Page 1

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
MK V
MK VI
MK VII
MK VIII
MK XXII
Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems
Line Maintenance Manual
Document No: 060-4199-180, Rev G
Release date: 29 Mar 2010
Honeywell International, Inc.
Redmond, Washington 98073-9701
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 1 of 68
Page 2
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
This document is an unpublished work.
Copyright 2005, 2010 Honeywell International, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This document and all information and expression contained herein are the
property of Honeywell and is provided to the recipient in confidence on a
“need to know” basis. Your use of this document is strictly limited to a
legitimate business purpose requiring the information contained therein.
Your use of this document constitutes acceptance of these terms.
Typed signatures constitute approval. Actual Signatures are on file at Honeywell in Redmond, WA.
DRAWN R. Halbert 23 FEB 00
CHECK
ENGR R. Halbert 23 FEB 00
MFG
QA
APVD G. Gilliland 23 FEB 00
APVD
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 2 of 68
Page 3
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
A
REVISIONS
SHT REV DESCRIPTION DATE
All Initial release.
23 FEB 00
PPROVED
R. Halbert
Reason 01 Severity 10
All A Direct update:
Incorporate –008 changes
Reason 01 Severity 10
All
All C Direct update to incorporate Airbus and Boeing part number
B Direct update to incorporate EGPWC/GNSSU part numbers
and troubleshooting information. Revised Level 2
descriptions.
Reason 01 Severity 10
changes, Revised Flight History Download Card P/Ns,
reformatted TOC and added the following RAAS-related
sections:
(1) Section 2.2.15
(2) “Application Software Version Invalid” and “RCD Failed”
(MK V/VII) aural annunciations to Table 3-2.
(3) Sections 3.8.42 and 3.8.43
(4) Appendix C
Reason 01 Severity 10
23 FEB 00
07 AUG 01
07 AUG 01
13 FEB 02
13 FEB 02
08 JAN 04
09 JAN 04
G. Gilliland
R. Henderson
L. Matter
B. Breen
G. Gilliland
J. Castro
L. Matter
All D 1) Deleted “Revisions Status of Sheets Index” table on
Sheet 3.
2) Section 3.2 (Troubleshooting Guide)
statement “(this sentence does not apply to internal
GPS engines)” after the existing sentence “If no faults
are present, verify that position data from the GPS, IRS,
or FMC is correct”.
3) Section 6.1.2 (Installation)
RAAS equipped EGPWC units.
4) Appendix C
- Revised Table B1-1 to C1-1.
- Revised Table B1-2 to C1-2.
- Table C1-2: Added note that “Operators/Installers must
refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness
(ICA) documentation to identify the approved RCD
configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having
RAAS installed”.
Reason 01 Severity 10
:
: Added step 6 to account for
: Added the
27 SEP 04
30 SEP 04
K. Christofferson
S. Wright
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 3 of 68
Page 4
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
A
REVISIONS
SHT REV DESCRIPTION DATE
PPROVED
All E Section 3.3.2 – added RAAS maintenance message to short
Level 1 Self-Test sequence and two notes, one to ensure
RAAS messages only occur if RAAS is activated and one to
explain the GPS NOT NAVIGATING enunciation.
Section 3.5 - added note to ensure RAAS message only
occurs if RAAS is activated.
Section 6.1.2 – modified step 6 to add Level 3 Self-Test.
Reason 01 Severity 10
All F Updated per ECO-65820
Updated document to include MK XXII helicopter EGPWS
and to include software -230-230 changes for RAAS and
newly introduced optional functions for Stabilized Approach
Monitor, Long Landing Monitor, Altimeter Monitor, and
Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor.
EFF PT: 10
All G Updated per ECO-87380
Updated document to include software -232-232 changes
for newly introduced function (Low Airspeed Monitor).
EFF PT: 14A DISP: USE
01 FEB 05
03 FEB 05
23 JUN 09
29 MAR 10
S. Wright
K. Christofferson
J. Mulkins
See AeroPDM
for additional
approvals
J. Mulkins
See AeroPDM
for additional
approvals
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 4 of 68
Page 5

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION.....................................................................................................................................................8
1.1 SCOPE......................................................................................................................................................................8
1.2 APPLICABILITY...........................................................................................................................................................8
1.3 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS..........................................................................................................................................9
2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ......................................................................................................................10
2.1 GENERAL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION..............................................................................................................................10
2.1.1 Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Computer (EGPWC).....................................................................11
2.2 OPERATION.............................................................................................................................................................11
2.2.1 Mode 1 – Excessive Descent Rate ...........................................................................................................11
2.2.2 Mode 2A/2B - Terrain Closure Rate..........................................................................................................11
2.2.3 Mode 3 - Descent After Takeoff ................................................................................................................11
2.2.4 Mode 4A/4B/4C - Unsafe Terrain Clearance ............................................................................................11
2.2.5 Mode 5 - Descent Below Glideslope.........................................................................................................12
2.2.6 Mode 6 - Advisory Callouts (optional) .......................................................................................................12
2.2.7 Mode 7 - Windshear Detection (Optional for MK V/VII only).....................................................................14
2.2.8 Envelope Modulation (not available in MK VI/VIII -001)............................................................................14
2.2.9 Terrain Clearance Floor and Runway Field Clearance Floor ...................................................................14
2.2.10 Terrain Alerting and Display (optional)......................................................................................................15
2.2.11 Peaks Display Mode (optional)..................................................................................................................16
2.2.12 Geometric Altitude (GPS Required)..........................................................................................................16
2.2.13 Weather Radar AutoTilt (MK V and MK VII only)......................................................................................16
2.2.14 System Display and Annunciation.............................................................................................................17
2.2.15 Runway Awareness and Advisory System (option for MK V and MK VII only).........................................17
2.2.16 Stabilized Approach Monitor (option for MK V and MK VII only) ..............................................................17
2.2.17 Altimeter Monitor (option for MK V and MK VII only) ................................................................................17
2.2.18 Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor (option for MK V and MK VII only)....................................................18
2.2.19 Long Landing Monitor (option for MK V and MK VII only).........................................................................18
2.2.20 Low Airspeed Monitor (MK V Boeing 737NG only)...................................................................................18
2.2.21 Lamp Format .............................................................................................................................................19
2.3 SYSTEM MAINTENANCE............................................................................................................................................20
2.3.1 Maintenance Philosophy...........................................................................................................................20
2.3.2 System Operation During an Inop Condition.............................................................................................20
2.3.3 BIT Description..........................................................................................................................................20
2.3.4 EGPWC Front Panel .................................................................................................................................21
2.3.5 Self-Test Functions....................................................................................................................................22
3 FAULT ISOLATION (TROUBLESHOOTING) .....................................................................................................23
3.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................23
3.2 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ......................................................................................................................................23
3.3 LEVEL 1 SELF-TEST - GO/NO GO TEST ....................................................................................................................24
3.3.1 Self-Test Preamble....................................................................................................................................24
3.3.2 Short Level 1 Self-Test..............................................................................................................................25
3.3.3 Long Level 1 Self-Test...............................................................................................................................26
3.4 LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST - CURRENT FAULTS...................................................................................................................26
3.4.1 Current Faults - Internal ............................................................................................................................27
3.4.2 Current Faults - External ...........................................................................................................................27
3.5 LEVEL 3 SELF-TEST - SYSTEM CONFIGURATION........................................................................................................33
3.6 LEVEL 4 SELF-TEST - FAULT HISTORY......................................................................................................................36
3.7 LEVEL 5 SELF-TEST - ALERT HISTORY......................................................................................................................37
3.8 LEVEL 6 SELF-TEST - DISCRETE INPUT TEST ............................................................................................................37
3.8.1 ARINC 552 / ALT 55 Radio Altitude Validity Flag Discretes.....................................................................38
3.8.2 GND Landing Gear Discrete .....................................................................................................................38
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 5 of 68
Page 6

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.3 +28V Landing Gear Discrete.....................................................................................................................38
3.8.4 GND Landing Flap Discrete or Flap Override...........................................................................................39
3.8.5 +28V Landing Flap or Flap Override Discrete...........................................................................................39
3.8.6 Flap Position Discretes..............................................................................................................................40
3.8.7 Self-Test Discrete......................................................................................................................................40
3.8.8 Steep Approach Discretes.........................................................................................................................40
3.8.9 GND ILS Tuned Discrete...........................................................................................................................41
3.8.10 +28V ILS Tuned Discrete..........................................................................................................................41
3.8.11 Glideslope Validity Discretes.....................................................................................................................41
3.8.12 GND Glideslope Inhibit Discrete................................................................................................................42
3.8.13 +28 V Glideslope Inhibit Discrete..............................................................................................................42
3.8.14 GND Glideslope Cancel Discrete..............................................................................................................42
3.8.15 Decision Height Discrete...........................................................................................................................42
3.8.16 Mode 6 Volume Control Discrete ..............................................................................................................43
3.8.17 Callouts Enable Discrete (MK V and MK VII only)....................................................................................43
3.8.18 GND Audio Suppress(Inhibit)/All Modes Inhibit Discrete..........................................................................43
3.8.19 +28 V Audio Suppress(Inhibit)/All Modes Inhibit Discrete.........................................................................43
3.8.20 AOA Validity Discretes (MK V and MK VII only) .......................................................................................44
3.8.21 Display Select Discretes............................................................................................................................44
3.8.22 Terrain Awareness & TCF Inhibit..............................................................................................................44
3.8.23 Simulator Reposition (MK V and MK VII only) ..........................................................................................44
3.8.24 Weather Radar On/Off...............................................................................................................................45
3.8.25 Localizer Validity Discretes (MK V and MK VII only).................................................................................45
3.8.26 Attitude Validity Discretes..........................................................................................................................45
3.8.27 Airspeed Validity Discrete .........................................................................................................................45
3.8.28 Barometric Altitude Rate Validity Discretes...............................................................................................46
3.8.29 Acceleration Self-Test In Progress Discrete .............................................................................................46
3.8.30 Longitudinal Acceleration Validity Discrete...............................................................................................46
3.8.31.......................................................................................................................................................................46
3.8.32 Normal Acceleration Validity Discrete.......................................................................................................46
3.8.33 Magnetic Heading Validity Discrete...........................................................................................................47
3.8.34 AOA Vane Heater Discrete .......................................................................................................................47
3.8.35 PLI Deselect Switch Discretes (MK V and MK VII only)............................................................................47
3.8.36 Autopilot Disconnect Discretes..................................................................................................................47
3.8.37 Tactical Select Discrete.............................................................................................................................48
3.8.38 Altitude Alert Discrete................................................................................................................................48
3.8.39 Corrected Barometric Altitude Validity Discrete........................................................................................48
3.8.40 Momentary Flap Override Discrete ...........................................................................................................48
3.8.41 Weight On Wheels Discrete......................................................................................................................49
3.8.42 GPWS Inhibit Discrete...............................................................................................................................49
3.8.43 RAAS EnABLE Discrete (MK V and MK VII Only) ....................................................................................49
3.8.44 RAAS Inhibit Discrete (MK V and MK VII Only) ........................................................................................49
3.8.45 Stabilized Approach Monitor Enable Discrete (MK V and MK VII Only)...................................................50
3.8.46 Stabilized Approach Monitor Inhibit Discrete (MK V and MK VII Only).....................................................50
3.8.47 Low Airspeed Monitor Inhibit Discrete (MK V – 737NG Only) ..................................................................50
4 MAINTENANCE PRACTICES..............................................................................................................................51
4.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................51
4.2 DATABASE UPDATE .................................................................................................................................................51
4.2.1 Database Update Frequency ....................................................................................................................51
4.2.2 Loading a Database ..................................................................................................................................51
4.3 FLIGHT HISTORY DOWNLOADING..............................................................................................................................52
4.3.1 Obtaining an EGPWS Flight History Download Card ...............................................................................52
4.3.2 Download Procedure.................................................................................................................................52
4.3.3 Transcription of the PCMCIA Card............................................................................................................53
4.4 PROGRAMMING THE CONFIGURATION MODULE (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII ONLY)........................................................54
4.4.1 Configuration Module Reprogramming (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)...................................................55
5 SERVICING ..........................................................................................................................................................57
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 6 of 68
Page 7

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
5.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................57
6 REMOVAL/INSTALLATION.................................................................................................................................57
6.1 EGPWC.................................................................................................................................................................57
6.1.1 Removal.....................................................................................................................................................57
6.1.2 Installation .................................................................................................................................................57
6.2 CONFIGURATION MODULE (MK VI, MK VIII, AND MK XXII ONLY)...............................................................................57
6.2.1 Removal.....................................................................................................................................................57
6.2.2 Installation .................................................................................................................................................57
6.3 DISPLAY SWITCHING RELAYS (IF INSTALLED).............................................................................................................58
6.3.1 Removal.....................................................................................................................................................58
6.3.2 Installation .................................................................................................................................................58
7 ADJUSTMENT/TEST ...........................................................................................................................................58
7.1 ADJUSTMENT ..........................................................................................................................................................58
7.2 TEST.......................................................................................................................................................................58
7.2.1 EGPWS Ground Tests ..............................................................................................................................58
8 INSPECTION/CHECK ..........................................................................................................................................59
8.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................59
9 CLEANING/PAINTING .........................................................................................................................................59
9.1 GENERAL................................................................................................................................................................59
10 REPAIRS ..............................................................................................................................................................59
10.1 GENERAL........................................................................................................................................................59
11 APPENDIX A: WINVIEWS ...................................................................................................................................60
12 APPENDIX B: TROUBLESHOOTING DO’S AND DO NOT’S............................................................................61
13 APPENDIX C: RAAS MAINTENANCE MESSAGES (AURAL & DISPLAYED).................................................62
14 APPENDIX D: STABILIZED APPROACH MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES .......................................64
15 APPENDIX E: ALTIMETER MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES..............................................................65
16 APPENDIX F: TAKEOFF FLAP CONFIGURATION MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES........................66
17 APPENDIX G: LONG LANDING MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES ......................................................67
18 APPENDIX H: LOW AIRSPEED MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES ......................................................68
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 7 of 68
Page 8
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 SCOPE
This document provides information about the Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS) with respect
to Line Maintenance Operations. This includes Description and Operation, Troubleshooting, Removal and
Installation, Adjustment and Test, and other related information. It is intended that the information in this document
be combined with detailed aircraft installation documentation for operator specific line maintenance procedures.
1.2 APPLICABILITY
This manual is applicable to the MK V, MK VI, MK VII, MK VIII, and MK XXII EGPWS with the following part
numbers and general description:
MK V EGPWC PART NUMBERS MK VII EGPWC PART NUMBERS
965-0976-003-XXX-XXX
965-0976-020-XXX-XXX
965-0976-040-XXX-XXX
965-0976-060-XXX-XXX
965-1676-XXX (Airbus P/N)
965-1690-XXX (Boeing P/N)
115 VAC, -40° to +70°
115 VAC, Internal 8 channel
GPS, -40° to +70°
28 VDC, -55° to +70°
115 VAC, Integral GNSSU,
-40° to +70°
115 VAC, -40° to +70°
115 VAC, -40° to +70°
965-1076-001-XXX-XXX
965-1076-020-XXX-XXX
965-1076-030-XXX-XXX
965-1076-040-XXX-XXX
965-1076-060-XXX-XXX
115 VAC, -40° to +70°
115 VAC, Internal 8 channel
GPS, -40° to +70°
28 VDC, Internal 8 channel
GPS, 55° to +70°
28 VDC, -55° to +70°
115 VAC, Integral GNSSU,
-40° to +70°
MK VI EGPWC PART NUMBERS MK VIII EGPWC PART NUMBERS MK XXII EGPWC PART NUMBERS
965-1176-XXX
965-1186-XXX
28 VDC, -55° to +70°
28 VDC, Internal 8 channel
GPS, -55° to +70°
965-1206-XXX
965-1216-XXX
28 VDC, -55° to +70°
28 VDC, Internal 8 channel
GPS, -55° to +70°
965-1590-XXX
965-1595-XXX
28 VDC, Internal 8 channel
GPS, -55° to +70°
28 VDC, Improved CPU,
Internal 8 channel GPS,
-55° to +70°
965-1180-XXX
965-1190-XXX
28 VDC, Improved CPU,
-55° to +70°
28 VDC, Improved CPU,
Internal 8 channel GPS,
-55° to +70°
965-1210-XXX
965-1220-XXX
TABLE 1-1 EGPWC Part Numbers
28 VDC, Improved CPU,
-55° to +70°
28 VDC, Improved CPU,
Internal 8 channel GPS,
-55° to +70°
NOTE: X’s represent variable values defining a specific application and configuration software version (i.e., -230-230 for MK V/VII
or -011 for MK VI/VIII/XXII original model or -026 for MK VI/VIII/XXII with improved CPU).
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 8 of 68
Page 9

