Page 1

Page 2

HLP-A Series
Page 3

Page 4

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
I. Introduction 1
1. Checks upon Delivery 2
2. Nameplate Description of HLP Series Inverter 3
II. Safety Precautions 4
1. Before the Power-up 4
2. During the Power-up 6
3. During the Operation 6
III. Standards and Specications 7
1. Particular Specications 7
2. General Specications 9
IV. Storage and Installation 11
1. Storage 11
2. Installation Site and Environment 11
3. Installation and Direction 11
V. Wiring 13
1. Main Circuit Wiring Schematic Diagram 13
2. Description of Terminal Block 14
3. Basic Connection Diagram 16
4. Precautions on Wiring 19
VI.Instruction of the Digital Operator 23
1. Description of the Digital Operator 23
2.Description of the panel type 24
3.List of the panel used in inverter 24
4.Description of Indicator Lamp Status 24
5. Description of Operation Examples 25
VII. Commissioning 27
1. Important Checks before the Commissioning 27
2. Commissioning Methods 27
VIII. Function List 28
IX. Descriptions of Functions 35
Page 5

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
X. Care & Maintenance, Fault Information and Troubleshooting 82
1. Precautions about Inspection and Maintenance 82
2. Periodical Inspection and Maintenance items 82
3. Fault Indication and Troubleshooting 82
4. Faults and Analysis 86
XI. Selection of Peripheral Devices and Disposition 88
1. Options 88
2. Disposition 89
XII. Appendices 93
Appendix 1: Simple Examples of Application 93
Appendix 2: Appearance and Installation Dimensions 100
Appendix 3: Appearance and Installation Dimensions 105
Appendix 4: Description of Parameter Setting for HLP-A Inverter 106
Appendix 5: User’s Records and Feedback 108
Page 6

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 1 -
I. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing and using the general-purpose inverter of HLP
series of multi-functions and high performance.
Please read carefully the operation manual before putting the inverter to
use so as to correctly install and operate the inverter, give full play to its
functions and ensure the safety. Please keep the operation manual handy
for future reference, maintenance, inspection and repair.
Due to the inverter of a kind of electrical and electronic product it
must be installed, tested and adjusted with parameters by specialized
engineering persons of motors.
The marks of
Danger
Caution
and other symbols in the manual
remind you of the safety and prevention cautions during the handling,
installation, running and inspection. Please follow these instructions to
make sure the safe use of the inverter. In case of any doubt please contact
our local agent for consultation. Our professional persons are willing and
ready to serve you.
The manual is subject to change without notice.
Danger
indicates wrong use may kill or injure people.
Caution
indicates wrong use may damage the inverter or
mechanical system.
Danger
● Be sure to turn off the input power supply before wiring.
● Do not touch any internal electrical circuit or component when the
charging lamp is still on after the AC power supply is disconnected,
which means the inverter still has high voltage inside and it is very
dangerous.
● Do not check components and signals on the circuit boards during
the operation.
● Do not dissemble or modify any internal connecting cord, wiring or
component of the inverter by yourself.
● Be sure to make correct ground connection of the earth terminal of
the inverter.
● Never remodel it or exchange control boards and components by
yourself. It may expose you to an electrical shock or explosion, etc.
Page 7
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 2 -
1. Checks upon Delivery
The inverter has been strictly and well packed before ex-work. In
consideration of various factors during the transportation special
attention should be paid to the following points before the assembly and
installation. If there is anything abnormal please notify the dealer or the
relevant people of our company.
● Check if the inverter has got any damage or deformation during the
transportation and handling.
● Check if there is one piece of HLPseries inverter and one copy of the
instruction manual available when unpacking it.
● Check the information on the nameplate to see if the specications
meet your order (Operating voltage and KVA value).
● Check if there is something wrong with the inner parts, wiring and
circuit board.
● Check if each terminal is tightly locked and if there is any foreign
article inside the inverter.
● Check if the operator buttons are all right.
● Check if the optional components you ordered are contained.
● Check if there is a certicate of qualication and a warranty card.
Caution
● Do not make any voltage-withstanding test with any component
inside the inverter. These semi-conductor parts are subject to the
damage of high voltage.
● Never connect the AC main circuit power supply to the output
terminals U.V W of the inverter.
● The main electric circuit boards of CMOS and IC of the inverter are
subject to the effect and damage of static electricity. Don’t touch the
main circuit boards.
● Installation, testing and maintenance must be performed by qualied
professional personnel.
● The inverter should be discarded as industrial waste. It is forbidden
to burn it.
Page 8

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 3 -
2. Nameplate Description of HLP Series Inverter
Hardware Version
Model: HLP A 01D5 43 C
Voltage Rating,43 means
3-phase 380V
Inverter Capacity,01D5 means 1.5KW
Serial No., A means A series
Trade Mark
MODEL:
Page 9

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 4 -
II. Safety Precautions
1. Before the Power-up
Caution
● Check to be sure that the voltage of the main circuit AC power supply
matches the input voltage of the inverter.
● The symbol,
E
, represents ground terminals. Be sure to make
correct ground connection of the earth terminals of the motor and the
inverter for safety.
● No contactor should be installed between the power supply and the
inverter to be used for starting or stopping of the inverter. Otherwise
it will affect the service life of the inverter.
Danger
● R.S.T terminals are power input terminals, never mixed with U.V.W
terminals. Be sure that the wiring of the main circuit is correct.
Otherwise it will cause damages of the inverter when the power is
applied to it.
● The terminal of
E
must be grounded separately and never
connected to line zero. Otherwise it will easily cause the protection
or errors of the inverter.
Caution
● Do not carry the front cover of the inverter directly when handling.
It should be handled with the base to prevent the fall-off of the front
cover and avoid the dropping of the inverter, which may possibly
cause the injuries to people and the damages to the inverter.
● Mount the inverter on a metal or other noncombustible material to
avoid the risk of re.
● Install the inverter in a safe location, avoiding high temperature,
direct sunlight, humid air or water.
● Keep the inverter from the reach of children or persons not
concerned.
● The inverter can only be used at the places accredited by our
company. Any unauthorized working environment may have the
risks of re, gas explosion, electric shock and other incidents.
● Install a heat sink or other cooling device when installing more than
one inverter in the same enclosure so that the temperature inside the
enclosure be kept below 40℃ to avoid overheat or the risk of re.
Page 10
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 5 -
● Be sure to turn off the power supply before dissembling or
assembling the operation keypanel and xing the front cover to avoid
bad contact causing faults or non-display of the operator.
● Do not install the inverter in a space with explosive gas to avoid the
risk of explosion.
● If the inverter is used at or above 1000m above seal level, the cooling
efciency will be worse, so please run it by de-rating.
● Do not install any contactor and other components of capacitor or
varistor on the output side of the inverter. Otherwise it will cause
malfunctions and damages of components of the inverter.
● Do not install any switch component like air circuit breaker or
contactor at the output of the inverter. If any of such components
must be installed because of the requirements of process and
others, it must be ensured that the inverter has no output when the
switch acts. In addition, it is forbidden to install any capacitor for
improvement of power factor or any varistor against thunder at the
output. Otherwise it will cause malfunctions, tripping protection and
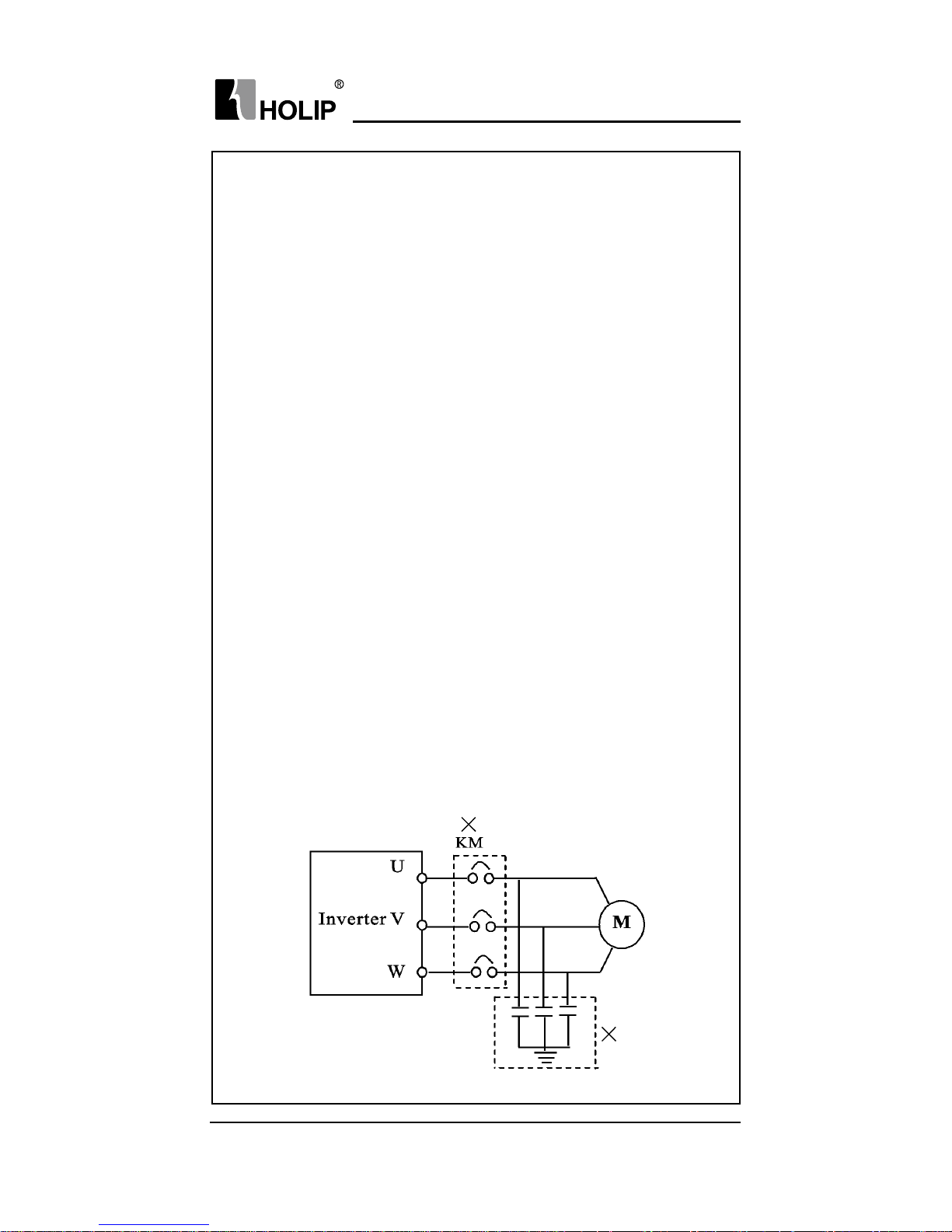
damages of components of the inverter. Please remove them as shown
in the below diagram.
● It will affect the service life of the inverter if a contact is connected
to the front end of input of the inverter to control its starts and stops.
Generally it is required to control it through FOR or REV terminals.
Special attention should be paid to its use in the case of frequent
starts and stops.
● Please use an independent power supply for the inverter. Do avoid
using the common power supply with an electrical welder and other
equipment with strong disturbance. Otherwise it will cause the
protection or even damage of the inverter.
Page 11

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 6 -
The user must strictly follow the instruction to operate and make wire
connection. Otherwise HOLIP will not responsible for the damages
due to wrong operation. The user will responsible for the damages
themselves.
Caution
● Do not touch the heat sink, braking resistor, or other heat elements.
These can become very hot.
● Be sure that the motor and machine is within the applicable speed
ranges before starting operation because the inverter is quite easy to
run from lower speed to higher speed.
● Do not check the signals on circuit boards while the inverter is
running to avoid danger.
● Be careful when changing the inverter settings. The inverter has been
adjusted and set before ex-work. Do not adjust it wantonly. Please
make proper adjustments according to the required functions.
● Do consider the vibration, noise and the speed limit of the motor
bearings and the mechanical devices when the inverter is running at
or above the frequency of 50Hz.
2. During the Power-up
Danger
● Do not plug the connectors of the inverter during the power up to
avoid any surge into the main control board due to plugging, which
might cause the damage of the inverter.
● Always have the protective cover in place before the power up to
avoid electrical shock injury.
3. During the Operation
Danger
● Never connect or disconnect the motor set while the inverter is in
running. Otherwise it will cause over-current trip and even burn up
the main circuit of the inverter.
● Never remove the front cover of the inverter while the inverter is
powered up to avoid any injury of electric shock.
● Do not come close to the machine when the fault restart function is
used to avoid anything unexpected. The motor may automatically
restart after its stop.
● The function of STOP Switch is only valid after setting, which is
different with the use of emergent stop switch. Please pay attention to
it when using it.
Page 12
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 7 -
III. Standards and Specications
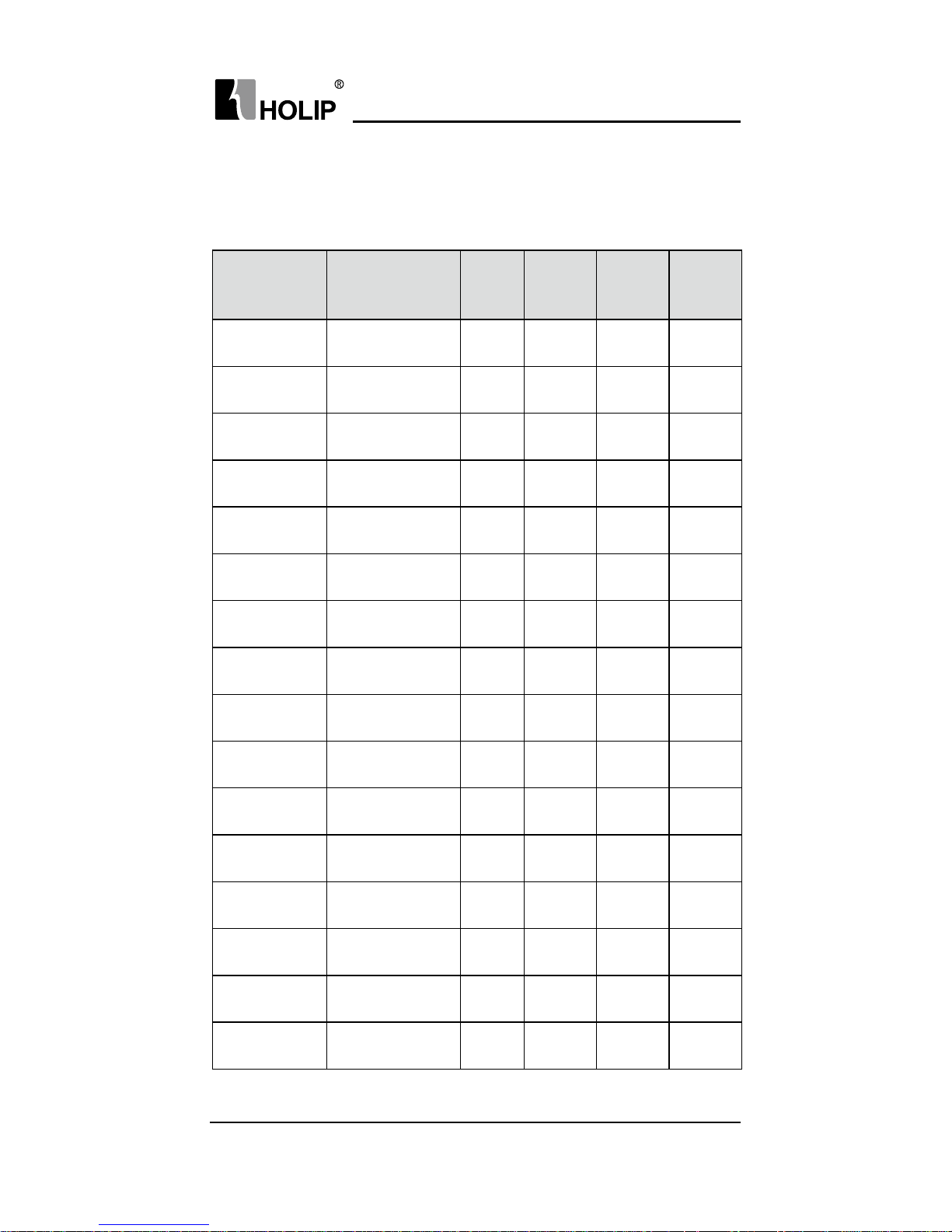
1. Particular Specications
Typ e
Input
Vol t age
Power
(KW)
Inverter
Capacity
( K VA)
Output
Current
(A)
Suitable
Motor
(KW)
HLPA00D 423C
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
0.4 1.0 2.5 0.4
HLPA0D7523C
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
0.75 2.0 5.0 0.75
HLPA01D52 3C
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
1.5 2.8 7.0 1.5
HLPA02D223B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
2.2 4.4 11 2.2
HLPA03D723B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
3.7 6.8 17 3.7
HLPA05D523B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
5.5 10 25 5.5
HLPA07D523B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
7.5 13.2 33 7.5
HLPA001123B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
11 19.6 49 11
HLPA001523B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
15 26 65 15
HLPA18D52 3B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
18. 5 32 80 18.5
HLPA002223B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
22 38.4 96 22
HLPA003023B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
30 52 130 30
HLPA003723B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
37 64 160 37
HLPA004523B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
45 72.8 182 45
HLPA005523B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
55 84 210 55
HLPA007523B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
75 114.4 286 75
Page 13
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 8 -
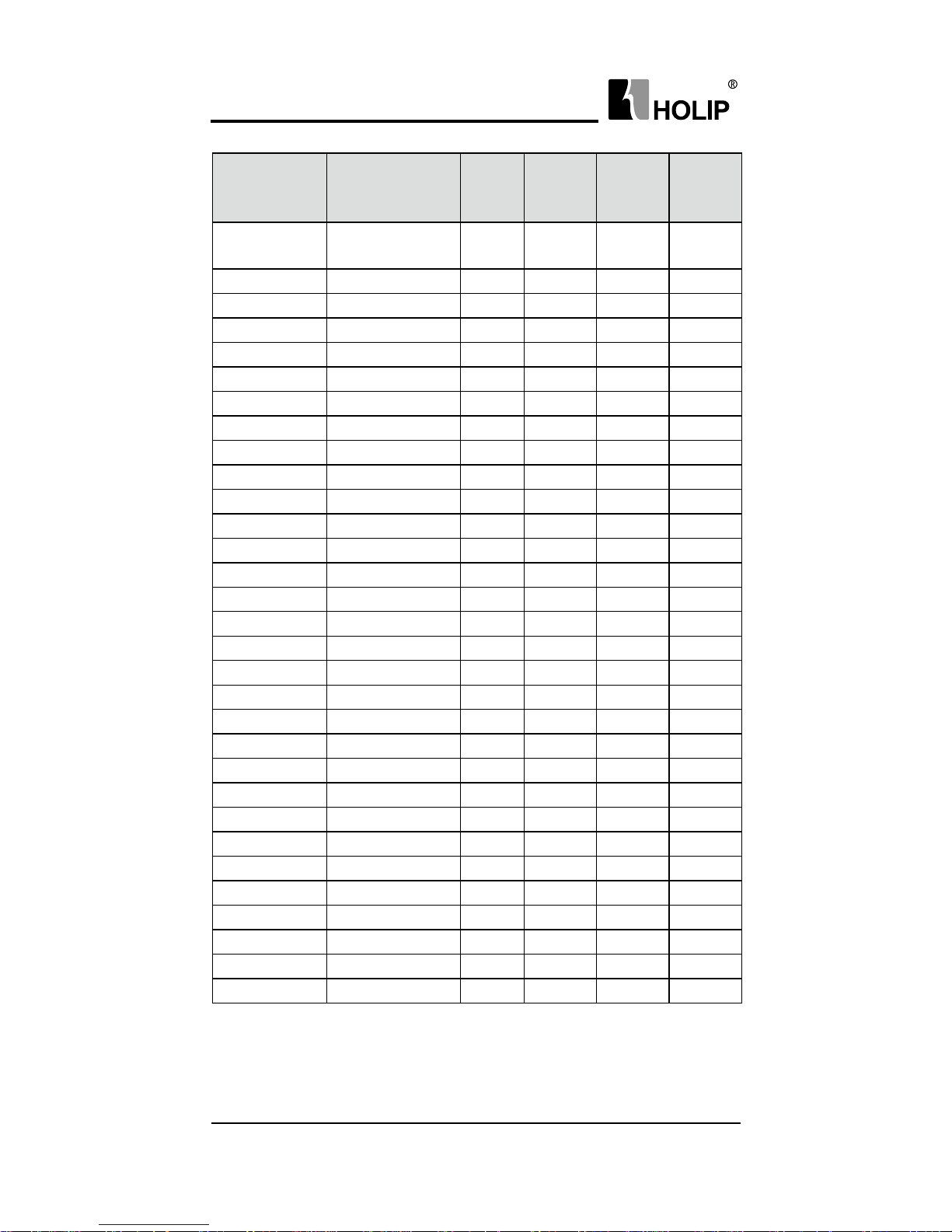
Typ e
Input
Vol t age
Power
(KW)
Inverter
Capacity
( K VA)
Output
Current
(A)
Suitable
Motor
(KW)
HLPA009023B
One & Three phase
220V 50Hz
90 137.2 343 90
HLPA0D7543C 3Φ380V 50Hz 0.75 2.2 2.7 0.75
HLPA01D543 C 3Φ380V 50Hz 1.5 3.2 4.0 1.5
HLPA02D243C 3Φ380V 50Hz 2.2 4.0 5.0 2.2
HLPA03D743B 3Φ380V 50Hz 3.7 6.8 8.5 3.7
HLPA05D543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 5.5 10 12.5 5.5
HLPA07D543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 7.5 14 17.5 7.5
HLPA001143B 3Φ380V 50Hz 11 19 24 11
HLPA001543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 15 26 33 15
HLPA18D543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 18.5 32 40 18. 5
HLPA002243B 3Φ380V 50Hz 22 37 47 22
HLPA003043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 30 52 65 30
HLPA003743B 3Φ380V 50Hz 37 64 80 37
HLPA004543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 45 72 91 45
HLPA0055 43B 3Φ380V 50Hz 55 84 110 55
HLPA007543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 75 116 152 75
HLPA009043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 90 134 176 90
HLPA011043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 110 160 210 110
HLPA0132 43B 3Φ380V 50Hz 132 193 253 132
HLPA016 0 43B 3Φ380V 50Hz 16 0 230 304 160
HLPA018 5 43B 3Φ380V 50Hz 185 260 340 185
HLPA0200 43B 3Φ380V 50Hz 200 290 380 200
HLPA022043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 220 325 426 220
HLPA025043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 250 381 480 250
HLPA028043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 280 427 540 280
HLPA030043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 300 450 580 300
HLPA0315 43B 3Φ380V 50Hz 315 460 605 315
HLPA034543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 345 502 660 345
HLPA037543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 375 544 715 375
HLPA040043B 3Φ380V 50Hz 400 582 765 400
HLPA041543B 3Φ380V 50Hz 415 604 795 415
Page 14
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 9 -
2. General Specications
Inverter Series HLP-A
Control Mode SPWM
Input Power
380±15% for 380V power;220 ±15%
for 220V power
5-Digits Display & Status
Indicator Lamp
Displaying frequency, current,
revolution, voltage, counter,
temperature, forward or reserve
running, and fault, etc.
Communication Control RS-485
Operation Temperature -10~40
℃
Humidity
0-95% Relative Humidity(without
dew
)
Vibration Below 0.5G
Frequency
Control
Range 0.10~400.00Hz
Accuracy
Digital:0.01%(-10~40
℃)
, Analog
:
0.1% (25±10
℃)
Setting Resolution
Digital:0.01Hz, Analog:1‰ of Max.
Operating Frequency
Output Resolution 0.01Hz
Operator Setting
Method
Press directly
to set.
Analog Setting
Method
External Voltage 0-5V, 0-10V, 4-20mA,
0-20mA.
Other Functions
Frequency lower limit, starting
frequency, stopping frequency, three
skip frequencies can be respectively
set.
General
Control
Ramp Control
Selectable 4-speed steps ramp-up and
-down time (0.1-6500s).
V/F Curve Set V/F curve at will
Torque Control
Torque increase is settable by max.
10.0%. The starting torque can reach
150% at 1.0Hz.
Multi-Inputs
6 multi-function input terminals
for 8–speed steps control, program
operation, switching of 4-speed Ramp,
UP/DOWN function, counter, external
emergency stop and other functions.
Page 15
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 10 -
Multi-Outputs
5 multi-function output terminals for
displaying of running, zero speed,
counter, external abnormity, program
operation and other information and
warnings.
Other Functions
AVR (auto voltage regulation),
Deceleration stop or free-stop, DC
brake, auto reset and restart, frequency
track, PLC control, traverse function,
drawing control, auto energy-savings,
carrier adjustable by max. 16KHz, etc.
Protection
Functions
Overload Protection
Electronic relay protection motor
Drive(for constant torque 150%/1
min. for the kinds of fan 120%/1min.
)
FUSE Protection FUSE broken, Motor stops.
Over-voltage
DC Voltage > 400V for 220V class
DC Voltage > 800V for 380V class
Low Voltage
DC Voltage < 200V for 220V class
DC Voltage < 400V for 380V class
Instant Stop and
Restart
Restarted by frequency track after
instantaneous stop.
Stall Prevention Anti-stall during Acc/Dec run
Output End Shorts Electronic circuit protecting
Other Functions
Fin over-heat protection, restriction
of reverse running, direct start after
power on, fault reset, parameter lock
PID, one-drive-more, etc.
Page 16

