Page 1

Reference Guide
ProtectTools Security Manager
Document Part Number: 389171-001
May 2005
Page 2

© Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The
only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing
herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Reference Guide
ProtectTools Security Manager
First Edition May 2005
Document Part Number: 389171-001
Page 3

Contents
1Introduction
ProtectTools Security Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Accessing the ProtectTools Security Manager . . . . . 1–2
Understanding Security Roles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–3
Managing ProtectTools Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–4
Creating a Secure Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–7
2 Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Basic Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Initializing the Smart Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Smart Card BIOS Security Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Enabling Smart Card BIOS Security Mode and
Setting the Smart Card Administrator Password. . . . 2–4
Changing the Smart Card Administrator
Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–6
Setting and Changing the Smart Card
User Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–7
Storing the Administrator or User
Card Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–8
General Tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
Updating BIOS Smart Card Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
Selecting the Smart Card Reader. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–10
Changing the Smart Card PIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–11
Backing Up and Restoring Smart Cards . . . . . . . . . 2–11
Reference Guide iii
Page 4

Contents
3 Embedded Security for ProtectTools
Basic Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Setup Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
Enabling the Embedded Security Chip . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
Initializing the Embedded Security Chip. . . . . . . . . . 3–3
Setting Up the Basic User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–4
General Tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–6
Using the Personal Secure Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–6
Encrypting Files and Folders. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–6
Sending and Receiving Encrypted E-mail. . . . . . . . . 3–7
Changing the Basic User Key Password . . . . . . . . . . 3–7
Advanced Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–8
Backing Up and Restoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–8
Changing the Owner Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–10
Enabling and Disabling Embedded Security . . . . . . 3–10
Migrating Keys with the Migration Wizard . . . . . . 3–12
4 BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Basic Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
General Tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
Managing Boot Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
Enabling and Disabling Device or
Security Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–3
Advanced Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
Managing ProtectTools Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–4
Managing Profiles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–7
Managing Computer Setup Passwords . . . . . . . . . . 4–11
iv Reference Guide
Page 5

5 Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Basic Concepts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–1
Setup Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Logging On to Credential Manger. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Registering Credentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
General Tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–7
Creating a Virtual Token . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–7
Changing the Windows Logon Password . . . . . . . . . 5–8
Changing a Token PIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
Managing Identity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–9
Locking the Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–11
Using Microsoft Network Logon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–12
Using Single Sign On . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–15
Advanced Tasks (Administrator Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–20
Specifying How Users and Administrators
Log On. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–20
Configuring Custom Authentication
Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–21
Configuring Credential Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–22
Configuring Credential Manager Settings. . . . . . . . 5–23
Contents
Glossary
Index
Reference Guide v
Page 6

Introduction
ProtectTools Security Manager
ProtectTools Security Manager software provides security
features that help protect against unauthorized access to the
computer, networks, and critical data. Enhanced security
functionality is provided by the following software modules:
■ Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
■ Embedded Security for ProtectTools
■ BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
■ Credential Manager for ProtectTools
The software modules available for your computer may vary
depending on your model. For example, Embedded Security for
ProtectTools requires that the Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
embedded security chip (select models only) be installed on your
computer, and Smart Card Security for ProtectTools requires an
optional smart card and reader.
1
ProtectTools software modules may be preinstalled, preloaded,
or available for download from the HP Web site. Visit
http://www.hp.com for more information.
The instructions in this guide are written with the assumption
✎
that you have already installed the applicable ProtectTools
software modules.
Reference Guide 1–1
Page 7

Introduction
Accessing the ProtectTools Security Manager
To access the ProtectTools Security Manager from the
Microsoft® Windows® Control Panel:
» Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager.
After you have configured the Credential Manager module,
✎
you can also open ProtectTools by logging on to Credential
Manager directly from the Windows logon screen. For more
information, refer to “Logging On to Windows with Credential
Manager,” in Chapter 5, “Credential Manager for
ProtectTools.”
1–2 Reference Guide
Page 8