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
MK V & MK VII EGPWC (left) and MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII EGPWC (right)
Figure 1-1 - Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Computers
1.3 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
The following documents are identified as additional EGPWS references:
MK V and MK VII:
965-0976-603 .........Product Specification for the EGPWS (MK V and MK VII)
060-4404-000………Product Description for Runway Awareness and Advisory System (RAAS) prior to -230-230
060-4564-000………Product Description, Flight Safety Functions of the EGPWS
993-0976-401 .........Interface Control Document for the Mark V EGPWS
993-1076-401 .........Interface Control Document for the Mark VII EGPWS
060-4199-125 .........Installation Design Guide for the MK V EGPWS
060-4199-225 .........Installation Design Guide for the MK VII EGPWS
060-4241-000 .........MK V and MK VII EGPWS Pilot Guide
060-4267-000 .........EGPWS Terrain Database Airport Coverage List (MK V and MK VII)
060-4353-000 .........EGPWS Terrain Database Obstacle Coverage Chart
MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII:
965-1176-601 .........Product Specification for the MK VI and MK VIII EGPWS (original model)
965-1180-601 .........Product Specification for the MK VI and MK VIII EGPWS (with improved CPU)
965-1590-601 .........Product Specification for the MK XXII EGPWS (original model)
965-1595-601 .........Product Specification for the MK XXII EGPWS (with improved CPU)
993-1176-401 .........Interface Control Document for the Mark VI/VIII/XXII EGPWS (original model)
993-1180-401 .........Interface Control Document for the Mark VI/VIII/XXII EGPWS (with improved CPU)
060-4314-125 .........Installation Design Guide for the MK VI/VIII EGPWS (original model)
060-4314-150………Installation Design Guide for the MK VI/VIII EGPWS (with improved CPU)
060-4314-225 .........Installation Design Guide for the MK XXII EGPWS (original model)
060-4314-250………Installation Design Guide for the MK XXII EGPWS (with improved CPU)
060-4314-000 .........MK VI and MK VIII EGPWS Pilot Guide
060-4314-200 .........MK XXII EGPWS Pilot Guide
060-4326-000 .........EGPWS Terrain Database Airport Coverage List (MK VI and MK VIII)
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 9 of 68
Page 10
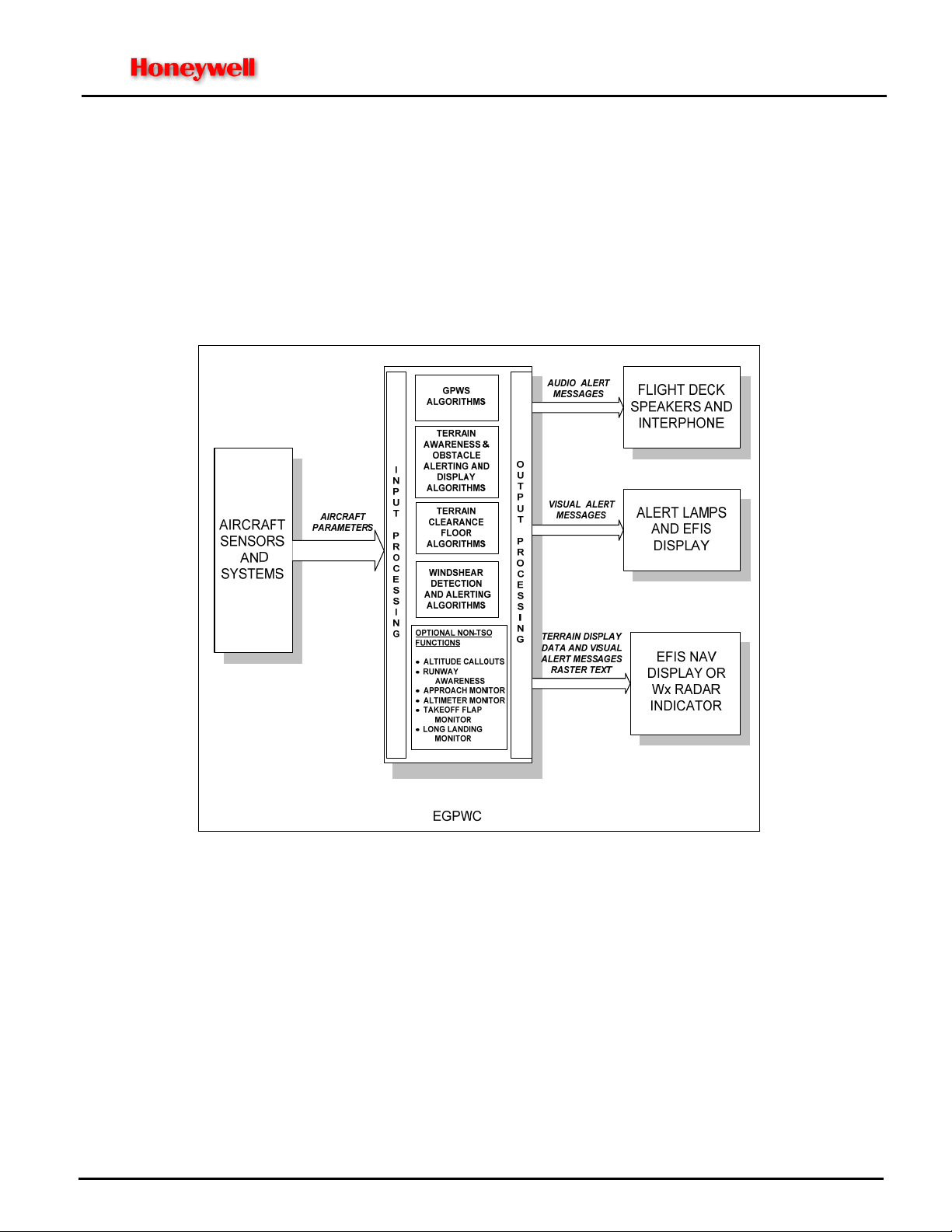
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
2.1 GENERAL SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The purpose for the Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS) is to help prevent accidents caused by
Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT), obstacles, or severe windshear. The Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning
Computer (EGPWC) accepts a variety of aircraft sensors and system inputs and applies alerting algorithms to
provide the flight crew with aural messages and visual annunciations when the boundaries of alerting envelopes are
exceeded. A graphic depiction of terrain and obstacles within the range selected on an EFIS or Weather Radar
display may be configured for enhanced situational awareness with respect to terrain and obstacles.
provides an overall system block diagram.
Figure 2-1
Figure 2-1: Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System
The EGPWS is comprised of the following:
• Aircraft sensors and systems providing input signals
• The Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Computer (EGPWC)
• Flight deck audio systems (speaker and interphone)
• Alert lamps and/or EFIS or EICAS displays (for alert and system status messages)
• EFIS Navigation Display (ND), Multi-Function Display (MFD), or Weather Radar Indicator for display of terrain
• Switching relay(s) when required for switching display inputs from weather display to terrain display
• GPS antenna for direct connection to EGPWC with internal GPS sensors
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 10 of 68
Page 11

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.1.1 ENHANCED GROUND PROXIMITY WARNING COMPUTER (EGPWC)
All EGPWS functions are processed by a single Line Replaceable Unit (LRU) called the Enhanced Ground
Proximity Warning Computer (EGPWC).
The MK V and MK VII EGPWC are digitally controlled computers housed in a 2 MCU ARINC 600-6 form factor
chassis intended for Air Transport type aircraft. Installation configuration is defined by program pin strapping in the
aircraft.
The MK VI and MK VIII EGPWC are digitally controlled computers housed in a non-ARINC form factor chassis
intended for Business and General Aviation and Regional Turboprop type aircraft. These models have fewer
interface and functional options. The installation configuration is defined in a programmed Configuration Module
installed in the aircraft.
The MK XXII EGPWC is a digitally controlled computer housed in a non-ARINC form factor chassis intended for
various rotorcraft. Similar to the MK VI and MK VIII EGPWC, this model has fewer interface and functional options.
The installation configuration is defined in a programmed Configuration Module installed in the helicopter.
The EGPWC receives information in AC, DC, discrete, and synchro analog formats, and RS-232, RS-422, ARINC
429 or ARINC 575 digital formats. Discrete signals can be either ground or +28V discretes. The EGPWC provides
discrete, audio and ARINC 429 outputs for alerts and system status, and video (ARINC 453/708) for terrain display.
The EGPWC is rack mounted and does not require any forced air cooling when operated within the normal
operating temperature range given in the Table 1-1.
2.2 OPERATION
2.2.1 MODE 1 – EXCESSIVE DESCENT RATE
Mode 1 provides audio and visual alerts for excessive descent rates into terrain. When the EGPWS caution alert
envelope is penetrated, the message “SINKRATE” is enunciated and EGPWS alert lights illuminate. Continuing the
excessive descent rate into the EGPWS warning alert envelope results in a “PULL-UP” enunciation and EGPWS
alert lights illuminated. Mode 1 is desensitized to eliminate unwanted (nuisance) alerts when the EGPWS
determines that the aircraft is above a Glideslope beam. In some fixed-wing applications, Mode 1 is also
desensitized when Steep Approach or Flap Override is active. In helicopter applications, Mode 1 is disabled when
autorotation is detected.
2.2.2 MODE 2A/2B - TERRAIN CLOSURE RATE
Mode 2 provides audio and visual alerts for dangerously high terrain closure rates. Two sub-modes, referred to as
Mode 2A and 2B, are defined. Mode 2A is active when flaps are not in the landing position and the aircraft is not on
an ILS approach within ± 2 dots of glideslope center. Mode 2B is active when the flaps are in the landing position or
while on an ILS approach within ± 2 dots of glideslope deviation. When the caution alert envelope is penetrated, the
message “TERRAIN, TERRAIN” is enunciated and EGPWS alert lights illuminate. Continuing the high terrain
closure rate into the warning alert envelope results in a “PULL-UP” enunciation and EGPWS alert lights illuminated.
2.2.3 MODE 3 - DESCENT AFTER TAKEOFF
Mode 3 provides audio and visual alerts for excessive altitude loss after takeoff, or after a go-around from below 245
feet above ground level (AGL), when flaps and gear are not in the landing configuration. Penetrating the Mode 3
alert envelope causes the voice message “DON’T SINK, DON’T SINK” and illumination of EGPWS alert lights.
2.2.4 MODE 4A/4B/4C - UNSAFE TERRAIN CLEARANCE
Mode 4 provides audio and visual alerts for unsafe terrain clearance with respect to phase of flight, height above
ground, and speed. Three sub-modes, referred to as Mode 4A, 4B, and 4C, are defined. Mode 4A is active during
cruise and approach with landing gear up. Mode 4B is active during cruise and approach with landing gear down
and flaps up. Mode 4C is active during takeoff when either gear or flaps are not in the landing configuration. The
aural enunciations for Mode 4A are “TOO LOW TERRAIN” or “TOO LOW GEAR” depending on airspeed. Mode 4B
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 11 of 68
Page 12
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
provides “TOO LOW TERRAIN” or “TOO LOW FLAPS” depending on airspeed. Mode 4C provides “TOO LOW
TERRAIN”. EGPWS alert lights are illuminated during these alerts.
2.2.5 MODE 5 - DESCENT BELOW GLIDESLOPE
Mode 5 provides audio and visual alerts for excessive glideslope deviation when the aircraft descends below the
glideslope beam on front-course ILS approaches. Two levels of alerting are provided. If the aircraft is below 1000
feet AGL and gets to or exceeds 1.3 dots glideslope deviation (fly-up), a ‘soft’ (reduced volume) “GLIDESLOPE” is
enunciated. Exceeding 2 dots below 300 feet AGL provides a hard (full volume) “GLIDESLOPE” enunciation.
EGPWS alert lights are illuminated during these alerts.
2.2.6 MODE 6 - ADVISORY CALLOUTS (OPTIONAL)
The EGPWC can be programmed to enunciate Mode 6 Advisory Callouts based on menu selectable options. Mode
6 includes Altitude Awareness, Minimums/Approaching Minimums, and Bank Angle type callouts as defined for
each EGPWS model (refer to an applicable Interface Control Document or Installation Design Guide). The menu
selected Advisory Callouts are defined and enabled in the installation configuration. If Altitude Callouts are not
enabled, only (DH based) “MINIMUMS” callouts will be provided. The MK XXII offers a tail strike advisory for
helicopters.
Only aural callouts are provided for Mode 6. EGPWS alert lights are NOT illuminated for Mode 6 callouts. The
following table identifies all of the Mode 6 Callouts that are available and the applicability to each model.
TABLE 2-1: MODE 6 CALLOUTS
CALLOUT DESCRIPTION
“DECISION HEIGHT“ At descent below minimums setting (DH)
“CHECK HEIGHT” At descent below minimums setting (DH)
“ALTITUDE-ALTITUDE” At descent below minimums setting (DH) with gear up
“MINIMUMS” At descent below minimums setting (DH)
“MINIMUM” At descent below minimums setting (DH)
“MINIMUMS-MINIMUMS” At descent below minimums setting (DH)
“DECIDE” At descent below minimums setting (DH)
“APPROACHING DECISION
HEIGHT”
At descent below minimums (DH altitude) setting plus
100 feet
“APPROACHING MINIMUMS” At descent below minimums setting (DH altitude) plus
80 feet
“PLUS HUNDRED” At descent below minimums setting (DH altitude) plus
100 feet
“FIFTY ABOVE” At descent below minimums setting (DH altitude) plus
50 feet
MODEL
V VI VII VIII XXII
#
•
# # # #
# # # #
#
•
#
•
# #
•
# #
•
# #
•
•
•
• • • • •
#
•
#
•
#
•
#
•
#
•
# #
•
# #
•
# #
•
# #
•
# #
•
“RADIO ALTIMETER” At descent below 2500 feet
“TWENTY FIVE HUNDRED” At descent below 2500 feet
“ONE THOUSAND” At descent below 1000 feet
“FIVE HUNDRED” At descent below 500 feet
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 12 of 68
#
•
•
#
•
•
• • • •
• • • •
# #
# #
#
#
Page 13
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
CALLOUT DESCRIPTION
500 TONE Provides 2 second 960 Hz tone at descent below 500
feet
SMART “FIVE HUNDRED” At descent below 500 feet (only) during non-precision
approach
“FIVE HUNDRED” Above field callout within 5 nm of a runway in the
database
“FIVE HUNDRED ABOVE” Above field callout within 5 nm of a runway in the
database
“FOUR HUNDRED” At descent below 400 feet
“THREE HUNDRED” At descent below 300 feet
“TWO HUNDRED” At descent below 200 feet
“ONE HUNDRED SIXTY” At descent below 160 feet
“ONE HUNDRED FIFTY” At descent below 150 feet
“ONE HUNDRED FORTY” At descent below 140 feet
“ONE HUNDRED THIRTY” At descent below 130 feet
“ONE HUNDRED TWENTY” At descent below 120 feet
MODEL
V VI VII VIII XXII
#
•
# #
•
• • • • •
#
#
• • • •
• • • •
#
•
•
#
•
•
#
#
#
#
• • • • •
# # # #
# # # #
# # # #
# # # #
# # # #
•
•
•
•
•
“ONE HUNDRED TEN” At descent below 110 feet
“ONE HUNDRED” At descent below 100 feet
100 TONE Provides 2 second 700 Hz tone at descent below 100
feet
“EIGHTY” At descent below 80 feet
“SIXTY” At descent below 60 feet
“FIFTY” At descent below 50 feet
“FOURTY” At descent below 40 feet
“THIRTY FIVE” At descent below 35 feet
35 TONE Provides 1 second 1400 Hz tone at descent below 35
feet
“THIRTY” At descent below 30 feet
“TWENTY” At descent below 20 feet
20 TONE Provides 1/2 second 2800 Hz tone at descent below
20 feet
“FIFTEEN” At descent below 15 feet
“TEN“ At descent below 10 feet
# # # #
• • • • •
#
•
#
•
#
•
# #
•
#
•
#
•
• • • • •
• • • • •
#
•
#
•
# #
•
# #
•
• • • • •
• • • • •
#
•
#
•
# #
•
# #
•
• • • • •
•
•
•
“FIVE” At descent below 5 feet
#
•
# #
•
# Not currently identified in any menu option for the model indicated.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 13 of 68
Page 14

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.2.6.1 EXCESSIVE BANK ANGLE CALLOUT
The Bank Angle Callout feature provides callout enunciation for excessive bank angles based on altitude and bank
angle limits defined by aircraft type. It is intended to enhance situational awareness during intentional or
unintentional maneuvering, and for protection against wing or engine strikes when close to the runway.
When the bank angle limit is reached, the aural callout “BANK ANGLE, BANK ANGLE” is given. Follow-on aural
messages are only provided when the aircraft roll angle increases an additional 20% from the previous callout.
Bank Angle Callouts are enabled by the installation configuration.
2.2.6.2 TAIL STRIKE CALLOUT
A tail strike alert function is provided by the MK XXII for applicable rotary wing aircraft based upon Radio Altitude,
Pitch Attitude, Pitch Rate and Barometric Altitude Rate. The voice message “Tail Too Low “ is provided continuously
while within the alert boundary. Unique alert boundaries are provided for applicable aircraft types.
2.2.7 MODE 7 - WINDSHEAR DETECTION (OPTIONAL FOR MK V/VII ONLY)
Mode 7 provides the flight crew with visual and aural alerts for windshear of sufficient magnitude to be potentially
hazardous to the aircraft. The system is capable of detecting severe decreasing performance shears (i.e.
increasing tailwind/decreasing headwind and/or downdraft) which present an immediate danger to the aircraft. The
system is also capable of detecting severe increasing performance shears (increasing headwind/decreasing tailwind
and/or up draft). While these shears may not present an immediate danger to the aircraft, these shears can indicate
that the atmospheric instability is such that an encounter with a severe decreasing performance shear is likely.
A detected increasing performance shear will result in an aural “CAUTION WINDSHEAR” enunciation and cockpit
light annunciation when enabled. A detected decreasing performance shear will result in an aural siren followed by
“WINDSHEAR, WINDSHEAR, WINDSHEAR” with a corresponding cockpit warning light annunciation.
2.2.8 ENVELOPE MODULATION (NOT AVAILABLE IN MK VI/VIII -001)
Envelope Modulation provides improved alert protection and expanded alerting margins at identified key locations
throughout the world. Due to terrain features at or near certain specific airports, normal operations have resulted in
nuisance or missed alerts at these locations in the past. With the introduction of accurate position information and a
terrain and airport database, it is now possible to identify these areas and adjust the normal alerting process to
compensate for the condition.
Modes 4, 5, and 6 are expanded at certain locations to provide alerting protection consistent with normal
approaches. Modes 1, 2, and 4 are desensitized at other locations to prevent nuisance alerts that result from
unusual terrain or approach procedures. In all cases, very specific information is used to correlate the aircraft
position and phase of flight prior to modulating the envelopes. This function is automatic and transparent to crew
operation.
2.2.9 TERRAIN CLEARANCE FLOOR AND RUNWAY FIELD CLEARANCE FLOOR
The Terrain Clearance Floor (TCF) alerting function adds an additional element of protection to the standard Ground
Proximity Warning System for fixed-wing aircraft. It creates an increasing terrain clearance envelope around the
airport runway to provide CFIT protection against situations where Mode 4 provides limited or no protection. TCF
alerts are based on current aircraft location, destination runway center point position, and Radio Altitude (altitude
AGL). TCF is active during takeoff, cruise, and final approach. TCF complements the existing Mode 4 protection by
providing an alert based on insufficient terrain clearance even when in landing configuration.
The TCF function is enhanced in all fixed-wing models (beginning with release –210-210 for the MK V/VII) with the
addition of a Runway Field Clearance Floor (RFCF) alerting function. RFCF is based on current aircraft location,
destination runway center point position, and Geometric Altitude or altitude Above Sea Level (ASL) relative to the
destination runway. RFCF provides short landing protection for runways that are significantly higher than the
surrounding terrain.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 14 of 68
Page 15

