Page 1

MC ToolKit
User Manual
Doc. No.: 34-ST-25-20
Release: 3
Last Revision Date: 9/06
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual i
9/06
Page 2

Notices and Trademarks
Copyright 2006 by Honeywell International Inc.
Release 3 September, 2006
Warranty/Remedy
Honeywell warrants goods of its manufacture as being free of defective materials and faulty workmanship. Contact
your local sales office for warranty information. If warranted goods are returned to Honeywell during the period of
coverage, Honeywell will repair or replace without charge those items it finds defective. The foregoing is Buyer's sole
remedy and is in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, including those of merchantability and
fitness for a particular purpose. Specifications may change without notice. The information we supply is believed
to be accurate and reliable as of this printing. However, we assume no responsibility for its use.
While we provide application assistance personally, through our literature and the Honeywell web site, it is up to the
customer to determine the suitability of the product in the application.
Industrial Measurement & Control
Honeywell
2500 W. Union Hills Drive
Phoenix, AZ 85027
Honeywell is a U.S. registered trademark of Honeywell
Other brand or product names are trademarks of their respective owners.
Page ii 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 3

About This Document
Contacts
World Wide Web
The following lists Honeywell’s World Wide Web sites that will be of interest to our industrial automation and
control customers.
Honeywell Organization WWW Address (URL/e-mail)
Corporate http://www.honeywell.com
Industrial Measurement and Control http://content.honeywell.com/imc/
International http://www.honeywell.com/Business/global.asp
Technical Assistance Center ACE@Honeywell.com
(e-mail)
Telephone
Contact us by telephone at the numbers listed below.
Organization Phone Number
United States and Canada Honeywell Inc.
Industrial Automation and Control
Technical Assistance Center
Solution Support Center
Asia Pacific Honeywell Asia Pacific Inc.
Hong Kong
Europe Honeywell PACE
Brussels, Belgium
Latin America Honeywell Inc.
Sunrise, Florida U.S.A.
1-800-343-0228 Sales
1-800-525-7439 Service
1-800-423-9883
1-602-313-3578
(852) 8298298
[32-2] 728-2111
(305) 364-2355
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual iii
9/06
Page 4

Symbol definitions
The following table lists those symbols used in this document to denote certain conditions.
Symbol Definition
This CAUTION symbol on the equipment refers the user to the Product Manual for
additional information. This symbol appears next to required information in the manual.
This WARNING symbol on the equipment refers the user to the Product Manual for
additional information. This symbol appears next to required information in the manual.
WARNING: risk of electrical shock. This symbol warns the user of a potential shock
hazard where HAZARDOUS LIVE voltages greater than 30 Vrms, 42.4 Vpeak, or 60
VDC may be accessible.
ATTENTION, Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) hazards. Observe precautions for
handling electrostatic sensitive devices
Protective Earth (PE) terminal. Provided for connection of the protective earth (green
or green/yellow) supply system conductor.
Functional earth terminal. Used for non-safety purposes such as noise immunity
improvement. NOTE: This connection shall be bonded to protective earth at the
source of supply in accordance with national local electrical code requirements.
Earth Ground. Functional earth connection. NOTE: This connection shall be bonded to
Protective earth at the source of supply in accordance with national and local electrical
code requirements.
Chassis Ground. Identifies a connection to the chassis or frame of the equipment shall
be bonded to Protective Earth at the source of supply in accordance with national and
local electrical code requirements.
Page iv 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 5

Contents
Introduction ................................................................................................................1
Purpose/Scope ....................................................................................................................................1
Product Description .............................................................................................................................2
Procedural Considerations ..................................................................................................................3
Transmitter Type and Communication Mode...................................................................................3
Type of Procedure and Prerequisites ..............................................................................................3
Special Equipment and/or Environment for Calibration...................................................................3
Transmitter/Communications Characteristics......................................................................................4
Honeywell Transmitter (Analog Mode) ............................................................................................4
General Procedures .................................................................................................10
Overview............................................................................................................................................10
Primer for MC Toolkit & SDC 625 Application Software ...................................................................10
Start-Up and Basic Operation and Navigation...............................................................................10
Input Methods: Letter, Numbers, Symbols ....................................................................................11
MC Toolkit Application Software Display Conventions .....................................................................13
Navigation ......................................................................................................................................13
Data Entry and Display ..................................................................................................................15
SDC 625 Application Software Display Conventions ...............................................16
Navigation..........................................................................................................................................16
Introduction........................................................................................................................................17
Summary of Operating Procedures...................................................................................................18
Procedural Considerations ................................................................................................................20
Input calibration..............................................................................................................................20
Output Calibration..........................................................................................................................20
MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters.........................................36
Introduction........................................................................................................................................36
General Procedures ..........................................................................................................................38
Procedural Considerations ................................................................................................................40
Input Calibration.............................................................................................................................40
Output Calibration..........................................................................................................................41
Using SDC 625 Application Software with all HART Transmitters and Devices....... 61
Introduction........................................................................................................................................61
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual v
9/06
Page 6

Messages and Diagnostic Codes............................................................................. 65
Messages and Diagnostic Codes......................................................................................................65
Reference Data ........................................................................................................ 75
Honeywell DE Fields and Values ......................................................................................................77
Honeywell HART Fields and Values .................................................................................................79
Generic HART Fields and Values .....................................................................................................82
XML Database (Samples) .................................................................................................................89
XML Sample - Honeywell DE ........................................................................................................89
XML Sample - non-Honeywell HART ............................................................................................89
MCT101 Maintenance..............................................................................................91
Modem Battery Replacement............................................................................................................91
MC Toolkit Software Installation/Maintenance ..................................................................................92
Overview 92
MCT202 Maintenance..............................................................................................93
Battery Replacement.........................................................................................................................93
SD Card Replacement.......................................................................................................................93
Replacement Parts................................................................................................... 93
MCT101 Replacement Parts .............................................................................................................93
MCT202 Replacement Parts .............................................................................................................95
Page vi 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 7

Tables
Table 1 DE Displays / Tasks Summary......................................................................................................................18
Table 2 DE Upload Procedures ..................................................................................................................................21
Table 3 DE Main Menu Procedures ...........................................................................................................................22
Table 4 Input Calibration (DE Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset Corrects ............................25
Table 5 Output Calibration - Loop Test......................................................................................................................30
Table 6 DE Output Calibration - Trim DAC Current.................................................................................................32
Table 7 DE Calibration - Apply Values......................................................................................................................34
Table 8 HART Displays / Tasks Summary ................................................................................................................39
Table 9 HART Device UPLOAD Procedure..............................................................................................................42
Table 10 Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedure...................................................................................................44
Table 11 Honeywell HART Diagnostics/Service Menu Procedures ..........................................................................49
Table 12 Honeywell HART Calibration - Zero Trim .................................................................................................51
Table 13 Honeywell HART Calibration - LRV and URV..........................................................................................53
Table 14 Honeywell HART Calibration - Reset corrects ...........................................................................................54
Table 15 Honeywell HART Calibration - Loop Test .................................................................................................55
Table 16 Honeywell HART Calibration - D/A Trim..................................................................................................56
Table 17 Honeywell HART Calibration - Apply Values............................................................................................58
Table 18 MC Toolkit/SDC 625 Error Messages.........................................................................................................65
Table 19 DE Messages ...............................................................................................................................................68
Table 20 HART Messages..........................................................................................................................................69
Table 21 ST 3000 Device Status Messages (DE).......................................................................................................71
Table 22 STT Device Status Messages (DE)..............................................................................................................72
Table 23 ST 3000 Device Status Messages (HART)..................................................................................................73
Table 24 STT Device Status Messages (HART) ........................................................................................................74
Table 25 Glossary.......................................................................................................................................................75
Table 26 DE Fields and Values ..................................................................................................................................77
Table 27 HART Fields and Values.............................................................................................................................79
Table 28 Generic HART Fields and Values...............................................................................................................82
Table 29 HART Universal Commands.......................................................................................................................87
Table 30 HART Common Practice Commands..........................................................................................................88
Table 31 Battery Removal and Replacement Procedure ............................................................................................91
Table 32 MCT101 Replacement Parts........................................................................................................................93
Table 33 MCT202 Replacement Parts........................................................................................................................95
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual vii
9/06
Page 8

Figures
Figure 1 Components of the MC Toolkit........................................................................................................................1
Figure 2 MCT202 (rugged and intrinsically safe models)..............................................................................................1
Figure 3 Honeywell ST 3000 Smart Transmitter - Analog mode...................................................................................4
Figure 4 Honeywell Analog Value Scaling ....................................................................................................................6
Figure 5 Honeywell DE Mode Value Scaling ................................................................................................................8
Figure 6 Honeywell (HART) Transmitter Diagram ........................................................................................................8
Figure 7 HART Point-point and Multi-Drop Value Scaling...........................................................................................9
Figure 8 Start-up - MC Toolkit Application.................................................................................................................10
Figure 9 Menu Tree - Honeywell DE Displays ............................................................................................................17
Figure 10 Menu Tree - Honeywell HART Displays.....................................................................................................36
Figure 11 Menu Tree: non-Honeywell HART Displays...............................................................................................37
Figure 12 HART Menus (Display Summary)...............................................................................................................38
Page viii 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 9

Purpose/Scope
This manual is intended to facilitate the use of the Honeywell MC Toolkit communications tool. It is
assumed that the user is skilled in the use and maintenance of process transmitters in process control, or
that he/she is under direct supervision of others with such skills.
The MC toolkit, with MC Toolkit Application Software and SDC 625 Application Software, enables
communication with several types of smart transmitters (pressure, temperature, etc) that are available for
use in the process control industry.
The emphasis of the information in this manual is directed primarily on the features and use of the
MC Toolkit in performing common maintenance tasks relating to transmitter devices, rather than on the
features and installation of specific transmitter devices.
It is recommended that that user should have the appropriate manuals available for specific transmitter
devices. For background information such as HART communications protocol and network wiring, it is
also recommended that the user should obtain publications available from agencies such s the HART
Communication Foundation.
Introduction
Ruggedized
Zone 2
Zone 1
Figure 1 Components of the MC Toolkit Figure 2 MCT202 (rugged and
intrinsically safe models)
This manual includes information of two types:
• background material that enables a skilled user to select the appropriate procedures in this manual and
to apply them in the appropriate sequence, and
• detailed descriptions of the MC Toolkit regarding functions, features, and procedures for applying
them
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 1
9/06
Page 10

Product Description
Product Description
The Honeywell MC Toolkit is a handheld communication package that enables convenient and reliable
communications with smart transmitters (temperature, pressure, and others). It consists of two software
applications – MC Toolkit Application Software and SDC 625 Application Software. The MC Toolkit
Application Software can be used to configure, monitor and calibrate Honeywell DE and HART
transmitters. The SDC 625 Application, utilizing HART Device Description (DD) technology, can be used
to configure, monitor and calibrated all HART devices – Honeywell or non-Honeywell devices. The MC
Toolkit can communicate to:
• any Honeywell analog transmitter with Honeywell proprietary digital communications protocol or with
DE (Digital Enhanced) communications protocol.
• any Honeywell transmitters with HART communications protocol
• Any HART transmitter from other manufacturers.
The MCT101 includes the following (separately orderable) components:
• a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant)
• a DE/HART Modem
• a Handheld Connector Cable that connects the PDA to the Modem
• Holster for PDA and Modem
• Honeywell MC Toolkit application software (CD ROM)
• Honeywell SDC 625 application software (on same CD ROM as MC Toolkit application software)
• Modem Battery
The MC Toolkit MCT202 version includes the following features:
• Ruggedized version- Environmentally hardened with no approvals.
• Zone 2 approvals: Intrinsically-safe version available with FM Class I, Div 2 and ATEX Zone 2 approvals.
• Zone 1 approvals: Intrinsically-safe version available with FM Class I, Div 1 and ATEX Zone 1 approvals.
The MCT202 includes the following components:
• An iroc PDA with integrated DE/HART modem
• Honeywell MC Toolkit CD ROM with MC Toolkit and SDC625 application software
• Test leads for the electrical connection from the PDA to the field device
All versions of the PDA incorporate the Microsoft Pocket PC 2003 or 2005 Operating System. Honeywell
software operates as an application package in the familiar MS Windows environment, and is virtually
identical for all versions of the PDA. The MC Toolkit application or SDC 625 application can run
simultaneously with other Pocket PC applications.
Page 2 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 11
Procedural Considerations
CAUTION! WARNING!
In some cases, the use of a field communicator with a transmitter that is connected on-line can have an
adverse effect on process operations.
Before using the MC Toolkit, be certain that you know the potential consequences of each procedure, and
that you use the appropriate safeguards to prevent problems. For example, if the transmitter is an element
of a control loop, the loop should be placed in the manual operating mode, and alarms and interlocks
("trips") should be disabled as appropriate before beginning the procedure.
The primary factors to be considered are separated into three categories under the following three headings.
The information under the following headings is intended as background for use of the DE Procedures and
HART Procedures, which are given in separate sections of this manual.
Transmitter Type and Communication Mode
The MC Toolkit can be used with various types of field transmitters, most of which can be operated in
more than one mode.
• Honeywell DE transmitter operating in Smart Analog Mode
Introduction
• Honeywell DE transmitter operating in Digital Enhanced (DE) Mode
• Honeywell (and other) HART transmitter operating in point-to-point (Analog w/ HART digital mode)
• Honeywell (and other) HART transmitter operating in multi-drop (HART-only digital mode)
The salient characteristics of each item listed, and the implications of each characteristic in procedures are
described under Transmitter/Communications Characteristics
Type of Procedure and Prerequisites
The MC Toolkit is designed to provide three basic functions:
• Monitoring
• Configuration
• Calibration
Depending on combinations of factors such as transmitter type, and communications mode, some
procedures such as monitoring the performance of a transmitter can be straightforward and innocuous, but
in some cases can also require special preparation and precautions.
Special Equipment and/or Environment for Calibration
Typically, a smart transmitter delivered by a major manufacturer today is designed to provide a high degree
of precision throughout its operating range, and has been calibrated to a high level of accuracy that is not
easy to duplicate in the user's plant process areas. Moreover, the design, materials, and manufacturing
process employed will ensure that the instrument will stay within calibration limits for an extended period.
Typically, calibration of a process-connected transmitter will degrade, rather than augment, the capability
of a smart transmitter. For this reason, the calibration procedures in this MC Toolkit User Manual include
a recommendation that the transmitter is removed from service and is calibrated only in a controlled
laboratory environment, using equipment whose precision is certified.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 3
9/06
Page 12

Transmitter/Communications Characteristics
Transmitter/Communications Characteristics
The characteristics of a typical Honeywell Smart Pressure Transmitter are summarized in Figure 3 through
Figure 7, following.
Honeywell Transmitter (Analog Mode)
Analog-to-Digital Sensing
As indicated by key number (1) in Figure 3, the sensor is a sealed assembly that typically includes three
separate sensors: Differential Pressure (DP), Static Pressure (SP) and Temperature (Temp).
Input Characterization
The sensor also includes a PROM, (2), which is Non-Volatile Memory (NVM) that stores
"characterization" constants written at the factory, and calibration constants, which can be written at the
factory and/or at the user's site. The data in NVM is used in an algorithm in the microprocessor, (3), which
is executed continuously to calculate the input value.
Figure 3 Honeywell ST 3000 Smart Transmitter - Analog mode
The characterization constants, which are written at the factory, are derived from highly precise testing of
the sensor's response over a range of temperatures, and from the Lower Range Limit (LRL) to the Upper
Range Limit (URL) of the sensor. The purpose of the characterization constants is to compensate for very
small inaccuracies in the sensor that are introduced by variations inherent in construction materials, and to
ensure that the calculated input is a high-fidelity representation of the analog input (linear or square root),
with a precise "zero" reference.
Input Calibration ("Corrects")
To optimize accuracy, the PROM includes storage for calibration constants: Correct Input Zero, Correct
LRV, and Correct URV.
The corrects constants provide for optimum accuracy in that they enable fine-tuning of the input
calculations, by first correcting at zero input, then bounding the input calculations at the user's operating
Page 4 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 13