Understanding Security Roles
In managing computer security (particularly for large
organizations), one important practice is to divide responsibilities
and rights among various types of administrators and users.
In a small organization or for individual use, these roles may
✎
all be held by the same person.
For ProtectTools, the security duties and privileges can be
divided into the following roles:
■ Security officer—Defines the security level for the company
or network and determines the security features to deploy,
such as smart cards, biometric readers, or USB tokens.
Many of the features in ProtectTools can be
✎
customized by the security officer in cooperation with
HP. For more information, visit
■ IT administrator—Applies and manages the security features
defined by the security officer. Can also enable and disable
some features. For example, if the security officer has
decided to deploy smart cards, the IT administrator can
enable smart card BIOS security mode.
http://www.hp.com.
Introduction
■ User—Uses the security features. For example, if the security
officer and IT administrator have enabled smart cards for the
system, the user can set the smart card PIN and use the card
for authentication.
Reference Guide 1–3
Page 9
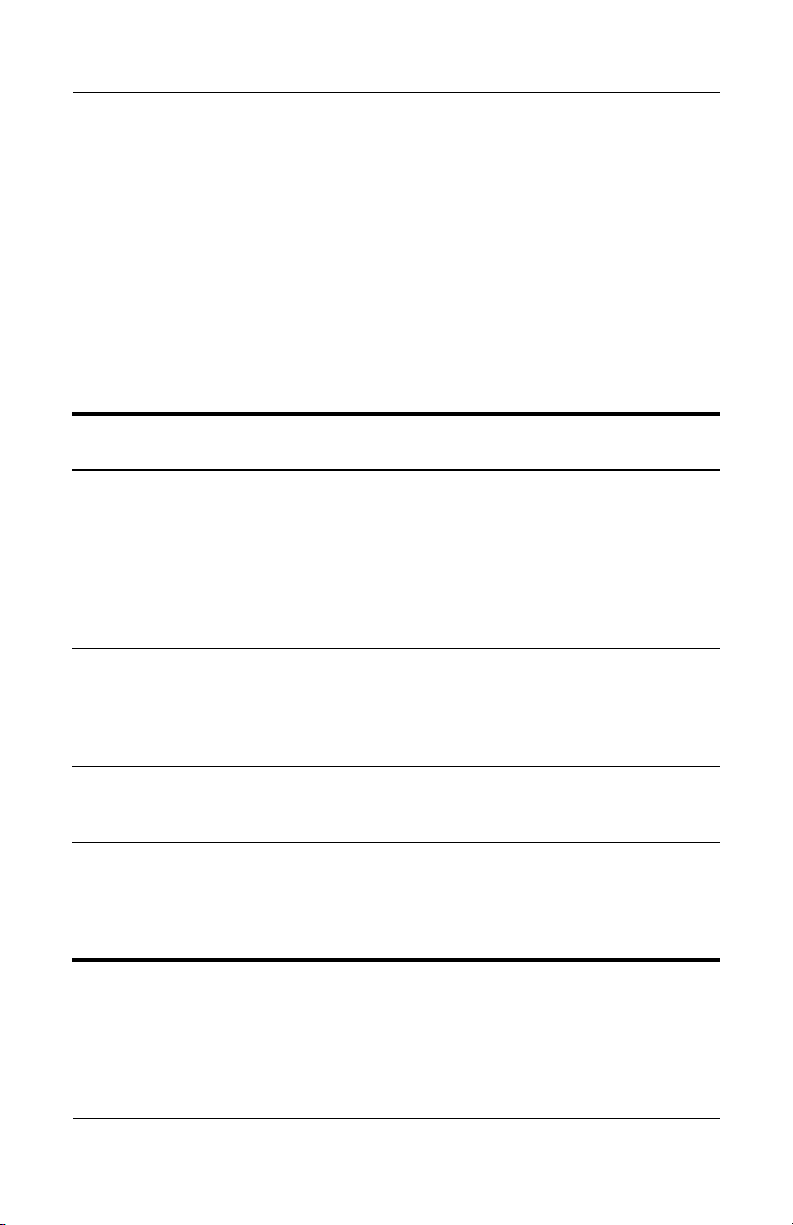
Introduction
Managing ProtectTools Passwords
Most of the ProtectTools Security Manager features are secured
by passwords. The following table lists the commonly used
passwords, the software module where the password is set, and
the password function.
The passwords that are set and used by IT administrators only are
indicated in this table as well. All other passwords may be set by
regular users or administrators.
Set in this
ProtectTools Password
ProtectTools Module Function
Computer Setup
administrator password
Also known as
✎
BIOS administrator,
BIOS Configuration, by
IT administrator
Protects access to the
Computer Setup utility.
f10 Setup, or
Security Setup
password
DriveLock master
password
DriveLock user password BIOS Configuration Protects access to the
Power-on password BIOS Configuration Protects access to the
BIOS Configuration, by
IT administrator
Protects access to the
internal hard drive that is
protected by DriveLock.
Is also used to remove
DriveLock protection.
internal hard drive that is
protected by DriveLock.
computer contents when
the computer is turned
on, restarted, or restored
from hibernation.
(Continued)
1–4 Reference Guide
Page 10
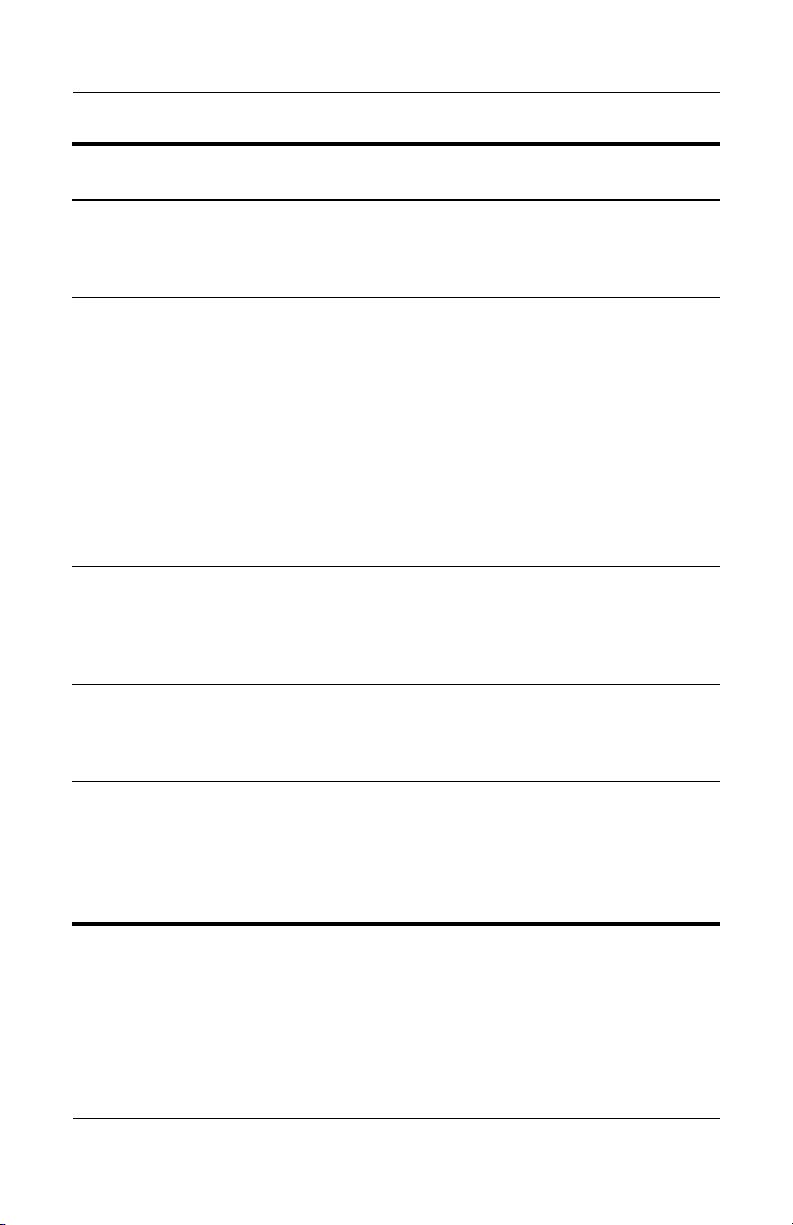
Set in this
ProtectTools Password
Profile password BIOS Configuration, by
ProtectTools Module Function
IT administrator
Introduction
Encrypts (and unlocks)
the profile where BIOS
system settings are
saved.
Smart card administrator
password
Also known as BIOS
✎
administrator card
password
Smart card PIN Smart Card Security Protects access to the
Smart card recovery file
password
Smart card user password
Also known as BIOS
✎
user card password
Smart Card Security,
by IT administrator
Smart Card Security Protects access to the
Smart Card Security Links the smart card to
Links the smart card to
the computer for
identification purposes.
Allows a computer
administrator to enable
or disable Computer
Setup passwords,
generate a new
administrator card, and
create recovery files to
restore user or
administrator cards.
smart card contents and
to computer access
when an optional smart
card and reader is used.
recovery file that
contains the BIOS
passwords.
the computer for
identification.
Allows a user to create a
recovery file to restore a
user card.
(Continued)
Reference Guide 1–5
Page 11
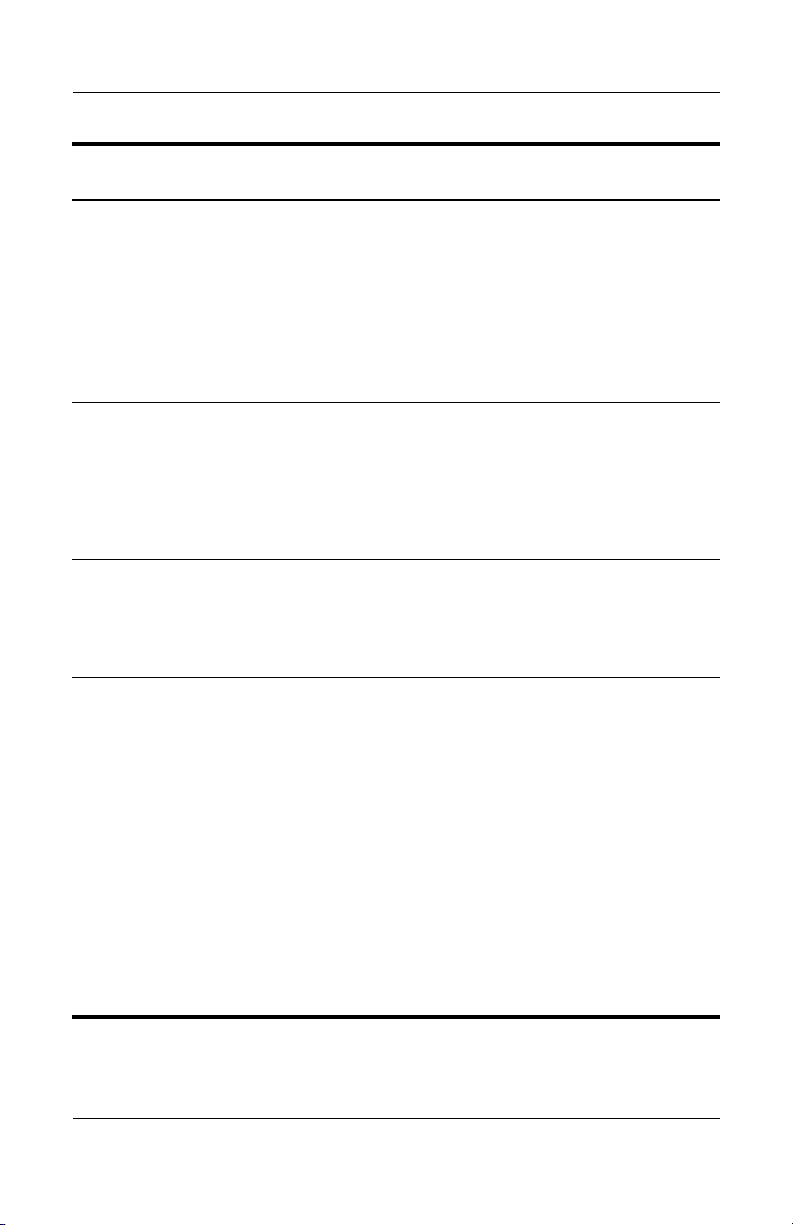
Introduction
ProtectTools Password
Basic User Key password
Also known as:
✎
Embedded Security
password
Emergency Recovery
Token password
Also known as:
✎
Emergency
Recovery Token Key
password
Set in this
ProtectTools Module Function
Embedded Security When enabled as the
BIOS power-on
authentication support
password, protects
access to the computer
contents when computer
is turned on, restarted,
or restored from
hibernation.
Embedded Security,
by IT administrator
Protects access to the
Emergency Recovery
Token, which is a
backup file for the
embedded security chip.
Owner password Embedded Security,
by IT administrator
Credential Manager logon
password
1–6 Reference Guide
Credential Manager This password offers
Protects the system and
the TPM chip from
unauthorized access to
all owner functions of
Embedded Security.
2 options:
■ It can be used in a
separate logon to
access Credential
Manager after logging
on to Microsoft
Windows.
■ It can be used in
place of the Windows
logon process,
allowing access to
Windows and
Credential Manager
simultaneously.
(Continued)
Page 12

ProtectTools Password
Credential Manager
recovery file password
Set in this
ProtectTools Module Function
Credential Manager,
by IT administrator
Protects access to the
Credential Manager
recovery file.
Introduction
Windows logon password Windows Control
Panel
Creating a Secure Password
When creating passwords, you must first follow any
specifications that are set by the program. In general, however,
consider the following guidelines to help you create strong
passwords and reduce the chances of your password being
compromised:
■ Use passwords with more than 6 characters, preferably more
than 8.
■ Mix the case of letters throughout your password.
■ Whenever possible, mix alphanumeric characters and include
special characters and punctuation marks.
■ Substitute special characters or numbers for letters in a
key word. For example, you can use the number 1 for letters
Ior L.
■ Combine words from 2 or more languages.
■ Split a word or phrase with numbers or special characters in
the middle, for example, “Mary2-2Cat45.”
■ Do not use a password that would appear in a dictionary.
Can be used in manual
logon or saved on the
smart card.
■ Do not use your name for the password, or any other personal
information, such as birth date, pet names, or mother's
maiden name, even if you spell it backwards.
Reference Guide 1–7
Page 13

Introduction
■ Change passwords regularly. You might change only a couple
■ If you write down your password, do not store it in a
■ Do not save the password in a file, such as an e-mail, on your
■ Do not share accounts or tell anyone your password.
of characters that increment.
commonly visible place very close to the computer.
computer.
1–8 Reference Guide
Page 14

