Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
FOR
MODEL 902 AUTOMATIC
ANALYZER
Copyright Hitachi, Ltd. 1997. All rights reserved. Printed in Japan. Part No. 713-9039 KN-K (H-LT)
Page 2

MODEL 902 AUTOMATIC ANALYZER
CONTENTS
1. PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................. 1-1
2. TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................. 2-1
3. FLOW PATH DIAGRAMS ........................................................................................ 3-1
4. BLOCK DIAGRAMS................................................................................................. 4-1
5. ISE ........................................................................................................................... 5-1
6. SWITCH SETTING................................................................................................... 6-1
7. EXPLANATION OF FUNCTION............................................................................... 7-1
8. MOTORS, DETECTORS AND FUSES .................................................................... 8-1
9. ANALYTICAL METHODS......................................................................................... 9-1
10. CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS............................................................................................... 10-1
11. CROSS WIRING REFERENCE ............................................................................... 11-1
12. INSTALLATION........................................................................................................ 12-1
13. MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION ........................................................................ 13-1
14. ADJUSTMENT SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................... 14-1
15. OEM......................................................................................................................... 15-1
16. SYSTEM INTERFACE.............................................................................................. 16-1
- i -
Page 3

1.PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
1.1 Overall System.........................................................................................................1-1
1.2 Sampling System.....................................................................................................1-2
1.3 Reagent System.......................................................................................................1-3
1.4 Reaction System......................................................................................................1-4
1.5 Photometic System..................................................................................................1-5
1.6 ISE (option)..............................................................................................................1-5
1.7 Installation Conditions..............................................................................................1-6
1.8 User Interface...........................................................................................................1-6
1.9 Dionized Water........................................................................................................1-6
1.10 Analytical Methods...................................................................................................1-7
1.11 Accuracy Methods....................................................................................................1-7
1.12 Data Storage............................................................................................................1-7
1.13 System Interface......................................................................................................1-8
1.14Options for Analyzer.................................................................................................1-8
1 - 0
Page 4

1.PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
1.1 Overall System
Configuration : Console type automatic analyzer, with analytical and operation units
integrated
Principle : Discrete type, random access, single-line multi-analysis system;
entire reaction monitoring system
Analytical methods : Colorimetry (absorbance measurement), ion selective electrode
method (ISE; option)
Throughput : Colorimetry ; 200 tests/hr (Photometry only max. 300 tests/hr
inclusive of ISE)
No. of analysis items: Colorimetry ; 36
ISE ; 3 (Na, K, Cl)
Serum indexes ; 3
Calculation items; 8
Reaction time : 10 minutes max.; 3, 4, 5, 10 minutes for concentration calculation
(same as Model 7070/7170)
Measurable samples : Serum (or blood plasma) and urine; one sample kind per channel
Application : Emergency (stat) and routine analyses
Test item selection : Via entry from operation panel, entry from system interface, entry
from no. of items settable (11 kinds)
1 - 1
Page 5

1.2 Sampling System
Sample container : Hitachi standard sample cup
Sample tube ;diameter 13 to 17 mm
length 75 to 100 mm
Sample disk : 60 positions
Outer row;35 positions (routine and stat samples)
(with free adapter, barcode reader attachable)
Inner row;25 positions (standard + control samples (22),
rinse solutions (3))
Detergents : 3 kinds
(W1;for sample probe rinsing) HITERGENT
(W2;for sample carryover evasion) ISE RINSE SOLUTION
(W3;for sample carryover evasion) HICARRYNON
Sampling mechanism : Pipetter driven by stepping motor
2 to 50 µL of sample/test (in 0.1 µL steps)
Pipetting mode : Normal ; prescribed volume discharged at cell
bottom
Aqueous sample; system water solution for sample probe
internal rinsing usable as STD-1
Sample pre-dilution not performed
Insufficient sample detection: Resistance detection method
Sample ID : Barcode reader (option)
Following code shemes are usable in combination; CODE 39,
CODE 128, INTERLEAVED 2 OF 5, NW7 (Modulas 10,
Modulas 16)
Automatic rerun : Auto rerun function not provided
Stat sample analysis : Routine sample analysis interruptible for stat sample analysis
Sample carryover : Sample carryover evasion function available; 2 kinds of
detergents settable on sample disk inner row
Sample conveyance : Can be sampled directly from belt-line
1 - 2
Page 6

1.3 Reagent System
Reagent disk : One disk, 40 positions
(20 positions each on inner and outer rows)
Reagent cooling : Cooling water circulating system (3 to 15°C) (option for China-
destined instrument)
Reagent bottle : 50 mL, 20 mL (adapter necessary)
(without barcode, concentrated reagent unusable)
Detergents : HITERGENT (50 mL); position 40 (fixed)
(for addition to reaction bath)
Detergent 1; for reagent probe, stirring rod rinsing, reagent
probe carryover evasion, reaction cell carryover
evasion
Detergent 2; for reagent probe carryover evasion, reaction cell
carryover evasion
(settable on reagent disk inner row)
ISE reagent : Internal standard solution(position 37 (fixed))
Diluent (position 38 (fixed))
Pipetting mechanism : Pipetter driven by stepping motor; 20 to 350 µL/test (in 1 µL
steps)
Reagent addition timing: 3 steps (0, 1.5 and 5 minutes); throughput is maintained even
when adding 3 reagents.
Carryover evasion : Rinsing for carryover evasion possible; throughput may decrease
by specifying carryover evasion.
1 - 3
Page 7

1.4 Reaction System
Reaction disk : Turntable type disk (10-minute reaction per rotation)
Reaction cell : Optical path length 6 mm (area 6 × 5 mm)
No. of reaction cells : 48
Reaction cell control : One rotation + one pitch feed (18 seconds)
Sample pipetting position: One position (fixed)
Reagent pipetting position: One position (fixed)
Reaction temperature : 37 ± 0.1°C (warm water circulating system)
Stirring : By means of stirring rod rotation
Timing for stirring; after each addition of R1,R2,R3
Stirring possible for a minimum volume of 100 µL
Stirring position : One position (fixed)
Reacting solution volume: Minimum; 250 µL (minimum required volume for photometry)
Maximum; 500 µL (temperature control, rinsing upper limit)
Photometric position : One position (fixed)
Cell rinsing : After completion of photometry (rinsing 3 times; rinsing with
detergent not performed)
Carryover evasion : Rinsing for carryover evasion possible; throughput may decrease
by specifying cell carryover evasion
1 -4
Page 8

1.5 Photometric System
Photometer : Multiwavelength photometer (absorptiometry)
Wavelengths : 12 wavelengths
(340, 376, 415, 450, 480, 505, 546, 570, 600, 660, 700, 800 nm)
Monochromator : Grating
Detector : Photodiode
Linearity : Up to 2.5 Abs (10 mm cell conversion)
Photometric method: Direct photometry of reaction cell (at one or two wavelengths)
Correction : Cell blank correction prior to analysis
(passed cell blank measurement alone)
1.6 ISE (option)
Electrodes : Flow cell type, liquid-membrane ISE cartridge
Reference electrode flow path: 1 MKCL, liquid flow path
Measuring temperature : 36°C ± 2°C (warm water circulating system)
System : Indirect (dilution) potentiometry, 50-times dilution
Measuring cycle : 36 sec/sample (18 sec for sample, 18 sec for internal
standard solution)
Measured items : Na, K, Cl
Measurable samples : Serum and urine
Linearity : Na;10 to 250 mmol/L
K ;1 to 100 mmol/L
Cl;10 to 250 mmol/L
Reagent bottle : Internal standard solution ; 50 mL max.
Diluent ; 50 mL max.
Reference electrode solution; 500 mL max.
1 - 5
Page 9

1.7 Installation Conditions
Power requirement : 230 V, 50/60 Hz, less than 1.5 kVA
Deionized water consumption: Less than 15 L/hr
Waste liquid drain : 2 systems (for concentrated and diluted liquids)
Ambient temperature/humidity: Temperature; 18 to 30°C
Humidity ; 20 to 80% (non-condensing)
Analyzer dimensions : 720 W × 720 D × 1085 H mm
Analyzer weight : Within 200 kg
BTU : 1300 kcal/hr max.
Noise (mean) in operation : < 55 dB
1.8 User Interface
Application : Routine analysis for Asia version
Display : Backlighted LCD; 256 × 128 dots, graphic
Keyboard : Touch screen keys (72 keys)
Printer : Thermal roll-paper printer (20 digits)
Multi-language
compatibility : Display; Japanese/English/Chinese/German/Spanish applicable
Printer; English alone
1.9 Deionised Water
Pressure : 0.5 to 3.5 kgf/cm
2
Conductivity: 1 µs/cm or less, germ-free
1 - 6
Page 10

1.10Analytical Methods
Assay modes : One-point
One-point end (+ prozone check)
Two-point rate
Two-point end (+ prozone check)
Three-point two-item
One-point rate two-item
Rate A (+ sample blank correction)
Rate A (+ serum indexes)
Rate B two-item (same wavelength)
Rate B two-item (different wavelengths)
ISE
Data alarms : Based on Model 7070/7170
Standard solution : 22 kinds max. (positions to be shared with control sera)
Calibration types : Linear (2-point linear)
K factor
4 parameter LOGIT-LOG
5 parameter LOGIT-LOG
Spline
Segmented line
Calibration method : At startup only; all points (FULL) and reagent-blank-corrected
calibration
Calculation channels : For 8 channels
Test-to-test compensation : For 8 channels
1.11Accuracy Control
Control serum : 5 kinds max. (positions shared with standard solutions)
1.12Data Storage
Routine sample data : 400 samples (in data disk)
Stat sample data : 50 samples (in data disk)
Control sample data : 5 kinds × 30 (in SRAM)
1 - 7
Page 11

1.13System Interface
Interface : RS-232C and current loop
Communication protocol: Based on Model 7070/7170
Communication details : Communication with host; communication details based on Model
7070/7170
1.14Options for Analyzer
ISE
Sample ID accessory : Model ; BL180
Maker ; Keyence
Barcode spec.; CODE 39, ITF, NW7 (Modulas 10, Modulas 16),
CODE 128
1 - 8
Page 12

2. TROUBLESHOOTING
2.1 Alarm Code Table ....................................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 LCD Display Alarm .....................................................................................2-24
2.2 Motor Control Alarms................................................................................................2-26
2.2.1 Operation Check Procedure at Occurrence of Alarm .................................2-27
2.3 Parameter Check .....................................................................................................2-29
2.3.1 Processing Flow .........................................................................................2-29
2.3.2 Details of Parameter Check........................................................................2-30
2.3.3 Details of Twin Test Simultaneous Analysis ...............................................2-34
2.4 Data Alarm...............................................................................................................2-35
2.4.1 Data Alarm Registratin Flow.......................................................................2-35
2.4.2 Data Alarm Code List..................................................................................2-36
2.4.3 Data Alarm Codes ......................................................................................2-37
2.4.4 ISE Data Alarms.........................................................................................2-49
2.4.5 Alarm Check Method..................................................................................2-52
2.4.6 Check and Set Alarm of Each Data............................................................2-60
2.4.7 Details of Data and Alarm Outputs Resulting from Calibration...................2-61
2.4.8 Output Check List for Each Photometry Assay CALIB. METHOD .............2-62
2.5 Retry Code Table.....................................................................................................2-64
2.5.1 Logging Program List......................................................................................2-65
2.6 Daily Alarm Trace.....................................................................................................2-67
2.6.1 Cumulative Alarm Trace.............................................................................2-69
2.6.2 Parameter Code List...................................................................................2-72
2.6.3 Communication Trace.................................................................................2-74
2.6.4 Cumulative Instrument Operation List.........................................................2-78
2.6.5 FD File Management..................................................................................2-79
2 - 0
Page 13
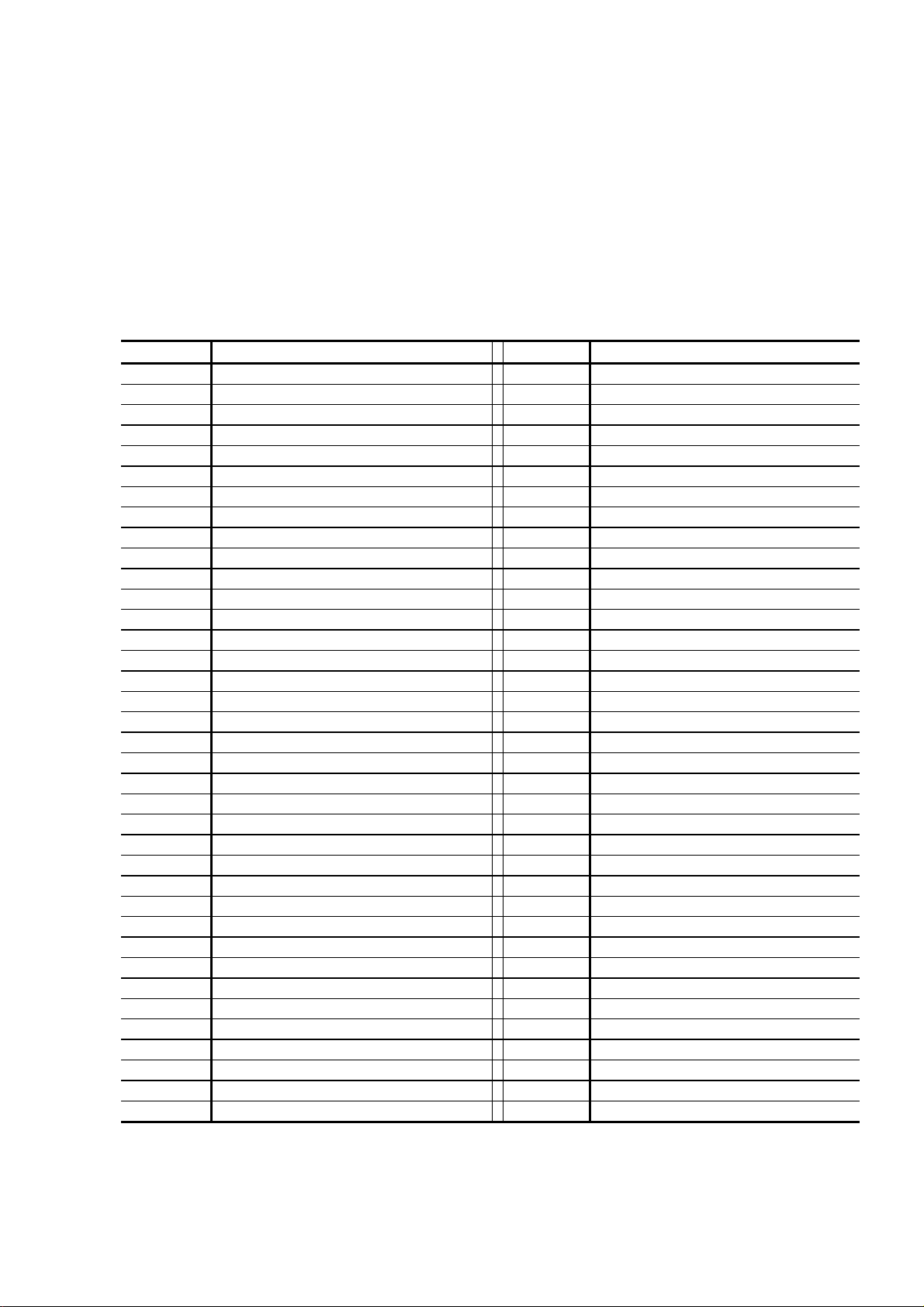
2. TROUBLESHOOTING
2.1 Alarm Code Table
Category Alarm Name Category Alarm Name
1 STIRRER 38 VAC. TANK
2 39
3 RINSE 40
4 41 LAMP
5 R.DISK 42
6 S.PROBE 43
7 44
8 S.DISK 45 CELL BNK1
9 46 CELL BNK2
10 47 ADC1 ?
11 S. SHORT 48 ADC2 ?
12 49 ADC3 ?
13 50 BARCODE 1
14 51
15 S. SYRINGE 52
16 REAG. PROBE 53
17 54 BARCODE 2
18 REAG. DISK 55
19 56
20 57 REAG. SHORT
21 58
22 R. SYRINGE 59 REAG. LEVEL
23 60
24 ISE SIPPER 61
25 62
26 ISE SYRING. 63
27 ISE STOP ? 64
28 TEMP CONT. 65
29 INC. WATER 66
30 REF. WATER 67 TS OVER
31 DIST. WATER 68 PATNT OVER
32 DIST. SENS. 69 SAMP. END
33 70
34 RESERVOIR 71 DC POWER
35 72 FUSE
36 73 POWER FAIL
37 SIPPER 74
2 - 1
(cont’d)
Page 14