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 11 -
IV. Storage and Installation
1. Storage
The inverter must be kept in its original package box before installation.
Pay attention to the followings when keeping it in storage if the inverter
is not used for the time being:
● It must be stored in a dry place without rubbish or dust.
● The suitable temperature for storage is between -20℃ and +65℃.
● The relative humidity required is 0-95% without condensation.
● There is no corrosive gas or liquid in the storage ambience.
● It’s better to lay the inverter on a rack and keep it in a proper package.
● It is better not to store the inverter for long time. Long time storage of
the inverter will lead to the deterioration of electrolytic capacity. If it
needs to be stored for a long time make sure to power it up one time
within a year and the power-up time should be at least above ve hours.
When powered up the voltage must be increased slowly with a voltage
regulator to the rated voltage value.
2. Installation Site and Environment
The inverter should be installed at the following location:
● Ambient temperature -5℃ to 40℃ with good ventilation.
● No water drop and low moisture.
● Free from direct sunshine, high temperature and heavy dust fall.
● Free from corrosive gas or liquid.
● Less dust, oil gas and metallic particles
● Free from vibration and easy for service and inspection.
● Free from the interference of electromagnetic noise.
Attention: The ambient conditions of the inverter will affect its
service life.
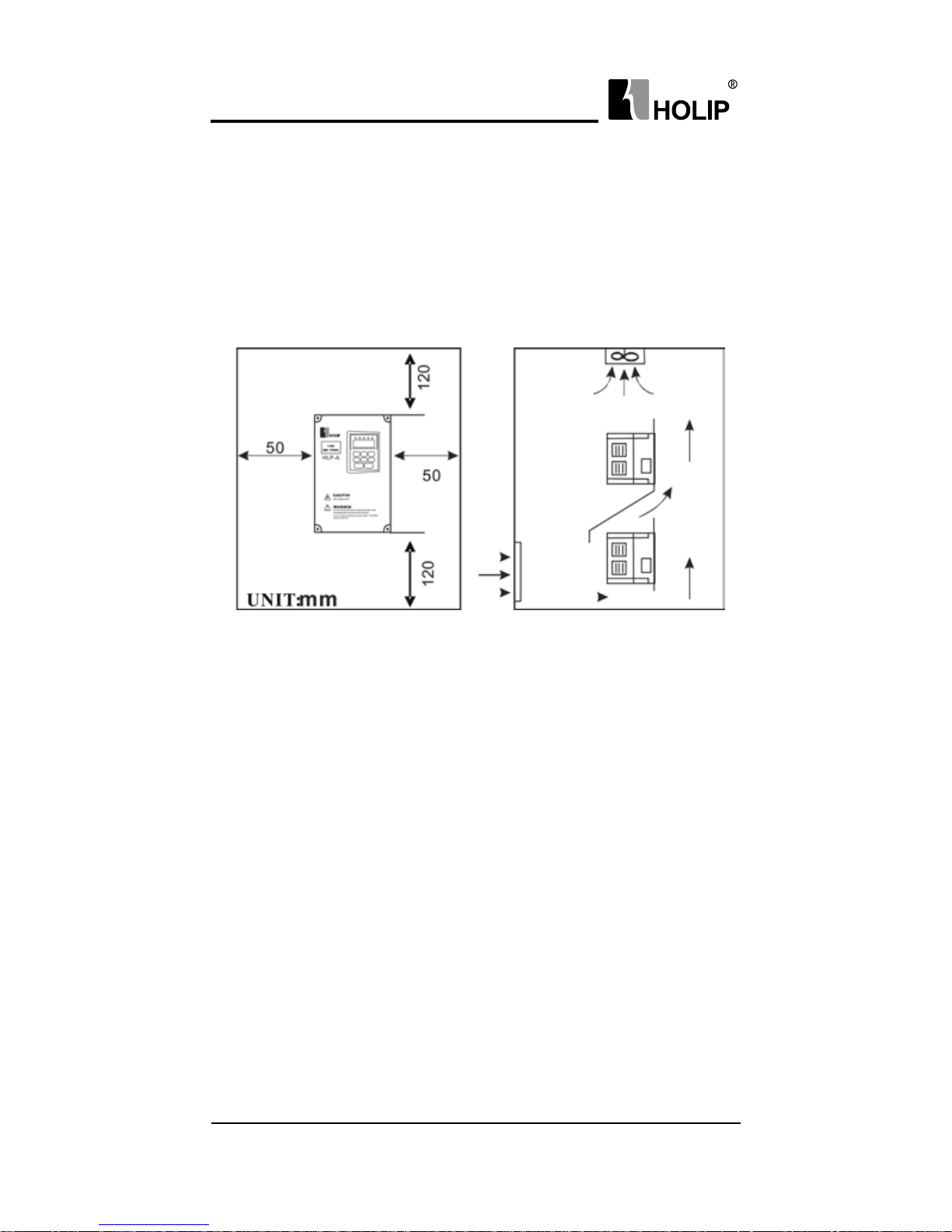
3. Installation and Direction
● There must be enough space left around the inverter for easy
maintenance and cooling. See Diagram 1.
● The inverter must be installed vertically with the smooth ventilation
for effective cooling.
● If there is any instability when installing the inverter, please put a at
Page 17
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 12 -
board under the inverter bottom base and install it again. If the inverter
is installed on a loose surface, stress may cause damage of parts in the
main circuit so as to damage the inverter.
● The inverter should be installed on non-combustible materials, such as
iron plate.
● If several inverters are installed, upper and lower, together in one
cabinet, please add heat dissipation plates and leave enough space
between the inverters. See Diagram.
Page 18
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 13 -
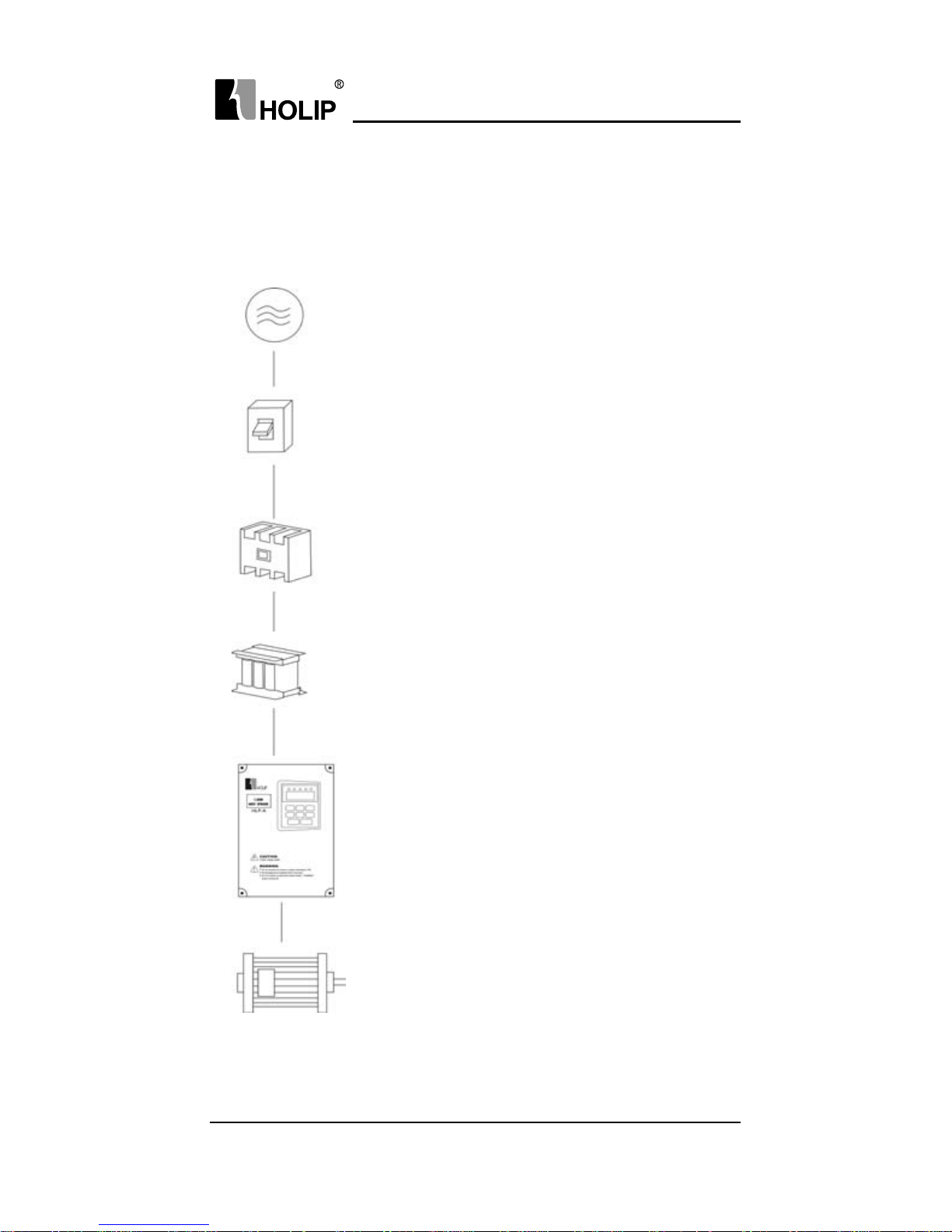
V. Wiring
1. Main Circuit Wiring Schematic Diagram
Power supply:
● Verify that the inverter’s rated voltage coincides
with AC power supply voltage to avoid a damage
of the inverter
No fuse breaker:
● Refer to the related list
Ground fault circuit interrupter:
● Use one of anti-high harmonic
Electromagnetic contactor:
● Note: Do not use the electromagnetic contactor as
the on/off button of power supply for the inverter
AC reactor:
● It is recommended to install an AC reactor for
power factor improvement if the input capacity is
more than 1000KVA.
Inverter:
● Be sure to make correct connections of the main
circuit wires and control signal wires of the
inverter.
● Be sure to make correct setting of parameters for
the inverter.
Page 19
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 14 -
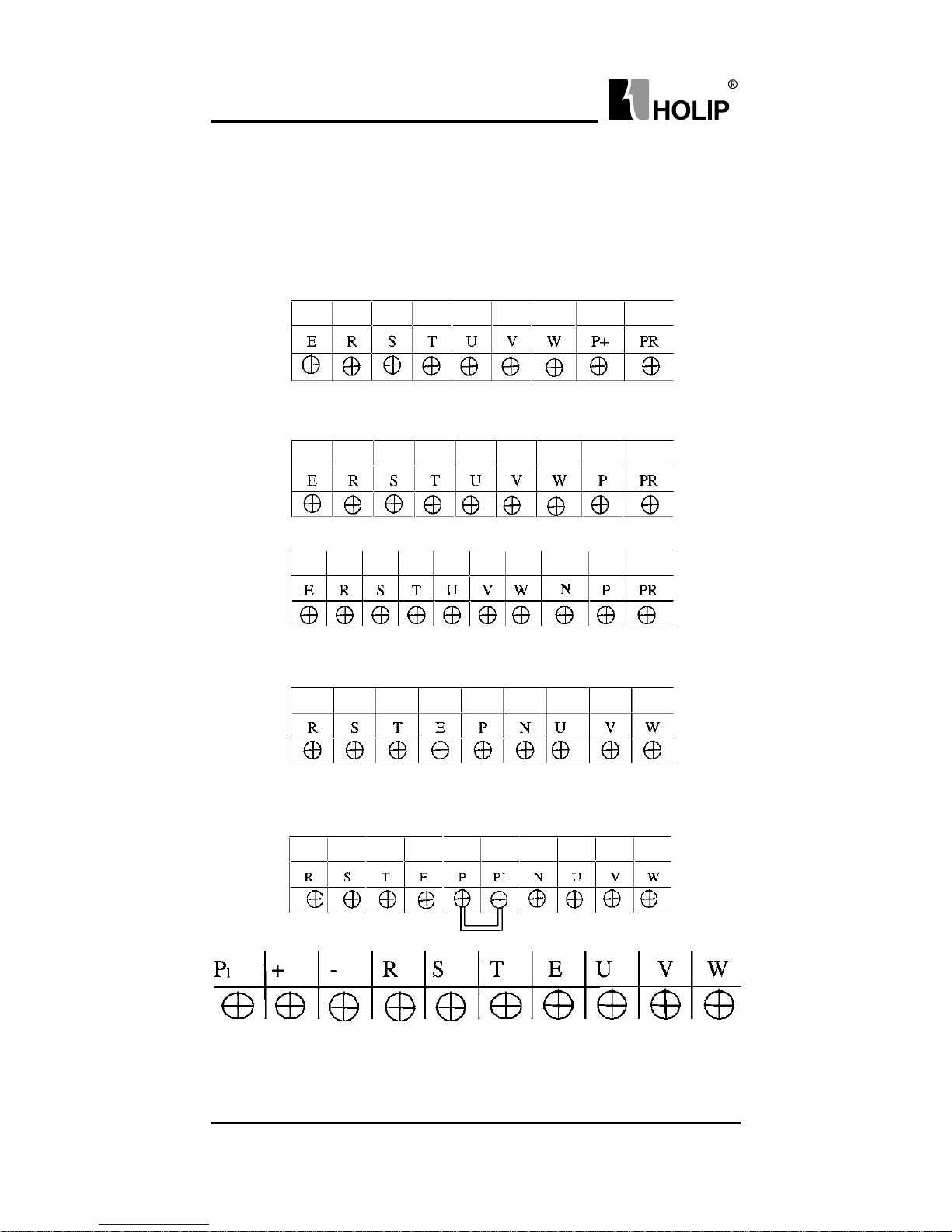
2. Description of Terminal Block
1)Arrangement of Main circuit Terminals
HLPA00D 423C-H L PA01D523C
HLPA0D7543C-HLPA02D243C
HLPA03D743B
HLPA02D223B-HLPA03D723B
HLPA05D543B-HLPA07D543B
HLPA001143B-HLPA003043B
HLPA05D523B-HLPA003023B
HLPA003743B-HLPA016043B
HLPA003723B-HLPA009023B
Cabinet HLPA013243BG-HLPA041543B
Page 20
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 15 -
2) Arrangement of Control Circuit Terminals
HLPA00D423C-HLPA01D523C HLPA0D7543C-HLPA02D243C
HLPA03D743B-HLPA041543B HLPA001123B-HLPA009023B
HLPA02D223B-HLPA03D723B
HLPA05D523B-HLPA07D523B
3) Function Description of Main circuit Terminals
Symbol Function Description
R.S.T
Input terminal of AC line power.(220V class, for both
single/three phase, single phase connected to any two
phases
)
U.V.W Output terminal of the inverter
P.P r Connector for braking resistor.
P1P
Connector for DC reactor (When using a DC reactor the
jumper shall be removed. A05D543B and A07D543B
internally jumped)
P (+)、N(-)Connecting terminal of external braking bank.
E
Ground terminal: the third method of grounding for 220V
and special grounding for 380 V of Electrical Engineering
Regulations.
4)Function Description of Control Circuit Terminals
Symbol Function Description Factory setting
FOR Multi-Input 1 Forward run
REV Multi-Input 2 Reverse run
RST Multi-Input 3 Reset
SPH Multi-Input 4 High speed
SPM Multi-Input 5 Middle Speed
SPL Multi-Input 6 Low Speed
DCM
Common Terminal of Digital
and Control Signals, +12v Power,
(EV、
P24)Ground
Page 21
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 16 -
Symbol Function Description Factory setting
EV +12V Power Supply
Max. output current
200mA
P24 +12V Power Supply
Max. output current
200mA
+10 Power Supply for Speed Setting +10V/20 m A
VI
Analog Voltage Frequency
Reference Input
0~+10V corresponding
to the highest operating
frequency
AI
Analog Current Frequency
Reference Input
4~20mA corresponding
to the highest operating
frequency
AO Output current
VO Output voltage
ACM
Common Terminal of Analog and
Control Signals
DRV
Multi-Output 1
(Optical couple output)
DC12V/100mA
UPF
Multi-Output 2
(Optical couple output)
FA
FBFCMulti-Output 3 (N/O or N/C) 3A/250VAC, 3A /30VDC
KA
KB
Multi-Output 4 (N/O) 3A/250VAC, 3A /30VDC
AM
Output terminals of digital
frequency
0~10V
RS+ RS- RS485 Communication port
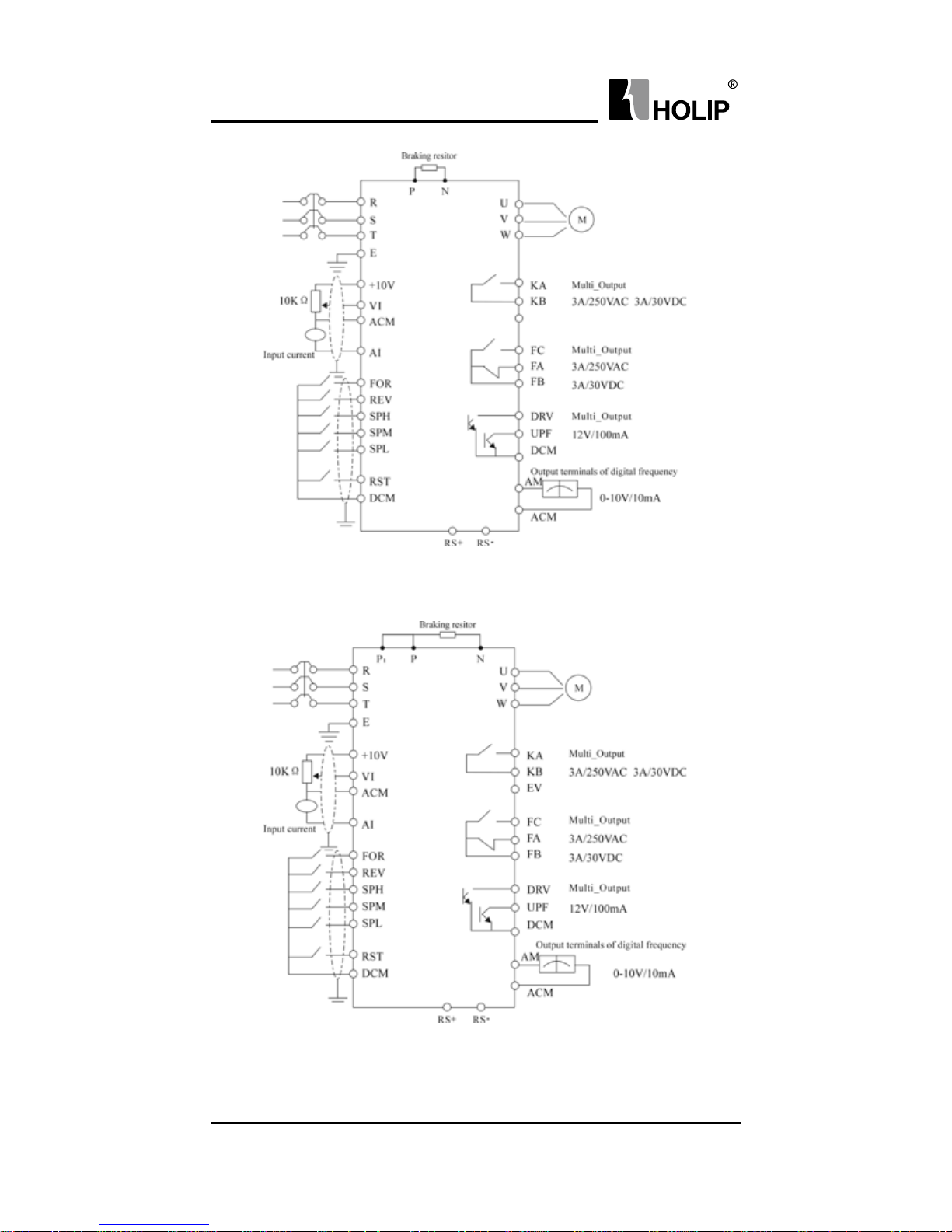
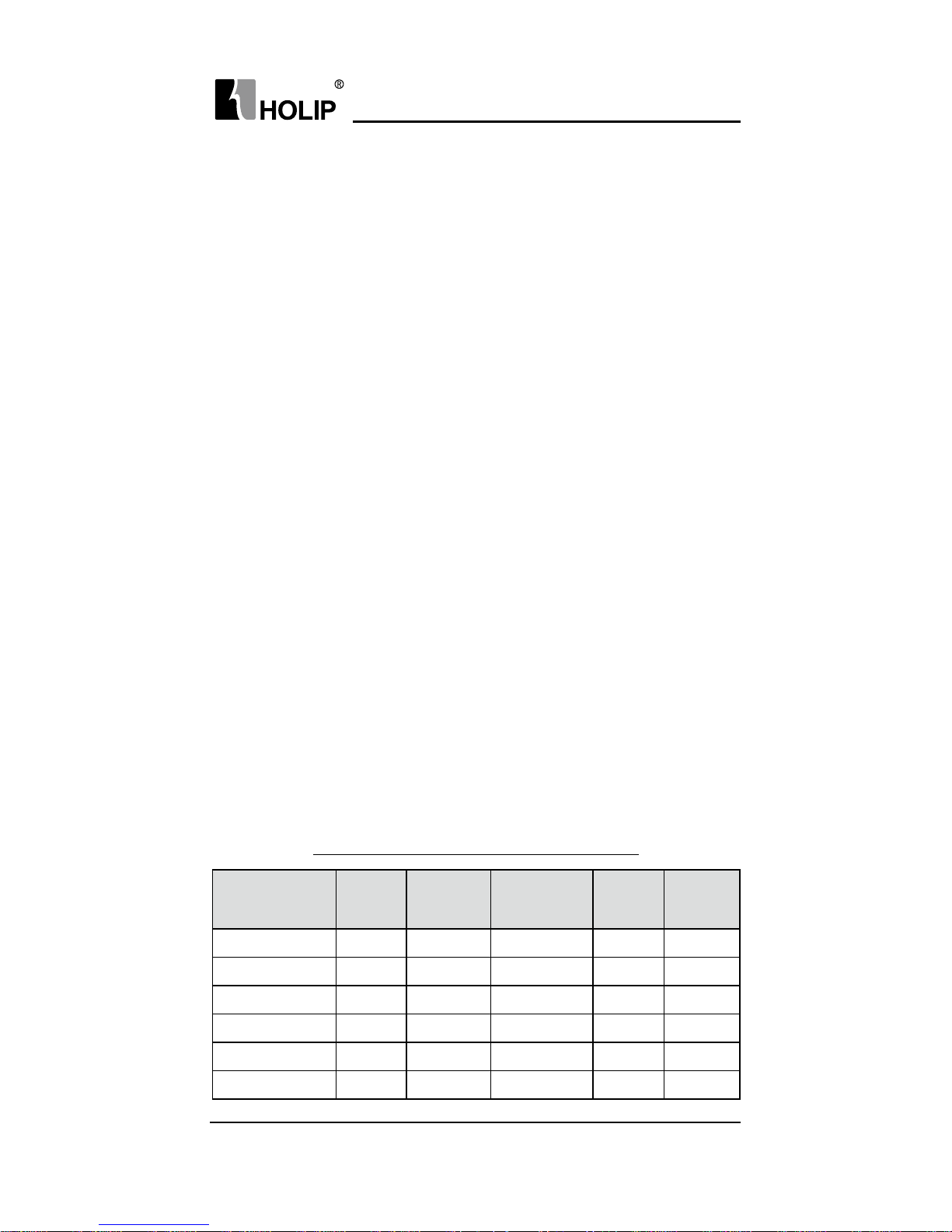
3. Basic Connection Diagram
The wiring of the inverter is divided into two parts, main circuit terminal
connections and control circuit terminal connections. The user can
see the main circuit terminals, and the control circuit terminals after
removing the cover of enclosure. The terminals must be connected
correctly as the following wiring circuit diagrams.
The following diagram shows the factory standard connection of Model
HLP-A
Page 22
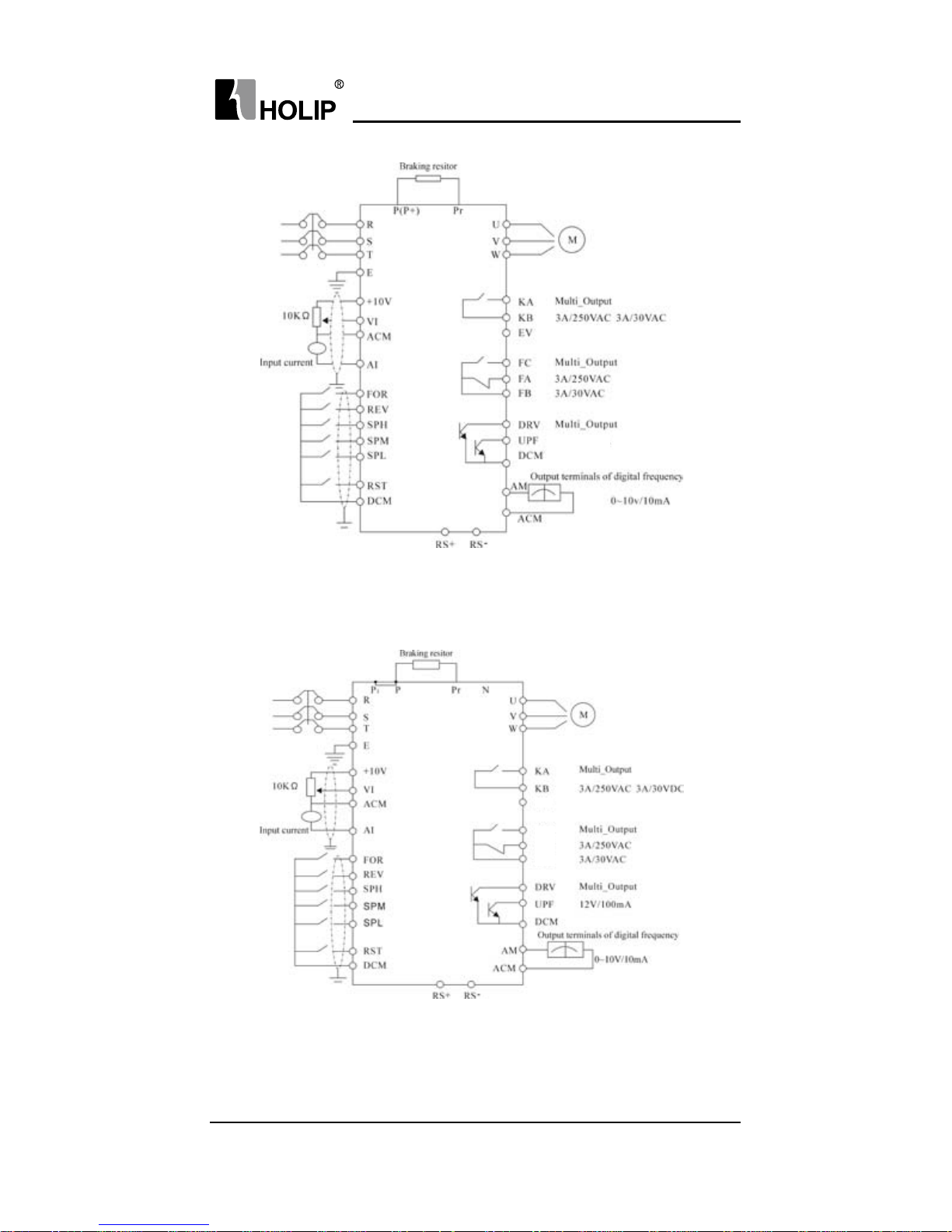
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 17 -
HLPA00D423C-HLPA03D723B
HLPA0D7543C-HLPA03D743B
HLPA05D543B-HLPA07D543B
FC
FA
FB
EV
12V/100mA
Page 23
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 18 -
HLPA001143B ~ H LPA003043B
HLPA05D523B~HLPA003023B
HLPA003743B ~HLPA041543B
HLPA003723B~H LPA009023B
EV( P24)
Page 24
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 19 -
4. Precautions on Wiring
1) For the main circuit wiring:
● While wiring the sizes and specications of wires should be selected
and the wiring should be executed according to the electrical
engineering regulations to ensure the safety.
● It is better to use shielded wire or wire and conduit for power cord and