Smart Card Security for
Basic Concepts
Smart Card Security for ProtectTools manages the smart card
setup and configuration for computers equipped with an optional
smart card reader.
With Smart Card Security, you can
■ Access smart card security features.
■ Initialize a smart card so that it can be used with other
ProtectTools modules, such as Credential Manager for
ProtectTools.
■ Work with the Computer Setup utility to enable smart card
authentication in a preboot environment, and to configure
separate smart cards for an administrator and a user. This
requires a user to insert the smart card and optionally enter
a PIN prior to allowing the operating system to load.
2
ProtectTools
■ Set and change the password used to authenticate users of
the smart card.
■ Back up and restore smart card BIOS passwords stored on the
smart card.
Reference Guide 2–1
Page 15

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Initializing the Smart Card
You must initialize the smart card before using it.
To initialize the smart card:
1. Insert the smart card into the reader.
2. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
3. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select Smart Card.
4. Click Initialize.
5. Type your name in the first box in the Initialize the smart
card dialog box.
6. Set and confirm the smart card PIN in the appropriate boxes.
The PIN code must be between 4 and 8 numeric characters.
To avoid losing access to the computer, do not forget the
Ä
smart card PIN. If you forget your smart card PIN, it may be
impossible to operate the computer. The smart card will be
locked and made unusable unless the smart card PIN is
entered correctly within 5 attempts. The count for these
attempts resets after the correct PIN is entered.
7. Click OK to complete the initialization.
2–2 Reference Guide
Page 16

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Smart Card BIOS Security Mode
When enabled, smart card BIOS security mode requires you to
use a smart card to log on to the computer.
The process of enabling smart card BIOS security mode involves
the following steps:
1. Enable Smart Card Power-on Authentication Support in
BIOS Configuration. Refer to “Enabling and Disabling Smart
Card Power-on Authentication Support,” in Chapter 4, “BIOS
Configuration for ProtectTools.”
Enabling this setting allows you to use a smart card for
✎
power-on authentication. The smart card BIOS
security mode features are unavailable until you enable
smart card power-on authentication support.
2. Enable smart card BIOS security mode in Smart Card
Security. Refer to “Enabling Smart Card BIOS Security
Mode and Setting the Smart Card Administrator Password,”
later in this chapter.
3. Set the smart card administrator password.
The smart card administrator password is set as part of the
✎
process of enabling smart card BIOS security mode.
The smart card administrator password is not the same as the
Computer Setup administrator password. The smart card
administrator password links the smart card to the computer for
identification purposes, and also allows you to do the following:
■ Enable or disable Computer Setup passwords
■ Create new administrator and user smart cards
■ Create a recovery file to restore either a user or administrator
smart card
The smart card administrator password cannot be set until smart
card BIOS security mode is enabled in Smart Card Security.
Reference Guide 2–3
Page 17

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Enabling Smart Card BIOS Security Mode and Setting the Smart Card Administrator Password
To enable smart card BIOS security mode and set the smart card
administrator password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select BIOS.
3. Under BIOS Security Mode, click Enable.
4. Click Next.
5. Enter the Computer Setup administrator password at the
prompt, and click Next.
6. Insert the new administrator smart card, and follow the
on-screen instructions. The instructions vary and may include
the following tasks:
❏ Initializing the smart card. Refer to “Initializing the Smart
Card” for detailed instructions.
❏ Setting the smart card administrator password. Refer to
“Storing the Administrator or User Card Password” for
detailed instructions.
❏ Creating a recovery file. Refer to “Creating a Recovery
File” for detailed instructions.
2–4 Reference Guide
Page 18

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Disabling Smart Card BIOS Security Mode
When disabling smart card BIOS security mode, the smart card
administrator and user passwords are disabled, and the use of the
smart card is no longer needed to access the computer.
If smart card BIOS security mode has previously been enabled,
✎
the button on the Smart Card Security BIOS page changes to
Disable.
To disable smart card security:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select BIOS.
3. Under BIOS Security Mode, click Disable.
4. Insert the card containing the current smart card administrator
password, and then click Next.
5. Enter the smart card PIN at the prompt and click Finish.
Reference Guide 2–5
Page 19

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Changing the Smart Card Administrator Password
The smart card administrator password is set as part of the
process for enabling smart card BIOS security mode. You can
change the smart card administrator password after it has been
set. Refer to “Smart Card BIOS Security Mode,” earlier in this
chapter, for more information about the smart card administrator
password.
The following procedure updates the smart card administrator
✎
password stored on the card and in Computer Setup.
To change the smart card administrator password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select BIOS.
3. Under BIOS Security Mode, next to BIOS administrator
card, click Change.
4. Enter the smart card PIN and click Next.
5. Insert the new administrator card and click Next.
6. Enter the smart card PIN and click Finish.
2–6 Reference Guide
Page 20

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Setting and Changing the Smart Card User Password
To set or change the smart card user password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select BIOS.
3. Under BIOS Security Mode, next to BIOS user card, click
the Set button.
If there is already a user password in Computer Setup,
✎
click the Change button.
4. Enter the smart card PIN and click Next.
5. Insert the new user card and click Next.
❏ If there is already a user password on the card, the
Finish dialog box is displayed. Omit steps 6 through 8
and go to step 9.
❏ If there is no user password on the card, the BIOS
Password Wizard opens.
6. In the BIOS Password Wizard, you can either
❏ Enter a password manually.
❏ Generate a random 32-byte password.
Using a known password enables you to create duplicate
✎
cards without using a recovery file. Generating a random
password offers more security; however, you must have a
recovery file to make backup cards.
Reference Guide 2–7
Page 21

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
7. Under Boot Requirements, select the check box if you
require the smart card PIN to be entered at startup.
If you do not require the smart card PIN to be entered at
✎
startup, clear this check box.
8. Enter the smart card PIN and click OK. The system prompts
you to create a recovery file.
It is highly recommended that you create a recovery
✎
file. For more information, refer to “Creating a
Recovery File,” later in this chapter.
9. Enter the smart card PIN in the Finish dialog box, and then
click Finish.
Storing the Administrator or User Card Password
If you want to create a backup card and have already set the
administrator password, you can store the password on the
new card.
CAUTION: This procedure updates only the password on the card and
Ä
not in Computer Setup. You will not be able to access the computer
with the new card.
To store the administrator or user card password:
1. Insert a smart card into the reader.
2. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
3. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select BIOS.
2–8 Reference Guide
Page 22

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
4. Under BIOS Password on Smart Card, click Store.
5. In the BIOS Password Wizard, you can either
❏ Enter a password manually.
❏ Generate a random 32-byte password.
Using a known password enables you to create duplicate
✎
cards without using a recovery file. Generating a random
password offers more security; however, you must have a
recovery file to make backup cards
6. Under Access Privilege, click either Administrator or User
for the type of card.
7. Under Boot Requirements, select the check box if you
require that the smart card PIN be entered at startup.
If you do not require the smart card PIN to be entered at
✎
startup, clear this check box.
8. Enter the smart card PIN and click OK.
9. Enter the smart card PIN again in the Finish dialog box, and
then click Finish. The system prompts you to create a
recovery file.
It is highly recommended that you create a smart card recovery
✎
file. For more information, refer to “Creating a Recovery File,”
later in this chapter.
Reference Guide 2–9
Page 23

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
General Tasks
Updating BIOS Smart Card Settings
To require a smart card PIN when you restart the computer:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Click the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select BIOS.
3. Under Smart Card BIOS Password Properties, click
Settings.
4. Select the check box to require a PIN at reboot.
To eliminate this requirement, clear the check box.
✎
5. Enter the smart card PIN and click OK.
Selecting the Smart Card Reader
Ensure that the correct smart card reader is selected in Smart Card
Security before using the smart card. If the correct reader is not
selected in Smart Card Security, some of the features may be
unavailable or incorrectly displayed.
To select the smart card reader:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select General.
3. Under Smart Card Reader, select the correct reader.
4. Insert the smart card into the reader. The reader information
is automatically refreshed.
2–10 Reference Guide
Page 24

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Changing the Smart Card PIN
To change the smart card PIN:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select Smart Card.
3. Click Change PIN.
4. Type your current smart card PIN.
5. Set and confirm the new PIN.
6. Click OK in the confirmation dialog box.
Backing Up and Restoring Smart Cards
After you have initialized a smart card and the card is ready for
use, it is highly recommended that you create a smart card
recovery file. The recovery file can be used to transfer the smart
card data from one smart card to another smart card. This file can
also be used to back up the original smart card or to restore the
data when a smart card is lost or stolen.
CAUTION: To avoid having a recovery file that does not match a smart
Ä
card with updated information, immediately create a new recovery file
and store it in a safe place. If you keep a backup smart card, you must
also update the information on the backup smart card by restoring the
new recovery file onto the backup smart card.
Reference Guide 2–11
Page 25

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Creating a Recovery File
To create a recovery file:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select Smart Card.
3. Under Recovery, click Create.
4. Enter the smart card PIN and click OK.
5. Enter the file path and file name in the Filename field.
To avoid loss of access to the computer, do not save the
Ä
recovery file on the computer hard drive; you will not be able
to access the file without the smart card. Also, a recovery file
saved on the hard drive may be accessible to others, posing a
security risk.
6. Set and confirm a recovery file password, and then click OK.
CAUTION: To prevent the loss of the smart card recovery file data, do
Ä
not forget the recovery file password. You cannot re-create your card
from the recovery file if you forget the password.
2–12 Reference Guide
Page 26

