Page 1

HPE iLO 5 User Guide
1.15
Abstract
This guide provides information about configuring, updating, and operating HPE ProLiant
Gen10 servers and HPE Synergy compute modules by using the HPE iLO 5 firmware. This
document is intended for system administrators, Hewlett Packard Enterprise representatives,
and Hewlett Packard Enterprise Authorized Channel Partners who are involved in configuring
and using Hewlett Packard Enterprise servers that include iLO 5.
Part Number: 880740-002a
Published: January 2018
Edition: 2
Page 2

©
Copyright 2012-2018 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
Notices
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for Hewlett
Packard Enterprise products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Hewlett Packard Enterprise required for possession,
use, or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer
Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government
under vendor's standard commercial license.
Links to third-party websites take you outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website. Hewlett Packard
Enterprise has no control over and is not responsible for information outside the Hewlett Packard
Enterprise website.
Acknowledgments
Microsoft® and Windows® are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and/or other countries.
Java® and Oracle® are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Google™ is a trademark of Google Inc.
Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.
Red Hat® is a registered trademark of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
SD is a trademark or registered trademark of SD-3C in the United States, other countries or both.
VMware® is a registered trademark or trademark of VMware, Inc. in the United States and/or other
jurisdictions.
Page 3

Contents
iLO.......................................................................................................... 16
Setting up iLO........................................................................................19
iLO key features..........................................................................................................................16
ROM-based configuration utility..................................................................................................17
iLO mobile app............................................................................................................................17
iLO RESTful API......................................................................................................................... 18
RESTful Interface Tool................................................................................................................18
iLO scripting and command line..................................................................................................18
Preparing to set up iLO............................................................................................................... 19
iLO network connection options....................................................................................... 19
NIC teaming with Shared Network Port configurations.................................................... 20
iLO IP address acquisition............................................................................................... 21
iLO access security.......................................................................................................... 21
iLO configuration tools..................................................................................................... 22
Initial setup steps: Process overview.......................................................................................... 23
Connecting iLO to the network....................................................................................................23
Setting up iLO by using the iLO 5 Configuration Utility............................................................... 24
Configuring a static IP address (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)............................................ 24
Managing local user accounts with the iLO 5 Configuration Utility.................................. 25
Logging in to iLO for the first time............................................................................................... 27
iLO default credentials................................................................................................................ 27
iLO licensed features.................................................................................................................. 27
iLO driver support........................................................................................................................28
Installing the iLO driver............................................................................................................... 28
Using the iLO web interface.................................................................30
iLO web interface........................................................................................................................ 30
Supported browsers....................................................................................................................30
Browser requirements.................................................................................................................30
Configuring the Internet Explorer JavaScript setting...................................................................30
Logging in to the iLO web interface ........................................................................................... 31
Cookie sharing between browser instances and iLO..................................................................31
iLO web interface........................................................................................................................ 33
Using the iLO controls.................................................................................................................33
Starting a remote management tool from the login page............................................................34
Changing the language from the login page............................................................................... 35
Viewing iLO information and logs....................................................... 36
Viewing iLO overview information...............................................................................................36
System information details............................................................................................... 36
System status details....................................................................................................... 37
Connection to HPE status................................................................................................ 38
Managing iLO sessions...............................................................................................................38
Session list details............................................................................................................38
iLO Event Log ............................................................................................................................ 39
Contents 3
Page 4

Viewing the event log....................................................................................................... 39
Saving the event log to a CSV file....................................................................................41
Clearing the event log...................................................................................................... 41
Integrated Management Log.......................................................................................................41
Viewing the IML................................................................................................................42
Marking an IML entry as repaired.................................................................................... 44
Adding a maintenance note to the IML............................................................................ 44
Saving the IML to a CSV file............................................................................................ 45
Clearing the IML...............................................................................................................45
Active Health System..................................................................................................................45
Active Health System data collection............................................................................... 46
Active Health System Log................................................................................................ 46
Downloading the Active Health System Log for a date range..........................................46
Downloading the entire Active Health System Log.......................................................... 47
Extracting the Active Health System Log by using curl....................................................48
Clearing the Active Health System Log............................................................................49
Viewing iLO self-test results........................................................................................................50
iLO self-tests.................................................................................................................... 50
Viewing general system information...................................................52
Viewing health summary information.......................................................................................... 52
Redundancy status.......................................................................................................... 52
Subsystem and device status.......................................................................................... 52
Subsystem and device status values............................................................................... 52
Viewing processor information....................................................................................................53
Processor details..............................................................................................................53
Viewing memory information.......................................................................................................54
Advanced Memory Protection details...............................................................................54
Memory Summary............................................................................................................56
Physical Memory Details..................................................................................................57
Logical Memory Details....................................................................................................57
Memory Details pane....................................................................................................... 58
Viewing network information....................................................................................................... 60
Physical Network Adapters.............................................................................................. 60
Logical Network Adapters................................................................................................ 62
Viewing the device inventory.......................................................................................................62
Device Inventory details................................................................................................... 62
Device status values........................................................................................................ 63
Viewing PCI slot details....................................................................................................63
Viewing storage information........................................................................................................63
Supported storage components....................................................................................... 64
Smart Array details...........................................................................................................64
Direct-attached storage details........................................................................................ 66
4 Contents
Managing firmware, OS software, and language packs.................... 68
Firmware updates....................................................................................................................... 68
Online firmware update.................................................................................................... 68
Online firmware update methods..................................................................................... 68
Offline firmware update.................................................................................................... 69
Offline firmware update methods..................................................................................... 69
Viewing and updating firmware from the iLO web interface........................................................70
Updating iLO or server firmware by using the Flash Firmware feature............................70
Viewing installed firmware information.............................................................................73
Replacing the active system ROM with the redundant system ROM...............................74
Page 5

iLO Repository............................................................................................................................ 74
Adding a component to the iLO Repository..................................................................... 74
Installing a component from the iLO Repository.............................................................. 75
Removing a component from the iLO Repository............................................................ 76
Viewing iLO Repository summary and component details...............................................76
Install Sets...................................................................................................................................77
Installing an install set...................................................................................................... 77
Removing an Install Set................................................................................................... 78
Viewing Install Sets.......................................................................................................... 78
System Recovery Set.......................................................................................................79
Installation Queue....................................................................................................................... 79
Viewing the Installation Queue.........................................................................................80
Removing a task from the Installation Queue.................................................................. 81
Installing language packs............................................................................................................81
Viewing software information...................................................................................................... 81
Product-related Software details...................................................................................... 82
Running Software details................................................................................................. 82
Installed Software details................................................................................................. 82
Configuring and using iLO Federation............................................... 83
iLO Federation............................................................................................................................ 83
Configuring iLO Federation.........................................................................................................83
Prerequisites for using the iLO Federation features.........................................................83
iLO Federation network requirements..............................................................................84
Configuring the multicast options for one iLO system at a time ...................................... 84
iLO Federation groups..................................................................................................... 85
Managing iLO Federation group memberships (local iLO system).................................. 87
Adding iLO Federation group memberships (multiple iLO systems)................................89
Configuring Enclosure iLO Federation Support............................................................... 92
Using the iLO Federation features.............................................................................................. 92
Selected Group list...........................................................................................................92
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file......................................................... 93
iLO Federation Multi-System view....................................................................................94
Viewing the iLO Federation Multi-System Map................................................................ 96
iLO Federation Group Virtual Media.................................................................................96
iLO Federation Group Power........................................................................................... 98
Configuring group power capping.................................................................................. 100
iLO Federation Group Firmware Update........................................................................102
Installing license keys (iLO Federation group) .............................................................. 105
iLO Integrated Remote Console........................................................ 107
.NET IRC requirements.............................................................................................................108
Microsoft .NET Framework.............................................................................................108
Microsoft ClickOnce....................................................................................................... 109
Starting the Integrated Remote Console...................................................................................109
Starting the .NET IRC.....................................................................................................109
Starting the .NET IRC from the Overview page............................................................. 109
Starting the Java IRC (Oracle JRE)................................................................................110
Starting the Java IRC (OpenJDK JRE)...........................................................................110
Starting the Java IRC from the Overview page.............................................................. 111
Acquiring the Remote Console..................................................................................................111
Using the Remote Console virtual power switch.......................................................................112
Virtual Power Button options.......................................................................................... 112
Using iLO Virtual Media from the Remote Console...................................................................113
Contents 5
Page 6

Shared Remote Console (.NET IRC only).................................................................................113
Joining a Shared Remote Console session....................................................................113
Console Capture (.NET IRC only).............................................................................................114
Viewing Server Startup and Server Prefailure sequences............................................. 114
Saving Server Startup and Server Prefailure video files................................................ 115
Capturing video files with the Remote Console..............................................................115
Viewing saved video files............................................................................................... 116
Remote Console hot keys......................................................................................................... 116
Creating hot keys............................................................................................................117
Keys for configuring Remote Console computer lock keys and hot keys.......................117
Resetting hot keys..........................................................................................................118
Viewing configured remote console hot keys (Java IRC only)....................................... 118
Configuring Remote Console Computer Lock settings............................................................. 119
Remote Console Computer Lock options.......................................................................119
Configuring the Integrated Remote Console Trust setting (.NET IRC)..................................... 119
Using a text-based Remote Console.................................................121
Using the iLO Virtual Serial Port............................................................................................... 121
Configuring the iLO Virtual Serial Port in the UEFI System Utilities...............................122
Configuring Linux to use the iLO Virtual Serial Port.......................................................122
Windows EMS Console with iLO Virtual Serial Port.......................................................125
Configuring Windows for use with the iLO Virtual Serial Port........................................ 125
Starting an iLO Virtual Serial Port session..................................................................... 126
Viewing the iLO Virtual Serial Port log........................................................................... 126
Text-based Remote Console (Textcons)................................................................................... 127
Customizing the Text-based Remote Console............................................................... 127
Using the Text-based Remote Console..........................................................................128
Using Linux with the Text-based Remote Console.........................................................129
Using iLO Virtual Media......................................................................130
iLO Virtual Media.......................................................................................................................130
Virtual Media operating system information..............................................................................131
Operating system USB requirement.............................................................................. 131
Configuring Windows 7 for use with iLO Virtual Media with Windows 7........................ 131
Operating system considerations: Virtual Floppy/USB key............................................132
Operating system considerations: Virtual CD/DVD-ROM.............................................. 132
Operating system considerations: Virtual Folder ...........................................................133
Using Virtual Media from the iLO web interface........................................................................133
Viewing Virtual Media status and port configuration...................................................... 134
Viewing connected local media......................................................................................134
Ejecting a local media device.........................................................................................135
Connecting scripted media.............................................................................................135
Viewing connected scripted media.................................................................................136
Ejecting scripted media.................................................................................................. 136
Remote Console Virtual Media................................................................................................. 136
Virtual Drives..................................................................................................................137
Create Media Image feature (Java IRC only).................................................................138
Using a Virtual Folder (.NET IRC only).......................................................................... 140
Setting up IIS for scripted Virtual Media....................................................................................140
Configuring IIS............................................................................................................... 140
Configuring IIS for read/write access............................................................................. 141
Inserting Virtual Media with a helper application............................................................142
Sample Virtual Media helper application........................................................................142
6 Contents
Page 7

Using the power and thermal features..............................................145
Server power-on....................................................................................................................... 145
Brownout recovery.................................................................................................................... 145
Graceful shutdown.................................................................................................................... 146
Power efficiency........................................................................................................................146
Power-on protection..................................................................................................................146
Power allocation (blade servers and compute modules).......................................................... 147
Managing the server power...................................................................................................... 147
Virtual Power Button options..........................................................................................148
Configuring the System Power Restore Settings......................................................................148
Auto Power-On...............................................................................................................148
Power-On Delay.............................................................................................................149
Viewing server power usage.....................................................................................................149
Power meter graph display options................................................................................150
Viewing the current power state.....................................................................................151
Viewing the server power history................................................................................... 152
Power settings.......................................................................................................................... 152
Configuring the Power Regulator settings......................................................................152
Configuring power caps................................................................................................. 153
Configuring battery backup unit settings........................................................................ 155
Configuring SNMP alert on breach of power threshold settings.................................... 155
Configuring the persistent mouse and keyboard............................................................156
Viewing power information........................................................................................................157
Power Supply Summary details..................................................................................... 157
Power Supplies list.........................................................................................................159
Power Discovery Services iPDU Summary ...................................................................160
Power Readings.............................................................................................................161
Power Microcontroller.....................................................................................................161
Battery Backup Unit details............................................................................................ 161
Smart Storage Battery details........................................................................................ 161
Power monitoring........................................................................................................... 162
High Efficiency Mode......................................................................................................162
Viewing fan information.............................................................................................................162
Fan details......................................................................................................................162
Fans............................................................................................................................... 163
Temperature information .......................................................................................................... 163
Viewing the temperature graph...................................................................................... 163
Viewing temperature sensor data...................................................................................164
Temperature monitoring................................................................................................. 164
Configuring iLO network settings..................................................... 166
iLO network settings................................................................................................................. 166
Viewing the network configuration summary.............................................................................166
Network configuration summary details......................................................................... 166
IPv4 Summary details.................................................................................................... 167
IPv6 Summary details.................................................................................................... 167
General network settings.......................................................................................................... 168
Configuring the iLO Hostname Settings.........................................................................168
NIC settings....................................................................................................................169
Configuring IPv4 settings.......................................................................................................... 171
IPv4 settings...................................................................................................................172
Configuring IPv6 settings.......................................................................................................... 173
IPv6 settings...................................................................................................................174
Contents 7
Page 8

iLO features that support IPv6....................................................................................... 175
Configuring iLO SNTP settings................................................................................................. 176
SNTP options................................................................................................................. 177
iLO clock synchronization.............................................................................................. 178
DHCP NTP address selection........................................................................................178
iLO NIC auto-selection..............................................................................................................178
NIC auto-selection support.............................................................................................179
iLO startup behavior with NIC auto-selection enabled................................................... 179
Enabling iLO NIC auto-selection.................................................................................... 180
Configuring NIC failover................................................................................................. 180
Viewing iLO systems in the Windows Network folder............................................................... 180
Managing remote support.................................................................. 182
HPE embedded remote support............................................................................................... 182
Device support............................................................................................................... 183
Data collected by HPE remote support.......................................................................... 183
HPE Proactive Care service...........................................................................................184
Prerequisites for remote support registration............................................................................184
Supported browsers....................................................................................................... 185
Setting up a ProLiant server for remote support registration......................................... 186
Insight Online direct connect network requirements...................................................... 187
Setting up the Insight Remote Support central connect environment............................ 187
Verifying access to Insight Online.................................................................................. 189
Registering for Insight Online direct connect ........................................................................... 189
Registering for Insight Online direct connect (step 1).................................................... 189
Registering for Insight Online direct connect (step 2).................................................... 190
Confirming registration is complete (iLO web interface)................................................ 191
Completing the optional post-registration steps............................................................. 191
Editing the web proxy settings (Insight Online direct connect only) .............................. 191
Registering for Insight Remote Support central connect ......................................................... 191
Unregistering from Insight Online direct connect ..................................................................... 192
Unregistering from Insight Remote Support central connect.................................................... 192
Remote support service events................................................................................................ 193
Service event transmission............................................................................................ 193
Using maintenance mode.............................................................................................. 193
Sending a test service event by using iLO..................................................................... 194
Viewing the Service Event Log.......................................................................................195
Clearing the Service Event Log......................................................................................196
Remote Support data collection................................................................................................196
Sending data collection information .............................................................................. 197
Sending Active Health System reporting information ....................................................197
Viewing data collection status in iLO..............................................................................198
Viewing Active Health System reporting status in iLO................................................... 198
Viewing data collection status in Insight Online............................................................. 198
Viewing data collection status in the Insight RS Console (Insight Remote Support
central connect only)...................................................................................................... 199
Registering a ProLiant server used as a host server for Insight Online direct connect............ 199
Changing the remote support configuration of a supported device.......................................... 200
Changing a supported device from central connect to direct connect........................... 200
Changing a supported device from direct connect to central connect remote support.. 200
8 Contents
Using the iLO administration features.............................................. 202
iLO user accounts..................................................................................................................... 202
Adding local user accounts............................................................................................ 202
Page 9

Editing local user accounts............................................................................................ 203
Deleting a user account................................................................................................. 203
iLO user account options............................................................................................... 204
iLO user privileges..........................................................................................................204
Password guidelines...................................................................................................... 205
IPMI/DCMI users............................................................................................................206
Viewing local user accounts...........................................................................................206
iLO directory groups..................................................................................................................206
Adding directory groups................................................................................................. 207
Editing directory groups................................................................................................. 207
Deleting a directory group.............................................................................................. 208
Directory group options.................................................................................................. 208
Directory group privileges.............................................................................................. 209
Viewing directory groups................................................................................................210
Boot Order.................................................................................................................................210
Configuring the server boot mode..................................................................................210
Configuring the server boot order.................................................................................. 210
Changing the one-time boot status.................................................................................211
Using the additional Boot Order page options............................................................... 212
Installing a license key by using a browser...............................................................................213
Viewing license information............................................................................................213
Lost license key recovery...............................................................................................214
iLO licensing...................................................................................................................214
Using Enterprise Secure Key Manager with iLO.......................................................................215
Configuring key manager servers.................................................................................. 215
Adding key manager configuration details..................................................................... 216
Testing the ESKM configuration..................................................................................... 216
Viewing ESKM events....................................................................................................217
Clearing the ESKM log...................................................................................................217
Language packs........................................................................................................................217
Selecting a language pack............................................................................................. 218
Configuring the default language settings......................................................................218
Configuring the current iLO web interface session language.........................................219
Uninstalling a language pack......................................................................................... 219
How iLO determines the session language....................................................................219
Firmware verification.................................................................................................................219
Configuring the firmware verification settings................................................................ 220
Running a firmware verification scan............................................................................. 221
Viewing firmware health status.......................................................................................221
iLO Backup & Restore.............................................................................................................. 222
What information is restored?........................................................................................ 222
Backing up the iLO configuration................................................................................... 223
Restoring the iLO configuration......................................................................................223
Restoring the iLO configuration after system board replacement.................................. 224
Using the iLO security features......................................................... 225
iLO security............................................................................................................................... 225
iLO access settings...................................................................................................................226
Configuring iLO service settings.................................................................................... 226
Configuring iLO access options..................................................................................... 228
iLO login with an SSH client...........................................................................................232
iLO Service Port........................................................................................................................233
Downloading the Active Health System Log through the iLO Service Port....................233
Connecting a client to iLO through the iLO Service Port................................................234
Configuring the iLO Service Port settings...................................................................... 234
Contents 9
Page 10

Configuring a client to connect through the iLO Service Port........................................ 235
iLO Service Port supported devices...............................................................................236
Sample text file for Active Health System Log download through iLO Service Port...... 236
Administering SSH keys........................................................................................................... 238
Authorizing a new SSH key by using the web interface.................................................238
Authorizing a new SSH key by using the CLI.................................................................238
Deleting SSH keys......................................................................................................... 239
Requirements for authorizing SSH keys from an HPE SIM server ............................... 239
SSH keys........................................................................................................................240
Supported SSH key format examples............................................................................ 240
CAC Smartcard Authentication................................................................................................. 241
Configuring CAC Smartcard Authentication settings..................................................... 242
Managing trusted certificates for CAC Smartcard Authentication.................................. 243
Certificate mapping........................................................................................................ 245
Administering SSL certificates.................................................................................................. 246
Viewing SSL certificate information................................................................................246
Obtaining and importing an SSL certificate....................................................................246
Directory authentication and authorization................................................................................249
Prerequisites for configuring authentication and directory server settings.....................249
Configuring Kerberos authentication settings in iLO...................................................... 249
Configuring schema-free directory settings in iLO......................................................... 250
Configuring HPE Extended Schema directory settings in iLO....................................... 252
Directory user contexts...................................................................................................253
Directory Server CA Certificate...................................................................................... 254
Local user accounts with Kerberos authentication and directory integration................. 254
Running directory tests.................................................................................................. 254
Configuring encryption settings.................................................................................................257
Enabling the Production or HighSecurity security state................................................. 257
Enabling the FIPS and SuiteB security states................................................................258
Connecting to iLO when using higher security states.................................................... 259
Configuring a FIPS-validated environment with iLO...................................................... 260
Disabling FIPS mode..................................................................................................... 260
Disabling SuiteB mode...................................................................................................261
iLO security states..........................................................................................................261
SSH cipher, key exchange, and MAC support...............................................................263
SSL cipher and MAC support.........................................................................................263
HPE SSO.................................................................................................................................. 265
Configuring iLO for HPE SSO........................................................................................ 265
Single Sign-On Trust Mode options............................................................................... 266
SSO user privileges........................................................................................................266
Adding trusted certificates..............................................................................................266
Extracting the HPE SIM SSO certificate........................................................................ 267
Importing a direct DNS name.........................................................................................267
Viewing trusted certificates and records.........................................................................268
Removing trusted certificates and records.....................................................................268
Configuring the Login Security Banner..................................................................................... 269
iLO security with the system maintenance switch.....................................................................269
Configuring iLO management settings.............................................271
10 Contents
Agentless Management and AMS............................................................................................ 271
Agentless Management Service............................................................................................... 272
Installing AMS................................................................................................................ 272
Verifying AMS installation...............................................................................................273
Restarting AMS.............................................................................................................. 274
System Management Assistant......................................................................................275
Page 11