ground the shielded layer or two ends of wire conduit.
● Be sure to install a Non Fuse Breaker (NFB) between the power
supply and the input terminals (R.S.T). (If using ground fault circuit
interrupter, please choose one corresponding to high frequency)
● Never connect AC power to the output terminal (U.V.W) of the
inverter.
● Output wires mustn’t be in touch of the metal part of the inverter
enclosure, or it will result in earth short-circuit.
● Phase-shifting capacitors, LC, RC noise filters, etc, can never be
connected to the output terminals of the inverter.
● The main circuit wire must be enough far away from other control
equipments.
● When the wiring between the inverter and the motor exceeds 15
meters for 220V class or 30 meters for 380V class, much higher dV/dT
will be produced inside the coil of the motor, which will cause the
destruction to the interlay or insulation of the motor. Please use a
dedicated AC motor for the inverter or add a reactor at the inverter.
● Please lower the carrier frequency when there is a longer distance
between the inverter and the motor. Because the higher the carrier
frequency is the bigger the leakage current of high-order harmonics in
the cables will be. The leakage current will have unfavorable effect on
the inverter and other equipment.
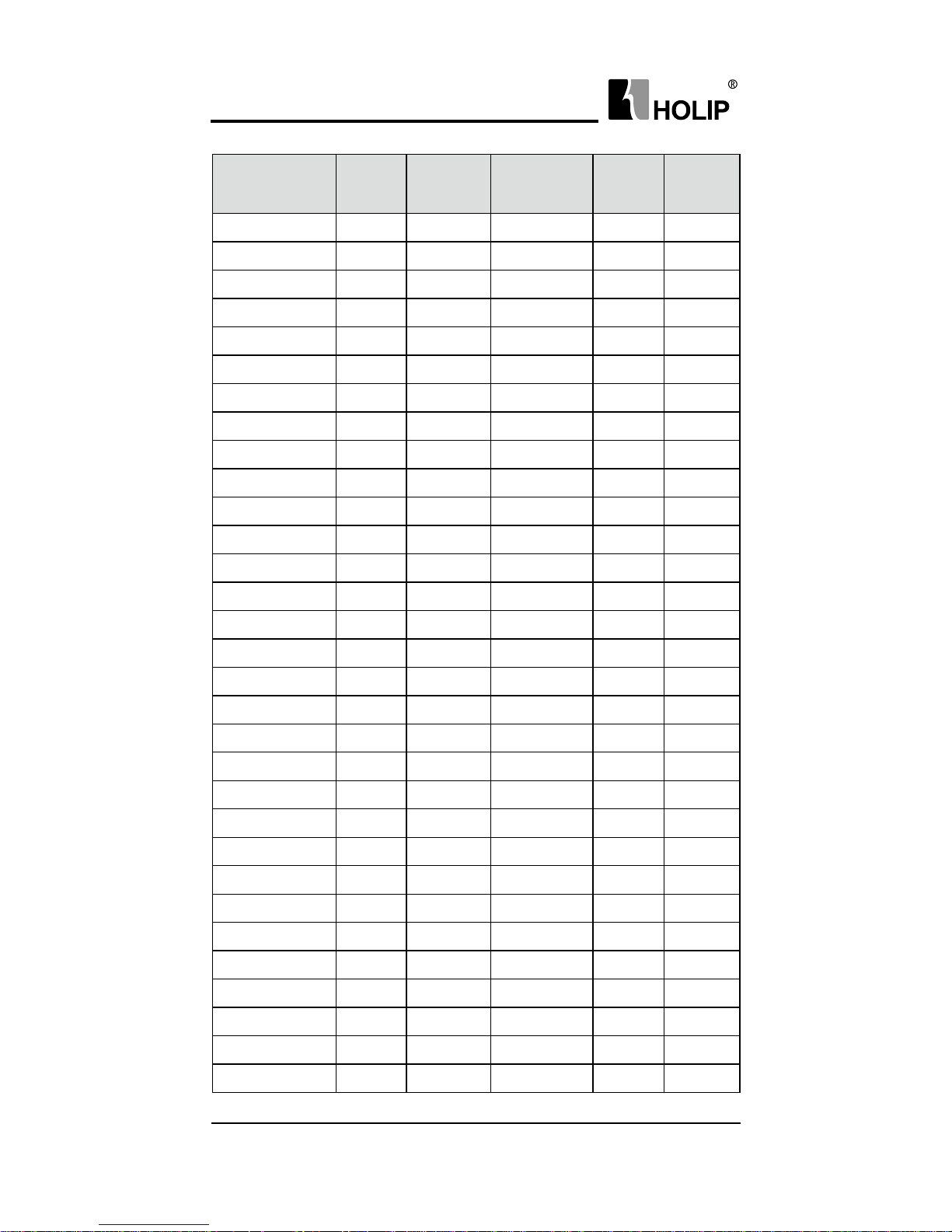
Specications of Non Fuse Breaker and Wire
Model NFB(A)
Input wire
mm
2
Output wire
mm
2
Control
wire
mm
2
Screw
HLPA00D 423C 16 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA0D7523C 16 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA01D52 3C 32 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA02D223B 32 4 4 1 M4
HLPA03D723B 40 6 6 1 M5
HLPA05D523B 63 6 6 1 M6
Page 25
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 20 -
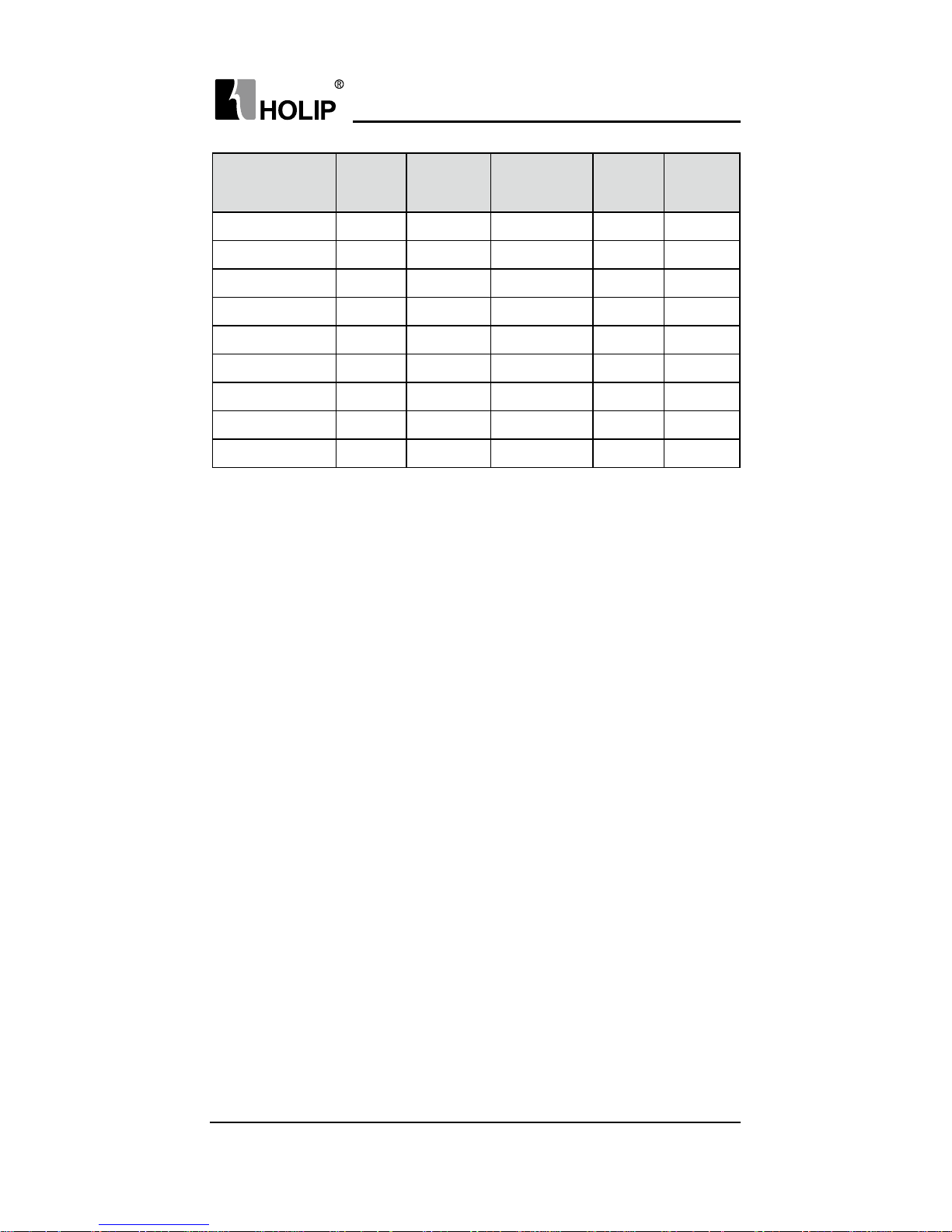
Model NFB(A)
Input wire
mm
2
Output wire
mm
2
Control
wire
mm
2
Screw
HLPA07D523B 63 6 6 1 M6
HLPA001123B 100 10 10 1 M6
HLPA001523B 16 0 25 25 1 M8
HLPA18D52 3B 160 25 25 1 M8
HLPA002223B 200 35 35 1 M10
HLPA003023B 250 70 70 1 M10
HLPA004523B 315 70 70 1 M10
HLPA005523B 400 95 95 1 M12
HLPA007523B 630 185 185 1 M12
HLPA009023B 630 240 240 1 M16
HLPA0D7543C 16 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA01D543 C 16 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA02D243C 16 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA03D743B 16 2.5 2.5 1 M4
HLPA05D543B 32 4 4 1 M5
HLPA07D543B 40 6 6 1 M5
HLPA001143B 63 6 6 1 M6
HLPA001543B 63 6 6 1 M6
HLPA18D543B 100 10 10 1 M6
HLPA002243B 100 16 16 1 M8
HLPA003043B 160 25 25 1 M8
HLPA003743B 16 0 25 25 1 M8
HLPA004543B 200 35 35 1 M10
HLPA0055 43B 200 35 35 1 M10
HLPA007543B 250 70 70 1 M10
HLPA009043B 315 70 70 1 M10
HLPA011043B 400 95 95 1 M12
HLPA0132 43B 400 150 150 1 M12
HLPA016 0 43B 630 185 185 1 M12
HLPA018 5 43B 630 240 240 1 M16
HLPA0200 43B 630 240 240 1 M16
Page 26
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 21 -
Model NFB(A)
Input wire
mm
2
Output wire
mm
2
Control
wire
mm
2
Screw
HLPA022043B 800 150×2 150×2 1 M16
HLPA025043B 800 150×2 150×2 1 M16
HLPA028043B 800 150×2 150×2 1 M16
HLPA030043B 800 150×2 150×2 1 M16
HLPA0315 43B 1000 185×2 150×2 1 M16
HLPA034543B 1000 185×2 150×2 1 M16
HLPA037543B 1200 240×2 185×2 1 M16
HLPA040043B 1200 240×2 185×2 1 M16
HLPA041543B 1200 240×2 185×2 1 M16
2) For control circuit wiring (signal line)
● The signal line should be separately laid in a different conduit with the
main circuit wire to avoid any possible interference.
● Please use the shielded cable with the size of 0.5-2mm2 for signal lines.
● Use the control terminals on the control panel correctly according to
your needs.
3) Grounding
● Grounding terminal E. Be sure to make correct grounding
220V class: The third grounding method (Grounding resistance should
be 100Ω or lower.)
380V class: The special third grounding method (Grounding resistance
should be 10Ω or lower.)
● Choose grounding wires according to the basic length and size of the
technical requirements of the electric equipment.
● Do avoid sharing grounding wire with other large power equipment
such as electric welder, power machine, etc. The grounding wire
should be kept away from the power supply wires for large power
equipment.
● The grounding method for several inverters together should be done as
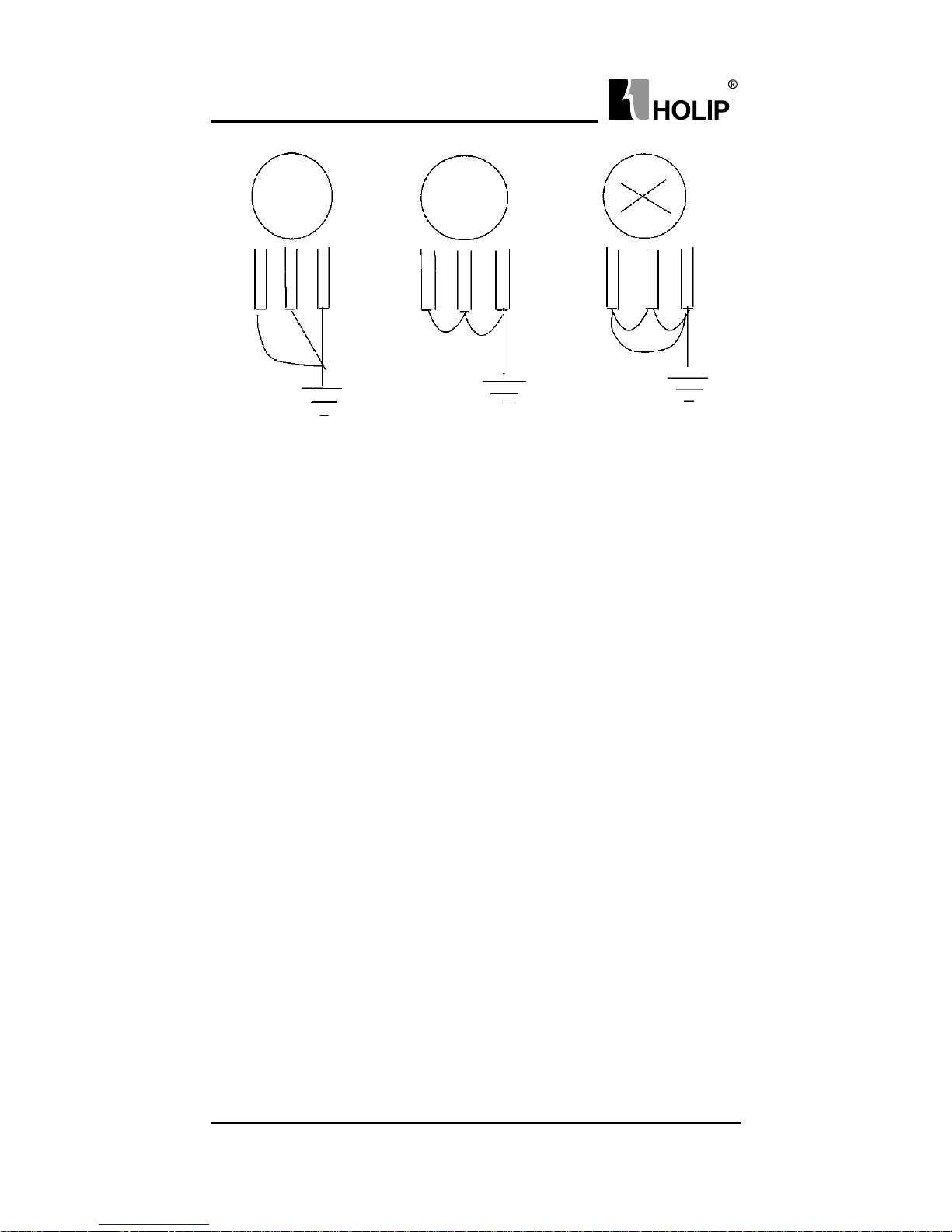
the rst and second diagrams below. Avoid the third loop.
● The grounding wire must be as shorter as possible.
Page 27
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 22 -
(1) Good (2) Good (3) Not good
Page 28
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 23 -
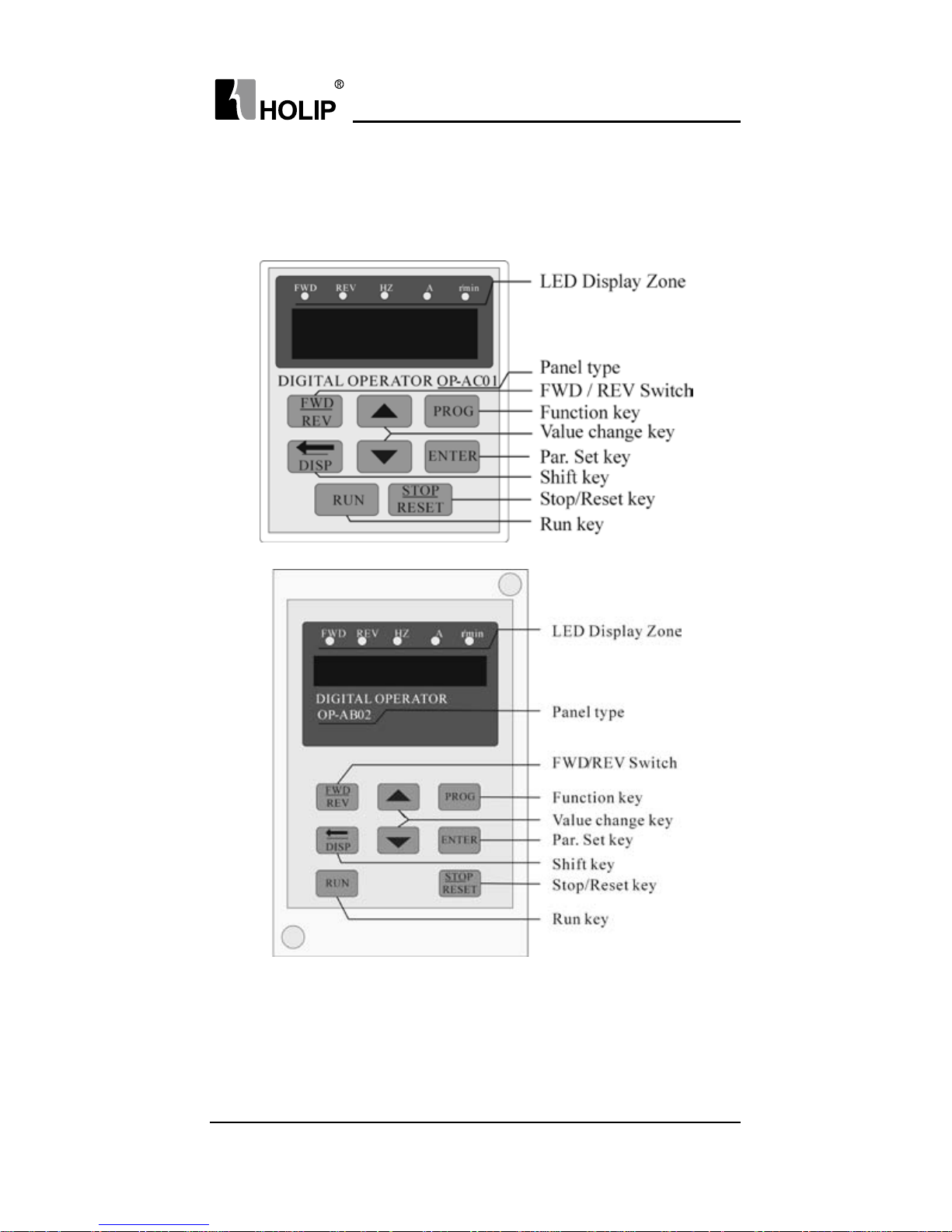
VI. Instruction of the Digital Operator
1. Description of the Digital Operator
Note:
The inverter of the hardware version C can use the panel OP-AC01,the
inverter of the hardware version B can use the panel OP-AB01 or OPAB02.
The panel OP-AB01 and OP-AB02 have the same function,but different
size,You can see the size in the appendix 3.
Page 29
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 24 -
2. Description of the panel type
3. List of the panel used in inverter
Model Specication Panel type
HLPA00D 423C 0.4KW/220V OP-AC01
HLPA0D7523C 0.75KW/220V OP-AC01
HLPA01D52 3C 1.5KW/220V OP-AC01
HLPA02D223B 2.2KW/220V OP-AB01
HLPA03D723B 3.7KW/220V OP-A B01
HLPA05D523B
|
HLPA009023B
5.5KW/220V
|
90KW/220V
OP-AB02
HLPA0D7543C 0.75KW/380V OP-AC01
HLPA01D543 C 1.5KW/380V OP-AC01
HLPA02D243C 2.2KW/380V OP-AC01
HLPA03D743B 3.7KW/380V OP-AB01
HLPA05D543B
|
HLPA041543B
5.5KW/380V
|
415KW/380V
OP-AB02
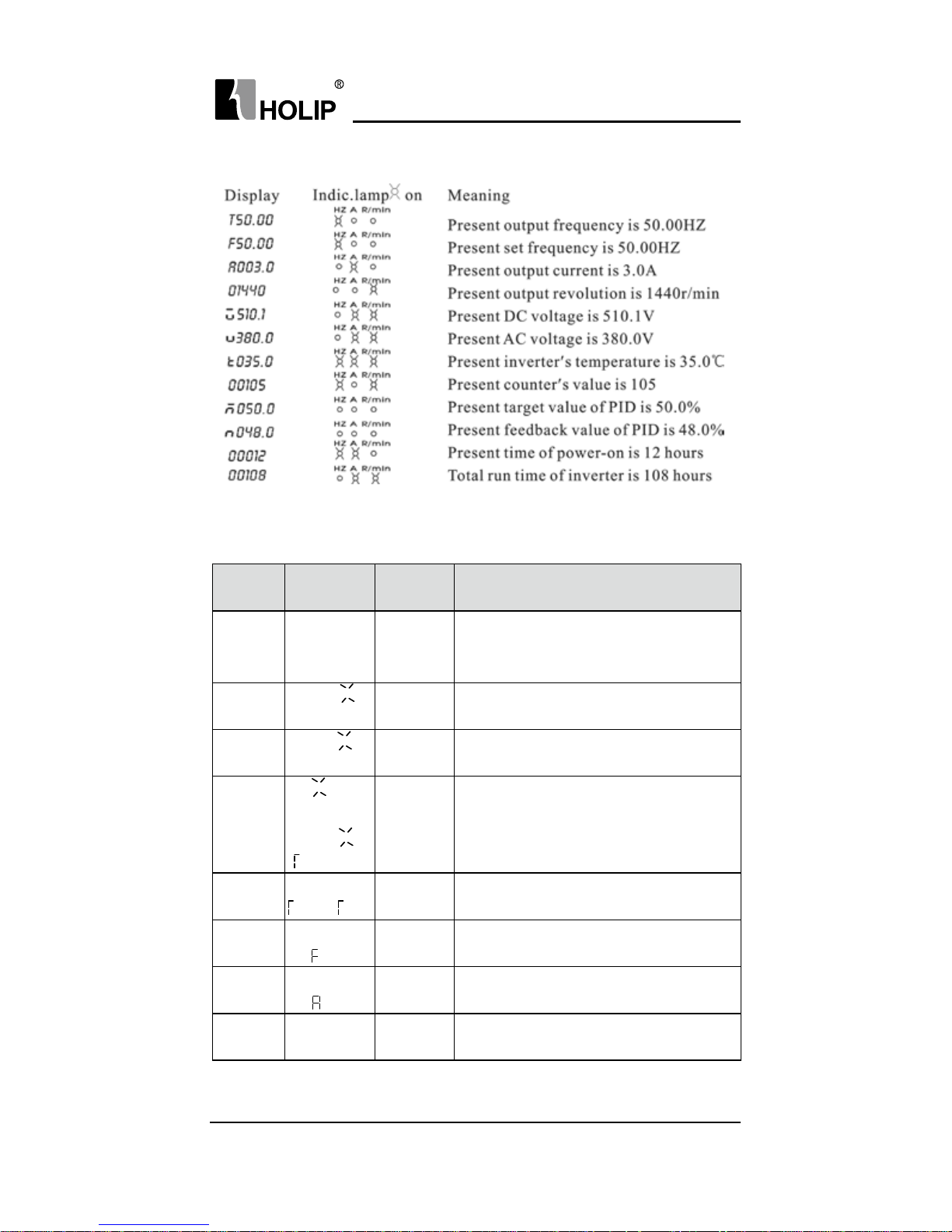
4.Description of Indicator Lamp Status
1) Description of Indicator Lamp Status
Indicator lamp Status Description
FOR on The motor is in forward rotation.
REV on The motor is in reverse rotation.
HZ on Displaying set frequency or output frequency.
A on Displaying output current.
r/min on Displaying rated motor revolution
A r/min on Displaying AC or DC voltage.
HZ r/min on Displaying counting value.
HZ A r/min on Displaying internal temperature of the inerter.
Page 30
HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 25 -
2) Description of Display Items
5. Description of Operation Examples
Procedures Displa y
Indicator
Lamp
Expla nation
Powe r up
↓
←
Ds p2.0
AXX.XX
FWD Hz
¢ ¤
Self detect when power-up,
display version no. display
running f requency
PROG
↓
CD000 FWD Hz
¢ ¤
Enter programming
Display the f unction of CD000
ENTER
↓
000.00 FWD Hz
¢ ¤
Display the content of CD000
←▲
ENTER
↓
PROG
50.00
END
C D 001
50.00(ash)
FWD Hz
¢ ¤
FWD Hz
¢ ¤
Change the content of CD000
Conrm changed value
Display END→CD001
Black from programming
↓
RUN 00.00→ 50.00
FWD Hz
¤ ¤ Display running and operating f requency
↓
DISP 50.0 0
FWD Hz
¤ ¤ Display running and operating f requency
↓
DISP 00 5.0
FWD A
¤ ¤
Monitor screen switching, display out put
current
↓
DISP 014 40
FWD r/min
¤ ¤ Monitor screen switching, display rotate speed
Page 31

