
Thu Jul 21 2011 14:14 GMT+0900
NT3261_Cover1.indd 1 11/07/27 18:03

1
UL Cautions, Warnings and Instructions xii
Warnings and Cautions for Troubleshooting and Maintenance
The warnings and instructions in this section summarize the procedures necessary to ensure an
inverter installation complies with Underwriters Laboratories
guidelines.
WARNING: Use 60/75C Cu wire only.
WARNING: Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than 100,000 rms
Symmetrical Amperes, 120V maximum.
WARNING: When protected by J class Fuses, or when Protected by Type E
Combination Motor
Controller Having An Interrupting Rating Not Less Than 100,000 rms Symmetrical Amperes, 120
Volts Maximum.
WARNING: Install device in pollution degree 2 environment.
WARNING: Maximum Surrounding Air Temperature 45C (004M),50C(007M).
WARNING: Solid state motor overload protection is provided in each model
WARNING: Integral solid state short circuit protection does not provide branch circuit protection.
Branch circuit protection must be provided in accordance with the National Electric Code and any
additional local codes
2
Terminal symbols and Screw size
Inverter Model Screw Size
Required
Torque (N-m)
Wire range
WJ200-004M M3.5 1.2 AWG12 (3.3mm2)
WJ200-007M M4 1.4 AWG10 (5.3mm2)
Fuse Sizes
The inverter shall be connected with a UL Listed Cartridge Nonrenewable fuse, rated 600Vac
with the current ratings as shown in the table below or Type E Combination Motor Controller
marking is to indicate that the unit shall be connected with, LS Industrial System Co., Ltd, Type E
Combination Motor Controller MMS Series with the ratings as shown in the table below:
Inverter Model
Fuse (UL-rated, class J, 600V ,
Maximum allowable current)
Type E C.M.C.
WJ200-004M
WJ200-007M
50A, AIC 200kA
MMS-32H,
120 V, 40 A
3
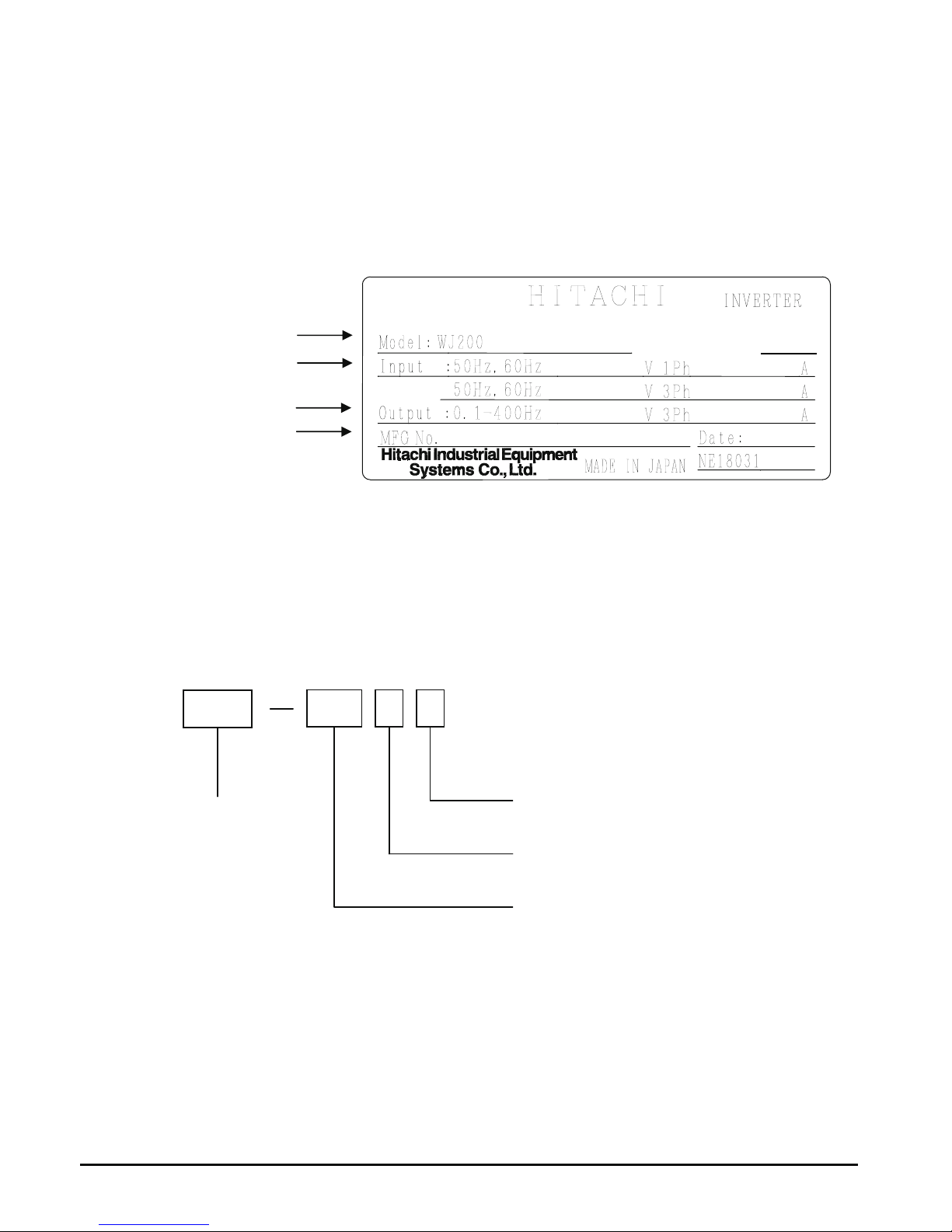
Inverter Specification Label
The Hitachi WJ200 inverters have product labels located on the right side of the housing,
as pictured below. Be sure to verify that the specifications on the labels match your power
source, and application safety requirements.
Inverter Specification Label
The model number for a specific inverter contains useful information about its operating
characteristics. Refer to the model number legend below:
100-120
200-240
14.0
3. 0
1104
14A_T12345_A_-001
-004MF
Model name
Input ratings
Output ratings
MFG number
Ver:2.0
WJ200
004 M F
Series name
Configuration type
F=with keypad
Input voltage:
M=Single-phase 100V class
A
pplicable motor capacity in kW
004=0.4kW
007=0.75kW
4
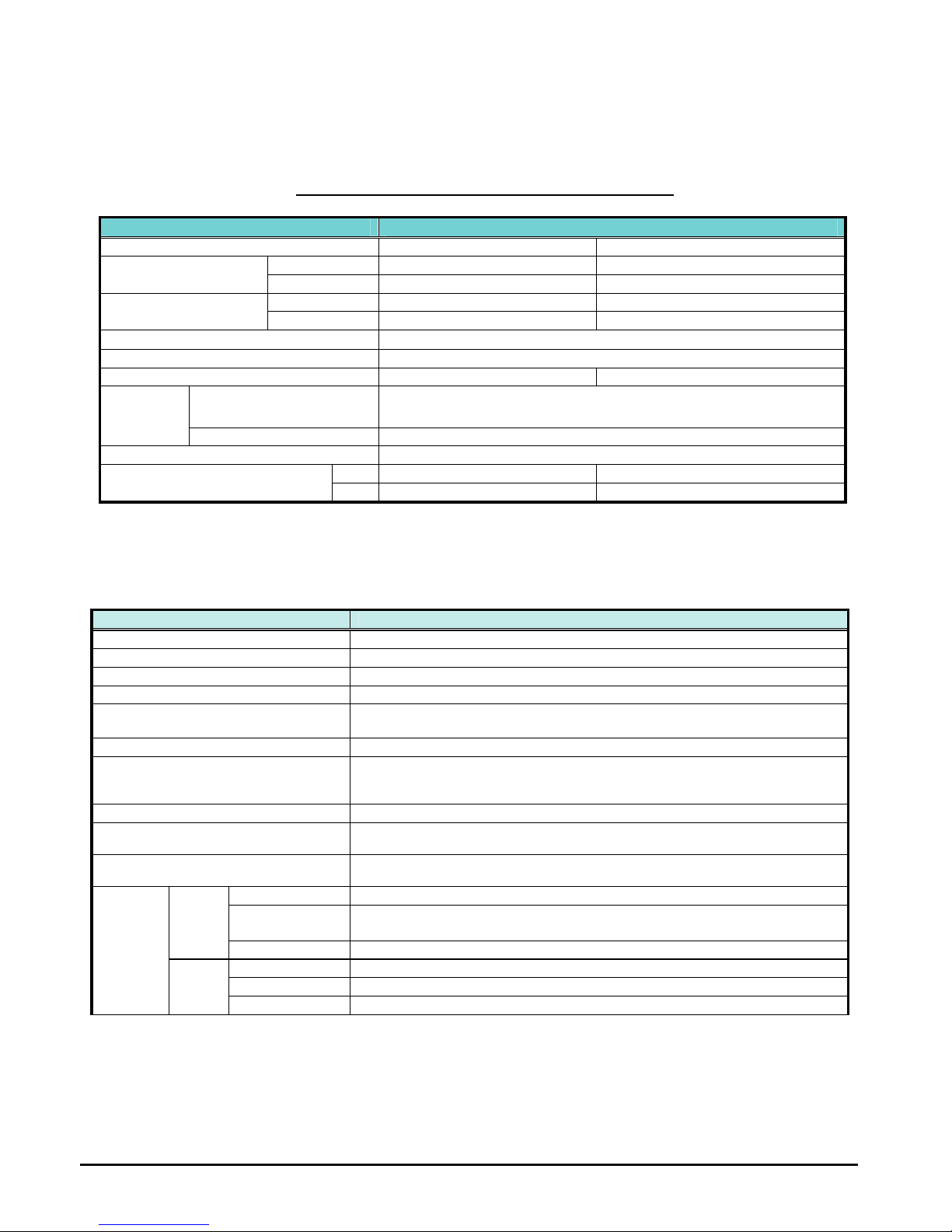
WJ200 Inverter Specifications
Model-specific tables for the Single-phase 100V class inverters
The following tables are specific to WJ200 inverters for the Single-phase 100V class model
groups. Note that “General Specifications” on page in this chapter
apply to both voltage
class groups. Footnotes for all specification tables follow the table below.
Item Single-phase 100V class Specifications
WJ200 inverters, 100V models 004MF 007MF
kW 0.4 0.75 Applicable motor size
HP
1/2 1
100V 1.0 1.7 Rated capacity (kVA)
120V 1.2 2.0
Rated input voltage
Single-phase: 100V to 120V 10%, 50/60Hz 5%
Rated output voltage *3 Three-phase: 200 to 240V (proportional to input voltage)
Rated output current (A) *12 3.0 (2.6) 5.0 (4.0)
Without resistor *6
100%:
50Hz
50%:
60Hz
Braking
With resistor 150%
DC braking Variable operating frequency, time, and braking force
kg 1.1 1.6 Weight
lb 2.4 3.5
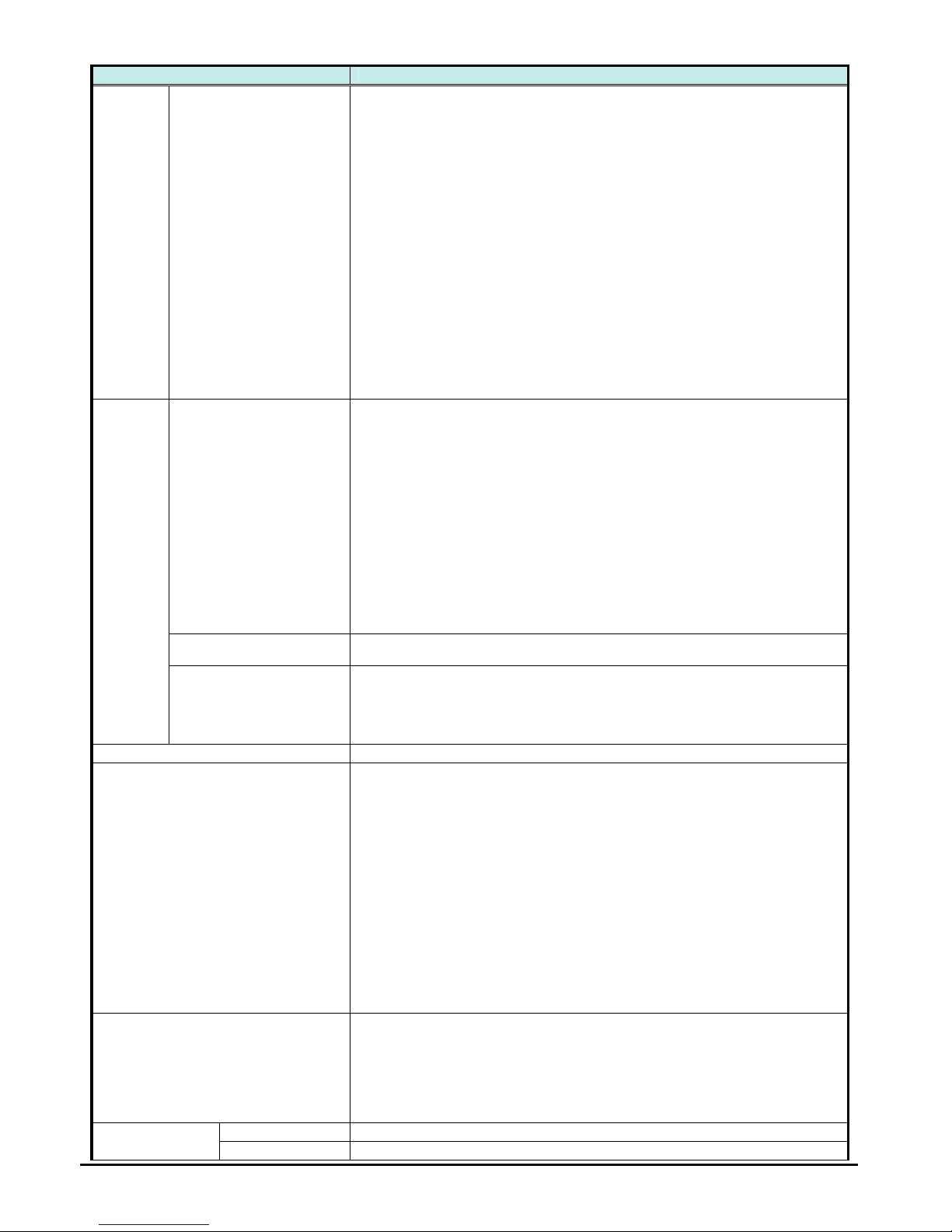
General Specifications
The following table applies to Single-phase 100V class WJ200 inverters.
Item General Specifications
Protective housing *1
IP20
Control method
Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control
Carrier frequency
2kHz to 15kHz (derating required depending on the model)
Output frequency range *4
0.1 to 400Hz
Frequency accuracy
Digital command: 0.01% of the maximum frequency
Analog command: 0.2% of the maximum frequency (25C 10C)
Frequency setting resolution
Digital: 0.01Hz; Analog: max. frequency/1000
Volt./Freq. characteristic
V/f control (constant torque, reduced torque, free-V/F): base freq. 30Hz~400Hz
adjustable,
Sensorless vector control, Closed loop control with motor encoder feedback
Overload capacity
60 sec. @150%
Acceleration/deceleration time
0.01 to 3600 seconds, linear and S-curve accel/decel, second accel/decel
setting available
Starting torque *5
200% @0.5Hz (IM: sensorless vector control)
50% @10% of base frequency (PM: sensorless vector control)
Operator panel
Up and Down keys / Value settings
External signal
*7
0 to 10 VDC (input impedance 10k Ohms), 4 to 20mA (input impedance 100
Ohms), Potentiometer (1k to 2k Ohms, 2W)
Freq.
setting
Via network
RS485 ModBus RTU, other network option
Operator panel
Run/Stop (Forward/Reverse run change by command)
External signal
Forward run/stop, Reverse run/stop
Input
signal
FWD/
REV run
Via network
RS485 ModBus RTU, other network option
5
Item General Specifications
Intelligent input terminal
Seven terminals,
sink/source changeable
by a short bar
68 functions assignable
FW (forward run command), RV (reverse run command), CF1~CF4 (multi-stage
speed setting), JG (jog command), DB (external braking), SET (set second
motor), 2CH (2-stage accel./decel. command), FRS (free run stop command),
EXT (external trip), USP (startup function), CS (commercial power switchover),
SFT (soft lock), AT (analog input selection), RS (reset), PTC (thermistor thermal
protection), STA (start), STP (stop), F/R (forward/reverse), PID (PID disable),
PIDC (PID reset), UP (remote control up function), DWN (remote control down
function), UDC (remote control data clear), OPE (operator control), SF1~SF7
(multi-stage speed setting; bit operation), OLR (overload restriction), TL (torque
limit enable), TRQ1 (torque limit changeover1), TRQ2 (torque limit
changeover2), BOK (Braking confirmation), LAC (LAD cancellation), PCLR
(position deviation clear), ADD (add frequency enable), F-TM (force terminal
mode), ATR (permission of torque command input), KHC (Cumulative power
clear), MI1~MI7 (general purpose inputs for EzSQ), AHD (analog command
hold), CP1~CP3 (multistage-position switches), ORL (limit signal of zero-return),
ORC (trigger signal of zero-return), SPD (speed/position changeover),
GS1,GS2 (STO inputs, safety related signals),
485 (Starting communication
signal), PRG (executing EzSQ program), HLD (retain output frequency), ROK
(permission of run command), EB (rotation direction detection of B-phase),
DISP (display limitation), NO (no function)
Intelligent output terminal
48 functions assignable
RUN (run signal), FA1~FA5 (frequency arrival signal), OL,OL2 (overload
advance notice signal), OD (PID deviation error signal), AL (alarm signal), OTQ
(over/under torque threshold), UV (under-voltage), TRQ (torque limit signal),
RNT (run time expired), ONT (power ON time expired), THM (thermal warning),
BRK (brake release), BER (brake error), ZS (0Hz detection), DSE (speed
deviation excessive), POK (positioning completion), ODc (analog voltage input
disconnection), OIDc (analog current input disconnection), FBV (PID second
stage output), NDc (network disconnect detection), LOG1~LOG3 (Logic output
signals), WAC (capacitor life warning), WAF (cooling fan warning), FR (starting
contact), OHF (heat sink overheat warning), LOC (Low load), MO1~MO3
(general outputs for EzSQ), IRDY (inverter ready), FWR (forward operation),
RVR (reverse operation), MJA (major failure), WCO (window comparator O),
WCOI (window comparator OI), FREF (frequency command source), REF (run
command source), SETM (second motor in operation), EDM (STO (safe torque
off) performance monitor), OP (option control signal), NO (no function)
Monitor output (analog)
Output freq., output current, output torque, output voltage, input power, thermal
load ratio, LAD freq., heat sink temperature, general output (EzSQ)
Output
signal
Pulse train output
(0~10Vdc, 32kHz max.)
[PWM output]
Output freq., output current, output torque, output voltage, input power, thermal
load ratio, LAD freq., heat sink temperature, general output (EzSQ)
[Pulse train output]
Output frequency, output current, pulse train input monitor
Alarm output contact
ON for inverter alarm (1c contacts, both normally open or closed available.)
Other functions
Free-V/f, manual/automatic torque boost, output voltage gain adjustment, AVR
function, reduced voltage start, motor data selection, auto-tuning, motor
stabilization control, reverse running protection, simple position control, simple
torque control, torque limiting, automatic carrier frequency reduction, energy
saving operation, PID function, non-stop operation at instantaneous power
failure, brake control, DC injection braking, dynamic braking (BRD), frequency
upper and lower limiters, jump frequencies, curve accel and decel (S, U,
inversed U,EL-S), 16-stage speed profile, fine adjustment of start frequency,
accel and decel stop, process jogging, frequency calculation, frequency
addition, 2-stage accel/decel, stop mode selection, start/end freq., analog input
filter, window comparators, input terminal response time, output signal
delay/hold function, rotation direction restriction, stop key selection, software
lock, safe stop function, scaling function, display restriction, password function,
user parameter, initialization, initial display selection, cooling fan control,
warning, trip retry, frequency pull-in restart, frequency matching, overload
restriction, over current restriction, DC bus voltage AVR
Protective function
Over-current, over-voltage, under-voltage, overload, brake resistor overload,
CPU error, memory error, external trip, USP error, ground fault detection at
power on, temperature error, internal communication error, driver error,
thermistor error, brake error, safe stop, overload at low speed, modbus
communication error, option error, encoder disconnection, speed excessive,
EzSQ command error, EzSQ nesting error, EzSQ execution error, EzSQ user
trip
Temperature
Operating (ambient): -10 to 40C(*8), / Storage: -20 to 65C(*9)
Operating
environment
Humidity
20 to 90% humidity (non-condensing)
6
Item General Specifications
Vibration *10
5.9m/s2 (0.6G), 10 to 55 Hz
Location
Altitude 1,000m or less, indoors (no corrosive gasses or dust)
Coating color
Black
Options
Remote operator unit, cables for the units, braking unit, braking resistor,
fieldbus
Footnotes for the preceding table and the tables that follow:
Note1: The protection method conforms to JIC C 0920.
Note2: The applicable motor refers to Hitachi standard 3-phase motor (4p). When using other
motors, care must be taken to prevent the rated motor current (50/60Hz) from exceeding the
rated output current of the inverter.
N
ote3: The output voltage decreases as the main supply voltage decreases (except when using
the AVR function). In any case, the output voltage cannot exceed the input power supply voltage.
In any case, the output voltage cannot exceed two times the input power supply voltage
Note4: To operate the motor beyond 50/60Hz, consult the motor manufacturer for the maximum
allowable rotation speed.
Note5: At the rated voltage when using a Hitachi standard 3-phase, 4-pole motor.
Note6: The braking torque via capacitive feedback is the average deceleration torque at the
shortest deceleration (stopping from 50/60Hz as indicated). It is not continuous regenerative
braking torque. The average deceleration torque varies with motor loss. This value decreases
when operating beyond 50Hz. If a large regenerative torque is required, the optional
regenerative braking unit and a resistor should be used.
Note7: The frequency command is the maximum frequency at 9.8V for input voltage 0 to
10VDC, or at 19.6mA for input current 4 to 20mA. If this characteristic is not satisfactory for
your application, contact your Hitachi representative.
Note8: If the inverter is operated outside the region shown in the graph in the derating curve,
the inverter may be damaged or its service life may be shortened. Set B083 Carrier Frequency
Adjustment in accordance with the expected output current level. See derating curve section
for the detailed information of the inverter operating range.
Note9: The storage temperature refers to the short-term temperature during transportation.
Note10: Conforms to the test method specified in JIS JIS C 60068-2-6 :2010(IEC
60068-2-6:2007). For the model types excluded in the standard specifications, contact your
Hitachi sales representative.
Note11: Watt losses are calculated values based on specification of main semi-conductors. You
must take suitable margin when designing cabinet based on these values. Otherwise there is a
possibility of heating trouble.
Note12: “When the ambient temperature exceeds 40C, output current must be limited to the
value in ( ).
Signal Ratings
Detailed ratings are in “Control Logic Signal Specifications” in Page 16.
Signal / Contact Ratings
Built-in power for inputs 24VDC, 100mA maximum
Discrete logic inputs 27VDC maximum
Discrete logic outputs 50mA maximum ON state current, 27 VDC maximum OFF state voltage
Analog output 10bit / 0 to 10VDC, 2mA
Analog input, current 4 to 19.6 mA range, 20mA nominal
Analog input, voltage
0 to 9.8 VDC range, 10VDC nominal, input impedance 10k
+10V analog reference 10VDC nominal, 10mA maximum
Alarm relay contacts 250 VAC, 2.5A (R load) max., 0.2A (I load, P.F.=0.4) max.
100 VAC, 10mA min
30 VDC, 3.0A (R load) max., 0.7A (I load, P.F.=0.4) max.)
5 VDC, 100mA min.
7
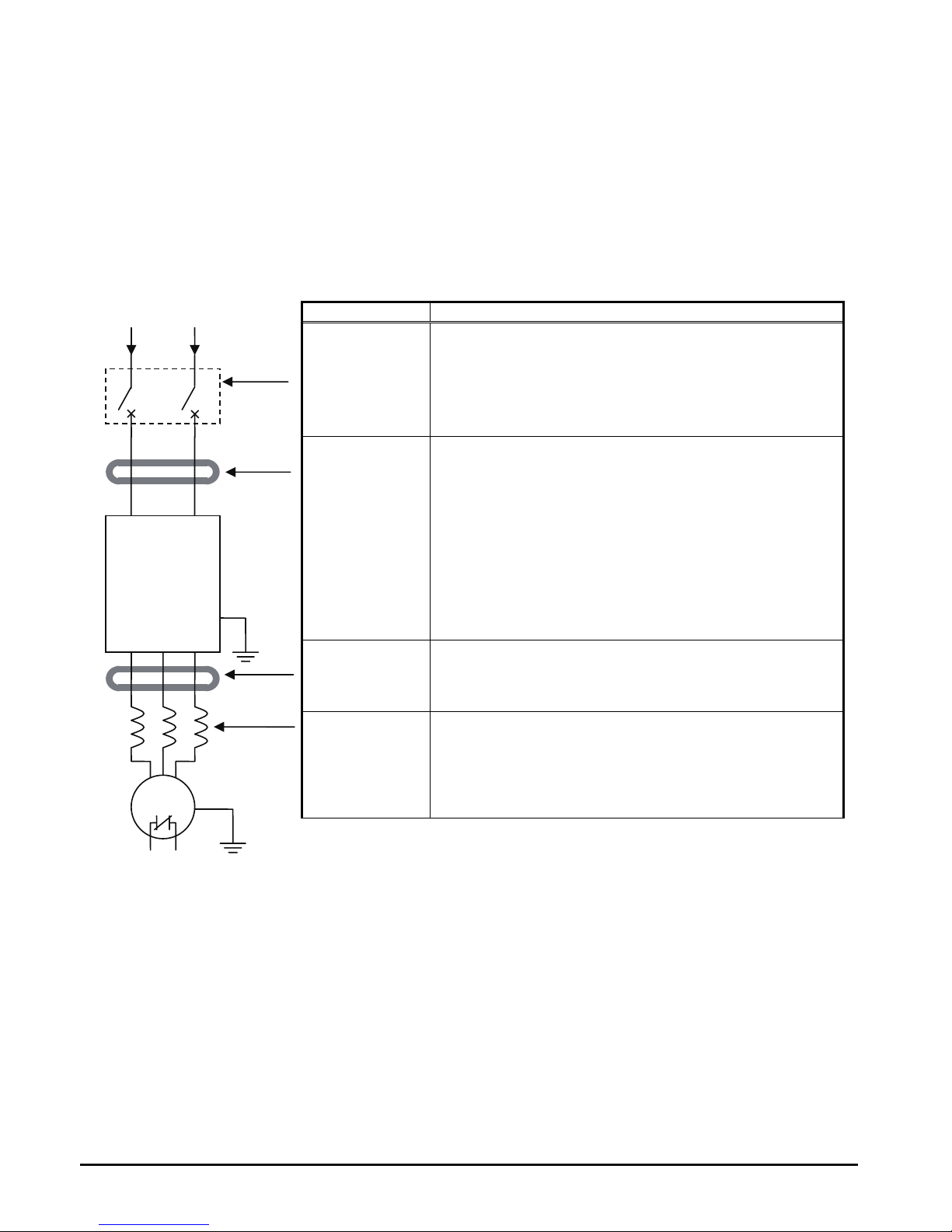
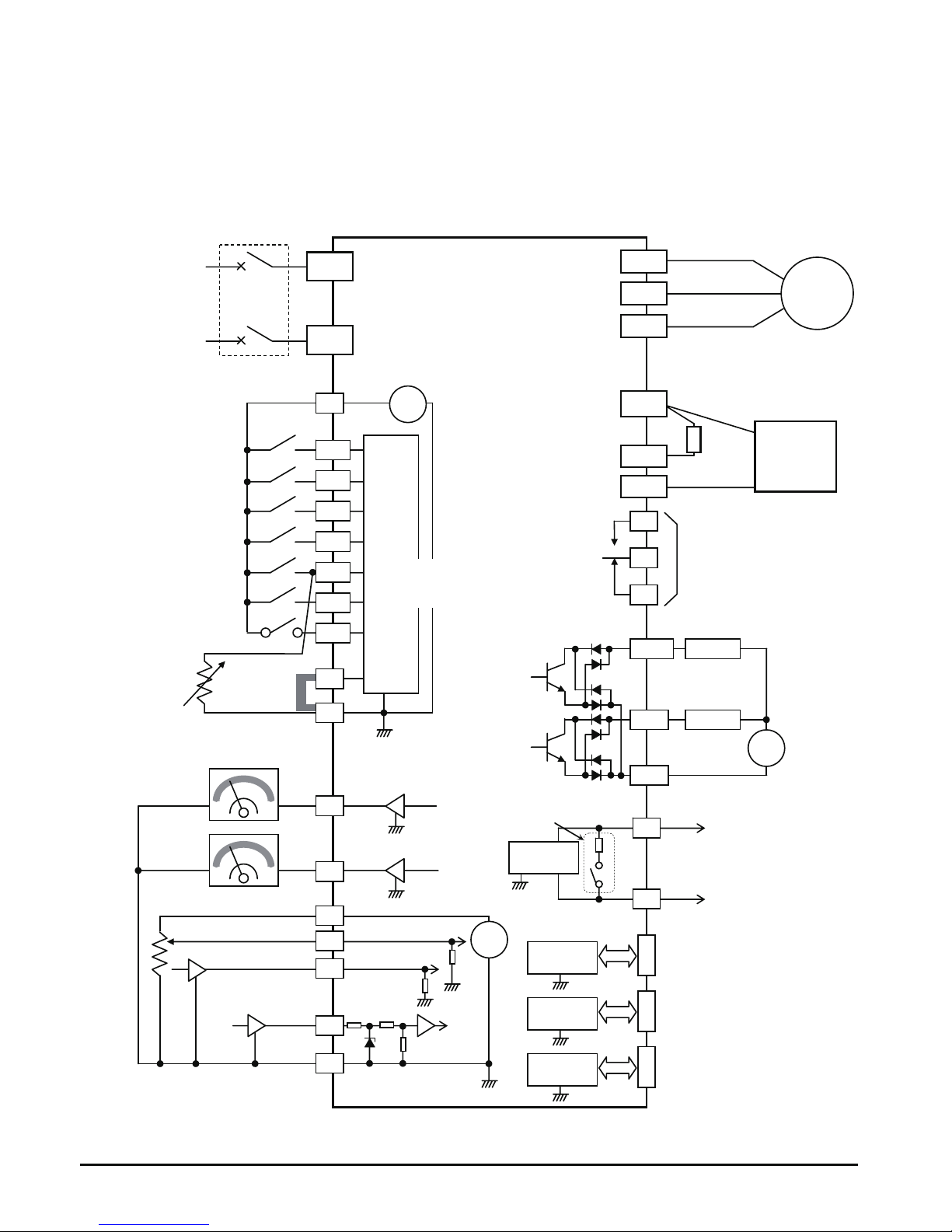
Basic System Description
A motor control system will obviously include a motor and inverter, as well as a circuit
breaker or fuses for safety. If you are connecting a motor to the inverter on a test bench
just to get started, that’s all you may need for now. But a system can also have a variety of
additional components. Some can be for noise suppression, while others may enhance the
inverter’s braking performance. The figure and table below show a system with all the
optional components you might need in your finished application.
Name Function
Breaker /
disconnect
A molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB), ground fault
interrupter (GFI), Type E Combination Motor
Controller(Type E C.M.C) or a fused disconnect device.
NOTE: The installer must refer to the NEC and local codes
to ensure safety and compliance.
Radio noise filter
Electrical noise interference may occur on nearby
equipment such as a radio receiver. This magnetic choke
filter helps reduce radiated noise (can also be used on
output).
Radio noise filter
Electrical noise interference may occur on nearby
equipment such as a radio receiver. This magnetic choke
filter helps reduce radiated noise (can also be used on
input).
Output-side
AC Reactor
This reactor reduces the vibration in the motor caused by
the inverter’s switching waveforms, by smoothing the
waveform to approximate commercial power quality. It is
also useful to reduce harmonics when wiring from the
inverter to the motor is more than 10m in length.
From power supply
Breaker,
MCCB or
GFI
M
Thermal
switch
L1 N
T1 T2 T3
Inverter
GND