Introduction
range. That is, corrections are applied at the Lower Range Value (LRV) and the Upper Range Value
(URV).
Factory calibration can be specified in the purchase order. Also, if precision equipment, suitable
environment, and required skill are available at the user's site, input calibration can be done locally.
Reset Corrects
In some cases, the calibration procedure yields unsatisfactory results such that the Corrects constants must
be removed from memory. The Reset Corrects erases all three corrects constants, so that only the factorywritten characterization constants will be retained in the PROM.
Digital Communication Path
As indicated at key number (4) in Figure 4, the Honeywell Smart Transmitter includes a path for digital
communications between the sensor (via the microprocessor) and the 4-20 mA current loop that connects
the transmitter to external communications devices such as process control equipment ("receiver") and/or to
a MC Toolkit.
Digital to-Analog Conversion and Transfer
The digital-to-analog converter (D/A) shown at key number (5) in Figure 3 is shown as a box with a dotted
line to indicate that analog output mode is a user-selectable feature, for use in an application whose
receiving equipment requires an analog input.
Note that the Digital I/O (Comm) (communications) box is shown in Figure 3 with solid line to indicate
that the digital communications path is available at all times, even when analog mode is selected.
Honeywell Transmitter Output - Analog Mode
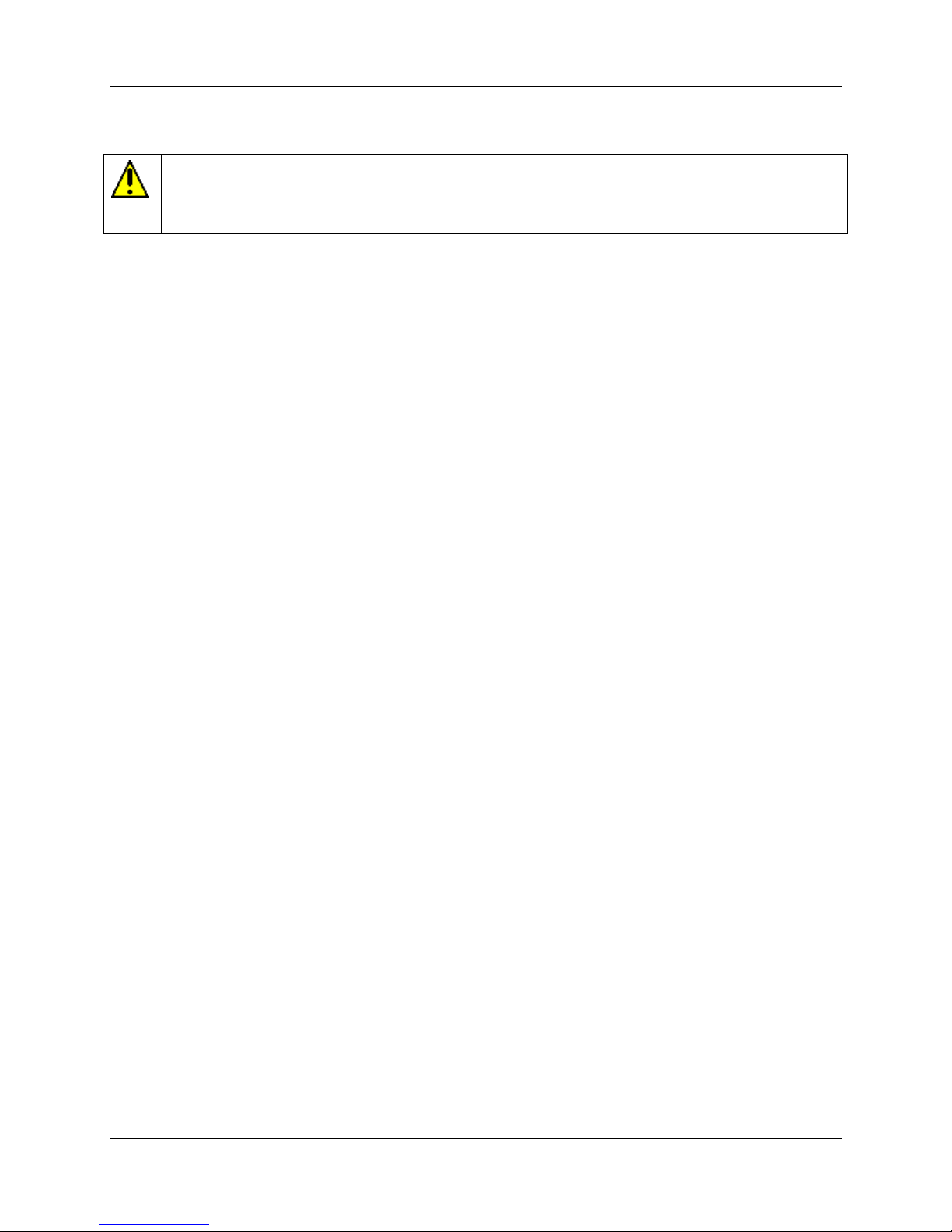
The diagram in Figure 4 provides an overview of a Honeywell transmitter operating in the analog mode.
Analog (PV Signal) Output
The vertical scale at the left of Figure 4 is an example of the available range (LRL to URL) of a pressure
transmitter sensor as built and characterized at the factory. The area of this scale that is highlighted in
white represents the configured process operating range (LRV to URV) - in this case, from 100 in H
225 in H
2
O.
Note that Engineering Units (EUs) shown in Figure 4 are included here only for reference. The transmitter
does not perform any conversion of the base units value to Engineering Units. All conversion to EUs is
performed in the MC Toolkit and/or in other receiving devices such as operating panels associated with
control equipment. Default conversion is to inches-H2O @39F.)
The output of a Honeywell transmitter operating in the analog mode is a scaled value (0% - 100%) of
current (4 mA to 20 mA), whose lower and upper limits correspond to the configured operating range
(LRV-URV), respectively.
At the right of Figure 4, "PVEULO", "PV", and "PVEUHI" are examples of parameter names that appear
on Honeywell control equipment, which are used as follows.
Parameter Name Parameter Description Display Examples
O to
2
PVEULO Process Value , Engineering Units, Low
PV Process Value
PVEUHI Process Value , Engineering Units, Low
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 5
9/06
PVEULO 100 in H20
PV 175 in H20
PVEUHI 225 in H20
Page 14
Transmitter/Communications Characteristics
Figure 4 Honeywell Analog Value Scaling
Digital (Communications Signal) Input/Output
As indicated at the right of Figure 4, communications between the MC Toolkit and the Honeywell Smart
Transmitter consist of digital pulse strings, with rapid transitions of current level between (approximately)
4 mA and 20 mA.
URVURV
Caution:
These rapid transitions provide for effective communications, but will interfere adversely with a transmitter
operating on-line in a control loop.
The MC Toolkit communicates digitally; exercise caution and good judgment when connecting the unit to
an on-line transmitter operating in the analog mode.
Honeywell Transmitter Output - Digital Enhanced Mode
Most of the operation of the Honeywell Smart Pressure Transmitter Digital Enhanced (DE) mode is similar
to that of operation in the analog mode. The essential characteristics of operation in DE mode are shown in
Figure 5.
As indicated at the right of Figure 5, output values of process variables, as well as digital communications,
are transferred to a receiving device digitally. The digital coding is Honeywell proprietary, which requires
the use of DE-capable Honeywell control equipment.
The use of DE mode offers several advantages:
process safety
Unlike in the analog mode, communications devices do not "bump" the
value of the PV.
accuracy is retained with less
maintenance
facilitates maintenance tasks
Digital communications are relatively immune to small variations in
circuit resistance or supply voltage.
Honeywell control systems include operating displays that enable direct
communication with transmitters operating in DE mode.
Page 6 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 15
Introduction
CAUTION:
Although it in not necessary to put a control loop in manual before communicating with a
transmitter operating in DE mode, caution is required if there is any potential for error in
identifying operating mode.
Honeywell HART Transmitters
Transmitters with HART capability have features that vary among manufacturers and with the
characteristics of specific devices. The MC Toolkit supports the HART Universal, Common Practice, and
Device Specific Commands that are implemented in Honeywell HART transmitters.
As the diagram in Figure 6 shows, the Honeywell HART Transmitter is virtually identical to non-HART
transmitters, except that the HART version includes a Digital I/O Modulator/Demodulator block (key
number (4) instead of the Honeywell DE communications block.
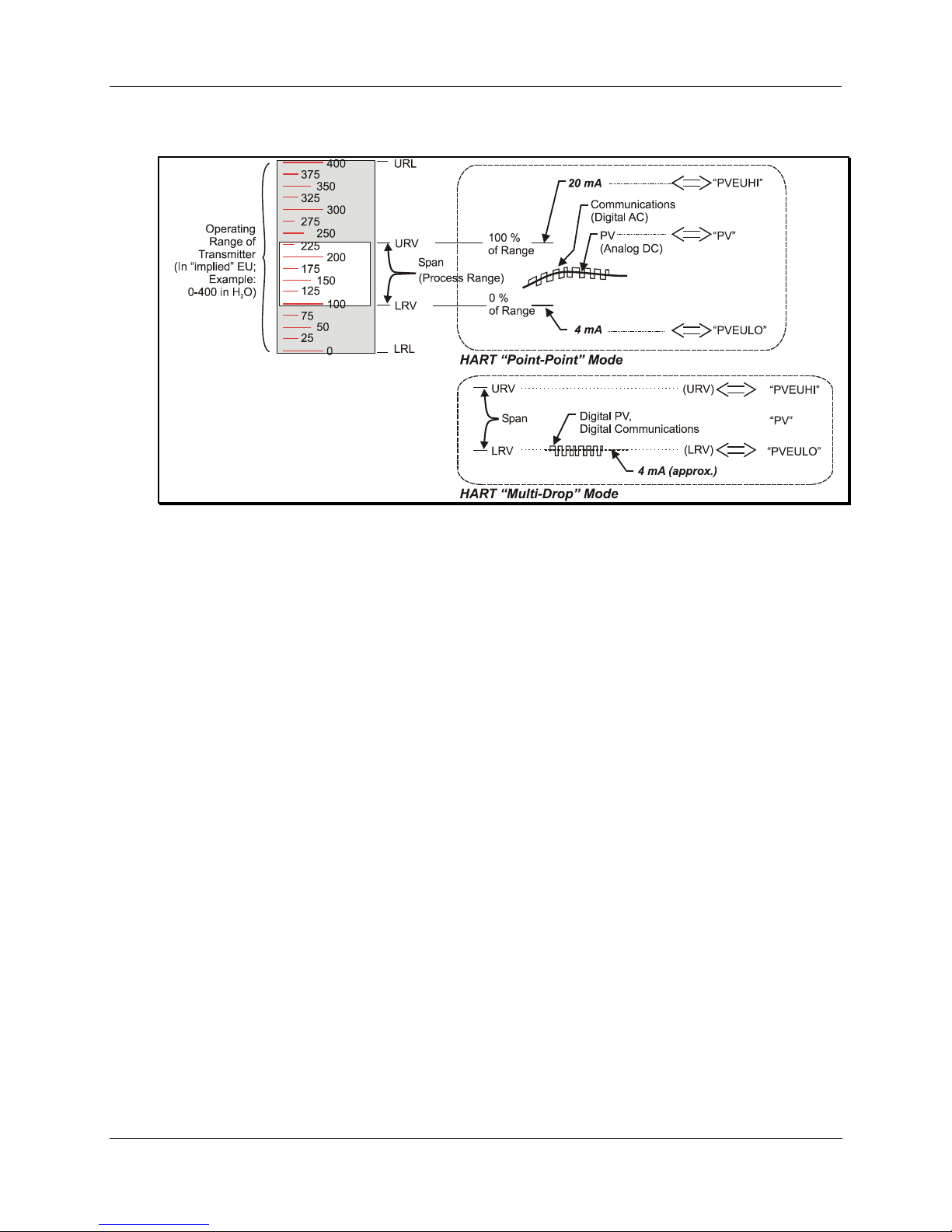
As indicated in Figure 7, the output of the HART includes two primary modes:
• Point-to-Point Mode, in which one transmitter is connected via a two-conductor, 4-20 mA current loop
to one receiver.
• Multi-Drop Mode, in which several transmitters are connected via a two-conductor network to a
multiplexed receiver device.
In point-to-point mode, the value of the primary PV is represented by a 4-20 mA current loop, almost
identical to that of the Honeywell Transmitter operating in analog mode. In this case however, the analog
signal is modulated by Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) methods, using frequencies and a current amplitude
that do not affect analog sensing at the receiver.
Note that the accuracy of the analog level must be precisely controlled for accurate sensing, but that HART
communications will not "bump" the process variables.
In multi-drop mode, up to 16 transmitters (addresses 0-15) can exist on the two-conductor network, which
precludes analog transmission methods. In this case, the same FSK modulation method is used for
conveying levels of PV (and other variables) and also for communications.
CAUTION:
Before connecting to a HART transmitter, ensure that the MC Toolkit is not set up for DE
communications, whose current amplitude can "bump" process variables in either point-topoint mode or in multi-drop mode.
Non-Honeywell HART Transmitters and Devices
HART-capable transmitters from any manufacturer and for any specific purpose are designed to commonagreement standards that provide for inter-operability.
Guidelines published by the HART Communication Foundation enables manufacturers to design devices
that communicate via a set of standard commands and responses.
The standard set of commands is an integral component of the Honeywell MC Toolkit that enables
communication with many HART transmitters from other manufacturers.
The MC Toolkit application software supports the HART Revision 5.0 Universal Commands and HART
Revision 5.0 Common Practice Commands. However, the MC Toolkit supports only a recommended
number of Common Practice commands. The MC Toolkit does not support device-specific commands for
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 7
9/06
Page 16
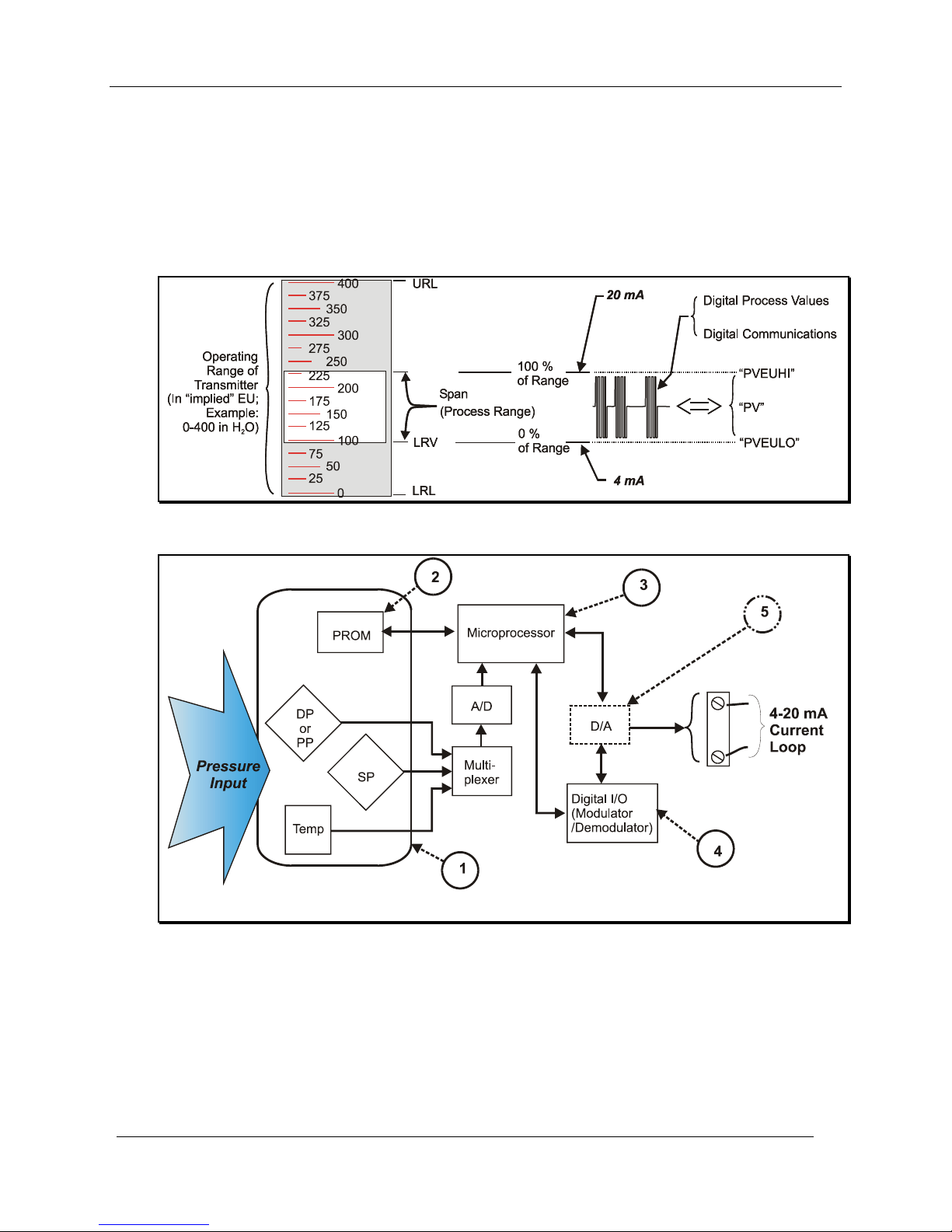
Transmitter/Communications Characteristics
non-Honeywell transmitters. For more information, refer to tables in the Reference Data section of this
manual.
It is recommended that the SDC 625 application software, based on DD-IDE/SDC-625 technology and
"OPEN" tools standard, be used with non-Honeywell HART devices. The SDC 625 is based on HART
Revision 5.0 and uses Device Descriptions stored in the Pocket PC to communicate to all universal,
common and specific device commands. MC Toolkit will come with all HART Registered (updated once
per quarter) Device Descriptions pre-loaded.
URVURV
Figure 5 Honeywell DE Mode Value Scaling
Figure 6 Honeywell (HART) Transmitter Diagram
Page 8 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 17
Introduction
Figure 7 HART Point-point and Multi-Drop Value Scaling
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 9
9/06
Page 18
General Procedures
Overview
The Honeywell MC Toolkit includes MC Toolkit application software and SDC 625 application software
running in the PDA, a general-purpose, hand-held computing device.
This section highlights some of the general-purpose features that facilitate use of the MC Toolkit software.
Primer for MC Toolkit & SDC 625 Application Software
The following is intended as a primer for using selected Pocket PC features with the MC Toolkit
application software.
Each of the following descriptions of features includes only the name of the feature and its functionality as
it is used with the MC Toolkit. The details of each feature are provided in the HELP information that is
included with the PDA.
As you become familiar with the MC Toolkit, you may want to explore other features that are listed and
described in the PDA HELP information.
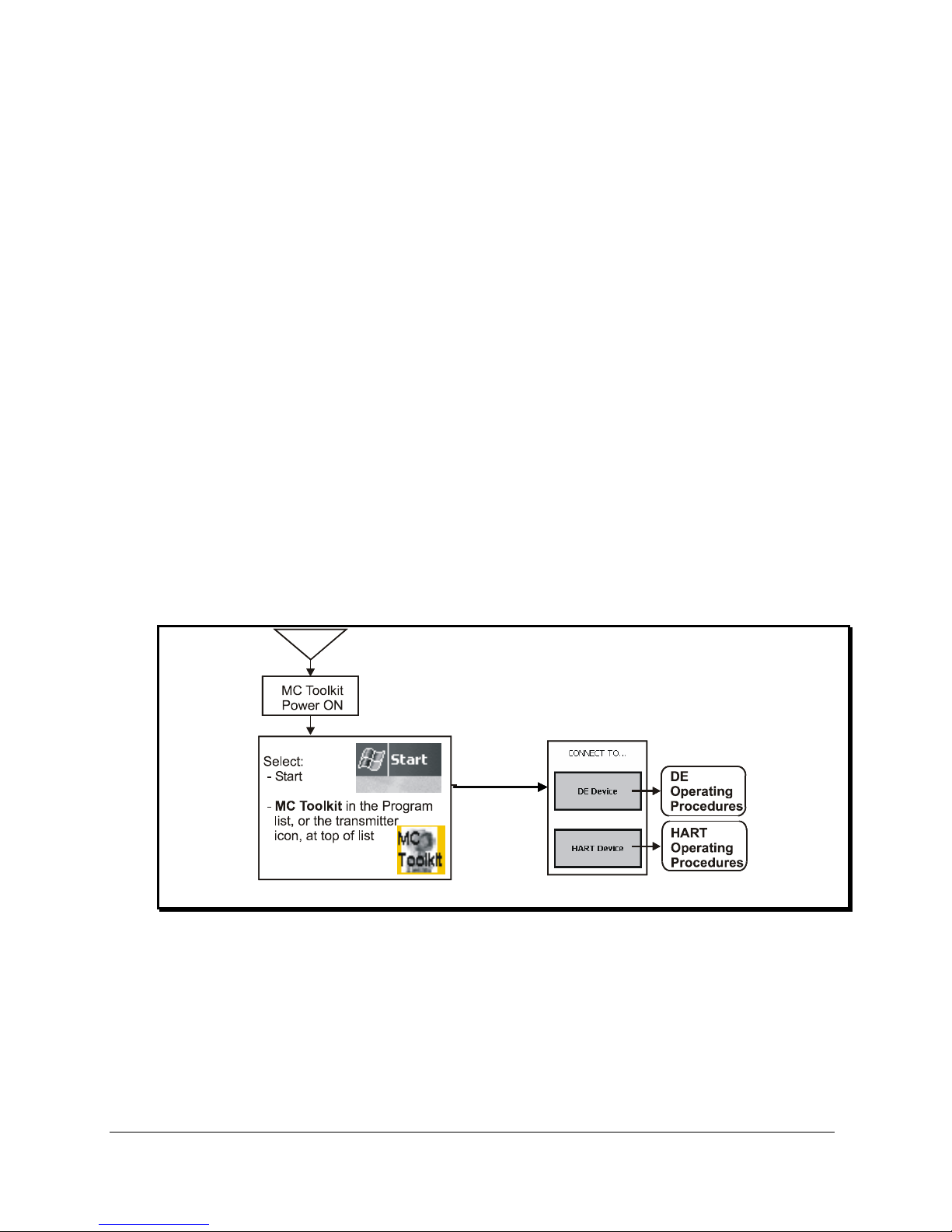
Start-Up and Basic Operation and Navigation
The sequence for starting the Pocket PC and the MC Toolkit application Software is illustrated in Figure 8
Start-up - MC Toolkit Application.
Figure 8 Start-up - MC Toolkit Application
Similarly to the MC toolkit application software, the SDC 625 application software can be started up. Turn
on the PDA and click on the SDC 625 icon. The SDC 625 icon can be found by selecting Start and then
Programs. The SDC 625 executable file can also be found in the Storage Card under File Explorer.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 10
9/06
Page 19

