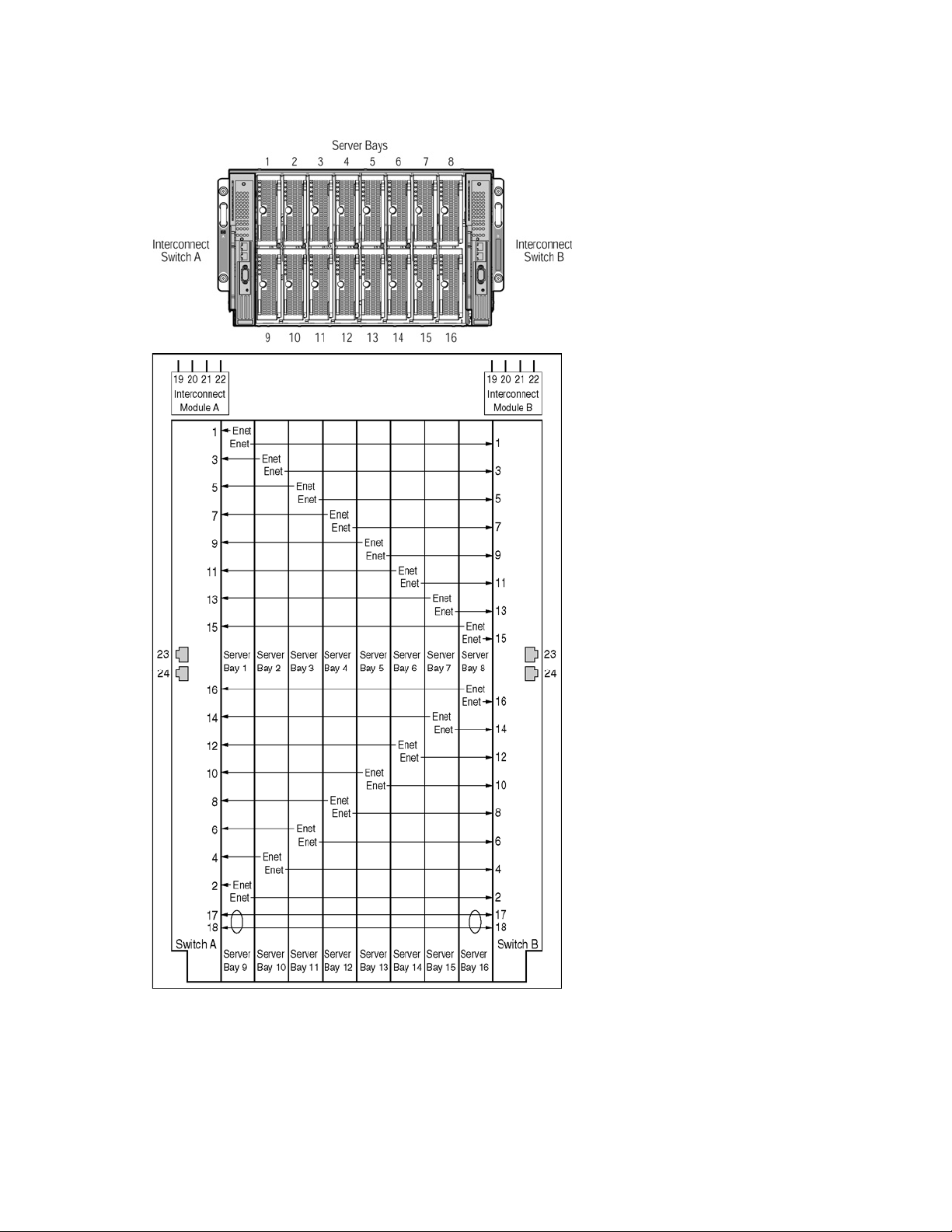
The following diagram illustrates the Ethernet signal connectivity between server bays and the interconnect bays
through the backplane for p-Class server enclosures with enhanced backplane components that support high-density
blade servers.
Figure 4 Ethernet signal connectivity for server enclosures with enhanced backplane components
The interconnect switch does not affect or determine NIC enumeration and the associated mapping of NIC interfaces
to interconnect switch ports. The numbering of the NICs on the server (for example, NIC 1, NIC 2, NIC 3) is
determined by the server type, the server operating system, and what NICs are enabled on the server.
Introduction 11
Page 12

HP Ethernet Connectivity Mapper utility (hpecm)
The HP Ethernet Connectivity Mapper is a utility used to determine the NIC name enumeration and the associated
mapping to switch ports. The physical connections between server blade network interface controllers (NICs) and
switch ports depend on the server blade type and the enclosure backplane type, as described above. The logical NIC
name enumeration depends on the operating system software (such as Local Area Connection, Local Area
Connection 2, etc. for Windows; eth0, eth1, etc. for Linux).
hpecm is a graphical tool which collects information about the contents of a ProLiant BL blade enclosure, including
enclosure type, blade type, and blade operating system (OS). It then displays the mapping between the switch or
patch panel ports and the OS enumeration (naming order) of the blade network interface controller (NIC) ports.
Configuration validation is performed as items are selected, so hpecm may also be used as an aid to configuration
and/or deployment planning.
To obtain the HP Ethernet Connectivity Mapper, download the Interconnect Switch Management Utilities from the HP
website (http://www.hp.com/support
). Search for GbE2.
GbE2 Interconnect Switches
Two GbE2 Interconnect Switches in the ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure provide switch redundancy and
redundant paths to the network ports on the server blades. Each GbE2 Interconnect Switch has six external Ethernet
ports and sixteen internal Gigabit Ethernet ports providing connectivity to the blade servers within the enclosure.
Each pair of GbE2 Interconnect Switches consolidates up to thirty-two 10/100/1000 Ethernet signals into one-toeight Gigabit ports (on the back of the system) plus four additional Gigabit Ethernet ports (on the front of the GbE2
Interconnect Switches). This design eliminates up to 31 network cables from the back of the server blade enclosure.
Redundant crosslinks
The two GbE2 Interconnect Switches are connected through redundant 10/100/1000 crosslinks. These two
crosslinks provide an aggregate throughput of 2 Gb/s for traffic between the GbE2 Interconnect Switches.
Redundant paths to server bays
Redundant Ethernet signals from each blade server are routed through the enclosure backplane to separate GbE2
Interconnect Switches within the enclosure. Two Ethernet signals are routed to Switch A and two are routed to Switch
B. This configuration provides redundant paths to each server bay.
Redundant Ethernet signals from each blade server are routed through the enclosure backplane to separate GbE2
Interconnect Switches within the enclosure. However, specific switch port to server mapping varies depending on
which type of server blade is installed. For example, for ProLiant BL20p series servers, two Ethernet signals are routed
to Switch A and two are routed to Switch B. This configuration provides redundant paths to each server bay.
On a heavily used system, using a single uplink port for 32 Ethernet signals can cause a traffic bottleneck. For
optimum performance, HP recommends that at least one uplink port per GbE2 Interconnect Switch be used.
The two front panel 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T ports per GbE2 Interconnect Switch may also be used for
additional uplink bandwidth to the network.
Supported technologies
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports the following technologies.
Layer 2 switching
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch uses 10/100/1000 Gigabit Layer 2 switching technology. Layer 2
refers to the Data Link layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model, which is concerned with moving data
packets across a network by enforcing Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). This layer
performs the following tasks:
• Ethernet packet framing
• Medium Access Control (MAC) addressing
• Physical medium transmission error detection
• Medium allocation (collision avoidance)
• Contention resolution (collision handling)
Introduction 12
Page 13

Layer 2 switching technology allows the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to look into data packets and redirect them based
on the destination MAC address. This reduces traffic congestion on the network because packets, instead of being
transmitted to all ports, are transmitted to the destination port only.
IEEE 802.1Q-based Virtual Local Area Network
The ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch provides support for a total of 255 IEEE 802.1Q Virtual Local Area
Networks (VLANs) for server grouping and isolation. A VLAN is a network segment configured according to a logical
scheme rather than a physical layout. VLANs can be used to combine any collection of local area network (LAN)
segments into an autonomous user group that appears as a single LAN.
VLANs also logically segment the physical network into different broadcast domains so that packets are forwarded
only between ports within the VLAN. This technology enhances performance by conserving bandwidth and improves
security by limiting traffic to specific domains. For example, you may want to isolate the server blade iLO ports from
the rest of the NICs. The iLO ports on interconnect Switch B can be assigned to their own VLAN and go to a
dedicated uplink or share an uplink using VLAN tagging.
IMPORTANT: The greater the number of VLANs, the greater the GbE2 Interconnect Switch central processing
unit (CPU) utilization. For maximum interconnect switch performance, HP recommends that you be judicious
when configuring the number of VLANs.
Spanning Tree Protocol
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), which allows the blocking of links
that form loops between switches in a network. When multiple links between switches are detected, a primary link is
established. Duplicated links are blocked from use and become standby links. If the primary link fails, the standby link
is activated.
In addition, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch provides a spanning tree domain per VLAN. The switch is compatible with
Cisco® PVST+ and Cisco PVST, when the other device is configured as untagged or configured to use 802.1q
tagging. Sixteen spanning tree domains are supported per GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
Release 2.0 also provides IEEE 802.1s-based MSTP and IEEE 802.1w-based RSTP.
Simple Network Management Protocol
Each GbE2 Interconnect Switch can be configured and monitored remotely from a Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP)-based network management station. The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports industry-standard SNMP
Management Information Bases (MIBs) and proprietary HP enterprise switch MIBs for fault detection and monitoring
of switch functionality. In addition, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports various environmental traps such as
temperature and fan failure traps.
To secure the management interface, the switch administrator can configure community strings with two levels of
access: Read and Read/Write. Access to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch can also be restricted to only management
stations that are members of a specific Internet Protocol (IP) network. This can be achieved by configuring the
address/mask of that specific network as a restricted management network address/mask.
Port mirroring
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch allows you to mirror one or multiple ports (source ports) to another port (destination
port) for network monitoring and troubleshooting purposes. This technology offers a way for network packet
analyzers to view the traffic moving through the GbE2 Interconnect Switches by providing a copy of the traffic that is
currently being passed through any other port. The packets are normally sent to a network packet analyzer or other
monitoring device attached to the mirror port.
Port trunking and load balancing
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports EtherChannel compatible IEEE 802.3ad (without LACP) port trunking allowing
several ports to be grouped together and act as a single logical link called a trunk. This feature provides a bandwidth
that is a multiple of the bandwidth of a single link. It also improves reliability since load balancing is automatically
applied to the ports in the trunked group. A link failure within the group causes the network traffic to be directed to
the remaining links in the group.
Trivial File Transfer Protocol support
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) support allows the GbE2 Interconnect Switch firmware to be upgraded by
downloading a new firmware file from a TFTP server to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Firmware images of the GbE2
Introduction 13
Page 14

Interconnect Switch can also be uploaded to a TFTP server, a configuration file can be downloaded into a GbE2
Interconnect Switch from a TFTP server, and configuration settings can be saved to the TFTP server.
Store and forward switching scheme
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch provides a store and forward switching scheme that allows each packet to be buffered
(stored) before it is forwarded to its destination. While this method creates latency, it improves reliability in a heavily
used interconnect switch. Packets that cannot be forwarded are saved immediately, rather than dropped, so that
packets behind them are less likely to be dropped in periods of heavy usage.
Bootstrap Protocol
By default, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is configured to obtain an IP address from a Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)
server during the boot process. The IP settings can also be manually configured by means of the serial interface. The
IP settings are configurable from the browser-based interface, but because the connection is based on an IP address
for these interfaces, users will have to reconnect with the newly assigned IP address.
Network Time Protocol
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch can maintain the current date and time. This information displays on the management
interfaces and is used to record the date and time of switch events. Current date and time information can be
manually set on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch or can be obtained through Network Time Protocol (NTP). NTP allows
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to send a request to a primary NTP server in each polling period asking for Greenwich
Mean Time (GMT).
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS)
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports the Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) method to
authenticate and authorize remote administrators for managing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. This method is based
on a client/server model. The Remote Access Server (RAS)—the switch—is a client to the back-end database server. A
remote user (the remote administrator) interacts only with the RAS, not the back-end server and database.
RADIUS authentication consists of the following components:
• A protocol with a frame format that utilizes User Datagram Protocol (UDP) over IP, based on Request For
Comments (RFC) 2138 and 2866
• A centralized server that stores all the user authorization information
• A client, in this case, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch, acting as the RADIUS client, communicates to the RADIUS server to authenticate and
authorize a remote administrator using the protocol definitions specified in Request For Comments (RFC) 2138 and
2866. Transactions between the client and the RADIUS server are authenticated using a shared key that is not sent
over the network. In addition, the remote administrator passwords are sent encrypted between the RADIUS client (the
switch) and the back-end RADIUS server.
The benefits of using RADIUS are:
• Authentication of remote administrators
• Identification of the administrator using name/password
• Authorization of remote administrators
• Determination of the permitted actions and customizing service for individual administrators
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus (TACACS+)
Starting with Release 2.0, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports the Terminal Access Controller Access Control
System Plus (TACACS+) method to authenticate, authorize, and account for remote administrators managing the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch. This method is based on a client/server model. The switch is a client to the back-end
TACACS+ AAA server. A remote user (the remote administrator) interacts only with the client, and not with the
back-end AAA server.
The TACACS+ AAA method consists of the following components:
• A protocol with a frame format that utilizes TCP over IP
• A centralized AAA server that stores all the user authentication, authorization, and accounting (of usage)
information
• A Network Access Server (NAS) or client (in this case, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch)
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch, acting as the TACACS+ client or NAS, communicates to the TACACS+ server to
authenticate, authorize, and account for user access. Transactions between the client and the TACACS+ server are
Introduction 14
Page 15