Configuring SNMP settings.......................................................................................................279
SNMP options................................................................................................................ 279
SNMPv3 authentication............................................................................................................ 280
Configuring SNMPv3 users............................................................................................281
Deleting an SNMPv3 user profile................................................................................... 281
Configuring the SNMPv3 Engine ID...............................................................................282
Configuring SNMP alerts.......................................................................................................... 282
SNMP alert settings........................................................................................................283
Using the AMS Control Panel to configure SNMP and SNMP alerts (Windows only).............. 283
SNMP traps...............................................................................................................................284
iLO AlertMail..............................................................................................................................289
Enabling AlertMail.......................................................................................................... 290
Disabling AlertMail..........................................................................................................290
Remote Syslog..........................................................................................................................291
Enabling iLO Remote Syslog......................................................................................... 291
Disabling iLO Remote Syslog........................................................................................ 292
Working with enclosures, frames, and chassis............................... 293
Using the Active Onboard Administrator...................................................................................293
Viewing OA information..................................................................................................293
Starting the OA GUI....................................................................................................... 293
Toggling the enclosure UID LED.................................................................................... 294
iLO option.......................................................................................................................294
Viewing frame information.........................................................................................................294
Frame details..................................................................................................................295
Toggling the frame UID LED.......................................................................................... 295
Server details................................................................................................................. 295
Toggling the server UID LED..........................................................................................296
Viewing chassis information......................................................................................................296
Power Supplies list.........................................................................................................296
Intelligent PDU details....................................................................................................297
Smart Storage Battery details........................................................................................ 297
Using iLO with other software products and tools..........................299
iLO and remote management tools...........................................................................................299
Starting a remote management tool from iLO................................................................ 299
Deleting a remote manager configuration...................................................................... 299
Using iLO with HPE OneView........................................................................................ 300
Starting Intelligent Provisioning from iLO..................................................................................301
IPMI server management..........................................................................................................301
Advanced IPMI tool usage on Linux...............................................................................302
Using iLO with HPE SIM........................................................................................................... 302
HPE SIM features...........................................................................................................303
Establishing SSO with HPE SIM.................................................................................... 303
iLO identification and association...................................................................................303
Receiving SNMP alerts in HPE SIM...............................................................................304
Configuring iLO and HPE SIM to use the same HTTP port........................................... 304
Reviewing iLO license information in HPE SIM............................................................. 305
Using iLO with HPE Insight Control server provisioning .......................................................... 305
Kerberos authentication and Directory services............................. 306
Kerberos authentication with iLO.............................................................................................. 306
Configuring Kerberos authentication..............................................................................306
Contents 11
Page 12

Configuring the iLO hostname and domain name for Kerberos authentication............. 306
Preparing the domain controller for Kerberos support................................................... 307
Generating a keytab file for iLO in a Windows environment.......................................... 307
Verifying that your environment meets the Kerberos authentication time requirement..309
Configuring Kerberos support in iLO..............................................................................310
Configuring supported browsers for single sign-on........................................................310
Directory integration..................................................................................................................312
Choosing a directory configuration to use with iLO...................................................................313
Schema-free directory authentication....................................................................................... 313
Prerequisites for using schema-free directory integration..............................................314
Process overview: Configuring iLO for schema-free directory integration..................... 315
Schema-free nested groups (Active Directory only).......................................................315
HPE Extended Schema directory authentication...................................................................... 315
Process overview: Configuring the HPE Extended Schema with Active Directory........ 315
Prerequisites for configuring Active Directory with the HPE Extended Schema
configuration...................................................................................................................316
Directory services support..............................................................................................317
Installing the iLO directory support software.................................................................. 317
Running the Schema Extender...................................................................................... 319
Directory services objects.............................................................................................. 320
Managing roles and objects with the Active Directory snap-ins..................................... 320
Sample configuration: Active Directory and HPE Extended Schema............................ 324
Directory-enabled remote management (HPE Extended Schema configuration).....................327
Roles based on organizational structure........................................................................327
How role access restrictions are enforced..................................................................... 328
User access restrictions................................................................................................. 329
Role access restrictions................................................................................................. 330
Tools for configuring multiple iLO systems at a time................................................................. 332
User login using directory services........................................................................................... 332
Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors (HPLOMIG)...................................333
Configuring directory authentication with HPLOMIG................................................................ 334
Discovering management processors............................................................................335
Optional: Upgrading firmware on management processors (HPLOMIG).......................337
Selecting directory configuration options....................................................................... 338
Naming management processors (HPE Extended Schema only)................................. 340
Configuring directories when HPE Extended Schema is selected.................................341
Configuring management processors (Schema-free configuration only)....................... 344
Setting up management processors for directories........................................................345
Importing an LDAP CA Certificate..................................................................................346
Running directory tests with HPLOMIG (optional)......................................................... 347
Directory services schema........................................................................................................349
HPE Management Core LDAP OID classes and attributes........................................... 349
Core class definitions..................................................................................................... 350
Core attribute definitions................................................................................................ 351
Lights-Out Management specific LDAP OID classes and attributes.............................. 354
Lights-Out Management attributes.................................................................................354
Lights-Out Management class definitions...................................................................... 354
Lights-Out Management attribute definitions................................................................. 355
Managing iLO reboots, factory reset, and NMI.................................357
12 Contents
Rebooting (resetting) iLO..........................................................................................................357
Rebooting (resetting) the iLO processor with the web interface ................................... 357
Rebooting (resetting) iLO with the iLO 5 Configuration Utility........................................357
Rebooting (resetting) iLO with the server UID button.................................................... 358
Reset iLO to the factory default settings................................................................................... 359
Page 13

Resetting iLO to the factory default settings (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)...................... 359
Generating an NMI....................................................................................................................360
Troubleshooting.................................................................................. 361
Using the iLO Virtual Serial Port with Windbg...........................................................................361
Using the Server Health Summary........................................................................................... 362
Server Health Summary details..................................................................................... 363
Event log entries....................................................................................................................... 364
Incorrect time stamp on iLO Event Log entries.........................................................................364
USB key attached to iLO Service Port fails to mount................................................................364
IML troubleshooting links.......................................................................................................... 365
Login and iLO access issues.................................................................................................... 365
iLO firmware login name and password not accepted .................................................. 365
iLO management port not accessible by name..............................................................365
Unable to access the iLO login page ............................................................................ 366
Unable to connect to iLO after changing network settings.............................................366
Unable to return to iLO login page after iLO reset ........................................................ 367
An iLO connection error occurs after an iLO firmware update ...................................... 367
Unable to connect to iLO processor through NIC ......................................................... 367
Unable to log in to iLO after installing iLO certificate .................................................... 367
Unable to connect to iLO IP address ............................................................................ 368
iLO TCP/IP communication fails ....................................................................................368
Secure Connection Failed error when using Firefox to connect to iLO..........................368
Certificate error when navigating to iLO web interface with Internet Explorer............... 369
Certificate error when navigating to iLO web interface with Chrome............................. 370
Certificate error when navigating to iLO web interface with Firefox............................... 370
iLO login page displays a Website Certified by an Unknown Authority message.......... 371
iLO inaccessible on a server managed by HPE OneView ............................................ 371
Unable connect to an iLO system with the iOS mobile app........................................... 372
iLO responds to pings intermittently or does not respond..............................................372
Running an XML script with iLO fails............................................................................. 373
Directory issues.........................................................................................................................373
Logging in to iLO with Kerberos authentication fails...................................................... 373
iLO credential prompt appears during Kerberos login attempt ......................................374
iLO credential prompt appears during Kerberos login by name attempt .......................375
A directory connection to iLO ends prematurely ........................................................... 375
Configured directory user contexts do not work with iLO login ..................................... 375
iLO directory user account does not log out after directory timeout expires ................. 376
Failure generating Kerberos keytab file for iLO Zero Sign In configuration................... 376
Error when running Setspn for iLO Kerberos configuration .........................................376
OpenLDAP authentication fails when configured with nested groups or posixgroups... 377
iLO Zero Sign In fails after domain controller OS reinstall ............................................ 377
Failed iLO login with Active Directory credentials ......................................................... 377
Directory Server DNS Name test reports a failure......................................................... 378
Ping Directory Server test reports a failure.................................................................... 378
Connect to Directory Server test reports a failure.......................................................... 378
Connect using SSL test reports a failure........................................................................379
Bind to Directory Server test reports a failure................................................................ 379
Directory Administrator Login test reports a failure........................................................ 379
User Authentication test reports a failure....................................................................... 380
User Authorization test reports a failure.........................................................................380
Directory User Contexts test reports a failure................................................................ 380
LOM Object Exists test reports a failure.........................................................................381
Remote Console issues............................................................................................................ 381
iLO Java IRC displays red X when Firefox is used to run Java IRC on Linux client ..... 381
Contents 13
Page 14

iLO Java IRC does not start .......................................................................................... 381
Cursor cannot reach iLO Remote Console window corners ......................................... 382
iLO Remote Console text window not updated correctly............................................... 382
Mouse or keyboard not working in iLO .NET IRC or Java IRC (Java Web Start).......... 382
Mouse or keyboard not working in iLO Java IRC (Java Applet).....................................383
iLO .NET IRC sends characters continuously after switching windows ........................ 384
iLO Java IRC displays incorrect floppy and USB key device information ..................... 384
Caps Lock out of sync between iLO and Java IRC .......................................................385
Num Lock out of sync between iLO and Shared Remote Console ............................... 385
Keystrokes repeat unintentionally during iLO Remote Console session........................385
Session leader does not receive connection request when iLO .NET IRC is in replay
mode ............................................................................................................................. 386
iLO Remote Console keyboard LED does not work correctly ....................................... 386
iLO .NET IRC becomes inactive or disconnects............................................................ 386
iLO .NET IRC failed to connect to server ...................................................................... 387
File not present after copy from server to iLO Virtual Media USB key ..........................388
iLO .NET IRC takes a long time to verify application requirements .............................. 388
iLO .NET IRC will not start ............................................................................................ 389
iLO .NET IRC cannot be shared ................................................................................... 389
iLO .NET IRC will not start in Firefox .............................................................................389
iLO .NET IRC will not start in Google Chrome .............................................................. 390
Unable to boot to DOS using a USB key mounted with the iLO Remote Console.........390
SSH issues................................................................................................................................391
Initial PuTTY input slow with iLO ...................................................................................391
PuTTY client unresponsive with iLO Shared Network Port............................................391
Text is displayed incorrectly when using an SSH connection to iLO.............................. 391
An SSH session fails to start or terminates unexpectedly..............................................392
Text-based Remote Console issues......................................................................................... 392
Unable to view Linux installer in text-based Remote Console....................................... 392
Unable to pass data through SSH terminal....................................................................392
VSP-driven selection during the serial timeout window sends output to BIOS
redirect instead of VSP.................................................................................................. 393
Scrolling and text appear irregular during BIOS redirection...........................................393
Remote Support issues.............................................................................................................393
SSL Bio Error during Insight RS registration..................................................................393
Server not identified by server name in Insight Online or Insight RS.............................394
Server OS name and version not listed in Insight RS or Insight Online.........................394
Connection error during Insight Online direct connect registration................................ 395
iLO session ends unexpectedly during iLO Insight Online direct connect registration...395
Server health status is red in Insight RS or Insight Online.............................................395
Server not identified by server name in Insight Online or Insight RS.............................396
Server information is overwritten when remote support data is sent to Hewlett
Packard Enterprise.........................................................................................................396
OS information displayed incorrectly in Insight Online...................................................397
Insight Online direct connect stopped working on a server with a replaced system
board.............................................................................................................................. 397
Duplicate central connect device records exist in Insight Online................................... 397
Device warranty is incorrectly listed as expired in Insight RS........................................ 398
Service events and collections display an incorrect time stamp in the Insight RS
Console.......................................................................................................................... 398
iLO Federation issues............................................................................................................... 399
Query errors occur on iLO Federation pages ................................................................399
A timeout error is displayed on the iLO Multi-System Map page .................................. 399
iLO Multi-System Map page displays a 502 error ......................................................... 400
iLO Multi-System Map page displays a 403 error ......................................................... 400
iLO peers are not displayed on iLO Federation pages...................................................401
iLO peers are displayed with IPv6 addresses on IPv4 networks................................... 401
14 Contents
Page 15

Firmware update issues............................................................................................................401
Unsuccessful iLO firmware update ............................................................................... 401
iLO firmware update error ............................................................................................. 402
iLO firmware update does not finish ..............................................................................402
iLO network Failed Flash Recovery............................................................................... 403
Licensing issues........................................................................................................................404
License key installation errors........................................................................................404
Unable to access Virtual Media or graphical Remote Console...................................... 404
Recovering an iLO license key.......................................................................................405
Agentless Management, AMS, and SNMP issues....................................................................406
AMS is installed but unavailable in iLO ......................................................................... 406
Unable to get SNMP information in HPE SIM................................................................ 406
Unable to receive HPE SIM alarms (SNMP traps) from iLO.......................................... 406
Websites.............................................................................................. 407
Support and other resources.............................................................409
Accessing Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support....................................................................... 409
Accessing updates....................................................................................................................409
Customer self repair..................................................................................................................410
Remote support........................................................................................................................ 410
Warranty information.................................................................................................................410
Regulatory information.............................................................................................................. 411
Documentation feedback...........................................................................................................411
Contents 15
Page 16

iLO
iLO 5 is a remote server management processor embedded on the system boards of HPE ProLiant
servers and Synergy compute modules. iLO enables the monitoring and controlling of servers from
remote locations. iLO management is a powerful tool that provides multiple ways to configure, update,
monitor, and repair servers remotely. iLO (Standard) comes preconfigured on Hewlett Packard Enterprise
servers without an additional cost or license.
Features that enhance server administrator productivity and additional new security features are licensed.
For more information, see the iLO licensing guide at the following website:
ilo-docs.
iLO key features
• Server health monitoring—iLO monitors temperatures in the server and sends corrective signals to
the fans to maintain proper server cooling. iLO also monitors installed firmware and software versions
and the status of fans, memory, the network, processors, power supplies, storage, and devices
installed on the system board.
• Agentless Management—With Agentless Management, the management software (SNMP) operates
within the iLO firmware instead of the host OS. This configuration frees memory and processor
resources on the host OS for use by server applications. iLO monitors all key internal subsystems, and
can send SNMP alerts directly to a central management server, even with no host OS installed.
http://www.hpe.com/support/
• Integrated Management Log—View server events and configure notifications through SNMP alerts,
remote syslogs, and email alerts.
• Learn more links—Troubleshooting information for supported events is available on the Integrated
Management Log page.
• Active Health System Log—Download the Active Health System log. You can send the log file to
Hewlett Packard Enterprise when you have an open support case or upload the log to the Active
Health System Viewer.
• iLO Federation management—Use the iLO Federation features to discover and manage multiple
servers at a time.
• Integrated Remote Console—If you have a network connection to the server, you can access a
secure high-performance console to manage the server from any location.
• Virtual Media—Remotely mount high-performance Virtual Media devices to the server.
• Power management—Securely and remotely control the power state of the managed server.
• Deployment and provisioning—Use Virtual Power and Virtual Media for tasks such as the
automation of deployment and provisioning.
• Power consumption and power settings—Monitor the server power consumption, configure server
power settings, and configure power capping on supported servers.
• Embedded remote support—Register a supported server for HPE remote support.
16 iLO
• User access—Use local or directory-based user accounts to log in to iLO. You can use CAC
smartcard authentication with local or directory-based accounts.
• Two-factor authentication—Two-factor authentication is supported with Kerberos and CAC
smartcard authentication.
• Secure Recovery—Validates the iLO firmware when power is applied. If the firmware is invalid, the
iLO firmware is flashed automatically (iLO Standard license).
Page 17

Validates the system ROM during server startup. If valid system ROM is not detected, the server is
prevented from booting. Recovery options include swapping the active and redundant ROM, and
initiating a firmware verification scan and recovery action (the iLO Advanced Premium Security Edition
license is required for scheduling and automated recovery).
• Firmware verification and recovery—Run scheduled or on-demand firmware verification scans and
configure recovery actions to implement when an issue is detected.
• iLO security states—Configure a security state that fits your environment. iLO supports the
Production security state (default) and high security states such as HighSecurity, FIPS, and SuiteB.
• iLO interface controls—For enhanced security, enable or disable selected iLO interfaces and
features.
• Firmware management—Save components to the iLO Repository and use SUM to configure install
sets and manage the installation queue.
• iLO Service Port—Use a supported USB Ethernet adapter to connect a client to the iLO Service Port
to access the server directly. Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends the HPE USB to Ethernet
Adapter (part number Q7Y55A). You can also connect a USB key to download the Active Health
System Log.
• IPMI—The iLO firmware provides server management based on the IPMI version 2.0 specification.
• iLO RESTful API and RESTful Interface Tool (iLOrest)—iLO 5 includes the iLO RESTful API, which
is Redfish API conformant.
• iLO Backup & Restore—Back up the iLO configuration and then restore it on a system with the same
hardware configuration.
• Intelligent System Tuning—Intelligent System Tuning for Gen10 servers consists of several features
to increase server performance. Jitter smoothing levels and balances frequency fluctuation in the
processor. Workload matching enables the use of preconfigured workload profiles to fine-tune server
resources. Core boosting works with selected Intel processors to enable higher performance across
more processor cores. For more information, see the HPE Gen10 Servers Intelligent System Tuning
white paper.
ROM-based configuration utility
You can use the iLO 5 Configuration Utility in the UEFI System Utilities to configure network parameters,
global settings, and user accounts.
The iLO 5 Configuration Utility is designed for the initial iLO setup, and is not intended for continued iLO
administration. You can start the utility when the server is booted, and you can run it remotely with the
Remote Console.
You can configure iLO to require users to log in when they access the iLO 5 Configuration Utility, or you
can disable the utility for all users. These settings can be configured on the Access Settings page.
Disabling the iLO 5 Configuration Utility prevents reconfiguration from the host unless the system
maintenance switch is set to disable iLO security.
To access the iLO 5 Configuration Utility, press F9 during POST to start the UEFI System Utilities. Click
System Configuration, and then click iLO 5 Configuration Utility.
iLO mobile app
The iLO mobile app provides access to your servers from a mobile device. The mobile app interacts
directly with the iLO processor, providing total control of the server at all times as long as the server is
plugged in. For example, you can access the server when it is in a healthy state or when it is powered off
ROM-based configuration utility 17
Page 18