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
When an aircraft penetrates either the TCF or the RFCF alert envelope, the aural message “TOO LOW TERRAIN”
will occur. This aural message will occur once when initial envelope penetration occurs, and one time thereafter for
each 20% degradation in either Altitude (AGL) or Altitude (ASL) depending on which envelope was violated (TCF or
RFCF respectively). EGPWS cockpit alert annunciations remain illuminated until the alert envelope is exited. The
TCF and RFCF functions are not available in the MK XXII.
2.2.9.1 RUNWAY DATABASE
The EGPWS Runway Database consists of data records for all airport runways offered for the coverage provided by
the Terrain Database. For the MK V and MK VII, all hard surface runways in the world 3500 feet or greater in length
are supported. For the MK VI, all runways 2000 feet or greater in length within the database region installed are
supported. The MK VIII has the ability to select >2000 foot or >3500 foot runway lengths. For the MK XXII, only
runways 2000 feet or greater with a published approach procedure are included. The database provides the means
of accessing the records of runways closest to the current aircraft position.
2.2.10 TERRAIN ALERTING AND DISPLAY (OPTIONAL)
The Terrain Alerting and Display (TAD) function monitors aircraft position with respect to local database-cataloged
terrain to provide rapid audio and visual alerts when a terrain threat is detected. Terrain threats are recognized and
annunciated when terrain violates specific computed envelope boundaries forward of the aircraft path. The terrain
database also includes obstacles (when and where available) providing similar annunciations when cataloged
obstacles violate the same envelope boundaries.
Terrain Alerting outputs (lights and audio) behaves in the same manner as the standard GPWS mode alerts. Either
caution or warning alerts will initiate a specific audio alert phrase. The caution aural is “CAUTION TERRAIN” or
“CAUTION OBSTACLE” and the warning aural is “TERRAIN, TERRAIN, PULL UP” or “OBSTACLE, OBSTACLE,
PULL UP” (minor variations exist).
Complementing the terrain threat alerts, the EGPWS also maintains a synthetic image of local terrain forward of the
aircraft for display on EFIS Navigation Displays (ND’s), Multi-Functional Displays (MFD’s), or Weather Radar
Indicators. The EGPWS may be configured to automatically de-select the Weather Display and pop-up a display of
the terrain threats when they occur. The logic used for these configurable controls also provides an external input
for predictive windshear alerts that can override a Terrain Display and revert to the weather display with the
corresponding windshear data.
The EGPWS provides up to two optional external displays outputs, each with independent range-scaling control in
the same fashion as weather radar with more than one indicator. Changes of range scaling to one display do not
affect the other display. Each of these two independent outputs may be used to drive more than one display.
2.2.10.1 TERRAIN AND OBSTACLE DATABASE
The EGPWS Terrain Database is the earth’s surface divided into grid sets and cells referenced to the geographic
(latitude/longitude) coordinate system of the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS-84). Elements of the grid sets
include the highest terrain altitude (above MSL) in each cells respective area. Grid sets vary in resolution
depending on geographic location. Because the overwhelming majority of “Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT)”
accidents occur near an airport, and the fact that aircraft operate in closer proximity to terrain near an airport, higher
resolution grids are used around airports. Lower resolution grids are used outside of airport areas where aircraft
altitude enroute makes CFIT accidents unlikely and for which detailed terrain features are not important to the flight
crew.
Digital Elevation Models (DEM’s) are available for most of the airports around the world today. In cases where data
is not currently available, DEM’s are generated from available topographic maps, sectional charts, and airline
approach plates. The process of acquiring, generating, assembling, and updating the database is governed by strict
configuration controls to insure the highest level of data integrity for generation of the EGPWS Terrain Database.
The EGPWS Terrain Database is organized in a flexible and expandable manner. Using digital compression
techniques, the complete database is stored in non-volatile memory within the LRU. Updates and additions are
easily accomplished via a PCMCIA card interface.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 15 of 68
Page 16

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The Obstacle Database (in MK V and MK VII -204-204 and later, and MK VI, MK VIII and MK XXII) is a separate file
included within the terrain database. Both files are loaded into the EGPWS in the terrain database PCMCIA card.
The obstacle database is accessed by the EGPWC application software only if obstacle alerting is enabled by
installation configuration. The obstacle data is processed by the EGPWS in the same fashion as terrain, and is
presented on the display as terrain (uses same coloring scheme).
MK V, MK VII, and MK VIII EGPWS utilize a worldwide Terrain Database. The MK VI EGPWS utilizes a regional
Terrain Database consisting of one of the following regions:
• the Americas Region (designated “N”) for all of North, Central, and South America,
• the Atlantic Region (designated “A”) covering Greenland, Europe, Africa, and Asia,
• the Pacific Region (designated “P”) covering Europe, East Africa, Asia, Australia, the Pacific Ocean (to 120W
longitude including most of the US west coast).
The MK XXII utilizes 11 regional databases. For either worldwide or regional Terrain Databases, the Obstacle
Database currently covers cataloged obstacles (see Section 1.3) that are 100 feet high or higher. The MK XXII
database of obstacles is unique in the inclusion of oil rigs.
2.2.11 PEAKS DISPLAY MODE (OPTIONAL)
As an enhancement to the “standard” EGPWS terrain display, the Peaks Mode (when enabled by the installation
configuration) allows terrain below the aircraft to be viewed on the EGPWS terrain display during all phases of flight
(for MK V and MK VII -206-206 and later, and MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII). At altitudes safely above terrain for the
chosen display range, the terrain is displayed independent of aircraft altitude emphasizing the highest and lowest
displayed elevations to provide enhanced situational awareness. This can be particularly valuable to the flight crew
in case of an unplanned descent or off-route deviation and for previewing terrain prior to or during descent.
The EGPWS terrain display uses colors and shading patterns corresponding to the vertical displacement between
terrain elevation and the current altitude of the aircraft. With the “standard” display, terrain more than 2000 feet
below the aircraft is not displayed typically leaving the terrain display blank during the enroute portion of flight. The
Peaks Mode Display adds additional density patterns and level thresholds based on terrain elevations relative to the
range and distribution of terrain in the display area. The Peaks Mode is thus a “merged” display applicable to all
phases of flight.
Within the Peaks Mode display, two elevation numbers indicate the highest and lowest terrain currently being
displayed. The elevation numbers indicate terrain in hundreds of feet Above Sea Level (ASL). The terrain elevation
numbers are displayed with the “highest” terrain number on top, and the “lowest” terrain number beneath it. The
“highest” terrain number is shown in the same color as the highest terrain color pattern on the display, and the
“lowest” terrain number is shown in the color of the lowest terrain color pattern shown on the display. A single
elevation number is displayed when there is no appreciable difference in terrain elevations such as when flying over
water (displayed blue on some display systems) or flat terrain. The elevation numbers on the display are also an
indication that the terrain display is selected.
2.2.12 GEOMETRIC ALTITUDE (GPS REQUIRED)
Geometric Altitude (for MK V and MK VII -206-206 and later, and MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII) is a computed
pseudo-Corrected Barometric Altitude (computed altitude “Above Sea Level” - ASL). This is designed to ensure
optimal operation of the EGPWS enhanced functions through all phases of flight and atmospheric conditions.
Geometric Altitude uses GPS Altitude, an improved pressure altitude calculation, Radio Altitude, and Terrain and
Runway elevation data to reduce or eliminate errors potentially induced into Corrected Barometric Altitude by
temperature extremes, non-standard altitude conditions, and altimeter miss-sets. Geometric Altitude also allows
continuous EGPWS operations in QFE environments without custom inputs or special operational procedures.
2.2.13 WEATHER RADAR AUTOTILT (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
MK V and MK VII EGPWS (-210-210 and later) provide an automatic Weather Radar tilt angle capability. The AutoTilt function uses aircraft altitude above the terrain and the terrain database to generate an optimum tilt angle for the
Weather Radar. The Auto-Tilt angle results in minimum ground clutter on the display while maintaining the optimum
weather detection capability. With manual tilt control, there can be over-scan where weather cells and terrain are
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 16 of 68
Page 17

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
below the antenna beam scan resulting in a blank display. Alternately, under-scan, where the antennas scan is
hitting the ground below the weather cells, results in ground clutter display. The calculated tilt angle is transmitted
on the ARINC 429-output bus (labels 061, 062, 063, 064, and 065) for any compatible Weather Radar system. See
the appropriate Part Number ICD for complete Label definitions.
2.2.14 SYSTEM DISPLAY AND ANNUNCIATION
In addition to the aural (voice) alerts provided over the cockpit speaker and interphone system, the EGPWS drives
cockpit annunciators and/or Electronic Flight Instrument Systems (EFIS) with system status and alert annunciations.
For some EFIS displays, the EGPWS is designed to interface and display the EGPWS terrain video as well as alert
annunciations directly onto the EFIS without the use of external relays or annunciators. This is referred to as an
“integrated” EFIS display. For other displays (some EFIS and all Radar Indicators), the terrain video is relay
switched into the display system externally taking the place of weather radar video. In this case, external switching
and annunciation is required. This is referred to as a “Bolt-On” display. The interface and display characteristics
are defined for each display system and programmed into the EGPWC as part of the configuration software.
Cockpit annunciations can vary somewhat aircraft to aircraft or operator to operator. In addition, several system
options are defined by the installation configuration. One of these is EGPWS lamp format. Two formats are
provided; Lamp Format 1 and Lamp Format 2. They are described and illustrated in the next page.
2.2.15 RUNWAY AWARENESS AND ADVISORY SYSTEM (OPTION FOR MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The Honeywell Runway Awareness and Advisory System (RAAS) offers significant safety enhancements for aircraft
equipped with Honeywell’s MK V or MK VII Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS). Honeywell’s
Runway Awareness and Advisory System is a software enhancement hosted in the EGPWS Unit. RAAS uses GPS
position data and the Honeywell EGPWS Database to provide aural advisories and alerts that supplement flight
crew awareness of position during ground operations and on approach to landing. EGPWS protection and operation
is unaltered by the addition of RAAS. RAAS installation is accomplished via a configuration database upload. The
installation does require that the EGPWS has a source of GPS data, software -218-218 (or -002 or -051) or later,
Terrain Database version 435 or later (454 or later if using software -230-230 or later), and the RAAS Configuration
Database (RCD) or Reloadable Customer Definitions (RCD) is loaded. When enabled, RAAS operates
automatically, without any action required from the flight crew. RAAS availability can be verified by performing an
EGPWS self test. See Appendix C for RAAS Maintenance Messages.
2.2.16 STABILIZED APPROACH MONITOR (OPTION FOR MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The Stabilized Approach Monitor function offers significant safety enhancements for aircraft equipped with
Honeywell’s MK V or MK VII Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS). Honeywell’s Stabilized
Approach Monitor is a software enhancement hosted in the EGPWS Unit. Stabilized Approach Monitor uses GPS
position data and the Honeywell EGPWS Database to provide aural advisories and alerts that supplement flight
crew awareness of unstabilized approach to landing. EGPWS protection and operation is unaltered by the addition
of Stabilized Approach Monitor. Stabilized Approach Monitor installation is accomplished via a configuration
database upload. The installation does require that the EGPWS has a source of GPS data, software -230-230 or
later, Terrain Database version 454 or later, and the Reloadable Customer Definitions (RCD) is loaded. When
enabled, Stabilized Approach Monitor operates automatically, without any action required from the flight crew.
Stabilized Approach Monitor availability can be verified by performing an EGPWS self test. See Appendix D for
Stabilized Approach Monitor Maintenance Messages.
2.2.17 ALTIMETER MONITOR (OPTION FOR MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The Altimeter Monitor function offers significant safety enhancements for aircraft equipped with Honeywell’s MK V or
MK VII Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS). Honeywell’s Altimeter Monitor is a software
enhancement hosted in the EGPWS Unit. Altimeter Monitor compares Corrected Altitude to the EGPWS blended
Geometric Altitude solution to provide aural advisories that supplement flight crew awareness of incorrect altimeter
setting or problems with the pressure altitude system. EGPWS protection and operation is unaltered by the addition
of Altimeter Monitor. Altimeter Monitor installation is accomplished via a configuration database upload. The
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 17 of 68
Page 18

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
installation does require that the EGPWS has a source of GPS data, software -230-230 or later, Terrain Database
version 454 or later, and the Reloadable Customer Definitions (RCD) is loaded. When enabled, Altimeter Monitor
operates automatically, without any action required from the flight crew. Altimeter Monitor availability can be verified
by performing an EGPWS self test. See Appendix E for Altimeter Monitor Maintenance Messages.
2.2.18 TAKEOFF FLAP CONFIGURATION MONITOR (OPTION FOR MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor function offers significant safety enhancements for aircraft equipped with
Honeywell’s MK V or MK VII Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS). Honeywell’s Takeoff Flap
Configuration Monitor is a software enhancement hosted in the EGPWS Unit. Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor
uses GPS position data, Flap angle inputs, and the Honeywell EGPWS Database to provide aural alerts that
supplement flight crew awareness of improper flap setting when the aircraft is aligned on a runway prior to takeoff.
EGPWS protection and operation is unaltered by the addition of Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor. Takeoff Flap
Configuration Monitor installation is accomplished via a configuration database upload. The installation does
require that the EGPWS has a source of GPS data, flap angle input, software -230-230 or later, Terrain Database
version 454 or later, and the Reloadable Customer Definitions (RCD) is loaded. When enabled, Takeoff Flap
Configuration Monitor operates automatically, without any action required from the flight crew. Takeoff Flap
Configuration Monitor availability can be verified by performing an EGPWS self test. See Appendix F for Takeoff
Flap Configuration Monitor Maintenance Messages.
2.2.19 LONG LANDING MONITOR (OPTION FOR MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The Long Landing Monitor function offers significant safety enhancements for aircraft equipped with Honeywell’s MK
V or MK VII Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS). Honeywell’s Long Landing Monitor is a
software enhancement hosted in the EGPWS Unit. Long Landing Monitor uses GPS position data and the
Honeywell EGPWS Database to provide aural alerts that supplement flight crew awareness of their position during a
landing when the aircraft has not touched down in a nominal amount of time and/or distance. EGPWS protection
and operation is unaltered by the addition of Long Landing Monitor. Long Landing Monitor installation is
accomplished via a configuration database upload. The installation does require that the EGPWS has a source of
GPS data, software -230-230 or later, Terrain Database version 454 or later, and the Reloadable Customer
Definitions (RCD) is loaded. When enabled, Long Landing Monitor operates automatically, without any action
required from the flight crew. Long Landing Monitor availability can be verified by performing an EGPWS self test.
See Appendix G for Long Landing Monitor Maintenance Messages.
2.2.20 LOW AIRSPEED MONITOR (MK V BOEING 737NG ONLY)
The Low Airspeed Monitor function offers significant safety enhancements for Boeing 737NG aircraft equipped with
Honeywell’s MK V Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning Systems (EGPWS). Honeywell’s Low Airspeed Monitor is
a software enhancement hosted in the EGPWS Unit. Low Airspeed Monitor uses Minimum Operating Speed and
Stick Shaker Speed input from the Stall Management and Yaw Damper computers to provide an aural alert that
supplements flight crew awareness that their airspeed had passes below 70% of the amber airspeed band.
EGPWS protection and operation is unaltered by the addition of Low Airspeed Monitor. Low Airspeed Monitor
installation is accomplished via an application software upload. The installation does require that the EGPWS has
software -232-232 or later loaded. When installed, Low Airspeed Monitor operates automatically, without any action
required from the flight crew. Low Airspeed Monitor availability can be verified by performing an EGPWS self test.
See Appendix H for Low Airspeed Monitor Maintenance Messages.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 18 of 68
Page 19

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.2.21 LAMP FORMAT
The EGPWS contains two different caution/warning lamp illumination formats as described below.
Lamp Format 1 provides EGPWS warning (red) and caution (amber) alert lamp drive logic such that:
• Only a Mode 5 “Glideslope” alert will activate the caution lamp output (amber).
• All other alerts (except “windshear” and Mode 6 callouts) will activate the warning lamp output (red).
“SINK RATE, SINK RATE”
“PULL UP”
“TERRAIN, TERRAIN”
“OBSTACLE, OBSTACLE”
“CAUTION TERRAIN”
“CAUTION OBSTACLE”
“TOO LOW TERAIN”
“TOO LOW GEAR”
“TOO LOW FLAPS”
“DON’T SINK”
“
GLIDESLOPE”
Modes 1-4, TA
All caution and
warning alerts
Mode 5 only
(RED)
PULL
UP
Push toTest
(AMBER)
BELOW
GS
Push to Cancel
Lamp Format 2 provides EGPWS warning (red) and caution (amber) alert lamp drive logic such that:
• Only the warning alerts containing the phrase “Pull Up” will activate the warning lamp output (red).
• All other alerts (except “windshear” and Mode 6 callouts) will activate the caution lamp output (amber).
(RED)
All Modes, TA
All warning alerts
All Modes, TA
All caution alerts
Note: Actual legends may vary.
EGPWS caution or warning alerts lamp driver outputs are activated for all Mode 1-5 GPWS alerts and Terrain or
Obstacle alerts when enabled. Windshear warning and caution alerts activate separate lamp outputs when
enabled.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 19 of 68
PULL
UP
Push to Test
(AMBER)
GPWS
Glideslope
Push to Cancel
PULL UP”
“
“SINK RATE, SINK RATE”
“TERRAIN, TERRAIN”
“OBSTACLE, OBSTACLE”
“CAUTION TERRAIN”
“CAUTION OBSTACLE”
“TOO LOW TERAIN”
“TOO LOW GEAR”
“TOO LOW FLAPS”
“DON’T SINK”
“GLIDESLOPE”
Page 20

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.3 SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
2.3.1 MAINTENANCE PHILOSOPHY
The EGPWS is an “on-condition” only maintenance system. No scheduled maintenance is required. This is
accomplished by both continuous Built-In-Test (BIT) and event initiated test functions. Event initiated test refers to
both power-up tests and manually activated Self-Tests. Results of these functions are indicated by system status
indicators and messages so that the systems functionality can be assessed.
Detected faults are indicated to the flight crew during normal flight operations by system status annunciators or flight
display (EFIS) messages in the cockpit (i.e., GPWS INOP or FAIL, W/S INOP or FAIL, TERR INOP or NOT
AVAILABLE). On the ground, system status indications are expanded to direct fault isolation to the fault source
whether internal or external to the EGPWC. Several levels of reporting are provided by the EGPWS Self-Test, and
multiple means are provided to access the information. The intent is to provide information that will encourage the
line mechanic to correct the real problem through clear fault messages and minimal effort.
2.3.2 SYSTEM OPERATION DURING AN INOP CONDITION
EGPWS continued airworthiness is predicated on system status indications. An indication of TERR INOP (only) or
NOT AVAILABLE (only) is likely to indicate a loss of necessary GPS data for performing Terrain Alerting and
Display functions, but has no effect on basic GPWS (Modes 1-7) functions. Additionally, a GPWS INOP (only)
indicates a loss of basic GPWS functions, but this could be limited to say Mode 4 only because of a loss of
necessary data required for that mode alone. In any case, the EGPWS will provide alerting based on the current
capability of the EGPWC and its inputs.
For the MK VI and MK XXII, consideration should be given to any operation that will cross the boundaries of the
regional database. Although this has no affect on the basic GPWS functions, the enhanced (TAD/TCF) functions
will become inoperative once the aircraft leaves the database region. This is indicated by the TERR INOP or NOT
AVAILABLE status indicator and the loss of terrain display when enabled and active.
2.3.3 BIT DESCRIPTION
The EGPWC contains an extensive BIT capability. The BIT functions provide high confidence that the Warning
Computer and interface signal sources are operating properly, and that the EGPWS will perform its intended
function. Detected failures are indicated via GPWS INOP, Windshear INOP, and Terrain INOP/NA annunciations
and on the ARINC 429 bus output. Failures detected during flight are saved in the flight history and are enunciated
during Level 4 of the cockpit Self-Test. BIT status is also available through the RS-232 port by use of a PC or
terminal.
If the EGPWC detects an internal Warning Computer fault, it will turn on all the INOP lights. If the EGPWC detects
an external input fault, it may or may not turn on the INOP light(s) depending on the input fault, the type of
installation, and whether the aircraft is airborne or on the ground.
The EGPWC BIT performs three types of functions: Operation Monitoring, Operation Tests, and Restricted Tests.
Operation Monitoring consists of software checks that are performed as part of the normal Warning Computer
processing. Operation Monitoring includes checks of data values and program flow control variables used for the
warning computations to ensure they are within expected ranges. The statuses of various EGPWC hardware subsystems are continuously verified including core processor checks, voice generator circuitry checks, and ARINC
429 wrap-around tests. Operation Monitoring also includes extensive testing of the input signals to ensure the
EGPWC is using proper data for its calculations.
Operation Tests run during normal operation without disrupting the EGPWC warning calculations or annunciations.
Operations Tests include CPU instruction set tests, A/D tolerance tests, ROM check-sum verification tests, and nondestructive RAM tests. Operation Tests are scheduled by the operating system to be performed between the
routines required for normal operation.
Restricted Tests destroy data or take an excessive amount of time to complete and cannot be run during normal
system operation. These tests are usually run during system power up or during a cockpit initiated Self-Test.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 20 of 68
Page 21