Input Methods: Letter, Numbers, Symbols
The PDA includes four methods for character input: Block Recognizer, Keyboard, Letter Recognizer, and
Transcriber.
In the Keyboard method, the user selects a text field in display, and then selects a character at a time from a
virtual keyboard. Using the keyboard involves familiar concepts that will enable quick and accurate
entries.
In the other three methods, the stylus is used to write the desired input directly onto the screen, and each
requires some adaptation of user skills. Of these, the Transcriber is probably the most efficient and easiest
to use.
Input Methods: Selections and Options (Examples)
Overview Display - Input Selection Display - Input Options
To select an input method, tap the
General Procedures
arrow
at the lower-right of
the display, then tap the name of the
desired input method.
To select an option for the selected
input method, select Settings from the
Start Menu, Input from the Settings
menu, and then select the desired
input options.
Note that the icon next to the selection
arrow changes with the method
selected.
Block Recognizer
Overview Display - Input Selection Display - Input Options
In the Block recognizer, the stylus is
used to write characters into a letter
pad (the box at bottom, on the left) or
a numeric pad (on the right).
The "
?" icon is a link to HELP; the
@$ icon is a link to a table of
symbols.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 11
9/06
Page 20
Primer for MC Toolkit & SDC 625 Application Software
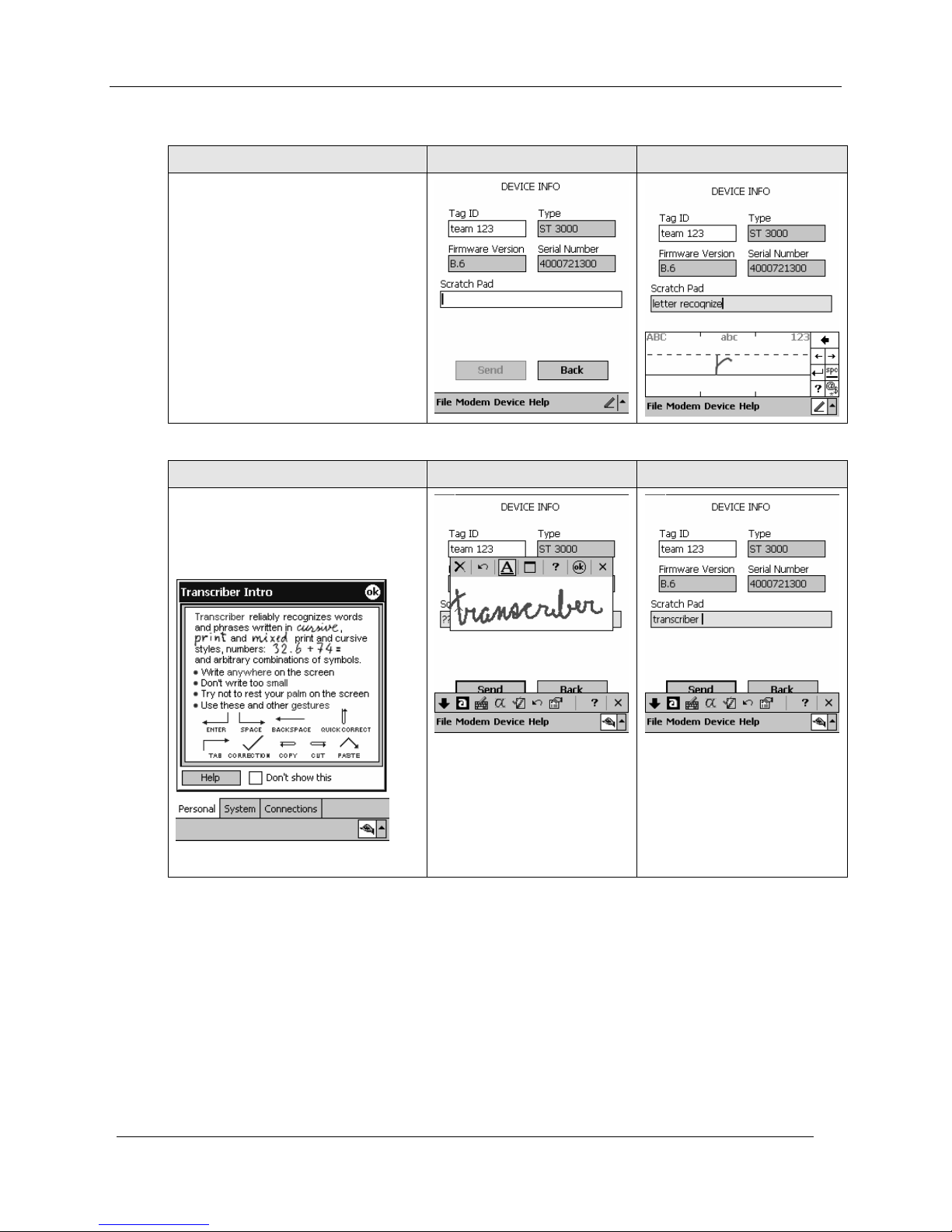
Letter Recognizer
Overview Empty Text Input Port Completing Entry
In the Letter Recognizer method,
characters are simply selected from a
virtual QWERTY keyboard.
As indicated at right, options include
small keys or large keys. Short-cut
options such as "gestures" (stylus
motion on the screen) and others are
also available via the Settings menu.
Transcriber
Overview Display - Input Selection Display - Input Options
Transcriber facilitates entry of text in
letters, numbers, and entire words.
Extensive HELP is provided for very
handy features.
Page 12 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 21

MC Toolkit Application Software Display Conventions
Navigation
Menu Buttons
In general, selecting a button in a display will call up the next-lower-level display, whose title is the same
or similar to the label on the button. A menu tree for Honeywell DE Displays is given Figure 9, and a
menu tree for HART display is given in Figure 10.
Back Button
In general, selecting the Back button at the bottom of any display will call up the next-higher-level
(previous) display.
In most displays, the Back button is at bottom-right or bottom-center. When it appears at bottom-left,
along with a left-pointing arrow, it indicates that selecting the Back button will necessitate a new Upload
of data from the transmitter to the MC Toolkit (~ 60 seconds).
Menu Bar
Menu Bar, Menu Selections, and HELP display
General Procedures
Menu
selections
The menu bar, at the bottom of each
display, enables the user to perform file,
diagnostic, and utility functions.
A typical display is shown below. Menu
selections are shown in detail at right
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 13
9/06
Page 22

MC Toolkit Application Software Display Conventions
Menu Bar, Menu Selections, and HELP display
File
Modem
Diagnostics
HELP
display
Exit
Closes the MC Toolkit application
Export
Enables export of database parameters in
XML format, which can be used by other
programs such as DocuMint. (Refer to the
Reference Data section for more
information.)
The Export selection is not available until a
transmitter database has been uploaded.
In DE Mode, the Connection State may be:
• Analog
• 4 Byte DE
• 6 Byte DE
In HART mode, the Connection State may
be:
• Burst Mode
• Not in Burst Mode
The Help display is available whenever the
MC Toolkit is active.
To export an XML file, select File, Export.
A popup message appears.
Select the
OK button.
It includes three groups of topics, each of
Selectable from the Help Menu
- General
- DE
- HART
Each group includes a list of topics. Each
topic (in blue, underlined letters) is
selectable to provide direct access to the
Help information.
Dragging the cursor in the scrollbar at right
enables viewing of all three groups of
topics. At the bottom of each group, a
Teh
Back to Top selection moves the display to
the beginning of the first group of topics.
Note:
The View, Find and (arrows) selections at
the bottom of the screen apply to the Help
that applies to the Pocket PC, and not to
the MC Toolkit application.
Page 14 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 23
General Procedures
Data Entry and Display
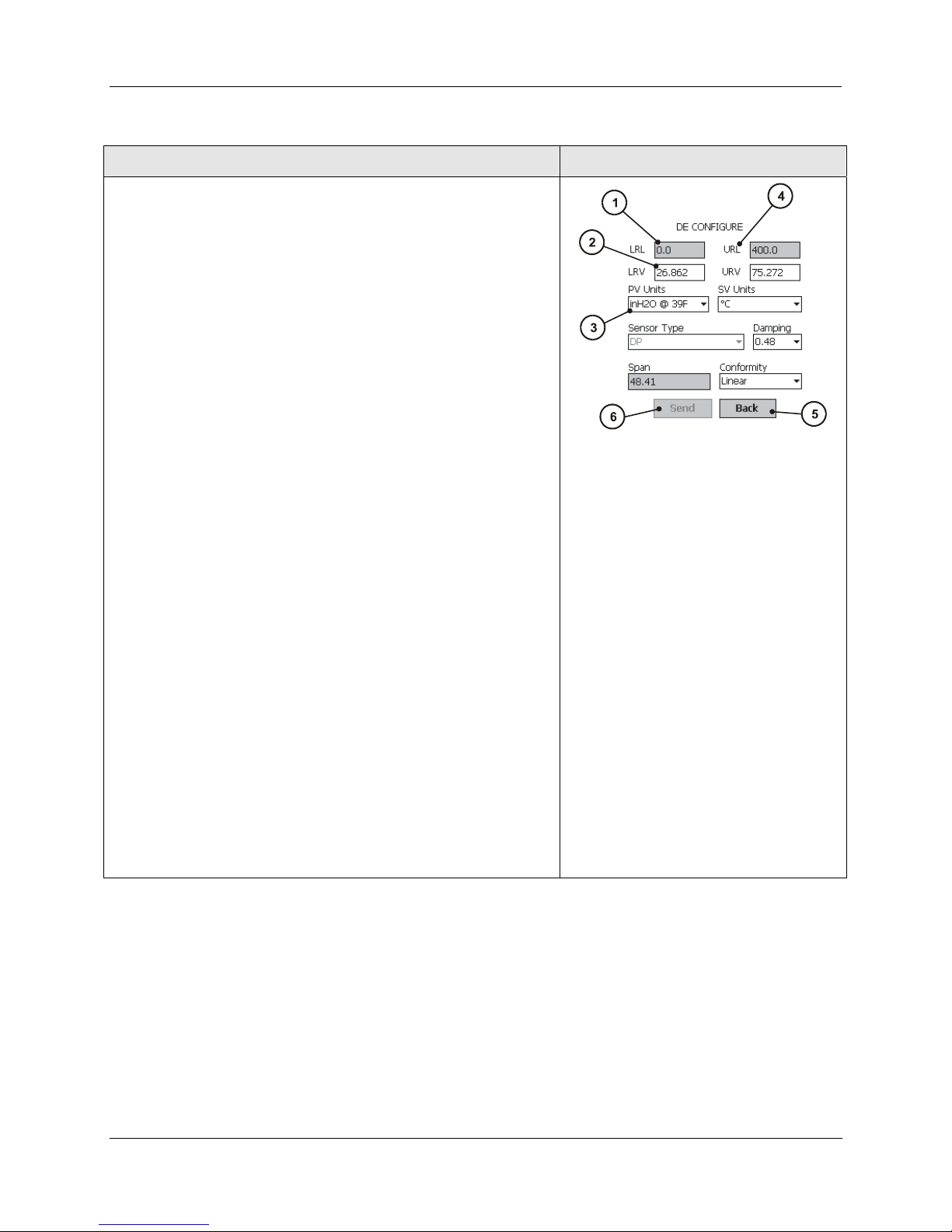
Key number / Description Illustration: Key Numbers
1. Box with no arrow and with gray background indicates a read-
only (R/ ) field. Numeric or text values in transmitter are
displayed only; user entry or modification is not permitted.
2. Box with white background and with no arrow indicates
Read/Write (R/W) text or numeric input field. Values previously
stored in memory (of the transmitter or of the MC Toolkit) are
displayed. The user can enter or modify values using an
appropriate Input Method (e.g., Keyboard).
Entering a new value turns the background yellow, indicating that
the value in the box is different from the value in memory.
When the Send button (6) is selected, the value in the box is
copied to memory in the transmitter, and the background color
returns to white.
If the user exits the screen before using the Send button, the
changes will be ignored.
3. Box with white background and arrow at right indicates a
read/write (R/W) selection list. The value previously selected
and stored in memory is displayed. Selecting the arrow at right
presents a list of available selections, and selecting an item from
the list places it in the selection box.
If the user exits the screen before using the Send button, the
changes will be ignored.
4. The label above the box indicates the meaning of the data inside
the box.
5. The Back button at the bottom of the display causes the display
that was viewed previously to return the screen.
6. The Send button is at half intensity when no values have been
changed. It changes to full intensity when one or more of the
boxes contain a changed value. Selecting the Send button when
it is highlighted will copy all changed values to memory, and the
button will return to half-intensity.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 15
9/06
Page 24
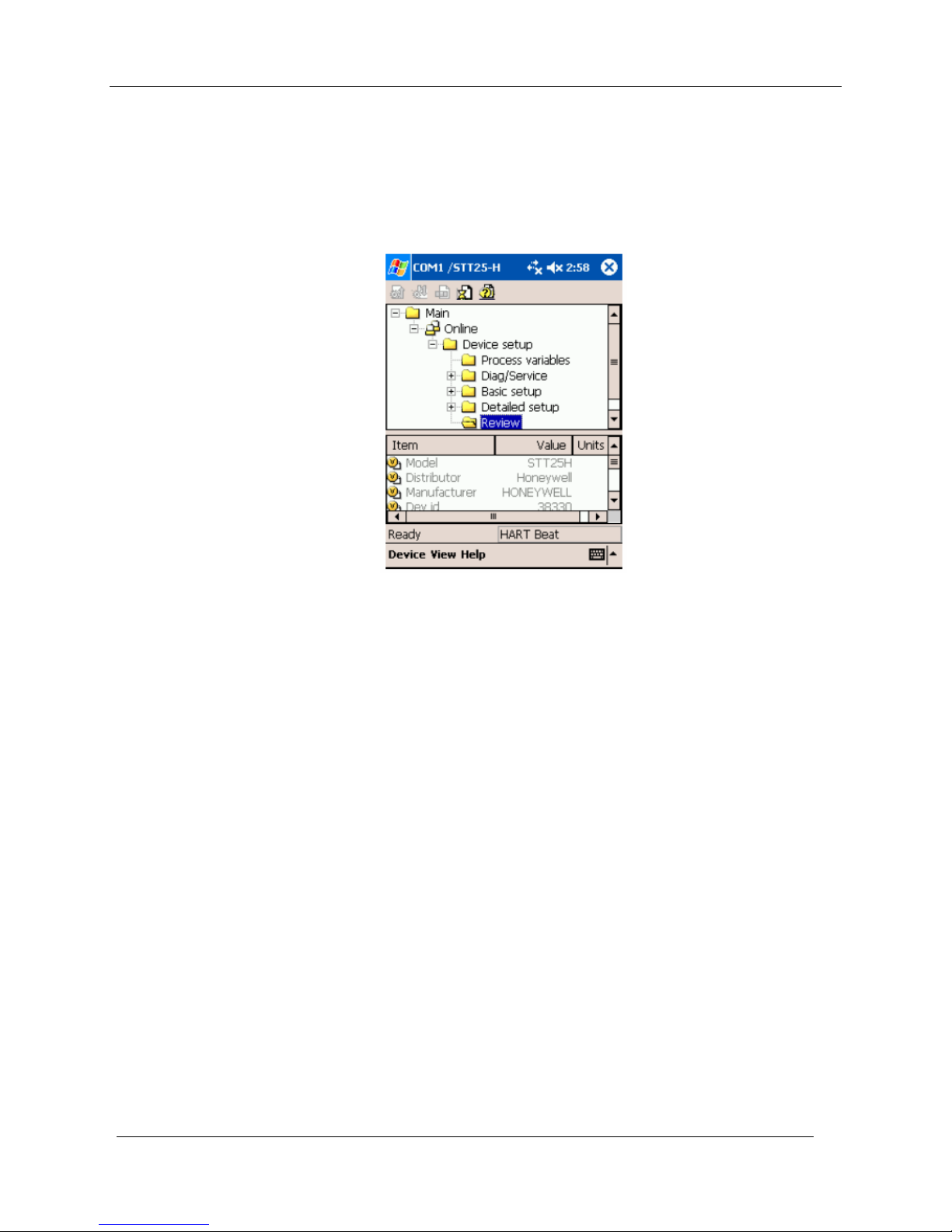
MC Toolkit Application Software Display Conventions
SDC 625 Application Software Display Conventions
Navigation
The SDC 625 Menu Bar can be located at the bottom of the Main screen. The menu selection consists of
the Device, View and Help options.
Device
The main purpose of the Device Menu is to Exit the program. Choosing Exit from the Device Menu will
end the SDC 625 program. Choose Preferences in the Device menu to access SDC Port Preferences.
View
The view selection can be used to check device/communication status by selecting Device Condition. One
can also view all HART Device Descriptions (DD) by selecting Available DDs. Device Descriptions,
obtained from the official HART communication CD-ROM, are listed by Manufacturer and Product. For
example, there is a folder listed as Honeywell. ST 3000 is listed as one product of four (with DD) under
this folder. Other Manufacturers with DDs are listed also. If you are working with a HART Device and
cannot find the DD in the list, please contact the Device Manufacturer. You can use the DD Copier
program when the manufacturer provides the device description.
Help
Choosing About SDC 625 will provide the Software Version.
Page 16 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 25