Category Alarm Name Category Alarm Name
75 MOTOR CONT. 114 ACI ERROR
76 MOTOR TOUT 115
77 116
78 117
79 118
80 119 FD WRITE ?
81 120 FD READ ?
82 121 NO FD
83 STANDARD ? 122
84 CALIB. 123 FD PROTECT
85 CALIB. SD ? 124
86 SENS. ? 125 PRINTER
87 126 SYSTEM I/F
88 127
89 128
90 ISE LEVEL 129
91 ISE NOISE 130 WATER EXG.
92 ISE PREP. 131
93 ISE SLOPE 132
94 ISE I. STD 133
95 REF. SHORT 134
96 TWIN TEST ? 135
97 136
98 CHEM. PARAM ? 137
99 CLB. PARAM ? 138
100 VOLUME ? 139
101 140 PANEL I/F
102 141 REAGNT ?
103 CMP. TEST ? 142
104 S. INDEXES ? 143
105 144
106 ON BOARD ? 145 CELL C. O.
107 REAG. POS ? 146 ISE C. O.
108 CLB (IS) POS 147
109 148
110 149
111 150
112 151
113 152
2 - 2
Page 15
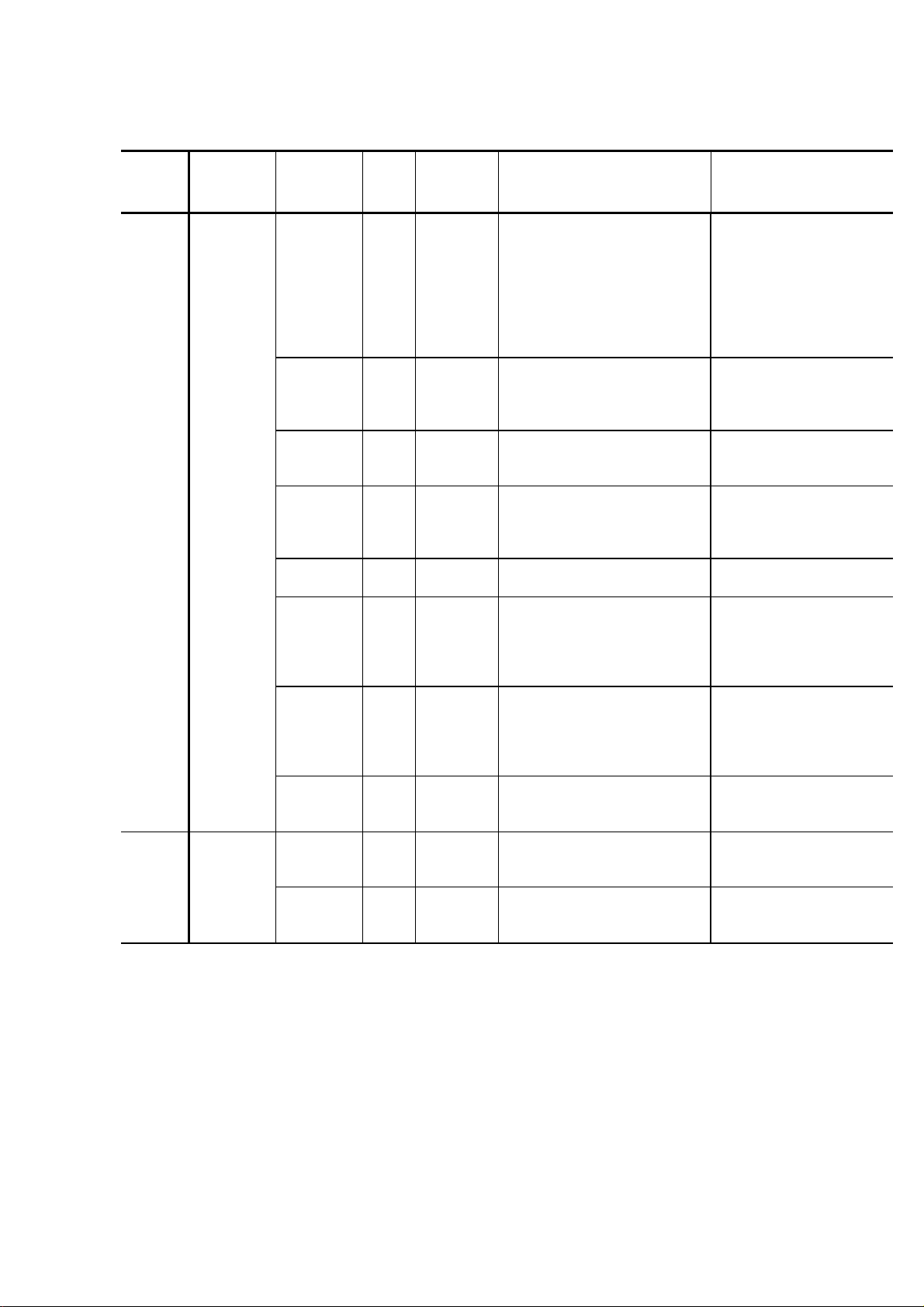
Alarm
Control
No.
1 to 8 STIRRER 1 1 STOP In ascending action of the
21,22 RINSE 3 1 STOP The rinsing mechanism does
Alarm Category
1 2 STOP In ascending action of the
1 3 STOP In descending action of the
1 4 STOP When the stirrer moves
1 5 STOP The stirrer does not come to
1 6 STOP At resetting, the stirrer does
1 7 STOP At resetting, the stirrer does
1 8 STOP In rotation of the stirrer, it is
3 2 STOP The rinsing mechanism does
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
stirrer, it does not reach the
upper dead point (on the
rinsing bath side).
(Alarm at the first upper
dead point after resetting will
be issued from other than
the cell side.)
stirrer, it does not reach the
upper dead point (on the cell
side).
stirrer, it does not leave the
upper dead point.
toward the rinsing bath, it
does not reach the rinsing
bath position.
the cell position.
not reach the rinsing bath
position (home position) in
its return movement to the
home position.
not leave the rinsing bath
position (home position) in
its departing movement
from the home position.
not set at the upper dead
point.
not reach the upper dead
point in ascending motion.
not leave the upper dead
point in descending motion.
Check the upper dead
point detector.
Same as above
Same as above
Check the home
detector.
Check the detector on
the cell side.
Check the home
detector.
Same as above
Check the upper dead
point detector.
Check the upper dead
point detector.
Same as above
2 - 3
Page 16

Alarm
Control
No.
Alarm Category
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
61 to 65 R. DISK 5 1 STOP The reaction disk cannot
recognize its stop position.
5 2 STOP The reaction disk does not
stop at the specified
position.
5 3 STOP At resetting, the reaction
disk cannot recognize its
home position.
5 4 STOP At resetting, the first cell
on reaction disk does not
stop at the specified
position.
5 5 STOP When the reaction disk
turns, the serum probe,
reagent probe, stirrer or
rinsing mechanism is not
set at the upper dead point
(on the cell side).
(When this alarm is
issued, another alarm (on
rinsing or stirring
mechanism) may concur.)
71 SAMPLE
PROBE
6 1 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 1)
The serum probe does not
reach the upper dead point
in ascending motion (on
other than the cell side).
(Alarm at the first upper
dead point after resetting
will be issued from other
than the cell side.)
72 to 85 SAMPLE
PROBE
6 2 STOP The serum probe does not
reach the upper dead point
in ascending motion (on
the cell side).
6 3 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 1)
The serum probe moves
down abnormally in
descending action (on
other than the cell side).
(±3 mm from cup bottom,
0 to 4 mm from cell
bottom)
6 4 STOP The serum probe moves
down abnormally in
descending action (on the
cell side).
6 5 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 1)
The serum probe does not
go down from the upper
dead point in descending
motion.
NOTE: 1. S.STOP may be issued only during operation.
(cont’d)
Check the detectors for
stop positions on the
inner and outer tracks.
Same as above
Check the home
detector.
Check the home
detector or inner/outer
track detector.
(1) Perform resetting.
(2) Check the upper
dead point detector
of the mechanism
which caused
alarm.
Check the upper dead
point detector.
Same as above
(1) Check the liquid
level detector.
(2) Replace the liquid
level detector PC
board.
Same as above
Check the upper dead
point detector.
2 - 4
Page 17

Alarm
Control
Alarm Category
No.
72 to 85 SAMPLE
6 6 STOP The serum probe does not
Sub-
code
Level Description Remedy
PROBE
6 7 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 1)
6 8 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 1)
6 9 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 2)
6 11 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 1)
6 12 WARNINGThe serum probe moves
6 13 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 2)
6 14 STOP In rotation of the serum
6 15 STOP In rotation of the serum
101 to
106
SAMPLE
DISK
8 1 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 2)
8 2 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 2)
8 3 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 2)
8 4 S.STOP/
STOP
(Note 2)
NOTE: 2. S.STOP may be issued only during operation.
go down from the upper
dead point in descending
motion (on the cell side).
Detection of abnormal
descending motion of the
serum probe remains on.
When serum probe turns to
the cell side, the cell position
cannot be detected.
When the serum probe turns
from the cell side to other
position, it does not come off
the cell position.
Before the probe goes down,
the liquid level detector is
already turned on.
down abnormally in
descending action (only at
turning of the serum probe in
adjustment).
In rotation of the serum
probe, it is not set at the
upper dead point.
probe from the reset
position, it does not come off
the reset position.
probe to the reset position, it
cannot detect the reset
position.
The sample disk cannot
detect the stop position on
outer track.
The sample disk does not
stop at the specified position
on outer track.
The sample disk cannot
detect the stop position on
inner track.
The sample disk does not
stop at the specified position
on inner track.
(cont’d)
Check the upper dead
point detector.
Refer to alarm code
6-3.
Check the home
detector.
Same as above
Refer to alarm code
6-3.
Same as above
Check the upper dead
point detector.
Check the home
detector.
Same as above
Check the outer track
detector.
Same as above
Check the inner track
detector.
Same as above
2 - 5
Page 18

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
Alarm Category
No.
101 to
106
SAMPLE
DISK
107 SAMPLE
DISK
251 to
310
551 to
552
561 to
568
SAMPLE
SHORT
SAMPLE
SYRINGE
REAGENT
PROBE
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
8 5 STOP At resetting, the sample disk
cannot detect the home
position.
8 6 STOP At resetting, the sample disk
does not stop at the specified
point of home position.
8 7 STOP At resetting, the sample disk
does not leave the home
position.
11 1 to 60WARNING In sipping from the sample
cup, sample on the sample
disk is inadequate.
Sub-code groups
Routine/
stat samples:1 to 35
Control STD:36 to 57
W1 to W3 :58 to 60
15 1 S.STOP/
STOP
15 2 S.STOP/
STOP
The serum syringe does not
reach the upper dead point.
The serum syringe does not
go down from the upper dead
point.
16 1 STOP The reagent probe does not
reach the upper dead point in
ascending motion.
16 2 STOP The reagent probe moves
down abnormally in
descending motion.
16 3 STOP The reagent probe does not
go down from the upper dead
point in descending motion.
16 4 WARNINGDetection of abnormal
descending motion of the
reagent probe remains on.
Check the home
detector.
Same as above
Check the home
detector.
Add sample.
Check the upper
dead point detector.
Same as above
Check the upper
dead point detector.
Check liquid level
detection.
Check the upper
dead point detector.
Check the
descending error
detector.
2 - 6
Page 19

Alarm
Control
No.
561 to
568
Alarm Category
REAGENT
PROBE
16 5 STOP When the reagent probe
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
turns toward the cell, it
cannot detect the cell
position.
16 6 STOP When the reagent probe
turns from the cell side to
other position, it does not
leave the cell position.
16 7 STOP Before the probe goes down,
the liquid level detector is
already turned on.
16 8 STOP In rotation of the reagent
probe, it is not set at the
upper dead point.
581 to
593
REAGENT
DISK
18 1 STOP The stop position of reagent
disk cannot be detected.
18 2 STOP The reagent disk does not
stop at the specified position.
18 3 STOP The home position of reagent
disk cannot be detected.
621 to
622
REAGENT
SYRINGE
22 1 STOP The reagent syringe does not
reach the upper dead point.
22 2 STOP The reagent syringe does not
move down from the upper
dead point.
641 ISE
SIPPER
24 1 STOP The sipper nozzle does not
reach the upper dead point
(during resetting/
operation).
642 ISE
SIPPER
661 to
662
ISE
SYRNG
671 ISE STOP
OK ?
24 2 WARNING/
STOP
(Note 4)
26 1 WARNING/
STOP
(Note 4)
26 2 WARNING/
STOP
(Note 4)
27 1 WARNING/
STOP
(Note 4)
The sipper nozzle does not
leave the upper dead point.
The sipper syringe does not
reach the upper dead point.
The sipper syringe does not
leave the upper dead point.
The ISE function is stopped
due to alarm.
(This warning is indicated
when restart in the sampling
stop status was attempted.)
NOTES: 3. S.STOP may be issued only during operation.
4. Though the photometry assay function works, the ISE function does not work.
(cont’d)
Check the home
detector.
Same as above
Check liquid level
detection.
Check the upper
dead point detector.
Check home
detection or count
detector.
Same as above
Check home
detection.
Check the upper
dead point detector.
Same as above
Check the upper
dead point detector of
ISE sipper.
Same as above
Check the upper
dead point detector of
ISE Syringe.
Check alarm log and
deal with the alarm.
2 - 7
Page 20