Restoring Smart Card Data
You can restore the smart card data from the recovery file. This is
especially useful if a card was lost or stolen, or if you want to
create a backup smart card. If you use a card with previous data
saved on it, the data will be overwritten.
Before you begin, you will need the following:
■ Access to a computer with Smart Card Security software
installed
■ Smart card recovery file
■ Smart card recovery file password
■ Smart card
To restore a smart card:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Smart Card Security.
2. Select the plus sign (+) to expand the Smart Card Security
menu, and then select Smart Card.
3. Insert the diskette or other media containing the smart card
recovery file.
Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
4. Insert a smart card into the reader. If the card is not
initialized, you will be prompted to initialize it. For detailed
instructions on initializing the smart card, refer to
“Initializing the Smart Card,” earlier in this chapter.
5. In the Recovery section, click Restore.
6. Ensure that the correct recovery file name is selected, and
enter the recovery file password.
7. Enter the smart card PIN.
8. Click OK. The original smart card contents are restored to
the new smart card.
Reference Guide 2–13
Page 27

Smart Card Security for ProtectTools
Creating a Backup Smart Card
It is highly recommended that you create duplicate smart cards
for backup purposes. Two methods can be used to create a backup
card, depending upon whether the smart card password was
manually or randomly generated.
To create a replacement smart card with a randomly generated
smart card password:
» Insert a smart card into the reader, and then load the
appropriate recovery file onto it. For more information, refer
to “Restoring Smart Card Data,” earlier in this chapter.
To create a replacement smart card with a manually generated
smart card password:
1. Initialize a new smart card. For instructions, refer to
“Initializing the Smart Card,” earlier in this chapter.
2. Store the administrator or user card password on the new
smart card. For instructions, refer to “Storing the
Administrator or User Card Password,” earlier in this chapter.
2–14 Reference Guide
Page 28

Embedded Security for
Basic Concepts
The integrated Trusted Platform Module (TPM) embedded
✎
security chip must be installed in your computer to use
Embedded Security for ProtectTools.
3
ProtectTools
Embedded Security for ProtectTools
unauthorized access to user data or credentials. This software
module provides the following security features:
■ Enhanced Microsoft Encryption File System (EFS) file
and folder encryption
■ Creation of a personal secure drive (PSD) for protecting
user data
■ Data management functions, such as backing up and
restoring the key hierarchy
■ Support for third-party applications (such as
Microsoft Outlook and Internet Explorer) for protected
digital certificate operations when using the Embedded
Security software
Reference Guide 3–1
protects against
Page 29

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
The TPM embedded security chip enhances and enables other
ProtectTools Security Manager security features. For example,
Credential Manager for ProtectTools can use the embedded chip
as an authentication factor when the user logs on to Windows.
On select models, the TPM embedded security chip also enables
enhanced BIOS security features accessed through BIOS
Configuration for ProtectTools.
Setup Procedures
CAUTION: To reduce security risk, it is highly recommended that your
Ä
IT administrator immediately initialize the embedded security chip.
Failure to initialize the embedded security chip could result in an
unauthorized user, a computer worm, or a virus taking ownership of the
computer and gaining control over the owner tasks, such as handling
the emergency recovery archive, and configuring user access settings.
Follow the steps in the following 2 sections to enable and
initialize the embedded security chip.
Enabling the Embedded Security Chip
The embedded security chip must be enabled in the Computer
Setup utility. This procedure cannot be performed in BIOS
Configuration for ProtectTools.
To enable the embedded security chip:
1. Open Computer Setup by turning on or restarting the
computer, and then pressing
Based Setup” message is displayed in the lower-left corner
of the screen.
2. If you have not set an administrator password, use the arrow
keys to select Security > Administrator password, and then
enter.
press
3. Type your password in the New password and Verify new
password boxes, and then press
3–2 Reference Guide
f10 while the “F10 = ROM
f10.
Page 30

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
4. In the Security menu, use the arrow keys to select
Embedded Security, and then press
enter.
5. Under Embedded Security, select Embedded security
device state and change to Enable.
6. Press
f10 to accept the changes to the Embedded Security
configuration.
7. To save your preferences and exit Computer Setup, use the
arrow keys to select File > Save Changes and Exit. Then
follow the instructions on the screen.
Initializing the Embedded Security Chip
In the initialization process for Embedded Security, you will
■ Set an owner password for the embedded security chip that
protects access to all owner functions on the embedded
security chip.
■ Set up the emergency recovery archive, which is a protected
storage area that allows reencryption of the Basic User Keys
for all users.
To initialize the embedded security chip:
1. Right-click the Embedded Security icon in the notification
area, at the far right of the taskbar, and then select
Embedded Security Initialization. The ProtectTools
Embedded Security Initialization Wizard opens.
2. Click Next.
3. Set and confirm an owner password, and then click Next. The
Setup Emergency Recovery dialog box opens.
4. Click Next to accept the default recovery archive location, or
click the Browse button to choose a different location, and
then click Next.
5. Set and confirm the emergency recovery token password, and
then click Next.
Reference Guide 3–3
Page 31

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
6. Click Browse and choose the location for the emergency
recovery archive, and then click Next.
7. Click Next on the “Summary” page.
❏ If you do not want to set up a basic user account at this
time, clear the Start the Embedded Security User
Initialization Wizard check box, and then click Finish.
You can start the wizard manually to set up a basic user
account at any time by following the instructions in the
next section.
❏ If you want to set up a basic user account, select the Start
the Embedded Security User Initialization Wizard
check box, and then click Finish. The Embedded Security
User Initialization Wizard opens. Refer to the instructions
in the next section for more details.
Setting Up the Basic User Account
Setting up a basic user account in Embedded Security
■ Produces a Basic User Key that protects encrypted data,
and sets a Basic User Key password to protect the Basic
User Key.
■ Sets up a personal secure drive (PSD) for storing encrypted
files and folders.
CAUTION: Safeguard the Basic User Key password. Encrypted data
Ä
cannot be accessed or recovered without this password.
To set up a basic user account and enable the user security
features:
1. If the Embedded Security User Initialization Wizard is not
open, select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools
Security Manager > Embedded Security > User Settings.
2. Under Embedded Security Features, click Configure. The
Embedded Security User Initialization Wizard opens.
3. Click Next.
3–4 Reference Guide
Page 32

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
4. Set and confirm the Basic User Key password, and then
click Next.
5. Click Next to confirm settings.
6. Select the security features you want, and then click Next.
7. Click Next again.
To use secure e-mail, you must first configure the e-mail
✎
client to use a digital certificate that is created with
Embedded Security. If a digital certificate is not available,
you must obtain one from a certification authority. For
instructions on configuring your e-mail and obtaining a
digital certificate, refer to the e-mail client online Help.
8. If more than one encryption certificate exists, select the
appropriate certificate, and then click Next.
9. Select the drive letter and label for your PSD, and then
click Next.
10. Select the size and location of the PSD, and then click Next.
11. Click Next on the “Summary” page.
12. Click Finish.
Reference Guide 3–5
Page 33

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
General Tasks
After the basic user account is set up, you can perform the
following tasks:
■ Encrypting files and folders
■ Sending and receiving encrypted e-mail
Using the Personal Secure Drive
After setting up the PSD, you are prompted to enter the Basic
User Key password at the next logon. If the Basic User Key
password is entered correctly, you can access the PSD directly
from Windows Explorer.
Encrypting Files and Folders
When working with encrypted files in Windows XP Professional,
consider the following rules:
■ Only files and folders on NTFS partitions can be encrypted.
Files and folders on FAT partitions cannot be encrypted.
■ System files and compressed files cannot be encrypted, and
encrypted files cannot be compressed.
■ Temporary folders should be encrypted, because they are
potentially of interest to hackers.
■ A recovery policy is automatically set up when you encrypt a
file or folder for the first time. This policy ensures that if you
lose your encryption certificates and private keys, you will be
able to use a recovery agent to decrypt your data.
3–6 Reference Guide
Page 34

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
To encrypt files and folders:
1. Right-click the file or folder that you want to encrypt.
2. Click Encrypt.
3. Click one of the following options:
❏ Apply changes to this folder only.
❏ Apply changes to this folder, subfolders, and files.
4. Click OK.
Sending and Receiving Encrypted E-mail
Embedded Security enables you to send and receive encrypted
e-mail, but the procedures vary depending upon the program you
use to access your e-mail. For more information, refer to the
Embedded Security online Help, and the online Help for your
e-mail.
Changing the Basic User Key Password
To change the Basic User Key password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > User Settings.
2. Under Basic User Key password, click Change.
3. Type the old password, and then set and confirm the new
password.
4. Click OK.
Reference Guide 3–7
Page 35

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
Advanced Tasks
Backing Up and Restoring
The Embedded Security backup feature creates an archive that
contains certification information to be restored in case of
emergency.
Creating a Backup File
To create a backup file:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > Backup.
2. Select Backup.
3. Click Browse to choose the location where the backup file
will be saved.
4. Select whether to add the emergency recovery archive to
the backup data.
5. Click Next.
6. Click Finish.
3–8 Reference Guide
Page 36

