Page 1

2910al
ProCurve Switches
W.14.01
Multicast and Routing Guide
www.procurve.com
Page 2

Page 3

HP ProCurve 2910al Switch
September 2009
W.14.03
Multicast and Routing Guide
Page 4

© Copyright 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company,
L.P. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. All Rights Reserved.
This document contains proprietary information, which is
protected by copyright. No part of this document may be
photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another
language without the prior written consent of HewlettPackard.
Publication Number
5992-5440
September 2009
Applicable Products
HP ProCurve 2910al-24G Switch J9145A
HP ProCurve 2910al-48G Switch J9147A
HP ProCurve 2910al-24G-PoE+ Switch J9146A
HP ProCurve 2910al-48G-PoE+ Switch J9148A
HP ProCurve 2-Port 10-GbE SFP+ al Module J9008A
HP ProCurve 2-Port 10-GbE CX4 al Module J9149A
HP ProCurve 10-GbE al Interconnect Kit J9165A
Trademark Credits
Microsoft, Windows, and Microsoft Windows NT are US
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this document is subject to
change without notice.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not
be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or
reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished
by Hewlett-Packard.
Warranty
See the Customer Support/Warranty booklet included with
the product.
A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your
Hewlett-Packard products and replacement parts can be
obtained from your HP Sales and Service Office or
authorized dealer.
Hewlett-Packard Company
8000 Foothills Boulevard, m/s 5551
Roseville, California 95747-5551
http://www.procurve.com
Page 5

Contents
Product Documentation
About Your Switch Manual Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Printed Publications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Electronic Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Software Feature Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
1 Getting Started
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Configuration and Operation Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Protocol Acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Command Syntax and Displayed Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Command Syntax Statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Command Prompts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Screen Simulations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Sources for More Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Getting Documentation From the Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Online Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Menu Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Need Only a Quick Start? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
IP Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
To Set Up and Install the Switch in Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
Physical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
iii
Page 6

2 Multimedia Traffic Control with IP
Multicast (IGMP)
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
IGMP General Operation and Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
IGMP Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
IGMP Operating Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Basic Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Number of IP Multicast Addresses Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Number of Multicast Filters Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
How IGMP Operates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Operation With or Without IP Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Automatic Fast-Leave IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Forced Fast-Leave IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Configuring Delayed Group Flush . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
IGMP Proxy Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
How IGMP Proxy Forwarding Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
CLI Commands for IGMP Proxy Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
VLAN Context Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
IGMP Proxy Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Operating Notes for IGMP Proxy Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
iv
Using the Switch as Querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Excluding Well-Known or Reserved
Multicast Addresses from IP Multicast Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
3 IP Routing Features
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Overview of IP Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
IP Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
IP Tables and Caches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
ARP Cache Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
IP Route Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Page 7

IP Forwarding Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
IP Route Exchange Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
IP Global Parameters for Routing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
ARP Age Timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
IP Interface Parameters for Routing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Configuring IP Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Changing the Router ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Configuring ARP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
How ARP Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Enabling Proxy ARP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Enabling Local Proxy ARP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Configuring Forwarding Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Changing the TTL Threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Enabling Forwarding of Directed Broadcasts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Configuring ICMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Disabling ICMP Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Disabling Replies to Broadcast Ping Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Disabling ICMP Destination Unreachable Messages . . . . . . . . . . 3-21
Disabling ICMP Redirects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Configuring Static IP Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Static Route Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Other Sources of Routes in the Routing Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Static IP Route Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Static Route States Follow VLAN States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
Configuring a Static IP Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
Configuring the Default Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-26
Configuring RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
Overview of RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
RIP Parameters and Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
RIP Global Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
RIP Interface Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
Configuring RIP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Enabling RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
v
Page 8

Enabling IP RIP on a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Changing the RIP Type on a VLAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Changing the Cost of Routes Learned on a VLAN Interface . . . . 3-30
Configuring RIP Redistribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Define RIP Redistribution Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Modify Default Metric for Redistribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Enable RIP Route Redistribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Changing the Route Loop Prevention Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-33
Displaying RIP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-33
Displaying General RIP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-34
Displaying RIP Interface Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-36
Displaying RIP Peer Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-37
Displaying RIP Redistribution Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-39
Displaying RIP Redistribution Filter (restrict) Information . . . . 3-39
Configuring IRDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-40
Enabling IRDP Globally . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-41
Enabling IRDP on an Individual VLAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-41
Displaying IRDP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
Configuring DHCP Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
DHCP Packet Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Unicast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Prerequisites for DHCP Relay Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Enabling DHCP Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Configuring an IP Helper Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Verifying the DHCP Relay Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Displaying the DHCP Relay Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Displaying DHCP Helper Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-46
Displaying the Hop Count Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-47
DHCP Option 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-48
Option 82 Server Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-49
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-50
General DHCP Option 82 Requirements and Operation . . . . . . . 3-51
vi
Page 9

Option 82 Field Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-52
Forwarding Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-54
Configuration Options for Managing DHCP Client Request
Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-54
Multiple Option 82 Relay Agents in a Client Request Path . . . . . 3-55
Validation of Server Response Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-56
Multinetted VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-57
Configuring Option 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-58
Example of Option 82 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-60
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-61
UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-63
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-63
Subnet Masking for UDP Forwarding Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-64
Configuring and Enabling UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . 3-65
Globally Enabling UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-65
Configuring UDP Broadcast Forwarding on Individual VLANs . 3-65
Displaying the Current IP Forward-Protocol Configuration . . . . . . . 3-67
Operating Notes for UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-68
Messages Related to UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-68
Index
vii
Page 10

viii
Page 11

Product Documentation
About Your Switch Manual Set
Note For the latest version of all ProCurve switch documentation, including
Release Notes covering recently added features, please visit the ProCurve
Networking Web site at www.procurve.com, click on Customer Care, and then
click on Manuals.
Printed Publications
The publications listed below are printed and shipped with your switch. The
latest version is also available in PDF format on the ProCurve Web site, as
described in the Note at the top of this page.
■ Read Me First—Provides software update information, product notes,
and other information.
■ HP ProCurve Switch Quick Setup—Provides quick start installation
instructions. See the Installation and Getting Started Guide for more
detailed information.
Electronic Publications
The latest version of each of the publications listed below is available in PDF
format on the ProCurve Web site, as described in the Note at the top of this
page.
■ Installation and Getting Started Guide—Explains how to prepare for
and perform the physical installation and connect the switch to your
network.
■ Management and Configuration Guide—Describes how to configure,
manage, and monitor basic switch operation.
■ Advanced Traffic Management Guide—Explains how to configure traffic
management features such as VLANs, MSTP, QoS, and Meshing.
■ Multicast and Routing Guide—Explains how to configure IGMP, PIM, IP
routing, and VRRP features.
■ Access Security Guide—Explains how to configure access security fea-
tures and user authentication on the switch.
■ IPv6 Configuration Guide—Describes the IPv6 protocol operations that
are supported on the switch.
■ Release Notes—Describe new features, fixes, and enhancements that
become available between revisions of the main product guide.
ix
Page 12

Software Feature Index
For the software manual set supporting your 2910al switch model, this feature
index indicates which manual to consult for information on a given software
feature.
Note This Index does not cover IPv6 capable software features. For information on
IPv6 protocol operations and features (such as DHCPv6, DNS for IPv6, Ping6,
and MLD Snooping), refer to the IPv6 Configuration Guide.
Intelligent Edge Software
Features
802.1Q VLAN Tagging X
802.1X Port-Based Priority X
802.1X Multiple Authenticated Clients Per Port X
Access Control Lists (ACLs) X
AAA Authentication X
Authorized IP Managers X
Authorized Manager List (Web, Telnet, TFTP) X
Auto MDIX Configuration X
BOOTP X
Config File X
Console Access X
Copy Command X
CoS (Class of Service) X
Management
and
Configuration
Advanced
Management
Traffic
Manual
Multicast and
Routing
Access
Security
Guide
Debug X
DHCP Configuration X
DHCP Option 82 X
DHCP Snooping X
x
Page 13

Intelligent Edge Software
Features
Management
and
Configuration
Manual
Advanced
Traffic
Management
Multicast and
Routing
Access
Security
Guide
DHCP/Bootp Operation
Diagnostic Tools
Downloading Software
Dynamic ARP Protection
Dynamic Configuration Arbiter
Eavesdrop Protection
Event Log X
Factory Default Settings
Flow Control (802.3x)
File Management
File Transfers
Friendly Port Names
Guaranteed Minimum Bandwidth (GMB)
GVRP
Identity-Driven Management (IDM)
IGMP
Interface Access (Telnet, Console/Serial, Web)
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
IP Addressing
IP Routing
Jumbo Packets
LACP
Link
LLDP
LLDP-MED
Loop Protection
MAC Address Management
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
xi
Page 14

Intelligent Edge Software
Features
MAC Lockdown X
Management
and
Configuration
Advanced
Management
Traffic
Manual
Multicast and
Routing
Access
Security
Guide
MAC Lockout
MAC-based Authentication
Management VLAN
Monitoring and Analysis
Multicast Filtering
Multiple Configuration Files
Network Management Applications (SNMP)
OpenView Device Management
Passwords and Password Clear Protection
ProCurve Manager (PCM)
Ping
Port Configuration
Port Monitoring
Port Security
Port Status
Port Trunking (LACP)
Port-Based Access Control (802.1X)
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Power over Ethernet (PoE+)
Protocol Filters
Protocol VLANS
Quality of Service (QoS)
RADIUS Authentication and Accounting
RADIUS-Based Configuration
Rate-Limiting X
RIP X
X
X
X
xii
X
X
X
Page 15

Intelligent Edge Software
Features
Management
and
Configuration
Manual
Advanced
Traffic
Management
Multicast and
Routing
Access
Security
Guide
RMON 1,2,3,9
Routing
Routing - IP Static
Secure Copy
sFlow
SFTP
SNMPv3
Software Downloads (SCP/SFTP, TFPT, Xmodem)
Source-Port Filters
Spanning Tree (STP, RSTP, MSTP)
SSHv2 (Secure Shell) Encryption
SSL (Secure Socket Layer)
Stack Management (3500yl/6200yl switches only)
Syslog
System Information
TACACS+ Authentication
Telnet Access
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
TFTP
Time Protocols (TimeP, SNTP)
Traffic Mirroring
Traffic/Security Filters
Troubleshooting
Uni-Directional Link Detection (UDLD)
UDP Forwarder
USB Device Support
VLANs
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
xiii
Page 16

Intelligent Edge Software
Features
Management
and
Configuration
Manual
Advanced
Traffic
Management
Multicast and
Routing
Access
Security
Guide
Voice VLAN
Web Authentication RADIUS Support
Web-based Authentication
Web UI
Xmodem
X
X
X
X
X
xiv
Page 17

Getting Started
Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Command Syntax Statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Command Prompts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Screen Simulations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Configuration and Operation Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Sources for More Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Getting Documentation From the Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Online Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1
Menu Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
Command Line Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Need Only a Quick Start? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
IP Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
To Set Up and Install the Switch in Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
Physical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1-1
Page 18

Getting Started
Introduction
Introduction
This guide is intended for use with the following switches:
■ HP ProCurve 2910al Switch
It describes how to use the command line interface (CLI), Menu interface, and
web browser to configure, manage, monitor, and troubleshoot switch operation. For an overview of other product documentation for the above switches,
refer to “Product Documentation” on page xi. You can download documentation from the ProCurve Networking web site, www.procurve.com.
Conventions
Configuration and Operation Examples
Unless otherwise noted, examples using a particular switch model apply to all
switch models covered by this guide.
Protocol Acronyms
IP Refers to the IPv4 protocol unless otherwise noted.
IPv6 Refers to the IPv6 protocol.
Command Syntax and Displayed Information
Command Syntax Statements
Syntax: ip < default-gateway < ip-addr >> | routing >
Syntax: show interfaces [port-list ]
■ Vertical bars ( | ) separate alternative, mutually exclusive elements.
■ Square brackets ( [ ] ) indicate optional elements.
■ Braces ( < > ) enclose required elements.
■ Braces within square brackets ( [ < > ] ) indicate a required element within
an optional choice.
1-2
Page 19

Getting Started
Conventions
■ Boldface indicates use of a CLI command, part of a CLI command syntax,
or other displayed element in general text. For example:
“Use the copy tftp command to download the key from a TFTP server.”
■ Italics indicate variables for which you must supply a value when execut-
ing the command. For example, in this command syntax, you must provide
one or more port numbers:
Syntax: aaa port-access authenticator < port-list >
Command Prompts
In the default configuration, your switch displays a CLI prompt similar to the
following example:
ProCurve 2910al#
To simplify recognition, this guide uses ProCurve to represent command
prompts for all switch models. For example:
ProCurve#
(You can use the hostname command to change the text in the CLI prompt.)
Screen Simulations
Displayed Text. Figures containing simulated screen text and command
output look like this:
ProCurve> show version
Image stamp:
Boot Image:
ProCurve>
Figure 1-1. Example of a Figure Showing a Simulated Screen
In some cases, brief command-output sequences appear without figure identification. For example:
ProCurve(config)# clear public-key
ProCurve(config)# show ip client-public-key
show_client_public_key: cannot stat keyfile
/sw/code/build/info
November 6, 2008 13:43:13
W.14.01
139
Primary
1-3
Page 20

Getting Started
Sources for More Information
Keys
Simulations of actual keys use a bold, sans-serif typeface with square brackets.
For example, the Tab key appears as
[Tab] and the “Y” key appears as [Y].
Sources for More Information
For information about switch operation and features not covered in this guide,
consult the following sources:
■ Feature Index—For information on which manual to consult for a given
software feature, refer to the “Software Feature Index” on page xii.
Note For the latest version of all ProCurve switch documentation referred to below,
including Release Notes covering recently added features, visit the ProCurve
Networking web site at www.procurve.com, click on Customer Care, and
then click on Manuals.
■ Software Release Notes—Release Notes are posted on the ProCurve
Networking web site and provide information on new software updates:
• new features and how to configure and use them
• software management, including downloading software to the switch
• software fixes addressed in current and previous releases
■ Product Notes and Software Update Information—The printed Read Me
First shipped with your switch provides software update information,
product notes, and other information.
■ Installation and Getting Started Guide—Use the Installation and Get-
ting Started Guide to prepare for and perform the physical installation.
This guide also steps you through connecting the switch to your network
and assigning IP addressing, as well as describing the LED indications for
correct operation and trouble analysis.
■ Management and Configuration Guide—Use this guide for information
on topics such as:
• various interfaces available on the switch
• memory and configuration operation
• interface access
• IP addressing
• time protocols
1-4
Page 21

Sources for More Information
Getting Started
• port configuration, trunking, traffic control, and PoE operation
• SNMP, LLDP, and other network management topics
• file transfers, switch monitoring, troubleshooting, and MAC address
management
■ Advanced Traffic Management Guide—Use this guide for information on
topics such as:
• VLANs: Static port-based and protocol VLANs, and dynamic GVRP
VLANs
• spanning-Tree: 802.1D (STP), 802.1w (RSTP), and 802.1s (MSTP)
• Quality-of-Service (QoS)
• Access Control Lists (ACLs)
■ Multicast and Routing Guide—Use this guide for information on topics
such as:
• IGMP
• IP routing
■ Access Security Guide—Use this guide for information on topics such as:
• Local username and password security
• Web-Based and MAC-based authentication
• RADIUS and TACACS+ authentication
• SSH (Secure Shell) and SSL (Secure Socket Layer) operation
• 802.1X access control
• Port security operation with MAC-based control
• Authorized IP Manager security
• Key Management System (KMS)
■ IPv6 Configuration Guide—Use this guide for information on topics
such as:
• Overview of IPv6 operation and features
• Configuring IPv6 addressing
• Using IPv6 management, security, and troubleshooting features
1-5
Page 22

Getting Started
Sources for More Information
Getting Documentation From the Web
To obtain the latest versions of documentation and release notes for your
switch:
1. Go to the ProCurve Networking web site at
2. Click on Customer Care.
3. Click on Manuals.
4. Click on the product for which you want to view or download a manual.
If you need further information on ProCurve switch technology, visit the
ProCurve Networking web site at:
Online Help
Menu Interface
If you need information on specific parameters in the menu interface, refer to
the online help provided in the interface. For example:
www.procurve.com
www.procurve.com
1-6
Online Help
for Menu
Figure 1-2. Online Help for Menu Interface
Page 23