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
Alarm Category
No.
681 TEMP
CONTROL
28 1 WARNING The water temperature of
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
incubation bath is higher
than 45.0°C.
28 2 WARNING The water temperature of
incubation bath is outside a
range of 37 ± 0.5°C.
(This is checked only at
operation.)
691 INCUBA-
TOR
29 1 WARNING The water level of
incubation bath is too low.
WATER
701 REF
WATER
30 1 WARNING A period of 24 hours has
passed since exchange of
incubation bath water.
711 DISTILLED
WATER
31 1 STOP The water level of distilled
water tank is too low.
(This alarm will not be
issued during initialization
and water exchange.)
712 DIST
WATER
721 DIST
WATER
SENSOR
724 RESER-
VOIR
31 2 WARNING The water level of distilled
water tank is too low.
32 1 WARNING The water level sensor in
distilled water tank is
abnormal.
34 1 WARNING The waste solution reservoir
is full.
771 SIPPER 37 1 STOP The negative pressure of
vacuum pump is too low.
781 VACUUM
TANK
811 to
813
PHOTOMETER LAMP
38 1 WARNING Water is accumulated in the
vacuum tank.
41 1 WARNING In passed cell blank
measurement, a value of
more than 3.3 Abs is
indicated in any one of 4
measurements.
(3 times or less)
41 2 S.STOP
(Restart
unallowable
41 3 S.STOP
(Restart
un-
In passed cell blank
measurement, a value of
more than 3.3 Abs is
indicated for all of ADC1,
)
ADC2 and λ
to λ12.
1
The above alarm code 41-1
is issued 10 times
consecutively.
allowable)
Check the thermistor
or thermostat of
heater.
Same as above
Replenish water or
check the drain
solenoid valve.
Exchange incubation
bath water.
Check the water level
sensor.
Same as above
Check float switch.
Check waste solution
tank detection.
Check vacuum level
at vacuum suction.
Check SV12 or SV14.
(1)Replace light
source lamp.
(2)Check 12 V
power supply.
2 - 8
Page 21

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
Alarm Category
No.
1231 CELL
BLANK
1241 to
1400
1441 to
PASS CELL
BLANK
ADC1? 47 1 WARNING Any one of I/O error,
1444
Subcode
45 1 S.STOP
Level Description Remedy
In passed cell blank
(Restart
unallowable)
measurement, any one of
ADC1, ADC2, λx and λy
differs from the reference
value (Note 5) by more than
0.1 Abs through 10
consecutive cycles.
(Counting is not made in
use for stopped cell blank
test.)
46 1 to 48WARNING In 4 passed cell blank
measurements, any one of
ADC1, ADC2, λx and λy
differs from the reference
value (Note 5) by more than
0.1 Abs twice or more.
(In case any one of those
values differs only once, the
average value of normal
data is treated as a value of
passed cell blank.)
boundary error of parameter
block pointer, I/O device
busy, channel error and I/O
device error (PC board not
mounted, device
inoperable, time-out) has
occurred.
47 2 WARNING •A/D count value remains
at 0.
•After A/D conversion,
interruption is impossible.
•The command or
parameter given to A/D
PC board is abnormal.
•A/D conversion cannot be
completed.
(Time-out occurs.)
(Reference voltage is
checked.)
47 3 WARNING The number of A/D starts
cannot be reset to 0.
(This is checked at reaction
measurement.)
(1)Carry out cell
washing.
(2)Replace the cell.
Same as above
Replace ECPU230 or
EMIO100 PC board.
(1)Replace Log Amp
PC board.
(2)Check 2 V and
6 V reference
voltages.
Same as above
2 - 9
Page 22

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
No.
1441 to
1444
1451 to
1453
1461 to
1462
1471 to
4506
Alarm Category
ADC1? 47 4 WARNING •A/D count for 2 V is
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
Same as above
abnormal.
•A/D count for 6 V is
abnormal.
Normal count for 2 V
(7547 < count value <
8341)
Normal count for 6 V
(22460 < count value <
25023)
(This is checked at
measurement of
reference voltage.)
ADC2? 48 1 WARNING Refer to alarm code 47-1. Replace ISE AMP PC
board.
48 2 WARNING Refer to alarm code 47-2. Same as above
48 3 WARNING Refer to alarm code 47-4.
Reference voltage for
ISE: 2 V and 8 V
Normal count for 2 V
(7547 < count value <
8341)
Normal count for 8 V
(30184 < count value <
33364)
Normal offset value
(22811 < count value <
40547)
ADC3? 49 1 WARNING Refer to alarm code 47-2. Replace EMIO100
49 2 WARNING •A/D count for 2 V is
abnormal.
Same as above
PC board.
Same as above
•A/D count for 6 V is
abnormal.
Normal count for 2 V
(12452 < count value <
13763)
Normal count for 6 V
(37356 < count value <
41288)
BARCODE1 50 1 to 35WARNING Data reception from the
barcode reader has not
been completed before ID
reception time-out.
(Sub-code indicates the
position No. on disk.)
Replace the label or
barcode reader.
2 - 10
Page 23

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
Alarm Category
No.
1801 to
BARCODE2 54 1 to 5WARNING An error has occurred in
1805
1931 to
1971
2231 to
2271
2781 to
2830
2851,
REAGENT
SHORT
REAGENT
LEVEL
UNASSIGNED
TS OVER 67 1 WARNING Because 400 samples are
2852
2861 PATIENT
SAMPLE
OVER
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
communication with the
barcode reader. (Parity
error, framing error or
overrun error)
Sub-code indication
1:Unassigned
2:Unassigned
3:Sample disk barcode
reader
4:Unassigned
5:Unassigned
57 1 to 40WARNING •The volume of reagent to
be sipped from a reagent
bottle is inadequate.
•The reagent volume is a
total amount of one kind
of reagent for each test
item.
(1)Sub-code indicates
position No.
(2)Positions 37 and 38
are used for ISE.
(3)Position 40 is used for
HITERGENT.
(4)Position 39 is used for
HIALKALI.
59 1 to 40WARNING Reagent volume is smaller
than the remaining reagent
check value specified with
system parameter.
registered in routine sample
test selecting information,
new test selecting
information cannot be
registered from the host.
68 1 WARNING Because 400 samples are
registered in routine sample
test selecting information, a
new routine sample cannot
be analyzed.
Check the
communication cable
of barcode reader.
Set new reagent.
Set reagent newly.
After completion of
analysis, register TS
again.
Same as above
2 - 11
Page 24

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
No.
2891 to
2894
Alarm Category
DC POWER 71 1 STOP 15 V DC power supply is
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
Replace the ±15 V
abnormal.
power supply
module.
71 2 STOP -15 V DC power supply is
Same as above
abnormal.
71 3 WARNING 12 V lamp power supply is
abnormal.
71 4 STOP 5 V power supply is abnormal.
71 11 E.STOP 24 V DC
Replace the 12 V
power supply.
5 V for other than
CPU board
2911 FUSE 72 1 E.STOP AC fuse has blown. Replace the F3
fuse.
2921 POWER
FAIL
2941 to
2973
MOTOR
CONTROL-
73 1 WARNING Power supply to the
instrument is interrupted
75 1 to 18 STOP Data cannot be written into
the motor controller.
Check power
supply.
Replace ECPU230.
LER
2991 to
3023
MOTOR
TIMEOUT
76 1 to 18 E.STOP Motor operation was
abnormal. Error has been
detected in the time-out check
of motor controller.
(1) Replace
ECPU230.
(2) Check the
mechanism
which caused
Sub-code Motor
alarm.
1 Reaction disk
2 Sample disk
3 Reagent disk
4 Rinsing mechanism
up/down
5 Sample arm
up/down
6 Sample arm
rotation
7 Reagent arm
up/down
8 Reagent arm
rotation
9 Stirrer up/down
10 Stirrer rotation
11 ISE sipper up/down
12 (Unassigned)
13 Serum syringe
14 Reagent syringe
15 ISE syringe
16 (Unassigned)
17 GMCNT
18 (Unassigned)
2 - 12
Page 25

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
No.
3101 to
3189
3251 to
3291
3401 to
3438
Alarm Category
Subcode
STANDARD? 83 1 to 40
(ch.)
CALIBRATION
84 1 to 40
(ch.)
CALIB.SD? 85 1 to 36
(ch.)
Level Description Remedy
WARNING <<Photometry assay>>
(1) In calibration, the
STD absorbance data
is indicated with
alarm.
(2) In calibration, data
calculation is
disabled.
(Photometry assay)
•Replace STD
sample.
•Check the
concentration
parameter.
(ISE assay)
Same as above
<<ISE assay>>
(1) In calibration, the
potential data of
standard or internal
standard solution is
indicated with ADC
error, insufficient
sample alarm, noise
alarm or level alarm.
(2) In calibration, data
calculation is
disabled.
(The result of calibration
is not updated nor saved
onto FD.)
WARNING <<Photometry assay>>
The factor value 'K'
determined in calibration
(Photometry assay)
(ISE assay)
Same as above
differs from the previous
value by more than ±20%.
<<ISE assay>>
The calibrator
concentration value and
slope value determined in
calibration differ from the
previous values by more
than the compensation
limit (%).
WARNING The mean error determined
in multi-point calibration is
Replace STD and
check again.
larger than the SD limit
(input value).
2 - 13
Page 26

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
No.
3551 to
3588
Alarm Category
SENSITIVITY?
Subcode
86 1 to 36
(ch.)
Level Description Remedy
WARNING In linear (with 2 to 6 points) or
nonlinear calibration, a
difference between the mean
STD (1) absorbance and the
mean STD (N)
(Note 7 )
The result of
calibration is not
updated nor saved
onto FD.
absorbance is smaller than
the sensitivity limit (input
value).
NOTES :
7.N:=2 for linear
(2points)
=2 to 6 for nonlinear
and linear (3 to 6
points)
(Span point input value)
8.If either STD (1) or STD
(N) alone has been
measured, the
absorbance value of the
other STD is checked
using the previous data.
4151 to
4153
4161 to
4163
ISE LEVEL 90 1 WARNING The mean potential value
(EAV) at three out of five
measurement points of
internal standard solution is
outside the following range.
(Internal standard)
Na:-90.0mV ≤ EAV ≤-10mV
⇒OK
90 2 WARNING K:-90.0mV ≤ EAV ≤ -10mV
⇒OK
90 3 WARNING Cl:100.0mV ≤ EAV ≤
180.0mV
⇒OK
ISE NOISE 91 1 WARNING A difference (FIV) between
maximum and minimum
potential values at three of
five measurement points of
internal standard solution is
outside the following range.
(Internal standard, sample)
Na:0.7mV < FIV(2) - FIV(4)
91 2 WARNING K :1.0mV < FIV(2) - FIV(4) Same as above
(1)Replace STD
and carry out
calibration.
(2)Replace the Na
electrode.
(1)Same as above
(2)Replace the K
electrode.
(1)Same as above
(2)Replace the Cl
electrode.
Carry out reagent
priming and check
for bubble
formation.
91 3 WARNING Cl:0.8mV < FIV(2) - FIV(4) Same as above
2 - 14
Page 27

Alarm
Control
No.
4171 to
4173
Alarm Category
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
ISE PREP. 92 1 WARNING Upon calibration, the slope
value is within the following
range.
Na : 45.0mV ≤ Slope value
≤ 49.9mV or
68.1mV ≤ Slope value
92 2 WARNING K : 45.0mV ≤ Slope value
≤ 49.9mV or
68.1mV ≤ Slope value
92 3 WARNING Cl : -39.9mV ≤ Slope value
≤ -35.0mV or
-68.1mV ≥ Slope value
(cont’d)
•Make sure that the
standard solution
and reagent are set
properly.
•Make sure that the
standard solution is
free from
concentration or
deterioration.
•Make sure that the
electrodes (Na, K,
Cl) are within their
guaranteed life.
4181 to
4183
4191 to
4193
ISE SLOPE 93 1 WARNING (1) In the result of
calibration, the slope
value is within the
following range.
(2) The response
characteristic of
electrode is poor (in case
carry-over rate (A) is as
indicated below).
Na : (1)SLOPE < 45.0mV
(2)0.232 < A
93 2 WARNING K : (1)SLOPE < 45.0mV
(2)0.160 < A
93 3 WARNING Cl : (1)SLOPE < -35.0mV
(2)0.490 < A
ISE I.STD 94 1 WARNING The concentration of internal
standard solution (C(IS)) is
within the following range.
Na : C(IS) < 120.0mEq/L or
160.0mEq/L < C(IS)
94 2 WARNING K : C(IS) < 3.0mEq/L or
7.0mEq/L < C(IS)
94 3 WARNING Cl : C(IS) < 80.0mEq/L or
120.0mEq/L < C(IS)
Refer to alarm
codes 92-1 to 3.
Same as above
Same as above
(1) Replace STD
and carry out
calibration
again.
(2) Replace t he
internal
standard
solution.
Same as above
Same as above
2 - 15
Page 28