authenticated using a shared key that is not sent over the network. In addition, the remote administrator passwords
are sent encrypted between the TACACS+ client (the switch) and the back-end TACACS+ server.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports:
• Only standard ASCII inbound login authentication. PAP, CHAP, or ARAP login methods are not supported. One-
time password authentication is also not supported.
• Authorization privilege levels of only 0, 3, and 6. These map to management levels of user, oper, and admin,
respectively.
• The accounting attributes of protocol, start_time, stop_time, and elapsed_time. For WebUI (BBI) users,
accounting stop records are only sent if the user presses the QUIT button.
Secure Shell and Secure Copy
Secure Shell (SSH) and Secure Copy (SCP) use secure tunnels to encrypt and secure messages between a remote
administrator and the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Telnet does not provide this level of security. The Telnet method of
managing a GbE2 Interconnect Switch does not provide a secure connection.
SSH is a protocol that enables remote administrators to log securely into the GbE2 Interconnect Switch over a network
to execute management commands.
SCP is typically used to copy files securely from one machine to another. SCP uses SSH for encryption of data on the
network. On a GbE2 Interconnect Switch, SCP is used to download and upload the switch configuration via secure
channels.
XModem
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports XModem for transferring files during direct dial-up communications. XModem
sends blocks of data in 128-byte blocks, and includes an error-detection system called a checksum. When the data is
received, the error detection system ensures that the entire message reached its destination. If not, the receiving
computer sends a request for retransmission of the data.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Snooping
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports IGMP Snooping for multicasting, starting with Release 2.0. Both Version 1and Version 2-based IGMP Snooping is supported. In addition, auto detection of the multicast router port and manual
configuration of the multicast router port is supported. For efficient multicast traffic management, the IGMP Filtering
option is supported.
Jumbo frames
By default, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch module supports jumbo frames up to 9216 bytes, which may help reduce
server central processing unit (CPU) utilization and may increase application throughput. No configuration is
required. The GbE2 Interconnect Switch does not fragment frames as they exit, or assemble packets into jumbo
frames as they enter the switch.
Auto-MDI/MDIX
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch Ethernet ports are medium dependent interface (MDI)/MDI crossover (MDIX) capable.
MDI/MDIX is a type of Ethernet port connection using twisted pair cabling. The medium dependent interface (MDI) is
the component of the media attachment unit (MAU) that provides the physical and electrical connection to the cabling
medium. An MDI crossover (MDIX) is a version of MDI that enables connection between like devices. MDI ports
connect to MDIX ports via straight-through twisted pair cabling whereas both MDI-to-MDI and MDIX-to-MDIX
connections use crossover twisted pair cabling. The GbE2 Interconnect Switch has the capability to automatically
detect the cable selection/type, making the distinction between a straight-through cable and a crossover cable
unimportant.
Auto-negotiation of duplex mode and speed
Auto-negotiation of duplex mode and speed can be configured on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Network adapters
that support multiple data speeds, such as Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet, choose the speed at which they run
through a procedure called auto-negotiation. Auto-negotiation involves probing the capability of the network using
low-level signaling techniques to select compatible Ethernet speeds. Auto-negotiation was originally developed to
make the migration from traditional Ethernet to Fast Ethernet products easier.
Introduction 15
Page 16
Redundant images in firmware
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch can store up to two different software images, called image1 and image2, as well as
boot software, called boot. When you download new software, you are given the ability to specify where it is to be
placed: either into image1, image2, or boot.
For example, if your active image is currently loaded into image1, you should probably load the new image software
into image2. This lets you test the new software and revert back to the original image stored in image1, if needed.
CAUTION: Unlike the firmware that has two images, there is only one image of boot supported. Upgrading the
boot image replaces the original boot image.
External components
This section describes the front panel of the ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch, the QuadT2 Interconnect
Module Panel, and the QuadSX Interconnect Module Panel.
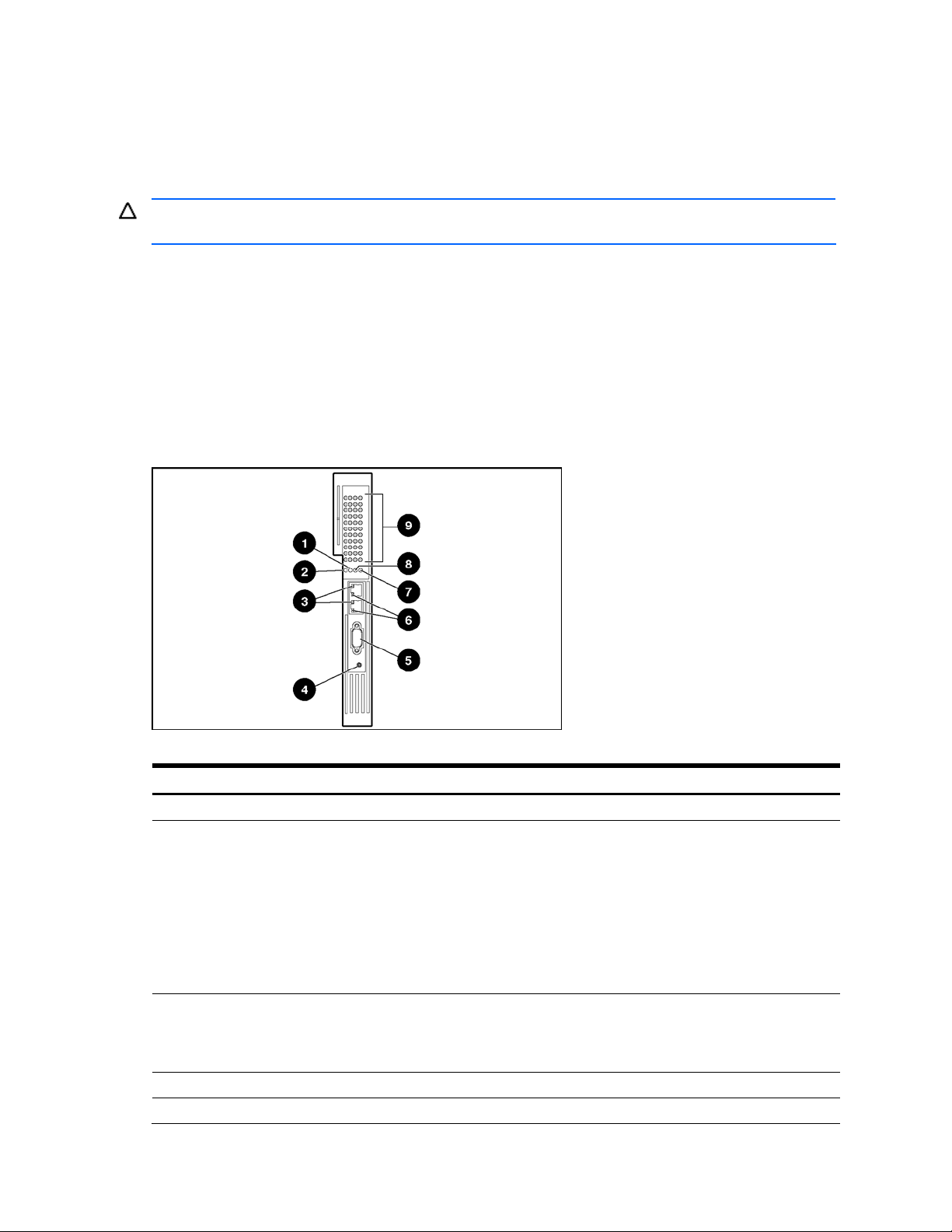
GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel
The front panel of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch has LEDs to indicate link activity, link speed, power status, and
management status. It has two RJ-45 connectors for 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T Ethernet management ports,
one RS-232 (DB-9) serial management port, and a power/reset (Pwr/Rst) button.
Figure 5 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel
Table 1 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel
Item Description Status
1 10G LED Reserved for future use
2 SAN LED Green = OctalFC Interconnect Module and Fibre Channel Signal Conditioning Card
match
Amber = OctalFC Interconnect Module and Fibre Channel Signal Conditioning Card
do not match
Off = No OctalFC Interconnect Module installed
Refer to the “HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit option” section in
the “Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch” chapter for information
about the GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit.
3 Front panel RJ-45
connector link speed LEDs
4 Pwr/Rst button Forces the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to power up or reboot
5 DB-9 connector Used to access the local management console
Amber = 1000 Mb/s
Green = 100 Mb/s
Off = 10 Mb/s
Introduction 16
Page 17
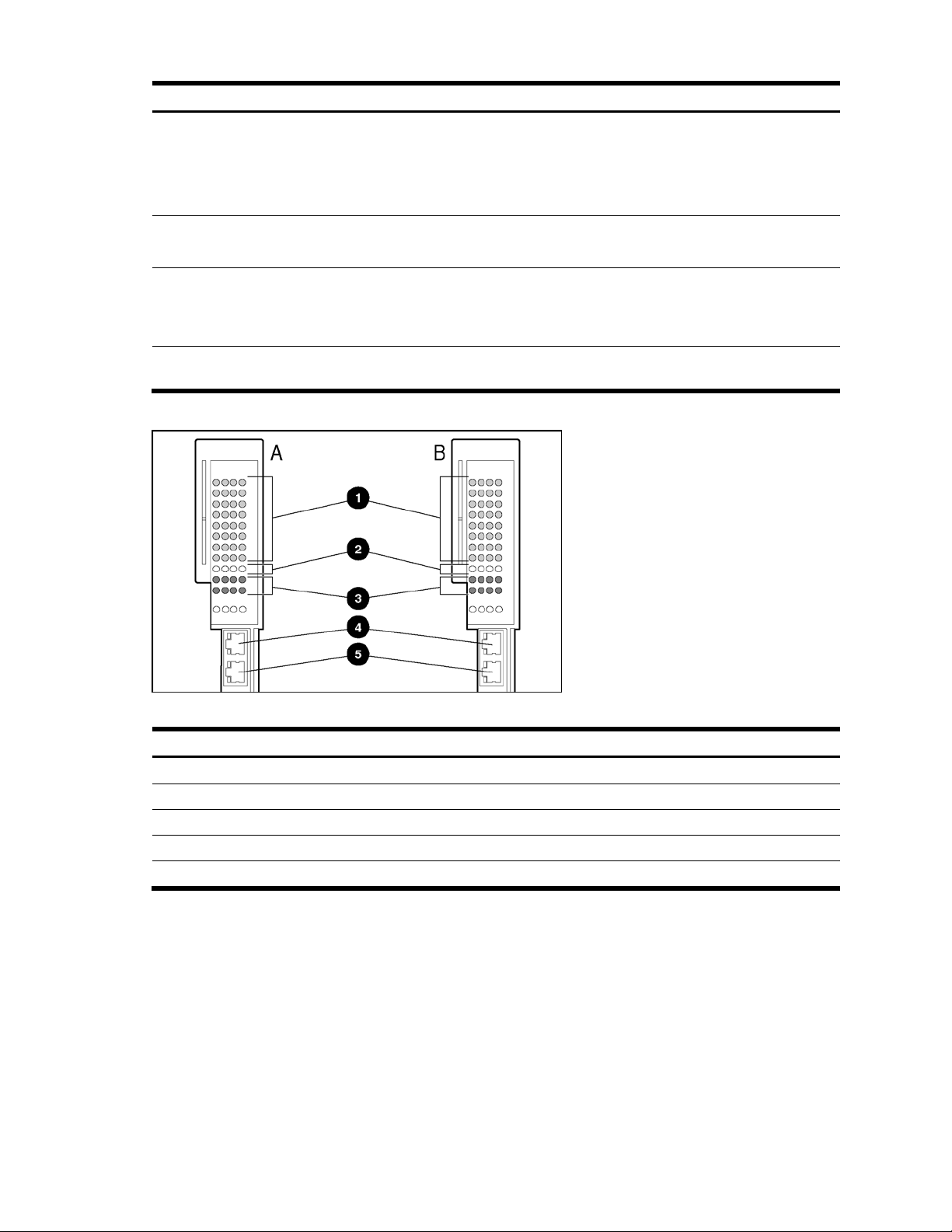
Table 1 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel
Item Description Status
6 Front panel RJ-45
connector link activity LEDs
7 Management status LED Flashing = Management session active
8 Power status LED Green = Power on
9 Link activity and speed
LEDs
Green = Link and no activity
Green flashing = Link and activity
Amber = Port disabled
Off = No link
Off = No management session active
Amber = Stand-by mode
Off = Power off
Refer to the following figures and tables for LED assignments and functions.
Figure 6 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel NIC LED assignments
Table 2 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel NIC LED assignments
Item Description
1 Downlink ports 1-16
2 Crosslink ports 17-18
3 Rear panel Uplink ports 19-22
4 Front panel RJ-45 port 23
5 Front panel RJ-45 port 24
Introduction 17
Page 18
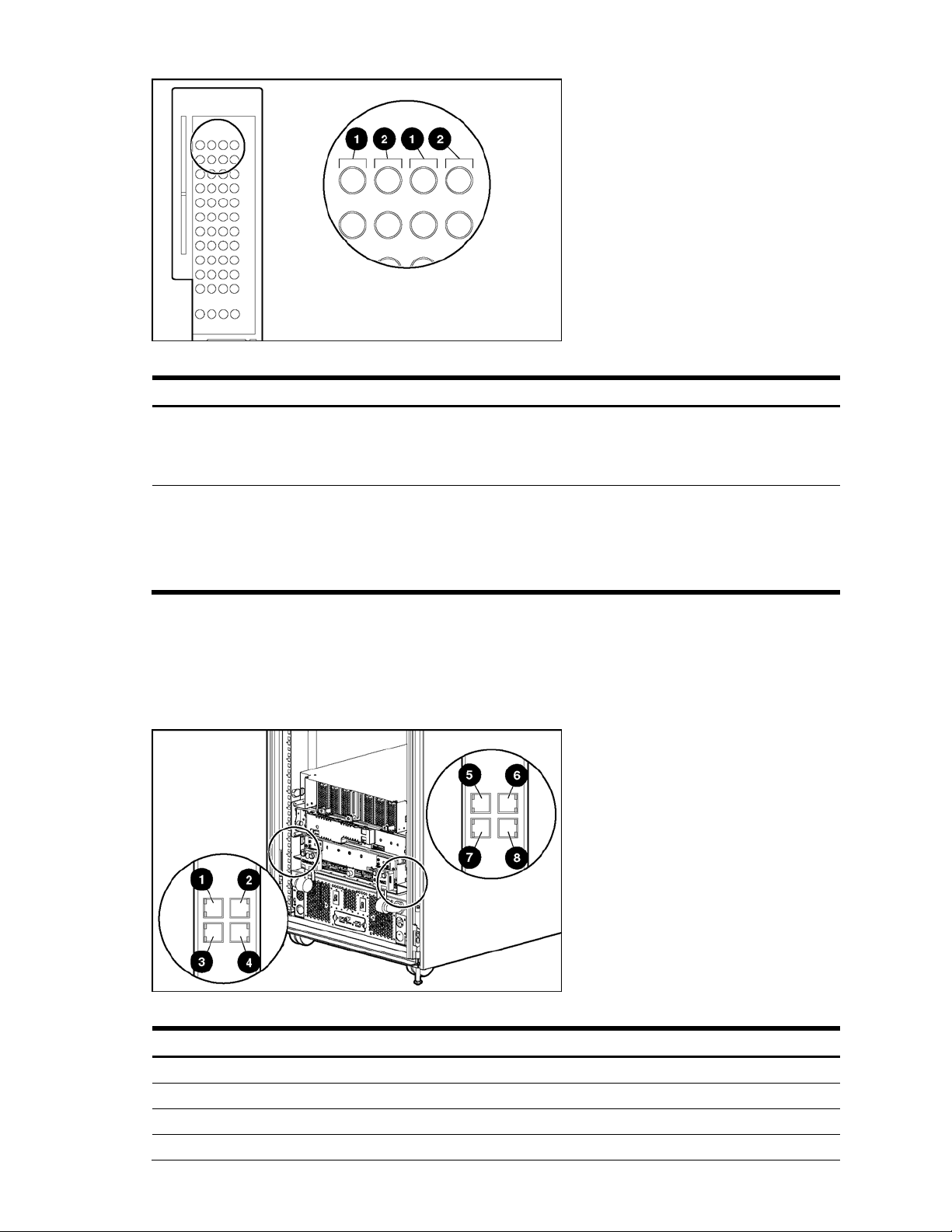
Figure 7 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel NIC LED functions
Table 3 GbE2 Interconnect Switch front panel NIC LED functions
Item LED Description Status
1 Link speed Amber = 1000 Mb/s
Green = 100 Mb/s
Off = 10 Mb/s
2 Link activity Green = Link and no activity
Green flashing = Link and activity
QuadT2 Interconnect Module panel
The QuadT2 Interconnect Modules are inserted into the bottom-left-most and bottom-right-most bays on the rear side of
the server blade enclosure. Each QuadT2 Interconnect Module has four RJ-45 connectors with link activity and speed
LEDs for uplink network cabling. Four RJ-45 connectors support Gigabit Ethernet connections for uplink connectivity.
Figure 8 QuadT2 Interconnect Module connectors
Table 4 QuadT2 Interconnect Module connectors
Amber = Port disabled
Off = No link
Item Description
1 Port 22 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch B
2 Port 21 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch B
3 Port 20 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch B
4 Port 19 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch B
Introduction 18
Page 19
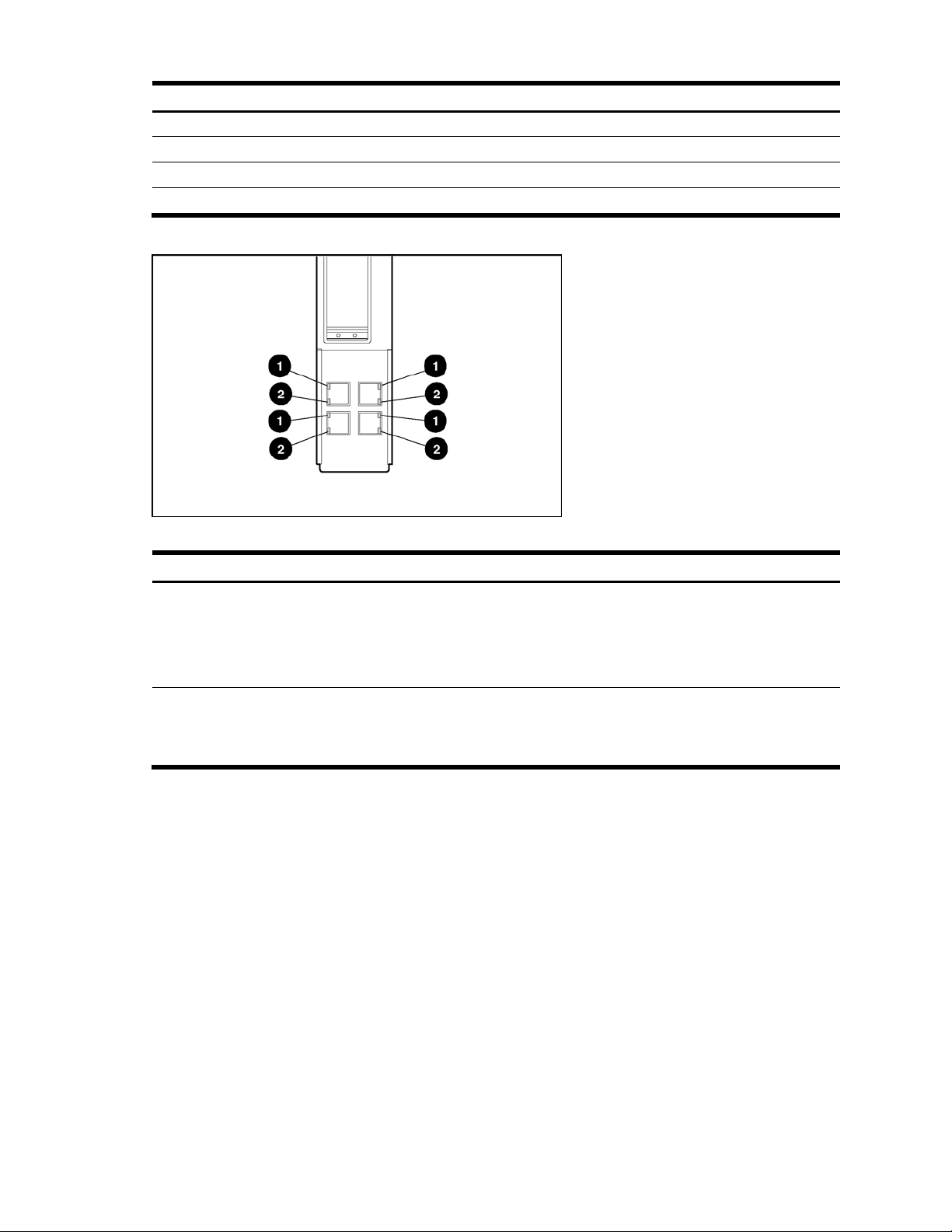
Table 4 QuadT2 Interconnect Module connectors
Item Description
5 Port 22 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch A
6 Port 21 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch A
7 Port 20 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch A
8 Port 19 RJ-45 connector for 10/100/1000 Mb uplink for Switch A
Figure 9 QuadT2 Interconnect Module LEDs
Table 5 QuadT2 Interconnect Module LEDs
Item LED Description Status
1 Link activity Green = Link and no activity
2 Link speed Amber = 1000 Mb/s
QuadSX Interconnect Module panel
The QuadSX Interconnect Modules are inserted into the bottom-left-most and bottom-right-most bays on the rear side of
the server blade enclosure. Each QuadSX Interconnect Module has four LC connectors with link activity LEDs for
uplink network cabling. The LC connectors support 1000SX Ethernet short-haul fiber connections for uplink
connectivity.
Green flashing = Link and activity
Amber = Port disabled
Off = No link
Green = 100 Mb/s
Off = 10 Mb/s
Introduction 19
Page 20
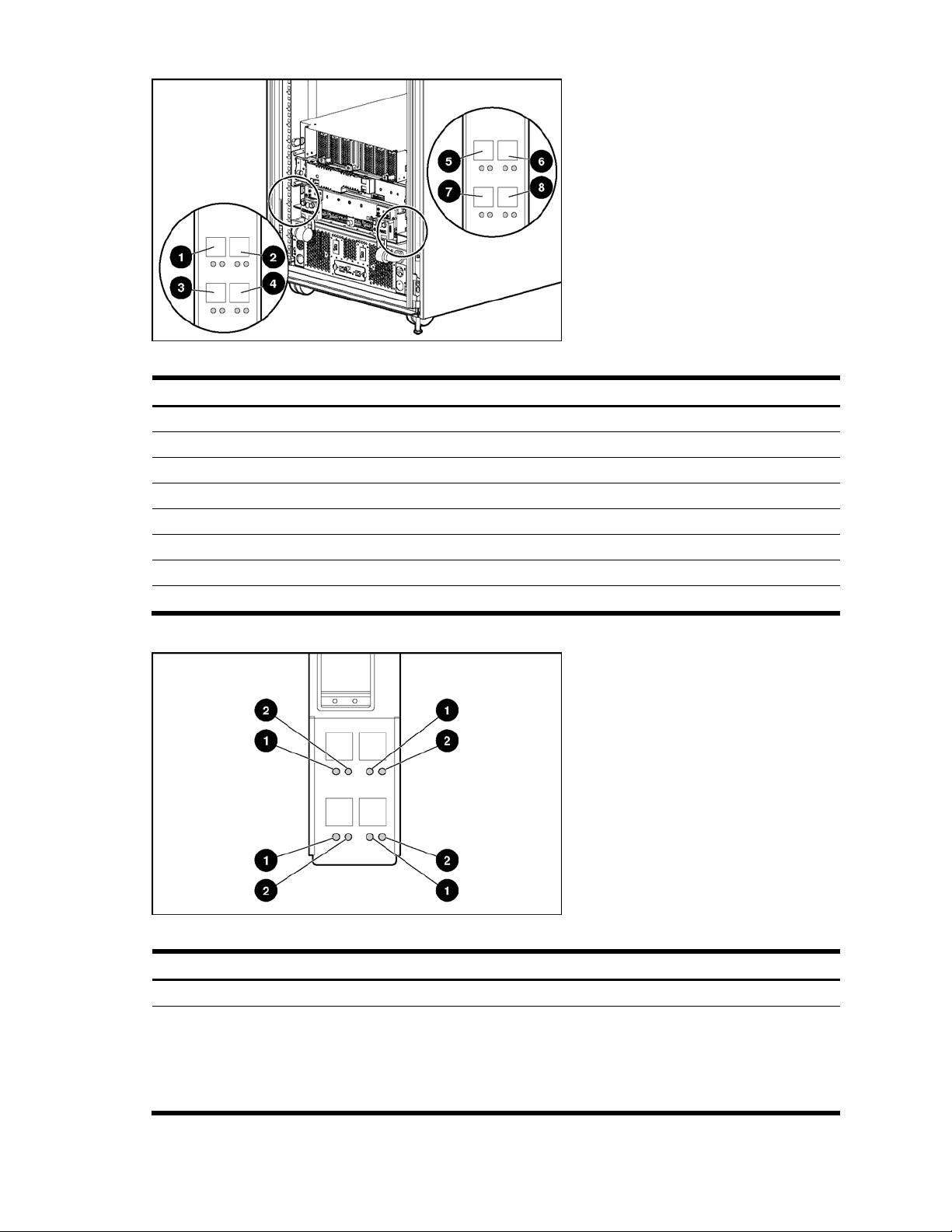
Figure 10 QuadSX Interconnect Module connectors
Table 6 QuadSX Interconnect Module connectors
Item Description
1 Port 22 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch B
2 Port 21 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch B
3 Port 20 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch B
4 Port 19 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch B
5 Port 22 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch A
6 Port 21 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch A
7 Port 20 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch A
8 Port 19 LC fiber connector for 1000SX uplink on Switch A
Figure 11 QuadSX Interconnect Module LEDs
Table 7 QuadSX Interconnect Module LEDs
Item LED Description Status
1 Link speed Amber = 1000 Mb/s
2 Link activity Green = Link and no activity
Green flashing = Link and activity
Amber = Port disabled
Off = No link
Introduction 20
Page 21

Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch
Overview
This chapter describes how to set up and install the ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switches and the
interconnect modules.
The setup and installation process includes the following tasks:
1. Installing the GbE2 Interconnect Switches and interconnect modules
2. Planning the GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration
3. Cabling the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the network
4. Powering up the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
5. Accessing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
6. Logging on and configuring the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
Installing the GbE2 Interconnect Switches and Interconnect Modules
This section describes how to:
• Install the hardware in a new GbE2 Interconnect Switch deployment
• Replace an existing ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch
• Upgrade from a ProLiant BL p-Class GbE Interconnect Switch
• Upgrade from a ProLiant BL p-Class RJ-45 Patch Panel
• Upgrade from a ProLiant BL p-Class RJ-45 Patch Panel 2
HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit option
The HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit option provides ProLiant BL20p G2 Fibre Channel signal
pass-through connectivity for the HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 and F-GbE2 Interconnect Kits. The GbE2 Storage
Connectivity Kit may be ordered separately and installed during a new deployment or later as an upgrade.
The GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit contains two ProLiant BL p-Class OctalFC Interconnect Modules that are inserted
into the top-left-most and top-right-most bays on the rear side of the server blade enclosure. Two ProLiant BL p-Class
Fibre Channel Signal Conditioning Cards are also included in the kit; one is installed in each GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
If you are installing the GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit, refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Storage Connectivity
Kit Quick Setup Instructions included with the GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit for more information.
Installation guidelines
Observe the following guidelines:
• Always install GbE2 Interconnect Switches in pairs. Each server blade enclosure requires two GbE2 Interconnect
Switches for proper connectivity. Both GbE2 Interconnect Switches are identical. They get their identities (Switch
A or Switch B) from the server blade enclosure slots they are plugged into.
• For proper operation, you must run like pairs in the interconnect slot.
• Always install the QuadT2 or QuadSX Interconnect Modules into the bottom-left-most and bottom-right-most bays
on the rear side of the server blade enclosure.
• Be sure that each interconnect module is fully seated. The latch/handle will drop into place when the module is
firmly seated.
• Always install the GbE2 Interconnect Switches into the interconnect bays, which are the left-most (side A) and
right-most (side B) bays on the front side of the server blade enclosure.
IMPORTANT: Record the switch MAC address printed on the MAC address label attached to your GbE2
Interconnect Switch. The MAC address can be used to find the IP address from a BOOTP server.
Installing a new GbE2 Interconnect Switch for a new deployment
To install a new GbE2 Interconnect Switch for a new deployment:
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 21
Page 22

1. Insert the interconnect modules into the bottom-left and bottom-right module bays on the rear side of the server
blade enclosure.
IMPORTANT: Be sure that the interconnect modules are fully seated. The latch/handle will drop into
place when the module is firmly seated.
Figure 12 Installing the QuadT2 or QuadSX Interconnect Modules
2. Slide one GbE2 Interconnect Switch into the right interconnect bay in the front side of the server blade enclosure
(1). The GbE2 Interconnect Switch in the right interconnect bay is referred to as Switch B.
3. Lock the ejector lever (2).
Figure 13 Installing the GbE2 Interconnect Switches
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 to insert the second GbE2 Interconnect Switch in the left interconnect bay. The GbE2
Interconnect Switch in the left interconnect bay is referred to as Switch A.
Replacing an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch
CAUTION: Removing a GbE2 Interconnect Switch from a powered enclosure will result in the loss of network
communications between the server blade network ports that are connected through this switch and the
segment of network infrastructure those ports need to communicate.
For continued blade server network communication and services availability, do the following before you
remove the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Redirect critical high-availability services or applications to use the
redundant network ports available on those blade servers that are connected through the redundant GbE2
Interconnect Switch in the enclosure.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 22
Page 23

IMPORTANT: If you are replacing an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch, or upgrading from a GbE
Interconnect Switch, an RJ-45 Patch Panel, or an RJ-45 Patch Panel 2, and you have strict security requirements:
Do not cable the GbE2 Interconnect Switch until after configuration.
Or
Connect the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the optional Diagnostic Station. The Diagnostic Station enables you
to power up, configure, and diagnose a ProLiant p-Class server blade or a ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect
Switch outside of the rack environment.
To replace an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch:
1. If possible, save the configuration file to a TFTP server for later retrieval. For more information on saving a
configuration file to a TFTP server, refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Command
Reference Guide.
2. On the front side of the ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure, release the ejector lever for the GbE2
Interconnect Switch.
3. Pull down on the ejector lever to unlock the GbE2 Interconnect Switch from the enclosure.
4. Slide the GbE2 Interconnect Switch out of the interconnect bay.
5. Slide the new GbE2 Interconnect Switch fully into the interconnect bay.
6. Close the ejector lever and let the switch boot up completely, so that network connectivity is established.
7. If you saved the configuration file to a TFTP server, download the configuration. For more information on
downloading a configuration file, refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Command
Reference Guide.
NOTE: Only replace the interconnect module if it is faulty, or if a different type of interconnect module is
required.
Upgrading from an existing GbE Interconnect Switch
CAUTION: Removing a GbE Interconnect Switch from a powered enclosure will result in the loss of network
communications between the server blade network ports that are connected through this switch and the
segment of network infrastructure those ports need to communicate.
For continued blade server network communication and services availability, do the following before you
remove the GbE Interconnect Switch. Redirect critical high-availability services or applications to use the
redundant network ports available on those blade servers that are connected through the redundant GbE
Interconnect Switch in the enclosure.
IMPORTANT: If you are replacing an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch, or upgrading from a GbE
Interconnect Switch, an RJ-45 Patch Panel, or an RJ-45 Patch Panel 2, and you have strict security requirements:
Do not cable the GbE2 Interconnect Switch until after configuration.
Or
Connect the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the optional Diagnostic Station. The Diagnostic Station enables you
to power up, configure, and diagnose a ProLiant p-Class server blade or a ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect
Switch outside of the rack environment.
IMPORTANT: By default, both the GbE Interconnect Switch and GbE2 Interconnect Switch have STP enabled
and have X-Connect ports (17 and 18) bundled in to a port trunk. During an upgrade from a GbE Interconnect
Switch to a GbE2 Interconnect Switch, there will be an STP convergence delay due to the topology change.
This causes a temporary interruption to packet forwarding on the attached Layer 2 switching network.
To upgrade from an existing GbE Interconnect Switch to a GbE2 Interconnect Switch:
1. On the rear side of the ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure, remove the interconnect module from the top-
left module bay.
2. On the front side of the server blade enclosure, release the ejector lever for the GbE Interconnect Switch in the
right interconnect bay.
3. Pull down on the ejector lever to unlock the GbE Interconnect Switch from the enclosure.
4. Slide the GbE Interconnect Switch out of the interconnect bay.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 23
Page 24