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 26 -
Note:
●
¢
means ashing. ¤ means bright.
● For monitoring AC, DC, T and other items they can be only switched and displayed
after the parameter setting.
● When it is powered up again after a power breakdown the inverter will display the
screen previous to the power breakdown after its self detection.
Procedures Displa y
Indicator
Lamp
Expla nation
↓
DISP 50.0 0
FWD Hz
¤ ¤
Switch to main screen, display running
f requency
↓
F/R
50.00→ 00.00
→ 50.00
REV Hz
¤ ¤
Switch of FWD.REV.rotation, display the
status of REV.rotation
↓
▲ 050.0 0
REV Hz
¤ ¤
Switch to adjustable f requency
↓
← ▼ 030.00
REV Hz
¤ ¤
Adjust running frequency
↓
ENTER 50.00→ 30.00
REV Hz
¤ ¤
Conrm the value, display running
f requency
↓
STOP 30.00→ 00.00
00.00 (ash)
REV Hz
¢ ¤
Stop
Page 32

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 27 -
VII. Commissioning
1. Important Checks before the Commissioning
● If there is any wrong connected wires? Pay special attention to the
terminal of U.V.W; Make sure the power supply wires are connected
to R.S.T, not U.V.W.
● If there is any metal powder or wires left on the base plate of the
inverter or the terminal block, which may cause short circuit.
● If screws are tightly locked and if the connecting parts are loose.
● If there is any short circuit or earth fault at outputs.
2. Commissioning Methods
The procedure of the operator is factory set up for the control mode of
HLP series. The commissioning can be carried out through the digital
operator. Generally, the commissioning can be conducted at 5.00 Hz.
Note: ¤means indicator is on;
means indicator lamps flash;
0
mean
digits ash.
Procedures Display Indicator Lamp Explanation
Power up
↓
←
Dsp2.0
AXX.XX
FWD Hz
¤
Self detect when powerup, display version
no. display running
frequency
↓
▲
00.0
0
FWD Hz
¤
Switch to adjustable
frequency
↓
← ▲
0
5
.00
FWD Hz
¤
Display the content of
CD000
↓
ENTER
05.00
FWD Hz
¤
Change the content of
CD000.conrm the
value
↓
RUN
05.00
FWD Hz
¤ ¤
Running at 5.00Hz
↓
STOP
05.00 (ash)
FWD Hz
¤
Stop
Page 33

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 28 -
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
Basic Parameters
CD000 Main Frequency 0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD001 Ma x . Voltage 0.1V—* 220/380
CD002 Base Frequency 0.01~400.00 Hz 50.00
CD003 Intermediate Voltage 0.1V—* *
CD004
Intermediate
Frequency
0.01~400.00 Hz 2.50/3.00
CD005 Mi n . Vol t a ge 0.1V~* *
CD006 Min. Frequency 0.01~20.00 Hz 0.50
CD007
Max Operating
Frequency
10.00~400.00 Hz 50.00
CD008 Reserved
CD009
Frequency Lower
Limit
0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD010 Parameter Lock 0: Invalid 1: Valid 0
CD011 Parameter Reset
00~10 08: Restore the
factory setting. No other
function.
00
CD012 Accel. Time 1 0.1~6500.0S *
CD013 Decel. Time 1 0.1~6500.0S *
CD 014 Accel. Time 2 0.1~6500.0S *
CD015 Decel. Time 2 0.1~6500.0S *
CD 016 Accel. Time 3 0.1~6500.0S *
CD017 Decel. Time 3 0.1~6500.0S *
CD 018 Accel. Time 4 0.1~6500.0S *
CD019 Decel. Time 4 0.1~6500.0S *
CD020
∫
CD030
Reserved
Applicable Parameters
CD0 31 Starting Mode
0: Start from Starting
Frequency
1: Frequency track start
0
CD032 Stopping Mode
0: Decelerating stop
1: Coasting stop
0
CD033
Source of Run
Commands
0: Operator
1: Exter nal terminal
2: Communication port
0
CD034
Source of Operating
Frequency
0: Operator
1: Exter nal terminal
2: Communication port
0
CD035 Carrier frequency 0~15 *
CD036 Jogging Frequency 0.00~400.00 Hz 5.00
VIII. Function List
Parameter and Function List (Part 1)
Page 34

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 29 -
Parameter and Function List (Part 2)
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
Applicable Parameters
CD037 Rev. Rotation Select
0: Rev Run forbidden;
1: Rev Run Enable
1
CD038 STOP key select
0: STOP Invalid
1: STOP Valid
1
CD039 S-Curve Time 0.0~ 6500.0S 0.0
CD040 Up/Down 0.01~2.50Hz 0.01
CD 0 41 Starting Frequency 0.10 ~10.00 Hz 0.50
CD042 Stopping Frequency 0.10 ~10.00 Hz 0.50
CD043
Auto Torque
Compensation
0.0~10.0% 2.0
CD044 Skip Frequency 1 0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD045 Skip Frequency 2 0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD046 Skip Frequency 3 0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD047
Skip Frequency
Range
0.10 ~10.00 Hz 0.50
CD048 Timer 1 time 0.1~10.0S 0.1
CD049 Timer 2 time 1~100S 1
Input and Output Terminals
*CD050 Multi-input 1(FOR) 0:Invalid; 1:Run;2:For
rotation; 3:Rev
rotation4:Stop; 5:FOR/
REV;6:Jog; 7;Jog For
rotation;8:Jog Rev
Rotation;9:Emergent
stop;10:Reset;
11:Reser ved;12:Overheat
of heat sink or
motor;13:Timer 1;14:Timer
2;15~16:Reserved;17:High
speed; 18:Middle
speed;19:Low
speed;20:Multi-speed1;21:
Multi-speed2;22: Multispeed3;23:Ramp select
1;24:Ramp select 2;25:Up
function;26:Down
function;27:Counter;
28:Counter
reset;29:Drawing;
30:AutoPLC
Start;31:AutoPLC
RST;32:PID Star;
02
*CD051 Multi-input 2(REV) 03
*CD052 Multi-input 3(RST) 10
*CD053 Multi-input 4(SPH) 17
*CD054 Multi-input 5(SPM) 18
*CD055 Mult i-i npu t 6 (SPL) 19
Page 35

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 30 -
Parameter and Function List (Part 3)
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
Input and Output Terminals
*CD056 Multi-output 1(DRV) 0: Invalid; 1: Run;
2: Fault indication;
3: Zero Speed;
4: Braking indication;
5: Set Frequency reach;
6: Arbitrary Frequency 1
reach;
7: Arbitrary Frequency 2
reach;
8: In Accel.; 9: In Decel.;
10: Inverter Overload alarm;
11: Motor Overload alarm;
12: Over-torque alarm;
13: Low voltage alarm;
14: Single stage end
indication;
15: Process end indication;
16: Counter reach;
17: Middle Counter Reach;
18: External Control Time 1
Reach;
19: External Control Time 2
Reach;
20: 4~20mA disconnected;
21~24: Reserved;
25: Auxiliary Pump 1;
26: Auxiliary Pump 2;
27: Drawing reach;
28:PID lower limit alarm;
29: PID upper limit alarm;
30: Fan act; 31: Reserved;
32: Braking resistor act
01
*CD057 Multi-output 2(UPF) 05
*CD058
Multi-output
3(Terminals of
FA,FB,FC)
02
*CD059
Multi-output
4(Terminals of
KA,KB)
00
CD060 Multi-output 5(AM)
Output of digital frequency
signals
0
CD 061 Uniform Frequency 1 0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD062 Uniform Frequency 2 0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD063
Uniform Frequency
Range
0.10 ~10.00 Hz 0.50
CD064 Counting value set 0~6550 0 0
CD065 Analog Input
0: 0~10V 1: 0~5V 2: 0~20mA
3: 4~20mA 4: 0~10V and
4~20mA stacked
0
CD066
Lower Analog
Frequency
0.00~400.00 Hz 0.00
CD067
Bias Direction at
Lower Frequency
0: Positive direction
1: Negative direction
0
CD068
Higher Analog
Frequency
0.00~600.00 Hz 50.00
Page 36

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 31 -
Parameter and Function List (Part 4)
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
Input and Output Terminals
CD069
Bias Direction at
Higher Frequency
0: Positive direction
1: Negative direction
0
CD070
Analog Negative Bias
Reversed
0:Not allowable
1:A llowable
0
CD071
AM Analog output
Gain
0~100% 100
CD072 Up/Down Function
0: Not memorized
1: Memorized
0
CD073 Up/Down Speed 0: 0.1HZ 1: 0.01HZ 0
CD074
Analog Filtering
Constant
0~50 20
CD075 Intermediate Counter 0~65500 0
Multi-speed and Simple PLC
CD076 PLC Operation
0: Normal run; 1: External
control 4 –speed; 2: External
control multi-speed; 3:
Disturbance; 4: Internal
control multi-speed; 5:
Drawing
0
CD077 AutoPLC
0: Stop after running for
one cycle; 1: Cycling run;
2: Auto stop after running
for one cycle (STOP for
intervention);3: Auto Run
and Cycling (STOP for
intervention)
0
CD078
PLC rotation
Direction
0~255 (0: For 1: Rev) 0
CD079 PLC Ramp Time 0~ 65535S 0
CD080 Frequency 2 0.00-400.00 Hz 15.00
CD 081 Frequency 3 0.00-400.00 Hz 20.00
CD082 Frequency 4 0.00-400.00 Hz 25.00
CD083 Frequency 5 0.00-400.00 Hz 30.00
CD084 Frequency 6 0.00-400.00 Hz 35.00
CD085 Frequency 7 0.00-400.00 Hz 40.00
CD086 Frequency 8 0.00-400.00 Hz 0.50
CD087 Timer 1 0.0-6500.0S 10.0
CD088 Timer 2 0.0-6500.0S 10.0
CD089 Timer 3 0.0-6500.0S 0.0
CD090 Timer 4 0.0-6500.0S 0.0
CD091 Timer 5 0.0-6500.0S 0.0
CD092 Timer 6 0.0-6500.0S 0.0
CD093 Timer 7 0.0-6500.0S 0.0
CD094 Timer 8 0.0-6500.0S 0.0
Page 37

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 32 -
Parameter and Function List (Part 5)
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
CD095 AutoPLC Memory 0~1 0
CD096
~
CD109
Reserved
Multi-speed and Easy PLC
CD110
Number of Auxiliary
Pump
0~2 0
CD111
Continuous
Operating Time of
Aux.Pumps
1~9000min 60
CD112
Interlocking Time of
Aux.Pumps
0.1~250S *
CD113
High Speed Running
Time
1~250S 60
CD114
Low Speed Running
Time
1~250S 60
CD115
Stopping Voltage
Level
1~150% 95
CD116
Lasting Time of
Stopping Voltage
Level
1~250S 30
CD117 Wakeup Level 1~150% 80
CD118 Sleep Frequency 0.00~400.00Hz 20.00
CD119
Lasting Time of Sleep
Frequency
1~250S 20
Parameters of Protection Functions
CD120
Over-voltage Stall
Prevention
0: Invalid 1: Valid 1
CD121
Stall Prevention Level
at Accel.
0~200% 150
CD122
Stall Prevention Level
at Constant Speed
0~200% 0
CD123
Stall Prevention Level
at Decel.
0~232% 0
CD124
Over-torque Detect
Mode
0~3 0
CD125
Over-torque Detect
Level
0~200% 0
CD126
Over-torque Detect
Time
0.1~20.0S 1.0
CD127
Decel. time for stall
prevention at constant
speed
5.0
CD128 Fault restar t time 1.0
CD129
Voltage rise time
during frequency
track
5
Page 38

