Page 1

HPE FlexNetwork 7500 Switch Series
Layer 3—IP Routing Configuratio n Guid e
Part number: 5200
Software
Document version: 6W101-20171020
version: 7500-CMW710-R7557P01
-1940a
Page 2

© Copyright 2017 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for Hewlett Packard
Enterprise products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. Hewlett
Packard Enterprise shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Hewlett Packard Enterprise required for possession, use, or
copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software
Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s
standard commercial license.
Links to third-party websites take you outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise website. Hewlett Packard
Enterprise has no control over and is not responsible for information outside the Hewlett Packard Enterprise
website.
Acknowledgments
Intel®, Itanium®, Pentium®, Intel Inside®, and the Intel Inside logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
Microsoft® and Windows® are trademarks of the Microsoft group of companies.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Java and Oracle are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
UNIX® is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Page 3

Contents
Configuring basic IP routing ··········································································· 1
Routing table ······················································································································································ 1
Dynamic routing protocols·································································································································· 2
Route preference ··············································································································································· 2
Load sharing ······················································································································································ 3
Route backup ····················································································································································· 3
Route recursion ·················································································································································· 3
Route redistribution ············································································································································ 3
Extension attribute redistribution ························································································································ 3
Setting the maximum lifetime for routes and labels in the RIB··········································································· 4
Setting the maximum lifetime for routes in the FIB ···························································································· 4
Enabling the RIB to flush route attribute information to the FIB ········································································· 5
Setting the maximum number of ECMP routes ·································································································· 5
Configuring RIB NSR ········································································································································· 6
Configuring IPv4 RIB NSR ························································································································· 6
Configuring IPv6 RIB NSR ························································································································· 6
Configuring inter-protocol FRR ·························································································································· 6
Configuring IPv4 RIB inter-protocol FRR ··································································································· 7
Configuring IPv6 RIB inter-protocol FRR ··································································································· 7
Configuring routing policy-based recursive lookup ···························································································· 7
Displaying and maintaining a routing table ········································································································ 8
Configuring static routing ············································································· 10
Configuring a static route ································································································································· 10
Configuring BFD for static routes ····················································································································· 11
Bidirectional control mode ························································································································ 11
Single-hop echo mode ····························································································································· 12
Configuring static route FRR ···························································································································· 13
Configuration guidelines ··························································································································· 13
Configuring static route FRR by specifying a backup next hop································································ 13
Configuring static route FRR to automatically select a backup next hop ················································· 14
Enabling BFD echo packet mode for static route FRR ············································································ 14
Displaying and maintaining static routes ·········································································································· 14
Static route configuration examples ················································································································· 15
Basic static route configuration example ·································································································· 15
BFD for static routes configuration example (direct next hop) ································································· 16
BFD for static routes configuration example (indirect next hop) ······························································ 19
Static route FRR configuration example ·································································································· 21
Configuring a default route ··········································································· 24
Configuring RIP ··························································································· 25
Overview ·························································································································································· 25
RIP route entries ······································································································································ 25
Routing loop prevention ··························································································································· 25
RIP operation ··········································································································································· 25
RIP versions ············································································································································· 26
Protocols and standards ·························································································································· 26
RIP configuration task list································································································································· 26
Configuring basic RIP ······································································································································ 27
Enabling RIP ············································································································································ 27
Controlling RIP reception and advertisement on interfaces ····································································· 28
Configuring a RIP version ························································································································ 29
Configuring RIP route control ··························································································································· 29
Configuring an additional routing metric ··································································································· 29
Configuring RIPv2 route summarization ·································································································· 30
Disabling host route reception ·················································································································· 31
i
Page 4

Advertising a default route ······················································································································· 31
Configuring received/redistributed route filtering······················································································ 32
Setting a preference for RIP ····················································································································· 32
Configuring RIP route redistribution ········································································································· 32
Tuning and optimizing RIP networks ··············································································································· 33
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 33
Setting RIP timers ···································································································································· 33
Enabling split horizon and poison reverse ······························································································· 34
Setting the maximum number of RIP ECMP routes ················································································· 34
Enabling zero field check on incoming RIPv1 messages ········································································· 35
Enabling source IP address check on incoming RIP updates·································································· 35
Configuring RIPv2 message authentication ····························································································· 35
Setting the RIP triggered update interval ································································································· 36
Specifying a RIP neighbor ························································································································ 36
Configuring RIP network management ···································································································· 37
Configuring the RIP packet sending rate ································································································· 37
Setting the maximum length of RIP packets ···························································································· 38
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing RIP packets ··················································································· 38
Configuring RIP GR ········································································································································· 38
Enabling RIP NSR············································································································································ 39
Configuring BFD for RIP ·································································································································· 39
Configuring single-hop echo detection (for a directly connected RIP neighbor) ······································ 40
Configuring single-hop echo detection (for a specific destination) ··························································· 40
Configuring bidirectional control detection ······························································································· 41
Configuring RIP FRR ······································································································································· 41
Configuration restrictions and guidelines ································································································· 41
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 42
Configuring RIP FRR ······························································································································· 42
Enabling BFD for RIP FRR ······················································································································ 42
Displaying and maintaining RIP ······················································································································· 42
RIP configuration examples ····························································································································· 43
Configuring basic RIP ······························································································································ 43
Configuring RIP route redistribution ········································································································· 46
Configuring an additional metric for a RIP interface················································································· 48
Configuring RIP to advertise a summary route ························································································ 49
Configuring RIP GR ································································································································· 52
Configuring RIP NSR ······························································································································· 52
Configuring BFD for RIP (single-hop echo detection for a directly connected neighbor) ························· 54
Configuring BFD for RIP (single hop echo detection for a specific destination) ······································· 57
Configuring BFD for RIP (bidirectional detection in BFD control packet mode) ······································· 59
Configuring RIP FRR ······························································································································· 62
Configuring OSPF························································································ 65
Overview ·························································································································································· 65
OSPF packets ·········································································································································· 65
LSA types ················································································································································· 65
OSPF areas ············································································································································· 66
Router types ············································································································································· 68
Route types ·············································································································································· 69
Route calculation ······································································································································ 69
OSPF network types ································································································································ 70
DR and BDR ············································································································································ 70
Protocols and standards ·························································································································· 71
OSPF configuration task list ····························································································································· 71
Enabling OSPF ················································································································································ 73
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 73
Configuration guidelines ··························································································································· 73
Enabling OSPF on a network ··················································································································· 74
Enabling OSPF on an interface················································································································ 74
Configuring OSPF areas ·································································································································· 75
Configuring a stub area ···························································································································· 75
Configuring an NSSA area ······················································································································· 76
ii
Page 5

Configuring a virtual link ··························································································································· 76
Configuring OSPF network types ····················································································································· 77
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 77
Configuring the broadcast network type for an interface·········································································· 77
Configuring the NBMA network type for an interface ··············································································· 77
Configuring the P2MP network type for an interface················································································ 78
Configuring the P2P network type for an interface··················································································· 79
Configuring OSPF route control ······················································································································· 79
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 79
Configuring OSPF route summarization ·································································································· 79
Configuring received OSPF route filtering ································································································ 80
Configuring Type-3 LSA filtering ·············································································································· 80
Setting an OSPF cost for an interface······································································································ 81
Setting the maximum number of ECMP routes ························································································ 82
Setting OSPF preference ························································································································· 82
Configuring discard routes for summary networks ··················································································· 82
Configuring OSPF route redistribution ····································································································· 83
Advertising a host route ··························································································································· 84
Excluding interfaces in an OSPF area from the base topology································································ 84
Tuning and optimizing OSPF networks ············································································································ 84
Configuration prerequisites ······················································································································ 84
Setting OSPF timers ································································································································ 85
Setting LSA transmission delay ··············································································································· 86
Setting SPF calculation interval ··············································································································· 86
Setting the LSA arrival interval ················································································································· 86
Setting the LSA generation interval·········································································································· 87
Disabling interfaces from receiving and sending OSPF packets ····························································· 87
Configuring stub routers ··························································································································· 88
Configuring OSPF authentication············································································································· 88
Adding the interface MTU into DD packets ······························································································ 89
Setting a DSCP value for OSPF packets ································································································· 90
Setting the maximum number of external LSAs in LSDB········································································· 90
Setting OSPF exit overflow interval·········································································································· 90
Enabling compatibility with RFC 1583······································································································ 90
Logging neighbor state changes ·············································································································· 91
Configuring OSPF network management ································································································ 91
Setting the LSU transmit rate ··················································································································· 92
Enabling OSPF ISPF ······························································································································· 93
Configuring prefix suppression ················································································································· 93
Configuring prefix prioritization ················································································································· 94
Configuring OSPF PIC ····························································································································· 94
Setting the number of OSPF logs ············································································································ 95
Filtering outbound LSAs on an interface ·································································································· 96
Filtering LSAs for the specified neighbor ································································································· 96
Configuring GTSM for OSPF ··················································································································· 96
Configuring OSPF GR······································································································································ 97
Configuring OSPF GR restarter ··············································································································· 97
Configuring OSPF GR helper ··················································································································· 98
Triggering OSPF GR ································································································································ 99
Configuring OSPF NSR ··································································································································· 99
Configuring BFD for OSPF····························································································································· 100
Configuring bidirectional control detection ····························································································· 100
Configuring single-hop echo detection ··································································································· 100
Configuring OSPF FRR·································································································································· 101
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 101
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 101
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 101
Advertising OSPF link state information to BGP ···························································································· 103
Displaying and maintaining OSPF ················································································································· 103
OSPF configuration examples ······················································································································· 104
Basic OSPF configuration example ······································································································· 104
OSPF route redistribution configuration example ·················································································· 107
iii
Page 6

OSPF route summarization configuration example ················································································ 109
OSPF stub area configuration example ································································································· 112
OSPF NSSA area configuration example ······························································································ 114
OSPF DR election configuration example ······························································································ 116
OSPF virtual link configuration example ································································································ 121
OSPF GR configuration example ··········································································································· 123
OSPF NSR configuration example········································································································· 125
BFD for OSPF configuration example ···································································································· 127
OSPF FRR configuration example ········································································································· 130
Troubleshooting OSPF configuration ············································································································· 133
No OSPF neighbor relationship established ·························································································· 133
Incorrect routing information ·················································································································· 133
Configuring IS-IS ······················································································· 135
Overview ························································································································································ 135
Terminology ··········································································································································· 135
IS-IS address format ······························································································································ 135
NET ························································································································································ 136
IS-IS area ··············································································································································· 137
IS-IS network types ································································································································ 138
IS-IS PDUs ············································································································································· 139
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 141
IS-IS configuration task list····························································································································· 141
Configuring basic IS-IS ·································································································································· 142
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 142
Enabling IS-IS ········································································································································ 143
Setting the IS level and circuit level ······································································································· 143
Configuring P2P network type for an interface ······················································································· 143
Configuring IS-IS route control ······················································································································· 144
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 144
Configuring IS-IS link cost ······················································································································ 144
Specifying a preference for IS-IS ··········································································································· 145
Configuring the maximum number of ECMP routes ··············································································· 146
Configuring IS-IS route summarization ·································································································· 146
Advertising a default route ····················································································································· 147
Configuring IS-IS route redistribution ····································································································· 147
Configuring IS-IS route filtering ·············································································································· 148
Configuring IS-IS route leaking ·············································································································· 149
Advertising IS-IS link state information to BGP ······················································································ 149
Tuning and optimizing IS-IS networks ··········································································································· 150
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 150
Specifying the interval for sending IS-IS hello packets ·········································································· 150
Specifying the IS-IS hello multiplier········································································································ 150
Specifying the interval for sending IS-IS CSNP packets ········································································ 151
Configuring a DIS priority for an interface ······························································································ 151
Disabling an interface from sending/receiving IS-IS packets ································································· 151
Enabling an interface to send small hello packets ················································································· 152
Configuring LSP parameters ·················································································································· 152
Controlling SPF calculation interval ······································································································· 155
Configuring convergence priorities for specific routes ··········································································· 156
Setting the LSDB overload bit ················································································································ 156
Configuring the ATT bit ·························································································································· 157
Configuring the tag value for an interface ······························································································ 157
Configuring system ID to host name mappings ····················································································· 158
Enabling the logging of neighbor state changes ···················································································· 159
Enabling IS-IS ISPF ······························································································································· 159
Enabling prefix suppression ··················································································································· 159
Configuring IS-IS network management ································································································ 160
Configuring IS-IS PIC ····························································································································· 160
Enhancing IS-IS network security ·················································································································· 161
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 162
Configuring neighbor relationship authentication ··················································································· 162
iv
Page 7

Configuring area authentication ············································································································· 162
Configuring routing domain authentication····························································································· 163
Configuring IS-IS GR ····································································································································· 163
Configuring IS-IS NSR ··································································································································· 164
Configuring BFD for IS-IS ······························································································································ 165
Configuring IS-IS FRR ··································································································································· 165
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 166
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 166
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 166
Displaying and maintaining IS-IS ··················································································································· 168
IS-IS configuration examples ························································································································· 169
Basic IS-IS configuration example ········································································································· 169
DIS election configuration example········································································································ 173
IS-IS route redistribution configuration example ···················································································· 177
IS-IS authentication configuration example···························································································· 181
IS-IS GR configuration example············································································································· 184
IS-IS NSR configuration example ·········································································································· 185
BFD for IS-IS configuration example ······································································································ 188
IS-IS FRR configuration example··········································································································· 191
Configuring BGP ························································································ 195
Overview ························································································································································ 195
BGP speaker and BGP peer ·················································································································· 195
BGP message types ······························································································································ 195
BGP path attributes ································································································································ 195
BGP route selection ······························································································································· 199
BGP route advertisement rules ·············································································································· 199
BGP load balancing ······························································································································· 200
Settlements for problems in large-scale BGP networks ········································································· 201
MP-BGP ················································································································································· 204
BGP multi-instance ································································································································ 205
BGP configuration views ························································································································ 205
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 207
BGP configuration task list ····························································································································· 208
Configuring basic BGP ··································································································································· 211
Enabling BGP ········································································································································· 212
Configuring a BGP peer ························································································································· 213
Configuring dynamic BGP peers ············································································································ 214
Configuring a BGP peer group ··············································································································· 217
Specifying the source address of TCP connections ··············································································· 227
Generating BGP routes ·································································································································· 228
Injecting a local network ························································································································· 228
Redistributing IGP routes ······················································································································· 230
Controlling route distribution and reception ··································································································· 232
Configuring BGP route summarization ··································································································· 232
Advertising optimal routes in the IP routing table ··················································································· 235
Advertising a default route to a peer or peer group················································································ 236
Configuring BGP to first send updates of the default route ···································································· 238
Limiting routes received from a peer or peer group ··············································································· 239
Configuring BGP route filtering policies ································································································· 241
Setting the BGP route sending rate ······································································································· 247
Configuring BGP route update delay ····································································································· 248
Configuring a startup policy for BGP route updates ··············································································· 248
Configuring BGP route dampening ········································································································ 249
Controlling BGP path selection ······················································································································ 251
Setting a preferred value for routes received ························································································· 251
Configuring preferences for BGP routes ································································································ 252
Configuring the default local preference ································································································ 254
Configuring the MED attribute ················································································································ 256
Configuring the NEXT_HOP attribute ···································································································· 260
Configuring the AS_PATH attribute ······································································································· 263
Ignoring IGP metrics during optimal route selection ·············································································· 269
v
Page 8

Configuring the SoO attribute ················································································································· 270
Tuning and optimizing BGP networks ············································································································ 271
Configuring the keepalive interval and hold time ··················································································· 271
Setting the session retry timer ················································································································ 273
Configuring the interval for sending updates for the same route ··························································· 274
Enabling BGP to establish an EBGP session over multiple hops ·························································· 275
Enabling immediate re-establishment of direct EBGP connections upon link failure ····························· 276
Enabling BGP ORF capabilities ············································································································· 276
Enabling 4-byte AS number suppression ······························································································· 278
Enabling MD5 authentication for BGP peers ························································································· 279
Enabling keychain authentication for BGP peers ··················································································· 280
Configuring BGP load balancing ············································································································ 281
Disabling BGP to establish a session to a peer or peer group ······························································· 282
Configuring GTSM for BGP ···················································································································· 283
Configuring BGP soft-reset ···················································································································· 284
Protecting an EBGP peer when memory usage reaches level 2 threshold ··········································· 290
Configuring an update delay for local MPLS labels ··············································································· 291
Flushing the suboptimal BGP route to the RIB ······················································································ 291
Setting a DSCP value for outgoing BGP packets ·················································································· 292
Disabling route recursion policy control for routes received from a peer or peer group ························· 292
Enabling per-prefix label allocation ········································································································ 293
Disabling optimal route selection for labeled routes without tunnel information ····································· 293
Configuring a large-scale BGP network ········································································································· 293
Configuring BGP community ·················································································································· 294
Configuring BGP route reflection ··········································································································· 296
Configuring a BGP confederation ·········································································································· 299
Configuring BGP GR ······································································································································ 300
Configuring BGP NSR···································································································································· 301
Enabling SNMP notifications for BGP ············································································································ 302
Enabling logging for session state changes ··································································································· 302
Enabling logging for BGP route flapping ········································································································ 303
Configuring BFD for BGP ······························································································································· 304
Configuring BGP FRR ···································································································································· 305
Configuring 6PE ············································································································································· 308
Configuring basic 6PE ···························································································································· 308
Configuring optional 6PE capabilities····································································································· 309
Configuring BGP LS ······································································································································· 311
Configuring basic BGP LS ····················································································································· 311
Configuring BGP LS route reflection ······································································································ 311
Specifying an AS number and a router ID for BGP LS messages ························································· 312
Configuring BMP ············································································································································ 312
Displaying and maintaining BGP···················································································································· 313
Displaying BGP ······································································································································ 313
Resetting BGP sessions ························································································································ 317
Clearing BGP information ······················································································································ 317
IPv4 BGP configuration examples ················································································································· 318
Basic BGP configuration example·········································································································· 318
BGP and IGP route redistribution configuration example ······································································ 322
BGP route summarization configuration example ·················································································· 325
BGP load balancing configuration example ··························································································· 328
BGP community configuration example ································································································· 331
BGP route reflector configuration example ···························································································· 334
BGP confederation configuration example····························································································· 336
BGP path selection configuration example ···························································································· 340
BGP GR configuration example ············································································································· 343
BFD for BGP configuration example ······································································································ 345
BGP FRR configuration example ··········································································································· 348
Multicast BGP configuration example ···································································································· 352
Dynamic BGP peer configuration example ···························································································· 356
BGP LS configuration example ·············································································································· 358
IPv6 BGP configuration examples ················································································································· 360
IPv6 BGP basic configuration example ·································································································· 360
vi
Page 9

IPv6 BGP route reflector configuration example ···················································································· 363
6PE configuration example ···················································································································· 366
BFD for IPv6 BGP configuration example ······························································································ 369
IPv6 BGP FRR configuration example ··································································································· 372
IPv6 multicast BGP configuration example ···························································································· 376
Troubleshooting BGP ····································································································································· 379
Symptom ················································································································································ 379
Analysis ·················································································································································· 379
Solution ·················································································································································· 379
Configuring PBR ························································································ 380
Overview ························································································································································ 380
Policy ······················································································································································ 380
PBR and Track ······································································································································· 381
PBR configuration task list ····························································································································· 382
Configuring a policy········································································································································ 382
Creating a node ······································································································································ 382
Setting match criteria for a node ············································································································ 382
Configuring actions for a node ··············································································································· 383
Configuring PBR ············································································································································ 383
Configuring local PBR ···························································································································· 383
Configuring interface PBR ······················································································································ 384
Displaying and maintaining PBR ···················································································································· 384
PBR configuration examples ·························································································································· 385
Packet type-based local PBR configuration example ············································································ 385
Packet type-based interface PBR configuration example ······································································ 386
EVPN-based service chain PBR configuration example ········································································ 388
Configuring IPv6 static routing ··································································· 395
Configuring an IPv6 static route ····················································································································· 395
Configuring BFD for IPv6 static routes ··········································································································· 395
Bidirectional control mode ······················································································································ 396
Single-hop echo mode ··························································································································· 396
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 static routes································································································ 397
IPv6 static routing configuration examples ···································································································· 397
Basic IPv6 static route configuration example ······················································································· 397
BFD for IPv6 static routes configuration example (direct next hop) ······················································· 399
BFD for IPv6 static routes configuration example (indirect next hop) ···················································· 402
Configuring an IPv6 default route······························································· 405
Configuring RIPng ····················································································· 406
Overview ························································································································································ 406
RIPng route entries ································································································································ 406
RIPng packets ········································································································································ 406
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 407
RIPng configuration task list··························································································································· 407
Configuring basic RIPng ································································································································ 407
Configuring RIPng route control ····················································································································· 408
Configuring an additional routing metric ································································································· 408
Configuring RIPng route summarization ································································································ 408
Advertising a default route ····················································································································· 409
Configuring received/redistributed route filtering···················································································· 409
Setting a preference for RIPng ··············································································································· 409
Configuring RIPng route redistribution ··································································································· 410
Tuning and optimizing the RIPng network ····································································································· 410
Setting RIPng timers ······························································································································ 410
Configuring split horizon and poison reverse ························································································· 411
Configuring zero field check on RIPng packets ····················································································· 411
Setting the maximum number of ECMP routes ······················································································ 412
Configuring the RIPng packet sending rate ··························································································· 412
Setting the interval for sending triggered updates ·················································································· 413
vii
Page 10