with a blank hard drive. As an IT administrator, you can troubleshoot problems and perform software
deployments from almost anywhere.
For more information about the iLO mobile app, see http://www.hpe.com/info/ilo/mobileapp.
iLO RESTful API
iLO includes the iLO RESTful API, which is Redfish API conformant. The iLO RESTful API is a
management interface that server management tools can use to perform configuration, inventory, and
monitoring tasks by sending basic HTTPS operations (GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, and PATCH) to the
iLO web server.
To learn more about the iLO RESTful API, see the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website (http://
www.hpe.com/info/restfulinterface/docs).
For specific information about automating tasks using the iLO RESTful API, see libraries and sample
code at http://www.hpe.com/info/redfish.
RESTful Interface Tool
The RESTful Interface Tool (iLOrest) is a scripting tool that allows you to automate HPE server
management tasks. It provides a set of simplified commands that take advantage of the iLO RESTful API.
You can install the tool on your computer for remote use or install it locally on a server with a Windows or
Linux Operating System. The RESTful Interface Tool offers an interactive mode, a scriptable mode, and a
file-based mode similar to CONREP to help decrease automation times.
For more information, see the following website:
http://www.hpe.com/info/resttool.
iLO scripting and command line
You can use the iLO scripting tools to configure multiple servers, to incorporate a standard configuration
into the deployment process, and to control servers and subsystems.
The iLO scripting and CLI guide describes the syntax and tools available for using iLO through a
command line or scripted interface.
18 iLO RESTful API
Page 19
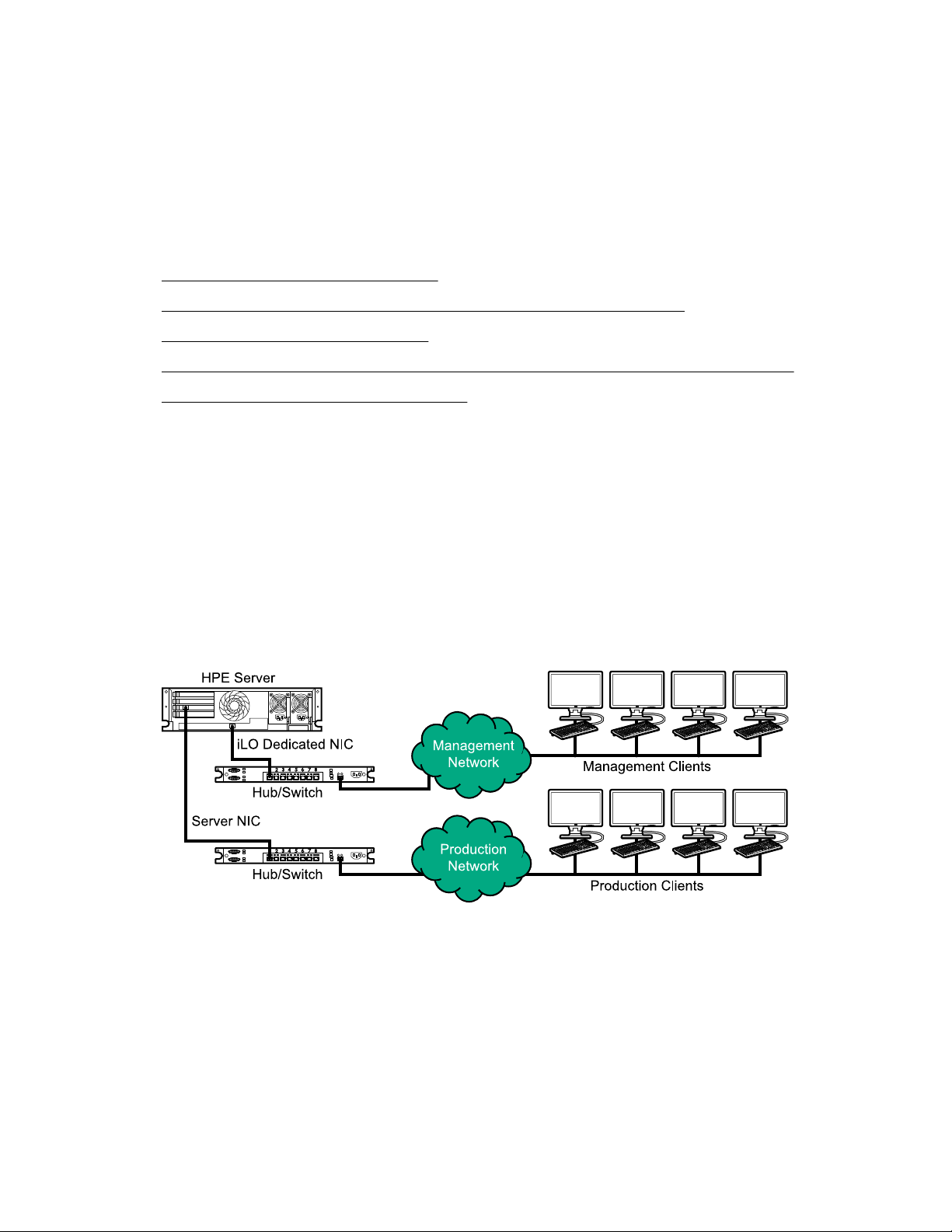
Setting up iLO
Preparing to set up iLO
Before setting up an iLO management processor, you must decide how to handle networking and
security. The following questions can help you configure iLO:
Procedure
1. How will iLO connect to the network?
2. Will NIC Teaming be used with the Shared Network Port configuration?
3. How will iLO acquire an IP address?
4. What access security is required, and what user accounts and privileges are needed?
5. What tools will you use to configure iLO?
iLO network connection options
Typically, iLO is connected to the network through a dedicated management network or a shared
connection on the production network.
Dedicated management network
In this configuration, the iLO port is on a separate network. A separate network improves performance
and security because you can physically control which workstations are connected to the network. A
separate network also provides redundant access to the server when a hardware failure occurs on the
production network. In this configuration, iLO cannot be accessed directly from the production network.
The Dedicated management network is the preferred iLO network configuration.
Figure 1: Dedicated management network
Production network
In this configuration, both the NIC and the iLO port are connected to the production network. In iLO, this
type of connection is called the Shared Network Port configuration. Certain Hewlett Packard Enterprise
embedded NICs and add-on cards provide this capability. This connection enables access to iLO from
anywhere on the network and it reduces the amount of networking hardware and infrastructure required
to support iLO.
There are some drawbacks to using this configuration.
Setting up iLO 19
Page 20
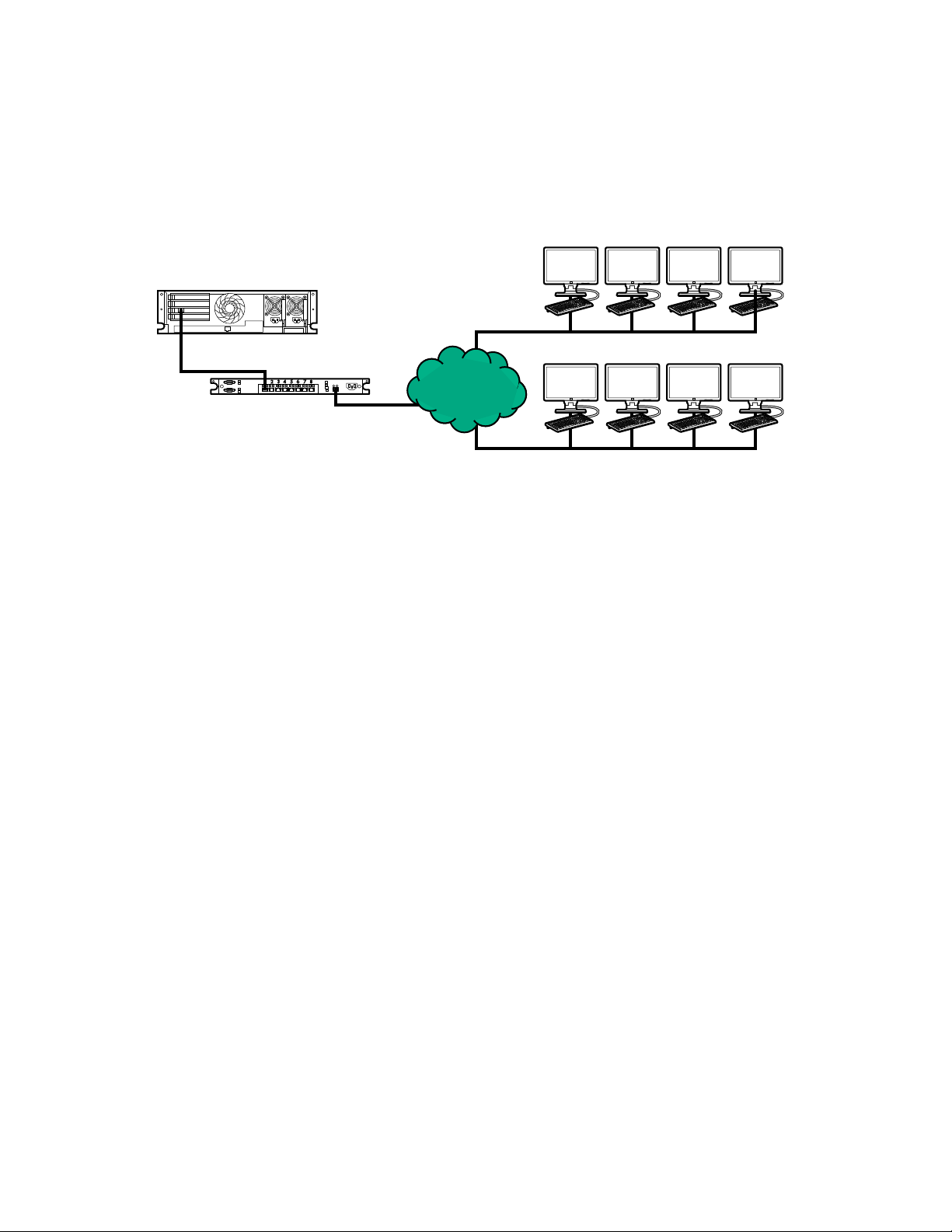
• With a shared network connection, traffic can hinder iLO performance.
Management Clients
Production Clients
Server NIC/iLO Shared Network Port
HPE Server
Hub/Switch
Management/
Production
Network
• During the server boot process and when the operating system NIC drivers are loading and unloading,
there are brief periods of time (2–8 seconds) when iLO cannot be reached from the network. After
these short periods, iLO communication is restored and iLO will respond to network traffic.
When this situation occurs, the Remote Console and connected iLO Virtual Media devices might be
disconnected.
Figure 2: Shared network connection
NIC teaming with Shared Network Port configurations
NIC teaming is a feature you can use to improve server NIC performance and reliability.
NIC teaming constraints
When you select a teaming mode to use when iLO is configured to use the Shared Network Port:
• iLO network communications will be blocked in the following conditions:
◦ The selected NIC teaming mode causes the switch that iLO is connected with to ignore traffic from
the server NIC/port that iLO is configured to share.
◦ The selected NIC teaming mode sends all traffic destined for iLO to a NIC/port other than the one
that iLO is configured to share.
• Because iLO and the server transmit and receive on the same switch port, the selected NIC teaming
mode must allow the switch to tolerate traffic with two different MAC addresses on the same switch
port. Some implementations of LACP (802.3ad) will not tolerate multiple MAC addresses on the same
link.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise NIC teaming modes
If your server is configured to use Hewlett Packard Enterprise NIC teaming, observe the following
guidelines.
Network Fault Tolerance
The server transmits and receives on only one NIC (the primary adapter). The other NICs (secondary
adapters) that are part of the team do not transmit server traffic and they ignore received traffic. This
mode allows the iLO Shared Network Port to function correctly.
Select the NIC/port iLO uses as the Preferred Primary Adapter.
20 NIC teaming with Shared Network Port configurations
Page 21
Transmit Load Balancing
The server transmits on multiple adapters but receives only on the primary adapter. This mode allows
the iLO Shared Network Port to function correctly.
Select the NIC/port iLO uses as the Preferred Primary Adapter.
Switch Assisted Load Balancing
This mode type refers to the following:
• HPE ProCurve Port Trunking
• Cisco Fast EtherChannel/Gigabit EtherChannel (Static Mode Only, no PAgP)
• IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation (Static Mode only, no LACP)
• Bay Network Multi-Link Trunking
• Extreme Network Load Sharing
In this mode, there is no concept of primary and secondary adapters. All adapters are considered
equal for the purposes of sending and receiving data. This mode is the most problematic for iLO
Shared Network Port configurations because traffic destined for iLO can be received on only one of
the server NIC/ports. To determine the constraints that your switch vendor places on their
implementation of switch assisted load balancing, see the switch vendor documentation.
For additional information, see the ProLiant Network Adapter Teaming support document.
For information about selecting a NIC teaming mode when your server uses another implementation of
NIC teaming, see NIC teaming constraints and the vendor documentation.
iLO IP address acquisition
To enable iLO access after it is connected to the network, the iLO management processor must acquire
an IP address and subnet mask. You can use a dynamic address or a static address.
Dynamic IP address
A dynamic IP address is set by default. iLO obtains the IP address and subnet mask from DNS or
DHCP servers. This method is the simplest.
If you use DHCP:
• The iLO management port must be connected to a network that is connected to a DHCP server,
and iLO must be on the network before power is applied. DHCP sends a request soon after power
is applied. If the DHCP request is not answered when iLO first boots, it will reissue the request at
90-second intervals.
• The DHCP server must be configured to provide DNS and WINS name resolution.
Static IP address
If DNS or DHCP servers are not available on the network, a static IP address is used. A static IP
address can be configured by using the iLO 5 Configuration Utility.
If you plan to use a static IP address, you must have the IP address before starting the iLO setup
process.
iLO access security
You can use the following methods to manage access to iLO:
iLO IP address acquisition 21
Page 22

Local accounts
Up to 12 user accounts can be stored in iLO. This configuration is ideal for small environments such
as labs and small-sized or medium-sized businesses.
Login security with local accounts is managed through the iLO Access Settings and user privileges.
Directory services
Up to six directory groups can be configured in iLO. Use a directory service to authenticate and
authorize iLO access. This configuration enables an unlimited number of users and easily scales to
the number of iLO devices in an enterprise.
If you plan to use directory services, consider enabling at least one local administrator account for
alternate access.
A directory provides a central point of administration for iLO devices and users, and the directory can
enforce a strong password policy.
CAC smartcard authentication
You can configure common access smartcards together with local accounts and directory services to
manage iLO user access.
iLO configuration tools
iLO supports various interfaces for configuration and operation. This guide discusses the following
interfaces:
iLO web interface
Use the iLO web interface when you can connect to iLO on the network by using a web browser. You
can also use this method to reconfigure an iLO management processor.
ROM-based setup
Use the iLO 5 Configuration Utility when the system environment does not use DHCP, DNS, or WINS.
Other configuration options not discussed in this guide follow:
Intelligent Provisioning
To start Intelligent Provisioning, press F10 during POST.
You can also access Always On Intelligent Provisioning through the iLO web interface. For more
information, see the Intelligent Provisioning user guide.
iLO RESTful API
A management interface that server management tools can use to perform configuration, inventory,
and monitoring of a supported server through iLO. For more information, see the following website:
http://www.hpe.com/info/redfish.
HPE OneView
A management tool that interacts with the iLO management processor to configure, monitor, and
manage ProLiant servers or Synergy compute modules. For more information, see the HPE OneView
user guide.
HPE Scripting Toolkit
This toolkit is a server deployment product for IT experts that provides unattended automated
installation for high-volume server deployments. For more information, see the Scripting Toolkit user
guide for Windows or Linux.
22 iLO configuration tools
Page 23

Scripting
You can use scripting to set up multiple iLO management processors. Scripts are XML files written for
a scripting language called RIBCL. You can use RIBCL scripts to configure iLO on the network during
initial deployment or from a deployed host.
The following methods are available:
• HPQLOCFG—A Windows command-line utility that sends RIBCL scripts over the network to iLO.
• HPONCFG—A local online scripted setup utility that runs on the host and passes RIBCL scripts to
the local iLO.
When iLO is configured to use the SuiteB security state, only HPONCFG for Linux is supported.
• Custom scripting environments (LOCFG.PL)—The iLO scripting samples include a Perl sample
that can be used to send RIBCL scripts to iLO over the network.
• SMASH CLP—A command-line protocol that can be used when a command line is accessible
through SSH or the physical serial port.
For more information about these methods, see the iLO scripting and command-line guide.
iLO sample scripts are available at the following website: http://www.hpe.com/support/ilo5.
Initial setup steps: Process overview
The iLO default settings enable you to use most features without additional configuration. However, the
configuration flexibility of iLO enables customization for multiple enterprise environments. This chapter
discusses the initial iLO setup steps.
Procedure
1. Connect iLO to the network.
2. If you are not using dynamic IP addressing, use the ROM-based setup utilities to configure a static IP
address.
3. If you will use the local accounts feature, use the ROM-based setup utilities to configure user
accounts.
4. Optional: Install an iLO license.
5. If necessary, install the iLO drivers.
Connecting iLO to the network
Connect iLO to the network through a production network or a dedicated management network.
iLO uses standard Ethernet cabling, which includes CAT 5 UTP with RJ-45 connectors. Straight-through
cabling is necessary for a hardware link to a standard Ethernet hub or switch.
For more information about setting up your hardware, see the server user guide.
More information
iLO network connection options on page 19
Initial setup steps: Process overview 23
Page 24
Setting up iLO by using the iLO 5 Configuration Utility
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends using the iLO 5 Configuration Utility to set up iLO for the first
time and to configure iLO network parameters for environments that do not use DHCP, DNS, or WINS.
NOTE:
If you can connect to iLO on the network by using a web browser, you can also use the iLO web interface
to configure iLO. Access iLO from a remote network client by using a supported browser and providing
the default DNS name, user name, and password.
Configuring a static IP address (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)
This step is required only if you want to use a static IP address. When you use dynamic IP addressing,
the DHCP server automatically assigns an IP address for iLO.
To simplify installation, Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends using DNS or DHCP with iLO.
Procedure
1. Optional: If you access the server remotely, start an iLO remote console session.
2. Restart or power on the server.
3. Press F9 in the server POST screen.
The UEFI System Utilities start.
4. Click System Configuration.
5. Click iLO 5 Configuration Utility.
6. Disable DHCP:
a. Click Network Options.
b. Select OFF in the DHCP Enable menu.
The IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address boxes become editable. When DHCP
Enable is set to ON, you cannot edit these values.
7. Enter values in the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway IP Address boxes.
8. To save the changes and exit, press F12.
The iLO 5 Configuration Utility prompts you to confirm that you want to save the pending
configuration changes.
9. To save and exit, click Yes - Save Changes.
The iLO 5 Configuration Utility notifies you that iLO must be reset in order for the changes to take
effect.
10. Click OK.
iLO resets, and the iLO session is automatically ended. You can reconnect in approximately 30
seconds.
11. Resume the normal boot process:
a. Start the iLO remote console.
24 Setting up iLO by using the iLO 5 Configuration Utility
Page 25

The iLO 5 Configuration Utility is still open from the previous session.
b. Press ESC several times to navigate to the System Configuration page.
c. To exit the System Utilities and resume the normal boot process, click Exit and resume system
boot.
Managing local user accounts with the iLO 5 Configuration Utility
Adding user accounts (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)
Procedure
1. Optional: If you access the server remotely, start an iLO remote console session.
2. Restart or power on the server.
3. Press F9 in the server POST screen.
The UEFI System Utilities start.
4. Click System Configuration, click iLO 5 Configuration Utility, click User Management, and then
click Add User.
5. Select the privileges for the new user.
To assign a privilege, select YES in the menu next to the privilege name. To remove a privilege,
select NO.
The Login privilege is assigned to every user by default, so it is not listed in the iLO 5 Configuration
Utility.
You cannot assign the Recovery Set privilege through the iLO 5 Configuration Utility, so it is not
available in the list.
6. Enter the user name and login name in the New User Name and Login Name boxes.
7. Enter the password.
a. Move the cursor to the Password box, and then press Enter.
The Enter your new password box opens.
b. Type the password, and then press Enter.
The Confirm your new password box opens.
c. Type the password again to confirm, and then press Enter.
The iLO 5 Configuration Utility confirms the new account creation.
8. To close the confirmation dialog box, click OK.
9. Create as many user accounts as needed, and then press F12 to save the changes and exit the
system utilities.
10. When prompted to confirm the changes, click Yes - Save Changes to exit the utility and resume the
boot process.
More information
iLO user privileges on page 204
iLO user account options on page 204
Managing local user accounts with the iLO 5 Configuration Utility 25
Page 26

Editing user accounts (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)
Procedure
1. Optional: If you access the server remotely, start an iLO remote console session.
2. Restart or power on the server.
3. Press F9 in the server POST screen.
The UEFI System Utilities start.
4. Click System Configuration, click iLO 5 Configuration Utility, click User Management, and then
click Edit/Remove User.
5. In the Action menu for the user you want to edit or remove, select Edit.
The account properties are displayed.
6. Update the Login Name.
7. Update the Password.
a. Move the cursor to the Password box, and then press Enter.
The Enter your new password box opens.
b. Type the password, and then press Enter.
The Confirm your new password box opens.
c. Type the password again to confirm, and then press Enter.
8. Modify the user account privileges.
To assign a privilege, select YES in the menu next to the privilege name. To remove a privilege,
select NO.
The Login privilege is assigned to every user by default, so it is not available in the iLO 5
Configuration Utility.
You cannot assign the Recovery Set privilege through the iLO 5 Configuration Utility, so it is not
available in the list.
9. Update as many user accounts as needed, and then press F12 to save the changes and exit the
system utilities.
10. When prompted to confirm the changes, click Yes - Save Changes to exit the utility and resume the
boot process.
More information
iLO user privileges on page 204
iLO user account options on page 204
Removing user accounts (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)
Procedure
1. Optional: If you access the server remotely, start an iLO remote console session.
2. Restart or power on the server.
3. Press F9 in the server POST screen.
26 Editing user accounts (iLO 5 Configuration Utility)
Page 27

The System Utilities start.
4. Click System Configuration, click iLO 5 Configuration Utility, click User Management, and then
click Edit/Remove User.
5. In the Action menu for the user you want to remove, select Delete.
The user name is marked to be deleted when you save the changes on this page.
6. If needed, mark other user accounts to delete, and then press F12 to save the changes and exit the
system utilities.
7. When prompted to confirm the changes, click Yes - Save Changes to exit the utility and resume the
boot process.
Logging in to iLO for the first time
Procedure
1. Enter https://<iLO hostname or IP address>.
HTTPS (HTTP exchanged over an SSL encrypted session) is required for accessing the iLO web
interface.
2. Enter the default user credentials, and then click Log In.
iLO default credentials
The iLO firmware is configured with a default user name, password, and DNS name. The default
information is on the serial label pull tab attached to the server that contains the iLO management
processor. Use these values to access iLO remotely from a network client by using a web browser.
• User name—Administrator
• Password—A random eight-character string
• DNS name—ILOXXXXXXXXXXXX, where the X characters represent the server serial number.
IMPORTANT:
Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends changing the default password after you log in to iLO for
the first time.
If you reset iLO to the factory default settings, use the default iLO account credentials to log in after
the reset.
iLO licensed features
iLO (Standard) is preconfigured on Hewlett Packard Enterprise servers without an additional cost or
license. Features that enhance productivity are licensed. For more information, see the iLO licensing
guide at the following website: http://www.hpe.com/support/ilo-docs.
To activate iLO licensed features, install an iLO license.
Logging in to iLO for the first time 27
Page 28

iLO driver support
iLO is an independent microprocessor running an embedded operating system. The architecture ensures
that most iLO functionality is available, regardless of the host operating system. The iLO driver enables
software such as HPONCFG and the Agentless Management Service to communicate with iLO. The
installed OS and system configuration determine the installation requirements.
Windows
When you use Windows with iLO, the following driver is available: iLO 5 Channel Interface Driver for
Windows.
This driver is required for the operating system to communicate with iLO. Install this driver in all
configurations.
Linux
When you use Linux with iLO, the following driver is available: hpilo.
This driver manages agent and tool application access to iLO.
hpilo is part of the Linux kernel for:
• SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 SP2
• SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 SUSE Installation Kit and later
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 errata kernel-3.10.0-514.6.1.el7
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.9 and later
hpilo is loaded automatically at startup.
On Ubuntu systems, hpilo is loaded automatically at startup after the Linux Management Component
Pack package is loaded.
VMware
When you use VMware with iLO, the following driver is available: ilo.
This driver manages Agentless Management Service, WBEM provider, and tool application access to iLO.
It is included in the customized Hewlett Packard Enterprise VMware images. For raw VMware images, the
driver must be installed manually.
Installing the iLO driver
Procedure
1. Obtain the iLO driver for your OS by downloading the Service Pack for ProLiant, or by downloading
the driver from the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website.
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SuSE Linux Enterprise Server, the driver is included in the Linux
distribution.
• For Windows—Use the SPP to install the iLO driver or download it from the Hewlett Packard
Enterprise Support Center at http://www.hpe.com/support/hpesc.
See the following websites for information about using the SPP:
28 iLO driver support
Page 29

