Hitachi HCS721050CLA382, 7K1000C, A7K2000, HCS721010CLA332, HCS721025CLA382 User Manual
...Page 1

Hitachi Global Storage Technologies
Models:
HDS721016CLA382
HDS721016CLA682
HDS721025CLA382
HDS721025CLA682
HDS721032CLA362
HDS721032CLA662
HDS721050CLA362
HDS721050CLA662
HDS721064CLA332
HDS721064CLA632
HDS721075CLA332
HDS721075CLA632
HDS721010CLA332
HDS721010CLA632
HUA722050CLA330/1
HUA722010CLA330/1
HCS721016CLA382
HCS721025CLA382
HCS721032CLA382
HCS721050CLA382
HCS721075CLA332
HCS721010CLA332
Hard Disk Drive Specification
Hitachi Deskstar 7K1000.C
Hitachi Ultrastar A7K2000
Hitachi CinemaStar 7K1000.C
3.5 inch Serial ATA hard disk drive
Revision 2.6 30. June. 2011
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
1
Page 2

Revision 2.6 (30 June 2011)
The following paragraph does not apply to the United Kingdom or any country where such provisions are
inconsistent with local law: HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECHNOLOGIES PROVIDES THIS
PUBLICATION "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some states do not allow disclaimer or express or implied
warranties in certain transactions, therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This publication could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to
the information herein; these changes will be incorporated in new editions of the publication. Hitachi may
make improvements or changes in any products or programs described in this publication at any time.
It is possible that this publication may contain reference to, or information about, Hitachi products (machines
and programs), programming, or services that are not announced in your country. Such references or
information must not be construed to mean that Hitachi intends to announce such Hitachi products,
programming, or services in your country.
Technical information about this product is available by contacting your local Hitachi Global Storage
Technologies representative or on the Internet at http://www.hitachigst.com
Hitachi Global Storage Technologies may have patents or pending patent applications covering subject matter
in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these patents.
© Copyright Hitachi Global Storage Technologies
Note to U.S. Government Users —Documentation related to restricted rights —Use, duplication or disclosure
is subject to restrictions set forth in GSA ADP Schedule Contract with Hitachi Global Storage Technologies.
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
2
Page 3

Table of contents
1 General ................................................................................................................................................................10
1.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Glossary ........................................................................................................................................... 11
1.3 General caution ............................................................................................................................... 11
1.4 References ....................................................................................................................................... 11
2 General features .................................................................................................................................................12
Part 1. Functional specification ....................................................................................................................... 13
3 Fixed disk subsystem description .......................................................................................................................14
3.1 Control Electronics ......................................................................................................................... 14
3.2 Head disk assembly ........................................................................................................................ 14
3.3 Actuator ........................................................................................................................................... 14
4 Drive characteristics ............................................................................................................................................15
4.1 Default logical drive parameters ................................................................................................... 15
4.2 Data sheet ....................................................................................................................................... 17
4.3 World Wide Name Assignment ...................................................................................................... 17
4.4 Drive organization .......................................................................................................................... 18
4.5 Performance characteristics .......................................................................................................... 19
5 Defect flagging strategy ......................................................................................................................................23
6 Specification ........................................................................................................................................................24
6.1 Electrical interface ......................................................................................................................... 24
6.2 Environment ................................................................................................................................... 28
6.3 DC power requirements ................................................................................................................. 30
6.4 Reliability ........................................................................................................................................ 32
6.5 Mechanical specifications............................................................................................................... 34
6.6 Vibration and shock ........................................................................................................................ 40
6.7 Acoustics .......................................................................................................................................... 43
6.8 Identification labels ........................................................................................................................ 43
6.9 Safety ............................................................................................................................................... 44
6.10 Electromagnetic compatibility ....................................................................................................... 45
Part 2. Interface Specification ......................................................................................................................... 46
7 General ................................................................................................................................................................47
7.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 47
7.2 Terminology ..................................................................................................................................... 47
7.3 Deviations From Standard............................................................................................................. 47
8 Registers .............................................................................................................................................................48
8.1 Alternate Status Register .............................................................................................................. 48
8.2 Command register .......................................................................................................................... 48
8.3 Cylinder High Register .................................................................................................................. 48
8.4 Cylinder Low Register .................................................................................................................... 49
8.5 Data Register .................................................................................................................................. 49
8.6 Device Control Register.................................................................................................................. 49
8.7 Drive Address Register ................................................................................................................... 50
8.8 Device/Head Register ..................................................................................................................... 50
8.9 Error Register ................................................................................................................................. 51
8.10 Features Register ........................................................................................................................... 52
8.11 Sector Count Register .................................................................................................................... 52
8.12 Sector Number Register ................................................................................................................. 52
8.13 Status Register ............................................................................................................................... 53
9 General Operation Descriptions ..........................................................................................................................54
9.1 Reset Response ............................................................................................................................... 54
9.2 Diagnostic and Reset considerations............................................................................................. 55
9.3 Sector Addressing Mode ................................................................................................................. 56
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
3
Page 4

9.4 Power Management Feature ......................................................................................................... 57
9.5 SMART Function ............................................................................................................................ 59
9.6 Security Mode Feature Set ............................................................................................................ 61
9.7 Host Protected Area Feature ......................................................................................................... 67
9.8 Write Cache Function ..................................................................................................................... 69
9.9 Reassign Function .......................................................................................................................... 70
9.10 Power-up in Standby feature set ................................................................................................... 71
9.11 Advanced Power Management feature set (APM) ....................................................................... 71
9.12 48-bit Address Feature Set ............................................................................................................ 72
9.13 Streaming feature Set .................................................................................................................... 73
9.14 SATA BIST (Built-in Self Test) ...................................................................................................... 75
9.15 SATA Interface Power Management ............................................................................................. 75
9.16 Software Setting Preservation ....................................................................................................... 76
9.17 SATA II Optional Features ............................................................................................................ 77
9.18 SCT Command Transport feature Set .......................................................................................... 81
10 Command Protocol ........................................................................................................................................100
10.1 PIO Data In commands ................................................................................................................ 100
10.2 PIO Data Out commands ............................................................................................................. 101
10.3 Non-Data commands .................................................................................................................... 101
10.4 DMA Data In commands and DMA Data Out commands ......................................................... 102
10.5 First-party DMA commands ........................................................................................................ 102
11 Command Descriptions .....................................................................................................................................103
11.1 Check Power Mode (E5h/98h) ...................................................................................................... 107
11.2 Configure Stream (51h) ................................................................................................................ 108
11.3 Device Configuration Overlay (B1h) ........................................................................................... 110
11.4 Download Microcode (92h) ........................................................................................................... 114
11.5 Execute Device Diagnostic (90h) ................................................................................................. 116
11.6 Flush Cache (E7h) ........................................................................................................................ 117
11.7 Flush Cache Ext (EAh)................................................................................................................. 118
11.8 Format Track (50h) ....................................................................................................................... 119
11.9 Format Unit (F7h) ........................................................................................................................ 121
11.10 Identify Device (ECh) ............................................................................................................... 122
11.11 Idle (E3h/97h) ............................................................................................................................ 133
11.12 Idle Immediate (E1h/95h) ........................................................................................................ 135
11.13 Initialize Device Parameters (91h) .......................................................................................... 136
11.14 Read Buffer (E4h) ..................................................................................................................... 137
11.15 Read DMA(C8h/C9h) ................................................................................................................ 138
11.16 Read DMA Ext (25h) ................................................................................................................. 140
11.17 Read FPDMA Queued (60h) ..................................................................................................... 142
11.18 Read Log Ext (2Fh) ................................................................................................................... 144
11.19 Read Multiple (C4h) .................................................................................................................. 157
11.20 Read Multiple Ext (29h) ........................................................................................................... 158
11.21 Read Native Max Address (F8h) .............................................................................................. 160
11.22 Read Native Max Address Ext (27h) ....................................................................................... 161
11.23 Read Sector(s) (20h/21h) ........................................................................................................... 163
11.24 Read Sector(s) Ext (24h) ........................................................................................................... 165
11.25 Read Stream DMA (2Ah) .......................................................................................................... 167
11.26 Read Stream PIO (2Bh) ............................................................................................................ 170
11.27 Read Verify Sector(s) (40h/41h)................................................................................................ 173
11.28 Read Verify Sector(s) Ext (42h) ................................................................................................ 175
11.29 Recalibrate (1xh) ....................................................................................................................... 177
11.30 Security Disable Password (F6h) ............................................................................................. 178
11.31 Security Erase Prepare (F3h) .................................................................................................. 180
11.32 Security Erase Unit (F4h) ........................................................................................................ 181
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
4
Page 5

11.33 Security Freeze Lock (F5h) ...................................................................................................... 183
11.34 Security Set Password (F1h) .................................................................................................... 184
11.35 Security Unlock (F2h) ............................................................................................................... 186
11.36 Seek (7xh) .................................................................................................................................. 188
11.37 Sense Condition (F0h : Vendor specific for Cinemastar) ........................................................ 189
11.38 Set Max Address (F9h) ............................................................................................................. 194
11.39 Set Max Address Ext (37h) ....................................................................................................... 200
11.40 Set Multiple (C6h) ..................................................................................................................... 202
11.41 Sleep (E6h/99h) ......................................................................................................................... 203
11.42 SMART Function Set (B0h) ..................................................................................................... 204
11.43 Standby (E2h/96h) .................................................................................................................... 222
11.44 Standby Immediate (E0h/94h) ................................................................................................. 224
11.45 Write Buffer (E8h) .................................................................................................................... 225
11.46 Write DMA (Cah/CBh) .............................................................................................................. 226
11.47 Write DMA FUA Ext (3Dh) ...................................................................................................... 228
11.48 Write DMA Ext (35h) ................................................................................................................ 230
11.49 Write FPDMA Queued (61h) .................................................................................................... 232
11.50 Write Log Ext (3Fh) .................................................................................................................. 234
11.51 Write Multiple (C5h) ................................................................................................................. 236
11.52 Write Multiple Ext (39h) .......................................................................................................... 238
11.53 Write Multiple FUA Ext (CEh) ................................................................................................ 240
11.54 Write Sector(s) (30h/31h) .......................................................................................................... 242
11.55 Write Sector(s) Ext (34h) .......................................................................................................... 244
11.56 Write Stream DMA (3Ah) ......................................................................................................... 246
11.57 Write Stream PIO (3Bh) ........................................................................................................... 249
11.58 Write Uncorrectable Ext (45h) ................................................................................................. 252
12 Timings ..........................................................................................................................................................254
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
5
Page 6

List of tables
Table 1 Type and Model# ........................................................................................................................ 10
Table 2 Formatted capacity .................................................................................................................... 15
Table 3 Formatted capacity --Continued-- ............................................................................................ 15
Table 4 Formatted capacity --Continued-- ............................................................................................ 15
Table 5 Formatted capacity --Continued-- ............................................................................................ 16
Table 6 Mechanical positioning performance ....................................................................................... 17
Table 7 World Wide Name Assignment ................................................................................................. 17
Table 8 Command overhead ................................................................................................................... 19
Table 9 Mechanical positioning performance ....................................................................................... 20
Table 10 Single Track Seek Time ........................................................................................................... 21
Table 11 Latency Time ............................................................................................................................ 21
Table 12 Drive ready time ...................................................................................................................... 21
Table 13 Mode transition times ............................................................................................................. 22
Table 14 Interface connector pins and I/O signals ............................................................................... 25
Table 15 Parameter descriptions ........................................................................................................... 27
Table 16 Temperature and humidity ..................................................................................................... 28
Table 17 Input voltage ............................................................................................................................ 30
Table 18 Power supply current of 2 Disk model ................................................................................... 30
Table 19 Power supply current of 1 Disk model ................................................................................... 31
Table 20 Power supply generated ripple at drive power connector..................................................... 31
Table 21 Physical Dimensions ............................................................................................................... 37
Table 22 Random vibration PSD profile break points (operating) ...................................................... 40
Table 23 Random vibration PSD profile break points (nonoperating) ................................................ 41
Table 24 Sinusoidal shock wave............................................................................................................. 42
Table 25 Rotational Shock ...................................................................................................................... 42
Table 26 Sound power levels .................................................................................................................. 43
Table 27 Alternate Status Register ....................................................................................................... 48
Table 28 Device Control Register........................................................................................................... 49
Table 29 Drive Address Register ............................................................................................................ 50
Table 30 Device/Head Register .............................................................................................................. 50
Table 31 Error Register .......................................................................................................................... 51
Table 32 Status Register ........................................................................................................................ 53
Table 33 Reset Response ........................................................................................................................ 54
Table 34 Default Register Values........................................................................................................... 55
Table 35 Diagnostic Codes ...................................................................................................................... 55
Table 36 Power conditions ...................................................................................................................... 58
Table 37 Command table for device lock operation -1 .......................................................................... 65
Table 38 Command table for device lock operation -2 .......................................................................... 66
Table 39 Phy Event Counter Identifiers ............................................................................................... 78
Table 40 READ LOG EXT Log Page 11h data structure definition .................................................... 80
Table 41 SCT Log Page and direction ................................................................................................... 81
Table 42 Identify Device Information Word 206 ................................................................................... 81
Table 43 Output Registers of SCT Command Using SMART ............................................................. 83
Table 44 Input Registers of SCT Command Using SMART ................................................................ 83
Table 45 Input Registers of SCT Command Using Write Log Ext ...................................................... 84
Table 46 Output Registers of SCT Command Using Write Log Ext ................................................... 84
Table 47 Key Sector Format ................................................................................................................... 85
Table 48 SCT Action Code List .............................................................................................................. 85
Table 49 Extended Status Code ............................................................................................................. 86
Table 50 Input Registers of SCT Data Transfer Using SMART .......................................................... 87
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
6
Page 7

Table 51 Input Registers of SCT Data Transfer using Read/Write Log Ext ....................................... 87
Table 52 Intput Registers of SCT Status Request Using SMART ...................................................... 88
Table 53 Input Registers of SCT Status Request Using Read Log Ext .............................................. 88
Table 54 Data Format of SCT Status Response ................................................................................... 90
Table 55 SCT Write Same (Inputs) ........................................................................................................ 91
Table 56 SCT Write Same (Outputs) ..................................................................................................... 91
Table 57 Error Recovery Control command (Inputs) ........................................................................... 94
Table 58 Error Recovery Control command (Onputs) .......................................................................... 94
Table 59 Feature Control command (Inputs) ........................................................................................ 95
Table 60 Feature Control command (Outputs) ..................................................................................... 95
Table 61 Feature Code List .................................................................................................................... 96
Table 62 SCT Data Table command (Inputs) ........................................................................................ 97
Table 63 SCT Data Table command (Outputs) ..................................................................................... 97
Table 64 Table ID .................................................................................................................................... 97
Table 65 Data Format of HDA Absolute Temperature History Table ................................................. 99
Table 66 Command Set ......................................................................................................................... 103
Table 67 Command Set --Continued-- ................................................................................................. 104
Table 68 Command Set (Subcommand) .............................................................................................. 105
Table 69 Check Power Mode Command (E5h/98h) ............................................................................ 107
Table 70 Configure Stream Command (51h) ...................................................................................... 108
Table 71 Device Configuration Overlay Command (B1h) .................................................................. 110
Table 72 Device Configuration Overlay Features register values .................................................... 110
Table 73 Device Configuration Overlay Data structure..................................................................... 112
Table 74 DCO error information definition......................................................................................... 113
Table 75 Download Microcode Command (92h) .................................................................................. 114
Table 76 Execute Device Diagnostic Command (90h) ........................................................................ 116
Table 77 Flush Cache Command (E7h) ............................................................................................... 117
Table 78 Flush Cache Ext Command (EAh) ....................................................................................... 118
Table 79 Format Track Command(50h) .............................................................................................. 119
Table 80 Format Unit Command (F7h) ............................................................................................... 121
Table 81 Identify Device Command (ECh) .......................................................................................... 122
Table 82 Identify device information ................................................................................................... 123
Table 83 Identify device information --Continued-- ........................................................................... 124
Table 84 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 125
Table 85 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 126
Table 86 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 127
Table 87 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 128
Table 88 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 129
Table 89 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 130
Table 90 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 131
Table 91 Identify device information --Continued— .......................................................................... 132
Table 92 Idle Command (E3h/97h) ...................................................................................................... 133
Table 93 Idle Immediate Command (E1h/95h) ................................................................................... 135
Table 94 Initialize Device Parameters Command (91h) .................................................................... 136
Table 95 Read Buffer Command (E4h) ................................................................................................ 137
Table 96 Read DMA Command (C8h/C9h).......................................................................................... 138
Table 97 Read DMA Ext Command (25h) ........................................................................................... 140
Table 98 Read FPDMA Queued Command (60h) ............................................................................... 142
Table 99 Read Log Ext Command (2Fh) ............................................................................................. 144
Table 100 Log Address Definition ........................................................................................................ 145
Table 101 General Purpose Log Directory .......................................................................................... 146
Table 102 Extended Comprehensive SMART Error Log ................................................................... 147
Table 103 Extended Error log data structure ..................................................................................... 148
Table 104 Command data structure .................................................................................................... 148
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
7
Page 8

Table 105 Error data structure ............................................................................................................ 149
Table 106 Extended Self-test log data structure ................................................................................ 150
Table 107 Extended Self-test log descriptor entry ............................................................................. 151
Table 108 Command Error information .............................................................................................. 152
Table 109 Read Stream Error Log ....................................................................................................... 153
Table 110 Stream Error Log entry ....................................................................................................... 154
Table 111 Write Stream Error Log ....................................................................................................... 155
Table 112 Streaming Performance Parameters log ............................................................................ 156
Table 113 Sector Time Array Entry (Linearly Interpolated) ............................................................. 156
Table 114 Position Array Entry (Linearly Interpolated) .................................................................... 156
Table 115 Access Time Array Entry (Linearly Interpolated) ............................................................. 156
Table 116 Read Multiple Command (C4h) .......................................................................................... 157
Table 117 Read Multiple Ext Command (29h) .................................................................................... 158
Table 118 Read Native Max ADDRESS (F8h) .................................................................................... 160
Table 119 Read Native Max Address Ext (27h) .................................................................................. 161
Table 120 Read Sector(s) Command (20h/21h) ................................................................................... 163
Table 121 Read Sector(s) Ext Command (24h) ................................................................................... 165
Table 122 Read Stream DMA Command (2Ah) .................................................................................. 167
Table 123 Read Stream PIO Command (2Bh) .................................................................................... 170
Table 124 Read Verify Sector(s) Command (40h/41h)........................................................................ 173
Table 125 Read Verify Sector(s) Ext Command (42h) ........................................................................ 175
Table 126 Recalibrate Command (1xh) ............................................................................................... 177
Table 127 Security Disable Password Command (F6h) ..................................................................... 178
Table 128 Password Information for Security Disable Password command .................................... 179
Table 129 Security Erase Prepare Command (F3h) ........................................................................... 180
Table 130 Security Erase Unit Command (F4h) ................................................................................ 181
Table 131 Erase Unit Information ....................................................................................................... 182
Table 132 Security Freeze Lock Command (F5h) ............................................................................... 183
Table 133 Security Set Password Command (F1h) ............................................................................ 184
Table 134 Security Set Password Information ................................................................................... 185
Table 135 Security Unlock Command (F2h) ....................................................................................... 186
Table 136 Security Unlock Information .............................................................................................. 187
Table 137 Seek Command (7xh)........................................................................................................... 188
Table 138 Sense Condition command (F0h) ........................................................................................ 189
Table 139 Set Features Command (EFh) ............................................................................................ 190
Table 140 Set Max ADDRESS (F9h) ................................................................................................... 194
Table 141 Set Max set Password ......................................................................................................... 196
Table 142 Set Max Set Password data contents ................................................................................. 196
Table 143 Set Max Lock........................................................................................................................ 197
Table 144 Set Max Unlock (F9h) ......................................................................................................... 198
Table 145 Set Max Freeze Lock (F9h) ................................................................................................. 199
Table 146 Set Max Address Ext Command (37h) ............................................................................... 200
Table 147 Set Multiple Command (C6h) ............................................................................................. 202
Table 148 Sleep Command (E6h/99h) ................................................................................................. 203
Table 149 SMART Function Set Command (B0h) .............................................................................. 204
Table 150 Log sector addresses ............................................................................................................ 207
Table 151 Device Attribute Data Structure ........................................................................................ 209
Table 152 Individual Attribute Data Structure .................................................................................. 210
Table 153 Device Attribute Thresholds Data Structure .................................................................... 214
Table 154 Individual Threshold Data Structure ................................................................................ 214
Table 155 SMART Log Directory ......................................................................................................... 215
Table 156 SMART summary error log sector ...................................................................................... 216
Table 157 Error log data structure ...................................................................................................... 217
Table 158 Command data structure .................................................................................................... 217
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
8
Page 9
Table 159 Error data structure ............................................................................................................ 218
Table 160 Self-test log data structure ................................................................................................. 219
Table 161 Selective self-test log data structure .................................................................................. 220
Table 162 Selective self-test feature flags ........................................................................................... 220
Table 163 SMART Error Codes ............................................................................................................ 221
Table 164 Standby Command (E2h/96h) ............................................................................................. 222
Table 165 Standby Immediate Command (E0h/94h) ......................................................................... 224
Table 166 Write Buffer Command (E8h) ............................................................................................. 225
Table 167 Write DMA Command (Cah/CBh) ...................................................................................... 226
Table 168 Write DMA FUA Ext Command (3Dh) .............................................................................. 228
Table 169 Write DMA Ext Command (35h) ........................................................................................ 230
Table 170 Write FPDMA Queued Command (61h) ............................................................................ 232
Table 171 Write Log Ext Command (3Fh) .......................................................................................... 234
Table 172 Write Multiple Command (C5h) ......................................................................................... 236
Table 173 Write Multiple Ext Command (39h) .................................................................................. 238
Table 174 Write Multiple FUA Ext Command (CEh) ........................................................................ 240
Table 175 Write Sector(s) Command (30h/31h) .................................................................................. 242
Table 176 Write Sector(s) Ext Command (34h) .................................................................................. 244
Table 177 Write Stream DMA Command (3Ah) ................................................................................. 246
Table 178 Write Stream PIO Command (3Bh) ................................................................................... 249
Table 179 Write Uncorrectable Ext Command (45h) ......................................................................... 252
Table 180 Timeout Values .................................................................................................................... 254
Table 181 Timeout Values --Continued-- ............................................................................................ 255
List of figures
Figure 1 PList physical format ..................................................................................................................... 23
Figure 2 Connector location (2 disk model shown) ........................................................................................ 24
Figure 3 the timing of COMRESET, COMINIT and COMWAKE .................................................................. 27
Figure 4 Limits of temperature and humidity ................................................................................................. 29
Figure 5 Top and side views with breather hole location and mechanical dimensions ....................................... 34
Figure 6 1D model Top and side views with breather hole location and mechanical dimensions ........................ 35
Figure 7 Bottom and side views with mounting hole locations ........................................................................ 36
Figure 8 Mounting hole locations (all dimensions are in mm) ......................................................................... 37
Figure 9 Connector locations ....................................................................................................................... 38
Figure 10 Initial Setting ......................................................................................................................... 62
Figure 11 Usual Operation ..................................................................................................................... 63
Figure 12 Password Lost ........................................................................................................................ 64
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
9
Page 10