General Procedures
Using MC Toolkit Application Software with Honeywell DE
Introduction
This section contains procedures for using the MC Toolkit application software to communicate with
Honeywell DE Transmitters.
For specific data relating to parameters involved in the procedures, refer to
Transmitters
Reference Data.
Figure 9 Menu Tree - Honeywell DE Displays
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 17
9/06
Page 26
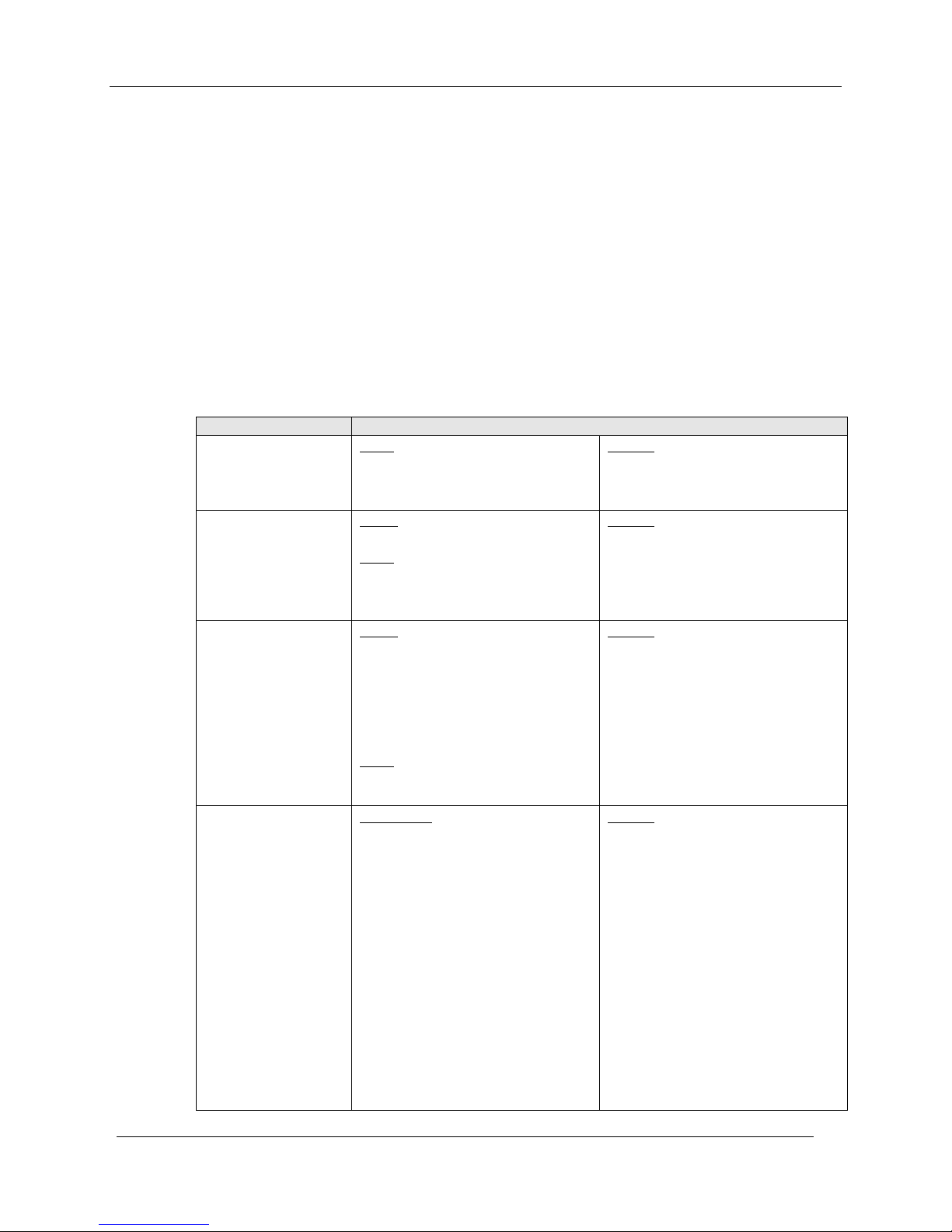
Summary of Operating Procedures
Summary of Operating Procedures
To access displays for Honeywell DE Transmitters:
• Start the MC Toolkit application; the CONNECT TO ... display will appear. (Refer to Figure 8
Start-up - MC Toolkit Application.)
• Upload the database from the transmitter. (The QUICK MONITOR display will enable viewing of
key parameters before taking the time for database uploading.) The DE MAIN MENU appears. (Refer
to Figure 9 Menu Tree - Honeywell DE Displays in this section.)
• Select the appropriate display from the DE MAIN MENU. (Refer to Table 3 DE Main Menu
Procedures in this section, and to the list of DE displays .)
The content of each display is summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 DE Displays / Tasks Summary
Menu Item Task
DEVICE INFO
GENERAL
DE CONFIGURE
CALIBRATION
Enter:
Device Type:
• Tag ID
• Message (in Scratch Pad)
Select:
• PV Type
Enter:
• Comm Mode
• Line Filter (STT)
• T/C Fault Detect (STT)
Select:
• PV Units
• SV Units
• Conformity (ST)
• Damping
• Sensor Type (STT)
• Linear
Enter:
• LRV
• URV
Enter/Select:
• Correct Input (Zero)
• Correct Input (LRV)
• Correct Input (URV)
• Reset Corrects (Zero, LRV, URV)
• Loop Test (Check
• Trim DAC Current (Calibrate
output current)
• Apply Values (that is, re-range
LRV and URV to PV input)
Observe (Read):
• Type
• Serial Number
• Firmware Version
Observe
• Failsafe Direction
Observe
• LRL
• URL
• Span
• Sensor Type (ST)
Observe
• Input at Zero, LRV, and URV
• (Verify) Reset Corrects
• Loop Current (continuity)
• Output Current level (at 0 %,
• Applied values of LRV and URV
(Read):
(Read):
(Read):
100%)
Page 18 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 27

Menu Item Task
LOCAL METER
Select:
• Meter Units (EU)
Enter:
• Custom Units
• (Custom) Flow (EU) value: Upper,
Lower
MONITOR
Auxiliary
Configuration
(STT 3000)
Observe
Select:
• Critical Status Latching
• Write Protection
• NAMUR
• CJ Compensation
Enter:
• CJ Temp
• Password (Write Protection)
• New Password
General Procedures
Observe
(Read):
• Meter Hardware Type
•
(Read):
• Input value
• Output value
• Secondary (Input) value
• Gross Status (code)
• Device Status (Messages)
Observe
(Read):
• High/Low PV Values
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 19
9/06
Page 28

Procedural Considerations
Procedural Considerations
Input calibration
Input calibration of pressure transmitters should be done only when necessary, and should be done only
under conditions that will ensure accuracy:
• The transmitter should be taken out of service, and should be moved to an area with favorable
environmental conditions: clean, dry, and temperature-controlled.
• The source for the input pressure must be very precise, and certified for correct operation.
• The procedures should be done by qualified personnel.
Details of requirements and procedure are given in Table 4.
Output Calibration
The Loop Test procedure is intended as a check for continuity and condition of components in the output
current loop. The Loop Test procedure is given in Table 5.
The Trim DAC Current procedure calibrates the output of the Digital to Analog converter for minimum
(0%) and maximum (100%) values of 4 mA and 20 mA, respectively. This procedure is used for
transmitters operating on-line in analog mode, to ensure proper operation of the transmitter with all
associated circuit components (wiring, power supply, control equipment, etc). It is necessary to use
precision test equipment (an ammeter or a voltmeter in parallel with precision resistor). The Trim DAC
procedure is given in Table 6.
The Apply Values procedure uses actual Process Variable input levels for calibrating the range of a
transmitter. To measure a liquid level for example, a sight-glass can be used to determine the minimum
(0%) and maximum (100%) level in a vessel. The Process Variable is carefully adjusted to stable
minimum and maximum levels, and the LRV and URV values are then set by commands from the MC
Toolkit. The DE Apply Values procedure is given in Table 7.
Page 20 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 29
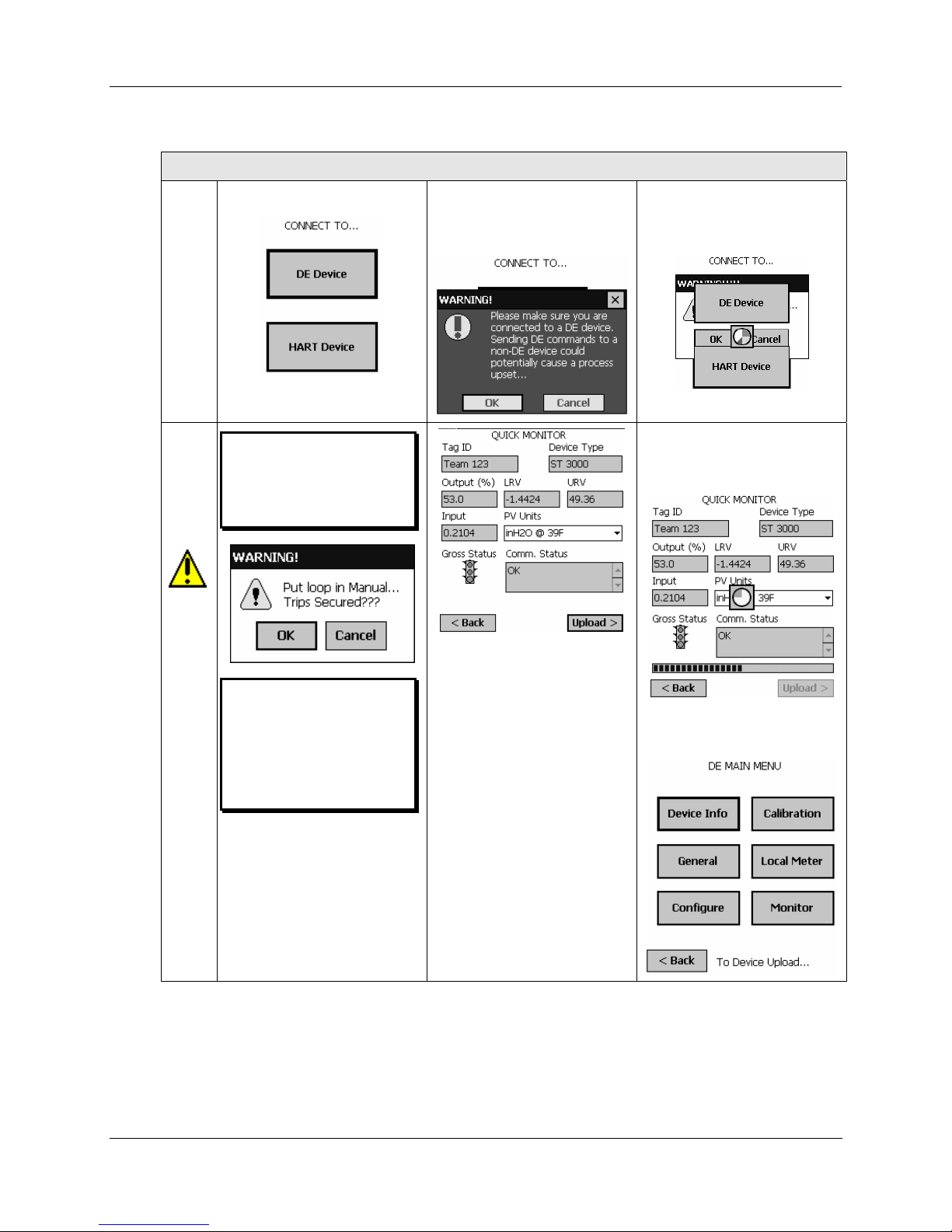
Table 2 DE Upload Procedures
General Procedures
DE Upload Procedures
Note:
This Warning appears only
if the transmitter is
configured for operation in
analog mode.
Select the DE Device button
This Warning message
appears.
If the MC Toolkit is connected
to a DE Device, select the
OK
button.
Select the
Upload button; the
wait cursor and progress bar
appear.
Use this display to
WARNING!
Before proceeding, if the
transmitter is part of a
control loop, ensure that
interlocks and alarms are
secured and that the loop is
in Manual control.
Then, select the OK button in
- Verify device
identification and to
monitor Gross Status
process conditions
- Select the desired Units
for the Process Variable
input using the PV Units
drop-down list.
Then, the Main Menu for an
ST 3000 Transmitter appears.
the popup message. The
display at right appears.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 21
9/06
Page 30
Procedural Considerations
Table 3 DE Main Menu Procedures
DE Main
Menu
(ST 3000)
DE Main Menu Procedures
(STT 3000)
Note:
This message appears if the
<Back button is selected if
the transmitter was set to
Output Mode (in Calibration
procedures), and the Output
was not later cleared.
Device
Info
General (ST 3000)
Tag ID (r/w)
User ID up to 8 alphanumeric characters (suggestion: relate
to functional process entities and/or plant areas).
Type (r)
Manufacturer's device type identifier (typically, a model
number)
Firmware Version (r)
Manufacturer's Firmware version identifier
Serial Number (r)
Manufacturer
Scratch Pad (r/w)
Up to 32 alphanumeric characters (suggestion: messages
to control room regarding observed/assigned operational
status)
(STT 3000)
PV Type (r/w)
Select: Dual Range
(STDC) or Single Range or
Single Range w/SV
Communication Mode
(r/w) Select: Analog or DE
4 Byte or DE 6 Byte
FS Direction (r)
(Upscale or Downscale;
selection is jumpered in the
transmitter).
Line Filter (r)
Select: 50hz or 60hz.
T/C Fault Detect (r/w):
Select: Enabled or
Disabled.
Page 22 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 31

DE
Configure
General Procedures
DE Main Menu Procedures
ST 3000
LRL (r): Lower Range Limit
URL (r): Upper Range Limit
LRV (r/w): Lower Range Value
URV (r/w): Upper Range Value
PV Units (r/w)
Selection of scaling value (default: inches of H2O@39)
SV Units (r/w)
Selection of scaling value (
Sensor Type (r)
0C/0
F)
Sensor Type associated with the transmitter
Damping (r/w)
STT 3000
Selection of level of digital noise reduction
Span (r)
Process Range (URL - LRL)
Conformity (r/w) (ST 3000)
Selection of conformity to input form: Linear or Square
Root
Linearization (r/w) (STT 3000)
Selection of conformity to input form: Linear or Non Linear
Calibration
Local
Meter
(ST 3000)
For more information, refer
to:
Table 4, Table 5, Table 6,
Table 7.
Meter Hardware (r)
Type designation of meter
associated with the transmitter
Meter Units (r/w)
Selection EUs for Local Meter
Custom Units (r/w)
(Refer to Transmitter User
Manual).
Flow EU Upper Value (r/w)
Selection of standard
Engineering Units for Flow
Upper Value
Flow EU Lower Value (r/w)
Selection of standard
Engineering Units for Flow
Lower Value
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 23
9/06
Page 32

Procedural Considerations
Local
Meter
(ST 3000
example)
DE Main Menu Procedures
Auxiliary
Configure
Monitor
Critical Status Latching
Enabled or Disabled.
Select
NAMUR
Enabled or Disabled.
Select
(Disable requires that Write
Protect is set to Not Write
Protected.)
CJ Temp.
Enter External Cold
Junction Temperature.
Select the
Read HI/LO
button to call up the READ
HIGH/LOW PV display.
SV (r)
Secondary Variable in
Engineering Units
Gross Status (r)
Gross transmitter status.
Select the
Device Status
button to call up the Device
Status display.
Select the Read button to
display the lowest and the
highest PV values since last
read.
Input (r)
Sensor input in Engineering
Units
Output (r)
Loop output as percent of
Span
Page 24 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Communication Status (r)
For status information, refer
to the section on
Messages and
Diagnostic Codes.
Page 33

General Procedures
Table 4 Input Calibration (DE Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset
Corrects
Input Calibration (De Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset Corrects
Requirements:
• Input source, with accuracy of at least
0.04%
• resistor, at least 250-ohms
• Voltmeter or Ammeter
• 24 Vdc Power Supply (nominal)
• Clean work area with suitable
environmental conditions.
• Pressure Transmitter must be level.
Overview of Procedures:
The Zero-Correct procedure establishes the
correct vertical positioning of the response
profile.
The LRV Correct and URV Correct
procedures establish the correct slope of the
response profile in the process operating
range by rotating the response profile
around the zero-reference point as a pivot.
The Zero-Correct procedure can be done at
any time during the Correct LRV and
Correct URV procedures in the same
calibration session.
The Correct LRV and Correct URV
procedure should never be performed
without first performing the Correct Input
(Zero) procedure in the same calibration
session.
Objective(s):
Using a precision PV input source as a reference, command
the transmitter to write calibration coefficients to NonVolatile Memory associated with transmitter input
hardware and software.
• Correct Input (Zero)
• Correct LRV
• Correct URV
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 25
9/06
Page 34