Alarm
Control
Alarm Category
No.
4201 to
4203
ISE
REAGENT
SHORT
4211 TWLN
TEST?
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
95 1 Unassigned
(Liquid level detection for
IS/DIL solution)
95 2 Unassigned (Same as
above)
95 3 WARNING The volume of reference
electrode solution is 30 mL
or less.
96 1 to 36
(ch.)
WARNING (1) when analyzing two
tests at a time, the
assigned method for
the corresponding test
is inadequate.
(2) Assignment of the
corresponding test is
being done or not
being done when
analysis for two tests is
not being made at the
same time.
(3) When analyzing two
tests at the same time,
the analytical
parameters are not
identical.
Sub-codes (1 to 36)
signify the channel
numbers.
(cont’d)
Replace the
reference electrode
solution with new
one.
Check the ISE
reagent volume.
•Start setting in
order from the
tests that are
designated by the
Measured Point of
the first half of the
1 channel 2 Test
Analysis Method (3
Point, 1 Point and
Rate, Rate B)
•When not
analyzing two tests
at the same time,
do not designate
'Two Test Analysis'
for the Analysis
Parameter.
•With the Analysis
Parameter screen
for the applicable
test, unify all the
parameters below
for the
Simultaneous 2
Test Analysis Test.
• Analytical Method
• Reaction Time
• Sample Volume
• Reagent
Pipetting volume
(R1-R3)
• Calibration
Method
• Calibration Point
• Standard solution
volume
• Standard solution
position
2 - 16
Page 29

Alarm
Control
No.
4511 to
4548
4661 to
4698
Alarm Category
CHEMISTRY
PARAMETER?
CALIBRATION
PARAMETER CALIB.
Sub-
code
98 1 to 36
(ch.)
99 1 to 36
(ch.)
Level Description Remedy
WARNING(1)The relationship
between assay code and
Correct the
parameter.
photometric point is
improper.
(2)The assigned
photometric point lags
behind the specified
reaction time.
(Operation is
impossible.)
WARNING (1)The relationship
between assay code and
Check parameter
and input it again.
calibration type is
improper.
(2)Necessary calibration
points for calibration
type are not input.
(3)Necessary standard
positions for calibration
are not input.
(4)The relationship
between calibration type
and calibration method
is improper.
(5)The standard
concentration values are
not set in ascending
order. (Except for STD
(3) and (4) for isozyme)
(6)Concentration value is
not zero when '99' is
entered for POS. of STD
(1).
1.The photometry assay
data in other than
manual mode is
checked.
2.Operation is
unallowable.
3.Check in (4) is made
with regard to
specifications of timeout calibration, lot-to-lot
calibration, bottle-tobottle calibration and
test selecting
information.
(cont’d)
2 - 17
Page 30

(cont’d)
Alarm
Control
No.
4811 to
4848
Alarm Category
VOLUME
CHECK?
Sub-
code
100 1 to 36
(ch.)
Level Description Remedy
WARNING (1)The total reagent
volume up to the last
photometric point is
more than 250 to
500 µL.
(2)The volumes of
reagents 1 to 3 are all
Check parameter.
If the improper
condition indicated
by alarm can be
detected, correction
and reentry are
required.
zero.
(3)The reagent volume
having a timing behind
the reaction time is not
zero.
(4)The total liquid volume
of sample and reagent is
less than 250 µL.
1.When '999' (stirring
only) is specified for
reagent volume, 0 µL is
taken for the volume.
However, when '999' is
specified for the reagent
volume having a timing
behind the reaction time,
an error occurs.
2.Operation is
unallowable.
3.The final liquid volume
is a total volume of
sample and reagent
within 250 to 500 µL.
5261 CMP. TEST 103 1 to 8 WARNING The setting of formula
number corresponding to
the relevant code is
improper.
(1)An unmeasurable test is
specified for
compensation.
(2)A compensated test is
not included in the
formula.
(3)In photometry assay for
compensated test, the
electrolyte parameter is
specified.
2 - 18
Call up calculation
item screen and
check the
compensation
formula on it.
Page 31

Alarm
Control
No.
5271 to
5356
Alarm Category
SERUM
INDEXES?
104 1 to 36
Subcode
(ch.)
Level Description Remedy
WARNING (1)Although the sub-code
corresponds to the
serum index
measurement test, the
rate-A assay is not
assigned.
(2)Although the sub-code
corresponds to the
serum index
measurement test and
sample blank is to be
corrected, reagent 2
discharge is specified.
(Analysis does not start.)
5431 ON BOARD? 106 1 WARNING There is no measurable
channel.
There is no channel for
which necessary reagent
has been prepared.
(Analysis does not start.)
5441 REAG.POS? 107 1 to 38WARNING (1)The reagent position
specified for a
photometry assay is
also specified for other
photometry assay.
(2)The same reagent
position is specified for
both carry-over cleaning
agent and photometry
assay or ISE test.
(Analysis does not
start.)
5481 CLB(IS)
POS.
108 1 WARNING When ISE is provided,
calibrator or control
positions are set at 55 to 57.
(Analysis does not start.)
5511 to
5516
ACI ERROR 114 1 to 6WARNING Barcode IC malfunctions.
1:Unassigned
2:Unassigned
3:Sample
4:Unassigned
5:Unassigned
6:Transfer
(cont’d)
Check parameter
for serum indexes.
Check each
parameter.
Check each
reagent.
Check the position
for control
calibration.
Replace RSDIST
PC board.
2 - 19
Page 32

Alarm
Control
No.
5561 to
5568
5571 to
5578
Alarm Category
FD-WRITE? 119 1 WARNING A hardware error has
119 2 WARNING A hardware error has
119 3 WARNING A hardware error has
119 4 WARNING A hardware error has
119 5 WARNING A hardware error has
119 6 WARNING A hardware error has
119 7 WARNING A hardware error has
119 8 WARNING A hardware error has
FD READ? 120 1 WARNING A hardware error has
120 2 WARNING A hardware error has
120 3 WARNING A hardware error has
120 4 WARNING A hardware error has
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
occurred in writing the
routine sample
measurement data.
occurred in writing the stat
sample measurement data.
occurred in writing the
control sample
measurement data.
occurred in writing the
individual or cumulative
alarm information.
occurred in writing the
parameter data.
occurred in execution of FD
formatting, copying into FD
or FDD cleaning.
occurred in writing the cell
blank data.
occurred in writing the
routine sample test
selecting information.
occurred in reading the
routine sample
measurement data.
occurred in reading the stat
sample measurement data.
occurred in reading the
control sample
measurement data.
occurred in reading the
individual or cumulative
alarm information.
(cont’d)
(1)Clean the FD.
(2)Replace the FD
with a new one.
(3)Replace the FD
drive.
Refer to alarm
category No. 119.
2 - 20
Page 33

Alarm
Control
No.
5571 to
5578
5581 FD NOT
5601 FD
5621 to
5625
Alarm Category
FD READ? 120 5 WARNING A hardware error has
INSERTED
PROTECT
PRINTER 125 1 WARNING Power supply is turned off
Subcode
120 6 WARNING A hardware error has
120 7 WARNING A hardware error has
120 8 WARNING A hardware error has
121 1,2 WARNING System disk is not set in
123 1,2 WARNING A write-protected disk is
125 2 WARNING Paper has run out or the
125 4 WARNING A hardware error has
125 5 WARNING A time-out error of the
Level Description Remedy
occurred in reading the
parameter data.
occurred in reading the
channel assignment.
occurred in reading the cell
blank data.
occurred in reading the
control parameter.
drive 1 or data disk is not
set in drive 2.
inserted.
or the connector is
disconnected.
printer head has risen.
occurred on the printer.
printer has occurred.
(cont’d)
Refer to alarm
category No. 119.
Insert the relevant
disk.
Unprotect the disk.
Check the power
supply or connector.
Set paper or lower
the printer head.
Check the printer
cable.
(1)Check the
printer cable.
(2)Replace the
printer.
2 - 21
Page 34

Alarm
Control
No.
5631 to
5643
Alarm Category
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
SYSTEM I/F 126 1 WARNING A reception time-out error
has occurred.
126 2 WARNING A transmission time-out
error has occurred.
126 3 WARNING A BCC error or checksum
error has occurred.
126 4 WARNING A parity error has occurred.
126 5 WARNING A framing error has
occurred.
126 6 WARNING An overrun error has
occurred.
126 7 WARNING Frame error
126 8 WARNING Text length error
126 9 WARNING Function character error
(cont’d)
(1)Check the cable
of system I/F.
(2)Check the
contents of
communication
trace.
(3)Check the
contents of
communication
by line analyzer.
(4)Check if a
change has
occurred in
system
parameters.
126 10 WARNING Sample information error
126 11 WARNING Test selecting information
error
126 12 WARNING Comment information error
126 13 WARNING Reception cannot continue
up to the end code because
an illegal character is
received from the host.
Example)A null code is
received from
the host.
5681 BATH
EXCHANGE
FAILURE
130 1 WARNING The start key has been
pressed despite failure in
incubation bath water
exchange.
5696 PANEL I/F 140 1 WARNING An error has occurred in
LCD display module
communication.
('Communication error'
appears on the LCD
display.)
5701 REAGENT? 141 1 to 36WARNING Either reagent positions R1
to R3 or reagent volume
alone is "0" (no
specification).
Do incubation bath
water exchange
again.
(1)Check the
communication
cable of LCD.
(2)Replace the
LCD.
Check and correct
the contents of
parameters R1 to
R3.
2 - 22
Page 35

Alarm
Control
No.
5771 CELL C. O. 145 1 to 10WARNING (1)More than 2 types of
5821 ISE C. O. 146 1 to 40WARNING R1 type is not specified for
Alarm Category
Subcode
Level Description Remedy
carry over evasion (cell)
are specified for 1 test.
(2)Sub-codes (1 to 10)
signify the evasion
types.
ISE test of Reagent Probe
Carry Over Evasion.
(cont’d)
Check and correct
the carry over
evasion (cell).
Check and correct
the Reagent Probe
carry over evasion.
2 - 23
Page 36

2.1.1 LCD Display Alarm
Output of Boot Error
Boot error is output to the console and the buzzer for small-size automatic analyzer (beeper is
used). Output is issued unconditionally to the console whenever connected. For the small-size
automatic analyzer, on the other hand, either of the destinations shown below is selected
depending on system. For selection method, refer to (3).
(1) Output to Console
Output to the console always uses a log message. This is because output cannot be
issued in the EAT format within a period from system start to EAT task start. Upon output,
a message is sent out line by line by scroll-up method as in the logging message of
VxWorks. Note that a line is fed before and after a message.
Output format is shown below. For contents of output, refer to (4).
(2) Buzzer Output for Small-Size Automatic Analyzer
The kinds of output are the same as the three kinds in the small-size immunological
system. Each output has a distinctive tone at the frequency indicated below.
1) Self Test Error : 50 Hz
2) Loading Error : 250 Hz
3) OS Initial Error : 1 Hz
Sounding : Continuous
(3) Distinction in Error Message Output
For distinction in error output of small-size automatic analyzer, the configuration register of
a flash memory is used.
According to the readout value of this register, output destination is distinguished as shown
below. The value is set by hardware. (No setting is required in software.)
Table 2-1 Flash-Memory Configuration Register
(0xf2000b)
Value Meaning
0x01 Output to small-size automatic analyzer
Bus error Other
2 - 24
Page 37

(4) Contents of Output
Output for the small-size automatic analyzer comes in 3 kinds described above. So, the
kinds of console output are listed below.
Table 2-2 Kinds of Console Message Output
Error Output Message
Self-test error 1. Self Test Error (0xXX)
XX: Self-test error code
Boot error 1. Rom Uncompress Error
2. F/D Boot Error (0xXXXXXXXX)
3. FROM Boot Error (0xXXXXXXXX)
XXXXXXXX: Boot error code (Refer to Section 5.)
OS initial error 1. OS Initial Error (Vect = 0xXX,PC=0xXXXXXXXX)
Vect = 0xXX: Vector No.
PC = 0xXXXXXXXX: Program counter
Note that EAT output is issued when possible.
2 - 25
Page 38

2.2 Motor Control Alarms
Alarm
Code
1 - 1 (3) - 4) 6 - 9 (4) - 5) 17 Unused
2 Unassigned 10 (5) - 6)
3 (4) - 5) 11 (7) - 8) 18 - 1 (2) - 3)
4 (2) - 2)ž3) 12 (6) - 7) (3) - 4)
5 (2) - 2)ž3) 14 Unassigned (2) - 2)
6 Unassigned 7 - 1 (2) - 3) (3) - 4)
7 (4) - 5) (3) - 4) 19 Unused
8 (8) - 9) (9) - A
9 Unassigned (10) - A 20 Unused
10 Unassigned 2 (2) - 3)
2 - 1 Unused 3 (3) - 4) 21 Unused
2 4 (2) - 3)
3 (10) - C 22 - 1 (1) - 1)
4 7 - 5 (1) - 1) 2 (4) - 5)
5 (2) - 2) 23 Unused
6 (9) - B
7 (10) - B 24 - 1 (1) - 1)
8 8 Unused 2 (4) - 5)
9 25 Unused
10 9 Unused
3 - 1 (3) - 4) 26 - 1 (1) - 1)
2 (4) - 5) 10 Unused 2 (4) - 5)
3 3
4 11 Unused 4
5
6 (OP) 12 Unused
7
8 13 Unused
9
10 14 Unused
4 Unused
5 - 1 (2) - 3) 15 - 1 (1) - 1)
2 (2) - 2) 3 Unassigned
3 (3) - 4) 4 Unassigned
4 (2) - 2) 16 - 1 (3) - 4)
5 (1) - 1) 2 (6) - 7)
6 Unassigned 3 (4) - 5)
6 - 1 (3) - 4) 4 (70 - 8)
2 (3) - 4) 5 (3) - 4)
3 (5) - 6) 6 (4) - 5)
4 (6) - 7) 7 (7) - 8)
5 (4) - 5) 8 (8) - 9)
6 (4) - 5) 9 Unassigned
7 (7) - 8) 10 Unassigned
8 (3) - 4)
Check
Procedure
(3) - 4) 13 (8) - 9) 2 (1) - 1)
(3) - 4) 15 Unassigned 3 (2) - 3)
(3) - 4) 2 (4) - 5) (*) : OPTION
Alarm
Code
Check
Procedure
Alarm
Code
Check
Procedure
2 - 26
Page 39

2.2.1
1. For items other than 7 and 8 ,
check whether the motor remains
running even after timeout.
NOTE:
If so, it should be identified as a
motor time out error.
2. Operation check method for 2-pitch
returning of sample disk.
3. Item 10 ; Operation check method
for 2-pitch feed of sample disk.
4. Item 9 ; Check at resetting.
2 - 27
Page 40

Notes:
1. In check procedure other than 7 and 8 ,
motor running status is checked after time-out.
When running, a motor time-out error occurs.
2. Operation check procedure at 2-pitch return of
the sample disk.
3. 10 is the operation check procedure at 2-pitch
feed of the sample disk.
4.
9 is the check at resetting.
.
2 - 28
Page 41