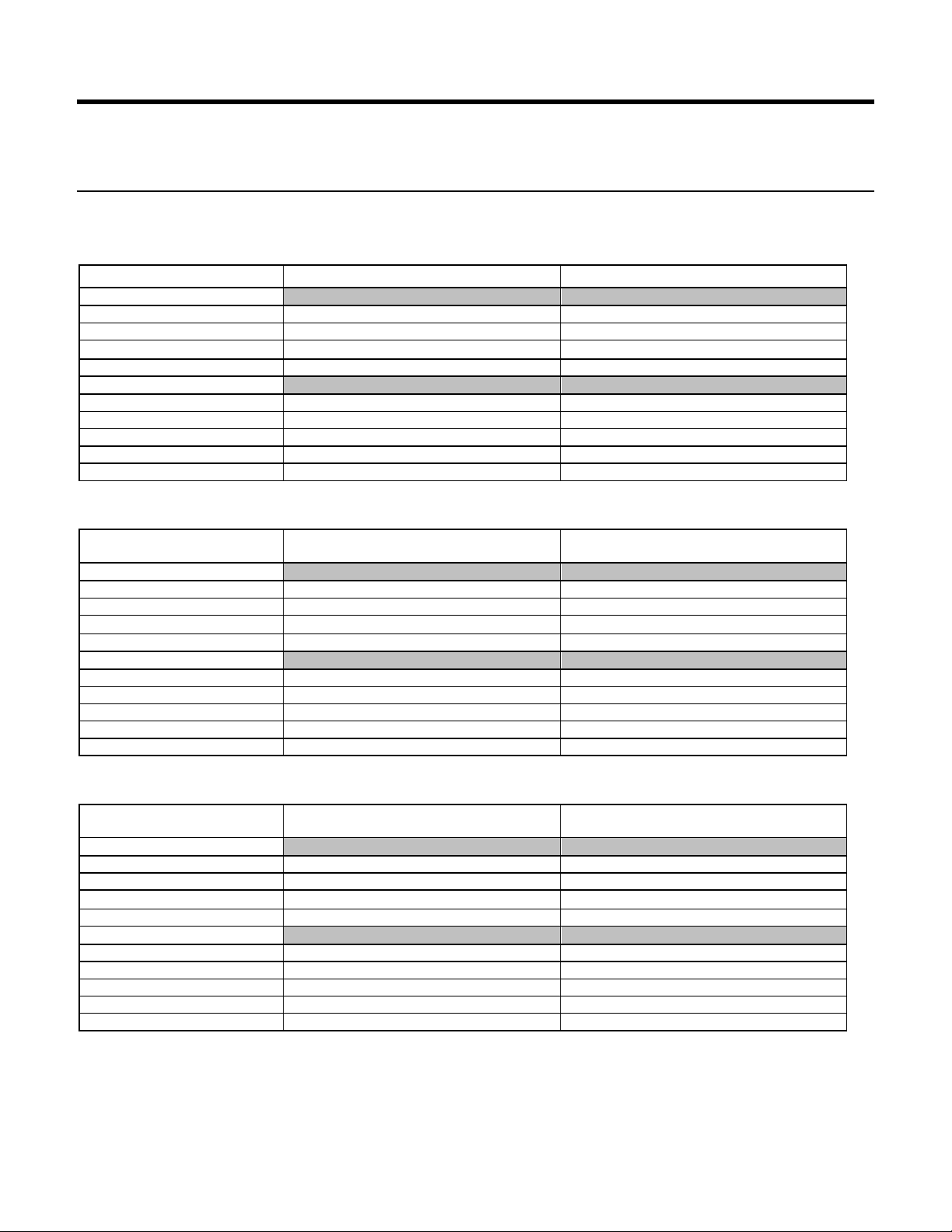
1 General
Capacity
Type
Cache
Model#
Deskstar
Ultrastar
CinemaStar
160GB
DS7SAC160
8MB
HDS721016CLA382
HDS721016CLA682
HCS721016CLA382
250GB
DS7SAC250
8MB
HDS721025CLA382
HDS721025CLA682
HCS721025CLA382
320GB
DS7SAC320
8MB
HCS721032CLA382
16MB
HDS721032CLA362
HDS721032CLA662
500GB
DS7SAC500
8MB
HCS721050CLA382
16MB
HDS721050CLA362
HDS721050CLA662
DS7SAC101
32MB
HUA722050CLA330/1
640GB
DS7SAC640
32MB
HDS721064CLA332
HDS721064CLA632
750GB
DS7SAC750
32MB
HDS721075CLA332
HDS721075CLA632
HCS721075CLA332
1TB
DS7SAC100
32MB
HDS721010CLA332
HDS721010CLA632
HCS721010CLA332
DS7SAC101
32MB
HUA722010CLA330/1
1.1 Introduction
This document describes the specifications of the Deskstar 7K1000.C, CinemaStar 7K1000.C and Ultrastar
A7K2000, an Hitachi Global Storage Technologies 3.5-inch 7200-rpm serial-ATA interface hard disk drive with the
following model numbers:
Table 1 Type and Model#
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
10
Page 11

1.2 Glossary
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
Kbpi 1,000 bits per inch
Ktpi 1,000 tracks per inch
Gbps 1,000,000,000 bits per second
Mbps 1,000,000 bits per second
MB/s 1,000,000 bytes per second
TB 1,000,000,000,000 bytes (for Drive Capacity)
GB 1,000,000,000 bytes(for Drive Capacity)
MB 1,048,576 bytes (for Memory Size)
KB 1,024 bytes (for Memory Size)
S.M.A.R.T. Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
DFT Drive Fitness Test
ADM Automatic Drive Maintenance
1.3 General caution
The drive can be damaged by shock or ESD (Electrostatic Discharge). Any damage sustained by the drive after
removal from the shipping package and opening the ESD protective bag are the responsibility of the user.
1.4 References
・ Serial ATA II: Extensions to Serial ATA 1.0
・ Serial ATA International Organization: Serial ATA Revision 2.60
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
11
Page 12
2 General features
Data capacities of 160 GB – 1 TB
Spindle speeds of 7200 RPM
Fluid Dynamic Bearing motor
Serial ATA interface
Sector format of 512 bytes/sector
Closed-loop actuator servo
Load/Unload mechanism, non head disk contact start/stop
Automatic Actuator lock
Interleave factor 1:1
Seek time of 14 ms(1Disk model) / 8.5 ms(2Disk model) typical without Command Overhead
Sector Buffer size of 8, 16 or 32 MB
(Upper 2024KB(8MB) / 2272.5KB(16MB)/ 2768.5KB(32MB) are used for firmware)
Ring buffer implementation
Write Cache
Native command queuing support
Advanced ECC On The Fly (EOF)
Automatic Error Recovery procedures for read and write commands
Self Diagnostics on Power on and resident diagnostics
Serial ATA Data Transfer 3Gbps / 6Gbps
CHS and LBA mode
Power saving modes/Low RPM idle mode (APM)
S.M.A.R.T. (Self Monitoring and Analysis Reporting Technology)
Support security feature
Quiet Seek mode
48 bit addressing feature
Adaptive Zone Formatting
RVS(Rotational Vibration Safeguard) (32MB cache model only)
SATA 2.6 compliant
Support bulk encryption(specific pn only)
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
12
Page 13

Part 1. Functional specification
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
13
Page 14

3 Fixed disk subsystem description
3.1 Control Electronics
The drive is electronically controlled by a microprocessor, several logic modules, digital/analog modules, and
various drivers and receivers. The control electronics performs the following major functions:
Controls and interprets all interface signals between the host controller and the drive.
Controls read write accessing of the disk media, including defect management and error recovery.
Controls starting, stopping, and monitoring of the spindle.
Conducts a power-up sequence and calibrates the servo.
Analyzes servo signals to provide closed loop control. These include position error signal and estimated
velocity.
Monitors the actuator position and determines the target track for a seek operation.
Controls the voice coil motor driver to align the actuator in a desired position.
Constantly monitors error conditions of the servo and takes corresponding action if an error occurs.
Monitors various timers such as head settle and servo failure.
Performs self-checkout (diagnostics).
3.2 Head disk assembly
The head disk assembly (HDA) is assembled in a clean room environment and contains the disks and actuator
assembly. Air is constantly circulated and filtered when the drive is operational. Venting of the HDA is accomplished
via a breather filter.
The spindle is driven directly by an in-hub, brushless, sensorless DC drive motor. Dynamic braking is used to quickly
stop the spindle.
3.3 Actuator
The read/write heads are mounted in the actuator. The actuator is a swing-arm assembly driven by a voice coil
motor. A closed-loop positioning servo controls the movement of the actuator. An embedded servo pattern supplies
feedback to the positioning servo to keep the read/write heads centered over the desired track.
The actuator assembly is balanced to allow vertical or horizontal mounting without adjustment.
When the drive is powered off, the actuator automatically moves the head to the actuator ramp outside of the disk
where it parks.
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
14
Page 15
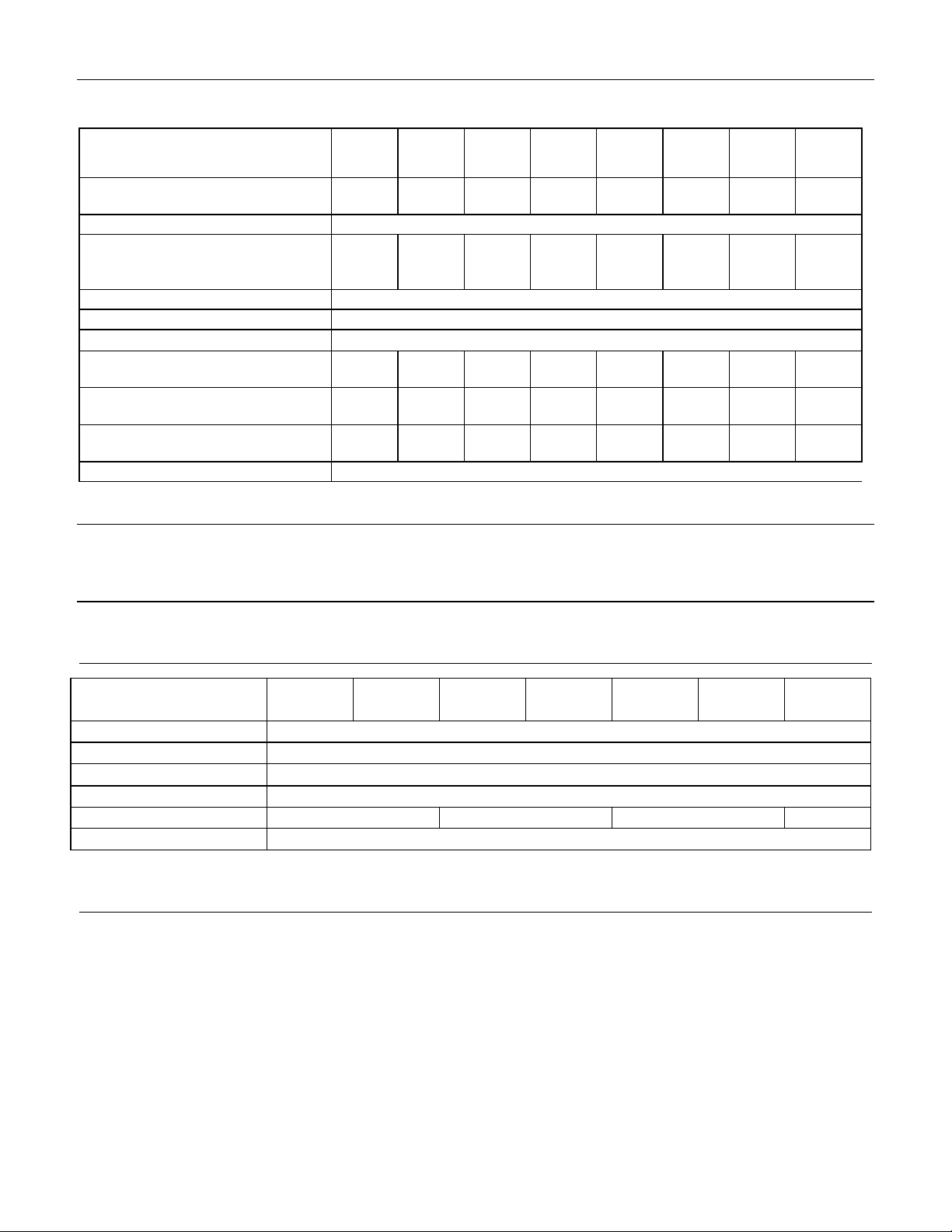
4 Drive characteristics
Description
160GB model
250GB model
Physical Layout
Label capacity (GB)
160
250
Bytes per Sector
512
512
Number of Heads 1 1
Number of Disks 1 1
Logical Layout
2
Number of Heads
16
16
Number of Sectors/ Track
63
63
Number of Cylinders
1
16,383
16,383
Number of Sectors
312,581,808
488,397,168
Total Logical Data Bytes
160,041,885,696
250,059,350,016
Description
320GB model
500GB model
Physical Layout
Label capacity (GB)
320
500
Bytes per Sector
512
512
Number of Heads 2 2 or 4
Number of Disks 1 1 or 2
Logical Layout
2
Number of Heads
16
16
Number of Sectors/ Track
63
63
Number of Cylinders
1
16,383
16,383
Number of Sectors
625,142,448
976,773,168
Total Logical Data Bytes
320,072,933,376
500,107,862,016
Description
640GB model
750GB model
Physical Layout
Label capacity (GB)
640
750
Bytes per Sector
512
512
Number of Heads 3 3 or 4
Number of Disks 2 2
Logical Layout
2
Number of Heads
16
16
Number of Sectors/ Track
63
63
Number of Cylinders
1
16,383
16,383
Number of Sectors
1.250,263,728
1,465,149,168
Total Logical Data Bytes
640,135,028,736
750,156,374,016
This section describes the characteristics of the drive.
4.1 Default logical drive parameters
The default of the logical drive parameters in Identify Device data is as shown below.
Table 2 Formatted capacity
Table 3 Formatted capacity --Continued--
Table 4 Formatted capacity --Continued--
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
15
Page 16

Description
1TB model
Physical Layout
Label capacity (GB)
1000
Bytes per Sector
512
Number of Heads
4
Number of Disks
2
Logical Layout
2
Number of Heads
16
Number of Sectors/ Track
63
Number of Cylinders
1
16,383
Number of Sectors
1,953,525,168
Total Logical Data Bytes
1,000,204,886,016
Table 5 Formatted capacity --Continued--
Notes:
1
Number of cylinders: For drives with capacities greater an 8.45 GB the IDENTIFY DEVICE information word 01
limits the number of cylinders to 16,383 per the ATA specification.
2
Logical layout: Logical layout is an imaginary drive parameter (that is, the number of heads) which is used to
access the drive from the system interface. The Logical layout to Physical layout (that is, the actual Head and
Sectors) translation is done automatically in the drive. The default setting can be obtained by issuing an IDENTIFY
DEVICE command
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
16
Page 17
4.2 Data sheet
Description
160GB
Model
250GB
Model
320GB
Model
500GB
Model
640GB
Model
750GB
3HD
Model
750GB
4HD
Model
1TB
Model
Max Data transfer rate (Mbps)
1484
1546
1484
1546
1484
1546
1484
1546
Interface transfer rate (MB/s)
300(SATA) 600(SATA)
Data buffer size1
8MB
8MB
8MB
16MB
8MB
16MB
32MB
32MB
32MB
32MB
32MB
Rotational speed (RPM)
7,200
Number of buffer segments (read)
up to 128
Number of buffer segments (write)
up to 112
Recording density- max (Kbpi)
1368
1429
1368
1429
1368
1429
1368
1429
Track density (Ktpi)
227
245
227
245
227
245 227
245
Areal density - max (Gbits/in2)
311
350
311
350
311
350 311
350
Number of data bands
30
Description of
160GB
Model
250GB
Model
320GB
Model
500GB
Model
640GB
Model
750GB
Model
1TB
Model
Organization
Hitachi GST
Manufacturing Site
Hitachi GST China Plant, China(GSP)
Product
Deskstar 7K1000.C/ CinemaStar 7K1000.C/ Ultrastar A7K2000
OUI
000CCAh
SHBU Block Assignment
35Ah
35Bh
35Ch
35Dh
Port/Node ID
11b
1
Upper 2024KB(8MB) / 2272.5KB(16MB)/ 2768.5KB(32MB) are used for firmware
Table 6 Mechanical positioning performance
4.3 World Wide Name Assignment
Table 7 World Wide Name Assignment
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
17
Page 18