8
Determining Wire and Fuse Sizes
The maximum motor currents in your application determines the recommended wire size.
The following table gives the wire size in AWG. The “Power Lines” column applies to the
inverter input power, output wires to the motor, the earth ground connection, and any other
components shown in the “Basic System Description” on page 7. The “Signal Lines”
column applies to any wire connecting to the two green connectors just inside the front
cover panel.
Motor Output Wiring Applicable equipment
kW HP
Inverter Model
Power
Lines
Signal Lines
Fuse (UL-rated,
class J, 600V ,
Maximum
allowable
current)
Typ e E
C.M.C.
0.4 1/2
WJ200-004MF
AWG12 /
3.3mm2
50A
MMS-32H,
120 V, 40 A
0.75
1
WJ200-007MF
AWG10 /
5.3mm
2
18 to 28
AWG / 0.14
to 0.75 mm
2
shielded wire
(see Note 4)
50A
MMS-32H,
120 V, 40 A
Note 1: Field wiring must be made by a UL-Listed and CSA-certified closed-loop terminal
connector sized for the wire gauge involved. Connector must be fixed by using
the crimping tool specified by the connector manufacturer.
Note 2: Be sure to consider the capacity of the circuit breaker to be used.
Note 3: Be sure to use a larger wire gauge if power line length exceeds 66ft. (20m).
Note 4: Use 18 AWG / 0.75mm
2
wire for the alarm signal wire ([AL0], [AL1], [AL2]
terminals).
Note 5: Type E Combination Motor Controller marking is to indicate that the unit shall be
connected with, LS Industrial System Co., Ltd, Type E Combination Motor
Controller MMS Series .
9
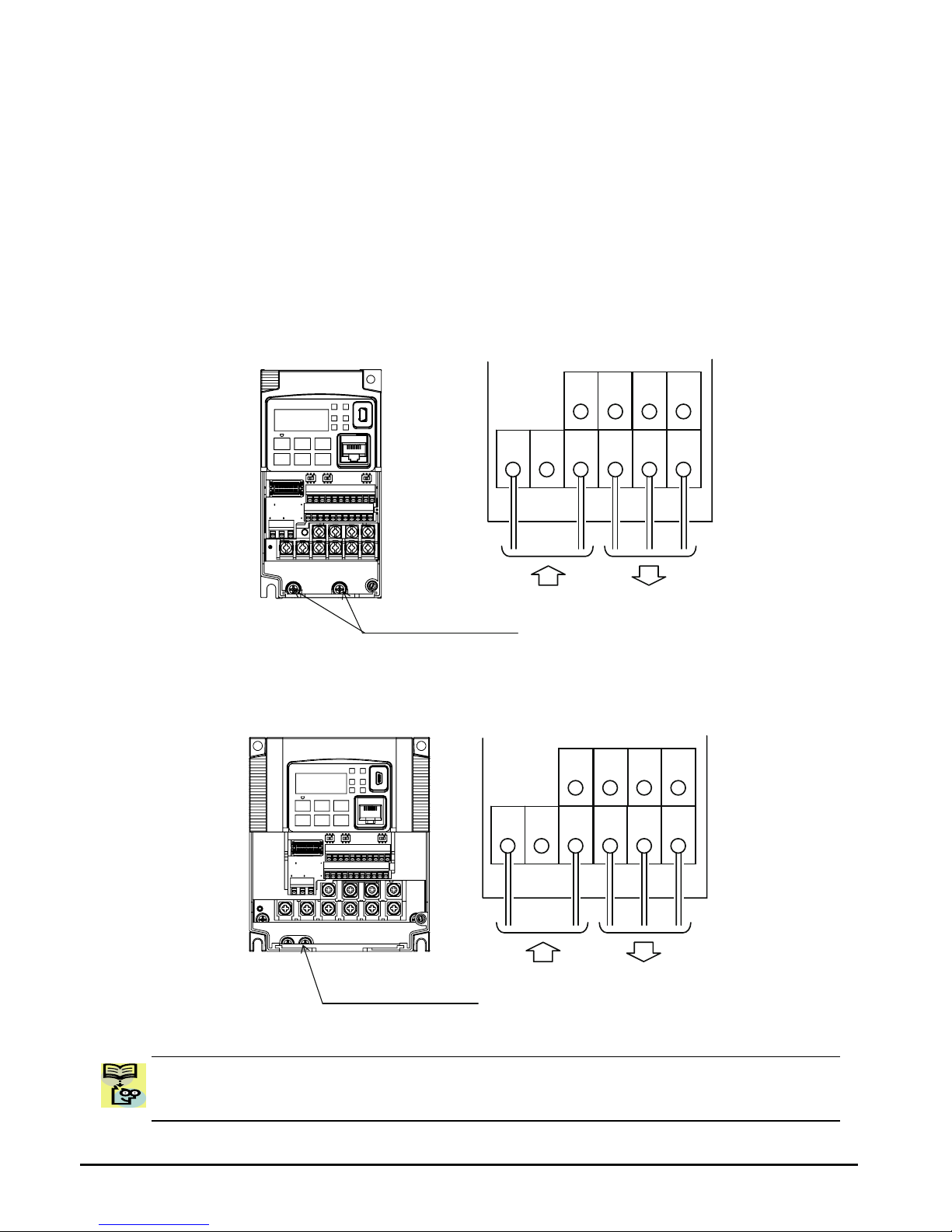
Wire the Inverter Input to a Supply
In this step, you will connect wiring to the input of the inverter. This Inverter is single-phase
power only. The power connection terminals are [L1] and [N]. So you must refer to the
specifications label (on the side of the inverter) for the acceptable power source
types!
Single-phase inverter models will have no connection to the [S/L2] terminal.
This is only used for three-phase models.
Note the use of ring lug connectors is
recommended
for a secure connection.
Single-phase 100V 0.4kW
Single-phase 100V 0.75kW
NOTE: An inverter powered by a portable power generator may
cause a distorted power
waveform, overheating the generator. In general, the generator capacity should be five
times that of the inverter (kVA).
Chassis Ground (M4)
Chassis Ground (M4)
Single-phase
L1
Power input Output to Motor
N U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
RB
P/+
-
Single-phase
Power input Output to Motor
L1
N U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
RB P/+
-
10
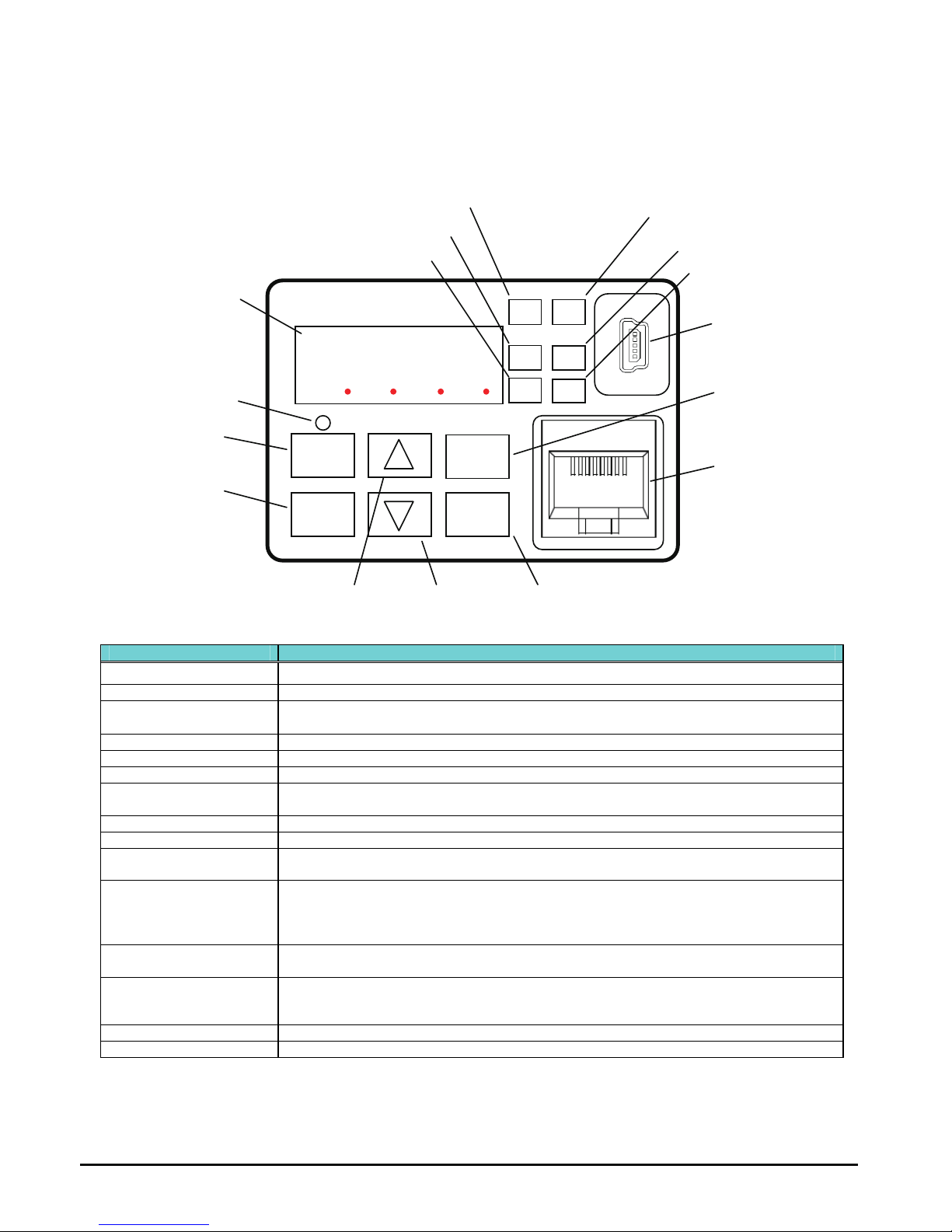
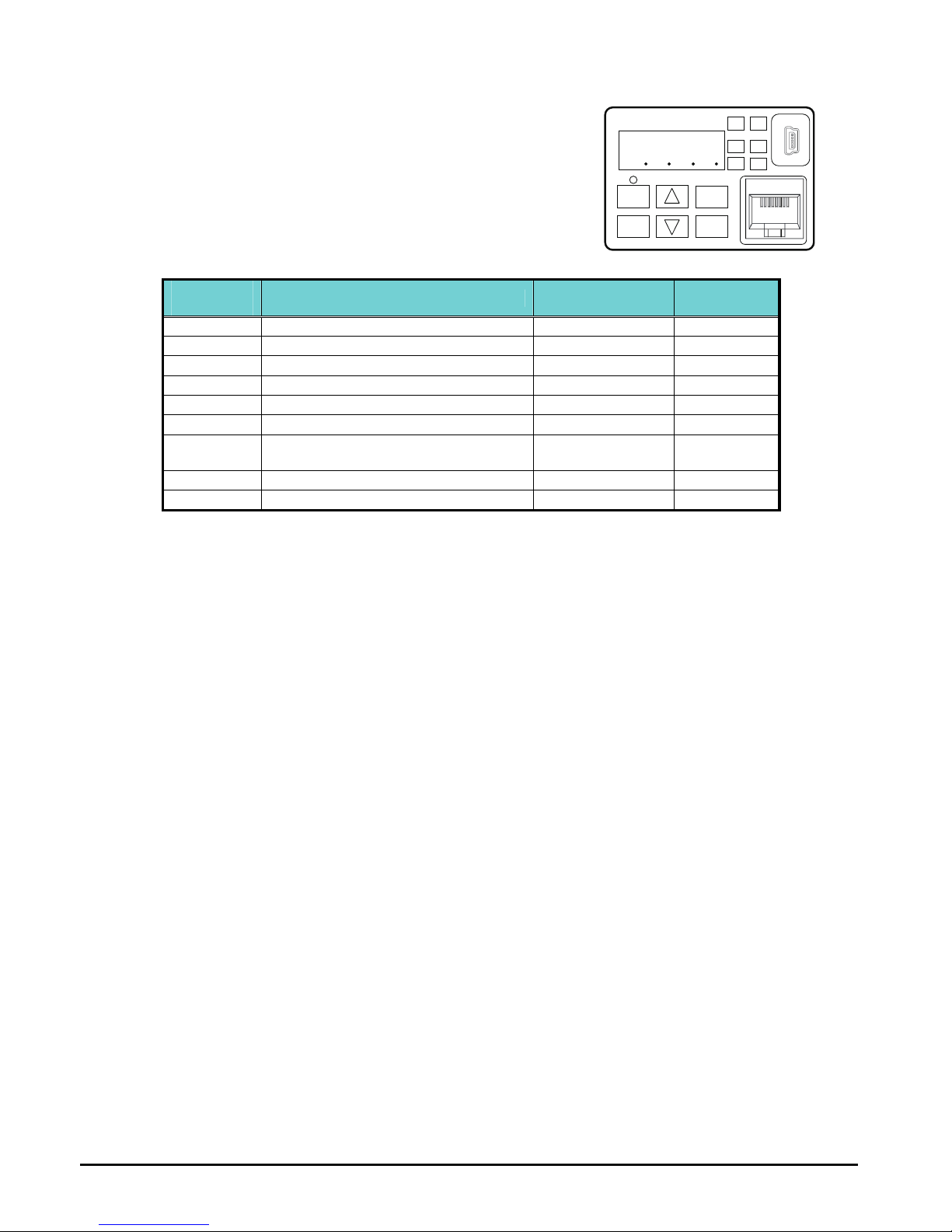
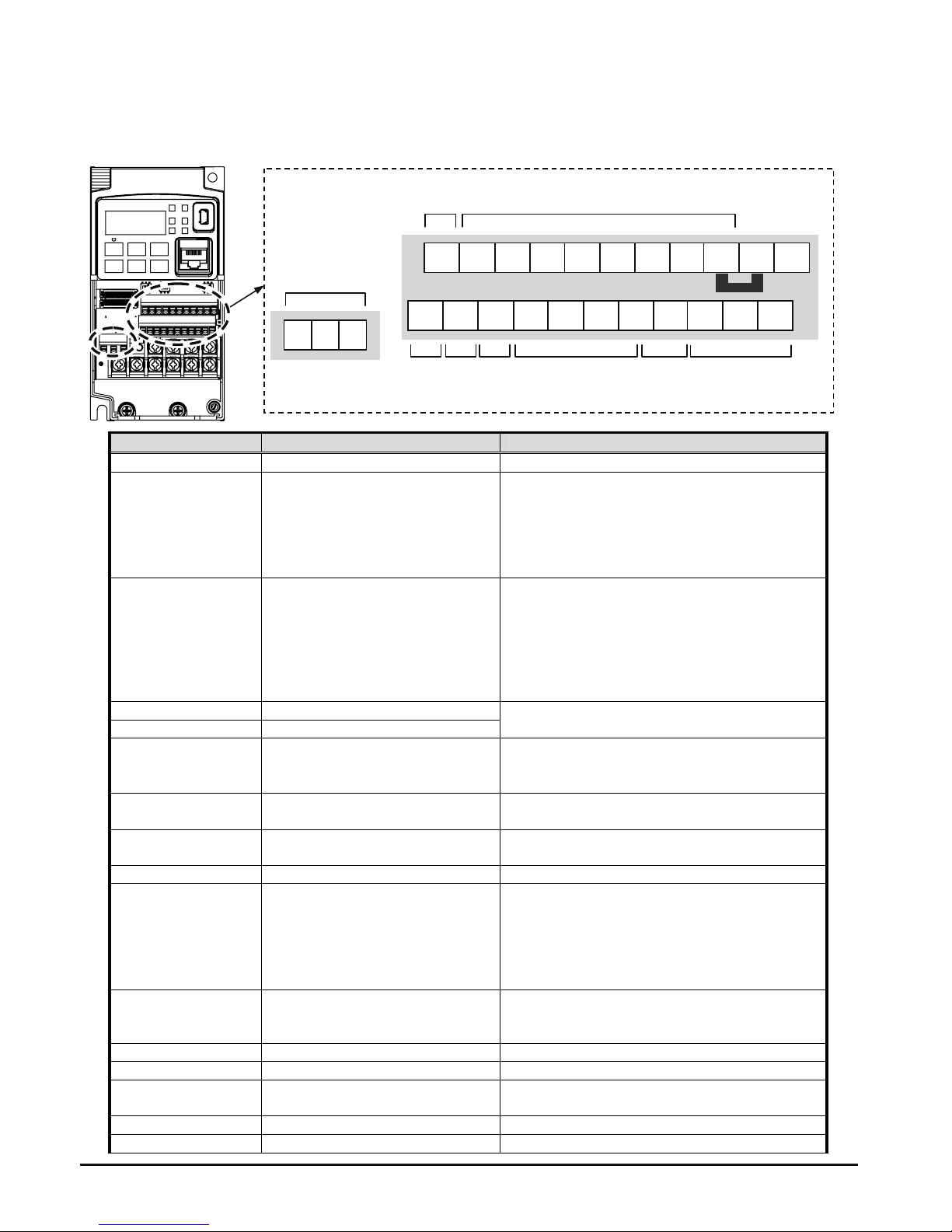
Using the Front Panel Keypad
Please take a moment to familiarize yourself with the keypad layout shown in the figure
below. The display is used in programming the inverter’s parameters, as well as monitoring
specific parameter values during operation.
Key and Indicator Legend
Items Contents
(1) POWER LED Turns ON (Green) while the inverter is powered up.
(2) ALARM LED Turns ON (Red) when the inverter trips.
(3) Program LED
¾ Turns ON (Green) when the display shows changeable parameter.
¾ Blinks when there is a mismatch in setting.
(4) RUN LED Turns ON (Green) when the inverter is driving the motor.
(5) Monitor LED [Hz] Turns ON (Green) when the displayed data is frequency related.
(6) Monitor LED [A] Turns ON (Green) when the displayed data is current related.
(7) Run command LED
Turns ON (Green) when the RUN command source is set to the operator. (Run key is
effective.)
(8) 7-seg LED Shows each parameter, monitors etc.
(9) RUN key Makes inverter run.
(10) STOP/RESET key
¾ Makes inverter stop, according to parameter setup.
¾ Reset the inverter when it is in trip situation
(11) ESC key
¾ Go to the top of next function group, when a function mode is shown
¾ Cancel the setting and return to the function code, when a data is shown
¾ Moves the cursor to a digit left, when it is in digit-to-digit setting mode
¾ Pressing for 1 second leads to display data of d001, regardless of current display.
(12) Up key
(13) Down key
¾ Increase or decrease the data.
¾ Pressing the both keys at the same time gives you the digit-to-digit edit.
(14) SET key
¾ Go to the data display mode when a function code is shown
¾ Stores the data and go back to show the function code, when data is shown.
¾ Moves the cursor to a digit right, when it is in digit-to-digit display mode
(15) USB connector Connect USB connector (mini-B) for using PC communication
(16) RJ45 connector Connect RJ45 jack for remote operator
1
2
RUN
ESC
STOP/
RESET
SET
8888
RUN
Hz A
PWR
ALM
PRG
(1) POWER LED
(2) ALARM LED
(8) 7-seg LED
(4) RUN LED
(10) STOP/RESET key
(15) USB connector
(3) Program LED
(16) RJ45 connector
(14) SET key
(13) Down key (12) Up key
(11) ESC key
(9) RUN key
(7) Run command LED
(5) Monitor LED [Hz]
(6) Monitor LED [A]
11
Keys, Modes, and Parameters
The purpose of the keypad is to provide a way to
change modes and parameters. The term function
applies to both monitoring modes and parameters.
These are all accessible through function codes that are
primary 4-character codes. The various functions are
separated into related groups identifiable by the
left-most character, as the table shows.
Function
Group
Type (Category) of Function Mode to Access
PRG LED
Indicator
“d” Monitoring functions Monitor
“F” Main profile parameters
Program
z
“A” Standard functions
Program
z
“b” Fine tuning functions
Program
z
“C” Intelligent terminal functions
Program
z
“H” Motor constant related functions
Program
z
“P” Pulse train input, torque, EzSQ, and
communication related functions
Program
z
“U” User selected parameters
Program
z
“E” Error codes
You can see from the following page how to monitor and/or program the parameters.
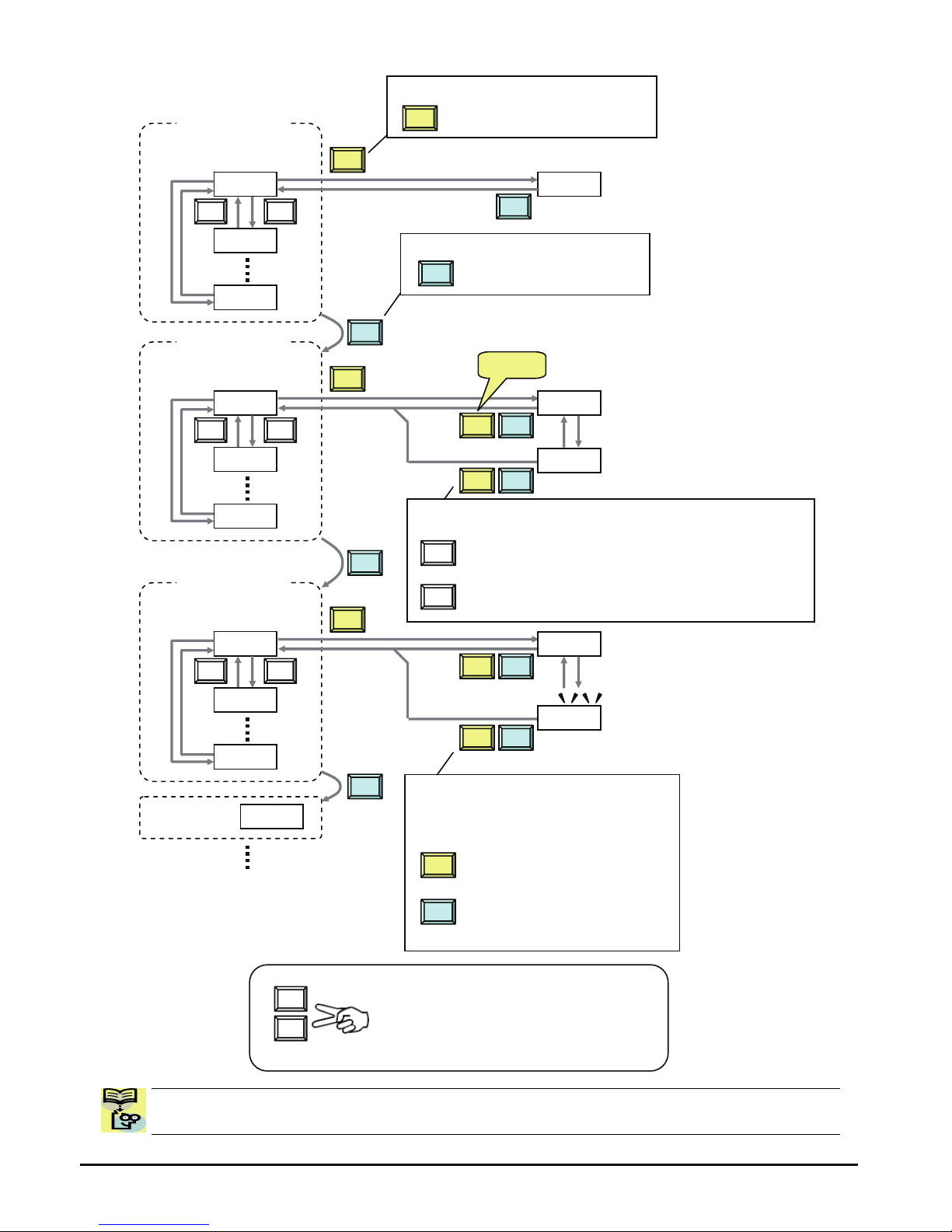
Keypad Navigation Map
The WJ200 Series inverter drives have many programmable functions and parameters.
Chapter 3 will cover these in detail, but you need to access just a few items to perform the
powerup test. The menu structure makes use of function codes and parameter codes to
allow programming and monitoring with only a 4-digit display and keys and LEDs. So, it is
important to become familiar with the basic navigation map of parameters and functions in
the diagram below. You may later use this map as a reference.
1
2
RUN
ESC
STOP/
RESET
SET
8888
RUN
Hz
A
PWR
ALM
PRG
12
NOTE: Pressing the [ESC] key will make the display go to the top of next function group,
regardless the display contents. (e.g. A021 Æ [ESC] Æ b001)
U
V
Press the both up and down key at the same
time in func. code or data display, then
single-digit edit mode will be enabled.
Refer to 2-34 for further information.
d001
V U
ESC
SET
Group "d"
Func. code display
0.00
d002
d104
F001
V U
Group "F"
Func. code display
F002
F004
50.00
50.01
SET
SET ESC
SET ESC
Save
A001
V U
Group "A"
Func. code display
A002
A165
00
01
SET
SET ESC
SET ESC
Data display
When data is changed, the display
starts blinking, which means that
new data has not been activated yet.
: Saves the data in EEPROM and
returns to func. code display.
: Cancels the data change and
returns to func. code display.
SET
ESC
Group "b"
b001
ESC
Func. code display
: Jumps to the next group
ESC
Func. code display
: Moves to data display
SET
ESC
ESC
Data display (F001 to F003)
Data does not blink because of real time synchronizing
: Saves the data in EEPROM
and returns to func. code display.
: Returns to func. code display without saving data.
SET
ESC
13
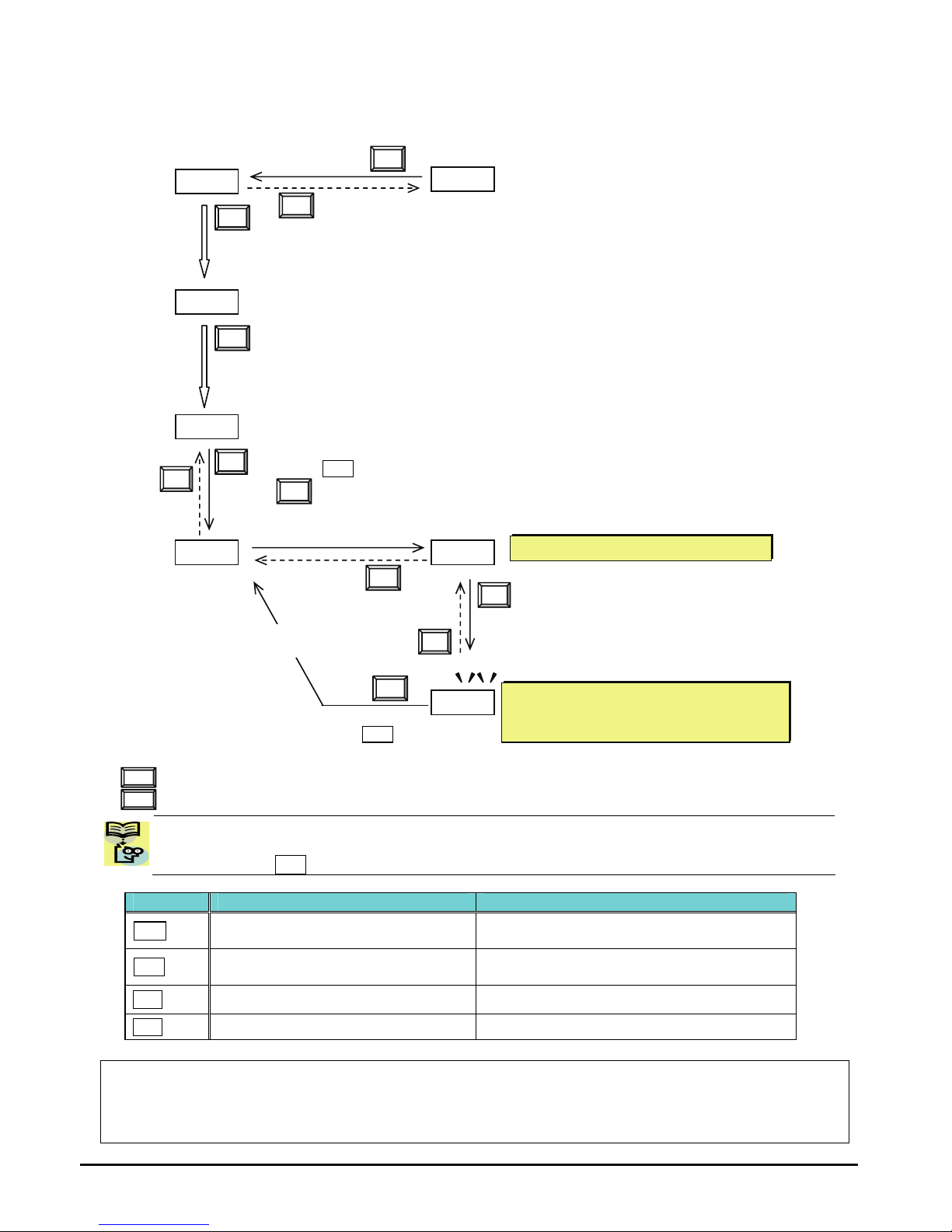
[Setting example]
After power ON, changing from 0.00 display to change the b083 (carrier frequency) data.
Function code dxxx are for monitor and not possible to change.
Function codes Fxxx other than F004 are reflected on the performance just after changing the data
(before pressing SET key), and there will be no blinking.
When a function code is shown… When data is shown…
ESC key Move on to the next function group
Cancels the change and moves back to the
function code
SET key Move on to the data display
Fix and stores the data and moves back to
the function code
U key
Increase function code Increase data value
V key
Decrease function code Decrease data value
Note
Keep pressing for more than 1 second leads to d001 display, regardless the display situation. But note that
the display will circulates while keep pressing the [ESC] key because of the original function of the key.
(e.g. F001 Æ A001 Æ b001 Æ C001 Æ …Æ displays 50.00 after 1 second)
b001
b083 5.0
Display is lit solidy
12.0
F001
d001
0.00
c Data of d001 will be shown on the
display after the first power ON
d Press [ESC] key to show
the function code
e Press [ESC] key to move
on to the function group F001
f Press [ESC] key twice to move
on to the function group b001.
g Press Up key to change increase
function code (b001
Æ b083)
h Press SET key to display the data of b083
i Press SET key to set
and save the data
When data is changed, the display
starts blinking, which means that new
data has not been activated yet.
ESC
U
V
SET
ESC
ESC
SET
ESC
U
V
:Fix and stores the data and moves back to the function code
:Cancels the change and moves back to the function code
SET
ESC
SET
i Press up key to increase the
data (5.0 Æ 12.0)
14
Connecting to PLCs and Other Devices
Hitachi inverters (drives) are useful in many types of applications. During installation, the
inverter keypad (or other programming device) will facilitate the initial configuration. After
installation, the inverter will generally receive its control commands through the control
logic connector or serial interface from another controlling device. In a simple application
such as single-conveyor speed control, a Run/Stop switch and potentiometer will give the
operator all the required control. In a sophisticated application, you may have a
programmable logic controller (PLC) as the system controller, with several connections to
the inverter.
It is not possible to cover all the possible types of application in this manual. It will be
necessary for you to know the electrical characteristics of the devices you want to connect
to the inverter. Then, this section and the following sections on I/O terminal functions can
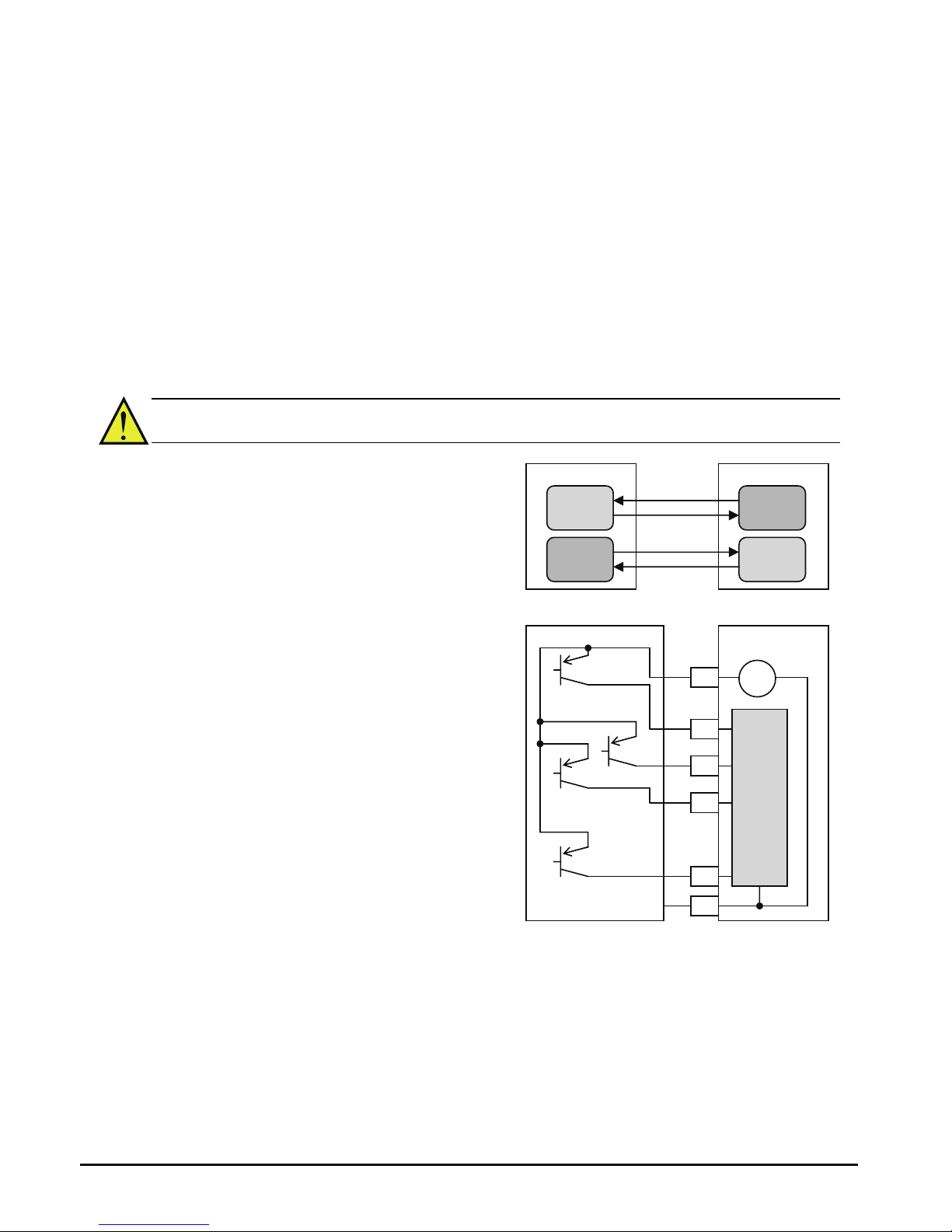
help you quickly and safely connect those devices to the inverter.
CAUTION: It is possible to damage the inverter or other devices if your application
exceeds the maximum current or voltage characteristics of a connection point.
The connections between the inverter and
other devices rely on the electrical input/output
characteristics at both ends of each connection,
shown in the diagram to the right.
The inverter’s configurable inputs accept either
a sourcing or sinking output from an external
device (such as PLC). This chapter shows the
inverter’s internal electrical component(s) at
each I/O terminal. In some cases, you will
need to insert a power source in the interface
wiring.
In order to avoid equipment damage and get
your application running smoothly, we
recommend drawing a schematic of each
connection between the inverter and the other
device. Include the internal components of
each device in the schematic, so that it makes
a complete circuit loop.
After making the schematic, then:
1. Verify that the current and voltage for each
connection is within the operating limits of
each device.
2. Make sure that the logic sense (active high or active low) of any ON/OFF connection is
correct.
3. Check the zero and span (curve end points) for analog connections, and be sure the
scale factor from input to output is correct.
4. Understand what will happen at the system level if any particular device suddenly
loses power, or powers up after other devices.
Other device
Input
circuit
Output
circuit
WJ200 inverter
Input
circuit
Output
circuit
signal
return
signal
return
Other device WJ200 inverter
Input
circuits
P24
1
2
3
7
L
24V
+ -
GND
…
…
15
Example Wiring Diagram
The schematic diagram below provides a general example of logic connector wiring, in
addition to basic power and motor wiring converted in Chapter 2. The goal of this chapter
is to help you determine the proper connections for the various terminals shown below for
your application needs.
Breaker, MCCB
or GFI
Power source,
1-phase,
inverter model
Input
circuits
24V
P24
+ -
1
2
3/GS1
4/GS2
5/PTC
Forward
Thermistor
Intelligent inputs,
7 terminals
GND for logic inputs
NOTE: For the wiring
of intelligent I/O and
analog inputs, be sure
to use twisted pair /
shielded cable. Attach
the shielded wire for
each signal to its
respective common
terminal at the inverter
end only.
Input impedance of
each intelligent input is
4.7k
[5] configurable as
discrete input or
thermistor input
AM
Meter
H
L
A
nalog reference
0~10VDC
4~20mA
GND for analog signals
WJ200
Moto
r
P/+
L1
N
U(T1)
V(T2)
W(T3)
-
AL1
AL0
AL2
Relay contacts,
type 1 Form C
6
7/EB
EO
Meter
Pulse train input
24Vdc 32kHz max.
RB
Brake
resistor
(optional)
11/ EDM
Load
Freq. arrival signal
Open collector output
Output circuit
GND for logic outputs
12
Load
+
CM2
L
L
+
O
OI
EA
A
pprx.10k
10Vdc
A
pprx.100
RS485
transceiver
RJ45 port
(Optional operator port)