2.3 Parameter Check
Parameter check is carried out on the channel for which test is selected on the CHANNEL
ASSIGNMENT screen at start of analysis.
2.3.1 Processing Flow
(1) At input of START key in STANDBY status.
Twin test
simultaneous analysis
parameter check
Check result?
NG
STOP
Analytical method
OK
check
Calibration parameter Serum index analytical
check method check
Volume check Reagent relationship check
1)
at carry-over cleaning
Upper/lower limit value CH, ACTIVATE check
check
Test-to-test Check result?
compensation check
Analytical mode check
1)
OK
NG
START
STOP
2 - 29
Page 42

2.3.2 Details of Parameter Check
Designation
No.
of Check
1 Check of
parameters
for twin test
simultaneous
analysis
Details of Check
The following are checked
for measurable (level 1,
Note 1) photometry tests.
(1) In case of twin test
simultaneous analysis,
the opposite test must
be specified properly.
• Two tests must form
a unique pair, and
one of them alone
must designate the
other.
(2) In case of other than
twin test simultaneous
analysis, tests must not
be paired.
(3) In case of twin test
simultaneous analysis,
two tests must be
identical in all of the
following parameters.
• Data mode
• STD POS.
• STD S. VOL
• Assay code
• Reaction time
• Sample volume
• Reagent volume
• Calibration type
• Calibration point
• Span point
Alarm
Display Subdivision
TWIN TEST? 1 to 37
(CH No.)
Remarks
Details of this check
are given in "Details
of twin test
simultaneous
analysis" in 2.3.3.
In case of twin test
simultaneous
analysis, an alarm
is issued if one of
two tests is not
registered or the
manual mode is
selected.
NOTE:
1. The term
'measurable'
indicates either
of the following
two levels.
Level 1:
Test registered
and manual
mode not
selected
Level 2:
Same as above
and reagent
provided
2 Assay code
check
The following are checked
for measurable (level 1)
photometry tests.
(1) Relationship between
assay code and
photometric point
(check of photometric
point input and input
range)
Refer to the analytical
method table in 1.1.1.
CHEM
PARAM?
2 - 30
1 to 37
(CH No.)
Page 43

Designation
No.
of Check
2 Assay code
check
3 Calibration
parameter
check
Details of Check
(2) Photometric points after
the specified reaction
time must not be set.
Refer to Note 6 in
"analytical method
table" of 1.1.1.
The following are checked
for measurable (level 1)
photometry tests.
(1) Relationship between
assay code and
calibration type
Refer to "relationship
between calibration type
and analytical method"
in 2.1.
(2) Entry must be made for
CALIB. POINTS
necessary for calibration
type.
Refer to "output by each
calibration method and
check table" in 2.7.
(3) Entry must be made for
STD POS. necessary
for calibration.
For STD specified by
measured STD No. in
"output by each
calibration method and
check table" of 2.7, it is
checked whether STD
POS. is input or not.
Alarm
Display Subdivision
CHEM
PARAM?
1 to 37
(CH No.)
CLB. PARAM? 1 to 37
(CH No.)
(cont’d)
Remarks
NOTES:
1. Checked
against the
specification of
calibration test
selecting
information.
2 - 31
Page 44

Designation
No.
of Check
3 Calibration
parameter
check
4 Volume
check
Details of Check
(4) The input value for
SPAN POINT must be
normal.
• When calibration
type is LINEAR (2 to
6-point) or LOGITLOG (3P or 4P)
1) The above input
value must not
equal 0.
2) The above input
value must not
exceed that for
CALIB. POINTS.
(5) Relationship between
calibration type and
calibration method
Refer to "output by each
calibration method and
check table" in 2.7.
(Note 2)
(6) STD CONC. must be
set in ascending order.
Check is made only for
necessary STD POS.
Note that isozyme STD
(3) and (4) are
excluded.
"=" is not regarded as in
ascending order.
(7) When '99' is entered for
POS. of STD (1),
CONC. must be 0.
The following are checked
for measurable photometry
tests.
(1) The total liquid volume
up to the final
photometric point must
be 500 µL or less.
(2) At least one of R1 to R3
volumes must not be 0.
(3) The reagent volume
having a timing behind
the reaction time is not 0.
(4) The minimum liquid
volume must be at least
250 µL.
Alarm
Display Subdivision
CLB. PARAM? 1 to 37
(CH No.)
VOLUME ? 1 to 37
(CH No.)
(cont’d)
Remarks
NOTES:
2. Checked
against the
specification of
calibration test
selecting
information.
When reagent
volume = 0, the
relevant reagent is
not used.
2 - 32
Page 45

Designation
No.
of Check
5 Test-to-test
compensation check
6 Serum index
analytical
method
check
7 Cell carry
over
8 ISE carry
over
Details of Check
For formula No. where
compensated test is
measurable:
(1) The compensation test
must be measurable.
In addition, when the
compensation test is
already registered as a
compensated test in any
preceding formula No.,
the check result for the
formula No. must be
OK.
(2) The compensated test
must be on the right
side of the formula.
(3) When the compensated
test is a photometry
test, no ISE test must
be registered for the
compensation test.
(1) The assay code for tests
for serum index
measurement must be
RATE-A. This check is
made only when the
tests are measurable.
(2) In the RATE-A test with
serum indexes, no R2
must be specified when
sample blank correction
is carried out.
(1) More than 2 types of
carry over evasion (cell)
are specified for 1 test.
(2) Sub-codes (1 to 10)
signify the evasion
types.
R1 type is not specified for
ISE test of Reagent Probe
Carry Over Evasion.
(cont’d)
Alarm
Remarks
Display Subdivision
CMP. TEST? 44 to 51
(FORMULA
No.)
This check is not
performed in case
of ORIGINAL ABS.
S. INDEXES? 1 to 37
(CH No.)
CELL. C. O. 1 to 10 Check and correct
the carry over
evasion (cell).
ISE C. O. 1 to 40 Check and correct
the Reagent Probe
carry over evasion.
2 - 33
Page 46

2.3.3 Details of Twin Test Simultaneous Analysis
∇ NG Note 2
CH = 1 to 37 Assay code P: Designates OK
for twin test opposite test.
Note 1 simultaneous Q: Designated by NG Note 2
P.Q
P.Q
P.Q
analysis opposite test. OK
P.Q
Designated
by one test
alone
Check result OK
Identical in
all parameters
with opposite
test Note 3
OK
Not paired
NGNote 2
NG Note 2
OK
NG Note 2
∆
NOTES: 1. Unmeasurable channels are excluded.
However, in twin test simultaneous analysis, alarm occurs when either
one of the two tests is unmeasurable.
2. Alarm is registered with a channel No. assigned for subdivision.
3. Refer to "Details of Parameter Check" in 2.3.2.
2 - 34
Page 47

2 - 35
Page 48

2.4.2 Data Alarm Code List
No. Data Alarm Remarks
Output String ISE
PRINTER C
R
T
1
ADC abnornal
2
Cell blank abnormal
3
Sample short
4
Reagent short
5
Absorbance over
6
Prozone error
7
Reaction limit over at all
points
8
Reaction limit over except 1
point
9
Reaction limit over except 2
or 3 points
10
Linearity abnormal at 9
points or more
11
Linearity abnormal at 8
points or less
12
Standard 1 absorbance
abnormal
13
Duplicate error
14
STD error
15
Sensitivity error
16
Calibration error
17
SD error
18
Noise error
19
Level error
20
Slope abnormal
21
Internal standard
concentration abnormal
22
Sample value abnormal
23
Test-to-test compensation
error
24
Test-to-test compensation
disabled
25
Calculation test error
26
Overflow
27
Calculation disabled
28
Expected value high limit
over
29
Expected value low limit over
30 Electrode preparation PREP. R
31 SD absorbance over >AMAX > >
ADC?
CELL?
SAMPLE
REAGN
ABS?
∗∗∗∗∗P
LIMT0
LIMT1
LIMT2
LIM.
LIM.8
S1ABS?
DUP
STD?
SENS
CALIB
SD?
NOISE
LEVEL
SLOPE?
I.STD
R.OVER
CMP.T
CMP.T!
CALC?
OVER
???
H
L
A
Q
V
T
Z
P
I
J
K
W
F
N
L
&
C
M
%
0
X
Photometry
Assay
S.
I/FRo
u
t
i
n
e
O
A
O
Q
O
V
O
T
O
Z
O
P
O
I
O
J
O
K
O
W
O
F
H
U
S
Y
B
G
N
L
E
O
D
O
&
C
O
O
O
M
O
%
O
0
X
O O O
S
C
S
R
S
C
S
t
o
T
o
t
o
T
a
n
D
u
a
n
D
t
t
t
t
t
r
i
r
o
n
o
l
e
l
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
•Data may become blank
space.
•Data may become blank
space.
•Prozone value is output to the
printer only when the monitor
is in the real time mode.
∗∗∗∗∗ indicates a prozone
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
value (5-digit).
O
O
O
O
O
O
•Data becomes blank space.
O
•Data becomes blank space
•Data becomes blank space.
•May concur with other alarm.
•May concur with other alarm.
O
•Data becomes blank space.
BM only
NOTES: 1. If any data caused multiple data alarms, the alarm registered first will be output.
2. When [Specify] is entered for measured value space parameter in the start condition screen.
2 - 36
Page 49

2.4.3 Data Alarm Codes
No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
ADC abnormal ADC? A The ADC value of main or
sub wavelength (only main
wavelength in single
wavelength photometry) is
zero.
Cell blank
abnormal
Sample short SAMPL V Before sample aspiration,
Reagent short REAGN T Before reagent aspiration,
CELL? Q (Photometry assay only)
Two or more of the four
passed cell blank values to
be used for CELL BLANK
are abnormal.
Note: Abnormal when the
difference from the
reference value
(value measured
with cell blank
function on the
maintenance
screen) is ± 0.1 Abs
or more.
the presence/absence of
sample is checked and it is
found that the sample is
absent.
the presence/absence of
reagent is checked and it is
found that the reagent is
absent.
• Perform measurement
again.
• Turn off the power switch,
and then turn it on.
• Perform cell blank
measurement once a
week or after
replacement of the light
source lamp or reaction
cuvette.
• Confirm the adequate
volume of HITERGENT.
After taking a proper
measure, exchange
incubation bath water
once.
• Rinse or replace the
reaction cuvette and
perform cell blank
measurement.
• After washing the light
transmitting window in the
incubation bath, perform
cell blank measurement.
• Inject the sample in a
volume of expected
consumption + 50 µL or
more into a standard cup.
• Insert the lead wire.
• Prepare and set reagent
newly.
• Insert the lead wire.
2 - 37
Page 50

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Absorbance over ABS? Z (Photometry assay)
The absorbance value to be
used for calculation after cell
blank correction exceeds 3.3
Abs. The absorbance is
checked for every
wavelength.
Prozone error
*****P
('*****'
indicates
a
prozone
value.)
P (Photometry assay only)
In 1-point or 2-point assay
with prozone check, the
prozone error is indicated if
'prozone' is detected.
Prozone check is performed
by comparing the prozone
value (hereafter referred to
as PC value) obtained from
calculation mentioned below
with the prozone limit value
preset on the chemistry
parameter screen. For the
lower prozone limit, the
prozone error is indicated if
the PC value is smaller. For
the upper prozone limit, the
error is indicated if the PC
value is larger.
In the event of prozone error,
the relevant PC value is also
printed out (only in real-time
monitor printing mode).
• In 1-point & rate, rate-A
or rate-B assay, check is
not carried out for the
interval to determine the
absorbance change rate
if an ascending reaction
setting is made for that
interval.
• Dilute the sample or
reduce its volume, and
then perform
measurement again.
• Set the sample correctly.
• Prepare the reagent
again.
• Prozone check values
are printed out only in
the real-time monitor
printing mode.
• Delution or retest with
decreased volume is
performed.
• For no-check, enter
‘-32000’ (lower limit) at
“Prozone limit value” on
the parameter setting
menu screen 1.
(cont’d)
2 - 38
Page 51

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Ep
Ep
−
Prozone error
*****P
('*****'
indicates
a
prozone
value)
P Shown below are the
expressions for calculation of
the PC value. Assuming that
the preset photometric points
are P1 and P2 and the
difference in absorbance
between two wavelengths at
photometric point P is E:
(1) In 1-point assay
PC value =Ep2, p
Ep2, p
2-1
1-1
-k
k: Liquid volume
correction factor
Note that k = 1 when
1 ≤ P1, P2 ≤ 5 or
6 ≤ P1, P2 ≤ 16 or
17 ≤ P1, P2 ≤ 33 or
34 ≤ P1, P2 ≤ 73.
Prozone check is not
carried out if P2 = 0.
(cont’d)
(2) In 2-point assay
PC value =
2 3
P2' P3
−
Ep Ep
−
4 3
P4 P3
−
Note that prozone check is
not carried out if P3 = 0 or
|Ep4 - Ep3| ≤ 100 × 10
- 4
Abs.
When P2' = 0, P2 is used.
In either case of (1) and (2),
prozone check is not made
for STD (1) measurement.
2 - 39
Page 52

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Reaction limit
over
(Photometry assay only)
In 2-point rate, 1-point & rate,
rate-A or rate-B assay, the
main wavelength absorbance
at the photometric point to be
used for calculation exceeds
the reaction limit value (value
• This alarm is issued
whenever the input
photometric range
values l and m for
calculation of the
absorbance change rate
do not satisfy l + 2 < m.
obtained after automatic
correction of input reaction
limit value). The error
condition varies depending
All points NG
Only one point
OK
Only two or three
points OK
LIMT 0
LIMT 1
LIMT 2
on the number of photometric
points within the reaction limit
I
range as shown below.
(1) The reaction limit is
exceeded at all points in
the input photometric
J
range.
(2) The reaction limit is
exceeded at the second
and subsequent points
K
excluding the first point.
(3) The reaction limit is
exceeded at the third and
subsequent points
excluding the first two
points, or at the fourth
and subsequent points
excluding the first three
points.
(Caution)
In 2-point rate assay, check
is made using not the input
photometric range values l
and m alone but all
photometric points between
l and m.
• Dilute the sample or
reduce its volume, and
then perform
measurement again.
• Prepare the reagent
again.
• Check for leakage or
clogging of the reagent
pipettor.
• Input correct values on
parameter registration
menu.
(cont’d)
2 - 40
Page 53