Configuring RIPng GR ··································································································································· 413
Configuring RIPng NSR ································································································································· 414
Configuring RIPng FRR ································································································································· 414
Configuration restrictions and guidelines ······························································································· 415
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 415
Configuring RIPng FRR ························································································································· 415
Enabling BFD for RIPng FRR ················································································································ 415
Displaying and maintaining RIPng ················································································································· 416
RIPng configuration examples ······················································································································· 416
Basic RIPng configuration example ······································································································· 416
RIPng route redistribution configuration example ·················································································· 419
RIPng GR configuration example··········································································································· 421
RIPng NSR configuration example ········································································································ 422
Configuring RIPng FRR ························································································································· 424
Configuring OSPFv3 ·················································································· 427
Overview ························································································································································ 427
OSPFv3 packets ···································································································································· 427
OSPFv3 LSA types ································································································································ 427
Protocols and standards ························································································································ 428
OSPFv3 configuration task list ······················································································································· 428
Enabling OSPFv3··········································································································································· 429
Configuring OSPFv3 area parameters ··········································································································· 430
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 430
Configuring a stub area ·························································································································· 430
Configuring an NSSA area ····················································································································· 430
Configuring an OSPFv3 virtual link ········································································································ 431
Configuring OSPFv3 network types ··············································································································· 431
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 432
Configuring the OSPFv3 network type for an interface ·········································································· 432
Configuring an NBMA or P2MP neighbor ······························································································ 432
Configuring OSPFv3 route control ················································································································· 432
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 432
Configuring OSPFv3 route summarization ····························································································· 433
Configuring OSPFv3 received route filtering ·························································································· 433
Configuring Inter-Area-Prefix LSA filtering ····························································································· 434
Setting an OSPFv3 cost for an interface ································································································ 434
Setting the maximum number of OSPFv3 ECMP routes ······································································· 435
Setting a preference for OSPFv3 ··········································································································· 435
Configuring OSPFv3 route redistribution ······························································································· 435
Tuning and optimizing OSPFv3 networks ······································································································ 437
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 437
Setting OSPFv3 timers ··························································································································· 437
Setting LSA transmission delay ············································································································· 437
Setting SPF calculation interval ············································································································· 438
Setting the LSA generation interval········································································································ 438
Setting a DR priority for an interface ······································································································ 439
Ignoring MTU check for DD packets ······································································································ 439
Disabling interfaces from receiving and sending OSPFv3 packets ························································ 439
Enabling logging for neighbor state changes ························································································· 440
Configuring OSPFv3 network management··························································································· 440
Setting the LSU transmit rate ················································································································· 441
Configuring stub routers ························································································································· 441
Configuring prefix suppression ··············································································································· 442
Configuring OSPFv3 authentication ······································································································· 443
Configuring OSPFv3 GR ································································································································ 444
Configuring GR restarter ························································································································ 444
Configuring GR helper ··························································································································· 444
Triggering OSPFv3 GR ·························································································································· 445
Configuring OSPFv3 NSR······························································································································ 445
Configuring BFD for OSPFv3 ························································································································· 445
Configuring OSPFv3 FRR ······························································································································ 446
viii
Page 11

Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 446
Configuration guidelines ························································································································· 447
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 447
Displaying and maintaining OSPFv3·············································································································· 448
OSPFv3 configuration examples···················································································································· 449
OSPFv3 stub area configuration example ····························································································· 449
OSPFv3 NSSA area configuration example ·························································································· 454
OSPFv3 DR election configuration example ·························································································· 456
OSPFv3 route redistribution configuration example··············································································· 459
OSPFv3 route summarization configuration example ············································································ 462
OSPFv3 GR configuration example ······································································································· 466
OSPFv3 NSR configuration example ····································································································· 467
BFD for OSPFv3 configuration example ································································································ 468
OSPFv3 FRR configuration example ····································································································· 470
Configuring IPv6 IS-IS ··············································································· 473
Overview ························································································································································ 473
Configuring basic IPv6 IS-IS ·························································································································· 473
Configuring IPv6 IS-IS route control ·············································································································· 474
Configuring IPv6 IS-IS link cost·············································································································· 475
Tuning and optimizing IPv6 IS-IS networks ··································································································· 476
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 476
Assigning a convergence priority to IPv6 IS-IS routes ··········································································· 476
Setting the LSDB overload bit ················································································································ 477
Configuring a tag value on an interface ································································································· 477
Controlling SPF calculation interval ······································································································· 478
Enabling IPv6 IS-IS ISPF ······················································································································· 478
Enabling prefix suppression ··················································································································· 478
Configuring BFD for IPv6 IS-IS ······················································································································ 479
Configuring IPv6 IS-IS FRR ··························································································································· 479
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 480
Configuration procedure ························································································································· 480
Enabling IPv6 IS-IS MTR ······························································································································· 482
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 IS-IS ··········································································································· 483
IPv6 IS-IS configuration examples ················································································································· 483
IPv6 IS-IS basic configuration example ································································································· 483
BFD for IPv6 IS-IS configuration example ····························································································· 487
IPv6 IS-IS FRR configuration example ·································································································· 490
Configuring IPv6 PBR ················································································ 494
Overview ························································································································································ 494
Policy ······················································································································································ 494
PBR and Track ······································································································································· 495
IPv6 PBR configuration task list ····················································································································· 495
Configuring an IPv6 policy ····························································································································· 496
Creating an IPv6 node ··························································································································· 496
Setting match criteria for an IPv6 node ·································································································· 496
Configuring actions for an IPv6 node ····································································································· 496
Configuring IPv6 PBR ···································································································································· 497
Configuring IPv6 local PBR ···················································································································· 497
Configuring IPv6 interface PBR ············································································································· 497
Displaying and maintaining IPv6 PBR············································································································ 497
IPv6 PBR configuration examples·················································································································· 498
Packet type-based IPv6 local PBR configuration example ···································································· 498
Packet type-based IPv6 interface PBR configuration example ······························································ 499
Configuring routing policies ········································································ 502
Overview ························································································································································ 502
Filters ····················································································································································· 502
Routing policy ········································································································································· 503
Configuring filters ··········································································································································· 503
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 503
ix
Page 12

Configuring an IP prefix list ···················································································································· 503
Configuring an AS path list ····················································································································· 504
Configuring a community list ·················································································································· 504
Configuring an extended community list ································································································ 505
Configuring a MAC list ··························································································································· 505
Configuring a routing policy···························································································································· 505
Configuration prerequisites ···················································································································· 505
Creating a routing policy ························································································································ 505
Configuring if-match clauses ·················································································································· 506
Configuring apply clauses ······················································································································ 507
Configuring the continue clause ············································································································· 509
Displaying and maintaining the routing policy ································································································ 509
Routing policy configuration examples ·········································································································· 510
Routing policy configuration example for IPv4 route redistribution ························································ 510
Routing policy configuration example for IPv6 route redistribution ························································ 513
Configuring DCN ······················································································· 515
Overview ························································································································································ 515
Basic concepts ······································································································································· 515
Basic features ········································································································································ 515
DCN configuration task list ····························································································································· 515
Enabling DCN ················································································································································ 516
Configuring the NE ID and NE IP ··················································································································· 516
Configuring DCN VPN···································································································································· 516
Enabling the automatic report feature ············································································································ 517
Configuring the source MAC address of LLDP frames ·················································································· 517
Advertising the LLDP management address ································································································· 518
Enabling the system to issue the generated ARP entry to a Layer 3 Ethernet subinterface after a port receives
an LLDP frame ··············································································································································· 518
DCN configuration examples ························································································································· 519
Document conventions and icons ······························································ 525
Conventions ··················································································································································· 525
Network topology icons ·································································································································· 526
Support and other resources ····································································· 527
Accessing Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support····························································································· 527
Accessing updates ········································································································································· 527
Websites ················································································································································ 528
Customer self repair ······························································································································· 528
Remote support ······································································································································ 528
Documentation feedback ······················································································································· 528
Index ·········································································································· 530
x
Page 13

Configuring basic IP routing
Criterion
Categories
The destination is a netw ork. T he subnet mask i s les s than 32
•
•
•
•
IP routing directs IP packet forwarding on routers based on a routing table. This chapter focuses on
unicast routing protoc ols. For more inf ormation about m ulticast routing protoco ls, see IP Multicast
Configuration Guide.
Routing table
A RIB contains the global routing information and related information, including route recursion, route
redistribution, and ro ute extension information. The r outer selects optimal routes from the routing
table and puts them into the FIB table. It uses the FIB table to forward packets. For more information
about the FIB table, see Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide.
Table 1 categorizes routes by different criteria.
Table 1 Route categories
• Network route—
Destination
bits.
• Host route—The destination is a host. The subnet mask is 32 bits.
Whether the
destination is directly
connected
Origin
• Direct route—The destination is directly connected.
• Indirect route—The destination is indirectly connected.
• Direct route—A direct route is discovered by the data link protocol on an
interface, and is also called an interface route.
• Static route—A static route is manually configured by an administrator.
• Dynamic route—A dy nami c route is dynamically discovered by a routing
protocol.
To view brief information about a routing table, use the display ip routing-table command.
<Sysname> display ip routing-table
Destinations : 9 Routes : 9
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
3.3.3.3/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
...
A route entry includes the following key items:
Destination—IP address of the destination host or network.
Mask—Mask length of the IP address.
Proto—Protocol that installed the route.
Pre—Preference of the route. Among routes to the same destination, the route with the highest
preference is optimal.
1
Page 14

•
•
•
Criterion
Categories
Route type
Preference
Cost—If multiple routes to a destination have the same preference, the one with the smallest
cost is the optimal route.
NextHop—Next hop.
Interface—Output interface.
Dynamic routing protocols
Static routes work well in small, stable networks. They are easy to configure and require fewer
system resources. However, in networks where topology changes occur frequently, a typical practice
is to configure a dynamic routing protocol. Compared with static routing, a dynamic routing protocol
is complicated to configure, requires more router resources, and consumes more network resources.
Dynamic routing protocols dynamically collect and report reachability information to adapt to
topology changes. They are suitable for large networks.
Dynamic routing protocols can be classified by different criteria, as shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Categories of dynamic routing protocols
Operation scope
Routing algorithm
Destination address
type
IP version
• IGPs—Work within an AS. Examples include RIP, OSPF, and IS-IS.
• EGPs—Work between ASs. The most popular EGP is BGP.
• Distance-vector protocols—Examples include RIP and BGP. BGP is also
considered a path-vector protocol.
• Link-state protocols—Examples include OSPF and IS-IS.
• Unicast routing protocols—Examples include RIP, OSPF, BGP, and IS-IS.
• Multicast routing protocols—Examples include PIM-SM and PIM-DM.
• IPv4 routing protocols—Examples include RIP, OSPF, BGP, and IS-IS.
• IPv6 routing protocols—Examples include RIPng, OSPFv3, IPv6 BGP, and
IPv6 IS-IS.
An AS refers to a group of routers that use the same routing policy and work under the same
administration.
Route preference
Routing protocols, includ in g stat ic and direc t r out ing, eac h b y defau lt have a preference. If they find
multiple routes to the sam e destinat ion, the router s elect s the r oute with the hig hest pref erence as
the optimal route.
The preference of a direct route is always 0 and cannot be changed. Y ou can configure a preference
for each static route and each dynamic routing protocol. The following table lists the route types and
default preferences. The smaller the value, the higher the preference.
Table 3 Route types and default route preferences
Direct route 0
Multicast static route 1
OSPF 10
IS-IS 15
Unicast static route 60
2
Page 15
Route type
Preference
RIP 100
OSPF ASE 150
OSPF NSSA 150
IBGP 255
EBGP 255
Unknown (route from an unt r u sted source) 256
Load sharing
A routing protocol might find multiple optimal equal-cost routes to the same destination. You can use
these routes to implement equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) load sharing.
Static routing, IPv6 static routing, RIP, RIPng, OSPF, OSPFv3, BGP , IPv6 BGP, IS-IS, and IPv6 IS-IS
support ECMP load sharing.
Route backup
Route backup can im prove network availability. Among m ultiple rout es to the s ame destin ation, the
route with the highest priority is the prim ary route and others are secondary routes.
The router forwards m atc hing packets through the prim ary route. W hen the primar y route fails, the
route with the highest preference among the secondary routes is selected to forward packets. When
the primary route recovers, the router uses it to forward packets.
Route recursion
To use a BGP, static, or RIP rout e t hat h as a n ind irec tl y co nnec t ed nex t ho p, a r o uter must perform
route recursion to find the output interface to reach the next hop.
Link-state routing pro tocols, such as O SPF and IS-IS, do not need route rec ursion, because th ey
obtain directly connected next hops through route calculation.
The RIB records and sa ves route recursion informati on, including brief information abo ut related
routes, recursive paths, and recur sion dep th.
Route redistribution
Route redistribution enables routing protocols to learn routing information from each other. A
dynamic routing pr otocol can redistribute routes from other routing protocols, including direct and
static routing. For more inform ation, see the respective chapt ers on those routi ng protocols i n this
configuration guide.
The RIB records redistribution relationships of routing protocols.
Extension attribute redistribution
Extension attribute redistribution enables routi ng protocols to learn route extension attri butes from
each other, including BGP extended comm unity attributes , OSPF area IDs , rout e types, and r outer
IDs.
3
Page 16

The RIB records extended attributes of each routing protocol and redistribution relationships of
Step
Command
Remarks
rib
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
different routing protocol extended attributes.
Setting the maximum lifetime for routes and labels in the RIB
Perform this task to prevent rout es of a certain protocol from being aged out due to slo w protocol
convergence resulting from a large number of route entries or long GR period.
The configuration takes effect at the next protocol or RIB process switchover.
To set the maximum lifetime for routes and labels in the RIB (IPv4):
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv4 address
family and enter its view.
4. Set the maximum lifetime for
IPv4 routes and labels in the
RIB.
To set the maximum route lifetime for routes and labels in the RIB (IPv6):
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv6 address
family and enter its view.
4. Set the maximum lifetime for
IPv6 routes and labels in the
RIB.
system-view
address-family ipv4
protocol
instance-name ]
system-view
rib
address-family ipv6
protocol
instance-name ]
protocol [
protocol [
instance
lifetime
instance
lifetime
seconds
seconds
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv4
address family exists.
By default, the maximum
lifetime for routes and labels
in the RIB is 480 seconds.
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv6
address family exists.
By default, the maximum
lifetime for routes and labels
in the RIB is 480 seconds.
Setting the maximum lifetime for routes in the FIB
When GR or NSR is disabled, FIB entries m ust be ret ained for s ome tim e after a protoco l proces s
switchover or RIB proces s switcho ver. When GR or NSR is enab led, FIB entri es m ust be removed
immediately after a pro toc o l or RIB process s witcho ver to avoid routin g is sues . Pe r f orm this task to
meet such requirements.
To set the maximum lifetime for routes in the FIB (IPv4):
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv4 address
family and enter its view.
system-view
rib
address-family ipv4
4
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv4
address family exists.
Page 17

Step
Command
Remarks
4. Set the maximum lifetime for
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
rib
Step
Command
Remarks
IPv4 routes in the FIB.
To set the maximum lifetime for routes in the FIB (IPv6):
fib lifetime
seconds
By default, the maximum
lifetime for routes in the FIB
is 600 seconds.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv6 address
family and enter its view.
4. Set the maximum lifetime for
IPv6 routes in the FIB.
system-view
rib
address-family ipv6
fib lifetime
seconds
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv6
address family exists.
By default, the maximum
lifetime for routes in the FIB
is 600 seconds.
Enabling the RIB to flush route attribute information to the FIB
This feature is a va ilabl e on l y f or BGP routes in the curr ent s of t ware vers io n. You can configure th is
feature when using sFlow to monitor BGP traffic. For more inform ation about BGP path attributes
—
and sFlow, see Layer 3
Configuration Guide.
To enable RIB to flush route attribute information to the FIB:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv4 address
family and enter its view.
4. Enable the RIB to flush route
attribute information to the
FIB.
IP Routing Configuration Guide and Network Management and Monitoring
N/A
N/A
address-family ipv4
flush route-attribute
protocol
By default, no RIB IPv4
address family exists.
By default, the RIB does not
flush route attribute
information to the FIB.
Setting the maximum number of ECMP routes
This configuration takes effect at reboot. Make sure the reboot does not impact your network.
To set the maximum number of ECMP routes:
1. Enter system view.
2. Set the maximum number of
ECMP routes.
system-view
max-ecmp-num
5
number
N/A
By default, the maximum
number of ECMP routes is
not set.
Page 18

Configuring RIB NSR
IMPORTANT:
Use this feature with protocol GR or NSR to avoid route timeouts and traffic interruption.
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
CAUTION:
This feature
faulty route, which might cause loops.
When an active/standby switchover occurs, nonstop routing (NSR) backs up routing information
from the active process to the standby process to a void routing flapping and ensure forwarding
continuity.
RIB NSR provides faster route convergence than protocol NSR during an active/standby switchover.
Configuring IP v4 RIB NSR
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv4 address
family and enter its view.
4. Enable IPv4 RIB NSR.
system-view
rib
address-family ipv4
non-stop-routing
Configuring IP v6 RIB NSR
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv4
address family exists.
By default, RIB NSR is
disabled.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv6 address
family and enter its view.
4. Enable IPv6 RIB NSR.
system-view
rib
address-family ipv6
non-stop-routing
Configuring inter-protocol FRR
Inter-protocol fast reroute (FRR) enables fast rerouting between routes of different protocols. A
backup next hop is automatically selected to reduce the service interruption time caused by
unreachable next hops. W hen the next hop of the prim ary link fails, the traffic is redirected to the
backup next hop.
Among the routes to the same destination in the RIB, a router adds the route with the highest
preference to the FIB tab le. For example, if a static route and an O SPF route in the RI B have the
same destination, the router adds the OSPF ro ute to the FI B table by def ault. The next hop of the
static route is selected as the backup next hop for the OSPF route. When the next hop of the OSPF
route is unreachable, the backup next hop is used.
uses the next hop of a route from a different protocol as the backup next hop for the
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv6
address family exists.
By default, RIB NSR is
disabled.
6
Page 19

Configuring IP v4 RIB inter-protoc ol FRR
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
rib
Step
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv4 address
family and enter its view.
4. Enable IPv4 RIB
inter-protocol FRR.
system-view
rib
address-family ipv4
inter-protocol fast-reroute
vpn-instance
[
vpn-instance-name ]
Configuring IP v6 RIB inter-protoc ol FRR
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv6 address
family and enter its view.
4. Enable IPv6 RIB
inter-protocol FRR.
system-view
address-family ipv6
inter-protocol fast-reroute
vpn-instance
[
vpn-instance-name ]
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv4
address family exists.
By default, inter-protocol
FRR is disabled.
If you do not specify a VPN
instance, inter-proto col FRR
is enabled for the public
network.
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv6
address family exists.
By default, inter-protocol
FRR is disabled.
If you do not specify a VPN
instance, inter-proto col FRR
is enabled for the public
network.
Configuring routing policy-based recursive lookup
When a route changes, the routing protocol has to perform a route recursion if the next hop is
indirectly connected. The routing protocol might select an incorrect path, which can cause traffic loss.
To prevent this problem, you can use a routing polic y to verify the recur sive route. If the recursive
route fails to m atch the routing policy, the routing protocol inval idates the rout e and marks it as
unreachable.
For the device to use exact routes to forward the traffic, make sure all desired routes can match the
routing policy.
To configure routing policy-based recursive lookup:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIB view.
3. Create the RIB IPv4 address
family and enter its view.
system-view
rib
address-family ipv4
7
N/A
N/A
By default, no RIB IPv4 address
family exists.
Page 20