USB
transceiver
USB (mini-B) port
(PC communication port)
USB power: Self power
L
L
Option port
controller
Option port connector
L
L
L
L
L
SP
SN
RS485
transceiver
Termination resistor (200)
(Change by slide switch)
Serial communication port
(RS485/ModBus)
L
PLC
Short bar
(Source type)
NOTE: Common for
RS485 is “L”.
Braking
unit (optional)
16
Control Logic Signal Specifications
The control logic connectors are located just behind the front housing cover. The relay
contacts are just to the left of the logic connectors. Connector labeling is shown below.
Terminal Name Description Ratings
P24 +24V for logic inputs 24VDC, 100mA. (do not short to terminal L)
PLC Intelligent input common To change to sink type, remove the short bar
between [PLC] and [L], and connect it
between [P24] and [L]. In this case,
connecting [L] to [1]~[7] makes each input
ON. Please remove the short bar when using
external power supply.
1
2
3/GS1
4/GS2
5/PTC
6
7/EB
Discrete logic inputs
(Terminal [3],[4],[5] and [7]
have dual function. See
following description and
related pages for the details.)
27VDC max. (use PLC or an external supply
referenced to terminal L)
GS1(3) Safe stop input GS1
GS2(4) Safe stop input GS2
Functionality is based on ISO13849-1
See appendix for the details.
PTC(5) Motor thermistor input Connect motor thermistor between PTC and
L terminal to detect the motor temperature.
Set 19 in C005.
EB(7) Pulse train input B 2kHz max.
Common is [PLC]
EA Pulse train input A 32kHz max.
Common is [L]
L (in upper row) *1 GND for logic inputs Sum of input [1]~[7] currents (return)
11/EDM Discrete logic outputs [11]
(Terminal [11] has dual
function. See following
description and related pages
for the details.)
50mA max. ON state current,
27 VDC max. OFF state voltage
Common is CM2
In case the EDM is selected, the functionality
is based on ISO13849-1
4VDC max. ON state voltage depression
12 Discrete logic outputs [12] 50mA max. ON state current,
27 VDC max. OFF state voltage
Common is CM2
CM2 GND for logic output 100 mA: [11], [12] current return
AM Analog voltage output 0~10VDC 2mA maximum
EO Pulse train output 10VDC 2mA maximum
32kHz maximum
L (in bottom row) *2 GND for analog signals Sum of [OI], [O], and [H] currents (return)
OI Analog current input 4 to 19.6 mA range, 20 mA nominal,
Analog
out
p
ut
Logic inputs
Logic
out
p
ut
Short bar
PLC
Analog
in
p
ut
Pulse
Train
input
Pulse
Train
out
put
RS485
comm.
RS485
comm.
P24 1 L 3 2
5 4 6
SN 7
12 11 AM CM2
OI L H O EA
SP EO
AL2AL1A
L0
Relay
contacts
17
Terminal Name Description Ratings
input impedance 100
O Analog voltage input 0 to 9.8 VDC range, 10 VDC nominal,
input impedance 10 k
H +10V analog reference 10VDC nominal, 10mA max.
SP, SN Serial communication terminal For RS485 Modbus communication.
AL0, AL1, AL2 *3 Relay common contact 250VAC, 2.5A (R load) max.
250VAC, 0.2A (I load, P.F.=0.4) max.
100VAC, 10mA min.
30VDC, 3.0A (R load) max.
30VDC, 0.7A (I load, P.F.=0.4) max.
5VDC, 100mA min.
Note 1: The two terminals [L] are electrically connected together inside the inverter.
Note 2: We recommend using [L] logic GND (to the right) for logic input circuits and [L]
analog GND (to the left) for analog I/O circuits.
Note 3: Refer to page 39 for details of trip signals.
Wiring sample of control logic terminal (source logic)
Note: If relay is connected to intelligent output, install a diode across the relay coil
(reverse-biased) in order to suppress the turn-off spike.
Sink/source logic of intelligent input terminals
Sink or source logic is switched by a short bar as below.
SP EO EA H O OI L AM CM2 12 11/EDM
Freq. meter
Variable resistor
for freq. setting
(1k
-2k
)
Short bar
(
source logic
)
RY
SN 7/EB 6 5/PTC 4/GS2 3/GS1
1 L PLC P24
RY
Short bar
PLC P24
L 1 2
Sink logic
Short bar
PLC P24 L
1 2
Source logic
18
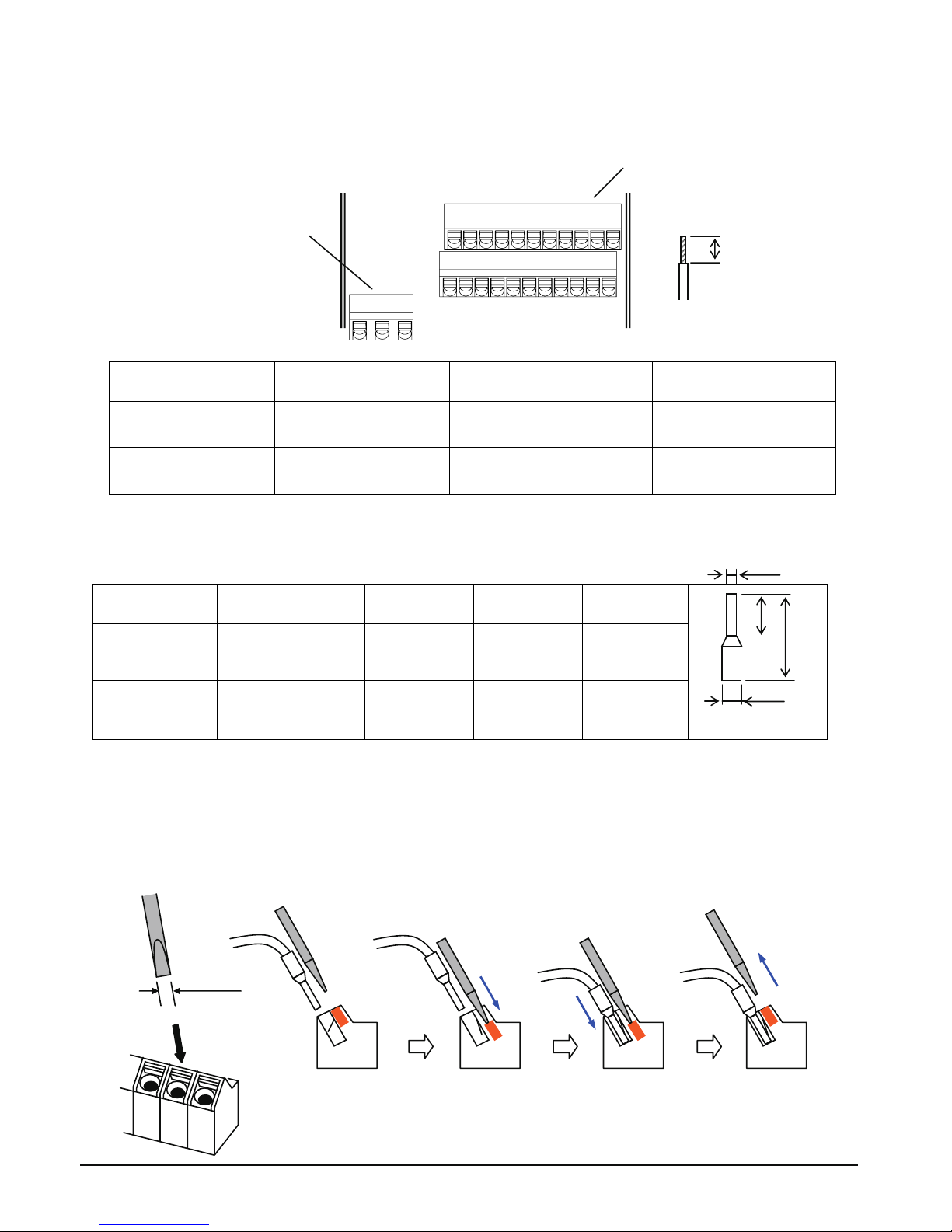
Wire size for control and relay terminals
Use wires within the specifications listed below. For safe wiring and reliability, it is recommended
to use ferrules, but if solid or stranded wire is used, stripping length should be 8mm.
Solid
mm
2
(AWG)
Stranded
mm2 (AWG)
Ferrule
mm2 (AWG)
Control logic
terminal
0.2 to 1.5
(AWG 24 to 16)
0.2 to 1.0
(AWG 24 to 17)
0.25 to 0.75
(AWG 24 to 18)
Relay terminal
0.2 to 1.5
(AWG 24 to 16)
0.2 to 1.0
(AWG 24 to 17)
0.25 to 0.75
(AWG 24 to 18)
Recommended ferrule
For safe wiring and reliability, it is recommended to use following ferrules.
* Supplier: Phoenix contact
Crimping pliers: CRIPMFOX UD 6-4 or CRIMPFOX ZA 3
How to connect?
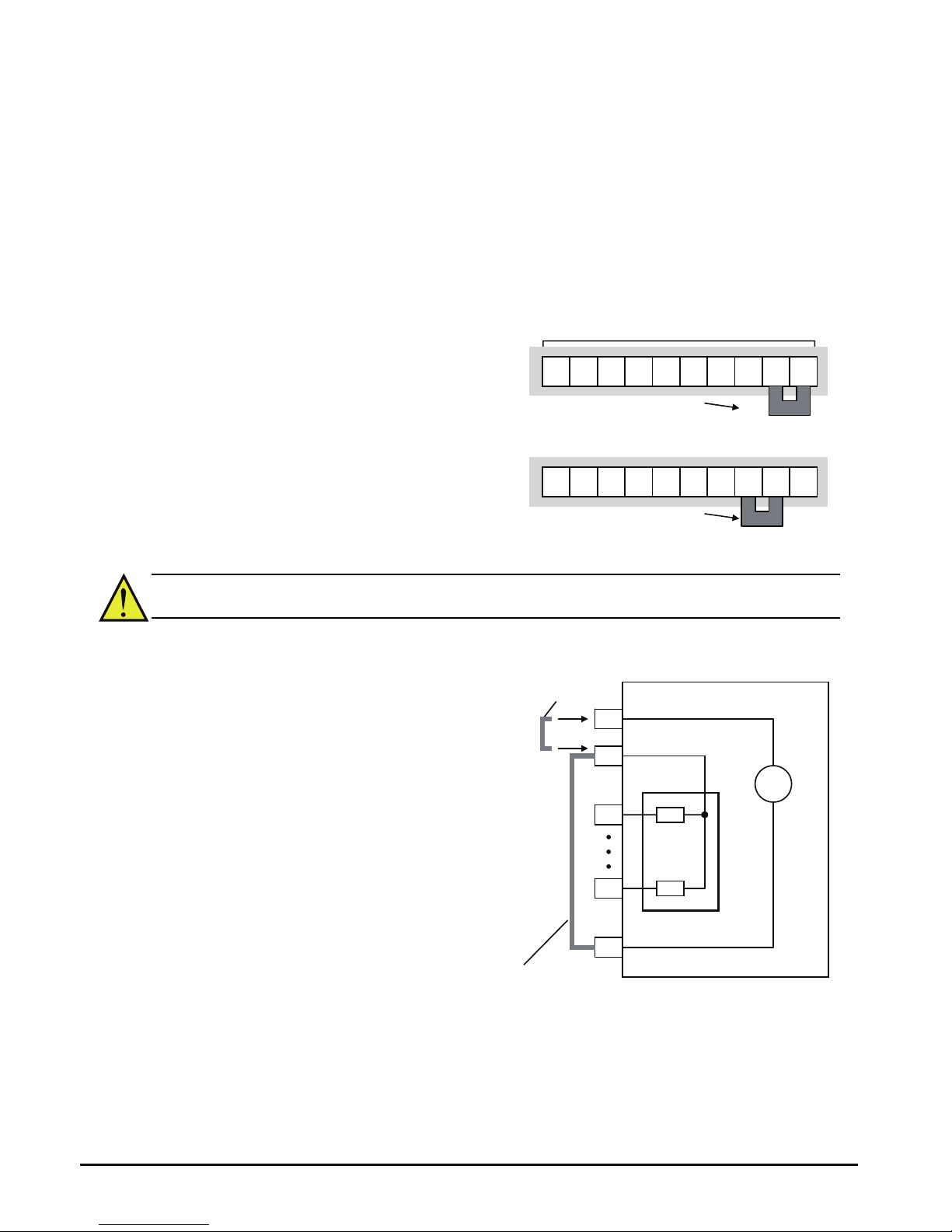
(1) Push down the orange actuating lever by a slotted screwdriver (width 2.5mm max.).
(2) Insert the conductor.
(3) Pull out the screwdriver then the conductor is fixed.
Wire size
mm
2
(AWG)
Model name of
ferrule *
L [mm] Φd [mm] ΦD [mm]
0.25 (24) AI 0.25-8YE 12.5 0.8 2.0
0.34 (22) AI 0.34-8TQ 12.5 0.8 2.0
0.5 (20) AI 0.5-8WH 14 1.1 2.5
0.75 (18) AI 0.75-8GY 14 1.3 2.8
Control logic terminal
Relay output terminal
8mm
Push down the
orange actuating
lever.
2.5mm
Insert in the
conductor.
Pull out the
screwdriver to fix
the conductor.
8
L
Φd
ΦD
19
Intelligent Terminal Listing
Intelligent Inputs
Use the following table to locate pages for intelligent input material in this chapter.
Input Function Summary Table
Symbol Code Function Name Page
FW 00 Forward Run/Stop
RV 01 Reverse Run/Stop
CF1 02 Multi-speed Select, Bit 0 (LSB)
CF2 03 Multi-speed Select, Bit 1
CF3 04 Multi-speed Select, Bit 2
CF4 05 Multi-speed Select, Bit 3 (MSB)
JG 06 Jogging
DB 07 External DC braking
SET 08 Set (select) 2nd Motor Data
2CH 09 2-stage Acceleration and Deceleration
FRS 11 Free-run Stop
EXT 12 External Trip
USP 13 Unattended Start Protection
CS 14 Commercial power source switchover
SFT 15 Software Lock
AT 16 Analog Input Voltage/Current Select
RS 18 Reset Inverter
PTC 19 PTC thermistor Thermal Protection
STA 20 Start (3-wire interface)
STP 21 Stop (3-wire interface)
F/R 22 FWD, REV (3-wire interface)
PID 23 PID Disable
PIDC 24 PID Reset
UP 27 Remote Control UP Function
DWN 28 Remote Control Down Function
UDC 29 Remote Control Data Clearing
OPE 31 Operator Control
SF1~SF7 32~38 Multi-speed Select,Bit operation Bit 1~7
OLR 39 Overload Restriction Source Changeover
TL 40 Torque Limit Selection
TRQ1 41 Torque limit switch 1
TRQ2 42 Torque limit switch 2
BOK 44 Brake confirmation
LAC 46 LAD cancellation
PCLR 47 Pulse counter clear
ADD 50 ADD frequency enable
F-TM 51 Force Terminal Mode
ATR 52 Permission for torque command input
KHC 53 Clear watt-hour data
MI1~MI7 56~62 General purpose input (1)~(7)
AHD 65 Analog command hold
CP1~CP3 66~68 Multistage-position switch (1)~(3)
ORL 69 Limit signal of zero-return
ORG 70 Trigger signal of zero-return
SPD 73 Speed/position changeover
GS1 77 STO1 input (Safety related signal)
GS2 78 STO2 input (Safety related signal)
485 81 Starting communication signal
PRG 82 Executing EzSQ program
HLD 83 Retain output frequency
ROK 84 Permission of Run command
EB 85 Rotation direction detection (phase B)
20
Use the following table to locate pages for intelligent input material in this chapter.
Input Function Summary Table
Symbol Code Function Name Page
DISP 86 Display limitation
NO 255 No assign
Intelligent Outputs
Use the following table to locate pages for intelligent output material in this chapter.
Input Function Summary Table
Symbol Code Function Name Page
RUN 00 Run Signal
FA1 01 Frequency Arrival Type 1–Constant Speed
FA2 02 Frequency Arrival Type 2–Over frequency
OL 03 Overload Advance Notice Signal
OD 04 PID Deviation error signal
AL 05 Alarm Signal
FA3 06 Frequency Arrival Type 3–Set frequency
OTQ 07 Over/under Torque Threshold
UV 09 Undervoltage
TRQ 10 Torque Limited Signal
RNT 11 Run Time Expired
ONT 12 Power ON time Expired
THM 13 Thermal Warning
BRK 19 Brake Release Signal
BER 20 Brake Error Signal
ZS 21 Zero Hz Speed Detection Signal
DSE 22 Speed Deviation Excessive
POK 23 Positioning Completion
FA4 24 Frequency Arrival Type 4–Over frequency
FA5 25 Frequency Arrival Type 5–Set frequency
OL2 26 Overload Advance Notice Signal 2
ODc 27 Analog Voltage Input Disconnect Detection
OIDc 28 Analog Voltage Output Disconnect Detection
FBV 31 PID Second Stage Output
NDc 32 Network Disconnect Detection
LOG1~3 33~35 Logic Output Function 1~3
WAC 39 Capacitor Life Warning Signal
WAF 40 Cooling Fan Warning Signal
FR 41 Starting Contact Signal
OHF 42 Heat Sink Overheat Warning
LOC 43 Low load detection
MO1~3 44~46 General Output 1~3
IRDY 50 Inverter Ready Signal
FWR 51 Forward Operation
RVR 52 Reverse Operation
MJA 53 Major Failure Signal
WCO 54 Window Comparator for Analog Voltage Input
WCOI 55 Window Comparator for Analog Current Input
FREF 58 Frequency Command Source
REF 59 Run Command Source
SETM 60 2nd Motor in operation
EDM 62
STO (Safe Torque Off) Performance Monitor
(Output terminal 11 only)
OP 63 Option control signal
no 255 Not used
21
Using Intelligent Input Terminals
Terminals [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6] and [7] are identical, programmable inputs for general use.
The input circuits can use the inverter’s internal (isolated) +24V field supply or an external
power supply. This section describes input circuits operation and how to connect them
properly to switches or transistor outputs on field devices.
The WJ200 inverter features selectable sinking or sourcing inputs. These terms refer to the
connection to the external switching device–it either sinks current (from the input to GND)
or sources current (from a power source) into the input. Note that the sink/source naming
convention may be different in your particular country or industry. In any case, just follow
the wiring diagrams in this section for your application.
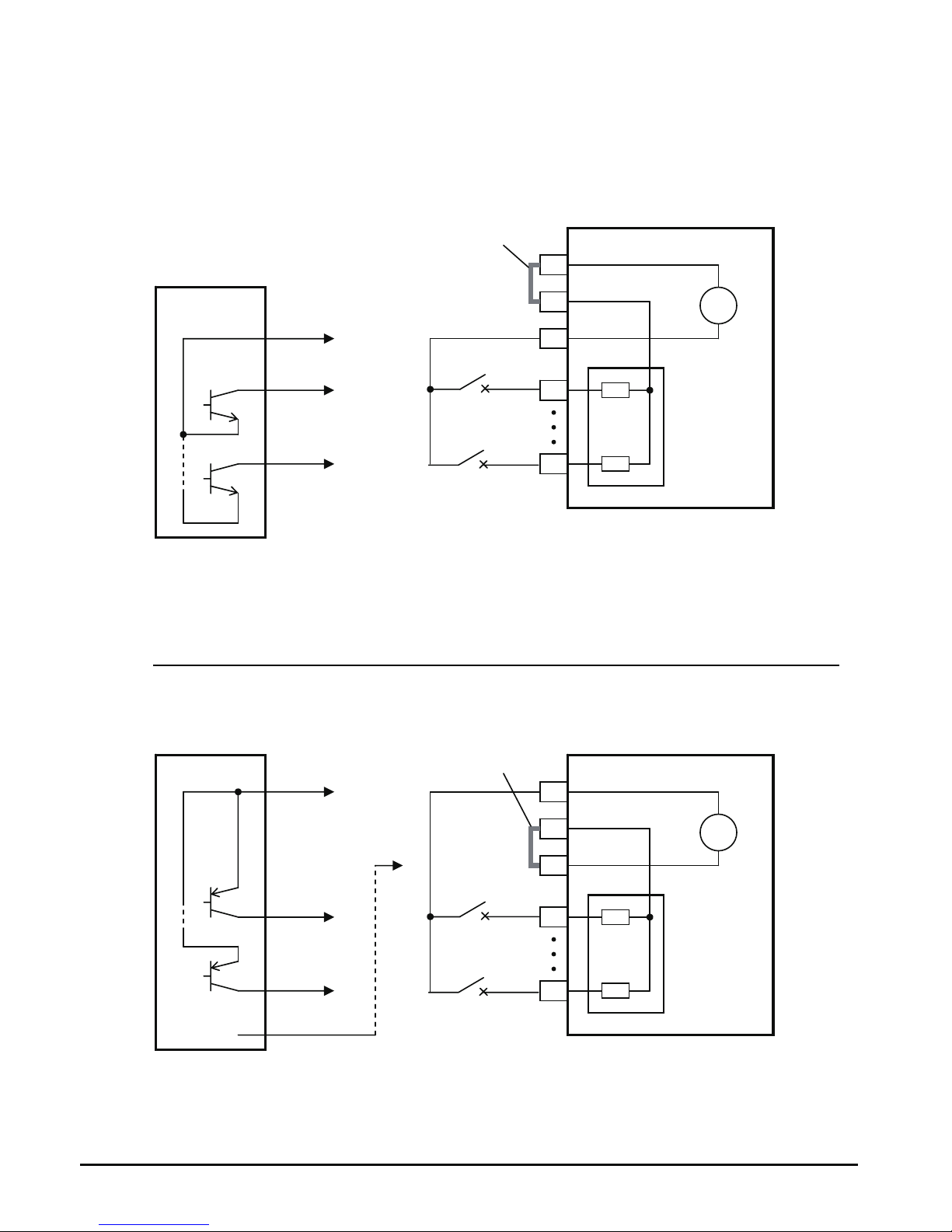
The inverter has a short bar (jumper) for
configuring the choice of sinking or sourcing
inputs. To access it, you must remove the
front cover of the inverter housing. In the
figure to the top right, the short bar is shown
as attached to the logic terminal block
(connector). If you need to change to the
source type connection, remove the short bar
and connect it as shown in the figure at the
bottom right.
CAUTION: Be sure to turn OFF power to the inverter before changing the short circuit bar
position. Otherwise, damage to the inverter circuitry may occur.
[PLC] Terminal Wiring – The [PLC]
terminal (Programmable Logic Control
terminal) is named to include various
devices that can connect to the inverter’s
logic inputs. In the figure to the right, note
the [PLC] terminal and the short bar
(jumper). Locating the short bar between
[PLC] and [L] sets the input logic source
type, which is the default setting for EU
and US versions. In this case, you
connect input terminal to [P24] to make it
active. If instead you locate the short bar
between [PLC] and [P24], the input logic
will be sink type. In this case, you
connect the input terminal to [L] to make
it active.
The wiring diagram on the following pages show the four combinations of using sourcing or
sinking inputs, and using the internal or an external DC supply.
WJ200 inverter
P24
1
7
L
24V
PLC
Input
circuits
+
-
Logic GND
Input common
Short bar for
sink logic
Short bar for
source logic
Logic inputs
5 4 3 2 1 L
PLC P24
Source logic connection
Short bar
7 6
5 4 3 2 1 L
PLC P24
Sink logic connection
Short bar
7 6
22
The two diagrams below input wiring circuits using the inverter’s internal +24V supply.
Each diagram shows the connection for simple switches, or for a field device with
transistor outputs. Note that in the lower diagram, it is necessary to connect terminal [L]
only when using the field device with transistors. Be sure to use the correct connection of
the short bar shown for each wiring diagram.
Sinking Inputs, Internal Supply
Short bar = [PLC] – [P24] position
GND
7
1
Field device
Open collector outputs,
NPN transistors
WJ200
P24
1
7
24V
PLC
Input
circuits
+
Logic GND
Input common
Short bar
Input switches
L
Sourcing Inputs, Internal Supply
Short bar = [PLC] – [L] position
Common to
[P24]
7
1
Field device
PNP transistor
sousing outputs
WJ200
P24
1
7
24V
PLC
Input
circuits
+
Logic GND
Input common
Short bar
Input switches
L
GND
to PNP bias
circuits
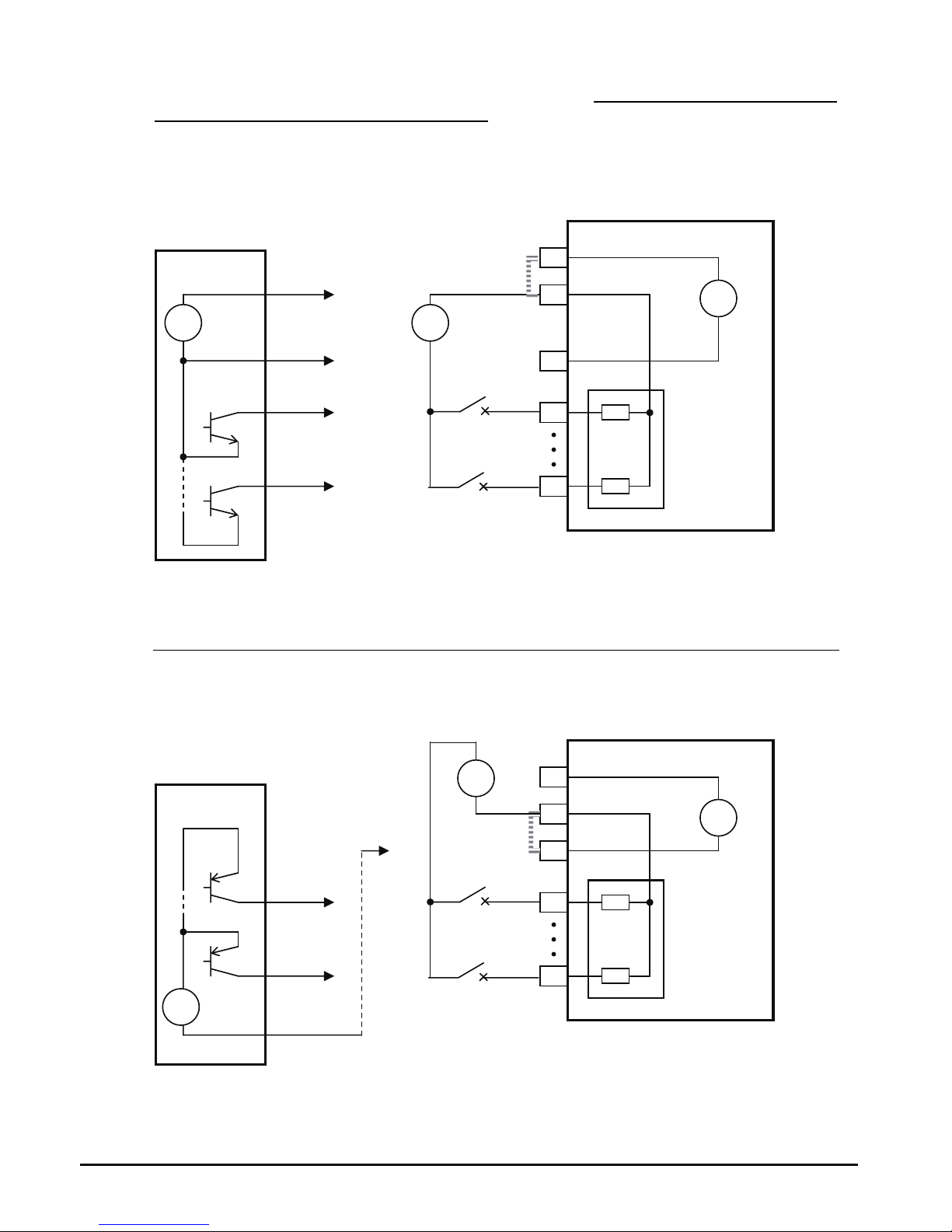
23
The two diagrams below show input wiring circuits using an external supply. If using the
“Sinking Inputs, External Supply” in below wiring diagram, be sure to remove the short bar,
and use a diode (*) with the external supply. This will prevent a power supply contention in
case the short bar is accidentally placed in the incorrect position. For the “Sourcing Inputs,
External Supply”, please connect the short bar as drawn in the diagram below.
Sinking Inputs, External Supply
Short bar = Removed
GND
7
1
Field device
Open collector outputs,
NPN transistors
WJ200
P24
1
7
24V
PLC
Input
circuits
+
Logic GND
Input common
Input switches
L
24V
+
+
24V
*
* Note: Make sure to remove the short circuit bar in case of
using an external power supply.
Sourcing Inputs, External Supply
Short bar = Removed
7
1
Field device
WJ200
P24
1
7
24V
PLC
Input
circuits
+
Input common
Input switches
L
GND
PNP transistor
sourcing outputs
24V
+
24V
+