Sources for More Information
Getting Started
Command Line Interface
If you need information on a specific command in the CLI, type the command
name followed by help. For example:
Figure 1-3. Example of CLI Help
Web Browser Interface
If you need information on specific features in the ProCurve Web Browser
Interface (hereafter referred to as the “web browser interface”), use the online
Help. You can access the Help by clicking on the Help text on top right side of
any of the web browser interface screens.
Figure 1-4. Help for Web Browser Interface
Note To access the online Help for the ProCurve web browser interface, you need
either ProCurve Manager (version 1.5 or greater) installed on your network
or an active connection to the World Wide Web. Otherwise, Online help for the
web browser interface will not be available.
1-7
Page 24

Getting Started
Need Only a Quick Start?
Need Only a Quick Start?
IP Addressing
If you just want to give the switch an IP address so that it can communicate
on your network, or if you are not using VLANs, ProCurve recommends that
you use the Switch Setup screen to quickly configure IP addressing. To do so,
do one of the following:
■ Enter setup at the CLI Manager level prompt.
Procurve# setup
■ In the Main Menu of the Menu interface, select
8. Run Setup
For more on using the Switch Setup screen, see the Installation and Getting
Started Guide you received with the switch.
1-8
To Set Up and Install the Switch in Your Network
Physical Installation
Use the ProCurve Installation and Getting Started Guide for the following:
■ Notes, cautions, and warnings related to installing and using the switch
and its related modules
■ Instructions for physically installing the switch in your network
■ Quickly assigning an IP address and subnet mask, set a Manager pass-
word, and (optionally) configure other basic features.
■ Interpreting LED behavior.
For the latest version of the Installation and Getting Started Guide for your
switch, refer to “Getting Documentation From the Web” on page 1-6.
1
Page 25

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP
Multicast (IGMP)
Contents
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
IGMP General Operation and Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
IGMP Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
IGMP Operating Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Basic Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Number of IP Multicast Addresses Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Number of Multicast Filters Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
2
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
How IGMP Operates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-12
Operation With or Without IP Addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
Automatic Fast-Leave IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Forced Fast-Leave IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Configuring Delayed Group Flush . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
IGMP Proxy Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
How IGMP Proxy Forwarding Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
CLI Commands for IGMP Proxy Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
VLAN Context Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
IGMP Proxy Show Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Operating Notes for IGMP Proxy Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
Using the Switch as Querier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
Excluding Well-Known or Reserved
Multicast Addresses from IP Multicast Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
2-1
Page 26

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
Overview
Overview
This chapter describes multimedia traffic control with IP multicast (IGMP) to
reduce unnecessary bandwidth usage on a per-port basis, and how to configure it with the switch’s built-in interfaces:
For general information on how to use the switch’s built-in interfaces, refer to
these chapters in the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch:
■ Chapter 3, “Using the Menu Interface”
■ Chapter 4, “Using the Command Line Interface (CLI)”
■ Chapter 5, “Using the ProCurve Web Browser Interface
■ Chapter 6, “Switch Memory and Configuration”
Note The use of static multicast filters is described in the chapter titled “Traffic/
Security Filters” in the Access Security Guide for your ProCurve switch.
2-2
Page 27

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
IGMP General Operation and Features
IGMP General Operation and Features
IGMP Features
Feature Default Menu CLI
view igmp configuration n/a — page 2-7
show igmp status for multicast
groups used by the selected
VLAN
enabling or disabling IGMP disabled — page 2-9
(Requires VLAN ID Context)
per-port packet control auto — page 2-10
IGMP traffic priority normal — page 2-11
querier enabled — page 2-11
fast-leave disabled — page 2-14
In a network where IP multicast traffic is transmitted for various multimedia
applications, you can use the switch to reduce unnecessary bandwidth usage
on a per-port basis by configuring IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol controls). In the factory default state (IGMP disabled), the switch simply
floods all IP multicast traffic it receives on a given VLAN through all ports on
that VLAN (except the port on which it received the traffic). This can result
in significant and unnecessary bandwidth usage in networks where IP multicast traffic is a factor. Enabling IGMP allows the ports to detect IGMP queries
and report packets and manage IP multicast traffic through the switch.
n/a — Yes
IGMP is useful in multimedia applications such as LAN TV, desktop conferencing, and collaborative computing, where there is multipoint communication; that is, communication from one to many hosts, or communication
originating from many hosts and destined for many other hosts. In such
multipoint applications, IGMP will be configured on the hosts, and multicast
traffic will be generated by one or more servers (inside or outside of the local
network). Switches in the network (that support IGMP) can then be configured to direct the multicast traffic to only the ports where needed. If multiple
VLANs are configured, you can configure IGMP on a per-VLAN basis.
Enabling IGMP allows detection of IGMP queries and report packets in order
to manage IP multicast traffic through the switch. If no other querier is
detected, the switch will then also function as the querier. (If you need to
disable the querier feature, you can do so through the IGMP configuration
MIB. Refer to “Changing the Querier Configuration Setting” on page 2-11.)
2-3
Page 28

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
IGMP General Operation and Features
Note IGMP configuration on the switches covered in this guide operates at the
VLAN context level. If you are not using VLANs, then configure IGMP in VLAN
1 (the default VLAN) context.
IGMP Terms
■ IGMP Device: A switch or router running IGMP traffic control
features.
■ IGMP Host: An end-node device running an IGMP (multipoint, or
multicast communication) application.
■ Querier: A required IGMP device that facilitates the IGMP protocol
and traffic flow on a given LAN. This device tracks which ports are
connected to devices (IGMP clients) that belong to specific multicast
groups, and triggers updates of this information. A querier uses data
received from the queries to determine whether to forward or block
multicast traffic on specific ports. When the switch has an IP address
on a given VLAN, it automatically operates as a Querier for that VLAN
if it does not detect a multicast router or another switch functioning
as a Querier. When enabled (the default state), the switch’s querier
function eliminates the need for a multicast router. In most cases,
ProCurve recommends that you leave this parameter in the default
“enabled” state even if you have a multicast router performing the
querier function in your multicast group. For more information, see
“How IGMP Operates” on page 2-12.
2-4
Page 29

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
IGMP General Operation and Features
IGMP Operating Features
Basic Operation
In the factory default configuration, IGMP is disabled. To enable IGMP
■ If multiple VLANs are not configured, you configure IGMP on the default
VLAN (DEFAULT_VLAN; VID = 1).
■ If multiple VLANs are configured, you configure IGMP on a per-VLAN
basis for every VLAN where this feature is to be used.
Enhancements
With the CLI, you can configure these additional options:
■ Forward with High Priority. Disabling this parameter (the default)
causes the switch or VLAN to process IP multicast traffic, along with other
traffic, in the order received (usually, normal priority). Enabling this
parameter causes the switch or VLAN to give a higher priority to IP
multicast traffic than to other traffic.
■ Auto/Blocked/Forward: You can use the console to configure individual
ports to any of the following states:
• Auto (the default): Causes the switch to interpret IGMP packets and
to filter IP multicast traffic based on the IGMP packet information for
ports belonging to a multicast group. This means that IGMP traffic
will be forwarded on a specific port only if an IGMP host or multicast
router is connected to the port.
• Blocked: Causes the switch to drop all IGMP transmissions received
from a specific port.
• Forward: Causes the switch to forward all IGMP and IP multicast
transmissions through the port.
■ Operation With or Without IP Addressing: This feature helps to
conserve IP addresses by enabling IGMP to run on VLANs that do not have
an IP address. See “Operation With or Without IP Addressing” on page
2-13.
■ Querier Capability: The switch performs this function for IGMP on
VLANs having an IP address when there is no other device in the VLAN
acting as querier. See “Using the Switch as Querier” on page 2-26.
2-5
Page 30

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
IGMP General Operation and Features
Notes Whenever IGMP is enabled, the switch generates an Event Log message
indicating whether querier functionality is enabled.
IP multicast traffic groups are identified by IP addresses in the range of
224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The maximum number of multicast groups is 256.
Incoming IGMP packets intended for reserved, or “well-known” multicast
addresses automatically flood through all ports (except the port on which the
packets entered the switch). For more on this topic, see “Excluding WellKnown or Reserved Multicast Addresses from IP Multicast Filtering” on page
2-27.
For more information, refer to “How IGMP Operates” on page 2-12.
Number of IP Multicast Addresses Allowed
The total of IGMP filters (addresses) and static multicast filters together is
2,047 (if data driven) or 2,048 otherwise, depending on the current max-vlans
configuration. If multiple VLANs are configured, then each filter is counted
once per VLAN in which it is used.
Number of Multicast Filters Allowed
2-6
The number of multicast filters allowed depends on the number of configured
VLANS:
■ 16 multicast filters if VLANs <= 1024
■ 8 multicast filters if VLANs > 1024
Page 31

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP
IGMP Commands Used in This Section
show ip igmp configuration page 2-7
ip igmp page 2-9
high-priority-forward page 2-11
auto <[ethernet] <port-list> page 2-10
blocked <[ethernet] <port-list> page 2-10
forward <[ethernet] <port-list> page 2-10
querier page 2-11
show ip igmp Refer to the section titled “Internet Group
Viewing the Current IGMP Configuration. This command lists the IGMP
configuration for all VLANs configured on the switch or for a specific VLAN.
Management Protocol (IGMP) Status” in appendix B
of the Management and Configuration Guide for your
switch.
Syntax:
show ip igmp config
Displays IGMP configuration for all VLANs on the switch.
show ip igmp vlan < vid > config
Displays IGMP configuration for a specific VLAN on the
switch, including per-port data.
(For IGMP operating status, refer to the section titled “Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Status” in appendix B, “Monitoring and Analyzing
Switch Operation” of the Management and Configuration Guide for you
switch.)
2-7
Page 32

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP
For example, suppose you have the following VLAN and IGMP configurations
on the switch:
VLAN ID VLAN Name IGMP
Enabled
1 DEFAULT_VLAN Yes No No
22 VLAN-2 Yes Yes Yes
33 VLAN-3 No No No
Forward with
High Priority
You could use the CLI to display this data as follows:
Figure 2-1. Example Listing of IGMP Configuration for All VLANs in the Switch
The following version of the show ip igmp command includes the VLAN ID
(vid) designation, and combines the above data with the IGMP per-port
configuration:
IGMP Configuration
for the Selected
VLAN
Querier
IGMP Configuration
On the Individual
Ports in the VLAN
Figure 2-2. Example Listing of IGMP Configuration for A Specific VLAN
2-8
Page 33

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP
Enabling or Disabling IGMP on a VLAN. You can enable IGMP on a
VLAN, along with the last-saved or default IGMP configuration (whichever
was most recently set), or you can disable IGMP on a selected VLAN.
Syntax:
[no] ip igmp
Enables IGMP on a VLAN. Note that this command must be
executed in a VLAN context.
For example, here are methods to enable and disable IGMP on the default
VLAN (VID = 1).
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1 ip igmp
Enables IGMP on VLAN 1.
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip igmp
Same as above.
ProCurve(config)# no vlan 1 ip igmp
Disables IGMP on vlan 1.
Note If you disable IGMP on a VLAN and then later re-enable IGMP on that VLAN,
the switch restores the last-saved IGMP configuration for that VLAN. For more
on how switch memory operates, refer to the chapter titled “Switch Memory
and Configuration” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your
switch.
You can also combine the ip igmp command with other IGMP-related commands, as described in the following sections.
2-9
Page 34

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP
Configuring Per-Port IGMP Traffic Filters.
Syntax: vlan < vid > ip igmp [auto < port-list > | blocked < port-list > |
forward < port-list >]
Used in the VLAN context, this command specifies how each
port should handle IGMP traffic. (Default: auto.)
Note: Where a static multicast filter is configured on a port,
and an IGMP filter created by this command applies to the
same port, the IGMP filter overrides the static multicast filter
for any inbound multicast traffic carrying the same multicast
address as is configured in the static filter. (Refer to the section
titled “Filter Types and Operation” in the “Port Traffic
Controls” chapter of the Management and Configuration Guide
for your switch.
For example, suppose you wanted to configure IGMP as follows for VLAN 1
on the 100/1000T ports on a module in slot 1:
Ports A1-A2 auto Filter multicast traffic. Forward IGMP traffic to hosts on these
Ports A3-A4 forward Forward all multicast traffic through this port.
Ports A5-A6 blocked Drop all multicast traffic received from devices on these ports.
ports that belong to the multicast group for which the traffic is
intended. (Also forward any multicast traffic through any of
these ports that is connected to a multicast router.)
Refer to the table below in the section on “Automatic Fast-Leave IGMP” for a
description of the default behavior of data-driven switches.
Depending on the privilege level, you could use one of the following commands to configure IGMP on VLAN 1 with the above settings:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1 ip igmp auto a1,a2 forward a3,a4
blocked a5,a6
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip igmp auto a1,a2 forward a3,a4 blocked
a5,a6
The following command displays the VLAN and per-port configuration resulting from the above commands.
ProCurve> show igmp vlan 1 config
2-10
Page 35

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
CLI: Configuring and Displaying IGMP
Configuring IGMP Traffic Priority.
Syntax: vlan < vid > ip igmp high-priority-forward
This command assigns “high” priority to IGMP traffic or
returns a high-priority setting to “normal” priority. (The
traffic will be serviced at its inbound priority.) (Default:
normal.)
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1 ip igmp high-priority-forward
Configures high priority for IGMP traffic on VLAN 1.
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip igmp high-priority-forward
Same as above command, but in the VLAN 1 context level.
ProCurve(vlan 1)# no ip igmp high-priority-forward
Returns IGMP traffic to “normal” priority.
ProCurve> show ip igmp config
Show command to display results of above high-priority
commands.
Configuring the Querier Function.
Syntax: [no] vlan <vid> ip igmp querier
This command disables or re-enables the ability for the switch
to become querier if necessary. The no version of the command
disables the querier function on the switch. The show ip igmp
config command displays the current querier command.
(Default Querier Capability: Enabled.)
2-11
Page 36

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
How IGMP Operates
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of
the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. IP manages multicast traffic by using
switches, multicast routers, and hosts that support IGMP. (In Hewlett-Packard’s implementation of IGMP, a multicast router is not necessary as long as
a switch is configured to support IGMP with the
of hosts, routers, and/or switches that send or receive multicast data streams
to or from the same source(s) is termed a multicast group, and all devices in
the group use the same multicast group address. The multicast group running
version 2 of IGMP uses three fundamental types of messages to communicate:
■ Query: A message sent from the querier (multicast router or switch)
asking for a response from each host belonging to the multicast group. If
a multicast router supporting IGMP is not present, then the switch must
assume this function in order to elicit group membership information
from the hosts on the network. (If you need to disable the querier feature,
you can do so through the CLI, using the IGMP configuration MIB. See
“Configuring the Querier Function” on page 2-11.)
■ Report (Join): A message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that
the host wants to be or is a member of a given group indicated in the report
message.
■ Leave Group: A message sent by a host to the querier to indicate that the
host has ceased to be a member of a specific multicast group.
querier feature enabled.) A set
Note on IGMP When an IGMPv3 Join is received by the switch, it accepts the host request
version 3
support
2-12
and begins to forward the IGMP traffic. This means that ports which have not
joined the group and are not connected to routers or the IGMP Querier will
not receive the group's multicast traffic.
The switch does not support the IGMPv3 “Exclude Source” or “Include
Source” options in the Join Reports. Rather, the group is simply joined from
all sources.
The switch does not support becoming a version 3 Querier. It will become a
version 2 Querier in the absence of any other Querier on the network.
An IP multicast packet includes the multicast group (address) to which the
packet belongs. When an IGMP client connected to a switch port needs to
receive multicast traffic from a specific group, it joins the group by sending
an IGMP report (join request) to the network. (The multicast group specified
Page 37