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
These tests primarily consist of more thorough hardware checks that would disrupt normal operation if continuously
run.
2.3.4 EGPWC FRONT PANEL
To aid in troubleshooting the EGPWS, the front panel of the Warning Computer provides indicators and user
interfaces as follows.
2.3.4.1 EGPWS STATUS LED’S
Three LED’s on the EGPWC front panel provide a high level indication of overall system status. These are:
• a yellow “External Fault” LED
• a green “Computer OK” LED
• a red “Computer Fail” LED
The yellow “External Fault” LED indicates that a fault external to the EGPWC exists. The green “Computer OK”
LED indicates that the EGPWC is operating correctly with no internal faults. The red “Computer Fail” LED indicates
that the EGPWC has an internal fault. Further explanation of internal and external faults is given in Section
and Section 3.4.2.
3.4.1
*Useful Tip #1 – The red Computer Fail LED illuminated does not guarantee
invalid strapping/wiring (MK V/VII only) to cause the LED to illuminate. Before returning a MK V/VII for repair,
bench test the unit with power/ground applied, making sure to ground the parity pin
does not illuminate during this bench test, the aircraft wiring is causing the Computer Fail condition.
the EGPWS is failed. It is possible for
. If the red Computer Fail LED
2.3.4.2 FRONT PANEL SELF-TEST INTERFACE (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The EGPWC front panel provides a Self-Test switch for activating Self-Test features described in Section 2.3.5.
This switch functions the same as cockpit Self-Test switches.
2.3.4.3 AUDIO JACK (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
The EGPWC front panel provides a headphone jack for use during Self-Test. The audio jack is a standard 600Ω
monophonic audio output compatible with a standard 2-connector ¼" audio plug headphones.
2.3.4.4 FRONT PANEL PCMCIA INTERFACE
For the MK V and MK VII, a PCMCIA card slot is provided in the front panel. For the MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII
the PCMCIA interface utilizes an external PCMCIA interface called a “SmartCable” connected to the front panel Test
Connector.
The PCMCIA interface provides a data downloading capability (either loading a new database from a PCMCIA Card
or downloading history data from the EGPWC to a Fault History Card).
2.3.4.5 FRONT PANEL TEST CONNECTOR
The EGPWC front panel Test Connector provides communications support capabilities intended for maintenance
and test functions. For the MK V and MK VII, this includes RS-232 and 422 communications. For the MK VI, MK
VIII, and MK XXII this includes RS-232, power, and signals used for PCMCIA (SmartCable) operation. These serve
as access to EGPWS signal monitoring, flight history, initiating BITE tests, updating databases, and other functions.
The interface is full duplex and is intended for human interaction using custom interface programs such as the
Honeywell WinVIEWS
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 21 of 68
©
utility (see Appendix A).
Page 22

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
2.3.5 SELF-TEST FUNCTIONS
The EGPWC supports a manually operated Self-Test sequence for indicating the operational status of the system.
The Self-Test aurally enunciates the EGPWS status and activates outputs (lights and displays) for visual
verification. The EGPWC Self-Test includes detailed configuration and status information for the EGPWC and
aircraft installation, maintenance information detailing the cause of detected faults, and historical information about
faults and alerts that occurred during previous flights. The Self-Test Function can only be accessed while on the
ground.
NOTE: Self-Test can be inhibited based on several configuration conditions (see Self-Test Preamble section 3.3.1).
EGPWS Self-Test is divided into six levels:
• Level 1 — Identifies the status of each of the major functions of the EGPWS. This is the normal pre-flight test
performed by the flight crew.
• Level 2 — Identifies all failures currently within the system. Level 2 is accessed by maintenance personnel to
help resolve INOP conditions.
• Level 3 — Identifies the configuration status of the Warning Computer and the installation.
• Level 4 — Identifies faults that have occurred during past flights. This information can be used to resolve
system problems reported by the flight crews.
• Level 5 — Identifies alerts that have occurred during past flights. This information can be used to resolve
system problems reported by the flight crews.
• Level 6 — Identifies state changes in the input discretes. This information can be used to verify the installation
and proper function of all discrete inputs.
Self-Test aural is heard over the cockpit speaker, cockpit interphone system, or through the headphone jack on the
EGPWC front panel (MK V and MK VII only). Details of these Self-Test levels are provided in Fault Isolation
Section 3.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 22 of 68
Page 23

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3 FAULT ISOLATION (TROUBLESHOOTING)
3.1 GENERAL
The troubleshooting methods provided in this section identify system and sensor or subsystem faults to the lowest
level possible. Additional fault isolation in the installation or associated sensors or subsystem should be performed
using the aircraft installation and wiring diagrams and other supporting documentation in accordance with
established maintenance procedures.
Do not remove or replace the EGPWC until all associated sensors or subsystems and their interfaces have been
verified per established maintenance procedures and the fault is isolated to the EGPWC. If the troubleshooting
methods determine that the EGPWC is faulty, then the EGPWC should be replaced per Section 6. Route the faulty
EGPWC to an authorized repair facility for repair.
3.2 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
In general, if any EGPWS Inoperative status is indicated, the EGPWC front panel LED’s should be checked. The
following table shows the recommended maintenance action in response to the front panel LED’s.
EXTERNAL
FAULT
OFF GREEN OFF Normal operation.
YELLOW GREEN OFF Troubleshoot external faults using the Level 2 Self-
OFF OFF OFF Ensure that the EGPWC is installed in the rack
OFF OFF RED Record the Level 2 Self-Test, if possible. Remove and
OFF GREEN RED Record the Level 2 Self-Test, if possible. Remove and
YELLOW OFF OFF Troubleshoot external faults using the Level 2 Self-
YELLOW OFF RED Troubleshoot external faults using the Level 2 Self-
YELLOW GREEN RED Record the Level 2 Self-Test, if possible. Troubleshoot
A Terrain INOP light rarely implies an external or internal failure of the EGPWC. The Terrain INOP light may turn on
if the required accuracy of the position information is not being received from the GPS, IRS, or the FMC. Therefore,
if the Terrain INOP light is reported to be on (or was on), perform a Level 2 Self-Test. If no faults are present, verify
that position data from the GPS, IRS, or FMC is correct (note: this sentence does not apply to internal GPS
engines).
COMPUTER
OK
COMPUTER
FAIL
CORRECTIVE ACTION
Test. DO NOT REMOVE OR REPLACE THE EGPWC
correctly and power to the EGPWC is turned on.
replace the EGPWC if required.
replace the EGPWC if required.
Test. DO NOT REMOVE OR REPLACE THE EGPWC
Test. Remove and replace the EGPWC if required.
external faults using the Level 2 Self-Test. Remove
and replace the EGPWC if required.
NOTE: The Computer Fail Light will illuminate during some ground test procedures that use the WinVIEWS
Software utility, even although no fault exists. The EGPWS Computer Fail Light will extinguish after testing
has completed.
The following sections detail the operation of the EGPWS Self-Test and its use in troubleshooting EGPWS faults,
when initiated by EGPWS Self-Test switches in the aircraft. Reference is made to a “short cancel” and a “long
cancel”. A “short cancel” is defined as depressing the Self-Test switch (either in the cockpit or on the EGPWC front
panel) for less than 2 seconds. A “long cancel” is defined as depressing the Self-Test switch (either in the cockpit or
on the EGPWC front panel) for more than 2 seconds (but not longer than 59 seconds or a fault is indicated and SelfTest is exited). The affect of these is indicated in each section.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 23 of 68
Page 24

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.3 LEVEL 1 SELF-TEST - GO/NO GO TEST
Level 1 Self-Test provides an overview of the current operational capability of the EGPWS. It is divided into 3
functions - the Preamble, Short Level 1 Self-Test, and Long Level 1 Self-Test as described in the following sections.
During Level 1 Self-Test, a Short Cancel terminates the Self-Test level and “CURRENT FAULTS” is enunciated to
indicate activation of Level 2 Self-Test. A Long Cancel terminates the entire Self-Test sequence exiting Self-Test.
3.3.1 SELF-TEST PREAMBLE
When Self-Test is initiated, the Preamble is performed. This first step in the Self-Test process checks for
configuration errors before starting the Short or Long Level 1 Self-Test process. If any are detected, the condition is
enunciated and the Self-Test process is automatically terminated (inhibited). These are listed below with the
associated probable cause and action.
TABLE 3-1: POSSIBLE PREAMBLE RESULTS
POSSIBLE SELF-TEST PREAMBLE RESULTS
Enunciation:
“PROGRAM PIN PARITY ERROR” (MK V or MK VII only)
Probable Cause: Wiring error in the program pins.
Action: Verify wiring to each program pin. Verify ODD parity selected.
Enunciation:
“AIRCRAFT TYPE INVALID” (MK V or MK VII only)
Probable Cause: Wiring error to the Aircraft Type program pins.
Action: Verify wiring to the Aircraft Type program pins.
Enunciation:
“CONFIGURATION TYPE INVALID” (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)
Probable Cause: The programmed configuration type is not a valid configuration.
Action: Correct and reprogram the Configuration Module (see Maintenance Practices section)
Enunciation:
“AIRCRAFT CONFIGURATION DATA BASE FAILED” (MK V or MK VII only)
Probable Cause: EGPWC internal Configuration database error.
Action:
Enunciation:
Pull power to the EGPWS for one minute and cycle power to clear all potential faults before
removing or replacing the EGPWC for repair (see Removal/Installation section)
“ APPLICATION DATA BASE FAILED” (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)
Probable Cause: EGPWC internal Application database error.
Action:
Enunciation:
Pull power to the EGPWS for one minute and cycle power to clear all potential faults before
removing or replacing the EGPWC for repair (see Removal/Installation section)
“AIRCRAFT CONFIGURATION DATA BASE CRC FAILED” (MK V or MK VII only)
Probable Cause: EGPWC internal configuration database error.
Action:
Pull power to the EGPWS for one minute and cycle power to clear all potential faults before
removing or replacing the EGPWC for repair (see Removal/Installation section)
Enunciation:
“ APPLICATION DATA BASE CRC FAILED” (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)
Probable Cause: EGPWC internal Application database error.
Action:
Enunciation:
Pull power to the EGPWS for one minute and cycle power to clear all potential faults before
removing or replacing the EGPWC for repair (see Removal/Installation section)
“CONFIGURATION MODULE READ ERROR” (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)
Probable Cause: The Configuration Module is faulty.
Verify Configuration Module connections. Cycle power to the EGPWC. If the problem
Action:
persists, reprogram the Configuration Module. IF the condition persist, replace the
Configuration Module. See Removal/Installation section.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 24 of 68
Page 25

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
POSSIBLE SELF-TEST PREAMBLE RESULTS
Enunciation:
Probable Cause: The Configuration Module is not programmed.
Action: Program the Configuration Module. See Maintenance Practices section.
Enunciation:
Probable Cause: The Configuration Module is not compatible with the EGPWC h/w or s/w or it’s faulty.
Action:
Enunciation:
Probable Cause: The “Audio Inhibit” or both “GPWS Inhibit” and “Terrain Inhibit” discrete inputs are true.
Action: Deselect or remove these inputs.
Enunciation:
Probable Cause: The “GPWS Inhibit” discrete input is true (selected) and “Terrain Inhibit” is not.
Action: Deselect or remove this input.
Enunciation:
Probable Cause: The “Steep Approach” input discrete(s) is enabled and active (selected).
Action: Deselect or remove this input (cockpit switch).
“CONFIGURATION MODULE NOT PROGRAMMED” (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)
“CONFIGURATION MODULE NOT COMPATIBLE” (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII only)
Verify Configuration Module connections. Cycle power to the EGPWC. If the problem
persists, reprogram or replace the Configuration Module (see Removal/Installation section).
“GPWS INHIBITED”, “TERRAIN INHIBITED”
“GPWS INHIBITED”
“SELF-TEST INHIBITED”
3.3.2 SHORT LEVEL 1 SELF-TEST
The Short Level 1 Self-Test is intended to provide a Go/No Go confidence test to indicate EGPWS functionality. It
indicates which Modes of the EGPWC are currently not available and activates system outputs. The short Level 1
Self-Test is a subset of the Long Level 1 Self-Test.
Upon successful completion of the preamble the short Self-Test is started. A Short Level 1 Self-Test sequence
(following the Preamble) is as follows:
• GPWS INOP, Windshear INOP, Terrain INOP (or Terrain Not Available) lights turn on *
• Amber caution (GPWS or Below G/S) lights turn on
• Voice: “GLIDESLOPE”
• Amber caution (GPWS or Below G/S) lights turns off
• G/S Cancel light turns on (if installed)
• G/S Cancel light turns off (if installed)
• Red Warning (Pull Up or GPWS) lights turns on
• Voice: “PULL UP”
• Red Warning (Pull Up or GPWS) lights turns off
• Red Windshear Warning lights turns on
• Voice: “(SIREN) WINDSHEAR, WINDSHEAR, WINDSHEAR”
• Red Windshear Warning lights turns off
• Amber Windshear Caution lights turns on (if installed)
• Amber Windshear Caution lights turns off (if installed)
• Red Warning (Pull Up or GPWS) lights turns on
• Voice: “TERRAIN, TERRAIN, PULL UP” (or “WARNING TERRAIN” for MK XXII)
• Terrain test pattern is displayed
• If RAAS is enabled, a RAAS Maintenance Message from Table C1-1 will be enunciated.
• If Stabilized Approach Monitor is enabled but inoperative or inhibited, it will be enunciated.
• If Altimeter Monitor is enabled but inoperative, it will be enunciated.
• If Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor is enabled but inoperative or inhibited, it will be enunciated.
• If Low Airspeed Monitor is enabled, a Maintenance Message from Table H1-1 will be enunciated.
• Red Warning (Pull Up or GPWS) lights turns off
• Terrain test pattern is turned off (after several sweeps)
• GPWS INOP, Windshear INOP, and Terrain INOP (or Terrain Not Available) lights turn off
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 25 of 68
Page 26

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
Installations that do not have the windshear function or the function enabled will not enunciate the windshear
message and illuminate windshear alert lights. Similarly, installations without the Terrain Alerting and Display (TAD)
function enabled will not have terrain lights and display or “TERRAIN” aural enunciation.
• NOTE: The general sequence of the LEVEL 1 SELF-TEST is the same for all installations. The actual
aural message and nomenclature of the Alert/warning lamps will vary.
• NOTE: Ensure that none
listed in Appendix C of this document is enunciated during the Level 1 Self-Test or terrain display range
changes (respectively) unless RAAS is activated for your aircraft. See the applicable aircraft AFMS and/or
Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICAW) documentation to determine if RAAS is activated.
• NOTE: An enunciation of “GPS NOT NAVIGATING” during the Level 1 Self-Test indicates that the Internal P-
xPress GPS engine has not acquired sufficient satellites to navigate. If this message is enunciated, ensure the
aircraft is in full view of the constellation for at least 20 minutes. If this does not resolve the enunciation, verify
all interfaces of the coax cable from the antenna to the EGPWC.
of the RAAS maintenance messages or RAAS On-Ground (display) status messages
3.3.3 LONG LEVEL 1 SELF-TEST
The Long Level 1 Self-Test is initiated by pressing and holding Self-Test until Self-Test voices start. The Long Level
1 Self-Test enunciates all configured and activated alert voices, including warning voices, caution voices, and
altitude callout voices immediately following the Short Level 1 Self-Test sequence above.
3.4 LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST - CURRENT FAULTS
Level 2 Self-Test provides enunciation of all faults existing at the time of the test request. Level 2 Self-Test is
initiated by pressing Self-Test within 3 seconds of the end of Level 1 Self-Test or following a short cancel during
Level 1 Self-Test.
If a fault is detected, it will be classified as either an internal or an external fault. Internal faults are defined as those
faults that originate within the EGPWC. Internal faults will turn on the red “COMPUTER FAIL” LED on the EGPWC
front panel. External faults are defined as those faults that originate from sources outside the EGPWC. External
faults will turn on the amber “EXTERNAL FAULT” LED on the EGPWC front panel.
Note that for the EGPWS/GNSSU (-060 MK V/VII), both internal and external fault lights will be lit if there is a
problem with the integral GNSSU subsystem.
If the EGPWC is connected to a GPS or GNSSU for position information (internal or external), various navigation
data status messages may also be listed during Level 2 Self Test. These messages indicate that there is a problem
with the position data, caused by antenna problems, satellite visibility or multi-path errors.
*Useful Tip #2 – Pressing the GPWS test switch for more than 2 seconds during Level 2 through 5 will bypass the
test information and will immediately jump to the end of that level (“PRESS TO CONTINUE” voice). GPWS INOP,
Windshear INOP, and Terrain INOP (or Terrain Not Available) lights are turned on (or remain on) for the duration of
the Level 2 Self-Test.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 26 of 68
Page 27

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.4.1 CURRENT FAULTS - INTERNAL
An internal fault indicates a problem with the EGPWC. The following table lists the internal fault messages and the
probable maintenance response.
Note: “NO FAULTS” is enunciated for Level 2 Self-Test if no faults are present.
TABLE 3-2: LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST - INTERNAL FAULTS
Enunciation:
Probable Cause: EGPWC failure
Action: Remove and replace the EGPWC.
ROM FAILED
RAM FAILED
NVM RAM FAILED
NVM FAILED
WATCHDOG TIMER TEST FAILED
EXCESSIVE WATCHDOG TIMEOUTS FAILURE
ANALOG CONVERTER FAILED*
VOICE GENERATOR FAILED
ARINC 429 TRANSMITTER FAILED
ARINC 429 RECEIVER FAILED
FLASH FILE SYSTEM WRITE FAILED (fixed by MK VI, VIII, XXII Hardware Mod 2)
APPLICATION DATABASE FAILED (DSP or CRC)
TERRAIN DATABASE FAILED (CRC or Runway or Mag. Var.)***
TERRAIN DATABASE NOT COMPATIBLE
ENVELOPE MODULATION DATABASE FAILED
CONFIGURATION DATABASE FAILED (MK V/VII)
APPLICATION DATABASE FAILED (MK VI/VIII/XXII )
CONFIGURATION DATABASE AAC DATA FAULT
SYSTEM OR MODE TASK FAILED
SUPPORT TASK FAILED
INTERNAL GPS FAILED**
APPLICATION SOFTWARE VERSION INVALID
RCD FAILED (MK V/VII)
Notes: If external faults also exist, these should be eliminated, and the internal faults rechecked before the EGPWC
is removed and replaced.
* Power unit on bench with parity pin strapped, and verify the failure is cleared.
** If the EGPWC incorporates the integral Mercury GNSSU (-060 hardware part numbers), both internal and
external faults will be indicated. This fault can also be indicated if there is no antenna connection to the GNSSU.
Before replacing the EGPWC/GNSSU, ensure that the antenna is connected and that no antenna wiring breaks
exist.
*** Invalid Latitude/Longitude causes a Mag Var table fault which may be annunciated as “Terrain Database Failed”
This can be caused by not connecting the GPS antenna.
3.4.2 CURRENT FAULTS - EXTERNAL
An external fault indicates a problem with an external sensor, system, or wiring. External faults are further broken
down in to sub-categories; Discrete Faults, ARINC 429 Bus Activity Faults, Analog Input Wire Monitoring Faults,
ARINC 429 Signal Faults, Analog Signal Faults, and Program Pin or Configuration Module Faults. The following
table provides a few examples of these.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 27 of 68
Page 28