24
CAUTION: Be sure to install a diode in between "P24" and "PLC" when connecting
multiple inverters with digital input wiring in common.
The power to the inverter control
circuits can be supplied externally as shown below. It is
possible to read and write parameters via the keypad with control power supplied in
this way, even though the drive itself is not powered. However it is NOT possible to
drive the motor.
To allow this capability, the inverter does not block current inflow to the control inputs.
When two or more inverters are connected together with common I/O wiring in this way,
it may result in unwanted activation of inputs. The use of diodes (rated 50V, 0.1A) as
shown will avoid this problem.
Short
bar
Inserting
diode
PLC
L
1
P24
PLC
L
1
Switch
OFF
Power ON
Power OFF
Input
ON
P24
PLC
L
P24
PLC
L
1
Switch
OFF
Power ON
Power OFF
Input
OFF
Short
bar
1
Switch
OFF
Switch
OFF
Input
OFF
Input
ON
P24
PLC
L
P24
PLC
L
P24
PLC
L
P24
PLC
L
1
1
1
Short
bar
In case of Source logic
Short
bar

25
Forward Run/Stop and Reverse Run/Stop Commands:
When you input the Run command via the terminal [FW], the inverter executes the Forward
Run command (high) or Stop command (low). When you input the Run command via the
terminal [RV], the inverter executes the Reverse Run command (high) or Stop command
(low).
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON Inverter is in Run Mode, motor runs forward
00
FW Forward Run/Stop
OFF Inverter is in Stop Mode, motor stops
ON Inverter is in Run Mode, motor runs reverse
01
RV Reverse Run/Stop
OFF Inverter is in Stop Mode, motor stops
Valid for inputs:
C001~C007
Required settings
A002 = 01
Notes:
When the Forward Run and Reverse Run
commands are active at the same time, the
inverter enters the Stop Mode.
When a terminal associated with either [FW] or
[RV] function is configured for normally closed,
the motor starts rotation when that terminal is
disconnected or otherwise has no input voltage.
Example (default input configuration shown see
page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
NOTE: The parameter F004, Keypad Run Key Routing, determines whether the single Run
key issues a Run FWD command or Run REV command. However, it has no effect on the
[FW] and [RV] input terminal operation.
WARNING: If the power is turned ON and the Run command is already active, the motor
starts rotation and is dangerous! Before turning power ON, confirm that the Run command
is not active.
RV FW
7654321L
PCS
P24
PLC