Step
Command
Remarks
4. Configure routing
Task
Command
verbose ]
policy-based recursive
lookup.
protocol
recursive-lookup route-policy
route-policy-name
protocol
nexthop
By default, routing policy-based
recursive lookup is not
configured.
Displaying and maintaining a routing table
Execute display commands in any view and reset commands in user view.
Display routing table information.
Display information about routes
permitted by an IPv4 basic ACL.
Display information about routes to a
specific destination address.
Display information about routes to a
range of destination addresses.
Display information about routes
permitted by an IP prefix list.
Display information about routes
installed by a protocol.
Display IPv4 route statistics.
Display brief IPv4 routing table
information.
Display the maximum number of
ECMP routes.
Display route attribute information in
the RIB.
Display RIB GR state information.
display ip routing-table
verbose ]
[
display ip routing-table [ vpn-instance
ipv4-acl-number [
display ip routing-table
ip-address [ mask-length | mask ] [
display ip routing-table
ip-address1 to ip-address2 [
display ip routing-table [ vpn-instance
prefix-list
display ip routing-table [ vpn-instance
protocol
display ip routing-table [ vpn-instance
statistics
display ip routing-table
summary
display max-ecmp-num
display rib attribute
display rib graceful-restart
prefix-list-name [
protocol [
verbose ]
vpn-instance
[
vpn-instance
[
vpn-instance
[
verbose ]
verbose ]
inactive
[ attribute-id ]
verbose ]
|
vpn-instance
[
longer-match
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
verbose ]
] [
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
acl
Display next hop information in the
RIB.
Display next hop informatio n fo r direct
routes.
Clear IPv4 route statistics.
Display IPv6 routing tab le information.
Display information about rout es to an
IPv6 destination address.
Display information about routes
permitted by an IPv6 basic ACL.
Display information about routes to a
range of IPv6 destination addr esses.
Display information about routes
permitted by an IPv6 prefix list.
display rib nib
display rib nib protocol
display route-direct nib
reset ip routing-table statistics protocol [ vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ] { protocol |
display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance
verbose ]
[
display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance
ipv6-address [ prefix-length ] [
display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance
acl
ipv6-acl-number [
display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance
ipv6-address1 to ipv6-address2 [
display ipv6 routing-table
prefix-list
8
self-originated
[
protocol [
[ nib-id ] [
verbose ]
prefix-list-name [
] [ nib-id ] [
verbose ]
verbose ]
all }
longer-match
vpn-instance
[
verbose ]
verbose
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
] [
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
]
verbose ]
Page 21
Task
Command
Display information about rout es
installed by an IPv6 protocol.
display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance
protocol
protocol [
inactive | verbose ]
vpn-instance-name ]
Display IPv6 route statistics.
Display brief IPv6 routing table
information.
Display route attribute information in
the IPv6 RIB.
Display IPv6 RIB GR state
information.
Display next hop information in the
IPv6 RIB.
Display next hop information for IPv6
direct routes.
Clear IPv6 route statistics.
display ipv6 routing-table [ vpn-instance
statistics
display ipv6 routing-table
vpn-instance
[
summary
display ipv6 rib attribute
[ attribute-id ]
display ipv6 rib graceful-restart
display ipv6 rib nib
display ipv6 rib nib protocol
display ipv6 route-direct nib
self-originated
[
protocol [
[ nib-id ] [
] [ nib-id ] [
verbose ]
verbose ]
reset ipv6 routing-table statistics protocol
vpn-instance-name ] { protocol |
all }
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance-name ]
verbose
vpn-instance
[
]
9
Page 22
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Configuring static routing
Static routes are m anuall y conf igured. If a net work 's topology is sim ple, you only nee d to co nfigure
static routes for the network to work correctly.
Static routes cannot ada pt t o net wor k topology changes. If a fault or a topological change oc c urs in
the network, the network administrator must modify the static routes manually.
Configuring a static route
Before you configure a static route, complete the following tasks:
Configure the physical parameters for related interfaces.
Configure the link-layer attributes for related interfaces.
Configure the IP addresses for related interfaces.
You can associate Track with a static route to m onitor the reachabil ity of the next hops. For m ore
information about Track, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
To configure a static route:
1. Enter system view.
2. (Optional.) Create a
static route group
and enter its view.
3. (Optional.) Add a
static route prefix to
the static route
group.
4. (Optional.) Return to
system view.
5. Configure a static
route.
ip route-static-group
prefix
dest-address { mask-length | mask }
quit
• Method 1:
ip route-static { dest-address { mask-length
| mask } | group group-name }
{ interface-type interface-number
[ next-hop-address ] | next-hop-address
[ recursive-lookup host-route ] [ track
track-entry-number ] | vpn-instance
d-vpn-instance-name next-hop-address
[ recursive-lookup host-route ] [ track
track-entry-number ] } [ permanent ]
[ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ]
[ description text ]
• Method 2:
ip route-static vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name { dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } | group group-name }
{ interface-type interface-number
[ next-hop-address ] | next-hop-address
[ recursive-lookup host-route ] [ public ]
[ track track-entry-number ] | vpn-instance
d-vpn-instance-name next-hop-address
[ recursive-lookup host-route ] [ track
track-entry-number ] } [ permanent ]
[ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ]
[ description text ]
group-name
N/A
By default, no static route
group is configured.
By default, no static route
prefix is added to the static
route group.
N/A
By default, no static route is
configured.
10
Page 23

Step
Command
Remarks
IMPORTANT:
Enabling BFD for a flapping route could worsen the situation.
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
6. (Optional.) Enable
periodic sending of
ARP requests to the
next hops of static
routes.
7. (Optional.)
Configure the
default preference
for static routes.
8. (Optional.) Delete all
static routes,
including the default
route.
ip route-static arp-request interval
ip route-static default-preference
default-preference
delete [ vpn-instance
static-routes all
vpn-instance-name ]
interval
Configuring BFD for static routes
BFD provides a general-purpose, standard, medium-, and protocol-independent fast failure
detection mechanis m. It can uniformly and quickly detec t th e failures of the b id ire c tiona l f orwarding
paths between two routers for protocols, such as routing protocols and MPLS.
By default, the device does
not send ARP requests to
the next hops of static
routes.
The default setting is 60.
To delete one static route,
use the
route-static
undo ip
command.
For more information about BFD, see High Availability Configuration Guide.
Bidirectional c ontrol mode
To use BFD bidirectional control detection between two devices, enable BFD control mode for each
device's static route destined to the peer.
To configure a static route and enable BFD control mode, use one of the following methods:
Specify an output interface and a direct next hop.
Specify an indirect next hop and a specific BFD packet source address for the static route.
To configure BFD control mode for a static route (direct next hop):
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure BFD
control mode for a
static route.
To configure BFD control mode for a static route (indirect next hop):
system-view
• Method 1:
ip route-static dest-address { mask-length |
mask } interface-type interface-number
next-hop-address bfd control-packet
[ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ]
[ description text ]
• Method 2:
ip route-static vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } interface-type
interface-number next-hop-address bfd
control-packet [ preference preference ] [ tag
tag-value ] [ description text ]
N/A
By default, BFD control
mode for a static route
is not configured.
11
Page 24
Step
Command
Remarks
IMPORTANT:
Do not use BFD for a static route with the output interface in spoofing state.
Step
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure BFD
control mode for a
static route.
system-view
• Method 1:
• Method 2:
Single-hop echo mode
With BFD echo mode enabled for a static route, the output interface sends BFD echo packets to the
destination device, which loops the packets back to test the link reachability.
ip route-static dest-address { mask-length |
mask } { next-hop-address bfd control-packet
bfd-source ip-address | vpn-instance
d-vpn-instance-name next-hop-address bfd
control-packet bfd-source ip-address }
[ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ]
[ description text ]
ip route-static vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } { next-hop-address bfd
control-packet bfd-source ip-address |
vpn-instance d-vpn-instance-name
next-hop-address bfd control-packet
bfd-source ip-address } [ preference
preference ] [ tag tag-value ] [ description
text ]
N/A
By default, BFD control
mode for a static route is
not configured.
To configure BFD echo mode for a static route:
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the
source address of
echo packets.
3. Configure BFD echo
mode for a static
route.
system-view
bfd echo-source-ip
• Method 1:
ip route-static dest-address { mask-length |
mask } interface-type interface-number
next-hop-address bfd echo-packet
[ preference preference ] [ tag tag-value ]
[ description text ]
• Method 2:
ip route-static vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } interface-type
interface-number next-hop-address bfd
echo-packet [ preference preference ] [ tag
tag-value ] [ description text ]
ip-address
N/A
By default, the source
address of echo packets is
not configured.
For more information a bout
this command, see High
Availability Command
Reference.
By default, BFD echo mode
for a static route is not
configured.
12
Page 25
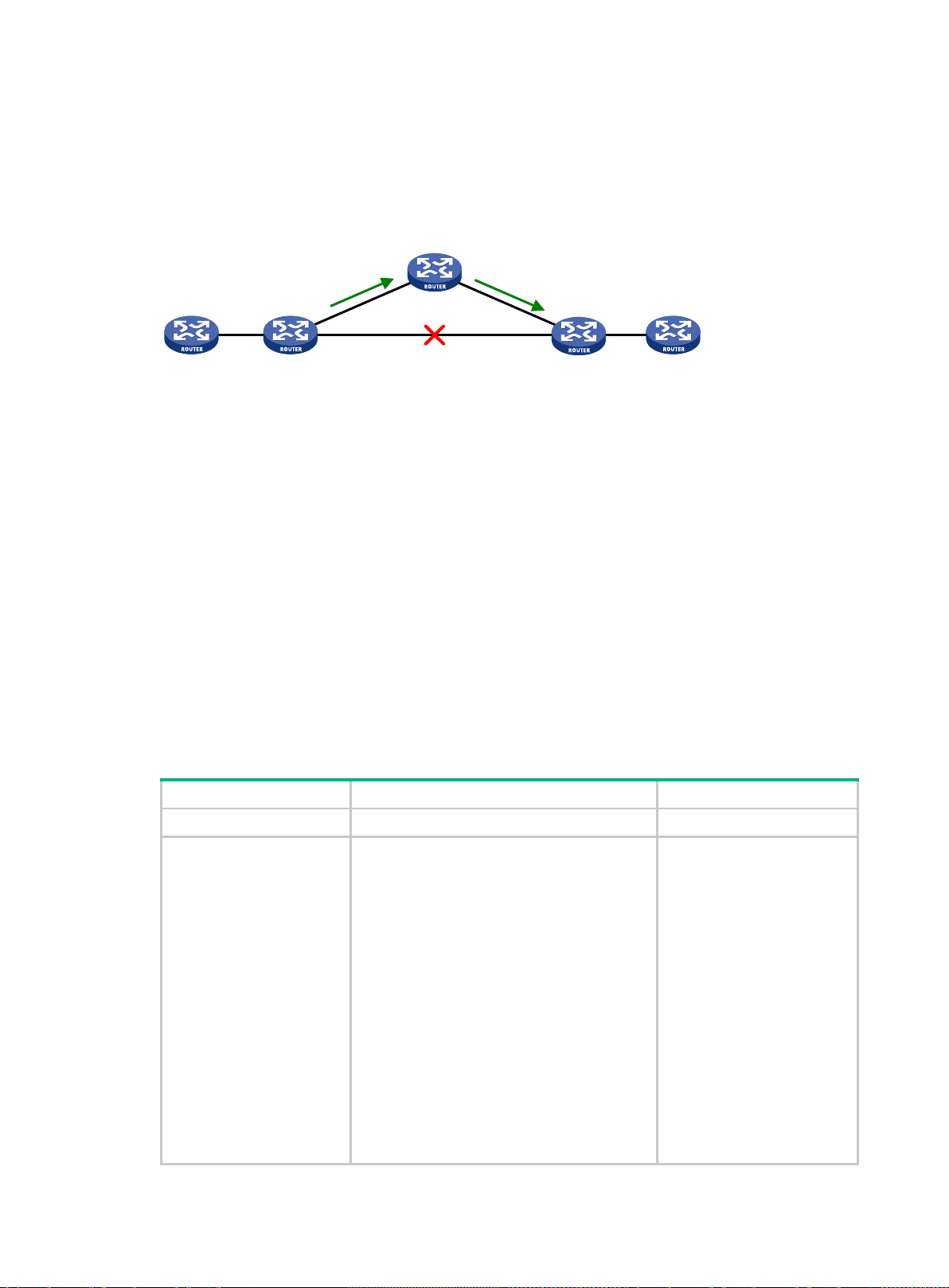
•
•
•
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
tag
description
Router A
Router B Router E
Backup nexthop:
Router C
Nexthop:
Router D
Configuring static route FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss and even routing loop. Static route fast reroute
(FRR) enables fast rerouting to minimize the impact of link or node failures.
Figure 1 Network diagram
As shown in Figure 1, upon a link failure, packets are directed to the backup next hop to avoid traffic
interruption. Y ou can either specify a backup next hop for FRR or enable FRR to automatically select
a backup next hop (which must be configured in advance).
Configuration guidelines
Do not use static route FRR and BFD (for a static route) at the same time.
Static route does not take effect when the backup output interface is unavailable.
Equal-cost routes do not support static route FRR.
The backup output interface and next hop must be different from the primary output interface
and next hop.
To change the backup output interface or next hop, you must first remove the current setting.
Static route FRR is available only when the state of primary link (with Layer 3 interfaces staying
up) changes from bidirectional to unidirectional or down.
Configuring static route FRR by specifying a backup next hop
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure static route
FRR.
system-view
• Method 1:
ip route-static dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } interface-type
interface-number [ next-hop-address
[ backup-interface interface-type
interface-number [ backup-nexthop
backup-nexthop-address ] ] ]
[ permanent ] [ preference preference ]
[ tag tag-value ] [ description text ]
• Method 2:
ip route-static vpn-instance
s-vpn-instance-name dest-address
{ mask-length | mask } interface-type
interface-number [ next-hop-address
[ backup-interface interface-type
interface-number [ backup-nexthop
backup-nexthop-address ] ] ]
[ permanent ] [ preference preference ]
[
tag-value ] [
N/A
By default, static route FRR
is disabled.
text ]
13
Page 26

Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Step
Command
Remarks
Task
Command
Configuring static route FRR to automatically select a backup next hop
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure static route FRR to
automatically select a
backup next hop.
ip route-static fast-reroute auto
N/A
By default, static route FRR is
disabled from automatically
selecting a backup next hop.
Enabling BFD echo packet mode for static route FRR
By default, static route F RR uses ARP to detec t primary link failures . Perform this task to enable
static route FRR to use BFD echo packet mode for fast failure detection on the primary link.
To enable BFD echo packet mode for static route FRR:
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the source IP
address of BFD echo
packets.
system-view
bfd echo-source-ip
ip-address
N/A
By default, the source IP address
of BFD echo packets is not
configured.
The source IP address cannot be
on the same network segment as
any local interface's IP address.
For more information about this
command, see High Availability
Command Reference.
3. Enable BFD echo packet
mode for static route FRR.
ip route-static
primary-path-detect bfd echo
By default, BFD echo mode for
static route FRR is disabled.
Displaying and maintaining static routes
Execute display commands in any view.
Display static route information.
Display static route next hop
information.
Display static routing table
information.
display ip routing-table protocol static
display route-static nib
display route-static routing-table
vpn-instance-name ] [ ip-address { mask-length | mask } ]
[ nib-id ] [
verbose ]
[
inactive
[
vpn-instance
verbose ]
|
14
Page 27
Vlan-int100
1.1.6.1/24
Host B
1.1.6.2/24
Vlan-int500
1.1.4.2/30
Vlan-int600
1.1.5.5/30
Vlan-int500
1.1.4.1/30
Vlan-int600
1.1.5.6/30
Vlan-int900
1.1.3.1/24
Vlan-int300
1.1.2.3/24
Host A
1.1.2.2/24
Host C
1.1.3.2/24
Switch B
Switch A
Switch C
Static route configuration examples
Basic static route configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 2, c onf i gure s tat ic routes on th e switches for interc onnections between an y t wo
hosts.
Figure 2 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes:
# Configure a default route on Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.4.2
# Configure two static routes on Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ip route-static 1.1.2.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.4.1
[SwitchB] ip route-static 1.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.5.6
# Configure a default route on Switch C.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.5.5
3. Configure the default gateways of Host A, Host B, and Host C as 1.1.2.3, 1.1.6.1, and 1.1.3.1. (Details not shown.)
Verifying the configuration
# Display static routes on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table protocol static
Summary Coun t : 1
Static Routing table Status : <Active>
Summary Coun t : 1
15
Page 28

Destination/M ask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/0 Static 60 0 1.1.4.2 Vlan500
Static Routing ta ble Status : <Inacti ve>
Summary Coun t : 0
# Display static routes on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display ip routing-table protocol static
Summary Coun t : 2
Static Routing table Status : <Acti ve >
Summary Coun t : 2
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
1.1.2.0/24 Static 60 0 1.1.4.1 Vlan500
Static Routing table Status : <Inac ti ve>
Summary Coun t : 0
# Use the ping command on Host B to test the reachability of Host A (Windows XP runs on the two
hosts).
C:\Documents an d Settings\Administrator>ping 1.1.2.2
Pinging 1.1.2.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 1.1 .2.2: bytes=32 tim e=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 1.1 .2.2: bytes=32 tim e=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 1.1 .2.2: bytes=32 tim e=1ms TTL=126
Reply from 1.1 .2.2: bytes=32 tim e=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 1.1.2.2:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 1ms
# Use the tracert command on Host B to test the reachability of Host A.
C:\Documents an d Settings\Administrator>tracert 1.1.2.2
Tracing rout e to 1.1.2.2 over a maxi mum of 30 hops
1 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 1.1.6.1
2 <1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 1.1.4.1
3 1 ms <1 ms <1 ms 1.1.2.2
Trace complete.
BFD for static routes configuration e x ample (direct next hop)
Network requirements
Configure the following, as shown in Figure 3:
16
Page 29

•
•
•
•
Device
Interface
IP address
Switch A Switch B
Switch C
BFD
L
2
Switch
Vlan-int10
Vlan
-int
11
Vlan-int11
Vlan
-int
13
Vlan-
int13
Vlan-int10
121.
1
.1
.0
/
24
120.1.1.0/24
Configure a static route to subnet 120.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
Configure a static route to subnet 121.1.1.0/ 24 on S wit c h B.
Enable BFD for both routes.
Configure a static route to subnet 120.1.1.0/24 and a static route to subnet 121.1.1.0/24 on
Switch C.
When the link between S witc h A and Switch B through the Layer 2 switch fai ls, B F D c an det ec t th e
failure immediately. Switch A then communicates with Switch B through Switch C.
Figure 3 Network diagram
Table 4 Interface and IP address assignment
Switch A VLAN-interface 10 12.1.1.1/24
Switch A VLAN-interface 11 10.1.1.102/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 10 12.1.1.2/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 13 13.1.1.1/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 11 10.1.1.100/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 13 13.1.1.2/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for the interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes and BFD:
# Configure static routes on Switch A and enable BFD control mode for the static route that
traverses the Layer 2 switch.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 10
[SwitchA-vlan-interface10] bfd min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchA-vlan-interface10] bfd min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchA-vlan-interface10] bfd detect-multiplier 9
[SwitchA-vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchA] ip route-static 120.1.1.0 24 vlan-interface 10 12.1.1.2 bfd control-packet
[SwitchA] ip route-static 120.1.1.0 24 vlan-interface 11 10.1.1.100 preference 65
[SwitchA] quit
# Configure static routes on Switch B and enable BFD control mode for the static route that
traverses the Layer 2 switch.
<SwitchB> sy stem-view
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 10
17
Page 30

[SwitchB-vlan-interface10] bfd min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchB-vlan-interface10] bfd min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchB-vlan-interface10] bfd detect-multiplier 9
[SwitchB-vlan-interface10] quit
[SwitchB] ip route-static 121.1.1.0 24 vlan-interface 10 12.1.1.1 bfd control-packet
[SwitchB] ip route-static 121.1. 1.0 24 vlan-interface 13 13.1.1.2 preference 65
[SwitchB] qu it
# Configure static routes on Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] ip rout e-static 120.1.1.0 24 13.1.1.1
[SwitchC] ip rout e-static 121.1.1.0 24 10.1.1.102
Verifying the configuration
# Display BFD sessions on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display bfd session
Total Session Nu m: 1 Up Session Num: 1 Init Mode: Active
IPv4 Session Working Under Ctrl Mode:
LD/RD SourceAddr DestAddr State Holdtime Interf ace
4/7 12.1.1.1 12.1.1.2 Up 2000ms Vlan10
The output shows that the BFD session has been created.
# Display the static routes on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table protocol static
Summary Coun t : 1
Static Routing table Status : <Acti ve >
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 Static 60 0 12.1.1 .2 Vlan10
Static Routing ta ble Status : <Inacti ve>
Summary Coun t : 0
The output shows that Swit ch A communicates with Sw itch B thr ough VLAN-interface 10. Then the
link over VLAN-interface 10 fails.
# Display static routes on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table protocol static
Summary Coun t : 1
Static Routing table Status : <Acti ve >
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 Static 65 0 10.1.1 .100 Vlan11
18
Page 31

•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Device
Interface
IP address
Switch A Switch B
Switch C
BFD
Vlan-int10
Vlan
-
int
11
Vlan-int11 Vlan-int13
Vlan-
int
13
Vlan-int10
121.1.1.0/24
120.1.1.0/24
Switch D
Vlan-int12
Vlan-int12
Loop1
1.1.1.9/32
Loop1
2.2.2.9/32
Static Routing ta ble Status : <Inacti ve>
Summary Coun t : 0
The output shows that Switch A communicates with Switch B through VLAN-interface 11.
BFD for static routes configuration example (indirect next hop)
Network requirements
Figure 4 shows the network topology as follows:
Switch A has a route to interface Loopback 1 (2.2.2.9/32) on Switch B, with the output interface
VLAN-interface 10.
Switch B has a route to interface Loopback 1 (1.1.1.9/32) on Switch A, with the output interface
VLAN-interface 12.
Switch D has a route to 1.1.1.9/32, with the output interface VLAN-interface 10, and a route to
2.2.2.9/32, with the output interfac e VLAN-interface 12.
Configure the following:
Configure a static route to subnet 120.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
Configure a static route to subnet 121.1.1.0/24 on Switch B.
Enable BFD for both routes.
Configure a static route to subnet 120.1.1.0/24 and a static route to subnet 121.1.1.0/24 on both
Switch C and Switch D.
When the link between Switch A and Switch B through Switch D fails, BFD can detect the failure
immediately. Switch A then communicates with Switch B through Switch C.
Figure 4 Network diagram
Table 5 Interface and IP address assignment
Switch A VLAN-interface 10 12.1.1.1/24
Switch A VLAN-interface 11 10.1.1.102/24
Switch A Loopback 1 1.1.1.9/32
Switch B VLAN-interface 12 11.1.1.1/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 13 13.1.1.1/24
Switch B Loopback 1 2.2.2.9/32
19
Page 32

Device
Interface
IP address
Switch C VLAN-interface 11 10.1.1.100/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 13 13.1.1.2/24
Switch D VLAN-interface 10 12.1.1.2/24
Switch D VLAN-interface 12 11.1.1.2/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static routes and BFD:
# Configure static routes on Switch A and enable BFD control mode for the static route that
traverses Switch D.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] bf d multi-hop min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchA] bf d multi-hop min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchA] bfd multi-hop detect-multiplier 9
[SwitchA] ip route-static 120.1.1.0 24 2.2.2.9 bfd control-packet bfd-source 1.1.1.9
[SwitchA] ip route-static 120.1.1.0 24 vlan-interface 11 10.1.1.100 preference 65
[SwitchA] quit
# Configure static routes on Switch B and enable BFD control mode for the static route that
traverses Switch D.
<SwitchB> sy stem-view
[SwitchB] bfd multi-hop min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchB] bfd multi-hop min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchB] bfd multi-hop detect-multiplier 9
[SwitchB] ip route-static 121.1.1.0 24 1.1.1.9 bfd control-packet bfd-source 2.2.2.9
[SwitchB] ip route-static 121.1. 1.0 24 vlan-interface 13 13.1.1.2 preference 65
[SwitchB] qu it
# Configure static routes on Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] ip rout e-static 120.1.1.0 24 13.1. 1.1
[SwitchC] ip rout e-static 121.1.1.0 24 10.1.1.102
# Configure static routes on Switch D.
<SwitchD> sy stem-view
[SwitchD] ip rout e-static 120.1.1.0 24 11.1.1.1
[SwitchD] ip rout e-static 121.1.1.0 24 12.1.1.1
Verifying the configuration
# Display BFD sessions on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display bfd session
Total Session Nu m: 1 Up Session Num: 1 Init Mode: Active
IPv4 Session Working Under Ctrl Mode:
LD/RD SourceAddr DestAddr State Holdtime Interf ace
4/7 1.1.1.9 2.2.2.9 Up 2000ms N/A
The output shows that the BFD session has been created.
20
Page 33