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 33 -
Parameter and Function List (Part 6)
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
Parameters of Motor Functions
CD130 Rated Motor Voltage
Set according to Motor
nameplate
*
CD131 Rated Motor Current
Set according to Motor
nameplate
*
CD132 Motor pole number. 02—60 04
CD133
Rated Motor
Revolution
00-9999r/min 14 40
CD134 Motor no-load current 0~100% 40
CD135
Motor slip
compensation
0—1000 0
CD136
~
CD139
Reserved
Parameters of Special Functions
CD14 0 DC Braking level 0.0~20.0% 2.0
CD141
DC Braking time at
start
0.0~25.0S 0.0
CD142
DC Braking time at
stop
0.0~25.0S 0.0
CD143 Frequency track time 0.0~20.0S 5.0
CD14 4
Current level for
frequency track
0~200% 150
CD145
Restart after
instantaneous Stop
0: Invalid 1: Frequency track 0
CD14 6
Allowable PowerBreakdown Time
0.1~5.0S 0.5
CD147
Number of Abnormal
Restart
0—10 00
CD14 8
Auto Voltage
Regulation
0: Invalid 1: Valid 1
CD149 Auto Energy Saving 0.0~20.0% 0.0
CD150
Proportional Constant
(P)
0.0~1000.0% 100.0
CD151 Integral Time (I) 0.1~* 5.0
CD152 Differential Time (D) 0.00~10.00S 0.00
CD153 Ta rge t value 0.0~100.0% *
CD154 Target value select
0: set by the operator 1:set by
external terminals (0-10V)
0
CD155 PID upper limit 0~100% 100
CD156 PID lower limit 0~100% 0
CD157
~
CD159
Reserved
CD16 0
Communication
Addresses
0-250 0
Page 39

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 34 -
Parameter and Function List (Part 7)
Categor y Code Function
Set Range & Function
Explanation
Factory
Setting
Commun ication
Funct ions
CD161
Communication Baud
Rate
0-3 1
CD162
Communication Data
Method
0-5 0
CD163
~
CD16 6
Reserved
Monitoring Parameters
CD167 Display Items 0-31 0
CD16 8 Display Items Open 0 -7 0
CD169
Voltage Rating of
Inverter
Set according to the model *
CD170
Rated Current of
Inverter
Set according to the model *
CD171 Sof t w a re Ver s ion *
CD172 Fault Record 1
Note: — means no fault
record.
——
CD173 Fault Record 2 ——
CD174 Fault Record 3 ——
CD175 Fault Record 4 ——
CD176 Fau lt Clear 00—10 (01 for Fault Clear) 00
Factory Setting
CD177 Inverter Model 0
CD178
Inverter Frequency
Standard
0: 50Hz 1: 60Hz *
CD179 Manufacture Date Year: Month: Week *
CD18 0 Serial No. *
CD181 Reserved
CD18 2
Communication
Protocol Select
0:Holip MODBUS
Communication Protocol
1:Standard MODBUS
Communication Protocol
0
CD183
~
CD250
Reserved
Page 40

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 35 -
IX. Descriptions of Functions
CD000 Main Frequency **
Set Range: 0.00 - 400.00 Hz Unit: 0.01 Hz Factor y Set ting: 0.00
In the digital operator mode, the inver ter will r un at the set value of CD000.
During running, the operating f requency can be changed by pressing ▲ or ▼.
During multi-speed running, the main f requency is taken as the f requency of
S p e e d 1.
In the exter nal cont rol multi-speed mode, if CD034 is set to 1, i.e. given by an
external terminal, Speed 1 will be given by the analog of the exter nal ter minal.
The setting of main frequency is limited by the maximum operating
f req ue nc y.
The related parameters of CD034, CD076 are adjustable during operation.
CD001 Max Voltage
Set Range: 0.1V-* Unit: 0.1V Factory Setting: 220/380
This parameter should be set according to the rated value of the motor’
s nameplate. The factor y setting is 380V for 380V class motor and 220V for
220V class motor. The setting range of this parameter is restricted by the
voltage rating of the inverter. In case of the motor relatively f ar away f rom the
inverter this set value can be increased properly.
CD002 Base Frequency
Set R a nge: 0.01— 400.00 Hz Un it: 0.01Hz Fac t or y Set t i n g: 50.00
This parameter must be set according to the rated frequency of operating
voltage on the motor’s nameplate. Under normal conditions do not change the
set value of base f requency at will. If it is equipped with a special motor this
value should be set properly according to the characteristics of the motor’s
parameters. Otherwise it may cause the damage to the equipment.
CD003 Intermediate voltage
Set Range: 0.1V—* Unit: 0.1V Factory Setting: *
This parameter is set for an intermediate voltage value of arbitrar y V/F curve.
If it is set improperly, it will cause over-current or under-torque of the motor,
or even tripping of the inverter. When the intermediate frequency is increased
the voltage will increase the output torque and at the same time also the output
current. When changing this parameter please pay attention to monitoring the
output current to avoid the inverter’s tripping due to over-current.
This set value of intermediate voltage is limited by the set value of max
voltage. When the voltage is increasing to a certain value at intermediate
Page 41

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 36 -
f requency the torque compensation will lose its f unction. When ad justing this
parameter the out put current of the inverter should be increased f rom low
to high slowly according to the load of machines until it meets the starting
requirement. Do not be quick to increase it by large amplitude. Otherwise it
might cause the tripping of the inverter or the damage of the machines.
CD004 Intermediate Frequency
Set Ra nge: 0.01-40 0.00 Hz Unit: 0.01 Hz Factor y Set t i ng: 2.50/3.00
No te: ** means this parameter is adjustable during operation.
This parameter is set for intermediate frequency of arbitrary V/F curve. If it is
set improperly, it will cause over-current or under-torque of the motor, or even
tripping of the inverter.
This set value of inter mediate f requency is limited by the set value of base
f req ue nc y.
Code
Model
CD003 CD005 C D012 C D 013 C D035
Code
Model
CD003 CD005 C D 012 C D 013 C D 0 35
A0 0D423C 15. 0 7.5 5 5 9 A 0 011 4 3 B 19 9.5 20 20 5
A0D7523C 14 .0 7 8 8 9 A 0 01543B 19 9.5 20 20 5
A01D 5 2 3 C 14. 0 7 10 10 8 A18 D 5 43 B 18 9 25 25 5
A02D223B 13.0 6.5 10 10 8 A002 243B 18 9 25 25 5
A03D723B 13. 0 6.5 15 15 7 A0030 43B 17 8.5 30 30 4
A05D523B 12.0 6.0 15 15 6 A0 03743B 16 8 35 35 4
A07D523B 11. 0 5.5 20 20 6 A004543B 16 8 40 40 4
A 0 011 2 3 B 10.0 5.0 25 25 5 A0 05543B 15 7.5 45 45 3
A 0 0152 3B 10.0 5.0 30 30 5 A007543B 15 7.5 50 50 3
A18 D 5 2 3 B 9.0 4.5 35 35 5 A009043B 14 7 75 75 2
A002223B 9.0 4.5 50 50 4 A 0 11 0 4 3 B 14 7 10 0 100 2
A003023B 8.0 4.0 70 70 4 A0132 43B 13 6.5 15 0 150 2
A003723B 7.0 3. 5 80 80 4 A 016 0 43 B 13 6.5 150 15 0 2
A0 04523B 6.0 3. 0 10 0 10 0 3 A 0185 4 3 B 12 6 200 200 2
A005523B 5.0 2.5 120 12 0 3 A020 0 43B 12 6 200 200 2
CD005 Min.Voltage
Set Range: 0.1V* Unit: 0.1V Factory Setting:*
This parameter is set for minimum starting voltage of V/F curve.
This set value of minimum voltage is limited by the voltage at the maximum
f req ue nc y.
CD006 Min.Frequeny
Set t i ng Ra nge: 0.01~20.00Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factory Set t i ng:0.50
This parameter is set for minimum starting frequency of V/F curve.
The f ollow ing chart is about V/F curve
、
Acceleration-Deceleration Time
and Factory Setting of Carrier of A series.
Page 42

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 37 -
Code
Model
CD003 CD005 C D012 C D 013 C D035
Code
Model
CD003 CD005 C D 012 C D 013 C D 0 35
A007523B 5.0 2.5 150 150 2 A02 2043B 11 5. 5 250 250 2
A009023B 5.0 2.5 150 150 2 A025043B 11 5.5 250 250 2
A0D7543C 22 11 8 8 9 A028043B 11 5.5 250 250 2
A01D 5 43C 22 11 10 10 8 A030043B 10 5 250 250 2
A0 2D243C 21 10 .5 15 15 8 A 0 315 43 B 10 5 250 250 2
A03D743B 21 10 . 5 15 15 7 A034543B 10 5 250 250 2
A05D543B 20 10 15 15 6 A037543B 10 5 250 250 2
A07D543B 20 10 20 20 6 A040043B 10 5 250 250 2
A 0 41543B 10 5 250 250 2
Note: ①Ramp Time 2 = Ramp Time 1 x 2
②
Ramp Time 3 = Ramp Time 2 x 2
③
Ramp Time 4 = Ramp Time 3 x 2
④
Min.Voltage Value = Intermediate Voltage Value/2
⑤
The intermediate frequency is 2.5 for the system of 50Hz.
⑥
The intermediate frequency is 3.0 for the system of 60Hz.
CD007 Max. Operating Frequency
Set R a nge: 10.00-400.00 Hz Un it: 0.01 Hz Factor y Set t ing: 50.00
This parameter is set for the maximum operating frequency of the inverter.
The following are several curves and set values of ten used for reference.
Specic curves must be set according to concrete characteristics of mechanical
load.
Cu rve of cons t a n t t or q u e Cu rve of lower to rq u e Cu r ve of hig h er t or q ue
CD008 Reserved
CD009 Frequency Lower Limit **
Set Range:0.00 ~ 400.00Hz Unit:0.01Hz Factor y Set t i ng:0.00
Page 43

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 38 -
CD011 Parameter Reset
Set Range: 00-10 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 00
When the value for a parameter is set improper or is abnormal for some
reasons this parameter can be set to 08 to restore it to the factory setting and
then reset. Af ter the parameters are locked (in case of CD010=1) the parameters
can’t be reset. They can only be reset af ter unlock. For related pa rameters ref er
t o C D010.
CD012 Accel. Ti m e 1 **
Set Ra nge: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factor y Setti ng: *
CD013 D e cel. Ti m e 1 **
Set Ra nge: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factor y Setting: *
CD 014 Ac c e l . T i m e 2 **
Set Ra nge: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Setting: *
CD015 Decel. Time 2 **
Set Range: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Set t ing: *
CD 016 Acc el. Ti m e 3 **
Set Range: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Set t ing: *
CD017 Decel. Time 3 **
Set Range: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Setting: *
C D 018 Ac c el. T i m e 4 **
Set Ra nge: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factor y Setti ng: *
CD019 Decel. Time 4 **
Set Range: 0.1—6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Set t ing: *
Ramp-up time means the time needed for the inverter to increase the
frequency f rom 0Hz to the maximum operating f requency (See t1 in the
This is set for preventing workers f rom f alse operation to avoid over-heat or
some other mechanical faults, which might be caused due to too low operating
f req ue nc y.
The setting of Frequency Lower Limit must be less than the set value of
CD 0 07.
CD010 Parameter Lock **
Set Range: 0-1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: I n va l id.
1: Valid, i.e. the parameters are locked. Except this para meter other pa rameters
can not be changed.
This parameter is set to prevent non-maintenance personnel f rom setting
other parameters by mistake. Af ter the parameters are locked the operating
frequency can be changed by pressing
or .
Page 44

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 39 -
HLP-A Series inverter have altogether 4 Ramp Times. For Ramp Time 2.3.4
the user can select the diff erent ramp up or down time through the external
terminals or switching of ramp time according to the act ual needs. In the
internal control multi-speed operation, diff erent ramp time can be selected
through easy PLC.
Generally the default of the inverter is Ramp Time 1, which is factor y set
depending on the model. Ramp Time 4 is for the jogging ramp time. For the
factory setting of parameters refer to the table in CD006.
The related parameters: CD050~CD055 and CD078.
CD020~CD030 Factory Reserved
CD031 Starting Mode
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
Two starting modes are available for the needs of different equipment.
0: Start from the starting frequency.
When CD141 is set to 0, i.e. DC braking is invalid at start, it starts running
from the starting f requency. When CD141 is set to any non-zero value, i.e. DC
braking is valid at start, itl rst performs a DC braking at start, and then starts
f rom the starting f requency.
For the related parameters refer to CD040, CD140 and CD141.
1: Start by frequency track
This setting can be used for the restarting of large inertia load. When
restarting, the inverter will trace the former frequency from the set f requency
downward. In case of large inertia equipment, when restarting, it can
implement the running command and track the former f requency right away
without waiting for the complete stop of the equipment to save time.
Note: When the inverter is restarted by frequency track, it will start tracking
the f requency f rom its set f requency downward, and search it at the highest
diagram). Ramp-down Time means the time needed for the inverter to
decrease the f requency f rom the maximum operating f requency to 0Hz (See
t 2 i n t h e d iag r a m).
Page 45

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 40 -
CD032 Stopping Mode
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
Two stopping modes are available for the needs of different equipment.
0: Decelerating Stop
When CD142 is set to 0, DC braking is invalid. When DC bra king is invalid,
the inverter will decelerate to the stopping frequency, and then stop outputs,
and the motor will coast to stop. When CD142 is set to any non-zero value, DC
braking is valid, and the inverter will rst decelerate to the stopping frequency,
and then stop by DC braking.
DC braking at stop is usually used for high position stop or f or positioning
control. It must be noticed that frequent uses of DC braking will cause over-
heat of the motor.
For the related parameters refer to CD042, CD140 and CD142.
1: Coasting Stop
When the inverter receives a STOP command, it will immediately stop output
and the motor will coast to stop. When the coasting stop mode is selected, DC
braking is invalid.
CD033 Source of Operation Commands
Set Range: 0—2 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: Set by the Operator
Operation commands are given via the digital operator.
1: Set by external terminals.
Operation commands are given via external terminals, i.e. multi-input
terminals
2: Set by communication ports.
Operation commands are given via communication ports.
speed. When restarting, the current becomes higher, and over-current or stall
may occur. So attention must be paid to the ad justment of current level of
frequency track. Generally, CD144 is adjusted around 100. The concrete value
can be set according to the characteristics of mechanical load.
Page 46

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 41 -
CD034 Source of Operating Frequency
Set Range: 0—2 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: Set by the operator. Operating frequency is given via the digital operator.
1: Set by external terminals. Operating f requency is controlled by analog
signals input via external terminals. The signal type is determined by CD065.
For the related parameters refer to CD065-CD070.
2: Set by communication ports. Operating f requency is given via the serial
communication.
CD035 Carrier Frequency (Note: 0-15 corresponds to 0-20KHz)
Set Range: 0-15 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: *
Carrier frequency is related to magnetic noise of motor, meanwhile the highlow of carrier f requency is related to the heating value of inverter and the
interference for environment. Following the chart:
Carrier Frequency
Elect romagnetic
Noise
Heating Capacity
Interference to the
Environment
Low
↓
High
High
↓
Low
Small
↓
Large
Little
↓
Great
Set Va l ue 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Carrier
Frequency
KHz
0.7 1 1. 5 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 10 11 13 15 17 20
As shown in the table above, the higher the carrier is, the lower the
electromagnetic noise of the motor will be, but the stronger its interf erence
to other systems will be and the greater the heating capacity of the inverter
will have. Under higher ambient temperature and heavier load of the motor
the carrier f requency should be decreased properly to improve the heat
characteristics of the inverter.
The factory setting of carrier f requency is depending on the model. For
specic data refer to the table in the description of CD006.
CD036 Jogging Frequency **
Set Range : 0.00 — 400.00Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factor y Set t ing: 5.0
The parameter set can realize the jogging f unction when the inverter is tested.
The jogging operation can be only achieved through the external terminals,
which can be set by multi-input terminals. Jogging f requency is limited by
the frequency upper/lower limits. While the jogging f unction is implemented,
other running commands are invalid. The ramp-up time of jogging f requency
Page 47

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 42 -
is set by Ramp-up Time 4. When the jog button is released the inverter
will stop output immediately. In case of jogging function please set the
corresponding multi-input terminals to 07 or 08.
This f unction is only valid at stop. It is invalid at running. For the related
pa ra meters ref e r to CD050-CD055.
CD037 Rev Rotation Select
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 1
0: Rev Rotation disable
1: Rev Rotation Enable
This f unction is suitable for the motor, which is not allowed to rotate reversely,
to prevent workers f rom false operation. When the reverse rotation is disabled,
the motor can only rotate f orward, not reverse.
CD038 STOP key
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 1
0: STOP i n va lid.
1: ST O P v a l i d .
This parameter set is only valid when CD033 is set to l or 2.
When the control mode is set f or external ter minals or com munication control,
STOP key on the panel can be chosen to be valid or invalid. When choosing it
as valid, STOP key can stop the inverter in running. When it needs to restart,
the former running signal must be released before restarting the inverter.
CD039 S-Curve Time
Set Range: 0.0— 6500.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Set ting: 0.0
This parameter ca n be set for no impact slow start or slow stop of the inverter
when starting or stopping. When starting S-curve the inverter will make
accelerating or decelerating curve of different speed rates according to Ramp
Ti me.
When CD039 is set as 0, S-cur ve is
invalid, i.e. it will accelerate or decelerate
in linear. Without consideration of
stall the actual accel/decal time =
(CD012+CD039)/2. The pa rameter is only
valid when CD012 is less than CD039.
Page 48

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 43 -
CD040 Up/Down
Set Range: 0.01~2.50Hz Unit:0.01Hz Factory Set t i ng:0.01
This parameter can be set in combination with CD073 for Up/Down of
external cont rol and the speed of increase and decrease.
the step length of Up/Down=(the set value of CD040/0.01)× UP/DOW N speed
CD041 Starting Frequency
Set Range: 0.10—10.00 Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factory Set ting: 0.50
Starting f requency is the initial f requency when the inverter is started. If the
starting f requency is set to 4.0Hz, the inverter will run between 4.0 Hz and the
maximum operating frequency after its start at 4.0Hz . The actual maximum
operating frequency is limited by the upper limit of frequency.
For the related parameters refer to CD031, CD140 and CD141.
CD042 Stopping Frequency
Set Range: 0.10—10.00 Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factor y Setting: 0.50
When stopping the inverter will decrease its f requency to the stopping
frequency and then stop running or start DC braking to stop.
If CD142 is set to 0, DC braking is invalid at stop and the inverter will stop
r u n ning.
If CD142 is set f or valid, the inverter will stop by DC braking.
For the related parameters refer to CD032, CD140 and CD142.
CD043 Auto Torque Compensation
Set Range: 0.0—10.0 % Un it: 0.1% Factor y Set ting: 2.0
This parameter can be
set for the auto output
of extra voltage
when the inverter is
running to achieve
higher torque, which
can compensate f or
the under-torque at
lower f requency. The
torque compensation should not be too big and it should be set slowly from low
to high according to the act ual sit uation.
Insuf cient compensation will result in the under-torque of the motor at lower
frequency. And over compensation will lead to too bigger torque, which will
produce a shock to the machine and even result in a trip of the inverter under
serious sit uation.
Page 49

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 44 -
CD044 Skip Frequency 1 **
CD045 Skip Frequency 2
CD046 Skip Frequency 3
Set Ra nge: 0.00 — 400.00 Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factory Setting: 0.00
CD047 Skip Frequency Range **
Set Range: 0.10—10.00 Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factor y Set ting: 0.50
These three f requency skipping points are set for avoiding a mechanical
resonance point. In case of CD047=0.1 , all skip f requencies are invalid. The
actual skip f requency range is two times that of CD047, as shown in the above
diagram.
CD048 Timer 1 Time
Set Range: 0.1~10.0S Unit: 0.1S Factory Set ting: 0.1
CD049 Timer 2 Time
Set Range: 1~100S Unit: 1S Factory Setting: 1
Timer 1 is a timer of 0.1s ~ 10.0s and Timer 2 is a timer of 1s ~ 100s. When the
timer start at multi-inputs is closed (on) the timer starts to count time. When it
reaches the set time the corresponding multi-output contact will act. When the
timer start is opened (of f ) the timer time at the multi-out put will be reset.
For example, set CD048=5.0s. When the exter nal control terminal (Multi-Input)
is valid the output terminal will be valid af ter ve (5.0) seconds, the signal of
which can be used to cont rol other cor responding signals.
Page 50

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 45 -
CD050 Mult i-input 1 (FOR f unction) Fa ctory Setting: 02
CD051 Multi-input 2 (REV function) Factory Setting: 03
CD052 Multi-input 3 (RST function) Factory Setting: 10
CD053 Multi-input 4 (SPH function) Factory Setting: 17
CD054 Mu lti-input 5 (SPM f unction) Fa ctory Sett ing: 18
CD055 Multi-input 6 (SPL function) Factory Setting: 19
Set Range: 00—32 Unit: No
00: Invalid. The terminal is set f or empty to prevent false actions.
01: RUN Running. It can be combined with other terminals to
compose multiple control modes.
02: FO R Fo r wa r d R o t at i o n
03: REV Reverse Rotation
04: STOP Stopping
05: FOR / R EV Switching of FOR /R EV rotation
06: J OG Jogg i n g
07: Jog FOR Rotation
08: Jo g R E V R o ta ti o n
09: Emergent Stop: Emergent stop. It can receive external emergent stop
command or other fault signals
10: RST Reset. This ter minal can be used f or reset af ter a f a ult is
removed.
11: R e s e r v e d
12: Over-heat of heat sink or motor: This contact can be used to detect over-heat
of the heat sink or motor to protect the motor and inver ter.
13: External Control Timer 1 Start: When the contact is closed, the timer will
start and begin to count time. When the timer reaches the
set point the corresponding multi-inputs will act.
14: External Control Timer 2 Star t
15 ~16: R e s e r v e d
17: High speed High, middle and low speed can compose three kinds of
operation mode
18: Middle speed with dif ferent f requencies. In the three terminals the high-
end sig nal has
19: Low speed priority. Low, Middle and High Speed are determined
respectively by Frequency 2, 3, 4.
20: Multi-speed 1 7-speed setting can be composed through Multi-speed 1, 2, 3.
21: M u l t i - s p e e d 2
22: M u lt i- s pe ed 3
23: Ramp Time 1: This terminal can be used to select the ramp time of the
inverter.
24: Ramp Time 2: 4 kinds of ramp time are available for choice.
25: UP Function When the switch of this terminal acts the f requency setting
Page 51