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Linearity
abnormal
LIN.
Number of
photometric
points in reaction
limit level range ≥
9
(Photometry assay only)
In 1-point & rate, rate-A or
W
rate-B assay, the absorbance
at each photometric point to
be used for calculation of the
absorbance change rate does
not satisfy the following
relational requirement.
• Make sure the sample
does not contain dust,
etc.
• Dilute the sample and
measure it again.
• If the stirring motor does
not rotate normally,
report to the
servicemen.
4 ≤ Number of
photometric
points in reaction
limit level range ≤
8
LIN. 8
∆E1− ∆E
≤ Linearity limit value
F
Where, ∆E: Absorbance
change rate determined from
absorbance at each
photometric point in reaction
limit level range by least
squares method
∆E
b
× 100
• The light source lamp
should not be used
beyond 750 hours.
• Replace the light source
lamp and perform cell
blank measurement.
∆E1: Absorbance change
rate in first half
∆Eb: Absorbance change
rate in second half
Assuming that the number of
photometric points in the
reaction limit level range is N,
∆E1, ∆Eb and linearity limit
value can be represented as
shown below.
LIMIT8 and LIN.LIMIT
values are both fixed.
(Unit: %,
(1) When N ≥ 9
Linearity limit
value LIMIT 8
value: LIN.LIMIT = 10,
LIMIT8 = 30)
(cont’d)
2 - 41
∆E f
∆E
b
Page 54

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
4 ≤ Number of
photometric
points in reaction
LIN. 8 F
(2) When 4 ≤ N ≤ 8
Linearity limit value LIN.
LIMIT
limit level range ≤
8
∆E f
∆E
b
Note that linearity check is
not carried out in the
following cases.
• The number of
photometric points in the
reaction limit level range
is three or less.
• |∆E|≤ 60
(× 10e - 4ABS/min)
• |∆Ef - ∆E
|≤ 60
b
(× 10e - 4ABS/min)
(cont’d)
Standard 1
absorbance
abnormal
S1ABS? H (Photometry assay) (Note 1)
In calibration, the mean value
of two measured absorbance
values of STD (1) is not
within the specified standard
1 absorbance range (input
value).
Value is absorbance with
End-point Assay, in the case
of late assay, is main wave O
length first absorbance.
Duplicate error DUP U (Photometry assay)
In calibration, this error is
indicated if the difference in
absorbance (or absorbance
change rate) between the first
and second measurements of
STD (i) is larger than the
DUPLICATE LIMIT (input
value).
(i = 1 to N: N indicates the
number of standards.)
• Prepare the standard
properly.
• Set the standard
properly.
• Unless check is desired,
input a value within
- 32000 to 32000 for
"standard 1 absorbance
range" on the parameter
registration menu 1
screen.
• Replace the seal piece
of pipettor.
• Check fastening of
joints.
• Unless check is desired,
input 32000 for
"duplicate limit
absorbance" on the
parameter registration
menu 1 screen.
2 - 42
Page 55

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
STD error STD? S (Photometry assay)
(1) In calibration, any one of
the following alarms is
encountered with the
measured STD
absorbances:
ADC abnormal, cell blank
abnormal, sample short,
reagent short,
absorbance over, reaction
limit over, linearity
abnormal, prozone error,
duplicate error,
calculation disabled and
standard 1 absorbance
abnormal.
(2) In calibration, calculation
is disabled before
completion.
(3) In non-linear calibration
(EXPONENTIAL and
Logit-Log5P), an extreme
value is found.
(4) After execution of non-
linear calibration
(SPLINE), the result of
extreme value/inflection
point check is NG.
• The parameters on the
screen and FD are not
updated.
(cont’d)
(ISE)
Calibration is invalid.
(Any one of the following
alarms is encountered: ADC
abnormal, sample short,
calculation disabled, noise
error and level error.)
2 - 43
Page 56

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Sensitivity error SENS Y (Photometry assay)
Sensitivity check is carried out
only for linear (2 to 6-point),
non-linear or isozyme P
calibration.
This error is indicated if the
difference in mean absorbance
between STD (1) and STD (N)
is smaller than SENSITIVITY
LIMIT (input value).
N: Linear (2-point)/
isozyme P calibration ..... 2
Non-linear/linear (3 to 6-
point) calibration ..... 2 to 6
(input value for SPAN
POINT)
Note, however, that N = 2
when CALIB. POINTS = 2 in
non-linear LOGIT-LOG
(3P)/(4P) calibration.
• The parameters on the
screen and FD are not
updated.
• Set the standard
solutions and reagent
properly.
• Prepare the standard
solutions newly.
• Check the sample
syringe for leakage,
clogging, etc.
• Unless check is
desired, input 0 for
"sensitivity limit
absorbance" on the
parameter registration
menu.
(cont’d)
For the mean absorbance of
STD (1) in span calibration, the
following data is used.
Linear ..... Previous S1 ABS
Non-linear ..... Previously
updated mean
absorbance
Sensitivity check is not made
in R.B. calibration.
SD error SD? G (Photometry assay)
This error is indicated upon
completion of non-linear
calibration or if the SD value in
linear (multi-point) calibration is
larger than SD LIMIT (input
value).
• Set in correct
concentration series.
• Replace the seal piece
of pipettor.
• Check fastening of
joints.
• Unless check is
desired, input 999.9
for "SD limit
absorbance" on the
parameter registration
menu.
2 - 44
Page 57

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Calibration error CALIB B (Photometry assay)
In linear (2 to 6-point) or
isozyme P calibration, the
calibration condition is checked
at calculation of parameter K.
This error is indicated if there is
a difference of ±20% or more
between the current and
previous K values.
• Same as in SENS
• Pay attention to
storage method and
the time period of
placement on the
sample disk.
• If the result is
satisfactory,
operation can be
continued. After
(ISE)
The calibration concentration or
slope level for display does not
satisfy the following expression.
|Previous value - current value|
(Previous value + current value )/2
×100% > COMPENSATE LIMIT
Noise error NOISE N (ISE)
This error is indicated if the
difference between the
maximum and minimum
potentials is within the following
range at three of the five
measuring points for each test
(on internal standard or sample).
measurement,
record parameters
on the maintenance
menu to store the K
value.
• Set reagent and
perform ISE priming
(with internal
standard solution
and diluent) once.
• Make sure O-ring is
fitted to each
electrode and its
holder and it is not
Na : 0.7mV < |FIV(2) - FIV(4)|
K : 1.0mV < |FIV(2) - FIV(4)|
Cl : 0.8mV < |FIV(2) - FIV(4)|
fitted doubly.
After reattaching,
perform ISE priming
(with reference
electrode solution).
• Replace the tube
and perform ISE
priming (with
reference electrode
solution) once.
• Clean the waste
solution drain path.
• Clean the syringe
and plunger and
replace the seal
piece.
(cont’d)
2 - 45
Page 58

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Level error LEVEL L (ISE)
This error is indicated if the
mean potential is outside the
following range at three of the
five measuring points for each
test (on internal standard).
•Set reagent and perform
ISE priming (with
reference electrode
solution) twice.
•Replace the electrode
and perform ISE
priming (with reference
Na: -90.0mV ≤ EAV ≤ -10mV
⇒ OK
K : -90.0mV ≤ EAV ≤ -10mV
⇒ OK
Cl : 100.0mV ≤ EAV ≤
180.0mV ⇒ OK
electrode solution)
once.
•Retighten the nipple.
Or after replacing the
rubber packing, perform
ISE priming (with
reference electrode
solution) once.
•Confirm the proper
combination of tube and
reagent.
•Plug in the cord
properly.
Slope abnormal SLOPE? E (ISE)
(1) The slope level for display
is within the following
range.
Na, K : SLOPE < 45.0mV,
Cl : SLOPE > -35.0mV
•Replace the electrode.
•Remove the probe and
correct clogging.
•Set properly.
•Confirm the proper
combination of tube and
reagent.
(2) Electrode response is
degraded.
(Carry-over rate is as
shown below.)
Na : 0.232 < A
K : 0.160 < A
Cl : 0.490 < A
Electrode
preparation
PREP. R Upon calibration, the slope
value is within the following
range.
•Make sure that the
standard solution and
reagent are set properly.
•Make sure that the
Na, K : 45.0mV ≤ Slope value
≤ 49.9mV or
68.1mV ≤ Slope value
Cl : -39.9mV ≤ Slope value
≤ -35.0mV or
-68.1mV ≤ Slope value
standard solution is free
from concentration or
deterioration.
•Make sure that the
electrodes (Na, K, Cl)
are within their
guaranteed life.
(cont’d)
2 - 46
Page 59

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Internal standard
concentration
abnormal
I. STD D (ISE)
The internal standard
concentration (C(IS)) is within
the following range.
Na : C(IS) < 120.0mEq/L or
•Confirm monthly flow
path washing.
•Replace the diluent and
internal standard
solution.
160.0mEq/L < C(IS)
K : C(IS) < 3.0mEq/L or
7.0mEq/L < C(IS)
CL : C(IS) < 80.0mEq/L or
120.0mEq/L < C(IS)
Calculation test
error
CALC?
%
Any data alarm other than
shown below is indicated for
the test to be used for
•Check the data alarm
name and take a proper
measure.
calculation.
Calculation disabled, test-to-
test compensation disabled,
expected value over
Overflow OVER
O
Concentration value (or activity
value) cannot be output within
the specified range of digit
•The data is left blank.
•Prepare appropriate
standard solution.
count.
Calculation
disabled
???
X
•In process of calculation, the
denominator becomes zero.
•An overflow occurs in
logarithmic or exponential
calculation.
•In isozyme Q-channel
concentration calculation, the
data alarm of 'calculation
disabled' is indicated for the
isozyme P-channel data or
the isozyme P channel is not
measured.
•The data is left blank.
•Determine the cause of
failure to color
development such as
improper kind of
standard solution, wrong
set position and
clogging of sample
probe.
•Dilute the sample or
reduce its volume and
perform analysis again.
•Calculation for a calculation
test has been attempted with
the data having a data
blanking alarm.
Expected value
over
L
H
The test result is outside the
expected value range (outside
mean value ± 2SD in case of a
control sample).
•Smaller than the lower limit
–
–
value
•Larger than the upper limit
•This alarm is not
indicated for serum
index.
•Correct setting on the
parameter registration
menu 1 screen.
value
(cont’d)
2 - 47
Page 60

No. Data Alarm Printer S. I/F Description Remedy
Sample value
abnormal
R. OVER
&
(ISE)
The sample concentration
(C(S)) is within the following
range.
Na : C(S) < 10.0mEq/L or
C(S) > 250.0mEq/L
K : C(S) < 1.0mEq/L or
C(S) > 100.0mEq/L
•Dilute the sample and
analyze it again.
•Direct measurement is
impossible. Utilize
standard addition
method, etc.
•Remove the probe and
correct clogging.
Cl : C(S) < 10.0mEq/L or
C(S) < 250.0mEq/L
Test-to-test
compensation
error
CMP.T
C
(1) In test-to-test
compensation calculation,
any data alarm other than
•Check the channel data
used for test-to-test
compensation.
shown below is indicated
for the compensation data.
(2) In isozyme Q-channel
concentration calculation,
any data alarm other than
shown below is indicated
for the isozyme P-channel
concentration.
Calculation disabled, testto-test compensation
disabled, overflow, random
error, systematic error, QC
error, expected value over
Test-to-test
compensation
disabled
CMP.T!
M
(1) In process of calculation for
test-to-test compensation,
the denominator becomes
zero.
(2) The test to be used for test-
to-test compensation is not
measured.
(3) Any test to be used for test-
to-test compensation has
•The data is left blank.
•Make sure masking is
not specified for the test
to be used for
compensation.
•Check the calculation
formula on the
parameter registration
menu 3 screen.
the data alarm of
'calculation disabled' or
'test-to-test compensation
disabled.'
(4) Any compensation test has
the data alarm which
leaves the data blank.
SD absorbance
over
>AMAX
>
At standard concentration of
“∞”, absorbance of sample or
absorbance change rate is over
or the same compared with
presumptive absorbance or
absorbance change rate.
(cont’d)
2 - 48
Page 61

2.4.4 ISE Data Alarms
Alarm Output
ISE
Priority Alarm Printout CRT S. I/F Remarks
Alarm on ISE data processing has 2 kinds shown below; calibration alarm and data alarm.
(1) Calibration Alarm
1 STD error STD?
2 Slope
abnormal
3 Electrode
preparation
4 Internal
standard
concentration
abnormal
5 Calibration
error
< Key >
N : Routine sample measurement
E : Stat sample measurement
C : Control sample measurement
STD : Calibration measurement
SLOPE?
PREP
I. STD
CALIB
Processing
N.E.C.R STD
–
–
–
–
–
S
E
R
D
B
×
×
×
×
×
on Operation
Monitor Screen
O O In calibration
measurement,
this alarm is set
at any of the
data alarms in
(2) (excluding
data alarms 6 to
9).
O O
O O
O O
O O
2 - 49
Page 62

(2) Data Alarm
Priority Alarm Printout CRT S. I/F Remarks
1 ADC
abnormal
2 Sample short SAMPLE V V
3 Noise error NOISE N N
4 Level error LEVEL L L
5 Sample value
abnormal
6 Calculation
disabled
7 Test-to-test
compensation
disabled
8 Test-to-test
compensation
error
9 Overflow OVER O O
ADC? A A
R.OVER & &
???
CMP.T! M M
CMP.T C C
× ×
ISE
Processing
N.E.C.R STD
O O O
O O
Alarm Output
on Operation
Monitor Screen
×
Registration is made on
the operation monitor in
ADC task.
At occurrence of this
alarm, the 'calculation
disabled' alarm is also set
(for making output data
blank).
O O O O
O O O O
O
O O
O
O
O
× × ×
× ×
× ×
Check is not performed in
ISE data processing.
× × ×
× ×
ISE
Check
Data
Alarm
O
×
×
O
2 - 50
Page 63

(3) Registration of Data Alarm "sample short"
Measured Sample
Other than STD (1) A
STD (1) A
NOTES: 1. A: Pre-detection is not made.
B: Pre-detection is made and at least either one of the following is encountered.
(i) The number of remaining pulses is zero.
(ii) Abnormal fall detection is activated within ±2 mm of the cup bottom level recognized
C: Other than A and B
(Pre-detection refers to liquid level detection till a time point just before sample aspiration
since start of probe fall.)
2.
O: Output
Alarm Issued in Sampling
(Note 1)
1st Time 2nd Time
B
C
B
C
Water
discharge
in probe adjustment.
×: Space
O: Issued
3.
×: Not issued
Data Output
(Note 2)
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
×
O
O
×
O
O
O
Data Alarm
(Note 3)
O
O
×
O
O
×
×
2 - 51
Page 64