Switch A Switch B
Switch C
Loop0
Vlan-int100
Vlan-
int200
Vlan-int200
Vlan-int100
Vlan
-int101
Vlan-int101
Loop0
Link A
Link B
# Display the static routes on Switch A.
<SwitchA> di splay ip routing-table protocol static
Summary Coun t : 1
Static Routing table Statu s : <Active>
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 Static 60 0 12.1.1 .2 Vlan10
Static Routing ta ble Status : <Inacti ve>
Summary Coun t : 0
The output shows that Swit ch A communicates with Sw itch B thr ough VLAN-interface 10. Then the
link over VLAN-interface 10 fails.
# Display static routes on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table protocol static
Summary Coun t : 1
Static Routing table Status : <Active>
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 Static 65 0 10.1.1 .100 Vlan11
Static Routing ta ble Status : <Inacti ve>
Summary Coun t : 0
The output shows that Switch A communicates with Switch B through VLAN-interface 11.
Static route FRR configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 5, conf igure static routes on Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C, and configure
static route FRR. When Link A becomes unidirectional, traffic can be switched to Link B immediately.
Figure 5 Network diagram
21
Page 34

Device
Interface
IP address
Table 6 Interface and IP address assignment
Switch A VLAN-interface 100 12.12.12.1/24
Switch A VLAN-interface 200 13.13.13.1/24
Switch A Loopback 0 1.1.1.1/32
Switch B VLAN-interface 101 24.24.24.4/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 200 13.13.13.2/24
Switch B Loopback 0 4.4.4.4/32
Switch C VLAN-interface 100 12.12.12.2/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 101 24.24.24.2/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure static route FRR on link A by using one of the following methods:
(Method 1.) Specify a backup next hop for static route FRR:
# Configure a static route on Switch A, and specify VLAN-interface 100 as the backup
output interface and 12.12.12.2 as the backup next hop.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 vlan-interfa ce 200 13.13.13.2
backup-interface vlan-interface 100 backup-nexthop 12.12.12.2
# Configure a static route on Switch B, and specify VLAN-interface 101 as the backup
output interface and 24.24.24.2 as the backup next hop.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 vlan-interfa ce 200 13.13.13.1
backup-interface vlan-interface 101 backup-nexthop 24.24.24.2
(Method 2.) Configure static route FRR to automatically select a backup next hop:
# Configure static routes on Switch A, and enable static route FRR.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 vlan-interfac e 200 13.13.13.2
[SwitchA] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 vl an-interface 100 12.12. 12.2 preference 70
[SwitchA] ip rout e-static fast -reroute auto
# Configure static routes on Switch B, and enable static route FRR.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 vlan-interfac e 200 13.13.13.1
[SwitchB] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 vl an-interface 101 24.24.24.2 preference 70
[SwitchB] ip route-static fast-reroute auto
3. Configure static routes on Switch C.
<SwitchC> system-view
[SwitchC] ip route-static 4.4.4.4 32 vlan-interfa ce 101 24.24.24.4
[SwitchC] ip route-static 1.1.1.1 32 vlan-interfa ce 100 12.12.12.1
Verifying the configuration
# Display route 4.4.4.4/32 on Switch A to view the backup next hop information.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table 4.4.4.4 verbose
Summary Coun t : 1
22
Page 35

Destination: 4. 4.4.4/32
Protocol: Static
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x0 Age: 04h20m37s
Cost: 0 Preference: 60
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x2 OrigAs: 0
NibID: 0x 26000002 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0x ffffffff Neighbor: 0. 0.0.0
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 13.13.13.2
Label: NULL RealNextHop: 13.13.13.2
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: 12.12.12.2
Tunnel ID: Inva lid Interface: Vlan-interface200
BkTunnel ID: Inva lid BkInterface: Vl an-interface100
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A
# Display route 1.1.1.1/32 on Switch B to view the backup next hop information.
[SwitchB] display ip routing-table 1.1.1.1 verbose
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination: 1.1.1.1/32
Protocol: Static
Process ID: 0
SubProtID: 0x0 Age: 04h20m37s
Cost: 0 Preference: 60
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x2 OrigAs: 0
NibID: 0x26000002 Last As: 0
AttrID: 0x ffffffff Neighbor: 0. 0.0.0
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 13.13.13.1
Label: NULL RealNextHop: 13.13.13.1
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: 24.24.24.2
Tunnel ID: Inva lid Interface: Vlan-interface200
BkTunnel ID: Inva lid BkInterface: Vlan-interface101
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A
23
Page 36

•
•
Configuring a default route
A default route is used to forward packets that do not match any specific routing entry in the routing
table. Without a def ault route, p ackets that do not m atch any routi ng entries ar e discarded and an
ICMP destination-unreachable packet is sent to the source.
A default route can be configured in either of the following ways:
The network administrator can configure a default route with both destinat ion an d mask being
0.0.0.0. For more information, see "
Some dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF, RIP, and IS-IS, can generate a default route.
For example, an upstream router running OSPF can generate a default route and advertise it to
other routers. These routers install the default route with the next hop being the upstream router.
For more information, see the respective chapters on these routing protocols in this
configuration guide.
Configuring static routing."
24
Page 37

•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Configuring RIP
Overview
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance-vector IGP suited to small-sized networks. It
employs UDP to exchange route inform ation through port 520.
RIP u ses a hop cou nt to measure the distanc e to a destination. The hop count fr om a router to a
directly connected net work is 0. T he hop count from a r outer to a direc tly connect ed router is 1. To
limit convergence tim e, RI P restr icts the val ue ran ge of t he metric from 0 to 15. A destination with a
metric value of 16 ( or greater) is considered unreachabl e. For this reason, RI P is not suitable f or
large-sized networks.
RIP route entries
RIP stores routing entries in a database. Each routing entry contains the following elements:
Destination address—IP address of a destination host or a network.
Next hop—IP address of the next hop.
Egress interface—Egress interface of the route.
Metric—Cost from the local router to the destination.
Route time—Time elapsed since the last update. The time is reset to 0 when the routing entry
is updated.
Route tag—Used for route control. For more information, see "Configuring routing policies."
Routing loop prevention
RIP uses the following mechanisms to prevent routing loops:
Counting to infinity—A destination with a metric value of 16 is considered unreachable. When
a routing loop occurs, the metric value of a route will increment to 16 to avoid endless looping.
Triggered updates—RIP immediately advertises triggered updates for topology changes to
reduce the possibility of routing loops and to speed up convergence.
Split horizon—Disables RIP from sending routes through the inter f ace where the routes were
learned to prevent routing loops and save bandwidth.
Poison reverse—Enables RIP to set the metric of routes received from a neighbor to 16 and
sends these routes back to the neighbor. The neighbor can delete such information from its
routing table to prevent routing loops.
RIP operation
RIP works as follows:
1. RIP sends request messages to neighboring routers. Neighboring routers return response messages that contain their routing tables.
2. RIP uses the received responses to update the local routing table and sends triggered update messages to its neighbors. All RIP routers on the network do this to learn latest routing information.
3. RIP periodically sends the local routing table to its neighbors. After a RIP neighbor receives the message, it updates its routing table, selects optimal routes, and sends an update to other neighbors. RIP ages routes to keep only valid routes.
25
Page 38

•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Tasks at a glance
RIP versions
There are two RIP versions, RIPv1 and RIPv2.
RIPv1 is a classful routing protocol. It advertises messages only through broadcast. RIPv1
messages do not car ry mask information, so RIPv1 c an only recognize natura l networks such as
Class A, B, and C. For this reason, RIPv1 does not support discontiguous subnets.
RIPv2 is a classless routing protocol. It has the following advantages over RIPv1:
Supports route tags to implement flexible route control through routing policies.
Supports masks, route summarization, and CIDR.
Supports designated nex t h ops to select the best ones on broadcast networks.
Supports multicasting route updates so only RIPv2 routers can receive these updates to reduce
resource consumption.
Supports plain text authentication and MD5 authentication to enhance security.
RIPv2 supports two trans mission modes: broadcast and m ulticast. Multicast is the default mode
using 224.0.0.9 as the multicast address. An interface operating in RIPv2 broadcast mode can also
receive RIPv1 messages.
Protocols and standards
RFC 1058, Routing Information Protocol
RFC 1723, RIP Version 2 - Carrying Additional Information
RFC 1721, RIP Version 2 Protocol Analysis
RFC 1722, RIP Version 2 Protocol Applicability Statement
RFC 1724, RIP Version 2 MIB Extension
RFC 2082, RIPv2 MD5 Authentication
RFC 2453, RIP Version 2
RIP configuration task list
Configuring basic RIP:
• (Required.) Enabling RIP
• (Optional.) Controlling RIP reception and advertisement on interfaces
• (Optional.) Configuring a RIP version
(Optional.) Configuring RIP route control:
• Configuring an additional routing metric
• Configuring RIPv2 route summarization
• Disabling host route reception
• Advertising a default route
• Configuring received/redistributed route filtering
• Setting a preference for RIP
• Configuring RIP route redistribution
26
Page 39

Tasks at a glance
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
(Optional.) Tuning and optimizing RIP networks:
• Setting RIP timers
• Enabling split horizon and poison reverse
• Setting the maximum number of RIP ECMP routes
• Enabling zero field check on incoming RIPv1 messa ges
• Enabling source IP address check on incoming RIP updates
• Configuring RIPv2 message authentication
• Setting the RIP triggered update interval
• Specifying a RIP neighbor
• Configuring RIP network management
• Configuring the RIP packet sending rate
• Setting the maximum length of RIP packets
• Setting the DSCP value for outgoing RIP packets
(Optional.) Configuring RIP GR
(Optional.) Enabling RIP NSR
(Optional.) Configuring BFD for RIP
(Optional.) Configuring RIP FRR
Configuring basic RIP
Before you configure basic RIP settings, complete the following tasks:
Configure the link layer protocol.
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring routers.
Enabling RIP
Follow these guidelin es when you enabl e RIP:
To enable multiple RIP processes on a router, you must specify an ID for each process. A RIP
process ID has only local significance. Two RIP routers having different process IDs can also
exchange RIP packets.
If you configure RIP settings in interface view before enabling RIP, the settings do not take
effect until RIP is enabled.
If a physical interface is attached to multiple networks, you cannot advertise these networks in
different RIP processes.
You cannot enable multiple RIP processes on a physical interface.
The rip enable command takes precedence over the network command.
Enabling RIP on a network
You can enable RIP on a net work and spec ify a w ildcard m ask for t he network . After that, only th e
interface attached to the network runs RIP.
To enable RIP on a network:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
27
N/A
Page 40

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
2. Enable RIP and enter RIP
view.
3. Enable RIP on a network.
Enabling RIP on an interface
1. Enter system view.
2. Enable RIP and enter RIP
view.
3. Return to system view.
4. Enter interface view.
5. Enable RIP on the interface.
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
network
[ wildcard-mask ]
system-view
rip
vpn-instance-name ]
quit
interface
interface-number
rip
exclude-subip
[
network-address
[ process-id ] [
interface-type
process-id
vpn-instance
vpn-instance
enable
]
By default, RIP is disabled.
By default, RIP is disabled on a
network.
network
The
can enable RIP on al l interf aces i n
a single process, but does not
apply to multiple RIP processes.
N/A
By default, RIP is disabled.
N/A
N/A
By default, RIP is disabled on an
interface.
0.0.0.0 command
Controlling RIP reception and adverti sement on interfaces
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Disable an interface from
sending RIP messages.
4. Return to system view.
5. Enter interface view.
6. Enable an interface to
receive RIP messages.
7. Enable an interface to send
RIP messages.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
silent-interface
interface-number |
quit
interface
interface-number
rip input
rip output
interface-type
vpn-instance
{ interface-type
all
N/A
N/A
By default, all RIP-enabled
interfaces can send RIP
messages.
}
The disabled interface can still
receive RIP messages and
respond to unicast requests
containing unknown ports.
N/A
N/A
By default, a RIP-enabled
interface can receive RIP
messages.
By default, a RIP-enabled
interface can send RIP
messages.
28
Page 41

•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
Configuring a RIP version
You can configure a global RIP version i n RI P view or an interface-specific R IP version i n interface
view.
An interface preferent ially us es the interf ace-spec ific RIP version. If no interf ace-spe cific versio n is
specified, the interf ace uses the global RIP version. If neither a global nor interfac e-specific RIP
version is configured, the interface sends RIPv1 broadcasts and can receive the following:
RIPv1 broadcasts and unicasts.
RIPv2 broadcasts, multicasts, and unicasts.
To configure a RIP version:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Specify a global RIP version.
4. Return to system view.
5. Enter interface view.
6. Specify a RIP version for the
interface.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
version
quit
interface
interface-number
rip version
multicast
{ 1 | 2 }
interface-type
] }
vpn-instance
{ 1 | 2 [
broadcast
Configuring RIP route control
N/A
N/A
By default, no global version is
specified. An interface sends
RIPv1 broadcasts, and can
receive RIPv1 broadcasts and
unicasts, and RIPv2 broadcasts,
multicasts, and unicasts.
N/A
N/A
By default, no interface-specific
RIP version is specified. The
interface sends RIPv1
|
broadcasts, and can receive
RIPv1 broadcasts and unicasts,
and RIPv2 br oadcasts, multicasts,
and unicasts.
Before you configure RIP route control, complete the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring routers.
Configure basic RIP.
Configuring an add i tional routing metric
An additional rout ing m etric (hop c ount) can b e added to the m etr ic of an inbound or outbound RIP
route.
An outbound additional m etric is added to the metr ic of a sent route, and it does not change the
route's metric in the routing table.
An inbound additional metric is added to the metric of a received route before the route is added into
the routing table, and the route's metric is changed. If the sum of the addition al metric and the
original metric is greater than 16, the metric of the route is 16.
To configure additional routing metrics:
29
Page 42

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
quit
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Specify an inbound
additional routing metric.
4. Specify an outbound
additional routing metric.
system-view
interface
interface-number
rip metricin
route-policy-name ]
rip metricout
route-policy-name ] value
interface-type
route-policy
[
value
route-policy
[
Configuring RI P v2 route summarization
Perform this task to summarize contiguous subnets into a summary network and sends the network
to neighbors. The smallest metric among all summarized routes is used as the metric of the
summary route.
Enabling RIPv2 automatic route summarization
Automatic summarization enables RIP v2 t o ge ner at e a natur a l net work for contiguous subnets. F or
example, suppose there are three subnet routes 10.1.1.0/24, 10.1.2.0/24, and 10.1.3.0/24.
Automatic summ ar ization a utomatically creates and advertises a summ ar y route 1 0.0.0 . 0/8 inste ad
of the more specific routes.
To enable RIPv2 automatic route summarization:
N/A
N/A
The default setting is 0.
The default setting is 1.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. (Optional.) Enable RIPv2
automatic route
summarization.
Advertising a summary route
Perform this task to manually configure a summary route.
For example, suppose cont iguous subne ts routes 10.1 .1.0/24, 10 .1.2 .0/24, an d 10.1.3 .0/24 ex ist in
the routing table. You can create a summary route 10.1.0.0/16 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 to advertise
the summary route instead of the more specific routes.
To configure a summary route:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
summary
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
By default, RIPv2 automatic route
summarization is enabled.
If subnets in the routing table are
not contiguous, disable automat ic
route summarization to advertise
more specific routes.
N/A
N/A
3. Disable RIPv2 automatic
route summarization.
4. Return to system view.
undo summary
30
By default, RIPv2 automatic route
summarization is enabled.
N/A
Page 43

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Step
Command
Remarks
NOTE:
The router enabled to advertise a default route does not accept default routes from RIP neighbors.
5. Enter interface view.
6. Configure a summary route.
interface
interface-number
rip summary-address
ip-address { mask-length | mask }
Disabling host r oute reception
Perform this task to disable RIPv2 from receiving host routes from the same network to save network
resources. This feature does not apply to RIPv1.
To disable RIP from receiving host routes:
1. Enter system view.
rip
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Disable RIP from receiving
host routes.
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
undo host-route
Advertising a default route
interface-type
vpn-instance
N/A
By default, no summary route is
configured.
N/A
N/A
By default, RIP receives host
routes.
You can advertise a defaul t route on all RIP interfaces in RIP view or on a specific RI P interface in
interface view. The interface view setting takes precedence over the RIP view settings.
To disable an interface from advertis ing a default route, use the rip default-route no-originate
command on the interface.
To configure RIP to advertise a default route:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Enable RIP to advertise a
default route.
4. Return to system view.
5. Enter interface view.
6. Configure the RIP interface
to advertise a default route.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
default-route
cost
[
cost-value |
route-policy-name ] *
quit
interface
interface-number
rip default-route
originate
route-policy
* |
interface-type
} [
no-originate
vpn-instance
only
{
route-policy
{ {
cost
cost-value |
route-policy-name ]
}
originate
|
only
|
N/A
N/A
}
By default, RIP does not adver tise
a default route.
N/A
N/A
By default, a RIP interface can
advertise a default route if the RIP
process is enabled to advertise a
default route.
31
Page 44

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Configuring received/redistributed route filtering
Perform this task to filter received and redistributed routes by using a filtering policy.
To configure route filtering:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Configure the filtering of
received routes.
4. Configure the filtering of
redistributed routes.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
filter-policy
gateway
prefix-list-name [
prefix-list-name ] }
[ interface-type interface-number ]
filter-policy
prefix-list
[ protocol [ process-id ] | interface-type
interface-number ]
prefix-list-name |
Setting a preference for RIP
If multiple IGPs find rou tes to the s ame destination, the r oute f oun d by the IGP that has the highest
priority is selected as the optimal route. Perform this task to assign a preference to RIP. The smaller
the preference value, the higher the priority.
vpn-instance
{ ipv4-acl-number |
gateway
{ ipv4-acl-number |
prefix-list-name }
import
prefix-list
export
N/A
N/A
By default, the filtering of
received routes is not
configured.
This command filters received
routes. Filtered routes are not
installed into the routing table or
advertised to neighbors.
By default, the filtering of
redistributed routes is not
configured.
This command filters
redistributed routes, including
routes redistributed with the
import-route
command.
To set a preference for RIP:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Set a preference for RIP.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
preference
route-policy
vpn-instance
{ preference |
route-policy-name } * The default setting is 100.
Configuring RI P route redistribution
Perform this task to configure RIP to redistribute routes from other routing protocols, including OSPF ,
IS-IS, BGP, static, and direct.
To configure RIP route redistribution:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
N/A
N/A
32
Page 45

Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
•
•
•
•
IMPORTANT:
To avoid unnecessary traffic or route flapping, configure identical RIP timer settings on RIP routers.
Step
Command
Remarks
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Redistribute routes from
another routing protocol.
4. (Optional.) Set a default cost
for redistributed routes.
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
import-route
[ as-number ] [ process-id |
all-processes | allow-ibgp
allow-direct
[
route-policy
tag
tag ] *
default cost
vpn-instance
protocol
]
cost
|
cost-value |
route-policy-name |
cost-value
N/A
By default, RIP route
redistribution is disabled.
This command can redistribute
only active routes. To view active
routes, use the
routing-table protocol
command.
The default setting is 0.
Tuning and optimizing RIP networks
Configuration prerequisites
Before you tune and optimize RIP networks, complete the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
Configure basic RIP.
Setting RIP timers
display ip
You can change the RIP network convergence speed by adjusting the following RIP timers:
Update timer—Specifies the interval between route updates.
Timeout timer—Specifies the route aging time. If no update for a route is received within the
aging time, the metric of the route is set to 16.
Suppress timer—Specifies how long a RIP route stays in suppressed state. When the metric
of a route is 16, the route enters the suppressed state. A suppressed route can be replaced by
an updated route that is received from the same neighbor before the suppress timer expires
and has a metric less tha n 16.
Garbage-collect timer—Specifies the interval from when the metric of a route becomes 16 to
when it is deleted from the routing table. RIP advertises the route with a metric of 16. If no
update is announced for that route before the garbage-collect timer expires, the route is deleted
from the routing table.
To set RIP timers:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
33
Page 46

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
By default:
• The garbage-collect timer is 120
• The suppress timer is 120
• The timeout timer is 180 seconds.
• The update timer is 30 seconds.
3. Set RIP timers.
timers { garbage-collect
garbage-collect-value |
suppress-value |
timeout-value |
update-value } *
update
suppress
timeout
Enabling split horizon and poison reverse
The split horizon and poison reverse functions can prevent routing loops.
If both split horizon and poison reverse are configured, only the poison reverse function takes effect.
Enabling split horizon
Split horizon disables RIP from sending routes through the interface where the routes were learned
to prevent routing loops bet ween adjacent routers.
To enable split horizon:
seconds.
seconds.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable split horizon.
system-view
interface
interface-number
rip split-horizon
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, split horizon is
enabled.
Enabling poison reverse
Poison reverse allows RIP to send routes through the interface where the routes were learned. The
metric of these routes is always set to 16 (unreachable) to avoid routing loops between neighbors.
To enable poison reverse:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable poison reverse.
system-view
interface
interface-number
rip poison-reverse
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, poison reverse is
disabled.
Setting the maxim um number of RIP ECMP routes
Perform this task to implement load sharing over ECMP routes.
To set the maximum number of RI P ECMP routes:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
34
N/A
Page 47