5. On the rear side of the server blade enclosure, insert the new interconnect module into the bottom-left module
bay.
6. On the front side of the server blade enclosure, slide a new GbE2 Interconnect Switch fully into the right
interconnect bay.
7. Close the ejector lever and let the switch boot up completely, so that network connectivity is established.
8. Repeat steps 1 through 4 to remove the interconnect module from the top-right module bay and the GbE
Interconnect Switch from the left interconnect bay.
9. Repeat steps 5 through 7 to insert the new interconnect module into the bottom-right module bay and the new
GbE2 Interconnect Switch into the left interconnect bay.
Upgrading from an RJ-45 Patch Panel or RJ-45 Patch Panel 2
CAUTION: Removing a patch panel from a powered enclosure will result in the loss of network
communications between the server blade network ports that are connected through this patch panel and the
segment of network infrastructure those ports need to communicate.
IMPORTANT: If you are replacing an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch, or upgrading from a GbE
Interconnect Switch, an RJ-45 Patch Panel, or an RJ-45 Patch Panel 2, and you have strict security requirements:
Do not cable the GbE2 Interconnect Switch until after configuration.
Or
Connect the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the optional Diagnostic Station. The Diagnostic Station enables you
to power up, configure, and diagnose a ProLiant p-Class server blade or a ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect
Switch outside of the rack environment.
To upgrade from an existing RJ-45 Patch Panel or RJ-45 Patch Panel 2:
1. From the rear side of the server blade enclosure, slide out the top and bottom patch panel modules (total of four)
from the module bays and unplug the cables.
2. From the front side of the ProLiant BL p-Class server blade enclosure, unlock the ejector lever and slide out the
patch panels (total of two) from the interconnect bays.
3. From the rear side of the server blade enclosure, insert the new interconnect modules that came with the GbE2
Interconnect Switch into the bottom-right and bottom-left module bays.
4. From the front side of the server blade enclosure, slide the one GbE2 Interconnect Switch into the left
interconnect bay.
5. Lock the ejector levers.
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 to install the second GbE2 Interconnect Switch in the right interconnect bay.
Planning the GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration
Before you configure the GbE2 Interconnect Switch, HP recommends that you plan the configuration. As you plan,
consider your default settings, security issues and privileges, and whether you want to configure each GbE2
Interconnect Switch manually or configure multiple GbE2 Interconnect Switches at the same time.
Default settings
The GbE2 Interconnect Switches ship with a default configuration in which all ports are enabled and assigned a
default VLAN with a VLAN ID (VID) equal to 1. This default configuration simplifies your initial setup by allowing you
to use a single uplink cable (from any external Ethernet connector) to connect your server blade enclosure to your
network. You need to assess your particular server environment to determine any requirements for other
considerations.
When planning the configuration, consider the default settings for the following parameters:
• Switch IP settings
• Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) settings
• Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) settings
• Port names and types
• Port trunking settings
• Interswitch X-Connect port settings
• Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) settings
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 24
Page 25

• User name and password settings
• Default access to various management interfaces
• Network Time Protocol (NTP) settings
IMPORTANT: Refer to the “Runtime switching software default settings” appendix for a complete list of default
configuration settings.
GbE2 Interconnect Switch security
When planning the GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration, secure access to the management interface by:
• Creating users with various access levels
• Enabling or disabling access to various management interfaces to fit the security policy
• Changing default SNMP community strings for read-only and read-write access
User, operator, and administrator access rights
To enable better GbE2 Interconnect Switch management and user accountability, three levels or classes of user access
have been implemented on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Levels of access to CLI, Web management functions, and
screens increase as needed to perform various GbE2 Interconnect Switch management tasks. Conceptually, access
classes are defined as follows:
• User interaction with the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is completely passive; nothing can be changed on the GbE2
Interconnect Switch. Users may display information that has no security or privacy implications, such as GbE2
Interconnect Switch statistics and current operational state information.
• Operators can only effect temporary changes on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. These changes will be lost
when the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is rebooted/reset. Operators have access to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
management features used for daily GbE2 Interconnect Switch operations. Because any changes an operator
makes are undone by a reset of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch, operators cannot severely impact GbE2
Interconnect Switch operation.
• Administrators are the only ones that may make permanent changes to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
configuration, changes that are persistent across a reboot/reset of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Administrators
can access GbE2 Interconnect Switch functions to configure and troubleshoot problems on the GbE2
Interconnect Switch. Because administrators can also make temporary (operator-level) changes as well, they
must be aware of the interactions between temporary and permanent changes.
Access to GbE2 Interconnect Switch functions is controlled through the use of unique surnames and passwords. Once
you are connected to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch via the local console, Telnet, or SSH, you are prompted to enter a
password. The default user names/password for each access level is listed in the following table.
NOTE: It is recommended that you change default GbE2 Interconnect Switch passwords after initial
configuration and as regularly as required under your network security policies. For more information, refer to
the “Setting Passwords” section in Chapter 3 of the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch
Command Reference Guide.
Table 8 User access levels
User account Description and tasks performed Password
User The user has no direct responsibility for
GbE2 Interconnect Switch management.
He or she can view all GbE2
Interconnect Switch status information
and statistics, but cannot make any
configuration changes to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch.
Operator The operator manages all functions of
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. The
operator can reset ports or the entire
GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
By default, the operator account is
disabled and has no password.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 25
user
Page 26

Table 8 User access levels
User account Description and tasks performed Password
Administrator The super user administrator has
complete access to all menus,
information, and configuration
commands on the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch, including the ability to change
both the user and administrator
passwords.
Manually configuring a GbE2 Interconnect Switch
A GbE2 Interconnect Switch can be configured manually using a command line interface, a browser-based interface,
or an SNMP interface. Refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Command Reference Guide for
more information on how to use these management interfaces to configure the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
After a GbE2 Interconnect Switch is configured, you can back up the configuration as a text file to a TFTP server. The
backup configuration file can then be downloaded from the TFTP server to restore the switch back to the original
configuration. This restoration may be necessary under one of the following conditions:
• The switch configuration becomes corrupted during operation.
• The switch must be replaced because of a hardware failure.
admin
Configuring multiple GbE2 Interconnect Switches
You can configure multiple GbE2 Interconnect Switches by using scripted command line interface (CLI) commands
through Telnet or by downloading a configuration file using a TFTP server.
Using scripted CLI commands through Telnet
The CLI, provided with the GbE2 Interconnect Switch, allows you to execute customized configuration scripts on
multiple switches. A configuration script can be tailored to one of the multiple switches, and then that configuration
can be deployed to other switches from a central deployment server.
Using a configuration file
If you plan for the base configuration of multiple GbE2 Interconnect Switches in your network to be the same, you can
manually configure one GbE2 Interconnect Switch, upload the configuration to a TFTP server, and use that
configuration as a base configuration template file.
GbE2 Interconnect Switch IP addresses are acquired by default using BOOTP, therefore, each GbE2 Interconnect
Switch has a unique IP address. Each GbE2 Interconnect Switch can be remotely accessed from a central deployment
server and an individual interconnect switch configuration can be downloaded to meet specific network requirements.
Refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Command Reference Guide for additional information
on using a TFTP server to upload and download configuration files.
Cabling the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
After installing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch hardware and planning the configuration, cable the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch to your network.
IMPORTANT: If you are replacing an existing GbE2 Interconnect Switch, or upgrading from a GbE
Interconnect Switch, an RJ-45 Patch Panel, or an RJ-45 Patch Panel 2, and you have strict security requirements:
Do not cable the GbE2 Interconnect Switch until after configuration.
Or
Connect the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the optional Diagnostic Station. The Diagnostic Station enables you
to power up, configure, and diagnose a ProLiant p-Class server blade or a ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect
Switch outside of the rack environment.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 26
Page 27

To connect the interconnect modules to the network:
1. Connect your network cables to the interconnect modules. For connector locations, refer to the “QuadT2
Interconnect Module panel” section or “QuadSX Interconnect Module panel” section in the “Introduction”
chapter.
2. Gather your network cables for the right side of the rack.
3. Insert the end of the cable-retaining bracket (provided with the bus bar and power bus boxes) into the cable
bracket (1).
4. Tighten the thumbscrew to secure the cable retaining bracket over the cables (2).
Figure 14 Installing the cable-retaining bracket
5. Repeat steps 2 through 4 for the network cables on the left side of the rack.
Powering up the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
If the server blade enclosure has power applied, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch automatically begins to power up
when installed. The power status LED on the front of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch starts out as amber to indicate that
power is connected to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. After 30 seconds, the power status LED turns to green to
indicate that the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is powered up. After the built in self-test flashes all LEDs, the active links
are illuminated, and the power status LED stays green.
You can manually force the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to power up by pressing the Pwr/Rst button through the access
hole in the front panel of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch while the power status LED is amber. HP recommends using a
small blunt object for this purpose.
CAUTION: Pressing the Pwr/Rst button while the power status LED is green will reset the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
IMPORTANT: If the server blade enclosure does not have power applied, refer to the system setup and
installation guide for the server blade enclosure.
Accessing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch can be accessed using the serial (DB-9) management port or an Ethernet connection.
• To access the GbE2 Interconnect Switch locally, use the front panel serial management port.
• To access the GbE2 Interconnect Switch through an Ethernet connection, use either the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch front panel RJ-45 ports or one of the following:
• The uplink RJ-45 ports in the QuadT2 Interconnect Module
• The uplink LC fiber ports in the QuadSX Interconnect Module
To access the GbE2 Interconnect Switch via an Ethernet connection, you need to assign it an IP address. By default,
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is set up to obtain its IP address from a BOOTP server existing on the attached network.
1. Access the BOOTP server and use the GbE2 Interconnect Switch MAC address to obtain the switch IP address.
The MAC address is printed on the MAC address label attached to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 27
Page 28
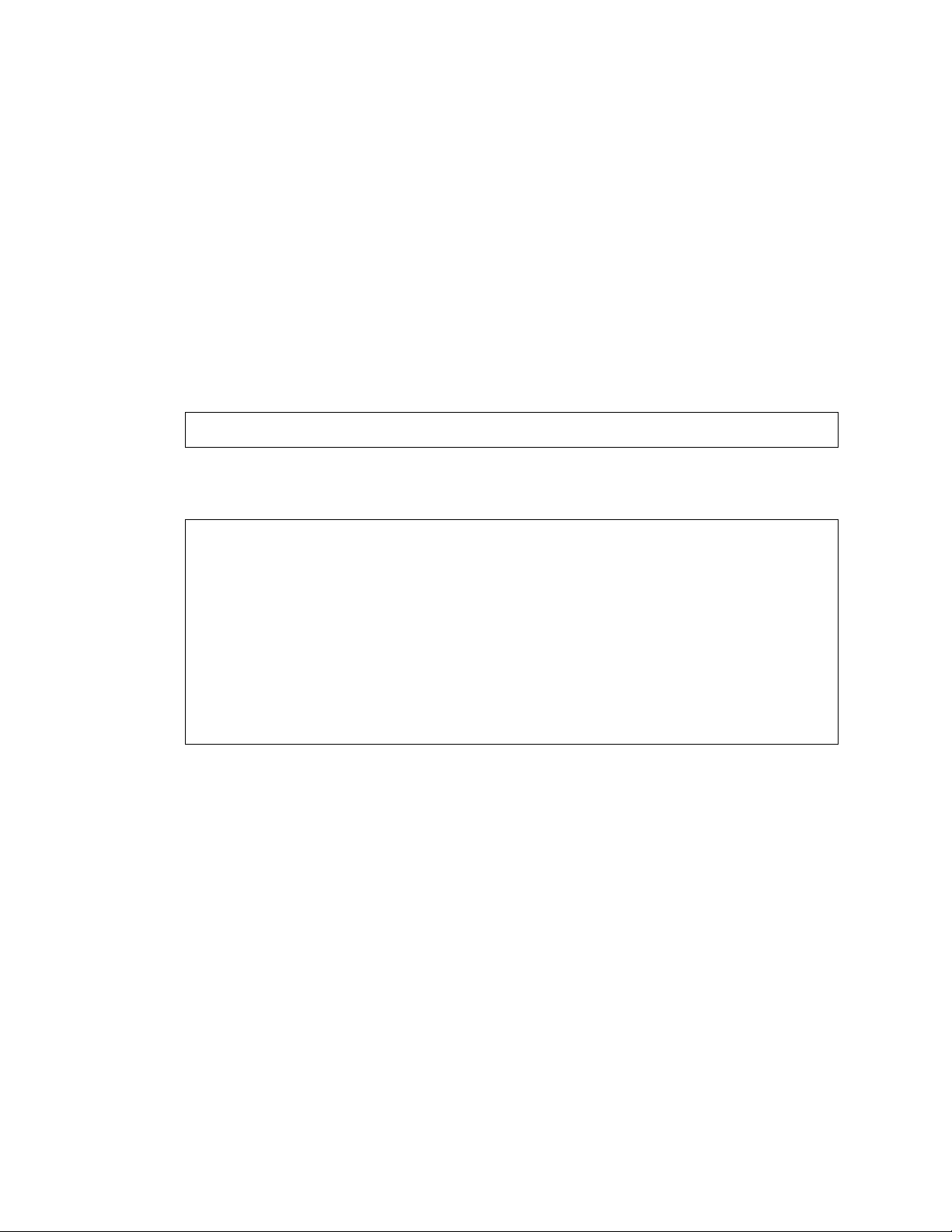
2. From a computer connected to the same network, use the IP address to access the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
using a Web browser or Telnet application. This allows you to access the GbE2 Interconnect Switch browserbased interface (BBI) or command line interface (CLI). Once you have accessed the GbE2 Interconnect Switch,
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch logon prompt is displayed.
If the GbE2 Interconnect Switch does not obtain the IP address by means of the BOOTP service, you can access the
switch locally and manually assign an IP address.
1. Connect the GbE2 Interconnect Switch DB-9 serial connector, using the null-modem cable (provided with the
following option kits: Scalable Busbar, Mini Busbar, and Power Bus Box), to a local client device (such as a
laptop computer) with VT100 terminal emulation software (such as Microsoft® Windows® HyperTerminal).
2. Open a VT100 terminal emulation session with the following settings: 9600 baud rate, eight data bits, no
parity, one stop bit, and no flow control.
3. Complete the following instructions to log on and configure the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Once you have
assigned an IP address, you can access the switch remotely.
Logging on and configuring the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
Do the following to log on to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
1. Connect to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch console. After connecting, the login prompt displays as shown below.
Enter password:
2. Enter admin as the default administrator password.
The Main Menu displays with administrator privileges:
[Main Menu]
info - Information Menu
stats - Statistics Menu
cfg - Configuration Menu
oper - Operations Command Menu
boot - Boot Options Menu
maint - Maintenance Menu
diff - Show pending config changes [global command]
apply - Apply pending config changes [global command]
save - Save updated config to FLASH [global command]
revert - Revert pending or applied changes [global command]
exit - Exit [global command, always available]
>> Main#
To help with the initial process of configuring your GbE2 Interconnect Switch, the software includes a Setup utility.
The Setup utility prompts you step-by-step to enter all the necessary information for basic configuration of the GbE2
Interconnect Switch. The Setup utility is activated manually from the command line interface any time after login.
Refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Command Reference Guide for information on how to
run the Setup utility, configure the IP address, change configuration settings, and monitor switch operation using one
of the following:
• Local RS-232 serial console management interface
• Remote Telnet console management interface
Refer to the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Browser-based Interface Reference Guide for
information on how to use the embedded browser-based (HTML) interface to manage the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
from anywhere on the network using a standard browser, such as Netscape Navigator or Microsoft Internet Explorer.
The “SNMP MIBs support” appendix provides information regarding the SNMP agents. This appendix also describes
how to use the MIBs to configure and monitor the GbE2 Interconnect Switch using a generic SNMP manager, such as
HP OpenView Network Node Manager or HP Systems Insight Manager.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 28
Page 29