4.4 Drive organization
4.4.1 Drive Format
Upon shipment from Hitachi Global Storage Technologies manufacturing the drive satisfies the sector continuity in
the physical format by means of the defect flagging strategy described in Section 5 on page 23 in order to provide
the maximum performance to users.
4.4.2 Cylinder allocation
Physical cylinder is calculated from the starting data track of 0. It is not relevant to logical CHS. Depending on the
capacity some of the inner zone cylinders are not allocated.
Data cylinder
This cylinder contains the user data which can be sent and retrieved via read/write commands and a spare area for
reassigned data.
Spare cylinder
The spare cylinder is used by Hitachi Global Storage Technologies manufacturing and includes data sent from a
defect location.
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
18
Page 19
4.5 Performance characteristics
Command type (Drive is in quiescent state)
Typical time (ms)
Typical time for NCQ
command (ms)
Read (Cache not hit)
0.5
0.5
Read (Cache hit)
0.1
0.2
Write
0.015
0.2
Seek
0.5
not applicable
Drive performance is characterized by the following parameters:
Command overhead
Mechanical positioning
- Seek time
- Latency
Data transfer speed
Buffering operation (Look ahead/Write cache)
All the above parameters contribute to drive performance. There are other parameters that contribute to the
performance of the actual system. This specification defines the characteristics of the drive, not the characteristics
of the system throughput which depends on the system and the application.
4.5.1 Command overhead
Command overhead is defined as the time required
from the time H->D Reg FIS w/ command bit is sent by host
to the time
PIO Set Up FIS is sent by device(PIO Read/Write)
DATA FIS is sent by device(DMA Read)
DMA Activate FIS is sent by device(DMA Write)
DMA Set Up FIS is sent by device(NCQ Read/Write)
Seek Start (Read cache not hit or Seek)
The table below gives average command overhead.
Table 8 Command overhead
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
19
Page 20
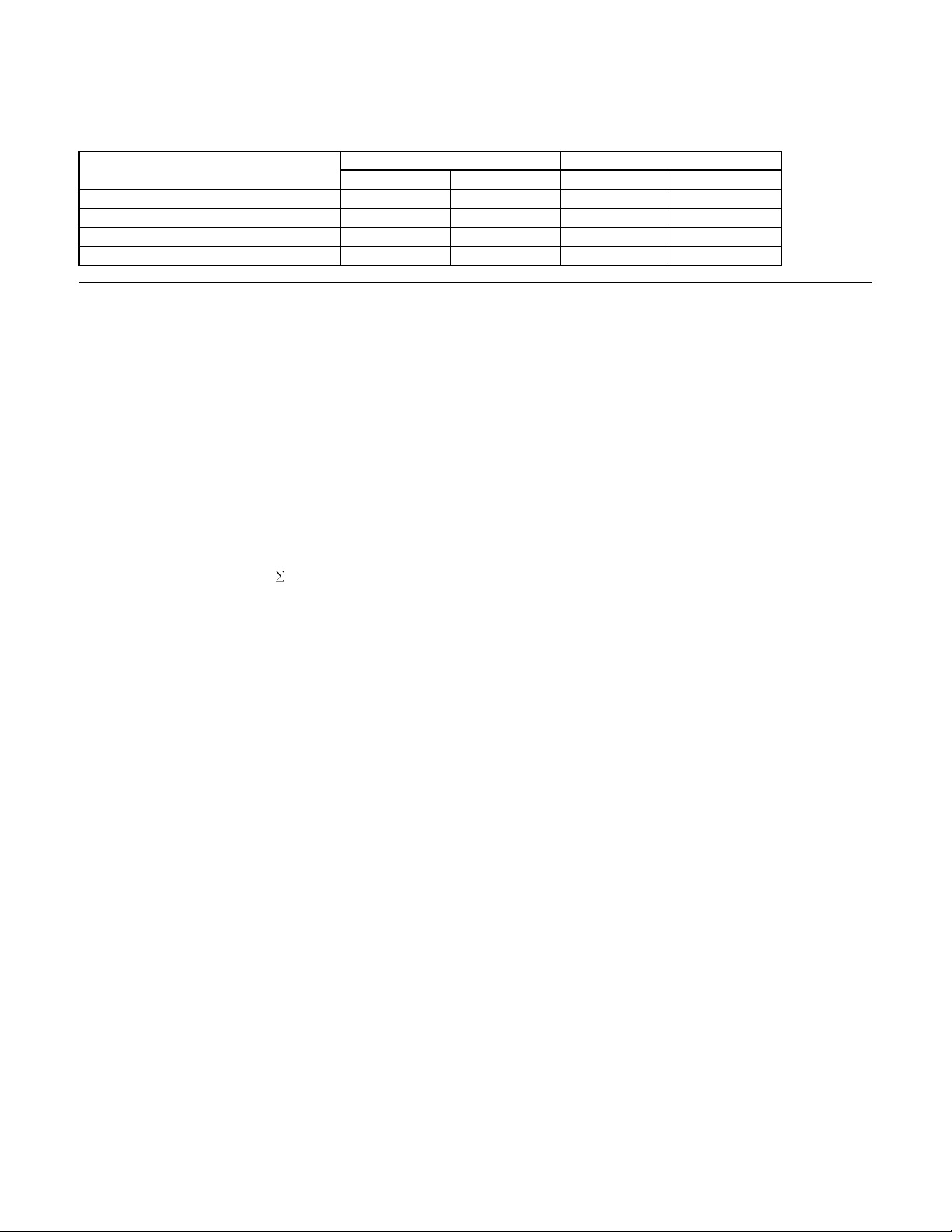
4.5.2 Mechanical positioning
Command Type
1 Disk model
2 Disk model
Typical (ms)
Max (ms)
Typical (ms)
Max (ms)
Read
14.0
14.7
8.5
9.2
Write
15.0
15.7
9.5
10.2
Read (Quiet Seek mode)
14.0
14.7
14.0
14.7
Write (Quiet Seek mode)
15.0
15.7
15.0
15.7
4.5.2.1 Average seek time (without command overhead, including settling)
Table 9 Mechanical positioning performance
The terms “Typical” and “Max” are used throughout this specification with the following meanings:
Typical. The average of the drive population tested at nominal environmental and voltage conditions.
Max. The maximum value measured on any one drive over the full range of the environmental and voltage
conditions. (See Section 6.2, “Environment” on page 28 and Section 6.3, “DC Power Requirements” on
page 30.)
Seek time is measured from the start of the motion of the actuator to the start of a reliable read or write
operation. "Reliable read or write" implies that error correction/recovery is not used to correct arrival
problems. The average seek time is measured as the weighted average of all possible seek combinations.
n=1
)
out
)
out
max.
(max. + 1 – n) (Tnin + Tn
Weighted Average =
__________________________________________________
(max. + 1) (Tnin + Tn
where: max = maximum seek length
n = seek length (1 to max)
Tn
Tn
= inward measured seek time for an n-track seek
in
= outward measured seek time for an n-track seek
out
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
20
Page 21
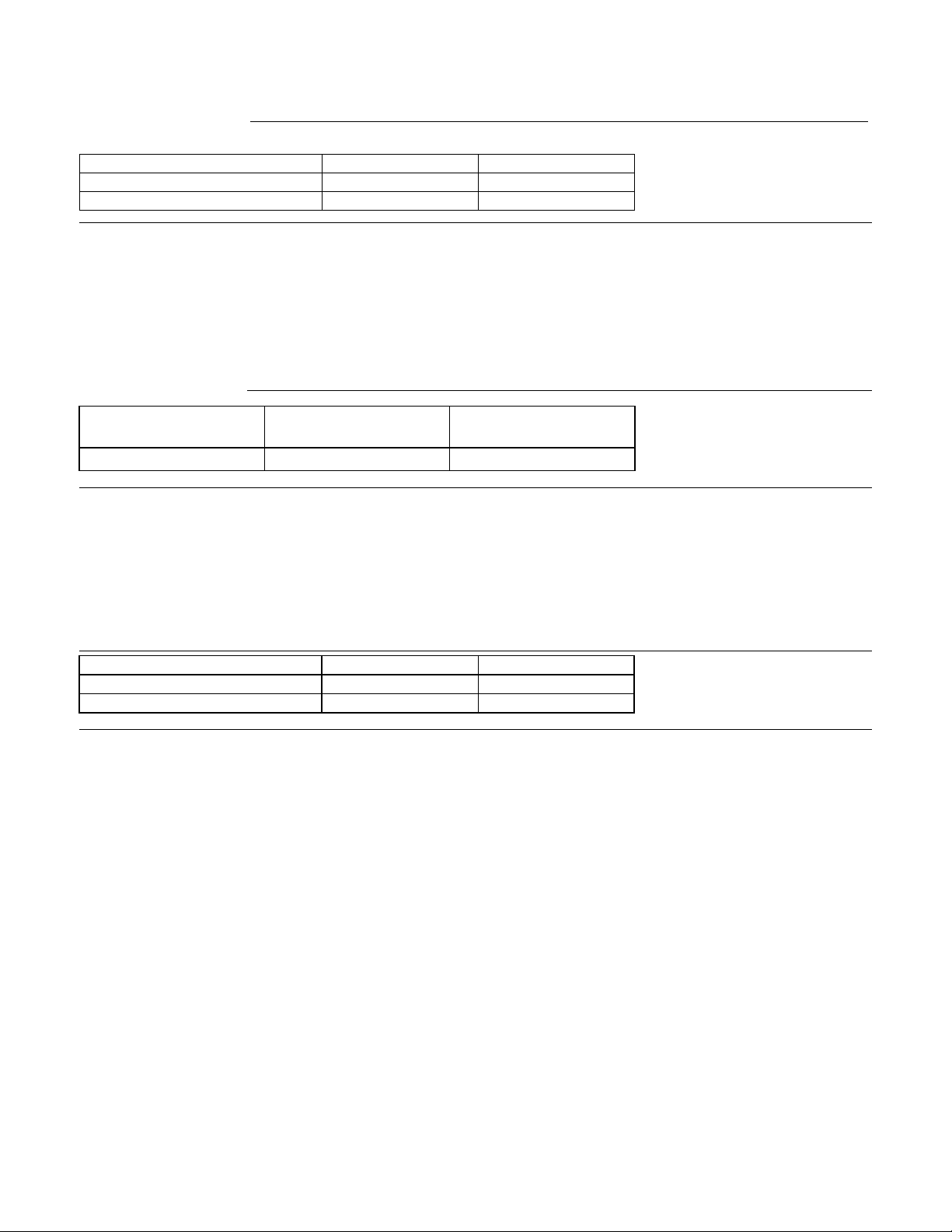
4.5.2.2 Single track seek time (without command overhead, including settling)
Function
Typical (ms)
Max (ms)
Read
0.8
1.5
Write
1.3
2.0
Rotational speed
Time for a revolution
(ms)
Average latency
(ms)
7200 RPM
8.3
4.17
Power on to ready
Typical (sec)
Maximum (sec)
1D model
8
20
2D model
10
20
Common to all models and all seek modes
Table 10 Single Track Seek Time
Single track seek is measured as the average of one (1) single track seek from every track with a random head
switch in both directions (inward and outward).
4.5.2.3 Average latency
Table 11 Latency Time
4.5.3 Drive ready time
Table 12 Drive ready time
Ready The condition in which the drive is able to perform a media access command (such as
read, write) immediately.
Power on This includes the time required for the internal self diagnostics.
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
21
Page 22
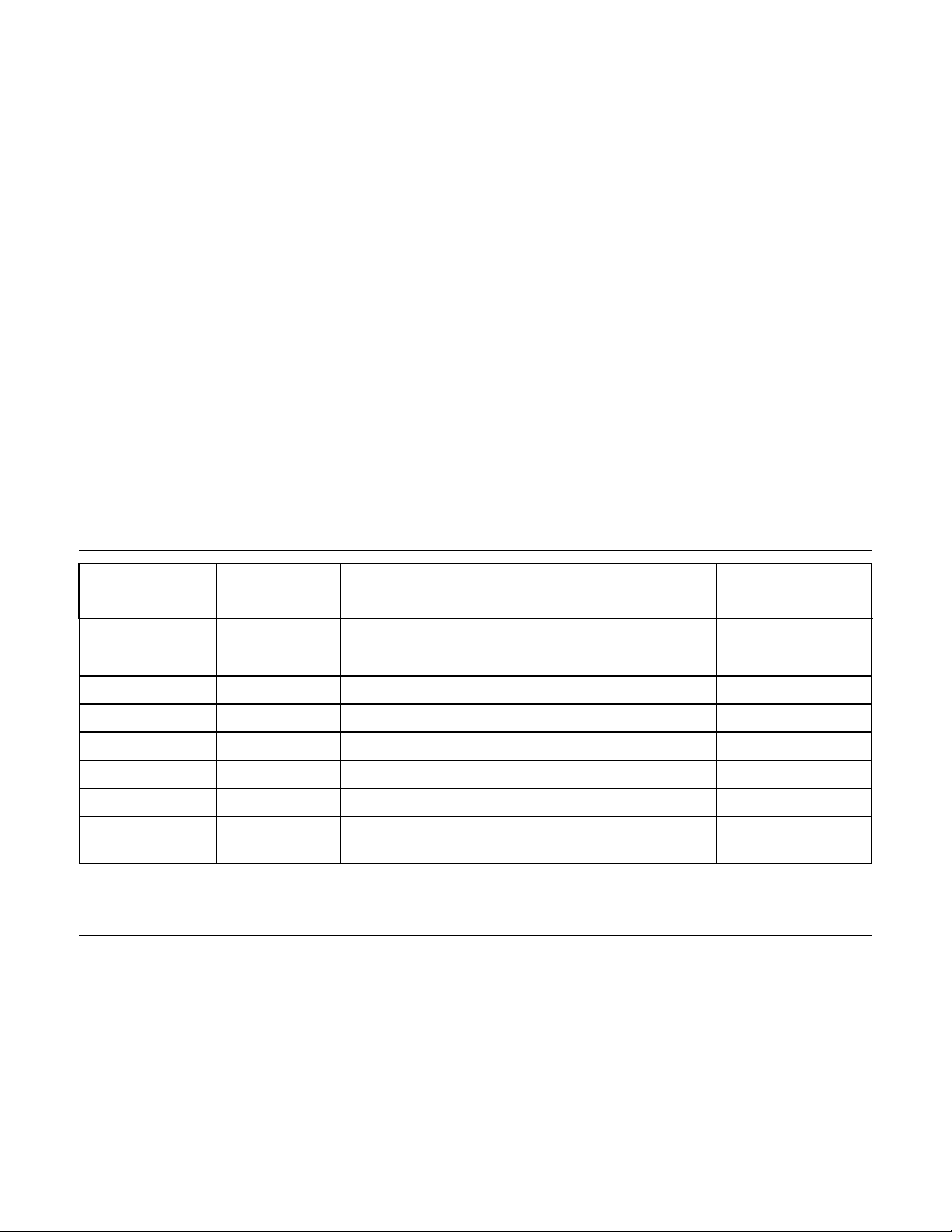
4.5.4 Operating modes
From
To
RPM
Typical Transition
time(sec)
Max Transition
time(sec)
Standby
Idle
0 -> 7200
8 (1Disk model)
10 (2Disk model))
20
Idle
Standby
7200 -> 0
Immediately
20
Standby
Sleep 0 Immediately
Immediately
Sleep
Standby
0
Immediately
Immediately
Unload idle
Idle
7,200
0.7
1
Idle
Unload Idle
7,200
0.7
1
Low RPM Idle
Idle
4500 -> 7200
3 (1 Disk model)
4 (2 Disk model)
10
Note: The command is processed immediately but there will be an actual spin down time reflecting the seconds
passed until the spindle motor stops.
Note: Low rpm idle mode is supported on specific drive PN, only.
4.5.4.1 Operating mode descriptions
Operating mode Description
Spin-up Start up time period from spindle stop or power down
Seek Seek operation mode
Write Write operation mode
Read Read operation mode
Unload Idle Spindle rotation at 7200 RPM with heads unloaded
Idle Spindle motor and servo system are working normally. Commands can be received
and processed immediately
Standby Actuator is unloaded and spindle motor is stopped. Commands can be received
immediately
Sleep Actuator is unloaded and spindle motor is stopped. Only soft reset or COMRESET can
change the mode to standby
Note: Upon power down or spindle stop a head locking mechanism will secure the heads in the OD parking position.
4.5.4.2 Mode transition times
Mode transition times are shown below.
Table 13 Mode transition times
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
22
Page 23

5 Defect flagging strategy
N N+1 N+2 N+3
defect defect
skip
skip
Media defects are remapped to the next available sector during the Format Process in manufacturing. The mapping
from LBA to the physical locations is calculated by an internally maintained table.
Shipped format
Data areas are optimally used.
No extra sector is wasted as a spare throughout user data areas.
All pushes generated by defects are absorbed by the spare tracks of the inner zone.
Figure 1 PList physical format
Defects are skipped without any constraint, such as track or cylinder boundary. The calculation from LBA to
physical is done automatically by internal table.
- Hitachi hard disk drive specifications –
23
Page 24
6 Specification
6.1 Electrical interface
6.1.1 Connector location
Refer to the following illustration to see the location of the connectors.
SATA
Figure 2 Connector location (2 disk model shown)
6.1.1.1 signal connector
The SATA signal connector is a 8-pin connector. Power connector is a 15-pin connector.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
24
Page 25
6.1.2 Signal definition
No.
Plug Connector pin definition
Signal
I/O
S1
GND
2nd mate
Gnd
S2
A+
Differential signal A from Phy
RX+
Input
S3
A- RX-
Input
Signal
S4
Gnd
2nd mate
Gnd
S5
B-
Differential signal B from Phy
TX-
Output
S6
B+ TX+
Output
S7
Gnd
2nd mate
Gnd
Key and spacing separate signal and power segments
P1
V33
3.3V power
3.3V
P2
V33
3.3V power
3.3V
P3
V33
3.3V power, pre-charge, 2nd Mate
3.3V
P4
Gnd
1st mate
Gnd
P5
Gnd
2nd mate
Gnd
P6
Gnd
2nd mate
Gnd
P7
V5
5V power,pre-charge,2nd Mate
5V
P8
V5
5V power
5V
Power
P9
V5
5V power
5V
P10
Gnd
2nd mate
Gnd
P11
Reserved
Support staggered spin-up and LED activity
Reserve
P12
Gnd
1st mate
Gnd
P13
V12
12V power,pre-chage,2nd mate
V12
P14
V12
12V power
V12
P15
V12
12V power
V12
SATA has receivers and drivers to be connected to Tx+/- and Rx +/- Serial data signal.
Defines the signal names of I/O connector pin and signal name.
Table 14 Interface connector pins and I/O signals
6.1.2.1 TX+ / TX-
These signal are the outbound high-speed differrential signals that are connected to the serial ATA cable
6.1.2.2 RX+ / RX-
These signals are the inbound high-speed differential signals that are connected to the serial ATA cable.
The following standard shall be referenced about signal specifications.
Serial ATA: High Speed Serialized AT Attachment Revision 2.6 15-Feb-2007
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
25
Page 26

6.1.2.3 5V PRECHARGE
+5 Vdc power that is available on the extended pins. This is used for pre-charging the I/O module.
The enclosure shall provide for a current limit of 4.5 A peak on each 5V pre-charge pin (R=1.1 Ohms).These
signals are the inbound high-speed differential signals that are connected to the serial ATA cable.
6.1.2.4 12V PRECHARGE
+12 Vdc power that is available on the extended pins. This is used for pre-charging the 12V circuitry in the I/O
Option slot module.
The enclosure shall be capable of supplying 2.4 A peak on each 12 V pre-charge pin (R=5 Ohms).+5 Vdc power
that is available on the extended pins. This is used for pre-charging the I/O module.
The enclosure shall provide for a current limit of 4.5 A peak on each 5V pre-charge pin (R=1.1 Ohms).These
signals are the inbound high-speed differential signals that are connected to the serial ATA cable.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
26
Page 27