26
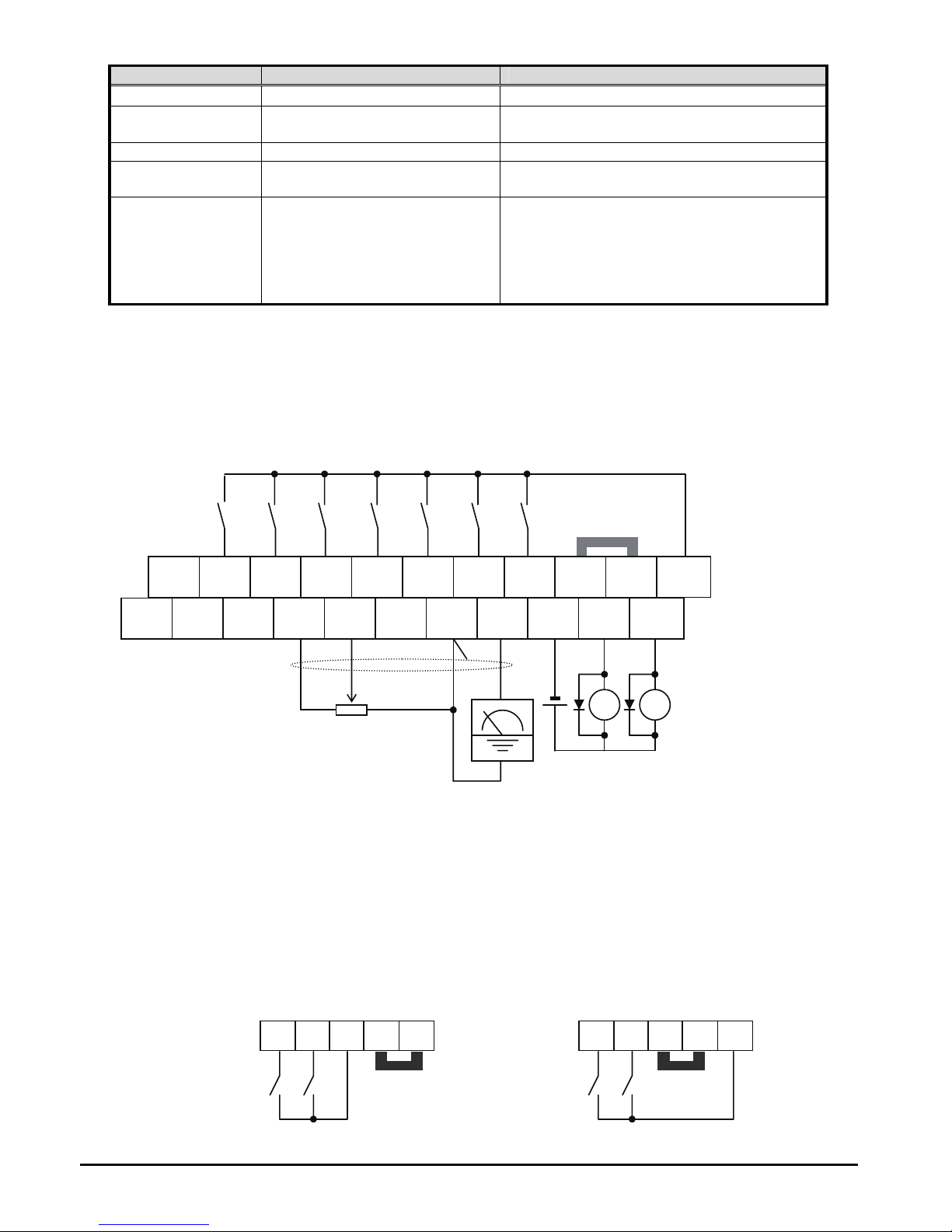
Multi-Speed Select ~Binary Operation
The inverter can store up to 16 different target
frequencies (speeds) that the motor output uses for
steady-state run condition. These speeds are accessible
through programming four of the intelligent terminals as
binary-encoded inputs CF1 to CF4 per the table to the
right. These can be any of the six inputs, and in any
order. You can use fewer inputs if you need eight or
fewer speeds.
NOTE: When choosing a subset of speeds to use,
always start at the top of the table, and with the
least-significant bit: CF1, CF2, etc.
The example with eight speeds in the
figure below shows how input switches
configured for CF1–CF3 functions can
change the motor speed in real time.
NOTE: Speed 0 depends on A001
parameter value.
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 0, logical 1
02
CF1 Multi-speed Select,
Bit 0 (LSB)
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 0, logical 0
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 1, logical 1
03
CF2 Multi-speed Select,
Bit 1
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 1, logical 0
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 2, logical 1
04
CF3 Multi-speed Select,
Bit 2
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 2, logical 0
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 3, logical 1
05
CF4 Multi-speed Select,
Bit 3 (MSB)
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 3, logical 0
Valid for inputs:
C001~C007
Required settings
F001, A001=02,
A020 to A035
Notes:
When programming the multi-speed settings,
be sure to press the SET key each time and then
set the next multi-speed setting. Note that when
the key is not pressed, no data will be set.
When a multi-speed setting more than 50Hz
(60Hz) is to be set, it is necessary to program the
maximum frequency A004 high enough to allow
that speed
Example (some CF inputs require input
configuration; some are default inputs):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
Multi-
speed
Input Function
CF4 CF3 CF2 CF1
Speed 0 0 0 0 0
Speed 1 0 0 0 1
Speed 2 0 0 1 0
Speed 3 0 0 1 1
Speed 4 0 1 0 0
Speed 5 0 1 0 1
Speed 6 0 1 1 0
Speed 7 0 1 1 1
Speed 8 1 0 0 0
Speed 9 1 0 0 1
Speed 10 1 0 1 0
Speed 11 1 0 1 1
Speed 12 1 1 0 0
Speed 13 1 1 0 1
Speed 14 1 1 1 0
Speed 15 1 1 1 1
Speed
0th
4th
6th
1st
2nd
5th
7th
3rd
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
[CF1]
[CF2]
[CF3]
[FW]
CF4 CF3 CF2 CF1
7654321L
PCS
P24
PLC

27
Two Stage Acceleration and Deceleration
When terminal [2CH] is turned ON, the inverter
changes the rate of acceleration and
deceleration from the initial settings (F002 and
F003) to use the second set of acceleration/
deceleration values. When the terminal is
turned OFF, the inverter is returned to the
original acceleration and deceleration time
(F002 acceleration time 1, and F003
deceleration time 1). Use A092 (acceleration
time 2) and A093 (deceleration time 2) to set
the second stage acceleration and deceleration
times.
In the graph shown above, the [2CH] becomes active during the initial acceleration. This
causes the inverter to switch from using acceleration 1 (F002) to acceleration 2 (A092).
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON Frequency output uses 2nd-stage acceleration and
deceleration values
09
2CH Two-stage Accelera-
tion and
Deceleration
OFF Frequency output uses the initial acceleration 1 and
deceleration 1 values
Valid for inputs:
C001~C007
Required settings
A092, A093, A094=00
Notes:
Function A094 selects the method for second
stage acceleration. It must be set = 00 to select
the input terminal method in order for the [2CH]
terminal assignment to operate.
Example (default input configuration shown see
page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
[2CH]
1
0
Output
frequency
t
[FW,RV]
1
0
Target
fre
q
uency
initial
second
2CH
7654321L
PCS
P24
PLC

28
Unattended Start Protection
If the Run command is already set when power is turned ON, the inverter starts running
immediately after powerup. The Unattended Start Protection (USP) function prevents that
automatic startup, so that the inverter will not run without outside intervention. When USP
is active and you need to reset an alarm and resume running, either turn the Run
command OFF, or perform a reset operation by the terminal [RS] input or the keypad
Stop/reset key.
In the figure below, the [USP] feature is enabled. When the inverter power turns ON, the
motor does not start, even though the Run command is already active. Instead, it enters
the USP trip state, and displays E 13 error code. This requires outside intervention to reset
the alarm by turning OFF the Run command per this example (or applying a reset). Then
the Run command can turn ON again and start the inverter output.
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON On powerup, the inverter will not resume a Run
command (mostly used in the US)
13
USP Unattended Start
Protection
OFF On powerup, the inverter will resume a Run
command that was active before power loss
Valid for inputs:
C001~C007
Required settings
(none)
Notes:
Note that when a USP error occurs and it is
canceled by a reset from a [RS] terminal input, the
inverter restarts running immediately.
Even when the trip state is canceled by turning
the terminal [RS] ON and OFF after an under
voltage protection E09 occurs, the USP function
will be performed.
When the running command is active
immediately after the power is turned ON, a USP
error will occur. When this function is used, wait
for at least three (3) seconds after the powerup to
generate a Run command.
Example (default input configuration shown see
page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
Inverter output frequency
0
t
Inverter power supply
1
0
Alarm output terminal
1
0
[USP] terminal
1
0
Run command [FW,RV]
1
0
Events:
E13
Alarm
cleared
Run
command
USP
7654321L
PCS
P24
PLC

29
Reset Inverter
The [RS] terminal causes the inverter to execute
the reset operation. If the inverter is in Trip Mode,
the reset cancels the Trip state. When the signal
[RS] is turned ON and OFF, the inverter executes
the reset operation. The minimum pulse width for
[RS] must be 12 ms or greater. The alarm output
will be cleared within 30 ms after the onset of the
Reset command.
WARNING: After the Reset command is given and the alarm reset occurs, the motor will
restart suddenly if the Run command is already active. Be sure to set the alarm reset after
verifying that the Run command is OFF to prevent injury to personnel.
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON The motor output is turned OFF, the Trip Mode is
cleared (if it exists), and powerup reset is applied
18
RS Reset Inverter
OFF Normal power ON operation
Valid for inputs:
C001~C007
Required settings
(none)
Notes:
While the control terminal [RS] input is ON, the
keypad displays alternating segments. After RS
turns OFF, the display recovers automatically.
Pressing the Stop/Reset key of the digital
operator can generate a reset operation only
when an alarm occurs.
Example (default input configuration shown see
page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
A terminal configured with the [RS] function can only be configured for normally open operation. The
terminal cannot be used in the normally closed contact state.
When input power is turned ON, the inverter performs the same reset operation as it does when a
pulse on the [RS] terminal occurs.
The Stop/Reset key on the inverter is only operational for a few seconds after inverter powerup when
a hand-held remote operator is connected to the inverter.
If the [RS] terminal is turned ON while the motor is running, the motor will be free running (coasting).
If you are using the output terminal OFF delay feature (any of C145, C147, C149 > 0.0 sec.), the [RS]
terminal affects the ON-to-OFF transition slightly. Normally (without using OFF delays), the [RS] input
causes the motor output and the logic outputs to turn OFF together, immediately. However, when any
output uses an OFF delay, then after the [RS] input turns ON, that output will remain ON for an additional
1 sec. period (approximate) before turning OFF.
[RS]
1
0
t
Alarm
signal
1
0
Approx. 30 ms
12 ms
minimum
RS
7654321L
PCS
P24
PLC

30
Using Intelligent Output Terminals
Run Signal
When the [RUN] signal is selected as an
intelligent output terminal, the inverter outputs
a signal on that terminal when it is in Run
Mode. The output logic is active low, and is
the open collector type (switch to ground).
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON when inverter is in Run Mode
00
RUN Run Signal
OFF when inverter is in Stop Mode
Valid for inputs:
11, 12, AL0 – AL2
Required settings
(none)
Notes:
The inverter outputs the [RUN] signal
whenever the inverter output exceeds the start
frequency specified by parameter B082. The start
frequency is the initial inverter output frequency
when it turns ON.
The example circuit for terminal [11] drives a
relay coil. Note the use of a diode to prevent the
negative going turn-off spike generated by the coil
from damaging the inverter’s output transistor.
Example for terminal [11] (default output
configuration shown see page 59):
Example for terminal [AL0], [AL1], [AL2] (requires
output configuration see page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
RY
Inverter output
terminal circuit
CM2 11
RUN
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2
Inverter logic
circuit board
RUN
[FW,RV]
1
0
Output
frequency
t
Run
signal
start freq.
B082
ON

31
Frequency Arrival Signals
The Frequency Arrival group of outputs helps coordinate external systems with the current
velocity profile of the inverter. As the name implies, output [FA1] turns ON when the output
frequency arrives at the standard set frequency (parameter F001). Output [FA2] relies on
programmable accel/ decel thresholds for increased flexibility. For example, you can have
an output turn ON at one frequency during acceleration, and have it turn OFF at a different
frequency during deceleration. All transitions have hysteresis to avoid output chatter if the
output frequency is near one of the thresholds.
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON when output to motor is at the constant frequency
01
FA1 Frequency Arrival
Type 1 – Constant
Speed
OFF when output to motor is OFF, or in any acceleration or
deceleration ramp
ON when output to motor is at or above the set frequency
thresholds for, even if in acceleration or decel ramps
02
FA2 Frequency Arrival
Type 2 – Over
frequency
OFF when output to motor is OFF, or during accel or decel
before the respective thresholds are crossed
ON when output to motor is at the set frequency
06
FA3 Frequency Arrival
Type 3 – Set
frequency
OFF when output to motor is OFF, or in any acceleration or
deceleration ramp
ON when output to motor is at or above the set frequency
thresholds for, even if in acceleration or decel ramps
24
FA4 Frequency Arrival
Type 4 – Over
frequency (2)
OFF when output to motor is OFF, or during accel or decel
before the respective thresholds are crossed
ON when output to motor is at the set frequency
25
FA5 Frequency Arrival
Type 5 – Set
frequency (2)
OFF when output to motor is OFF, or in any acceleration or
deceleration ramp
Valid for inputs:
11, 12, AL0 – AL2
Required
settings
C042, C043, C045, C046,
Notes:
For most applications you will need to use
only one type of frequency arrival outputs (see
examples). However, it is possible assign both
output terminals to output functions [FA1] and
[FA2]
For each frequency arrival threshold, the
output anticipates the threshold (turns ON early)
by 1.5Hz
The output turns OFF as the output
frequency moves away from the threshold,
delayed by 0.5Hz
The example circuit for terminal [11] drives a
relay coil. Note the use of a diode to prevent the
negative going turn-off spike generated by the
coil from damaging the inverter’s output
transistor
Example for terminal [11] (default output configuration
shown see page 59):
Example for terminal [AL0], [AL1], [AL2] (requires
output configuration see page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
RY
Inverter output
terminal circuit
CM2 11
FA1
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2
Inverter logic
circuit board
FA1

32
Frequency arrival output [FA1] uses the
standard output frequency (parameter
F001) as the threshold for switching. In
the figure to the right, Frequency Arrival
[FA1] turns ON when the output
frequency gets within Fon Hz below or
Fon Hz above the target constant
frequency, where Fon is 1% of the set
maximum frequency and Foff is 2% of
the set maximum frequency. This
provides hysteresis that prevents output
chatter near the threshold value. The
hysteresis effect causes the output to
turn ON slightly early as the speed
approaches the threshold. Then the
turn-OFF point is slightly delayed. Note
the active low nature of the signal, due to
the open collector output.
Frequency arrival output [FA2/FA4]
works the same way; it just uses two
separate thresholds as shown in the
figure to the right. These provide for
separate acceleration and deceleration
thresholds to provide more flexibility than
for [FA1]. [FA2/FA4] uses C042/C045
during acceleration for the ON threshold,
and C043/C046 during deceleration for the
OFF threshold. This signal also is active
low. Having different accel and decel
thresholds provides an asymmetrical
output function. However, you can use
equal ON and OFF thresholds, if desired.
Frequency arrival output [FA3/FA5] works
also the same way, only difference is
arriving at set frequency.
FA1
signal
Output
freq.
Fon
F001
F001
Foff
Fon
ON
Foff
ON
0
Fon=1% of max. frequency
Foff=2% of max. frequency
FA2/FA4
signal
Output
freq.
thresholds
C042/C045
ON
0
C043/C046
Fon
Foff
Fon=1% of max. frequency
Foff=2% of max. frequency
FA3/FA5
signal
Output
freq.
thresholds
C042/C045
0
C043/C046
Fon
Foff
Fon=1% of max. frequency
Foff=2% of max. frequency
Foff
Fon
ON ON

33
Alarm Signal
The inverter alarm signal is active when a fault has
occurred and it is in the Trip Mode (refer to the
diagram at right). When the fault is cleared the alarm
signal becomes inactive.
We must make a distinction between the alarm signal
AL and the alarm relay contacts [AL0], [AL1] and [AL2].
The signal AL is a logic function, which you can assign
to the open collector output terminals [11], [12], or the
relay outputs.
The most common (and default) use of the relay is for AL, thus the labeling of its terminals.
Use an open collector output (terminal [11] or [12]) for a low-current logic signal interface
or to energize a small relay (50 mA maximum). Use the relay output to interface to higher
voltage and current devices (10 mA minimum).
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name State Description
ON when an alarm signal has occurred and has not
been cleared
05
AL Alarm Signal
OFF when no alarm has occurred since the last clearing
of alarm(s)
Valid for inputs:
11, 12, AL0 – AL2
Required settings
C031, C032, C036
Notes:
By default, the relay is configured as normally
closed (C036=01). Refer to the next page for an
explanation.
In the default relay configuration, an inverter
power loss turns ON the alarm output. the alarm
signal remains ON as long as the external control
circuit has power.
When the relay output is set to normally
closed, a time delay of less than 2 seconds occurs
after powerup before the contact is closed.
Terminals [11] and [12] are open collector
outputs, so the electric specifications of [AL] are
different from the contact output terminals [AL0],
[AL1], [AL2].
This signal output has the delay time (300 ms
nominal) from the fault alarm output.
The relay contact specifications are in “Control
Logic Signal Specifications” on page 4–6. The
contact diagrams for different conditions are on
the next page.
Example for terminal [11] (default output
configuration shown see page 59):
Example for terminal [AL0], [AL1], [AL2] (requires
output configuration see page 59):
See I/O specs on page 16,17.
Run Stop
RUN
STOP
RESET
Trip
STOP
RESET
Fault
Fault
A
larm signal active
RY
Inverter output
terminal circuit
CM2 11
A
L
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2
Inverter logic
circuit board
A
L

34
The alarm relay output can be configured in two main ways:
Trip/Power Loss Alarm – The alarm relay is configured as normally closed (C036=01)
by default, shown below (left). An external alarm circuit that detects broken wiring also
as an alarm connects to [AL0] and [AL1]. After powerup and short delay (< 2 seconds),
the relay energizes and the alarm circuit is OFF. Then, either an inverter trip event or
an inverter power loss will de-energize the relay and open the alarm circuit
Trip Alarm – Alternatively, you can configure the relay as normally open (C036=00),
shown below (right). An external alarm circuit that detects broken wiring also as an
alarm connects to [AL0] and [AL2]. After powerup, the relay energizes only when an
inverter trip event occurs, opening the alarm circuit. However, in this configuration, an
inverter power loss does not open the alarm circuit.
Be sure to use the relay configuration that is appropriate for your system design. Note that
the external circuits shown assume that a closed circuit = no alarm condition (so that a
broken wire also causes an alarm). However, some systems may require a closed circuit =
alarm condition. In that case, then use the opposite terminal [AL1] or [AL2] from the ones
shown.
N.C. contacts (C036=01) N.O. contacts (C036=00)
During normal operation When an alarm occurs or
when power is OFF
During normal operation
or when power is OFF
When an alarm occurs
Power Run Mode AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2 Power Run Mode AL0-AL1 AL0-AL2
ON Normal Closed Open ON Normal Open Closed
ON Trip Open Closed ON Trip Closed Open
OFF – Open Closed OFF – Open Closed
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2
AL1
Power
supply
Load
AL0 AL2

35
Analog Input Operation
The WJ200 inverters provide for analog input to
command the inverter frequency output value.
The analog input terminal group includes the [L],
[OI], [O], and [H] terminals on the control
connector, which provide for Voltage [O] or
Current [OI] input. All analog input signals must
use the analog ground [L].
If you use either the voltage or current analog
input, you must select one of them using the logic
input terminal function [AT] analog type. Refer to
the table on next page showing the activation of
each analog input by combination of A005 set
parameter and [AT] terminal condition. The [AT]
terminal function is covered in “Analog Input
Current/Voltage Select” in section 4. Remember
that you must also set A001 = 01 to select analog
input as the frequency source.
NOTE: If no logic input terminal is configured for the [AT] function, then inverter recognizes
that [AT]=OFF and MCU recognizes [O]+[OI] as analog input.
Using an external potentiometer is a common way to
control the inverter output frequency (and a good way
to learn how to use the analog inputs). The
potentiometer uses the built-in 10V reference [H] and
the analog ground [L] for excitation, and the voltage
input [O] for the signal. By default, the [AT] terminal
selects the voltage input when it is OFF.
Take care to use the proper resistance for the
potentiometer, which is 1~2 k
, 2 Watts.
Voltage Input – The voltage input circuit uses
terminals [L] and [O]. Attach the signal cable’s
shield wire only to terminal [L] on the inverter.
Maintain the voltage within specifications (do not
apply negative voltage).
Current Input – The current input circuit uses
terminals [OI] and [L]. The current comes from a
sourcing type transmitter; a sinking type will not
work! This means the current must flow into
terminal [OI], and terminal [L] is the return back to
the transmitter. The input impedance from [OI] to
[L] is 100 Ohms. Attach the cable shield wire only
to terminal [L] on the inverter.
AM H O OI L
+V Ref.
Voltage input
Current input
A
GND
AM H O OI L
Freq.
settin
g
A001
V/I input
select
[AT]
Å
+
-
4-20 mA
0-10 V
AM H O OI L
1 to 2k, 2W
0 to 9.6 VDC,
0 to 10V nominal
AM H O OI L
+
-
4 to 19.6 mA DC,
4 to 20mA nominal
AM H O OI L
Å
See I/O specs on page 21,22.