2.4.5 Alarm Check Method
(1) Photometry Assay Calibration Check
(a) SD check of approximate expression
When SD in the difference between the automatically generated calibration curve
and the measured absorbance value in non-linear calibration is larger than "SD limit
absorbance," comment SD? is printed. SD value is printed under the test name in
the result of calibration. Unless check is desired, input 999.9.
(b) Duplication check
In measurement of reagent blank and standard solution, comment DUP is printed
when the difference in absorbance between two measurements is larger than
"duplicate limit absorbance." Unless check is desired, input 32000.
(c) Sensitivity check
When the difference in absorbance between reagent blank (STD1) and standard
solution (having the maximum concentration if there are multiple standard
solutions), comment SENS is printed. Unless check is desired, input 0.
(d) Standard solution 1 absorbance check
When the absorbance of reagent blank (standard solution 1) exceeds "standard 1
absorbance range," comment S1 ABS is printed. In an end-point assay test, the
absorbance value on the left side of calibration result printout is checked and that
on the right side is checked in a rate-assay test. Unless check is desired, input 32000 to 32000.
2 - 52
Page 65

(2) Reaction Limit Level Check
When concentration or enzyme activity is abnormally high in a rate assay test, correct
data is unobtainable because the substrate or coenzyme in reagent is consumed
completely. Therefore, the upper or lower reaction limit absorbance is set for check .
Check is made on the absorbance at the main wavelength alone.
< Relationship between Alarm Name and Photometric Point >
When 4 points or more over the specified photometric range are within the reaction limit,
measurement is carried out normally. In case no point, 1 point or 2 points are within the
reaction limit, a reference value is obtained depending on an absorbance change
between the first two points. In case 3 points are within the reaction limit (with comment
LIMT2), the value obtained depending on an absorbance change among the first three
points is printed as a reference value.
ABS.
Input photometric range
(with comment LIMT0)
ABS.
Input photometric range
(with comment LIMT2)
ABS.
Reaction limit level
Time
Input photometric range
(with comment LIMT1)
ABS.
Time
Input photometric range
(with comment LIMT2)
Fig. 2-1 Reaction Limit Level Check
Time
Reaction limit
level
Time
< Automatic Correction of Reaction Limit Level >
The instrument corrects the input reaction limit level by adding an absorbance value due
to sample turbidity, etc.
Reaction limit level = Input reaction limit absorbance value + (L1 - LB)
L1: Sample absorbance at photometric point 1
LB: Reagent blank absorbance at photometric point 1
When L1 - LB ≤ 0, automatic calibration will not be performed.
2 - 53
Page 66

(a) Electrolyte compensable range check.
When the ratio of change in calibrator concentration or slope value from the
previous one is larger than the input value, comment CALIB is printed. Unless
check is desired, input 200%.
(b) Calibration check
When calibration factor K has changed by 20% or more from the previous value,
comment CALIB is printed (check value is fixed at 20%).
(c) STD check
If any of the following alarms occurs on calibration data, comment STD? is printed.
• ADC abnormal (ADC?) • Reaction limit over (LIMT0, 1, 2)
• Cell blank abnormal (CELL?) • Reaction linearity abnormal (LIN. or LIN.8)
• Sample short (SAMPL) • Duplicate error (DUP)
• Reagent short (REAGN) • Standard 1 absorbance abnormal
(S1ABS?)
• Absorbance over (ABS!) • Calculation disabled (???)
• Prozone error (xxxxxP)
(d) Measure to be taken on printout of comment
When comment STD? or SENS is indicated, calibration curve will not be updated.
Therefore, recalibration is necessary. In case of CALIB or SD!, sample
measurement is allowed after making sure the result of calibration is normal. In this
case, however, the result of calibration will not be saved automatically onto the
floppy disk. Before turning off power supply, parameters should be recorded on the
maintenance screen.
Table 2-1 Handling of Calibration Result with Comment
Printed
Comment
STD? Not updated
SENS Not updated
CALIB Updated
SD ! Updated
Calibration Result
(display on screen)
(previous result remains)
(previous result remains)
(to new result)
(to new result)
Alarm Name on
Operation Monitor Screen
Calibration curve generation disabled
(code 70-1 to 49)
Standard solution sensitivity abnormal
(code 73-1 to46)
Calibration abnormal
(code 70-1 to 49)
Calibration SD abnormal
(code 72-1 to 46)
Automatic Saving onto
Floppy Disk
The reagent blank (S1ABS)
and calibration factor (K) of
the relevant test are not
saved automatically onto
floppy disk.
2 - 54
Page 67

(3) Reaction Linearity Check
∆Af−∆Ab
In a rate assay test, the linearity in absorbance change is checked.
Check value varies with the number of points (N) in photometric range.
Fig. 2-2 Reaction Linearity Check
< When N ≥ 9 >
The difference in absorbance change quantity between the first-half 6 points (5 sections)
and the latter-half 6 points is obtained and then divided with the overall absorbance
change quantity. When the result of this calculation exceeds the limit in linearity check,
comment LIN. is printed together with the result of measurement.
∆
A
× 100 > Linearity limit value.....LIN.
< When 4 ≤ N ≤ 8 >
The difference in absorbance change quantity between the first-half 3 points (2 sections)
and the latter-half 3 points is obtained and then divided with the overall absorbance
change quantity. When the result of this calculation exceeds the limit in linearity check,
comment LIN.8 is printed together with the result of measurement.
9
Af
∆
∆
• ∆Af, ∆Ab and ∆A in the above formula are all converted into absorbance change in a minute
• In the following cases, reaction linearity is not checked.
9
Ab
− ∆
9
A
by the least squares method.
a) The number of photometric points (N) within the reaction limit is 3 or less ("reaction limit
b) Absorbance change in a minute is 60 × 10-4 Abs or less, or |∆Af - ∆Ab| is equal to or
× 100 > Linearity limit value.....LIN.8
over" will occur).
smaller than 60 × 10-4.
2 - 55
Page 68

(4) Prozone Check
In immunological reaction, the absorbance of calibration curve falls at high concentrations
so that correct data is unobtainable (this is called "zone phenomenon or prozone effect").
Therefore, prozone check is performed by the two methods below and a data comment is
indicated when required.
< Antigen Readdition Method >
In 1-point assay, a small amount (approx. 50 µL) of sample containing antigen is readded
for the second reagent (R2 to R4) to check the change in absorbance before and after
addition (the dashed line in Fig. 2-3 indicates that absorbance falls due to excessive
antigen).
< Reaction Rate Ratio Method >
In 2-point assay, check is performed according to the ratio of the initial reaction rate after
addition of antiserum to the mean reaction rate.
Check Abs.
R1
(antiserum)
Rn (antigen)
Time
Fig. 2-3 Antigen Readdition Method
R1
(1st reagent)
Fig. 2-4 Reaction Rate Ratio Method
Rn (nth reagent) Time
2 - 56
Page 69

Absorbance for concentration
calculation
Prozone check value
(PC value)
Antigen Readdition Method
(1-point assay)
Al + A
2
l-1
Al + A
2
l-1
Ax =
Am + A
PC = -k
m-1
2
Reaction Rate Ratio Method
(2-point assay)
Am + A
Ax = -k
2
(Am - An)/(m-n)
PC = × 100
(Ap - An)/(p-n)
m-1
Al + A
2
l-1
< Judgment >
In case of 'limit value - above,' comment xxxP (xxx indicates PC value) is printed when PC
value is larger than the limit value. In case of 'limit value - below,' the comment is printed
when PC value is smaller than the limit value.
• Prozone check will not be performed in the following cases.
(1) In STD (1) measurement (2) |Ap - Am| < 100 × 10-4 Abs
2 - 57
Page 70

(5) ISE Calibration Alarm Check
Alarm Name Alarm Check Method (alarm setting condition)
Standard error Calibration is invalid.
(Any of the following alarms has occurred; ADC abnormal, sample short,
calculation disabled, noise error and level error.)
Slope abnormal (1) The slope for display is within the following range.
Na, K : Slope < 45.0 mV
Cl : Slope > -35.0 mV
(2) Electrode response is degraded (carry-over ratio is as given below).
Na : 0.232 < A
K : 0.160 < A
Cl : 0.490 < A
ISE prepare (1) The slope for display is within the following range.
Na, K : 45.0 mV ≤ Slope ≤ 49.9 mV or
68.1 mV ≤ Slope
Cl : -39.9 mV ≤ Slope ≤ -35.0 mV or
-68.1 mV ≥ Slope
(2) Electrode response is degraded (carry-over ratio is as given below).
Na : 0.154 < A
K : 0.107 < A
Cl : 0.330 < A
Internal standard
concentration
abnormal
Calibration
abnormal
The concentration of internal standard solution (C(IS)) is within the following
range.
Na : C (IS) < 120.0 mEq/L or 160.0 mEq/L < C (IS)
K : C (IS) < 3.0 mEq/L or 7.0 mEq/L < C (IS)
Cl : C (IS) < 80.0 mEq/L or 120.0 mEq/L < C (IS)
On each of the calibrator concentration and slope for display, the previous and
current values are compared and the result exceeds the COMPENSATE LIMIT
value.
Previous value - Current value
× 100 (%) > COMPENSATE Limit
(Previous value + Current value)/2
2 - 58
Page 71

(6) ISE Data Alarm Check
Alarm Name Alarm Check Method
ADC abnormal The result of ADC is abnormal. (Checked in ADC task)
Sample short Sample volume is inadequate. (Checked in control task)
Noise error This alarm is issued when a difference between maximum and minimum
potential values at three out of five measurement points in each test is within
the following range (on internal standard and sample).
Na : 0.7 mVFIV (2) - FIV (4)
K : 1.0 mVFIV (2) - FIV (4)
Cl : 0.8 mVFIV (2) - FIV (4)
Level error This alarm is issued when a difference between maximum and minimum
potential values at three out of five measurement points in each test is within
the following range (on internal standard).
Na : -90.0 mV ≤ EAV ≤ -10 mV ⇒ OK
K : -90.0 mV ≤ EAV ≤ -10 mV ⇒ OK
Cl : 100.0 mV ≤ EAV ≤ 180.0 mV ⇒ OK
Sample value abnormal The sample concentration (C(S)) is within the following range.
Na : C (S) < 10 mEq/L or C (S) > 250 mEq/L
K : C (S) < 1 mEq/L or C (S) > 100 mEq/L
Cl : C (S) < 10 mEq/L or C (S) > 250 mEq/L
Calculated disabled Due to zero division, log-X, etc.
2 - 59
Page 72

2.4.6 Check and Set Alarm of Each Data
(1) Calibration
Priority
Data Kind
Potential of internal
standard solution
Low potential of
standard solution
High potential of
standard solution
Calibrator potential Na
Slope value (for
display)
Concentration of
internal standard
solution
Calibrator
concentration
Correction factor Na
Na
K
Cl
Na
K
Cl
Na
K
Cl
K
Cl
Na
K
Cl
Na
K
Cl
Na
K
Cl
K
Cl
1 2 3 4 5 6
Noise error Level error
ADC
abnormal
↑ ↑ ↑
↑ ↑ ↑
Slope
abnormal
Internal
standard
concentration
abnormal
Calibration
abnormal
Calculatio
n disabled
Sample
short
Preparation
abnormal
Calculation
disabled
Calculation
disabled
Noise
error
Calibration
abnormal
Level error
Calculation
disabled
(2) Routine Sample Measurement (1st), Stat Sample Measurement (1st) and Control Sample
Measurement
Data Kind
Sample
concentration
Priority
Na
K
Cl
1 2 3 4 5 6
ADC
abnormal
Sample
short
Noise error Level error Sample
value
abnormal
Calculatio
n disabled
If multiple data alarms concur, the one with the highest priority will be indicated.
2 - 60
Page 73

2.4.7 Details of Data and Alarm Outputs Resulting from Calibration
C3
disabled
Sample error factors
Standard
solution
LOW
Standard
solution
HIGH
Standard
solution
CALIBRATOR
IS
L2
IS
L3
IS
M1
E
L2
E
L3
IS
M2
IS
M3
IS
C1
E
M2
E
M3
IS
C2
IS
C3
IS
C4
E
C2
E
ADC
Noise
Level
ADC
ADC
Sample short
Noise
Level
Level
ADC
Noise
Level
ADC
Sample short
Level
ADC
Noise
Level
ADC
Sample short
Level
Calculation error factors
Slope abnormal
Slope
IS
concentration
Preparation abnormal
Calibration abnormal
Calculation disabled
Internal standard
concentration
Calculation disabled
Noise errror
Level error
ADC error
Sample short
Noise error
ADC error
Sample short
Noise error
ADC error
Sample short
Noise error
Level error
STD error
Slope abnormal
Preparation
abnormal
Calibration
abnormal
Calculation
disabled
Internal standard
concentration
abnormal
Calculation
Calibration
abnormal
Calcuration
disabled
Calcuration
disabled
IS
potential
Low
potential
High
potential
Calibration
potential
Slope
Internal
standard
concentration
Calibration
concentration
Correction
factor
Calibrator
concentration
Correction
factor
Calibration abnormal
Calculation disabled
Calculation disabled
2 - 61
Page 74

2 - 62
Page 75

(1) List of Calibration Output Media
Output Medium
Output Data
Calibration curve
parameters
(S1ABS, K, A, B, C)
SD value
Serum index blank CALIBRATION LIST
Blank level
Absorbance or absorbance
change rate
Initial or final observance
CALIBRATION LIST
CRT
(screen name)
×
× × ×
×
×
PRT S. I/F
× ×
CALIBRATION MONITOR
× ×
CALIBRATION MONITOR
CALIBRATION MONITOR
NOTE: In plotting of measured absorbance values, the currently measured STD alone is
taken.
(2) Relationship between Alarm and Output in Calibration
Data Alarm Name
S1ABS error No No
DUPLICATE error No No
STD error No Yes
SENSITIVE error No Yes
CALIB error Yes Yes
SD error Yes Yes
No alarm Yes No
Updating of Screen
Parameter
Screen Display
of Alarm
Remarks
O
O
O
NOTE: For CALIB and SD errors, "∗" is output on logging for discrimination.
2 - 63
Page 76