6.1.3 Out of band signaling(SATA)
C O M R E S E T /C O M IN IT
t1
t2
t3
t4
C O M W A K E
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
Nominal (ns)
t1
ALINE primitives
106.7
t2
Spacing
320
t3
ALIGN primitives
106.7
t4
Psacing
106.7
Figure 3 the timing of COMRESET, COMINIT and COMWAKE
Table 15 Parameter descriptions
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
27
Page 28
6.2 Environment
Operating conditions
Temperature
Relative humidity
Maximum wet bulb temperature
Maximum temperature gradient
Altitude
CinemaStar : 0 to 70°C (See notes)
Deskstar/Ultrastar : 0 to 60°C (See notes)
8 to 90% non-condensing
29.4°C non-condensing
20°C/Hour
–300 to 3,048 m
Non-Op conditions
Temperature
Relative humidity
Maximum wet bulb temperature
Maximum temperature gradient
Altitude
-40 to 70°C
5 to 95% non-condensing
35°C non-condensing
30°C/Hour
–300 to 12,000 m
6.2.1 Temperature and humidity
Table 16 Temperature and humidity
Notes:
1. CinemaStar : Temperature tested at the top cover (AV streaming application usage)
Deskstar/Ultrastar : The system is responsible for providing sufficient ventilation to maintain a surface
temperature below 65°C at the center of the top cover of the drive.
2. Non condensing conditions should be maintained at any time.
3. Maximum storage period within shipping package is one year,
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
28
Page 29
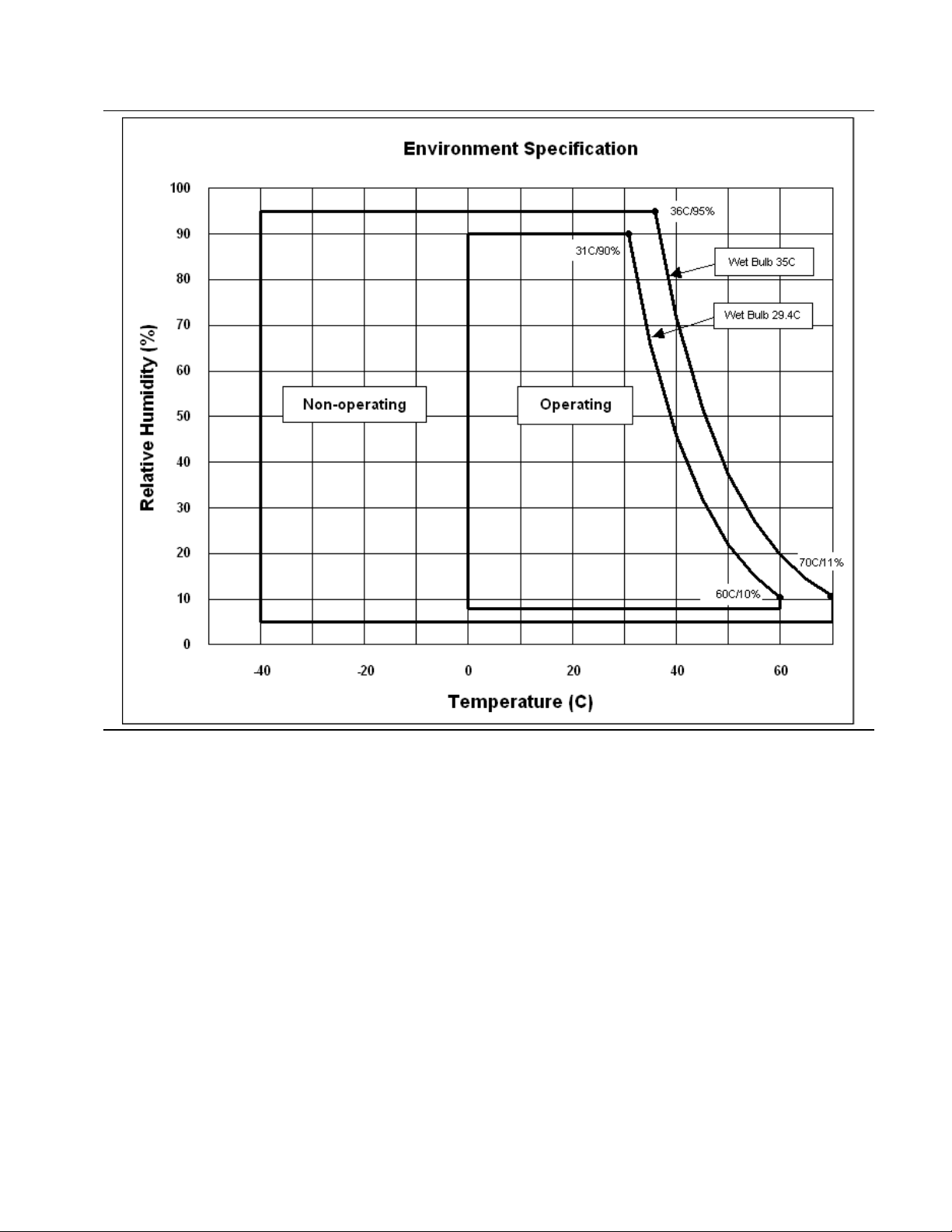
Figure 4 Limits of temperature and humidity
Note: Storage temperature range is 0 to 70°C
6.2.2 Corrosion test
The drive shows no sign of corrosion inside and outside of the hard disk assembly and is functional after being
subjected to seven days at 50°C with 90% relative humidity.
6.2.3 Atmospheric condition
Environments that contain elevated levels of corrosives (e.g. hydrogen sulfide, sulfur oxides, or hydrochloric
acid) should be avoided. Care must be taken to avoid using any compound/material in a way that creates an
elevated level of corrosive materials in the atmosphere surrounding the disk drive. Care must also be taken to
avoid use of any organometallic (e.g. organosilicon or organotin) compound/material in a way that creates
elevated vapor levels of these compounds/materials in the atmosphere surrounding the disk drive.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
29
Page 30
6.3 DC power requirements
Input voltage
During run and spin up
Absolute max
spike voltage
Supply rise time
+5 Volts Supply
5V ± 5%
–0.3 to 5.5V
0 to 5sec
+12 Volts Supply
12V ±10%
–0.3 to 15.0V
0 to 5sec
Power supply current of
2 Disk model
+5 Volts [mA]
+12 Volts [mA]
Total
[W]
(values in milliamps. RMS)
Pop Mean
Pop Mean
Idle average
230
270
4.4
Idle ripple (peak-to-peak)
200
400
Low RPM idle
170
100
2.1
Low RPM idle ripple
100
250
Unload idle average
170
250
3.9
Unload idle ripple
100
300
Random R/W average1
330
560
8.4
(8.6) *1
(580) *1
Random R/W peak
1100
1700
Random R/W average(Quiet Seek)
350
330
5.7
Random R/W peak(Quiet Seek)
1100
1500
Start up (max)
1100
1800
Standby average
160
7
0.9
Sleep average
160
7
0.9
Damage to the drive electronics may result if the power supply cable is connected or disconnected to the legacy
Power connector while power is being applied to the drive (no hot plug/unplug is allowed). If SATA power supply
cable is connected or disconnected to the SATA power connector, hot plug/unplug is allowed.
6.3.1 Input voltage
Table 17 Input voltage
Caution : To avoid damage to the drive electronics, power supply voltage spikes must not exceed
specifications.
6.3.2 Power supply current (typical)
Table 18 Power supply current of 2 Disk model
*1 : for Ultrastar only
Except for a peak of less than 100 s duration
1
Random R/W : 35 IOPS / 16 Blocks Random Write and Random Read
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
30
Page 31

Power supply current of
1 Disk models
+5 Volts [mA]
+12 Volts [mA]
Total
[W]
(values in milliamps. RMS)
Pop Mean
Pop Mean
Idle average
220
210
3.6
Idle ripple (peak-to-peak)
200
300
Low RPM Idle
160
90
1.9
Low RPM Idle Ripple
100
250
Unload Idle average
160
200
3.2
Unload Idle Ripple
100
300
Random R/W average1(Quiet Seek)
350
400
6.6
Random R/W peak(Quiet Seek)
1100
1200
Start up (max)
1100
1900
Standby average
160
7
0.9
Sleep average
160
7
0.9
Table 19 Power supply current of 1 Disk model
Maximum (mV pp)
MHz
+5V DC
200
0-10
+12V DC
250
0-10
1
Random R/W : 35 IOPS / 16 Blocks Random Write and Random Read
6.3.3 Power supply generated ripple at drive power connector
Table 20 Power supply generated ripple at drive power connector
During drive start up and seeking 12-volt ripple is generated by the drive (referred to as dynamic loading). If the
power of several drives is daisy chained together, the power supply ripple plus the dynamic loading of the other
drives must remain within the above regulation tolerance. A common supply with separate power leads to each
drive is a more desirable method of power distribution.
To prevent external electrical noise from interfering with the performance of the drive, the drive must be held by
four screws in a user system frame which has no electrical level difference at the four screws position and has
less than ±300 millivolts peak to peak level difference to the ground of the drive power connector.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
31
Page 32

6.4 Reliability
6.4.1 Data integrity
No more than one sector is lost at Power loss condition during the write operation when the write cache option is
disabled. If the write cache option is active, the data in write cache will be lost. To prevent the loss of customer
data, it is recommended that the last write access before power off be issued after setting the write cache off.
6.4.2 Cable noise interference
To avoid any degradation of performance throughput or error rate when the interface cable is routed on top or
comes in contact with the HDA assembly, the drive must be grounded electrically to the system frame by four
screws. The common mode noise or voltage level difference between the system frame and power cable ground
or AT interface cable ground should be in the allowable level specified in the power requirement section.
6.4.3 Load/Unload
The product supports a minimum of 300,000 normal load/unloads in a 40° C environment.
Load/unload is invoked by transition of the HDD's power mode.
Idle <-> unload idle
Idle <-> Low rpm idle*
*Note: Low rpm idle mode is supported on specific drive PN, only.
6.4.4 Start/stop cycles
The drive withstands a minimum of 50,000 start/stop cycles in a 40° C environment and a minimum of 10,000
start/stop cycles in extreme temperature or humidity within the operating range. .
6.4.5 Preventive maintenance
None
6.4.6 Data reliability
Probability of not recovering data is 1 in 10
Ultrastar model.
ECC On The Fly correction
1 Symbol : 10 bits
No Interleave
34 symbol ECC
This implementation always recovers 16 random errors and a 310-bit continuous burst error
14
bits read for Deskstar/CinemaStar models, 1 in 1015 bits read for
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
32
Page 33

6.4.7 Required Power-Off Sequence
The required BIOS sequence for removing power from the drive is as follows:
Step 1: Issue one of the following commands.
Standby
Standby immediate
Sleep
Note: Do not use the Flush Cache command for the power off sequence because this command does not
invoke Unload
Step 2: Wait until the Command Complete status is returned. In a typical case 350 ms are required for the
command to finish completion; however, the BIOS time out value needs to be 30 seconds considering error
recovery time.
Step 3: Terminate power to HDD.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
33
Page 34

6.5 Mechanical specifications
6.5.1 Physical dimensions
Figure 5 Top and side views with breather hole location and mechanical dimensions
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
34
Page 35

Figure 6 1D model Top and side views with breather hole location and mechanical dimensions
All dimensions are in millimeters.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
35
Page 36

Figure 7 Bottom and side views with mounting hole locations
All dimensions in the above figure are in millimeters.
The breather hole must be kept uncovered in order to keep the air pressure inside of the disk enclosure equal to
external air pressure.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
36
Page 37

The following table shows the physical dimensions of the drive.
Height (mm)
Width (mm)
Length (mm)
Weight (grams)
1 Disk model
Weight (grams)
2 Disk model
26.1 MAX
101.6 ± 0.25
147 MAX
400 MAX
680 MAX
Side View
(5)(6) (7)
Bottom View
(1)(2)
(3)
(4)
I/F Connector
(4X) Max. penetration 4.0 mm
(6X) Max. penetration 4.5 mm
Thread
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
6-32UNC
41.28±0.5
44.45±0.2
95.25±0.2
6.35±0.2
28.5±0.5
60.0±0.2
41.6±0.2
Table 21 Physical Dimensions
6.5.2 Hole locations
The mounting hole location and size for the hard disk drive is shown below.
Figure 8 Mounting hole locations (all dimensions are in mm)
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
37
Page 38

6.5.3 Connector locations
Figure 9 Connector locations
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
38
Page 39

6.5.4 Drive mounting
The drive will operate in all axes (6 directions). Performance and error rate will stay within specification limits if
the drive is operated in the other orientations from which it was formatted.
For reliable operation, the drive must be mounted in the system securely enough to prevent excessive motion or
vibration of the drive during seek operation or spindle rotation, using appropriate screws or equivalent mounting
hardware.
The recommended mounting screw torque is 0.6 - 1.0 Nm (6-10 Kgf.cm).
The recommended mounting screw depth is 4 mm maximum for bottom and 4.5 mm maximum for horizontal
mounting.
Drive level vibration test and shock test are to be conducted with the drive mounted to the table using the bottom
four screws.
6.5.5 Heads unload and actuator lock
Heads are moved out from disks (unload) to protect the disk data during shipping, moving, or storage. Upon
power down, the heads are automatically unloaded from disk area and the locking mechanism of the head
actuator will secure the heads in unload position.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
39
Page 40

6.6 Vibration and shock
Frequency
5 Hz
17 Hz
45 Hz
48 Hz
62 Hz
65 Hz
150 Hz
200 Hz
500 Hz
RMS
(G)
x10
–3
[G2/Hz]
0.02
1.1
1.1
8.0
8.0
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.67
All vibration and shock measurements recorded in this section are made with a drive that has no mounting
attachments for the systems. The input power for the measurements is applied to the normal drive mounting
points.
6.6.1 Operating vibration
6.6.1.1 Random vibration (Linear)
The test is 30 minutes of random vibration using the power spectral density (PSD) levels shown below in each of
three mutually perpendicular axes. The disk drive will operate without non-recoverable errors when subjected to
the above random vibration levels.
Table 22 Random vibration PSD profile break points (operating)
The overall RMS (root mean square) level is 0.67 G.
6.6.1.2 Swept sine vibration (Linear)
The drive will meet the criteria shown below while operating in the specified conditions:
No errors occur with 0.5 G 0 to peak, 5 to 300 to 5 Hz sine wave, 0.5 oct/min sweep rate with 3-minute
dwells at two major resonances
No data loss occurs with 1 G 0 to peak, 5 to 300 to 5 Hz sine wave, 0.5 oct/min sweep rate with 3-minute
dwells at two major resonances
6.6.1.3 Random vibration (Rotational)
The drive will meet the criteria shown below while operating in the specified conditions:
Less than 20% Performance degradation for Random Write/Read/Verify @12.5Rad/sec^2(’10-300Hz
Flat)
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
40
Page 41

6.6.2 Nonoperating vibration
Frequency
2 Hz
4 Hz
8 Hz
40 Hz
55 Hz
70 Hz
200 Hz
G2/Hz
0.001
0.03
0.03
0.003
0.01
0.01
0.001
The drive does not sustain permanent damage or loss of previously recorded data after being subjected to the
environment described below
6.6.2.1 Random vibration
The test consists of a random vibration applied for each of three mutually perpendicular axes with the time
duration of 10 minutes per axis. The PSD levels for the test simulate the shipping and relocation environment
shown below. The overall RMS (Root Mean Square) level of vibration is 1.04 G.
Table 23 Random vibration PSD profile break points (nonoperating)
6.6.2.2 Swept sine vibration
2 G (Zero to peak), 5 to 500 to 5 Hz sine wave
0.5 oct/min sweep rate
3 minutes dwell at two major resonances
6.6.3 Operating shock
The drive meets the following criteria while operating in the conditions described below. The shock test consists
of 10 shock inputs in each axis and direction for total of 60. There must be a delay between shock pulses long
enough to allow the drive to complete all necessary error recovery procedures.
No error occurs with a 10 G half-sine shock pulse of 11 ms duration in all models.
No data loss occurs with a 30 G half-sine shock pulse of 4 ms duration in all models.
No data loss occurs with a 70 G half-sine shock pulse of 2 ms duration.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
41
Page 42

6.6.4 Nonoperating shock
Models
Accleration level (G)
Duration (ms)
1D/2D models
350
2
All models
150
11
Duration
Rad/sec2
1 ms
30,000
2 ms
20,000
The drive will operate with no degradation of performance after being subjected to shock pulses with the
following characteristics.
6.6.4.1 Trapezoidal shock wave
Approximate square (trapezoidal) pulse shape
Approximate rise and fall time of pulse is1 ms
Average acceleration level is 50 G. (Average response curve value during the time following the 1 ms rise
time and before the 1 ms fall with a time "duration of 11 ms")
Minimum velocity change is 4.23 meters/second
6.6.4.2 Sinusoidal shock wave
The shape is approximately half-sine pulse. The figure below shows the maximum acceleration level and
duration.
Table 24 Sinusoidal shock wave
6.6.5 Nonoperating Rotational shock
All shock inputs shall be applied around the actuator pivot axis.
Table 25 Rotational Shock
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
42
Page 43

6.7 Acoustics
Mode
Typical / Max
1 disk model
2 disk model
Idle
2.5 / 2.7
2.4 / 2.5
Operating
Performance seek mode
N/A
2.9/ 3.1
Quiet seek mode
2.7 / 3.0
2.5 / 2.7
The upper limit criteria of the octave sound power levels are given in Bels relative to one picowatt and are shown
in the following table. The sound power emission levels are measured in accordance with ISO 7779.
Table 26 Sound power levels
Mode definition:
Idle mode. The drive is powered on, disks spinning, track following, unit ready to receive and respond to
interface commands.
Operating mode. Continuous random cylinder selection and seek operation of the actuator with a dwell
time at each cylinder. The seek rate for the drive is to be calculated as shown below:
Dwell time = 0.5 x 60/RPM
Seek rate = 0.4 / (Average seek time + Dwell time)
6.8 Identification labels
The following labels are affixed to every drive shipped from the drive manufacturing location in accordance with
the appropriate hard disk drive assembly drawing:
A label containing the Hitachi logo, the Hitachi Global Storage Technologies part number, and the
statement “Made by Hitachi Global Storage Technologies Inc.” or Hitachi Global Storage
Technologies approved equivalent
A label containing the drive model number, the manufacturing date code, the formatted capacity, the
place of manufacture, UL/CSA/TUV/CE/C-Tick mark logos
A bar code label containing the drive serial number
A label containing the jumper pin description
A user designed label per agreement
The above labels may be integrated with other labels.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
43
Page 44

6.9 Safety
6.9.1 UL and CSA standard conformity
The product is qualified per UL60950-1:2005 Second Edition and CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.60950-1-07 Second
Edition, for use in Information Technology Equipment including Electric Business Equipment.
The UL recognition or the CSA certification is maintained for the product life.
The UL and C-UL recognition mark or the CSA monogram for CSA certification appear on the drive.
6.9.2 German Safety Mark
The product is approved by TUV on Test requirement: EN 60950-1:2006+A11 but the GS mark is not
applicable to internal devices such as this product.
6.9.3 Flammability
The printed circuit boards used in this product are made of material with the UL recognized flammability rating of
V-1 or better. The flammability rating is marked or etched on the board. All other parts not considered electrical
components are made of material with the UL recognized flammability rating of V-2 minimum basically.
6.9.4 Safe handling
The product is conditioned for safe handling in regards to sharp edges and corners.
6.9.5 Substance restriction requirements
The product complies with the Directive 2002/95/EC of the European Parliament on the restrictions of the use of
the certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (RoHS).
6.9.6 Secondary circuit protection
Spindle/VCM driver module includes 12 V over current protection circuit.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
44
Page 45

6.10 Electromagnetic compatibility
When installed in a suitable enclosure and exercised with a random accessing routine at maximum data rate,
the drive meets the following worldwide EMC requirements:
United States Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Rules and Regulations (Class B), Part 15. (A
6 dB buffer shall be maintained on the emission requirements).
European Economic Community (EEC) directive number 76/889 related to the control of radio frequency
interference and the Verband Deutscher Elektrotechniker (VDE) requirements of Germany
(GOP).Spectrum Management Agency (SMA) EMC requirements of Australia. The SMA has approved
two forms of C-Tick Marking for Hitachi Global Storage Technologies.
6.10.1 CE Mark
The product is declared to be in conformity with requirements of the following EC directives under the sole
responsibility of Hitachi Global Storage Technologies Japan Ltd:
Council Directive 2004/108/EC on the approximation of laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic
compatibility.
6.10.2 C-Tick Mark
The product complies with the following Australian EMC standard:
Limits and methods of measurement of radio disturbance characteristics of information technology, AS/NZS
3548 : 1995 Class B.
6.10.3 BSMI Mark
The product complies with the Taiwan EMC standard “Limits and methods of measurement of radio
disturbance characteristics of information technology equipment, CNS 13438 Class B.”
6.10.4 KC Mark
The product complies with the Korea EMC standard. The regulation for certification of information and
communication equipment is based on “Telecommunications Basic Act” and “Radio Waves Act” Korea EMC
requirement are based technically on CISPR22 measurement standards and limits. KC standards are likewise
based on IEC standards.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
45
Page 46

Part 2. Interface Specification
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
46
Page 47