36
The following table shows the available analog input settings. Parameter A005 and the
input terminal [AT] determine the External Frequency Command input terminals that are
available, and how they function. The analog inputs [O] and [OI] use terminal [L] as the
reference (signal return).
A005
[AT] Input Analog Input Configuration
ON [OI]
00
OFF [O]
ON Integrated POT on external panel
02
OFF [O]
ON Integrated POT on external panel
03
OFF [OI]
Other Analog Input-related topics:
· “Analog Input Settings”
· “Additional Analog Input Settings”
· “Analog Signal Calibration Settings”
· “Analog Input Current/Voltage Select”
· “ADD Frequency Enable”
· “Analog Input Disconnect Detect”

37
Pulse Train Input Operation
The WJ200 inverter is capable of accepting pulse train input signals, that are used for
frequency command, process variable (feedback) for PID control, and simple positioning.
The dedicated terminal is called “EA” and “EB”. Terminal “EA” is a dedicated terminal, and
the terminal “EB” is an intelligent terminal, that has to be changed by a parameter setting.
Terminal Name Description Ratings
EA Pulse train input A For frequency command, 32kHz max.
Reference voltage: Common is [L]
EB
(Input terminal 7)
Pulse train input B
(Set C007 to 85 )
27Vdc max.
For frequency command, 2kHz max.
Reference voltage: Common is [PLC]
(1) Frequency Command by pulse train input
When using this mode, you should set A001 to 06. In this case the frequency is detected by
input-capture, and calculated based on the ratio of designated max. frequency (under
32kHz). Only an input terminal “EA” will be used in this case.
(2) Using for process variable of PID control
You can use the pulse train input for process variable (feedback) of PID control. In this
case you need to set A076 to 03. Only “EA” input terminal is to be used.
(3) Simple positioning by pulse train input
This is to use the pulse train input like an encoder signal. You can select three types of
operation.
Analog
outpu
t
Logic input
L
o
gic
outpu
t
Sho
rt
bar
PLC
Analog
in
pu
t
Pulse
input
Pulse
Train
output
RS485
co
mm.
RS485
co
mm.
P24 1 L 3 2
5 4 6
SN 7
12 11
AM
CM2 OI L
H O EA
SP EO
AL2AL1A
L0
Relay contact
Train

38
Analog Output Operation
In inverter applications it is useful to monitor the
inverter operation from a remote location or from the
front panel of an inverter enclosure. In some cases,
this requires only a panel-mounted volt meter. In other
cases, a controller such as a PLC may provide the
inverter’s frequency command, and require inverter
feedback data (such as output frequency or output
current) to confirm actual operation. The analog output
terminal [AM] serves these purposes.
The inverter provides an analog voltage output on terminal [AM] with terminal [L] as analog
GND reference. The [AM] can output inverter frequency or current output value. Note that
the voltage range is 0 to +10V (positive-going only), regardless of forward or reverse motor
rotation. Use C028 to configure terminal [AM] as indicated below.
Func. Code Description
00
Inverter output frequency
01
Inverter output current
02
Inverter output torque
03
Digital output freqnency
04
Inverter output goltage
05
Inverter input power
06
Electronic Thermal Load
07
LAD frequency
08
Digital current monitor
10
Cooling fin temperature
12
General purpose
15
Pulse train
C028
16
Option
AM H O OI L
+-
A
GND
A
nalog
Voltage
Output
10VDC
full scale,
2mA max
See I/O specs on page 21,22

39
The [AM] signal offset and gain are adjustable, as indicated below.
Func. Description Range Default
C106
[AM] output gain 0.~255. 100.
C109
[AM] output offset 0.0~10.0 0.0
The graph below shows the effect of the gain and offset setting. To calibrate the [AM]
output for your application (analog meter), follow the steps below:
1. Run the motor at the full scale speed, or most common operating speed.
a. If the analog meter represents output frequency, adjust offset (C109) first, and then
use C106 to set the voltage for full scale output.
b. If [AM] represents motor current, adjust offset (C109) first, and then use BC106 to set
the voltage for full scale output. Remember to leave room at the upper end of the
range for increased current when the motor is under heavier loads.
NOTE: As mentioned above, first adjust the offset, and then adjust the gain. Otherwise the
required performance cannot be obtained because of the parallel movement of the offset
adjustment.
Full scale (FS)
Hz or A
A
M output
10V
0
1/2 FS
5V
C106=0~255
AM output gain adjustment
Full scale (FS)
Hz or A
A
M output
10V
0
1/2 FS
5V
C109=0~10
Parallel
movement
AM output offset adjustment

40
Monitoring functions
NOTE:. Mark “9” in b031=10 shows the accessible parameters when b031 is set “10”, high
level access.
“d” Function
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Units
D001
Output frequency monitor
Real time display of output frequency
to motor from
0.0 to 400.0Hz
If b163 is set high, output frequency
(F001) can be changed by up/down
key with d001 monitoring.
Hz
D002
Output current monitor
Filtered display of output current to
motor, range is
0 to 655.3 ampere (~99.9 ampere for
1.5kW and less)
A
D003
Rotation direction monitor
Three different indications:
“F” Forward
“o” Stop
“r” Reverse
D004
Process variable (PV),
PID feedback monitor
Displays the scaled PID process
variable (feedback) value (A075 is
scale factor),
0.00 to 10000
% times
constant
D005
Intelligent input
terminal status
Displays the state of the intelligent
input terminals:
D006
Intelligent output
terminal status
Displays the state of the intelligent
output terminals:
ON
OFF
Relay
12 11
ON
OFF
7 6 5 4
3
2 1
Terminal numbers

41
“d” Function
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Units
D007
Scaled output
frequency monitor
Displays the output frequency scaled
by the constant in B086.
Decimal point indicates range:
0 to 3999
Hz times
constant
d008
Actual frequency monitor
Displays the actual frequency, range
is -400 to 400 Hz
Hz
d009
Torque command monitor
Displays the torque command, range
is -200 to 200 %
%
d010
Torque bias monitor
Displays the torque bias value, range
is -200 to 200 %
%
d012
Output torque monitor
Displays the output torque, range is
-200 to 200 %
%
D013
Output voltage monitor
Voltage of output to motor,
Range is 0.0 to 600.0V
V
d014
Input power monitor
Displays the input power, range is 0
to 999.9 kW
KW
d015
Watt-hour monitor
Displays watt-hour of the inverter,
range is 0 to 9999000
D016
Elapsed RUN time monitor
Displays total time the inverter has
been in RUN mode in hours.
Range is 0 to 9999 / 1000 to 9999 /
100 to 999 (10,000 to 99,900)
hours
D017
Elapsed power-on time
monitor
Displays total time the inverter has
been powered up in hours.
Range is 0 to 9999 / 1000 to 9999 /
100 to 999 (10,000 to 99,900)
hours
D018
Heat sink temperature monitor
Temperature of the cooling fin, range
is -20~150
C
d022
Life check monitor
Displays the state of lifetime of
electrolytic capacitors on the PWB
and cooling fan.
d023
Program counter monitor
[EzSQ]
Range is 0 to 1024
d024
Program number monitor
[EzSQ]
Range is 0 to 9999
d025
User monitor 0
[EzSQ]
Result of EzSQ execution, range is
–2147483647~2147483647
d026
User monitor 1
[EzSQ]
Result of EzSQ execution, range is
–2147483647~2147483647
d027
User monitor 2
[EzSQ]
Result of EzSQ execution, range is
–2147483647~2147483647
d029
Positioning command monitor
Displays the positioning command,
range is –268435455~+268435455
d030
Current position monitor
Displays the current position, range
is –268435455~+268435455
d050
Dual monitor
Displays two different data
configured in b160 and b161.
d060
Inverter mode monitor
Displays currently selected inverter
mode :
I-C:IM CT mode/I-v:IM VT mode/
P:PM
Lifetime expired
Normal
Electrolytic caps
Cooling fan

42
“d” Function
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Units
D080
Trip counter
Number of trip events,
Range is 0. to 65530
events
D081
Trip monitor 1
D082
Trip monitor 2
D083
Trip monitor 3
d084
Trip monitor 4
d085
Trip monitor 5
d086
Trip monitor 6
Displays trip event information:
Error code
Output frequency at trip point
Motor current at trip point
DC bus voltage at trip point
Cumulative inverter operation
time at trip point
Cumulative power-ON time at
trip point
d090
Warning monitor Displays the warning code
D102
DC bus voltage monitor
Voltage of inverter internal DC bus,
Range is 0.0 to 999.9
V
d103
BRD load ratio monitor
Usage ratio of integrated brake
chopper, range is 0.0~100.0%
%
D104
Electronic thermal monitor
Accumulated value of electronic
thermal detection, range is from
0.0~100.0%
%
Main Profile Parameters
NOTE:. Mark “9” in b031=10 shows the accessible parameters when b031 is set “10”, high
level access.
“F” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
F001
Output frequency setting
Standard default target frequency
that determines constant motor
speed, range is 0.0 / start
frequency to maximum frequency
(A004)
9
0.0 Hz
F002
Acceleration time (1)
9
10.0 sec.
F202
Acceleration time (1),
2
nd
motor
Standard default acceleration,
range is 0.01 to 3600 sec.
9
10.0 sec.
F003
Deceleration time (1)
9
10.0 sec.
F203
Deceleration time (1),
2
nd
motor
Standard default deceleration,
range is 0.01 to 3600 sec.
9
10.0 sec.
F004
Keypad RUN key routing
Two options; select codes:
00 Forward
01 Reverse
U
00

43
Standard Functions
NOTE:. Mark “9” in b031=10 shows the accessible parameters when b031 is set “10”, high
level access.
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
A001
Frequency source
U
02
A201
Frequency source,
2
nd
motor
Eight options; select codes:
00 POT on ext. operator
01 Control terminal
02 Function F001 setting
03 ModBus network input
04 Option
06 Pulse train input
07 via EzSQ
10 Calculate function output
U
02
A002
Run command source
U
02
A202
Run command source,
2
nd
motor
Five options; select codes:
01 Control terminal
02 Run key on keypad,
or digital operator
03 ModBus network input
04 Option
U
02
A003
Base frequency
Settable from 30 Hz to
the maximum frequency(A004)
U
60.0 Hz
A203
Base frequency,
2
nd
motor
Settable from 30 Hz to
the 2
nd
maximum
frequency(A204)
U
60.0 Hz
A004
Maximum frequency
Settable from the base
frequency to 400 Hz
U
60.0 Hz
A204
Maximum frequency,
2
nd
motor
Settable from the 2
nd
base
frequency to 400 Hz
U
60.0 Hz
A005
[AT] selection
Three options; select codes:
00...Select between [O] and [OI]
at [AT] (ON=OI, OFF=O)
02...Select between [O] and
external POT at [AT]
(ON=POT, OFF=O)
03...Select between [OI] and
external POT at [AT]
(ON=POT, OFF=OI)
U
00
A011
[O] input active range start
frequency
The output frequency
corresponding to the analog
input range starting point,
range is 0.00 to 400.0
U
0.00 Hz
A012
[O] input active range end
frequency
The output frequency
corresponding to the analog
input range ending point,
range is 0.0 to 400.0
U
0.00 Hz
A013
[O] input active range start
voltage
The starting point (offset) for the
active analog input range,
range is 0. to 100.
U
0. %
A014
[O] input active range end
voltage
The ending point (offset) for the
active analog input range,
range is 0. to 100.
U
100. %

44
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
A015
[O] input start frequency
enable
Two options; select codes:
00Use offset (A011 value)
01Use 0Hz
U
01
A016
Analog input filter
Range n = 1 to 31,
1 to 30 : ×2ms filter
31: 500ms fixed filter with ±
0.1kHz hys.
U
8. Spl.
A017
Simple sequence function
selection(EzSQ)
00...Disable
01...PRG terminal
02...Always
9
00
a019
Multi-speed operation
selection
Select codes:
00...Binary operation (16 speeds
selectable with 4 terminals)
01...Bit operation (8 speeds
selectable with 7 terminals)
U
00
A020
Multi-speed freq. 0
Defines the first speed of
a multi-speed profile, range is 0.0
/ start frequency to 400Hz
A020 = Speed 0 (1st motor)
9
0.0 Hz
A220
Multi-speed freq. 0,
2
nd
motor
Defines the first speed of
a multi-speed profile or a 2nd
motor, range is 0.0 / start
frequency to 400Hz
A220 = Speed 0 (2nd motor)
9
0.0 Hz
Defines 15 more speeds,
range is 0.0 / start frequency to
400 Hz.
A021=Speed 1 ~ A035=Speed15
9
See next
row
Hz
A021
to
A035
Multi-speed freq. 1 to 15
(for both motors)
A021 ~ A035
9
0.0 Hz
A038
Jog frequency
Defines limited speed for jog,
range is from start frequency to
9.99 Hz
9
6.00 Hz
A039
Jog stop mode
Define how end of jog stops the
motor; six options:
00Free-run stop (invalid during
run)
01Controlled deceleration
(invalid during run)
02DC braking to stop(invalid
during run)
03Free-run stop (valid during
run)
04Controlled deceleration
(valid during run)
05DC braking to stop(valid
during run)
U
04
A041
Torque boost select
U
00
A241
Torque boost select, 2nd motor
Two options:
00Manual torque boost
01Automatic torque boost
U
00
A042
Manual torque boost value
Can boost starting torque
between 0 and 20% above
9
1.0 %

45
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
A242
Manual torque boost value, 2nd
motor
normal V/f curve,
range is 0.0 to 20.0%
9
1.0 %
A043
Manual torque boost
frequency
9
5.0 %
A243
Manual torque boost
frequency,
2nd motor
Sets the frequency of the V/f
breakpoint A in graph (top of
previous page) for torque boost,
range is 0.0 to 50.0%
9
5.0 %
A044
V/f characteristic curve
U
00
A244
V/f characteristic curve,
2
nd
motor
Six available V/f curves;
00Constant torque
01Reduced torque (1.7)
02Free V/F
03Sensorless vector (SLV)
U
00
A045
V/f gain
9
100. %
A245
V/f gain, 2nd motor
Sets voltage gain of the inverter,
range is 20. to 100.%
9
100. %
a046
Voltage compensation gain for
automatic torque boost
9
100.
a246
Voltage compensation gain for
automatic torque boost,
2nd
motor
Sets voltage compensation gain
under automatic torque boost,
range is 0. to 255.
9
100.
a047
Slip compensation gain for
automatic torque boost
9
100.
a247
Slip compensation gain for
automatic torque boost,
2nd motor
Sets slip compensation gain
under automatic torque boost,
range is 0. to 255.
9
100.
A051
DC braking enable
Three options; select codes:
00Disable
01Enable during stop
02Frequency detection
U
00
A052
DC braking frequency
The frequency at which DC
braking begins,
range is from the start frequency
(B082) to 60Hz
U
0.5 Hz
A053
DC braking wait time
The delay from the end of
controlled deceleration to start
of DC braking (motor free runs
until DC braking begins),
range is 0.0 to 5.0 sec.
U
0.0 sec.
A054
DC braking force for
deceleration
Level of DC braking force,
settable from 0 to 100%
U
50. %
A055
DC braking time for
deceleration
Sets the duration for DC braking,
range is from 0.0 to 60.0
seconds
U
0.5 sec.
A056
DC braking / edge or level
detection for [DB] input
Two options; select codes:
00Edge detection
01Level detection
U
01
a057
DC braking force at start
Level of DC braking force at
start, settable from 0 to 100%
U
0. %

46
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
a058
DC braking time at start
Sets the duration for DC braking,
range is from 0.0 to 60.0
seconds
U
0.0 sec.
a059
Carrier frequency during DC
braking
Carrier frequency of DC braking
performance, range is from 2.0 to
15.0kHz
U
5.0 sec.
A061
Frequency upper limit
Sets a limit on output frequency
less than the maximum
frequency (A004).
Range is from frequency lower
limit (A062) to maximum
frequency (A004).
0.0 setting is disabled
>0.0 setting is enabled
U
0.00 Hz
A261
Frequency upper limit,
2nd motor
Sets a limit on output frequency
less than the maximum
frequency (A204).
Range is from frequency lower
limit (A262) to maximum
frequency (A204).
0.0 setting is disabled
>0.0 setting is enabled
U
0.00 Hz
A062
Frequency lower limit
Sets a limit on output frequency
greater than zero.
Range is start frequency (B082)
to frequency upper limit (A061)
0.0 setting is disabled
>0.0 setting is enabled
U
0.00 Hz
A262
Frequency lower limit,
2nd motor
Sets a limit on output frequency
greater than zero.
Range is start frequency (B082)
to frequency upper limit (A261)
0.0 setting is disabled
>0.0 setting is enabled
U
0.00 Hz
A063
A065
A067
Jump freq. (center) 1 to 3
Up to 3 output frequencies can
be defined for the output to jump
past to avoid motor resonances
(center frequency)
Range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.0
0.0
0.0
Hz
A064
A066
A068
Jump freq. width (hysteresis) 1
to 3
Defines the distance from the
center frequency at which the
jump around occurs
Range is 0.0 to 10.0 Hz
U
0.5
0.5
0.5
Hz
A069
Acceleration hold frequency
Sets the frequency to hold
acceleration, range is 0.0
to 400.0Hz
U
0.00 Hz
A070
Acceleration hold time
Sets the duration of acceleration
hold, range is 0.0 to 60.0
seconds
U
0.0 sec.
A071
PID enable
Enables PID function,
three option codes:
00PID Disable
01PID Enable
02PID Enable with reverse
output
U
00

47
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
A072
PID proportional gain
Proportional gain has a range of
0.00 to 25.00
9
1.0
A073
PID integral time constant
Integral time constant has
a range of 0.0 to 3600 seconds
9
1.0 sec.
A074
PID derivative time constant
Derivative time constant has
a range of 0.0 to 100 seconds
9
0.00 sec.
A075
PV scale conversion
Process Variable (PV), scale
factor (multiplier), range of 0.01
to 99.99
U
1.00
A076
PV source
Selects source of Process
Variable (PV), option codes:
00[OI] terminal (current in)
01[O] terminal (voltage in)
02ModBus network
03Pulse train input
10Calculate function output
U
00
A077
Reverse PID action
Two option codes:
00PID input = SP-PV
01PID input = -(SP-PV)
U
00
A078
PID output limit
Sets the limit of PID output as
percent of full scale,
range is 0.0 to 100.0%
U
0.0 %
a079
PID feed forward selection
Selects source of feed forward
gain, option codes:
00Disabled
01[O] terminal (voltage in)
02[OI] terminal (current in)
U
00
A081
AVR function select
U
02
a281
AVR function select,
2
nd
motor
Automatic (output) voltage
regulation, selects from three
type of AVR functions, three
option codes:
00AVR enabled
01AVR disabled
02AVR enabled except during
deceleration
U
02
A082
AVR voltage select
U
200 V
a282
AVR voltage select,
2
nd
motor
200V class inverter settings:
200/215/220/230/240
U
200 V
a083
AVR filter time constant
Define the time constant of the
AVR filter, range is 0 to 10 sec.
U
0.300 sec.
a084
AVR deceleration gain
Gain adjustment of the braking
performance, range is 50
to 200%
U
100. %
A085
Energy-saving operation mode
Two option codes:
00Normal operation
01Energy-saving operation
U
00
A086
Energy-saving mode tuning Range is 0.0 to 100 %.
U
50.0 %

48
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
A092
Acceleration time (2)
9
10.00 sec.
A292
Acceleration time (2),
2
nd
motor
Duration of 2nd segment of
acceleration, range is:
0.01 to 3600 sec.
9
10.00 sec.
A093
Deceleration time (2)
9
10.00 sec.
A293
Deceleration time (2),
2
nd
motor
Duration of 2
nd
segment of
deceleration, range is:
0.01 to 3600 sec.
9
10.00 sec.
A094
Select method to switch to
Acc2/Dec2 profile
U
00
A294
Select method to switch to
Acc2/Dec2 profile, 2
nd
motor
Three options for switching from
1st to 2nd accel/decel:
002CH input from terminal
01Transition frequency
02Forward and reverse
U
00
A095
Acc1 to Acc2 frequency
transition point
U
0.0 Hz
A295
Acc1 to Acc2 frequency
transition point, 2
nd
motor
Output frequency at which
Accel1 switches to Accel2, range
is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.0 Hz
A096
Dec1 to Dec2 frequency
transition point
U
0.0 Hz
A296
Dec1 to Dec2 frequency
transition point, 2
nd
motor
Output frequency at which
Decel1 switches to Decel2,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.0 Hz
A097
Acceleration curve selection
Set the characteristic curve of
Acc1 and Acc2, five options:
00linear
01S-curve
02U-curve
03Inverse U-curve
04EL S-curve
U
01
A098
Deceleration curve selection
Set the characteristic curve of
Dec1 and Dec2, options are
same as above (a097)
U
01
A101
[OI] input active range start
frequency
The output frequency
corresponding to the analog
input range starting point,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.00 Hz
A102
[OI] input active range end
frequency
The output frequency
corresponding to the current
input range ending point,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.0 Hz
A103
[OI] input active range start
current
The starting point (offset) for the
current input range,
range is 0. to 100.%
U
20. %
A104
[OI] input active range end
current
The ending point (offset) for the
current input range,
range is 0. to 100.%
U
100. %
A105
[OI] input start frequency
select
Two options; select codes:
00Use offset (A101 value)
01Use 0Hz
U
00

49
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
a131
Acceleration curve constant Range is 01 to 10.
U
02
a132
Deceleration curve constant Range is 01 to 10.
U
02
A141
A input select for calculate
function
Seven options:
00Operator
01VR
02Terminal [O] input
03Terminal [OI] input
04RS485
05Option
07Pulse train input
U
02
A142
B input select for calculate
function
Seven options:
00Operator
01VR
02Terminal [O] input
03Terminal [OI] input
04RS485
05Option
07Pulse train input
U
03
A143
Calculation symbol
Calculates a value based on the
A input source (A141 selects) and
B input source (A142 selects).
Three options:
00ADD (A input + B input)
01SUB (A input - B input)
02MUL (A input * B input)
U
00
A145
ADD frequency
An offset value that is applied to
the output frequency when the
[ADD] terminal is ON.
Range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
9
0.00 Hz
A146
ADD direction select
Two options:
00Plus (adds A145 value to the
output frequency setting)
01Minus (subtracts A145 value
from the output frequency
setting)
U
00
a150
Curvature of EL-S-curve at the
start of acceleration
Range is 0 to 50%
U
10. %
a151
Curvature of EL-S-curve at the
end of acceleration
Range is 0 to 50%
U
10. %
a152
Curvature of EL-S-curve at the
start of deceleration
Range is 0 to 50%
U
10. %
a153
Curvature of EL-S-curve at the
end of deceleration
Range is 0 to 50%
U
10. %
a154
Deceleration hold frequency
Sets the frequency to hold
deceleration, range is 0.0
to 400.0Hz
U
0.0 Hz
a155
Deceleration hold time
Sets the duration of deceleration
hold, range is 0.0
to 60.0 seconds
U
0.0 sec.

50
“A” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
a156
PID sleep function action
threshold
Sets the threshold for the action,
set range 0.0~400.0 Hz
U
0.00 Hz
a157
PID sleep function action delay
time
Sets the delay time for
the action, set range
0.0~25.5 sec
U
0.0 sec.
A161
[VR] input active range start
frequency
The output frequency
corresponding to the analog
input range starting point,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.00 Hz
A162
[VR] input active range end
frequency
The output frequency
corresponding to the current
input range ending point,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.00 Hz
A163
[VR] input active range start %
The starting point (offset) for the
current input range,
range is 0. to 100.%
U
0. %
A164
[VR] input active range end %
The ending point (offset) for the
current input range,
range is 0. to 100.%
U
100. %
A165
[VR] input start frequency
select
Two options; select codes:
00Use offset (A161 value)
01Use 0Hz
U
01

51
Fine Tuning Functions
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
B001
Restart mode on power failure
/ under-voltage trip
Select inverter restart method,
Five option codes:
00Alarm output after trip, no
automatic restart
01Restart at 0Hz
02Resume operation
after frequency matching
03Resume previous freq. after
freq. matching, then decelerate
to stop and display trip info
04Resume operation after active
freq. matching
U
00
B002
Allowable under-voltage power
failure time
The amount of time a power input
under-voltage can occur without
tripping the power failure alarm.
Range is 0.3 to 25 sec.
If under-voltage exists longer than
this time, the inverter trips, even if
the restart mode is selected.
U
1.0 sec.
B003
Retry wait time before motor
restart
Time delay after under-voltage
condition goes away, before the
inverter runs motor again.
Range is 0.3 to 100 seconds.
U
1.0 sec.
B004
Instantaneous power failure /
under-voltage trip alarm
enable
Three option codes:
00Disable
01Enable
02Disable during stop and
decelerates to a stop
U
00
B005
Number of restarts on power
failure / under-voltage trip
events
Two option codes:
00Restart 16 times
01Always restart
U
00
b007
Restart frequency threshold
Restart the motor from 0Hz if the
frequency becomes less than this
set value during the motor is
coasting, range is 0 to 400Hz
U
0.00 Hz
b008
Restart mode on over voltage /
over current trip
Select inverter restart method,
Five option codes:
00Alarm output after trip, no
automatic restart
01Restart at 0Hz
02Resume operation after
frequency matching
03Resume previous freq. after
active freq. matching, then
decelerate to stop and display
trip info
04Resume operation after active
freq. matching
U
00
b010
Number of retry on over
voltage / over current trip
Range is 1 to 3 times
U
3
times
b011
Retry wait time on over voltage
/ over current trip
Range is 0.3 to 100 sec.
U
1.0 sec.