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
TABLE 3-3: CURRENT FAULTS - EXTERNAL (EXAMPLES)
FAULT EXAMPLE REASON
ARINC 429 Bus Fault GPS BUS 1 INACTIVE No expected input labels received for more
than 4 seconds
ARINC 429 Signal
Fault
ARINC 429 Signal
Fault
Analog Signal Fault RADIO ALTIMETER 1 WIRING
AOA UNREASONABLE FAULT AOA is not within 4 degrees of waterline
Discrete Input Faults FLAP SWITCH FAULT Indicates Landing Flaps for > 60 seconds with
GEAR SWITCH FAULT Indicates Landing Gear for > 60 seconds with
AUDIO CANCEL INVALID Discrete selected for > 30 seconds.
TERRAIN INHIBIT INVALID Discrete selected for > 60 seconds.
GPWS INHIBIT INVALID Discrete selected for > 60 seconds.
ALL MODES INHIBIT INVALID Discrete configured to suppress both audio
GLIDESLOPE CANCEL INVALID Discrete selected for > 15 seconds.
ILS SELECT INVALID More than 1 discrete selected for > 5
FLAP ANGLE UNREASONABLE Invalid combination selected for > 30
RANGE UNREASONABLE No valid range provided for > 5 seconds.
SELF-TEST INVALID Discrete selected for > 60 seconds.
AIR GROUND INVALID Indicates On-Ground for > 60 seconds with an
MOMENTARY TERRAIN
ILS BUS 1 GLIDESLOPE FAULT FW The SSM of the input data indicates
Failure/Warning
Note: Only the RS232 present Status will
report the ‘FW” part of the fault.
ILS BUS 1 GLIDESLOPE FAULT UPD The input label is not meeting the required
update rate.
Note: Only the RS232 present Status will
report the ‘UPD” part of the fault.
Open wire monitoring has detected no
FAULT
connection.
during takeoff roll (60-90 knots). Incorrect
Aircraft Configuration or AOA potentiometer is
Worn.
an airspeed > 250 knots, or indicates Not
Landing Flaps for more than 2 seconds with
“Too Low Flaps” message below 100 feet.
an airspeed > 290 knots, or indicates Not
Landing Gear for more than 2 seconds with
“Too Low Gear” message below 100 feet.
and visual outputs and selected for > 60
seconds.
Or if aircraft type is configured for ‘Audio
Inhibit Monitoring’ then activation for > 60
seconds to inhibit only audio will cause this
fault.
seconds.
seconds.
airspeed > 290 knots.
Selected for > 15 seconds.
SELECT 1 (or 2) INVALID
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 28 of 68
Page 29

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
TABLE 3-4: LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST - EXTERNAL FAULTS
THE FOLLOWING EXTERNAL FAULTS ARE AVAILABLE IN LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST:
Enunciation:
“<BUS> Inactive”
Example: GPS BUS 1 Inactive
Probable Cause:
Action:
Enunciation:
Input source not powered or a wiring problem exists between source LRU and the
EGPWC.
Verify input source LRU is powered. Verify wiring from the source LRU. Verify program pin
configuration.
“<BUS><SIGNAL> FAULT”
Example: ILS BUS 1 GLIDESLOPE FAULT
Probable Cause:
Input signal SSM = Fail Warning, or Input signal is not being transmitted (incorrect update
rate).
Action: Repair input signal.
Enunciation:
“<SIGNAL> FAULT ESE” (See Table 3-5 for other failure codes)
Probable Cause: External signal is outside reasonable limits
Action: Verify signal scaling
Enunciation:
“<BUS> WIRING FAULT”
Example: RADIO ALTIMETER 1 WIRING FAULT
Probable Cause: Open wire monitor has detected no connection from the source LRU.
Action: Verify wiring from the source LRU.
Enunciation:
“FLAP SWITCH FAULT”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the flap discrete input.
Action: Verify wiring from the flap override switch and/or flap input discretes.
Enunciation:
“GEAR SWITCH FAULT”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the gear discrete input.
Action: Verify wiring from the gear override switch and/or gear input discrete.
Enunciation:
“AUDIO CANCEL INVALID”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the audio cancel input.
Action: Verify wiring from the audio cancel switch.
Enunciation:
“ALL MODES INHIBIT INVALID”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the audio cancel input.
Action: Verify wiring from the audio cancel input.
Enunciation:
“GLIDESLOPE CANCEL INVALID”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the glideslope cancel input.
Action: Verify wiring from the glideslope cancel input.
Enunciation:
“ILS SELECT INVALID”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the ILS Select inputs.
Action: Verify wiring from the ILS Select switches.
Enunciation:
“FLAP ANGLE UNREASONABLE”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the flap discrete input(s).
Action: Verify wiring from the flap-input discrete(s).
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 29 of 68
Page 30

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
THE FOLLOWING EXTERNAL FAULTS ARE AVAILABLE IN LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST:
Description:
SELF-TEST INVALID (WinVIEWS ONLY)
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the Self-Test input.
Action: Verify wiring from the Self-Test discrete.
Enunciation:
“MOMENTARY TERRAIN SELECT 1 (or 2) INVALID”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the Terrain Select inputs.
Action: Verify wiring from the terrain “ON” switches.
Enunciation:
“PROGRAM PIN READ ERROR”
Probable Cause: Wiring error to the program pins.
Action: Verify wiring to each program pin.
Enunciation:
“CALLOUTS OPTION INVALID”
Probable Cause: Wiring error to the Callout Options program pins.
Action: Verify wiring to the Callout Options program pins.
Enunciation:
“AUDIO MENU INVALID”
Probable Cause: Wiring error to the Audio Menu program pins.
Action: Verify wiring to the Audio Menu program pins.
Enunciation:
“PROGRAM PIN <XX> INVALID” (where XX is a number)
Probable Cause: Invalid option selected.
Action: Verify wiring to all program pins.
Description: “CONFIGURATION MODULE READ ERROR” (WinVIEWS ONLY)
Probable Cause: The Configuration Module is faulty.
Action: Cycle power to EGPWC. If fault persists, reprogram or replace the Configuration Module.
Description: “CONFIGURATION MODULE NOT PROGRAMMED” (WinVIEWS ONLY)
Probable Cause: The Configuration Module is new, or never has been programmed.
Action: Reprogram the Configuration Module. See Appendix C.
Description: “CONFIGURATION MODULE NOT COMPATIBLE (WinVIEWS ONLY)
Probable Cause: The Configuration Module is faulty.
Action:
Cycle power to the EGPWC. If the persist reprogram the Configuration Module. If the
condition persist, replace the Program Module. See Appendix C.
Description: “SUPPORT TASK FAILED”
Probable Cause: Fault History Memory Full.
Action: Erase Fault History.
Description: “SYSTEM OR MODE TASKED FAILED”
Probable Cause: Conflicting Configuration of the same channel.
Action: Check configuration of channels.
Description: “MOMENTARY FLAP OVERRIDE INVALID”
Probable Cause: Electrical short at the Flap Override input.
Action: Verify wiring from the Flap Override Switch.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 30 of 68
Page 31

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
TABLE 3-5: GENERAL FAILURE CODE IDENTIFIERS
For example, if the Computed Airspeed from Air Data Computer #1 is failed (i.e., SSM = Fail Warning), the following
messages would be enunciated:
“CURRENT FAULTS”
“EGPWC OK”
“EXTERNAL FAULTS”
“AIR DATA BUS 1 COMPUTED AIRSPEED FAULT”
“PRESS TO CONTINUE”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 31 of 68
Page 32
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
NOTE: Before attempting to correct an external fault, verify that the EGPWS installation configuration matches the
aircraft configuration. If the installation configuration and aircraft configuration does not match, check the Program
Pin or Configuration Module connections being sure to cycle power to the EGPWC in the process. If an incorrect
aircraft configuration exists, the Program Pins must be changed or the Configuration Module may need to be
reprogrammed (see Maintenance Practices) or replaced (see Removal/Installation section).
If the unit is a MK V or MK VII with integral GNSSU (-060 part number), and external faults are indicated on GPS
signals (e.g., GPS BUS 1 LATITUDE FAULT), an internal fault may exist. In this case both fault lights will be on and
the message INTERNAL GPS FAULT will also be indicated. This condition can also be caused by a disconnected or
broken antenna wire. Ensure good antenna connection before replacing the EGPWS/GNSSU.
If no faults are detected, the following messages will be enunciated:
“CURRENT FAULTS”
“NO FAULTS”
“PRESS TO CONTINUE”
If no faults are detected, but the GPS or GNSSU are not navigating properly, navigation status messages may be
enunciated as follows:
“CURRENT FAULTS”
“NO FAULTS”
Navigation Status Messages “PRESS TO CONTINUE”
The list of possible navigation problems is listed in Table 3–6. In these instances, no fault lamps will be lit on the
unit, however, TERRAIN INOP or TERRAIN UNAVAILABLE will be indicated on the Flight Deck.
TABLE 3-6: LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST – NAVIGATION STATUS MESSAGES
THE FOLLOWING GPS STATUS MESSAGES ARE AVAILABLE IN LEVEL 2 SELF-TEST:
Enunciation:
“TERRAIN AWARENESS NO VALID LATITUDE”
Probable Cause: GPS/GNSSU has not acquired a sufficient number of satellites.
Action:
Enunciation:
Remove aircraft from hanger and wait 5 to 20 minutes for the GPS/GNSSU acquire a
sufficient number of satellites. Verify cabling and antenna connection for the GPS/GNSSU.
“TERRAIN AWARENESS NO VALID LONGITUDE”
Probable Cause: GPS/GNSSU has not acquired a sufficient number of satellites.
Action:
Enunciation:
Remove aircraft from hanger and wait 5 to 20 minutes for the GPS/GNSSU acquire a
sufficient number of satellites. Verify cabling and antenna connection for the GPS/GNSSU.
“TERRAIN INOP”
Probable Cause: GPS/GNSSU has not acquired a sufficient number of satellites.
Action:
Remove aircraft from hanger and wait 5 to 20 minutes for the GPS/GNSSU to acquire
sufficient number of satellites. Verify cabling and antenna connection for the GPS/GNSSU.
Description: “TERRAIN AWARENESS-POSITION ERROR”
Probable Cause:
GPS/GNSSU has not acquired a sufficient number of satellites
or ARINC [743A / 743] setting incorrect.
Remove aircraft from hanger and wait 5 to 20 minutes for the GPS/GNSSU to acquire
Action:
sufficient number of satellites. Verify cabling and antenna connection for the GPS/GNSSU.
Verify correct 743A / 743 configuration.
Enunciation:
Probable Cause:
“TERRAIN CLEARANCE FLOOR POSITION ERROR”
GPS/GNSSU has not acquired a sufficient number of satellites
or ARINC [743A / 743] setting incorrect.
Remove aircraft from hanger and wait 5 to 20 minutes for the GPS/GNSSU to acquire
Action:
sufficient number of satellites. Verify cabling and antenna connection for the GPS/GNSSU.
Verify correct 743A / 743 configuration.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 32 of 68
Page 33

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.5 LEVEL 3 SELF-TEST - SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
A Level 3 Self-Test enunciates EGPWC configuration information. Level 3 is accessed while the aircraft is on the
ground by pressing the EGPWS test switch within 3 seconds of the “PRESS TO CONTINUE” message at the end of
the Level 2 test. The message “SYSTEM CONFIGURATION” will be enunciated when Level 3 starts.
During a Level 3 Self-Test, a short cancel bumps the enunciation to the next Level 3 item (e.g. from terrain database
information to envelope modulation database information). A long cancel terminates the Self-Test level and “PRESS
TO CONTINUE” is enunciated for proceeding to Level 4 Self-Test.
TABLE 3-7: LEVEL 3 SELF-TEST INFORMATION
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS GIVEN IN THE LEVEL 3 SELF-TEST:
1. Part Number
2. Mod Status
3. Serial Number
4. Application Software Version or (only for PNs 965-1676-XXX and 965-1690-XXX) Software Version
5. Configuration Software Version (only for PNs 965-0976-XXX or 965-1076-XXX)
6. Terrain Database Version
7. Envelope Modulation Database Version
8. Boot Code Version
9. RAAS RCD Part Number (MK V/VII and RAAS enabled only)
10. Aircraft Type
11. Audio Menu
12. Altitude Callout Menu
13.
All other selected options from installation configuration. Note that only those features that are enabled or disabled
from the basic configuration are enunciated. The order of the enunciation will vary depending on Aircraft
configuration.
“SMART CALLOUT SELECTED”
“AUDIO DECLUTER DISABLED”
“ARINC 743 GPS SELECTED”
“WINDSHEAR CAUTION WITH VOICE SELECTED”
“TERRAIN CLEARANCE FLOOR DISABLED”
“TERRAIN AWARENESS DISABLED”
“BANK ANGLE SELECTED”
“OBSTACLE AWARENESS SELECTED”
“PEAKS ENABLED”
“INTERNAL GPS SELECTED”
“FLASH “L” “A” “M” “P” “S” SELECTED” -204-204 software versions and earlier
"FLASHING LAMP SELECTED" -206-206 software versions and later
“POP-UP DISABLED”
“FLAP “R” ”E” “V” SELECTED” -204-204 software versions and earlier
"FLAP REVERSAL SELECTED" -206-206 software versions and later
"FLAP “W” “O” “W” REVERSAL SELECTED" (MK XXII)
“MODE SIX LOW VOLUME SELECTED” (discrete)/ “MODE 6 Low Volume Program Pin Selected “ (pp12)
“AUDIO INHIBIT MONITOR SELECTED”
“EGPWS INHIBITED”
“GLIDESLOPE INHIBITED”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 33 of 68
Page 34

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS GIVEN IN THE LEVEL 3 SELF-TEST:
“IRS 1 ATTITUDE MODE SELECTED”
“ MODE 6 INOP-NO Decision Height” (approaching minimums in menu).
“STEEP APPROACH ACTIVATED”
“STEEP APPROACH ENABLED”
“STEEP APPROACH SELECTED”
“VISUAL SUPPRESS ENABLED”
“ALTERNATE VOLUME 1 SELECTED”
“QFE SELECTED”
“ALTN G/S CANCEL”
“OPTIONAL INPUTS SELECTED”
“SINGLE GPS SELECTED”
“DUAL GPS SELECTED”
“SINGLE GPIRS SELECTED”
“DUAL GPIRS SELECTED”
“DUAL ILS SELECTED”
“DUAL RA SELECTED”
“TRIPLE RA SELECTED”
““WINDSHEAR DISABLED”
“WINDSHEAR INOP DISABLED”
“SIM REPOSITION ENABLED”
“BANK ANGLE DISABLED”
“ALTERNATE RA 1 SELECTED “
“ALTERNATE RA 2 SELECTED “
“ALTN GPS BUS SPEED SELECTED “
“PWS OPTION 1 SELECTED “
“’PWS OPTION 2 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE POP UP SELECTED “
“BANK ANGLE OPTION 1 SELECTED”
“BANK ANGLE OPTION 2 SELECTED”
“CONFIGURATION OPTION 1 SELECTED”
“CONFIGURATION OPTION 2 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE MODE 4B REV SELECTED”
“LAMP FORMAT 2 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 1 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 2 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 3 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 4 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 5 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 6 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 7 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 8 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE DISPLAY 9 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE VOLUME 2 SELECTED”
“ALTERNATE MODE 6 VOLUME” SELECTED”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 34 of 68
Page 35

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS GIVEN IN THE LEVEL 3 SELF-TEST:
“GPS ALTITUDE REF WGS84 SELECTED”
“AUTOROTATION CALLOUT X SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“NORMAL POPUP RANGE X SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“LOW ALTITUDE POPUP RANGE X SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“MODE 6B ALWAYS ON SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“NORMAL TERRAIN WITH AIRSPEED SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“LOW ALTITUDE WITH AIRSPEED SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“SAR LOW ALTITUDE SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“AUDIO INHIBIT TIME X” (MK XXII)
“INHIBIT ALL EXCEPT MINIMUMS TYPE CALLOUT AND 100 CALLOUT SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“INHIBIT ALL EXCEPT MINIMUMS TYPE CALLOUT SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“INHIBIT TOO LOW GEAR SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“INHIBIT RUNWAY CALLOUTS 50 AND BELOW SELECTED” (MK XXII)
“ALTERATE DECISION HEIGHT SELECTED” (MK XXII)
* “RUNWAY AWARENESS ENABLE SET” OR “RUNWAY AWARENESS ENABLED”
* “APPROACH MONITOR ENABLED”
* “FLAPS MONITOR ENABLED”
* “ALTIMETER MONITOR ENABLED”
* “LONG LANDING ENABLED”
* “AIRSPEED LOW INHIBITED”
*Ensure that none
enunciated during the Level 3 Self-Test or terrain display range changes (respectively) unless these optional
functions are activated for your aircraft. See the applicable aircraft AFMS and/or Instructions for Continued
Airworthiness (ICAW) documentation to determine if these functions are activated.
of these maintenance messages above or listed in Appendix C through H of this document are
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 35 of 68
Page 36

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.6 LEVEL 4 SELF-TEST - FAULT HISTORY
Level 4 Self-Test provides enunciation of the faults recorded over the last 10 flight legs. Level 4 Self-Test is initiated
by pressing the cockpit Self-Test button within 3 seconds of the end of Level 3 Self-Test.
If any faults were recorded in the last ten flight legs then voice sequence as described in the following table will be
enunciated. Otherwise, the message “NO FAULTS” will be enunciated.
During Level 4 Self-Test, a Short Cancel bumps the enunciation to the next flight leg with faults (if any).
During Level 4 Self-Test, a Long Cancel terminates the Self-Test level and “PRESS TO CONTINUE” is enunciated
for proceeding to Level 5 Self-Test.
TABLE 3-8: LEVEL 4 SELF-TEST INFORMATION
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS GIVEN IN THE LEVEL 4 SELF-TEST:
Enunciate the number of the most recent flight leg with faults as “FLIGHT X”, where “X” is a number from 1
1.
to 10 where 1 is the most recent flight leg
2. Enunciate any internal faults stored for leg X
3. Enunciate any external faults stored for leg X
4. Increment to next oldest leg with faults (if any) and repeat the above sequence
5. Test proceeds to the next flight leg that contains a fault.
For Example:
If a fault occurred within the previous 10 flight legs the aural messages enunciated will be the same as given in
Level 2 with the added information of which flight leg the fault occurred. For example, if radio altimeter bus 1 failed 4
flights earlier the messages would be:
“FLIGHT 4”
“EGPWC OK”
“EXTERNAL FAULTS”
“RADIO ALTIMETER BUS 1 INACTIVE”
“PRESS TO CONTINUE’
Note that flight 1 is the most recent flight.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 36 of 68
Page 37