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
in the join request is determined by the requesting application running on the
IGMP client.) When a networking device with IGMP enabled receives the join
request for a specific group, it forwards any IP multicast traffic it receives for
that group through the port on which the join request was received. When the
client is ready to leave the multicast group, it sends a Leave Group message
to the network and ceases to be a group member. When the leave request is
detected, the appropriate IGMP device will cease transmitting traffic for the
designated multicast group through the port on which the leave request was
received (as long as there are no other current members of that group on the
affected port).
Thus, IGMP identifies members of a multicast group (within a subnet) and
allows IGMP-configured hosts (and routers) to join or leave multicast groups.
IGMP Data. To display data showing active group addresses, reports, queries, querier access port, and active group address data (port, type, and
access), refer to the section titled “Internet Group Management Protocol
(IGMP) Status” in appendix B, “Monitoring and Analyzing Switch Operation”
of the Management and Configuration Guide for you switch.).
Operation With or Without IP Addressing
You can configure IGMP on VLANs that do not have IP addressing. The benefit
of IGMP without IP addressing is a reduction in the number of IP addresses
you have to use and configure. This can be significant in a network with a large
number of VLANs. The limitation on IGMP without IP addressing is that the
switch cannot become Querier on any VLANs for which it has no IP address—
so the network administrator must ensure that another IGMP device will act
as Querier. It is also advisable to have an additional IGMP device available as
a backup Querier. See the following table.
Table 2-1.Comparison of IGMP Operation With and Without IP Addressing
IGMP Function Available With IP Addressing
Configured on the VLAN
Forward multicast group traffic to any port on
the VLAN that has received a join request for
that multicast group.
Forward join requests (reports) to the Querier. Yes None
Configure individual ports in the VLAN to Auto
(the default)/Blocked, or Forward.
Available
Without IP
Addressing?
Yes None
Yes None
Operating Differences Without an IP Address
2-13
Page 38

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
IGMP Function Available With IP Addressing
Configured on the VLAN
Configure IGMP traffic forwarding to normal or Yes None
high-priority forwarding.
Age-Out IGMP group addresses when the last
IGMP client on a port in the VLAN leaves the
group.
Support Fast-Leave IGMP and Forced FastLeave IGMP (below).
Support automatic Querier election. No Querier operation not available.
Operate as the Querier. No Querier operation not available.
Available as a backup Querier. No Querier operation not available.
Available
Without IP
Addressing?
Yes
Yes
Operating Differences Without an IP Address
Requires that another IGMP device in the VLAN has an IP
address and can operate as Querier. This can be a multicast router or another switch configured for IGMP operation. (ProCurve recommends that the VLAN also include
a device operating as a backup Querier in case the device
operating as the primary Querier fails for any reason.
Automatic Fast-Leave IGMP
Fast-Leave IGMP. Depending on the switch model, Fast-Leave is enabled or
disabled in the default configuration.
Switch Model Data- IGMP Fast- Default IGMP Behavior
or Series Driven Leave Setting
IGMP
Included?
Switch 8212zl
Switch 6400cl
Switch 6200yl
Switch 5400zl
Switch 5300xl
Switch 4200vl
Switch 3500yl
Switch 3400cl
Switch 2910al
Switch 2500
Switch 2600
Switch 2600-
PWR
Switch 4100gl
Switch 6108
Yes Always Drops unjoined mulitcast traffic except for
Enabled always-fowarded traffic toward the Querier or
multicast routers, and out of IGMP-forward
ports. Selectively forwards joined multicast
traffic, except on IGMP-forward ports, which
forward all multicast traffic.
No Disabled in
the Default
Configuration
IGMP Fast-Leave disabled in the default
configuration. Floods unjoined multicast traffic
to all ports. Selectively forwards joined
multicast traffic, except on IGMP-forward
ports, which forward all multicast traffic.
2-14
On switches that do not support Data-Driven IGMP, unregistered multicast
groups are flooded to the VLAN rather than pruned. In this scenario, FastLeave IGMP can actually increase the problem of multicast flooding by
Page 39

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
removing the IGMP group filter before the Querier has recognized the IGMP
leave. The Querier will continue to transmit the multicast group during this
short time, and because the group is no longer registered the switch will then
flood the multicast group to all ports.
On ProCurve switches that do support Data-Driven IGMP (“Smart” IGMP),
when unregistered multicasts are received the switch automatically filters
(drops) them. Thus, the sooner the IGMP Leave is processed, the sooner this
multicast traffic stops flowing.
Because of the multicast flooding problem mentioned above, the IGMP FastLeave feature is disabled by default on all ProCurve switches that do not
support Data-Driven IGMP. (See the table above.) The feature can be enabled
on these switches via an SNMP set of this object:
hpSwitchIgmpPortForceLeaveState.<vid>.<port number>
However, this is not recommended as this will increase the amount of multicast flooding during the period between the client’s IGMP Leave and the
Querier’s processing of that Leave. For more information on this topic refer
to “Forced Fast-Leave IGMP” on page page 2-17.
Automatic Fast-Leave Operation. If a switch port has the following characteristics, then the Fast-Leave operation will apply:
1. Connected to only one end node
2. The end node currently belongs to a multicast group; i.e. is an IGMP client
3. The end node subsequently leaves the multicast group
Then the switch does not need to wait for the Querier status update interval,
but instead immediately removes the IGMP client from its IGMP table and
ceases transmitting IGMP traffic to the client. (If the switch detects multiple
end nodes on the port, automatic Fast-Leave does not activate—regardless of
whether one or more of these end nodes are IGMP clients.)
2-15
Page 40

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
In the next figure, automatic Fast-Leave operates on the switch ports for IGMP
clients “3A” and “5A”, but not on the switch port for IGMP clients “7A” and 7B,
Server “7C”, and printer “7D”.
Fast-Leave IGMP
automatically operates on
the ports connected to
IGMP clients 3A and 5A,
but does not operate on
the port connected to
Switch 7X because the
switch detects multiple
end nodes on that port.
Routing
Switch
Acting as
Querier
Fast-Leave IGMP
activates on these
two ports.
A1 A3
3A
Switch
Figure 2-3. Example of Automatic Fast-Leave IGMP Criteria
When client “3A” running IGMP is ready to leave the multicast group, it
transmits a Leave Group message. Because the switch knows that there is only
one end node on port A3, it removes the client from its IGMP table and halts
multicast traffic (for that group) to port A3. If the switch is not the Querier, it
does not wait for the actual Querier to verify that there are no other group
members on port A3. If the switch itself is the Querier, it does not query port
A3 for the presence of other group members.
A4
5A
A6
7A
Fast-Leave IGMP does
not activate on this port.
7B
Switch 7X
Server
7C
Printer
7D
2-16
Note that Fast-Leave operation does not distinguish between end nodes on
the same port that belong to different VLANs. Thus, for example, even if all of
the devices on port A6 in figure 2-3 belong to different VLANs, Fast-Leave does
not operate on port A6.
Default (Enabled) IGMP Operation Solves the “Delayed Leave”
Problem. Fast-leave IGMP is enabled by default. When Fast-leave is disabled
and multiple IGMP clients are connected to the same port on an IGMP device
(switch or router), if only one IGMP client joins a given multicast group, then
later sends a Leave Group message and ceases to belong to that group, the
switch automatically retains that IGMP client in its IGMP table and continues
forwarding IGMP traffic to the IGMP client until the Querier triggers confirmation that no other group members exist on the same port. This delayed leave
operation means that the switch continues to transmit unnecessary multicast
traffic through the port until the Querier renews multicast group status.
Page 41

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
Configuring Fast-Leave IGMP.
Syntax: [no] ip igmp fastleave < port-list >
Enables IGMP fast-leaves on the specified ports in the selected
VLAN. The no form of the command disables IGMP fast-leave
on the specified ports in the selected VLAN. Use show running
to display the ports per-VLAN on which Fast-Leave is
disabled.
How IGMP Operates
Forced Fast-Leave IGMP
When enabled, Forced Fast-Leave IGMP speeds up the process of blocking
unnecessary IGMP traffic to a switch port that is connected to multiple end
nodes. (This feature does not activate on ports where the switch detects only
one end node). For example, in figure 2-3, even if you configured Forced FastLeave on all ports in the switch, the feature would activate only on port A6
(which has multiple end nodes) when a Leave Group request arrived on that
port.
When a port having multiple end nodes receives a Leave Group request from
one end node for a given multicast group “X”, Forced Fast-Leave activates and
waits a small amount of time to receive a join request from any other group
“X” member on that port. If the port does not receive a join request for that
group within the forced-leave interval, the switch then blocks any further
group “X” traffic to the port.
Configuring Forced Fast-Leave IGMP
Syntax: [no] vlan < vid > ip igmp forcedfastleave <port-list>
Enables IGMP Forced Fast-Leave on the specified ports in the
selected VLAN, even if they are cascaded. (Default: Disabled.)
The no form of the command disables Forced Fast-Leave on the
specified ports in the selected VLAN. Use show running to
display the ports per-VLAN on which Forced Fast-Leave is
enabled.
To view a non-default IGMP forced fast-leave configuration on a VLAN, use
the show running-config command. (The show running-config output does not
include forced fast-leave if it is set to the default of 0.)
Forced fast-leave can be used when there are multiple devices attached to a
port.
2-17
Page 42

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
Configuring Delayed Group Flush
When enabled, this feature continues to filter IGMP groups for a specified
additional period of time after IGMP leaves have been sent. The delay in
flushing the group filter prevents unregistered traffic from being forwarded
by the server during the delay period. In practice, this is rarely necessary on
the switches covered in this guide, which support data-driven IGMP. (DataDriven IGMP, which is enabled by default, prunes off any unregistered IGMP
streams detected on the switch.)
Syntax: igmp delayed-flush < time-period >
Where leaves have been sent for IGMP groups, enables the switch
to continue to flush the groups for a specified period of time.
This command is applied globally to all IGMP-configured
VLANs on the switch. Range: 0 - 255; Default: Disabled (0).
Syntax: show igmp delayed-flush
Displays the current igmp delayed-flush setting.
IGMP Proxy Forwarding
Note For more information about PIM-DM and PIM-SM, see the chapters “PIM-DM
(Dense Mode)” and “PIM-SM (Sparse Mode)” in this guide.
When a network has a border router connecting a PIM-SM domain to a PIM-DM
domain, the routers that are completely within the PIM-DM domain have no
way to discover multicast flows in the PIM-SM domain. When an IGMP join
occurs on a router entirely within the PIM-DM domain for a flow that originates within the PIM-SM domain, it is never forwarded to the PIM-SM domain.
The IGMP proxy is a way to propagate IGMP joins across router boundaries.
The proxy triggers the boundary router connected to a PIM-SM domain to
query for multicast flows and forward them to the PIM-DM domain. IGMP
needs to be configured on all VLAN interfaces on which the proxy is to be
forwarded or received and PIM-DM must be running for the traffic to be
forwarded.
You can configure an IGMP proxy on a selected VLAN that will forward IP
joins (reports) and IGMP leaves to the upstream border router between the
two multicast domains. You must specify the VLANs on which the proxy is
enabled as well as the address of the border router to which the joins are
forwarded.
2-18
Page 43

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
How IGMP Proxy Forwarding Works
The following steps illustrate how to flood a flow from the PIM-SM domain
into the PIM-DM domain when an IGMP join for that flow occurs in the
PIM-DM domain (refer to figure 2-4).
1. Routing Switch 1 is configured with the IGMP proxy forwarding function
to forward joins towards Border Router 1. Routing Switch 1 is also
configured to forward joins from VLAN 1 toward Border Router 2, as is
VLAN 4 on Routing Switch 3.
2. VLAN 2 on Routing Switch 2 is configured to forward joins toward Border
Router 1.
3. When the host connected in VLAN 1 issues an IGMP join for multicast
address 235.1.1.1, the join is proxied by Routing Switch 1 onto VLAN 2 and
onto VLAN 4. The routing information table in Routing Switch 1 indicates
that the packet to Border Router 1 and Border Router 2 is on VLAN 2 and
VLAN 4, respectively.
2-19
Page 44

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
Routing Switch
2
VLAN 2
Routing Switch 1
VLAN 1
Initial IGMP
join
For 235.1.1.1
Border
router 1
Proxy joins towards Border router 2
PIM SM DOMAIN
VLAN 3
Routing Switch 3
V
LA
N
4
Multicast traffic source
(Multicast address
235.1.1.1
PIM DM DOMAIN
Proxy joins
towards Border
router 1
V
Border
router 2
5
N
A
L
Figure 2-4. IGMP Proxy Example
4. Routing Switch 2 then proxies the IGMP join into VLAN 3, which is
connected to Border Router 1.
5. Border Router 1 uses PIM-SM to find and connect to the multicast traffic
for the requested traffic. The traffic is flooded into the PIM-DM network
where it is routed to the original joining host.
6. Additionally, the join was proxied from Routing Switch 3 to Border Router
2. At first, both border routers will flood the traffic into the PIM-DM
domain. However, PIM-DM only forwards multicasts based on the shortest reverse path back to the source of the traffic as determined by the
unicast routing tables (routing FIB). Only one multicast stream is sent to
the joining host. This configuration provides a redundant link in case the
first link fails.
2-20
Page 45

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
CLI Commands for IGMP Proxy Configuration
Syntax: [no] igmp-proxy-domain <domain-name> [<border-router-ip-address>
<mcast-range | all>]
Add or leave a multicast domain. The no form of the command
is used to remove a multicast domain. All VLANs associated
with the domain must first be removed for this command to
work. See the no form of igmp-proxy in the VLAN context command.
domain-name
User-defined name to associate with the PIM border router and
multicast range that is being sent to toward the border router.
border-router-ip-addr
The IP address of the border router toward which IGMP proxy
packets are sent. Not required for the no form of the command.
Note: The current routing FIB determines the best path towards the
border router and therefore the VLAN that a proxy is sent out on.
<low-bound-ip-address | all>
The low boundary (inclusive) of the multicast address range
to associate with this domain (for example, 234.0.0.1).
If all is selected, the multicast addresses in the range of
224.0.1.0 - 239.255.255.255 will be included in this domain.
Note: Addresses 224.0.0.0 - 224.0.0.255 are never used since these
addresses are reserved for protocols.
<high-bound-ip-address>
The high boundary (inclusive) of the multicast address range
to associate with this domain (for example, 236.1.1.1)
The following example shows the IGMP proxy border IP address
(111.11.111.111) being configured.
ProCurve(config)# igmp-proxy-domain Bob 111.11.111.111
Figure 2-5. An example of the IGMP Proxy Border IP Address Command
2-21
Page 46

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
The example below shows the lower and upper boundaries of the multicast
address range associated with the domain named Bob.
ProCurve(config)# igmp-proxy-domain Bob 111.11.111.111 234.0.0.1
ProCurve(config)# igmp-proxy-domain Bob 111.11.111.111 236.1.1.1
Figure 2-6. Setting the Lower and Upper Bounds for Multicasting
VLAN Context Command
The following command is performed when in VLAN context mode. When a
query occurs on the upstream interface, an IGMP join will be sent for all
multicast addresses that are currently joined on the downstream interface.
Syntax: [no] igmp-proxy <domain-name>
Tells the VLAN which IGMP proxy domains to use with joins
on the VLAN. The no version of the command with no domain
name specified removes all domains associated with this
VLAN.
Note: Multiple different domains may be configured in the same VLAN
context where the VLAN is considered the downstream interface. The
domain name must exist prior to using this command to add the domain.
Note If the unicast routing path to the specified IP address was through the VLAN
specified, then no proxy IGMP would occur, that is, a proxy is not sent back
out on the VLAN that the IGMP join came in on.
If no unicast route exists to the border router, then no proxy IGMP packets
will be sent.
2-22
Page 47