◦ SPP documentation: http://www.hpe.com/info/spp/documentation.
◦ SPP Custom Download hosted service: http://www.hpe.com/servers/spp/custom.
• For VMware—Download the iLO driver from the vibsdepot section of the Software Delivery
Repository website: http://www.hpe.com/support/SDR-Linux.
Follow the installation instructions provided with the software.
• For Ubuntu—Subscribe to the Linux Management Component Pack at http://www.hpe.com/
support/SDR-Linux.
Setting up iLO 29
Page 30

Using the iLO web interface
iLO web interface
You can use the iLO web interface to manage iLO. You can also use a Remote Console, XML
configuration and control scripts, SMASH CLP, or the iLO RESTful API.
For more information, see the iLO and iLO RESTful API documentation at the following website:
www.hpe.com/support/ilo-docs.
Supported browsers
iLO 5 supports the latest versions of the following browsers:
• Microsoft Edge
• Mozilla Firefox
• Google Chrome mobile and desktop
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 11
Browser requirements
The iLO web interface requires a browser that meets the following requirements:
• JavaScript—The iLO web interface uses client-side JavaScript extensively.
This setting is not enabled by default in all versions of Internet Explorer. To check or change this
setting, see Configuring the Internet Explorer JavaScript setting on page 30.
• Cookies—Cookies must be enabled for certain features to function correctly.
http://
• Pop-up windows—Pop-up windows must be enabled for certain features to function correctly. Verify
that pop-up blockers are disabled.
• TLS—To access the iLO web interface, you must enable TLS 1.0 or later in your browser.
Configuring the Internet Explorer JavaScript setting
Some versions of Internet Explorer have JavaScript disabled by default. Use the following procedure to
enable JavaScript.
Procedure
1. Start Internet Explorer.
2. Select Tools > Internet options.
3. Click Security.
4. Click Custom level.
5. In the Scripting section, set Active scripting to Enable.
30 Using the iLO web interface
Page 31

6. Click OK.
7. Refresh your browser window.
Logging in to the iLO web interface
Procedure
1. Enter https://<iLO host name or IP address>.
When you access the iLO web interface, you must use HTTPS (HTTP exchanged over an SSL
encrypted session).
The iLO login page opens. If a
NOTICE section.
2. Do one of the following:
• Enter a directory or local account login name and password, and then click Log In.
• Click the Zero Sign In button.
If iLO is configured for Kerberos network authentication, the Zero Sign In button is displayed below
the Log In button. You can use the Zero Sign In button to log in without entering a user name and
password.
• Connect a smartcard, and then click the Log in with Smartcard button.
If iLO is configured for CAC Smartcard Authentication, the Log in with Smartcard button is
displayed below the Log In button.
Do not enter a login name and password when you use CAC Smartcard Authentication.
More information
iLO default credentials on page 27
login security banner is configured, the banner text is displayed in the
Cookie sharing between browser instances and iLO
When you browse to iLO and log in, one session cookie is shared with all open browser windows that
share the iLO URL in the browser address bar. As a consequence, all open browser windows share one
user session. Logging out in one window ends the user session in all the open windows. Logging in as a
different user in a new window replaces the session in the other windows.
This behavior is typical of browsers. iLO does not support multiple users logged in from two different
browser windows in the same browser on the same client.
Shared instances
When the iLO web interface opens another browser window or tab (for example, a help file), this window
shares the connection to iLO and the session cookie.
When you are logged into the iLO web interface, and you open a new browser window manually, a
duplicate instance of the original browser window opens. If the domain name in the address bar matches
the original browser session, the new instance shares a session cookie with the original browser window.
Cookie order
Logging in to the iLO web interface 31
Page 32

During login, the login page builds a browser session cookie that links the window to the appropriate
session in the iLO firmware. The firmware tracks browser logins as separate sessions listed on the
Session List page.
For example, when User1 logs in, the web server builds the initial frames view, with User1 listed as the
active user, menu items in the navigation pane, and page data in the right pane. When User1 clicks from
link to link, only the menu items and page data are updated.
While User1 is logged in, if User2 opens a browser window on the same client and logs in, the second
login overwrites the cookie generated in the User1 session. Assuming that User2 is a different user
account, a different current frame is built, and a new session is granted. The second session appears on
the Session List page as User2.
The second login has effectively orphaned the first session by overriding the cookie generated during the
User1 login. This behavior is the same as closing the User1 browser without clicking the Log Out button.
The User1 orphaned session is reclaimed when the session timeout expires.
Because the current user frame is not refreshed unless the browser is forced to refresh the entire page,
User1 can continue navigating by using the browser window. However, the browser is now operating by
using the User2 session cookie settings, even though it might not be readily apparent.
If User1 continues to navigate in this mode (User1 and User2 sharing a process because User2 logged in
and reset the session cookie), the following might occur:
• User1 session behaves consistently with the privileges assigned to User2.
• User1 activity keeps User2 session alive, but User1 session can time out unexpectedly.
• Logging out of either window causes both sessions to end. The next activity in the other window can
redirect the user to the login page as if a session timeout or premature timeout occurred.
• Clicking Log Out from the second session (User2) results in the following warning message:
Logging out: unknown page to display before redirecting the user to the login page.
• If User2 logs out and then logs back in as User3, User1 assumes the User3 session.
• If User1 is at login, and User2 is logged in, User1 can alter the URL to redirect to the index page. It
appears as if User1 has accessed iLO without logging in.
These behaviors continue as long as the duplicate windows are open. All activities are attributed to the
same user, using the last session cookie set.
Displaying the current session cookie
After logging in, you can force the browser to display the current session cookie by entering the following
in the URL navigation bar:
javascript:alert(document.cookie)
The first field visible is the session ID. If the session ID is the same among the different browser windows,
these windows are sharing iLO session.
You can force the browser to refresh and reveal your true identity by pressing F5, selecting View >
Refresh, or clicking the Refresh button.
Best practices for preventing cookie-related issues
• Start a new browser for each login by double-clicking the browser icon or shortcut.
• To close an iLO session before you close the browser window, click the Log Out button.
32 Using the iLO web interface
Page 33

iLO web interface
The iLO web interface groups similar tasks for easy navigation and workflow. The interface is organized
with a navigation tree in the left pane. To use the web interface, click an item in the navigation tree, and
then click the name of the tab you want to view.
The following branches are available in the navigation tree only if your server type or configuration
supports them:
• If you have a ProLiant server blade, the BL c-Class branch is included.
• If you have a Synergy compute module, the Synergy Frame branch is included.
• If you have a ProLiant XL server, the Chassis branch is included.
• When a remote management tool is used with iLO, the <Remote Management Tool Name> branch is
included.
Using the iLO controls
iLO control icons
When you log in to the iLO web interface, the iLO controls are available from any iLO page.
• Power icon—Click this icon to access the Virtual Power Button features.
• UID icon—Click this icon to turn the UID LED on and off.
• Language—Click this icon to select a language for the current iLO web interface session.
iLO web interface 33
Page 34

To view or modify the language settings, click the language icon, and then select Settings.
• Health icon—Click this icon to view the overall health status for the server fans, temperature sensors,
and other monitored subsystems. For all components except the Agentless Management Service
(AMS), click a component to view additional details.
• User icon—Click this icon to do the following:
◦ To log out of the current iLO web interface session, click the user icon, and then select Logout.
◦ To view the active iLO sessions, click the user icon, and then select Sessions.
◦ To view or modify iLO user accounts, click the user icon, and then select Settings.
• Help icon—Click this icon to view online help for the current iLO web interface page.
• Ellipsis icon—This icon is displayed on the Firmware & OS Software page when the browser
window is too small to show the full page. To access the Update Firmware and Upload to iLO
Repository options, click this icon. These options are available on all Firmware & OS Software tabs.
iLO navigation pane
iLO has a collapsible navigation pane that is accessible from each page.
• To toggle between showing and hiding the navigation pane, click the icon in the top left corner of the
iLO web interface.
• To hide the navigation pane, click the X icon.
• To show the navigation pane, click the icon in the top left corner of the iLO web interface.
• The navigation pane shows a thumbnail of the Remote Console. To start a Remote Console, click the
thumbnail and select a console option from the menu.
• For servers with monitors, click the Remote Console thumbnail in the navigation pane, and then select
Wake-Up Monitor to wake up a monitor that is in sleep mode.
Starting a remote management tool from the login page
Prerequisites
iLO is under the control of a remote management tool.
Procedure
1. Navigate to the iLO login page.
34 Starting a remote management tool from the login page
Page 35

When iLO is under the control of a remote management tool, the iLO web interface displays a
message similar to the following:
This system is being managed by <remote management tool name>. Changes made
locally in iLO will be out of sync with the centralized settings, and
could affect the behavior of the remote management system.
2. The name of the remote management tool is a link. To start the remote management tool, click the
link.
Changing the language from the login page
If a language pack is installed, use the language menu on the login screen to select the language for the
iLO session. This selection is saved in a browser cookie for future use.
Prerequisites
A language pack is installed.
Procedure
1. Navigate to the iLO Login page.
2. Select a language from the Language menu.
Changing the language from the login page 35
Page 36

Viewing iLO information and logs
Viewing iLO overview information
Procedure
Navigate to the Information page.
The iLO Overview page displays high-level details about the server and the iLO subsystem, as well as
links to commonly used features.
System information details
• Server Name—The server name defined by the host operating system. To navigate to the Access
Settings page, click the Server Name link.
• Product Name—The product with which this iLO processor is integrated.
• UUID—The universally unique identifier that software uses to identify this host. This value is assigned
when the system is manufactured.
• UUID (Logical)—The system UUID that is presented to host applications. This value is displayed only
when set by other software. This value might affect operating system and application licensing. The
UUID (Logical) value is set as part of the logical server profile that is assigned to the system. If the
logical server profile is removed, the system UUID value reverts from the UUID (Logical) value to the
UUID value. If no UUID (Logical) value is set, this item is not displayed.
• Server Serial Number —The server serial number, which is assigned when the system is
manufactured. You can change this value by using the ROM-based system utilities during POST.
• Serial Number (Logical)—The system serial number that is presented to host applications. This value
is displayed only when set by other software. This value might affect operating system and application
licensing. The Serial Number (Logical) value is set as part of the logical server profile that is
assigned to the system. If the logical server profile is removed, the serial number value reverts from
the Serial Number (Logical) value to the Server Serial Number value. If no Serial Number
(Logical) value is set, this item is not displayed.
• Chassis Serial Number—The serial number of the chassis that contains the server node.
This value is displayed only for server nodes in an HPE Apollo chassis.
• Product ID—This value distinguishes between different systems with similar serial numbers. The
product ID is assigned when the system is manufactured. You can change this value by using the
ROM-based system utilities during POST.
• System ROM—The version of the active system ROM.
• System ROM Date—The date of the active system ROM.
• Redundant System ROM—The version of the redundant system ROM. If a system ROM update fails
or is rolled back, the redundant system ROM is used. This value is displayed only if the system
supports redundant system ROM.
• Integrated Remote Console—Provides links to start the .NET IRC or Java IRC for remote, out-ofband communication with the server console. For information about the available remote console
options, see iLO Integrated Remote Console on page 107.
36 Viewing iLO information and logs
Page 37

• License Type—The level of licensed iLO firmware functionality.
• iLO Firmware Version—The version and date of the installed iLO firmware. To navigate to the
Firmware Update page, click the iLO Firmware Version link.
• IP Address—The network IP address of the iLO subsystem.
• Link-Local IPv6 Address—The SLAAC link-local address of the iLO subsystem. To navigate to the
Network Summary page, click the Link-Local IPv6 Address link. This value is displayed only for iLO
Dedicated Network Port configurations.
• iLO Hostname—The fully qualified network name assigned to the iLO subsystem. By default, the
hostname is ILO, followed by the system serial number and the current domain name. This value is
used for the network name and must be unique.
System status details
• System Health—The server health indicator. This value summarizes the condition of the monitored
subsystems, including overall status and redundancy (ability to handle a failure). Lack of redundancy
in any subsystem at startup will not degrade the system health status. To navigate to the Health
Summary page, click the System Health link.
• Server Power—The server power state (ON or OFF). To access the Virtual Power Button features,
click the Server Power icon.
• UID Indicator—The state of the UID LED. The UID LED helps you identify and locate a server,
especially in high-density rack environments. The possible states are UID ON, UID OFF, and UID
BLINK.
If the iLO Service Port is in use, UID BLINK status includes the Service Port status. The possible
values are UID BLINK (Service Port Busy), UID BLINK (Service Port Error), and UID BLINK
(Service Port Finished).
To turn the UID LED on or off, click the UID Indicator icon, click the UID control at the top of the iLO
web interface window, or use the UID buttons on the server chassis.
When the UID is blinking, and then it stops blinking, the status reverts to the previous value (UID ON
or UID OFF). If a new state is selected while the UID LED is blinking, that state takes effect when the
UID LED stops blinking.
CAUTION:
The UID LED blinks automatically to indicate that a critical operation is underway on the host,
such as Remote Console access or a firmware update. Do not remove power from a server
when the UID LED is blinking.
• TPM Status or TM Status—The status of the TPM or TM socket or module.
The possible values are Not Supported, Not Present, or Present-Enabled.
Trusted Platform Modules and Trusted Modules are computer chips that securely store artifacts used
to authenticate the platform. These artifacts can include passwords, certificates, or encryption keys.
You can also use a TPM or TM to store platform measurements to make sure that the platform
remains trustworthy.
On a supported system, ROM decodes the TPM or TM record and passes the configuration status to
iLO, the iLO RESTful API, the CLP, and the XML interface.
System status details 37
Page 38

• Module Type—The TPM or TM type and specification version. The possible values are TPM 1.2, TPM
2.0, TM 1.0, Not Specified, and Not Supported. This value is displayed when a TPM or TM is
present on a server.
• SD-Card Status—The status of the internal SD card. If present, the number of blocks in the SD card
is displayed.
• Access Panel Status—The state of the access panel. The possible states are OK (the access panel
is installed) and Intrusion (the access panel is open). This value is displayed only on servers that are
configured for chassis intrusion detection.
• iLO Date/Time—The internal clock of the iLO subsystem.
Connection to HPE status
This section shows the remote support registration status for supported servers.
The possible status values follow:
• Registered to Remote Support—The server is registered.
• Registration incomplete—The server is registered for Insight Online direct connect remote support,
but step 2 of the registration process is incomplete.
• Not registered—The server is not registered.
• Unable to retrieve the HPE Remote Support information—The registration status could not be
determined.
• Remote Support Registration Error—A remote support connection error occurred.
Managing iLO sessions
Prerequisites
Administer User Accounts privilege
Procedure
1. Navigate to the Information page, and then click the Session List tab.
The Session List page displays information about the active iLO sessions.
2. Optional: To disconnect one or more sessions, click the check box next to each session you want to
disconnect, and then click Disconnect Session.
Session list details
iLO displays the following details in the Current Session and Session List tables:
• User—The iLO user account name.
• IP—The IP address of the computer used to log in to iLO.
• Login Time—The date and time that the iLO session started.
• Access Time—The date and time that iLO was last active in the session.
• Expires—The date and time that the session will end automatically.
38 Connection to HPE status
Page 39

• Source—The session source (for example, Remote Console, web interface, ROM-based setup utility,
iLO RESTful API, or SSH).
• Privilege icons (current user only)—The privileges assigned to the current user account.
iLO Event Log
The event log provides a record of significant events recorded by the iLO firmware.
Logged events include major server events such as a server power outage or a server reset, and iLO
events such as unauthorized login attempts. Other logged events include successful or unsuccessful
browser and Remote Console logins, virtual power and power-cycle events, clearing the log, and some
configuration changes, such as creating or deleting a user.
iLO provides secure password encryption, tracking all login attempts and maintaining a record of all login
failures. The Authentication Failure Logging setting allows you to configure logging criteria for failed
authentications. The event log captures the client name for each logged entry to improve auditing
capabilities in DHCP environments, and records the account name, computer name, and IP address.
For a list of the errors that might appear in the event log, see the error messages guide for your server.
Viewing the event log
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the iLO Event Log tab.
2. Optional: Use the event log sort, search, and filter features to customize the log view.
The total number of recorded events is always displayed above the filter icon. When filters are applied,
the number of events that meet the filter criteria is displayed below the filter icon.
3. Optional: To view the event details pane, click an event.
Event log details
• ID—The event ID number. Events are numbered in the order in which they are generated.
By default, the event log is sorted by the ID, with the most recent event at the top.
• Severity—The importance of the detected event.
• Description—The description identifies the component and detailed characteristics of the recorded
event. If the iLO firmware is rolled back to an earlier version, the description UNKNOWN EVENT TYPE
might be displayed for events recorded by the newer firmware. You can resolve this issue by updating
the firmware to the latest supported version, or by clearing the event log.
• Last Update—The date and time when the latest event of this type occurred. This value is based on
the date and time stored by the iLO firmware.
If the iLO firmware did not recognize the date and time when an event was updated, [NOT SET] is
displayed.
• Count—The number of times this event has occurred (if supported).
In general, important events generate an event log entry each time they occur. They are not
consolidated into one event log entry.
iLO Event Log 39
Page 40

When less important events are repeated, they are consolidated into one event log entry, and the
Count and Last Update values are updated. Each event type has a specific time interval that
determines whether repeated events are consolidated or a new event is logged.
• Category—The event category. For example, Administration, Configuration, or Security.
Event log icons
iLO uses the following icons to indicate event severity:
Critical—The event indicates a service loss or imminent service loss. Immediate attention is
•
needed.
•
Caution—The event is significant but does not indicate performance degradation.
• Informational—The event provides background information.
Unknown—The event severity could not be determined.
•
Event log event pane details
• Initial Update—The date and time when the first event of this type occurred. This value is based on
the date and time stored by the iLO firmware.
If iLO did not recognize the date and time when the event was first created, [NOT SET] is displayed.
• Event Code—A unique identifier for an event within a given event class displayed in hexadecimal
format.
Customizing the event log view
Sorting events
Click a column heading to sort the event log table by that column.
To change the display to ascending or descending order, click the column heading again.
Event filters
To access the event log filters, click .
• To filter by severity, select a severity level from the Severity menu.
• To filter by event category, select a value in the Category menu.
• To change the displayed date and time for events, select a value in the Time menu. Choose from the
following:
◦ Show Default—Display UTC time.
◦ Show Local Time—Display the iLO web interface client time.
◦ Show ISO Time—Display UTC time in ISO 8601 format.
40 Event log icons
Page 41

• To filter by the last update date, select a value in the Last Update menu.
• To set the filters back to the default values, click Reset filters.
Searching for an event
To search for events based on dates, event ID, or description text, click , and then enter text in the
search box.
Saving the event log to a CSV file
Use a supported browser to export the event log to a CSV file.
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the iLO Event Log tab.
2. Click the CSV icon
3. In the CSV Output window, click Save, and then follow the browser prompts to save or open the file.
Clearing the event log
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the iLO Event Log tab.
2. Click .
3. When prompted to confirm the request, click OK.
The event log is cleared of all previously logged information and an event is recorded in the log.
Integrated Management Log
The IML provides a record of historical events that have occurred on the server. Events are generated by
the system ROM and by services such as the iLO driver. Logged events include server-specific
information such as health and status information, firmware updates, operating system information, and
ROM-based POST codes.
Entries in the IML can help you diagnose issues or identify potential issues. Preventative action might
help to avoid disruption of service.
iLO manages the IML, which you can access through a supported browser, even when the server is off.
The ability to view the log when the server is off can be helpful when troubleshooting remote host server
issues.
Examples of the types of information recorded in the IML follow:
• Fan inserted
• Fan removed
• Fan failure
Saving the event log to a CSV file 41
Page 42