52
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
B012
Level of electronic thermal
U
A
B212
Level of electronic thermal,
2
nd
motor
Set a level between 20% and 100%
for the rated inverter current.
U
Rated
current for
each
inverter
model *1
A
B013
Electronic thermal
characteristic
U
01
B213
Electronic thermal
characteristic, 2
nd
motor
Select from three curves, option
codes:
00Reduced torque
01Constant torque
02Free setting
U
01
b015
Free setting electronic thermal
~freq.1
Range is 0 to 400Hz
U
0.0 Hz
b016
Free setting electronic thermal
~current1
Range is 0 to inverter rated current
Amps
U
0.00
Amps
b017
Free setting electronic thermal
~freq.2
Range is 0 to 400Hz
U
0.0 Hz
b018
Free setting electronic thermal
~current2
Range is 0 to inverter rated current
Amps
U
0.00
Amps
b019
Free setting electronic thermal
~freq.3
Range is 0 to 400Hz
U
0.0 Hz
b020
Free setting electronic thermal
~current3
Range is 0 to inverter rated current
Amps
U
0.00
Amps
B021
Overload restriction operation
mode
U
01
B221
Overload restriction operation
mode, 2
nd
motor
Select the operation mode during
overload conditions, four options,
option codes:
00Disabled
01Enabled for acceleration and
constant speed
02Enabled for constant speed
only
03Enabled for acceleration and
constant speed, increase speed
at regen.
U
01
B022
Overload restriction level
U
Rated
current
x 1.5
Amps
B222
Overload restriction level,
2
nd
motor
Sets the level of overload restriction,
between 20% and 200% of the rated
current of the inverter, setting
resolution is 1% of rated current
U
Rated
current
x 1.5
Amps
B023
Deceleration rate at overload
restriction
U
1.0 sec.
B223
Deceleration rate at overload
restriction, 2
nd
motor
Sets the deceleration rate when
inverter detects overload, range is
0.1 to 3000.0, resolution 0.1
U
1.0 sec.
b024
Overload restriction operation
mode 2
Select the operation mode during
overload conditions, four options,
option codes:
00Disabled
01Enabled for acceleration and
constant speed
02Enabled for constant speed
only
03Enabled for acceleration and
constant speed, increase speed
at regen.
U
01

53
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
b025
Overload restriction level 2
Sets the level of overload restriction,
between 20% and 200% of the rated
current of the inverter, setting
resolution is 1% of rated current
U
Rated
current
x 1.5
b026
Deceleration rate 2 at overload
restriction
Sets the deceleration rate when
inverter detects overload, range is
0.1 to 3000.0, resolution 0.1
U
1.0 sec.
b027
OC suppression selection
Two option codes:
00Disabled
01Enabled
U
01
B028
Current level of active freq.
matching
Sets the current level of active freq.
matching restart, range is
0.2*inverter rated current to
2.0*inverter rated current, resolution
0.1
U
Rated
current
A
B029
Deceleration rate of active
freq. matching
Sets the deceleration rate when
active freq. matching restart, range
is 0.1 to 3000.0, resolution 0.1
U
0.5 sec.
B030
Start freq. of active freq.
matching
Three option codes:
00freq at previous shutoff
01start from max. Hz
02start from set frequency
U
00
B031
Software lock mode selection
Prevents parameter changes, in five
options, option codes:
00all parameters except B031 are
locked when [SFT] terminal is
ON
01all parameters except B031 and
output frequency F001 are
locked when [SFT] terminal is
ON
02all parameters except B031 are
locked
03all parameters except B031 and
output frequency F001 are
locked
10High level access including
B031
See appendix C for the accessible
parameters in this mode.
U
01
B033
Motor cable length parameter Set range is 5 to 20.
U
10.
b034
Run/power ON warning time
Range is,
0.:Warning disabled
1. to 9999.:
10~99,990 hrs (unit: 10)
1000 to 6553:
100,000~655,350 hrs (unit: 100)
U
0.
Hrs.
B035
Rotation direction restriction
Three option codes:
00No restriction
01Reverse rotation is restricted
02Forward rotation is restricted
U
00
b036
Reduced voltage start
selection
Set range, 0 (disabling the function),
1 (approx. 6ms) to 255 (approx.
1.5s)
U
2

54
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
b037
Function code display
restriction
Seven option codes:
00Full display
01Function-specific display
02User setting (and b037)
03Data comparison display
04Basic display
05Monitor display only
U
04
b038
Initial display selection
000Func. code that SET key
pressed last displayed.(*)
001~030d001~d030 displayed
201F001 displayed
202B display of LCD operator
U
001
B039
Automatic user parameter
registration
Two option codes:
00Disable
01Enable
U
00
B040
Torque limit selection
Four option codes:
00Quadrant-specific setting mode
01Terminal-switching mode
02Analog voltage input mode(O)
U
00
B041
Torque limit 1 (fwd/power)
Torque limit level in forward
powering quadrant, range is 0 to
200%/no(disabled)
U
200 %
b042
Torque limit 2 (rev/power)
Torque limit level in forward
powering quadrant, range is 0 to
200%/no(disabled)
U
200 %
B043
Torque limit 3 (rev/power)
Torque limit level in reverse
powering quadrant, range is 0 to
200%/no(disabled)
U
200 %
B044
Torque limit 4 (fwd/regen.)
Torque limit level in forward regen.
quadrant, range is 0 to
200%/no(disabled)
U
200 %
b045
Torque LAD STOP selection
Two option codes:
00Disable
01Enable
U
00
b046
Reverse run protection
Two option codes:
00No protection
01Reverse rotation is protected
U
01
b049
Dual Rating Selection It is not possible to change.
U
00
B050
Controlled deceleration on
power loss
Four option codes:
00Trips
01Decelerates to a stop
02Decelerates to a stop with DC
bus voltage controlled
03Decelerates to a stop with DC
bus voltage controlled,
then restart
U
00
B051
DC bus voltage trigger level of
ctrl. decel.
Setting of DC bus voltage to start
controlled decel. operation. Range is
0.0 to 1000.0
U
220.0 V
B052
Over-voltage threshold of ctrl.
decel.
Setting the OV-LAD stop level of
controlled decel. operation. Range is
0.0 to 1000.0
U
360.0 V
B053
Deceleration time of ctrl. decel. Range is 0.01 to 3600.0
U
1.0 sec.

55
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
B054
Initial freq. drop of ctrl. decel.
Setting of initial freq. drop.
Range is 0.0 to 10.0 Hz
U
0.0 Hz
B060
Maximum-limit level of window
comparator (O)
Set range, {Min.-limit level (b061) +
hysteresis width (b062)x2} to 100 %
(Minimum of 0%)
U
100. %
B061
Minimum-limit level of window
comparator (O)
Set range, 0 to {Max.-limit level
(b060) - hysteresis width
(b062)x2} % (Maximum of 0%)
9
0. %
B062
Hysteresis width of window
comparator (O)
Set range, 0 to {Max.-limit level
(b060) - Min.-limit level (b061)}/2 %
(Maximum of 10%)
9
0. %
B063
Maximum-limit level of window
comparator (OI)
Set range, {Min.-limit level (b064 +
hysteresis width (b065)x2} to 100 %
(Minimum of 0%)
9
100. %
B064
Minimum-limit level of window
comparator (OI)
Set range, 0 to {Max.-limit level
(b063) - hysteresis width
(b065)x2} % (Maximum of 0%)
9
0. %
b065
Hysteresis width of window
comparator (OI)
Set range, 0 to {Max.-limit level
(b063) - Min.-limit level (b064)}/2 %
(Maximum of 10%)
9
0. %
b070
Operation level at O
disconnection
Set range, 0 to 100%, or “no”
(ignore)
U
no
b071
Operation level at OI
disconnection
Set range, 0 to 100%, or “no”
(ignore)
U
no
b075
Ambient temperature setting
Set range is,
-10~50 C
9
40
C
B078
Watt-hour clearance
Two option codes:
00OFF
01ON (press STR then clear)
9
00
b079
Watt-hour display gain
Set range is,
1.~1000.
9
1.
B082
Start frequency
Sets the starting frequency for the
inverter output, range is 0.10 to 9.99
Hz
U
0.50 Hz
B083
Carrier frequency
Sets the PWM carrier (internal
switching frequency), range is 2.0 to
15.0 kHz
U
2.0 kHz
B084
Initialization mode (parameters
or trip history)
Select initialized data, five option
codes:
00Initialization disabled
01Clears Trip history
02Initializes all Parameters
03Clears Trip history and
initializes all parameters
04Clears Trip history and
initializes all parameters and
EzSQ program
U
00
B085
Country for initialization
Select default parameter values for
country on initialization, two option
codes:
00area A 01area B
U
00
B086
Frequency scaling conversion
factor
Specify a constant to scale the
displayed frequency for D007
monitor, range is 0.01 to 99.99
U
1.00

56
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
B087
STOP key enable
Select whether the STOP key on the
keypad is enabled, three option
codes:
00Enabled
01Disabled always
02 Disabled for stop
U
00
B088
Restart mode after FRS
Selects how the inverter resumes
operation when free-run stop (FRS)
is cancelled, three options:
00Restart from 0Hz
01Restart from frequency
detected from real speed of
motor (freq. matching)
02Restart from frequency
detected from real speed of
motor (active freq. matching)
U
00
b089
Automatic carrier frequency
reduction
Three option codes:
00Disabled
01Enabled, depending on the
output current
02Enabled, depending on the
heat-sink temperature
U
01
b090
Dynamic braking usage ratio
Selects the rate of use (in %) of the
regenerative braking resistor per
100 sec. intervals, range is 0.0 to
100%.
0%: Function disabled
>0%: Enabled, per value
U
0.0 %
B091
Stop mode selection
Select how the inverter stops the
motor, two option codes:
00DEC (decelerate to stop)
01FRS (free-run to stop)
U
00
B092
Cooling fan control
Selects when the fan is ON during
inverter operation, four options:
00Fan is always ON
01Fan is ON during run, OFF
during stop (5 minute delay
from ON to OFF)
02Fan is temperature controlled
U
01
B093
Clear elapsed time of cooling
fan
Two option codes:
00Count
01Clear
U
00
b094
Initialization target data
Select initialized parameters, four
option codes:
00All parameters
01All parameters except in/output
terminals and communication.
02Only registered parameters
in Uxxx.
03All parameters except
registered parameters in Uxxx
and b037.
U
00
b095
Dynamic braking control
(BRD) selection
Three option codes:
00Disable
01Enable during run only
02Enable always
U
01

57
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
b096
BRD activation level
Range is:
330 to 380V (200V class)
U
360 V
b097
BRD resistor value Min.Resistance to 600.0
U
Min.
Resistance
Ohm
B100
Free V/F setting, freq.1 Set range, 0 ~ value of b102
U
0. Hz
b101
Free V/F setting, voltage.1 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
b102
Free V/F setting, freq.2 Set range, value of b100 ~b104
U
0. Hz
b103
Free V/F setting, voltage.2 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
b104
Free V/F setting, freq.3 Set range, value of b102 ~b106
U
0. Hz
b105
Free V/F setting, voltage.3 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
b106
Free V/F setting, freq.4 Set range, value of b104 ~b108
U
0. Hz
b107
Free V/F setting, voltage.4 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
b108
Free V/F setting, freq.5 Set range, value of b108 ~b110
U
0. Hz
b109
Free V/F setting, voltage.5 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
b110
Free V/F setting, freq.6 Set range, value of b108 ~b112
U
0. Hz
b111
Free V/F setting, voltage.6 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
b112
Free V/F setting, freq.7 Set range, b110 ~ 400
U
0. Hz
b113
Free V/F setting, voltage.7 Set range, 0 ~ 800V
U
0.0 V
B120
Brake control enable
Two option codes:
00Disable
01Enable
U
00
b121
Brake Wait Time for Release Set range: 0.00 to 5.00 sec
U
0.00 sec.
b122
Brake Wait Time for
Acceleration
Set range: 0.00 to 5.00 sec
U
0.00 sec.
b123
Brake Wait Time for Stopping Set range: 0.00 to 5.00 sec
U
0.00 sec.
b124
Brake Wait Time for
Confirmation
Set range: 0.00 to 5.00 sec
U
0.00 sec.
b125
Brake release freq. Set range: 0 to 400Hz
U
0.00 sec.
b126
Brake release current
Set range: 0~200% of inverter rated
current
U
(rated
current)
A
b127
Braking freq. setting Set range: 0 to 400Hz
U
0.00 Hz
B130
Deceleration overvoltage
suppression enable
00Disabled
01Enabled
02Enabled with accel.
U
00
B131
Decel. overvolt. suppress level
DC bus voltage of suppression.
Range is:
200V class330 to 395
U
380 V
b132
Decel. overvolt. Suppress
const.
Accel. rate when b130=02.
Set range: 0.10 ~ 30.00 sec.
U
1.00 sec.
B133
Decel. overvolt. Suppress
proportional gain
Proportional gain when b130=01.
Range is: 0.00 to 5.00
9
0.20

58
“b” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
B134
Decel. overvolt. Suppress
integral time
Integration time when b130=01.
Range is: 0.00 to 150.0
9
1.0 sec.
b145
GS input mode
Two option codes:
00No trip (Hardware shutoff only)
01Trip
U
00
b150
Display ex.operator connected
When an external operator is
connected via RS-422 port, the
built-in display is locked and shows
only one "d" parameter configured
in:
d001 ~ d030
U
001
b160
1st parameter of Dual Monitor
U
001
b161
2nd parameter of Dual Monitor
Set any two "d" parameters in b160
and b161, then they can be
monitored in d050. The two
parameters are switched by
up/down keys.
Set range: d001 ~ d030
U
002
b163
Frequency set in monitoring
Two option codes:
00Freq. set disabled
01Freq. set enabled
9
00
b164
Automatic return to the initial
display
10 min. after the last key operation,
display returns to the initial
parameter set by b038. Two option
codes:
00Disable
01Enable
9
00
b165
Ex. operator com. loss action
Five option codes:
00Trip
01Trip after deceleration to a stop
02Ignore
03Coasting (FRS)
04Decelerates to a stop
9
02
b166
Data Read/Write select
00 Read/Write OK
01 Protected
U
00
b171
Inverter mode selection
Three option codes:
00No function
01Std. IM (Induction Motor)
03PM(Permanent Magnet Motor)
U
00
b180
Initialization trigger
(*)
This is to perform initialization by
parameter input with b084, b085 and
b094. Two option codes:
00Initialization disable
01Perform initialization
U
00
b190
Password Settings A
0000(Invalid Password)
0001-FFFF(Password)
U
0000
b191
Password authentication A 0000-FFFF
U
0000
b192
Password Settings B
0000(Invalid Password)
0001-FFFF(Password)
U
0000
b193
Password authentication B 0000-FFFF
U
0000

59
Intelligent Terminal Functions
“C” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
C001
Input [1] function
Select input terminal [1] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
00
[FW]
C002
Input [2] function
Select input terminal [2] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
01
[RV]
C003
Input [3] function
[GS1 assignable]
Select input terminal [3] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
02
[CF1]
C004
Input [4] function
[GS2 assignable]
Select input terminal [4] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
03
[CF2]
C005
Input [5] function
[PTC assignable]
Select input terminal [5] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
09
[2CH]
C006
Input [6] function
Select input terminal [6] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
18
[RS]
C007
Input [7] function
Select input terminal [7] function,
68 options (see next section)
U
13
[USP]
C011
Input [1] active state
U
00
C012
Input [2] active state
U
00
C013
Input [3] active state
U
00
C014
Input [4] active state
U
00
C015
Input [5] active state
U
00
C016
Input [6] active state
U
00
C017
Input [7] active state
Select logic conversion, two option
codes:
00normally open [NO]
01normally closed [NC]
U
00
C021
Output [11] function
[EDM assignable]
U
01
[FA1]
C022
Output [12] function
48 programmable functions
available for logic (discrete) outputs
(see next section)
U
00
[RUN]
C026
Alarm relay function
48 programmable functions
available for logic (discrete) outputs
(see next section)
U
05
[AL]
C027
[EO] terminal selection
(Pulse/PWM output)
13 programmable functions:
00Output frequency (PWM)
01Output current (PWM)
02Output torque (PWM)
03Output frequency (Pulse train)
04Output voltage (PWM)
05Input power (PWM)
06Electronic thermal load ratio
(PWM)
07LAD frequency (PWM)
08Output current (Pulse train)
10Heat sink temperature (PWM)
12General output (PWM)
15Pulse train input monitor
16Option(PWM)
U
07

60
“C” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
C028
[AM] terminal selection
(Analog voltage output
0...10V)
11 programmable functions:
00Output frequency
01Output current
02Output torque
04Output voltage
05Input power
06Electronic thermal load ratio
07LAD frequency
10Heat sink temperature
11Output torque (with code)
13General output
16Option
U
07
[LAD]
C030
Digital current monitor
reference value
Current with digital current monitor
output at 1,440Hz
Range is 20%~200% of rated
current
9
Rated
current
A
C031
Output [11] active state
U
00
C032
Output [12] active state
U
00
C036
Alarm relay active state
Select logic conversion, two option
codes:
00normally open [NO]
01normally closed [NC]
U
01
C038
Output mode of low current
detection
Two option codes:
00During acceleration,
deceleration and constant speed
01During constant speed only
U
01
C039
Low current detection level
Set the level of low load detection,
range is 0.0 to 2.0*inverter rated
current
U
INV rated
current
A
C040
Output mode of overload
warning
Two option codes:
00During accel., decel. And
constant speed
01During constant speed only
U
01
C041
Overload warning level
Sets the overload warning signal
level between 0% and 200% (from
0 to two time the rated current of
the inverter)
U
Rated current
x 1.15
A
C241
Overload warning level, 2nd
motor
Sets the overload warning signal
level between 0% and 200% (from
0 to two time the rated current of
the inverter)
U
Rated current
x 1.15
A
C042
Frequency arrival setting
for acceleration
Sets the frequency arrival setting
threshold for the output frequency
during acceleration,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.0 Hz
C043
Frequency arrival setting
for deceleration
Sets the frequency arrival setting
threshold for the output frequency
during deceleration,
range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.0 Hz
C044
PID deviation level
Sets the allowable PID loop error
magnitude (absolute value),
SP-PV, range is 0.0 to 100%
U
3.0 %
C045
Frequency arrival setting 2
for acceleration
Set range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.00 Hz
C046
Frequency arrival setting 2
for deceleration
Set range is 0.0 to 400.0 Hz
U
0.00 Hz

61
“C” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
C047
Pulse train input/output
scale conversion
If EO terminal is configured as
pulse train input (C027=15), scale
conversion is set in C047.
Pulse-out = Pulse-in (C047)
Set range is 0.01 to 99.99
9
1.00
C052
PID FBV output
high limit
When the PV exceeds this value,
the PID loop turns OFF the PID
second stage output, range is 0.0
to 100%
U
100.0 %
C053
PID FBV output
low limit
When the PV goes below this
value, the PID loop turns ON the
PID second stage output, range is
0.0 to 100%
U
0.0 %
C054
Over-torque/under-torque
selection
Two option codes:
00Over-torque
01Under-torque
U
00
C055
Over/under-torque level
(Forward powering mode)
Set range is 0 to 200%
U
100. %
C056
Over/under-torque level
(Reverse regen. mode)
Set range is 0 to 200%
U
100. %
C057
Over/under-torque level
(Reverse powering mode)
Set range is 0 to 200%
U
100. %
C058
Over/under-torque level
(Forward regen. mode)
Set range is 0 to 200%
U
100. %
C059
Signal output mode of
Over/under-torque
Two option codes:
00During accel., decel. And
constant speed
01During constant speed only
U
01
C061
Electronic thermal warning
level
Set range is 0 to 100%
Setting 0 means disabled.
U
90 %
C063
Zero speed detection level Set range is 0.0 to 100.0Hz
U
0.00 Hz
C064
Heat sink overheat warning
Set range is 0 to 110 C
U
100.
C
C071
Communication speed
Eight option codes:
032,400 bps
044,800 bps
059,600 bps
0619,200 bps
0738,400 bps
0857,600 bps
0976,800 bps
10115,200 bps
U
05 baud
C072
Modbus address
Set the address of the inverter on
the network. Range is 1 to 247
U
1.
C074
Communication parity
Three option codes:
00No parity
01Even parity
02Odd parity
U
00
C075
Communication stop bit
Two option codes:
11 bit
22 bit
U
1 bit

62
“C” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
C076
Communication error
select
Selects inverter response to
communications error.
Five options:
00Trip
01Decelerate to a stop and trip
02Disable
03Free run stop (coasting)
04Decelerates to a stop
U
02
C077
Communication error
time-out
Sets the communications watchdog
timer period.
Range is 0.00 to 99.99 sec
0.0 = disabled
U
0.00 sec.
C078
Communication wait time
Time the inverter waits after
receiving a message before it
transmits.
Range is 0. to 1000. ms
U
0. msec.
C081
O input span calibration
Scale factor between the external
frequency command on terminals
L–O (voltage input) and the
frequency output,
range is 0.0 to 200%
9
100.0 %
C082
OI input span calibration
Scale factor between the external
frequency command on terminals
L–OI (voltage input) and the
frequency output,
range is 0.0 to 200%
9
100.0 %
C085
Thermistor input (PTC)
span calibration
Scale factor of PTC input.
Range is 0.0 to 200%
9
100.0 %
C091
Debug mode enable
Displays debug parameters.
Two option codes:
00Disable
01Enable <Do not set>
(for factory use)
9
00
C096
Communication selection
00Modbus-RTU
01 EzCOM
02 EzCOM<administrator>
U
00
C098
EzCOM start adr. of master 01-08
U
01
C099
EzCOM end adr. of master 01-08
U
01
C100
EzCOM starting trigger
00 Input terminal
01 Always
U
00
C101
Up/Down memory mode
selection
Controls speed setpoint for the
inverter after power cycle.
Two option codes:
00Clear last frequency (return to
default frequency F001)
01Keep last frequency adjusted
by UP/DWN
U
00

63
“C” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
C102
Reset selection
Determines response to Reset
input [RS].
Four option codes:
00Cancel trip state at input signal
ON transition, stops inverter if
in Run Mode
01Cancel trip state at signal OFF
transition, stops inverter if in
Run Mode
02Cancel trip state at input ON
transition, no effect if in
Run Mode
03Clear the memories
only related to trip status
U
00
C103
Restart mode after reset
Determines the restart mode after
reset is given, three option codes:
00Start with 0 Hz
01Start with freq. matching
02Start with active freq. matching
U
00
C104
UP/DWN clear mode
Freq. set value when UDC signal is
given to the input terminal, two
option codes:
000 Hz
01Original setting (in the
EEPROM memory at power on)
U
00
C105
EO gain adjustment Set range is 50 to 200%
9
100. %
C106
AM gain adjustment Set range is 50 to 200%
9
100. %
C109
AM bias adjustment Set range is 0 to 100%
9
0. %
C111
Overload warning level 2
Sets the overload warning signal
level between 0% and 200% (from
0 to two time the rated current of
the inverter)
9
Rated current
x 1.15
A
C130
Output [11] on delay
U
0.0 sec.
C131
Output [11] off delay
Set range is 0.0 to 100.0 sec.
U
0.0 sec.
C132
Output [12] on delay
U
0.0 sec.
C133
Output [12] off delay
Set range is 0.0 to 100.0 sec.
U
0.0 sec.
C140
Relay output on delay
U
0.0 sec.
C141
Relay output off delay
Set range is 0.0 to 100.0 sec.
U
0.0 sec.
C142
Logic output 1 operand A
U
00
C143
Logic output 1 operand B
All the programmable functions
available for logic (discrete) outputs
except LOG1 to LOG3, OPO, no
U
00
C144
Logic output 1 operator
Applies a logic function to calculate
[LOG] output state,
Three options:
00[LOG] = A AND B
01[LOG] = A OR B
02[LOG] = A XOR B
U
00
C145
Logic output 2 operand A
U
00
C146
Logic output 2 operand B
All the programmable functions
available for logic (discrete) outputs
except LOG1 to LOG3, OPO, no
U
00

64
“C” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
C147
Logic output 2 operator
Applies a logic function to calculate
[LOG] output state,
Three options:
00[LOG] = A AND B
01[LOG] = A OR B
02[LOG] = A XOR B
U
00
C148
Logic output 3 operand A
U
00
C149
Logic output 3 operand B
All the programmable functions
available for logic (discrete) outputs
except LOG1 to LOG3, OPO, no
U
01
C150
Logic output 3 operator
Applies a logic function to calculate
[LOG] output state,
Three options:
00[LOG] = A AND B
01[LOG] = A OR B
02[LOG] = A XOR B
U
00
C160
Input [1] response time
U
1.
C161
Input [2] response time
U
1.
C162
Input [3] response time
U
1.
C163
Input [4] response time
U
1.
C164
Input [5] response time
U
1.
C165
Input [6] response time
U
1.
C166
Input [7] response time
Sets response time of each input
terminal, set range:
0 (x 2 [ms]) to 200 (x 2 [ms])
(0 to 400 [ms])
U
1.
C169
Multistage speed/position
determination time
Set range is 0. to 200. (x 10ms)
U
0. msec.
Input Function Summary Table – This table shows all thirty-one intelligent input functions
at a glance. Detailed description of these functions, related parameters and settings, and
example wiring diagrams are in “Using Intelligent Input Terminals” on page 27.
Input Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON Inverter is in Run Mode, motor runs forward
00
FW FORWARD Run/Stop
OFF Inverter is in Stop Mode, motor stops
ON Inverter is in Run Mode, motor runs reverse
01
RV Reverse Run/Stop
OFF Inverter is in Stop Mode, motor stops
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 0, logical 1
02
CF1
Multi-speed Select,
Bit 0 (LSB)
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 0, logical 0
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 1, logical 1
03
CF2
Multi-speed Select,
Bit 1
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 1, logical 0
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 2, logical 1
04
CF3
Multi-speed Select,
Bit 2
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 2, logical 0
ON Binary encoded speed select, Bit 3, logical 1
05
CF4
Multi-speed Select,
Bit 3 (MSB)
OFF Binary encoded speed select, Bit 3, logical 0
ON
Inverter is in Run Mode, output to motor runs at
jog parameter frequency
06
JG Jogging
OFF Inverter is in Stop Mode
ON DC braking will be applied during deceleration
07
DB External DC braking
OFF DC braking will not be applied
ON
The inverter uses 2nd motor parameters for
generating frequency output to motor
08
SET
Set (select) 2nd Motor
Data
OFF
The inverter uses 1st (main) motor parameters
for generating frequency output to motor