IGMP Proxy Show Command
Syntax: show igmp-proxy < entries | domains | vlans >
Shows the currently active IGMP proxy entries, domains, or
vlans.
ProCurve(config)# show igmp-proxy entries
Total number of multicast routes: 2
Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
Multicast Address Border Address VID Multicast Domain
----------------- -------------- ----- ------
234.43.209.12 192.168.1.1 1 George
235.22.22.12 15.43.209.1 1 SAM
226.44.3.3 192.168.1.1 2 George
Figure 2-7. Example Showing Active IGMP Proxy Entries
ProCurve(config)# show igmp-proxy domains
Total number of multicast domains: 5
Multicast Domain Multicast Range Border Address Active entries
--------------- ------------------- ---------------- ---- George 225.1.1.1/234.43.209.12 192.168.1.1 2
SAM 235.0.0.0/239.1.1.1 15.43.209.1 1
Jane 236.234.1.1/236.235.1.1 192.160.1.2 0
Bill ALL 15.43.209.1 0
Figure 2-8. Example Showing IGMP Proxy Domains
2-23
Page 48

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
How IGMP Operates
ProCurve(config)# show igmp-proxy vlans
IGMP PROXY VLANs
VID Multicast Domain Active entries
------ ---------------- --------------
1 George 1
1 Sam 1
1 Jane 0
2 George 1
4 George 0
4 Bill 0
Figure 2-9. Example Showing Active IGMP Proxy VLANs
Operating Notes for IGMP Proxy Forwarding
■ You can configure up to 12 multicast domains. These domains will indicate
a range of multicast addresses and the IP address of the PIM-SM/PIM-DM
border router.
■ You must give each domain a unique name, up to 20 characters long.
■ The domains may have overlapping multicast ranges.
■ The IP address of the border router may be the same or different in each
configured domain.
■ Duplicate IGMP joins are automatically prevented, or leaves that would
remove a flow currently joined by multiple hosts.
■ Range overlap allows for redundant connectivity and the ability for mul-
ticasts to arrive from different border routers based on the shortest path
back to the source of the traffic.
■ The configured domain names must be associated with one or more
VLANs for which the proxy joins are to be done.
■ All routers in the path between the edge router receiving the initial IGMP
packets and the border router have to be configured to forward IGMP
using IGMP proxy.
■ All upstream and downstream interfaces using IGMP proxy forwarding
require IGMP and PIM to be enabled.
■ You must remove all VLAN associations with the domain name before that
domain name can be removed.
2-24
Page 49

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
■ The appropriate border routers must be used for each VLAN, or PIM-DM
How IGMP Operates
will not forward the traffic. This could occur when multiple border routers
exist. It may be necessary to configure multiple overlapping domains if
the multicast source address can generate the same multicast address and
have different best paths to the PIM-DM domain.
Caution Be careful to avoid configuring a IGMP forward loop, as this would leave the
VLANs in a joined state forever once an initial join is sent from a host. For
example, a join is issued from the host in VLAN 2 and routing switch 2 will
proxy the join onto VLAN 1. Routing switch 3 will then proxy the join back
onto VLAN 2 and increment its internal count of the number of joins on VLAN
2. Even after the host on VLAN 2 issues a leave, the proxy join will continue
to remain and refresh itself each time a query occurs on VLAN 2. This type of
loop could be created with multiple routers if an IGMP proxy is allowed to get
back to the VLAN of the router that initially received the IGMP join from a
host. (See figure 2-10.)
PIM SM DOMAIN
Routing Switch 1
(Border router)
Routing Switch 2 Routing Switch 3
Figure 2-10. Proxy Loop Scenario
PIM DM DOMAIN
VLAN 1
Proxy VLAN 2 to 1
Proxy VLAN 1 to 2
VLAN 2
2-25
Page 50

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
/15/
Using the Switch as Querier
Using the Switch as Querier
The function of the IGMP Querier is to poll other IGMP-enabled devices in an
IGMP-enabled VLAN to elicit group membership information. The switch
performs this function if there is no other device in the VLAN, such as a
multicast router, to act as Querier. Although the switch automatically ceases
Querier operation in an IGMP-enabled VLAN if it detects another Querier on
the VLAN, you can also use the switch’s CLI to disable the Querier capability
for that VLAN.
Note A Querier is required for proper IGMP operation. For this reason, if you disable
the Querier function on a switch, ensure that there is an IGMP Querier (and,
preferably, a backup Querier) available on the same VLAN.
If the switch becomes the Querier for a particular VLAN (for example, the
DEFAULT_VLAN), then subsequently detects queries transmitted from
another device on the same VLAN, the switch ceases to operate as the Querier
for that VLAN. If this occurs, the switch Event Log lists a pair of messages
similar to these:
I 01/15/01 09:01:13 igmp: DEFAULT_VLAN: Other Querier detected
I 01/15/01 09:01:13 igmp: DEFAULT_VLAN: This switch is no longer Querie
In the above scenario, if the other device ceases to operate as a Querier on the
default VLAN, then the switch detects this change and can become the Querier
as long as it is not pre-empted by some other IGMP Querier on the VLAN. In
this case, the switch Event Log lists messages similar to the following to
indicate that the switch has become the Querier on the VLAN:
I 01
I 01/15/01 09:22:00 igmp: DEFAULT_VLAN: This switch has been elected
2-26
01 09:21:55 igmp: DEFAULT_VLAN: Querier Election in process
Page 51
Excluding Well-Known or Reserved Multicast Addresses from IP Multicast Filtering
Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
Excluding Well-Known or Reserved
Multicast Addresses from IP Multicast
Filtering
Each multicast host group is identified by a single IP address in the range of
224.0.0.0 through 239.255.255.255. Specific groups of consecutive addresses
in this range are termed “well-known” addresses and are reserved for predefined host groups. IGMP does not filter these addresses, so any packets the
switch receives for such addresses are flooded out all ports assigned to the
VLAN on which they were received (except the port on which the packets
entered the VLAN).
The following table lists the 32 well-known address groups (8192 total
addresses) that IGMP does not filter on.
Table 2-2.IP Multicast Address Groups Excluded from IGMP Filtering
Groups of Consecutive
Addresses in the Range of
224.0.0.X to 239.0.0.X*
224.0.0.x 232.0.0.x 224.128.0.x 232.128.0.x
225.0.0.x 233.0.0.x 225.128.0.x 233.128.0.x
226.0.0.x 234.0.0.x 226.128.0.x 234.128.0.x
227.0.0.x 235.0.0.x 227.128.0.x 235.128.0.x
228.0.0.x 236.0.0.x 228.128.0.x 236.128.0.x
229.0.0.x 237.0.0.x 229.128.0.x 237.128.0.x
230.0.0.x 238.0.0.x 230.128.0.x 238.128.0.x
231.0.0.x 239.0.0.x 231.128.0.x 239.128.0.x
* X is any value from 0 to 255.
Groups of Consecutive
Addresses in
224.128.0.X to 239.128.0.X*
the Range of
2-27
Page 52

Multimedia Traffic Control with IP Multicast (IGMP)
Excluding Well-Known or Reserved Multicast Addresses from IP Multicast Filtering
Notes IP Multicast Filters. This operation applies to the ProCurve Series 5400zl
switches, the Series 3500yl switches, the switch 6200yl, the switch 8212zl,
the Series 2910al switches, the Series 5300xl switches, as well as the 1600M,
2400M, 2424M, 4000M, and 8000M, but not to the Series 2500, 2650, Series
4100gl, Series 4200vl, or 6108 switches (which do not have static traffic/
security filters).
IP multicast addresses occur in the range from 224.0.0.0 through
239.255.255.255 (which corresponds to the Ethernet multicast address range
of 01005e-000000 through 01005e-7fffff). Where a switch has a static Traffic/
Security filter configured with a “Multicast” filter type and a “Multicast
Address” in this range, the switch will use the static filter unless IGMP learns
of a multicast group destination in this range. In this case, IGMP dynamically
takes over the filtering function for the multicast destination address(es) for
as long as the IGMP group is active. If the IGMP group subsequently deactivates, the switch returns filtering control to the static filter.
Reserved Addresses Excluded from IP Multicast (IGMP) Filtering.
Traffic to IP multicast groups in the IP address range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255
will always be flooded because addresses in this range are “well known” or
“reserved” addresses. Thus, if IP Multicast is enabled and there is an IP
multicast group within the reserved address range, traffic to that group will
be flooded instead of filtered by the switch.
2-28
Page 53

IP Routing Features
Contents
Overview of IP Routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
IP Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
IP Tables and Caches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
ARP Cache Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
IP Route Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
IP Forwarding Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
IP Route Exchange Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
IP Global Parameters for Routing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-8
ARP Age Timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
IP Interface Parameters for Routing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
3
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Configuring IP Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Changing the Router ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Configuring ARP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
How ARP Works . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Enabling Proxy ARP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Enabling Local Proxy ARP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
CLI Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Configuring Forwarding Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Changing the TTL Threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Enabling Forwarding of Directed Broadcasts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Configuring ICMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Disabling ICMP Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Disabling Replies to Broadcast Ping Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
Disabling ICMP Destination Unreachable Messages . . . . . . . . . . 3-21
Disabling ICMP Redirects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Configuring Static IP Routes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
3-1
Page 54

IP Routing Features
Contents
Static Route Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Other Sources of Routes in the Routing Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Static IP Route Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Static Route States Follow VLAN States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
Configuring a Static IP Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-24
Configuring the Default Route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-26
Configuring RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
Overview of RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
RIP Parameters and Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
RIP Global Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
RIP Interface Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-28
Configuring RIP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Enabling RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Enabling IP RIP on a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Changing the RIP Type on a VLAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Changing the Cost of Routes Learned on a VLAN Interface . . . . 3-30
Configuring RIP Redistribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Define RIP Redistribution Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Modify Default Metric for Redistribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Enable RIP Route Redistribution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Changing the Route Loop Prevention Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-33
Displaying RIP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-33
Displaying General RIP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-34
Displaying RIP Interface Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-36
Displaying RIP Peer Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-37
Displaying RIP Redistribution Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-39
Displaying RIP Redistribution Filter (restrict) Information . . . . 3-39
3-2
Configuring IRDP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-40
Enabling IRDP Globally . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-41
Enabling IRDP on an Individual VLAN Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-41
Displaying IRDP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
Configuring DHCP Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
DHCP Packet Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Unicast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Page 55

IP Routing Features
Contents
Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Prerequisites for DHCP Relay Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Enabling DHCP Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Configuring an IP Helper Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Verifying the DHCP Relay Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Displaying the DHCP Relay Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-45
Displaying DHCP Helper Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-46
Displaying the Hop Count Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-47
DHCP Option 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-48
Option 82 Server Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-49
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-50
General DHCP Option 82 Requirements and Operation . . . . . . . 3-51
Option 82 Field Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-52
Forwarding Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-54
Configuration Options for Managing DHCP Client Request
Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-54
Multiple Option 82 Relay Agents in a Client Request Path . . . . . 3-55
Validation of Server Response Packets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-56
Multinetted VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-57
Configuring Option 82 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-58
Example of Option 82 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-60
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-61
UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-63
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-63
Subnet Masking for UDP Forwarding Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-64
Configuring and Enabling UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . 3-65
Globally Enabling UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-65
Configuring UDP Broadcast Forwarding on Individual VLANs . 3-65
Displaying the Current IP Forward-Protocol Configuration . . . . . . . 3-67
Operating Notes for UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-68
Messages Related to UDP Broadcast Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-68
3-3
Page 56

IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
Overview of IP Routing
The switches covered in this guide offer the following IP routing features, as
noted:
■ IP Static Routes – up to 256 static routes
■ RIP (Router Information Protocol) – supports RIP Version 1, Version 1
compatible with Version 2 (default), and Version 2
■ IRDP (ICMP Router Discovery Protocol) – advertises the IP addresses of
the routing interfaces on this switch to directly attached host systems
■ DHCP Relay – allows you to extend the service range of your DHCP
server beyond its single local network segment
Throughout this chapter, the switches covered in this guide are referred to as
“routing switches”. When IP routing is enabled on your switch, it behaves just
like any other IP router.
Basic IP routing configuration consists of adding IP addresses, enabling IP
routing, and, enabling a route exchange protocol, such as Routing Information
Protocol (RIP).
3-4
For configuring the IP addresses, refer to the chapter titled “Configuring IP
Addresses” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch.
The rest of this chapter describes IP routing and how to configure it in more
detail. Use the information in this chapter if you need to change some of the
IP parameters from their default values or you want to view configuration
information or statistics.
Page 57

IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
IP Interfaces
On the routing switches, IP addresses are associated with individual VLANs.
By default, there is a single VLAN (Default_VLAN) on the routing switch. In
that configuration, a single IP address serves as the management access
address for the entire device. If routing is enabled on the routing switch, the
IP address on the single VLAN also acts as the routing interface.
Each IP address on a routing switch must be in a different subnet. You can
have only one VLAN interface that is in a given subnet. For example, you can
configure IP addresses 192.168.1.1/24 and 192.168.2.1/24 on the same routing
switch, but you cannot configure 192.168.1.1/24 and 192.168.1.2/24 on the same
routing switch.
You can configure multiple IP addresses on the same VLAN.
The number of IP addresses you can configure on an individual VLAN interface
is 32.
You can use any of the IP addresses you configure on the routing switch for
Telnet, Web management, or SNMP access, as well as for routing.
Note All ProCurve devices support configuration and display of IP address in
classical subnet format (example: 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0) and Classless
Interdomain Routing (CIDR) format (example: 192.168.1.1/24). You can use
either format when configuring IP address information. IP addresses are
displayed in classical subnet format only.
IP Tables and Caches
The following sections describe the IP tables and caches:
■ ARP cache table
■ IP route table
■ IP forwarding cache
The software enables you to display these tables.
3-5
Page 58
IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
ARP Cache Table
The ARP cache contains entries that map IP addresses to MAC addresses.
Generally, the entries are for devices that are directly attached to the routing
switch.
An exception is an ARP entry for an interface-based static IP route that goes
to a destination that is one or more router hops away. For this type of entry,
the MAC address is either the destination device’s MAC address or the MAC
address of the router interface that answered an ARP request on behalf of the
device, using proxy ARP.
ARP Cache. The ARP cache contains dynamic (learned) entries. The software places a dynamic entry in the ARP cache when the routing switch learns
a device’s MAC address from an ARP request or ARP reply from the device.
The software can learn an entry when the switch or routing switch receives
an ARP request from another IP forwarding device or an ARP reply. Here is
an example of a dynamic entry:
IP Address MAC Address Type Port
1 207.95.6.102 0800.5afc.ea21 Dynamic 6
Each entry contains the destination device’s IP address and MAC address.
To configure other ARP parameters, see “Configuring ARP Parameters” on
page 3-14.
IP Route Table
The IP route table contains routing paths to IP destinations.
Note The default gateway, which you specify when you configure the basic IP
information on the switch, is used only when routing is not enabled on the
switch.
Routing Paths. The IP route table can receive the routing paths from the
following sources:
■ A directly-connected destination, which means there are no router hops
to the destination
■ A static IP route, which is a user-configured route
■ A route learned through RIP
3-6
Page 59

-
IP Routing Features
i
0
Overview of IP Routing
Administrative Distance. The IP route table contains the best path to a
destination. When the software receives paths from more than one of the
sources listed above, the software compares the administrative distance of
each path and selects the path with the lowest administrative distance. The
administrative distance is a protocol-independent value from 1 – 255.
The IP route table is displayed by entering the CLI command show ip route
from any context level in the console CLI. Here is an example of an entry in
the IP route table:
Destination Gateway VLAN Type Sub-Type Metric D
----------------- --------------- ---- --------- ---------- -------- -
10.10.10.1/32 10.10.12.1 connected 1
Each IP route table entry contains the destination’s IP address and subnet
mask and the IP address of the next-hop router interface to the destination.
Each entry also indicates route type. The type indicates how the IP route table
received the route.
To configure a static IP route, see “Configuring a Static IP Route” on page 3-24
IP Forwarding Cache
The IP forwarding cache provides a fast-path mechanism for forwarding IP
packets. The cache contains entries for IP destinations. When an ProCurve
routing switch has completed processing and addressing for a packet and is
ready to forward the packet, the device checks the IP forwarding cache for an
entry to the packet’s destination.
■ If the cache contains an entry with the destination IP address, the device
uses the information in the entry to forward the packet out the ports listed
in the entry. The destination IP address is the address of the packet’s final
destination. The port numbers are the ports through which the destination
can be reached.
■ If the cache does not contain an entry, the software can create an entry in
the forwarding cache.
Each entry in the IP forwarding cache has an age timer. The age interval
depends on the number of entries in the table. The age timer ranges from 12
seconds (full table) to 36 seconds (empty table). Entries are only aged if they
are not being utilized by traffic. If you have an entry that is always being used
in hardware, it will never age. If there is no traffic, it will age in 12-36 seconds.
The age timer is not configurable.
3-7
Page 60

IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
Note You cannot add static entries to the IP forwarding cache.
IP Route Exchange Protocols
The switch supports the Routing Information Protocol (RIP).
These protocols provide routes to the IP route table. You can use one or more
of these protocols, in any combination. The protocols are disabled by default.
For configuration information, see “Configuring RIP” on page 3-27.
IP Global Parameters for Routing Switches
The following table lists the IP global parameters and the page where you can
find more information about each parameter.
Table 3-1. IP Global Parameters for Routing Switches
Parameter Description Default See page
Router ID The value that routers use to identify themselves to
other routers when exchanging route information.
RIP does not use the router ID.
Address
Resolution
Protocol
(ARP)
ARP age The amount of time the device keeps a MAC address
Proxy ARP An IP mechanism a router can use to answer an ARP
A standard IP mechanism that routers use to learn
the Media Access Control (MAC) address of a
device on the network. The router sends the IP
address of a device in the ARP request and receives
the device’s MAC address in an ARP reply.
learned through ARP in the device’s ARP cache. The
device resets the timer to zero each time the ARP
entry is refreshed and removes the entry if the timer
reaches the ARP age. (Can be set using the menu
interface to be as long as 1440 minutes. Go to Menu
> Switch Configuration > IP Config.)
See “ARP Age Timer” on page 3-9.
request on behalf of a host, by replying with the
router’s own MAC address instead of the host’s.
The lowestnumbered IP
address
configured on the
lowest-numbered
routing interface.
Enabled 3-14
Five minutes. n/a
Disabled 3-16
3-13
3-8
Page 61

IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
Parameter Description Default See page
Time to Live
(TTL)
Directed
broadcast
forwarding
ICMP Router
Discovery
Protocol
(IRDP)
The maximum number of routers (hops) through
which a packet can pass before being discarded.
Each router decreases a packet’s TTL by 1 before
forwarding the packet. If decreasing the TTL causes
the TTL to be 0, the router drops the packet instead
of forwarding it.
A directed broadcast is a packet containing all ones
(or in some cases, all zeros) in the host portion of the
destination IP address. When a router forwards
such a broadcast, it sends a copy of the packet out
each of its enabled IP interfaces.
Note: You also can enable or disable this parameter
on an individual interface basis. See table 3-2 on
page 3-12.
An IP protocol that a router can use to advertise the
IP addresses of its router interfaces to directly
attached hosts. You can enable or disable the
protocol at the Global CLI Config level.
You also can enable or disable IRDP and configure
the following protocol parameters on an individual
VLAN interface basis at the VLAN Interface CLI
Config level.
• Forwarding method (broadcast or multicast)
• Hold time
• Maximum advertisement interval
• Minimum advertisement interval
• Router preference level
64 hops Refer to the
chapter titled
“Configuring IP
Addressing” in
the Management
and Configuration
Guide.
Disabled 3-18
Disabled 3-40
3-41
Static route An IP route you place in the IP route table. No entries 3-22
Default
network
route
The router uses the default network route if the IP
route table does not contain a route to the
destination. Enter an explicit default route (0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0 or 0.0.0.0/0) as a static route in the IP route
table.
None configured 3-26
ARP Age Timer
The ARP age is the amount of time the switch keeps a MAC address learned
through ARP in the ARP cache. The switch resets the timer to zero each time
the ARP entry is refreshed and removes the entry if the timer reaches the ARP
age.
3-9
Page 62
IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
You can increase the ARP age timeout maximum to 24 hours or more with this
command:
Syntax: [no] ip arp-age <[1...1440] | infinite>
Allows the ARP age to be set from 1 to 1440 minutes (24
hours). If the option “infinite” is configured, the internal ARP
age timeout is set to 99,999,999 seconds (approximately 3.2
years). An arp-age value of 0 (zero) is stored in the
configuration file to indicate that “infinite” has been
configured. This value also displays with the show commands
and in the menu display (Menu > Switch Configuration >
IP Config).
Default: 20 minutes.
ProCurve(config)# ip arp-age 1000
Figure 3-1. Example of Setting the ARP Age Timeout to 1000 Minutes
To view the value of ARP Age timer, enter the show ip command as shown in
Figure 3-2.
ProCurve(config)# show ip
Internet (IP) Service
IP Routing : Disabled
Default Gateway : 15.255.120.1
Default TTL : 64
Arp Age
Domain Suffix
DNS server :
VLAN | IP Config IP Address Subnet Mask Proxy ARP
-------------------- + ---------- --------------- --------------- -------- DEFAULT_VLAN | Manual 15.255.111.13 255.255.248.0 No
: 1000
:
Figure 3-2. Example of show ip Command Displaying ARP Age
You can also view the value of the ARP Age timer in the configuration file.
3-10
Page 63

ProCurve(config)# show running-config
Running configuration:
; J9146A Configuration Editor; Created on release #W.14.XX
hostname "8200LP"
module 2 type J8702A
module 3 type J8702A
module 4 type J8702A
ip default-gateway 15.255.120.1
ip arp-age 1000
snmp-server community "public" Unrestricted
snmp-server host 16.180.1.240 "public"
vlan 1
name "DEFAULT_VLAN"
untagged B1-B24,C1-C24,D1-D24
ip address 15.255.120.85 255.255.248.0
exit
gvrp
spanning-tree
Figure 3-3. Example Showing ip arp-age Value in the Running Config File
IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
You can set or display the arp-age value using the menu interface (Menu >
Switch Configuration > IP Config).
ProCurve 12-June-2007 14:45:31
===========================- TELNET - MANAGER MODE ======================
IP Routing : Disabled
Default Gateway : 15.255.120.1
Default TTL : 64
Arp Age : 1000
IP Config [Manual] : Manual
IP Address : 15.255.111.11
Subnet Mask : 255.255.248.0
Actions-> Cancel Edit Save Help
Switch Configuration - Internet (IP) Service
Figure 3-4. Example of the Menu Interface Displaying the ARP Age Value
3-11
Page 64
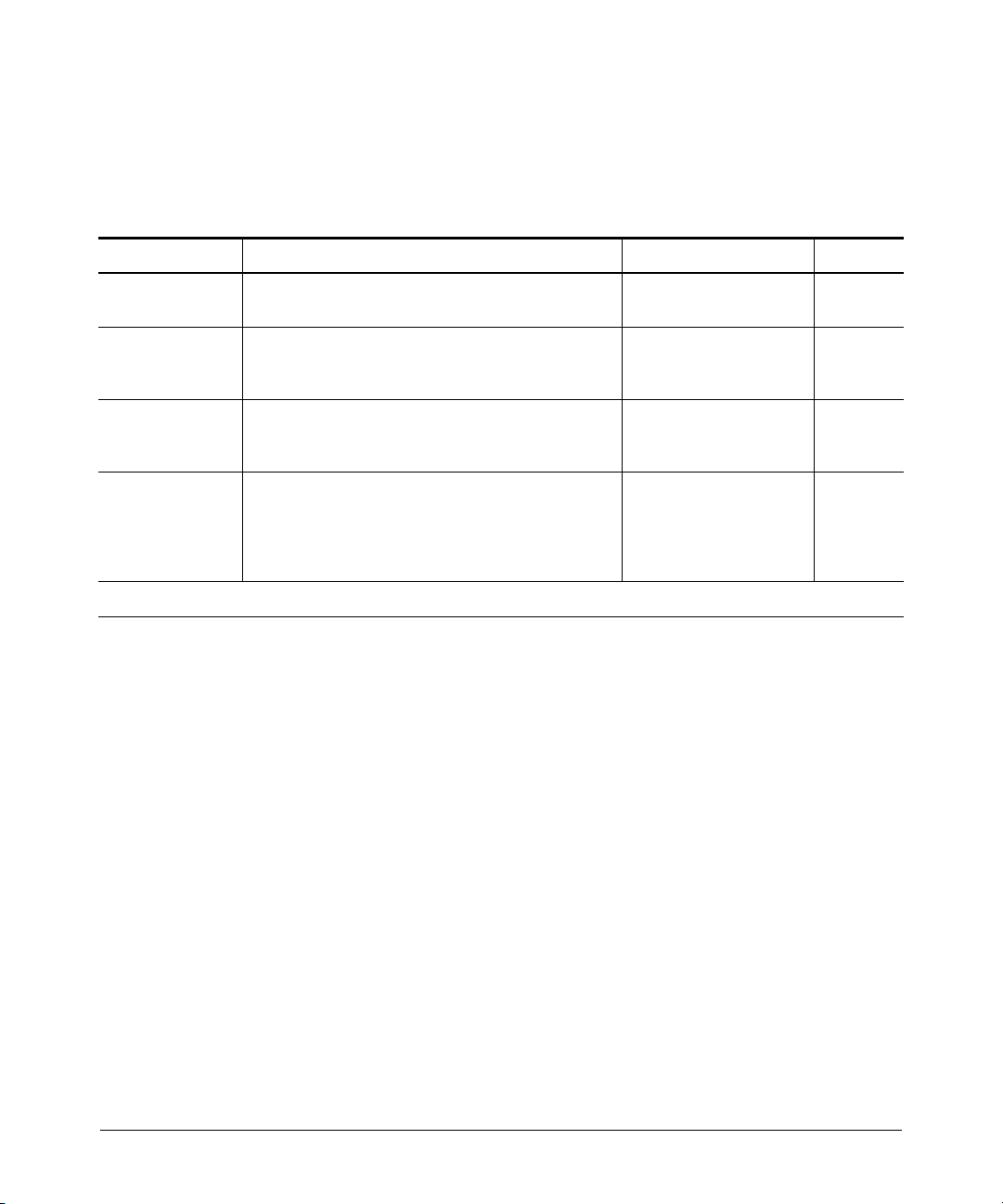
IP Routing Features
Overview of IP Routing
IP Interface Parameters for Routing Switches
Table 3-2 lists the interface-level IP parameters for routing switches.
Table 3-2. IP Interface Parameters – Routing Switches
Parameter Description Default See page
IP address A Layer 3 network interface address; separate IP
addresses on individual VLAN interfaces.
Metric A numeric cost the router adds to RIP routes learned
ICMP Router
Discovery
Protocol (IRDP)
IP helper address The IP address of a UDP application server (such as a
*
Refer to the chapter titled “Configuring IP Addressing” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your switch.
on the interface. This parameter applies only to RIP
routes.
Locally overrides the global IRDP settings. See table 31 on page 3-8 for global IRDP information.
BootP or DHCP server) or a directed broadcast
address. IP helper addresses allow the routing switch
to forward requests for certain UDP applications from
a client on one subnet to a server on another subnet.
None configured *
1 (one) 3-29
Disabled 3-41
None configured 3-45
3-12
Page 65

Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
IP Routing Features
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing
Switches
The following sections describe how to configure IP parameters. Some parameters can be configured globally while others can be configured on individual
VLAN interfaces. Some parameters can be configured globally and overridden
for individual VLAN interfaces.
Note This section describes how to configure IP parameters for routing switches.
For IP configuration information when routing is not enabled, refer to the
chapter titled “Configuring IP Addressing” in the Management and Configu-
ration Guide for your routing switch.
Configuring IP Addresses
You can configure IP addresses on the routing switch’s VLAN interfaces.
Configuring IP addresses is described in detail in the chapter titled “Configuring IP Addressing” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your
switch.
Changing the Router ID
In most configurations, a routing switch has multiple IP addresses, usually
configured on different VLAN interfaces. As a result, a routing switch’s identity
to other devices varies depending on the interface to which the other device
is attached. Some routing protocols identify a routing switch by just one of
the IP addresses configured on the routing switch, regardless of the interfaces
that connect the routing switches. This IP address is the router ID.
Note Routing Information Protocol (RIP) does not use the router ID.
If no router ID is configured, then, by default, the router ID on a ProCurve
routing switch is the first IP address that becomes physically active at reboot.
This is usually the lowest numbered IP interface configured on the device.
However, if no router ID is configured and one or more user-configured
loopback interfaces are detected at reboot, then the lowest-numbered (userconfigured) loopback interface becomes the router ID. If the lowestnumbered loopback interface has multiple IP addresses, then the lowest of
these addressees will be selected as the router ID. Once a router ID is selected,
it will not automatically change unless a higher-priority interface is configured
on the routing switch. (User-Configured loopback interfaces are always higher
3-13
Page 66

IP Routing Features
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
priority than other configured interfaces.) However, you prefer, you can
explicitly set the router ID to any valid IP address, as long as the IP address
is not in use on another device in the network.
Reconfiguring the Router ID (Optional). If you want to change the
router ID setting, do the following:
1. Go to the global config context. When you do so, the CLI prompt will
appear similar to the following:
ProCurve(config)#_
2. Use ip router-id < ip-addr > to specify a new router ID. (This IP address must
be unique in the routing switch configuration.)
For more information on the router ID, refer to “IP Global Parameters for
Routing Switches” on page 3-8 and “Changing the Router ID” on page 3-13.
To change the router ID, enter a command such as the following:
ProCurve(config)# ip router-id 209.157.22.26
Syntax: Syntax: ip router-id < ip-addr >
The < ip-addr > can be any valid, unique IP address.
Note You can specify an IP address used for an interface on the ProCurve routing
switch, but do not specify an IP address in use by another device.
Configuring ARP Parameters
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a standard IP protocol that enables an
IP routing switch to obtain the MAC address of another device’s interface
when the routing switch knows the IP address of the interface. ARP is enabled
by default and cannot be disabled.
How ARP Works
A routing switch needs to know a destination’s MAC address when forwarding
traffic, because the routing switch encapsulates the IP packet in a Layer 2
packet (MAC layer packet) and sends the Layer 2 packet to a MAC interface
on a device directly attached to the routing switch. The device can be the
packet’s final destination or the next-hop router toward the destination.
3-14
Page 67

Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
IP Routing Features
The routing switch encapsulates IP packets in Layer 2 packets regardless of
whether the ultimate destination is locally attached or is multiple router hops
away. Since the routing switch’s IP route table and IP forwarding cache
contain IP address information but not MAC address information, the routing
switch cannot forward IP packets based solely on the information in the route
table or forwarding cache. The routing switch needs to know the MAC address
that corresponds with the IP address of either the packet’s locally attached
destination or the next-hop router that leads to the destination.
For example, to forward a packet whose destination is multiple router hops
away, the routing switch must send the packet to the next-hop router toward
its destination, or to a default route or default network route if the IP route
table does not contain a route to the packet’s destination. In each case, the
routing switch must encapsulate the packet and address it to the MAC address
of a locally attached device, the next-hop router toward the IP packet’s
destination.
To obtain the MAC address required for forwarding a datagram, the routing
switch does the following:
■ First, the routing switch looks in the ARP cache (not the static ARP table)
for an entry that lists the MAC address for the IP address. The ARP cache
maps IP addresses to MAC addresses. The cache also lists the port
attached to the device and, if the entry is dynamic, the age of the entry. A
dynamic ARP entry enters the cache when the routing switch receives an
ARP reply or receives an ARP request (which contains the sender’s IP
address and MAC address). A static entry enters the ARP cache from the
static ARP table (which is a separate table) when the interface for the
entry comes up.
To ensure the accuracy of the ARP cache, each dynamic entry has its own
age timer. The timer is reset to zero each time the routing switch receives
an ARP reply or ARP request containing the IP address and MAC address
of the entry. If a dynamic entry reaches its maximum allowable age, the
entry times out and the software removes the entry from the table. Static
entries do not age out and can be removed only by you.
■ If the ARP cache does not contain an entry for the destination IP address,
the routing switch broadcasts an ARP request out all its IP interfaces. The
ARP request contains the IP address of the destination. If the device with
the IP address is directly attached to the routing switch, the device sends
an ARP response containing its MAC address. The response is a unicast
packet addressed directly to the routing switch. The routing switch places
the information from the ARP response into the ARP cache.
3-15
Page 68