• Fan degraded
• Fan repaired
• Fan redundancy lost
• Fans redundant
• Power supply inserted
• Power supply removed
• Power supply failure
• Power supplies redundancy lost
• Power supplies redundant
• Temperature over threshold
• Temperature normal
• Automatic shutdown started
• Automatic shutdown canceled
• Drive failure
Viewing the IML
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Integrated Management Log tab.
2. Optional: Use the IML sort, search, and filter features to customize the log view.
The total number of recorded events is always displayed above the filter icon. When filters are applied,
the number of events that meet the filter criteria is displayed below the filter icon.
3. Optional: To view the event details pane, click an event.
IML details
• The first column on the left side of the web interface displays an active check box next to each event
with Critical or Caution status. Use this check box to select an event to mark as repaired.
• ID—The event ID number. Events are numbered in the order in which they are generated.
By default, the IML is sorted by the ID, with the most recent event at the top. A factory reset will reset
the counter.
• Severity—The importance of the detected event.
• Class—Identifies the type of event that occurred, for example, UEFI, environment, or system revision.
• Description—The description identifies the component and detailed characteristics of the recorded
event.
If the iLO firmware is rolled back, the description UNKNOWN EVENT TYPE might be displayed for
events recorded by the newer firmware. You can resolve this issue by updating the firmware to the
latest supported version, or by clearing the log.
42 Viewing the IML
Page 43

• Last Update—The date and time when the latest event of this type occurred. This value is based on
• Count—The number of times this event has occurred (if supported).
• Category—The event category. For example, Hardware, Firmware, or Administration.
IML icons
iLO uses the following icons to indicate IML event severity:
•
• Caution—The event is significant but does not indicate performance degradation.
the date and time stored by the iLO firmware.
If iLO did not recognize the date and time when an event was updated, [NOT SET] is displayed.
In general, important events generate an IML entry each time they occur. They are not consolidated
into one event log entry.
When less important events are repeated, they are consolidated into one IML entry, and the Count
and Last Update values are updated. Each event type has a specific time interval that determines
whether repeated events are consolidated or a new event is logged.
Critical—The event indicates a service loss or an imminent service loss. Immediate attention is
needed.
• Informational—The event provides background information.
• Repaired—An event has undergone corrective action.
• Unknown—The event severity could not be determined.
IML event pane details
• Initial Update—The date and time when the first event of this type occurred. This value is based on
the date and time stored by the iLO firmware.
If iLO did not recognize the date and time when the event was first created, [NOT SET] is displayed.
• Event Code—A unique identifier for an event within a given event class (displayed in hexadecimal
format).
• Learn More— Click the link displayed here to access troubleshooting information for supported
events.
• Recommended Action— A short description of the recommended action for a failure condition.
Customizing the IML view
Sorting events
Click a column heading to sort the IML table by that column.
To change the display to ascending or descending order, click the arrow next to the column heading.
Event filters
To access the event log filters, click .
IML icons 43
Page 44

• To filter by severity, select a severity level from the Severity list.
• To filter by class, select a class from the Class list.
• To filter by event category, select a value in the Category list.
• To change the displayed date and time for events, select a value in the Time menu. Choose from the
following:
◦ Show Default—Display UTC time.
◦ Show Local Time—Display the iLO web interface client time.
◦ Show ISO Time—Display UTC time in ISO 8601 format.
• To filter by the Last Update date, select a value in the Last Update menu.
• To set the filters back to the default values, click Reset filters.
Searching for an event
To search for events based on dates, event IDs, or description text, click , and then enter text in the
search box.
Marking an IML entry as repaired
Use this feature to change the status of an IML entry from Critical or Caution to Repaired.
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Investigate and repair the issue.
2. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Integrated Management Log tab.
3. Select the log entry.
To select an IML entry, click the check box next to the entry in the first column of the IML table. If a
check box is not displayed next to an IML entry, that entry cannot be marked as repaired.
4. Click .
The iLO web interface refreshes, and the selected log entry status changes to Repaired.
Adding a maintenance note to the IML
Use maintenance notes to create log entries about maintenance activities such as upgrades, system
backups, periodic system maintenance, or software installations.
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
44 Marking an IML entry as repaired
Page 45

Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Integrated Management Log tab.
2. Click .
The Enter Maintenance Note window opens.
3. Enter the text that you want to add as a log entry, and then click OK.
You can enter up to 227 bytes of text. You cannot submit a maintenance note without entering some
text.
An Informational log entry with the class Maintenance is added to the IML.
Saving the IML to a CSV file
Use a supported browser to export the IML to a CSV file.
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Integrated Management Log tab.
2. Click the CSV icon .
3. In the CSV Output window, click Save, and then follow the browser prompts to save or open the file.
Clearing the IML
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Integrated Management Log tab.
2. Click .
3. When prompted to confirm the request, click OK.
The IML is cleared of all previously logged information and an event is recorded in the IML.
Active Health System
The Active Health System monitors and records changes in the server hardware and system
configuration.
The Active Health System provides:
• Continuous health monitoring of over 1600 system parameters
• Logging of all configuration changes
• Consolidated health and service alerts with precise time stamps
• Agentless monitoring that does not affect application performance
Saving the IML to a CSV file 45
Page 46

Active Health System data collection
The Active Health System does not collect information about your operations, finances, customers,
employees, or partners.
Examples of information that is collected:
• Server model and serial number
• Processor model and speed
• Storage capacity and speed
• Memory capacity and speed
• Firmware/BIOS and driver versions and settings
The Active Health System does not parse or change OS data from third-party error event log activities (for
example, content created or passed through the OS).
Active Health System Log
The data collected by the Active Health System is stored in the Active Health System Log. The data is
logged securely, isolated from the operating system, and separate from customer data.
When the Active Health System Log is full, new data overwrites the oldest data in the log.
It takes less than 5 minutes to download the Active Health System Log and send it to a support
professional to help you resolve an issue.
When you download and send Active Health System data to Hewlett Packard Enterprise, you agree to
have the data used for analysis, technical resolution, and quality improvements. The data that is collected
is managed according to the privacy statement, available at http://www.hpe.com/info/privacy.
You can also upload the log to the Active Health System Viewer. For more information, see the Active
Health System Viewer documentation at the following website: http://www.hpe.com/support/ahsv-docs.
Downloading the Active Health System Log for a date range
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Active Health System Log tab.
The Active Health System Log is inaccessible when it is being used by Intelligent Provisioning, the iLO
Service Port, or the Active Health System download CLI tool.
2. Enter the range of days to include in the log. The default value is seven days.
a. Click the From box.
A calendar is displayed.
b. Select the range start date on the calendar.
c. Click the To box.
A calendar is displayed.
d. Select the range end date on the calendar.
To reset the range to the default values, click the Reset icon .
3. Optional: Enter the following information to include in the downloaded file:
46 Active Health System data collection
Page 47

• Support case number
• Contact name
• Phone number
• Email address
• Company name
The contact information you provide will be treated in accordance with the Hewlett Packard Enterprise
privacy statement. This information is not written to the log data stored on the server.
4. Click Download.
5. Save the file.
6. If you have an open support case, you can email the log file to gsd_csc_case_mngmt@hpe.com.
Use the following convention for the email subject: CASE: <case number>.
Files that are larger than 25 MB must be compressed and uploaded to an FTP site. If needed, contact
Hewlett Packard Enterprise for FTP site information.
7. Optional: Upload the file to the Active Health System Viewer.
For more information, see http://www.hpe.com/servers/ahsv.
Downloading the entire Active Health System Log
It might take a long time to download the entire Active Health System Log. If you must upload the Active
Health System Log for a technical issue, Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends downloading the log
for the specific range of dates in which the problem occurred.
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Active Health System Log tab.
The Active Health System Log is inaccessible when it is being used by Intelligent Provisioning, the iLO
Service Port, or the Active Health System download CLI tool.
2. Click Show Advanced Settings.
3. Optional: Enter the following information to include in the downloaded file:
• Support case number
• Contact name
• Phone number
• Email address
• Company name
The contact information that you provide will be treated in accordance with the Hewlett Packard
Enterprise privacy statement. This information is not written to the log data stored on the server.
4. Click Download Entire Log.
5. Save the file.
Downloading the entire Active Health System Log 47
Page 48

6. If you have an open support case, you can email the log file to gsd_csc_case_mngmt@hpe.com.
Use the following convention for the email subject: CASE: <case number>.
Files that are larger than 25 MB must be compressed and uploaded to an FTP site. If needed, contact
Hewlett Packard Enterprise for FTP site information.
7. Optional: Upload the file to the Active Health System Viewer.
For more information, see http://www.hpe.com/servers/ahsv.
Extracting the Active Health System Log by using curl
iLO supports extracting the Active Health System Log with the curl command-line tool.
Procedure
1. Install curl.
2. You can download curl from the following website: http://curl.haxx.se/.
3. Open a command window.
4. Enter a command similar to the following examples.
IMPORTANT:
When you enter these commands, ensure that you do not use spaces or other unsupported
characters.
If required by your command line environment, special characters such as the ampersand must
be preceded by the escape character. See the command line environment documentation for
more information.
• To download the Active Health System Log for a range of dates:
curl "https://<iLO_IP_address>/ahsdata/ahs.ahs?from=<yyyy-mm-dd>&to=
<yyyy-mm-dd>" -k -v -u <username>:<password> -o <filename>.ahs
• To download the Active Health System Log for the last seven days, and add a Hewlett Packard
Enterprise support case number to the log header:
curl "https://<iLO_IP_address>/ahsdata/ahs.ahs?days=<number_of_days>
&case_no=<number>" -k -v -u <username>:<password> -o <filename>.ahs
• To download the Active Health System Log for the last seven days, and include a case number and
contact information:
curl "https://<iLO_IP_address>/ahsdata/ahs.ahs?days=<number_of_days>
&case_no=<number>&contact_name=<name>&phone=<phone_number>&email=
<email_address>&co_name=<company>" -k -v -u <username>:<password>
-o <filename>.ahs
• To download the entire Active Health System Log:
curl "https://<iLO_IP_address>/ahsdata/ahs.ahs?downloadAll=1" -k -v
-u <username>:<password> -o <filename>.ahs
48 Extracting the Active Health System Log by using curl
Page 49

5. The file is saved to the specified path.
6. Close the command window.
curl command usage with iLO
When you use curl to extract the Active Health System log, the command components include the
following:
Options
<iLO IP address>
Specifies the iLO IP address.
from=<yyyy-mm-dd>&to=<yyyy-mm-dd>
Represents the start and end date of the range of dates to include in the log. Enter dates in the format
year-month-day, for example, 2017-07-29 for July 29, 2017.
days=<number of days>
Specifies that you want to download the log file for the last <number of days> from today's date.
downloadAll=1
Specifies that you want to download the entire log.
–k
Specifies that HTTPS warnings will be ignored.
–v
Specifies verbose output.
-u <username>:<password>
Specifies your iLO user account credentials.
–o <filename>.ahs
Specifies the output file name and path.
case_no=<HPE support case number>
Specifies a Hewlett Packard Enterprise support case number to add to the log header.
Options for adding contact information to the downloaded log
phone=<phone number>
Specifies a phone number to add to the log header.
email=<email address>
Specifies an email address to add to the log header.
contact_name=<contact name>
Specifies a contact name to add to the log header.
co_name=<company name>
Insert your company name in the log header.
Clearing the Active Health System Log
If the log file is corrupted, or if you want to clear and restart logging, use the following procedure to clear
the Active Health System Log.
curl command usage with iLO 49
Page 50

Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Active Health System Log tab.
The Active Health System Log is inaccessible when it is being used by Intelligent Provisioning, the
Active Health System download CLI tool, or the iLO Service Port.
2. Click Show Advanced Settings.
3. Scroll to the Clear Log section, and then click Clear.
4. When prompted to confirm the request, click OK.
iLO notifies you that the log is being cleared.
5. Reset iLO.
Resetting iLO is required because some Active Health System data is recorded to the log only during
iLO startup. Performing this step ensures that a complete set of data is available in the log.
6. Reboot the server.
Rebooting the server is required because some information, such as the operating system name and
version, is logged at server startup. Performing this step ensures that a complete set of data is
available in the log.
Viewing iLO self-test results
The iLO Self-Test Results section displays the results of internal iLO diagnostic tests, including the test
name, status, and notes.
The tests that are run are system-dependent. Not all tests are run on all systems. To see the tests that
are performed on your system, view the list on the Diagnostics page.
If a status is not reported for a test, the test is not listed.
Procedure
Click Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Diagnostics tab.
iLO self-tests
Self-test details
Self-Test
The tested function.
Status
The test status.
50 Viewing iLO self-test results
Page 51

• Pass—The test was successful.
• Fail—The test detected a problem. A reboot, firmware or software update, or service might be
required.
•
Informational—Supplemental data about the tested system is provided in the Notes column.
Notes
A test might include supplemental information in the Notes column.
For some tests, this column displays the versions of other system programmable logic, such as the
System Board PAL or the Power Management Controller.
iLO self-test types
The tests that are run are system-dependent. Not all tests are run on all systems. The possible tests
include:
• Cryptographic—Tests security features.
• NVRAM data—Tests the subsystem that retains nonvolatile configuration data, logs, and settings.
• Embedded Flash—Tests the state of the system that can store configuration, provisioning, and
service information.
• Host ROM—Checks the BIOS to determine whether it is out-of-date compared to the management
processor.
• Supported Host—Checks the management processor firmware to determine whether it is out of date
for the server hardware.
• Power Management Controller—Tests functions related to power measurement, power capping, and
power management.
• CPLD—Tests the programmable hardware in the server.
• ASIC Fuses—Compares a known data pattern against expected data manufactured into the iLO chip
to make sure that the chip was manufactured properly and that operating settings meet tolerances.
Viewing iLO information and logs 51
Page 52

Viewing general system information
Viewing health summary information
The Health Summary page displays the status of monitored subsystems and devices. Depending on the
server configuration, the information on this page varies.
If the server is powered off, the system health information on this page is current as of the last power off.
Health information is updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
Procedure
Click System Information in the navigation tree.
Redundancy status
Redundancy status is displayed for the following:
• Fan Redundancy
• Power Status
Subsystem and device status
Summarized status information is displayed for the following:
• Agentless Management Service
• BIOS/Hardware Health
• Fans
• Memory
• Network
• Power Supplies (nonblade servers only)
• Processors
• Storage
• Temperatures
• Smart Storage Battery Status (supported servers only)
Subsystem and device status values
The Health Summary page uses the following status values:
• Redundant—There is a backup component for the device or subsystem.
• OK—The device or subsystem is working correctly.
Not Redundant—There is no backup component for the device or subsystem.
•
52 Viewing general system information
Page 53

• Not Available—The component is not available or not installed.
• Degraded—The device or subsystem is operating at a reduced capacity.
iLO displays the power supply status as Degraded when mismatched power supplies are installed.
If you power on a server with nonredundant fans or power supplies, the system health status is listed
as OK. However, if a redundant fan or power supply fails while the system is powered on, the system
health status is listed as Degraded until you replace the fan or power supply.
• Failed Redundant—The device or subsystem is in a nonoperational state.
• Failed—One or more components of the device or subsystem are nonoperational.
• Other—For more information, navigate to the System Information page of the component that is
reporting this status.
• Link Down—The network link is down.
• Unknown—The iLO firmware has not received data about the device status. If iLO was reset when
the server was powered off, some subsystems display the status Unknown because the status cannot
be updated when the server is powered off.
• Not Installed—The subsystem or device is not installed.
Viewing processor information
The Processor Information page displays the available processor slots, the type of processor installed
in each slot, and a summary of the processor subsystem.
If the server is powered off, the system health information on this page is current as of the last power off.
Health information is updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
Procedure
Click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Processors tab.
Processor details
The following information is displayed for each processor:
• Processor Name—The name of the processor.
• Processor Status—The health status of the processor.
• Processor Speed—The speed of the processor.
• Execution Technology—Information about the processor cores and threads.
• Memory Technology—The processor memory capabilities.
• Internal L1 cache—The L1 cache size.
• Internal L2 cache—The L2 cache size.
• Internal L3 cache—The L3 cache size.
Viewing processor information 53
Page 54

Viewing memory information
The Memory Information page displays a summary of the system memory. When server power is off,
AMP data is unavailable, and only memory modules present at POST are displayed.
If the server is powered off, the system health information on this page is current as of the last power off.
Health information is updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
Procedure
1. Click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Memory tab.
The Memory page displays details for the following:
• Advanced Memory Protection (AMP)
• Memory Summary
• Physical Memory
• Logical Memory
2. Optional: By default, empty memory sockets are hidden in the Physical Memory table. To view the
empty memory sockets, click show empty sockets. When empty memory sockets are displayed, click
hide empty sockets to hide them.
3. Optional: To view additional memory details, select a memory module.
The Memory Details pane is displayed.
Advanced Memory Protection details
AMP Mode Status
The status of the AMP subsystem.
• Other/Unknown—The system does not support AMP, or the management software cannot
determine the status.
• Not Protected—The system supports AMP, but the feature is disabled.
• Protected—The system supports AMP. The feature is enabled but not engaged.
• Degraded—The system was protected, but AMP is engaged. Therefore, AMP is no longer
available.
• DIMM ECC—The system is protected by DIMM ECC only.
• Mirroring—The system is protected by AMP in the mirrored mode. No DIMM faults have been
detected.
• Degraded Mirroring—The system is protected by AMP in the mirrored mode. One or more DIMM
faults have been detected.
• On-line Spare—The system is protected by AMP in the hot spare mode. No DIMM faults have
been detected.
• Degraded On-line Spare—The system is protected by AMP in the hot spare mode. One or more
DIMM faults have been detected.
54 Viewing memory information
Page 55

• RAID-XOR—The system is protected by AMP in the XOR memory mode. No DIMM faults have
been detected.
• Degraded RAID-XOR—The system is protected by AMP in the XOR memory mode. One or more
DIMM faults have been detected.
• Advanced ECC—The system is protected by AMP in the Advanced ECC mode.
• Degraded Advanced ECC—The system is protected by AMP in the Advanced ECC mode. One
or more DIMM faults have been detected.
• LockStep—The system is protected by AMP in the LockStep mode.
• Degraded LockStep—The system is protected by AMP in the LockStep mode. One or more
DIMM faults have been detected.
• A3DC—The system is protected by AMP in the A3DC mode.
• Degraded A3DC—The system is protected by AMP in the A3DC mode. One or more DIMM faults
have been detected.
Configured AMP Mode
The active AMP mode. The following modes are supported:
• None/Unknown—The management software cannot determine the AMP fault tolerance, or the
system is not configured for AMP.
• On-line Spare—A single spare bank of memory is set aside at boot time. If enough ECC errors
occur, the spare memory is activated and the memory that is experiencing the errors is disabled.
• Mirroring—The system is configured for mirrored memory protection. All memory banks are
duplicated in mirrored memory, as opposed to only one for online spare memory. If enough ECC
errors occur, the spare memory is activated and the memory that is experiencing the errors is
disabled.
• RAID-XOR—The system is configured for AMP with the XOR engine.
• Advanced ECC—The system is configured for AMP with the Advanced ECC engine.
• LockStep—The system is configured for AMP with the LockStep engine.
• Online Spare (Rank Sparing)—The system is configured for Online Spare Rank AMP.
• Online Spare (Channel Sparing)—The system is configured for Online Spare Channel AMP.
• Intersocket Mirroring—The system is configured for mirrored intersocket AMP between the
memory of two processors or boards.
• Intrasocket Mirroring—The system is configured for mirrored intrasocket AMP between the
memory of a single processor or board.
• A3DC—The system is configured for AMP with the A3DC engine.
Supported AMP Modes
• RAID-XOR—The system can be configured for AMP using the XOR engine.
• Dual Board Mirroring—The system can be configured for mirrored advanced memory protection
in a dual memory board configuration. The mirrored memory can be swapped with memory on the
same memory board or with memory on the second memory board.
Viewing general system information 55
Page 56

• Single Board Mirroring—The system can be configured for mirrored advanced memory
protection in a single memory board.
• Advanced ECC—The system can be configured for Advanced ECC.
• Mirroring—The system can be configured for mirrored AMP.
• On-line Spare—The system can be configured for online spare AMP.
• LockStep—The system can be configured for LockStep AMP.
• Online Spare (Rank Sparing)—The system can be configured for Online Spare Rank AMP.
• Online Spare (Channel Sparing)—The system can be configured for Online Spare Channel AMP.
• Intersocket Mirroring—The system can be configured for mirrored intersocket AMP between the
memory of two processors or boards.
• Intrasocket Mirroring—The system can be configured for mirrored intrasocket AMP between the
memory of a single processor or board.
• A3DC—The system can be configured for A3DC AMP.
• None—The system cannot be configured for AMP.
Memory Summary
The Memory Summary section shows a summary of the memory that was installed and operational at
POST.
Location
The slot or processor on which the memory board, cartridge, or riser is installed. Possible values
follow:
• System Board—There is no separate memory board slot. All DIMMs are installed on the
motherboard.
• Board <Number>—There is a memory board slot available. All DIMMs are installed on the
memory board.
• Processor <Number>—The processor on which the memory DIMMs are installed.
• Riser <Number>—The riser on which the memory DIMMs are installed.
Number of Sockets
The number of present memory module sockets.
Total Memory
The capacity of the memory, including memory recognized by the operating system and memory used
for spare, mirrored, or XOR configurations.
Speed
The memory module speed.
Operating Voltage
The voltage at which the memory operates.
56 Memory Summary
Page 57