Procedural Considerations
Input Calibration (De Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset Corrects
Set-Up On Bench
A typical bench set-up is shown at right.
Connect the MC Toolkit as indicated, and
establish communication with the
transmitter.
For these procedures, components in the
current loop are not critical, provided that
they support reliable communication
between the transmitter and the MC Toolkit.
If a Honeywell ST 3000 Pressure
Transmitter is being calibrated, positioning
(leveling) is important, because the meter
body contains fluids that can affect zero
sensing.
Enter
(configure)
values for
LRV and
URV
From the DE MAIN MENU, select Configure to call up the
DE CONFIGURE display.
a. Use the
PV Units to select the appropriate Engineering
Units.
b. Using the keyboard, enter the desired LRV and URV
values.
c. Select the Send button to copy all newly entered values to
the transmitter. When the copy operation is complete,
Send will be displayed in half intensity.
Page 26 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 35

Input Calibration (De Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset Corrects
Call up
Calibration
display
Correct
Input at
Zero
Navigate to the DE
Calibration display as
follows.
Select Back (go to DE Main
Menu), then select the
Calibration button.
Select Corr. Input (zero).
This message appears.
General Procedures
As indicated below, this procedure will shift the slope up
or down to eliminate the error at the zero reference. The
slope (angle) of the response is unchanged.
NOTE:
The PV Input (Zero) refers
to a known standard such
as zero pressure (e.g.: vent
`
both sides of a DP
transmitter).
Select Yes in the message box
above; this message appears.
At this point, ensure that the value of the PV applied at the
input is exactly Zero.
Then, select the OK button in the popup message.
This action sends the Correct Input (Zero) command to the
transmitter, which adjusts the input calculation.
Wait until this message
appears.
When the transmitter has
completed the Zero
Correction, this message
appears.
Select the
OK button to
acknowledge.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 27
9/06
Page 36

Procedural Considerations
Input Calibration (De Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset Corrects
Correct
Input at
LRV
(ST 3000)
Select the
button. This message appears.
Adjust the PV input pressure
to the exact value of the LRV
entered in the DE
CONFIGURE display.
Correct LRV
Select the
OK button; this
message appears.
Observe the input pressure
at the applied value; when
it is stable, select the
button.
OK
When the transmitter has
completed the LRV
correction, this message
appears.
Select
OK to
acknowledge.
Correct
Input at
LRV
(STT 3000)
Correct
Input at
URV
(ST 3000)
Correct
Input at
URV
(STT 3000)
Select the Correct LRV
button. This message appears.
Select the
Correct URV
button. This message appears.
Select the Correct URV
button. This message appears.
Adjust the input
temperature to the exact
value of the LRV entered in
the DE CONFIGURE
display.
Adjust the PV input
pressure to the exact value
of the URV entered in the
DE CONFIGURE display.
Select the
OK button.
Adjust the input
temperature to the exact
value of the URV entered
in the DE CONFIGURE
display.
Select the
OK button; this
message appears.
Select the
OK button to
acknowledge
When the transmitter has
completed the URV
correction, this message
appears.
OK to
Select
acknowledge.
Select the
OK button; this
message appears.
Page 28 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Select the
OK button to
acknowledge
Page 37

General Procedures
Input Calibration (De Transmitters) - Correct Input (Zero), LRV, URV; Reset Corrects
Reset
Corrects
Note:
This function commands
the transmitter to
overwrite all user input
corrections with factory
default
("characterization")
values.
It is intended for use only
when excessive
corrections render the
transmitter inaccurate.
If corrects should not be
overwritten with factory
values, select the
No button.
If corrects need to be
overwritten, select the
button. The timer will
appear briefly, indicating the
operation is performed.
Yes
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 29
9/06
Page 38

Procedural Considerations
Table 5 Output Calibration - Loop Test
Output Calibration - Loop Test
Objective
Loop Test
Verify the integrity of
electrical components in
the output current loop.
Connect the MC Toolkit
as indicated, and establish
communication with the
transmitter.
For these procedures,
values of components in
the current loop are not
critical, provided that
they support reliable
communication between
the transmitter and the
MC Toolkit.
In the Output Calibration
box, select the
Loop Test
button; the display at
right appears.
Select the desired
constant-level Output:
%, 100 %, or Other (any
0
of 0 % - 100 %).
Select the
Select the
Set button.
Yes button, and
observe the output current at
0%, 100%, or Other (userentered) %.
Note:
If the transmitter is in
Analog mode, you can
observe the output on
an externally
connected meter or on
a Local Meter.
To view the Monitor display,
navigate Back from the
LOOP TEST display and
select the MONITOR
display.
This popup appears; select
Yes to continue.
Example:
DE output (100 %), as
viewed on the MC Toolkit.
In DE Mode, the
output can be observed
on the Local Meter or
on the Monitor display
on the MC Toolkit.
Page 30 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 39

Example
Output Calibration - Loop Test
The displays at right
illustrate a
Set Output
selection and setting of
Other, at 57 %.
General Procedures
!!
Unintended
exit in
Output
Mode?
!!
Caution:
If Yes was selected as
above in the
CONFIRM! popup
message, it is possible
to exit MC Toolkit
application while the
Output is fixed at
constant current.
This message at right
appears if the user performs
an operation on the MC
Toolkit that will terminate
the connection to the
transmitter while the
transmitter is in output mode.
Select
Yes button only if
constant-current Output with
the MC Toolkit is intended.
Otherwise, select the No
button, go back to the LOOP
TEST display, and select the
Clear Output button.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 31
9/06
Page 40

Procedural Considerations
Table 6 DE Output Calibration - Trim DAC Current
DE Output Calibration - Trim DAC Current
Overview
of
Objectives
For a DE transmitter operating in analog mode in a user's application, calibrate the analog
output current to the PV input range. That is, adjust the output such that 4 mA corresponds
to 0% (LRV), and 20 mA corresponds to 100% (URV).
Call up
display
In the DE MAIN
MENU, select the
Calibration button.
Select the Trim DAC Curr.
button; this display appears.
The CALIBRATION
menu appears.
Page 32 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 41

DE Output Calibration - Trim DAC Current
General Procedures
Trim
Output
Current
Select the
Set Output To 0% button or the 100% button.
The message popup at right appears.
Caution:
In Output Mode, output current is fixed at 0% or
100%. Ensure that the loop is in Manual control.
Select the Yes button, and at the meter, observe the level
of loop current.
NOTE:
On the voltmeter, 4 mA corresponds to 1 volt.
Using the MC Toolkit, adjust the loop current to the
Zero Percent level (4 mA). If the current is low, tap the
Increment button; if it is high, tap the Decrement
button, and observe the change on the meter.
NOTE:
If the error is large, you can accelerate the
adjustment rate by changing the Step Size to 10 or
to 100.
When the zero current level (4 mA) is achieved, select
the Set Output To 100 % button.
NOTE:
On the voltmeter, 20 mA corresponds to 5 volts.
Change
display
while in
Output
Mode
Use the Increment and/or Decrement buttons to adjust
the output current to 20 mA.
When the 100% current level (20 mA) is achieved,
select the Clear Output button. (Note that the button
changes to half intensity.)
If you select the Back button before selecting the Clear
Output button, the display at right will appear.
If you are sure that you want to remain in Output Mode
while viewing other displays, select the
Yes button;
otherwise, select the No button, and the Clear Output
button
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 33
9/06
Page 42

Procedural Considerations
Table 7 DE Calibration - Apply Values
DE Calibration - Apply PV values to Set LRV and Set URV
Overview
of
Objectives:
• Manually set the Process Variable input to 0%, and apply this value to Set LRV;
• Manually set the Process Variable input to 100%, and apply this value to Set URV.
NOTE:
This procedure applies to DE Transmitters operating in DE Mode as well as to those
operating in Analog (current) Mode.
On the DE MAIN MENU,
select the
Calibration
button.
In the Apply Values group,
select the
Set LRV button.
The popup message at right
appears.
Note:
The value of the Input
indicated in this message
updates only when the
popup message is called
up.
To update this value,
select the No button, and
again select the Set LRV
button in the
CALIBRATION
display.
Page 34 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 43

DE Calibration - Apply PV values to Set LRV and Set URV
Set LRV
Set URV
Verify
settings
While observing the PV value at the physical process
element, (using a sight glass, for example) adjust the
Process Variable to the desired Minimum (0 %) level,
then select Set LRV
If the displayed value is satisfactory, select Yes to
copy the Input Value to the LRV in the transmitter. If
not, select NO and repeat this step.
While observing the PV value at the physical process
element, (using a sight glass, for example) adjust the
process variable to the desired Maximum level, then
select Set URV.
If the displayed value is satisfactory, select Yes to
copy the Input Value to the URV in the transmitter. If
not, select NO and repeat this step.
The results of the
Set LRV and Set
URV actions can be
verified by calling
up the DE
CONFIGURE
display.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 35
9/06
Page 44

Introduction
MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Introduction
This section contains procedures for using the MC Toolkit application software to communicate with
Honeywell and non-Honeywell Transmitters with HART communications protocol. In some cases, the
Honeywell transmitters differ somewhat from non-Honeywell transmitters, separate procedures are
provided as appropriate. It is recommended that you use SDC 625 application software when
communicating with non-Honeywell devices. For specific data relating to parameters involved in the
procedures, refer to
Reference Data.
Figure 10 Menu Tree - Honeywell HART Displays
Page 36 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 45

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Figure 11 Menu Tree: non-Honeywell HART Displays
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 37
9/06
Page 46

General Procedures
Honeywell HART Transmitters
Figure 12 HART Menus (Display Summary)
Other HART Transmitters
General Procedures
To access displays for HART Transmitters:
• Start the MC Toolkit application; the CONNECT TO ... display will appear. (Refer to Figure 8
Start-up - MC Toolkit Application).
• Upload the database from the transmitter. (Refer to Table 9 in this section.)
− (The QUICK MONITOR display will enable viewing of key parameters before beginning other
procedures.)
− The HART MAIN MENU appears.
• Select the appropriate display from the HART MAIN MENU. (Refer to Table 10 Honeywell HART
Main Menu Procedure in this section, and to the following task list.)
NOTE:
Although some of the MC Toolkit displays (and procedures) for Honeywell transmitters differ from those
for non-Honeywell transmitters, the MC toolkit automatically provides the appropriate displays. Although
the user is not required to make any selections in the displays, he must be aware of transmitter type to select
the appropriate procedures in this manual.
Page 38 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 47

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Table 8 HART Displays / Tasks Summary
Menu Item Task
DEVICE INFO
BASIC SETUP
OUTPUT
CONDITION
ALARM (STT 3000)
DIAGNOSTICS
/SERVICE
CALIBRATION
Enter:
Device Type:
• Tag ID
• Message
• Descriptor
Enter:
• LRV
• URV
Select:
• Damping
• PV Sensor Units (ST 3000,
STT25H, Generic
• PV1 & PV2 Units(STT25T)
• SV units (ST 3000)
• Transfer Function (ST 3000,
Generic)
• CJT Units (STT25H, STT25T)
• PV Units Type (Generic)
Select:
• Poll Adrs (0-15)
• Scaled D/A Trim (Output
Calibration procedure)
• NAMUR (STT 3000)
Select:
• Break Detect (STT25H)
• Latching Alarm
• Clear Latching
• XS Delta Detection (STT25T
Select (Procedure):
• Master Reset
• Device Status
• Monitor (Output: mA, %; PV, PV2
[STT25T}, SV)
• Write Protect (Enter/Change
Password) (STT25H)
Select (Procedure):
Input Calibration
• Zero Trim (ST 3000 and Generic)
• Correct Input LRV (ST3000 and
STT25H)
• Correct Input URV (ST3000 and
STT25H)
• Reset Corrects (ST3000 and
STT25H)
Output Calibration
• Loop Test
• D/A Trim
Input (Re-Range to PV)
• Apply Values (LRV, URV)
Observe (Read):
• Model
• Device ID
• Manufacturer
Observe
(Read):
• LRL
• URL
• Sensor Type (ST 3000)
Observe
(Read):
• PV Output
• PV2 (STT25T)
• Alarm Direction
• Requested Preambles
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 39
9/06
Page 48

Procedural Considerations
Menu Item Task
Local Meter
(ST 3000 only)
Sensor
(STT 3000)
EXTENDED INFO
DYNAMIC VARS
BURST MODE
SPEC. MONITOR
Select:
• Meter Units (EU)
Enter:
• Custom Units (conversion constant)
• (Custom) EU Flow: Low/High
Select:
• Sensor Type
• Line Filter
• CJ Mode Comp
• Mode Selection (STT25T)
• Match PV’s (STT25T)
Observe (Read):
Enter:
• Primary Variable Code
• Secondary Variable Code
• Tertiary Variable Code
• Quaternary variable Code
Select:
• Burst Mode
• Burst Options
Select:
• No. of Var's Query
• Device variable
Observe
• Meter Type
Observe
• RTD Wire Selection (STT25H)
• Universal Rev.
• Software Rev.
• Field Device Rev.
• Poll Address
• PROM ID
• # Req. Preams
• PV Sensor S/N
• Final Assembly #
Observe (Read)_:
• Values of selected variables
(Read):
(Read):
Procedural Considerations
The details of procedures vary with device type. This section contains a set of procedures for Honeywell
HART Transmitters, and separate set of procedures for non-Honeywell HART devices.
Input Calibration
Input calibration of transmitters should be done only when necessary, and should be done only under
conditions that will ensure accuracy:
• The transmitter should be taken out of service, and should be moved to an area with favorable
environmental conditions: clean, dry, and temperature-controlled.
• The source for the input pressure must be very precise, and must be certified for correct operation.
• The procedures should be done by qualified personnel.
For Honeywell HART devices, input calibration procedures are given in Table 12 through Table 14, and
for non-Honeywell HART devices, consult the manufacturer’s User Manual..
Page 40 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 49

Output Calibration
The Loop Test procedure is intended as a check for continuity and condition of components in the output
current loop. The procedure for Honeywell HART devices is given in Table 15, and for non-Honeywell
devices consult the manufacturer’s User Manual.
The D/A Trim procedure calibrates the output of the Digital to Analog converter for minimum (0%) and
maximum (100%) values of 4 mA and 20 mA, respectively. This procedure is used for transmitters
operating on-line in analog mode, to ensure proper operation of the transmitter with all associated circuit
components (wiring, power supply, control equipment, etc). It is necessary to use precision test equipment
(a voltmeter and in-circuit resistor or an ammeter).
The procedure for Honeywell HART devices is given in Table 16, and for non-Honeywell devices consult
the manufacturer’s User Manual.
The Apply Values procedure uses actual Process Variable input levels for calibrating the range of a
transmitter. To measure a liquid level for example, a sight-glass can be used to determine the minimum
(0%) and maximum (100%) level in a vessel. The PV is carefully adjusted to stable minimum and
maximum levels, and the LRV and URV values are then set by commands from the MC Toolkit.
For Honeywell HART devices, the procedure is given in Table 17, and for non-Honeywell devices consult
the manufacturer’s User Manual.
MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 41
9/06
Page 50

Procedural Considerations
Table 9 HART Device UPLOAD Procedure
HART Device UPLOAD Procedure
Initiate
Connection
Device
Polling and
Selection
(Refer to Figure 8.)
Select the
button; this display
appears.
HART Device
Select the
OK button to
initiate communications.
If you know the address of
the device on the HART
network, select it in the
Address drop-down box.
- or -
If you don't know the
address of the device, select
the POLL button.
The MC toolkit will look
for devices on all addresses
(0-15), and will then list the
addresses of all transmitters
that respond.
When the POLL button is
selected, the MC toolkit
will look for devices on all
addresses (0-15), and will
then list the addresses of all
transmitters that respond.
Note that at this point, the
UPLOAD button is half
intensity (inactive).
Page 42 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Select the device from the
list.
Page 51

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
HART Device UPLOAD Procedure
Initiate
Upload
HART MAIN
MENU
Select the UPLOAD button.
A wait cursor and a
progress bar appear while
the database is copied from
the device to the MC
ToolKit (~ 10 seconds).
Then, the HART MAIN
MENU appears.
The MC Toolkit
automatically determines
the type of transmitter
device, and includes the
appropriate MENU content
for Honeywell or nonHoneywell devices.
HART STT 25T
HART QUICK MONITOR
(Honeywell
HART ST 3000)
When the Quick Monitor
display appears, use it to
HART ST3000, STT25H,
GENERIC
Then, select the
Close
button.
(non-Honeywell HART
Device)
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 43
9/06
(Honeywell)
HART STT25H STT25T
Page 52

Procedural Considerations
Table 10 Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedure
Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedures
Menu
styles:
Device
Info
ST 3000 HART
Note that the
Sensor functions are not
Alarm and
available.
Tag ID - Enter up to 8
characters
Message - Enter up to 32
characters
Descriptor - Enter up to 16
characters
STT25H, STT25T
Note that the
Local Meter
function is not available
ST3000, Generic
STT25H, STT25T
Device
Info
(Extended
Info)
Extended Info – Calls up the
Extended Info display
Page 44 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 53

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedures
Basic
Setup
Honeywell ST 3000
Honeywell STT25H
Output
Condition
Transfer Function - Linear or Square Root
(select)
SV Units - Engineering Units for
Secondary Variable (select)
CJT Units - Engineering Units for Cold
Junction Temperature (select)
PV1 and PV2 Sensor Units (r/w) -
Engineering Units
LRL - Lower Range Limit; URL - Upper Range Limit (read)
LRV - Lower Range Value ; URV - Upper Range Value (enter or read)
PV Sensor Units (r/w) - Engineering Units (select)
Damping - Filtering factor for process "noise" (in seconds - select)
PV Output (r)
PV2 (r) (STT25T Only)
Alarm Direction - Failsafe
Upscale | Downscale)
(
jumpered or switched in
field
device)
Scaled D/A Trim - (Refer to
Table 16 for more
information.)
NAMUR (STT25H,
STT25T)– Select output
levels:
Standard or NAMUR
HART Output
Poll Address
To change the Poll Address
(0-15) of the connected
device:
• Select the desired address
from the pull-down list
• Select the
Req. Preambles - Number
Send button.
of preambles required
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 45
9/06
Page 54