IP Routing Features
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
ARP requests contain the IP address and MAC address of the sender, so
all devices that receive the request learn the MAC address and IP address
of the sender and can update their own ARP caches accordingly.
Note: The ARP request broadcast is a MAC broadcast, which means the
broadcast goes only to devices that are directly attached to the routing
switch. A MAC broadcast is not routed to other networks. However, some
routers, including ProCurve routing switches, can be configured to reply
to ARP requests from one network on behalf of devices on another
network. See “Enabling Proxy ARP” below.
Note If the routing switch receives an ARP request packet that it is unable to deliver
to the final destination because of the ARP time-out and no ARP response is
received (the routing switch knows of no route to the destination address),
the routing switch sends an ICMP Host Unreachable message to the source.
Enabling Proxy ARP
Proxy ARP allows a routing switch to answer ARP requests from devices on
one network on behalf of devices in another network. Since ARP requests are
MAC-layer broadcasts, they reach only the devices that are directly connected
to the sender of the ARP request. Thus, ARP requests do not cross routers.
3-16
For example, if Proxy ARP is enabled on a routing switch connected to two
subnets, 10.10.10.0/24 and 20.20.20.0/24, the routing switch can respond to an
ARP request from 10.10.10.69 for the MAC address of the device with IP
address 20.20.20.69. In standard ARP, a request from a device in the 10.10.10.0/
24 subnet cannot reach a device in the 20.20.20.0 subnet if the subnets are on
different network cables, and thus is not answered.
An ARP request from one subnet can reach another subnet when both subnets
are on the same physical segment (Ethernet cable), since MAC-layer broadcasts reach all the devices on the segment.
Proxy ARP is disabled by default on ProCurve routing switches. To enable
Proxy ARP, enter the following commands from the VLAN context level in the
CLI:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip proxy-arp
To again disable IP proxy ARP, enter the following command:
ProCurve(vlan-1)# no ip proxy-arp
Page 69

Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
Syntax: [no] ip proxy-arp
IP Routing Features
Enabling Local Proxy ARP
When the Local Proxy ARP option is enabled, a switch responds with its MAC
address to all ARP request on the VLAN. All IP packets are routed through and
forwarded by the switch. The switch prevents broadcast ARP requests from
reaching other ports on the VLAN.
Notes Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) redirects will be disabled on
interfaces on which local proxy ARP is enabled.
CLI Commands
To enable local proxy ARP, you must first enter vlan context, for example:
ProCurve(config) vlan 1
Then enter the command to enable local proxy ARP:
ProCurve(vlan-1)ip local-proxy-arp
Syntax: [no] ip local-proxy-arp
Enables the local proxy ARP option. You must be in VLAN
context to execute this command. When enabled on a VLAN,
the switch responds to all ARP requests received on the VLAN
ports with its own hardware address.
The no option disables the local proxy ARP option.
Default: Disabled
Execute the show ip command to see which VLANs have local proxy ARP
enabled.
3-17
Page 70

IP Routing Features
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
ProCurve(vlan-1)# show ip
Internet (IP) Service
IP Routing : Disabled
Default TTL : 64
Arp Age : 20
Domain Suffix :
DNS server :
VLAN | IP Config IP Address Subnet Mask Proxy ARP
-------------------- + ---------- --------------- --------------- -------- DEFAULT_VLAN | DHCP/Bootp 15.255.157.54 255.255.248.0 Yes Yes
VLAN2100 | Disabled
Figure 3-5. Local Proxy ARP is Enabled on the Default VLAN
Configuring Forwarding Parameters
The following configurable parameters control the forwarding behavior of
ProCurve routing switches:
■ Time-To-Live (TTL) threshold
■ Forwarding of directed broadcasts
All these parameters are global and thus affect all IP interfaces configured on
the routing switch.
To configure these parameters, use the procedures in the following sections.
3-18
Changing the TTL Threshold
The configuration of this parameter is covered in the chapter titled, “Configuring IP Addressing” in the Management and Configuration Guide for your
routing switch.
Enabling Forwarding of Directed Broadcasts
A directed broadcast is an IP broadcast to all devices within a single directlyattached network or subnet. A net-directed broadcast goes to all devices on a
given network. A subnet-directed broadcast goes to all devices within a given
subnet.
Page 71

Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
IP Routing Features
Note A less common type, the all-subnets broadcast, goes to all directly-attached
subnets. Forwarding for this broadcast type also is supported, but most
networks use IP multicasting instead of all-subnet broadcasting.
Forwarding for all types of IP directed broadcasts is disabled by default. You
can enable forwarding for all types if needed. You cannot enable forwarding
for specific broadcast types.
To enable forwarding of IP directed broadcasts, enter the following CLI
command:
ProCurve(config)# ip directed-broadcast
Syntax: [no] ip directed-broadcast
ProCurve software makes the forwarding decision based on the routing
switch's knowledge of the destination network prefix. Routers cannot determine that a message is unicast or directed broadcast apart from the destination network prefix. The decision to forward or not forward the message is by
definition only possible in the last-hop router.
To disable the directed broadcasts, enter the following CLI command:
ProCurve(config)# no ip directed-broadcast
3-19
Page 72

IP Routing Features
Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
Configuring ICMP
You can configure the following ICMP limits:
■ Burst-Normal – The maximum number of ICMP replies to send per
second.
■ Reply Limit – You can enable or disable ICMP reply rate limiting.
Disabling ICMP Messages
ProCurve devices are enabled to reply to ICMP echo messages and send ICMP
Destination Unreachable messages by default.
You can selectively disable the following types of Internet Control Message
Protocol (ICMP) messages:
■ Echo messages (ping messages) – The routing switch replies to IP pings
from other IP devices.
■ Destination Unreachable messages – If the routing switch receives an
IP packet that it cannot deliver to its destination, the routing switch
discards the packet and sends a message back to the device that sent the
packet to the routing switch. The message informs the device that the
destination cannot be reached by the routing switch.
■ Address Mask replies – You can enable or disable ICMP address mask
replies.
3-20
Disabling Replies to Broadcast Ping Requests
By default, ProCurve devices are enabled to respond to broadcast ICMP echo
packets, which are ping requests. You can disable response to ping requests
on a global basis using the following CLI method.
To disable response to broadcast ICMP echo packets (ping requests), enter
the following command:
ProCurve(config)# no ip icmp echo broadcast-request
Syntax: [no] ip icmp echo broadcast-request
If you need to re-enable response to ping requests, enter the following
command:
ProCurve(config)# ip icmp echo broadcast-request
Page 73

Configuring IP Parameters for Routing Switches
IP Routing Features
Disabling ICMP Destination Unreachable Messages
By default, when a ProCurve device receives an IP packet that the device
cannot deliver, the device sends an ICMP Unreachable message back to the
host that sent the packet. The following types of ICMP Unreachable messages
are generated:
■ Administration – The packet was dropped by the ProCurve device due to
a filter or ACL configured on the device.
■ Fragmentation-needed – The packet has the “Don’t Fragment” bit set in
the IP Flag field, but the ProCurve device cannot forward the packet
without fragmenting it.
■ Host – The destination network or subnet of the packet is directly
connected to the ProCurve device, but the host specified in the destination
IP address of the packet is not on the network.
■ Network – The ProCurve device cannot reach the network specified in
the destination IP address of the packet.
■ Port – The destination host does not have the destination TCP or UDP
port specified in the packet. In this case, the host sends the ICMP Port
Unreachable message to the ProCurve device, which in turn sends the
message to the host that sent the packet.
■ Protocol – The TCP or UDP protocol on the destination host is not
running. This message is different from the Port Unreachable message,
which indicates that the protocol is running on the host but the requested
protocol port is unavailable.
■ Source-route-failure – The device received a source-routed packet but
cannot locate the next-hop IP address indicated in the packet’s SourceRoute option.
Note Disabling an ICMP Unreachable message type does not change the ProCurve
device’s ability to forward packets. Disabling ICMP Unreachable messages
prevents the device from generating or forwarding the Unreachable messages.
To disable all ICMP Unreachable messages, enter the following command:
ProCurve(config)# no ip icmp unreachable
Syntax: [no] ip icmp unreachable
3-21
Page 74

IP Routing Features
Configuring Static IP Routes
Disabling ICMP Redirects
You can disable ICMP redirects on the ProCurve routing switch only on a
global basis, for all the routing switch interfaces. To disable ICMP redirects
globally, enter the following command at the global CONFIG level of the CLI:
ProCurve(config)# no ip icmp redirects
Syntax: [no] ip icmp redirects
Configuring Static IP Routes
This feature enables you to create static routes (and null routes) by adding
such routes directly to the route table. This section describes how to add static
and null routes to the IP route table.
Static Route Types
You can configure the following types of static IP routes:
■ Standard – the static route consists of a destination network address or
host, a corresponding network mask, and the IP address of the next-hop
IP address.
■ Null (discard) – the Null route consists of the destination network
address or host, a corresponding network mask, and either the reject or
blackhole keyword. Typically, the null route is configured as a backup
route for discarding traffic if the primary route is unavailable. By default,
when IP routing is enabled, a route for the 127.0.0.0/8 network is created
to the null interface. Traffic to this interface is rejected (dropped). This
route is for all traffic to the “loopback” network, with the single exception
of traffic to the host address of the switch’s loopback interface (127.0.0.1/
32). Figure 3-6 on page 3-26 illustrates the default Null route entry in the
switch’s routing table.
Note On a single routing switch you can create one null route to a given destination.
Multiple null routes to the same destination are not supported.
3-22
Page 75

IP Routing Features
Configuring Static IP Routes
Other Sources of Routes in the Routing Table
The IP route table can also receive routes from these other sources:
■ Directly-connected networks: One route is created per IP interface. When
you add an IP interface, the routing switch automatically creates a route
for the network the interface is in.
■ RIP: If RIP is enabled, the routing switch can learn about routes from the
advertisements other RIP routers send to the routing switch. If the RIP
route has a lower administrative distance than any other routes from
different sources to the same destination, the routing switch places the
route in the IP route table. (Refer to “Administrative Distance” on page 3-
7.)
■ Default route: This is a specific static route that the routing switch uses
if other routes to the destination are not available. See “Configuring the
Default Route” on page 3-26.
Static IP Route Parameters
When you configure a static IP route, you must specify the following
parameters:
■ The IP address and network mask for the route’s destination network or
host.
■ The route’s path, which can be one of the following:
• the IP address of a next-hop router.
• a “null” interface. The routing switch drops traffic forwarded to the
null interface.
The routing switch also applies default values for the route’s administrative
distance (page 3-7). In the case of static routes, this is the value the routing
switch uses to compare a static route to routes from other route sources to
the same destination before placing a route in the IP route table. The default
administrative distance for static IP routes is 1, but can be configured to any
value from 1 - 255.
The fixed administrative distance values ensure that the routing switch always
prefers static IP routes over routes from other sources to the same destination.
3-23
Page 76

IP Routing Features
Configuring Static IP Routes
Static Route States Follow VLAN States
IP static routes remain in the IP route table only so long as the IP interface to
the next-hop router is up. If the next-hop interface goes down, the software
removes the static route from the IP route table. If the next-hop interface
comes up again, the software adds the route back to the route table.
This feature allows the routing switch to adjust to changes in network topology. The routing switch does not continue trying to use routes on unreachable paths but instead uses routes only when their paths are reachable.
For example, the following command configures a static route to 207.95.7.0
(with a network mask of 255.255.255.0), using 207.95.6.157 as the next-hop
router’s IP address.
ProCurve(config)# ip route 207.95.7.0/24 207.95.6.157
A static IP route specifies the route’s destination address and the next-hop
router’s IP address or routing switch interface through which the routing
switch can reach the destination. (The route is added to the routing switch’s
IP route table.)
In the above example, routing switch “A” knows that 207.95.6.157 is reachable
through port A2, and assumes that local interfaces within that subnet are on
the same port. Routing switch “A” deduces that IP interface 207.95.7.188 is
also on port A2. The software automatically removes a static IP route from
the route table if the next-hop VLAN used by that route becomes unavailable.
When the VLAN becomes available again, the software automatically re-adds
the route to the route table.
3-24
Configuring a Static IP Route
This feature includes these options:
■ Static Route: configure a static route to a specific network or host
address
■ Null Route: configure a “null” route to discard IP traffic to a specific
network or host address:
• discard traffic for the destination, with ICMP notification to sender
• discard traffic for the destination, without ICMP notification to
sender
Page 77

