Honda Power Equipment FCX User Manual

Emergency Response Guide
Prepared for Fire Service, Law Enforcement, Emergency Medical, and Professional
Towing Personnel by American Honda Motor Co., Inc.
Honda Fuel Cell Vehicle


Contents
Key Components
1
Vehicle Description
Type, Size, and Materials 2
Curb Weight 2
Fuel Cell Module 2
Hydrogen Tanks 2
High-Voltage Electric Motors 3
Power Control Unit 3
12-Volt Battery 3
Capacitor Module 4
High-Voltage Cables 4
Built-In Safety Features
Occupant Protection Features 5
Crash Detection System 5
Hydrogen Tank Safety Valves 5
Hydrogen Line Sensors 6
Manual Hydrogen Shut-Off Valve 6
Potential Hazards
Flammable Fluid 7
Hydrogen Properties and Potential Hazards 7
Electric Shock Potential 8
Capacitor Electrolyte 8
Emergency Procedures
Incidents Involving Fire 9
Submerged or Partially Submerged Vehicle 9
Damaged Vehicle 10
Best Method for Preventing Current Flow and Hydrogen Leakage 11
Second-Best Method for Preventing Current Flow and
Hydrogen Leakage 12
Least-Desirable Method for Preventing Current Flow and
Hydrogen Leakage 14
Extricating Occupants 16
Emergency Towing
Using the Towing Hook 17
Using the Tie-Downs 18