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.7 LEVEL 5 SELF-TEST - ALERT HISTORY
Level 5 Self-Test provides enunciation of the alerts (cautions and warnings) recorded over the last 10 flight legs.
Level 5 Self-Test is initiated by pressing the cockpit Self-Test button within 3 seconds of the end of Level 4 SelfTest.
If any alerts were recorded in the last ten flight legs then voice sequence as described in the following table will be
enunciated. Otherwise, the message “NO WARNINGS” will be enunciated.
During Level 5 Self-Test, a Short Cancel bumps the enunciation to the next flight leg with faults (if any).
During Level 5 Self-Test, a Long Cancel terminates the Self-Test level and “PRESS TO CONTINUE” is enunciated
for proceeding to Level 6 Self-Test.
TABLE 3-9: LEVEL 5 SELF-TEST INFORMATION
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION IS GIVEN IN THE LEVEL 5 SELF-TEST:
1. Enunciate the number of the most recent flight leg with alerts as “FLIGHT X”, where “X” is a number from 1
to 10 where 1 is the most recent flight leg
2. Enunciate any alerts stored for leg X
3. Increment to next oldest leg with alerts (if any) and repeat the above sequence
For Example:
If a glideslope alert were given 7 flight legs earlier, the messages would be:
“WARNING HISTORY”
“FLIGHT 7”
“GLIDESLOPE”
“PRESS TO CONTINUE”
3.8 LEVEL 6 SELF-TEST - DISCRETE INPUT TEST
Level 6 Self-Test provides enunciation of any changes in the status of discrete inputs for verification proper function
and discrete input wiring. Level 6 Self-Test is initiated by pressing the cockpit Self-Test button within 3 seconds of
the end of Level 5 Self-Test. The results are indicated in the following sections.
If a state change occurs on any discrete input (other than the Self-Test input as it is directly tested in its use to
control the test sequences), the EGPWC will annunciate the functional name of the discrete followed by its new
state. For example, if the Glideslope Cancel discrete input in the current configuration is defined as ground =
cancel, and the discrete transitions from open to ground, Level 6 Self-Test will say: “GLIDESLOPE CANCELED”. If
the input is only momentarily grounded Level 6 Self-Test will say: “GLIDESLOPE CANCELED - GLIDESLOPE
ENABLED.”
NOTE: Not all discretes are used in an installation; therefore, unused discretes shall not apply. See aircraft wiring
diagrams to determine applicable discretes.
During Level 6 Self-Test the message “DISCRETE INPUT TEST - PRESS TO CANCEL” is enunciated every 60
seconds. This provides additional evidence; along with the continued illumination of the INOP lights/fail
annunciations, that Self-Test is still in progress.
During Level 6 Self-Test, a Short Cancel or Long Cancel terminates Self-Test and “END OF SELF-TEST” is
enunciated. As with all Self-Test levels, if the aircraft goes in air, then Self-Test is terminated.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 37 of 68
Page 38

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.1 ARINC 552 / ALT 55 RADIO ALTITUDE VALIDITY FLAG DISCRETES
Three Radio Altitude validity flags may be used by the EGPWS, one for each of the three possible ARINC 552 or
ALT 55 Radio Altimeters inputs.
Type Validity from ARINC 552 or ALT 55 Radio Altimeter.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Radio Altitude Validity Discrete #1
Radio Altitude Validity Discrete #2
Radio Altitude Validity Discrete #3
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Radio Altimeter 1 Valid”
“Radio Altimeter 1 Invalid”
“Radio Altimeter 2 Valid”
“Radio Altimeter 2 Invalid”
“Radio Altimeter 3 Valid”
“Radio Altimeter 3 Invalid”
3.8.2 GND LANDING GEAR DISCRETE
Type Supplied by landing gear or landing gear selector handle position-sensitive switch. This input can
be paralleled with, or used exclusively by a Gear Override Switch if an alternate source of Gear
Position is used.
Signal Status: Landing Gear Down or Landing Gear Up
Fault monitoring: Indication of landing gear selected for more than 60 seconds at airspeeds above 290 knots will
result in a gear switch fault which will cause a GPWS INOP indication.
Note: This can be caused either by a gear switch fault or by the Gear Override switch being left in the on position.
Landing Gear Discrete
or Gear Override
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
“Landing Gear Down”
“Landing Gear Up”
3.8.3 +28V LANDING GEAR DISCRETE
Type Supplied by landing gear or landing gear selector handle position-sensitive switch. This input can
be paralleled with, or used exclusively by a Gear Override Switch if an alternate source of Gear
Position is used.
Signal Status: Landing Gear Down or Landing Gear Up
Fault monitoring: Indication of landing gear selected for more than 60 seconds at airspeeds above 290 knots will
result in a gear switch fault which will cause a GPWS INOP indication.
Note: This can be caused either by a gear switch fault or by the Gear Override switch being left in the on position.
+28 V Landing Gear Discrete
or Gear Override
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 38 of 68
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
“28V Landing Gear Down”
“28V Landing Gear Up”
Page 39

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.4 GND LANDING FLAP DISCRETE OR FLAP OVERRIDE
Type: Supplied by Flap or Flap selector handle switch. This input can be paralleled with, or used
exclusively by a Flap Override Switch if an alternate source of Flap Position is used.
Signal Status: Landing Flaps or Not Landing Flaps
Fault monitoring: Indication of landing flaps selected for more than 60 seconds at airspeeds above 250 knots will
result in a flap switch fault which will cause a GPWS INOP indication.
Note: This can be caused either by a flap switch fault or by the Flap Override switch being left in the on position.
GND Landing Flaps Discrete
or Flap Override
Note: If Flap Reversal Program Pin is enabled for MK VII EGPWC, the Audio readout will be:
GND Landing Flaps Discrete
or Flap Override
Not Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
“Flaps Selected”
“Flaps Not Selected”
“Flaps Selected”
“Flaps Not Selected”
3.8.5 +28V LANDING FLAP OR FLAP OVERRIDE DISCRETE
Type: Supplied by Flap or Flap selector handle switch. This input can be paralleled with, or used
exclusively by a Flap Override Switch if an alternate source of Flap Position is used.
Signal Status: Landing Flaps or Not Landing Flaps
Fault monitoring: Indication of landing flaps selected for more than 60 seconds at airspeeds above 250 knots will
result in a flap switch fault which will cause a GPWS INOP indication.
Note: This can be caused either by a flap switch fault or by the Flap Override switch being left in the on position.
+28 V Landing Flaps Discrete
or Flap Override
Note: If Flap Reversal Program Pin is enabled for MK VII EGPWC, the Audio readout will be:
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
“28V Flaps Selected”
“28V Flaps Not Selected”
GND Landing Flaps Discrete
or Flap Override
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 39 of 68
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
“Flaps Selected”
“Flaps Not Selected”
Page 40

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.6 FLAP POSITION DISCRETES
Up to four flap position discretes are typically supplied from the flap selector handle switch.
Type: Supplied by Flap selector handle switch.
Signal Status: Flap position selected.
Fault monitoring: Depending on the installation, activation of more than one, or none of these discretes for more
than 30 seconds will result in a Flap Unreasonable indication.
Flap Position Discrete #1 Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Flap Position Discrete #2 Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Flap Position Discrete #3 Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Flap Position Discrete #4 Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Flap 1 True”
“Flap 1 False”
“Flap 2 True”
“Flap 2 False”
“Flap 3 True”
“Flap 3 False”
“Flap 4 True”
“Flap 4 False”
3.8.7 SELF-TEST DISCRETE
Type: Supplied by momentary actuated cockpit self-test switch
Signal Status: Self-Test or Normal
Fault monitoring: Activation of this input continuously for more than 60 seconds will result in the "Self-Test Invalid”
fault which will cause a GPWS INOP indication.
Note: This input is used to start and stop the Level 6 Self-Test, there is no audio output for this discrete in Level 6.
3.8.8 STEEP APPROACH DISCRETES
To activate Steep Approach, both of the Steep Approach discretes must be selected. Discrete #1 should be enabled
if Steep Approach is to be used, and can be permanently enabled. Discrete #2 should be selected in flight when
starting a steep approach, it should not be permanently selected. On ground Self-Test is inhibited if Steep Approach
is active.
3.8.8.1 STEEP APPROACH DISCRETE #1 (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Steep Approach Enabled
Signal Status: Steep Approach Enabled or Disabled
Steep Approach Discrete #1
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 40 of 68
Level 6 Audio readout
Enabled =>
Disabled =>
“Steep Approach Enabled”
“Steep Approach Disabled”
Page 41

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.8.2 STEEP APPROACH DISCRETE #2
Type: Steep Approach Selected
Signal Status: Steep Approach Selected or Not Selected
Steep Approach Discrete #2
Selected =>
Not Selected =>
3.8.9 GND ILS TUNED DISCRETE
Type: Supplied by ILS/VOR Mode Selector.
Signal Status: ILS tuned or VOR tuned
GND ILS Tuned Discrete #1
GND ILS Tuned Discrete #2
ILS Tuned =>
ILS Not Tuned =>
ILS Tuned =>
ILS Not Tuned =>
3.8.10 +28V ILS TUNED DISCRETE
Type: Supplied by ILS/VOR Mode Selector.
Signal Status: ILS tuned or VOR tuned
+28 V ILS Tuned Discrete #1
+28 V ILS Tuned Discrete #2
ILS Tuned =>
ILS Not Tuned =>
ILS Tuned =>
ILS Not Tuned =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Steep Approach Selected”
“Steep Approach Not
Selected”
Level 6 Audio readout
“ILS 1 Tuned”
“ILS 1 Not Tuned”
“ILS 2 Tuned”
“ILS 2 Not Tuned”
Level 6 Audio readout
“28V ILS 1 Tuned”
“28V ILS 1 Not Tuned”
“28V ILS 2 Tuned”
“28V ILS 2 Not Tuned”
3.8.11 GLIDESLOPE VALIDITY DISCRETES
Two Glideslope Validity Discretes may be used by EGPWS, one for each possible ARINC 547 Glideslope Receiver
input.
Type: Validity from ARINC 547 Glideslope receiver.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Glideslope Validity Discrete #1
Glideslope Validity Discrete #2
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 41 of 68
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Glideslope 1 Valid”
“Glideslope 1 Invalid”
“Glideslope 2 Valid”
“Glideslope 2 Invalid”
Page 42

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.12 GND GLIDESLOPE INHIBIT DISCRETE
Type: Switch for inhibit of Glideslope mode
Signal Status: Glideslope Inhibit or Not Inhibit
Fault monitoring: Mode 5 will be disabled and “Glideslope” will not be enunciated during cockpit Self-Test and the
long vocabulary test if inhibited.
Glideslope Inhibit Discrete
Not Inhibit =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Inhibit =>
“Glideslope Inhibit True”
“Glideslope Inhibit False”
3.8.13 +28 V GLIDESLOPE INHIBIT DISCRETE
Type: Switch for inhibit of Glideslope mode
Signal Status: Glideslope Inhibit or Not Inhibit
Fault monitoring: Mode 5 will be disabled and “Glideslope” will not be enunciated during cockpit Self-Test and the
long vocabulary test if inhibited.
+28V Glideslope Inhibit Discrete
Not Inhibit =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Inhibit =>
“28V Glideslope Inhibit True”
“28V Glideslope Inhibit
False”
3.8.14 GND GLIDESLOPE CANCEL DISCRETE
Type: Supplied by momentarily actuated cockpit Glideslope mode manual inhibit switch.
Signal Status: Glideslope is canceled if glideslope function is active
Fault monitoring: Activation of this input for more than 15 seconds will result in the ‘Glideslope Cancel Invalid’ fault
which will cause a GPWS INOP indication. Typically, the Glideslope cancel can only be selected
below 2000 feet AGL. However, some configurations only allow it below 1000 feet AGL.
Glideslope Cancel Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
Cancel =>
Normal =>
“Glideslope Canceled”
“Glideslope Enabled”
3.8.15 DECISION HEIGHT DISCRETE
Type: Decision Height Bug switch
Signal Status: Less than Decision Height or Greater than Decision Height
DH Discrete
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 42 of 68
Less Than DH =>
Greater Than DH =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Below DH”
“Above DH”
Page 43

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.16 MODE 6 VOLUME CONTROL DISCRETE
Type: Mode 6 low volume select switch
Signal Status: Low Volume Select or Normal Volume
“Low Volume” in this case refers to the -6db volume level used during Self-Test. “Normal Volume” refers to the level
of the selected call-out menu.
Mode 6 Low Volume Discrete
Low Volume =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Mode 6 Low Volume”
Normal =>
“Mode 6 Normal Volume”
3.8.17 CALLOUTS ENABLE DISCRETE (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Mode 6 Altitude callouts enable switch
Signal Status: Callouts Enable or Callouts Disable with optional Minimums only
Altitude Callouts Enable Discrete
Voice Enabled =>
Voice Disabled =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Callouts Enabled”
“Callouts Disabled”
3.8.18 GND AUDIO SUPPRESS(INHIBIT)/ALL MODES INHIBIT DISCRETE
The function of this discrete is controlled by program pin. This discrete always inhibits all audio except for the
Windshear warning. If configured to suppress visual the input will also suppress all visuals except for the Windshear
warning. If configured to also suppress visuals, activation of this input for more than 60 seconds will always result in
the ‘All Modes Inhibit” fault which will cause GPWS and Terrain INOP indications. As a function of selected aircraft
type this discrete can also cause the All Modes Inhibit fault after 60 seconds even if it is only configured to suppress
audio.
Type: Analog discrete input from a flight deck mounted switch
Signal Status: Audio Suppress enabled or disabled/All Modes Inhibit enable or disable
GND Audio Inhibit Discrete
GPWS Inhibit =>
Not Inhibit =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Audio Inhibit”
“Audio Not Inhibit”
3.8.19 +28 V AUDIO SUPPRESS(INHIBIT)/ALL MODES INHIBIT DISCRETE
The function of this discrete is controlled by program pin. This discrete always inhibits all audio except for the
Windshear warning. If configured to suppress visual the input will also suppress all visuals except for Windshear
warning. If configured to also suppress visuals, activation of this input for more than 60 seconds will always result in
the ‘All Modes Inhibit” fault which will cause GPWS and Terrain INOP indications. As a function of selected aircraft
type this discrete can also cause the All Modes Inhibit fault after 60 seconds even if it is only configured to suppress
audio.
Type: Analog discrete input from a flight deck mounted switch
Signal Status: Audio Suppress enabled or disabled/All Modes Inhibit enable or disable
+28V Audio Inhibit Discrete
GPWS Inhibit =>
Not Inhibit =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“28V Audio Inhibit”
“28V Audio Not Inhibit”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 43 of 68
Page 44
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.20 AOA VALIDITY DISCRETES (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Two AOA validity discretes may be used by EGPWS, one for each source of AOA. Input will come from either an
AOA Indication System or a Stall Warning Computer, depending on the type being used by the aircraft.
Type: Fail Flag from AOA Indication System or a Stall Warning Computer
Signal Status: Fail or Not Fail
AOA Validity Discrete #1
AOA Validity Discrete #2
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“AOA 1 Valid”
“AOA 1 Invalid”
“AOA 2 Valid”
“AOA 2 Invalid”
3.8.21 DISPLAY SELECT DISCRETES
Type: Supplied by momentarily actuated cockpit manual switch. Two types are supported:
Type 1: momentary make/break switch
Type 2: toggle type switch
Signal Status: Terrain Awareness Display (TAD) activated if not active or TAD canceled if currently active.
Display Select Discrete #1
Display Select Discrete #2
Level 6 Audio readout
True =>
False =>
True =>
False =>
“Display Discrete 1 True”
“Display Discrete 1 False”
“Display Discrete 2 True”
“Display Discrete 2 False”
3.8.22 TERRAIN AWARENESS & TCF INHIBIT
Type: Switch for inhibit of Terrain Awareness & TCF functions
Signal Status: Terrain Awareness & TCF Inhibit or Not Inhibit
“Terrain Inhibited” will be enunciated during cockpit Self-Test if inhibited.
Fault monitoring: For some installations, activation of this input for more than 5 seconds will activate the Terrain
Monitor (refer to the Terrain Display Configuration Data table for each aircraft type).
Terrain Awareness & TCF Inhibit
Level 6 Audio readout
Disabled =>
Normal =>
“Terrain Off”
“Terrain On”
3.8.23 SIMULATOR REPOSITION (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Switch for activating Simulator Reposition
Signal Status: Reposition or Normal
If the Simulator Reposition program pin option is activated, then this discrete can be used to ‘preset’ the EGPWS to
match simulator initial conditions.
Simulator Reposition Discrete
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 44 of 68
Reposition =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Simulator Reposition On”
Normal =>
“Simulator Reposition Off”
Page 45

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.24 WEATHER RADAR ON/OFF
Type: WXR On/Off switch input
Signal Status: Radar turned on or off
WXR #1 On Discrete
WXR #2 On Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
On =>
Off =>
On =>
Off =>
“Weather On”
“Weather Off”
“Weather 2 On”
“Weather 2 Off”
3.8.25 LOCALIZER VALIDITY DISCRETES (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Two Localizer validity discretes may be used by EGPWS, one for each possible ARINC 547 Localizer Receiver
input.
Type: Validity from ARINC 547 Localizer receiver.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Localizer Validity Discrete #1
Localizer Validity Discrete #2
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Localizer 1 Valid”
“Localizer 1 Invalid”
“Localizer 2 Valid”
“Localizer 2 Invalid”
3.8.26 ATTITUDE VALIDITY DISCRETES
Two Attitude validity discretes may be used by EGPWS, one for each possible Attitude sensor.
Type: Validity from Attitude sensor.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Attitude Validity Discrete #1
Attitude Validity Discrete #2
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Attitude 1 Valid”
“Attitude 1 Invalid”
“Attitude 2 Valid”
“Attitude 2 Invalid”
3.8.27 AIRSPEED VALIDITY DISCRETE
Airspeed validity discrete may be used by EGPWS for the Airspeed sensor.
Type: Validity from Airspeed sensor.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Airspeed Validity Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Airspeed Valid”
“Airspeed Invalid”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 45 of 68
Page 46
EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.28 BAROMETRIC ALTITUDE RATE VALIDITY DISCRETES
Two Barometric Altitude Rate validity discretes may be used by EGPWS, one for each possible barometric rate
sensor.
Type: Validity from barometric rate sensor.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Barometric Altitude Rate Validity Discrete #1
Barometric Altitude Rate Validity Discrete #2
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Altitude Rate1 Valid”
“Altitude Rate1 Invalid”
“Altitude Rate 2 Valid”
“Altitude Rate 2 Invalid”
3.8.29 ACCELERATION SELF-TEST IN PROGRESS DISCRETE
Indicates that Accelerometers are in Self-Test mode.
Type: Self-Test status from acceleration sensor.
Signal Status: Acceleration Self-Test Active or Inactive
Acceleration Self-Test In Progress
In Progress =>
Not in Progress =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Acceleration Self-Test Active
Acceleration Self-Test Inactive
3.8.30 LONGITUDINAL ACCELERATION VALIDITY DISCRETE
Longitudinal Acceleration validity discrete may be used by EGPWS for the Acceleration sensor.
Type: Validity from Acceleration sensor.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Longitudinal Acceleration Validity
Discrete
Invalid =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
“Longitudinal Acceleration Valid”
“Longitudinal Acceleration Invalid”
3.8.31
3.8.32 NORMAL ACCELERATION VALIDITY DISCRETE
Normal Acceleration validity discrete may be used by EGPWS for the Acceleration sensor.
Type: Validity from Acceleration sensor.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Normal Acceleration Validity Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Normal Acceleration Valid”
“Normal Acceleration Invalid”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 46 of 68
Page 47