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Set the maximum number of
RIP ECMP routes.
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
maximum load-balancing
number
vpn-instance
N/A
By default, the maximum number
of RIP ECMP routes equals the
maximum number of ECMP
routes supported by the system.
Enabling zero field check on incoming RIPv1 messages
Some fields in the RIPv1 message must be set to zero. These fields are called "zero fields." Y ou can
enable zero field check on incoming RIPv1 messages. If a zero field of a message contains a
non-zero value, RIP does not process the message. If you are certain that all messages are
trustworthy, disable zero field check to save CPU resources.
This feature does not apply to RIPv2 packets, because they have no zero fields.
To enable zero field check on incoming RIPv1 messages:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Enable zero field check on
incoming RIPv1 messages.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
checkzero
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
The default setting is enabled.
Enabling source IP address check on incoming RIP updates
Perform this task to enable source IP address check on incoming RIP updates.
Upon receiving a message, RIP compares the source IP address of the message with the IP address
of the receiving interface. If they are not in the same network segment, RIP discards the message.
To enable source IP address check on incoming RIP updates:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Enable source IP address
check on incoming RIP
messages.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
validate-source-address
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
By default, this function is
enabled.
Configuring RI P v2 message authent i c ation
Perform this task to enable authentication on RIPv2 messages. This feature does not apply to RIPv1
because RIPv1 does not support authentic ation. A lthough you can sp ecify an authent ication m ode
for RIPv1 in interface view, the configuration does not take effect.
RIPv2 supports two authentication modes: simple authenticat ion and MD 5 auth ent icat ion.
To configure RIPv2 message authentication:
35
Page 48

Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Configure RIPv2
authentication.
system-view
interface
rip authentication-mode
cipher
{
cipher
{
plain }
interface-type interface-number
plain
|
|
string }
} string key-id |
plain
} string } |
md5
{
simple { cipher
rfc2082
{
rfc2453
Setting the RIP t riggered update inter v al
Perform this task to avoid network overh ead and red uce system r esource consum ption caused b y
frequent RIP triggered updates.
You can use the timer triggered comm and to set the maximum interval, minim um interval, and
incremental interval for sending RIP triggered updates.
For a stable network, the minimum-interval is used.
If network changes become frequent, the incremental interval incremental-interval is used to
extend the triggered update sending int er val unti l the maximum-interval is reached.
To set the triggered update interval:
1. Enter system view.
N/A
N/A
By default, RIPv2
authentication is not
|
configured.
N/A
rip
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Set the RIP triggered
update interval.
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
timer triggered
[ minimum-interval [ incremental-interval ] ]
Specifying a RIP nei ghbor
Typically RIP m essages are sent in broadcast or multicast. To enable RIP on a link that does n ot
support broadcast or multicast, you must manually specify RIP neighbors.
Follow these guidelines when you specify a RIP neighbor:
Do not use the peer ip-address command when the neighbor is directly connected. Otherwise,
the neighbor might receive both unicast and multicast (or broadcast) messages of the same
routing information.
If the specified neighbor is not directly connected, disable source address check on incoming
updates.
To specify a RIP neighbor:
vpn-instance
maximum-interval
N/A
By default:
• The maximum interval
is 5 seconds.
• The minimum interval is
50 milliseconds.
• The incremental interval
is 200 milliseconds.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
vpn-instance
36
N/A
N/A
Page 49

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
3. Specify a RIP neighbor.
4. Disable source IP
address check on
inbound RIP updates
peer
ip-address
undo validate-source-address
Configuring RI P network management
You can use network management software to manage the RIP process to which MIB is bound.
To configure RIP network management:
1. Enter system view.
2. Bind MIB to a RIP
process.
system-view
rip mib-binding
process-id
Configuring the RIP packet sending rat e
Perform this task to set the interval for sending RIP packets and the maximum number of RIP
packets that can be sent at each interval. This feature can avoid excessive RIP packets from
affecting system performance and consuming too much bandwidth.
By default, RIP does not
unicast updates to any
peer.
By default, source IP
address check on inbound
RIP updates is enabled.
N/A
By default, MIB is bound to the
RIP process with the smallest
process ID.
To configure the RIP packet sending rate:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Set the interval for sending
RIP packets and the
maximum number of RIP
packets that can be sent at
each interval.
4. Return to system view.
5. Enter interface view.
6. Set the interval for sending
RIP packets and the
maximum number of RIP
packets that can be sent at
each interval.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
output-delay
quit
interface
interface-number
rip output-delay
count
vpn-instance
count
time
interface-type
time
count
count
N/A
N/A
By default, an interface sends up
to three RIP packets every 20
milliseconds.
N/A
N/A
By default, the interface uses the
RIP packet sending rate
configured for the RIP process
that the interface runs.
37
Page 50

CAUTION:
The supported maximum length of RIP packets varies by vendor
avoid compatibility issues.
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
Setting the maximum l ength of RIP packet s
. Use this feature with caution to
The packet length of RI P pack et s determines how m an y routes c a n be car r ied in a R I P pack et. S et
the maximum length of RIP packets to make good use of link bandwidth.
When authentication is enabled, follow these guidelines to ensure packet forwarding:
For simple authentication, the maximum length of RIP packets must be no less than 52 bytes.
For MD5 authentication (with packet format defined in RFC 2453), the maximum length of RIP
packets must be no less than 56 bytes.
For MD5 authentication (with packet format defined in RFC 2082), the maximum length of RIP
packets must be no less than 72 bytes.
To set the maximum length of RIP packets:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Set the maximum length of
RIP packets.
system-view
interface
interface-number
rip max-packet-length
interface-type
value
N/A
N/A
By default, the maximum l ength of
RIP packets is 512 bytes.
Setting the DSCP value for outgoing RIP packets
The DSCP value specifies the precedence of outgoing packets.
To set the DSCP value for outgoing RIP packets:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Set the DSCP value for
outgoing RIP packets.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
dscp
dscp-value
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
By default, the DSCP value for
outgoing RIP packets is 48.
Configuring RIP GR
GR ensures forwar ding cont inuity wh en a r outing prot ocol res tarts or an act ive/standb y switc hover
occurs.
Two routers are required to complete a GR process. The following are router roles in a GR process:
GR restarter—Graceful restarting router. It must have GR capability.
GR helper—A neighbor of the GR restarter. It helps the GR restarter to complete the GR
process.
After RIP restarts on a router, the router must learn RIP routes again and update its FIB table, which
causes network disconnections and route reconvergence.
38
Page 51

IMPORTANT:
You cannot enable RIP NSR on a device that acts as GR restarter.
Step
Command
Remarks
IMPORTANT:
A device that has RIP NSR enabled cannot act as GR restarter.
Step
Command
Remarks
With the GR feature, the restarting router (known as the GR restarter) can notify the event to its GR
capable neighbors. G R capable neighb ors (known as GR helpers) maintain their adj acencies with
the router within a GR interval. During this process, the FIB table of the router does not change. After
the restart, the router contacts its neighbors to retrieve its FIB.
By default, a RIP-enabled device acts as the GR helper. Perform this task on the GR restarter.
To configure GR on the GR restarter:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Enable GR for RIP.
4. (Optional.) Set the GR
interval.
Enabling RIP NSR
Nonstop Routing (N SR) allows the device to back up the routing information from the acti ve RIP
process to the standb y RIP process. After an active/st andby switchover, NSR can complete rout e
regeneration without tearing down adjacencies or impacting forwarding services.
NSR does not require the cooperation of neighboring devices to recover routing information, and it is
typically used more often than GR.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
graceful-restart
graceful-restart interv al
vpn-instance
interval
N/A
N/A
By default, RIP GR is disabled.
By default, the GR interval is 60
seconds.
To enable RIP NSR:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Enable RIP NSR.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
non-stop-routing
Configuring BFD for RIP
RIP detects route failures b y periodically sending requests. If it receives no response for a route
within a certain tim e, RIP consid ers the r oute unre achabl e. To speed up convergence, perf orm this
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
By default, RIP NSR is disabled.
RIP NSR enabled for a RIP
process takes effect only on that
process. As a best practice,
enable RIP NSR for each process
if multiple RIP processes exist.
39
Page 52

•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
task to enable BFD for RIP. For mor e information about BFD, see Hi gh Availability Configuration
Guide.
RIP supports the following BFD detection modes:
Single-hop echo detection—Detection mode for a direct neighbor. In this mode, a BFD
session is established only when the directly connected neighbor has route information to send.
Single-hop echo detection for a specific destination—In this mode, a BFD session is
established to the specified RIP neighbor when RIP is enabled on the local interface.
Bidirectional control detection—Detection mode for an indirect neighbor. In this mode, a
BFD session is established only when both ends have routes to send and BFD is enabled on
the receiving interface.
Configuring single-hop echo detection (for a direct l y connected RIP neighbor)
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the source IP
address of BFD echo
packets.
3. Enter interface view.
4. Enable BFD for RIP.
bfd echo-source-ip
interface
interface-number
rip bfd enable
interface-type
ip-address
N/A
By default, the source IP address
of BFD echo packets is not
configured.
N/A
By default, BFD for RIP is
disabled.
Configuring single-hop echo detection (for a specifi c destination)
When a unidirectional link occurs between the local device and a specific neighbor, BFD can detect
the failure. The local device will not receive or send any RIP packets through the interface connected
to the neighbor to impr ove c onverg enc e s pe ed. When the link rec overs , the i nterface can send RIP
packets again.
This feature applies to RIP neighbors that are directly connected.
To configure BFD for RIP (single hop echo detection for a specific destination):
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the source IP
address of BFD echo
packets.
3. Enter interface view.
4. Enable BFD for RIP.
bfd echo-source-ip
interface
interface-number
rip bfd enable destination
ip-address
interface-type
40
ip-address
N/A
By default, no source IP address
is configured for BFD echo
packets.
N/A
By default, BFD for RIP is
disabled.
Page 53

Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
•
Router A Router B
Router E
Backup nexthop
:
Router C
Nexthop
: Router D
Configuring bidirectional control detection
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Specify a RIP neighbor.
4. Enter interface view.
5. Enable BFD on the RIP
interface.
system-view
rip
vpn-instance-name ]
peer
interface
interface-number
rip bfd enable
Configuring RIP FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause pack et loss and even routing lo op until RIP completes
routing convergence based on the new network topology . FRR enables fast rerouting to minimize the
impact of link or node failures.
[ process-id ] [
ip-address
interface-type
vpn-instance
N/A
N/A
By default, RIP does not unicast
updates to any peer.
Because the
command does not remove the
neighbor relationship
immediately, executing the
command cannot bring down the
BFD session immediately.
N/A
By default, BFD is disabled on a
RIP interface.
undo peer
Figure 6 Network diagram for RIP FRR
As shown in Figure 6, configure FRR on Router B by using a routing policy to specify a backup next
hop. When the primary link fails, RIP directs packets to the backup next hop. At the same time, RIP
calculates the shortest path based on the new network topology, and forwards packets over that path
after network convergence.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
RIP FRR takes effect only for RIP routes learned from directly connected neighbors.
RIP FRR is available only when the state of primary link (with Layer 3 interfaces staying up)
changes from bidirectional to unidirectional or down.
Equal-cost routes do not support RIP FRR.
41
Page 54

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Task
Command
Configuration p r erequisites
You must specify a next hop by using the apply fast-reroute backup-interface command in a
routing policy and ref erence the routi ng policy for FRR. For mor e information about ro uting policy
configuration, see "Configuring routing policies."
Configuring RIP FRR
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter RIP view.
3. Configure RIP FRR.
system-view
rip
[ process-id ] [
vpn-instance-name ]
fast-reroute route-policy
route-policy-name
Enabling BFD for RIP FRR
By default, RIP FRR does not use BFD to detect primary link failures. T o speed up RIP convergence,
enable BFD single-hop echo detection for RIP FRR to detect pr imary link failures.
To configure BFD for RIP FRR:
1. Enter system view.
2. Configure the source IP
address of BFD echo
packets.
system-view
bfd echo-source-ip
vpn-instance
ip-address
N/A
N/A
By default, RIP FRR is disabled.
N/A
By default, the source IP address
of BFD echo packets is not
configured.
The source IP address cannot be
on the same network segment as
any local interface's IP address.
For more information about this
command, see High Availability
Command Reference.
3. Enter interface view.
4. Enable BFD for RIP FRR.
interface
interface-number
rip primary-path-detect bfd
echo
interface-type
Displaying and maintaining RIP
Execute display commands in an y view and exec ute reset commands in user view.
Display RIP current status and configuration
information.
Display active routes in the RIP database.
Display RIP GR information.
42
display rip
display rip
{ mask-length | mask } ]
display rip
N/A
By default, BFD for RIP FRR is
disabled.
[ process-id ]
process-id
[ process-id ]
database
[ ip-address
graceful-restart
Page 55

Task
Command
display rip
non-stop-routing
Vlan-int
102
2.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int100
1.1
.1.2
/24
Vlan-
int102
10.1.1.2
/24
Vlan
-int100
1.1.1.1/24
Vlan-
int101
10.2.1.1/24
Vlan-
int
101
3
.1.1
.1/
24
Switch A Switch B
Display RIP interface information.
Display neighbor information for a RIP process.
Display RIP NSR information.
Display routing information for a RIP process.
Reset a RIP process.
Clear the statistics for a RIP process.
RIP configuration examples
Configuring basic RIP
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 7, enable RIPv2 on all interfaces on Switch A and Switch B. Conf igure S witch B
to not advertise route 10.2.1.0/24 to Switch A, and to accept only route 2.1.1.0/24 from Switch A.
Figure 7 Network diagram
display rip
process-id
interface-number ]
display rip
interface-number ]
process-id
[ process-id ]
display rip
process-id
{ mask-length | mask } [
statistics
reset rip
reset rip
]
process-id
process-id
process
statistics
interface [
neighbor
route
[ ip-address
verbose
interface-type
[ interface-type
peer
] |
ip-address |
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP by using either of the following methods:
(Method 1) # Enable RIP on the specified networks on Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] rip
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 2.0.0.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 3.0.0.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
(Method 2) # Enable RIP on the specified interfaces on Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] rip
[SwitchB-rip-1] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface100] rip 1 enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 101
43
Page 56

[SwitchB-Vlan-interface101] rip 1 enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface101] quit
[SwitchB] interface vlan-interface 102
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface102] rip 1 enable
[SwitchB-Vlan-interface102] quit
# Display the RIP routing table of Switch A.
[SwitchA] display rip 1 route
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
D - Direct, O - Optimal, F - Flush to RIB
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- Peer 1.1.1.2 on Vlan-interface100
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
10.0.0.0/8 1.1.1.2 1 0 RAOF 11
Local route
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
2.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
3.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
The output shows that RIPv1 uses a natural mask.
3. Configure a RIP version: # Configure RIPv2 on Switch A.
[SwitchA] rip
[SwitchA-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchA-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
# Configure RIPv2 on Switch B.
[SwitchB] rip
[SwitchB-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchB-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchB-rip-1] quit
# Display the RIP routing table on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display rip 1 route
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
D - Direct, O - Optimal, F - Flush to RIB
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Peer 1.1.1.2 on Vlan-interface100
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
10.0.0.0/8 1.1.1.2 1 0 RAOF 50
10.2.1.0/24 1.1.1.2 1 0 RAOF 16
10.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.2 1 0 RAOF 16
Local route
Destina tion/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
2.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
3.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
44
Page 57

NOTE:
After RIPv2 is configured, RIPv1 routes might still exist in the routi
out.
The output shows that RIPv2 uses classless subnet masks.
ng table until they are aged
# Display the RIP routing table on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display rip 1 route
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
D - Direct, O - Optimal, F - Flush to RIB
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- Peer 1.1.1.1 on Vlan-interface100
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
2.1.1.0/24 192.168.1.3 1 0 RAOF 19
3.1.1.0/24 192.168.1.3 1 0 RAOF 19
Local route
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
10.2.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
4. Configure route filtering: # Reference IP prefix lists on Switch B to filter received and redistributed routes.
[SwitchB] ip pr efix-list aaa inde x 10 permit 2.1.1.0 24
[SwitchB] ip pr efix-list bbb index 10 deny 10.2.1.0 24
[SwitchB] ip pr efix-list bbb inde x 11 permit 0.0.0.0 0 less-equal 32
[SwitchB] ri p 1
[SwitchB-rip-1] filter-policy prefix -list aaa impo rt
[SwitchB-rip-1] filter-policy prefix -list bbb export
[SwitchB-rip-1] quit
# Display the RIP routing table on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display rip 100 route
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- Peer 1.1.1.2 on Vlan-interface100
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
10.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.2 1 0 RAO F 19
Local route
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
2.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
3.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
# Display the RIP routing table on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display rip 1 route
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed , G - Garbage-collect
D - Direct, O - Optimal, F - Flush to RIB
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
45
Page 58

Eth1/1
Vlan-int100
11.1.1.2/24
Vlan-int200
12.3.1.2/24
Vlan-int200
12
.3.1.1/24
Vlan-int400
16.4.1.1/24
Vlan
-int101
10.2.1.1/24
Vlan-int100
11.1.1.1/24
Switch A
Switch B
Switch C
RIP 100 RIP 200
Peer 1.1.1.1 on Vlan-interface100
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
2.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.3 1 0 RAOF 19
Local route
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
10.2.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
Configuring RI P route redistribution
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 8, Swit ch B communicates with S witch A through RIP 100 and with Switch C
through RIP 200.
Configure RIP 200 to redistribute direct routes and routes from RIP 100 on Switch B so Switch C can
learn routes destined for 10.2.1.0/24 and 11.1.1.0/24. Switch A cannot learn routes destined for
12.3.1.0/24 and 16.4.1.0/24 .
Figure 8 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP:
# Enable RIP 100, and configure RIPv2 on Switch A.
<SwitchA> sy stem-view
[SwitchA] ri p 100
[SwitchA-rip-100] network 10.0.0.0
[SwitchA-rip-100] network 11.0.0.0
[SwitchA-rip-100] version 2
[SwitchA-rip-100] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-100] quit
# Enable RIP 100 and RIP 200, and configure RIPv2 on Switch B.
<SwitchB> sy stem-view
[SwitchB] ri p 100
[SwitchB-rip-100] network 11.0.0.0
[SwitchB-rip-100] version 2
[SwitchB-rip-100] undo summary
[SwitchB-rip-100] quit
[SwitchB] ri p 200
[SwitchB-rip-200] network 12.0.0.0
[SwitchB-rip-200] version 2
[SwitchB-rip-200] undo summary
46
Page 59

[SwitchB-rip-200] quit
# Enable RIP 200, and configure RIPv2 on Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] ri p 200
[SwitchC-rip-200] network 12.0.0.0
[SwitchC-rip-200] network 16.0.0.0
[SwitchC-rip-200] version 2
[SwitchC-rip-200] undo summary
[SwitchC-rip-200] quit
# Display the IP routing table on Switch C.
[SwitchC] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 13 Routes : 13
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
12.3.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Vlan200
12.3.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Vlan200
12.3.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
12.3.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Vlan200
16.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Vlan400
16.4.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Vlan400
16.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
16.4.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Vlan400
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
3. Configure route redistribution: # Configure RIP 200 to redistribute routes from RIP 100 and direct routes on Switch B.
[SwitchB] ri p 200
[SwitchB-rip-200] import-route rip 100
[SwitchB-rip-200] import-route direct
[SwitchB-rip-200] quit
# Display the IP routing table on Switch C.
[SwitchC] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 15 Routes : 15
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.2.1.0/2 4 RIP 100 1 12.3.1.1 Vlan200
11.1.1.0/2 4 RIP 100 1 12.3.1.1 Vlan200
12.3.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Vlan200
12.3.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Vlan200
12.3.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
12.3.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 12.3.1.2 Vlan200
16.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Vlan400
47
Page 60

Switch B
Switch C
Switch A
Switch D Switch E
Vlan-int100
1.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int100
1.1.1.2/24
Vlan-int200
1.1.2.1/24
Vlan-int200
1.1.2.2/24
Vlan-int400
1.1.3.1/24
Vlan-int300
1.1.4.1/24
Vlan-int400
1.1.3.2/24
Vlan-int300
1.1.4.2/24
Vlan-int500
1.1.5.1/24
Vlan-int500
1.1.5.2/24
16.4.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Vlan400
16.4.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
16.4.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 16.4.1.1 Vlan400
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Configuring an add i tional metric for a R IP interface
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 9, run RIPv2 on all the interfaces of Switch A, Switch B, Switch C, Switch D, and
Switch E.
Switch A has two links to Switch D. The link from Switch B to Switch D is more stable than that from
Switch C t o Switch D. Conf igure an additional m etric for RIP routes received from VLAN-interface
200 on Switch A so Switch A prefers route 1.1.5.0/24 learned from Switch B.
Figure 9 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP:
# Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] rip 1
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchA-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
# Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> sy stem-view
[SwitchB] rip 1
[SwitchB-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[SwitchB-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchB-rip-1] undo summary
# Configure Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchB] rip 1
[SwitchC-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] version 2
48
Page 61