Supporting software and special considerations
The following supporting software is available to assist you in configuring and managing the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
• Server Blade and Power Management Module Firmware—Provides firmware and installation instructions
required for proper rack location operation.
• Utilities package and documentation—Provides utilities and documentation for GbE2 Interconnect Switch
management. The utilities and documentation are located at http://www.hp.com/support
• GbE2 Interconnect Switch Firmware Upgrade Smart Component (for Microsoft Windows only)—Provides quick
and easy installation of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch firmware, firmware upgrade tool, and readme file. A
SoftPaq is available for use with Linux operating systems.
The utilities package and documentation, and the SoftPaq listed above, are available at
http://www.hp.com/support
.
.
Setting up and installing the GbE2 interconnect switch 29
Page 30

HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory
Compliance Notices
Class A equipment
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15
of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at personal expense.
Modifications
The FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made to this device that are not expressly
approved by Hewlett-Packard Company may void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Cables
Connections to this device must be made with shielded cables with metallic RFI/EMI connector hoods in order to
maintain compliance with FCC Rules and Regulations.
Canadian Notice (Avis Canadien)
Class A equipment
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du
Canada.
HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices 30
Page 31

European Union Regulatory Notice
This product complies with the following EU Directives:
• Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
• EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
CE Compliance of this product is valid only if powered with the correct HP-provided and CE marked AC adapter.
If this product has telecommunication functionality, it also complies with the essential requirements of:
• R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
*For a notified body number refer to the product regulatory label.
Compliance with these directives implies conformity to harmonized European standards (European Norms) which are
listed on the EU Declaration of Conformity issued by Hewlett-Packard for this product or product family.
The telecommunications functionality of this product may be used in the following EU and EFTA countries:
Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland,
Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovak
Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and United Kingdom.
Notice for use in France and Italy
Italy:
E'necessaria una concessione ministeriale anche per l'uso del prodotto. Verifici per favore con il proprio distributore
o direttamente presso la Direzione Generale Pianificazione e Gestione Frequenze.
License required for use. Verify with your dealer or directly with General Direction for Frequency Planning and
Management (Direzione Generale Pianificazione e Gestione Frequenze).
France:
L'utilisation de cet equipement (2.4GHz Wireless LAN) est soumise a certaines restrictions: Cet equipement peut etre
utilise a l'interieur d'un batiment en utilisant toutes les frequences de 2400 a 2483.5MHz (Chaine 1-13). Pour une
utilisation en environement exterieur, vous devez utiliser les frequences comprises entre 2454-2483.5MHz (Chaine
10-13). Pour les dernieres restrictions, voir http://www.art-telecom.fr
For 2.4 GHz Wireless LAN operation of this product certain restrictions apply: This product may be used indoor for
the entire 2400-2483.5 MHz frequency band (channels 1-13). For outdoor use, only 2454-2483.5 MHz frequency
band (channels 10-13) may be used. For the latest requirements, see http://www.art-telecom.fr
Notice for products incorporating 5GHz Wireless LAN devices
Frequency availability for 802.11a or 802.11h Wireless LAN is not currently harmonized throughout the European
Union. For compliance requirements, users should verify with their supplier, local HP office or Telecommunications
authority.
.
.
HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices 31
Page 32

BSMI Notice
Japanese Notice
Korean Notice
HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices 32
Page 33

HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices
Class A equipment
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15
of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at personal expense.
Modifications
The FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made to this device that are not expressly
approved by Hewlett-Packard Company may void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Cables
Connections to this device must be made with shielded cables with metallic RFI/EMI connector hoods in order to
maintain compliance with FCC Rules and Regulations.
Canadian Notice (Avis Canadien)
Class A equipment
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du
Canada.
HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices 33
Page 34

European Union Regulatory Notice
This product complies with the following EU Directives:
• Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
• EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
CE Compliance of this product is valid only if powered with the correct HP-provided and CE marked AC adapter.
If this product has telecommunication functionality, it also complies with the essential requirements of:
• R&TTE Directive 1999/5/EC
*For a notified body number refer to the product regulatory label.
Compliance with these directives implies conformity to harmonized European standards (European Norms) which are
listed on the EU Declaration of Conformity issued by Hewlett-Packard for this product or product family.
The telecommunications functionality of this product may be used in the following EU and EFTA countries:
Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland,
Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovak
Republic, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and United Kingdom.
Notice for use in France and Italy
Italy:
E'necessaria una concessione ministeriale anche per l'uso del prodotto. Verifici per favore con il proprio distributore
o direttamente presso la Direzione Generale Pianificazione e Gestione Frequenze.
License required for use. Verify with your dealer or directly with General Direction for Frequency Planning and
Management (Direzione Generale Pianificazione e Gestione Frequenze).
France:
L'utilisation de cet equipement (2.4GHz Wireless LAN) est soumise a certaines restrictions: Cet equipement peut etre
utilise a l'interieur d'un batiment en utilisant toutes les frequences de 2400 a 2483.5MHz (Chaine 1-13). Pour une
utilisation en environement exterieur, vous devez utiliser les frequences comprises entre 2454-2483.5MHz (Chaine
10-13). Pour les dernieres restrictions, voir http://www.art-telecom.fr
For 2.4 GHz Wireless LAN operation of this product certain restrictions apply: This product may be used indoor for
the entire 2400-2483.5 MHz frequency band (channels 1-13). For outdoor use, only 2454-2483.5 MHz frequency
band (channels 10-13) may be used. For the latest requirements, see http://www.art-telecom.fr
Notice for products incorporating 5GHz wireless LAN devices
Frequency availability for 802.11a or 802.11h Wireless LAN is not currently harmonized throughout the European
Union. For compliance requirements, users should verify with their supplier, local HP office or Telecommunications
authority.
.
.
HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices 34
Page 35

BSMI Notice
Japanese Notice
Korean Notice
Laser compliance
The fiber optic module contains a laser that is classified as a “Class 1 Laser Product” in accordance with US FDA
regulations and the IEC 60825-1. The product does not emit hazardous laser radiation.
WARNING! Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein or
in the laser product’s installation guide may result in hazardous radiation exposure. To reduce the risk of
exposure to hazardous radiation:
Do not try to open the module enclosure. There are no user-serviceable components inside.
Do not operate controls, make adjustments, or perform procedures to the laser device other than those
specified herein.
Allow only HP Authorized Service technicians to repair the unit.
The Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration implemented
regulations for laser products on August 2, 1976. These regulations apply to laser products manufactured from
August 1, 1976. Compliance is mandatory for products marketed in the United States. This device is classified as a
Class 1 laser product as defined by IEC 60825-1.
HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit Regulatory Compliance Notices 35
Page 36

Technical specifications
Table 9 General specifications
Standards IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet
Protocols CSMA/CD
Data transfer rates
Ethernet Half-Duplex: 10 Mb/s
IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T Ethernet
IEEE 802.3z 1000Base-SX Ethernet
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
IEEE 802.3ac Frame Extensions for VLAN
IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Protocol (No LACP support)
IEEE 802.3x Full-Duplex Flow Control
ANSI/IEEE 802.3 Nway Auto-Negotiation
Full-Duplex: 20 Mb/s
Fast Ethernet Half-Duplex: 100 Mb/s
Full-Duplex: 200 Mb/s
Gigabit Ethernet Half-Duplex: 1000 Mb/s
Full-Duplex: 2000 Mb/s
Connectors
GbE2 Interconnect Switch 2 RJ-45, 1 DB-9
QuadT2 Interconnect Module 4 RJ-45
QuadSX Interconnect Module 4 SFP fiber transceivers with LC connectors
10Base-T Two Pair UTP Category 3, 4, 5 (100 m)
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm STP (100 m)
100Base-TX Two Pair or Four Pair UTP Category 5 (100 m)
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm STP (100 m)
1000Base-T Four Pair UTP Category 5e (100 m)
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm STP (100 m)
1000Base-SX 50/125 µm Multimode Fiber with 400 MHz/Km rating has a maximum
distance of 500 meters.
50/125 µm Multimode Fiber with 500 MHz/Km rating has a maximum
distance of 550 meters.
62.5/125 µm Multimode Fiber with 160 MHz/Km rating has a maximum
distance of 220 meters.
62.5/125 µm Multimode Fiber with 200 MHz/Km rating has a maximum
distance of 275 meters.
Technical specifications 36
Page 37

Table 9 General specifications
Number of ports per GbE2 Interconnect
Switch
16 x 10/100/1000-Mb/s Nway Ports dedicated to server blade for GbE2
Interconnect Switch communications
2 x 10/100/1000-Mb/s Nway Ports dedicated to communications between
GbE2 Interconnect Switches A and B
4 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T RJ-45 ports or 4 1-Gigabit LC ports
(depending on C-GbE2 or
F-GbE2 kit options)
2 x 10Base-T/100Base-TX/1000Base-T RJ-45
front panel management ports, or additional uplink ports
1 x serial RS-232 DB-9 front-panel management port
Table 10 Physical and environmental specifications
DC inputs -48V: 2350 mA maximum per GbE2 Interconnect Switch
Power consumption 112W maximum per GbE2 Interconnect Switch
Operating temperature 10 to 35 degrees Celsius
Storage temperature -30 to 60 degrees Celsius
Operating humidity 20% to 80% RH noncondensing
Storage humidity 5% to 95% RH noncondensing
GbE2 Interconnect Switch dimensions 28.0 in. x 10.4 in. x 1.6 in.
Interconnect Module dimensions Top Module (Fibre Channel Signals):
7.4 in. x 3.5 in. x 1.6 in.
Bottom Module (Ethernet Signals):
7.4 in. x 2.25 in. x 1.6 in.
Weight 12 lb (GbE2 Interconnect Switch and Interconnect Module)
EMI FCC Class A
ICES-003 Class A
AS/NZS 3548 Class A
VCCI Class A
Safety UL/CUL Listed Accessory
CE
Technical specifications 37
Page 38

Table 11 Performance specifications
Transmission method Store-and-forward
Memory 128MB main, 32MB flash, and 2 MB shared packet buffer
memory per GbE2 Interconnect Switch
MAC address table size 2K per GbE2 Interconnect Switch
Packet forwarding rate 1,488,095 packets per second with 64 byte packets per port
(for 1000 Mb/s)
Maximum external port packet forwarding rate 6 X 1Gig port = 6 X 1,488,095 = 8,928,570 pps per GbE2
Interconnect Switch
Best downlink external port packet forwarding rate ratio 16 : 6
Interswitch x-connects across enclosure backplane 2 X 1Gig ports bundled in Port Trunk of 2Gig size
MAC address learning Automatic update
Forwarding table age time Maximum age: 1 to 65535 seconds
Default: 300 seconds
Technical specifications 38
Page 39

Runtime switching software default settings
This section provides the default settings for the GbE2 Interconnect Switch:
• Table 12 contains general default settings for both Switch A and Switch B
• Table 13 contains port names, VLANs, STP, trunking default settings for Switch A and Switch B
Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Switch A and Switch B are configured with the following general default settings:
Table 12 Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Setting Value
Notice None
Banner None
User Names/Passwords User Name:
• user—Enabled
• oper—Disabled
• admin—Enabled (cannot be
disabled)
BOOTP Service Enabled
IP Address (if manual IP option is
selected)
Subnet Mask (if manual IP option is
selected)
Primary Default Gateway 0.0.0.0
Secondary Default Gateway 0.0.0.0
Primary DNS Server Address 0.0.0.0
Secondary DNS Server Address 0.0.0.0
Default Domain Name None
Management Network/Mask 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
Switch Software Image on Next Boot Image1
Switch Config File on Next Boot Active
Display Hostname (sysName) in CLI
Prompt
Idle Timeout 5 minutes
Telnet Status Enabled
Telnet Port 23
Web Status Enabled
Web Port 80
Backpressure Disabled
Port State Enabled
Port Speed/Duplex Auto
Flow Control Receive & Transmit
STP STG 1—Enabled with Default VLAN (VID=1)
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
Disabled
Password:
• user
• None
• admin
Port 1-16 (Server Ports) STP—Disabled at Port Level
STG 2-16—Disabled
Bridge Max Age 20 seconds
Runtime switching software default settings 39
Page 40

Table 12 Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Setting Value
Bridge Hello Time 2 seconds
Bridge Forward Delay 15 seconds
Bridge Priority 32768
MAC Address Aging Time 300 seconds
Port Priority 128
Path Cost 4
Static VLAN Entry Default VLAN (VID = 1)
Port VID 1 for all ports
Port Trunking Trunk Group 1, Enabled with Port 17
and 18
Port Trunking Load Sharing Algorithm The algorithm selects the following as forwarding ports for forwarding traffic:
1 For forwarding IP Packets—modulus of XOR of last 3 bits of Source and last 3
bits of Destination IP address
2 For forwarding non-IP packets—modulus of XOR of last 3 bits of Source and
last 3 bits of Destination MAC address
3 For forwarding broadcast, multicast packets, and unknown unicast packets—
the lowest active port number in the trunk group
Port Mirroring—Mirror Status Disabled
Port Mirroring—Mirror Port None Selected
Port Mirroring—Mirror Port Traffic
Direction
Port Mirroring—Monitoring Port None Selected
SNMP Read/Write
SNMP System Name None
SNMP System Location None
SNMP System Contact None
SNMP Community String/Access Right Public = read-only
SNMP Trap Host 1 0.0.0.0
SNMP Trap Host 1 Community String Public
SNMP Trap Host 2 0.0.0.0
SNMP Trap Host 2 Community String Public
SNMP Authentication Traps Disabled
SNMP Link Up/Down Traps Enabled
Security IP Network/Mask 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
TFTP Server IP Address 0.0.0.0
TFTP Port Number 69
Firmware Upgrade File name = none
Configuration File from TFTP Server File name = none
Configuration File to TFTP Server File name = none
PING Tool Target address = undefined
Trace Route Tools Target address = undefined
Serial Port Baud Rate 9600
None Selected
Private = read/write
Default tries = 5
Runtime switching software default settings 40
Page 41