Syntax: [no] ip route < dest-ip-addr >/< mask-length >
<next-hop-ip-addr | vlan <vlan-id> | reject | blackhole >
[metric < metric>] [ distance<1-255> ] [tag-value <tagval>]
Allows the addition and deletion of static routing table entries.
A route entry is identified by a destination (IP address/Mask
Length) and next-hop pair. The next-hop can be either a
gateway IP address, a VLAN, or the keyword “reject” or “blackhole”.
A gateway IP address does not have to be directly reachable
on one of the local subnets. If the gateway address is not
directly reachable, the route is added to the routing table as
soon as a route to the gateway address is learned.
dest-ip-addr >/ The route destination and network mask
< mask-bits length for the destination IP address.
Alternatively, you can enter the mask itself.
For example, you can enter either 10.0.0.0/24 or
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 for a route destination of
10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0.
next-hop-ip- This IP address is the gateway for reaching the
addr destination. The next-hop IP address is not
required to be directly reachable on a local
subnet. (If the next-hop IP address is not
directly reachable, the route will be added to
the routing table as soon as a route to this
address is learned.)
reject Specifies a null route where IP traffic for the
specified destination is discarded and an
ICMP error notification is returned to the
sender.
blackhole Specifies a null route where IP traffic for the
specified destination is discarded and no
ICMP error notification is returned to the
sender.
distance Specifies the administrative distance to asso-
ciate with a static route. If not specified, this
value is set to a default of 1. For more on this
topic, refer to “Administrative Distance” on
page 3-7. (Range: 1 - 255)
IP Routing Features
Configuring Static IP Routes
The no form of the command deletes the specified route for the specified
3-25
Page 78
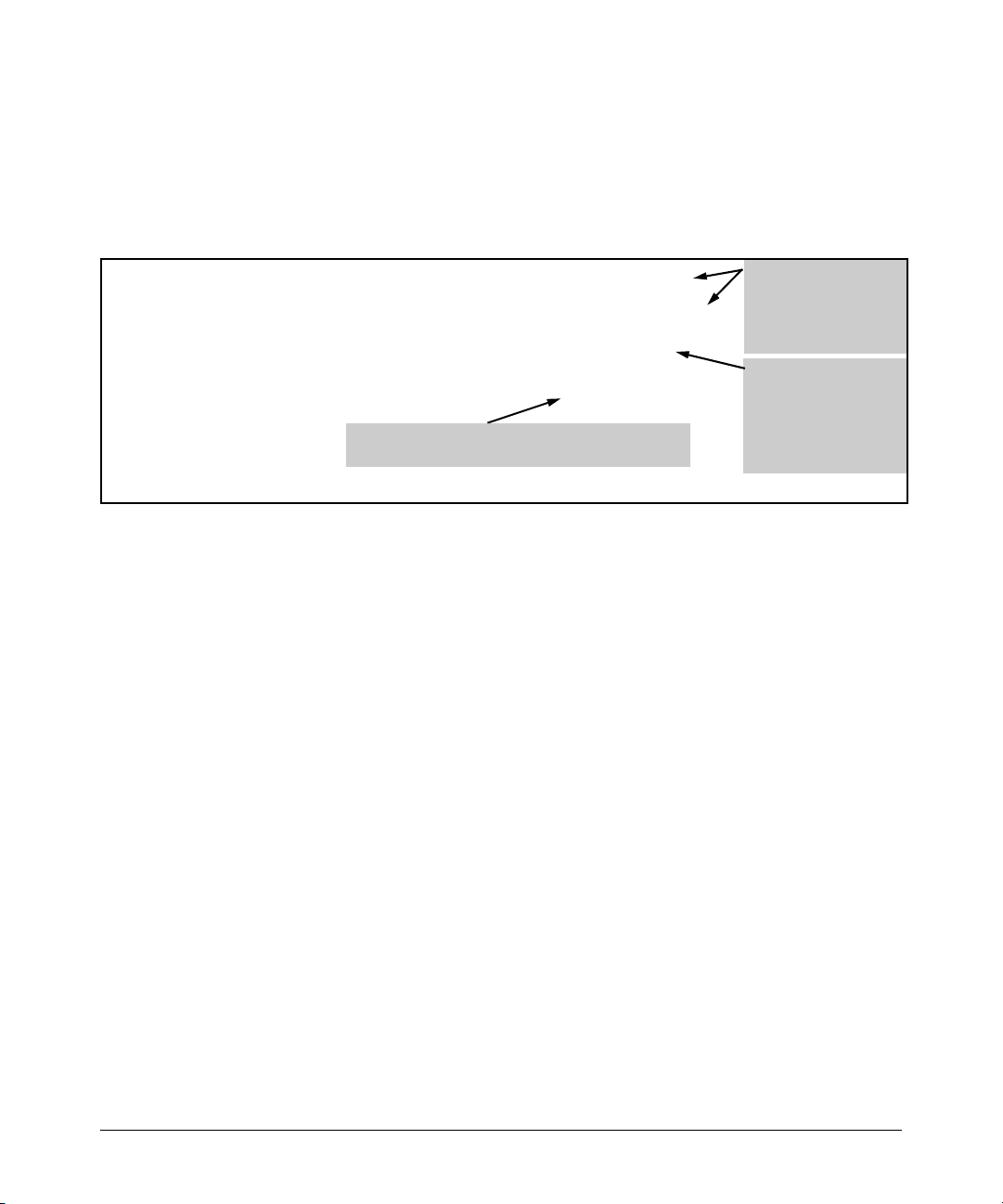
IP Routing Features
Configuring Static IP Routes
destination next-hop pair.
The following example configures two static routes for traffic delivery and
identifies two other null routes for which traffic should be discarded instead
of forwarded.
ProCurve(config)# ip route 10.10.40.0/24 10.10.10.1
ProCurve(config)# ip route 10.10.50.128/27 10.10.10.1
ProCurve(config)# ip route 10.10.20.177/32 reject
ProCurve(config)# ip route 10.10.30.0/24 blackhole
Configures a null route to drop traffic for the 10.50.10.0
network without any ICMP notification to the sender.
Figure 3-6. Example of Configuring Static Routes
Configuring the Default Route
You can also assign the default route and enter it in the routing table. The
default route is used for all traffic that has a destination network not reachable
through any other IP routing table entry. For example, if 208.45.228.35 is the
IP address of your ISP router, all non-local traffic could be directed to the ISP
by entering this command:
ProCurve(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0/0 208.45.228.35
Configures static
routes to two different
network destinations
using the same nexthop router IP address.
Configures a null route
to drop traffic for the
device at 10.50.10.177
and return an ICMP
notification to the
sender.
3-26
Page 79

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
Configuring RIP
This section describes how to configure RIP using the CLI interface.
To display RIP configuration information and statistics, see “Displaying RIP
Information” on page 3-33.
Overview of RIP
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is an IP route exchange protocol that uses
a distance vector (a number representing distance) to measure the cost of a
given route. The cost is a distance vector because the cost often is equivalent
to the number of router hops between the ProCurve routing switch and the
destination network.
A ProCurve routing switch can receive multiple paths to a destination. The
software evaluates the paths, selects the best path, and saves the path in the
IP route table as the route to the destination. Typically, the best path is the
path with the fewest hops. A hop is another router through which packets
must travel to reach the destination. If the ProCurve routing switch receives
a RIP update from another router that contains a path with fewer hops than
the path stored in the ProCurve routing switch's route table, the routing switch
replaces the older route with the newer one. The routing switch then includes
the new path in the updates it sends to other RIP routers, including ProCurve
routing switches.
RIP routers, including ProCurve routing switches, also can modify a route's
cost, generally by adding to it, to bias the selection of a route for a given
destination. In this case, the actual number of router hops may be the same,
but the route has an administratively higher cost and is thus less likely to be
used than other, lower-cost routes. A RIP route can have a maximum cost of
15. Any destination with a higher cost is considered unreachable. Although
limiting to larger networks, the low maximum hop count prevents endless
loops in the network.
The switches covered in this guide support the following RIP types:
■ Ver sion 1
■ V1 compatible with V2
■ Version 2 (the default)
3-27
Page 80

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
Not e ICMP Host Unreachable Message for Undeliverable ARPs. If the
routing switch receives an ARP request packet that it is unable to deliver to
the final destination because of the ARP timeout and no ARP response is
received (the routing switch knows of no route to the destination address),
the routing switch sends an ICMP Host Unreachable message to the source.
RIP Parameters and Defaults
The following tables list the RIP parameters, their default values, and where
to find configuration information.
RIP Global Parameters
3-3 lists the global RIP parameters and their default values.
Table 3-3. RIP Global Parameters
Parameter Description Default
RIP state Routing Information Protocol V2-only. Disabled
auto-summary Enable/Disable advertisement of summarized routes. Enabled
metric Default metric for imported routes. 1
redistribution RIP can redistribute static and connected routes. (RIP
redistributes connected routes by default, when RIP is
enabled.)
Disabled
RIP Interface Parameters
3-4 lists the VLAN interface RIP parameters and their default values.
Table 3-4. RIP Interface Parameters
Parameter Description Default
RIP version The version of the protocol that is supported on the
interface.
The version can be one of the following:
• Version 1 only
• Version 2 only
• Version 1 or version 2
V2-only
3-28
Page 81

IP Routing Features
Parameter Description Default
Configuring RIP
metric A numeric cost the routing switch adds to RIP routes
learned on the interface. This parameter applies only
to RIP routes.
IP address The routes that a routing switch learns or advertises
can be controlled.
loop
prevention
receive Define the RIP version for incoming packets V2-only
send Define the RIP version for outgoing packets V2-only
The method the routing switch uses to prevent routing
loops caused by advertising a route on the same
interface as the one on which the routing switch
learned the route.
• Split horizon - the routing switch does not
advertise a route on the same interface as the one
on which the routing switch learned the route.
• Poison reverse - the routing switch assigns a cost
of 16 (“infinite” or “unreachable”) to a route before
advertising it on the same interface as the one on
which the routing switch learned the route.
1
The routing switch
learns and
advertises all RIP
routes on all RIP
interfaces
Poison reverse
Configuring RIP Parameters
Use the following procedures to configure RIP parameters on a system-wide
and individual VLAN interface basis.
Enabling RIP
RIP is disabled by default. To enable it, use one of the following methods.
When you enable RIP, the default RIP version is RIPv2-only. You can change
the RIP version on an individual interface basis to RIPv1 or
RIPv1-or-v2 if needed.
To enable RIP on a routing switch, enter the following commands:
ProCurve(config)# ip routing
ProCurve(config)# router rip
ProCurve(rip)# exit
ProCurve(config)# write memory
Syntax: [no] router rip
3-29
Page 82

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
Note IP routing must be enabled prior to enabling RIP. The first command in the
preceding sequence enables IP routing.
Enabling IP RIP on a VLAN
To enable RIP on all IP addresses in a VLAN, use ip rip in the VLAN context.
when the command is entered without specifying any IP address, it is enabled
in all configured IP addresses of the VLAN.
To enable RIP on a specific IP address in a VLAN, use ip rip [< ip-addr >| all ] in
the VLAN context and enter a specific IP address. If you want RIP enabled on
all IP addresses, you can specify all in the command instead of a specific IP
address.
Changing the RIP Type on a VLAN Interface
When you enable RIP on a VLAN interface, RIPv2-only is enabled by default.
You can change the RIP type to one of the following on an individual VLAN
interface basis:
■ Version 1 only
■ Version 2 only (the default)
■ Version 1 - or - version 2
3-30
To change the RIP type supported on a VLAN interface, enter commands such
as the following:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip rip v1-only
ProCurve(vlan-1)# exit
ProCurve(config)# write memory
Syntax: [no] ip rip < v1-only | v1-or-v2 | v2-only >
Changing the Cost of Routes Learned on a VLAN Interface
By default, the switch interface increases the cost of a RIP route that is learned
on the interface. The switch increases the cost by adding one to the route's
metric before storing the route.
You can change the amount that an individual VLAN interface adds to the
metric of RIP routes learned on the interface.
Page 83

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
Note RIP considers a route with a metric of 16 to be unreachable. Use this metric
only if you do not want the route to be used. In fact, you can prevent the switch
from using a specific interface for routes learned though that interface by
setting its metric to 16.
To increase the cost a VLAN interface adds to RIP routes learned on that
interface, enter commands such as the following:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip rip metric 5
These commands configure vlan-1 to add 5 to the cost of each route learned
on the interface.
Syntax: ip rip metric < 1-16 >
Configuring RIP Redistribution
You can configure the routing switch to redistribute connected and static
routes into RIP. When you redistribute a route into RIP, the routing switch can
use RIP to advertise the route to its RIP neighbors.
To configure redistribution, perform the following tasks:
1. Configure redistribution filters to permit or deny redistribution for a route
based on the destination network address or interface. (optional)
2. Enable redistribution
Define RIP Redistribution Filters
Route redistribution imports and translates different protocol routes into a
specified protocol type. On the switches covered in this guide, redistribution
is supported for static routes and directly connected routes. Redistribution of
any other routing protocol into RIP is not currently supported. When you
configure redistribution for RIP, you can specify that static or connected
routes are imported into RIP routes.
To configure for redistribution, define the redistribution tables with “restrict”
redistribution filters. In the CLI, use the restrict command for RIP at the RIP
router level.
Note Do not enable redistribution until you have configured the redistribution
filters. Otherwise, the network might get overloaded with routes that you did
not intend to redistribute.
3-31
Page 84

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
Example: To configure the switch to filter out redistribution of static or
connected routes on network 10.0.0.0, enter the following commands:
ProCurve(config)# router rip
ProCurve(rip)# restrict 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
ProCurve(rip)# write memory
Note The default configuration permits redistribution for all default connected
routes only.
Syntax: restrict < ip-addr > < ip-mask > | < ip-addr /< prefix length >
This command prevents any routes with a destination address that is included
in the range specified by the address/mask pair from being redistributed by
RIP.
Modify Default Metric for Redistribution
The default metric is a global parameter that specifies the cost applied to all
RIP routes by default. The default value is 1. You can assign a cost from 1 – 15.
Example: To assign a default metric of 4 to all routes imported into RIP, enter
the following commands:
ProCurve(config)# router rip
ProCurve(rip)# default-metric 4
Syntax: default-metric < value >
The < value > can be from 1 – 15. The default is 1.
Enable RIP Route Redistribution
Note Do not enable redistribution until you have configured the redistribution
filters. Otherwise, the network might get overloaded with routes that you did
not intend to redistribute.
To enable redistribution of connected and static IP routes into RIP, enter the
following commands.
ProCurve(config)# router rip
ProCurve(rip)# redistribute connected
3-32
Page 85

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
ProCurve(rip)# redistribute static
ProCurve(rip)# write memory
Syntax: [no] redistribute < connected | static >
Changing the Route Loop Prevention Method
RIP can use the following methods to prevent routing loops:
■ Split horizon - the routing switch does not advertise a route on the same
interface as the one on which the routing switch learned the route.
■ Poison reverse - the routing switch assigns a cost of 16 (“infinity” or
“unreachable”) to a route before advertising it on the same interface as
the one on which the routing switch learned the route. This is the default.
These loop prevention methods are configurable on an individual VLAN
interface basis.
Note These methods are in addition to RIP's maximum valid route cost of 15.
Poison reverse is enabled by default. Disabling poison reverse causes the
routing switch to revert to Split horizon. (Poison reverse is an extension of
Split horizon.) To disable Poison reverse on an interface, and thereby enable
Split horizon, enter the following:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1
ProCurve(vlan-1)# no ip rip poison-reverse
Syntax: [no] ip rip poison-reverse
Entering the command without the “no” option will re-enable Poison reverse.
Displaying RIP Information
All RIP configuration and status information is shown by the CLI command
show ip rip and options off that command. The following RIP information can
be displayed:
RIP Information Type Page
General Information
Interface Information
Peer Information
3-34
3-36
3-37
3-33
Page 86

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
RIP Information Type Page
Redistribute Information
Restrict Information
3-39
3-39
Displaying General RIP Information
To display general RIP information, enter show ip rip at any context level. The
resulting display will appear similar to the following:
3-34
Figure 3-7.Example of General RIP Information Listing
The display is a summary of Global RIP information, information about
interfaces with RIP enabled, and information about RIP peers. The following
fields are displayed:
■ RIP protocol – Status of the RIP protocol on the router. RIP must be
enabled here and on the VLAN interface for RIP to be active. The default
is disabled.
■ Auto-summary – Status of Auto-summary for all interfaces running RIP.
If auto-summary is enabled, then subnets will be summarized to a class
network when advertising outside of the given network.
Page 87

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
■ Default Metric – Sets the default metric for imported routes. This is the
metric that will be advertised with the imported route to other RIP peers.
A RIP metric is a measurement used to determine the 'best' path to
network; 1 is the best, 15 is the worse, 16 is unreachable.
■ Route changes – The number of times RIP has modified the routing
switch’s routing table.
■ Queries – The number of RIP queries that have been received by the
routing switch.
■ RIP Interface Information – RIP information on the VLAN interfaces
on which RIP is enabled.
• IP Address – IP address of the VLAN interface running rip.
• Status – Status of RIP on the VLAN interface.
• Send mode – The format of the RIP updates: RIP 1, RIP 2, or RIP 2
version 1 compatible.
• Recv mode – The switch can process RIP 1, RIP 2, or RIP 2 version
1 compatible update messages.
• Metric – The path “cost”, a measurement used to determine the 'best'
RIP route path; 1 is the best, 15 is the worse, 16 is unreachable.
• Auth – RIP messages can be required to include an authentication
key if enabled on the interface.
■ RIP Peer Information – RIP Peers are neighboring routers from which
the routing switch has received RIP updates.
• IP Address – IP address of the RIP neighbor.
• Bad routes – The number of route entries which were not processed
for any reason.
• Last update timeticks – How many seconds have passed since we
received an update from this neighbor.
Syntax: show ip rip
3-35
Page 88

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
Figure 3-8.Example of Show IP RIP Interface Output
Displaying RIP Interface Information
To display RIP interface information, enter the show ip rip interface command
at any context level. The resulting display will appear similar to the following:
See “RIP Interface Information” on the previous page for definitions of these
fields.
You can also display the information for a single RIP VLAN interface, by
specifying the VLAN ID for the interface, or specifying the IP address for the
interface.
3-36
Displaying RIP interface information by VLAN ID: For example, to
show the RIP interface information for VLAN 1000, use the show ip rip interface
vlan < vid > command.
Figure 3-9. Example of RIP Interface Output by VLAN
Page 89