[SwitchC-rip-1] undo summary
# Configure Switch D.
<SwitchD> sy stem-view
[SwitchD] rip 1
[SwitchD-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[SwitchD-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchD-rip-1] undo summary
# Configure Switch E.
<SwitchE> sy stem-view
[SwitchE] rip 1
[SwitchE-rip-1] network 1.0.0.0
[SwitchE-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchE-rip-1] undo summary
# Display all active routes in the RIP database on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display rip 1 database
1.0.0.0/8, auto-summary
1.1.1.0/24, cost 0, next hop 1.1.1.1, RIP-interface
1.1.2.0/24, cost 0, next hop 1.1.2.1, RIP-interface
1.1.3.0/24, cost 1, next hop 1.1.1.2
1.1.4.0/24, cost 1, next hop 1.1.2.2
1.1.5.0/24, cost 2, next hop 1.1.1.2
1.1.5.0/24, cost 2, next hop 1.1.2.2
The output shows two RIP routes destined for network 1.1.5.0/24, with the next hops as Switch
B (1.1.1.2) and Switch C (1.1.2.2), and with the same cost of 2.
3. Configure an additional metric for a RIP interface: # Configure an inbound additional metric of 3 for RIP-enabled interface VLAN-interface 200 on
Switch A.
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface200] rip metricin 3
# Display all active routes in the RIP database on Switch A.
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface200] display rip 1 database
1.0.0.0/8, auto-summary
1.1.1.0/24, cost 0, next hop 1.1.1.1, RIP-interface
1.1.2.0/24, cost 0, next hop 1.1.2.1, RIP-interface
1.1.3.0/24, cost 1, next hop 1.1.1.2
1.1.4.0/24, cost 2, nexthop 1.1.1.2
1.1.5.0/24, cost 2, next hop 1.1.1.2
The output shows that only one RIP route reaches network 1.1.5. 0/2 4, with the nex t hop as
Switch B (1.1.1.2) and a cost of 2.
Configuring RIP to advertise a summary route
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 10, Sw itch A and Switch B run OSPF, Switc h D runs RIP, and Switch C r uns
OSPF and RIP. Configure RIP to redistribute OSPF routes on Switch C so Switch D can learn routes
destined for networks 10.1.1.0/24, 10.2.1.0/24, 10.5.1.0/24, and 10.6.1.0/24.
To reduce the routin g tabl e size o f Swit ch D, configure route summarization on Switch C to advertise
only the summary route 10.0.0.0/8 to Switch D.
49
Page 62

Switch A
Vlan-int100
10.2.1.2/24
Switch C
Vlan-int100
10.2.1.1/24
Vlan-int300
11.3.1.2/24
Switch D
RIP
OSPF
Switch B
Vlan-int200
10.1.1.2/24
Vlan-int200
10.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int300
11.3.1.1/24
Vlan-int400
11.4.1.2/24
Vlan-int500
10.6.1.2/24
Vlan-int600
10.5.1.2/24
Figure 10 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic OSPF:
# Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ospf
[SwitchA-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.5.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchA-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
# Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> sy stem-view
[SwitchB] ospf
[SwitchB-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0 .0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0 .0] network 10.6.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchB-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
# Configure Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] ospf
[SwitchC-ospf-1] area 0
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0 .0] network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255
[SwitchC-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
[SwitchC-ospf-1] quit
3. Configure basic RIP: # Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] rip 1
[SwitchC-rip-1] network 11.3.1.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchC-rip-1] undo summary
# Configure Switch D.
<SwitchD> sy stem-view
[SwitchD] rip 1
50
Page 63

[SwitchD-rip-1] network 11.0.0.0
[SwitchD-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchD-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchD-rip-1] quit
# Configure RIP to redistribute routes from OSPF process 1 and direct routes on Switch C.
[SwitchC-rip-1] import-route direct
[SwitchC-rip-1] import-route ospf 1
[SwitchC-rip-1] quit
# Display the IP routing table on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 15 Routes : 15
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.1.1.0/2 4 RIP 100 1 11.3.1.1 Vlan300
10.2.1.0/2 4 RIP 100 1 11.3.1.1 Vlan300
10.5.1.0/2 4 RIP 100 1 11.3.1.1 Vlan300
10.6.1.0/2 4 RIP 100 1 11.3.1.1 Vlan300
11.3.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 11.3. 1.2 Vlan300
11.3.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 11.3.1.2 Vlan300
11.3.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
11.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 11.4.1.2 Vlan400
11.4.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 11.4.1.2 Vlan400
11.4.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.2 55/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
4. Configure route summarization: # Configure route summarization on Switch C and advertise only the summary route 10.0.0.0/8.
[SwitchC] interfac e vlan-interface 300
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface300] rip summary-address 10.0.0.0 8
# Display the IP routing table on Switch D.
[SwitchD] display ip routing-table
Destinations : 12 Routes : 12
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
0.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
10.0.0.0/8 RIP 100 1 11.3.1.1 Vlan300
11.3.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 11.3.1.2 Vlan300
11.3.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 11.3.1.2 Vlan300
11.3.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
11.4.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 11.4.1.2 Vlan400
11.4.1.0/32 Direct 0 0 11.4.1.2 Vlan400
11.4.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
51
Page 64

•
•
Vlan-int100
192.1.1.1/24
Vlan-int100
192.1.1.3/24
Vlan-int100
192.1.1.2/24
GR helper GR helper
GR restarter
Switch A
Switch CSwitch B
Router ID: 1.1.1.1
Router ID: 2.2.2.2
Router ID: 3.3.3.3
127.0.0.0/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
127.255.255.2 55/32 Direct 0 0 127.0.0.1 InLoop0
Configuring RI P GR
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 11, Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C all run RIPv2.
Enable GR on Switch A. Switch A acts as the GR restarter.
Switch B and Switch C act as GR helpers to synchronize their routing tables with Switch A by
using GR.
Figure 11 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses and subnet masks for interfaces on the switches. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure RIPv2 on the switches to ensure the following: (Details not shown.)
Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C can communicate with each other at Layer 3.
Dynamic route update can be implemented among them with RIPv2.
3. Enable RIP GR on Switch A.
<SwitchA> sy stem-view
[SwitchA] rip
[SwitchA-rip-1] graceful-restart
Verifying the configuration
# Trigger a routing protocol restart or active/standby switchover and display GR status on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display rip graceful-restart
RIP process: 1
Graceful Restart capability : Enabled
Current GR state : Normal
Graceful Restart period : 60 seconds
Graceful Restart remaining time : 0 seco nds
Configuring RI P N S R
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 12, Switch A, Switch B, and Switch S all run RIPv2.
52
Page 65

Loop 0
22.22.22.22/32
Vlan-int100
12.12.12.1/24
Vlan-int100
12.12.12.2/24
Vlan-int200
14.14.14.2/24
Vlan-int200
14.14.14.1/24
Loop 0
44.44.44.44/32
Switch S
Switch A
Switch B
Enable RIP NSR on Switch S to ensure correct routing when an active/standby switchover occurs on
Switch S.
Figure 12 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses and subnet masks for interfaces on the switches. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure RIPv2 on the switches to ensure the following: (Details not shown.)
Switch A, Switch B, and Switch S can communicate with each other at Layer 3.
Dynamic route update can be implemented among them with RIPv2.
3. Enable RIP NSR on Switch S.
<SwitchS> sy stem-view
[SwitchS] ri p 100
[SwitchS-rip-100] non-stop-routing
[SwitchS-rip-100] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Perform an active/standby switchover on S witch S .
[SwitchS] placement reoptimize
Predicted ch anges to the placeme nt
Program Current location New location
--------------------------------------------------------------------lb 0/0 0/0
lsm 0/0 0/0
slsp 0/0 0/0
rib6 0/0 0/0
routepolicy 0/0 0/0
rib 0/0 0/0
staticroute6 0/0 0/0
staticroute 0/0 0/0
eviisis 0/0 0/0
ospf 0/0 1/0
Continue? [y /n]:y
Re-optimization of the placement start . You will be notified on completion
Re-optimizati on of the placement co mp lete. Use 'display placement' to view th e new
placement
# Display neighbor information and route information on Switch A.
[SwitchA] display rip 1 neighbor
Neighbor Addre ss: 12.12.12.2
Interface : Vlan-interface200
Version : RIPv2 Last update: 00h00m13s
Relay nbr : No BFD session: None
Bad packets: 0 Bad routes : 0
[SwitchA] display rip 1 route
53
Page 66

•
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
D - Direct, O - Optimal, F - Flush to RIB
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- Peer 12.12.12.2 on Vlan-interface200
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
14.0.0.0/8 12.12.12.2 1 0 RAOF 16
44.0.0.0/8 12.12.12.2 2 0 RAOF 16
Local route
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
12.12.12.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
22.22.22.22/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
# Display neighbor information and route information on Switch B.
[SwitchB] display rip 1 neighbor
Neighbor Addre ss: 14.14.14.2
Interface : Vlan-interface200
Version : RIPv2 Last update: 00h00m32s
Relay nbr : No BFD session: None
Bad packets: 0 Bad routes : 0
[SwitchB] display rip 1 route
Route Flags: R - RIP, T - TRIP
P - Permanent, A - Aging, S - Suppressed, G - Garbage-collect
D - Direct, O - Optimal, F - Flush to RIB
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- Peer 14.14.14.2 on Vlan-interface200
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
12.0.0.0/8 14.14.14.2 1 0 RAOF 1
22.0.0.0/8 14.14.14.2 2 0 RAOF 1
Local route
Destination/Mask Nexthop Cost Tag Flags Sec
44.44.44.44/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
14.14.14.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 0 RDOF -
The output shows that the neighbor and route information on Switch A and Switch B keep unchanged
during the active/standby switchover on Switch S. The traffic from Switch A to Switch B has not been
impacted.
Configuring BFD for RIP (single-ho p echo detection for a directly connected neighbor)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 13, VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A and Switch C runs RIP process 1.
VLAN-interface 200 of Switch A runs RIP process 2. VLAN-interface 300 of Switch C and
VLAN-interface 200 and VLAN-interface 300 of Switch B run RIP process 1.
Configure a static route destined for 100.1.1.1/24 and enable static route redistribution into RIP
on Switch C. This allows Switch A to learn two routes destined for 100.1.1.1/24 through
VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 200 respectively, and uses the one through
VLAN-interface 100.
54
Page 67

•
Vlan
-int100
192.168.1.1/24
BFD
Switch A
Switch C
Vlan-int100
192.168.1.2/24
L2 switch
Vlan-int300
192.168.3.1/24
Vlan-int300
192.168.3.2/24
Vlan-int200
192.168.2.2/24
Vlan-int200
192.168.2.1/24
Switch B
Enable BFD for RIP on VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A. When the link over VLAN-interface 100
fails, BFD can quickly detect the failure and notify RIP. RIP deletes the neighbor relationship
and route information learned on VLAN-interface 100, and uses the route destined for 100.1.1.1
24 through VLAN-interf ac e 200.
Figure 13 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP:
# Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> sy stem-view
[SwitchA] rip 1
[SwitchA-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchA-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 192.168.1.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] rip bfd enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] rip 2
[SwitchA-rip-2] version 2
[SwitchA-rip-2] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-2] network 192.168.2.0
[SwitchA-rip-2] quit
# Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] rip 1
[SwitchB-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchB-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchB-rip-1] network 192.168.2.0
[SwitchB-rip-1] network 192.168.3.0
[SwitchB-rip-1] quit
# Configure Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] rip 1
55
Page 68

[SwitchC-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchC-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchC-rip-1] netwo rk 192.168.1.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] netwo rk 192.168.3.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] import-route static
[SwitchC-rip-1] quit
3. Configure BFD parameters on VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A.
[SwitchA] bf d echo-source-ip 11.11.11.11
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd detect-multiplier 7
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] quit
4. Configure a static route on Switch C.
[SwitchC] ip route-static 120.1.1.1 24 null 0
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFD session information on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display bfd session
Total Session Nu m: 1 Up Session Num: 1 Init Mode: Active
IPv4 Session Working Under Echo Mode:
LD SourceAddr DestAddr State Holdtime Interface
4 19 2.168.1.1 192.168.1. 2 Up 2000ms Vlan100
# Display RIP routes destined for 120.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table 120.1.1.0 24
Summary coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 RIP 100 1 192.168.1.2 Vlan-interface100
The output shows that Switch A communicates with Switch C through VLAN-interface 100. Then the
link over VLAN-interface 100 fails.
# Display RIP routes destined for 120.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table 120.1.1.0 24
Summary coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
120.1.1.0/24 RIP 100 1 192.168.2.2 Vlan-interface200
The output shows that Switch A communicates with Switch C through VLAN-interface 200.
56
Page 69

•
•
Switch A Switch C
Vlan-int200
192.168.3.1/24
Vlan-int200
192.168.3.2/24
Vlan-int100
192.168.2.2/24
Vlan-int100
192.168.2.1/24
Switch B
RIP packets
BFD session
Fault
Configuring BFD for RIP (single hop echo detection for a specific destination)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 14, VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A and Switch B runs RIP process 1.
VLAN-interface 200 of Switch B and Switch C runs RIP process 1.
Configure a static route destined for 100.1.1.0/24 and enable static route redistribution into RIP
on both Switch A and Switch C. This allows Switch B to learn two routes destined for
100.1.1.0/24 through VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 200. The route redistributed from
Switch A has a smaller cost than that redistributed from Switch C, so Switch B uses the route
through VLAN-interface 200.
Enable BFD for RIP on VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A, and specify VLAN-interface 100 of
Switch B as the destination. When a unidirectional link occurs between Switch A and Switch B,
BFD can quickly detect the link failure and notify RIP. Swit c h B then deletes the neighbor
relationship and the route information learned on VLAN-interface 100. It does not receive or
send any packets from VLAN-interface 100. When the route learned from Switch A ages out,
Switch B uses the route destined for 100.1.1.1 24 through VLAN-interface 200.
Figure 14 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP and enable BFD on the interfaces:
# Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] rip 1
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 192.168.2.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] import-route static
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] rip bfd enable destination 192.168.2.2
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] rip 1
[SwitchB-rip-1] network 192.168.2.0
57
Page 70

[SwitchB-rip-1] network 192.168.3.0
[SwitchB-rip-1] quit
# Configure Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] rip 1
[SwitchC-rip-1] network 192.168.3.0
[SwitchC-rip-1 ] import-route static cost 3
[SwitchC-rip-1] quit
3. Configure BFD parameters on VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A.
[SwitchA] bfd echo-source-ip 11.11.11.11
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd min-echo-receive-interval 500
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] return
4. Configure static routes: # Configure a static route on Switch A.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 null 0
# Configure a static route on Switch C.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 100.1.1.0 24 null 0
Verifying the configuration
# Display BFD session information on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display bfd session
Total Session Nu m: 1 Up Session Num: 1 Init Mode: Active
IPv4 session working under Echo mode:
LD SourceAddr DestAddr State Holdtime Interface
3 192.168.2.1 192.168.2.2 Up 2000ms vlan100
# Display routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Switch B.
<SwitchB> display ip routing-table 100.1. 1. 0 24 verbose
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination: 100.1.1.0/24
Protocol: RIP
Process ID: 1
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h02m47s
Cost: 1 Preference: 100
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x2 OrigAs: 0
NibID: 0x12000002 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0xffffffff Neighbor: 19 2.168.2.1
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 192.1 68.2.1
Label: NULL RealNex tHop: 192.168.2.1
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: N/A
58
Page 71

•
•
•
•
Tunnel ID: Inva lid Interface: vlan-interface 100
BkTunnel ID: Inva lid BkInterface: N/A
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A
# Display routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Switch B when the link between Switch A and Switch B
fails.
<SwitchB> display ip routing-table 100.1. 1. 0 24 verbose
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination: 100.1.1.0/24
Protocol: RIP
Process ID: 1
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h21m23s
Cost: 4 Preference: 100
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x 2 OrigAs: 0
NibID: 0x12000002 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0xffffffff Neighbor: 19 2.168.3.2
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 192.1 68.3.2
Label: NULL RealNex tHop: 192.168.3. 2
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: N/A
Tunnel ID: Inva lid Interface: vlan-interface 200
BkTunnel ID: Inva lid BkInterface: N/A
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A
Configuring BFD for RIP (bidirectional detection in BFD control packet mode)
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 15, VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A and VLAN-interface 200 of Switch C run RIP
process 1.
VLAN-interface 300 of Switch A runs RIP process 2. VLAN-interface 400 of Switch C, and
VLAN-interface 300 and VLAN-interface 400 of Switch D run RIP process 1.
Configure a static route destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
Configure a static route destined for 101.1.1.0/24 on Switch C.
Enable static route redistribution into RIP on Switch A and Switch C. This allows Switch A to
learn two routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 through VLAN-interface 100 and VLAN-interface 300.
It uses the route through VLAN-interface 100.
Enable BFD on VLAN-interface 100 of Switch A and VLAN-interface 200 of Switch C.
When the link over VLAN-interface 100 fails, BFD c an quick ly detect the link failur e and notif y RIP.
RIP deletes the neighbor relationship and the route information received learned on VLAN-interface
100. It uses the route destined for 100.1.1.0/24 through VLAN-interface 300.
59
Page 72

Device
Interface
IP address
100.1.1.0/24
101.1.1.0/24
Switch C
Switch A
Vlan-
int100
Vlan-int100
Switch B
Vlan-int200
BFD
Vlan-int200
Switch D
Vlan-int300
Vlan-int300
Vlan-int
400
Vlan
-
int400
Figure 15 Network diagram
Table 7 Interface and IP address assignment
Switch A VLAN-interface 300 192.168.3.1/24
Switch A VLAN-interface 100 192.168.1.1/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 100 192.168.1.2/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 200 192.168.2.1/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 200 192.168.2.2/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 400 192.168.4.2/24
Switch D VLAN-interface 300 192.168.3.2/24
Switch D VLAN-interface 400 192.168.4.1/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses for interfaces. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure basic RIP and enable static route redistribution into RIP so Switch A and Switch C
have routes to send to each other:
# Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> sy stem-view
[SwitchA] rip 1
[SwitchA-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchA-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 192.168.1.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] network 101.1.1.0
[SwitchA-rip-1] peer 192.168.2.2
[SwitchA-rip-1] undo validate-source-address
[SwitchA-rip-1] import-route static
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] rip bfd enable
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
[SwitchA] rip 2
[SwitchA-rip-2] version 2
60
Page 73

[SwitchA-rip-2] undo summary
[SwitchA-rip-2] network 192.168.3.0
[SwitchA-rip-2] quit
# Configure Switch C.
<SwitchC> sy stem-view
[SwitchC] rip 1
[SwitchC-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchC-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchC-rip-1] network 192.168.2.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] netwo rk 192.168.4.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] network 100.1.1.0
[SwitchC-rip-1] peer 192.168.1.1
[SwitchC-rip-1] undo validate-source-address
[SwitchC-rip-1] import-route static
[SwitchC-rip-1] quit
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] rip bfd enable
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] quit
# Configure Switch D.
<SwitchD> sy stem-view
[SwitchD] rip 1
[SwitchD-rip-1] version 2
[SwitchD-rip-1] undo summary
[SwitchD-rip-1] netwo rk 192.168.3.0
[SwitchD-rip-1] netwo rk 192.168.4.0
3. Configure BFD parameters: # Configure Switch A.
[SwitchA] bfd session init-mode active
[SwitchA] interface vlan-inte rface 100
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] bfd detect-mul tiplier 7
[SwitchA-Vlan-interface100] quit
# Configure Switch C.
[SwitchC] bfd session init-mode acti ve
[SwitchC] interface vlan-interface 200
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] bfd min-transmit-interval 500
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] bfd min-receive-interval 500
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] bfd detect-mul tiplier 7
[SwitchC-Vlan-interface200] quit
4. Configure static routes: # Configure a static route to Switch C on Switch A.
[SwitchA] ip route-static 192.168.2.0 24 vlan-interface 100 192.168.1. 2
[SwitchA] quit
# Configure a static route to Switch A on Switch C.
[SwitchC] ip route-static 192.168.1.0 24 vlan-interf ace 200 192.168.2.1
61
Page 74

Device
Interface
IP address
Switch A Switch B
Switch C
Loop0
Vlan-int100
Vlan-int200
Vlan-int200
Vlan-int100
Vlan-int101
Vlan-int101
Loop0
Link A
Link B
Verifying the configuration
# Display the BFD session information on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display bfd session
Total Session Nu m: 1 Up Session Num: 1 Init Mode: Active
IPv4 session working under Ctrl mode:
LD/RD Sou rceAddr DestAddr State Holdtime Interface
513/513 192.168.1.1 192.168.2.2 Up 1700ms vlan100
# Display RIP routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table 100.1. 1. 0 24
Summary coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
100.1.1.0/24 RIP 100 1 192.168.2.2 vlan-interface 100
The output shows that Switch A communicates with Switch C through VLAN-interface 100. Then the
link over VLAN-interface 100 fails.
# Display RIP routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Switch A.
<SwitchA> display ip routing-table 100.1.1.0 24
Summary coun t : 1
Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost NextHop Interface
100.1.1.0/24 RIP 100 2 192.168.3.2 vlan-interface 300
The output shows that Switch A communicates with Switch C through VLAN-interface 300.
Configuring RI P FRR
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 1 6, Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C run RIP v2. Configure RIP FRR so that
when Link A becomes unidirectional, services can be switched to Link B immediately.
Figure 16 Network diagram
Table 8 Interface and IP address assignment
Switch A VLAN-interface 100 12.12.12.1/24
62
Page 75