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 46 -
of the inver ter will be increased or decreased by one unit.
When the switch of the terminal is hold the f requency will
increase or decrease rapidly to a point and then i ncrease or
decrease
26: Down Function at even speed. When the power is up again af ter the power
breakdown the changed frequency will not be memorized.
27: Counter Pulse When this terminal is set for the counter it can receive the
pulse signal of ≤250HZ and counts.
28: Counter Reset When this contact acts it will clear the present counting
values displayed, restore C00 and restar t counting.
29: Drawing Start When this contact is triggered the drawing action starts.
30:AutoPLC Start This contact can be used to achieve the function of
AutoPLC start.
31: AutoPLC Reset Suspend This contact can be used to achieve the f unction
of AutoPLC clear suspend.
32: PID Valid When t his contact is closed, PID f unction starts. PID
Function start is only valid during operation.
Explanation:
1. Three multi-function terminals can be used for the connection method of
three-wire system for the realization of switching of FOR/REV rotation,
which is extensively applied in the cases of FOR /R EV switching of
photoelectric switches.
①
Select FOR, REV and RST.
②
Parameter setting:
CD033=1 for exter nal control CD050=02 f or FOR rotation
CD051= 03 f or R EV Rot a t ion CD052=04 f or Stop
③
Action Descr iption:
When triggering FOR, the inverter will rotate forward
(st a r t);
When triggering REV, the inverter will rotate reverse;
When pressing STOP, the inverter will stop.
①
Select FOR,REV
②
Parameter Setting:
CD033=1 for external control CD050=01 for Run f unction
CD051= 05 f or F/ R f unct ion
While K2 is of f, the inverter will rotate forward.
While K2 is on, the inverter will rotate reverse.
2. RUN, DCM, F/R can be used for Start, Stop and switching of FOR /REV:
Page 52

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 47 -
3. Description of Ramp Time 1 and 2:
1) This f unction is only valid when CD076 is set to 0, 1 and 2. Under the
disturbance and internal control multi-speed it is invalid.
2) Any two multi-inputs can be combined for 4 kinds of ramp time for
selection.
3) The related multi-inputs are set for Ramp Time 1, 2. Take the terminals of
SPH and SPM as example, when SPH CD053 is set to 23 and SPM CD054 is
set to 24, SPH and SPM are now Ramp Time 1, 2.
SPH SPM Result
OFF OFF Ramp Time 1
ON OFF Ramp Time 2
OFF ON Ramp Time 3
ON ON Ramp Time 4
4. Function description of High, Middle and low speed terminals:
RUN SPL SPM SPH Result
ON OFF OFF OFF
Main speed, the frequency runs at the set
value of CD000.
ON ON OFF OFF
Low speed, the frequency runs at the set
value of CD080.
ON ON/OFF ON OFF
Middle speed, the frequency runs at the set
value of CD081.
ON ON/OFF ON/OFF ON
High speed, the frequency runs at the set
value of CD082.
H.Speed
Page 53

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 48 -
Note:
( 1 ) This f unction is only valid when CD076 is set to 1, i.e. for 4-Speed of
exter nal cont rol.
( 2 ) Low, middle and high speed f requency are determined by Frequency 2,3, 4.
( 3 ) Ramp time is determined by Ramp Select terminal.
( 4 ) When all high, middle and low speeds have signal inputs it will give
priority in the sequence of high, middle and low speed.
5. Description of UP and DOWN Function:
UP DOWN Result
ON OFF Frequency increase
OFF ON Frequency decrease
ON ON Not increase or decrease
Note:
( 1 )
The f unction of UP and DOWN is only valid when the operator is
selected for the source of the operating f requency, i.e. CD034=0.
( 2 )
When the UP terminal is closed the f requency of the inverter will
increase.
( 3 )
When the DOWN terminal is closed the f requency of the inverter will
dec r ease.
( 4 )
When both UP and DOWN terminals are closed at the same time the
f requency will neither increase nor decrease. It is regarded as invalid.
( 5 )
When the f requency reaches the max operating f requency it will stop
increasing.
( 6 )
When the f requency reaches the min f requency or its lower limit, it will
stop decreasing.
( 7 )
Af ter a power breakdown the set value of CD000 will be memorized
instead of the f requency.
Page 54

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 49 -
( 8 )
When using the f unction of UP and DOWN, the keys of
△ ▽
of t he
panel are valid. Af ter changing the values it needs to press SET (ENTER) key
for conrmation and then the inverter can implement the action. Meanwhile
the value will write to CD000, which will be memorized af ter a power
breakdown.
( 9 )
When keeping pressing UP or DOWN, the frequency will increase or
decrease rapidly to a point and then increase or decrease at even speed.
(
10 ) The value changed by UP or DOWN can be set through CD072 for
conrmation of whether it should be memorized or not memorized. For details
refer to CD072.
6. Function Description of Multi-speed 1, 2 and 3:
They are only valid when CD076 is set to 2. For details refer to CD076.
7. Function Description of Counter
:
Note:
(1) The signal width triggered should not be lower than 2 msec (t1 、 t2≥2msec) .
(2) When the counting value is reached the corresponding multi-output contact
will act.
(3) This counter can only count again after reset.
(4) When reaching to 65535 the counter will not count again.
8. Description of AutoPLC Clear Suspend:
For details refer to 10. Example Application of AutoPLC Suspend in Appendix
1 and the description of related parameters in CD095.
*CD056 Multi-Output 1 (DRV function) Factory Setting: 01**
*CD057 Multi-Output 2 (UPF function) Factory Setting: 05
*CD058 Multi-Output 3 (FA, FB, FC function) Factory Setting: 02
*CD059 Multi-Output 4 (KA, KB function) Factory Setting: 00
Set Range: 00 —32 Unit: 1
00: Invalid: The terminal is set for no f unction to prevent f alse actions.
01: In Run: The contact will act when the inverter has output or receives the
r u nning command.
Page 55

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 50 -
02: Fault Indication: The contact will act when the inverter detects abnormal
conditions.
03: Zero Speed: The contact will act when the output frequency of the inverter
is less than its starting f requency.
04: DC Braking indication: The contact will act when the inverter is in DC
braking.
05: Set Frequency reach: The contact will act when the output f requency of the
inverter reaches the set frequency.
06: Uniform Frequency 1 Reach: The contact will act when the output
frequency of the inverter reaches the designated frequency (CD061).
07: Uniform Frequency 2 reach: The contact will act when the output
frequency of the inverter reaches the designated frequency (CD062).
08: In Accel: The contact will act when the inverter is in ramp-up.
09: In Decel: The contact will act when the inverter is in ramp-down.
10: Inverter Over-load Alarm: The contact will act when the inverter detects
over-load.
11: Motor Overload Alarm: The contact will act when the inverter detects over-
load of the motor.
12: In Over-torque Detect: The contact will act when the inverter detects over-
torque.
13: Low Voltage Alarm: The contact will act when the inverter detects low
volt age.
14: Single Step End: The contact will act and generate one pulse when the
inverter nishes a single step in implementation of program operation.
15: Process End: The contact will act and generate one pulse when the inverter
f inishes all the steps (i.e. af ter one cycle) in implementation of program
operation.
16: Set Counter Reach: The contact will act when the inverter implements the
external counter and the counting value is equal to the set value (CD064).
17: Middle Counter Reach: The contact will act when the inverter implements
the external counter and the counting value is greater than or equal to the
set va lu e (CD075).
18: External Control Timer 1 reach: The contact will act when the timer reaches
the set va l ue.
19: External Control Timer 2 reach:
20: 4~20mA disconnected: When AI input signal is opened the contact will act.
21~24: Reserved.
25: Auxiliary Pump 1: This contact controls the starting and stopping of
au x ilia ry pu mps. For det ails ref er to Ope r a tion of Multi- pu m ps.
26: A u x il i a r y P u m p 2
27: Drawing reach: The contact will act when the drawing action is nished.
The contact will automatically reset when the inverter stops.
Page 56

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 51 -
28: PID Lower Limit Alarm: This contact will act when the PID feedback is
smaller than the lower limit (the set value of CD156).
29: PID Upper Limit Alarm: This contact will act when the PID feedback is
greater than the upper limit (the set value of CD155).
30: Fan act: When the temperature of the inverter is increased or it is in
running, this contact will act.
31: Electromagnetic Relay Act: When the contact pulls in, the corresponding
multi-f unction terminal will act.
32: Braking Resistor Act: When the inverter is in r u nning and the DC voltage
reaches the braking voltage the contact will act.
CD060 Multi-Output AM **
Set Range: 0—7 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
Functions: Output terminal of digital f requency, generating pulse or 0—10V
analog. In combination with CD071 it can be connected with a corresponding
instrument with the measuring range below 10 to be used for external
monitor ing.
0 : 0~10V analog output, corresponding to output f requency. 0~10V
corresponds to 0~Maximum operating frequency
1 : 0~10V analog output, corresponding to output current. 0~10V corresponds
to 0~two times of the rated cur rent of the inverter.
2 : Analog output, corresponding to DC bus voltage. 0~10V corresponds to
0~1000V.
3 : Analog output, corresponding to AC output voltage. 0~10V corresponds to
0~510V/255V.
(Note: The machine type of three phase, 380V corresponds to 510V and the
machine ty pe of single phase, 220V corresponds to 255V)
4 : Pulse Output, corresponding to operating frequency: 1 Pulse/Hz, (50% of
capacity ratio )
5 : Pulse Output, corresponding to operating f requency: 2 Pulse /Hz, (50% of
capacity ratio )
6 : Pulse Output, corresponding to operating frequency: 3 Pulse /Hz, (50% of
capacity ratio )
7 : Pulse Output, corresponding to operating f requency: 6 Pulse /Hz, (50% of
capacity ratio )
Page 57

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 52 -
CD061 Unif or m Freq uency 1 **
CD062 Uniform Frequency 2
Set Range: 0.00—400.00 Hz Unit: 0.01 Hz Factor y Setting: 0.00
CD063 Uniform Frequency Range **
Se t Ra n ge: 0.10—10.00 H z Unit: 0.01 Hz Fa c t or y Set ti n g: 0.50
When the output f requency is more than the uniform f requency the
corresponding multi-outputs will act. The uniform frequency range acts as a
hyster esis loo p.
When the inverter is in the operation of multi-pumps, CD061 (Uniform
Frequency 1) is used as high speed f requency and CD062 is set as low speed
operating f requency. The definitions of the corresponding multi-function
contacts are changed.
When out put F. is higher than uniform F, the corresp. multiout puts act.The
unifor m F. range is uaed as hysteresis LOOP.
CD064 Counting Value **
Set Range: 0—65500 Unit: 1 Factor y Setting: 0
An external ter minal of multi-f unction can be used as a trigger for the
counter. When the counter reaches the set value of CD064 the corresponding
multi-output contact will act. After the counter is cleared and reset it will start
counting again. A proximity switch or optoelectronic switch can be used for
the trigger ing signals.
CD065 Analog Input
Set Range: 0—7 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: 0~10V 1: 0~5V 2: 0~20mA
3: 4~20mA 4: 0-10V and 4-20mA stacked 5-7: Invalid
This parameter can be set for different analog input signals.
When CD065=4, t he out put f reque ncy =1/2 (U/ Uma x + I /Ima x )× 50Hz
Page 58

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 53 -
Among which: U: Analog Voltage; U
max
: Ma xi m u m A na log Vol t a ge;
I: A nalog Cu r re n t; I
max
: Maximum Analog Cu r rent.
For example, When +10V and 20mA are respectively entered for the analog
input, the output f requency of the inverter is 50Hz.
CD066 Lower Analog Frequency
Set Range: 0.00—400.00 Hz Unit: 0.01 Hz Factor y Setting: 0.00
CD067 Bias Direction at Lower Frequency
Set R a nge: 0—1 Un it: 1 Factor y Set ting: 0
0: Positive direction
1: Negative direction
Bias direction means the instr uction of FOR/REV rotation command. Positive
bias indicates for ward rotation while negative bias indicates reverse rotation.
For details refer to the diagram in CD070.
CD068 Higher Analog Frequency
Set Range: 0.00—600.00 Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factor y Setting: 50.00
CD069 Bias Direction at Higher Frequency
Set Ra nge: 0—1 Unit: 1 Fact or y Set t i ng: 0
0: Positive direction
1: Negative direction
Bias direction means the instr uction of FOR/REV rotation command. Positive
bias indicates for ward rotation while negative bias indicates reverse rotation.
For details refer to the diagram in CD070.
CD070 Analog Negative Bias Reverse
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: Negative bias Rev is not allowable.
1: Negative bias Rev is allowa ble.
The parameter group is set for the measuring range and zero point of the
external analog terminals and can be combined for any kind of curve to
control the operation of the motor.
Setting: CD066=50 CD067=1 CD068=50
CD069=0 CD070=1
Note: this curve can be easily used in
complicated applications in combination with
other curves. When using it the instruction
of FOR/REV run f rom external terminals is
still valid. When switching, the curve will turn
reverse.
Page 59

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 54 -
Setting: CD066=50 CD067=0 CD068=0
CD069=0 CD070=0
Note: this curve is a kind of special
application of reverse ramp setting. When
usi ng transmit ter for the con t rol of pressu re,
temperatu re and others and while the control
has higher pressure and output signals but
requiring the corresponding commands of stop
or deceleration on the inverter this curve can
satisf y the demand properly.
Setting: CD066=10 CD067=1 CD068=40
CD069=0 CD070=1
Note: this method is used extensively. The user
can use it exibly.
Setting: CD066=10 CD067=1 CD068=40
CD069=0 CD070=1
Note; this curve is the extension of the above
cu r ve. 2V~10V (4.8m A~20mA) corresponds to
0Hz~ 40HZ; t he signal of 0V~2V(4~ 4.8mA)is
invalid. It can be used to avoid noice
disturbance. In harsh environment it is better
not to use sig nals below 1V f or setting the
operating frequency of the inverter.
CD071 AM Analog Output Gain
Set Range: 0.0—100.0% Unit: 1% Factor y Set t i ng: 100.0
This parameter can be used to adjust the output voltage value of Multi-output
6 to adapt to frequency meters with different measuring range and also
used to correct a f requency meter. For example, for an externally connected
f requency meter with the measuring range of 0~5V, a multi-f unction terminal
can be used to display its operating f requency. Then it can be corrected with
this parameter. It can be achieved by setting CD071=50 .
Page 60

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 55 -
CD072 UP/DOWN Function
Set Range: 0-1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: Not memor ized 1: Memorized
This parameter can be set for the selection of whether the values changed by
the UP or DOWN shall be memorized or not af ter stop. The changed values
whether to be memorized or not means when they are changed by UP or
DOWN du ring operation and the inver ter is restarted af ter stop these changed
values shall be memorized or not af ter restart. When CD072 is set to 0, the
changed value will not be memorized and when it is set to 1, the changed values
will be memorized. The set values of CD000 will be memorized af ter restart.
For the related parameters refer to CD050-CD055.
CD073 UP/DOWN Speed
Set Range: 0-1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: 0.1H z . M i n i m u m U P / DO W N s p e e d is 0.1H z .
1: 0.01H z. M i n i m u m U P/ DO W N s p e e d is 0.01H z.
Through the changes of this set value the UP/DOWN speed unit can be
ad justed to meet the needs of dif f erent customers.
CD074 Analog Filtering Constant
Set Range: 0-50 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 20
The setting of this parameter is related to the analog responding speed. The
higher the value of CD074 is set, the lower the analog responding speed will be.
CD075 Intermediate Counter
Set Range: 0-65500 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
Ref er t o CD06 4.
CD076 PLC Operation
Set Range: 0—5 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: Normal operation, i.e. the inverter is running in the normal control mode.
1: Exter nal control 4-Speeds (Refer to the f unction description and diagram of
three terminals of high, middle and low speed in C050~C055)
2: External control multi-speeds
Page 61

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 56 -
Multi-f unction Terminals Results
Mult i-speed 1Mult i-speed 2Mult i-speed
3
OFF OFF OFF
Main f requency and f requencies
are determined by CD000 or
potentiometer.
ON OFF OFF
Multi-speed 1 and f requency are
deter mined b y CD080.
OFF ON OFF
Multi-speed 2 and frequency are
d e t e r m i n e d b y C D 0 81.
ON ON OFF
Multi-speed 3 and frequency are
det e r mi ned by CD082.
OFF OFF ON
Multi-speed 4 and f requency are
d e t e r m i ne d b y C D0 83.
ON OFF ON
Multi-speed 5 and frequency are
deter mi ned by CD084.
OFF ON ON
Multi-speed 6 and f requency are
d e te r m i ne d b y CD085.
ON ON ON
Multi-speed 7 and f requency are
deter mi ned by CD086.
Note:
①
It is only valid to realize the external control 8-Speeds operation when
Multi-inputs are set for Multi-speed 1, 2, 3 and CD076 is set to 2.
②
Multi-speed 1, 2, 3 can be used to make up 7-Speeds and 8-Speeds adding
the main frequency .
③
The f requencies of Speed Step 1 ~ Step 7 are determined by CD080~CD086.
④
Each ramp time is determined by the external multi-function terminal.
⑤
The directions of each program operation are determined by the external
Page 62

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 57 -
multi-function terminals.
⑥
This main frequency can be set in two ways. One method is to set it
through CD000 and another is to set it through the potentiometer.
When CD034 is set to 1 the f requency of Main Frequency is set by the
potentiometer. For the related parameters refer to CD000,CD034 and
CD080~CD086.
Note:
①
The f requency at each inection point is determined by CD000 and CD080.
②
Skip Frequency is determined by CD086.
③
Running Time is determined by Timer CD087 and CD088.
④
The related parameters: CD000, CD080~CD088.
4: Internal control Multi-speeds
Note:
①
Main speed and 7-speeds composes 8-speeds.
②
The ramp time of each speed step is set by PLC Ramp Time CD079. Refer
to the detail descriptions of CD079.
③
Running Time is set by Timer CD087~CD094. For the control steps not to
3: Disturbance (Traverse f unction)
This is a special parameter in the chemical fiber and printing and dying
industries to realize the traverse f unction. Except the commands of stop,
external faults and emergency stop all other commands are not accepted at
r u n ning.
Page 63

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 58 -
be used the timer can be set to 0.
④
Running direction of each speed step is determined by CD078.
⑤
In the internal control multi-speed operation the running time and
direction are determined by the setting of internal parameters. Any switching
of external time and FOR/REV rotation is invalid.
5: D r a w i n g
This is a special parameter f or the constant speed of unwinding and rewinding.
By using this function the linear speed constant in certain accuracy can be
realized.
Note:
①
Through triggering of the external multi-f unction terminal the drawing
action begins.
②
In implementation of the d rawing action the actual run ning time is
T = C D 08 7 ×10 .
③
when the drawing action is nished the inverter will run at the constant
seed of CD081 and the corresponding multi-output contact will act at the same
time. Until receiving the STOP command the inverter will stop running and
the multi-output contact will reset.
CD077 Auto PLC
Set Range: 0—3 Unit: 1 Factory Setti ng: 0
0: Stop af ter the program runs one cycle.
1: Cycling r unning.
2: Stop after it runs one cycle automatically (STOP for intervention) .
3: Auto running and cycling (STOP for intervention)
This parameter setting is only valid when CD076 is set to 4. For relevant
parameters refer to CD000, CD076 and CD078~CD094.
Page 64

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 59 -
Explanation:
1. Stop after the program runs one cycle.
When the command of auto program operation is given, the inverter will
run with each set value of internal parameters. It will run for one cycle and
then stop automatically. The inverter will not restar t and run until it receives
another command of operation.
2. Cycling run.
When the command of operation is given, the inverter will run in sequence
with the f requency of every speed step and running time set by each of
the internal parameters and will recycle. Du ring the cycling run, except the
commands of stop, external faults and emergency stop, all other commands
will not be accepted.
3. Stop after it runs one cycle automatically (STOP for intervention)
Note:
①
When the command of auto program operation is given the inverter will
run with each parameters. But it will stop rst and then restart at changing of
each step and will stop automatically af ter running for one cycle. The inverter
will not restart and run until it receives another command of operation.
②
The f requencies of each speed step are set by CD000 and CD080~CD086.
③
The running times of each speed step are set by CD087~CD094.
④
The running direction is set by CD078.
CD078 PLC Running Direction
Set Range: 0—255 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
This parameter is only valid when CD076 is set to 4. This parameter setting
determine the r unning direction of each f requency of CD080~CD086 and
CD000 in the program operation. The setting method is as f ollows:
The rotation direction is set rst in the binary 8 bits mode, and then converted
to a decimal value for the setting of this parameter. For instance:
Page 65

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 60 -
0: For. 1: Rev.
Ma i n Speed (CD000) For.
Frequency 1 (CD080) Rev.
Frequency 2 (CD081) For.
Frequency 3 (CD082) Rev.
Frequency 4 (CD083) For.
Frequency 5 (CD084) For.
Frequency 6 (CD085) Rev.
Frequency 7 (CD086) For.
T h e p a r a m e t e r v a l u e 010 01010 i s c o n v e r t e d t o a d e c i m a l v a l u e:
1× 2
6
+1× 23+1× 21=64+8+2=74
Then CD078=74
CD079 PLC Ramp Time
Set Range: 0~65535S Unit: 1S Factory Setting: 0
This parameter is only valid when CD076 is set to 4.
This parameter is set to determine the ramp time values for Step 1~4 of the
internal control multi-speed. The setting method is as follows:
①
Determine each Ramp Time in the binar y 2 bit mode
Bi t1 Bit0 Ramp Time
0 0 R a m p T i m e 1 C D 012 , CD 013
0 1 R a m p T i m e 2 CD 014, C D 015
1 0 R a m p Ti me 3 CD 016, C D017
1 1 R a m p Ti me 4 CD 018, CD 019
②
Determine the Ramp time of each speed step in the binary 16 bit mode
Step 8 Step 7 Step 6 Step 5 Step 4 Step 3 Ste p 2 Step 1
t8 t7 t6 t5 t4 t3 t2 t1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1
t1 Select Ramp Time 4
t2 Select Ra mp Time 1
t3 Select Ramp Time 3 The setting value:
t4 Select Ramp Time 2 1×2
0
+1× 21+1× 25+1× 26=99
Page 66

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 61 -
t5 Select Ramp Time 1 So CD079 is set to 99
t6 Select Ramp Time 1 Attach: 2
0
=1 21=2 22=4 23=8
t7 Select Ramp Time 1 2
4
=16 25=32 26=64 27=128
t8 Select Ramp Time 1
CD080 Frequency 2 Factory Setting 15.00**
CD081 Frequency 3 Factory Setting 20.00
CD082 Frequency 4 Factory Setting 25.00
CD083 Frequency 5 Factory Setting 30.00
CD084 Frequency 6 Factory Setting 35.00
CD085 Frequency 7 Factory Setting 40.00
CD086 Frequency 8 Factory Setting 0.50
Set Range: 0.00 — 400.00 Hz Unit: 0.01 Hz
This parameter is set in combination of the multi-inputls to select 4-speeds of
external control, multi-speeds of external control or multi-speeds of internal
control. For the relevant parameters refer to the description of CD076 and
CD087~CD094.
CD087 Timer 1 Factory Setting 10.0**
CD088 Timer 2 Factory Setting 10.0
CD089 Timer 3 Factory Setting 0.0
CD090 Timer 4 Factory Setting 0.0
CD091 Timer 5 Factory Setting 0.0
CD092 Timer 6 Factory Setting 0.0
CD093 Timer 7 Factory Setting 0.0
CD094 Timer 8 Factory Setting 0.0
Set Ra nge: 0.0 — 6500.0S Unit: 0.1S
This parameter is set for the internal control multi-speeds and the running
time of drawing f unction. For the relevant parameter refer to CD076 and
CD080~CD088.
CD095 AutoPLC Memory Function
Set Range: 0—1 Factory Setting: 0
0: N o t m e mor i z e d
1: M e m o r i z e d
This parameter is set to determine whether the inverter is to realize the
suspending f u nction in AutoPLC mode. I n case of CD095=1 it can memorize
the status in which the inverter is running and will memorize it at stop or
fail. It will continue to run when returning to normal. In case of CD095=0 it
will not memorize. For specic applications refer to Example Application 10 in
A p p e n d i x 1.
Page 67