65
Input Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON
Frequency output uses 2nd-stage acceleration and
deceleration values
09
2CH
2-stage Acceleration
and Deceleration
OFF
Frequency output uses standard acceleration and
deceleration values
ON
Causes output to turn OFF, allowing motor to free run
(coast) to stop
11
FRS Free-run Stop
OFF
Output operates normally, so controlled deceleration
stop motor
ON
When assigned input transitions OFF to ON, inverter
latches trip event and displays
E 12
12
EXT External Trip
OFF
No trip event for ON to OFF, any recorded trip events
remain in history until reset
ON
On powerup, the inverter will not resume a Run
command (mostly used in the US)
13
USP
Unattended Start
Protection
OFF
On powerup, the inverter will resume a Run command
that was active before power loss
ON Motor can be driven by commercial power
14
CS
Commercial power
source switchover
OFF Motor is driven via the inverter
ON
The keypad and remote programming devices are
prevented from changing parameters
15
SFT Software Lock
OFF The parameters may be edited and stored
ON
16
AT
Analog Input
Voltage/Current Select
OFF
Refer to “Analog Input Settings” on page 41.
ON
The trip condition is reset, the motor output is turned
OFF, and powerup reset is asserted
18
RS Reset Inverter
OFF Normal power-ON operation
ANLG
When a thermistor is connected to terminal [5] and [L],
the inverter checks for over-temperature and will cause
trip event and turn OFF output to motor
19
PTC
PTC thermistor
Thermal Protection
(C005 only)
OPEN
A disconnect of the thermistor causes a trip event, and
the inverter turns OFF the motor
ON Starts the motor rotation
20
STA Start
(3-wire interface)
OFF
No change to present motor status
ON Stops the motor rotation
21
STP Stop
(3-wire interface)
OFF No change to present motor status
ON Selects the direction of motor rotation: ON = FWD.
While the motor is rotating, a change of F/R will start a
deceleration, followed by a change in direction
22
F/R FWD, REV
(3-wire interface)
OFF Selects the direction of motor rotation: OFF = REV.
While the motor is rotating, a change of F/R will start a
deceleration, followed by a change in direction
ON Temporarily disables PID loop control. Inverter output
turns OFF as long as PID Enable is active (A071=01)
23
PID PID Disable
OFF Has no effect on PID loop operation, which operates
normally if PID Enable is active (A071=01)
ON Resets the PID loop controller. The main consequence
is that the integrator sum is forced to zero
24
PIDC PID Reset
OFF No effect on PID controller
ON Accelerates (increases output frequency) motor from
current frequency
27
UP Remote Control UP
Function (motorized
speed pot.)
OFF Output to motor operates normally
ON Decelerates (decreases output frequency) motor from
current frequency
28
DWN Remote Control Down
Function (motorized
speed pot.)
OFF Output to motor operates normally

66
Input Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON Clears the UP/DWN frequency memory by forcing it to
equal the set frequency parameter F001. Setting C101
must be set=00 to enable this function to work
29
UDC Remote Control Data
Clearing
OFF UP/DWN frequency memory is not changed
ON
Forces the source of the output frequency setting A001
and the source of the Run command A002 to be from
the digital operator
31
OPE Operator Control
OFF
Source of output frequency set by A001 and source of
Run command set by A002 is used
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 1, logical 1
32
SF1 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 1
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 1, logical 0
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 2, logical 1
33
SF2 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 2
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 2, logical 0
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 3, logical 1
34
SF3 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 3
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 3, logical 0
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 4, logical 1
35
SF4 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 4
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 4, logical 0
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 5, logical 1
36
SF5 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 5
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 5, logical 0
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 6, logical 1
37
SF6 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 6
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 6, logical 0
ON Bit encoded speed select, Bit 7, logical 1
38
SF7 Multi-speed Select,
Bit operation Bit 7
OFF Bit encoded speed select, Bit 7, logical 0
ON Perform overload restriction
39
OLR Overload Restriction
Source Changeover
OFF Normal operation
ON
Setting of b040 is enabled
40
TL Torque Limit Selection
OFF Max. torque is limited with 200%
ON
41
TRQ1 Torque limit switch 1
OFF
ON
42
TRQ2 Torque limit switch 2
OFF
Torque limit related parameters of Powering/regen, and
FW/RV modes are selected by the combinations of
these inputs.
ON
Brake wait time (b124) is valid
44
BOK Brake confirmation
OFF
Brake wait time (b124) is not valid
ON Set ramp times are ignored. Inverter output
immediately follows the freq. command.
46
LAC LAD cancellation
OFF Accel. and/or decel. is according to the
set ramp time
ON Clear the position deviation data
47
PCLR Pulse counter clear
OFF Maintain the position deviation data
ON
Adds the A145 (add frequency) value
to the output frequency
50
ADD ADD frequency enable
OFF
Does not add the A145 value to the
output frequency
ON Force inverter to use input terminals
for output frequency and Run command sources
51
F-TM Force Terminal Mode
OFF
Source of output frequency set by A001 and source of
Run command set by A002 is used
ON Torque control command input is enabled
52
ATR Enable torque
command input
OFF Torque control command input is disabled
ON Clear watt-hour data
53
KHC Clear watt-hour data
OFF No action
ON General purpose input (1) is made ON under EzSQ
56
MI1 General purpose input
(1)
OFF General purpose input (1) is made OFF under EzSQ
ON General purpose input (2) is made ON under EzSQ
57
MI2 General purpose input
(2)
OFF General purpose input (2) is made OFF under EzSQ

67
Input Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON General purpose input (3) is made ON under EzSQ
58
MI3 General purpose input
(3)
OFF General purpose input (3) is made OFF under EzSQ
ON General purpose input (4) is made ON under EzSQ
59
MI4 General purpose input
(4)
OFF General purpose input (4) is made OFF under EzSQ
ON General purpose input (5) is made ON under EzSQ
60
MI5 General purpose input
(5)
OFF General purpose input (5) is made OFF under EzSQ
ON General purpose input (6) is made ON under EzSQ
61
MI6 General purpose input
(6)
OFF General purpose input (6) is made OFF under EzSQ
ON General purpose input (7) is made ON under EzSQ
62
MI7 General purpose input
(7)
OFF General purpose input (7) is made OFF under EzSQ
ON Analog command is held
65
AHD Analog command hold
OFF Analog command is not held
ON
66
CP1 Multistage-position
switch (1)
OFF
ON
67
CP2 Multistage-position
switch (2)
OFF
ON
68
CP3 Multistage-position
switch (3)
OFF
Multistage position commands are set according to the
combination of these switches.
ON Limit signal of homing is ON
69
ORL Limit signal of homing
OFF Limit signal of homing is OFF
ON Starts homing operation
70
ORG Trigger signal of
homing
OFF No action
ON Speed control mode
73
SPD Speed/position
changeover
OFF Position control mode
ON
77
GS1 GS1 input
OFF
ON
78
GS2 GS2 input
OFF
EN60204-1 related signals:
Signal input of “Safe torque off” function.
ON Starts EzCOM
81
485 Start EzCOM
OFF No execution
ON Executing EzSQ program
82
PRG Executing EzSQ
program
OFF No execution
ON Retain the current output frequency
83
HLD Retain output
frequency
OFF No retention
ON Run command permitted
84
ROK Permission of Run
command
OFF Run command is not permitted
ON Forward rotation
85
EB Rotation direction
detection (C007 only)
OFF Reverse rotation
ON
Only a parameter configured in b038 is shown
86
DISP Display limitation
OFF All the monitors can be shown
ON (input ignored)
255
no No function
OFF (input ignored)

68
Output Function Summary Table – This table shows all functions for the logical outputs
(terminals [11], [12] and [AL]) at a glance. Detailed descriptions of these functions, related
parameters and settings, and example wiring diagrams are in “Using Intelligent Output
Terminals” on page 36.
Output Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON When the inverter is in Run Mode
00
RUN Run Signal
OFF When the inverter is in Stop Mode
ON When output to motor is at the set frequency
01
FA1 Frequency Arrival Type
1–Constant Speed
OFF When output to motor is OFF, or in any
acceleration or deceleration ramp
ON When output to motor is at or above the set freq,
even if in accel (C042) or decel (C043) ramps
02
FA2 Frequency Arrival Type
2–Over frequency
OFF When output to motor is OFF,
or at a level below the set frequency
ON When output current is more than the set
threshold (C041) for the overload signal
03
OL Overload Advance
Notice Signal 1
OFF When output current is less than the set threshold
for the deviation signal
ON When PID error is more than the set threshold for
the deviation signal
04
OD Output Deviation
for PID Control
OFF When PID error is less than the set threshold for
the deviation signal
ON When an alarm signal has occurred and has not
been cleared
05
AL Alarm Signal
OFF When no alarm has occurred since the last
cleaning of alarm(s)
ON When output to motor is at the set frequency,
during accel (C042) and decel (C043).
06
FA3 Frequency Arrival Type
3–Set frequency
OFF When output to motor is OFF,
or is not at a level of the set frequency
ON Estimated motor torque exceeds
the specified level
07
OTQ Over/under Torque
Signal
OFF Estimated motor torque is lower than
the specified level
ON Inverter is in Undervoltage
09
UV Undervoltage
OFF Inverter is not in Undervoltage
ON Torque limit function is executing
10
TRQ Torque Limited Signal
OFF Torque limit function is not executing
ON Total running time of the inverter exceeds
the specified value
11
RNT Run Time Expired
OFF Total running time of the inverter does not exceed
the specified value
ON Total power ON time of the inverter exceeds
the specified value
12
ONT Power ON time Expired
OFF Total power ON time of the inverter does not
exceed the specified value
ON Accumulated thermal count exceeds
the C061 set value
13
THM Thermal Warning
OFF Accumulated thermal count does not exceed the
C061 set value
ON Output for brake release
19
BRK Brake Release Signal
OFF No action for brake
ON Brake error has occurred
20
BER Brake Error Signal
OFF Brake performance is normal

69
Output Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON Output frequency falls below the threshold
specified in C063
21
ZS Zero Hz Speed
Detection Signal
OFF Output frequency is higher than the threshold
specified in C063
ON Deviation of speed command and actual speed
exceeds the specified value P027.
22
DSE Speed Deviation
Excessive
OFF Deviation of speed command and actual speed
does not exceed the specified value P027.
ON Positioning is completed
23
POK Positioning Completion
OFF Positioning is not completed
ON When output to motor is at or above the set freq.,
even if in accel (C045) or decel (C046) ramps
24
FA4 Frequency Arrival Type
4–Over frequency
OFF When output to motor is OFF, or at a level below
the set frequency
ON When output to motor is at the set frequency,
during accel (C045) and decel (C046).
25
FA5 Frequency Arrival Type
5–Set frequency
OFF When output to motor is OFF, or is not at a level of
the set frequency
ON When output current is more than the set
threshold (C111) for the overload signal
26
OL2 Overload Advance
Notice Signal 2
OFF When output current is less than the set threshold
for the deviation signal
ON
When the [O] input value < B070 setting (signal
loss detected)
27
ODc Analog Voltage Input
Disconnect Detection
OFF When no signal loss is detected
ON
When the [OI] input value < B071 setting (signal
loss detected)
28
OIDc Analog Current input
Disconnect Detection
OFF When no signal loss is detected
ON Transitions to ON when the inverter is in RUN
Mode and the PID Process Variable (PV) is less
than the Feedback Low Limit (C053)
31
FBV PID Second Stage
Output
OFF Transitions to OFF when the PID Process Variable
(PV) exceeds the PID High Limit (C052), and
transitions to OFF when the inverter goes from
Run Mode to Stop Mode
ON When the communications watchdog timer (period
specified by C077) has time out
32
NDc Network Disconnect
Detection
OFF When the communications watchdog timer is
satisfied by regular communications activity
ON
When the Boolean operation specified by C143
has a logical “1” result
33
LOG1 Logic Output Function 1
OFF
When the Boolean operation specified by C143
has a logical “0” result
ON
When the Boolean operation specified by C146
has a logical “1” result
34
LOG2 Logic Output Function 2
OFF
When the Boolean operation specified by C146
has a logical “0” result
ON
When the Boolean operation specified by C149
has a logical “1” result
35
LOG3 Logic Output Function 3
OFF
When the Boolean operation specified by C149
has a logical “0” result
ON Lifetime of internal capacitor has expired.
39
WAC Capacitor Life Warning
Signal
OFF Lifetime of internal capacitor has not expired.

70
Output Function Summary Table
Option
Code
Terminal
Symbol
Function Name Description
ON Lifetime of cooling fan has expired.
40
WAF Cooling Fan Warning
Signal
OFF Lifetime of cooling fan has not expired.
ON Either FW or RV command is given to the inverter
41
FR Starting Contact Signal
OFF No FW or RV command is given to the inverter, or
both are given to the inverter
ON Temperature of the heat sink exceeds a specified
value (C064)
42
OHF Heat Sink Overheat
Warning
OFF Temperature of the heat sink does not exceed a
specified value (C064)
ON Motor current is less than the specified value
(C039)
43
LOC Low load detection
OFF Motor current is not less than the specified value
(C039)
ON General output 1 is ON
44
MO1 General Output 1
OFF General output 1 is OFF
ON General output 2 is ON
45
MO2 General Output 2
OFF General output 2 is OFF
ON General output 3 is ON
46
MO3 General Output 3
OFF General output 3 is OFF
ON Inverter can receive a run command
50
IRDY Inverter Ready Signal
OFF Inverter cannot receive a run command
ON Inverter is driving the motor in forward direction
51
FWR Forward Rotation
OFF Inverter is not driving the motor in forward
direction
ON Inverter is driving the motor in reverse direction
52
RVR Reverse Rotation
OFF Inverter is not driving the motor in reverse
direction
ON Inverter is tripping with major failure
53
MJA Major Failure Signal
OFF Inverter is normal, or is not tripping with major
failure
ON Analog voltage input value is inside of the window
comparator
54
WCO Window Comparator for
Analog Voltage Input
OFF Analog voltage input value is outside of the
window comparator
ON Analog current input value is inside of the window
comparator
55
WCOI Window Comparator for
Analog Current Input
OFF Analog current input value is outside of the
window comparator
ON Frequency command is given from the operator
58
FREF Frequency Command
Source
OFF Frequency command is not given from the
operator
ON Run command is given from the operator
59
REF Run Command Source
OFF Run command is not given from the operator
ON 2nd motor is being selected
60
SETM 2nd Motor Selection
OFF 2
nd
motor is not being selected
ON STO is being performed
62
EDM STO (Safe Torque Off)
Performance Monitor
(Output terminal 11
only)
OFF STO is not being performed
ON (output terminal for option card)
63
OPO Option card output
OFF (output terminal for option card)
ON -
255
no Not used
OFF -

71
Motor Constants Functions
“H” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
H001
Auto-tuning selection
Three option codes:
00Disabled
01Enabled with motor stop
02Enabled with motor rotation
U
00
H002
Motor constant selection
U
00
H202
Motor constant selection,
2
nd
motor
Four option codes:
00Hitachi standard motor
02Auto tuned data
U
00
H003
Motor capacity
U
kW
H203
Motor capacity,
2
nd
motor
Eleven selections:
0.1/0.2/0.4/0.75/1.5/2.2/3.7/
5.5/7.5/11/15/18.5
U
Specified by
the capacity
of each
inverter
model
kW
H004
Motor poles setting
U
4 poles
H204
Motor poles setting,
2
nd
motor
Four selections:
2 / 4 / 6 / 8 / 10
U
4 poles
H005
Motor speed response
constant
9
100.
H205
Motor speed response
constant, 2
nd
motor
Set range is 1 to 1000
9
100.
H006
Motor stabilization constant
9
100.
H206
Motor stabilization
constant, 2nd motor
Motor constant (factory set),
range is 0 to 255
9
100.
H020
Motor constant R1
(Hitachi motor)
U
ohm
H220
Motor constant R1,
2nd motor (Hitachi motor)
0.001~65.535 ohms
U
ohm
H021
Motor constant R2
(Hitachi motor)
U
ohm
H221
Motor constant R2,
2nd motor
(Hitachi motor)
0.001~65.535 ohms
U
ohm
H022
Motor constant L
(Hitachi motor)
U
mH
H222
Motor constant L,
2nd motor
(Hitachi motor)
0.01~655.35mH
U
mH
H023
Motor constant I0
(Hitachi motor)
U
A
H223
Motor constant I0,
2nd motor
(Hitachi motor)
0.01~655.35A
U
A
H024
Motor constant J
(Hitachi motor)
U
kgm2
H224
Motor constant J,
2nd motor
(Hitachi motor)
0.001~9999 kgm
2
U
Specified by
the capacity
of each
inverter
mode
kgm
2
H030
Motor constant R1
(Auto tuned data)
U
ohm
H230
Motor constant R1,
2nd motor
(Auto tuned data)
0.001~65.535 ohms
U
ohm
H031
Motor constant R2
(Auto tuned data)
0.001~65.535 ohms
U
Specified by
the capacity
of each
inverter
mode
ohm

72
“H” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
H231
Motor constant R2,
2nd motor
(Auto tuned data)
U
ohm
H032
Motor constant L
(Auto tuned data)
U
mH
H232
Motor constant L,
2nd motor
(Auto tuned data)
0.01~655.35mH
U
mH
H033
Motor constant I0
(Auto tuned data)
U
A
H233
Motor constant I0,
2nd motor
(Auto tuned data)
0.01~655.35A
U
A
H034
Motor constant J
(Auto tuned data)
U
kgm2
H234
Motor constant J,
2nd motor
(Auto tuned data)
0.001~9999 kgm
2
U
kgm2
H050
Slip compensation P gain
for V/f control with FB
0.00-10.00
U
0.2 Times
H051
Slip compensation I gain
for V/f control with FB
0.-1000.
U
2. s
PM Motor Constants Functions
“H” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
H102
PM motor code setting
00Hitachi standard
(Use H106-H110 at motor
constants)
01Auto-Tuning
(Use H109-H110, H111-H113
at
motor constants)
U
00
H103
PM motor capacity
0.1/0.2/0.4/0.55/0.75/1.1/1.5/2.2/3.0
/3.7/
4.0/5.5/7.5/11.0/15.0/18.5
U
kW
dependent
kW
H104
PM motor pole setting
2/4/6/8/10/12/14/16/18/20/22/24/26/
28/
30/32/34/36/38/40/42/44/46/48
U
kW
dependent
Poles
H105
PM Rated Current
(0.00-1.00)×Rated current of
the inverter [A]
U
kW
dependent
A
H106
PM const R(Resistance) 0.001-65.535 [Ω]
U
kW
dependent
ohm
H107
PM const Ld
(d-axis inductance)
0.01-655.35 [mH]
U
kW
dependent
mH
H108
PM const Lq
(q-axis inductance)
0.01-655.35 [mH]
U
kW
dependent
mH
H109
PM const Ke
(Induction voltage constant)
0.0001-6.5535 [V/(rad/s)]
U
kW
dependent
V/(rad/s)
H110
PM const J(Moment of
inertia)
0.001-9999.000 [kgm
2
]
U
kW
dependent
kgm2
H111
PM const R (Resistance,
Auto)
0.001-65.535 [Ω]
U
kW
dependent
ohm

73
“H” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
H112
PM const Ld
(d-axis inductance, Auto)
0.01-655.35 [mH]
U
kW
dependent
mH
H113
PM const Lq
(q-axis inductance, Auto)
0.01-655.35 [mH]
U
kW
dependent
mH
H116
PM Speed Response 1-1000 [%]
U
100
%
H117
PM Starting Current 20.00-100.00 [%]
U
70.00[%]
%
H118
PM Starting Time 0.01-60.00 [s]
U
1.00[s]
s
H119
PM Stabilization Constant 0-120 [%]
U
100[%]
%
H121
PM Minimum Frequency 0.0-25.5 [%]
9
8.0 [%]
%
H122
PM No-Load Current 0.00-100.00 [%]
9
10.00 [%]
%
H123
PM Starting Method Select
00 Normal
01 Initial Magnet Position
Estimation
U
0
H131
PM Initial Magnet Position
Estimation 0V Wait Times
0-255
U
10
H132
PM Initial Magnet Position
Estimation Detect Wait
Times
0-255
U
10
H133
PM Initial Magnet Position
Estimation Detect Times
0-255
U
30
H134
PM Initial Magnet Position
Estimation Voltage Gain
0-200
U
100

74
Expansion Card Functions
“P” parameters will be appeared when the expansion option is connected.
“P” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
P001
Reaction when option card
error occurs
Two option codes:
00…Inverter trips
01…Ignores the error (Inverter
continues operation)
U
00
P003
[EA] terminal selection
Three option codes:
00…Speed reference (incl. PID)
01…For control with encoder
feedback
02…Extended terminal for EzSQ
U
00
P004
Pulse train input mode
selection for feedback
Four option codes:
00…Single-phase pulse [EA]
01…2-phase pulse (90 difference) 1
([EA] and [EB])
02…2-phase pulse (90 difference) 2
([EA] and [EB])
03…Single-phase pulse [EA] and
direction signal [EB]
U
00
P011
Encoder pulse setting
Sets the pulse number (ppr) of the
encoder, set range is 32~1024
pulses
U
512.
P012
Simple positioning selection
Two option codes:
00…simple positioning deactivated
01…simple positioning activated
U
00
p015
Creep Speed
Set range is start frequency (b082)
~10.00 Hz
U
5.00
Hz
P026
Over-speed error detection
level
Set range is 0~150%
U
115.0
%
P027
Speed deviation error
detection level
Set range is 0~120 Hz
U
10.00
Hz
P031
Deceleration time Input Type
00…Operator
03…EzSQ
U
00
P033
Torque command input
selection
Six option codes:
00…Analog voltage input [O]
01…Analog current input [OI]
03…Operator, 06…Option
U
00
P034
Torque command level input Set range is 0~200%
9
0.
%
p036
Torque bias mode selection
Five option codes:
00…No bias 01…Operator
U
00
p037
Torque bias value setting Range is –200~200%
9
0.
%
p038
Torque bias polar selection
Two option codes:
00…According to the sign
01…According to the rotation
direction
05…Option
U
00
p039
Speed limit of Torque control
(Forward rotation)
Set range is 0.00~120.00Hz
9
0.00
Hz
p040
Speed limit of Torque control
(Forward rotation)
Set range is 0.00~120.00Hz
9
0.00
Hz

75
“P” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
p041
Speed / Torque control
switching time
Set range is 0 to 1000 ms
U
0.
ms
P044
Communication watchdog
timer
(for option)
Set range is 0.00 to 99.99s
U
1.00
s
P045
Inverter action on
communication error
(for option)
00 (tripping),
01 (tripping after decelerating and
stopping the motor),
02 (ignoring errors),
03 (stopping the motor after
free-running),
04 (decelerating and stopping
the motor)
U
00
P046
DeviceNet polled I/O:
Output instance number
0-20
U
1
P048
Inverter action on
communication idle mode
00 (tripping),
01 (tripping after decelerating and
stopping the motor),
02 (ignoring errors),
03 (stopping the motor after
free-running),
04 (decelerating and stopping the
motor)
U
00
P049
Motor poles setting for RPM
0/2/4/6/8/10/12/14/16/18/20/22/24/26
/28/
30/32/34/36/38/40/42/44/46/48
U
0
p055
Pulse train input frequency
scale setting
Sets the pulse numbers at max.
frequency, set range is 1.0~32.0 kHz
U
25.0
kHz
p056
Pulse train input frequency
filter time constant setting
Set range is 0.01~2.00 sec.
U
0.10
sec.
p057
Pulse train input bias setting Set range is –100~100 %
U
0.
%
p058
Limitation of the pulse train
input setting
Set range is 0~100 %
U
100.
%
P060
Multistage position 0
9
0
P061
Multistage position 1
9
0
P062
Multistage position 2
9
0
P063
Multistage position 3
9
0
P064
Multistage position 4
9
0
P065
Multistage position 5
9
0
P066
Multistage position 6
9
0
P067
Multistage position 7
P073 to P072
(Displayed higher 4-digits only)
9
0
P068
Homing mode selection
00…Low speed mode
01…High speed mode
9
00
P069
Homing direction
00…Forward rotation side
01…Reverse rotation side
9
01
P070
Low speed homing freq. 0 to 10Hz
9
5.00 Hz
P071
High speed homing freq. 0 to 400Hz
9
5.00 Hz
P072
Position range (Forward)
0 to +268435455(Higher 4-digits
displayed)
9
+268435
455
P073
Position range (Reverse)
–268435455 to 0(Higher 4-digits
displayed)
9
-2684354
55

76
“P” Function Defaults
Func.
Code
Name Description
Run
Mode
Edit
Initial data Units
P075
Positioning mode selection
00…With limitation
01…No limitation (shorter route)
P004 is to be set 00 or 01
U
00
P077
Encoder disconnection
timeout
0.0 to 10.0 s
9
1.0 sec.
p100
~
P131
EzSQ user parameter
U(00) ~ U(31)
Each set range is 0~65535
9
0.
P140
EzCOM number of data 1 to 5
9
5
P141
EzCOM destination 1 address 1 to 247
9
1
P142
EzCOM destination 1 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P143
EzCOM source 1 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P144
EzCOM destination 2 address 1 to 247
9
2
P145
EzCOM destination 2 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P146
EzCOM source 2 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P147
EzCOM destination 3 address 1 to 247
9
3
P148
EzCOM destination 3 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P149
EzCOM source 3 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P150
EzCOM destination 4 address 1 to 247
9
4
P151
EzCOM destination 4 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P152
EzCOM source 4 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P153
EzCOM destination 5 address 1 to 247
9
5
P154
EzCOM destination 5 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
P155
EzCOM source 5 register 0000 to FFFF
9
0000
 Loading...
Loading...