Table 12 Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Setting Value
Serial Port Data Bit 8
Serial Port Parity Bit None
Serial Port Stop Bit 1
Serial Port Flow Control None
Default VLAN Default VLAN (VID=1) with all ports
assigned including CPU, STG=1
NTP State Disabled
NTP Server 0.0.0.0
NTP Resync Interval 720 minutes
GMT Timezone Offset -06:00
Daylight Savings Time State Disabled
System Up Time 0 days 00 :00 :00
Current Time RTC or NTP (00 :00 :00)
Date None
Syslog Host 0.0.0.0
Syslog Host 2 0.0.0.0
Syslog Host Severity 7
Syslog Host 2 Severity 7
Syslog Console Output Disabled
Log console—Enabled
system—Enabled
mgmt—Enabled
cli—Enabled
stp—Enabled
vlan—Enabled
ssh—Enabled
ntp—Enabled
ip—Enabled
web—Enabled
RSA Server Key Autogen Interval 0
RSA Server Key Autogen Disabled
SSH Server On
SCP-only Administrator Password admin
SSH Server Port 22
SCP Apply and Save Disabled
RADIUS Server Off
RADIUS Secret None
Primary RADIUS Server 0.0.0.0
Secondary RADIUS Server 0.0.0.0
RADIUS Server Port 1645
RADIUS Server Retries 3
Runtime switching software default settings 41
Page 42

Table 12 Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Setting Value
RADIUS Server Timeout 3
RADIUS Backdoor for Telnet Access Disabled
Re-ARP Period in Minutes 10
MSTP Disabled
MSTP Default Mode RSTP
MSTP Region Name None
MSTP Region Version 1
MSTP Max Hop Count 20
CIST Bridge Max Age 20 seconds
CIST Bridge Hello Time 2 seconds
CIST Bridge Forward Delay 15 seconds
CIST Bridge Priority 32768
CIST MAC Address Aging Time 300 seconds
CIST Port Priority 128
CIST Port Path Cost 20000
MSTP Link Type Auto
MSTP Edge Port Enabled: Ports 1-16
TACACS+ Service Off
TACACS+ Primary Secret None
TACACS+ Secondary Secret None
Primary TACACS+ Server 0.0.0.0
Secondary TACACS+ Server 0.0.0.0
TACACS+ Server Port 49
TACACS+ Server Retries 3
TACACS+ Server Timeout 5 seconds
TACACS+ Backdoor for Telnet Access Disabled
IGMP Snooping Disabled
IGMP VLANs None
IGMP Report Timeout 10 seconds
IGMP Multicast Router Timeout 255 seconds
IGMP Robust 2
Aggregate IGMP Report Disabled
IGMP Fastleave Disabled
IGMP Fastleave VLANs None
IGMP Filtering Disabled
IGMP Filters None
Static Multicast Router Port None
Uplink Failure Detection (UFD) Off
UFD Failure Detection Pair Disabled
UFD Link To Monitor – Port None
UFD Link To Monitor – Trunk None
Runtime switching software default settings 42
Page 43

Table 12 Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Setting Value
UFD Link to Disable – Ports None
UFD Link To Disable -- Trunks None
RMON History Group Number None
RMON History Interface MIB to Monitor None
RMON History Number of Requested
Buckets
RMON History Polling Interval 1800
RMON History Owner None
RMON Event Group Number None
RMON Event Description None
RMON Event Type None
RMON Alarm Group Number None
RMON Alarm MIB to Monitor None
RMON Alarm Interval 1800
RMON Alarm Sample Type abs
RMON Alarm Type either
RMON Alarm Rising Threshold 0
RMON Alarm Falling Threshold 0
RMON Alarm Rising Event Index 0
RMON Alarm Falling Event Index 0
RMON Alarm Owner Null
IP Forwarding Disabled
RIP Disabled
Configurable User Name – admpw admin
Configurable User Name – opw Disabled
Configurable User Name – usrpw user
Configurable User Name – UID 1-10 Disabled
Uplink Fast Disabled
LACP Disabled
THASH – enable SIP and DIP
SNMPv1 – Read community string: public
SNMPv1 – Write community string: private
SNMPv1 – SNMP state machine timeout: 5
SNMPv1 – authentication traps: disabled
SNMPv1 – Uplink Failure Detection
traps:
SNMPv1 – link up/down traps: enabled
SNMPv1 – v1/v2 access: enabled
802.1x – 8021x disabled
802.1x – mode force-auth
802.1x – qtperiod 60
802.1x – txperiod 30
30
disabled
Runtime switching software default settings 43
Page 44

Table 12 Switch A and Switch B: general default settings
Setting Value
802.1x – suptmout 30
802.1x – syrtmout 30
802.1x – maxreq 2
802.1x – raperiod 3600
802.1x – reauth off
IGMP off
MCAST/BCAST/UCAST off
SNMPv3 – SNMP access read/write enabled
SNMPv3 – v1v2 access enabled
SNMPv3 – adminmd5 authentication = md5, privacy = des
SNMPv3 – adminsha authentication = sha, privacy = des
SNMPv3 – v1v2only authentication = none, privacy = none
SNMPv3 – admingrp level=authPriv,
users=adminmd5,
adminsha, rview, wview, nview=iso
SNMPv3 – v1v2grp level=noAuthNoPriv,
users=v1v2only,
rview, wview=iso,
nview=v1v2only
SNMPv3 – iso subtree = 1, included
SNMPv3 – v1v2only subtree=1, included
subtree=1.3.6.1.6.3.15, excluded
subtree=1.3.6.1.6.3.16, excluded
subtree=1.3.6.1.6.3.18, excluded
OSPF Disabled
FTP – port 21 (not configurable)
Browser upgrade option Enabled, (not configurable)
STP Fast Disabled
VRRP off
HTTPS Port Disabled
Runtime switching software default settings 44
Page 45

Switch A and Switch B: port names, VLANs, STP, trunking default settings
IMPORTANT: If you have the ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2 Interconnect Kit option with the QuadSX Interconnect
Modules, the management interface supports only 1000M/Full and Auto options for the Speed/Duplex fields
for Gigabit uplink ports. The fiber QuadSX Interconnect Module supports only 1000-Mb/s (Gigabit) speed, and
not 10-Mb/s or 100-Mb/s.
Switch A and Switch B are configured with the following factory default settings for port names, VLANs, STP, and
trunking.
Table 13 Switch A and Switch B: port names, VLANs, STP, and trunking default settings
Port type Port
no.
Server 1 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 2 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 3 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 4 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 5 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 6 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 7 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 8 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 9 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 10 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 11 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 12 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 13 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 14 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 15 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Server 16 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
X-Connect 17 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
X-Connect 18 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Uplink 19 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Speed PVID Tag
(Y/N)
VLAN name Port name STP Trunk group
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
Downlink1 Disabled
Downlink2 Disabled
Downlink3 Disabled
Downlink4 Disabled
Downlink5 Disabled
Downlink6 Disabled
Downlink7 Disabled
Downlink8 Disabled
Downlink9 Disabled
Downlink10 Disabled
Downlink11 Disabled
Downlink12 Disabled
Downlink13 Disabled
Downlink14 Disabled
Downlink15 Disabled
Downlink16 Disabled
XConnect1 Enabled 1
XConnect2 Enabled 1
Uplink1 Enabled
Runtime switching software default settings 45
Page 46

Table 13 Switch A and Switch B: port names, VLANs, STP, and trunking default settings
Port type Port
no.
Uplink 20 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Uplink 21 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Uplink 22 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Front Panel 23 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Front Panel 24 10/100/1000 (Auto) 1 N Default
Speed PVID Tag
(Y/N)
VLAN name Port name STP Trunk group
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
VLAN
Uplink2 Enabled
Uplink3 Enabled
Uplink4 Enabled
FrontPanel1 Enabled
FrontPanel2 Enabled
Runtime switching software default settings 46
Page 47

Performing a serial download
Introduction
You can perform a serial download of the new GbE2 Interconnect Switch Operating System firmware, or Boot Code
firmware if you want to upgrade a GbE2 Interconnect Switch directly from any existing operating system (OS) or Boot
Code images.
This procedure requires the following:
• A computer running terminal emulation software
• A standard null modem cable with a female DB-9 connector
• A GbE2 Interconnect Switch OS firmware and/or Boot Code images
Serial upgrade of boot code firmware image procedure
Use the following procedure to perform a serial upgrade of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch Boot Code firmware image,
usually named pGbE2_b_100.bin.
1. Using the null modem, connect the console port of a GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the serial port of your PC that
supports XModem/1K XModem.
2. Start HyperTerminal (part of Microsoft Windows) or equivalent terminal emulation application (depending on
your computer operating system), and set the following parameters for terminal emulation console:
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
3. Power on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
4. Hold the Shift key down and press the D key repeatedly during the Memory Test, until the following message
displays:
Memory Test ................
Xmodem Mode
Starting POST...
Checking MP I2c................................... PASSED.
Checking PCI bus.................................. PASSED.
Checking Interrupt................................ PASSED.
Post Passed.
Disabling watchdog for xmodem.
ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch - PPCBoot 2.x.x.
To download GbE2 Switch Boot Code or GbE2 Switch OS Image use 1K Xmodem at
115200
NOTE: You can perform serial downloads at 57600 baud rate by pressing the Shift-F keys or at 115200
baud rate by pressing the Shift-D keys.
Performing a serial download 47
Page 48

5. After you see the message displayed in step 4, reconfigure your terminal emulation console with the following
parameters.
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 115200
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
6. Press Enter several times on the keyboard of the PC that is connected to the console port of the GbE2
Interconnect Switch. When the console port is successfully communicating with the PC, indicating readiness for
image transfer, you see continuous C’s:
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
7. Make sure that the new Switch Boot Code firmware file is available on the computer. This file can be
downloaded from the CD that is shipped with the GbE2 Interconnect Switch or from
http://www.hp.com/support
8. Select <Transfer-Send File> from the menu and choose the following options in the send file window:
file: pGbE2_b_100.bin (100 represents the version number of Switch Boot
Code firmware)
protocol: 1K XMODEM
The send file window displays progress of the file transfer. It takes about seven minutes for the transfer to
complete.
.
NOTE: Although slower, XModem also works if you choose not to use 1K MODEM.
9. After completing the transfer, a message displays how many bytes transferred, followed by another message
displaying the status of image extraction. Do not power cycle the switch during this process. After extracting the
image, it is updated to flash and a message with a progress indicator displays as shown.
CAUTION: Do not power off the GbE2 Interconnect Switch until you see the message: “Change your
baud rate to 9600 bps and power cycle the switch,” otherwise, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch will be
inoperable.
ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch - PPCBoot 2.x.x.
To download GbE2 Switch Boot Code or GbE2 Switch OS Image use 1K Xmodem at
115200
Total bytes transferred: 0x380000
Extracting images ... Do *NOT* power cycle the switch
Updating flash ...
#########################################################
Change your baud rate to 9600 bps and power cycle the switch
10. Change the baud rate to 9600 and power off the GbE2 Interconnect Switch, wait for a few seconds, and
power on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch boots with the new version of the Boot Code image that was just downloaded.
Performing a serial download 48
Page 49

Serial upgrade of operating system firmware procedure
Use the following procedure to perform a serial upgrade of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch Operating System firmware
image usually named pGbE2_100.bin.
1. Using the null modem cable, connect the console port of a GbE2 Interconnect Switch to the serial port of your
PC that supports XModem/1K XModem.
2. Start HyperTerminal (part of Microsoft Windows) or equivalent terminal emulation application (depending on
your computer operating system) and set the following parameters for terminal emulation console:
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 9600
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
3. Power on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
4. Hold the Shift key down and press the D key repeatedly during the Memory Test, until the following message
displays:
Memory Test ................
Xmodem Mode
Starting POST...
Checking MP I2c................................... PASSED.
Checking PCI bus.................................. PASSED.
Checking Interrupt................................ PASSED.
Post Passed.
Disabling watchdog for xmodem.
ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch - PPCBoot 2.x.x.
To download GbE2 Switch Boot Code or GbE2 Switch OS Image use 1K Xmodem at
115200
NOTE: You can perform serial downloads at 57600 baud rate by pressing the Shift-F keys or at 115200
baud rate by pressing the Shift-D keys.
5. After the message in step 4 displays, reconfigure your terminal emulation console with the following
parameters.
Parameter Value
Baud Rate 115200
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
Performing a serial download 49
Page 50

6. Press Enter several times on the keyboard of the PC that is connected to the console port of the GbE2
Interconnect Switch. When the console port is successfully communicating with the PC, indicating readiness for
image transfer, you see continuous C’s:
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
7. Make sure that the new Switch Operating System firmware file is available on the computer. This file can be
downloaded from the CD that is shipped with the GbE2 Interconnect Switch or from
http://www.hp.com/support
8. Select <Transfer-Send File> from the menu and choose the following options in the send file window:
file: pGbE2_100.bin (100 represents the version number of Switch Operating
System firmware)
protocol: 1K XMODEM
The send file window displays the progress of the file transfer. It takes about five minutes for the transfer to
complete.
NOTE: Although slower, XModem also works if you choose not to use 1K MODEM.
9. After completing the transfer, a message displays how many bytes transferred, followed by another message
displaying the status of image extraction. Do not power cycle the switch during this process.
.
CAUTION: Do not power off the GbE2 Interconnect Switch until you see the message: “Change your baud rate
to 9600 bps and the power cycle switch”, otherwise, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch will be inoperable.
Performing a serial download 50
Page 51

10. After extracting the image, the system prompts you to select which current operating system image (image1 or
image2) needs to be updated by the new operating system image. It also provides an option (n) not to update
any and to quit the update procedure.
Depending on your selection, 1 or 2, the system updates image1 or image2 on the flash and a message with a
progress indicator displays as shown below. If you select n, the system aborts the update procedure and
prompts you to reset the baud rate and power cycle the switch.
ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch - PPCBoot 2.x.x.
To download GbE2 Switch Boot Code or GbE2 Switch OS Image use 1K Xmodem
at 115200
Total bytes transferred: 0x1ef400CCCCCCCCCCCCCC
Extracting images ... Do *NOT* power cycle the switch
Please choose the GbE2 Switch OS Image to upgrade [1|2|n] : 1
Updating GbE2 Switch OS Image 1 @ ff800000
###############################
Switch set to boot image 1
Change your baud rate to 9600 bps and power cycle the switch
OR
ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch - PPCBoot 2.x.x.
To download GbE2 Switch Boot Code or GbE2 Switch OS Image use 1K Xmodem at
115200
Total bytes transferred: 0x1ef400
Extracting images ... Do *NOT* power cycle the switch
Please choose the GbE2 Switch OS Image to upgrade [1|2|n] : 2
Updating GbE2 Switch OS Image 2 @ ff800000
###############################
Switch set to boot image 2
Change your baud rate to 9600 bps and power cycle the switch
OR
ProLiant p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch - PPCBoot 2.x.x.
To download GbE2 Switch Boot Code or GbE2 Switch OS Image use 1K Xmodem at
115200
Total bytes transferred: 0x1ef400
Extracting images ... Do *NOT* power cycle the switch
Please choose the GbE2 Switch OS Image to upgrade [1|2|n] : n
No update.
Change your baud rate to 9600 bps and power cycle the switch
11. Change the baud rate to 9600 and power off the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Wait for a few seconds, and
power on the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
During bootup the GbE2 Interconnect Switch the following prompt displays:
Press <Ctrl>-o to use the other image…
If you want to use the other operating system image, press the Ctrl-o keys.
Performing a serial download 51
Page 52