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
Restoring Certification Data from the Backup File
To restore data from the backup file:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > Backup.
2. Click Restore.
3. Click Browse to select the backup file from the stored
location.
4. Click Next.
5. Select whether to start the Embedded Security User
Initialization Wizard.
❏ If you choose to start the initialization wizard, click
Finish, and then follow the on-screen instructions to
complete the initialization. For more information, refer
to “Setting Up the Basic User Account,” earlier in this
chapter.
❏ If you choose not to start the initialization wizard, click
Finish.
Reference Guide 3–9
Page 37

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
Changing the Owner Password
To change the owner password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > Advanced.
2. Under Owner Password, click Change.
3. Type the old owner password, and then set and confirm the
new owner password.
4. Click OK.
Enabling and Disabling Embedded Security
It is possible to disable the Embedded Security features if you
want to work without the security function.
The Embedded Security features can be enabled or disabled at
2 different levels.
■ Temporary disabling—With this option, embedded security
is automatically reenabled on Windows restart. This option
is available to all users by default.
■ Permanent disabling—With this option, the owner password
is required to reenable Embedded Security. This option is
available only to administrators.
3–10 Reference Guide
Page 38

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
Temporarily Disabling Embedded Security
To temporarily disable Embedded Security:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > User Settings.
2. Under Embedded Security, click Disable.
Enabling Embedded Security After Temporary Disable
Embedded Security will automatically be reenabled upon
Windows restart if it was disabled through User Settings.
If you log off your Windows account but do not restart the
✎
computer, the Embedded Security features will still be disabled
when you or another user logs on to Windows, until the
computer is restarted.
Permanently Disabling Embedded Security
To permanently disable Embedded Security:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > Advanced.
2. Under Embedded Security, click Disable.
3. Enter your owner password at the prompt, and then click OK.
Reference Guide 3–11
Page 39

Embedded Security for ProtectTools
Enabling Embedded Security After Permanent Disable
To enable Embedded Security after permanently disabling it:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Embedded Security > Advanced.
2. Under Embedded Security, click Enable.
3. Enter your owner password at the prompt, and then click OK.
Migrating Keys with the Migration Wizard
Migration is an advanced administrator task that allows the
management, restoration, and transfer of keys and certificates.
For details on migration, refer to the Embedded Security
online Help.
3–12 Reference Guide
Page 40

BIOS Configuration for
Basic Concepts
BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools provides access to the
Computer Setup utility security and configuration settings. This
gives users Windows access to system security features that are
managed by Computer Setup.
With BIOS Configuration, you can
■ Manage power-on passwords and administrator passwords.
■ Configure other preboot authentication features, such as
enabling smart card passwords and embedded security
authentication.
■ Enable and disable hardware features, such as CD-ROM boot
or different hardware ports.
4
ProtectTools
■ Configure boot options, which includes enabling MultiBoot
and changing the boot order.
Many of the features in BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
✎
are also available in the Computer Setup utility.
Reference Guide 4–1
Page 41

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
General Tasks
BIOS Configuration allows you to manage various computer
settings that would otherwise be accessible only by pressing
f10 at startup and entering the Computer Setup utility.
Managing Boot Options
You can use BIOS Configuration to manage various settings
for tasks that run when you turn on or restart the computer.
To manage boot options:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Enter your Computer Setup administrator password at the
BIOS administrator password prompt, and click OK.
The BIOS administrator password prompt is displayed only
✎
if you have already set the Computer Setup administrator
password. For more information about setting the Computer
Setup administrator password, refer to “
Administrator Password
Setting the
,” later in this chapter.
3. Select or clear the Enable Quick boot check box.
4. Select the delays (in seconds) for
Express Boot Popup.
5. Select or clear the Enable MultiBoot check box.
6. If you have enabled MultiBoot, select the boot order by
selecting a boot device, and then clicking Move Up or
Move Down to adjust its order in the list.
7. Click Apply and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
4–2 Reference Guide
f10 and f12, and for
Page 42

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Enabling and Disabling Device or Security Options
To enable or disable devices or security options:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Enter your Computer Setup administrator password at the
BIOS administrator password prompt, and then click OK.
3. Click Device Options.
4. Select or clear any combination of the following options:
❏ NumLock at Boot
❏ Swapping Fn/Ctrl Keys
❏ Multiple Pointing Devices
❏ USB Legacy Support
❏ Automatic SpeedStep Functionality Support
❏ Fan Always on While on AC Power
5. Select the parallel port mode from the drop-down box.
6. Click Security.
7. Select or clear any combination of the following options:
❏ Serial Port
❏ Infrared Port
❏ Parallel Port
❏ SD Slot
❏ CD-ROM Boot
❏ Floppy Boot
❏ Internal Network Adapter Boot
8. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes and exit.
Reference Guide 4–3
Page 43

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Advanced Tasks
Managing ProtectTools Settings
Some of the features of ProtectTools Security Manager can be
managed in BIOS Configuration.
Enabling and Disabling Smart Card Power-on Authentication Support
Enabling this option allows you to use the smart card for user
authentication when you turn on the computer.
To enable smart card power-on authentication support:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Enter your Computer Setup administrator password at the
BIOS administrator password prompt, and then click OK.
3. Select Security.
4. Click Advanced.
5. Under Smart Card Security, select the Enable Smart Card
Power-on Authentication Support check box.
To disable smart card power-on authentication, clear this
✎
check box.
6. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
4–4 Reference Guide
Page 44

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Enabling and Disabling Power-on Authentication Support for Embedded Security
Enabling this option allows the system to use the TPM embedded
security chip (if available) for user authentication when you turn
on the computer.
To enable power-on authentication support for embedded
security:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Enter your Computer Setup administrator password at the
BIOS administrator password prompt, and then click OK.
3. Select Security.
4. Click Advanced.
5. Under Embedded Security, select the Enable Power-on
Authentication Support check box.
To disable power-on authentication for embedded security,
✎
clear this check box.
6. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
Reference Guide 4–5
Page 45

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Enabling and Disabling Automatic DriveLock Hard Drive Protection
When this option is enabled, the DriveLock passwords will be
generated and protected by the TPM embedded security chip. The
DriveLock master password is set to match the Computer Setup
administrator password, and the DriveLock user password is
generated randomly by the TPM and protected by the TPM.
The option to enable Automatic DriveLock is unavailable unless
■ The computer has a TPM security chip installed and
initialized. For instructions on how to enable and initialize the
TPM security chip, refer to “Enabling the Embedded Security
Chip” and “Initializing the Embedded Security Chip” in
Chapter 3, “Embedded Security for ProtectTools.”
■ No DriveLock passwords have already been enabled.
If you have already manually set DriveLock passwords on your
✎
computer, you must first disable them before you can set
Automatic DriveLock protection.
To enable or disable Automatic DriveLock protection:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Enter your Computer Setup administrator password at the
BIOS administrator password prompt, and then click OK.
3. Select Security.
4. Click Advanced.
5. Under Embedded Security, select the Enable Automatic
DriveLock Protection check box.
To disable power-on authentication for Embedded Security,
✎
clear this check box.
6. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
4–6 Reference Guide
Page 46

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Managing Profiles
After you have set your preferences in BIOS Configuration for
ProtectTools, you can save the settings under a named profile.
The settings are saved in a file which is encrypted with a
password that you provide. This profile can then be applied to
multiple platforms.
You must restart your computer for these settings to take effect.
✎
Managing Profiles Using the Command Line
You can use the command line interface to manage profiles for
BIOS configuration. From the command line, you can
■ Change the setting to display the “Profiles” page in BIOS
Configuration for ProtectTools, which is hidden by default.
■ Access and open a profile scheme
■ Apply profiles across multiple computers
To access and modify profile settings from the command line:
1. Select Start > Run.
2. Enter
3. Click OK.
4. At the command prompt, use the
Reference Guide 4–7
cmd.exe in the Open box.
cd command to navigate
to the following path for the BIOS Configuration utility:
C:\Program Files\HPQ\HP BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Page 47

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
5. Enter hpqsetup.exe, and add switches to customize the request,
as shown in the following table.
Switch(es) Function Example
/f
and
/k
These 2 switches
✎
are used
together.
/f: Specify INI file path
/k: Specify the
password for decrypting
the file created in the
BIOS Configuration tool
Hpqsetup.exe /fc:\test.ini
/kxxxx
(where
test
is the name
of the INI file, and
is the password)
xxxx
/p Display the “Profiles”
page on the BIOS
Configuration page of
ProtectTools, which is
hidden by default
(requires restart of
ProtectTools)
6. Press
enter.
Hpqsetup.exe /p
4–8 Reference Guide
Page 48

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Saving a New Profile Scheme
To save a new profile scheme:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Click Profiles.
If the “Profiles” page is not visible, you must change
✎
the display setting from the command line. For
instructions, refer to
Command Line,” in the previous section.
3. Click Save As.
4. Type a name for the profile in the dialog box.
5. Set and confirm a password to encrypt the file.
6. Click OK in the Add Profile dialog box.
7. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
“Managing Profiles Using the
Deleting a Profile Scheme
To delete a profile scheme:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Profiles.
3. Select the profile you want to delete from the drop-down list.
4. Click Delete.
5. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
The INI file created by that profile is deleted from the following
location:
C:\Program Files\HPQ\HP BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools \INIFiles
Reference Guide 4–9
Page 49