7 General
Device
Device indicates HDS7210xxCLA3yz / HUA7220xxCLA33z /
HCS5C10xxCLA382 / HCS7210xxCLA3y2 / HDS5C10xxCLA382
Host
Host indicates the system that the device is attached to.
Check Power Mode
Check Power Mode command returns FFh to Sector Count Register when the
device is in Idle mode. This command does not support 80h as the return value.
COMRESET
COMRESET response is not the same as that of Power On Reset. Refer to
section 5.1, “Reset Response” for detail.
Download
Download command is aborted when the device is in security locked mode.
COMRESET response time
During 500ms from Power On Reset, COMINIT is not returned within 10ms as a
response to COMRESET.
Streaming Commands
When the device is in standby mode, Streaming Commands can‟t be completed
while waiting for the spindle to reach operating speed even if execution time
exceeds specified CCTL(Command Completion Time Limit). The minimum CCTL
is 50ms.CCTL is set to 50ms when the specified value is shorter than 50ms. For
HCS7210xxCLA3y2 and HCS5C10xxCLA382, the minimum CCTL is 100ms.
Error Recover Control
(SCT Command set)
When the device is in standby mode, any command where error recovery time
limit is specified can‟t be completed while waiting for the spindle to reach operating
speed even if execution time exceeds specified recovery time limit. The minimum
time limit is 6.5 second. When the specified time limit is shorter than 6.5 second,
the issued command is aborted. For HCS7210xxCLA3y2 and
HCS5C10xxCLA382, the minimum time limit is 0.3 second.
7.1 Introduction
This specification describes the host interface of HDS7210xxCLA3yz / HUA7220xxCLA33z /
HCS5C10xxCLA382 / HCS7210xxCLA3y2 / HDS5C10xxCLA382
.
The interface conforms to the following working documents of Information technology with certain limitations
described in the chapter 0 “Deviations from Standard” on page 47
– Serial ATA II: Extensions to Serial ATA Revision 2.6
7.2 Terminology
7.3 Deviations From Standard
The device conforms to the referenced specifications, with deviations described below.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
47
Page 48

8 Registers
Alternate Status Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
BSY
RDY
DF
DSC
/SERV
DRQ
COR
IDX
ERR
In Serial ATA, the host adapter contains a set of registers that shadow the contents of the traditional device
registers, referred to as the Shadow Register Block. Shadow Register Block registers are interface registers
used for delivering commands to the device or posting status from the device. About details, please refer to the
Serial ATA Specification.
In the following cases, the host adapter sets the BSY bit in its shadow Status Register and transmits a FIS to the
device containing the new contents.
Command register is written in the Shadow Register Block
Device Control register is written in the Shadow Register Block with a change of state of the SRST bit
COMRESET is requested
8.1 Alternate Status Register
Table 27 Alternate Status Register
This register contains the same information as the Status Register. The only difference is that reading this
register does not imply interrupt acknowledge or clear a pending interrupt. See 8.13 "Status Register" on the
page 53 for the definition of the bits in this register.
8.2 Command register
This register contains the command code being sent to the device. Command execution begins immediately
after this register is written. The command set is shown in Table 66 Command Set on page 103.
All other registers required for the command must be set up before writing the Command Register.
8.3 Cylinder High Register
This register contains the high order bits of the starting cylinder address for any disk access. At the end of the
command, this register is updated to reflect the current cylinder number.
In LBA Mode this register contains Bits 16-23. At the end of the command, this register is updated to reflect the
current LBA Bits 16-23.
The cylinder number may be from zero to the number of cylinders minus one.
When 48-bit addressing commands are used, the "most recently written" content contains LBA Bits 16-23, and
the "previous content" contains Bits 40-47. The 48-bit Address feature set is described in 9.12.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
48
Page 49

8.4 Cylinder Low Register
Device Control Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
HOB - - - 1
SRST
-IEN
0
Bit Definitions
HOB
HOB (high order byte) is defined by the 48-bit Address feature set. A write to
any Command Register shall clear the HOB bit to zero.
SRST (RST)
Software Reset. The device is held reset when RST=1. Setting RST=0
reenables the device.
The host must set RST=1 and wait for at least 5 microseconds before setting
RST=0, to ensure that the device recognizes the reset.
-IEN
Interrupt Enable. When -IEN=0, and the device is selected, device interrupts to
the host will be enabled. When -IEN=1, or the device is not selected, device
interrupts to the host will be disabled.
This register contains the low order bits of the starting cylinder address for any disk access. At the end of the
command, this register is updated to reflect the current cylinder number.
In LBA Mode this register contains Bits 8-15. At the end of the command, this register is updated to reflect the
current LBA Bits 8-15.
The cylinder number may be from zero to the number of cylinders minus one.
When 48-bit addressing commands are used, the "most recently written" content contains LBA Bits 8-15, and
the "previous content" contains Bits 32-39.
8.5 Data Register
This register is used to transfer data blocks between the device data buffer and the host. It is also the register
through which sector information is transferred on a Format Track command, and configuration information is
transferred on an Identify Device command.
All data transfers are 16 bits wide, except for ECC byte transfers, which are 8 bits wide. Data transfers are PIO
only.
The register contains valid data only when DRQ=1 in the Status Register.
8.6 Device Control Register
Table 28 Device Control Register
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
49
Page 50

8.7 Drive Address Register
Drive Address Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
HIZ
-WTG
-H3
-H2
-H1
-H0
-DS1
-DS0
Bit Definitions
HIZ
High Impedance. This bit is not driven and will always be in a high impedance state.
-WTG
-Write Gate. This bit is 0 when writing to the disk device is in progress.
-H3,-H2,-H1,-H0
-Head Select. These four bits are the one's complement of the binary coded address
of the currently selected head. -H0 is the least significant.
-DS1
-Drive Select 1. Drive select bit for device 1, active low. DS1=0 when device 1 (slave)
is selected and active.
-DS0
-Drive Select 0. Drive Select bit for device 0, active low. DS0=0 when device 0
(master) is selected and active.
Device/Head Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
1 L 1
DRV
HS3
HS2
HS1
HS0
Bit Definitions
L
Binary encoded address mode select. When L=0, addressing is by CHS mode. When
L=1, addressing is by LBA mode.
DRV
Device. This product ignores this bit.
HS3,HS2,HS1,HS0
Head Select. These four bits indicate binary encoded address of the head. HS0 is the
least significant bit. At command completion, these bits are updated to reflect the
currently selected head.
The head number may be from zero to the number of heads minus one.
In LBA mode, HS3 through HS0 contain bits 24-27 of the LBA. At command
completion, these bits are updated to reflect the current LBA bits 24-27.
Table 29 Drive Address Register
This register contains the inverted drive select and head select addresses of the currently selected drive.
8.8 Device/Head Register
Table 30 Device/Head Register
This register contains the device and head numbers.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
50
Page 51

8.9 Error Register
Error Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
ICRCE
UNC
0
IDNF
0
ABRT
TK0NF
AMNF
Bit Definitions
ICRCE (CRC)
Interface CRC Error. ICRCE=1 indicates a CRC error occurred during FIS transmission or
FIS reception.
UNC
Uncorrectable Data Error. UNC=1 indicates an uncorrectable data error has been
encountered.
IDNF (IDN)
ID Not Found. IDN=1 indicates the requested sector's ID field could not be found.
ABRT (ABT)
Aborted Command. ABT=1 indicates the requested command has been aborted due to a
device status error or an invalid parameter in an output register.
TK0NF (T0N)
Track 0 Not Found. T0N=1 indicates track 0 was not found during a Recalibrate command.
AMNF (AMN)
Address Mark Not Found. This product does not report this error. This bit is always zero.
Table 31 Error Register
This register contains status from the last command executed by the device, or a diagnostic code.
At the completion of any command except Execute Device Diagnostic, the contents of this register are valid
always even if ERR=0 in the Status Register.
Following a power on, a reset, or completion of an Execute Device Diagnostic command, this register contains a
diagnostic code. See 0 on page 55 for the definition.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
51
Page 52

8.10 Features Register
This register is command specific. This is used with the Set Features command, SMART Function Set command
and Format Unit command.
8.11 Sector Count Register
This register contains the number of sectors of data requested to be transferred on a read or write operation
between the host and the device. If the value in the register is set to 0, a count of 256 sectors (in 28-bit
addressing) or 65,536 sectors (in 48-bit addressing) is specified.
If the register is zero at command completion, the command was successful. If not successfully completed, the
register contains the number of sectors which need to be transferred in order to complete the request.
The contents of the register are defined otherwise on some commands. These definitions are given in the
command descriptions.
8.12 Sector Number Register
This register contains the starting sector number for any disk data access for the subsequent command.
The sector number is from one to the maximum number of sectors per track.
In LBA mode, this register contains Bits 0-7. At the end of the command, this register is updated to reflect the
current LBA Bits 0-7.
When 48-bit commands are used, the "most recently written" content contains LBA Bits 0-7, and the "previous
content" contains Bits 24-31.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
52
Page 53

8.13 Status Register
Status Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
BSY
DRDY
DF
DSC
/SERV
DRQ
CORR
IDX
ERR
Bit Definitions
BSY
Busy. BSY=1 whenever the device is accessing the registers. The host should not read or
write any registers when BSY=1. If the host reads any register when BSY=1, the contents of
the Status Register will be returned.
DRDY (RDY)
Device Ready. RDY=1 indicates that the device is capable of responding to a command.
RDY will be set to 0 during power on until the device is ready to accept a command. If the
device detects an error while processing a command, RDY is set to 0 until the Status Register
is read by the host, at which time RDY is set back to 1.
DF
Device Fault. This product does not support DF bit. DF bit is always zero.
DSC
Device Seek Complete. DSC=1 indicates that a seek has completed and the device head is
settled over a track. DSC is set to 0 by the device just before a seek begins. When an error
occurs, this bit is not changed until the Status Register is read by the host, at which time the
bit again indicates the current seek complete status.
When the device enters into or is in Standby mode or Sleep mode, this bit is set by device in
spite of not spinning up.
SERV (SRV)
Service. This product does not support SERV bit.
DRQ
Data Request. DRQ=1 indicates that the device is ready to transfer a word or byte of data
between the host and the device. The host should not write the Command register when
DRQ=1.
CORR (COR)
Corrected Data. Always 0.
IDX
Index. IDX=1 once per revolution. Since IDX=1 only for a very short time during each
revolution, the host may not see it set to 1 even if the host is reading the Status Register
continuously. Therefore, the host should not attempt to use IDX for timing purposes.
ERR
Error. ERR=1 indicates that an error occurred during execution of the previous command.
The Error Register should be read to determine the error type. The device sets ERR=0 when
the next command is received from the host.
Table 32 Status Register
This register contains the device status. The contents of this register are updated whenever an error occurs and
at the completion of each command.
If the host reads this register when an interrupt is pending, it is considered to be the interrupt acknowledge. Any
pending interrupt is cleared whenever this register is read.
If BSY=1, no other bits in the register are valid.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
53
Page 54

9 General Operation Descriptions
Power On Reset (POR)
The device executes a series of electrical circuitry diagnostics, spins
up the HDA, tests speed and other mechanical parametric, and sets
default values.
COMRESET
COMRESET is issued in Serial ATA bus.
The device resets the interface circuitry as well as Soft Reset.
Soft Reset (Software Reset)
SRST bit in the Device Control Register is set, and then is reset.
The device resets the interface circuitry according to the Set Features
requirement.
POR
COMRESET
Soft Reset
Aborting Host interface
- o o
Aborting Device operation
-
(*1)
(*1)
Initialization of hardware
o x x
Internal diagnostic
o x x
Spinning spindle
o x x
Initialization of registers (*2)
o o o
Reverting programmed parameters to default
o
(*3)
(*3)
- Number of CHS
(set by Initialize Device Parameter)
- Multiple mode
- Write cache
- Read look-ahead
- ECC bytes
Disable Standby timer
o x x
Power mode
(*5)
(*4)
(*4)
9.1 Reset Response
There are three types of reset in ATA as follows:
The actions of each reset are shown in Table 33.
o ---- execute
x ---- not execute
Table 33 Reset Response
Table Notes
(*1) Execute after the data in write cache has been written.
(*2) Default value on POR is shown in 0 Default Register Values on page55.
(*3) The Set Features command with Feature register = CCh enables the device to revert these
parameters to the power on defaults.
(*4) In the case of Sleep mode, the device goes to Standby mode. In other case, the device does
not change current mode.
(*5) Idle when Power-Up in Standby feature set is disabled. Standby when Power-Up in Standby
feature set is enabled.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
54
Page 55

9.1.1 Register Initialization
Register
Default Value
Error
Diagnostic Code
Sector Count
01h
Sector Number
01h
Cylinder Low
00h
Cylinder High
00h
Device/Head
00h
Status
50h
Alternate Status
50h
Code
Description
01h
No error Detected
02h
Formatter device error
03h
Sector buffer error
04h
ECC circuitry error
05h
Controller microprocessor error
Table 34 Default Register Values
After power on, hard reset, or software reset, the register values are initialized as shown in Table 34.
Table 35 Diagnostic Codes
The meaning of the Error Register diagnostic codes resulting from power on, hard reset or the Execute Device
Diagnostic command is shown in Table 35.
9.2 Diagnostic and Reset considerations
In each case of Power on Reset, COMRESET, Soft reset, and EXECUTE DEVICE DIAGNOSTIC command, the
device is diagnosed. And Error register is set as shown in Table 35.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
55
Page 56

9.3 Sector Addressing Mode
Device/Head
<---
LBA
bits
27-24
Cylinder High
<---
LBA
bits
23-16
Cylinder Low
<---
LBA
bits
15- 8
Sector Number
<---
LBA
bits
7- 0
All addressing of data sectors recorded on the device's media is by a logical sector address. The logical CHS
address for HDS7210xxCLA3yz / HUA7220xxCLA33z / HCS5C10xxCLA382 / HCS7210xxCLA3y2 /
HDS5C10xxCLA382 is different from the actual physical CHS location of the data sector on the disk media. All
addressing of data sectors recorded on the device's media.
HDS7210xxCLA3yz / HUA7220xxCLA33z / HCS5C10xxCLA382 / HCS7210xxCLA3y2 /
HDS5C10xxCLA382 support both Logical CHS Addressing Mode and LBA Addressing Mode as the sector
addressing mode.
The host system may select either the currently selected CHS translation addressing or LBA addressing on a
command-by-command basis by using the L bit in the DEVICE/HEAD register. So a host system must set the L
bit to 1 if the host uses LBA Addressing mode.
9.3.1 Logical CHS Addressing Mode
The logical CHS addressing is made up of three fields: the cylinder number, the head number and the sector
number. Sectors are numbered from 1 to the maximum value allowed by the current CHS translation mode but
can not exceed 255(0FFh). Heads are numbered from 0 to the maximum value allowed by the current CHS
translation mode but can not exceed 15(0Fh). Cylinders are numbered from 0 to the maximum value allowed by
the current CHS translation mode but cannot exceed 65535(0FFFFh).
When the host selects a CHS translation mode using the INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS command, the
host requests the number of sectors per logical track and the number of heads per logical cylinder. The device
then computes the number of logical cylinders available in requested mode.
The default CHS translation mode is described in the Identify Device Information. The current CHS translation
mode also is described in the Identify Device Information.
9.3.2 LBA Addressing Mode
Logical sectors on the device shall be linearly mapped with the first LBA addressed sector (sector 0) being the
same sector as the first logical CHS addressed sector (cylinder 0, head 0, sector 1). Irrespective of the logical
CHS translation mode currently in effect, the LBA address of a given logical sector does not change. The
following is always true:
LBA = ( (cylinder * heads_per_cylinder + heads)
* sectors_per_track ) + sector - 1
where heads_per_cylinder and sectors_per_track are the current translation mode values.
On LBA addressing mode, the LBA value is set to the following register.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
56
Page 57

9.4 Power Management Feature
The power management feature set permits a host to modify the behavior in a manner which reduces the power
required to operate. The power management feature set provides a set of commands and a timer that enables a
device to implement low power consumption modes.
HDS7210xxCLA3yz / HUA7220xxCLA33z / HCS5C10xxCLA382 / HCS7210xxCLA3y2 /
HDS5C10xxCLA382 implement the following set of functions.
1. A Standby timer
2. Idle command
3. Idle Immediate command
4. Sleep command
5. Standby command
6. Standby Immediate command
9.4.1 Power Mode
The lowest power consumption when the device is powered on occurs in Sleep Mode. When in sleep mode, the
device requires a reset to be activated.
In Standby Mode the device interface is capable of accepting commands, but as the media may not immediately
accessible, there is a delay while waiting for the spindle to reach operating speed.
In Idle Mode the device is capable of responding immediately to media access requests.
In Active Mode the device is under executing a command or accessing the disk media with read look-ahead
function or writes cache function.
9.4.2 Power Management Commands
The Check Power Mode command allows a host to determine if a device is currently in, going to or leaving
standby mode.
The Idle and Idle Immediate commands move a device to idle mode immediately from the active or standby
modes. The idle command also sets the standby timer count and starts the standby timer.
The Standby and Standby Immediate commands move a device to standby mode immediately from the active or
idle modes. The standby command also sets the standby timer count.
The Sleep command moves a device to sleep mode. The device's interface becomes inactive at the completion
of the sleep command. A reset is required to move a device out of sleep mode. When a device exits sleep mode
it will enter Standby mode.
9.4.3 Standby timer
The standby timer provides a method for the device to automatically enter standby mode from either active or
idle mode following a host programmed period of inactivity. If the device is in the active or idle mode, the device
waits for the specified time period and if no command is received, the device automatically enters the standby
mode.
If the value of SECTOR COUNT register on Idle command or Standby command is set to 00h, the standby timer
is disabled.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
57
Page 58

9.4.4 Interface Capability for Power Modes
Mode
BSY
RDY
Interface active
Media
Active x x Yes
Active
Idle 0 1 Yes
Active
Standby 0 1 Yes
Inactive
sleep x x No
Inactive
Each power mode affects the physical interface as defined in the following table:
Table 36 Power conditions
Ready (RDY) is not a power condition. A device may post ready at the interface even though the media may not
be accessible.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
58
Page 59

9.5 SMART Function
The intent of Self-monitoring, analysis and reporting technology (SMART) is to protect user data and prevent
unscheduled system downtime that may be caused by predictable degradation and/or fault of the device. By
monitoring and storing critical performance and calibration parameters, SMART devices employ sophisticated
data analysis algorithms to predict the likelihood of near-term degradation or fault condition. By alerting the host
system of a negative reliability status condition, the host system can warn the user of the impending risk of a
data loss and advise the user of appropriate action.
9.5.1 Attributes
Attributes are the specific performance or calibration parameters that are used in analyzing the status of the
device. Attributes are selected by the device manufacturer based on that attribute's ability to contribute to the
prediction of degrading or faulty conditions for that particular device. The specific set of attributes being used
and the identity of these attributes is vendor specific and proprietary.
9.5.2 Attribute values
Attribute values are used to represent the relative reliability of individual performance or calibration attributes.
The valid range of attribute values is from 1 to 253 decimal. Higher attribute values indicate that the analysis
algorithms being used by the device are predicting a lower probability of a degrading or faulty condition existing.
Accordingly, lower attribute values indicate that the analysis algorithms being used by the device are predicting
a higher probability of a degrading or faulty condition existing.
9.5.3 Attribute thresholds
Each attribute value has a corresponding attribute threshold limit which is used for direct comparison to the
attribute value to indicate the existence of a degrading or faulty condition. The numerical values of the attribute
thresholds are determined by the device manufacturer through design and reliability testing and analysis. Each
attribute threshold represents the lowest limit to which its corresponding attribute value can be equal while still
retaining a positive reliability status. Attribute thresholds are set at the device manufacturer's factory and cannot
be changed in the field. The valid range for attribute thresholds is from 1 through 253 decimal.
9.5.4 Threshold exceeded condition
If one or more attribute values, whose Pre-failure bit of their status flag is set, are less than or equal to their
corresponding attribute thresholds, then the device reliability status is negative, indicating an impending
degrading or faulty condition.
9.5.5 SMART commands
The SMART commands provide access to attribute values, attribute thresholds and other logging and reporting
information.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
59
Page 60