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 62 -
CD096~CD109 Reserved
This parameter is set for the number of auxiliary pump. The start or stop
of the auxiliary pumps is controlled by using the multi-output contacts and
Auxiliary Pump 1 or Auxiliary Pump 2 is controlled through the peripheral
con t rol circuit.
*CD110 Number of Auxiliary Pump
Set Range: 0—2 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
In case of two pumps with only one pump in duty, in order to ensure each
pump to work evenly, it will be switched to another pump when its running
time reaches the set value of CD111.
*CD111 Continuous Running Time of Auxiliary Pumps
Set Range: 1—9000min Unit: 1min Factory Setting: 60
This parameter is set to determine the interlocking time of two auxiliary
pumps when switching with each other.
*CD112 Interlocking Time of Auxiliary Pump
Set Range: 0.1~250.0S Unit: 0.1S Fact or y Setting: *
In the application of water supply with constant pressure, when the master
pump is running at the f requency of high speed (set by CD061) due to
larger water volume and the high speed r unning time (CD113) is reached, the
corresponding multi-function contacts act and the auxiliary pumps start.
*CD113 High Speed Running Time
Set Range: 1~250S Unit:1S Factory Setting:60
In the application of water supply with constant pressure, when the master
pump is running at the f requency of low speed (set by CD062) due to
smaller water volume and the low speed running time (CD114) is reached, the
corresponding multi-function contacts act and the auxiliary pumps stop.
*CD114 Low Speed Running Time
Set Range: 1~250S Unit:1S Factory Setting:60
Page 68

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 63 -
CD113 and CD114 must be used in combination of CD061, CD062 and multioutputs. Their main function is to increase or decrease the number of auxiliary
pu m p.
This parameter is set for the voltage level of the master pump entering into
sleep mode. For details refer to the following description.
*CD115 Stopping Voltage Level
Set Range:0~150% Unit:1% Factory Setting:95
This parameter is set for the lasting time under the stopping voltage level
bef ore entering into sleep mode. For details refer to the following description.
*CD116 Lasting Time of Stopping Voltage Level
Set Range:1~250S Unit:1S Factory Setting:30
This parameter is set f or the wakeup voltage level f rom sleep to wakeup.
*CD117 Wakeup Voltage Level
Set Range:1~150% Unit:1% Factory Setting:80
This parameter is set for the lowest operating f requency entering into sleep
mode.
*CD118 Sleep Frequency
Set Range: 0.00~400.00Hz Unit: 0.01Hz Factory Setting:20.00
This parameter is set for the lasting time to run at sleep f requency when
entering into sleep mode.
*CD119 Lasting Time of Sleep Frequency
Set Range: 1~250S Unit: 1S Factory Setting:20
Page 69

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 64 -
The following is the block diagram of multi pumps operation:
Page 70

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 65 -
0: Over-voltage stall prevention invalid
1: Over-voltage stall prevention valid.
When the inverter is in deceleration, due to the eff ect of load inertia, the motor
will produce a return energy to the inverter and cause the DC voltage of the
CD120 Over-voltage Stall Prevention
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 1
F≥CD061
P≥CD115
T≥CD116
F≥CD061
T≥CD113
Page 71

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 66 -
inverter to increase. So when the f unction of over-voltage stall prevention is
started, if the DC voltage of the inverter becomes too high, the inver ter will
stop decelerating till the voltage at DC decreases below the set value, then the
inver ter will go on to decelerate and the ramp-down time will be extended
automatically.
When the inverter is in ramp-up, due to overload or too short ramp-up time,
the output current of the inverter will go up quickly and exceed the set
standard level. When this happens, the inverter will stop accelerating. When
the current returns under its set value, the inverter will go on to accelerate.
CD121 Stall Prevention Level at Ramp-up
Set Range: 0—200% Unit: 1% Factory Set ting: 150
100% current is the rated current of t he motor. When t his parameter is set to 0,
the stall prevention f unction is invalid.
When the inverter is running at constant speed, due to load uctuation and
other reasons, the cur rent will increase. When the current exceeds its set
standard value, the inverter will lower the output frequency. When the output
current returns to its normal range, the inverter will accelerate again to its set
f req ue nc y.
CD122 Stall Prevention Level at Constant Speed
Set Range: 0—200% Unit: 1% Factory Setting: 0
100% current is the Rated Current of the motor. When t his parameter is set to
0 the stall prevention f unction is invalid.
R ef e r t o C D12 0 .
CD123 Stall Prevention Level at Deceleration
Set Range:0~232% Unit:1% Factory Setting:0
Page 72

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 67 -
100% current is the rated current of the motor.
0: When reaching the frequency it starts to detect over-torque and when over-
torque is detected it continues to run.
1: When reaching the f requency it starts to detect over-torque and when over-
torque is detected it stop running.
2: It detects over-torque during running and when over-torque is detected it
continues to run.
3: It detects over-torque during running and when over-torque is detected it
st op r un ning.
CD124 Over-torque Detect Mode
Set Range: 0—3 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
When the output current exceeds the over-torque detection level and also
exceeds half of the set time of over-torque detection (factory setting: 1.0s), the
over-torque detection will indicate, and the corresponding multi-f unction
alar m contact will act. When it exceeds the set time, the inverter will turn to
self-protection. When this parameter is set to 0, the over-torque detection will
be invalid
CD125 Over-torque Detect Level
Set Range: 0—200% Unit: 1% Factory Setting: 0
When the inverter detects that the output current has exceeded the motor
current set value, the inverter begins to calculate the over-torque time. When
the over-torque time has exceeded half of the set detect time, the corresponding
multi-function output contact will act, and produce the over-torque alarm,
while the inverter will keep running. When the over-torque time has exceeded
the set detect time (set by CD126), the inverter will turn to self-protection,
display the fault information and stop output..
For the related parameters refer to CD125.
CD126 Over-torque Detect Time
Set Ra nge: 0.1—20.0s Unit: 0.1s Factor y Set ting: 1.0
Page 73

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 68 -
When the inverter is used for the loads of kinds of fan and pump CD122 can
be set to 120. When the current of the inverter is greater than 120% the output
frequency will decrease and the current will also decrease accordingly. After
the current returns to normal the frequency will return to normal slowly, so as
to achieve the stall prevention f unction. The decreasing speed of the f requency
is determined by CD127. For the Related parameters refer to CD 122.
CD127 Decel. Time for Stall Prevention at Constant Speed
Factory Setting: 5.0
When the inver ter is set for f ault restart and if it has a fault trip with the time
exceeding the set value of CD128 the inver ter will restart. When using this
f unction pay more attention to the safety.
CD128 Fault Restart Time Factory Setting: 1.0
When the starting mode of the inverter is set to f requency track there is a
process of voltage rise during the f requency track. When the voltage is rising
rapidly the current will be higher and the tracking process will be faster.
When the voltage is rising slowly the current will be lower and the tracking
process will be slower. In general practice this value of CD129 is set lower for
the inverter of smaller power and set higher for the inverter of larger power.
CD129 Voltage Rise Time during frequency track Factory Setting: 5
It is set according to the rated voltage value of the nameplate of the motor. For
the inverters of 230V class the factory setting is 220, while for the inverters of
400 V class the f actor y setting is 380.
CD130 Rated Motor Voltage Unit: 0.1V Factory Setting: *
It is set according to the rated value of the nameplate of the motor. This
parameter can be used to restrict the output current of the inverter to prevent
over-current and protect the motor. If the current of the motor has exceeded
this value the inverter of AC motor will turn to self-protection.
CD131 Rated Motor Current Unit: 0.1A Factory Setting: *
This parameter is set for the number of the motor’s pole according to the
nameplate of the motor.
CD132 Motor Pole Number
Set Range: 02—10 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 04
Page 74

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 69 -
This is set according to the act ual revolution of the motor. The displayed value
is the same as this set value. It can be used as a monitoring parameter, which is
convenient to the user. This set value corresponds to the revolution at 50Hz.
CD133 Rated Motor Revolution
Set Range: 0~9999r/min Unit: 1r/min Factory Setting: 1440
The setting of motor no-load current will affect the value of slip compensation.
The current is 100% of the rated cur rent of the motor.
CD134 Motor No-load Current
Set Range:0~100% Unit:1% Factory Setting:40
When the inverter drives the motor the slip becomes bigger due to the increase
of load. This parameter can be set for slip compensation to decrease the slip
and make the r u nning speed of the motor closer to the synchronous revolution
0~1000 is cor responding to 0~10% .
CD135 Motor Slip Compensation
Set Range: 0—1000 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
This parameter is set f or the DC braking voltage to the motor at start and stop.
It can be ad justed for dif ferent braking voltage. When ad justing the parameter
it must be increased slowly f rom lower value to high value until the sufcient
braking torque is achieved.
The voltage at maximum frequency is 100% voltage.
CD140 DC Braking Voltage Level
Set Ra nge: 0.0 —20.0% Unit: 0.1% Factory Setting: 2.0
CD136—CD139 Reserved
This parameter is set f or DC Bra king at
start and the lasting time of DC Braking
current to the motor. If it is set to zero it
means DC braking is invalid.
DC braking at start is normally used
in the application, in which the load is
movable when the machine is at stop, such
as windmill. Because of the load existing before the inverter drives, the motor
is often in coasting with an uncertain rotation direction. So the DC braking can
be executed before starting the motor to prevent the inverter f rom tripping.
This setting is valid only when CD031 is set to 0. For the related pa rameters
refer to CD031, CD140 and CD041.
CD141 DC Braking Time at Start
Set Range: 0.0—25.0S Unit: 0.1S Factor y Setting: 0.0
Page 75

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 70 -
Note: When this parameter is set to any
non-zero value it star ts DC brake at
stop and sends the DC braking time to
the motor. DC braking at stop is often
used for a high-level stop or positioning
control. When this parameter is set to
zero it closes DC braking at stop.
This setti ng is valid when CD032 is set
to 0. For the related parameters refer to CD032, CD042 and CD140.
CD142 DC Braking Time at stop
Set Range: 0.0~25.0S Unit: 0.1S Factor y Setting: 0.0
This parameter is set as f requency track time when the inverter is started
by frequency track after an external abnormality or temporary power
breakdown. For starting or stopping of some large inertia load, if restarting a
machine af ter its complete stop, it will waste much time because of its large
inertia of load. But if the frequency track is started, it is not necessary to wait
for the machine to come to a f ull stop for restart. The inverter will t race the
frequency f rom high to low with the set frequency. Af ter searching it will
continue to accelerate to reach the set frequency.
CD143 Frequency Track Time
Set Range: 0.1—20.0S Unit: 0.1S Factor y set ting:5.0
When the inverter is tracing the frequency this set value is taken as the level
for output current. When the output current is higher than this level the
inverter will decrease the frequency to restore the current below the level and
then it will execute the frequency track again.
CD144 Current Level for Frequency Track
Set Range: 0—200% Unit: 1% Factory Setting: 150
0: Invalid, i.e. the inverter will not restart after an instantaneous power
brea kdow n.
1: Start by frequency track. Refer to CD143.
CD145 Restart af ter Instantaneous Stop
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
This parameter is set for the maximum allowable power f ailure time. If
exceeding the set time the inver ter will continue to stop output af ter power on.
To restart the inver ter it needs to follow the general starting procedures.
CD146 Allowable Power-Breakdown Time
Set Ra nge: 0.1—5.0S Un it: 0.1S Factor y Setti ng: 0.5
Page 76

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 71 -
Af ter the abnormal conditions (such as over-cur rent and over-voltage) happens
the inverter will automatically reset and restart. If the starting mode is set to
normal mode it will start according to the normal procedures. If it is set to star t
by f requency track it will start in the f requency track mode. Af ter starting
it will restore the set number again if there is no more abnormality happened
within 60 seconds. If there is still any error and it reaches the set number the
inverter will stop output. It can only be started after reset. When CD147 is set
to zero the inverter will not carry out the f unctions of automatic reset and
restar t.
CD147 Number of Abnormal Restart
Set Range: 00—10 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 00
0: Invalid
1: V a l i d
When the input power is not stable and if the voltage is too high the operation
of the motor with the power exceeding the rated voltage will cause increase
of the temperature of the motor, damage of its insulation and unstable output
torque. This auto voltage regulation can automatically stabilize the output
voltage within the rated voltage range of the motor under the condition of
unstable output power supply
When this function is set to invalid the output voltage will uctuate.
CD148 Auto Voltage Regulation
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 1
When it is set to zero this function is invalid. When Auto energy saving
f unction is started the inverter will r un at the f ull voltage during ramp-up or
-down. During the operation at constant speed the inverter can automatically
calculate the optimum voltage value according to the power of load and supply
power to the load to achieve the goal of energy saving.
CD149 Auto Energy Saving
Set Ra nge: 0.0 —20.0% Unit: 0.1% Factory Set ting: 0.0
Auto energy saving can reduce the normal output voltage by max 30%. For
the load with f requent changes or closing to f ull load, this f unction is not
suitable.
Page 77

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 72 -
This proportional constant is set for the er ror value gain. In case of I=0, D=0, it
is only for proportional control.
*CD150 Proportional Constant (P) **
Set Range:0~1000.0% Unit:0.1% Factory Set ting:100.0
The integral time (I) is set for the responding speed f or PID. The larger the
I value is set the slower the responding speed will be. To the contrary, if the
responding speed is quick but the integral time value is set too small, it will
cause oscillation.
*CD151 I n t eg r a l Ti m e ( T ) **
Set Range:0.1~1000.0S Unit:0.1S Factor y Setti ng:.5.0
This dif ferential time (D) is set for the depression operation of PID. The larger
the D value is, the more obvious the depression operation will be. When D is set
to zero, this f unction is invalid.
*CD152 Dif ferential Time (D) **
Set Range: 0.00~10.00s Unit: 0.01s Factor y Setting: 0
This target value can be set through external voltage signal or the digital
operator.100% target value is corresponding to the analog frequency at +10V.
PID closed-loop control is usually used in the process control with physical
quantity not changing fast, such as the controls of pressure and temperature,
etc. The feedback signal is usually taken from temperature transmitter, or
pressure tra nsmitter, etc. Under PID control, t he feed back signal input pat h is
the a nalog current sig nal of 4-20m A.
PID closed-loop control is valid when Multi-input PID is sta r ted.
PID Cont rol Block Diagra m:
*CD153 Target Value **
Set Range: 0.0 ~100.0% Unit: 1% Factory Setting: *
Page 78

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 73 -
General operating methods of PID control:
(1) Choose the correct transmitter (with the output specication of standard
current signal 4-20mA).
(2) Set the right target value.
(3) If the output does not have oscillation, increase the proportional constant (P).
(4) If the out put does not have oscillation, decrease the integral time (Ti).
(5) If the output do not have oscillation, increase the dif f erential time (Td).
(6) Concrete applications can be refer red to the example application
descriptions in Appendix 1.
1. Suppress the Over Output
a: Decrease the diff erential time (D value)
b: Increase the integral time (I value)
2. Suppress t he oscillation
a: Decrease the dif ferential time (D value) or set it to zero.
b: Decrease Proportional Constant (P value)
The target value can be set through the selection of the panel or external
analog. The external analog is 0~10V signal or given by the potentiometer.
When CD154=0, the target value of PID is the value set by CD153.
When CD154=1,the target value of PID is the value of the exter nal analog 0-10V
(corresponding to 0-100%), the setting of CD153 is invalid.
*CD154 PID Target Value **
Set Range: 0~1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting:0
Page 79

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 74 -
When PID feedback value is more than the set value of CD155 the
corresponding multi-output will act and the inverter will not stop.
*CD155 PID Upper Limit **
S e t R a n g e: 0 ~10 0 % Un it: 1% Fa ct or y Se t t i ng:100
When PID feedback value is less than the set value of CD156 the corresponding
multi-output will act and the inverter will not stop.
*CD156 PID Lower Limit **
Set Range: 0~100% Unit: 1% Factory Setting:0
When the inverter is set for RS-485 Communication interface control, each of
the inverters will be set for its individual identication number through CD160.
00: No communication f unction.
01~250: Address for the inverters
CD160 Communication Addresses
Set Range:0~250 Unit:1 Factory Setting:0
CD157~CD159 Rese r ve d
0: 4800 b/s 1: 9600 b/s 2: 19200 b/s 3: 38400 b/s
CD161 Com m u nica t i o n B a n d R at e
Set Range:0~3 Unit:* Factory Setting:1
0: 8N1 For ASCII 1: 8E1 For ASCII 2: 8O1 For ASCII
3: 8N1 Fo r RT U 4: 8E1 For RT U 5: 8O1 Fo r RTU
CD162 Communication Data Method
Set Range:0~5 Unit:* Factory Setting:0
CD16 3 ~ C D166 R e se r v e d
HOLIP MODBUS Communication Protocol
When using the RS485 communication interface, each of the inverters must
be set for its own add ress so that the computer can use this individual address
to carry out the control.
1: The communication protocol has two kinds of control mode:
(1) RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) mode
(2) ASCII (American Standard Code for information interchange) mode
Information of codes:
RTU mode: Each of 8-bit data is composed of two 4-bit (hexadecimal), for
Page 80

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 75 -
exa m pl e: 64 H
ASCII mode: Each of 8-bit data is composed of two ASC IIbyte, for example:
One 1-bit data 64H (hexadecimal) is composed of ASC II byte“64”, included“6”
(36H) a nd “4”(34H).
Byte 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
ASCII
code
30H 31H 32H 33H 34H 35H 36H 37H
Byte 8 9 A B C D E F
ASCII
code
38H 39H 41H 42H 43H 44H 45H 46H
2: Communication Data Method
(1) 8 N1 F o r A S C I I C D16 2 = 0
(2)
8E1 For ASCII C D162=1
⑶
8O1 For ASCII C D162=2
(4)
8N1 F o r R T U C D16 2 = 3
Page 81

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 76 -
(5)
8E1 F o r R T U C D16 2 = 4
(6)
8O1 Fo r R T U C D16 2 = 5
3: Communication Document Formats
3.1 A S C I I Mo d e
Communication Document Forms
STX
“ : ”
(3A H )
ADDR FU NC LEN
DATA
( n -1)
....
DATA
0
CRC
END
CR(0DH)
LF(0A H )
(1) STX: Sta r ting u n it “ : ” (3AH)
(2) ADDR communication address,8-bit data is composed of
two ASC II byte.
00: Broadcast mode is MODBUS
01~250: Address of the corresponding inverters.
(3) FUNC: Function code 8-bit data is composed of two ASC II byte.
01: FUNC READ, Read the data of f unction code
02: FUNC WRIT, write the data of f unction code
03: Write cont rol data
04: Read control status data
05: Write inverter frequency data
06: R ese r ve d
07: Re se r ve d
08: L o o p t e s t
a: Read f unction code data
For m a t:
ADDR 01 LEN FU NC Data
ADDR=0 means no answer
ADDR≠0 means a reply from inverter of this address
When inverter reply normal, the for mat as follows~
ADDR 01 LEN FU NC Data
Page 82

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 77 -
If DATA is one word, t he LEN=3, If DATA is one byte, the LEN=2 .
When inverter has no this f unction code or reply no effect, the format as
f ollows :
ADDR 81H 01 FU NC
b : Write f unction code data
Format :
ADDR 02 LEN FU NC Data
ADDR=0 for broadcast, it write to all inverter, but no reply.
ADDR≠0, set data and reply from inverter of this address.
When the setting is incorrect or the inverter does not have this function, the
format ret u r ned is as follows:
ADDR 81H 01 FU NC
c: Co n tr ol c o m ma nd s
Fo r ma t:
ADDR 03 LEN CNTR
ADDR=0 for broadcast, it write to all inverter, but no reply
ADDR≠0, reply and return.
CNTR
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
jog r jogf jog r/f stop rev for run
When the setting is correct it will return to present control status.
For mat: ADDR 03 LEN CNST
CNST
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Track start Brak ing r/f jog gi n g running r/f jog run
When the check is not correct,
ADDR 83H 01 CNST
d: Rea d stat us value
Format :
A DDR 04 01 CFG
A DDR=0, no reply
ADDR≠0, reply.
CFG=0~7, reply single data
0 : Set F 1 : Out F 2 : Out A 3 : RoTT
4 : DCV 5 : ACV 6 : Cont 7 : Tmp
For example: read agreed f requency
Send : 01 04 03 00 CRC
Retu r n : 01 04 03 13 88 CRC
I n w h i c h , 13 88 a r e d a t a
13 for high order, while 88 for low order.
(4) LEN : data length, It means the length of D(n-1)…D0, Length set: when one
Page 83

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 78 -
word, LEN=3, when one byte or <1by te, LE N=2
.
(5) DATA: <Data characters> data content. 2n ASCII compose n bytes, it have
f ty ASC II at most.
(6) LRC : longit udinal red undancy check
ASCII mode: Get LRC methods is that add ADDR to the last data, if the result
is more than 256,then the result subtract 256 until the result is less then 256 (if
the result is 128H, take 28H), then 100H subtract the result get LRC.
(7) For example: write 30.00Hz to inverter of 01 ( write to CD000 )
STX ADDR FU NC LEN DATA LRC END
“:”
“0”
“1”
“0”
“2”
“0”
“3”
“0” “0” “0”
“B” “B” “8”
“3” “7” “CR” “LF”
3A H 3 0 H 31 H 30 H 32H 30 H 33H
30H 30H 30H
42H 42H 38H
33H 37H 0DH 0AH
Calculate LRC: 01H+02H+03H+00H+0BH+B8H=C9H
C9H subtracted f rom 100H: 37H
So the sent data is following: 3AH 30H 31H 30H 32H 30H 33H 30H 30H 30H
42H 42H 38H 33H 37H 0DH 0AH
3.2 R T U M o d e
Quiet ADDR FUNC LEN D
( n -1)~D(0)
CRC Quiet
>50ms >50ms
(1) Quiet: the time of no data is more than 50 ms
(2) ADDR: Communication add ress, 8-bit data
(3) FUNC: Function code, 8-bit data, ref er to 3.1-3
(4) LEN: Data length, the length of D~n-1~~D0
(5) DATA: data content, n*8-bit
(6) LRC: Longitudinal Redu ndancy Check
RTU mode: get CRC~cyclical Redundancy Check~.
The CRC calculation method is following:
(1) make a 16-bit register and set value 0FFFFH(call CRC register)
(2) done rst byte of data Exclusive OR with low byte of 16-bit CRC register
and save the result to CRC register
(3) done 1 bit right shif t with CRC register and ll zero to lef t bit, then check
low bit of CRC register.
(4) if t he low bit is zero, then do repeat setp3, else CRC register do Exclusive
O R w i t h 0A 0 01H .
(5) done repeat step 3 and 4,until CRC register done right shif t 8 times, then the
byte is fully done.
(6) done repeat step 2 to 5 for the next byte of data, until process completely
Page 84