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.33 MAGNETIC HEADING VALIDITY DISCRETE
A Magnetic Heading validity discrete may be used by EGPWS for the Magnetic Heading sensor.
Type: Validity from Magnetic Heading sensor.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Magnetic Heading Validity Discrete
Invalid =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
“Magnetic Heading Valid”
“Magnetic Heading Invalid”
3.8.34 AOA VANE HEATER DISCRETE
An AOA Vane Heater Discrete may be used by EGPWS for indication of vane heat for flight history recording.
Type: Heater Flag from AOA vane.
Signal Status: Vane Heater On or Vane Heater off
AOA Vane Heater Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
True =>
False =>
“AOA Vane Heater On”
“AOA Vane Heater Off”
3.8.35 PLI DESELECT SWITCH DISCRETES (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
PLI deselect switch discretes may be used by EGPWS for de-activating the PLI select relays to remove EGPWS PLI
indication from the ADI.
Type: momentary make/break switch
Signal Status: EGPWS PLI deselected
PLI Deselect Switch #1
PLI Deselect Switch #2
Pressed =>
Not Pressed =>
Pressed =>
Not Pressed =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“PLI Deselect Switch 1 True”
“PLI Deselect Switch 1 False”
“PLI Deselect Switch 2 True”
“PLI Deselect Switch 2 False”
3.8.36 AUTOPILOT DISCONNECT DISCRETES
Autopilot Disconnect discretes may be used by EGPWS for indication that the Autopilot has been disconnected.
Type: Autopilot Disconnected
Signal Status: Autopilot Connected or Not Connected
Autopilot Disconnect #1
Autopilot Disconnect #2
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 47 of 68
Connected =>
Not Connected =>
Connected =>
Not Connected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Autopilot 1 Selected”
“Autopilot 1 Not
Selected”
“Autopilot 2 Selected”
“Autopilot 2 Not
Selected”
Page 48

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.37 TACTICAL SELECT DISCRETE
Tactical Select discrete may be used by EGPWS for an indication that the Tactical Select switch has been pressed.
Type: momentary make/break switch
Signal Status: Tactical Select Selected or Not Selected
Tactical Select Discrete
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
Selected =>
“Tactical Selected”
“Tactical Not Selected”
3.8.38 ALTITUDE ALERT DISCRETE
Altitude Alert discrete may be used by EGPWS for an indication that the Altitude Alert is selected.
Type: Discrete for activating the Altitude Alert tone.
Signal Status: Altitude Alert Selected or Deselected
Altitude Alert Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
True =>
False =>
“Altitude Alert Selected”
“Altitude Alert Deselected”
3.8.39 CORRECTED BAROMETRIC ALTITUDE VALIDITY DISCRETE
Corrected Barometric Altitude Validity Discrete may be used by EGPWS to determine when the Corrected Altitude
input is invalid.
Type: Validity from Corrected Barometric Altitude computer.
Signal Status: Valid or Invalid
Corrected Barometric Alt Valid
Level 6 Audio readout
Valid =>
Invalid =>
“Corrected Altitude Valid”
“Corrected Altitude Invalid”
3.8.40 MOMENTARY FLAP OVERRIDE DISCRETE
Flap Override Discrete may be used by EGPWS to determine when Flap Override has been selected.
Type: Momentary make/break switch.
Signal Status: Selected or Not Selected
Momentary Flap Override Discrete
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 48 of 68
Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Flap Override”
“Not Flap Override”
Page 49

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.41 WEIGHT ON WHEELS DISCRETE
Weight On Wheels Discrete may be used by EGPWS to determine if the aircraft is on the ground.
Type: Weight On Wheels Status
Signal Status: On Ground or Not On Ground
Weight On Wheels Discrete
Selected =>
Not Selected =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“On Ground”
“Not On Ground”
3.8.42 GPWS INHIBIT DISCRETE
This discrete inhibits all audio and visual except for Windshear, Terrain Awareness and TCF.
Type: Analog discrete input from a flight deck mounted switch
Signal Status: GPWS enabled or disabled
Fault monitoring: Activation of this input for more than 5 seconds will result in the ‘GPWS Inhibit’ fault which will
cause a GPW INOP indication.
GPWS Inhibit Discrete
GPWS Inhibit =>
Not Inhibit =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“GPWS Inhibit”
“GPWS Not Inhibit”
3.8.43 RAAS ENABLE DISCRETE (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Discrete for enabling RAAS functionality
Signal Status: RAAS Enabled or Disabled
RAAS Enable Discrete
True =>
False =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Runway Awareness Enabled”
“Runway Awareness Disabled”
3.8.44 RAAS INHIBIT DISCRETE (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Discrete for inhibiting RAAS functionality, also inhibits Long Landing Monitor and Takeoff Flap
Configuration Monitor
Signal Status: RAAS Inhibit or Not Inhibit
RAAS Inhibit Discrete
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 49 of 68
True =>
False =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Runway Awareness Inhibit”
“Runway Awareness Not Inhibit”
Page 50

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
3.8.45 STABILIZED APPROACH MONITOR ENABLE DISCRETE (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Discrete for enabling Stabilized Approach Monitor functionality
Signal Status: Approach Monitor Enabled or Disabled
Stabilized Approach Monitor Enable
Discrete
True =>
False =>
Level 6 Audio readout
“Approach Monitor Enabled”
“Approach Monitor Disabled”
3.8.46 STABILIZED APPROACH MONITOR INHIBIT DISCRETE (MK V AND MK VII ONLY)
Type: Discrete for inhibiting Stabilized Approach Monitor functionality
Signal Status: Approach Monitor Inhibit or Not Inhibit
Stabilized Approach Monitor Inhibit Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
True =>
False =>
“Approach Monitor Inhibit”
“Approach Monitor Not Inhibit”
3.8.47 LOW AIRSPEED MONITOR INHIBIT DISCRETE (MK V – 737NG ONLY)
Type: Discrete for inhibiting Low Airspeed Monitor functionality
Signal Status: Low Airspeed Monitor Inhibit or Not Inhibit
Low Airspeed Monitor Inhibit Discrete
Level 6 Audio readout
True =>
False =>
“Low Airspeed Inhibit True”
“Low Airspeed Inhibit False”
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 50 of 68
Page 51

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
4 MAINTENANCE PRACTICES
4.1 GENERAL
Normal maintenance activities performed on the EGPWS should follow standard industry maintenance practices.
System maintenance practices may include; updating a database, downloading flight history data, and programming
or reprogramming the MK VI, MK VIII or MK XXII Configuration Module. These are addressed in the following
sections.
4.2 DATABASE UPDATE
The Enhanced Ground Proximity Warning System (EGPWS) uses Terrain, Obstacle, Runway, and Envelope
Modulation databases to provide enhanced functions. These are periodically updated, as new data becomes
available. The Terrain, Obstacle, and Runway databases are typically combined and loaded into the EGPWS as
one database, however it is possible that individual database updates could be provided. The procedure for loading
a database update is the same in all cases and this section will address them as a database update generically.
For each new (updated) database, Honeywell will provide notification of the new database via a Service Information
Letter (SIL). The SIL will be sent to all registered EGPWS customers, or they will be available for Internet download
from Honeywell Technical Publication website or the EGPWS website at www.egpws.com
description of the changes in the database, as compared to the previous database, so that each customer can
determine the applicability of the database update to their operations. For example, a Terrain database update
involving only terrain in South America will be of no value to a domestic U.S. airline. Thus, the domestic U.S. airline
would not need the database update. The SIL will also contain instructions on how to obtain the new Terrain
Database and any required modifications. Database updates are coordinated with the FAA prior to SIL release via
a Honeywell “minor mod” notification process. Installation and verification of terrain databases is addressed in a
generic Service Bulletin.
. The SIL will contain a
EGPWS databases are not identified on the EGPWC nameplate as a part of the unit part number. However, for the
MK V and MK VII, there is a label on the inside of the front panel maintenance door that can be used for identifying
the installed terrain database. For the MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII a separate label is placed on the unit front
panel identifying the installed Terrain database version number and for the MK VI and MK XXII the database region
(see section 2.2.10.1). Otherwise, the installed databases can be determined in the Level 3 Self-Test (see Section
3.5) which should always be used to confirm the current database version.
4.2.1 DATABASE UPDATE FREQUENCY
Honeywell is continually striving to improve the EGPWS databases. New terrain, obstacle, or runway data is
obtained by many different means, evaluated and verified, before it is processed into an EGPWS database. When
sufficient or significant new data is available, Honeywell will release a database update.
Honeywell is committed to investigating reported nuisance alerts. When nuisance alerts result from database
problems (accuracy or resolution) Honeywell will make corrections to the database. Nuisance alerts can also result
in changes to the Envelope Modulation database, although this tends to be less frequently updated.
It is up to the EGPWS customer to determine if a specific database update is applicable to their operation.
Honeywell recommends always operating with the latest database.
NOTE: Some database updates may require a hardware or software mod. Any required modification information
will be identified in the associated database SIL.
Operators can visit the EGPWS website Database page and enroll in a distribution list that sends e-mail notification
when a new database is released. Also on this website page is a Future Content and Schedule document the gives
details on the expected release dates for 3-4 future databases.
4.2.2 LOADING A DATABASE
A database is loaded into the EGPWC via the PCMCIA card slot in the front panel in the MK V and MK VII. In the
MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII a “Smart Cable” data-loader is connected to the Test connector on the front panel.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 51 of 68
Page 52

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
The database may be loaded either while the EGPWC is on the aircraft or on a bench provided the appropriate
power is applied.
Each Honeywell database Service Information Letter includes reference to the procedure for loading the database in
the EGPWC. Refer to the SIL for this information.
4.3 FLIGHT HISTORY DOWNLOADING
In flight, the EGPWC records detected faults, and data prior to and following an alert. This flight history data can be
downloaded from the EGPWC via the PCMCIA interface. With this data, Honeywell can analyze the flight history
when necessary to help in the troubleshooting process, or analyzing special or unique events.
4.3.1 OBTAINING AN EGPWS FLIGHT HISTORY DOWNLOAD CARD
To obtain a Flight History Download (PCMCIA) Card necessary for this procedure, order the following part number:
For MK V and MK VII EGPWS (P/Ns 965-0976-xxx-xxx-xxx/965-1676-xxx/965-1690-xxx and 965-1076-xxx-xxx-
xxx), order Flight History Download Card p/n 718-1592-001.
For MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII EGPWS (P/Ns 965-11xx-xxx, 965-12xx-xxx, and 965-159x-xxx), order Flight
History Download Card p/n 718-1593-001.
NOTE: A Honeywell programmed and formatted PCMCIA Card is required to initiate the download sequence and
record the data. The Download Cards (p/n 718-1592-001 and 718-1593-001) are not interchangeable.
Also, database update cards can not be used for flight history downloading.
4.3.2 DOWNLOAD PROCEDURE
1. For the MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII access and connect Smart Cable p/n 951-0386-001 to Test Connector J3
on the EGPWC front panel.
For the MK V or MK VII, access and open the front panel door on the EGPWC.
2. Apply power to the EGPWC.
3. Verify that the COMPUTER OK LED is ON.
NOTE: If the COMPUTER FAIL LED is ON, the integrity of the Downloaded Data cannot be assured.
NOTE: If the EXTERNAL FAULT LED is ON, this will not interfere with the Download process.
4. On the EGPWC front panel or Smart Cable (see Figures x-x and x-x), verify the:
• IN PROG LED is extinguished.
• CARD CHNG LED is extinguished.
• XFER COMP LED is extinguished.
• XFER FAIL LED is extinguished.
5. Verify that the PCMCIA Card has its Write Protect Function Selector in the OFF (in- board) position.
NOTE: The PCMCIA Card Write Protect Selector is fragile and should be moved only with the minimum amount
of force.
6. Insert PCMCIA Card into the PCMCIA Card slot.
For the MK V or MK VII, ensure the notch on the bottom of the PCMCIA Card is in the down position. Push the
card in carefully until the PUSH TO EJECT button on the front Panel is fully extended. This will be when the
face of the button is nearly level with the rear of the inserted PCMCIA Card.
For the MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII, the label on the card and on the Smart Cable should both be oriented in
the same direction. The PCMCIA Card will only insert about half the card length.
CAUTION: Excessive force will damage the internal connector.
7. While loading is in progress, the IN PROG LED illuminates and the COMPUTER OK LED turns OFF.
8. When loading is complete, the IN PROG LED will turn OFF and the XFER COMP LED will turn ON.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 52 of 68
Page 53

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
NOTE: This operation should require no more than 10 minutes.
NOTE: If the XFER FAIL LED turns ON instead of the XFER COMP LED, then a different Flight History
Download PCMCIA Card must be obtained from Honeywell for the Data Download.
9. Remove the PCMCIA Card,
For the MK V or MK VII, depress the PUSH TO EJECT button on the EGPWC front panel.
For the MK VI or MK VIII, and MK XXII, carefully grasp the card and pull from the Smart Cable.
NOTE: The EGPWS should automatically return to its normal operating mode upon removal of the card.
10. Verify that the COMPUTER OK LED illuminates (allow up to 3 minutes for the light to come on).
11. Procedure is complete. Close the EGPWC front panel door or disconnect the Smart Cable as appropriate.
NOTE: Flight History Download Cards can only be used once.
4.3.3 TRANSCRIPTION OF THE PCMCIA CARD
For transcription of a Flight History Download Card, contact Honeywell Technical Operations to arrange delivery of
the data or the card
a) via email
aerotechsupport@honeywell.com
b) via toll-free (US/Canada) telephone 800-601-3099 (select option 2):
c) via direct dial telephone 602-365-3099
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 53 of 68
Page 54

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
4.4 PROGRAMMING THE CONFIGURATION MODULE (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII ONLY)
Programming the EGPWS Configuration Module is accomplished using WinVIEWS on a PC connected to the
EGPWC via the RS-232 interface. Prior to this activity, the necessary and desired configuration should be
determined based on the MK VI, MK VIII, or MK XXII Installation Design Guide referenced in Section 1.3. Utilize a
copy of Appendix E, Table 5.2 in the IDG for recording the associated installation Category ID information.
For programming the Configuration Module, the following procedure is used:
1. Verify EGPWC interface to P2 connector (including Configuration Module) and RS-232 interface to PC.
2. Power EGPWC and PC and start WinVIEWS.
3. With WinVIEWS active in the Terminal Mode, Configuration sub-mode commands are available for the
programming purpose. Type “CFG” at the prompt. At this point, the CFG > prompt is displayed and the
program and EGPWC are ready for entering the program command and data string. “HELP” or “?” will display a
list of the commands and their description. “CUW” is the necessary command for entering the identified ID’s for
each category.
4. Using the Category ID’s chosen from the ICD (refer to completed Table 5.2), create a command string with the
following structure:
CUW 0/15 # # # # # # # # # # # # # # #/
• CUW<space>0 is the command and version number. CUW writes the category ID’s defined by version 0
definition (0 is the only version currently available) to the Configuration Module via the EGPWC without a
CRC (checksum) value attached (this is generated by the EGPWC when the data is transmitted).
• /15 indicates the beginning of the data string (/) with 15 being the total number of categories to follow.
• <space><Cat 1 ID#><space><Cat 2 ID#>…<Cat 15 ID#>/ - each Cat ID # is the chosen ID for the
associated category with the first being category 1 and the last being category 15 in order. The following
slash indicates the end of the data.
Note: If 15 ID’s don’t follow “/15”, the error message “Invalid Parameter. Not enough category ID’s.
Configuration update failed, please try again” will be given. The value entered for each category must
be an available ID for the associated category or a similar error message will be given. If the number of
categories provided is less than 15 (e.g., “/8 # …#/” with eight ID’s defined), then the remaining
categories (9 through 15) will be set to 0.
5. After completing the data string as defined above, pressing ENTER results in a question; “Confirm this data
reflects configuration to be programmed (Y/N)”. Pressing the Y key sends the data to the EGPWC to write to
the Configuration Module. Following the writing of the Configuration Module the EGPWC is automatically
rebooted in order for the configuration to take affect.
Note: If when the ENTER key is pressed the question response is not given (cursor just moves to the next
line), pressing any character key should provide the proper response.
Pressing the N key results in the message “Command aborted – No configuration module change has been
made”. If necessary, revise the data to correct or change as necessary and continue as above. The backspace
key can be used to make corrections.
6. Following the successful writing to the Configuration Module (no messages) and EGPWC reboot, pressing
Control Z (Ctrl Z) restarts the WinVIEWS terminal mode communication.
7. There are a couple ways to now confirm the Configuration Module programming with the following being the
preferred. As above, type “CFG” to restart the Configuration sub-mode. At the CFG > prompt, type “CMR”
<ENTER>. Each Category and its associated ID is read from the Configuration Module and listed on the
display. Alternately, when not in the Configuration sub-mode, the command “PS” (Present Status) will display
EGPWC and configuration data.
8. Configuration Module programming is complete.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 54 of 68
Page 55

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
4.4.1 CONFIGURATION MODULE REPROGRAMMING (MK VI, MK VIII, MK XXII ONLY)
Reprogramming the EGPWS Configuration Module is accomplished similar to the programming process above.
Prior to reprogramming, the desired new configuration should be determined based on the MK VI, MK VIII, or MK
XXII Interface Design Guide (IDG) document referenced in Section 1.3.
For reprogramming the Configuration Module, the following procedure is used:
1. Verify EGPWC interface to P2 connector (including Configuration Module) and RS-232 interface to PC.
2. Power EGPWC and PC and start WinVIEWS.
3. With WinVIEWS active in the Terminal Mode, start the Configuration sub-mode by typing “CFG” at the prompt.
At this point, either all the ID’s can be rewritten using the CUW command as before, or individual categories can
be changed as follows:
4. At the CFG > prompt use the CAT command with the following structure:
• CAT<space><category #><space><ID#><space><T or F>
• <category #> is the ICD Category to change (example 7)
• <ID#> is the new ID to change to (example 92)
• <T or F> is True or False for rebooting the EGPWC. Use “T” if only one category is to be changed and the
EGPWC will reboot following ENTER. Use “F” if another individual ID is to be changed by another CAT
operation.
Example:
CFG >CAT 7 92 T
5. After inputting the desired change information, pressing ENTER will transmit the data to the EGPWC to write to
the Configuration Module. If a reboot is commanded (T), then the EGPWC will reboot at the completion of the
write process. If a reboot is not commanded (F), then the message “Writing to configuration module…Category
7 ID updated successfully.” is given and the CFG > prompt is again displayed. At this point, the Configuration
Module has been changed, but the change will not be effective until the EGPWC is rebooted. Additional
changes can be made with the final change set to command the EGPWC reboot (or cycle EGPWC power to
reboot).
6. Verification of the changes made is the same as before. As above, type “CFG” to restart the Configuration submode. At the CFG > prompt, type “CMR” <ENTER>. Each Category and its associated ID is read from the
Configuration Module and listed on the display. Alternately, when not in the Configuration sub-mode, the
command “PS” (Present Status) will display EGPWC and configuration data.
7. Configuration Module reprogramming is complete.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 55 of 68
Page 56