9.5.6 Off-line Read Scanning
The device provides the off-line read scanning feature with reallocation. This is the extension of the off-line data
collection capability. The device performs the entire read scan with reallocation for the marginal sectors to
prevent the user data lost.
If interrupted by the host during the read scanning, the device services the host command.
9.5.7 Error Log
Logging of reported errors is supported. The device provides information on the last five errors that the device
reported as described in SMART error log sector. The device may also provide additional vendor specific
information on these reported errors. The error log is not disabled when SMART is disabled. Disabling SMART
shall disable the delivering of error log information via the SMART READ LOG SECTOR command.
If a device receives a firmware modification, all error log data is discarded and the device error count for the life
of the device is reset to zero.
9.5.8 Self-test
The device provides the self-test features which are initiated by SMART Execute Off-line Immediate command.
The self-test checks the fault of the device, reports the test status in Device Attributes Data and stores the test
result in the SMART self-test log sector as described in SMART self-test log data structure. All SMART attributes
are updated accordingly during the execution of self-test.
If interrupted by the host during the self-tests, the device services the host command.
If the device receives a firmware modification, all self-test log data is discarded.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
60
Page 61

9.6 Security Mode Feature Set
Security Set Password
('F1'h)
Security Unlock
('F2'h)
Security Erase Prepare
('F3'h)
Security Erase Unit
('F4'h)
Security Freeze Lock
('F5'h)
Security Disable Password
('F6'h)
Device Locked mode
The device disables media access commands after power on. Media access
commands are enabled by either a security unlock command or a security erase
unit command.
Device Unlocked mode
The device enables all commands. If a password is not set this mode is entered
after power on, otherwise it is entered by a security unlock or a security erase
unit command.
Device Frozen mode
The device enables all commands except those which can update the device
lock function, set/change password. The device enters this mode via a Security
Freeze Lock command. It cannot quit this mode until power off.
High level security
When the device lock function is enabled and the User Password is forgotten the
device can be unlocked via a Master Password.
Maximum level security
When the device lock function is enabled and the User Password is forgotten
then only the Master Password with a Security Erase Unit command can unlock
the device. Then user data is erased.
Security Mode Feature Set is a powerful security feature. With a device lock password, a user can prevent
unauthorized access to hard disk device even if the device is removed from the computer.
The following commands are supported for this feature.
9.6.1 Security mode
Following security modes are provided.
9.6.2 Security Level
Following security levels are provided.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
61
Page 62

9.6.3 Password
Master Password
When the Master Password is set, the device does NOT enable the Device Lock
Function, and the device can NOT be locked with the Master Password, but the Master
Password can be used for unlocking the device locked.
Identify Device Information word 92 contains the value of the Master Password Revision
Code set when the Master Password was last changed. Valid values are 0001h through
FFFEh.
User Password
The User Password should be given or changed by a system user. When the User
Password is set, the device enables the Device Lock Function, and then the device is
locked on next power on reset or hard reset.
< Setting Password >
POR
Set Password with User Password
Normal operation
Power off
< No Setting Password >
POR
Normal operation
Power off
POR Device locked mode
POR Device unlocked mode
(Ref.)
Figure 10 Initial Setting
This function can have 2 types of passwords as described below.
The system manufacturer/dealer who intends to enable the device lock function for the end users, must set the
master password even if only single level password protection is required.
9.6.4 Operation example
9.6.4.1 Master Password setting
The system manufacturer/dealer can set a new Master Password from default Master Password using the
Security Set Password command, without enabling the Device Lock Function.
The Master Password Revision Code is set to FFFEh as shipping default by the HDD manufacturer
9.6.4.2 User Password setting
When a User Password is set, the device will automatically enter lock mode the next time the device is powered
on.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
62
Page 63

9.6.4.3 Operation from POR after User Password is set
POR
Device Locked mode
Unlock CMD Erase Prepare Media access
command (*1)
Non-Media access
command (*1)
Password
Match ?
Complete
Erase Unit
Lock function
Disable
Enter Device
Unlock mode
Erase Unit
Password
Match ?
Normal operation : All commands are available
Freeze Lock command
Enter Device Frozen mode
Normal Operation except Set Password,
Disable Password, Erase Unit, Unlock commands.
Reject
Complete
N
Y
N
Y
When Device Lock Function is enabled, the device rejects media access command until a Security Unlock
command is successfully completed.
Figure 11 Usual Operation
(*1) Refer to 9.6.5 on the page .65
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
63
Page 64

9.6.4.4 User Password Lost
User Password Lost
LEVEL ?
High
Unlock CMD with Master Password
Maximum
Normal operation
Erase Prepare Command
Erase Unit Command
with Master Password
Normal operation but data lost
If the User Password is forgotten and High level security is set, the system user can't access any data. However,
the device can be unlocked using the Master Password.
If a system user forgets the User Password and Maximum security level is set, data access is impossible.
However, the device can be unlocked using the Security Erase Unit command to unlock the device and erase all
user data with the Master Password.
Figure 12 Password Lost
9.6.4.5 Attempt limit for SECURITY UNLOCK command
The SECURITY UNLOCK command has an attempt limit. The purpose of this attempt limit is to prevent that
someone attempts to unlock the drive by using various passwords many times.
The device counts the password mismatch. If the password does not match, the device counts it up without
distinguishing the Master password and the User password. If the count reaches 5, EXPIRE bit (bit 4) of Word
128 in Identify Device information is set, and then SECURITY ERASE UNIT command and SECURITY
UNLOCK command are aborted until a hard reset or a power off. The count and EXPIRE bit are cleared after a
power on reset or a hard reset.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
64
Page 65

9.6.5 Command Table
Command
Locked Mode
Unlocked Mode
Frozen Mode
Check Power Mode
Executable
Executable
Executable
Configure Stream
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Execute Device Diagnostic
Executable
Executable
Executable
Device Configuration Restore
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Device Configuration Freeze Lock
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Device Configuration Identify
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Device Configuration Set
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Download Microcode
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Flush Cache
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Flush Cache Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Format Track
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Identify Device
Executable
Executable
Executable
Idle
Executable
Executable
Executable
Idle Immediate
Executable
Executable
Executable
Initialize Device Parameters
Executable
Executable
Executable
Read Buffer
Executable
Executable
Executable
Read DMA
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read DMA Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read FPDMA Queued
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Log Ext
Executable
Executable
Executable
Read Multiple
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Multiple Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Native Max Address
Executable
Executable
Executable
Read Native Max Ext
Executable
Executable
Executable
Read Sector(s)
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Sector(s) Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Stream DMA
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Stream PIO
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Verify Sector(s)
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Read Verify Sector(s) Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Recalibrate
Executable
Executable
Executable
SCT Read/Write Long
Command aborted
Command aborted
Command aborted
SCT Write Same
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
SCT Error Recovery Control
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
SCT Feature Control
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
SCT Data Table
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
SCT Read Status
Executable
Executable
Executable
Security Disable Password
Command aborted
Executable
Command aborted
Security Erase Prepare
Executable
Executable
Command aborted
This table shows the device's response to commands when the Security Mode Feature Set (Device lock
function) is enabled.
Table 37 Command table for device lock operation -1
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
65
Page 66

Command
Locked Mode
Unlocked Mode
Frozen Mode
Security Erase Unit
Executable
Executable
Command aborted
Security Freeze Lock
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Security Set Password
Command aborted
Executable
Command aborted
Security Unlock
Executable
Executable
Command aborted
Seek
Executable
Executable
Executable
Set Features
Executable
Executable
Executable
Set Max Address
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Set Max Address Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Set Multiple Mode
Executable
Executable
Executable
Sleep
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Disable Operations
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Enable/Disable Attributes Autosave
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Enable Operations
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Execute Off-line Immediate
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Read Attribute Values
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Read Attribute Thresholds
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Return Status
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Save Attribute Values
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Read Log Sector
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Write Log Sector
Executable
Executable
Executable
SMART Enable/Disable Automatic Off-Line
Executable
Executable
Executable
Standby
Executable
Executable
Executable
Standby Immediate
Executable
Executable
Executable
Write Buffer
Executable
Executable
Executable
Write DMA
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write DMA Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write DMA FUA Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write FPDMA Queued
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Log Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Multiple
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Multiple Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Multiple FUA Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Sector(s)
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Sector(s) Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Stream DMA
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Stream PIO
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Write Uncorrectable Ext
Command aborted
Executable
Executable
Table 38 Command table for device lock operation -2
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
66
Page 67

9.7 Host Protected Area Feature
Read Native Max ADDRESS
('F8'h)
Set Max ADDRESS
('F9'h)
Capacity (native)
:
6,498,680,832
byte (6.4GB)
Max LBA (native)
:
12,692,735
(0FFFFFh)
Required size for protected area
:
206,438,400
byte
Required blocks for protected area
:
403,200
(062700h)
Customer usable device size
:
6,292,242,432
byte (6.2GB)
Customer usable sector count
:
12,289,536
(BB8600h)
LBA range for protected area
:
BB8600h to C1ACFFh
Host Protected Area Feature is to provide the 'protected area' which can not be accessed via conventional
method. This 'protected area' is used to contain critical system data such as BIOS or system management
information. The contents of entire system main memory may also be dumped into 'protected area' to resume
after system power off.
The LBA/CYL changed by following command affects the Identify Device Information.
The following set of commands is implemented for this function.
9.7.1 Example for operation (In LBA mode)
Assumptions:
For better understanding, the following example uses actual values for LBA, size, etc. Since it is just an example,
these values could be different.
Device characteristics
1. Shipping HDDs from HDD manufacturer
When the HDDs are shipped from HDD manufacturer, the device has been tested to have usable capacity
of 6.4GB besides flagged media defects not to be visible by system.
2. Preparing HDDs at system manufacturer
Special utility software is required to define the size of protected area and store the data into it.
The sequence is:
Issue Read Native Max Address command to get the real device maximum LBA. Returned value shows
that native device Maximum LBA is 12,692,735 (C1ACFFh) regardless of the current setting.
Make entire device be accessible including the protected area by setting device Maximum LBA as
12,692,735 (C1ACFFh) via Set Max Address command. The option could be either nonvolatile or
volatile.
Test the sectors for protected area (LBA >= 12,289,536 (BB8600h)) if required.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
67
Page 68

Write information data such as BIOS code within the protected area.
Change maximum LBA using Set Max Address command to 12,289,535 (BB85FFh) with nonvolatile
option.
From this point, the protected area cannot be accessed till next Set Max Address command is issued.
Any BIOSes, device drivers, or application software access the HDD as if that is the 6.2GB device
because the device acts exactly the same as real 6.2GB device does.
3. Conventional usage without system software support
Since the HDD works as 6.2GB device, there is no special care to use this device for normal use.
4. Advanced usage using protected area
The data in the protected area is accessed by following.
Issue Read Native Max Address command to get the real device maximum LBA. Returned value shows
that native device Maximum LBA is 12,692,735 (C1ACFFh) regardless of the current setting.
Make entire device be accessible including the protected area by setting device Maximum LBA as
12,692,735 (C1ACFFh) via Set Max Address command with volatile option. By using this option,
unexpected power removal or reset will not make the protected area remained accessible.
Read information data from protected area.
Issue hard reset or POR to inhibit any access to the protected area.
9.7.2 Security extensions
1. Set Max Set Password
2. Set Max Lock
3. Set Max Freeze Lock
4. Set Max Unlock.
The Set Max Set Password command allows the host to define the password to be used during the current
power on cycle. The password does not persist over a power cycle but does persist over a hardware or software
reset. This password is not related to the password used for the Security Mode Feature set. When the password
is set the device is in the Set_Max_Unlocked mode. The Set Max Lock command allows the host to disable the
Set Max commands (except set Max Unlock) until the next power cycle or the issuance and acceptance of the
Set Max Unlock command. When this command is accepted the device is in the Set_Max_Locked mode. The
Set Max Unlock command changes the device from the Set_Max_Locked mode to the Set_Max_Unlocked
mode. The Set Max Freeze Lock command allows the host to disable the Set Max commands (including Set
Max UNLOCK) until the next power cycle. When this command is accepted the device is in the Set_Max_Frozen
mode.
The IDENTIFY DEVICE response word 83, bit 8 indicates that this extension is supported if set, and word 86, bit
8 indicate the Set Max security extension enabled if set.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
68
Page 69

9.8 Write Cache Function
Write cache is a performance enhancement whereby the device reports as completing the write command
(Write Sector(s), Write Multiple and Write DMA) to the host as soon as the device has received all of the data
into its buffer. And the device assumes responsibility to write the data subsequently onto the disk.
While writing data after completed acknowledgment of a write command, soft reset or hard reset does not
affect its operation. But power off terminates writing operation immediately and unwritten data are to be lost.
Soft reset, Standby (Immediate) command and Flush Cache commands during writing the cached data are
executed after the completion of writing to media. So the host system can confirm the completion of write
cache operation by issuing Soft reset, Standby (Immediate) command or Flush Cache command to the
device before power off.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
69
Page 70

9.9 Reassign Function
The reassign Function is used with read commands and write commands. The sectors of data for reassignment
are prepared as the spare data sector.
This reassignment information is registered internally, and the information is available right after completing the
reassign function. Also the information is used on the next power on reset or hard reset.
If the number of the spare sector reaches 0 sectors, the reassign function will be disabled automatically.
The spare tracks for reassignment are located at regular intervals from Cylinder 0. As a result of reassignment,
the physical location of logically sequenced sectors will be dispersed.
9.9.1 Auto Reassign Function
The sectors those show some errors may be reallocated automatically when specific conditions are met. The
spare tracks for reallocation are located at regular intervals from Cylinder 0. The conditions for auto-reallocation
are described below.
Non recovered write errors
When a write operation can not be completed after the Error Recovery Procedure (ERP) is fully carried out, the
sector(s) are reallocated to the spare location. An error is reported to the host system only when the write cache
is disabled and the auto reallocation is failed.
If the write cache function is ENABLED, and when the number of available spare sectors reaches 0 sectors,
both auto reassign function and write cache function are disabled automatically.
Non recovered read errors
When a read operation is failed after defined ERP is fully carried out, a hard error is reported to the host system.
This location is registered internally as a candidate for the reallocation. When a registered location is specified
as a target of a write operation, a sequence of media verification is performed automatically. When the result of
this verification meets the criteria, this sector is reallocated.
Recovered read errors
When a read operation for a sector failed once then recovered at the specific ERP step, this sector of data is
reallocated automatically. A media verification sequence may be run prior to the relocation according to the
pre-defined conditions.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
70
Page 71

9.10 Power-up in Standby feature set
Power-Up In Standby feature set allows devices to be powered-up into the Standby power management state to
minimize inrush current at power-up and to allow the host to sequence the spin-up of devices.
This feature set will be enabled/disabled via the SET FEATURES command. The enabling of this feature set
shall be persistent after power cycle.
A device needs a SET FEATURES subcommand to spin-up to active state when the device has powered-up into
Standby. The device remains in Standby until the SET FEATURES subcommand is received.
If power-up into Standby is enabled, when an IDENTIFY DEVICE is received while the device is in Standby as a
result of powering up into Standby, the device shall set word 0 bit 2 to one to indicate that the response is
incomplete, then only words 0 and 2 are correctly reported.
The IDENTIFY DEVICE information indicates the states as follows:
identify device information is complete or incomplete
this feature set is implemented
this feature set is enabled or disabled
the device needs the Set Features command to spin-up into active state
9.11 Advanced Power Management feature set (APM)
This feature allows the host to select an advanced power management level. The advanced power management
level is a scale from the lowest power consumption setting of 01h to the maximum performance level of FEh.
Device performance may increase with increasing advanced power management levels. Device power
consumption may increase with increasing advanced power management levels. The advanced power
management levels contain discrete bands, described in the section of Set Feature command in detail. This
feature set uses the following functions:
1. A SET FEATURES subcommand to enable Advanced Power Management
2. A SET FEATURES subcommand to disable Advanced Power Management
Advanced Power Management is independent of the Standby timer setting. If both Advanced Power
Management and the Standby timer are set, the device will go to the Standby state when the timer times out or
the device‟s Advanced Power Management algorithm indicates that the Standby state should be entered.
The IDENTIFY DEVICE response word 83, bit 3 indicates that Advanced Power Management feature is
supported if set. Word 86, bit 3 indicates that Advanced Power Management is enabled if set. Word 91, bits 7-0
contain the current Advanced Power Management level if Advanced Power Management is enabled.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
71
Page 72

9.12 48-bit Address Feature Set
The 48-bit Address feature set allows devices with capacities up to 281,474,976,710,655 sectors. This allows
device capacity up to 144,115,188,075,855,360 bytes. In addition, the number of sectors that may be transferred
by a single command are increased by increasing the allowable sector count to 16 bits.
Commands unique to the 48-bit Address feature set are:
Flush Cache Ext
Read DMA Ext
Read FPDMA Queued
Read Multiple Ext
Read Native Max Address Ext
Read Sector(s) Ext
Read Verify Sector(s) Ext
Set Max Address Ext
Write DMA Ext
Write DMA FUA Ext
Write FPDMA Queued
Write Multiple Ext
Write Multiple FUA Ext
Write Sector(s) Ext
Write Uncorrectable Ext
The 48-bit Address feature set operates in LBA addressing only. Devices also implement commands using
28-bit addressing, and 28-bit and 48-bit commands may be intermixed.
In a device, the Features, the Sector Count, the Sector Number, the Cylinder High, and the Cylinder Low
registers are a two-byte-deep FIFO. Each time one of these registers is written, the new content written is placed
into the "most recently written" location and the previous content is moved to "previous content" location.
The host may read the "previous content" of the Features, the Sector Count, the Sector Number, the Cylinder
High, and the Cylinder Low registers by first setting the High Order Bit (HOB, bit 7) of the Device control register
to one and then reading the desired register. If HOB in the Device Control register is cleared to zero, the host
reads the "most recently written" content when the register is read. A write to any Command Block register shall
cause the device to clear the HOB bit to zero in the Device Control register. The "most recently written" content
always gets written by a register write regardless of the state of HOB in the Device Control register.
Support of the 48-bit Address feature set is indicated in the Identify Device response bit 10 word 83. In addition,
the maximum user LBA address accessible by 48-bit addressable commands is contained in Identify Device
response words 100 through 103.
When the 48-bit Address feature set is implemented, the native maximum address is the value returned by a
Read Native Max Address Ext command. If the native maximum address is equal to or less than 268,435,455, a
Read Native Max Address shall return the native maximum address. If the native maximum address is greater
than 268,435,455, a Read Native Max Address shall return a value of 268,435,455.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
72
Page 73

9.13 Streaming feature Set
The Streaming feature set is an optional feature set that allows a host to request delivery of data from a
contiguous logical block address range within an allotted time. This places a priority on time to access the data
rather than the integrity of the data. Streaming feature set commands only support 48-bit addressing.
A device that implements the Streaming feature set shall implement the following minimum set of commands:
Configure Stream
Read Stream PIO
Write Stream PIO
Read Stream DMA
Write Stream DMA
Read Log Ext
Support of the Streaming feature set is indicated in Identify Device work 84 bit 4.
Note that PIO versions of these commands limit the transfer rate (16.6 MB/s), provide no CRC protection, and
limit status reporting as compared to a DMA implementation.
9.13.1 Streaming commands
The streaming commands are defined to be time critical data transfers rather than the standard data integrity
critical commands. Each command shall be completed within the time specified in the Configure Stream
command or in the streaming command itself in order to ensure the stream requirements of the AV type
application. The device may execute background tasks as long as the Read Stream and Write Stream command
execution time limits are still met.
Using the Configure Stream command, the host may define the various stream properties including the default
Command Completion Time Limit (CCTL) to assist the device in setting up its caching for best performance. If
the host does not use a Configure Stream command, the device shall use the CCTL specified in each streaming
command, and the time limit is effective for one time only. If the CCTL is not set by Configure Stream command,
the operation of a streaming command with a zero CCTL is device vendor specific. If Stream ID is not set by a
Configure Stream command, the device shall operate according to the Stream ID set by the streaming
command. The operation is device vendor specific.
The streaming commands may access any user LBA on a device. These commands may be interspersed with
non-streaming commands, but there may be an impact on performance due to the unknown time required to
complete the non-streaming commands.
The streaming commands should be issued using a specified minimum number of sectors transferred per
command, as specified in word 95 of the Identify Device response. The transfer length of a request should be
a multiple of the minimum number of sectors per transfer.
The host provided numeric stream identifier, Stream ID, may be used by the device to configure its resources to
support the streaming requirements of the AV content. One Stream ID may be configured for each read and
write operation with different command completion time limits be each Configure Stream command.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
73
Page 74