Physical Memory Details
The Physical Memory Details section shows the physical memory modules on the host that were
installed and operational at POST. Unpopulated module positions are also listed. Various resilient memory
configurations can change the actual memory inventory from what was sampled at POST. In systems that
have a high number of memory modules, all module positions might not be listed.
Location
The slot or processor on which the memory module is installed.
Status
The memory module status and whether the module is in use.
Size
The size of the memory module, in MB.
Speed
The memory module speed.
Technology
The memory module technology. Possible values follow:
• Unknown—Memory technology cannot be determined.
• N/A—Not present.
• Synchronous
• RDIMM
• UDIMM
• LRDIMM
• NVDIMM
• NVDIMM-N
• R-NVDIMM
Logical Memory Details
This section shows the HPE Scalable Persistent Memory devices that were configured and operational at
POST.
Location
The processor and/or the region for the logical device. For example, PROC 1,2 Spanned Logical
NVDIMM, or PROC 1 Logical NVDIMM 1.
Status
The logical memory status.
Size
The size of the logical memory, in MB.
Speed
The logical memory speed.
Physical Memory Details 57
Page 58

Technology
The logical memory technology. Possible values follow:
• NVDIMM
• NVDIMM-N
• R-NVDIMM
Memory Details pane
Physical Memory
Manufacturer
The memory module manufacturer.
HPE Memory
Indicates whether the memory module is HPE SmartMemory. Yes is displayed for HPE
SmartMemory, and No is displayed for other memory types, including HPE memory that is not
SmartMemory.
Part Number
The memory module part number.
This value is displayed only for HPE Memory modules.
Type
The type of memory installed. Possible values follow:
• Other—Memory type cannot be determined.
• Board—Memory module is permanently mounted (not modular) on a system board or memory
expansion board.
• DDR4
• N/A—Memory module is not present.
Minimum Voltage
The minimum voltage at which the memory module can operate.
Ranks
The number of ranks in the memory module.
Error Correction
The type of error correction used by the memory module.
Data Width Bits
The memory module data width in bits.
Bus Width Bits
The memory module bus width in bits.
Channel
The channel number in which the memory module is connected.
58 Memory Details pane
Page 59

Memory Controller
The memory controller number.
Slot
The memory module slot number.
Socket
The memory module socket number.
State
The memory state.
Vendor ID
The memory vendor ID.
Armed
The current backup-ready status of the NVDIMM-N, if available.
Last Operation
The status of the last operation.
Media Life
The percentage of media life left.
Logical Memory
Name
The memory module product name.
Manufacturer
The memory module manufacturer.
Power Backup Unit Bays
The number of battery backed unit bays that provide backup power to the logical DIMM.
Type
The type of memory installed.
The only possible value for logical memory is Logical.
Minimum Voltage
The minimum voltage at which the memory module can operate.
Ranks
The number of ranks in the memory module.
Error Correction
The type of error correction used by the memory module.
Data Width Bits
The memory module data width in bits.
Bus Width Bits
The memory module bus width in bits.
Viewing general system information 59
Page 60

Memory Media
The proprietary media source of the memory module. For example, NAND or Proprietary.
State
The memory state.
Armed
The current backup-ready status of an NVDIMM-N, if available.
Last Operation
The status of the last operation.
Media Life
The percentage of media life left.
Viewing network information
If the server is powered off, the health status information on this page is current as of the last power off.
Health information is updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
To view a full set of data on this page, ensure that AMS is installed and running. The server IP address,
add in network adapters, and the server NIC status are displayed only if AMS is installed and running on
the server.
The information on this page is updated when you log in to iLO. To refresh the data, log out of iLO, and
then log back in.
Procedure
1. Click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Network tab.
2. Optional: To expand or collapse the information on this page, click Expand All or Collapse All,
respectively.
Physical Network Adapters
Integrated and add-in NICs and Fibre Channel adapters
This section displays the following information about the integrated and add-in NICs and Fibre Channel
adapters in the server:
• Adapter number—The adapter number, for example, Adapter 1 or Adapter 2.
• Location—The location of the adapter on the system board.
• Firmware—The version of the installed adapter firmware, if applicable. This value is displayed for
system NICs (embedded and stand-up) only.
• Status—The NIC status.
◦ On Windows servers:
If the NIC has never been plugged in to a network, iLO displays the status Unknown.
If the NIC has been plugged in to a network, and is now unplugged, iLO displays the status Link
Down.
◦ On Linux servers:
60 Viewing network information
Page 61

If NetworkManager is used to manage the NIC, the default status is Up and the link status is
displayed in iLO.
If Linux legacy utilities are used to manage the NIC, iLO displays the link status only if the NIC is
configured by an administrator. If the NIC is not configured, iLO displays the status Unknown.
◦ On VMware servers:
If iLO cannot communicate with the NIC port, it displays the status Unknown.
If the NIC driver reports the status link_down, iLO displays the status Down.
If the NIC driver reports the status link_up, iLO displays the status Up.
• Port—The configured network port. This value is displayed for system NICs (embedded and stand-up)
only.
• MAC Address—The port MAC address.
• IPv4 Address—For system NICs (embedded and stand-up), the server IP address (if available).
• IPv6 Address—For system NICs (embedded and stand-up), the server IP address (if available).
• Status—The port status.
• Team/Bridge—If a port is configured for NIC teaming, the name of the configured link between the
physical ports that form a logical network adapter. This value is displayed for system NICs (embedded
and stand-up) only.
Fibre Channel host bus adapters or converged network adapters
The following information is displayed for Fibre Channel host bus adapters or converged network
adapters:
• Physical Port—The physical network port number.
• WWNN—The port world-wide node name.
• WWPN—The world-wide port name.
• Status—The port status.
Boot progress and boot targets
The following information about the boot progress and boot targets is displayed when DCI connectivity is
available:
• Port—The configured virtual port number.
• Boot Progress—The current boot status.
• Boot Targets
◦ WWPN—The world-wide port name.
◦ LUN ID—The logical unit number ID.
Viewing general system information 61
Page 62

Logical Network Adapters
This section displays the following information about network adapters that use NIC teaming to combine
two or more ports into a single logical network connection:
• Adapter name—The name of the configured link between the physical ports that form the logical
network adapter.
• MAC Address—The logical network adapter MAC address.
• IP Address—The logical network adapter IP address.
• Status—The logical network adapter status.
The following information is displayed for the ports that form each logical network adapter:
• Members—A sequential number assigned to each port that forms the logical network adapter.
• MAC Address—The MAC address of the physical adapter port.
• Status—The status of the physical adapter port.
Viewing the device inventory
The Device Inventory page displays information about devices installed on the system board. Some
examples of the devices listed on this page include installed adapters, PCI devices, SATA controllers, and
Smart Storage batteries.
If the server is powered off, the health status information on this page is current as of the last power on.
Health information is updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
The following information is displayed only if AMS is installed and running on the server: Firmware version
and status of add-in network adapters, network-attached storage details, and Smart Storage Battery
status.
If the iLO firmware cannot retrieve the network adapter product name or part number directly from the
device, it attempts to collect that information from AMS.
Procedure
Click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Device Inventory tab.
Device Inventory details
• Location—The device install location.
• Product Name—The device product name.
• Product Part Number—The device part number.
This column displays the value Various when the actual part number of the listed device depends on
internally installed graphics devices that differ by server model.
• Assembly Number—The device part number (Hewlett Packard Enterprise devices) or the EEPROM
Board Info data (third-party devices).
• Serial Number—The device serial number.
• Product Version—The device product version.
62 Logical Network Adapters
Page 63

• Firmware Version—The installed device firmware version.
• Status—The device status.
Device status values
The Device Inventory page uses the following status values:
• OK—The device is working correctly.
• Other—The device status could not be determined.
• No Supporting CPU—The CPU that supports the device slot is not installed.
• Not Installed—A device is not installed.
• Link Down—The network link is down.
• Failed—One or more components of the device are nonoperational.
• Degraded—The device is operating at a reduced capacity.
• Warning—The device is operating at a reduced capacity.
• Unknown—The iLO firmware has not received data about the device status.
Viewing PCI slot details
Procedure
1. Click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Device Inventory tab.
2. Move the cursor over the Location column for a listed PCI slot.
PCI slot tooltip details
• Type—The PCI slot type.
• Bus Width—The PCI slot bus width.
• Length—The PCI slot length.
• Characteristics 1—Information about the PCI slot, for example, voltage and other support
information.
• Characteristics 2—Information about the PCI slot, for example, voltage and other support
information.
Viewing storage information
If the server is powered off, the system health information on this page is current as of the last power off.
Health information is updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
To view a full set of data on this page, ensure that AMS is installed and running. SAS/SATA controller
information is displayed only if AMS is installed and running on the server.
Device status values 63
Page 64

The information displayed on this page depends on your storage configuration. Some storage
configurations will not display information for every category.
Fibre Channel adapters are not listed on this page. To view information about Fibre Channel adapters,
click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Network tab.
Procedure
1. Click System Information in the navigation tree, and then click the Storage tab.
2. Optional: To expand or collapse the data, click Expand All or Collapse All, respectively.
3. Smart Array controllers only: For the controller you want to view, select one of the following options:
• Logical View—View configured logical drives and associated physical drives. This view does not
show physical drives that are not configured as part of an array, or spare drives.
• Physical View—View physical drives. This view does not show logical drives.
Supported storage components
The Storage Information page displays information about the following storage components:
• Smart Array controllers, drive enclosures, the attached logical drives, and the physical drives that
constitute the logical drives.
• Hewlett Packard Enterprise and third-party storage controllers that manage direct-attached storage,
and the attached physical drives.
iLO 5 supports the following products:
◦ HPE ML/DL Server M.2 SSD Enablement Kit
◦ HPE 12G SAS Expander
◦ HPE Dual 8GB MicroSD EM USB Kit
◦ NVMe drives
Smart Array controllers are listed first on the page, followed by other Hewlett Packard Enterprise and
third-party storage controllers.
Smart Array details
iLO displays information about controllers, enclosures, logical drives, and physical drives.
iLO can monitor 256 physical drives total and 256 logical drives total.
Controllers
This section provides the following details for each Smart Array controller.
• Controller location—Slot number or system board
• Top-level controller status (displayed on the left of the controller location)—A combination of the
controller hardware status and the status of cache modules, enclosures, and physical, logical, and
spare drives associated with the controller. If the controller hardware status is OK, and any associated
hardware has a failure, the top-level controller status changes to Major Warning or Degraded,
64 Supported storage components
Page 65

depending on the failure type. If the controller hardware has a Failed status, the top-level controller
status is Failed.
• Controller Status—Controller hardware status (OK or Failed)
• Serial Number
• Model
• Firmware Version
• Controller Type
• Cache Module Status
• Cache Module Serial Number
• Cache Module Memory
• Encryption Status—Indicates whether encryption is enabled in the controller.
The following values are possible:
◦ Enabled
◦ Not Enabled
◦ Enabled-Local Mode—This value is displayed when you do not use a remote key management
server.
• Encryption ASIC Status—Indicates whether the ASIC encryption self tests for the controller passed
or failed. A failed status indicates that the controller is not encrypted.
• Encryption Critical Security Parameter NVRAM Status—Indicates whether the controller
successfully detected the critical security parameter NVRAM. A failed status means that the controller
is not encrypted.
The encryption settings for a Smart Array controller can be configured by using the Smart Storage
Administrator software.
Drive enclosures
This section provides the following information about the drive enclosures attached to a Smart Array
controller.
• Enclosure port and box numbers
• Status
• Drive Bays—The number of drive bays
• Serial Number
• Model
• Firmware Version
Some enclosures do not have all the listed properties, and some storage configurations do not have drive
enclosures.
Viewing general system information 65
Page 66

Logical drives
When the Logical View option is selected, the following information is listed for the logical drives
attached to a Smart Array controller.
• Logical drive number
• Status
• Capacity
• Fault Tolerance
• Logical Drive Type
• Encryption Status
Logical drives must be configured through the Smart Storage Administrator software before they can be
displayed on this page.
Physical drives
The information listed in this section depends on whether the Logical View or Physical View option is
selected. In the Logical View, physical drives that are configured as part of an array are listed. In the
Physical View, all physical drives are listed.
When a physical drive has a Failed status, this status does not affect the overall storage health status.
Only logical drives affect the storage health status.
The following information is listed for the physical drives attached to a Smart Array controller:
• Physical drive port, box, and bay numbers
• Status
• Serial Number
• Model
• Media Type
• Capacity
• Location
• Firmware Version
• Drive Configuration
• Encryption Status
Direct-attached storage details
Controllers
This section provides the following information about the Hewlett Packard Enterprise and third-party
storage controllers that manage direct-attached storage.
• Controller location
• Top-level controller status—The top-level controller status (displayed on the left of the controller
location) is a combination of the controller hardware status and the status of the enclosures, physical
drives, and spare drives associated with the controller. If the controller hardware status is OK, and any
66 Direct-attached storage details
Page 67

associated hardware has a failure, the top-level controller status changes to Major Warning or
Degraded, depending on the failure type. If the controller hardware has a Failed status, the top-level
controller status is Failed.
• Controller Status—Controller hardware status (OK or Failed)
• Serial Number
• Model
• Firmware Version
• Controller Type
Physical Drives
This section provides information about physical drives attached to Hewlett Packard Enterprise and thirdparty storage controllers.
When a physical drive has a Failed status, this status does not affect the overall storage health status.
Only logical drives affect the storage health status.
• Physical drive location
• Status
• Serial Number
• Model
• Media Type
• Capacity
• Location
• Firmware Version
• Drive Configuration
• Encryption Status
Viewing general system information 67
Page 68

Managing firmware, OS software, and language packs
Firmware updates
Firmware updates enhance server and iLO functionality with new features, improvements, and security
updates.
You can update firmware by using an online or offline firmware update method.
Online firmware update
When you use an online method to update firmware, you can perform the update without shutting down
the server operating system. Online firmware updates can be performed in-band or out-of-band.
In-band
Firmware is sent to iLO from the server host operating system.
The iLO 5 Channel Interface Driver is required for in-band firmware updates.
During a host-based firmware update, if iLO is set to the Production security state, it does not verify
user credentials or privileges because the host-based utilities require a root (Linux and VMware) or
Administrator (Windows) login.
When iLO is configured to use the HighSecurity, FIPS, or SuiteB security states, user credentials are
required.
When you use HPONCFG version 5.1.0 or later with iLO 5 1.15 or later, you must have the following
privileges: Login, Configure iLO Settings, and Administer User Accounts.
The iLO Online ROM Flash Component and HPONCFG are examples of online in-band firmware
update methods.
Out-of-band
Firmware is sent to iLO over a network connection. Users with the Configure iLO Settings privilege
can update firmware by using an out-of-band method. If the system maintenance switch is set to
disable iLO security, any user can update firmware with an out-of-band method.
The iLO web interface, HPQLOCFG, HPLOMIG, the iLO RESTful API, LOCFG.PL, and SMASH CLP
are examples of online out-of-band firmware update methods.
Online firmware update methods
In-band firmware updates
• Online ROM Flash Component—Use an executable file to update firmware while the server is
running. The executable file contains the installer and the firmware package.
You can download online ROM flash components for iLO and server firmware at the following
website: http://www.hpe.com/support/ilo5.
This option is supported when iLO is configured to use the Production security state.
• HPONCFG—Use this utility to update firmware by using XML scripts. Download the iLO or server
firmware image and the Update_Firmware.xml sample script. Edit the sample script with your
setup details, and then run the script.
68 Managing firmware, OS software, and language packs
Page 69

Sample scripts are available at http://www.hpe.com/support/ilo5. For more information about
scripting, see the iLO scripting and CLI guide.
When iLO is configured to use the SuiteB security state, only HPONCFG for Linux is supported.
Out-of-band firmware updates
• iLO web interface—Download a supported firmware file and install it by using the iLO web
interface. You can update firmware for a single server or an iLO Federation group.
• iLO RESTful API—Use the iLO RESTful API and a REST client such as the RESTful Interface
Tool to update firmware.
For more information, see http://www.hpe.com/info/restfulinterface/docs.
• HPQLOCFG—Use this utility to update firmware by using XML scripts. Download the iLO or server
firmware image and the Update_Firmware.xml sample script. Edit the sample script with your
setup details, and then run the script.
Sample scripts are available at http://www.hpe.com/support/ilo5. For more information about
scripting, see the iLO scripting and CLI guide.
• HPLOMIG (also called Directories Support for ProLiant Management Processors)—You do not
need to use directory integration to take advantage of the HPLOMIG firmware update capabilities.
HPLOMIG can be used to discover multiple iLO processors and update their firmware in one step.
• SMASH CLP—Access SMASH CLP through the SSH port, and use standard commands to view
firmware information and update firmware.
For more information about SMASH CLP, see the iLO scripting and CLI guide.
Offline firmware update
When you use an offline method to update the firmware, you must reboot the server by using an offline
utility.
The SPP, SUM, the Scripting Toolkit for Windows, and the Scripting Toolkit for Linux are examples of
offline firmware update methods.
Offline firmware update methods
You can use the following offline firmware update methods:
SPP
Use the SPP to install firmware. For more information, see the following website: http://
www.hpe.com/info/spp/documentation.
SUM
SUM is a tool for firmware, driver, and software maintenance on supported servers and other nodes.
You can use SUM together with iLO to access the iLO Repository and manage install sets and the
installation queue.
Scripting Toolkit
Use the Scripting Toolkit to configure several settings within the server and update firmware. This
method is useful for deploying to multiple servers. For instructions, see the Scripting Toolkit user
guide for Windows or Linux.
Offline firmware update 69
Page 70

Viewing and updating firmware from the iLO web interface
The iLO web interface supports the following firmware and software management features:
• Viewing installed firmware.
• Viewing installed software.
• Using the Flash Firmware controls to install firmware on the local managed server.
• Using the Group Firmware Update feature to install firmware on multiple servers in an iLO Federation
group.
• Accessing the iLO with integrated Smart Update features. This version of iLO supports the following
actions:
◦ Manage the iLO Repository and add saved components to the installation queue.
◦ View and remove install sets and add them to the installation queue.
Use SUM to configure install sets. For more information, see the SUM documentation.
◦ View and remove components from the installation queue.
The best practice is to use SUM to manage the installation queue. You can use the iLO web
interface to update the queue by adding or removing an individual component. For more
information, see the SUM documentation.
You can access the iLO Repository and the Flash Firmware controls from all tabs on the Firmware & OS
Software page.
Updating iLO or server firmware by using the Flash Firmware feature
You can update firmware from any network client by using the iLO web interface. A signed file is required.
You can also initiate a component update from the iLO Repository page.
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Obtain an iLO firmware or server firmware file.
2. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click Update Firmware.
If the Update Firmware option is not displayed, click the ellipsis icon in the top right corner of the iLO
web interface, then click Update Firmware.
3. Select the Local file or Remote file option.
4. Depending on the option you selected, do one of the following:
• In the Local binary file box, click Browse (Internet Explorer or Firefox) or Choose Files
(Chrome), and then specify the location of the firmware component.
• In the Remote binary file URL box, enter the URL for a firmware component on an accessible
web server.
70 Viewing and updating firmware from the iLO web interface
Page 71

5. Optional: To save a copy of the component to the iLO Repository, select the Also store in iLO
Repository check box.
6. To start the update process, click Flash.
Depending on the server configuration, iLO notifies you that:
• When you update the iLO firmware, iLO will reboot automatically.
Some types of server firmware might require a server reboot, but the server will not reboot
automatically.
• A TPM or TM is installed in this server. Before you initiate a system ROM or iLO firmware update,
suspend or back up any software that stores information on the TPM or TM. For example, if you
use drive encryption software, suspend it before initiating a firmware update. Failure to follow
these instructions might result in losing access to your data.
7. Do one of the following:
• If a TPM or TM message was not displayed, click OK.
• If a TPM or TM message was displayed, verify that any software that stores data on the TPM or
TM is suspended or backed up, and then click OK.
The iLO firmware receives, validates, and then flashes the firmware image.
When you update the iLO firmware, iLO reboots and closes your browser connection. It might take
several minutes before you can re-establish a connection.
8. For iLO firmware updates only: To start working with the new firmware, clear your browser cache,
and then log in to iLO.
9. For server firmware updates only: If the firmware type requires a system reset or server reboot for
the new firmware to take effect, take the appropriate action. For more information, see
Requirements for firmware update to take effect on page 72.
10. Optional: To confirm that the new firmware is active, check the firmware version on the Installed
Firmware page.
You can also check the iLO firmware version on the Overview page.
Supported firmware types
Many types of firmware update are supported, depending on the server platform. These types include:
• iLO
• System ROM/BIOS
• Chassis
• Power Management Controller
• Programmable Logic (CPLD)
• Backplane
• Language Packs
Supported firmware types 71
Page 72