SNMP MIBs support
Introduction
Management and statistics information is stored in the GbE2 Interconnect Switch in the Management Information Base
(MIB). The GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports several standard MIBs. Values for MIB objects can be retrieved with
any SNMP-based network management software.
In addition to the standard MIBs, the switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended
Management Information Base. The proprietary MIB is retrieved by specifying the MIB Object-Identifier (OID) at the
network manager station.
MIB values can be either read-only or read/write variables.
• Read-only MIB variables can be constants that are programmed into the switch or variables that change while
the switch is in operation. Examples of read-only constants include the number and types of ports. Examples of
read-only variables are the statistics counters, such as the number of errors that have occurred or how many
kilobytes of data have been received and forwarded through a port.
• Read/write MIB variables are usually related to user-customized configurations. Examples include the IP address
of the switch, Spanning Tree Algorithm parameters, and port status.
SNMP manager software
If you use third-party vendor SNMP software to manage the switch, you can access proprietary enterprise MIBs for the
switch. The MIBs can be found in the utilities on the HP website (http://www.hp.com/support
If your software provides functions to browse or modify MIBs, you can also change the MIB values (if the MIB
attributes permit the write operation). This process can be quite involved, because you must use the MIB OIDs,
available in the MIB files, and retrieve them one by one.
Use an SNMP manager, such as HP OpenView Network Node Manager or HP Systems Insight Manager, to access
the enterprise-specific MIBs. Compile the MIBs into the MIB database and then use a MIB browser to navigate through
them. For detailed information, access the individual descriptions of each MIB or refer to the documentation that came
with your SNMP manager software.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch SNMP agent supports SNMP Version 1. Security is provided through SNMP community
strings. The default community strings are “public” for SNMP GET operation and “private” for SNMP SET operation.
Users may specify up to two trap hosts for receiving SNMP traps. The agent will send the SNMP trap to the specified
hosts when appropriate. Traps will not be sent if there is no host specified.
Supported MIBs
The SNMP agent for the GbE2 Interconnect Switch supports the following MIBs:
• bt2Network.mib— Layer 3 configuration information including IP interface, gateway, Domain Name System
(DNS), IGMP, and static Mrouter
• bt2Physical.mib— Layer 2 configuration information including VLAN, trunk groups, spanning tree
configuration, port mirroring, Forwarding Database (FDB) table, MSTP/RSTP, and Uplink Failure Detection
(UFD)
• bt2Switch.mib— General switch configuration information including statistics, system information, port
configuration, RADIUS, Network Time Protocol (NTP), syslog, trap host, Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP),
hardware information, TACACS+, secondary Radius server, and Uplink Failure Detection (UFD)
• bt2trap.mib—GbE2 Interconnect Switch trap information
• hpswitchpl.mib—HP GbE2 Interconnect Switch MIB root definition
• rfc1213.mib—MIB-II for network management of TCP/IP-based internets; Layer 3 IP information/data
• rfc1215.mib—Coldstart, warmstart, linkup trap definitions
• rfc1493.mib—Bridge traps, standard spanning tree, and other Layer 2 switch data
• rfc1573.mib—Defines the IANAifType textual convention, and thus the enumerated values of the ifType
object defined in MIB-II's ifTable
• rfc1757.mib—Remote Network Monitoring (RMON) MIB
• rfc2037.mib—SNMP network management entity MIB for use with multiple STPs
• cpqrack.mib—Rack location information
).
SNMP MIBs support 52
Page 53

• cpqsinfo.mib—Switch identification information
• cpqhost.mib—Switch identification information
• bt2Network.mib
• bt2Physical.mib
• bt2Switch.mib
• bt2acl.mib
• bt2qos.mib
• bt2trap.mib
• cpqhost.mib
• cpqrack.mib
• cpqsinfo.mib
• dot1x.mib
• hpswitchpl.mib
• ieee8023ad.mib
• rfc1213.mib
• rfc1493.mib
• rfc1573.mib
• rfc1643.mib
• rfc1757.mib
• rfc1850.mib
• rfc1907.mib
• rfc2037.mib
• rfc2571.mib
• rfc2572.mib
• rfc2573.mib
• rfc2574.mib
• rfc2575.mib
• rfc2576.mib
Supported traps
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch SNMP agent supports the following generic traps as defined in RFC 1215:
• ColdStart
• WarmStart
• LinkDown
• LinkUp
• AuthenticationFailure
• Failover
The SNMP agent also supports two spanning tree traps as defined in RFC 1493:
• NewRoot
• TopologyChange
SNMP MIBs support 53
Page 54

The following are the enterprise SNMP traps supported in the GbE2 Interconnect Switch:
Table 14 Supported enterprise SNMP traps
Trap name Description
bt2SwDefGwUp
bt2SwDefGwDown
bt2SwDefGwInService
bt2SwDefGwNotInService
bt2SwLoginFailure
bt2SwPrimaryPowerSupplyFailure
bt2SwVrrpNewMaster
bt2SwVrrpNewBackup
bt2SwVrrpAuthFailure
bt2SwRackLocationChange
bt2SwTempExceedThreshold
bt2SwTempReturnThreshold
bt2SwApplyComplete
Signifies that the default gateway is alive.
Signifies that the default gateway is down.
Signifies that the default gateway is up and in service.
Signifies that the default gateway is alive but not in service.
Signifies that someone failed to enter a valid
username/password combination.
Signifies that the primary power supply failed.
Indicates that the sending agent has transitioned to Master
state.
Indicates that the sending agent has transitioned to Backup
state.
Signifies that a packet has been received from a router whose
authentication key or authentication type conflicts with this
router’s authentication key or authentication type.
Implementation of this trap is optional.
Signifies that the GbE2 Interconnect Switch has had a
location change.
Signifies that the switch temperature has exceeded maximum
safety limits.
Indicates that the switch temperature has returned below
maximum safety limits.
Signifies that the new configuration has been applied.
bt2SwSaveComplete
bt2SwFwDownloadSucess
bt2SwFwDownloadFailure
bt2SwFanFailure
bt2SwFanFailureFixed
bt2SwUfdfoLtMFailure
bt2SwUfdfoLtMUP
Signifies that the new configuration has been saved.
Signifies that the firmware has been downloaded to
[image1|image2|boot image].
Signifies that the firmware downloaded failed to
[image1|image2|boot image].
Indicates that the fan failure has been detected.
Indicates that the fan failure has been fixed.
Signifies that an LtM link is down.
Signifies that an LtM link is up.
SNMP MIBs support 54
Page 55

Safe Mode configuration
Introduction
GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration files are specified in text format. Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) or Secure
Copy (SCP) services can to be used to upload and download these text-based configuration files. When these
configuration files are downloaded and applied to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
interprets the contents and applies it to the system as active configuration.
The configuration settings can be saved to NVRAM, and they become the backup configuration for the GbE2
Interconnect Switch. These settings are then used every time the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is rebooted.
IMPORTANT: The TFTP server must be running TFTP server software to perform a file transfer. TFTP server
software is included as part of the Windows utilities package.
When inserting a new or replacement GbE2 Interconnect Switch into a production/real-time environment, you must
be certain that the GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration is compatible with the production network. Since the
factory default switch configuration may not be same as the production configuration, it may compromise the security
aspects and VLAN isolation used by the production network.
A new or replacement GbE2 Interconnect Switch should be preconfigured in a "safe mode" such that it addresses
these security concerns and still allows the administrator to configure the switch and finalize switch deployment on the
production network. The administrator can simply download a final configuration template with the safe mode
configuration to deploy the GbE2 Interconnect Switch in the production environment.
User account information
User password information is not saved in the configuration file for security reasons and must be managed by the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch administrator. User account information can be manually added to the configuration file
after it is uploaded, or it can be re-entered using the CLI.
Safe Mode
When inserting a new or replacement GbE2 Interconnect Switch into a production environment, you must be certain
that the GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration is compatible with the production network. Compatibility with a
network can include items such as:
• Specific configuration of the network in general—problems, such as loops, can occur within the network without
specifically enabling Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
• Security of connected network entities—security issues can arise as a result of configuration items, including
such attributes as subnet-to-subnet communication and blade-to-blade communication where communication
between these entities is not acceptable
• Security of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch—these attributes include controlled access to the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch such as user-password and SNMP read-write community strings
• Other configuration attributes, such as VLAN settings
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch factory default, as well as previously configured GbE2 Interconnect Switches, may not
have configurations that are compatible with the production network.
If the configuration of the GbE2 Interconnect Switch is not compatible with the production network, the GbE2
Interconnect Switch may be pre-configured in a pre-production network environment before inserting in to production
environment. Also, the GbE2 Interconnect Switch can booted up using the Diagnostic Station for preconfiguration, to
make it ready for production network.
There are several preconfiguration options:
• Configure the GbE2 Interconnect Switch for its exact position in the production network.
• Partially configure the GbE2 Interconnect Switch so that it is compatible with multiple positions in the production
network. The configuration can then be completed for the GbE2 Interconnect Switch through scripting, manual
operation, or a configuration download. This more globally appropriate configuration is called a safe mode
configuration. Note that a single safe mode configuration may or may not be appropriate for all production
environments. A spare GbE2 Interconnect Switch, however, configured to a safe mode, may be appropriate for
multiple production environments.
Safe Mode configuration 55
Page 56

GbE2 Interconnect Switch replacement scenario using a Safe Mode configuration
When an in-production GbE2 Interconnect Switch fails:
1. Remove the failed GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
2. Insert the spare GbE2 Interconnect Switch that was previously configured for safe operation.
3. Upgrade to new firmware if appropriate.
4. Download the correct configuration for that particular GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
Safe Mode configuration file templates
An example template configuration file, named Safe_Mode_GbE2, has been provided as a basis to create an
appropriate safe mode configuration. This file, delivered with the GbE2 Interconnect Switch Management Utilities
package, is located on the utilities and user documentation CD included in the interconnect kit and at
http://www.hp.com/support
NOTE: The template provided is only an example, and should not be used in a production environment without
modifications required for your specific production network. This template has commented sections such as for
IP configuration, password protection, and port selection.
.
Safe Mode configuration file template modification
To modify the safe mode configuration file template:
1. Review the readme file.
2. Copy the example safe mode template to a new file with custom name.
3. Perform modifications appropriate for your production environment. Your environment may require additional
settings such as VLAN configuration, IP settings, password settings, TFTP/SCP settings, and so on.
Applying the Safe Mode template configuration file
Use one of the following methods to apply the file to your GbE2 Interconnect Switch and set the switch in Safe Mode.
Method 1: Via the switch serial port using command line interface (CLI)
1. Power up the switch using the Diagnostic Station or by inserting the switch in a non-production blade enclosure.
Log in to the switch CLI via the serial console as Admin.
2. Open the Safe_Mode_GbE2 template configuration file using any text editor, such as Microsoft WordPad,
and make the changes as suggested by the comments in that template configuration file.
3. Copy all the content from the template configuration file with your edits and paste it as a command to the switch
CLI.
4. Issue the /apply command on the CLI.
5. Issue the /save command, and type y when prompted.
6. Power up the switch by inserting it into a production blade enclosure. This boots up the switch in Safe Mode,
with all ports except uplink port 19 disabled.
7. Access any of the switch management interfaces through uplink port 19, and complete the switch configuration
appropriate for your production network. Or, you can use the serial port to complete the switch configuration
appropriate for your production network.
Safe Mode configuration 56
Page 57

Method 2: Via any switch management interface using TFTP functionality
1. Power up the switch using the Diagnostic Station or by inserting the switch in a non-production blade enclosure.
After resetting the switch to factory settings (if required), login to the switch CLI via the serial console as Admin.
2. If the switch cannot get BootP assigned IP settings, configure the switch IP address settings so that it can access
a TFTP server on the attached network.
3. Open the Safe_Mode_GbE2 template configuration file using any text editor, such as Microsoft WordPad, and
make the changes as suggested by the comments in that template configuration file.
4. From any switch management interface, enable TFTP download of the template configuration file with your
edits.
5. Apply the changes and save to flash.
6. Power up the switch by inserting it into a production blade enclosure. This boots up the switch in Safe Mode
with all ports except uplink port 19 disabled.
7. Access any of the switch management interfaces through uplink port 19, and complete the switch configuration
appropriate for your production network. Or, you can use the serial port to complete the switch configuration
appropriate for your production network.
Safe Mode configuration 57
Page 58

Electrostatic discharge
Overview
To prevent damage to the system, be aware of the precautions you need to follow when setting up the system or
handling parts. A discharge of static electricity from a finger or other conductor may damage system boards or other
static-sensitive devices. This type of damage may reduce the life expectancy of the device.
To prevent electrostatic damage, observe the following precautions:
• Avoid hand contact by transporting and storing products in static-safe containers.
• Keep electrostatic-sensitive parts in their containers until they arrive at static-free workstations.
• Place containers on a grounded surface before removing the contents.
• Avoid touching pins, leads, or circuitry.
• Always be properly grounded when touching a static-sensitive component or assembly.
Grounding methods
There are several methods for grounding. Use one or more of the following methods when handling or installing
electrostatic-sensitive parts:
• Use a wrist strap connected by a grounded cord. Wrist straps are flexible straps with a minimum of 1 megohm
±10 percent resistance in the ground cords. To provide proper ground, wear the strap snug against the skin.
• Use heel straps, toe straps, or boot straps. Wear the straps on both feet when standing on conductive floors or
dissipating floor mats.
• Use conductive field service tools.
• Use a portable field service kit with a folding static-dissipating work mat.
If you do not have any of the suggested equipment for proper grounding, have an HP authorized reseller install the
part.
NOTE: For more information on static electricity or assistance with product installation, contact your HP
authorized reseller.
Electrostatic discharge 58
Page 59