9.13.1.1 Urgent bit
The Urgent bit in the Read Stream and Write Stream commands specifies that the command should be
completed in the minimum possible time by the device and shall be completed within the specified Command
Completion Time Limit.
9.13.1.2 Flush to Disk bit
The Flush to Disk bit in the Write Stream command specifies that all data for the specified stream shall be
flushed to the media before posting command completion. If a host requests flushes at times other than the
end of each Allocation Unit, streaming performance may be degraded. The Set Features command to
enable/disable caching shall not affect caching for streaming commands.
9.13.1.3 Not Sequential bit
The Not Sequential bit specifies that the next read stream command with the same Stream ID may not be
sequential in LBA space. This information helps the device with pre-fetching decisions.
9.13.1.4 Read Continuous bit
If the Read Continuous bit is set to one for the command, the device shall transfer the requested amount of data
to the host within the Command Completion Time Limit even if an error occurs. The data sent to the host by
the device in an error condition is vendor specific.
9.13.1.5 Write Continuous bit
If the Write Continuous bit is set to one for the command, and an error is encountered, the device shall complete
the request without posting an error. If an error cannot be resolved within the Command Completion Time Limit,
the erroneous section on the media may be unchanged or may contain undefined data. A future read of this
area may not report an error, even though the data is erroneous.
9.13.1.6 Handle Streaming Error bit
The Handle Streaming Error bit specifies to the device that this command starts at the LBA of a recently reported
error section, so the device may attempt to continue its corresponding error recovery sequence where it left off
earlier. This mechanism allows the host to schedule error recovery and defect management for content critical
data.
9.13.2 Streaming Logs
The Streaming Data Transfer feature set requires two error logs and one performance log. These logs are
accessed via the Read Log Ext command; the information included in the error logs is volatile and is not
maintained across power cycles, hard resets, or sleep. These error logs are 512 bytes in length and retain the
last 31 errors that occurred during any Streaming Data transfer.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
74
Page 75

9.14 SATA BIST (Built-in Self Test)
The device supports the following BIST modes, and begins operations when it receives BIST Activate FIS.
F – Far End Analog Loopback.
L – Far End Retimed Loopback
T – Far End Transmit only
A – ALIGN Bypass (valid only in combination with T bit)
S – Bypass Scrambling (valid only in combination with T bit)
9.15 SATA Interface Power Management
The device supports both receiving host-initiated interface power management requests and initiating
interface power management. The device initiates interface power management when the device enters its
power saving mode whose power consumption is lower than Normal Idle mode.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
75
Page 76

9.16 Software Setting Preservation
When a device is enumerated, software will configure the device using SET FEATURES and other commands.
These software settings are often preserved across software reset but not necessarily across hardware reset.
In Parallel ATA, only commanded hardware resets can occur, thus legacy software only reprograms settings that
are cleared for the particular type of reset it has issued. In Serial ATA, COMRESET is equivalent to hard reset
and a non-commanded COMRESET may occur if there is an asynchronous loss of signal. Since COMRESET
is equivalent to hardware reset, in the case of an asynchronous loss of signal some software settings may be
lost without legacy software knowledge. In order to avoid losing important software settings without legacy
driver knowledge, the software settings preservation ensures that the value of important software settings is
maintained across a COMRESET. Software settings preservation may be enabled or disabled using SET
FEATURES with a subcommand code of 06h. If a device supports software settings preservation, the feature
shall be enabled by default.
9.16.1 COMRESET Preservation Requirements
The software settings that shall be preserved across COMRESET are listed below. The device is only required
to preserve the indicated software setting if it supports the particular feature/command the setting is associated
with.
INITIALIZE DEVICE PARAMETERS: Device settings established with the INITIALIZE DEVICE
PARAMETERS command.
Power Management Feature Set Standby Timer: The Standby timer used in the Power Management
feature set.
Read/Write Stream Error Log: The Read Stream Error Log and Write Stream Error Logs (accessed using
READ LOG EXT and WRITE LOG EXT).
Security mode state: The security mode state established by Security Mode feature set commands (refer
to section 6.13 of the ATA/6 specification). The device shall not transition to a different security mode state
based on a COMRESET. For example, the device shall not transition from the SEC5: Unlocked / not
Frozen state to state SEC4: Security enabled / Locked when a COMRESET occurs, instead the device shall
remain in the SEC5: Unlocked / not Frozen state.
SECURITY FREEZE LOCK: The Frozen mode setting established by the SECURITY FREEZE LOCK
command.
SECURITY UNLOCK: The unlock counter that is decremented as part of a failed SECURITY UNLOCK
command attempt.
SET ADDRESS MAX (EXT): The maximum LBA specified in SET ADDRESS MAX or SET ADDRESS
MAX EXT.
SET FEATURES (Write Cache Enable/Disable): The write cache enable/disable setting established by the
SET FEATURES command with subcommand code of 02h or 82h.
SET FEATURES (Set Transfer Mode): PIO, Multiword, and UDMA transfer mode settings established by
the SET FEATURES command with subcommand code of 03h.
SET FEATURES (Advanced Power Management Enable/Disable): The advanced power management
enable/disable setting established by the SET FEATURES command with subcommand code of 05h or 85h.
The advanced power management level established in the Sector Count register when advanced power
management is enabled (SET FEATURES subcommand code 05h) shall also be preserved.
SET FEATURES (Read Look-Ahead): The read look-ahead enable/disable setting established by the SET
FEATURES command with subcommand code of 55h or AAh.
SET FEATURES (Reverting to Defaults): The reverting to power-on defaults enable/disable setting
established by the SET FEATURES command with a subcommand code of CCh or 66h.
SET MULTIPLE MODE: The block size established with the SET MULTIPLE MODE command.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
76
Page 77

9.17 SATA II Optional Features
There are several optional features defined in SATA II. The following shows whether these features are
supported or not.
9.17.1 Asynchronous Signal Recovery
The device supports asynchronous signal recovery defined in SATA II.
9.17.2 Device Power Connector Pin 11 Definition
SATA II specification defines that Pin 11 of the power segment of the device connector may be used to
provide the host with an activity indication and disabling of staggered spin-up. The device does not support
both usage of Pin 11.
9.17.3 Phy Event Counters
Phy Event Counters are an optional feature to obtain more information about Phy level events that occur on the
interface. This information may aid designers and integrators in testing and evaluating the quality of the interface.
A device indicates whether it supports the Phy event counters feature in IDENTIFY (PACKET) DEVICE Word 76,
bit 10. The host determines the current values of Phy event counters by issuing the READ LOG EXT command
with a log page of 11h. The counter values shall not be retained across power cycles. The counter values shall
be preserved across COMRESET and software resets.
The counters defined can be grouped into three basic categories: those that count events that occur during Data
FIS transfers, those that count events that occur during non-Data FIS transfers, and events that are unrelated to
FIS transfers. Counters related to events that occur during FIS transfers may count events related to
host-to-device FIS transfers, device-to-host FIS transfers, or bi-directional FIS transfers. A counter that records
bi-directional events is not required to be the sum of the counters that record the same events that occur on
device-to-host FIS transfers and host-to-device FIS transfers.
Implementations that support Phy event counters shall implement all mandatory counters, and may support any
of the optional counters as shown in 0. Note that some counters may increment differently based on the speed
at which non-Data FIS retries are performed by the host and device. Implementations may record CRC and
non-CRC error events differently. For example, there is a strong likelihood that a disparity error may cause a
CRC error. Thus, the disparity error may cause both the event counter that records non-CRC events and the
event counter that records CRC events to be incremented for the same event. Another example implementation
difference is how a missing EOF event is recorded; a missing EOF primitive may imply a bad CRC even though
the CRC on the FIS may be correct. These examples illustrate that some Phy event counters are sensitive to the
implementation of the counters themselves, and thus these implementation sensitive counters cannot be used
as an absolute measure of interface quality between different implementations.
9.17.3.1 Counter Reset Mechanisms
There are two mechanisms by which the host can explicitly cause the Phy counters to be reset.
The first mechanism is to issue a BIST Activate FIS to the device. Upon reception of a BIST Activate FIS the
device shall reset all Phy event counters to their reset value. The second mechanism uses the READ LOG EXT
command. When the device receives a READ LOG EXT command for log page 11h and bit 0 in the Features
register is set to one, the device shall return the current counter values for the command and then reset all Phy
event counter values.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
77
Page 78

9.17.3.2 Counter Identifiers
Identifier
(Bits 11:0)
Mandatory /
Optional
Description
000h
Mandatory
No counter value; marks end of counters in the page
001h
Mandatory
Command failed and ICRC bit set to one in Error register
002h
Optional
R_ERR response for Data FIS
003h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Device-to-Host Data FIS)
004h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Host-to-Device Data FIS)
005h
Optional
R_ERR response for Non-data FIS
006h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Device-to-Host Non-data FIS)
007h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Host-to-Device Non-data FIS)
008h
Optional
Not supported (Device-to-Host non-Data FIS retries)
009h
Optional
Transitions from drive PhyRdy to drive PhyNRdy
00Ah
Mandatory
Signature Device-to-Host Register FISes sent due to a COMRESET
00Bh
Optional
CRC errors within a Host-to-Device FIS
00Dh
Optional
Non-CRC errors within a Host-to-Device FIS
00Fh
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Host-to-Device Data FIS due to CRC
errors)
010h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Host-to-Device Data FIS due to
non-CRC errors)
012h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Host-to-Device Non-data FIS due to
CRC errors)
013h
Optional
Not supported (R_ERR response for Host-to-Device Non-data FIS due to
non-CRC errors)
Each counter begins with a 16-bit identifier. 0 defines the counter value for each identifier. Any unused counter
slots in the log page should have a counter identifier value of 0h.
Optional counters that are not implemented shall not be returned in log page 11h. A value of „0‟ returned for a
counter means that there have been no instances of that particular event. There is no required ordering for event
counters within the log page; the order is arbitrary and selected by the device vendor.
For all counter descriptions, „transmitted‟ refers to items sent by the device to the host and „received‟ refers to
items received by the device from the host.
Bits 14:12 of the counter identifier convey the number of significant bits that counter uses. All
counter values consume a multiple of 16-bits. The valid values for bits 14:12 and the
corresponding counter sizes are:
1h 16-bit counter
2h 32-bit counter
3h 48-bit counter
4h 64-bit counter
Any counter that has an identifier with bit 15 set to one is vendor specific. This creates a vendor specific range of
counter identifiers from 8000h to FFFFh. Vendor specific counters shall observe the number of significant bits
14:12 as defined above.
Table 39 Phy Event Counter Identifiers
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
78
Page 79

9.17.3.2.1 Counter Definitions
The counter definitions in this section specify the events that a particular counter identifier
represents.
9.17.3.2.1.1 Identifier 000h
There is no counter associated with identifier 000h. A counter identifier of 000h indicates that
there are no additional counters in the log page.
9.17.3.2.1.2 Identifier 001h
The counter with identifier 001h returns the number of commands that returned an ending status
with the ERR bit set to one in the Status register and the ICRC bit set to one in the Error register.
9.17.3.2.1.3 Identifier 002h
The counter with identifier 002h returns the sum of (the number of transmitted Device-to-Host
Data FISes to which the host responded with R_ERRP) and (the number of received Host-toDevice Data FISes to which the device responded with R_ERRP).
9.17.3.2.1.4 Identifier 005h
The counter with identifier 005h returns the sum of (the number of transmitted Device-to-Host
non-Data FISes to which the host responded with R_ERRP) and (the number of received Host-toDevice non-Data FISes to which the device responded with R_ERRP). Retries of non-Data FISes
are included in this count.
9.17.3.2.1.5 Identifier 009h
The counter with identifier 009h returns the number of times the device transitioned into the
PHYRDY state from the PHYNRDY state, including but not limited to asynchronous signal events,
power management events, and COMRESET events. If interface power management is enabled,
then this counter may be incremented due to interface power management transitions.
9.17.3.2.1.6 Identifier 00Ah
The counter with identifier 00Ah returns the number of transmitted Device-to-Host Register FISes
with the device reset signature in response to a COMRESET, which were successfully followed by
an R_OK from the host.
9.17.3.2.1.7 Identifier 00Bh
The counter with identifier 00Bh returns the number of received Host-to-Device FISes of all types
(Data and non-Data) to which the device responded with R_ERRP due to CRC error.
9.17.3.2.1.8 Identifier 00Dh
The counter with identifier 00Dh returns the number of received Host-to-Device FISes of all types
(Data and non-Data) to which the devices responded with R_ERRP for reasons other than CRC
error.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
79
Page 80

9.17.3.3 READ LOG EXT Log Page 11h
Byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0
Reserved
1
Reserved
2
Reserved
3
Reserved
… … n
Counter n Identifier
n+1
n+2
Counter n Value
n +
Counter
n Length
… … 508
Reserved
509
510
511
Data Structure Checksum
READ LOG EXT log page 11h is one page (512 bytes) in length. The first Dword of the log page contains
information that applies to the rest of the log page. Software should continue to process counters until a counter
identifier with value 0h is found or the entire page has been read. A counter identifier with value 0h indicates that
the log page contains no more counter values past that point. Log page 11h is defined in Table 40.
Table 40 READ LOG EXT Log Page 11h data structure definition
Counter n Identifier
Phy event counter identifier that corresponds to Counter n Value. Specifies the particular event counter
that is being reported. The Identifier is 16 bits in length.
Valid identifiers are listed in Table 40.
Counter n Value
Value of the Phy event counter that corresponds to Counter n Identifier. The number of significant bits is
determined by Counter n Identifier bits 14:12 (as defined in section 4.3.2). The length of Counter n Value
shall always be a multiple of 16-bits. All counters are one-extended. For example, if a counter is only
physically implemented as 8-bits when it reaches the maximum value of 0xFF, it shall be one-extended to
0xFFFF. The counter shall stop (and not wrap to zero) after reaching its maximum value.
Counter n Length
Size of the Phy event counter as defined by bits 14:12 of Counter n Identifier.
The size of the Phy event counter shall be a multiple of 16-bits.
Data Structure Checksum
The data structure checksum is the 2‟s complement of the sum of the first 511 bytes in the data structure.
Each byte shall be added with unsigned arithmetic and overflow shall be ignored. The sum of all 512
bytes of the data structure will be zero when the checksum is correct.
Reserved All reserved fields shall be cleared to zero
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
80
Page 81

9.18 SCT Command Transport feature Set
Log page E0h
Log Page E1h
Write log page
Issue Command
Send Data to the drive
Read log page
Return Status
Received Data from the drive
Word
Description
206
SCT Command set support
15-12
Vendor Specific
11-6
Reserved
5 Action Code 5 (SCT Data Table) supported
4 Action Code 4 (Features Control) supported
3 Action Code 3 (Error Recovery Control) supported
2 Action Code 2 (SCT Write Same) supported
1 Obsolete
0 SCT Feature Set supported (includes SCT status)
9.18.1 Overview
9.18.1.1 Introduction
SMART Command Transport (SCT) is the method for the drive to receive commands using log page E0h and
transporting data using log page E1h. These log pages are used as follows:
Table 41 SCT Log Page and direction
There are two ways to access the log pages: using SMART READ/WRITE LOG and READ/WRITE LOG EXT.
Both sets of commands access the same log pages and provide the same capabilities.
The log directory for log pages E0h and E1h should report a length of one. The length of log page E1h does not
indicate the length of an SCT data transfer.
If SMART is supported, but not enabled, the drive supports SMART READ/WRITE LOG for Log page E0h and
E1h.
If security is enabled and password has not been issued to unlock the device, all SCT commands will fail.
9.18.1.2 Capability definition
Capability Identification is performed by issuing Identify Device command. Word 206 of Identify Data is used to
determine if SCT is enabled and which SCT Action Codes are supported.
Table 42 Identify Device Information Word 206
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
81
Page 82

9.18.1.3 SCT Command Nesting and intermingling with Standard commands
In general, standard ATA commands can be intermingled with SCT Commands but SCT commands cannot be
nested. SCT commands that do not require a follow-on data transfer operation never have an issue with being
intermixed with any ATA commands or each other. SCT commands that do require data transfer, on the other
hand, may not be nested; that is, if a key command that requires a data transfer is issued, all data transfer - to or
from the host - must complete before another SCT command is issued. In most cases, however, ATA
read/write commands may be inserted in between SCT data transfers, that is, between complete SMART Read
Log/Write Log commands. Furthermore, any reset (power-on, software or hardware) will cause the SCT
command to be aborted.
9.18.1.4 Resets
In an SCT command is executing, any reset including Soft Reset, Hard Reset, COMRESET, and Power-On
Reset all cause the command to be terminated. This could result in partial command execution or data loss.
There is no indication once the drive becomes ready that the previous command was terminated.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
82
Page 83

9.18.2 SCT Command Protocol
Command Block Output Registers
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Feature
D6h
Sector Count
01h
Sector Number
E0h
Cylinder Low
4Fh
Cylinder High
C2h
Device/Head
- - - D - - - - Command
B0h
Command Block Input Registers (Success)
Command Block Input Registers (Error)
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Error
00h
Error
04h
Sector Count
Depends on command
(LSB)
Sector Count
Extended Status code
(LSB)
Sector Number
Depends on command
(MSB)
Sector Number
Extended Status code
(MSB)
Cylinder Low
Number of sectors to
transfer (LSB)
Cylinder Low
Number of sectors to
transfer (LSB)
Cylinder High
Number of sectors to
transfer (MSB)
Cylinder High
Number of sectors to
transfer (MSB)
Device/Head
- - - - - - -
- Device/Head
- - - - - - -
-
Status
50h
Status
51h
9.18.2.1 Command Transport
SCT Command Transport occurs when a 512-byte data packet (called “Key Sector”) is created and the written to
SMART or extended log page E0h. The key sector specifies Action and Function Codes along with the
parameters that are required to perform the action.
9.18.2.1.1 Issue SCT Command Using SMART
Table 43 Output Registers of SCT Command Using SMART
Table 44 Input Registers of SCT Command Using SMART
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
83
Page 84

9.18.2.1.2 Issue SCT Command Using Write Log Ext
Command Block Output Registers
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Feature
Current
Reserved
Previous
Reserved
Sector Count
Current
01h
Previous
00h
LBA Low
Current
E0h
Previous
Reserved
LBA Mid
Current
00h
Previous
00h
LBA High
Current
Reserved
Previous
Reserved
Device/Head
- - - D - - -
-
Command
3Fh
Command Block Input Registers (Success)
Command Block Input Registers (Error)
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Error
00h
Error
04h
Sector Count
HOB=0
Depends on command
(LSB)
Sector Count
HOB=0
Extended Status Code
(LSB)
HOB=1
Reserved
HOB=1
Reserved
LBA Low
HOB=0
Depends on command
(MSB)
LBA Low
HOB=0
Extended Status Code
(MSB)
HOB=1
Reserved
HOB=1
Reserved
LBA Mid
HOB=0
Number of sectors (LSB)
LBA Mid
HOB=0
Number of sectors (LSB)
HOB=1
Reserved
HOB=1
Reserved
LBA High
HOB=0
Number of sectors (MSB)
LBA High
HOB=0
Number of sectors (MSB)
HOB=1
Reserved
HOB=1
Reserved
Device/Head
- - - - - - -
- Device/Head
- - - - - - - - Status
50h
Status
51h
Table 45 Input Registers of SCT Command Using Write Log Ext
All ATA “previous” registers are reserved in Write Log Ext responses.
Table 46 Output Registers of SCT Command Using Write Log Ext
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
84
Page 85

9.18.2.1.3 Key Sector Format
Byte
Field
Words
Description
1:0
Action Code
1
This field defines the command type and
generally specifies the type of data being
accessed, such as sector or physical action
being performed, such as seek.
3:2
Function Code
1
This field specifies the type of access, and
varies by command. For example, this can
specify read, write, verify, etc.
X:4
Parameter1
Depends on command
Depends on command
Y:x+1
Parameter2
Depends on command
Depends on command
… … …
…
Total Words
256
Action Code
Block Data
TF Data
Description
0000h
- - Reserved
0001h
Read/Write
Y
Long Sector Access (Not Supported)
0002h
Write
N
SCT Write Same
0003h
- Y Error Recovery Control
0004h
- Y Features Control
0005h
Read
N
SCT Data Table
0006h-BFFFh
- - Reserved
C000h-FFFFh
- - Vendor Specific
An SCT command (Key Sector) is always 512 bytes long. Table below shows the generic format of an SCT
command.
Table 47 Key Sector Format
The action codes are defined in Table below.
Table 48 SCT Action Code List
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
85
Page 86