Procedural Considerations
Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedures
Alarm
Diagnostics
/Service
Menu
Break Detect(STT25H) -
select Disabled or Enabled
When Enabled, the
transmitter checks for open
Thermocouple.
Latching Alarm - select
Disabled or Enabled
When Enabled, the output
remains in Failsafe until the
critical status condition is
cleared, and the transmitter
is reset.
When Disabled, if the
transmitter goes to Failsafe,
the transmitter will clear
Failsafe as soon as the
critical status condition is
cleared.
Refer Table 11 for more
information.
Click on the
Clear Latching button to
clear the Failsafe condition
if the Latching Alarm is
Enabled.
XS Delta Detection
(STT25T) – Select On or
Off. When On, if the
difference (Delta) between
PV1 and PV2 exceeds the
Delta Alarm value, the
device goes into Failsafe,
and a critical alarm is raised.
When Off, if the Delta
Alarm value is exceeded,
the device will not go into
failsafe, and a non-critical
alarm is raised.
Calibration
Menu
Refer to:
Table 12 - Zero Trim (not
supported for STT25T or
STT25H)
Table 14 - Reset Corrects
Refer to:
Table 13 - Corr. Input LRV
and Corr. Input URV
(ST3000 and STT25H)
Table 17 - Apply Values
(ST3000 and (STT25H)
Table 15 - Loop Test
Table 16 - D/A Trim
Page 46 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 55

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedures
Local
Meter
Sensor
(STT25H
Local Meter refers to a
meter installed integrally in
an ST 3000 transmitter, or to
a remote-mounted meter that
is associated with the
ST 3000 transmitter.
Meter Units - Engineering
Units associated with the
Local Meter
Sensor Type - Select from list. (See Reference Data section
for more information.)
Line Filter - Select: 50 Hz/60 Hz.
RTD Wire - If the sensor is an RTD type, this field indicates
whether it is a 3-wire or a 4-wire RTD.
CJ Mode Comp. (STT25H) - (Cold Junction Mode
Compensation); select Internal CJ/External CJ.
For more information, refer
to the user manuals(s) for
the transmitter and/or for the
Remote Meter Assembly
(RMA 3000).
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 47
9/06
Page 56

Procedural Considerations
Honeywell HART Main Menu Procedures
Sensor
(STT25T)
Mode Selection – Select from list. If changing the Mode
requires a change to the sensor type, select from the Sensor
Type and then select Send. (Note that, if RTD/RTD Mode is
selected, only PT1000 Sensor Type is available.)
The Sensor Type may be changed with no change to Mode
selection.
Whenever the Sensor Type is changed, the Sensor Units
Selection display appears. If having changed the Sensor Type
requires a change to the Sensor Units, select from the list and
then select Send; if a change is not required, select Cancel.
Delta Alarm (r/w) - Enter the magnitude of the difference
between PV1 and PV2 at which the Delta Alarm will trip.
Delta (r) – the value of [PV1-PV2], as calculated in the
STT25T transmitter.
PV1 & PV2 Units (r) – Last –selected Sensor Unit
Match PV’s – When ON, the value of PV1 is assigned to the
PV2.
Line Filter - Select: 50 Hz/60 Hz.
CJ Mode Comp - Select: Internal CJ or External CJ.
Page 48 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 57

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Table 11 Honeywell HART Diagnostics/Service Menu Procedures
Honeywell HART Diagnostics/Service Menu Procedures
Menu
Master
Reset
Monitor
Master Reset is the
functional equivalent of
cycling power on the
transmitter. No parameters
are changed.
Select the
Master Reset
button, then confirm by
selecting the
Yes button.
The Monitor display enables
viewing of transmitter status
and of the value of the
output.(in engineering units
and in percent)
Delta (STT25T) – Magnitude
of the difference between
PV1 and PV2
PV - Primary variable
PV2 (STT25T) – Primary
Variable 2
SV - Secondary variable
TV - Tertiary variable
(generic)
QV - Quaternary variable
(generic)
Selecting the
Device Status
button calls up the DEVICE
STATUS display (see
above).
For status information, refer
to the section on Messages
and Diagnostic Codes.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 49
9/06
Page 58

Procedural Considerations
Honeywell HART Diagnostics/Service Menu Procedures
Device
Status
Write
Protect
The Critical status block lists
the conditions that render the
transmitter device inoperable.
The Non-Critical status
block lists advisories of
conditions that are
noteworthy, but that do not
cause non-operability.
Refer to the section on
Messages and Diagnostic
Codes.
The
Write Protect function
is available for the
Honeywell STT 25H
Temperature Transmitter.
Provides write protection for
all parameters.
To enable write protection,
select
Write protected, then
select the Send button.
To disable Write Protection,
select Not write protected,
enter the password, and then
select the Send button.
The password can be
changed only when Not
Write Protected.
Change Password,
To
select the Start button, type
in the new password, and
then select the
Send button.
Page 50 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 59

Table 12 Honeywell HART Calibration - Zero Trim
Honeywell HART Calibration Zero Trim
MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Overview
of
Objectives
(Applies to
ST 3000)
Requirements:
• Input source, with accuracy of at
least 0.04%
• resistor, at least 250-ohms
• Voltmeter or Ammeter
• 24 Vdc Power Supply (nominal)
• Clean work area with suitable
environmental conditions.
• Pressure Transmitter must be level.
Overview of Procedures:
The Zero-Correct procedure establishes
the correct vertical positioning of the
response profile.
The LRV Correct and URV Correct
procedures establish the correct slope of
the response profile by rotating the
response profile around the zeroreference point as a pivot.
The Zero-Correct procedure can be done
at any time during the Correct LRV and
Correct URV procedures in the same
calibration session.
Objective(s):
Using a precision PV input source as a reference,
command the transmitter to write calibration
coefficients to NVM associated with transmitter
input hardware and software.
• Correct Input (Zero)
• Correct LRV
• Correct URV
The Correct LRV and Correct URV
procedure should never be performed
without first performing the Correct
Input (Zero) procedure in the same
calibration session.
The transmitter should be removed from
service and moved to a clean area.
The input source should be derived from
a precision input source such as a deadweight tester.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 51
9/06
Page 60

Procedural Considerations
Honeywell HART Calibration Zero Trim
Menu
Zero Trim
Honeywell ST 3000
(Note - Zero Trim is
available.)
NOTE:
This procedure will
change LRV and URV
settings.
Select Zero Trim. The first
of a series of Pop-Up
messages appears.
Honeywell STT 3000
(Note - no Zero Trim.)
To acknowledge the
message, select the Yes
button; another message
appears.
Apply the zero-reference
input source to the sensor.
Select the
OK button, and
wait for this message:
Select the
following message should
appear.
OK button; the
Page 52 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 61

Table 13 Honeywell HART Calibration - LRV and URV
MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Correct
LRV
(St3000
and
STT25H)
Correct
URV
(ST3000
and
STT25H)
Corr. Input LRV
Select
Connect precision input
pressure source, and set to
the desired Lower Range
Value.
Correct Input URV.
Select
Connect precision input
pressure source, and set to
the desired Upper Range
Value.
Ensure that pressure input
source is correct and is not
The LRV value is stored in
the transmitter.
varying.
Then, to set the LRV
parameter in the transmitter
to the applied value, select
OK in the pop-up window.
Ensure that pressure input
source is correct and is not
The URV value is stored in
the transmitter.
varying.
Then, to set the LRV
parameter in the transmitter
to the applied value, select
OK in the pop-up window.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 53
9/06
Page 62

Procedural Considerations
Table 14 Honeywell HART Calibration - Reset corrects
Reset
Corrects
(ST3000
and
STT25H)
Note:
This function commands
the transmitter to
overwrite all user input
corrections with factory
default
("characterization")
values.
It is intended for use only
when excessive
corrections render the
transmitter inaccurate.
Select the
button.
Reset Corrects
.
Page 54 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 63

Table 15 Honeywell HART Calibration - Loop Test
Honeywell HART Calibration - Loop Test
MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Loop Test
This function verifies the
integrity of the physical
components of analog
output loop current in a
process application
To observe output current
levels, connect a voltmeter
or current meter into the
current loop.
Observe the meter, and
Yes in the popup
select
message to command the
transmitter to go to the
selected current level.
To return to the inputdependent current level,
select
Clear Output; this
popup message appears.
Back button is
If the
selected before using the
Clear Output command, the
message at right appears.
To go back to the
Calibration Menu, select
OK in the popup, select the
Clear Output button, then
select the
Back button.
Select the desired current
level, then select
Set Output.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 55
9/06
Page 64

Procedural Considerations
Table 16 Honeywell HART Calibration - D/A Trim
Honeywell HART Calibration - D/A Trim
D/A Trim
Calibrate
4 mA
Output
NOTE:
This procedure
calibrates the value of
the analog output
current at minimum
(0%) and maximum
(100%) values.
To begin, select the D/A
Trim button on the
Calibration menu.
.
Connect a voltmeter or
ammeter into the current
loop.
Then, select the
OK button
in the popup; the next
message popup appears.
This display appears.
Observe the meter, and
select the
OK button in the
popup message to
command the transmitter to
go to 4.0 mA output.
In the Meter Value field,
key-in the value (in
milliamps) observed on the
meter, as indicated in the
example at right.
Select the Start D/A Trim
button. A popup message
appears.
In this example, the
observed value of 1.038 V
is converted to 4.152 mA.
Note: If you are using a
voltmeter, use the calculator
to convert the voltage value
to mA.
Send; the keyed-in
Select
value is copied to the
transmitter output
algorithm.
If the observed value is
4.000 mA, select
Yes. The
popup message shown at
right appears.
Select
OK to proceed to 20.0
mA calibration.
Again, observe the resulting
mA output on the connected
meter.
If the observed value is not
4.000 mA, select
No in the
popup message, enter the
observed current value, and
select Send. Repeat until
the observed value is 4.000
mA.
Page 56 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 65

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Honeywell HART Calibration - D/A Trim
Calibrate
20 mA
Output
(Example 1)
Calibrate
20 mA
Output
(Example 2)
The 20 mA calibration
display appears.
Again, observe the resulting
mA output on the connected
meter.
In the example at right,
meter indication of 4.97 V
is converted to 19.80 mA
and entered into the
Value
field.
Select
Send to copy the
entered value to the
transmitter output
algorithm.
In the example at right, the
corrected value was 5.02 V
(20.08 mA).
This new value is entered
and
Send is selected again.
Meter
The new value is observed
as 5.00 V (20.00 mA),
which is entered into the
Meter Value field.
When the Send button is
selected, this display
appears.
The calibration is
completed, but the 20.00
mA calibration value is
retained until
OK in the
popup message is selected.
When the
OK button is
selected, the output current
goes back to tracking the
input value, and the popup
message disappears.
Select
Back to return to the
CALIBRATION menu.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 57
9/06
Page 66

Procedural Considerations
Table 17 Honeywell HART Calibration - Apply Values
Honeywell HART Calibration - Apply Values
Overview
of
Objectives
(Adjust
and View
Process
Variable
input value
at LRV.)
• Manually set Process Variable input to 0%, and apply this value to Set LRV (output) at
4 MA.
• Manually set Process Variable input to 100%, and apply this value to set URV (output)
at 20 mA.
This function uses actual
Select the Send button.
process values to calibrate
input of LRV and URV.
This popup message
appears.
Physically observe the value
of the Process Variable, and
adjust it manually to the
desired LRV value.
Select the
Apply Values
button on the Calibration
menu; the display at right
appears.
Page 58 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 67

MC Toolkit Software with Honeywell HART Transmitters
Honeywell HART Calibration - Apply Values
Apply
Values:
LRV
(Write
input value
as LRV.)
Select the OK button. The display at right
appears.
The Current Applied Process Value field
shows the value of the Process Value. A
new sample of the input level is displayed
each time the user selects the Read New
Value button.
Adjust the process variable to the desired
value while repeatedly selecting the Read
New Value button to monitor and verify
the input value.
When the Process Variable
is stabilized at the desired
input level, select the Set
New Value button.
The popup at right appears.
Select the OK button to
write the input value as the
LRV calibration value; and
the popup message box will
disappear.
(Adjust
and View
Process
Variable
input value
at URV.)
Select the 20 mA button.
The popup at right appears.
This display at right is the
same one used for applying
PV input as LRV value.
Adjust the PV input to the
desired URV level while
using the Read New
Value button for
monitoring.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 59
9/06
Page 68

Procedural Considerations
Honeywell HART Calibration - Apply Values
(Write
input value
as URV.)
When the PV is stabilized,
select the Set as New
Value button. This popup
at right appears.
Select the OK button to
write the input value as the
URV calibration value; and
the popup message box will
disappear.
Page 60 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 69

Using SDC 625 Application Software with all HART
Introduction
This section contains procedures for using the SDC 625 application software to communicate to any device
with HART communications protocol. It is recommended that you use SDC 625 application software when
communicating with non-Honeywell devices. After double-clicking on the SDC 625 icon, the following
screen often appears. Choose “ignore”, it is an indicator that a configuration may have changed.
Using SDC 625 Application Software with all HART Transmitters and Devices
Transmitters and Devices
The following is the main screen for the SDC 625 application software. It is “Tree View” based solely on
the devices DD – Device Description.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 61
9/06
Page 70

Introduction
As you browse through the “tree”, different values will appear in the bottom section of the main screen.
Since the DD (Device Description) file can be different for each field device, SDC 625 Main screen will
look different for many devices. Some field devices will require relatively few configurations commands
and therefore the main screen will have a simple structure. Other devices, which require more configuration
commands, will have a relatively complex main screen structure. The following table depicts the basic
structure of a Device Setup menu for a Honeywell STT 250 temperature transmitter:
Device Setup Submenu item Description/Purpose
Process Variables Used to monitor the PV in engineering units, PV
in%, PV analog output and Cold Junction
Temperature
Diag/Service Used to perform a Loop Test or D/A trim.
Submenus include Device Status, Calibration and
Write Protect.
Basic Setup View Tag, change PV damping or CJ Temperature
units. In Device Information: view Tag,
Manufacturer, Model, Device I.D. and Write Protect
status. Change Sensor units using the PV Snsr Unit
Method.
Detailed Setup
Review View Model, Distributor, Manufacturer, Device I.D.,
Submenus are Sensors, Signal Condition, Output
Condition, Device Information and Alarm. In
Sensors, one can change sensor, view sensor
type, change the line filter or change compensation.
In Signal Condition, on can change PV Damping,
LRV or URV. Can view PV % range. In Output
Condition, one can view alarm direction, perform a
loop test, perform a D/A trim or turn Namur alarm
on or off. In Device Information, on can view the
Model, view and change the Tag, view and/or enter
a Message. One can also view the software
revision. In Alarm, one can view or change Break
detection, view or change Latching Alarm, clear
Latch and view alarm direction.
Tag, Message, Universal rev, Fld dev rev, software
rev, Poll addr and Num req preams.
The following screen provides an example of some Items that can be edited.
Page 62 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 71

Using SDC 625 Application Software with all HART Transmitters and Devices
1. Clicking on the Value field can modify the bold items. They are typically orange icons like Tag
above.
2. The green icons (Enter values above) are also editable. Click on them as well to open.
3. The blue icons (like PV Snsr Unit above) represent methods and can be run by choosing them and
following the instructions.
The following screen is an example of how to make a change to a value such as the Tag I.D.
1. This screen appears after choosing a bolded value (orange icon) such as Tag. You can highlight
the value (STT25-H) and then delete it by using the keyboard. Clicking on the Keyboard button in
the lower right corner opens the keyboard. Press “Set” once finished.
2. The Backspace (top right on the keyboard) button can be used to remove blank characters if
desired.
3. New values can be entered into the Textbox using the keyboard.
After making a change (such as the Tag I.D.) the following screen will appear:
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 63
9/06
Page 72

Introduction
The following screen shows an example of a Method. A method, identified by a blue icon, is a step-by-step
procedure to execute a change. For, example the SDC 625 uses a Method to change the Engineering units
or to put a pressure transmitter into output mode.
1. After choosing Set on the previous screen, the new tag under Value is highlighted. You have
made a change on the Pocket PC, but it has not been downloaded to the device yet.
2. Click on the Upload button (short Arrow on previous screen) to send the new tag to the device.
3. You can choose the next button to the right of the Upload button (long arrow on previous screen)
if you want to clear the new tag value and revert back to the current value (STT25H) in the device.
1. The method above allows one to change the engineering units of a field device.
When you have fully configured the device or made the changes you need to make, you can exit the
SDC625 program in the following way: Click on Device, and then Exit.
Page 64 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 73

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Table 18 MC Toolkit/SDC 625 Error Messages
MC TOOLKIT/SDC 625 ERROR MESSAGES
MESSAGE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Another Secondary master has been
detected! HART Protocol does not
support more than one secondary
master on the HART Network.
Checksum error on Modem Response! A noisy environment can cause this error. Repeat the command again.
Com Port Read Timeout! Ensure that the Honeywell supplied modem cable is used and that the
Com read Error!
Error writing to Com Port!
Error writing to Com Port!
EscapeCom function Error!
GetCommState Error!
Host Failed to get good response from
the Modem!
Remove one of the secondary masters from the network.
connections are secure.
Make sure the modem has a good battery.
Make sure ActiveSync is not running.
If several programs are active, try closing one or more open programs.
Stop the MC Toolkit application by doing File | Exit and restart the
program.
Use the Pocket PC hardware reset. See your Pocket PC documentation
reset the unit. Caution for MCT101 Users: If the Symbol PPT 2800
computer is reset, it will lose all its installed programs and data. The
program will have to be installed again.
MCT101 Users, make sure you are using a Honeywell approved Pocket
PC.
MCT101 Users: ensure that the Honeywell supplied modem cable is
used and that the connections are secure.
Make sure the modem has a good battery.
Invalid Command number from the
Modem!
Invalid Handle Value! Make sure ActiveSync is not running.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 65
9/06
Communications problem between the Pocket PC and the modem.
Repeat the command again.
If Several programs are active, try closing one or more open programs.
Stop the MC Toolkit application by doing File | Exit and restart the
program.
Use the Pocket PC hardware reset. See your Pocket PC documentation
reset the unit. Caution for MCT101 Users: If the Symbol PPT 2800
computer is reset, it will lose all its installed programs and data. The
program will have to be installed again.
Make sure you are using a Honeywell approved Pocket PC.
Page 74