Requirements for firmware update to take effect
• iLO firmware or language pack—Requires an iLO reset, which is triggered automatically.
• System ROM (BIOS)—Requires a server reboot.
• Chassis firmware (Power Management) and Edgeline Chassis Controller Firmware—Take effect
immediately.
• System Programmable Logic Device (CPLD)—Requires a server reboot.
• Power Management Controller and NVMe Backplane Firmware—Do not require a server reboot or a
system reset.
The NVMe firmware version will be displayed in the iLO web interface after the next server reboot.
Obtaining the iLO firmware image file
You can download an iLO firmware image file and use it to update a single server or multiple servers in an
iLO Federation group.
The BIN file from the iLO Online ROM Flash Component is required for updating the iLO firmware with the
Flash Firmware or Group Firmware Update features.
Procedure
1. Navigate to the following website: http://www.hpe.com/support/hpesc.
2. To locate and download the iLO Online ROM Flash Component file, follow the onscreen instructions.
Download a Windows or Linux component.
3. Extract the BIN file.
• For Windows components: Double-click the downloaded file, and then click the Extract button.
Select a location for the extracted files, and then click OK.
• For Linux components: Depending on the file format, enter one of the following commands:
◦ #sh ./CP00XXXX.scexe –unpack=/tmp/
◦ #rpm2cpio <firmware_file_name>.rpm | cpio -id
The name of the iLO firmware image file is similar to iLO 5_<yyy>.bin, where <yyy> represents
the firmware version.
Obtaining supported server firmware image files
Procedure
1. Navigate to the following website: http://www.hpe.com/support/hpesc.
2. To locate and download an Online ROM Flash Component file, follow the onscreen instructions.
3. Double-click the downloaded file, and then click the Extract button.
4. Select a location for the extracted files, and then click OK.
72 Requirements for firmware update to take effect
Page 73

Server firmware file type details
• When you update the system ROM, you must use a signed image or the signed ROMPAQ image:
◦ Signed image example:
http://<server.example.com:8080>/<wwwroot>/P79_1.00_10_25_2013.signed.flash
◦ Signed ROMPAQ image example:
http://<server.example.com>/<wwwroot>/CPQPJ0612.A48
• The Power Management Controller, chassis firmware, and NVMe backplane files use the file
extension .hex. For example, the file name might be similar to ABCD5S95.hex.
• The System Programmable Logic Device (CPLD) firmware file uses the file extension .vme.
Viewing installed firmware information
Procedure
Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree.
The Installed Firmware page displays firmware information for various server components. If the server
is powered off, the information on this page is current as of the last power off. Firmware information is
updated only when the server is powered on and POST is complete.
Firmware types
The firmware types listed on the Installed Firmware page vary based on the server model and
configuration.
For most servers, the system ROM and iLO firmware are listed. Other possible firmware options include
the following:
• Power Management Controller
• Server Platform Services Firmware
• Smart Array
• Intelligent Platform Abstraction Data
• Smart Storage Battery
• TPM or TM firmware
• SAS Programmable Logic Device
• System Programmable Logic Device
• Intelligent Provisioning
• Networking adapters
• NVMe Backplane firmware
• Innovation Engine (IE) firmware
• Drive firmware
Viewing installed firmware information 73
Page 74

• Power Supply firmware
• Embedded Video Controller
Firmware details
The Installed Firmware page displays the following information for each listed firmware type:
• Firmware Name—The name of the firmware.
• Firmware Version—The version of the firmware.
• Location—The location of the component that uses the listed firmware.
Replacing the active system ROM with the redundant system ROM
Prerequisites
• The server supports redundant system ROM.
• Virtual Power and Reset privilege
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree.
2. On the Installed Firmware page, click the swap icon next to the Redundant System ROM details.
iLO prompts you to confirm the request.
3. Click OK.
The change will take effect after the next server reboot.
iLO Repository
The iLO Repository is a secure storage area in the nonvolatile flash memory embedded on the system
board. This flash memory is called the iLO NAND. Use SUM or iLO to manage signed software and
firmware components in the iLO Repository.
iLO, the UEFI BIOS, SUM, and other client software can retrieve these components and apply them to
supported servers. Use SUM to organize the stored components into install sets and SUM or iLO to
manage the installation queue.
To learn more about how iLO, SUM, and the BIOS work together to manage software and firmware, see
the SUM documentation.
Adding a component to the iLO Repository
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click Upload to iLO Repository.
74 Firmware details
Page 75

If the Upload to iLO Repository option is not displayed, click the ellipsis icon in the top right corner of
the iLO web interface, then click Upload to iLO Repository.
2. Select the Local file or Remote file option.
3. Depending on the option you selected, do one of the following:
• In the Local binary file box, click Browse (Internet Explorer or Firefox) or Choose Files (Chrome),
and then specify the location of the firmware component.
• In the Remote binary file URL box, enter the URL for a firmware component on an accessible web
server.
4. For firmware components specified by multiple files only: Select the I have a component signature
file check box.
5. If you selected the check box in the previous step, do one of the following:
• In the Local component signature file box, click Browse (Internet Explorer or Firefox) or Choose
Files (Chrome), and then specify the location of the component signature file.
• In the Remote component signature file URL box, enter the URL for a component signature file
on an accessible web server.
6. Click Upload.
iLO notifies you that uploading a component with the same name as an existing component will
replace the existing component. Components that are part of the Recovery Set are protected and
cannot be replaced by uploading a new component with the same name. To replace a Recovery Set
component, log in with an account that has the Recovery Set privilege, and then delete the recovery
install set.
7. Click OK.
The upload starts. The upload status is displayed at the top of the iLO web interface.
Installing a component from the iLO Repository
You can add a component to the installation queue from the iLO Repository page.
When you add a component to the installation queue, it is added to the end of the queue. After other
queued items are complete, the added component is installed when the software that initiates updates for
the component type detects the installation request. To determine the software that can initiate an update,
check the component details on the iLO Repository and Installation Queue pages.
If a component in a previously queued task is waiting to start or finish, a new queued component might be
delayed indefinitely. For example, if a queued update must wait until the UEFI BIOS detects it during
server POST, but the server is not restarted, then the updates that follow in the queue will not be installed.
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click iLO Repository.
2. Click the install component icon next to the component you want to install.
Installing a component from the iLO Repository 75
Page 76

iLO notifies you that the component will be added to the end of the installation queue, and prompts
you to confirm the request.
3. Click Yes, add to the end of the queue.
If the installation queue is empty, and iLO can initiate the component installation, the button is labeled
Yes, install now.
The update is initiated after existing queued tasks finish and the software that initiates installation for
the selected component type detects a pending installation.
If the installation queue is empty and iLO can initiate the update, the update begins immediately.
Removing a component from the iLO Repository
Prerequisites
• Configure iLO Settings privilege
• The component is not in an install set.
• The component is not part of a queued task.
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click the iLO Repository tab.
2. Click the remove component icon .
iLO prompts you to confirm the request.
3. Click Yes, remove.
The component is removed.
Viewing iLO Repository summary and component details
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click the iLO Repository tab.
2. Optional: To view detailed component information, click an individual component.
iLO Repository details
iLO Repository storage details
The Summary section of the iLO Repository page displays the following details about the iLO
Repository storage use:
• Capacity—Total iLO Repository storage capacity
• In use—Used storage
• Free space—Available iLO Repository storage
• Components—Number of saved components in the iLO Repository
76 Removing a component from the iLO Repository
Page 77

iLO Repository contents
The Contents section of the iLO Repository page displays the following details about each firmware or
software component:
• Name
• Version
iLO Repository individual component details
When you click an individual component, the following details are displayed:
• Name—Component name
• Version—Component version
• File name—Component file name
• Size—Component size
• Uploaded—Upload date and time
• Installable by—The software that can initiate an update with the component.
• In use by install set or task?—Whether the component is part of an install set.
Install Sets
An install set is a group of components that can be applied to supported servers with a single command.
Use SUM to create install sets. You can use iLO to view existing install sets in the iLO web interface.
Saving an install set when you deploy from SUM keeps all the components on the iLO system for
immediate use at a later time to restore or roll back a component version without needing to find the
original SPP.
To learn more about how iLO, SUM, and the BIOS work together to manage software and firmware, see
the SUM documentation.
Installing an install set
You can add an install set to the installation queue from the Install Sets page.
When you add an install set to the installation queue, iLO adds a task to the end of the installation queue
for each component or command in the install set. After other queued items are complete, the install set
contents are installed when the software that initiates updates for each component type detects the
installation request. To determine the software that can initiate an update, check the component details.
If a component in a previously queued task is waiting to start or finish, a new queued component might be
delayed indefinitely. For example, if a queued update must wait until the UEFI BIOS detects it during
server POST, but the server is not restarted, then the updates that follow in the queue will not be installed.
Prerequisites
• Configure iLO Settings privilege
• No components in the install set are queued as part of another installation task.
Install Sets 77
Page 78

Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click Install Sets.
2. Click the install icon next to the install set you want to install.
iLO notifies you that the contents of the install set will be added to the end of the installation queue,
and prompts you to confirm the request.
3. Click Yes, add to the end of the queue.
If the installation queue is empty, and iLO can initiate the updates in the install set, the button is
labeled Yes, install now.
The updates are initiated after existing queued tasks finish and the software that initiates installation
for the selected component types detects a pending installation.
If the installation queue is empty and iLO can initiate the requested updates, the update begins
immediately.
Removing an Install Set
Prerequisites
• Configure iLO Settings privilege for unprotected install sets.
• Recovery Set privilege for removing the protected install set.
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click Install Sets.
2. Click the remove install set icon .
iLO prompts you to confirm the request.
3. Click Yes, remove.
The install set is removed.
Viewing Install Sets
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click the Install Sets tab.
2. Optional: Click an install set to view detailed information.
Install Set details
Install Set summary details
The Install Sets tab displays the following details about each install set:
• Name—The install set name.
• Components/Commands—The components and commands in the install set.
78 Removing an Install Set
Page 79

Use the install set icons to add an install set to the installation queue or to remove an install set. The
protected install set is displayed with a lock icon.
Individual install set details
When you click an individual install set, the following details are displayed:
• Name—The install set name.
• Created—The creation date and time.
• Description—A description of the install set.
• Component/Commands—The components and commands in the install set.
• System Recovery Set?—Indicates whether the install set can be edited or deleted. This status is
used for the System Recovery Set. Only one System Recovery Set can exist at a time.
System Recovery Set
By default, a System Recovery Set is included with every server. User accounts with the Recovery Set
privilege can configure this install set.
The following firmware components are included in the default System Recovery Set:
• System ROM (BIOS)
• iLO firmware
• System Programmable Logic Device (CPLD)
• Innovation Engine
• Server Platform Services (SPS) Firmware
If the default System Recovery Set is deleted, a user with the Recovery Set privilege can use SUM to
create an install set, and then designate it as the System Recovery Set by using the iLO RESTful API.
For instructions, see the SUM user guide. Only one System Recovery Set can exist at a time.
Installation Queue
The installation queue is an ordered list of components that were added to the queue individually or as
parts of an install set. Use SUM to manage the queue. You can view queued tasks and add single
components to the queue from the iLO web interface.
When you add a component to the installation queue, it is added to the end of the queue. After other
queued items are complete, the added component is installed when the software that initiates updates for
the component type detects the installation request. To determine the software that can initiate an update,
check the component details on the iLO Repository and Installation Queue pages.
If a component in a previously queued task is waiting to start or finish, a new queued component might be
delayed indefinitely. For example, if a queued update must wait until the UEFI BIOS detects it during
server POST, but the server is not restarted, then the updates that follow in the queue will not be installed.
To learn more about how iLO, SUM, and the BIOS software work together to manage software and
firmware, see the SUM documentation.
System Recovery Set 79
Page 80

Viewing the Installation Queue
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click the Installation Queue tab.
2. Optional: To view detailed information, click an individual task.
Queued task details
Task summary details
The Installation Queue tab displays the following details about each task:
State
Status of the task. The possible values follow:
• In progress—The task is being processed.
• Expired—The task is expired. Subsequent tasks will not run until this task is removed from the
queue.
• Exception—The task could not complete. Subsequent tasks will not run until this task is removed
from the queue.
• Complete—The task completed successfully.
• Pending—The task will run when the software that initiates updates for the component type
detects the installation request.
Name
The task name.
Starts
The task start date and time.
Expires
The task expiration date and time.
Individual task details
When you click an individual task, the following details are displayed:
• Name—The task name.
• State—Task status.
• Result—Task results, if available.
• Installable by—The software that can initiate an update with the selected component.
• Start time—The task start date and time.
• Expiration—The task expiration date and time.
80 Viewing the Installation Queue
Page 81

Removing a task from the Installation Queue
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click Installation Queue.
2. Click the remove component icon .
iLO prompts you to confirm the request.
3. Click Yes, remove.
The component is removed.
Installing language packs
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Download a language pack from the following website: http://www.hpe.com/support/ilo5.
2. To extract the contents, double-click the downloaded file.
The language pack file name is similar to the following: lang_<language>_<version>.lpk.
3. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click Update Firmware.
The Flash Firmware controls appear.
4. Click Browse (Internet Explorer or Firefox) or Choose Files (Chrome).
5. Select a language pack, and then click Open.
6. Optional: To save a copy of the language pack file to the iLO Repository, select the Also store in iLO
Repository check box.
7. Click Flash.
iLO prompts you to confirm the installation request.
8. Click OK.
iLO installs the selected language pack, reboots, and closes your browser connection.
It might take several minutes before you can re-establish a connection.
Viewing software information
Prerequisites
To display a complete set of data on this page, AMS must be installed.
Removing a task from the Installation Queue 81
Page 82

Procedure
1. Click Firmware & OS Software in the navigation tree, and then click the Software tab.
2. Optional: To update the software information data, click .
The information on this page is cached in the browser, and iLO displays the date and time of the last
update. If 5 minutes or more have passed since the page was updated, click to update the page
with the latest information.
Product-related Software details
This section lists all the HPE software on the managed server. The list includes Hewlett Packard
Enterprise and Hewlett Packard Enterprise-recommended third-party software that was added manually
or by using the SPP.
• Name—The name of the software.
• Version—The software version.
The versions of the displayed firmware components indicate the firmware versions available in the
firmware flash components that are saved on the local operating system. The displayed version might
not match the firmware running on the server.
• Description—A description of the software.
Running Software details
This section lists all the software that is running or available to run on the managed server.
• Name—The name of the software.
• Path—The file path of the software.
Installed Software details
The Installed Software list displays the name of each installed software program.
82 Product-related Software details
Page 83

Configuring and using iLO Federation
iLO Federation
iLO Federation enables you to manage multiple servers from one system using the iLO web interface.
When configured for iLO Federation, iLO uses multicast discovery and peer-to-peer communication to
enable communication between the systems in an iLO Federation group.
When an iLO Federation page loads, a data request is sent from the iLO system running the web
interface to its peers, and from those peers to other peers until all data for the selected iLO Federation
group is retrieved.
iLO supports the following features:
• Group health status—View server health and model information.
• Group Virtual Media—Connect scripted media for access by the servers in an iLO Federation group.
• Group power control—Manage the power status of the servers in an iLO Federation group.
• Group power capping—Set dynamic power caps for the servers in an iLO Federation group.
• Group firmware update—Update the firmware of the servers in an iLO Federation group.
• Group license installation—Enter a license key to activate iLO licensed features on the servers in an
iLO Federation group.
• Group configuration—Add iLO Federation group memberships for multiple iLO systems.
Any user can view information on iLO Federation pages, but a license is required for using the following
features: Group Virtual Media, Group power control, Group power capping, Group configuration, and
Group firmware update.
Configuring iLO Federation
Prerequisites for using the iLO Federation features
Procedure
• The network configuration meets the iLO Federation requirements.
• The multicast options are configured for each iLO system that will be added to an iLO
Federation group.
If you use the default multicast option values, configuration is not required.
• iLO Federation group memberships are configured.
All iLO systems are automatically added to the DEFAULT group.
• Enclosure support for iLO Federation is configured in the Onboard Administrator software (ProLiant
server blades only).
This setting is enabled by default.
For more information, see the iLO Federation user guide.
Configuring and using iLO Federation 83
Page 84

iLO Federation network requirements
• Servers that will be used with iLO Federation must use the iLO Dedicated Network Port configuration.
The iLO Federation features cannot be used with the iLO Shared Network Port configuration.
• Optional: iLO Federation supports both IPv4 and IPv6. If both options have valid configurations, you
can configure iLO to use IPv4 instead of IPv6. To configure this setting, clear the iLO Client
Applications use IPv6 first check box on the iLO Dedicated Network Port - IPv6 Settings page.
• Configure the network to forward multicast traffic if you want to manage iLO systems in multiple
locations.
• Ensure that multicast traffic is enabled if the switches in your network include the option to enable or
disable it. This configuration is required for iLO Federation and other Hewlett Packard Enterprise
products to discover the iLO systems on the network.
• For iLO systems that are separated by Layer 3 switches, configure the switches to forward SSDP
multicast traffic between networks.
• Configure the network to allow multicast traffic (UDP port 1900) and direct HTTP (TCP default port 80)
communication between iLO systems.
• For networks with multiple VLANs, configure the switches to allow multicast traffic between the
VLANs.
• For networks with Layer 3 switches:
◦ For IPv4 networks: Enable PIM on the switch and configure it for PIM Dense Mode.
◦ For IPv6 networks: Configure the switch for MLD snooping.
Configuring the multicast options for one iLO system at a time
Use the following procedure to configure the multicast options for each iLO system that will be added to
an iLO Federation group. If you use the default values, configuration is not required.
You can use the iLO RESTful API or RIBCL scripts to view and configure multicast options for multiple
iLO systems.
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree.
The Setup tab is displayed.
2. For iLO Federation Management, select Enabled or Disabled.
3. For Multicast Discovery, select Enabled or Disabled.
4. Enter a value for Multicast Announcement Interval (seconds/minutes).
5. Select a value for IPv6 Multicast Scope.
To ensure that multicast discovery works correctly, make sure that all iLO systems in the same group
use the same value for IPv6 Multicast Scope.
6. Enter a value for Multicast Time To Live (TTL).
84 iLO Federation network requirements
Page 85

To ensure that multicast discovery works correctly, make sure that all iLO systems in the same group
use the same value for Multicast Time to Live (TTL).
7. Click Apply.
Network changes and changes you make on this page take effect after the next multicast
announcement.
Multicast options
• iLO Federation Management—Enables or disables the iLO Federation features. The default setting
is Enabled. Selecting Disabled disables the iLO Federation features for the local iLO system.
• Multicast discovery—Enables or disables multicast discovery. The default setting is Enabled.
Selecting Disabled disables the iLO Federation features for the local iLO system.
Disabling multicast discovery is not supported on Synergy compute modules. To limit the impact of
multicast traffic on a network with Synergy compute modules, adjust the IPv6 Multicast Scope and
Multicast Time To Live (TTL) settings.
• Multicast Announcement Interval (seconds/minutes)—Sets the frequency at which the iLO system
announces itself on the network. Each multicast announcement is approximately 300 bytes. Select a
value of 30 seconds to 30 minutes. The default value is 10 minutes. Selecting Disabled disables the
iLO Federation features for the local iLO system.
• IPv6 Multicast Scope—The size of the network that will send and receive multicast traffic. Valid
values are Link, Site, and Organization. The default value is Site.
• Multicast Time To Live (TTL)—Specifies the number of switches that can be traversed before
multicast discovery stops. The default value is 5.
iLO Federation groups
iLO Federation group memberships for local iLO systems
When you configure group memberships for a local iLO system, you specify the privileges that members
of a group have for configuring the local managed server.
For example, if you add the local iLO system to group1 and assign the Virtual Power and Reset privilege,
the users of other iLO systems in group1 can change the power state of the managed server.
If the local iLO system does not grant the Virtual Power and Reset privilege to group1, the users of other
iLO systems in group1 cannot use the group power control features to change the power state of the
managed server.
If the system maintenance switch is set to disable iLO security on the local iLO system, the users of other
iLO systems in group1 can change the state of the managed server, regardless of the assigned group
privileges.
Group memberships for the local iLO system are configured on the iLO Federation page Setup tab.
You can perform the following tasks for a local iLO system:
• View group memberships.
• Add and edit group memberships.
• Remove group memberships.
Multicast options 85
Page 86

iLO Federation group memberships for a set of iLO systems
When you add group memberships for multiple iLO systems at one time, you specify the privileges that
members of the group have for configuring the other members of the group.
For example, if you configure group2 based on the DEFAULT group, and you assign the Virtual Power
and Reset privilege, the users of iLO systems in group2 can change the power state of all the servers in
the group.
You can add group memberships for multiple iLO systems on the Group Configuration page.
You can perform the following tasks for a group of iLO systems:
• Create a group with the same members as an existing group, but with different privileges.
• Create a group with members that you select by using the iLO Federation filters.
iLO Federation group privileges
When an iLO system is added to a group, the group can be granted the following privileges:
• Login— Group members can log in to iLO.
• Remote Console—Group members can remotely access the managed server Remote Console,
including video, keyboard, and mouse control.
• Virtual Power and Reset—Group members can power-cycle or reset the host system. These
activities interrupt the system availability.
• Virtual Media—Group members can use scripted Virtual Media with the managed server.
• Host BIOS—Group members can configure the host BIOS settings by using the UEFI System
Utilities.
• Configure iLO Settings—Group members can configure most iLO settings, including security
settings, and can remotely update firmware.
• Administer User Accounts—Group members can add, edit, and delete iLO user accounts.
• Host NIC—Group members can configure the host NIC settings.
• Host Storage—Group members can configure the host storage settings.
• Recovery Set—Group members can manage the recovery install set.
This privilege is not available if you start a session when the system maintenance switch is set to
disable iLO security.
iLO Federation group characteristics
• All iLO systems are automatically added to the DEFAULT group, which is granted the Login privilege
for each group member. You can edit or delete the DEFAULT group membership.
• iLO Federation groups can overlap, span racks and data centers, and can be used to create
management domains.
• An iLO system can be a member of up to 10 iLO Federation groups.
86 iLO Federation group memberships for a set of iLO systems
Page 87