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Applying a Profile Scheme
You can apply any profile scheme to a new platform through
HP BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools.
To apply a profile scheme:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Profiles.
3. Select the profile scheme you want to apply from the
drop-down list.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click OK. The
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\BIOS
Configuration\INIFiles
XXX.ini file is saved at the following location:
Applying a Profile Scheme Across Multiple Computers
An IT administrator can use the HPQSetup application and a
deployment tool to apply a BIOS Configuration profile across
multiple platforms over a network. The HPQSetup application
can be used only with a deployment tool, and only from the
command line. For more information, refer to “Managing Profiles
Using the Command Line,” earlier in this document.
4–10 Reference Guide
Page 50

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Managing Computer Setup Passwords
You can use BIOS Configuration to set and change the power-on
and administrator passwords in Computer Setup, and also to
manage various password settings.
CAUTION: The passwords you set through the “Passwords” page in
Ä
BIOS Configuration are saved immediately upon clicking the Apply or
OK button in the ProtectTools window. Make sure you remember what
password you have set, because you will not be able to undo a
password setting without supplying the previous password.
The power-on password can protect your notebook from
unauthorized use.
After you have set a power-on password, the Set button on the
✎
“Passwords” page is replaced by a Change button.
The Computer Setup administrator password protects the
configuration settings and system identification information in
Computer Setup. After this password is set, it must be entered to
access Computer Setup. If you have set an administrator
password, you will be prompted for the password before opening
the BIOS Configuration portion of ProtectTools.
After you have set an administrator password, the Set button on
✎
the “Passwords” page is replaced by a Change button.
Reference Guide 4–11
Page 51

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Setting the Power-On Password
To set the power-on password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Passwords.
3. Under Power-On Password, select Set.
4. Type and confirm the password in the Enter Password and
Verify Password boxes.
5. Click OK in the Passwords dialog box.
6. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
Changing the Power-On Password
To change the power-on password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Passwords.
3. Under Power-On Password, click Change.
4. Type the current password in the Old Password box.
5. Set and confirm the new password in the Enter New
Password box.
6. Click OK in the Passwords dialog box.
7. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
4–12 Reference Guide
Page 52

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Setting the Administrator Password
To set the Computer Setup administrator password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Passwords.
3. Under Administrator Password, select Set.
4. Set and confirm the password in the Enter Password and
Confirm Password boxes.
5. Click OK in the Passwords dialog box.
6. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
Changing the Administrator Password
To change the Computer Setup administrator password:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Passwords.
3. Under Administrator Password, click Change.
4. Type the current password in the Old Password box.
5. Type and confirm the new password in the Enter New
Password and Verify New Password boxes.
6. Click OK in the Passwords dialog box.
7. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
Reference Guide 4–13
Page 53

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Setting Password Options
You can use BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools to set password
options to enhance the security of your system.
Enabling and Disabling Stringent Security
CAUTION: To prevent the computer from becoming permanently
Ä
unusable, record your configured administrator password, power-on
password, or smart card PIN in a safe place away from your computer.
Without these passwords or PIN, the computer cannot be unlocked.
Enabling stringent security provides enhanced protection for
the power-on and administrator passwords and other forms of
power-on authentication.
To enable or disable stringent security:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Passwords.
3. Select the Enable Stringent Security check box.
If you want to disable stringent security, clear this
✎
check box.
4. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
4–14 Reference Guide
Page 54

BIOS Configuration for ProtectTools
Enabling and Disabling Power-on
Authentication on Windows Restart
This option allows you to enhance security by requiring users to
enter a power-on, TPM, DriveLock, or smart card password when
Windows restarts.
To enable or disable power-on authentication on Windows restart:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > BIOS Configuration.
2. Select Passwords.
3. Select the Enable Power-on Authentication on Windows
restart check box.
If you want to disable power-on authentication on Windows
✎
restart, clear this check box.
4. Click Apply, and then click OK in the ProtectTools window
to save your changes.
Reference Guide 4–15
Page 55

Credential Manager for
Basic Concepts
Credential Manager for ProtectTools has security features that
provide protection against unauthorized access to your computer.
These features include the following:
■ Alternatives to passwords when logging on to Microsoft
Windows, such as using a smart card or biometric reader
to log on to Windows.
■ Single Sign On feature that automatically remembers
credentials for Web sites, applications, and protected
network resources.
■ Support for optional security devices, such as smart cards
and biometric readers.
■ Support for additional security settings, such as requiring
authentication with an optional security device to unlock the
computer.
5
ProtectTools
Reference Guide 5–1
Page 56

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Setup Procedures
Logging On to Credential Manger
Depending upon the configuration, you can log on to Credential
Manager in any of the following ways:
■ Credential Manager Logon Wizard (preferred)
■ Credential Manager icon in the notification area
■ ProtectTools Security Manager
If you use the Credential Manager Logon prompt on the
✎
Windows Logon screen to log in to Credential Manager, you
are logged in to Windows at the same time.
Logging On for the First Time
The first time you open Credential Manager, log on with your
regular Windows Logon password. A Credential Manager
account is then automatically created with your Windows logon
credentials.
After logging on to Credential Manager, you can register
additional credentials, such as a fingerprint or a smart card.
At the next logon, you can select the logon policy and use any
combination of the registered credentials.
5–2 Reference Guide
Page 57

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Using the Credential Manager Logon Wizard
To log on to Credential Manger using the Credential Manager
Logon Wizard:
1. Open the Credential Manager Logon Wizard in any of the
following ways:
❏ From the Windows logon screen
❏ From the notification area, by double-clicking the
ProtectTools icon.
❏ From the “Credential Manager” page of Protect Tools
Security Manager, by clicking the Log On link on the
upper right side of the window.
2. Enter your user name in the User name box, and then
click Next.
3. Select the authentication method you want to use, and then
click Next.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions for logging on with your
selected authentication method.
5. Click Finish.
Reference Guide 5–3
Page 58

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Creating a New Account
You can use the Credential Manager Logon Wizard to create a
new user account. Before you begin, you must be logged on to
Windows with an administrator account, but not logged on to
Credential Manager.
To create a new account:
1. Open Credential Manager by double-clicking the icon in the
notification area. The Credential Manager Logon Wizard
opens.
2. On the “Introduce Yourself” page, click the More button,
and then click Sign Up for a New Account.
3. Click Next.
4. On the “Registration” page, type the user name, first and
last name of the user, and the account description. Then
click Next.
5. On the “Authentication Methods” page, select the
authentication methods you want to register (and clear the
check boxes for those you do not want to register), and
then click Next.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to register the selected
credentials.
7. Click Finish.
5–4 Reference Guide
Page 59

Registering Credentials
You can use the “My Identity” page to register your various
authentication methods, or credentials. After they have been
registered, you can use these methods to log on to Credential
Manager.
Registering Fingerprints
To register fingerprints:
1. Connect the fingerprint reader to your computer.
2. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
3. Click My Identity.
4. Under I Want To, click Register Fingerprints.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the
registration.
Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Reference Guide 5–5
Page 60

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Registering a Smart Card or Token
To register a smart card or token:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Register
Credentials.
4. Click the authentication method you want to register, and
then click Next.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the
registration.
Registering Other Credentials
To register other credentials:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Register
Credentials.
4. Click the authentication method you want to register, and
then click Next.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the
registration.
5–6 Reference Guide
Page 61

General Tasks
All users have access to the “My Identity” page in Credential
Manager. From the “My Identity” page, you can
■ Create and register authentication credentials.
■ Manage passwords.
■ Manage Microsoft Network accounts.
■ Manage single sign on credentials.
Creating a Virtual Token
A virtual token works very much like a smart card or USB token.
The token is saved either on the computer hard drive or in the
Windows registry. When you log on with a virtual token, you are
asked for a user PIN to complete the authentication.
To create a new virtual token:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
Credential Manager for ProtectTools
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Register
Credentials.
4. Click Next.
5. Click Virtual Token, and then click Next.
6. Click Create New, and then click Next.
7. Enter a name and location for the virtual token file (or
click the Browse button to find a file location), and then
click Next.
8. Set and confirm a master PIN and a user PIN.
9. Click Finish.
Reference Guide 5–7
Page 62

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Changing the Windows Logon Password
You can change your Windows logon password from the
“My Identity” page in Credential Manager.
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click Change Windows Logon
Password.
4. Type your old password in the Old password box.
5. Set and confirm your new password in the New password
and Confirm password boxes.
6. Click Finish.
Changing a Token PIN
You can change the PIN for a smart card or virtual token from the
“My Identity” page in Credential Manager.
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Change
Tok en P IN .
4. Click Next.
5. Select the token for which you want to change the PIN, and
then click Next.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the PIN
change.
5–8 Reference Guide
Page 63

Managing Identity
Backing Up an Identity
It is recommended that you back up your identity in Credential
Manager, in case of data loss or accidental removal.
To back up an identity:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Backup
Identity.
4. Click Next.
5. Select the elements you want to back up, and then click Next.
6. On the “Device Type” page, select the device type you want
to use to store the backup, and then click Next.
You will need to know the password or PIN code for the
✎
device you select for the backup file.
Credential Manager for ProtectTools
7. Follow the on-screen instructions for the device you selected,
and then click Finish.
Reference Guide 5–9
Page 64