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
MC TOOLKIT/SDC 625 ERROR MESSAGES
Memory Error If several programs are active, try closing one or more open programs.
Too many programs installed in the Pocket PC. Check the Pocket PC
free memory. Uninstall programs if need to release memory.
Too many data files in the Pocket PC. Check the Pocket PC free
memory. Delete unused data files to release memory.
Use the Pocket PC hardware reset. See your Pocket PC documentation
reset the unit. Caution for MCT101 Users: If the Symbol PPT 2800
computer is reset, it will lose all its installed programs and data. The
program will have to be installed again.
Message length is longer than
expected
Message length is shorter than
expected
Modem bad checksum This could indicate a defective modem. Repeat the command again. If
Modem Buffer overflow
Modem busy
Modem framing error
Modem illegal command
Modem illegal data
Modem network error
Modem Transmitter Serial Error!
No Response from the Transmitter Make sure that the MC Toolkit field connections are connected to the
Communications problem between the Pocket PC computer and the
modem. Repeat the command again.
the problem persist contact Honeywell TAC.
Communications problem between the Pocket PC computer and the
modem. Repeat the command again.
transmitter.
Verify the transmitter is wired correctly and that it is powered.
If connected to a DE transmitter, make sure the polarity of the cables
connecting to the transmitter is correct.
If connected to a HART transmitter, make sure the address number is
correct.
Resume Monitor Thread Failed! Close all the other running applications.
Page 66 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Make sure the correct protocol for the transmitter is selected.
A defective transmitter can also cause this error message.
Verify that a 250 ohm resistor in series with the transmitter.
Restart MC Toolkit application.
Page 75

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
MC TOOLKIT/SDC 625 ERROR MESSAGES
Serial Port is not Available
SetCommMask Error!
SetCommState Error!
SetCommTimeouts Error!
Suspend monitor Thread Failed!
Upload Cannot Continue.
Too Many bytes received on ComPort! Repeat the command. If the problem persist contact Honeywell TAC.
Transmitter-Modem Receive Buffer
overflow!
Unknown Error! MCT101 Users: This could indicate a defective modem. Repeat the
COM Port Initialization Failed MCT101 Users: Please check the COM Port of the PPC to which
No HARTDE Modem Present
HARTDE Modem Protocol set failed MCT101 Users: Unable to set the HART Protocol in Modem. Please
Make sure ActiveSync is not running.
If Several programs are active, try closing one or more open programs.
Stop the MC Toolkit application by doing File | Exit and restart the
program.
Use the Pocket PC hardware reset. See your Pocket PC documentation
reset the unit. Caution: If the Symbol PPT 2800 computer is reset, it will
lose all its installed programs and data. The program will have to be
installed again.
Make sure you are using a Honeywell approved Pocket PC.
System failed to suspend the monitor function
This could indicate a software problem with the MC Toolkit Software.
Repeat the command again. If the problem persist contact Honeywell
TAC.
command again. If the problem persist contact Honeywell TAC.
HARTDE Modem is connected. Some other application may be using the
same.
MCT101 Users: HART/DE Modem is not detected. Please check the
Modem connection to PPC & Modem battery.
check the Modem. Remove the Modem battery and re-install.
Failed to create Burst Message
Handler thread
Error In Communication with Device,
Closing the Device.
No Device found, Do You want to Retry MCT101 Users: Device is not detected. Please check the Modem
Could not find XXXX.fms, Loading
Generic DD...
Unable to Load Generic DD
(0x268005XX)..
Too many applications may be running. Please close some of the
application and restart SDC.
MCT101 Users: This could be a problem with device connection. Please
check the Modem connection with PPC, Modem connection with Device,
Modem battery and Device power.
connection with PPC & Device, Modem battery and Device power.
If the above things are perfect, try to change different device detection
options from Preference dialog box under Device/Preferences menu,
restart the SDC.
Unable to find the connected Device DD in the DD Library of PPC. You
can still perform Generic operations with the device with Generic DD
loaded. For utilizing full functionalities of the device, update the Device
DD in the DD Library of PPC (in the memory card) and try again.
Generic DD not available in the DD Library of PPC. Please update your
DD Library of PPC. If the problem persist contact Honeywell TAC
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 67
9/06
Page 76

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Table 19 DE Messages
DE MESSAGES
Write NVM Failed Write to transmitter Non-Volatile Memory failed.
Unknown Device MC Toolkit does not support this transmitter.
Invalid Range User-entered value is too high or too low.
Invalid Request This transmitter does not support the command requested.
NACK MC Toolkit sensed Non-Acknowledgement of message to the
Transmitter.
Illegal Operation Typically caused by an invalid parameter or an attempt to perform an
operation in a mode not allowed by the transmitter.
Transmitter in Local Mode Transmitter in Factory Mode
Transmitter is Busy Transmitter was communicating when MC Toolkit sent message to
transmitter.
Invalid operation on Write Protected
Field
Undefined Gross Status Byte from the
Transmitter
Gross Status Reserved Bit Set The transmitter has reported a status indication not understood by MC
Data Inaccessible Unable to access the parameter value.
Bad character in Scratchpad The scratchpad contains an invalid data byte.
Invalid Float value Value is not a valid floating point value.
Value Out of Range User-entered number is too high or too low.
Transmitter is in DE Mode. D/A Trim is
allowed only in Analog Mode.
The transmitter is in Output Mode. Are
you sure you want to terminate the
connection?
The changes you have made are about
to be sent to the transmitter. Continue?
Please make sure you are connected to
a DE device. Sending DE commands to
a non-DE device could potentially cause
a process upset.
Attempt to write to a protected field.
The transmitter has reported a status indication not understood by MC
Toolkit.
Toolkit.
DE mode is digital only (no digital-to-analog conversion).
User tried to Exit MC Toolkit application while the DE Transmitter is still
in Output Mode.
Values entered into this display will be written into transmitter memory.
DE communications (~ 4-20 mA amplitude) could cause erroneous
transmission in non-DE protocols.
Leaving the Main Menu will require an
upload in order to return. Are you sure
you want to do this?
Put loop in Manual ... Trips secured? Changing values of transmitter parameters can cause process upset.
Conformity must be square root to
select this unit.
Page 68 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
A new Upload will require approximately 60-second wait.
Units for Flow indications are available only when Square Root
conformity is selected.
Page 77

DE MESSAGES
Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Are you sure you wand to Reset All
Corrects to factory defaults?
Are you sure you want to place the
transmitter in output mode (?)
Square Root is not allowed for GP and
AP Sensor Types.
Executing Reset All Corrects will overwrite all user input calibration
values (Zero, LRV, URV) with factory-default values.
In Output Mode, output current will be set to the selected constant
value, rather than to calculated
Square Root conformity is available only for FLOW (DP) input
applications.
Table 20 HART Messages
HART MESSAGES
Bad Manufacturer Code MC Toolkit does not recognize the manufacturer code from the
transmitter.
Bad Status code from the transmitter MC Toolkit does not recognize the status code from the
transmitter.
Bad Start character on HART Message! First byte in HART response message is not a valid byte(valid
bytes:0x02,0x82,0x06,0x86,0x01,0x81)
Device specific command error Possible error codes 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15.
Subset of these is defined for commands. If any value other than
these subset values, this message is displayed.
Error code 02: Invalid Selection The selection is not valid.
Error code 03: Passed parameter too large Entered value is too large.
Error code 04: Passed parameter too small Entered value is too small.
Error code 05: Too few data bytes received Internal error. Repeat command.
Error code 06: Wrong Password! The password entered is incorrect.
Error code 07: In Write Protect Mode The transmitter is in Write Protect Mode.
Error Code 08: Set to Nearest Possible Value Set to Nearest Possible Value
Error Code 09: Applied process too high Applied process too high or out of range.
Error code 09: LRV too high LRV is too high or out of range.
Error Code 09: Not in Proper Current Mode Not in Proper Current Mode
Error Code 10: Applied process too low Applied process too low or out of range.
Error code 10: LRV too low LRV too low or out of range.
Error Code 11: Excess correction attempted Attempted correction value is out of range.
Error Code 11: Invalid Transmitter variable Selected variable is invalid for this transmitter.
Error Code 11: Transmitter in Multidrop Mode! Action could not be completed because the transmitter is in
multidrop mode.
Error code 11: URV too high URV too high or out of range.
Error Code 12: Invalid Units Invalid Units
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 69
9/06
Page 78

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
HART MESSAGES
Error code 12: URV too low URV too low or out of range.
Error code 13: Parameter out of limits Parameter is out of the valid range.
Error code 14: Span Too Small Span Too Small
Error Code 14: Warning: New LRV pushed
URV over Sensor Limit
Error code 16: Access restricted Access to the parameter is not allowed.
Error code 32: Device is Busy! Device is currently busy; try command again.
Error Code 64: Command not implemented in
the Transmitter!
Error on Burst Response! The burst message contained a communications error.
HART Communication Error! MC Toolkit detected a communications error in the HART
Invalid command number from the Transmitter.
Please make sure that another secondary
master is not on the network!
Manufacturer Code not be found Manufacturer Code not be found
No device found! No HART devices could be found on the network.
Non primary variable out of limits Process applied to the non-primary variable is outside the
Parity Error! Bit 6 on first response code byte set. MC Toolkit detected a
Overrun Error! Bit 5 on first response code byte set
Framing Error! Bit 4 on first response code byte set. MC Toolkit detected a
The new URV has caused the URV to go over the sensor limits.
Action is not supported by the transmitter.
message.
The HART protocol supports only one secondary master on the
network.
operating limits of the field device.
communications error in the HART message.
communications error in the HART message.
Checksum Error! Bit 3 on first response code byte set
Reserved Field Error! Bit 2 on first response code byte set
Receive Buffer Overflow! Bit 1 on first response code byte set
Primary variable out of limits Process applied to the primary variable is outside the operating
limits of the field device.
Undefined Response code for the command
associated with the current operation!
Response code (First byte) value 1 is returned from the
transmitter. This response value is undefined in the currently
supported HART devices
Page 70 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 79

Table 21 ST 3000 Device Status Messages (DE)
ST3000 DEVICE STATUS MESSAGES (DE)
Meter Body Fault
Characterization PROM Fault or bad checksum
SUSPECT INPUT: The input process data seems wrong
Messages and Diagnostic Codes
CRITICAL
NON CRITICAL
Electronics Fault(A). MDU/DAC Compensation Fault
Electronics Fault(B)-RAM Fault
Electronics Fault(C)-NVM Fault
Electronics Fault(D)-NVM Fault
Electronics Fault(E)-NVM Fault
Meter Body Sensor Over Temperature(>125C)
ZERO correction value is outside the acceptable limits for accurate operation
SPAN correction value is outside the acceptable limits for accurate operation
Transmitter is in the OUTPUT mode and is using a fixed output that is "not from the
process"
Meter Body Overload
Meter Body Fault: The pressure input is greater than two times the URL of the
transmitter
Calibration correction values are Reset to Factory default
Data for the DAC Temperature compensation is corrupted
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 71
9/06
Page 80

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Table 22 STT Device Status Messages (DE)
STT DEVICE STATUS MESSAGES (DE)
Power up self test failure
Isolated Microprocessor Communications Failure: An electronics failure was detected on
the isolated electronics
An open circuit detected at the input. Note: Power cycling is not required to reset this
critical status
CRITICAL
Factory calibration data is corrupted
User Configuration data is corrupted
Isolated microprocessor NVM write failure
User NVM write failure
STT body ambient temperature out of specification (-40 to +85 deg C)
Uncertain or inconsistent input reading
Input measurement is out of specification for this STT Configuration
Low quality CJ compensation temperature reading
NON CRITICAL
The zero correction value is outside the acceptable limits for accurate operation
The SPAN correction value is outside the acceptable limits for accurate operation
The transmitter is in the OUTPUT MODE and using a fixed output that is ""not from the
process""
User correction active
Suspect Input
Backup thermocouple is active
Input Status not Latched
Custom Input Sensor
Redundant T/C Mode
Delta Temperature Mode
4 wire RTD mode
Page 72 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 81

Table 23 ST 3000 Device Status Messages (HART)
ST3000 DEVICE STATUS MESSAGES (HART)
Invalid Database
PROM Failure
Suspect Input
Messages and Diagnostic Codes
CRITICAL
NON CRITICAL
DAC Diode Fault
NVM Fault
RAM Fault
PROM Fault
PAC Fault
Sensor Over-temperature
Excess Zero Correction
Excess Span Correction
In Output Mode
M.B. Overload
Meter Body Fault
Corrects Reset
No DAC Temp. Compensation
Primary variable out of limits
Non primary variable out of limits
Loop current saturated - Analog output 1 and its digital representation are outside the
operating limits of the field device.
Loop current fixed - Analog output 1 and its digital representation are in fixed mode and
are not responding to input changes.
Cold Start A reset or self test of the device has occurred, or power has been removed or
applied.
Configuration changed
Device Malfunction - Field device has malfunctioned due to a hardware error or failure.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 73
9/06
Page 82

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Table 24 STT Device Status Messages (HART)
STT25H DEVICE STATUS MESSAGES (HART)
RAM Failure
ADC Failure
CRITICAL
NON CRITICAL
INFORMATION
Input Open
Factory Calibration Corrupted
User Configuration Corrupted
Ambient Temp. Out of Range
Uncertain Input
Input Out of Spec.
Output Saturated
In Current Fixed Mode
User Correct Active
Suspect Input
Non-Latched
4 Wires RTD/Ohm
Primary variable out of limits
Non primary variable out of limits
Loop current saturated
Loop current fixed
Cold Start
Configuration changed
Device Malfunction
STT25T DEVICE STATUS MESSAGES (HART)
Hardware Failure
Input open
CRITICAL
NON CRITICAL
NVM Calibration Failed
NVM Configuration Failed
XS Delta
Sensor 1 failed
Sensor 2 Failed
XS Delta
CJ Over Temp
Input out of spec
Output Saturated
In Output Mode
Page 74 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 83

Reference Data
Table 25 Glossary
Item Definition Description
Conformity
Response form of
User selection of PV conversion algorithm: Linear or Square Root
sensor.
D/A Trim
Digital to Analog
Trim
Adjustment to digital-to analog (output) conversion algorithm that
aligns minimum and maximum values of scaled digital range to
minimum (0%) and maximum (100%) values of analog output.
Damping
Digital algorithm in transmitter MPU that reduces noise in a PV that
is generated in the process or induced in transmitter components.
EU
Engineering
Units
A standard scale of values, selected by the user from a standard set for
convenient display and interpretation.
Input 1. Physical property (e.g., pressure) applied to a sensor
2. Digital value, calculated in the transmitter, that represents
magnitude of the physical input
Local Meter
A device associated with a single transmitter and installed locally (in
the transmitter housing) or remotely (in a separate housing) that
displays variables sensed or calculated in the transmitter.
Loop Test
(In Analog Mode only) a set of commands from the HHC that causes
the transmitter to provide 0% (4 mA) and 100% (20 mA) for testing
proper operation of all components of the current loop.
LRL
Lower Range
Limit
Minimum value in the useful range of the physical property of a
transmitter at which a sensor can operate.
LRV
Lower Range
Minimum value in a continuous range of "normal" process values.
Value
Match PV’s
Toggle for PV
When On, the value of PV2 is set to the value of PV1.
Matching
Meter Units
User-selected scale of values that provides for convenient
interpretation of values in the associated transmitter.
Output
Analog or digital value, calculated from the input, that is transferred
from the transmitter to a receiver (e.g., process control equipment)
PV Process Variable
Measured magnitude of a primary physical property such as pressure
or temperature.
PV Input
Physical property such as pressure or temperature, applied to an input
sensor
PV Units
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 75
9/06
Process Variable
Units
Standard scale of values of a PV, selected by the user for convenient
display and interpretation.
Page 84

Messages and Diagnostic Codes
Item Definition Description
Sensor Type
Standardized designation of the physical design property of a sensor
(e.g., DP, AP for pressure TC, RTD for temperature.)
Span
The continuous range of values in the "normal" operating range of PV
values (that is, URV-LRV).
SV Secondary Variable
A measured physical value of a physical property (e.g., temperature)
that relates to the measured primary physical property (e.g., pressure).
SV Units
URL
URV
Secondary Variable
Units
Upper Range
Limit
Upper Range
Standard scale of values of an SV, chosen by the user for convenient
display and interpretation.
Minimum value in the useful range of the physical property of a
transmitter sensor can operate.
Maximum value in a continuous range of "normal" process values.
Value
SEND
Command from the HHC to copy the values of displayed parameters
to either the transmitter to which it is connected, or to (NV? memory)
in the HHC.
XS Delta
Detection
Toggle for Delta
Alarm enabling
If XS Delta Detection is On and the Delta Alarm value is exceeded,
the PV output goes to the Failsafe value and a Critical Status message
is enunciated.
If Off and the Delta Alarm value is exceeded, the PV output is not
affected and a Non-Critical Status message is enunciated.
76 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 85

Reference Data
Honeywell DE Fields and Values
Table 26 DE Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
Device Info Tag ID Tag id (8 chars.)
Type Transmitter type
Firmware version Firmware version of the transmitter
Serial number Serial number of transmitter
Scratch pad 32 chars.
General PV Type
Dual Range
Single Range
(STDC)
Communication mode Analog DE 4 byte DE 6 byte
Failsafe Direction Upscale Downscale
Line Filter (STT only) 50 Hz 60 Hz
T/C Fault Detect (STT only) Enabled Disabled
DE Configure LRL, URL, LRV, URV Floating point
PV Units (STT only) °C
K °R
°F
PV Units (ST only) InH2O @ 39F
InH2O @ 68F
MmHg @ 0C
Psi
KPa
MPa
mBar
bar
g/cm²
kg/cm²
SV Units °C °F
Sensor Type (STT only) T/C J
T/C K
T/C T
T/C S
T/C R
T/C E
T/C B
T/C N
RTD-PT100J
Millivolts
RTD-PT100D
RTD-PT200
RTD-PT500
RTD-Ni500
Sensor Type (ST only) DP AP GP
Damping (STT only) 0.00
0.30
0.70
3.10
6.30
12.70
1.50
DE Configure
(continued)
Damping (ST only) 0.00
0.16
0.32
1.00
2.00
4.00
0.48
Single Range
w/SV
inHg @ 32F
mmH2O @ 4C
mH2O @ 4C
ATM
InH2O @ 60F
RTD-Cu10
RTD-Cu25
T/C–RH
Radiamatic
T/C–W5W26
T/C–W3W25
Ohms
T/C-NiNiMo
25.50
51.10
102.30
8.00
16.0
32.0
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 77
9/06
Page 86