RJ-45 pin specification
When connecting the HP ProLiant BL p-class GbE2 Interconnect Switch to a switch, bridge, or hub, an Ethernet cable
is necessary.
The following figure displays the standard RJ-45 receptacle/connector for 10/100 Mb/s and Gigabit over Copper
ports. Table 15 indicates the pin number and wire color assignments for the switch-to-network adapter card
connection, and the Ethernet cable for the switch-to-switch, switch-to-hub, or switch-to-bridge connection. Table 16
provides the same information for the Gigabit over Copper ports.
NOTE: A cable configured for Gigabit over Copper can also be used on a 10/100-Mb/s connection.
Figure 15 Standard RJ-45 receptacle/connector for 10/100 Mb/s and gigabit over copper
Table 15 RJ-45 connector pin assignment for 10/100 Mb/s
Contact Media direct interface signal Color match
1 Tx + (transmit) White/Orange
2 Tx - (transmit) Orange/White
3 Rx + (receive) White/Green
4 Not used Blue/White
5 Not used White/Blue
6 Rx – (receive) Green/White
7 Not used White/Brown
8 Not used Brown/White
Table 16 RJ-45 connector pin assignment for gigabit over copper
Contact Media direct interface signal Color match
1 BI_DA+ White/Orange
2 BI_DA- Orange/White
3 BI_DB+ White/Green
4 BI_DC+ Blue/White
5 BI_DC- White/Blue
6 BI_DB- Green/White
7 BI_DD+ White/Brown
8 BI_DD- Brown/White
RJ-45 pin specification 59
Page 60

Troubleshooting
This section provides information on solutions to problems that may occur during the configuration and operation of a
ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch. The following tables provide steps to take before calling your service
representative.
Following are four tables with basic troubleshooting information:
• Setting up and accessing—Table 17 contains general troubleshooting information about setting up and
accessing the GbE2 Interconnect Switch. Topics covered include LEDs, cables, failure of the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch to get IP settings, failure to connect to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch remotely, and what to do if you
forget your administrator user name and password.
• Configuring—Table 18 contains general troubleshooting information about configuring the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch. Topics covered include configuring VLANs and XConnect ports.
• Using a TFTP server—Table 19 contains general troubleshooting information about using a TFTP server to back
up GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration or to configure multiple GbE2 Interconnect Switches.
• Upgrading firmware using the serial port—Table 20 contains general troubleshooting information about
upgrading system firmware using the serial console port.
For additional troubleshooting information, refer to
• “Performing a serial download" appendix in this guide
• Appendix A: Troubleshooting Tools, in the HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect Switch Application Guide
• The following website: http://www.hp.com/support
Table 17 Troubleshooting: Setting up and accessing
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
Forgot the administrator user name and
password that you configured on the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
The Power LED on the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch is not on.
The Power LED on the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch stays amber for more than 30
seconds and GbE2 Interconnect Switch
does not boot.
No link LED displays, even after you
plug the Category 5 cable in the RJ-45
connector of the external port.
Unknown Call HP technical support at
1-800-652-6672 or your service
representative to get a backdoor
password.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch is not
seated properly.
The server blade enclosure is not
powered up.
There is a faulty LED. Check the console to see if GbE2
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch fuse is
blown.
The standby mode time out function is
malfunctioning.
The cable is not properly plugged in. Check the cable at both ends to ensure
The cable or connector heads are faulty. Replace the cable with another tested
Make sure that the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch is inserted completely and seated
properly.
Make sure that the server blade
enclosure is powered up and all the
power connections are intact.
Interconnect Switch is booted.
Send for repair.
Force the GbE2 Interconnect Switch to
boot by pressing the Pwr/Rst button.
that it is plugged in and seated properly.
cable.
Troubleshooting 60
Page 61

Table 17 Troubleshooting: Setting up and accessing
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
The RJ-45 connector on the switch or LED
is faulty.
• After checking and replacing the
cable, if no link LED displays, check
whether the port is transferring data.
If yes, the LED is faulty. If no, it
could be a faulty RJ-45 connector.
Call your service representative.
• This could be caused by using a
crossover cable instead of a
straight-through cable.
Cannot access the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch serial console interface using null
modem connection from a PC Terminal
Emulation Program.
An error message that the GbE2
Interconnect Switch failed to complete
the system self-testing is displayed on the
serial console screen.
The keyboard locks up when using
HyperTerminal to log on to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch through the console
interface.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch fails to get
its IP settings from the BOOTP server,
even though by default it is configured
for BOOTP.
IMPORTANT: If you are running in
spanning tree mode, it can take up to
2½ minutes for the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch to get its IP settings.
Cannot connect to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch console interface
remotely using Telnet.
The null modem cable is faulty. Make sure that you use the null modem
cable provided by HP with this
hardware.
The connection settings do not match the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch serial settings.
The system diagnostic tests failed. Note the reason for the failure from the
Scroll lock is on. Press the Scroll Lock key on the keyboard
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch is not
connected properly to the network.
The BOOTP server is not available on
the network or VLAN that is attached to
the switch management port.
The BOOTP server cannot offer IP
settings to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
because no IP addresses are available.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch timed out
its request for IP settings.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch IP address
may not be configured or correct.
Make sure that the PC Terminal
Emulation session settings match the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch serial settings.
serial console screen message and call
your service representative.
and make sure that the scroll lock is off.
Check the cable and connections and
make sure that there is network
connectivity between the GbE2
Interconnect Switch and the BOOTP
server.
Make sure that the BOOTP server is
present on the network or VLAN
attached to the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
Add additional IP addresses as
necessary.
Reset the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
• From the serial console interface,
make sure that the GbE2
Interconnect Switch IP address is
configured and valid on your
network.
• Use the correct IP address to
establish the Telnet connection with
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
The setting allowing access to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch using the Telnet
interface is disabled.
The management network address/mask
(if used) does not contain the IP address
of your management station.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the Telnet interface is enabled.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the Management Network
Address/Mask contains the IP address of
your management station.
Troubleshooting 61
Page 62

Table 17 Troubleshooting: Setting up and accessing
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
Password is not accepted by the GbE2
Interconnect Switch using the remote
console interface immediately after a
reboot.
Cannot connect to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch console interface
remotely using SSH.
Cannot connect to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch remotely using the
Web interface.
Cannot connect to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch SNMP interface.
The management network address/mask
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch is still
working on network convergence.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch IP address
may not be configured or correct.
The setting allowing access to the GbE2
Interconnect Switch using the SSH
interface is disabled.
The management network address/mask
(if used) does not contain the IP address
of your management station.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch IP address
may not be configured or correct.
Access to the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
using the Web interface is disabled.
The Proxy server settings are configured
on your Internet browser and your proxy
server does not know the GbE2
Interconnect Switch IP address.
The management network address/mask
(if used) does not contain the IP address
of your management station.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch IP address
may not be configured or correct.
(if used) does not contain the IP address
of your management station.
Wait up to 10 seconds, and the
password should be accepted.
• From the serial console interface,
make sure that the GbE2
Interconnect Switch IP address is
configured and valid on your
network.
• Use the correct IP address to
establish the SSH connection with
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the SSH interface is enabled
and all its settings are configured
correctly.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the Management Network
Address/Mask contains the IP address of
your management station.
• From the serial console interface,
make sure that the GbE2
Interconnect Switch IP address is
configured and valid on your
network.
• Use the correct IP address to
establish the Web connection with
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the Web interface is enabled.
Disable the manual proxy settings on
your Web browser and let it
automatically find Web servers using the
IP address.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the Management Network
Address/Mask contains the IP address of
your management station.
• From the serial console interface,
make sure that the GbE2
Interconnect Switch IP address is
configured and valid on your
network.
• Use the correct IP address to
establish the SNMP connection with
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
From the serial console interface, make
sure that the Management Network
Address/Mask contains the IP address of
your management station.
Troubleshooting 62
Page 63

Table 18 Troubleshooting: Configuring
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
After connecting more than one port to
another switch or destination device, the
port activity LEDs continuously indicate
activity.
While configuring VLANs, you cannot
enable a port in multiple VLANs.
While assigning the ports to VLANs, the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch does not let
the user enable two adjacent ports into
two different VLANs.
Because there are multiple links across
this device and the destination device,
they form loops, which cause broadcast
storms.
A port can be part of only one VLAN
unless the port is a tagged port.
The ports could be two adjacent ports
that are bundled in a Port Trunk.
Enable STP if you want multiple links.
This setting prevents loops and maintains
standby links for resilience in case of
primary link failure.
Make sure that you enable the port as a
tagged port.
Two ports that are assigned to a Port
Trunk cannot be assigned to two
different VLANs. Either break the trunk to
assign it two different VLANs or assign
the ports to one VLAN.
Troubleshooting 63
Page 64

Table 19 Troubleshooting: Using a TFTP server
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
While using TFTP to download firmware,
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch fails to
connect to the TFTP server, or after
connection the download fails.
While using TFTP to download or upload
a configuration file, the GbE2
Interconnect Switch fails to connect to
the TFTP server, or after connection the
download or upload fails.
The configuration file is not found on the
The TFTP server was started with a
The TFTP server is not available to
connect to or there is connectivity failure
between the switch and TFTP server.
The firmware file is not found on the
TFTP server. The file name could be
wrong.
The TFTP server was started with a
configured directory.
The TFTP server is not available to
connect or there is a connectivity failure
between the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
and the TFTP server.
TFTP server. The file name could be
wrong.
configured directory.
• Make sure that the IP address of the
TFTP server is correct.
• Make sure that the TFTP server exists
on the same network and VLAN as
the GbE2 Interconnect Switch.
• Make sure that you can ping the
TFTP server from the GbE2
Interconnect Switch and vice versa.
• Make sure that a valid firmware file
exists on the TFTP server to
download to the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
• On the GbE2 Interconnect Switch,
check the file name you configured
to download.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch must be
configured using the full path name, if it
is not in the directory specified in the
TFTP server.
• Make sure that the TFTP server exists
on the same network or VLAN as
that of the switch.
• Make sure that you can ping the
TFTP server from the switch and vice
versa.
• Make sure that the IP address of the
TFTP server is correct.
• Make sure that a valid configuration
file exists on the TFTP server to
download to the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
• On the GbE2 Interconnect Switch,
check the file name you configured
to download or upload.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch must be
configured using the full path name, if it
is not in the directory specified in the
TFTP server.
Troubleshooting 64
Page 65

Table 20 Troubleshooting: Upgrading firmware using the serial port
Problem Possible cause Possible solution
After forcing the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch into the download mode, the
console screen displays a message to
change the baud rate for your terminal
emulation session for XModem transfer
and does not display CCCC….
After starting to download the firmware
file, the download fails.
The GbE2 Interconnect Switch
configuration is corrupt.
Your terminal emulation session baud
rate does not match the GbE2
Interconnect Switch serial console baud
rate in the download mode.
The firmware file is not the correct one
or is corrupt.
An error was made when saving the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch configuration.
Change the baud rate of your terminal
emulation session to match the GbE2
Interconnect Switch serial console baud
rate in the download mode.
IMPORTANT: The baud rate for the
GbE2 Interconnect Switch serial console
in the download mode and runtime
mode are two separate settings.
Obtain the latest firmware file that is
specified for this GbE2 Interconnect
Switch.
Reboot the GbE2 Interconnect Switch
and reload the factory settings. This
action clears all settings and restores
them to the initial values that were
present when the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch was purchased. Refer to the HP
ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Interconnect
Switch Command Reference Guide for
more information.
After reloading the factory settings,
reconfigure the GbE2 Interconnect
Switch settings.
Troubleshooting 65
Page 66

Index
A
accessing switch: procedure, 27;
RADIUS authentication, 14
administrator account password, 26
architecture, switch, 10
B
Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP): overview,
14
BSMI regulatory notice, 32, 35
C
cabling of switch: procedures, 26;
reduction feature, 6, 10
Canadian regulatory notice, 30, 33
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
Collision Detection (CSMA/CD), 12
configuration: features, 8; manual, 26;
multiple switches, 26; planning for,
24; safe mode, 55
crosslinks, redundant, 12
CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple
Access with Collision Detection), 12
D
data transfer rates, 36
default settings: parameters to set, 24
diagnostics tools, 8
downloading software, 16
E
emulation software, 47, 49
Ethernet ports/connectors: features, 6;
locations, 18; specifications, 36
eXtensible Markup Language (XML),
55
external components, overview, 16
F
failover features, 8
features, 6
Federal Communications Commission
(FCC) notice, 30, 33
Fibre Channel signal pass-through
connectivity, 21
front panel components, overview, 16
G
GbE2 Storage Connectivity Kit, 21
H
hardware installation, 21
HP ProLiant BL p-Class C-GbE2
Interconnect Kit: features, 5
HP ProLiant BL p-Class F-GbE2
Interconnect: Kit features, 5
HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2
Interconnect Switch: architecture,
10; external components, 16;
installing, 21; SNMP MIBs support,
52; supported technologies, 12;
troubleshooting, 60
HP ProLiant BL p-Class GbE2 Storage
Connectivity Kit, 21
I
IEEE 802.1Q-based VLAN, 13
IEEE/ANSI standards, specifications,
36
image, downloading, 16
installation: cabling, 26; hardware,
21; initial power-up, 27; overview,
21; planning configuration, 24
Integrated Lights Out (iLO): switch
architecture, 12; VLAN features, 13
interconnect modules: accessing switch
with, 27; cabling procedure, 27;
QuadSX, 5, 19; QuadT2, 5, 18
IP addresses: BOOTP sources for, 14;
TFTP server, 26
J
Japanese regulatory notice, 32, 35
K
Korean regulatory notice, 35
L
laser device regulatory compliance
notice, 35
Layer 2-based packet forwarding, 12
load balancing, 13
local area network (LAN), 13
M
Management Information Bases
(MIBs), 52
manual configuration, 26
mirroring of ports, overview, 13
multiple-switch configuration, 26
N
new deployment installation, 22
O
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI)
model, 12
operator account password, 25
P
packets, forwarding technology, 12
patch panels, upgrading from, 24
performance features, 6
port trunking, 13
ports: locations, 18; mirroring of, 13;
specifications, 37
power-up procedures, initial, 27
protocols, network: BOOTP, 14;
overview, 13; specifications, 36
Q
QuadSX Interconnect Module:
location, 19; overview, 5
QuadT2 Interconnect Module:
location, 18; overview, 5
R
RADIUS, authentication, 14
redundancy features: crosslinks, 12;
overview, 8
regulatory compliance notices, 30, 33
remote access to switch, 28
Remote monitoring (RMON), 7
replacing existing GbE2 switch, 23
replacing interconnect switch, safe
mode, 55
RJ-45 connectors: location, 18; pin
specifications, 59
RJ-45 patch panels, upgrading from,
24
RMON (remote monitoring), 7
S
safe mode: compatibility with network,
55; configuration file templates, 55,
56; switch replacement scenario, 56
security: overview, 25; RADIUS
authentication, 14
Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP): overview, 13; SNMP MIBs
support, 52
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP):
overview, 8, 13
specifications: RJ-45 pin, 59
Index 66
Page 67

standards, IEEE/ANSI, 36
store and forward switching scheme,
14
switch replacement, safe mode, 56
T
templates, safe mode: location, 56;
modification, 56
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
server: multiple switch
configurations, 26; overview, 13;
XML configuration, 55
troubleshooting, 60
trunking feature, overview, 13
U
upgrading from a GbE Interconnect
Switch, 23
upgrading from RJ-45 patch panels,
24
user account password, 25
users, XML configuration, 55
V
virtual local area networks (VLANs):
features, 13
VLAN ID, 24
X
XModem, 47, 49
Index 67
 Loading...
Loading...