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Restoring an Identity
To restore an identity:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Restore
Identity.
4. Click Next.
5. On the “Device Type” page, select the device type where the
backup was stored, and then click Next.
6. Follow the on-screen instructions for the device you selected,
and then click Finish.
7. Click Yes at the confirmation dialog box.
Removing an Identity from the System
You can delete your identity entirely from Credential Manager.
This does not affect the Windows user account.
✎
To remove your identity from the system:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Select My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Remove My
Identity from the System.
4. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box. The identity is
logged off and removed from the system.
5–10 Reference Guide
Page 65

Locking the Computer
To secure your computer when you are away from your desk, use
the Lock Workstation feature. This prevents unauthorized users
from gaining access to your computer. Only you and members of
the administrators group on your computer can unlock it.
For added security, you can configure the Lock Workstation
✎
feature to require a smart card, biometric reader, or token to
unlock the computer. For more information, refer to
“Configuring Credential Manager Settings,” later in this
chapter.
To lock the computer:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under I Want To, click More, and then click Lock
Workstation. The Windows logon screen is displayed. You
must use a Windows password or the Credential Manager
Logon Wizard to unlock the computer.
Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Reference Guide 5–11
Page 66

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Using Microsoft Network Logon
You can use Credential Manager to log on to Windows, either at
a local computer or on a network domain. When you log on to
Credential Manager for the first time, the system automatically
adds your local Windows user account as the network account
for the Network Logon service. Refer to “Logging On for the
First Time,” earlier in this chapter, for more information.
Logging On to Windows with Credential Manager
You can use Credential Manager to log on to a Windows network
or local account.
1. From the Windows logon screen, select Log on to
Credential Manager.
2. Click Next on the “Welcome” page, if it is displayed.
3. Type your user name in the User name box.
If you want this to be the default user name, select Use this
✎
name next time you log on.
4. Select Credential Manager from the Log on to list.
5. Click Next. On the “Logon Policy” page, select the
authentication method you want to use.
If you want this method to be the default method, select Use
✎
this policy next time you log on.
6. Follow the instructions for the authentication method you
selected. If your authentication information is correct, you
will be logged on to your Windows account and to Credential
Manager.
5–12 Reference Guide
Page 67

Adding Accounts
You can add additional local or domain accounts after logging on
to Credential Manager.
To add an account:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Microsoft Network Logon, click Add a Network
Account.
4. Set the user name for the new account in the User name box.
5. Click the domain from the list of available domains.
6. Type and confirm the password.
If you want this to be your default user account, select Use
✎
these credentials by default.
7. Click Finish.
Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Removing Accounts
You can remove local or domain accounts after logging on to
Credential Manager.
To remove an account:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Microsoft Network Logon, click Manage Network
Accounts.
4. Click the account you want to remove, and then click
Remove.
5. In the confirmation dialog box, click Yes .
Reference Guide 5–13
Page 68

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Setting a Default User
You can set or change the default user after logging on to
Credential Manager.
To set a default user:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Microsoft Network Logon, click Manage Network
Accounts.
4. Click the account you want to be the default, and then click
Properties.
5. On the Set Up Account tab of the Account Properties
dialog box, select the Use these credentials by default
check box.
6. Click Apply and then click OK.
5–14 Reference Guide
Page 69

Using Single Sign On
Credential Manager has a Single Sign On feature that stores
user names and passwords for multiple Internet and Windows
applications, and automatically enters logon credentials when
you access a registered application.
Security and privacy are important features of Single Sign On.
✎
All credentials are encrypted and are available only after
successful logon to Credential Manager.
You can also configure Single Sign On to validate your
✎
authentication credentials with a smart card, biometric reader,
or token, before logging on to a secure site or application. This
is particularly useful when logging on to applications or Web
sites that contain personal information, such as bank account
numbers. For more information, refer to “Configuring
Credential Manager Settings,” later in this chapter.
Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Reference Guide 5–15
Page 70

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Registering a New Application
Credential Manager prompts you to register any application that
you launch while you are logged on to Credential Manager. You
can also register an application manually.
Using Automatic Registration
To register an application with automatic registration:
1. Open an application that requires you to log on.
2. On the Credential Manager Single Sign On dialog box,
click Options to configure the following settings for the
registration:
❏ Do not suggest to use SSO with this site or application.
❏ Fill in credentials only. Do not submit.
❏ Ask confirmation before submitting credentials.
3. Click Yes to complete the registration.
Using Manual (Drag and Drop) Registration
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Single Sign On, click Register New Application.
4. Run the application you want to register until you reach the
page with the password box.
5. On the “Drag and Drop Registration” page of the SSO
Registration Wizard, select the type of activity you want to
automate.
In most cases, the activity you want to automate will be the
✎
Logon dialog.
5–16 Reference Guide
Page 71

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
6. Click and drag the icon from the wizard page over the area
of the application where the password box is located. Release
the pointer when the area is highlighted.
You will not see the finger icon move across the page,
✎
but when you drag the pointer over the logon box in the
application, a rectangular icon is displayed.
7. On the “Application Information” page of the SSO
Registration Wizard, enter the name and description for
the application.
8. Click Finish.
9. Enter the logon credential—for example, the user name and
password—into the application box.
10. In the confirmation dialog box, confirm or modify the
credential name, and then click Ye s .
Managing Applications and Credentials
Modifying Application Properties
To modify application properties:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Single Sign On, click Manage Applications and
Credentials.
4. Click the application entry you want to modify, and then
click Properties.
a. Click the General tab to modify the application name and
description. Change the settings by selecting or clearing
the check boxes next to the appropriate settings.
b. Click the Script tab to view and edit the SSO application
script.
5. Click OK to save your changes.
Reference Guide 5–17
Page 72

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Removing Applications from Single Sign On
To remove applications from Single Sign On:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Single Sign On, click Manage Applications and
Credentials.
4. Click the application entry you want to remove, and then
click Remove.
5. Click Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
6. Click OK.
Exporting Applications
You can export applications to create a backup copy of the Single
Sign On application script. This file can then be used to recover
the Single Sign On data. This acts as a supplement to the identity
backup file, which contains only the credential information.
To export an application:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Single Sign On, click Manage Applications and
Credentials.
4. Click the application entry you want to export. Then click
More, and then click Export Application.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the export.
6. Click OK.
5–18 Reference Guide
Page 73

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Importing Applications
To import an application:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Single Sign On, click Manage Applications and
Credentials.
4. Click the application entry you want to import. Then click
More, and then click Import Application.
5. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the import.
6. Click OK.
Modifying Credentials
To modify credentials:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click My Identity.
3. Under Single Sign On, click Manage Applications and
Credentials.
4. Click the application entry you want to modify, and then
click More.
5. Select any of the following options:
❏ Add New Credentials
❏ Delete Credentials
❏ Delete Unused Credentials
❏ Edit Credentials
6. Follow the on-screen instructions.
7. Click OK to save changes.
Reference Guide 5–19
Page 74

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Advanced Tasks (Administrator Only)
The “Authentication and Credentials” page and the “Advanced
Settings” page of Credential Manager are available only to those
users with administrator rights. From these pages, you can
■ Specify how users and administrators log on.
■ Configure credential properties.
■ Configure Credential Manager program settings.
Specifying How Users and Administrators Log On
From the “Authentication and Credentials” page, you can specify
which type or combination of credentials are required of either
users or administrators.
To specify how users or administrators log on:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click Authentication and Credentials.
3. Click the Authentication tab.
4. Click the category (Users or Administrators) from the
category list.
5. Click the type or combination of authentication methods
from the list.
6. Click OK.
7. Click Apply, and then click OK to save your changes.
5–20 Reference Guide
Page 75

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Configuring Custom Authentication Requirements
If the set of authentication credentials you want is not listed on
the Authentication tab of the “Authentication and Credentials”
page, you can create custom requirements.
To configure custom requirements:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click Authentication and Credentials.
3. Click the Authentication tab.
4. Click the category (Users or Administrators) from the
category list.
5. Click Custom from the list of authentication methods.
6. Click Configure.
7. Select the authentication methods you want to use.
8. Choose the combination of methods by clicking one of the
following:
❏ Use AND to combine the authentication methods
(Users will have to authenticate with all of the methods
you checked each time they log on.)
❏ Use OR to combine the authentication methods
(Users will be able to choose any of the selected methods
each time they log on.)
9. Click OK.
10. Click Apply, and then click OK to save your changes.
Reference Guide 5–21
Page 76

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Configuring Credential Properties
From the Credentials tab of the “Authentication and
Credentials” page, you can view the list of available
authentication methods, and modify the settings.
To configure the credentials:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click Authentication and Credentials.
3. Click the Credentials tab.
4. Click the credential type you want to modify.
❏ To register the credential, click Register, and then follow
the on-screen instructions.
❏ To delete the credential, click Clear, and then click Ye s in
the confirmation dialog box.
❏ To modify the credential properties, click Properties, and
then follow the on-screen instructions.
5. Click Apply, and then click OK.
5–22 Reference Guide
Page 77