• There is no limit on the number of iLO systems that can be in a group.
• You must have the Configure iLO Settings privilege to configure group memberships.
• You can use the iLO web interface to configure group memberships for a local iLO system or a group
of iLO systems.
• You can use RIBCL XML scripts to view and configure group memberships.
For more information, see the iLO Federation user guide.
• You can use the iLO RESTful API to configure group memberships.
For more information, see the iLO RESTful API documentation at the following website: http://
www.hpe.com/support/restfulinterface/docs.
• Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends installing the same version of the iLO firmware on iLO
systems that are in the same iLO Federation group.
Managing iLO Federation group memberships (local iLO system)
Viewing iLO Federation group memberships (local iLO system)
Procedure
Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree.
You can also use RIBCL scripts to view information about groups. For more information, see the iLO
Federation user guide.
The Group Membership for this iLO table lists the name of each group that includes the local iLO
system, and the privileges granted to the group by the local iLO system.
Adding iLO Federation group memberships
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree.
The Setup tab is displayed.
2. Click Join Group.
3. Enter the following information:
• Group Name—The group name, which can be 1 to 31 characters long.
• Group Key—The group password, which can be from the configured minimum password length to
31 characters long.
• Group Key Confirm—Confirm the group password.
Managing iLO Federation group memberships (local iLO system) 87
Page 88

If you enter the name and key for an existing group, the local iLO system is added to that group. If you
enter the name and key for a group that does not exist, the group is created and the local iLO system
is added to the new group.
4. Select from the following privileges:
• Login
• Remote Console
• Virtual Power and Reset
• Virtual Media
• Host BIOS
• Configure iLO Settings
• Administer User Accounts
• Host NIC
• Host Storage
• Recovery Set
The privileges granted to the group by the local iLO system control the tasks that users of other iLO
systems in the group can perform on the managed server.
5. Click Join Group.
Editing iLO Federation group memberships
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree.
The Setup tab displays the existing group memberships for the local iLO system.
2. Select a group membership, and then click Edit.
3. To change the group name, enter a new name in the Group Name box.
The group name can be 1 to 31 characters long.
4. To change the group key, select the Change Group Key check box, then enter a new value in the
Group Key and Group Key Confirm boxes.
The group key can be from the configured minimum password length to 31 characters long.
5. Select or clear the check boxes for the privileges you want to update.
The privileges granted to the group by the local iLO system control the tasks that users of other iLO
systems in the group can perform on the managed server.
For more information about the available privileges, see iLO Federation group privileges on page
86.
88 Editing iLO Federation group memberships
Page 89

6. Click Update Group.
7. If you updated the group name or group key, update them on the other systems in the affected group.
Removing a local iLO system from an iLO Federation group
Prerequisites
Configure iLO Settings privilege
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree.
The Setup tab shows the group membership for the local iLO system.
2. Select the check box next to the group membership that you want to delete.
3. Click Delete.
4. When prompted to confirm the request, click OK.
Adding iLO Federation group memberships (multiple iLO systems)
Adding an iLO Federation group based on an existing group
Use this procedure to create an iLO Federation group with the same members as an existing group. For
example, you might want to create a group that contains the same systems that are in the DEFAULT
group, but with different privileges.
Prerequisites
• Configure iLO Settings privilege
• An iLO license that supports this feature is installed.
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Configuration tab.
If no iLO Federation groups exist, this page displays the following message: There are no
configured groups. Use the iLO Federation Setup page to create a group.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
All of the systems in the selected group will be added to the group you create on this page.
3. Enter the following information:
• Group Name—The group name, which can be 1 to 31 characters long.
• Group Key—The group password, which can be from the configured minimum password length to
31 characters long.
• Group Key Confirm—Confirm the group password.
If you enter the name of a group that exists, iLO prompts you to enter a unique group name.
4. Select from the following privileges:
Removing a local iLO system from an iLO Federation group 89
Page 90

• Administer User Accounts
• Remote Console Access
• Virtual Power and Reset
• Virtual Media
• Configure iLO Settings
• Login Privilege
This step defines the privileges that members of the group have for configuring the other members of
the group.
5. Optional: Enter the Login Name and Password for a user account on the remote systems you want to
manage.
This information is required if the selected group does not have the Configure iLO Settings privilege on
the remote systems you want to manage.
To enter credentials for multiple remote systems, create a user account with the same login name and
password on each system.
6. Click Create Group.
The group creation process takes a few minutes. The group will be fully populated within the amount
of time configured for the Multicast Announcement Interval.
Creating a group from a filtered set of servers
Use this procedure to create an iLO Federation group from a list of filtered servers. For example, you
might want to create a group that contains all servers with a specific version of the iLO firmware.
When you create a group from a list of filtered servers, only the servers listed in the Affected Systems
list at the time the group is created are added to the group. If you configure servers that meet the filter
criteria after the group is created, they are not added to the group.
Prerequisites
• Configure iLO Settings privilege
• An iLO license that supports this feature is installed.
Procedure
1. Create a set of systems by using the filters on the iLO Federation pages.
2. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Configuration tab.
The filters you apply when you create a set of systems are listed at the top of the page. To remove a
filter, click the filter name.
If no iLO Federation groups exist, this page displays the following message: There are no
configured groups. Use the Setup page to create a group.
3. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
All of the systems in the selected group that meet the selected filter criteria will be added to the new
group.
4. Enter the following information:
90 Creating a group from a filtered set of servers
Page 91

• Group Name—The group name, which can be 1 to 31 characters long.
• Group Key—The group password, which can be from the configured minimum password length to
31 characters long.
• Group Key Confirm—Confirm the group password.
5. Select from the following privileges:
• Administer User Accounts
• Remote Console Access
• Virtual Power and Reset
• Virtual Media
• Configure iLO Settings
• Login Privilege
This step defines the privileges that members of the group have for configuring the other members of
the group.
6. Optional: Enter the Login Name and Password for a user account on the remote systems you want to
manage.
This information is required if the selected group does not have the Configure iLO Settings privilege on
the remote systems you want to manage.
To enter credentials for multiple remote systems, create a user account with the same login name and
password on each system.
7. To save the configuration, click Create Group.
The group creation process takes a few minutes. The group will be fully populated within the amount
of time configured for the Multicast Announcement Interval.
Servers affected by a group membership change
The Affected Systems section on the Group Configuration page provides the following details about
the servers affected when you make a group membership change:
• Server Name—The server name defined by the host operating system.
• Server Power—The server power state (ON or OFF).
• UID Indicator—The state of the UID LED. The UID LED helps you identify and locate a server,
especially in high-density rack environments. The possible states are UID ON, UID OFF, and UID
BLINK.
• iLO Hostname—The fully qualified network name assigned to the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO
web interface for the server, click the link in the iLO Hostname column.
• IP Address—The network IP address of the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO web interface for the
server, click the link in the IP Address column.
Click Next or Prev (if available) to view more servers in the list.
More information
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file on page 93
Servers affected by a group membership change 91
Page 92

Configuring Enclosure iLO Federation Support
If you want to use iLO Federation with server blades in a BladeSystem c-Class enclosure, the Enable
Enclosure iLO Federation Support option must be enabled in the Onboard Administrator software. This
setting is required to allow peer-to-peer communication between the server blades in an enclosure. The
Enable Enclosure iLO Federation Support option is enabled by default.
Procedure
1. Log in to the Onboard Administrator web interface (https://<OA hostname or IP address>).
2. Select Enclosure Information > Enclosure Settings > Network Access in the navigation tree.
The Protocols tab is displayed.
3. Select the Enable Enclosure iLO Federation Support check box, and then click Apply.
You can also use the CLI to enable or disable the Enable Enclosure iLO Federation Support option.
To enable the option, enter ENABLE ENCLOSURE_ILO_FEDERATION_SUPPORT. To disable the
option, enter DISABLE ENCLOSURE_ILO_FEDERATION_SUPPORT. For more information, see the
Onboard Administrator CLI user guide.
Verifying server blade support for iLO Federation
Procedure
1. Log in to the Onboard Administrator web interface (https://<OA hostname or IP address>).
2. Select Device Bays > <Device Name> > iLO in the navigation tree.
3. Verify that iLO Federation Capable is set to Yes.
Using the iLO Federation features
Selected Group list
All of the iLO Federation pages except for Setup have a Selected Group list.
92 Configuring Enclosure iLO Federation Support
Page 93

When you select a group from the Selected Group list:
• The servers affected by a change on the Group Virtual Media, Group Power, Group Firmware
Update, Group Licensing, and Group Configuration pages are listed in the Affected Systems
table.
• The information displayed on iLO Federation pages applies to all the servers in the selected group.
• The changes you make on iLO Federation pages apply to all the servers in the selected group.
• The selected group is saved in a cookie and remains persistent, even when you log out of iLO.
After you select a group, you can filter the servers in the list to view server information or perform actions
on a subset of the servers in the group.
Selected Group list filters
When you filter the list of servers:
• The information displayed on iLO Federation pages applies to all the servers in the selected group that
meet the filter criteria.
• The changes you make on iLO Federation pages apply to all the servers in the selected group that
meet the filter criteria.
• The filter settings are saved in a cookie and remain persistent, even when you log out of iLO.
Selected Group list filter criteria
You can use the following criteria to filter the servers in a group:
• Health status—Click a health status link to select servers with a specific health status.
• Model—Click a server model number link to select servers matching the selected model.
• Server name—Click a server name to filter by an individual server.
• Firmware Information—Click a firmware version or flash status to select servers matching the
selected firmware version or status.
• TPM or TM Option ROM Measuring—Click an Option ROM Measuring status to include or exclude
servers matching the selected Option ROM Measuring status.
• License usage—If an error message related to a license key is displayed, click the license key to
select servers that use that license key.
• License type—Click a license type to select servers with the selected license type installed.
• License status—Click a license status to select servers with an installed license matching the
selected status.
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file
The following iLO Federation pages allow you to export information to a CSV file:
• Multi-System View
• Multi-System Map
• Group Virtual Media
Selected Group list filters 93
Page 94

• Group Power
• Group Firmware Update
• Group Licensing
• Group Configuration
Procedure
1. Navigate to a page that supports the file export feature.
2. Click View CSV.
3. In the CSV Output window, click Save, and then follow the browser prompts to save or open the file.
If multiple pages of servers are included in the list, the CSV file will contain only the servers that are
currently displayed on the iLO web interface page.
If a query error occurred, the systems that did not respond to the query are excluded from the iLO web
interface page and the CSV file.
iLO Federation information export options
You can export the following information from the iLO Federation pages:
Systems with critical or degraded status
Export this list from the Multi-System View page.
iLO peers list
Export this list from the Multi-System Map page.
Affected systems list
Export the list of systems affected by an iLO Federation action on the following pages:
• Group Virtual Media
• Group Power
• Group Firmware Update
• Group Licensing
• Group Configuration
The export feature is not supported on the Group Power Settings page.
iLO Federation Multi-System view
The Multi-System View page provides a summary of the server models, server health, and critical and
degraded systems in an iLO Federation group.
94 iLO Federation information export options
Page 95

Viewing server health and model information
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Multi-System View tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
3. Optional: To filter the list of servers, click a health status, server model, or server name link.
Server health and model details
• Health—The number of servers in each listed health status. The percentage of the total number of
servers in each listed health status is also displayed.
• Model—The list of servers, grouped by model number. The percentage of the total number of servers
for each model number is also displayed.
• Critical and Degraded Systems—The list of servers in the critical or degraded state.
Viewing servers with critical and degraded status
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Multi-System View tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
3. Optional: To filter the list of servers, click a health status, server model, or server name link.
4. Click Next or Previous (if available) to view more servers in the Critical and Degraded Systems list.
More information
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file on page 93
Critical and degraded server status details
• Server Name—The server name defined by the host operating system.
• System Health—The server health status.
• Server Power—The server power status (ON or OFF).
• UID Indicator—The state of the server UID LED. The UID LED helps you identify and locate a server,
especially in high-density rack environments. The possible states are UID ON, UID OFF , and UID
BLINK.
• System ROM—The installed System ROM version.
• iLO Hostname—The fully qualified network name assigned to the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO
web interface for the server, click the link in the iLO Hostname column.
• IP Address—The network IP address of the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO web interface for the
server, click the link in the IP Address column.
Viewing server health and model information 95
Page 96

Viewing the iLO Federation Multi-System Map
The Multi-System Map page displays information about the peers of the local iLO system. The local iLO
system identifies its peers through multicast discovery.
When an iLO Federation page loads, a data request is sent from the iLO system running the web
interface to its peers, and from those peers to other peers until all the data for the selected group is
retrieved.
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Multi-System Map tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
More information
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file on page 93
iLO peer details
• #—The peer number.
• iLO UUID—The iLO system UPnP UUID.
• Last Seen—The time stamp of the last communication from the server.
• Last Error—A description of the most recent communication error between the listed peer and the
local iLO system.
• Query Time (seconds)—When a timeout occurs, this value can be used to identify systems that are
not responding quickly. This value applies to the most recent query.
• Node Count—When an error occurs, this value can indicate how much data might be missing. A
value of zero indicates that the most recent query timed out. This value applies to the most recent
query.
• URL—The URL for starting the iLO web interface for the listed peer.
• IP—The peer IP address.
iLO Federation Group Virtual Media
Group Virtual Media enables you to connect scripted media for access by the servers in an iLO
Federation group.
• Scripted media only supports 1.44 MB floppy disk images (IMG) and CD/DVD-ROM images (ISO).
The image must be on a web server on the same network as the grouped iLO systems.
• Only one of each type of media can be connected to a group at the same time.
• You can view, connect, and eject scripted media, and you can boot from CD/DVD-ROM disk images.
When you use scripted media, you save a floppy disk or CD/DVD-ROM disk image to a web server
and connect to the disk image by using a URL. iLO accepts URLs in HTTP or HTTPS format. iLO does
not support FTP.
• Before you use the Virtual Media feature, review the Virtual Media operating system considerations.
96 Viewing the iLO Federation Multi-System Map
Page 97

Connecting scripted media for groups
Prerequisites
• An iLO license that supports this feature is installed.
• Each member of the selected iLO Federation group has granted the Virtual Media privilege to the
group.
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Virtual Media tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
The scripted media you connect will be available to all systems in the selected group.
3. Enter the URL for the scripted media disk image in the Scripted Media URL box in the Connect
Virtual Floppy section (IMG files) or the Connect CD/DVD-ROM section (ISO files).
4. Select the Boot on Next Reset check box if you want the servers in the group to boot to this disk
image only on the next server reboot.
The image will be ejected automatically on the second server reboot so that the servers do not boot to
it twice.
If this check box is not selected, the image remains connected until it is manually ejected, and the
servers boot to it on all subsequent server resets, if the system boot options are configured
accordingly.
If a server in the group is in POST when you enable the Boot on Next Reset check box, an error
occurs because you cannot modify the server boot order during POST. Wait for POST to finish, and
then try again.
5. Click Insert Media.
iLO displays the command results.
Viewing scripted media status for groups
Procedure
Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Virtual Media tab.
Scripted media details
When scripted media is connected to the systems in an iLO Federation group, the following details are
listed in the Virtual Floppy Status section and Virtual CD/DVD-ROM Status section:
• Media Inserted—The Virtual Media type that is connected. Scripted Media is displayed when
scripted media is connected.
• Connected—Indicates whether a Virtual Media device is connected.
• Image URL—The URL that points to the connected scripted media.
The Virtual Floppy Status and Virtual CD/DVD-ROM Status sections are displayed only when media is
connected.
Connecting scripted media for groups 97
Page 98

Ejecting a scripted media device
Prerequisites
• An iLO license that supports this feature is installed.
• Each member of the selected iLO Federation group has granted the Virtual Media privilege to the
group.
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Virtual Media tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
The scripted media device that you eject will be disconnected from all the systems in the selected
group.
3. Click Eject Media in the Virtual Floppy Status section or the Virtual CD/DVD-ROM Status section.
Servers affected by a Group Virtual Media action
The Affected Systems section provides the following details about the servers affected when you initiate
a Group Virtual Media action:
• Server Name—The server name defined by the host operating system.
• Server Power—The server power state (ON or OFF).
• UID Indicator—The state of the UID LED. The UID LED helps you identify and locate a server,
especially in high-density rack environments. The possible states are UID ON, UID OFF, and UID
BLINK.
• iLO Hostname—The fully qualified network name assigned to the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO
web interface for the server, click the link in the iLO Hostname column.
• IP Address—The network IP address of the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO web interface for the
server, click the link in the IP Address column.
Click Next or Prev (if available) to view more servers in the list.
More information
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file on page 93
iLO Federation Group Power
The Group Power feature enables you to manage the power of multiple servers from a system running
the iLO web interface. Use this feature to do the following:
• Power off, reset, or power-cycle a group of servers that are in the ON or Reset state.
• Power on a group of servers that are in the OFF state.
• View the list of servers that will be affected when you click a button in the Virtual Power Button
section of the Group Power page.
98 Ejecting a scripted media device
Page 99

Changing the power state for a group of servers
The Virtual Power Button section on the Group Power page summarizes the current power state of the
servers in a group. The summary information includes the total number of servers that are in the ON,
OFF, or Reset state. The System Power summary indicates the state of the server power when the page
is first opened. Use the browser refresh feature to update the System Power information.
Prerequisites
• An iLO license that supports this feature is installed.
• Each member of the selected iLO Federation group has granted the Virtual Power and Reset privilege
to the group.
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Power tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
iLO displays the grouped servers by power state with a counter that shows the total number of servers
in each state.
3. To change the power state of a group of servers, do one of the following:
• For servers that are in the ON or Reset state, click one of the following buttons:
◦ Momentary Press
◦ Press and Hold
◦ Reset
◦ Cold Boot
For servers that are in the OFF state, click the Momentary Press button.
The Press and Hold, Reset, and Cold Boot options are not available for servers that are in the OFF
state.
4. When prompted to confirm the request, click OK.
iLO displays a progress bar while the grouped servers respond to the Virtual Power Button action. The
progress bar indicates the number of servers that successfully processed the command.
The Command Results section displays the command status and results, including error messages
related to the power state change.
Virtual Power Button options
• Momentary Press—The same as pressing the physical power button.
Some operating systems might be configured to initiate a graceful shutdown after a momentary press,
or to ignore this event. Hewlett Packard Enterprise recommends using system commands to complete
Changing the power state for a group of servers 99
Page 100

a graceful operating system shutdown before you attempt to shut down by using the Virtual Power
Button.
• Press and Hold—The same as pressing the physical power button for 5 seconds and then releasing
it.
The servers in the selected group are powered off as a result of this operation. Using this option might
circumvent a graceful operating system shutdown.
This option provides the ACPI functionality that some operating systems implement. These operating
systems behave differently, depending on a short press or long press.
• Reset—Forces the servers in the selected group to warm-boot: CPUs and I/O resources are reset.
Using this option circumvents a graceful operating system shutdown.
• Cold Boot—Immediately removes power from the servers in the selected group. Processors, memory,
and I/O resources lose main power. The servers will restart after approximately 6 seconds. Using this
option circumvents a graceful operating system shutdown.
Servers affected by the Virtual Power Button
The Affected Systems list provides the following details about the servers affected when you initiate a
Virtual Power Button action:
• Server Name—The server name defined by the host operating system.
• Server Power—The server power state (ON or OFF).
• UID Indicator—The state of the UID LED. The UID LED helps you identify and locate a server,
especially in high-density rack environments. The possible states are UID ON, UID OFF, and UID
BLINK.
• iLO Hostname—The fully qualified network name assigned to the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO
web interface for the server, click the link in the iLO Hostname column.
• IP Address—The network IP address of the iLO subsystem. To open the iLO web interface for the
server, click the link in the IP Address column.
Click Next or Prev (if available) to view more servers in the list.
More information
Exporting iLO Federation information to a CSV file on page 93
Configuring group power capping
Prerequisites
• An iLO license that supports this feature is installed.
• Each member of the selected iLO Federation group has granted the Configure iLO Settings privilege
to the group.
Procedure
1. Click iLO Federation in the navigation tree, and then click the Group Power Settings tab.
2. Select a group from the Selected Group menu.
100 Servers affected by the Virtual Power Button
 Loading...
Loading...