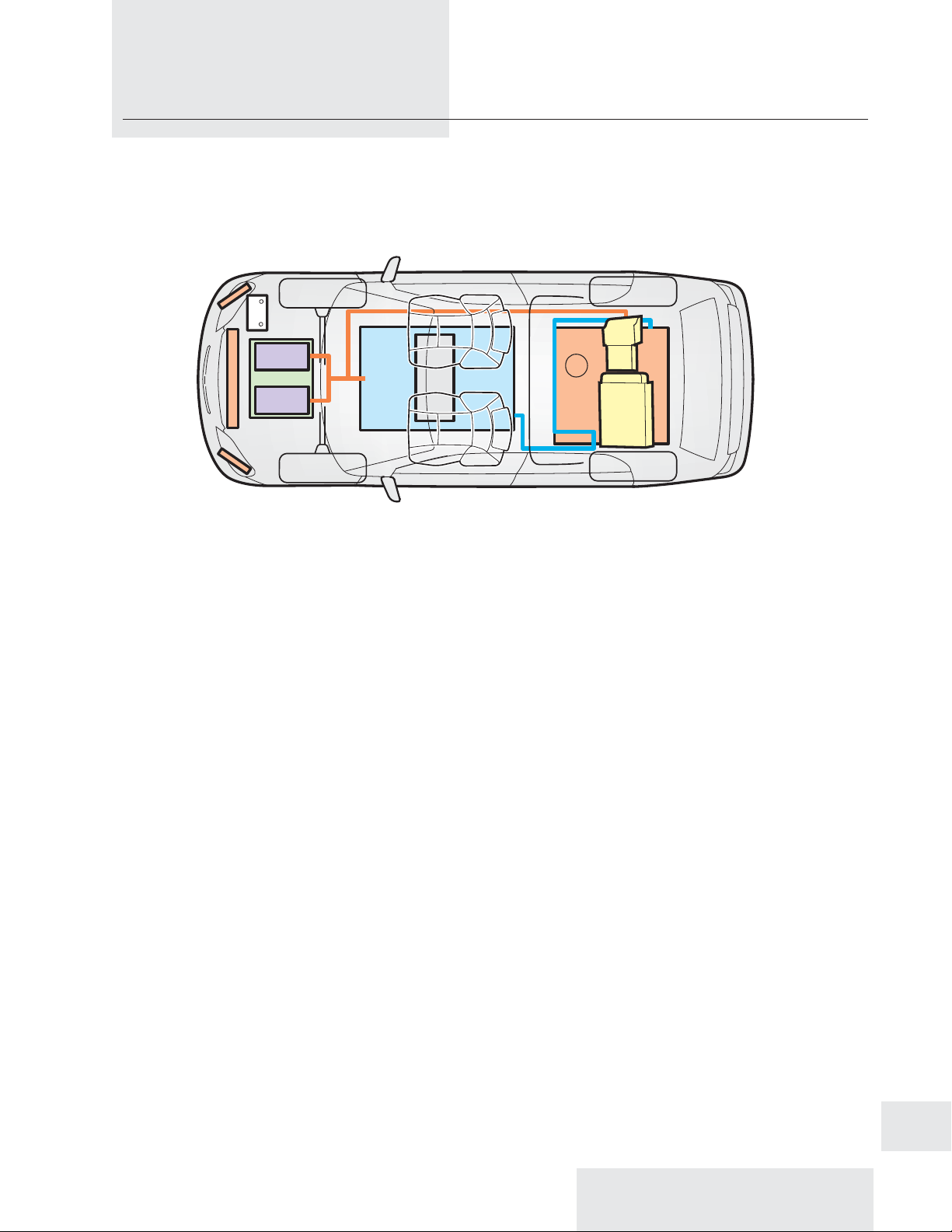
Key Components

Type, Size, and Materials
The Honda FCX is a 2-door, 4-passenger hatchback
electric vehicle that uses fuel cells to generate
power. The FCX can be easily identified by the
words “Fuel Cell Power” across the bottom of the
rear window, a blue and white compressed hydrogen
decal on the right side of the rear hatch, and the
words “Fuel Cell Power” and the FCX logo on the
driver’s and passenger’s doors. The chassis and
most components are made of steel and aluminum.
A few parts are made of plastic.
Curb Weight
The curb weight of the Honda FCX is 3,700 pounds
(1,680 kg).
Fuel Cell Module
The main power source for the FCX is a fuel cell
module, which is housed inside a strong steel box
under the passenger compartment floor. This
module contains many individual fuel cells that
combine hydrogen from onboard tanks with oxygen
from the air intake units to produce electricity. The
only by-products of this process are heat and water;
the water is released through the exhaust pipe.
Hydrogen Tanks
The hydrogen used by the fuel cell module is
compressed to 5,000 psi and stored in two tanks.
The tanks are under the rear floor of the vehicle.
They are made of nonflammable materials and
certified to have passed the same rigid impact tests
as tanks in cars fueled by compressed natural gas
(CNG).
At 5,000 psi, the total capacity of the tanks is 9.44
2
pounds (4.28 kg) of hydrogen.
3
Vehicle Description Continued
High-Voltage Electric Motors
Electricity generated by the fuel cell
module powers these four high-voltage
motors:
• The propulsion motor drives the front
wheels
• An air compressor motor supplies air to
the fuel cells
• A water pump motor cools the fuel cell
module
• An air conditioning motor powers the
air conditioning system
Turning the key switch to the Accessory (I)
or Lock (0) position turns off all the
motors. However, the air compressor motor