Honeywell DE Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
Span Floating point (URV – LRV)
Linearization (STT only) Linear Non-Linear
Conformity (ST only) Linear Square Root
Auxiliary
Critical Status Latching Enabled Disabled
Configure
(STT only)
NAMUR Enabled Disabled
CJ Compensation Internal External
CJ Temperature Floating point
Write Protection Enabled Disabled
Password Write protection password (4 digits)
Change Password
New Password 4 digits
(STT only)
Confirm New Password 4 digits
Monitor Input Transmitter input in engineering units (floating point)
Output Transmitter output in percent (floating point)
SV Secondary variable (floating point)
Device Status Gross Status Critical Non-Critical
Invalid
Database
Critical Critical status strings
Non-Critical Non-critical status strings
Local Meter (ST
only)
Meter Hardware
Full Functional
Meter
No Meter, Local
Span & Zero
No Meter
Installed
Meter, NO
Local Span or
Zero
Meter Units %
inH2O @ 39F
mmHg @ 0C
psi
kPa
mBar
bar
g/cm²
kg/cm²
mmH2O @ 4C
mHg @ 0C
mH2O 4C
GPM
GPH
Custom
mPa
Custom Units 8 characters
Flow EU Upper Value Floating point
Flow EU Lower Value Floating point
78 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 87

Honeywell HART Fields and Values
Table 27 HART Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
Device Info Tag ID 8 chars
Model Transmitter type
Device ID Transmitter’s device ID
Manufacturer String
Message 32 chars
Descriptor 16 chars
Extended Info Universal Rev. Numerical
Software Rev. Numerical
Field Device Rev. Numerical
Poll Address Numerical
# Req. Preams Numerical
PV Sensor S/N Numerical
Final Assembly # Numerical
PROM ID Numerical
Basic Setup LRL, URL, LRV, URV Floating point
PV Sensor Units
Sensor Type (ST only) DP AP GP
SV Units °C
Transfer Function Linear Square root
Damping (ST only) 0.00
Damping (STT only) Floating point between 0 and 100
PV Sensor Units (ST
only)
(STT only)
InH2O @ 68F
InHg @ 0C
FtH2O @ 68F
MmH2O @ 68F
MmHg @ 0C
Psi
°C
°F
°F
0.16
0.32
0.48
Bar
Mbar
g/cm²
kg/cm²
pascals
kPa
°R
Kelvin
°R Kelvin
1.00
2.00
4.00
Reference Data
Torr
ATM
InH2O @ 60F
MPa
InH2O @ 4C
MmH2O @ 4C
MV
Ohms
8.00
16.0
32.0
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 79
9/06
Page 88

Honeywell HART Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
Output Condition
PV Output Floating point
PV2 (STT25T only)
Alarm Direction High Low
NAMUR (STT only) Enabled Disabled
Poll Address 0 - 15
Req. Preambles Numerical
Device Status Critical String
Non-Critical String
Info (STT25H only) String
Monitor Output (ma) Output current (floating point)
Output (%) Output percent (floating point)
PV
Primary variable output in engineering units (floating
point)
PV2 (STT25T only)
Primary variable 2 output in engineering units (floating
point)
SV Secondary variable in engineering units (floating point)
Local Meter (ST only) Meter Hardware Meter Installed
No Meter
Installed
Meter Units % of Span
inH2O @ 4C
mmHg @ 0C
psi
kPa
mBar
bar
g/cm²
kg/cm²
mmH2O @ 4C
inHg @ 0C
mH2O @ 4C
gal/min
gal/hr
Custom
mPa
Custom Units 8 chars
Flow EU High Floating point
Flow EU Low Floating point
Alarm (STT only)
Break Detect (STT25H
only)
Enabled
Disabled
Latching Alarm Enabled
Disabled
XS Delta On
Off
Sensor (STT only)
Sensor Type (STT25H
only)
MV
T/C-E
T/C-J
T/C-K
T/C-T
T/C-S
T/C-R
T/C-B
JPT 100
PT100
PT200
Ohms
T/C-N
80 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 89

Dialog Field Value
Sensor Type (STT25T
only)
T/C-J
T/C-K
T/C-T
T/C-E
Line Filter 50 Hz 60 Hz
RTD Wire (STD25H) 3 Wire 4 Wire Sensor (STT only)
(continued)
CJ Mode Compensation
Internal CJ External CJ
(STT25H)
Compensation
(STT25T)
Write Protect (STT25H
only)
Write Protect Write protected
Not write
protected
Password 4 chars
New Password 4 chars
Reference Data
PT100 (RTD)
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 81
9/06
Page 90

Generic HART Fields and Values
Generic HART Fields and Values
Table 28 Generic HART Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
Device Info Tag ID 8 chars
Model Transmitter type
Device ID Transmitter’s device ID
Manufacturer String
Message 32 chars
Descriptor 16 chars
Extended Info Universal Rev. Numerical
Software Rev. Numerical
Field Device Rev. Numerical
Hardware Revision Numerical
# Req. Preams Numerical
PV Sensor S/N Numerical
Final Assembly # Numerical
Physical Signaling Code Numerical
Basic Setup LRL, URL, LRV, URV Floating point
Minimum Span Floating point
Damping Floating point
PV Units Type
Temperature
Pressure
Volumetric flow
Velocity
Volume
Length
Time
Mass
PV Sensor Units
Mass flow
Mass per volume
Viscosity
Electromagnetic
unit of electric
potential
Electrostatic unit of
current
Electromagnetic
unit of resistance
Energy
Power
Radial velocity
Miscellaneous
Generic
Temperature
82 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Pressure
degC
degF
inH2O @ 39F
inHg @ 32F
ftH2O @ 68F
mmH2O @ 68F
mmHg @ 0C
psi
degR
bar
Mbar
g/cm²
kg/cm²
Pascals
KPa
Kelvin
torr
ATM
inH2O @ 60F
MPa
inH2O @ 4C
mmH2O @ 4C
Page 91

Dialog Field Value
Basic Setup
(Continued)
Volumetric Flow
ft³/min
gal/min
l/min
ImpGal/min
m³/hr
gal/s
MillionGal/day
l/s
MillionL/day
ft³/s
Velocity ft/s
m/s
Volume gal
liter
Imperial Gal
m³
bbl
Length ft
meter
Time min
sec
Mass gram
kg
Metric Ton
Mass Flow g/s
g/min
g/hr
kg/s
kg/min
kg/hr
kg/day
Mass Per Volume SGU
g/cm³
kg/m³
lb/gal
lb/ft³
g/ml
Electromagnetic Unit of
Electric Potential
Electrostatic Unit of
Viscosity centistokes centipoises
mV
mA
Current
Electromagnetic Unit of
Ohm kOhms
Resistance
Basic Setup
Energy newton-meter kilowatt hour btu
Reference Data
ft³/day
m³/s
m³/day
ImperialGal/hr
ImperialGal/day
norm. m³/hr
norm. l/hr
std. ft³/min
ft³/hr
in/s
in/min
bushel
yd³
ft³
in³
m³/min
bbl/s
bbl/min
bbl/hr
bbl/day
gal/hr
ImperialGal/s
l/hr
gal/day
ft/min
m/hr
normal m³
normal liter
std ft³
hectoliter
liquid bbl
in
mm
cm
hr day
lb
Short Ton
MetTon/min
MetTon/hr
MetTon/day
lb/s
lb/min
lb/hr
kg/l
g/l
lb/in³
ShTon/yd³
degTwaddell
Long Ton
ounce
lb/day
ShTon/min
ShTon/hr
ShTon/day
LTon/hr
LTton/day
degBaum (heavy)
degBaum (light)
degAPI
ug/l
ug/m³
V
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 83
9/06
Page 92

Generic HART Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
(Continued)
deka therm
foot pound force
Miscellaneous Hz
uMho
Percent,
pH
mSiemen/cm
uSiemen/cm
Newton
degBrix
% solids/wt
Generic Use Enumeration
Not Used
Transfer Function Linear
Square Root
Sq. Root 3rd Power
Sq. Root 5th Power
Special Curve
PV Output Floating point
Alarm Direction High Low
NAMUR Not applicable for Generic HART transmitter
Poll Address 0 - 15
Req. Preambles Numerical
Dynamic
Variable Map
Primary Var. Code Numerical
Secondary Var. Code Numerical
Tertiary Var. Code Numerical
Quaternary Var. Code Numerical
Diagnostics/
Service
Master Reset Performs a Master Reset of device
Device Status Displays the Device Status screen
Self Test Performs a Self Test of the device
Monitor Displays the Monitor screen
Device Status
Status Byte Status Byte 0 - Status Byte 15
Status Bit
Status Bit 0 - Status Bit 7
OK
Non Critical Status (Field
Device Status)
Primary Variable
Out of Limits
Non Primary
Variable Out of
Limits
Loop Current
Saturated
Mjoule Mcalorie
% solids/vol
degBalling
proof/vol
proof/mass
parts/million
degrees
radian
% consistency
volume %
None
ml/l
ul/l
% LEL
ppb
% SteamQual
ftin16
ft³/lb
pFarads
% plato
Special
Unknown
Square
Discrete(switch)
Sq. Rt+Spec. Curve
Sq. Rt 3rd+Spec.
Curve
Loop Current Fixed
More Status
Available
Cold Start
Sq. Rt 5th+Spec.
Curve
Not Used
None
Unknown
Configuration
Changed
Device
Malfunction
84 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 93

Dialog Field Value
Monitor Output (mA) Floating point
Output (%) Floating point
PV Floating point
SV Floating point
TV Floating point
QV Floating point
Comm. Status String value
Device Status Displays the Device Status screen
Calibration Zero Trim Performs a Zero Trim
Apply Values Displays the Apply Values screen
Loop Test Displays the Loop Test screen
D/A Trim Displays the D/A Trim screen
Apply Values,
Set the (output current to) 4 mA 20 mA
screen 1
Apply Values,
screen 2
Set As New Value
Current Applied Process
Value
Floating point
Sets the LRV or URV equal to the value in the Current Applied
Process Value edit box.
Read New Value Updates the Current Applied Process Value edit box
Loop Test Mode Normal Output Mode
Choose Analog Output
4 mA 20 mA Other
Level
Other Floating point
Set Output Sets the device output
Clear Output Clears the Output Mode
D/A Trim
Field Device Will Be
Scaled From
Floating Point
Change Scale Activates the 2 edit boxes mentioned above.
Start D/A Trim Starts the D/A Trim process
Meter Value Floating point
Burst Mode Burst Mode Off
On
Burst Options PV
Specific
Monitor
Number of Device
Variables to Query
1 - 4
Not Used
None
% Range and
Current
Unknown
Special
All PVs and
Current
Dev. Var. 1 0 - 22
Dev. Var. 2 0 - 22
Dev. Var. 3 0 - 22
Reference Data
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 85
9/06
Page 94

Generic HART Fields and Values
Dialog Field Value
Dev. Var. 4 0 - 22
Dev. Var. 1 Floating point
Dev. Var. 2 Floating point
Dev. Var. 3 Floating point
Dev. Var. 4 Floating point
86 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 95

Table 29 HART Universal Commands
Command Number Function
0 Read Unique Identifier
1 Read Primary Variable
2 Read Current and % of Range
3 Read Current and Four Dynamic Variables
6 Write Polling Address
12 Read Message
13 Read Tag, Descriptor, Date
14 Read PV Sensor information
15 Read Output information
16 Read final assembly number
17 Write Message
18 Write Tag, Descriptor, Date
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 87
9/06
Page 96

Table 30 HART Common Practice Commands
Command Number Function
33 Read Transmitter Variables
34 Write Damping Value
35 Write Range Values
36 Set Upper Range Value
37 Set Lower Range Value
40 Enter/Exit fixed current mode
41 Perform Device Self-test
42 Perform Master Reset
43 Set(trim) PV Zero
44 Write PV Units
45 Trim DAC Zero
46 Trim DAC Gain
47 Write Transfer Function
48 Read additional device status
50 Read Dynamic Variable Assignments
51 Write Dynamic Variable Assignments
53 Write Transmitter Variable Units
105 Read Burst mode configuration
107 Write Burst Device Variables
108 Write Burst mode command number
109 Burst mode control
88 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 97

Reference Data
XML Database (Samples)
XML database files that can be exported from the MC Toolkit application to Documint (or other XML file
utility) includes thirteen items. The specific content of each file depends on the type of field device from which
it is exported, but the form of each item is the same for all devices.
Example:
<Field name="Bus Type">HART</Field>
<Field name="
Parameter Name">Parameter Value</Field>
Two samples of XML files are given below - one for a Honeywell STT 3000 Smart Temperature Transmitter,
and the other for a non-Honeywell (or "generic") device by Smar.
An explanation of the parameters/values for each XML item is given in the table that follows the samples.
XML Sample - Honeywell DE
*******************************************************
<Record>
<Field name="Bus Type">DE</Field>
<Field name="Device">STT 3000</Field>
<Field name="Tag ID">XXXXXXXX</Field>
<Field name="Serial Number">B125340037</Field>
<Field name="Manufacturer">Honeywell</Field>
<Field name="Model Number">1.5</Field>
<Field name="Transfer Function">1</Field>
<Field name="Input Range : In Low">-20.0</Field>
<Field name="Input Range : In High">107.5</Field>
<Field name="Input Range : In Units">0</Field>
<Field name="Output Range : Out Low">4.00</Field>
<Field name="Output Range : Out High">20.00</Field>
<Field name="Output Range : Out Units">mA</Field>
</Record>
XML Sample - non-Honeywell HART
*********************************************************
<Database>
<Table name="Instrument">
<Record>
<Field name="Bus Type">HART</Field>
<Field name="Device">Generic</Field>
<Field name="Tag ID">SMAR</Field>
<Field name="Serial Number">816923</Field>
<Field name="Manufacturer">62</Field>
<Field name="Model Number">12345</Field>
<Field name="Transfer Function">0</Field>
<Field name="Input Range : In Low">-10.0</Field>
<Field name="Input Range : In High">100.0</Field>
<Field name="Input Range : In Units">39</Field>
<Field name="Output Range : Out Low">1.00</Field>
<Field name="Output Range : Out High">5.00</Field>
<Field name="Output Range : Out Units">58</Field>
</Record>
*******************************************************
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 89
9/06
Page 98

XML Database (Samples)
Field # Parameter Name Parameter Description
Bus Type
1
2
Device
Protocol type
Classification of device type: Honeywell DE (ST 3000,
STT3000, Honeywell HART (STT25H), or generic (nonHoneywell) HART
Tag ID
3
Serial Number
4
Manufacturer
5
User-defined identifier
Serial Number of device (assigned by Manufacturer)
a. Name of Manufacturer (Honeywell)
b. Numeric Code for Manufacturer's Name
Model Number
6
a. Firmware Version (Honeywell DE Transmitter)
b. Final assembly number (Honeywell HART and generic
HART)
Transfer Function
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Input Range : In Low
Input Range : In High
Input Range : In Units
Output Range : Out Low
Output Range : Out High
Output Range : Out Units
Code for output form (0= Linear; 1= Square Root)
LRV
URV
Code for Engineering Units (PV Input)
Output Range 0 % value (1 V or 4 mA)
Output Range 100 % value (5 V or 20 mA)
a. mA or Volts (Honeywell DE)
b. Numeric Code for Engineering Units (HART)
90 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
Page 99

MCT101 Maintenance
Modem Battery Replacement
The battery should be replaced:
• when, in the Modem Diagnostics display (in the Modem Status box) one of these messages appears
− Modem Battery: Low
− Modem Battery: Unknown (after checking wiring connections)
• in periodic maintenance, when voltmeter test indicates low voltage.
WARNING !!
Never remove the cover of the battery compartment, or attempt battery replacement in areas
designated as having a potentially Explosive atmosphere.
Table 31 Battery Removal and Replacement Procedure
Step Action
MCT101 Maintenance
WARNING !!
Do not perform this procedure in an area designated as having a potentially explosive
atmosphere.
1
2
Remove the screw that holds the battery cover in place, and remove the cover from the
battery compartment.
Press lightly on the bottom of the battery as shown in the picture below, rotating the battery
outward at the top. Note the orientation of the battery in the compartment, and then remove
it from the case.
3 Noting orientation of the new battery and the terminals, insert the new battery into the case.
4 Replace the cover and the retaining screw.
Release 3 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual 91
9/06
Page 100

MC Toolkit Software Installation/Maintenance
MC Toolkit Software Installation/Maintenance
Overview
The MC Toolkit application software and SDC 625 application software, as well as all available HART
device Descriptions (DD), have been pre-loaded into the PDA’s memory chip at the factory. The MCT101
is ready to use once the necessary batteries (included) are installed in the DE/HART Modem and PDA. It is
recommended that you review the PDA manufacturer’s documentation for general use requirements such as
battery charging requirements and configuration options.
The MCT202 should be unpacked per the separate safety instruction sheet.
We have also included a CD-ROM that includes the MC Toolkit application software and SDC 625
application software, should you ever need to reload it.
To establish a partnership between your desktop PC and the PDA, follow the PDA manufacturer’s
documentation on how to install ActiveSync and establish a connection. The ActiveSync software is
provided on the PDA manufacturer’s CD-ROM disk, or it can be obtained directly from Microsoft at:
http://www.microsoft.com/pocketpc/downloads/activesync.asp
Note:
The handheld computer needs to be connected to the MC Toolkit Modem for the MC Toolkit software to
operate correctly. If the modem is not connected to the handheld computer, an error message will appear.
Use the short interface cable provided for this purpose.
DD Copier
The DD (Device Description) Copier can be used to place a Device Description (.fms file) into the right
folder in the MC Toolkit Device Description file structure.
1. Obtain the Device Description (.fms file) and place into an existing folder on the PDA. For
example, the. fms file could be placed in a folder on the Storage Card in File Explore. You can use
File Explorer to view folders/files.
2. Use File Explorer to find DD Copier. DD Copier will be in the following directory: My
Device\Storage Card\Honeywell SDC.
3. Selection DD Copier to open the program
4. Select File from the menu at the bottom, and select open.
5. Locate the stored .fms file from Step 1 above.
6. Select (highlight) the .fms file and select OK at the bottom of the screen. This will copy the .fms
file into the PDA’s Device Description file structure.
92 34-ST-25-20 MC Toolkit User Manual Release 3
9/06
 Loading...
Loading...