Status Code
Definition
0000h
Command complete without error
0001h
Invalid Function Code
0002h
Input LBA out of range
0003h
Request sector count overflow. The number of sectors requested to transfer
(Sector Count register) in the read or write log command is larger than required by
SCT command.
0004h
Invalid Function code in Error Recovery command
0005h
Invalid Selection code in Error Recovery command
0006h
Host read command timer is less than minimum value
0007h
Host write command timer is less than minimum value
0008h
Background SCT command was aborted because of an interrupting host command
0009h
Background SCT command was terminated because of unrecoverable error
000Ah
Invalid Function code in Long Sector Access command
000Bh
SCT data transfer command was issued without first issuing an SCT command
000Ch
Invalid Function code in Feature Control command
000Dh
Invalid Feature code in Feature Control command
000Eh
Invalid New State value in Feature Control command
000Fh
Invalid Option Flags in Feature Control command
0010h
Invalid SCT Action code
0011h
Invalid Table ID (table not supported)
0012h
Command was aborted due to drive security being locked
0013h
Invalid revision code
0017h
Blocking SCT Write Same command was terminated because of unrecoverable
error
0018h-BFFFh
Reserved
C000h-C002h
Vendor Specific
C003h
Overlay switch failure in Long Sector Access command
C004h
Read Long failure
C005h
Write Long failure
C006h
Write Cache enable failure
C007h-FFEFh
Vendor Specific
FFF0h-FFFEh
Reserved
FFFFh
SCT command executing in background
9.18.2.1.4 Extended Status Code
Table 49 Extended Status Code
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
86
Page 87

9.18.2.2 Data transfer
Command Block Output Registers
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Feature
D5h(Read)/D6h(Write)
Sector Count
Number of sectors to be
transferred
Sector Number
E1h
Cylinder Low
4Fh
Cylinder High
C2h
Device/Head
- - - D - - - - Command
B0h
Command Block Output Registers
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Feature
Current
Reserved
Previous
Reserved
Sector Count
Current
01h
Previous
00h
LBA Low
Current
E1h
Previous
Reserved
LBA Mid
Current
00h
Previous
00h
LBA High
Current
Reserved
Previous
Reserved
Device/Head
- - - D - - -
-
Command
2Fh(Read)/3Fh(Write)
Once an SCT command has been issued, status can be checked and data can be transferred. Data transfer
uses log page E1h.
9.18.2.2.1 Read/Write SCT Data Using SMART
Table 50 Input Registers of SCT Data Transfer Using SMART
9.18.2.2.2 Read/Write SCT Data Using Read/Write Log Ext
Table 51 Input Registers of SCT Data Transfer using Read/Write Log Ext
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
87
Page 88

9.18.2.3 SCT Status Request
Command Block Output Registers
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Feature
D5h
Sector Count
01h
Sector Number
E0h
Cylinder Low
4Fh
Cylinder High
C2h
Device/Head
- - - D - - -
-
Command
B0h
Command Block Output Registers
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Feature
Current
Reserved
Previous
Reserved
Sector Count
Current
01h
Previous
00h
LBA Low
Current
E0h
Previous
Reserved
LBA Mid
Current
00h
Previous
00h
LBA High
Current
Reserved
Previous
Reserved
Device/Head
- - - D - - - - Command
2Fh
Once an SCT command has been issued, a status is reported in the ATA registers. This status indicates that the
command was accepted or that an error occurred. This ATA status return does not indicate successful
completion of the SCT actions. Some commands can take several minutes or even hours to execute. In this
case, the host can determine execution progress by requesting SCT status.
Log page E0h contains the status information. Reading log page E0h retrieves the status information. The SCT
status may be acquired any time that the host is allowing to send a command to the device. This command will
not change the power state of the drive, nor terminate any background activity, including any SCT command in
progress.
9.18.2.3.1 SCT Status Request Using SMART
Table 52 Intput Registers of SCT Status Request Using SMART
9.18.2.3.2 SCT Status Request Using Read Log Ext
Table 53 Input Registers of SCT Status Request Using Read Log Ext
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
88
Page 89

9.18.2.3.3 Format of SCT Status Response
Byte
Type
Field Name
Value
Description
1:0
Word
Format Version
0003h
Status Response format version number
3:2
Word
SCT Version
Manufacturer‟s vendor specific
implementation version number
5:4
Word
SCT Spec.
0001h
Highest level of SCT Technical Report
supported
9:6
DWord
Status Flags
Bit 0 : Segment Initialized Flag
If this bit is set to 1, an SCT Write Same
command write to all LBAs of the drive has
completed without error. This bit shall be
cleared to 0 when any user LBA is written,
even if write cache is enabled. This bit is
alse cleared if the capacity of the drive is
changed via SETMAX, SETMAX EXT or
DCO. This bit is preserved through a power
cycle.
Bit 1-31 : Reserved
10
Byte
Drive Status
0 = Active waiting for a command
1 = Stand-by
2 = Sleep
3 = DST executing in background
4 = SMART ODC executing in background
5 = SCT executing in background
13:11
Byte[3]
reserved
00h
15:14
Word
Extended Status
Code
Status Of last SCT command issued.
FFFFh if SCT command executing in
background.
17:16
Word
Action Code
Action code of last SCT command issued. If
the Extended Status Code is FFFFh, this is
the Action Code of the command that is
current executing.
19:18
Word
Function Code
Function code of last SCT command
issued. If the Extended Status Code is
FFFFh, this is the Function Code of the
command that is current executing.
39:20
Byte[20]
reserved
00h
47:40
QWord
LBA
Current LBA of SCT command executin in
background. If there is no command
currently executing in the background, this
field is undefined.
199:48
Byte[152]
00h
200
Byte
HDA Temp
Current HDA temperature in degrees
Celsius. This is a 2‟s complement number.
80h indicates that this value is invalid.
201
Byte
Min Temp
Minimum HDA temperature in degrees
Celsius. This is a 2‟s complement integer.
80h indicates that this value is invalid.
202
Byte
Max Temp
Maximum HDA temperature in degrees
Celsius. This is a 2‟s complement number.
80h indicates that this value is invalid.
203
Byte
Life Min Temp
Minimum HDA temperature in degrees
Celsius seen for the life of the device. This
is a 2‟s complement integer. 80h indicates
that this value is invalid.
204
Byte
Life Max Temp
Maximum HDA temperature in degrees
Celsius seen for the life of the drive. This is
a 2‟s complement number. 80h indicates
that this value is invalid.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
89
Page 90

205
Byte
Reserved
00h
209:206
Dword
Over Limit Count
Number of temperature recording Intervals
since the last power-on reset where the
recorded temperature was greater than Max
Op Limit. See table 93 for information about
this Interval.
213:210
Dword
Under Limit Count
Number of temperature recording Intervals
since the last power-on reset where the
recorded temperature was less than Min Op
Limit. See table 93 for information about this
Interval.
479:214
Byte[275]
Reserved
00h
511:480
Byte[32]
Vendor Specific
00h
Table 54 Data Format of SCT Status Response
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
90
Page 91

Word
Name
Value
Description
0
Action Code
0002h
This action writes a pattern or sector of data repeatedly to
the media. This capability could also be referred to as “Write
All” or “Write Same”.
1
Function Code
0001h
Repeat Write Pattern (Background Operation)
0002h
Repeat Write Sector (Background Operation)
0101h
Repeat Write Pattern (Blocking Operation)
0102h
Repeat Write Sector (Blocking Operation)
5:2
Start LBA
QWord
First LBA
9:6
Count
QWord
Number of sectors to fill
11:10
Pattern
DWord
If the Function Code is 0001h, this field contains a 32-bit
pattern that is written on the media starting at the location
specified in words two through five
255:12
reserved
0000h
Command Block Input Registers (Success)
Error
00h
Sector Count
Reserved
Sector Number
Reserved
Cylinder Low
Number of sectors to transfer (LSB) = 01h
Cylinder High
Number of sectors to transfer (MSB) = 00h
Device/Head
reserved
Status
50h
9.18.3 SCT Command Set
9.18.3.1 SCT Write Same (action code : 0002h)
Inputs: (Key Sector)
Table 55 SCT Write Same (Inputs)
Outputs: (TF Data)
Table 56 SCT Write Same (Outputs)
The SCT Write Same command will begin writing sectors from Start LBA in incrementing order until Count
sectors have been written. A Count of zero means apply operation from Start LBA until the last user LBA on the
drive is reached. The HPA feature determines the last user LBA. This command will not write over a hidden
partition when hidden partitions are enabled using the Host Protected Area drive capabilities. Automatic sector
reassignment is permitted during the operation of this function.
If Start LBA or Start LBA + Count go beyond the last user LBA then an error is reported and the SCT command
is not executed. Issuing this command with a value of zero for Start LBA and Count will cause all LBAs of the
drive to be written the specified pattern.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
91
Page 92

Once the key sector has been issued, if the Function Code was 0002h or 0102h and the TF Data indicates that
the drive is ready to receive data, log page E1h should be written to transfer the data.
This command can change the Segment Initialized Flag. If the command writes all the user addressable sectors
and completes without encountering an error or being aborted, then the “Segment Initialized Flag” (bit 0 of the
Status Flags in the SCT Status. See0) shall be set to 1. A write to any user addressable sector on the drive
(except another complete write all), shall cause the Segment Initialized Flag to be cleared. Reallocations as a
result of reading data (foreground or background) do not clear the Segment Initialized Flag.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
92
Page 93

Implementation note for Background Operation (Function code = 0001h, 0002h)
Possible Extended Status Code for Background Operation (Function code = 0001h, 0002h)
0008h
Background SCT command was aborted because of an interrupting host command
0009h
Background SCT command was terminated because of unrecoverable error
FFFFh
SCT command executing in background
Command Block Input Registers (Error)
Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Error
04h
Sector Count
Extended Status code
(LSB)
Sector Number
Extended Status code
(MSB)
Cylinder Low
N/A
Cylinder High
N/A
Device/Head
- - - - - - -
-
Status
51h
Possible Extended Status Code for Blocking Operation (Function code = 0101h, 0102h)
0017h
Blocking SCT Write Same command was terminated because of unrecoverable
error
In this mode, the drive will return command completion status when the drive finished receiving data.
Any command, including IDENTIFY DEVICE, other than SCT Status, issued to the drive while this command is
in progress will terminate the SCT Write Same command. The incoming command is executed.
Use the SCT Status command to retrieve status information about the current SCT command. Example status
information includes: command active or complete, current LBA, and errors. When this command is in progress,
the SCT status error code will be FFFFh, and set to 0000h if the command completes without error. It will be less
than FFFFh and grater the 0000h if the command terminated prematurely for any reason.
Implementation note for Blocking Operation (Function code = 0101h, 0102h)
In this mode, the drive will return command completion status when the drive finished the SCT Write Same
operation.
Outputs for Error
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
93
Page 94

9.18.3.2 Error Recovery Control command (action code : 0003h)
Word
Name
Value
Description
0
Action Code
0003h
Set the read and write error recovery time
1
Function Code
0001h
Set New Value
0002h
Return Current Value
2
Selection Code
0001h
Read Timer
0002h
Write Timer
3
Value
Word
If the function code is 0001h, then this field contains the
recovery time limit in 100ms units. The minimum SCT
timeout value is 65 (=6.5 second). When the specified time
limit is shorter than 6.5 second,the issued command is
aborted.
255:4
reserved
0000h
Command Block Input Registers (Success)
Error
00h
Sector Count
If Function Code was 0002h, then this is the LSB of the requested recovery limit.
Otherwise, this field is reserved.
Sector Number
If Function Code was 0002h, then this is the MSB of the requested recovery limit.
Otherwise, this field is reserved.
Cylinder Low
reserved
Cylinder High
reserved
Device/Head
reserved
Status
50h
Inputs: (Key Sector)
Table 57 Error Recovery Control command (Inputs)
Outputs: (TF Data)
Table 58 Error Recovery Control command (Onputs)
The Error Recovery Control command can be used to set time limits for read and write error recovery. For
non-queued commands, these timers apply to command completion at the host interface. For queued
commands where in order data delivery is enabled, these timers begin counting when the device begins to
execute the command, not when the command is sent to the device. These timers do not apply to streaming
commands, or to queued commands when out-of-order data delivery is enabled.
These command timers are volatile. The default value is 0 (i.e. disable command time-out).
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
94
Page 95

9.18.3.3 Feature Control Command (action code : 0004h)
Word
Name
Value
Description
0
Action Code
0004h
Set or return the state of drive features described in 0
1
Function Code
0001h
Set state for a feature
0002h
Return the current state of a feature
0003h
Return feature option flags
2
Feature Code
Word
See 0 for a list of the feature codes
3
State
Word
Feature code dependent value
4
Option Flags
Word
Bit15:1 = Reserved
If the function code is 0001h, setting bit 0 to one causes the
requested feature state change to be preserved across
power cycles.
If the function code is 0001h, setting bit 0 to zero causes the
requested feature state change to be volatile. A hard reset
causes the drive to revert to default, or last non-volatile
setting.
255:5
reserved
0000h
Command Block Input Registers (Success)
Error
00h
Sector Count
If Function Code was 0002h, then this is the LSB of Feature State.
If Function Code was 0003h, then this is the LSB of Option Flags.
Otherwise, this field is reserved.
Sector Number
If Function Code was 0002h, then this is the MSB of Feature State.
If Function Code was 0003h, then this is the MSB of Option Flags.
Otherwise, this field is reserved.
Cylinder Low
reserved
Cylinder High
reserved
Device/Head
reserved
Status
50h
Inputs: (Key Sector)
Table 59 Feature Control command (Inputs)
Outputs: (TF Data)
Table 60 Feature Control command (Outputs)
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
95
Page 96

Feature Code
State Definition
0001h
0001h : Allow write cache operation to be determined by Set Feature command
0002h : Force write cache enabled
0003h : Force write cache disabled
If State 0001h is selected, the ATA Set Feature command will determine the operation
state of write cache. If State 0002h or 0003h is selected, write cache will be forced into
the corresponding operation state, regardless of the current ATA Set Feature state.
Any attempt to change the write cache setting through Set Feature shall be accepted,
but otherwise ignored, and not affect the operation state of write cache and complete
normally without reporting an error.
In all cases, bit 5 of word 85 in the Identify Device information will reflect the true
operation state of write cache, one indicating enabled and zero indicating disabled.
The default state is 0001h.
0002h
0001h : Enable Write Cache Reordering
0002h : Disable Write Cache Reordering
The default state is 0001h.
The drive does not return error for setting state 0002h, but the state is ignored.
0003h
Set time interval for temperature logging.
0000h is invalid.
0001h to FFFFh logging interval in minutes.
This value applies to the Absolute HDA Temperature History queue. Issuing this
command will cause the queue to be reset and any prior values in the queue will be
lost. Queue Index shall be set to zero and the first queue location will be set to the
current value. All remaining queue locations are set to 80h. The Sample Period, Max
Op Limit, Over Limit, Min Op Limit and Under Limit values are preserved.
Default value is 0001h.
0004h-CFFFh
Reserved
D000h-FFFFh
Vendor Specific
Table 61 Feature Code List
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
96
Page 97

9.18.3.4 SCT Data Table Command (action code : 0005h)
Word
Name
Value
Description
0
Action Code
0005h
Read a data table
1
Function Code
0001h
Read Table
2
Table ID
Word
See 0 for a list of data tables
255:2
reserved
0000h
Command Block Input Registers (Success)
Error
00h
Sector Count
reserved
Sector Number
reserved
Cylinder Low
Number of sectors to transfer (LSB) = 01h
Cylinder High
Number of sectors to transfer (MSB) = 00h
Device/Head
reserved
Status
50h
Table ID
Description
0000h
Invalid
0001h
Reserved
0002h
HDA Temperature History Table (in absolute degree C). See 0
0003h-CFFFh
Reserved
D000h-FFFFh
Vendor Specific
Inputs: (Key Sector)
Table 62 SCT Data Table command (Inputs)
Outputs: (TF Data)
Table 63 SCT Data Table command (Outputs)
Table 64 Table ID
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
97
Page 98

Byte
Size
Field Name
Description
1:0
Word
Format
Version
Data table format version (=0002h)
3:2
Word
Sampling
Period
Absolute HDA Temperature sampling period
in minutes.
0000h indicates sampling is disabled.
5:4
Word
Interval
Timer interval between entries in the history
queue.
6
Byte
Max Op Limit
Maximum recommended continuous
operating temperature. This is a one byte 2‟s
complement number that allows a range
from -127°C to +127°C to be specified. 80h
is an invalid value. This is a fixed value.
7
Byte
Over Limit
Maximum temperature limit. This is a one
byte 2‟s complement number that allows a
range from -127°C to +127°C to be
specified. 80h is an invalid value. This is a
fixed value.
8
Byte
Min Op Limit
Minimum recommended continuous
operating limit. This is a one byte 2‟s
complement number that allows a range
from -127°C to +127°C to be specified. 80h
is an invalid value. This is a fixed value.
9
Byte
Under Limit
Minimum temperature limit. This is a one
byte 2‟s complement number that allows a
range from -127°C to +127°C to be
specified. 80h is an invalid value. This is a
fixed value.
29:10
Byte[20]
Reserved
31:30
Word
Queue Size
Number of entry locations in history queue.
This value is 128.
33:32
Word
Queue Index
Last updated entry in queue. Queue Index is
zero-based, so Queue Index 0000h is the
first location in the buffer (at offset 34). The
most recent temperature entered in the
buffer is at Queue Index + 34.
See Note 1 and Note 2.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
98
Page 99

(Queue Size+33):34
Byte[Queue Size]
Queue Buffer
This is a circular buffer of absolute HDA
Temperature values. These are one byte 2‟s
complement numbers, which allow a range
from -127°C to +127°C to be specified. A
value of 80h indicates an initial value or a
discontinuity in temperature recording.
The Actual time between samples may vary
because commands may not be interrupted.
The sampling period is the minimum time
between samples. See Not 1.
If the host changes the logging interval using
the volatile option, the interval between
entries in the queue may change between
power cycles with no indication to the host.
511:(Queue Size
+34)
Byte[512-Queue
Size-34]
Reserved
Note 1 – The Absolute HDA Temperature History is preserved across power cycles with the requirement
that when the drive powers up, a new entry is made in the history queue of 80h, an invalid absolute
temperature value. This way an application viewing the history can see the discontinuity in temperature
result from the drive being turned off.
Note 2 – When the Absolute HDA Temperature history is cleared, for new drives or after changing the
Logging Interval, the Queue Index shall be set to zero and the first queue location shall be set to the current
Absolute HDA Temperature value. All remaining queue locations are set to 80h.
Table 65 Data Format of HDA Absolute Temperature History Table
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
99
Page 100

10 Command Protocol
The commands are grouped into different classes according to the protocols followed for command execution.
The command classes with their associated protocols are defined below.
Please refer to Serial ATA Revision 1.0a (Section 9. device command layer protocol) and Serial ATA II:
Extensions to Serial ATA 1.0a (Section 4. Command layer) about each protocol.
For all commands, the host must first check if BSY=1, and should proceed no further unless and until BSY=0.
For all commands, the host must also wait for RDY=1 before proceeding.
A device must maintain either BSY=1 or DRQ=1 at all times until the command is completed. The INTRQ signal
is used by the device to signal most, but not all, times when the BSY bit is changed from 1 to 0 during command
execution.
A command shall only be interrupted with a COMRESET or software reset. The result of writing to the Command
register while BSY=1 or DRQ=1 is unpredictable and may result in data corruption. A command should only be
interrupted by a reset at times when the host thinks there may be a problem, such as a device that is no longer
responding.
Interrupts are cleared when the host reads the Status Register, issues a reset, or writes to the Command
Register.
The device timeout values are described in the Section12 on the page 254.
10.1 PIO Data In commands
These commands are:
Device Configuration Identify
Identify Device
Read Buffer
Read Log Ext
Read Multiple
Read Multiple Ext
Read Sector(s)
Read Sector(s) Ext
Read Stream PIO
SMART Read Attribute Values
SMART Read Attribute Thresholds
SMART Read Log Sector
Execution includes the transfer of one or more 512 byte sectors of data from the device to the host.
Hitachi hard disk drive specifications
100
 Loading...
Loading...