Device
Interface
IP address
Switch A VLAN-interface 200 13.13.13.1/24
Switch A Loopback 0 1.1.1.1/32
Switch B VLAN-interface 101 24.24.24.4/24
Switch B VLAN-interface 200 13.13.13.2/24
Switch B Loopback 0 4.4.4.4/32
Switch C VLAN-interface 100 12.12.12.2/24
Switch C VLAN-interface 101 24.24.24.2/24
Configuration procedure
1. Configure IP addresses and subnet masks for interfaces on the switches. (Details not shown.)
2. Configure RIPv2 on the switches to make sure Switch A, Switch B, and Switch C can
communicate with each other at Layer 3. (Details not shown.)
3. Configure RIP FRR: # Configure Switch A.
<SwitchA> system-view
[SwitchA] ip prefix-list abc index 10 permit 4.4.4.4 32
[SwitchA] route-policy frr permit node 10
[SwitchA-route-policy-frr-10] if-match ip address prefix-list abc
[SwitchA-route-policy-frr-10] apply fast-reroute backup-interface vlan-interface
100 backup-nexthop 12.12.12.2
[SwitchA-route-policy-frr-10] quit
[SwitchA] rip 1
[SwitchA-rip-1] fast-reroute route-policy frr
[SwitchA-rip-1] quit
# Configure Switch B.
<SwitchB> system-view
[SwitchB] ip prefix-list abc index 10 permit 1.1.1.1 32
[SwitchB] route-policy frr permit node 10
[SwitchB-route-policy-frr-10] if-match ip address prefix-list abc
[SwitchB-route-policy-frr-10] apply fast-reroute backup-interface vlan-interface
101 backup-nexthop 24.24.24.2
[SwitchB-route-policy-frr-10] quit
[SwitchB] rip 1
[SwitchB-rip-1] fast-reroute route-policy frr
[SwitchB-rip-1] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Display route 4.4.4.4/32 on Switch A to view the backup next hop information.
[SwitchA] display ip routing-table 4.4.4.4 verbose
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination: 4.4.4.4/32
Protocol: RIP
Process ID: 1
63
Page 76

SubProtID: 0x 1 Age: 04h20m37s
Cost: 1 Preference: 100
IpPre: N/ A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x 2 OrigAs: 0
NibID: 0x26000002 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0xffffffff Neighbor: 13 .13.13.2
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 13.13 .13.2
Label: NULL RealNex tHop: 13.13.13.2
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: 12.12.12.2
Tunnel ID: Inva lid Interface: Vlan-interface200
BkTunnel ID: Inva lid BkInterface: Vlan-interface100
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A
# Display route 1.1.1.1/32 on Switch B to view the backup next hop information.
[SwitchB] display ip routing-table 1.1.1.1 verbose
Summary Coun t : 1
Destination: 1.1.1.1/32
Protocol: RIP
Process ID: 1
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 04h20m37s
Cost: 1 Preference: 100
IpPre: N/A QosLocalID: N/A
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x2 OrigAs: 0
NibID: 0x26000002 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0xffffffff Neighbor: 13 .13.13.1
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 13.13.13.1
Label: NULL RealNex tHop: 13.13.13.1
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: 24.2 4.24.2
Tunnel ID: Inva lid Interface: Vlan-interface200
BkTunnel ID: Inva lid BkInterface: Vlan-interface101
FtnIndex: 0x0 TrafficIndex: N/A
Connector: N/A
64
Page 77

•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Configuring OSPF
Overview
Open Shortest Path F irst (OSPF) is a link-state IGP developed by the OSPF work ing group of the
IETF. OSPF version 2 is used for IPv4. OSPF refers to OSPFv2 throughout this chapter.
OSPF has the following features:
Wide scope—Supports multiple network sizes and several hundred routers in an OSPF routing
domain.
Fast convergence—Advertises routing updates instantly upon network topology changes.
Loop free—Computes routes with the SPF algorithm to avoid routing loops.
Area-based network partition—Splits an AS into multiple areas to facilitate management.
This feature reduces the LSDB size on routers to save memory and CPU resources, and
reduces route updates transmitted between areas to save bandwidth.
ECMP routing—Supports multiple equal-cost routes to a destination.
Routing hierarchy—Supports a 4-level routing hierarchy that prioritizes routes into intra-area,
inter-area, external Type-1, and external Type-2 routes.
Authentication—Supports area- and interface-based packet authentication to ensure secure
packet exchange.
Support for multicasting—Multicasts protocol packets on some types of links to avoid
impacting other devices.
OSPF packets
OSPF messages are carried directly over IP. The protocol number is 89.
OSPF uses the following packet types:
Hello—Periodically sent to find and maintain neighbors, containing timer values, information
about the DR, BDR, and known neighbors.
Database description (DD)—Describes the digest of each LSA in the LSDB, exchanged
between two routers for data synchronization.
Link state request (LSR)—Requests needed LSAs from a neighbor. After exchanging the DD
packets, the two routers know which LSAs of the neighbor are missing from their LSDBs. They
then exchange LSR packets requesting the missing LSAs. LSR packets contain the digest of
the missing LSAs.
Link state update (LSU)—Transmits the requested LSAs to the neighbor.
Link state acknowledgment (LSAck)—Acknowledges received LSU packets. It contains the
headers of received LSAs (an LSAck packet can acknowledge multiple LSAs).
LSA types
OSPF advertises routing inform ation in Link State Advertisem ents (LSAs). The f ollowing LSAs are
commonly used:
Router LSA—Type-1 LSA, originat ed b y all routers and flooded throughout a single area only.
This LSA describes the collected states of the router's interfaces to an area.
65
Page 78

•
•
•
•
•
•
Area 0
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
Area 4
Network LSA—Type-2 LSA, originated for broadcast and NBMA networks by the designated
router, and flooded throughout a single area only. This LSA contains the list of routers
connected to the network.
Network Summary LSA—Type-3 LSA, originated by Area Border Routers (ABRs), and
flooded throughout the LSA's associated area. Each summary-LSA describes a route to a
destination outside the area, yet still inside the AS (an inter-area route).
ASBR Summary LSA—Type-4 LSA, originated by ABRs and flooded throughout the LSA's
associated area. Type 4 summary-LSAs describe routes to Autonomous System Boundary
Router (ASBR).
AS External LSA—Type-5 LSA, originated by ASBRs, and flooded throughout the AS (except
stub and NSSA areas). Each AS-external-LSA describes a route to another AS.
NSSA LSA—Type-7 LSA, as defined in RFC 1587, originated by ASBRs in NSSAs and flooded
throughout a single NSSA. NSSA LSAs describe routes to other ASs.
Opaque LSA—A proposed type of LSA. Its format consists of a standard LSA header and
application specific information. Opaque LSAs are used by the OSPF protocol or by some
applications to distribute information into the OSPF routing domain. The opaque LSA includes
Type 9, T ype 10, and Type 1 1. The Type 9 opaque LSA is flooded into the local subnet, the Type
10 is flooded into the local area, and the Type 11 is flooded throughout the AS.
OSPF areas
In large OSPF routing domains, SPF route computations consume too many storage and CPU
resources, and enormous OSPF packets generated for route synchronization occupy excessive
bandwidth.
To resolve these issues, OSPF splits an AS into multiple areas. Each area is identified by an area ID.
The boundaries between areas are routers rather than links. A network segment (or a link) can only
reside in one area as shown in Figure 17.
You can configure route summarization on ABRs to reduce the num ber of LSAs a dvert is ed t o oth er
areas and minimize the effect of topology changes.
Figure 17 Area-based OSPF network partition
66
Page 79

•
•
Area 0
Area 1
Area 2
ABRABR
Transit area
Virtual link
Area 0
Area
1
Virtual link
R2
R1
Backbone area and virtual links
Each AS has a bac kbone area that distrib utes routing information between non-back bone areas.
Routing information between non-backbone areas must be forwarded by the backbone area. OSPF
has the following requirements:
All non-backbone areas must maintain connectivity to the backbone area.
The backbone area must maintain connectivity within itself.
In practice, these requirements might not be met due to lack of physical links. OSPF virtual links can
solve this issue.
A virtual link is established bet we en t wo AB Rs thr oug h a non-backbone area. It mus t be c onf igure d
on both ABRs to take effect. The non-backbone area is called a transit area.
As shown in Figure 18, Area 2 has no direct physical link to the backbone Area 0. Y ou can configure
a virtual link between the two ABRs to connect Area 2 to the backbone area.
Figure 18 Virtual link application 1
Virtual links can also be used as redundant links. If a physical link failure breaks the internal
connectivity of the backbone area, you can configure a virtual link to replace the failed physical link,
as shown in Figure 19.
Figure 19 Virtual link application 2
The virtual link between the two ABRs acts as a point-to-point connection. You can configure
interface param eters, such as hello inter val, on the virtual link as they are c onfig ured on a ph ysical
interface.
The two ABRs on the virtual link unicast O SPF packets to each o ther, and the OSPF router s in
between convey these OSPF packets as normal IP packets.
Stub area and totally stub area
A stub area does not distribute Type-5 LSAs to r educe the r outing tab le size and LS As advertised
within the area. The ABR of the stub area advertises a def ault route in a Type-3 LSA so that the
routers in the area can reach external networks through the default route.
To further reduce the rout ing ta ble s ize a nd ad vert ised LS As, you ca n co nfigure the s tub ar ea as a
totally stub area. T he ABR of a totally stub are a does not advertise inter -area routes or external
67
Page 80

•
•
•
•
NSSA
Area
2
Type 7
Type 5
Type
5
Type 5
Type 5
Area 0
Area 1
NSSA
ABR
ABR
NSSA
ASBR
ASBR
RIP
RIP
routes. It advertises a default route in a Type-3 LSA so that the routers in the area can reach external
networks through the default route.
NS SA area and totally NSSA area
An NSSA area does not import AS external LSAs (Type-5 LSAs) but can import Type-7 LSAs
generated by the NSSA ASBR. The NSSA ABR translates Type-7 LSAs into Type-5 LSAs and
advertises the Type-5 LSAs to other areas.
As shown in Figure 20, the OSPF AS contains Area 1, Area 2, and Area 0. The other two ASs run RIP .
Area 1 is an NSSA area where the ASBR redistributes RIP routes in Type-7 LSAs into Area 1. Upon
receiving the Type-7 LSAs, the NSSA ABR translates them to Type-5 LSAs, and advertises the
Type-5 LSAs to Area 0.
The ASBR of Area 2 redistributes RIP routes in Type-5 LSAs into the OSPF routing domain.
However, Area 1 does not receive Type-5 LSAs because it is an NSSA area.
Figure 20 NSSA area
Router types
OSPF routers are classified into the following types based on their positions in the AS:
Internal router—All interfaces on an internal router belong to one OSPF area.
ABR—Belongs to more than two areas, one of which must be the backbone area. ABR
connects the backbone area to a non-backbone area. An ABR a nd the backbone area can be
connected through a physical or logical link.
Backbone router—No less than one interface of a backbone router must reside in the
backbone area. All ABRs and internal routers in Area 0 are backbone routers.
ASBR—Exchanges routing information with another AS is an ASBR. An ASBR might not resi de
on the border of the AS. It can be an internal router or an ABR.
68
Page 81

•
•
•
•
•
•
Area 1
Area 2
Area 3
Area 4
Backbone router
ASBR
IS-IS
RIP
Internal router
ABR
Area 0
Figure 21 OSPF router types
Route types
OSPF prioritizes routes into the following route levels:
Intra-area route.
Inter-area route.
Type-1 external route.
Type-2 external route.
The intra-area and inter -area routes des cribe the network topology of the AS . The external routes
describe routes to external ASs.
A Type-1 ex ternal r oute ha s high cred ibil ity. The cost of a Type-1 external route = the cost f rom the
router to the corresponding ASBR + the cost from the ASBR to the destination of the external route.
A Type-2 ex ternal route has low credibility. OSPF considers that t he cost from the ASBR to the
destination of a Type-2 external route is much greate r than the cost from the A SBR to an OSPF
internal router. The cost of a Type-2 external route = the cost from the ASBR to the destination of the
Type-2 external route. If two T yp e-2 routes to the same destination have the same cost, OSPF takes
the cost from the router to the ASBR into consideration to determine the best route.
Route calculation
OSPF computes routes in an area as follows:
Each router generates LSAs based on the network topology around itself, and sends them to
other routers in update packets.
Each OSPF router collects LSAs from other routers to compose an LSDB. An LSA describes
the network topology around a router, and the LSDB describes the entire network topology of
the area.
69
Page 82

•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Each router transforms the LSDB to a weighted directed graph that shows the topolog y of the
area. All the routers within the area have the same graph.
Each router uses the SPF algorithm to compute a shortest path tree that shows the routes to the
nodes in the area. The router itself is the root of the tree.
OSPF network types
OSPF classifies networks into the following types, depending on different link layer protocols:
Broadcast—By default, OSPF considers the network type as broadcast. On a broadcast
network, hello, LSU, and LSAck packets are multicast to 224.0.0.5 that identifies all OSPF
routers or to 224.0.0.6 that identifies the DR and BDR. DD packets and LSR packets are
unicast.
NBMA—OSPF packets are unicast on an NBMA network.
P2MP—No link is P2MP type by default. P2MP must be a conversion from other network types
such as NBMA. On a P2MP network, OSPF packets are multicast to 224.0.0.5.
P2P—On a P2P network, OSPF packets are multicast to 224.0.0.5.
The following are the differences between NBMA and P2MP networks:
NBMA networks are fully meshed. P2MP networks are not required to be fully meshed.
NBMA networks require DR and BDR election. P2MP networks do not have DR or BDR.
On an NBMA network, OSPF packets are unicast, and neighbors are manually configured. On a
P2MP network, OSPF packets are multicast by default, and you can configure OSPF to unicast
protocol packets.
DR and BDR
DR and BDR mechanism
On a broadcast or NBMA network, any two routers must establish an adjacency to exchange routing
information with each other. If n routers are present on the network, n(n-1)/2 adjacencies are
established. Any topology change on the network results in an increase in traffic for route
synchronization, which consumes a large amount of system and bandwidth resources.
Using the DR and BDR mechanisms can solve this problem.
DR—Elected to advertise routing information among other routers. If the DR fails, routers on the
network must elect another DR and synchronize information with the new DR. Using this
mechanism without BDR is time-consuming and is prone to route calculation errors.
BDR—Elected along with the DR to establish adjacencies with all other routers. If the DR fails,
the BDR immediately becomes the new DR, and other routers elect a new BDR.
Routers other than the DR and BDR are called DR Others. They do not establish adjac encies with
one another, so the number of adjacencies is reduced.
The role of a router is subnet (or interface) specific. It might be a DR on one interface and a BDR or
DR Other on another interface.
As shown in Figure 22, solid lines are Ethernet p hysical links, and dashed lines represent OSPF
adjacencies. With the DR and BDR, only seven adjacencies are established.
70
Page 83

NOTE:
I
are different concepts. After startup, OSPF sends a hello packet
on each OSPF interface. A receiving router checks parameters in the packet. If the parameters
match its own, the receiving router considers the sending router an OSPF neighbor. Two OSPF
neig
e their LSDBs through exchange
of DD packets and LSAs.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
DR BDR
DR other DR otherDR other
Physical links Adjacencies
Figure 22 DR and BDR in a network
n OSPF, neighbor and adjacency
hbors establish an adjacency relationship after they synchroniz
DR and BDR election
DR election is performed on broadcast or NBMA networks but not on P2P and P2MP networks.
Routers i n a broadcast or NBMA network elect the D R and BDR by router priorit y and ID. R outers
with a router priority value higher than 0 are candidates for DR and BDR election.
The election votes are hello packets. Each router sends the DR elected by itself in a hello packet to
all the other routers. If two routers on the network declare themselves as the DR, the router with the
higher router priority wins. If router priorities are the same, the router with the higher router ID wins.
If a router with a higher router priority becomes active after DR and BDR election, the router cannot
replace the DR or BDR until a new elect ion is performed. Therefore, t h e DR of a network might not
be the router with the highe st prior ity, and the BDR might not b e the rou ter with the s econd high est
priority.
Protocols and standards
RFC 1765, OSPF Database Overflow
RFC 2328, OSPF Version 2
RFC 3101, OSPF Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) Option
RFC 3137, OSPF Stub Router Advertisement
RFC 4811, OSPF Out-of-Band LSDB Resynchronization
RFC 4812, OSPF Restart Signaling
RFC 4813, OSPF Link-Local Sig na ling
OSPF configuration task list
To run OSPF, you must first en able OSPF o n t he rout er. Make a prop er conf igur ation plan to a void
incorrect settings that can result in route blocking and routing loops.
To configure OSPF, perform the following tasks:
71
Page 84

Tasks at a glance
(Required.) Enabling OSPF
(Optional.) Configuring OSPF areas:
• Configuring a stub area
• Configuring an NSSA area
• Configuring a virtual link
(Optional.) Configuring OSPF network types:
• Configuring the broadcast network type for an interface
• Configuring the NBMA network type for an interface
• Configuring the P2MP network type for an interface
• Configuring the P2P network type for an interface
(Optional.) Configuring OSPF rout e contr ol:
• Configuring OSPF route summarization
Configuring route summarization on an ABR
Configuring route summarization on an ASBR
• Configuring received OSPF route filtering
• Configuring Type-3 LSA filtering
• Setting an OSPF cost for an interface
• Setting the maximum number of ECMP routes
• Setting OSPF preference
• Configuring discard routes for summary networks
• Configuring OSPF route redistribution
Redistributing routes from another routing protocol
Redistributing a default route
Configuring default parameters for redistributed routes
• Advertising a host route
• Excluding interfaces in an OSPF area from the base topology
72
Page 85

Tasks at a glance
(Optional.) Tuning and optimizing OSPF networks:
• Setting OSPF timers
• Setting LSA transmission delay
• Setting SPF calculation interval
• Setting the LSA arrival interval
• Setting the LSA generation interval
• Disabling interfaces from receiving and sending OSPF packets
• Configuring stub routers
• Configuring OSPF authentication
• Adding the interface MTU into DD packets
• Setting a DSCP value for OSPF packets
• Setting the maximum number of external LSAs in LSDB
• Setting OSPF exit overflow interval
• Enabling compatibility with RFC 1583
• Logging neighbor state changes
• Configuring OSPF network manage ment
• Setting the LSU transmit rate
• Enabling OSPF ISPF
• Configuring prefix suppression
• Configuring prefix prioritization
• Configuring OSPF PIC
• Setting the number of OSPF logs
• Filtering outbound LSAs on an interface
• Filtering LSAs for the specified neighbor
• Configuring GTSM for OSPF
(Optional.) Configuring OSPF G R
• Configuring OSPF GR restarter
• Configuring OSPF GR helper
• Triggering OSPF GR
(Optional.) Configuring OSPF N SR
(Optional.) Configuring BFD for OSPF
(Optional.) Configuring OSPF F RR
(Optional.) Advertising OSPF link state information to BGP
Enabling OSPF
Enable OSPF before you perform other OSPF configuration tasks.
Configuration p rerequisites
Configure the link layer pro tocol and I P addresses for interf aces to ens ure I P connec tivit y bet ween
neighboring nodes.
Configuration guidelines
To enable OSPF on an interface, you can enable OSPF on the network where th e inter f ac e res ides
or directly enable OSPF on that interface. If you configure both, the latter takes precedence.
73
Page 86

•
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
You can specify a global router ID, or specify a router ID when you create an OSPF process.
If you specify a router ID when you create an OSPF proces s , any two routers in an AS must
have different router IDs. A common practice is to specify the IP address of an interface as the
router ID.
If you specify no router ID when you create the OSPF process, the global router ID is used. As
a best practice, specify a router ID when you create the OSPF process.
OSPF supports multiple processes and VPNs.
To run multiple OSPF processes, you must specify an ID for each process. The process IDs
take effect locally and has no influence on packet exchange between routers. Two routers with
different process IDs can exchange packets.
You can configure an OSPF process to run in a specified VPN instance. For more information
about VPN, see MPLS Configuration Guide.
Enabling OSPF on a network
1. Enter system view.
2. (Optional.) Configure a
global router ID.
3. Enable an OSPF process
and enter OSPF view.
4. (Optional.) Configure a
description for the OSPF
process.
5. Create an OSPF area and
enter OSPF area view.
6. (Optional.) Configure a
description for the area.
7. Specify a network to
enable the interface
attached to the network to
run the OSPF process in
the area.
system-view
router id
ospf [
router-id
vpn-instance
vpn-instance-name ] *
description
area
description
network
wildcard-mask
router-id
process-id |
router-id |
area-id
ip-address
text
text
N/A
By default, no global router ID is
configured.
If no global router ID is configured, the
highest loopback interface IP addre ss, if
any, is used as the router ID. If no loop back
interface IP address is available, the
highest physical interface IP a ddres s is
used, regardless of th e in t erfa ce status (up
or down).
By default, OSPF is disabled.
By default, no description is configured for
the OSPF process.
As a best practice, configure a description
for each OSPF process.
By default, no OSPF areas exist.
By default, no description is configured for
the area.
As a best practice, configure a description
for each OSPF area.
By default, no network is specified.
A network can be added to only one area.
Enabling OSPF on an interface
1. Enter system view.
system-view
74
N/A
Page 87

Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
2. Enter interface view.
3. Enable an OSPF process
on the interface.
interface
interface-number
ospf
area-id [
interface-type
process-id
exclude-subip ]
Configuring OSPF areas
Before you configure an OSPF area, perform the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
Enable OSPF.
Configuring a stub area
You can configure a non-b ack bone area at an AS e dge as a stub ar ea. To do so, execute the stub
command on all routers attached to the area. The routing table size is reduced because Type-5 LSAs
will not be flooded w ith in the stub area. The ABR gen e r ates a default route into th e stub area so all
packets destined outside of the AS are sent through the default route.
area
N/A
By default, OSPF is disabled on an
interface.
If the specified OSPF process and area do
not exist, the command creates the OSPF
process and area. Disabl ing a n OSP F
process on an interf ace does not delet e the
OSPF process or the area.
To further reduce the routing table size and routing information exchanged in the stub area, configure
a totally stub area b y using the stub no-summary c ommand on th e ABR. AS ex ternal routes and
inter-area routes will not be distri buted into the area. All the pac kets destine d outside of the AS or
area will be sent to the ABR for forwarding.
A stub or totally stub area cannot have an ASBR because external routes cannot be distributed into
the area.
To configure an OSPF stub area:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter area view.
4. Configure the area as a
stub area.
5. (Optional.) Set a cost for
the default route advertised
to the stub area.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
area
stub
default-route-advertise-alwa
[
ys
|
default-cost
vpn-instance
area-id
no-summary
router-id
] *
cost-value
N/A
N/A
N/A
By default, no stub area is configured.
The default setting is 1.
default-cost
The
takes effect only on the ABR of a stub
area or totally stub area.
cost command
75
Page 88