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
An example CUW command/data string, its definition, and the corresponding CWR list is provided below.
CUW command/data string:
CFG > CUW 0/15 2 3 2 0 0 3 95 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0/
Above Configuration defined:
Category 1 Aircraft/Mode Type: 2
Category 2 Air Data Source: 3
Category 3 Position Source: 2
Category 4 Altitude Callouts Menu: 0 (All callouts)
Category 5 Audio Menu: 0 (Basic menu)
Category 6 Display Configuration: 3
Category 7 Select Group #1 Options: 95
Steep Approach Enabled: True
TA&D Alternate Pop-Up: False (Pop-Up on Caution or Warning)
Peaks Mode Enable: True
Obstacle Awareness Enabled: True
Bank Angle Enable: True
Flap Reversal: True
GPS Altitude Reference: MSL (required for internal GPS source, Cat 3 ID 2)
Category 8 Radio Altitude Input Select: 1
Category 9 Navigation Input Select: 0
Category 10 Attitude Input Select: 0
Category 11 Heading Input Select: 0
Category 12 Windshear Select type: 0
Category 13 Discrete I/O Type Select: 0
Category 14 Audio output Level Select: 0 (Equiv. to MK VI GPWS output level)
Category 15 Undefined 0
CWR list: (based on above configuration)
CFG > CMR
CONFIGURATION MODULE:
Format Version: 0
Category 1 ID: 2
Category 2 ID: 3
Category 3 ID: 2
Category 4 ID: 0
Category 5 ID: 0
Category 6 ID: 3
Category 7 ID: 95
Category 8 ID: 1
Category 9 ID: 0
Category 10 ID: 0
Category 11 ID: 0
Category 12 ID: 0
Category 13 ID: 0
Category 14 ID: 0
Category 15 ID: 0
CRC: 1565805624
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 56 of 68
Page 57

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
5 SERVICING
5.1 GENERAL
The EGPWS does not require any servicing.
6 REMOVAL/INSTALLATION
6.1 EGPWC
6.1.1 REMOVAL
1. Remove power to the EGPWC.
2. (MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII only) Disconnect aircraft connectors from the front of the unit.
3. Turn hold-down counterclockwise and unlatch from EGPWC.
4. Remove EGPWC from aircraft equipment rack.
6.1.2 INSTALLATION
1. Ensure power is off to the EGPWC rack.
2. Position EGPWC in mounting tray and secure with hold-down latch (rotate clockwise).
3. (MK VI, MK VIII, and MK XXII only) Connect aircraft connectors to the front of the unit ensuring that each is
properly latched.
4. Provide power to EGPWC and all required sensors and subsystems.
5. Perform a Level 1 Self-Test per Section
6. If RAAS or any other optional function is installed, refer to Level 1 and Level 3 Self-Test messages in Appendix
C through G to validate the RCD version installed.
3.3 to verify EGPWC operation.
6.2 CONFIGURATION MODULE (MK VI, MK VIII, AND MK XXII ONLY)
Refer to the appropriate Installation Design Guide referenced in Section 1.3 for Configuration Module illustrations.
6.2.1 REMOVAL
1. Remove power to the EGPWC.
2. Disconnect the P2 aircraft connector from the unit.
3. Remove two screws holding Configuration Module to P2 connector.
4. Separate Configuration Module from P2 connector and access wires.
5. De-pin six Configuration Module wires and detach ground wire to free Configuration Module from P2 connector.
6.2.2 INSTALLATION
1. Ensure that power is off to the EGPWC.
2. Pin six Configuration Module wires to P2 connector (see applicable aircraft wiring diagrams).
3. Connect the Configuration Module housing ground wire to a wire harness shield termination within the P2
connector harness.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 57 of 68
Page 58

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
4. Align the Configuration Module housing to the P2 connector ensuring that wires are properly contained within
the connector assembly.
5. Install the two screws securing the Configuration Module to the P2 connector.
6. Connect the P2 connector assembly to the EGPWC.
7. Provide power to EGPWC and all required sensors and subsystems.
8. Program the Configuration Module per the instructions in Section 4.4 and any appropriate aircraft drawings that
define the proper values to use.
9. Perform EGPWS Level 1, 2, and 3 Self-Test per Section 3.3 to 3.5 to verify system function and proper
configuration per aircraft drawings.
6.3 DISPLAY SWITCHING RELAYS (IF INSTALLED)
Refer to appropriate EGPWS aircraft wiring and mechanical drawings.
6.3.1 REMOVAL
1. Remove power to the EGPWC.
2. Remove power to the Weather Radar system.
3. Remove power to the EGPWS/Weather Radar display switching relays.
4. Access and remove the display switching relay(s) using standard maintenance practices.
6.3.2 INSTALLATION
1. Ensure that EGPWC, Weather Radar, and display switching relay power is removed.
2. Mount relay(s) and secure.
3. Provide power to the EGPWC and all required sensors and subsystems.
4. Provide power to the Weather Radar system.
5. Provide power to the display switching relays.
6. Perform a Level 1 Self-Test per Section
3.3 to verify relay operation.
7 ADJUSTMENT/TEST
7.1 ADJUSTMENT
The EGPWS does not require any adjustments.
7.2 TEST
Line maintenance testing for the EGPWS consists of functional verification of the EGPWC and associated
interfaces. For EGPWC functional verification, see the Fault Isolation Section 3. Associated interfaces are verified
through EGPWS ground tests as described in the following section.
7.2.1 EGPWS GROUND TESTS
All EGPWS Ground Tests are developed by the installer to meet aircraft specific interfaces. Examples of Ground
Test are available from Honeywell via the EGPWS website. To obtain a copy of a sample Ground Test Procedure,
please visit
Procedures sub-page.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 58 of 68
www.egpws.com, select the Installation Information page, then select the Ground and Flight Test
Page 59

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
8 INSPECTION/CHECK
8.1 GENERAL
The EGPWS does not require any specific periodic inspection or checks. The system should be inspected for
integrity and checked for wear/tear during the course of routine aircraft maintenance inspections.
9 CLEANING/PAINTING
9.1 GENERAL
The EGPWS does not contain any elements that required cleaning or painting on the aircraft. Any cleaning or
painting of the EGPWC should be performed by an authorized EGPWS repair facility.
10 REPAIRS
10.1 GENERAL
No on-aircraft repairs are identified for the EGPWS. If a problem is found with a unit, remove and replace the unit
per the removal and installation procedures and route the unit to an authorized repair facility for repair.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 59 of 68
Page 60

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
11 APPENDIX A: WINVIEWS
WinVIEWS (Windows Virtual Interface to the Enhanced Warning System) is a software tool developed by Honeywell
to monitor or view values within the EGPWC, and perform certain test interface functions.
Overview:
The WinVIEWS software provides a monitor function that does not alter the operation of the EGPWS.
The monitoring of the values assists in the testing of the EGPWS by allowing the operator to quickly determine if the
correct signal and scaling is being used by the EGPWS. Additionally, WinVIEWS provides a detailed status of the
software configuration and input signals, which enables quick identification of system anomalies. WinVIEWS is also
utilized for programming the Configuration Module in MK VI, MK VIII, and MKXXII applications.
To obtain a copy of the WinVIEWS software, please visit
www.egpws.com, select the Installation Information page,
then select the Diagrams, Drawings & Software sub-page. WinVIEWS is available as a self extracting .zip file. A
User’s Guide is available there as well.
In addition to the WinVIEWS software, a command file may be utilized. The command file is a simple text file that
includes each Current Value Table (CVT) Item used in a test procedure. The file must be ‘text only’ such as those
created in the Microsoft Windows NotePad program. It should have a filename extension of .wvc or .cmd. The
webpage mentioned above also contains generic command files for use in ground and flight testing the various
EGPWS models.
To use WinVIEWS a RS-232 cable (PN 704-2670-001 is required) to connect the PC 9-pin comm port to the
EGPWC 15-pin test port.
Typical WinVIEWS operation with the EGPWC:
1. Connect the PC to the EGPWC via the RS-232 cable defined above.
2. On the PC, start the WinVIEWS program (requires Windows 95 or later).
3. WinVIEWS opens in the Terminal Mode. Various commands are available in this mode. Type “HELP” or “?” for
command help. In particular, CVT Items may be added or deleted to/from the display to assist with system
analysis.
4. Under the File Menu select the “Load Command File” option and load the appropriate Command File.
5. Use F6 to select the Display Mode: each CVT item listed in the Command File will be continuously updated at a
rate of at least once per second. The value shown for each CVT Item listed is the current value used by the
EGPWS. F6 toggles between the Display and Terminal Modes.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 60 of 68
Page 61

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
12 APPENDIX B: TROUBLESHOOTING DO’S AND DO NOT’S
DO use built-in self test levels to find the exact nature of the fault.
DO use our free WinVIEWS program to quickly access Self Test Level 1, 2, and 3 info
DO remember to look at the front panel LEDs
Green Computer OK LED means “don’t remove”
Amber External Fault LED means “don’t remove”
Red Computer means “possibly remove”
DO NOT use cockpit INOP lamps for troubleshooting
INOP indications are merely a pilot’s indication of which EGPWS functions are inactive, they are not positive
indication of internal EGPWS faults. Experience shows External (non-EGPWS) faults are responsible for
INOPs illumination 99% of the time.
DO NOT remove unit if front panel green Computer OK LED is illuminated
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 61 of 68
Page 62

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
13 APPENDIX C: RAAS MAINTENANCE MESSAGES (AURAL & DISPLAYED)
TABLE C1-1: RAAS MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test Level 1
(Annunciated
after Terrain
Awareness part
of Self-Test)
Self-Test Level 1 “Runway Awareness Not Available”
Self-Test Level 1
Self-Test Level 1 “Runway Awareness INOP” RAAS enabled but the function is inoperative
Self-Test Level 1 “Runway Awareness R-T-O” RAAS enabled and functioning, but RAAS
Except where noted, all maintenance
message voices are Male
“Runway Awareness OK - Feet”
“Runway Awareness OK - Metres”
Note: Feet and Metres will be annunciated in the
gender voice option (Male or Female) selected for
RAAS.
“Runway Awareness Inhibited”
MESSAGE
NOTES:
All volume levels at same volume as
existing EGPWS Self-Test messages
RAAS enabled, functioning, has good position
information, and is at a validated airport.
Distances annunciated in Feet.
RAAS enabled, functioning, has good position
information, and is at a validated airport.
Distances annunciated in Metres.
RAAS enabled, but the system either has no
position information, the accuracy of the position
information is insufficient to allow RAAS to
function, or the aircraft is at airport that has not
been validated in the EGPWS Terrain Database
RAAS enabled, but the advisories have been
inhibited with the activation of an external
input/switch.
advisories (other than distance remaining) are
temporarily inhibited because RAAS has
detected a Rejected Take-Off condition. To clear
this message and enable RAAS advisories, the
aircraft must be taxied off the runway area.
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Self-Test Level 3 Software -228-228 and earlier:
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 62 of 68
“Runway Awareness Enable Set”
“Runway Awareness Enabled”
“RAAS RCD Part Number XXX-XXXX-XXX “
Software -230-230 and on:
“RCD Part Number XXX-XXXX-XXX “
where X is the 10-digit installation-specific RCD
part number.
RCD Enable Key is set. The RCD is not loaded.
RCD is loaded and RAAS Enable Key is set.
Note: This message replaces the “Runway
Awareness Enable Set” message.
Allows verification that the correct RCD is
loaded into the EGPWS.
Page 63

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
TABLE C1-2: RAAS DISPLAYED MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test
Level 1
(Displayed as
part of the
EGPWS SelfTest Pattern )
On-Ground
status
DISPLAYED MESSAGE
RAAS Display messages are displayed OnGround only. To initiate, change the display
range. Message displayed only the selected
channel.
RCDxyz12 (magenta)*
* May be green depending on display
1
SEE NOTE BELOW
RAAS-OK-FT (green)
RAAS-OK-M (green)
RAAS-N/AVBL (amber)
NOTES:
Displayed immediately above or below the TDB
Version display.
RCD version “xyz12” is the last 5 digits of the 10digit RCD software part number (labeled on
PCMCIA card).
RAAS enabled, functioning, has good position
information, and is at a validated airport. Distances
annunciated in Feet.
RAAS enabled, functioning, has good position
information, and is at a validated airport.
Distances annunciated in Metres.
RAAS enabled, but the system either has no
position information, the accuracy of the position
information is insufficient to allow RAAS to
function, or the aircraft is at airport that has not
been validated in the EGPWS Terrain Database
(last item only applicable to -228-228 and earlier)
RAAS-NA-xxxx (amber)
RAAS-RTO (green)
RAAS-INOP (amber)
RAAS enabled, but the aircraft is at an airport
(ICAO code “xxxx”) that has not been validated in
the EGPWS Terrain Database (applicable only to 230-230 and later)
RAAS enabled but advisories are inhibited
because a RAAS Rejected Take-Off was detected
RAAS enabled but function is Inoperative
NOTE: Operators/Installers must refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICA) documentation to
identify the approved RCD configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having RAAS installed.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 63 of 68
Page 64

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
14 APPENDIX D: STABILIZED APPROACH MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
TABLE D-1: STABILIZED APPROACH MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test Level 1
Self-Test Level 1 “Approach Monitor INOP” Stabilized Approach Monitor enabled but the
Self-Test Level 2 “Approach Monitor Approach Speed Undefined” Stabilized Approach Monitor “Too Fast” function
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Self-Test Level 3 “RCD Part Number XXX-XXXX-XXX “
Except where noted, all maintenance
message voices are Male
“Approach Monitor Inhibited”
“Approach Monitor Enabled”
where X is the 10-digit installation-specific RCD
part number.
MESSAGE
NOTES:
All volume levels at same volume as
existing EGPWS Self-Test messages
Stabilized Approach Monitor enabled, but the
advisories have been inhibited with the
activation of an external input/switch
function is inoperative
is enabled but the aircraft does not provide a
source of Approach Speed
RCD Enable Key is set and loaded RCD
activates Stabilized Approach Monitor function.
Allows verification that the correct RCD is
loaded into the EGPWS.
NOTE: Operators/Installers must refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICA) documentation to
identify the approved RCD configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having Stabilized Approach
Monitor installed.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 64 of 68
Page 65

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
15 APPENDIX E: ALTIMETER MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
TABLE E-1: ALTIMETER MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test Level 1 “Altimeter Monitor INOP” Altimeter Monitor enabled but the function is
Self-Test Level 2 “Altimeter Monitor GPS Signal Undefined” Altimeter Monitor function is enabled but the
Self-Test Level 2
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Self-Test Level 3 “RCD Part Number XXX-XXXX-XXX “
Except where noted, all maintenance
message voices are Male
“Altimeter Monitor Static Air Temperature
Undefined”
“Altimeter Monitor Enabled”
where X is the 10-digit installation-specific RCD
part number.
MESSAGE
NOTES:
All volume levels at same volume as
existing EGPWS Self-Test messages
inoperative
aircraft does not provide a source of GPS
Altimeter Monitor function is enabled but the
aircraft does not provide a source of SAT
RCD Enable Key is set and loaded RCD
activates Altimeter Monitor function.
Allows verification that the correct RCD is
loaded into the EGPWS.
NOTE: Operators/Installers must refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICA) documentation to
identify the approved RCD configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having Altimeter Monitor
installed.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 65 of 68
Page 66

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
16 APPENDIX F: TAKEOFF FLAP CONFIGURATION MONITOR MAINTENANCE
MESSAGES
TABLE F-1: TAKEOFF FLAP CONFIGURATION MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test Level 1
Self-Test Level 1 “Flaps Monitor INOP” Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor enabled but
Self-Test Level 2 “Flaps Monitor Flap Angle Undefined” Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor function is
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Self-Test Level 3 “RCD Part Number XXX-XXXX-XXX “
Except where noted, all maintenance
message voices are Male
“Flaps Monitor Inhibited”
“Flaps Monitor Enabled”
where X is the 10-digit installation-specific RCD
part number.
MESSAGE
NOTES:
All volume levels at same volume as
existing EGPWS Self-Test messages
Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor enabled, but
the advisories have been inhibited with the
activation of an external input/switch. NOTE –
the EGPWS does not support a dedicated
Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor inhibit, but
activation of a defined RAAS inhibit will also
inhibit Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor.
the function is inoperative
enabled but the aircraft does not provide a
source of Flap Position
RCD Enable Key is set and loaded RCD
activates Takeoff Flap Configuration Monitor
function.
Allows verification that the correct RCD is
loaded into the EGPWS.
NOTE: Operators/Installers must refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICA) documentation to
identify the approved RCD configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having Takeoff Flap
Configuration Monitor installed.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 66 of 68
Page 67

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
17 APPENDIX G: LONG LANDING MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
TABLE G-1: LONG LANDING MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test Level 1
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Self-Test Level 3 “RCD Part Number XXX-XXXX-XXX “
Except where noted, all maintenance
message voices are Male
“Runway Awareness Inhibited” (only if RAAS
enabled at same time as Long Landing Monitor)
“Long Landing Enabled”
where X is the 10-digit installation-specific RCD
part number.
MESSAGE
NOTES:
All volume levels at same volume as
existing EGPWS Self-Test messages
Long Landing Monitor enabled, but the
advisories have been inhibited with the
activation of an external input/switch. NOTE –
the EGPWS does not support a dedicated Long
Landing Monitor inhibit, but activation of a
defined RAAS inhibit will also inhibit Long
Landing Monitor.
RCD Enable Key is set and loaded RCD
activates Long Landing Monitor function.
Allows verification that the correct RCD is
loaded into the EGPWS.
NOTE: Operators/Installers must refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICA) documentation to
identify the approved RCD configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having Long Landing Monitor
installed.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 67 of 68
Page 68

EGPWS LINE MAINTENANCE MANUAL
18 APPENDIX H: LOW AIRSPEED MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
TABLE H-1: LOW AIRSPEED MONITOR MAINTENANCE MESSAGES
MAINT.
FUNCTION
Self-Test Level 1 ”Airspeed Low” Low Airspeed Monitor enabled, functioning, has
Self-Test Level 1
Self-Test Level 1 “Airspeed Low INOP” Low Airspeed Monitor enabled but the function
Self-Test Level 3
(Annunciated at
end of Selected
Options )
Except where noted, all maintenance
message voices are Male
“Airspeed Low Inhibited”
“Airspeed Low Inhibited”
MESSAGE
NOTES:
All volume levels at same volume as
existing EGPWS Self-Test messages
all required input information.
Low Airspeed Monitor enabled, but the advisory
have been inhibited via aircraft wiring.
is inoperative.
Low Airspeed Monitor enabled, but the advisory
have been inhibited via aircraft wiring.
NOTE: Operators/Installers must refer to their Instructions for Continued Airworthiness (ICA) documentation to
identify the approved configurations specific to their aircraft type/model having Low Airspeed Monitor
installed.
CAGE CODE: 97896 SCALE: NONE SIZE: A DWG NO.: 060-4199-180 REV: G SHEET 68 of 68
 Loading...
Loading...