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Configuring Credential Manager Settings
From the “Advanced Settings” page, you can access and modify
various settings using the following tabs:.
■ General—Allows you to modify the settings for basic
configuration.
■ Single Sign On—Allows you to modify the settings for how
Single Sign On works for the current user, such as how it
handles detection of logon screens, automatic logon to
registered dialogs, and password display.
■ Services and Applications—Allows you to view the available
services and modify the settings for those services.
■ Biometric Settings—Allows you to select the fingerprint
reader software and adjust the security level of the fingerprint
reader.
■ Smart Cards and Tokens—Allows you to view and modify
properties for all available smart cards and tokens.
To modify Credential Manager settings:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click Advanced Settings.
3. Click the appropriate tab for the settings you want to modify.
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to modify the settings.
5. Click Apply, and then click OK to save your changes.
Reference Guide 5–23
Page 78

Credential Manager for ProtectTools
Example 1—Using the “Advanced Settings”
Page to Allow Windows Logon from
Credential Manager
To enable logging on to Windows from Credential Manager:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click Advanced Settings.
3. Click the General tab.
4. Select the Use Credential Manager to log on to Windows
check box.
5. Click Apply, and then click OK to save your changes.
6. Restart the computer.
Example 2—Using the “Advanced Settings”
Page to Require User Verification Before
Single Sign On
To require Single Sign On to verify your credentials before
logging on to a registered dialog box or Web page:
1. Select Start > All Programs > HP ProtectTools Security
Manager > Credential Manager.
2. Click Advanced Settings.
3. Click the Single Sign On tab.
4. Under When registered logon dialog or Web page is
visited, select the Validate user before submitting
credentials check box.
5. Click Apply, and then click OK to save your changes.
6. Restart the computer.
5–24 Reference Guide
Page 79

Glossary
The following terms are used in this document and throughout
the ProtectTools Security Manager.
Authentication—Process of verifying whether a user is
authorized to perform a task, for example, accessing a computer,
modifying settings for a particular program, or viewing
secured data.
Automatic DriveLock—Security feature that causes the
DriveLock passwords to be generated and protected by the TPM
Embedded Security chip. When the user is authenticated by the
TPM embedded security chip during startup by entering the
correct TPM Basic User Key password, the BIOS unlocks the
hard drive for the user.
Biometric—Category of authentication credentials that use a
physical feature, such as a fingerprint, to identify a user.
BIOS profile—Group of BIOS configuration settings that can
be saved and applied to other accounts.
BIOS security mode—Setting in Smart Card Security that, when
enabled, requires the use of a smart card and a valid PIN for user
authentication.
Certification authority—Service that issues the certificates
required to run a public key infrastructure.
Credentials—Method by which a user proves eligibility for a
particular task in the authentication process.
Cryptographic service provider (CSP)—Provider or library
of cryptographic algorithms that can be used in a well-defined
interface to perform particular cryptographic functions.
Reference Guide Glossary–1
Page 80

Glossary
Cryptography—Practice of encrypting and decrypting data so
that it can be decoded only by specific individuals.
Decryption—Procedure used in cryptography to convert
encrypted data into plain text.
DriveLock—Security feature that links the hard drive to a user
and requires the user to correctly enter the DriveLock password
when the computer starts up.
Digital certificate—Electronic credentials that confirm the
identity of an individual or a company by binding the identity of
the digital certificate owner to a pair of electronic keys that are
used to sign digital information.
Digital signature—Data sent with a file that verifies the sender
of the material, and that the file has not been modified after it
was signed.
Domain—Group of computers that are part of a network and
share a common directory database. Domains are uniquely
named, and each has a set of common rules and procedures.
Emergency recovery archive—Protected storage area that
allows the re-encryption of basic user keys from one platform
owner key to another.
Encryption—Procedure, such as use of an algorithm, employed
in cryptography to convert plain text into cipher text in order to
prevent unauthorized recipients from reading that data. There are
many types of data encryption, and they are the basis of network
security. Common types include Data Encryption Standard and
public-key encryption.
Encryption File System (EFS)—System that encrypts all files
and subfolders within the selected folder.
Identity—In the ProtectTools Credential Manager, a group of
credentials and settings that is handled like an account or profile
for a particular user.
Migration—a task that allows the management, restoration, and
transfer of keys and certificates.
Glossary–2 Reference Guide
Page 81

Glossary
Network account—Windows user or administrator account,
either on a local computer, in a workgroup, or on a domain.
Personal secure drive (PSD)—Provides a protected storage area
for sensitive data.
Power-on authentication—Security feature that requires some
form of authentication, such as a smart card, security chip, or
password, when the computer is turned on.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)—Standard that defines the
interfaces for creating, using, and administering certificates and
cryptographic keys.
Reboot—Process of restarting the computer.
Single Sign On—Feature that stores authentication data and
allows you to use the Credential Manager to access Internet and
Windows applications that require password authentication.
Smart card—Small piece of hardware, similar in size and shape
to a credit card, which stores identifying information about the
owner. Used to authenticate the owner to a computer.
Smart card administrator password—Password that links an
administrator smart card with the computer in Computer Setup
for identification at startup or restart. This password can be set
manually by the administrator or randomly generated.
Smart card user password—Password that links a user smart
card with the computer in Computer Setup for identification at
startup or restart. This password can be set manually by the
administrator or randomly generated.
Stringent security—Security feature in BIOS Configuration that
provides enhanced protection for the power-on and administrator
passwords and other forms of power-on authentication.
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) embedded security chip
(select models only)—Integrated security chip that can protect
highly sensitive user information from malicious attackers. It is
the root-of-trust in a given platform. The TPM provides
cryptographic algorithms and operations that meets the Trusted
Computing Group (TCG) specifications.
Reference Guide Glossary–3
Page 82

Glossary
USB token—Security device that stores identifying information
about a user. Like a smart card or biometric reader, it is used to
authenticate the owner to a computer.
Virtual token—Security feature that works very much like a
smart card and reader. The token is saved either on the computer
hard drive or in the Windows registry. When you log on with a
virtual token, you are asked for a user PIN to complete the
authentication.
Windows user account—Profile for an individual authorized
to log on to a network or to an individual computer.
Glossary–4 Reference Guide
Page 83

Index
A
account
basic user
Credential Manager
Automatic DriveLock
3–4
5–4
4–6
B
backup
embedded security
identity
single sign on
smart card
basic user account
Basic User Key password
changing
definition
setting
biometric readers
BIOS administrator card
password
changing
definition
setting
BIOS administrator password
changing
definition
setting
5–9
2–11
3–7
1–6
3–5
2–6
1–5
2–4
4–13
1–4
4–13
3–8
5–18
3–4
5–5
BIOS Configuration for
ProtectTools
BIOS smart card security
BIOS user card password
definition
setting and changing
boot options
4–1
2–3
1–5
2–7
4–2
C
command line 4–7
Computer Setup administrator
password
changing
definition
setting
Credential Manager
account
logon password
logon wizard
recovery file password
Credential Manager for
ProtectTools
4–13
1–4
4–13
5–4
1–6
5–3
1–7
5–1
D
default user 5–14
device options
4–3
Reference Guide Index–1
Page 84

Index
disabling
Automatic DriveLock
device options
embedded security
power-on authentication
4–4
smart card authentication
4–4
smart card BIOS security
2–5
stringent security
DriveLock passwords
4–3
4–6
3–11
4–14
1–4
E
Embedded Security for
ProtectTools
emergency recovery
emergency recovery token
password
definition
setting
enabling
Automatic DriveLock
device options
embedded security
power-on authentication
4–4
smart card authentication
4–4
smart card BIOS security
2–3
stringent security
TPM chip
encrypting files and folders
3–6
3–1
3–3
1–6
3–3
4–6
4–3
3–11
4–14
3–2
F
F10 Setup password 1–4
fingerprints
I
identity 5–9
initializing
embedded security chip
smart card
5–5
3–3
2–2
L
locking workstation 5–11
M
managing
identity
profiles
My Identity
5–9
4–7
5–9
N
network account 5–13
O
owner password
changing
definition
setting
3–10
1–6
3–3
P
passwords
guidelines
managing
personal secure drive (PSD)
3–6
1–7
1–4
Index–2 Reference Guide
Page 85

Index
power-on authentication
enabling and disabling
on Windows restart
power-on password
definition
setting and changing
profile password
definition
setting
profiles
applying
deleting
displaying menu
saving
properties
application
authentication
credential
ProtectTools Security
Manager
1–4
1–5
4–9
4–10
4–9
4–8
4–9
5–17
5–20
5–22
1–1
R
recovery
identity
Single Sign On
smart cards
registering
application
credentials
5–10
5–19
2–13
5–16
5–5
4–4
4–15
4–12
S
security setup password 1–4
Single Sign On
automatic registration
exporting applications
5–18
manual registration
modifying application
properties
removing applications
5–18
smart card administrator
password
changing
definition
setting
smart card BIOS security
smart card PIN
changing
definition
smart card recovery file
password
definition
setting
Smart Card Security for
ProtectTools
smart card user password
definition
setting and changing
storing
stringent security
5–17
2–6
1–5
2–3
2–11
1–5
1–5
2–12
2–1
1–5
2–8
4–14
5–16
5–16
2–3
2–7
Reference Guide Index–3
Page 86

Index
T
TPM chip
enabling
initializing
3–2
3–3
V
virtual token 5–7
W
Windows logon password 1–7
Windows network account
5–13
Index–4 Reference Guide
 Loading...
Loading...