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Configuring an NSSA area
A stub area can not import external routes , but an NSSA area can import external routes into the
OSPF routing domain while retaining other stub area characteristics.
Do not configure the backbone area as an NSSA area or totally NSSA area.
To configure an NSSA area, configure the nssa command on all the routers attached to the area.
To configure a totally NSS A area, configure the nssa c ommand on all the r outers attached to the
area and configure t he nssa no-summary com mand on the ABR. T he A BR of a tota lly NSSA area
does not advertise inter-area routes into the area.
To configure an NSSA area:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter area view.
4. Configure the area as an
NSSA area.
5. (Optional.) Set a cost for
the default route advertised
to the NSSA area.
Configuring a virtual link
Virtual links are configured for connecting backbone area routers that have no direct physic al links.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
area
nssa [ default-route-advertise
cost
[
route-policy
type
no-summary
[ [ [
translate-ignore-checking-bac
[
kbone
translator-stability-interval
value ] *
default-cost
vpn-instance
area-id
cost-value |
type ] * |
translate-always
translate-never
] ] |
router-id
nssa-only
route-policy-name |
no-import-route
suppress-fa
|
cost-value
|
|
]
] |
N/A
N/A
N/A
|
By default, no area is configured as
an NSSA area.
The default setting is 1.
This command takes effect only on
the ABR/ASBR of an NSSA or
totally NSSA area.
To configure a virtual link:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter area view.
4. Configure a virtual link.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
area
vlink-peer
seconds |
{ {
cipher | plain
{
keychain-name |
plain
|
seconds |
vpn-instance
area-id
router-id [
hello
hmac-md5
} string } |
trans-delay
seconds |
md5
|
} string |
76
router-id
simple
retransmit
dead
} key-id
keychain
cipher
{
seconds ] *
N/A
N/A
N/A
By default, no virtual links exist.
Configure this command on both
ends of a virtual link. The
dead
intervals must be identical on
both ends of the virtual link.
hello
and
Page 89

•
•
•
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Configuring OSPF network types
OSPF classifies net work s into four types, including broadc ast, N BMA, P2MP, and P2P. The def aul t
network type of an interface on the device is broadcast.
When you change the network type of an interface, follow these guidelines:
When an NBMA network becomes fully meshed, change the network type to broadcast to avoid
manual configuration of neighbors.
If any routers in a broadcast network do not support multicasting, change the network type to
NBMA.
An NBMA network must be fully meshed. OSPF requires that an NBMA network be fully
meshed. If a network is partially meshed, change the network type to P2MP.
If a router on an NBMA network has only one neighbor, you can change the network type to P2P
to save costs.
Two broadcast-, NBMA-, and P2MP-interfaces can establish a neighbor relationship only when they
are on the same network segment.
Configuration p rerequisites
Before you configure OSPF network types, perform the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
Enable OSPF.
Configuring the broadcast network type for an interface
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Configure the OSPF network
type for the interface as
broadcast.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ospf network-type broadcast
interface-type
N/A
N/A
By default, the network type of an
interface is broadcast.
Configuring the NB M A network type for an interface
After you configure the network type as NBMA, you must specify neighbors and their router priorities
because NBMA interfaces cannot find neighbors by broadcasting hello packets .
To configure the NBMA network type for an interface:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Configure the OSPF
network type for the
interface as NBMA.
interface
interface-number
ospf network-type nbma
interface-type
77
N/A
N/A
By default, the network type of an
interface is broadcast.
Page 90

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
4. (Optional.) Set a router
priority for the interface.
5. Return to system view.
6. Enter OSPF view.
7. Specify a neighbor and
set its router priority.
ospf dr-priority
quit
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
peer
ip-address [
priority ]
priority
router-id
vpn-instance
dr-priority
The default setting is 1.
The router priority configured with this
command is for DR election.
N/A
N/A
By default, no neighbor is specified.
The priority configured with this
command indicates whether a
neighbor has the election right or not.
If you configure the ro uter pr iority for a
neighbor as 0, the local router
determines the neighbor has no
election right, and does not send hello
packets to this neighbor. However, if
the local router is the DR or BDR, it
still sends hello packets to the
neighbor for neighbor relationship
establishment.
Configuring the P2MP network type for an interface
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Configure the OSPF
network type for the
interface as P2MP.
4. Return to system view.
5. Enter OSPF view.
6. (Optional.) Specify a
neighbor and set its router
priority.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ospf network-type p2mp
unicast
[
quit
ospf [
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
peer
cost-value ]
interface-type
]
process-id |
vpn-instance
ip-address [
router-id
cost
N/A
N/A
By default, the network type of an
interface is broadcast.
After you configure the OSPF
network type for an interface as
P2MP unicast, all packets are
unicast over the interface. The
interface cannot broadcast hello
packets to discover neighbors, so
you must manually specify the
neighbors.
N/A
N/A
By default, no neighbor is specified.
This step must be performed if the
network type is P2MP unicast, and
is optional if the network type is
P2MP.
78
Page 91

Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Configuring the P2P network type for an interface
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Configure the OSPF
network type for the
interface as P2P.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ospf network-type p2p
peer-address-check ]
[
interface-type
Configuring OSPF route control
This section describes how to control the advertisement and reception of OSPF routing information,
as well as route redistribution from other protocols.
Configuration p rerequisites
Before you configure OSPF route control, perform the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
Enable OSPF.
Configure filters if routing information filtering is needed.
Configuring OSPF route summarization
N/A
N/A
By default, the network type of an
interface is broadcast.
Route summarization enables an ABR or ASBR to summarize cont iguous networks into a single
network and advertise the network to other areas.
Route summarizatio n reduces the routing inform ation exchanged b etween areas and the size of
routing tables, and improves routing performance. For example, three internal networks 19.1.1.0/24,
19.1.2.0/24, and 19.1.3.0/ 24 are available within an area. You can summar ize the three networks
into network 19.1.0.0/16, and advertise the summary network to other areas.
Configuring route summarization on an ABR
After you configure a s ummary route on an ABR, t he ABR generates a summary LSA instead of
specific LSAs. The sc ale of LSDBs on r o uter s in ot her areas and th e inf lu enc e of topo logy changes
are reduced.
To configure route summarization on an ABR:
1. Enter system view.
ospf [
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter OSPF area view.
4. Configure ABR route
summarization.
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
area
abr-summary
{ mask-length | mask } [
not-advertise
vpn-instance
area-id
router-id
ip-address
cost
] [
cost-value ]
advertise
N/A
N/A
N/A
By default, route summ arizatio n is
|
not configured on an ABR.
79
Page 92

•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
Configuring route summarization on an ASBR
Perform this task to enabl e an ASBR to summarize external routes withi n the specified address
range into a single rou te. The ASBR advertises only the summar y route to reduce the number of
LSAs in the LSDB.
An ASBR can summarize routes in the following LSAs:
Type-5 LSAs.
Type-7 LSAs in an NSSA area.
Type-5 LSAs translated by the ASBR (also an ABR) from Type-7 LSAs in an NSSA area.
If the ASBR (ABR) is not a translator, it cannot summarize routes in Type-5 LSAs translated
from Type-7 LS As .
To configure route summarization on an ASBR:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Configure ASBR route
summarization.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
|
*
asbr-summary
{ mask-length | mask } [
cost-value |
nssa-only
|
router-id
vpn-instance-name ]
ip-address
not-advertise
tag
tag ] *
router-id
cost
|
Configuring received OSPF route filtering
Perform this task to filter routes calculated using received LSAs.
The following filtering methods are available:
Use an ACL or IP prefix list to filter routing inf ormation by destination address .
Use the gateway keyword to filter routing information by next hop.
Use an ACL or IP prefix list to filter routing information by destination address. At the same time
use the gateway keyword to filter routing information by next hop.
Use a routing policy to filter routing information.
To configure OSPF to filter routes calculated using received LSAs:
N/A
N/A
By default, route summarization is
not configured on an ASBR.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Configure OSPF to
filter routes
calculated using
received LSAs.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
filter-policy
prefix-list-name ] |
prefix-list
|
prefix-list-name ] |
route-policy-name }
vpn-instance-name ] *
{ ipv4-acl-number [
prefix-list-name [
router-id
gateway
route-policy
import
Configuring Type-3 LSA filtering
Perform this task to filter Type-3 LSAs advertised to an area on an ABR.
80
router-id |
gateway
prefix-list-name
gateway
N/A
N/A
By default, OSPF accepts all
routes calculated using received
LSAs.
Page 93

Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
T o configure Type-3 LSA filtering:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter area view.
4. Configure Type-3 LSA
filtering.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
|
*
area
area-id
filter
{ ipv4-acl-number |
prefix-list-name |
route-policy-name } {
import
}
router-id
vpn-instance-name ]
route-policy
export
Setting an OSPF cost for an interface
Set an OSPF cost for an interface by using either of the following methods:
Set the cost value in interface view.
Set a bandwidth reference value for the interface. OSPF computes the cost with this formula:
Interface OSPF cost = Bandwidth reference value (100 Mbps) / Expected interface bandwidth
(Mbps). The expected bandwidth of an interface is configured with the bandwidth command
(see Interface Command Reference).
If the calculated cost is greater than 65535, the value of 65535 is used. If the calculated cost
is less than 1, the value of 1 is used.
If no cost or bandwidth reference value is configured for an interface, OSPF computes the
interface cost based on the interface bandwidth and default bandwidth reference value.
router-id
prefix-list
|
N/A
N/A
N/A
By default, the ABR does not
filter Type-3 LSAs.
To set an OSPF cost for an interface:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Set an OSPF cost for
the interface.
To set a bandwidth reference value:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Set a bandwidth
reference value.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ospf cost
system-view
ospf [
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
bandwidth-reference
interface-type
cost-value
process-id |
vpn-instance
router-id
value
N/A
N/A
By default, the OSPF cost is calculated
according to the interface bandwidth.
For a loopback interface, the O SPF cost
is 0 by default.
N/A
N/A
The default setting is 100 Mbps.
81
Page 94

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Setting the maxim um number of ECMP routes
Perform this task to implement load sharing over ECMP routes.
To set the maximum number of ECMP routes:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Set the maximum number of
ECMP routes.
system-view
ospf [
|
maximum load-balancing
Setting OSPF preference
A router can ru n multiple ro uting protoco ls, and each protocol is assigned a pr eference. If multip le
routes are available to the same destination, the one with the highest protocol preference is selected
as the best route.
To set OSPF preference:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
|
process-id |
vpn-instance
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] * N/A
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] * N/A
router-id
router-id
number
N/A
N/A
By default, the maximum
number of ECMP routes
equals the maximum number
of ECMP routes supported by
the system.
3. Set a preference for
OSPF.
preference
route-policy
ase
[
] { preference |
route-policy-name } *
By default, the preference of OSPF
internal routes is 10 and the preference
of OSPF external routes is 150.
Configuring discard routes for summary networks
Perform this task on an A BR or ASBR to spec ify whether to gener ate discard routes for summar y
networks. You can also specify a preference for the discard routes.
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Configure discard routes
for summary networks.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
discard-route
{ preference |
internal
suppression
vpn-instance
{ preference |
router-id
external
{
suppression
} } *
N/A
} |
N/A
By default:
• The ABR or ASBR generates
discard routes for summary
networks.
• The preference of discard
routes is 255.
82
Page 95

IMPORTANT:
The
allow
it with caution.
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Configuring OSPF route redistribution
On a router running OSPF and other routing protocols, you can configure OSPF to redistribute static
routes, direct routes, or r ou tes f r om other pr otoc ols, s u c h as RIP, IS-IS, and BGP. OSPF advertises
the routes in Type-5 LSAs or T y pe-7 LSAs. In addition, you can configure OSPF to filter redistributed
routes so that OSPF advertises only permitted routes.
import-route bgp command redistributes only EBGP routes. Because the import-route bgp
-ibgp co mmand redistributes both EBGP and IBGP routes, and might cause routing loops, use
Redistributing routes from another routing protocol
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Configure OSPF to
redistribute routes from
another routing protocol.
4. (Optional.) Configure
OSPF to filter
redistributed routes.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
import-route
[ process-id |
allow-ibgp
cost-value |
route-policy-name |
*
filter-policy
prefix-list
[ protocol [ process-id ] ]
] [
prefix-list-name }
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] *
protocol [ as-number ]
all-processes
allow-direct
nssa-only
tag
{ ipv4-acl-number |
Redistributing a default route
router-id |
|
cost
|
route-policy
|
type
tag |
export
type ]
N/A
N/A
By default, no route
redistribution is configured.
This command redistributes only
active routes. To view
information about active routes,
use the
protocol
By default, OSPF accept s all
redistributed routes.
display ip routing-table
command.
The import-route command cannot redistribute a default external route. Perform this task to
redistribute a default route.
To redistribute a default route:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Redistribute a default
route.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
default-route-advertise
permit-calculate-other
cost-value |
route-policy-name |
default-route-advertise
cost
cost-value ]
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] *
route-policy
type
[ [
] |
type ] *
[
Configuring default parameters for redistributed routes
Perform this task to configure default param eters for redistributed r outes, including cost, t ag, and
type. T ags identify information about protocols. For example, when redistributing BGP routes, OSPF
uses tags to identify AS IDs.
To configure the default parameters for redistributed routes:
router-id |
always
|
cost
summary
N/A
N/A
By default, no default route is
redistributed.
This command is applicable
only to VPNs. The PE router
advertises a default route in a
Type-3 LSA to a CE router.
83
Page 96

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
•
•
•
•
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Configure the default
parameters for
redistributed routes
(cost, upper limit, tag,
and type).
system-view
ospf [
vpn-instance
default { cost
type } *
Advertising a host r oute
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter area view.
4. Advertise a host route.
process-id |
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
area
area-id
host-advertise
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] *
cost-value |
router-id
vpn-instance
ip-address cost
router-id |
tag
tag |
N/A
N/A
type
By default, t he cost is 1, the tag
is 1, and the type is Type-2.
N/A
N/A
N/A
By default, no host route is
advertised.
Excluding interfaces in an OSPF area from the base topology
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Enter area view.
4. Exclude interfaces from the
base topology.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
area
capability default-exclusion
vpn-instance
area-id
router-id
N/A
N/A
N/A
By default, interfaces in an OSPF
area belong to the base topology.
Tuning and optimizing OSPF networks
You can use one of the following methods to optimize an OSPF network:
Change OSPF packet timers to adjust the convergence speed and network load. On low-speed
links, consider the delay time for sending LSAs.
Change the SPF calculation interval to reduce resource consumption caused by frequent
network changes.
Configure OSPF authentication to improve security.
Configuration p rerequisites
Before you configure OSPF network optimization, perform the following tasks:
Configure IP addresses for interfaces to ensure IP connectivity between neighboring nodes.
84
Page 97

•
•
•
•
•
Step
Command
Remarks
Enable OSPF.
Setting OSPF timers
An OSPF interface includes the following timers:
Hello timer—Interval for sending hello packets. It must be identical on OSPF neighbors.
Poll timer—Interval for sending hello packets to a neighbor that is down on the NBMA network.
Dead timer—Interval within which if the interface does not receive any hello packet from the
neighbor, it declares the neighbor is down.
LSA retransmission timer—Interval within which if the interface does not receive any
acknowledgment packets after sending an LSA to the neighbor, it retransmits the LSA.
To set OSPF timers:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Set the hello interval.
4. Set the poll interval.
5. Set the dead interval.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ospf timer hello
ospf timer poll
ospf timer dead
interface-type
seconds
seconds
seconds
N/A
N/A
By default:
• The hello interval on P2P and
broadcast interfaces is 10
seconds.
• The hello interval on P2MP and
NBMA interfaces is 30 seconds.
The default hello interval is restored
when the n etwork type f or an in terface is
changed.
The default setting is 120 seconds.
The poll interval is a minimum of four
times the hello interval.
By default:
• The dead interval on P2P and
broadcast interfaces is 40
seconds.
• The dead interval on P2MP and
NBMA interfaces is 120 seconds.
The dead interval must be a minimum of
four times the hello interval on an
interface.
The default dead interval is restored
when the n etwork type f or an in terface is
changed.
6. Set the retransmission
interval.
ospf timer retransmit
85
interval
The default setting is 5 seconds.
A retransmission interval setting that is
too small can cause unnecessary LSA
retransmissions. This interval is ty pically
set bigger th an the round-trip time of a
packet between two neighbors.
Page 98

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
system-view
Step
Command
Remarks
Setting LSA transmission delay
To avoid LSAs from aging out durin g transmission, se t an LSA retransmission dela y especially for
low speed links.
To set the LSA transmission delay on an interface:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter interface view.
3. Set the LSA transmi ssi on
delay.
system-view
interface
interface-number
ospf trans-delay
interface-type
Setting SPF ca lculation interv al
LSDB changes result in SPF calculations. When the topology changes frequently, a large amount of
network and router resources are occ up ied by SPF calculat ion. You can adjust the SPF c alc ulat io n
interval to reduce the impact.
For a stable network, the minimum interval is used. If network c hanges becom e f requent, the SPF
calculation in terval is incremented by the incremental interva l × 2
maximum interval is reached. The value n is the number of calculation times.
To set the SPF calculation interval:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
vpn-instance
router-id
seconds
N/A
N/A
The default setting is 1 second.
n-2
for each c alculation until the
N/A
N/A
3. Set the SPF
calculation interval.
spf-schedule-interval
maximum-interval
[ minimum-interval
[ incremental-interval ] ]
Setting the LSA arrival interval
If OSPF receives an LSA that has the same LSA type, LS ID, and router ID as the previously received
LSA within the LSA arrival interval, OSPF discards the LSA to save bandwidth and route resources.
To set the LSA arrival interval:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
vpn-instance
86
router-id
By default:
• The maximum interval is 5
seconds.
• The minimum interval is 50
milliseconds.
• The incremental interval is 200
milliseconds.
N/A
N/A
Page 99

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
3. Set the LSA arrival interval.
lsa-arrival-interval
interval
Setting the LSA generation interval
Adjust the LSA generation interval to protect network resources and routers from being overwhelmed
by LSAs at the time of frequent network changes.
The default setting is 1000
milliseconds.
Make sure this interval is smaller
than or equal to the interval set with
lsa-generation-interva
the
command.
l
For a stable network, the minimum interval is used. If network changes become f requent, the LS A
generation interval is increm ented by the incremental inter val × 2
n-2
for each generation until the
maximum interval is reached. The value n is the number of generation times.
To set the LSA generation interval:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Set the LSA
generation interval.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
lsa-generation-interval
maximum-interval [ minimum-interval
[ incremental-interval ] ]
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] *
router-id |
N/A
N/A
By default:
• The maximum interval is 5
seconds.
• The minimum interval is 50
milliseconds.
• The incremental interval is 200
milliseconds.
Disabling interf aces from receivin g and sending OSPF packets
T o enhance OSPF adaptability and reduce resource consumption, you can set an OSPF interface to
"silent." A silent OSPF interface bloc ks OSPF packets and cannot establish any OSPF neighbor
relationship. However, other interfaces on the router can still advertise direct routes of the interface in
Router LSAs.
To disable interfaces from receiving and sending routing information:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
router-id |
vpn-instance-name ] *
vpn-instance
router-id
87
N/A
N/A
Page 100

Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
Step
Command
Remarks
3. Disable interfaces from
receiving and sending
OSPF packets.
silent-interface
interface-number |
Configuring stub routers
A stub router is used for traffic control. It repor ts its status as a stub router to neig hboring OSPF
routers. The neighbor ing routers can h ave a route to t he stub router, but they do not use the stub
router to forward data.
Router LSAs from the stub router might contain different link type values. A value of 3 means a link to
a stub network, and the c os t of the link will not be cha nged b y def ault. To set the cost of the link to
65535, specify the include-stub keyword in the stub-router command. A value of 1, 2 or 4 means a
point-to-point link, a link to a transit network, or a virtual link. On such links, a maximum cost value of
65535 is used. Neighbors do not send packets to the stub router as long as they have a route with a
smaller cost.
{ interface-type
all
}
By default, an OSPF interface can
receive and send OSPF packets.
silent-interface
The
disables only the interfaces
associated with the current
process rather than other
processes. Multiple OSPF
processes can disable the same
interface from receiving and
sending OSPF packets.
command
To configure a router as a stub router:
1. Enter system view.
2. Enter OSPF view.
3. Configure the router as
a stub router.
system-view
ospf [
process-id |
vpn-instance
stub-router [ external-lsa
[ max-metric-value ] |
on-startup
[ seconds ] } |
[ max-metric-value ] ] *
router-id
vpn-instance-name ] *
{ seconds |
summary-lsa
Configuring OSPF authentication
Perform this task to configure OSPF ar ea and int erf ac e authentication.
OSPF adds the configured key into sent packets, and uses the key to authenticate received packets.
Only p ackets that pass the authentication can be received. If a pack et fails the authentication, the
OSPF neighbor relationship cannot be established.
If you configur e OSPF authentication f or both an area and an interface in that area, the interface
uses the OSPF authentication configured on it.
Configuring OSPF area authentication
router-id |
include-stub
wait-for-bgp
N/A
N/A
By default, the router is not
|
configured as a stub router.
A stub router is not related to a
stub area.
You must configure the same authentication mode and key on all the routers in an area.
To configure OSPF area authent icat ion:
1. Enter system view.
system-view
88
N/A
 Loading...
Loading...