may continue running for up to 10 seconds.
Power Control Unit
The power control unit (PCU) is located
under the hood directly under the two air
intake units. The PCU controls the
generation and use of high-voltage
electrical power and contains high-voltage
components.
12-Volt Battery
A conventional 12-volt battery is located
under the hood, on the passenger side of
the vehicle. This battery powers the lights,
audio system, and other standard electrical
components. It also supplies power to start
the fuel cell system.
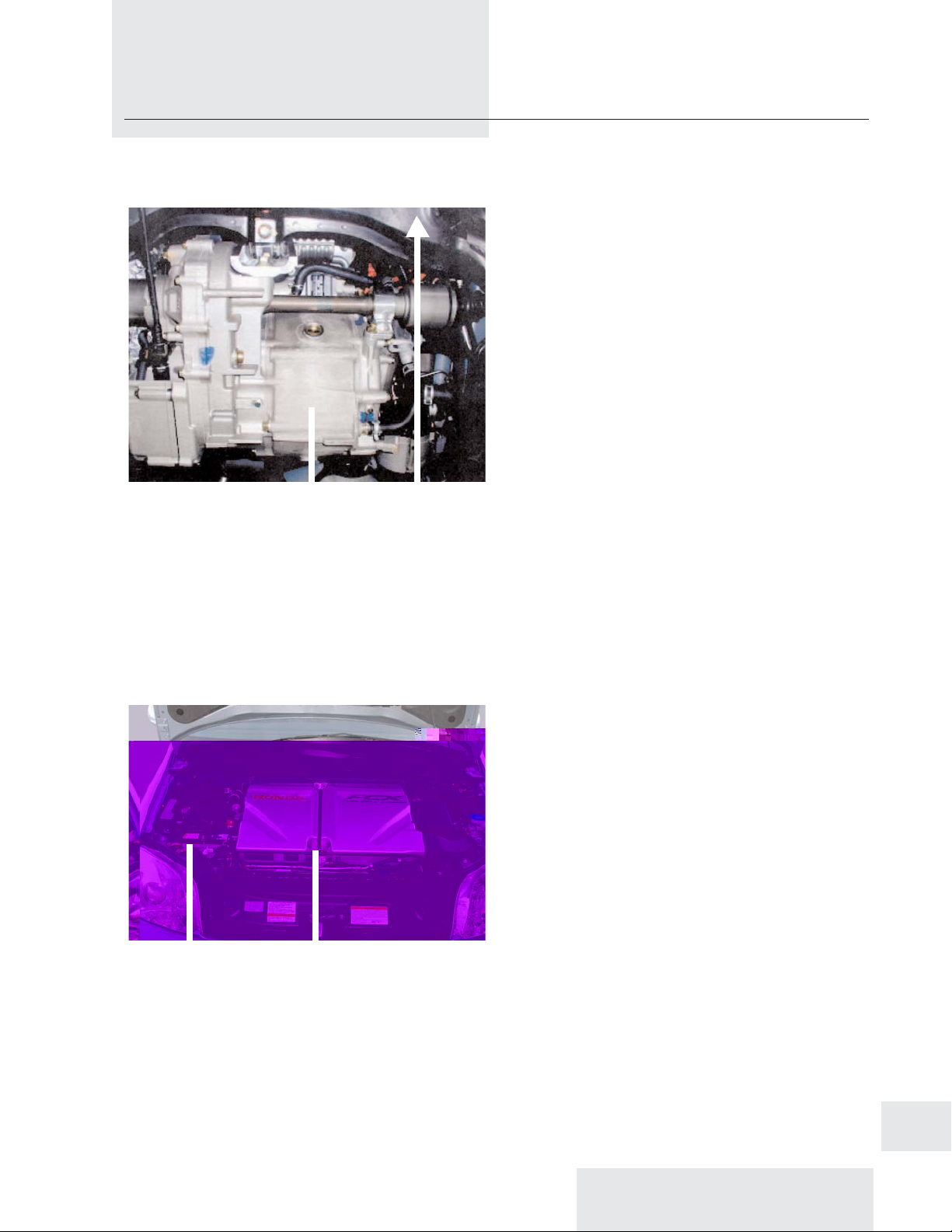
Propulsion Motor Front of Car
12V Battery Power Control Unit

4
Capacitor Module
Two integrated capacitor assemblies make up
the capacitor module. Somewhat like a
battery, the capacitor module provides longterm storage for electrical power generated
by the fuel cells or regenerated by the
propulsion motor. This power is available to
provide extra current when needed, such as
during acceleration. Each capacitor assembly
has many individual cells. Specifications for
the capacitor module are
Weight: 150 pounds (68.6 kg)
Total Voltage: 400 volts
Capacity: 8.0 farads
The capacitor module is housed inside a
strong, sealed protective box, between the
rear seat and the cargo area. The module
contains high-voltage even when the fuel cell
module and the key switch are turned off.
The entire unit is electrically insulated from
the vehicle body.
High-Voltage Cables
Electrical energy comes from the fuel cell
module and the capacitor module to the
various electrical components through 21
high-voltage cables. Most of these cables are
concealed behind or within various
components. Any high voltage cable visible
under the hood or from under the car can be
easily identified by its orange protective
cover.
Vehicle Description Continued
One of Two Assemblies in the
Capacitor Module
High-Voltage Cables
(driver’s-side under-hood view)
 Loading...
Loading...