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 79 -
all data. The last data of CRC register is CRC value. When send CRC value in
command data, low bytes must change the sequence with high bytes, i.e. low
bytes will be sent rst.
(7) Example 1: Write 30.00Hz to inverter of 01
Command data
ADDR FUNC LEN DATA CRC
01H 02H 03H 00H 0BH B8H 7FH 0CH
Sent data: 01H 02H 03H 00H 0BH B8H 7FH 0CH
(8) E x a m ple 2:
The following is that get CRC value with C language. The f unction has
two para meters:
Unsig ned cha r *da t a ← the point of data buffer
Unsigned cha r length ← number of data buffer
This f unction will send back the CRC value with unsigned integer
for mat.
Unsigned int crc_chk (unsigned char *data, u nsigned char length)
{
i n t j;
unsigned int reg_crc=0xffff;
while (length--){
reg_crc^=*data=++;
for( j=0; j<8;j+ +){
if (reg _crc&0×01){/*LSB(b0)=1*/
reg _crc=(reg _crc>>1)^0xa001;
}e l s e{
reg _crc=reg _crc>>1;
}
}
}
return reg_crc;
}
This para meter is only valid when Bit 2 is set to 1 in CD168. For the details ref er
t o C D168.
0: Inverter Temperature
1: Counter Value
2: PI D Ta r ge t Va l u e
3: P I D F e e d b a c k Va l u e
4: Present running time of power up (Unit: Hour)
CD167 Display Items
Set Range: 0 —31 Unit: 1 Factor y Setting: 0
Page 85

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 80 -
5: Total running time of power up(Unit: Hour)
6 -31: I n v a l i d
This parameter is set for selection of displaying of DC voltage, AC voltage
and other items so that the customer can monitor and view them in sequence
through the switch key.
It can be is set rst in the binary 3 bits mode, and then converted to a decimal
va l u e.
CD168 Display Items Open
Set Range: 0—7 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: In valid 1: Valid
DC Volt a ge
AC Vol ta ge
Select to display items of
C D16 7.
In the contents displayed the factory setting is to show output f requency, set
frequency, output current and output revolution through the switch key. If it is
necessary to view and monitor other items they can be set through CD167 and
C D16 8.
Factor y setting is depending on the model. It can be observed, but not set.
CD169 Voltage Rating of Inverter Unit: 1V Factory Setting: *
It is depending on the model and can’t be changed.
CD170 Rated Current of Inverter Unit: 1A Factory Setting: *
It ca n be obser ved, but not set.
CD171 Software Version Factory Setting: *
When it has no f ault record it shows ——. Af ter access to this parameter the
fault display can be checked.
CD172 Fault Record 1 Factory Setting: ————
CD173 Fault Record 2 Factory Setting: ————
CD174 Fault Record 3 Factory Setting: ————
CD175 Fault Record 4 Factory Setting: ————
Page 86

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 81 -
01 is for f ault clear. Others have no f unction.
CD176 Fault Clear **
Set Range: 00—10 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 00
0: Constant torque 1: For kinds of fan. It can be observed, but not changed.
CD177 Inverter Model
Set Range: 0—1 Unit: 1 Factory Setting: 0
0: 50Hz 1: 60Hz It is factory setting. It can be obser ved, but not set.
0: Holip MODBUS Com mu nicat ion Protocol
1: Sta ndard MODBUS Communication Protocol
It is factory setting. It can be observed, but not set.
CD179 Manufacture date Factory Setting: *
Week
Mont h
Yea r
CD180 Serial No. Factory Set ting: *
C D181 Re s e r v e d
CD183~CD250 Reserved
It is factory setting. It can be observed, but not set.
Note:
* means the said parameter has a variety of set values or should be set
specically according to concrete conditions.
** means the said parameter can be set during the operation.
CD178 Inverter Frequency Standard
Set Range:0~1 Unit:1 Factory Setting:*
CD182 Communication Protocol Select
Set Range:0-1 Unit:1 Factory Setting:0
Page 87

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 82 -
X. Care & Maintenance, Fault Information and
Troubleshooting
Periodical maintenances and inspections will keep your inverter in its normal
state for long time.
1. Precautions about Inspection and Maintenance
● Be sure to turn off the power supply to the inverter (R.S.T) rst before the
inspection and maintenance.
● After conrming the main circuit power supply has been turned off and
the display has disappeared, wait until the internal indicator lamp for high
voltage goes out before perf or ming the inspection and maintenance.
● During the inspection, do not pull out or wrongly distribute the internal
power supply, wires and cables. Other wise it will cause malf u nction or
damage to the inverter.
● Do not leave any screw or other part inside the inverter during the
installation, or it will result in the short circuit of circuit board.
● Keep the inverter clean, f ree f rom dust, oil mist and moisture af ter the
installation.
2. Periodical Inspection and Maintenance items
● Check whether the power supply voltage conforms to the rated voltage of
the inverter.
(Pay special attention to that whether there is any damage on the power
supply wires and the motor.)
● Check whether the wiring terminals and the connectors are tight
(Check whether the power supply wires and terminal connection wires have
any broken strand).
● Check whether there is dust, iron lings or corrosive uid in the inverter.
● Measuring the insulation impedance of the inverter is forbidden.
● Examine the output voltage, output current and output frequency of the
inverter.
(The measuring results should not have too big difference.)
● Check whether the ambient temperature of the inverter is between -5℃ and
40℃ and whether the installation environment has good ventilation.
● Check whether the humidity is kept below 90% (without condensation).
● Check whether the motor makes unusual noises or abnormal vibration in
r u n ning.
(The inver ter should not be installed in a place with high vibration.)
● Please make periodical cleaning of vent holes.
3. Fault Indication and Troubleshooting
Page 88

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 83 -
The inverter of HLP series is relatively perfective with the protection f unctions
of overload, inter-phase shor t circuit, earth short circuit, under-voltage,
overheating and over-cur rent, etc. When a protection f unction happens with
the inverter please check the reasons of faults according to the inf or mation
listed in the table below. The inverter can be restarted af ter the disposal. If the
f ault cannot be disposed please contact the local dist ributor.
Fau l t
Display
Fault Contents &
Descr iption
Disposal methods
E.OC.A
Over-current
during ramp-up
1: Check whether the motor has got short
circuit or par tial short circuit and whether the
insulation of output wire is good.
2: Extend the ramp-up time.
3: The conguration of the inverter is not
reasonable. The inver ter’s capacity should be
increased.
4: Decrease the torque and increase the set
va l u e.
E.OC.n
Over-current at
constant speed
1: Check whether the motor has got short circuit
and whether the insulation of the output wires
is good.
2: Check whether the motor is blocked and
whether there is a sudden change of mechanical
load.
3: Check whether the inverter’s capacity is too
small and increase its capacity.
4: Check whether there is a sudden change in
the power su p ply voltage.
E.OC.d
E.OC.S
Over-current at
decel
Over-current at
stop
1: Check whether the insulation of the out put
wires is good and whether the motor has got
short circuit.
2: Extend the Ramp-down Time.
3: Replace it with an inverter of larger capacity.
4: DC braking is too high. Decrease DC braking.
5: The inverter has f ailure. Please send it to the
factor y for repair.
E.G F.S
E.G F.a
E.G F. n
E.G F.d
Short circuit to
ear th
1: Check whether the connection wire of the
motor has got short circuit.
2: Check whether the insulation of the out put
wires is good.
3: Please send it f or repair.
Page 89

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 84 -
Fau l t
Display
Fault Contents &
Descr iption
Disposal methods
E.o u.S
E.o u.a
E.o u.n
E.o u.d
Over-voltage at stop
Over-voltage at
accel
Over-voltage at
constant speed
Over-voltage at
decel
1: Extend the Ramp-down Time or add a
braking resistor.
2: Improve the mains supply voltage and check
whether there is any sudden change in the
volt age.
E.L u.s
E.Lu.A
E.Lu.n
E.L u.d
Low voltage
1: Check whether the input voltage is normal.
2: Check whether there is sudden change in
load.
3: Check whether there is any phase missing.
E.OH.S
E.OH.A
E.OH.n
E.OH.d
Overheat of
inverter
1: Check whether the f an is blocked and
whether there is any foreign matter stuck in
the cooling ns.
2: Check whether the ambient temperature is
nor m al.
3: Check whether there is enough space for
ventilation and good air convection.
E.OL.A
E.OL.n
E.OL.d
Inver ter overload
150 % P e r m i n u t e
1: Check whether the capacity of the inverter is
lower. Otherwise it should be increased.
2: Check whether there is any jamming in the
mechanical load.
3: The setting of V/F curve is bad. Set it again.
E.OA.A
E.OA.n
E.OA.d
Motor overload
150 % P e r m i n u t e
1: Check whether there is any sudden change in
the mechanical load.
2: The equipped motor is too small.
3: The motor is hot and the insulation becomes
bad.
4: Check whether the voltage has big
uctuation.
5: Check whether there is any phase missing.
6: The mechanical load is increased.
E.O T. A
E.O T. n
E.O T.d
Motor over-torque
1: Check whether there is any uctuation in the
mechanical load.
2: Check whether the equipped motor is smaller.
E.bS.A
E.bS.n
E.bS.d
E.bS.S
No f eedback f rom
auxiliary coil of
the electromagnetic
contactor
Please contact the factor y.
Page 90

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 85 -
Fau l t
Display
Fault Contents &
Descr iption
Disposal methods
E.bT.A
E.bT.n
E.bT.d
Braking transistor
damage
Please send it f or repair.
E.EC.S
E.EC.n
E.EC.d
E.EC.A
CPU f ault Please contact the factory.
E.EE.S
E.EE.n
E.EE.d
E.EE.A
E
2
Prom f ault Please contact the f actor y.
Er External interferences Isolate the interference source
ES Emergency Stop In Emergency Stop
20 4-20mA wire broken Join the broken wires
Pr Setting error Correct the setting
DCb DC braking stat us In DC braking
Note: (1) Fault Code Form as follows:
Stat us
Alarm message
Fau l t
S: A t st o p pi n g
Y A: At accel.
N: At constant speed run
D: A t de c el.
(2) Code Comparison Table:
Apr Parameter setting bad Check parameter ,reset
A.OL Motor Load Alarming
Check load and setup
parameter of motor current
A.OT Over Torque Alarming
Reset over torque level
parameter
A.OA
Inverter Overload
Alarming
Correctly set V/F curve to
check load
Page 91

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 86 -
4. Faults and Analysis
(1) W hen RU N key is pressed, the motor does not r un.
1) The setting of operation mode is wrong, i.e., under the operation mode of
external control terminals, the inverter is started by the digital operator or
under the operation mode of the digital operator it is star ted by the exter nal
cont rol ter minals.
2) The frequency reference is too low or not set.
3) The peripheral wiring is wrong. For example, the setting of wiring of two-
wire system and three-wire system and other related parameters have er rors.
4) The setting of multi-f unction terminals is wrong (in the external control).
5) The inverter is in the fault protection.
6) The motor f ails.
7) The inverter fails.
(2) The parameters cannot be set.
1) Password locks. Please decrypt it rst before resetting.
2) The inverter is in running.
3) The connection of the connecting parts is abnormal. The communication of
the digital operator is abnor mal. Take out the operator af ter power-of f and
then mount it again for a trial.
(3) The motor cannot rotate reverse.
Reverse rotation is disabled.
(4) The motor rotates in the opposite direction.
The output line is wrongly connected. Please change any two lines of U.V.W
over.
(5) The deceleration of the motor is too slow.
1) The setting of Ramp-down Time is too long. Decrease Ramp-down Time.
2) Add a braking resistor.
3) A d d a DC b r ak e.
(6) Over-heat of the motor
1) The load is too large. The actual torque has exceeded the rated torque of the
motor. It is recommended to increase the capacity of the motor.
2) The ambient temperat ure is too high. In a place with higher temperatu re the
motor will be burn out. Please decrease the temperature around the motor.
3) The phase to phase withstand voltage of the motor is insuf cient.
The switch actions of the inverter will make the winding coil of the motor
produce shock wave. Typically the maximum shock voltage will reach 3
times that of input power of the inverter. Please select a motor with higher
Page 92

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 87 -
phase to phase withstand voltage against shock than the maximum shock
volt age.
(7) The starting of the inverter interferes other control devices
1) Decrease the carrier frequency and reduce the number of actions of internal
switches.
2) Install a noise lter at the power input of the inverter.
3) Install a noise lter at the output of the inverter.
4) Make correct grounding for the inverter and the motor.
5) Use metal conduit to tube the cable to shield it.
6) Make separate wiring for the main circuit wires and control wires.
(8) When the fan starts the inverter detected an over-current stall.
1) At start the fan rotates idly. Please set it for DC braking at start.
2) When DC braking at start has been set increase the DC braking value.
(9) The machine has the noise of vibration or roar
1) The vibration f requency of mechanical system resonates with the carrier.
Adjust the carrier to avoid the point of resonance.
2) The vibration f requency of mechanical system resonates with the output
frequency of the inverter.
a. Set it f or skip f unction to avoid the point of resonance.
b. Put rubber vibration isolator on the base plate of motor.
Page 93

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 88 -
XI. Selection of Peripheral Devices and
Disposition
1. Options
Descr iption Functions
NFB or Ground fault
interrupter for wire
connection
Protect the wiring of the inverter. Be sure to install
a breaker at the power. Please select a ground fault
circuit interrupter against high-order harmonics.
Elect romagnetic
contactor
In order to prevent the braking resistor f rom
bur ning out, please add an electromagnetic
contactor and connect a surge absorber to the coil
when using it.
Surge a bsorber
Absorb the switching surge current f rom the
electromagnetic contactor and control relays.
Isolating t ra nsfor mer
Its f unction of isolating the input and output of the
inverter is effective to reduce the interference to
other electric devices.
DC reactor Improve the input power factor of the inverter.
AC reactor
Improve the input power factor of the inverter and
prevent the shock of surge voltage.
Braking resistor, braking
unit
Consume the regenerating energy of the motor and
shorten the ramp-down time.
1) Leakage switch
There is earth static capacity inside of the inverter and the motor as well as
the input and output leads. Due to higher carrier frequency of the inverter the
inverter has higher earth leakage current, especially for the inverters of large
capacity series. When using a leakage switch it may sometimes result in the
error action of the protective circuit. So when using a leakage switch attention
should be paid to its selection and the proper reduction of carrier f requency
and shortening the leads, etc.
2) AC r eactors
An AC reactor can constrict the high-order harmonic of input cur rent of the
inverter to improve its input power factor and prevent the shock of surge. It is
recommended to use an input AC reactor under the f ollowing circumstances:
a~Three-phase power supply is in unbalance.
b~Any equipment with thyristor or power f actor compensation unit with
switching control is connected to the same power supply.
Page 94

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 89 -
3) DC r ea c t or s
It is necessar y to install a DC reactor when the capacity of power supply is
more than 1000 KVA or the mains power capacity is higher than the rated
capacity of the inverter. A DC reactor is also needed for the case with higher
demand on the improvement of power factor of power supply. This DC
reactor can be used together with an AC reactor to achieve the obvious effect
of decreasing high-order harmonic at input. If it is necessary to install a DC
reactor please contact the local distributor.
2. Disposition
1) DC Reactors Disposition
DC Reactor Model
Matched Power
(W)
Rated Current
(A)
Inductance
(mH)
DCL-37 37 10 0 0.7
DCL- 45 45 120 0.58
DCL -55 55 14 6 0.47
DCL-75 75 200 0.35
DCL-90 90 2 38 0.29
D C L -110 110 291 0.24
D C L -132 132 326 0. 215
D C L -16 0 16 0 395 0.17 7
DCL-200 200 494 0.14 2
DCL-220 220 557 0.12 6
DCL-280 280 700 0.10
DC L -300 300 800 0.08
D C L -315 315 800 0.08
DC L -345 345 660 0.07
DCL-375 375 715 0.064
DCL-400 400 765 0.058
D C L - 415 415 795 0.053
Page 95

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 90 -
Connection
①
Remove the jumpers of P and P1 terminals.
②
Connect DC reactor to Terminals P and P1 as shown in the following
diagram:
DC Reactor
Note: HLP inverter of above
37KW has connectors. The
inverter of below 37KW must
not be connected with it.
The f unction of DC reactor is to restrict the AC component stacked with DC
reactor to a specied value to suppress the mains harmonics and improve the
power factor of the inverter.
2) AC Reactors Disposition
AC Reactor Model
Matched Power
(W)
Rated Current
(A)
Inductance
(mH)
HKSG2-24 11 24 0.52
HK SG2-34 15 34 0.397
H K SG 2-38 18 . 5 38 0.352
HKSG2-50 22 50 0.26
HKSG2-60 30 60 0.24
HKSG2-75 37 75 0. 2 35
H K SG 2- 91 45 91 0.17
H K S G 2 -11 2 55 112 0.16
H K SG 2 -15 0 75 150 0 .11 2
H K S G 2-18 0 90 18 0 0 .10
HKSG2-220 110 220 0.09
HKSG2-265 132 265 0.08
HK SG2-30 0 160 30 0 0.07
H K SG 2-360 200 (185) 360 0.06
HKSG2-400 220 400 0.05
HKSG2-560 280 560 0.03
HKSG2-640 315 640 0.0 215
HKSG2-700 345 700 0.019
HKSG2-750 375 750 0.017
HKSG2-800 400 800 0 . 015
HKSG2-860 415 860 0.012
Page 96

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 91 -
AC Reactor
The incoming reactor is also named shif t-changing reactor and it is used for
the incoming wire of the mains with AC f lowing inside. Its function is to
suppress the harmonics of the inverter feedback to the mains.
Inverter Model
Bra king resistor
Specication
Braking torque
10 % ED
Special Motor
KW
W Ω
HL PA00D423C 80 200 125 0.4
HLPA0D7523C 10 0 200 125 0.75
H L P A 01D 523C 300 10 0 12 5 1. 5
HL PA02D223C 30 0 70 125 2.2
HLPA0D7543C 80 750 125 0.75
H L P A 01D 5 4 3C 300 400 125 1.5
HL PA02D243C 30 0 250 12 5 2.2
HLPA03D743B 400 150 125 3.7
HL PA05D543B 500 10 0 12 5 5.5
HLPA07D543B 1000 75 12 5 7.5
H L P A 0 0 11 4 3 B 1000 50 125 11
H L PA 0 015 43B 15 0 0 40 125 15
H L P A 18 D 5 43B 4800 32 12 5 18 . 5
HL PA0022 43B 4800 27.2 125 22
HL PA0030 43B 6000 20 125 30
HLPA003743B 9600 16 125 37
HL PA004543B 9600 13.6 125 45
H L PA 0 05543B 12000 20/2 125 55
HLPA007543B 18000 13. 6 / 2 125 75
HLPA009043B 18000 20/3 125 90
H L P A 0 11 0 4 3 B 18000 20/3 12 5 11 0
H L P A 0132 4 3B 24000 20/4 125 132
Page 97

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 92 -
Inverter Model
Bra king resistor
Specication
Braking torque
10 % ED
Special Motor
KW
W Ω
H L P A 016 0 43B 36000 13.6 / 4 125 16 0
H L P A 0185 4 3B 45000 13.6 / 5 12 5 185
HLPA020043B 45000 13.6 / 5 125 200
HLPA022043B 48000 13.6 /5 125 220
HL PA0250 43B 48000 13.6 / 5 125 250
HL PA0280 43B 57600 13.6 / 6 125 280
HL PA030 0 43B 57600 13.6 / 6 125 30 0
For the braking resistor used for the machines of above 315 KW please contact
t he f a c to r y.
For the inverter of above 11KW to realize quick brake a braking unit must be
added.
Note:
1: Please select the resistor value and operating f requency given by our
com pa n y.
2: If it causes any damage to the inverter and other devices due to the use of
any braking resistor and braking model group not supplied by our company,
we will take no responsibility.
3: Be sure to consider the safety and ignitability of the environment when
installing a braking resistor. The distance to the inverter should be at least 100
mm.
4: If it is necessary to change the resistor value and power value, please contact
the local distributor.
5: In need of a braking resistor a separate order must be placed. Please contact
the local distributor for details.
Page 98

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 93 -
XII. Appendices
Appendix 1: Simple Examples of Application
1. Disturbance Function (Generation of Triangle Wave)
A curve as in lef t is generated.
Parameter setting:
CD076=3 CD000=30
CD080=27 CD086=0.5
C D 0 8 7 = 10 C D 0 8 8 = 10
2. Drawing Function
Parameter setting:
CD076=5 CD000=25 CD080=50 CD081=30
CD087=720 CD052=29 CD033=1
Note:
①
When triggered by external multi-f unction terminals (as RST in the
diagram), the drawing action starts to be implemented.
②
In implementation of drawing action the running time T=CD087×10S
③
FOR/ REV Rotation of the Motor Controlled by One Potentiometer.
Page 99

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 94 -
Parameter setting:
CD033=1 CD034=1 CD066=50 CD068=50
CD067=1 CD069=0 CD070=1
4. Internal Control 8 Speed Run
A curve as shown in the following diagram is established. Internal cont rol
8-speed run will stop after running for one cycle.
Parameter setting:
CD076=4 CD000=30 CD080=50 CD081=30
CD082=20 CD083=40 CD084=10 CD085=35
CD086=15 CD078=36 CD077=0 CD012=5
CD013=5 CD033=1 CD079=0 CD050=1
CD087-CD094=15
Note:
1. The r un ni ng t ime of each speed is set by CD087-CD094=15.
2. Auto cycling CD077=1
3. Af ter the running command is given it will run with the set curve for one
cycle and stop.
Page 100

HLP-A Series
HLP-A Series
- 95 -
5. Linkage of Multi Pumps
At tent ion:
①
The frequency of the main inverter can be set by the potentiometer.
②
The proportion relation of the inverters can be ad justed by CD068.
For exa mple: For F
Inverter1
: F
Inverter2
: F
Inverter3
=1 : 2 : 3 the para mete rs of CD068 can
be adjusted.
Fr eq u e nc y 1 : C D068 =50, Fr eq u e nc y 2 : C D068 =100, F re q ue n cy 3 : C D068=150. I n
case of the analog of 10V, the corresponding frequencies are respectively 50Hz,
100H z, 150H z wit h t he propor tion of .1 : 2 : 3.
③
For easy operation and ad justment a f ine tuning potentiometer can be
added. For concrete application please consult.
 Loading...
Loading...