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
The information in this display includes the following fields, which are defined
under ““RIP Interface Information” on page 3-35: IP Address, Status, Send
mode, Recv mode, Metric, and Auth.
The information also includes the following fields:
■ Bad packets received – The number of packets that were received on
this interface and were not processed for any reason.
■ Bad routes received – The number of route entries that were received
on this interface and were not processed for any reason.
■ Sent updates – The number of RIP routing updates that have been sent
on this interface.
Displaying RIP interface information by IP Address: For example, to
show the RIP interface information for the interface with IP address 100.2.0.1,
enter the show ip rip interface command as shown below:
Figure 3-10. Example of Show IP RIP Interface Output by IP Address
The information shown in this display has the same fields as for the display
for a specific VLAN ID. See the previous page for the definitions of these fields.
Syntax: show ip rip interface [ip-addr | vlan < vlan-id >]
Displaying RIP Peer Information
To display RIP peer information, enter the show ip rip peer command at any
context level.
3-37
Page 90
IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
The resulting display will appear similar to the following:
ProCurve# show ip rip peer
RIP peer information
IP Address Bad routes Last update timeticks
--------------- ----------- ---------------------
100.1.0.100 0 1
100.2.0.100 0 0
100.3.0.100 0 2
100.10.0.100 0 1
Figure 3-11. Example of Show IP RIP Peer Output
This display lists all neighboring routers from which the routing switch has
received RIP updates. The following fields are displayed:
■ IP Address – IP address of the RIP peer neighbor.
■ Bad routes – The number of route entries that were not processed for
any reason.
■ Last update timeticks – How many seconds have passed since the
routing switch received an update from this peer neighbor.
Displaying RIP information for a specific peer: For example, to show
the RIP peer information for the peer with IP address 100.1.0.100, enter show
ip rip peer 100.1.0.100.
ProCurve# show ip rip peer 100.0.1.100
RIP peer information for 100.0.1.100
3-38
IP Address : 100.1.0.100
Bad routes : 0
Last update timeticks : 2
Figure 3-12. Example of Show IP RIP Peer < ip-addr > Output
This display lists the following information for a specific RIP peer:
■ IP Address – IP address of the RIP peer neighbor.
■ Bad routes – The number of route entries which were not processed for
any reason.
Page 91

IP Routing Features
Configuring RIP
■ Last update timeticks – How many seconds have passed since the
routing switch received an update from this neighbor.
Displaying RIP Redistribution Information
To display RIP redistribution information, enter the show ip rip redistribute
command at any context level:
ProCurve# show ip rip redistribute
RIP redistributing
Route type Status
--------- ----- connected enabled
static disabled
Figure 3-13. Example of Show IP RIP Redistribute Output
RIP automatically redistributes connected routes that are configured on
interfaces that are running RIP, and all routes that are learned via RIP. The
router rip redistribute command, described on page 3-31, configures the routing
switch to cause RIP to advertise connected routes that are not running RIP or
static routes. The display shows whether RIP redistribution is enabled or
disabled for connected or static routes.
Displaying RIP Redistribution Filter (restrict) Information
To display RIP restrict filter information, enter the show ip rip rest rict command
at any context level:
ProCurve(config)# show ip rip restrict
RIP restrict list
IP Address Mask
--------------- --------------
Figure 3-14. Example of Show IP RIP Restrict Output
3-39
Page 92

IP Routing Features
Configuring IRDP
The display shows if any routes, identified by the IP Address and Mask fields
are being restricted from redistribution. The restrict filters are configured by
the router rip restrict command described on page 3-31.
Configuring IRDP
The ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP) is used by ProCurve routing
switches to advertise the IP addresses of their router interfaces to directly
attached hosts. IRDP is disabled by default. You can enable the feature on a
global basis or on an individual VLAN interface basis.
When IRDP is enabled, the routing switch periodically sends Router Advertisement messages out the IP interfaces on which the feature is enabled. The
messages advertise the routing switch's IP addresses to directly attached
hosts who listen for the messages. In addition, hosts can be configured to
query the routing switch for the information by sending Router Solicitation
messages.
Some types of hosts use the Router Solicitation messages to discover their
default gateway. When IRDP is enabled on the ProCurve routing switch, the
routing switch responds to the Router Solicitation messages. Some clients
interpret this response to mean that the routing switch is the default gateway.
If another router is actually the default gateway for these clients, leave IRDP
disabled on the ProCurve routing switch.
3-40
IRDP uses the following parameters. If you enable IRDP on individual VLAN
interfaces, you can configure these parameters on an individual VLAN interface basis.
■ Packet type - The routing switch can send Router Advertisement
messages as IP broadcasts or as IP multicasts addressed to IP multicast
group 224.0.0.1. The default packet type is IP broadcast.
■ Hold time - Each Router Advertisement message contains a hold time
value. This value specifies the maximum about of time the host should
consider an advertisement to be valid until a newer advertisement arrives.
When a new advertisement arrives, the hold time is reset. The hold time
is always longer than the maximum advertisement interval. Therefore, if
the hold time for an advertisement expires, the host can reasonably
conclude that the router interface that sent the advertisement is no longer
available. The default hold time is three times the maximum message
interval.
Page 93

IP Routing Features
Configuring IRDP
■ Maximum message interval and minimum message interval - when
IRDP is enabled, the routing switch sends the Router Advertisement
messages every 450-600 seconds by default. The time within this interval
that the routing switch selects is random for each message and is not
affected by traffic loads or other network factors. The random interval
minimizes the probability that a host will receive Router Advertisement
messages from other routers at the same time. The interval on each IRDPenabled routing switch interface is independent of the interval on other
IRDP-enabled interfaces. The default maximum message interval is 600
seconds. The default minimum message interval is 450 seconds.
■ Preference - If a host receives multiple Router Advertisement messages
from different routers, the host selects the router that send the message
with the highest preference as the default gateway. The preference can be
a number from -4294967296 to 4294967295. The default is 0.
Enabling IRDP Globally
To enable IRDP globally, enter the following command:
ProCurve(config)# ip irdp
This command enables IRDP on the IP interfaces on all ports. Each port uses
the default values for the IRDP parameters.
Enabling IRDP on an Individual VLAN Interface
To enable IRDP on an individual VLAN interface and configure IRDP parameters, enter commands such as the following:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip irdp maxadvertinterval 400
This example shows how to enable IRDP on a specific interface (VLAN 1) and
change the maximum advertisement interval for Router Advertisement
messages to 400 seconds.
Syntax: [no] ip irdp [broadcast | multicast] [holdtime <seconds>] [maxadvertinterval
< seconds >] [minadvertinterval < seconds >] [preference < number >]
■ broadcast | multicast - This parameter specifies the packet type the routing
switch uses to send the Router Advertisement.
• broadcast - The routing switch sends Router Advertisements as IP
broadcasts.
3-41
Page 94

IP Routing Features
Configuring IRDP
• multicast - The routing switch sends Router Advertisements as multi-
cast packets addressed to IP multicast group 224.0.0.1. This is the
default.
■ holdtime < seconds > - This parameter specifies how long a host that
receives a Router Advertisement from the routing switch should consider
the advertisement to be valid. When a host receives a new Router Advertisement message from the routing switch, the host resets the hold time
for the routing switch to the hold time specified in the new advertisement.
If the hold time of an advertisement expires, the host discards the advertisement, concluding that the router interface that sent the advertisement
is no longer available. The value must be greater than the value of the
maxadvertinterval parameter and cannot be greater than 9000. The default
is three times the value of the maxadvertinterval parameter.
■ maxadvertinterval - This parameter specifies the maximum amount of time
the routing switch waits between sending Router Advertisements. You can
specify a value from 1 to the current value of the holdtime parameter. The
default is 600 seconds.
■ minadvertinterval - This parameter specifies the minimum amount of time
the routing switch can wait between sending Router Advertisements. The
default is three-fourths (0.75) the value of the maxadvertinterval parameter. If you change the maxadvertinterval parameter, the software automatically adjusts the minadvertinterval parameter to be three-fourths the
new value of the maxadvertinterval parameter. If you want to override the
automatically configured value, you can specify an interval from 1 to the
current value of the maxadvertinterval parameter.
■ preference < number > - This parameter specifies the IRDP preference level
of this routing switch. If a host receives Router Advertisements from
multiple routers, the host selects the router interface that sent the
message with the highest preference as the host's default gateway. The
valid range is -4294967296 to 4294967295. The default is 0.
3-42
Page 95
Displaying IRDP Information
To display IRDP information, enter show ip irdp from any CLI level.
ProCurve# show ip irdp
Status and Counters - ICMP Router Discovery Protocol
Global Status : Disabled
IP Routing Features
Configuring DHCP Relay
VLAN Name Status Advertising Min int Max int Holdtime Preference
-------------- -------- ------------ ------- ------- -------- -----------
DEFAULT_VLAN Enabled multicast 450 600 1800 0
VLAN20 Enabled multicast 450 600 1800 0
VLAN30 Enabled multicast 450 600 1800 0
Address (sec) (sec) (sec)
Figure 3-15.Example of Output for Show IP IRDP
Configuring DHCP Relay
Overview
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is used for configuring
hosts with IP address and other configuration parameters without user intervention. The protocol is composed of three components:
■ DHCP client
■ DHCP server
■ DHCP relay agent
The DHCP client sends broadcast request packets to the network; the DHCP
servers respond with broadcast packets that offer IP parameters, such as an
IP address for the client. After the client chooses the IP parameters, communication between the client and server is by unicast packets.
ProCurve routing switches provide the DHCP relay agent to enable communication from a DHCP server to DHCP clients on subnets other than the one
the server resides on. The DHCP relay agent transfers DHCP messages from
DHCP clients located on a subnet without a DHCP server to other subnets. It
also relays answers from DHCP servers to DHCP clients.
3-43
Page 96

IP Routing Features
Configuring DHCP Relay
The DHCP relay agent is transparent to both the client and the server. Neither
side is aware of the communications that pass through the DHCP relay agent.
As DHCP clients broadcast requests, the DHCP relay agent receives the
packets and forwards them to the DHCP server. During this process, the DHCP
relay agent increases the hop count by one before forwarding the DHCP
message to the server. A DHCP server includes the hop count from the DHCP
request that it receives in the response that it returns to the client.
DHCP Packet Forwarding
The DHCP relay agent on the routing switch forwards DHCP client packets to
all DHCP servers that are configured in the table administrated for each VLAN.
Unicast Forwarding
The packets are forwarded using unicast forwarding if the IP address of the
DHCP server is a specific host address. The DHCP relay agent sets the
destination IP address of the packet to the IP address of the DHCP server and
forwards the message.
Broadcast Forwarding
3-44
The packets are forwarded using broadcast forwarding if the IP address of the
DHCP server is a subnet address or IP broadcast address (255.255.255.255).
The DHCP relay agent sets the DHCP server IP address to broadcast IP address
and will be forwarded to all VLANs with configured IP interfaces (except the
source VLAN).
Prerequisites for DHCP Relay Operation
For the DHCP Relay agent to work on the switch, you must complete the
following steps:
1. Enable DHCP Relay on the routing switch (the default setting).
2. Ensure that a DHCP server is servicing the routing switch.
3. Enable IP Routing on the routing switch.
4. Ensure that there is a route from the DHCP server to the routing switch
and back.
5. Configure one or more IP helper addresses for specified VLANs to forward
DHCP requests to DHCP servers on other subnets.
Page 97

IP Routing Features
Configuring DHCP Relay
Enabling DHCP Relay
The DHCP Relay function is enabled by default on a ProCurve routing switch.
However, if DHCP has been disabled, you can re-enable it by entering the
following command at the global configuration level:
ProCurve(config)# dhcp-relay
To disable the DHCP Relay function, enter the no form of the command:
ProCurve(config)# no dhcp-relay
Configuring an IP Helper Address
To add the IP address of a DHCP server for a specified VLAN on a routing
switch, enter the ip helper-address command at the VLAN configuration level
as in the following example:
ProCurve(config)# vlan 1
ProCurve(vlan-1)# ip helper-address <ip-addr>
To remove the DHCP server helper address, enter the no form of the
command:
ProCurve(vlan-1)# no ip helper-address < ip-addr >
Operating Notes
■ You can configure up to 4000 IP helper addresses on a routing switch. The
helper addresses are shared between the DHCP relay agent and UDP
forwarder feature.
■ A maximum of sixteen IP helper addresses is supported in each VLAN.
Verifying the DHCP Relay Configuration
Displaying the DHCP Relay Setting
Use the show config command (or show running for the running-config file) to
display the current DHCP Relay setting.
3-45
Page 98

IP Routing Features
Configuring DHCP Relay
ProCurve# show config
Startup configuration:
; J9146A Configuration Editor; Created on release #W.14.XX
hostname “ProCurve”
cdp run
module 1 type J8702A
ip default-gateway 18.30.240.1
snmp-server community “public” Unrestricted
vlan 1
name “DEFAULT_VLAN”
untagged A1
ip address 18.30.240.180 255.255.248.0
no untagged A2-A24
exit
no dhcp-relay
no dhcp-relay hop-count-increment
Non-Default DHCP Relay and Hop
Count Increment settings
Figure 3-16. Displaying Startup Configuration with DHCP Relay and Hop Count
Increment Disabled
Displaying DHCP Helper Addresses
To display the list of currently configured IP Helper addresses for a specified
VLAN on the switch, enter the show ip helper-address vlan command.
Syntax: show ip helper-address [vlan <vlan-id>]
Displays the IP helper addresses of DHCP servers
configured for all static VLANS in the switch or on a
specified VLAN, regardless of whether the DHCP Relay
feature is enabled. The vlan <vlan-id> parameter
specifies a VLAN ID number.
The following command lists the currently configured IP Helper addresses for
VLAN 1.
Figure 3-17. Displaying IP Helper Addresses
3-46
Page 99

IP Routing Features
Configuring DHCP Relay
Displaying the Hop Count Setting
To verify the current setting for increasing the hop count in DHCP requests,
enter the show dhcp-relay command. Note that the current setting is displayed
next to DHCP Request Hop Count Increment.
ProCurve# show dhcp-relay
Status and Counters - DHCP Relay Agent
DHCP Relay Agent Enabled : Yes
DHCP Request Hop Count Increment: Disabled
Option 82 Handle Policy : Replace
Remote ID : MAC Address
Client Requests Server Responses
Valid Dropped Valid Dropped
-------- --------- -------- --------1425 2 1425 0
Figure 3-18. Example of show dhcp-relay Command Showing Hop Count
Increment
3-47
Page 100

IP Routing Features
Configuring DHCP Relay
DHCP Option 82
Option 82 is called the Relay Agent Information option and is inserted by the
DHCP relay agent when forwarding client-originated DHCP packets to a
DHCP server. Servers recognizing the Relay Agent Information option may
use the information to implement IP address or other parameter assignment
policies. The DHCP Server echoes the option back verbatim to the relay agent
in server-to-client replies, and the relay agent strips the option before
forwarding the reply to the client.
The “Relay Agent Information” option is organized as a single DHCP option
that contains one or more “sub-options” that convey information known by
the relay agent. The initial sub-options are defined for a relay agent that is colocated in a public circuit access unit. These include a “circuit ID” for the
incoming circuit, and a “remote ID” which provides a trusted identifier for the
remote high-speed modem.
The routing switch can operate as a DHCP relay agent to enable communication between a client and a DHCP server on a different subnet. Without Option
82, DHCP operation modifies client IP address request packets to the extent
needed to forward the packets to a DHCP server. Option 82 enhances this
operation by enabling the routing switch to append an Option 82 field to such
client requests. This field includes two suboptions for identifying the routing
switch (by MAC address or IP address) and the routing switch port the client
is using to access the network. A DHCP server with Option 82 capability can
read the appended field and use this data as criteria for selecting the IP
addressing it will return to the client through the usual DHCP server response
packet. This operation provides several advantages over DHCP without
Option 82:
■ An Option 82 DHCP server can use a relay agent’s identity and client
source port information to administer IP addressing policies based on
client and relay agent location within the network, regardless of whether
the relay agent is the client’s primary relay agent or a secondary agent.
■ A routing switch operating as a primary Option 82 relay agent for DHCP
clients requesting an IP address can enhance network access protection
by blocking attempts to use an invalid Option 82 field to imitate an
authorized client, or by blocking attempts to use response packets with
missing or invalid Option 82 suboptions to imitate valid response packets
from an authorized DHCP server.
■ An Option 82 relay agent can also eliminate unnecessary broadcast traffic
by forwarding an Option 82 DHCP server response only to the port on
which the requesting client is connected, instead of broadcasting the
DHCP response to all ports on the VLAN.
3-48
 Loading...
Loading...