2.5 Retry Code Table
Code Description Remarks
Allowable
Retry Count
1 Alarm fuse blown 1/50 ms
2 12 V for lamp 1/4.5 sec Check is not made when lamp is turned
off (during initialization, water exchange
or sleep).
3 15 V for CPU rack 1/50 ms
4 -15 V for CPU rack 1/50 ms
14 Liquid in vacuum tank 1/4.5 sec
15 Vacuum pressure abnormal 1/4.5 sec Check is not made within 10 sec after
vacuum pump turns on.
16 Waste solution tank 1/4.5 sec
17 Incubation bath water inadequate 100/4.5 sec Checked in the following statuses;
standby, operation, sampling stop.
18 Distilled water short 1) 10/6 sec Water supply
2) 50/6 sec Warning
3) 150/6 sec STOP
19 Distilled water sensor abnormal 1/6 sec Check is not made during initialization,
water exchange or wake-up.
31 GPCNT1 10 Only at power-on
32 GPCNT2 10 Only at power-on
33 GPCNT3 10 Only at power-on
34 GPCNT4 10 Only at power-on
35 GPCNT5 10 Only at power-on
36 GPCNT6 10 Only at power-on
37 GPCNT7 10 Only at power-on
38 GPCNT8 10 Only at power-on
46 GMCNT1 10 Only at power-on
47 GMCNT2 10 Only at power-on
48 GMCNT3 10 Only at power-on
49
50 ADC controller 1 Only at power-on
71 Checksum error detected in operation
unit
72 Checksum error detected in analyzing
unit
102
103
104
105
106
107
1
1
2 - 64
Page 77

2.5.1 Logging Program List
No. Function Output Method Processing
1 Monitor printout Real time printout: Specify "print" on
the start condition menu screen.
Printout is made when the specified
values in all tests for one sample are
calculated during operation.
Batch printout: Specify sample
number on the data monitor screen.
2 Calibration result
printout
3 Remaining
reagent volume
printout
4 Cell blank printout Specify "cell blank" on the
5 Reproducibility
check printout
6 Cumulative
mechanism
information
printout
7 Parameter printout Specify "parameter" on the
8 Program check
printout
9 ISE check printout Specify "ISE" check on the mechanism
10 Photometer check
printout
11 Alarm trace
printout (DAILY)
12 Alarm trace
printout
(CUMULATIVE)
13 Original Abs.
printout
14 Communication
trace printout
15 Work sheet
printout
16 Barcode Reader
check
Printout is made when "calibration" is
selected on the start condition menu
screen and the result of calibration is
output.
Specify "remaining reagent volume
printout" on the start condition menu
screen.
maintenance screen.
Specify "reproducibility check" on the
maintenance screen.
Specify "cumulative mechanism
information" on the mechanism check
menu screen.
maintenance screen.
Specify "program check" on the
mechanism check menu screen.
check menu screen.
Specify "photometer check" on the
maintenance screen.
Specify "alarm trace information" on
the mechanism check menu screen.
Specify "alarm trace information" on
the mechanism check menu screen.
Printout is made when "original Abs." is
specified on the system parameter
screen and operation is executed.
Specify "communication trace printout"
on the mechanism check menu screen.
Specify "work sheet printout" on the TS
registration screen of routine analysis.
Specify "Barcode Reader" check on
the mechanism check menu screen
Real time
and batch
Real time
Batch
Batch
Batch
Batch
Batch
Batch
Real time
Batch
Batch
Batch
Real time
Batch
Batch
Real time
Printout Stop
by Stop Key
O
(In batch mode
alone)
×
×
O
O
×
O
×
×
O
(Note 1)
O
O
×
(Note 2)
O
O
×
NOTES: 1. The stop key is invalid during printout.
2. The stop key need be pressed to stop analysis.
(1) Initialization of Printer
2 - 65
Page 78

Effected when power supply is turned on or there is a printer alarm at start of printing
one processing.
(2) Paper Feed
• At end of printout
At the end of each printout (in batch mode of No. 1 and in Nos. 3 to 15), paper is
fed by 3 lines.
(Paper is also fed when printout is stopped by stop key input.)
(3) Page Length
Page length is not determined.
(4) Printing Performance
4 lines/sec (80 characters/sec), 2.54 cm/6 lines, paper feed in pitches of 4.23 mm/line
(1/6 inch)
(5) Printing System
Numerals are right-justified with space at leading positions unless there is a
comment.
(6) Printout with No Blank Space
• Channel number is not registered in keyed-in information.
• Measured data is unavailable.
(7) For Leaving Blank Space
Overflow has occurred at the location where measured data is to be printed.
2 - 66
Page 79

2.6 Daily Alarm Trace
(1) Outline
The alarm and retry data from power-on to present time point are printed when "daily" in
"alarm trace data" is specified on the mechanism check menu screen.
(2) Details of Printout
(a) Title
The title "Daily Alarm Trace," date and time are printed.
The printing order of year, month and day depends on the date printout order
specification.
(b) Time (24-hour base)
Time when alarm and retry data has been saved onto FD.
(c) Instrument status
Numerical value representing the instrument status. For details, refer to Table
2-2.
(d) Occurrence count
Indicates how many times the same alarm/retry data as that in a single cycle has
occurred successively (in the number of cycles within 1 to 999).
(e) Identification character
'A' is printed out for alarm data, and 'R' for retry data. Printout is not made when
there is no data in each case.
(f) Alarm data
The alarm data is printed out in the order of main alarm code (3-digit integer), sub
alarm code (3-digit integer) and time of occurrence up to 10 kinds. If 10 kinds are
exceeded, excess ones are not stored. However, they are saved as cumulative data.
Time of occurrence: Time on the basis of operation cycle (000 to 179) when the
alarm has occurred (in 100 msec).
(g) Retry data
The retry data is printed out in the order of retry code (3-digit integer), retry count (3digit integer) and time of occurrence up to 10 kinds. If 10 kinds are exceeded, excess
ones are not stored. However, they are saved as cumulative data.
(h) Key operation data
The key operation data is printed out in the order of key operation code (3-digit
integer), key operation count (3-digit integer) and time of key operation (3-digit
integer). Printout is made only once.
2 - 67
Page 80

Table 2-2 Instrument Status Code Table
Blank row is the unassigned one.
Code Instrument Status Code Instrument Status Code Instrument Status
1 Initialization 23 45 Incubation bath water
exchange
2 Standby
(including parameter check)
3 Preparation for operation 25 47 Probe position adjustment
4 Operation 26 48 Probe position adjustment
5 Sampling stop 27 49 Probe position adjustment
6 28 50 Probe position adjustment
7 29 T/M stop 51 Probe position adjustment
8 Stop 30 Emergency stop 52 Mechanism check
9 31 53 Barcode Reader check
10 32 54 ISE check (internal standard
11 33 Rinsing (cell) 55
12 34 Rinsing (ISE) 56
13 35 Rinsing (all) 57
14 36 58
15 37 Photometer check 59
16 38 ISE priming (IS) 60
17 39 61
18 40 62 Routine sampling stop
19 41 ISE priming (REF) 63
20 42 64
21 43 Cell blank 65 Mechanism resetting during
22 44 66
24 46 Resetting
(sample probe rotation)
(sample probe up/down)
(reagent probe rotation)
(reagent probe up/down)
(stirrer)
electromotive force
measurement)
(restart unallowable)
operation
2 - 68
Page 81

(3) Printout System
(a) Data is printed out in the sequential order starting from the newest data.
(b) When the alarm/retry data in a single cycle does not reach 10 kinds, it is printed out
closely with no blank line left.
(c) When there is no alarm data or retry data, its title alone is printed.
(4) Notes
(a) Printout can be stopped in steps of cycle by stop key input.
(b) Up to 500-cycle data starting from the oldest one is saved onto FD. However, if the
same data has recurred in consecutive cycles, storage is made as one-cycle data.
(c) In case of FD error, processing is terminated with the title alone printed.
2.6.1 Cumulative Alarm Trace
(1) Outline
The alarm data and retry data saved in the FD are printed when "cumulative" in "alarm
trace data" is specified on the mechanism check menu screen.
(2) Details of Printout
(a) Title
The title "Cumul. Alarm Trace," date and time are printed.
The printing order of year, month and day depends on the date printout order
specification.
(b) Final alarm occurrence date/time
The printing order of occurrence date depends on the date printout order
specification. Time printout is fixed to 24-hour base.
(c) Identification character
'A' is printed out for alarm data, 'R' for retry data and 'K' for key operation. Printout is
not made when there is no data in each case.
(d) Alarm data
The alarms, which have occurred in a day, are printed out in the order of main alarm
code (3-digit integer), sub alarm code (3-digit integer) and occurrence count (3-digit
integer) up to 20 kinds.
(Occurrence count: The cumulative number of identical alarms which have occurred
in a day)
(e) Retry data
The retries, which have occurred in a day, are printed out in the order of retry code
(3-digit integer) and retry count (3-digit integer) up to 20 kinds.
2 - 69
Page 82

(f) Key operation data
The key operation data is printed out in the order of key operation code (3-digit
integer), key operation count (3-digit integer) and time of key operation (3-digit
integer). Printout is made up to 16 kinds.
(3) Printout System
(a) Data is printed out in the sequential order starting from the newest data.
(b) When the alarm/retry data in a day does not reach 20 kinds, it is printed out closely
with no blank line left.
(c) When there is no alarm data or retry data, its title alone is printed.
(4) Notes
(a) Printout can be stopped in steps of day by stop key input.
(b) The data obtained from power-on to power-off is taken as daily data and the data for
up to 256 days is saved onto FD starting from the newest data. In case of continuous
energization, however, a day's data is automatically closed when the day changes
and subsequent data is treated as for the following day.
(c) In case of FD error, processing is terminated with the title alone printed.
2 - 70
Page 83

Alarm Trace Printout (DAILY)
Instrument status
Occurrence count
Time of occurrence
Retry count (or sub alarm code)
Retry code (or main alarm code)
Alarm Trace Printout (CUMULATIVE)
Main
code
Occurrence count
Sub code
Retry circuit
Retry code
2 - 71
Page 84

2.6.2 Parameter Code List
2 - 72
Page 85

(1) Parameter Printout
Table 2-3 Contents of Printout
Numerical
Input from
Screen
0 Title
1 to 37 Photometry assay parameter
38 to 40 ISE parameter
99 8calculation tests
8 compensation tests
Control positions (1 to 5)
Serum indexes
Printing order
Printing format (when with card printer)
Set test
Carry-over evasion
System parameter
DIP switch data
Contents of Printout Without ISE With ISE Remarks
O O
O O
×
O
(× for ISE-
related tests)
( O: Printed ×: Not printed )
O
O
(2) Program Check Printout
Program version No.
2 - 73
Page 86

2.6.3 Communication Trace
(1) Outline
The contents of communication between the analyzer and external system are printed
according to the specification of "communication trace printout" on the mechanism check
menu screen.
(2) Printing Items and Their Contents
Details are given in Table 2-4.
Table 2-4 Printing Items and Their Contents
Printing Item Contents
Title Title "Communication Trace," date and time are printed.
The printing order of year, month and day depends on the
date printout order specification.
Time Communication start time – Communication end time
(hour, minute, second) (hour, minute, second)
Communication mode Transmission
Reception
Error message Refer to Table 2-5.
Example of communication text Refer to the system I/F specification.
AU → HOST
HOST → AU
2 - 74
Page 87

(3) Printout System
In printout of
(a) Printout order
Sequential printout starting from the latest communication
(b) Presence/absence of error message and printout system
Details are given in Table 2-5.
Table 2-5 Presence/Absence of Error Message and Printout System
Error
Message
None Both transmission
BCC SUM
PARITY
FRAMING
OVER RUN
FRAME
LENGTH
CHAR1
CHAR2
CHAR3
CHAR4
TIME OUT Both transmission
NOTE: Control codes and corresponding character strings are listed in Table 2-8.
Communication
Mode
and reception
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
HOST → AU
and reception
Contents
of Error
None (normal) Only communication
BCC error or
checksum error
Parity error All data printed
Framing error All data printed
Overrun error All data printed
Frame error All data printed
Text length error All data printed
Function character
error
Sample data error All data printed
Test selecting
information error
Comment error All data printed
Transmission or
reception time-out
error
Printout System
(communication
text example)
function No. and
sample data
All data printed
All data printed
All data printed
Only time point,
communication
mode and error
message printed
communication text
(example), an ASCII
control code is
converted into a
character string and
printed, and then
line is fed and
communication text
is printed.
Remarks
(Note)
(4) Notes
(a) Printout is terminated by stop key input. Printout can be stopped after the contents of
trace in one cycle have been printed.
(b) A text is printed on two lines when it is longer than 20 characters.
2 - 75
Page 88

Table 2-6 Control Codes and Corresponding Character Strings Printed
Control Code (NEX) Character String Use in AU (Analyzer Unit)
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
0A
0B
0C
0D
0E
0F
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
1A
1B
1C
1D
1E
1F
NUL
SOM
STX
ETX
EOT
ENQ
ACK
BEL
BS
NT
LF
VT
FF
CR
S0
S1
DLE
DC1
DC2
DC3
DC4
NAK
SYN
ETB
CAN
EM
SUB
ESC
FS
GS
RS
US
O
O
O
O
2 - 76
Page 89

(5) Communication Trace Printout
5 0 5 0
Communication Trace
94/07/25 16:30
08:11:17 – 08:11:18
AU–>HOST
:A 10110ABCDEFG
08:11:11 – 08:11:12
HOST–>AU
:A 10110ABCDEFG
08:05:08 – 08:05:09
AU–>HOST
:A 10210ABCDEFG
08:05:00 – 08:05:01
HOST–>AU
?
08:04:10 – 08:04:11
AU–>HOST
:A 10210ABCDEFG
08:03:00 – 08:03:01
HOST–>AU CHAR. ERR
:A 05105ABCDEFGHIJKL
A0101010101010101010
10104
Communication start and end time points
Communication mode and error message
Communication text example
2 - 77
Page 90

2.6.4 Cumulative Instrument Operation List
1. Routine; Routine sample 3. Cont.; Control serum
2. Calib.; Calibration solution 4. STAT; Stat sample
Total number of tests
Number of analyzed samples
2 - 78
Page 91

2 - 79
Page 92

3. FLOW PATH DIAGRAMS
3.1 List of Solenoid Valves.............................................................................................3-1
3.2 Overall Piping Diagramm..........................................................................................3-2
3.3 Flow Rate at Each Location .....................................................................................3-3
3.4 WASH ...................................................................................................................3-4
3.4.1 Details of WASH Processing......................................................................3-5
3.5 Carry-over Evasion Function....................................................................................3-6
3 - 0
Page 93

3. FLOW PATH DIAGRAMS
3.1 List of Solenoid Valves
SV No.
SV 1 2-way A2-5617 Open 24 V DC CKD Water supply intake 713-0321
SV 2 2-way HB-11-X0185 Open 24 V DC CKD Sample syringe 713-1059
SV 3 2-way HB-11-X0185 Open 24 V DC CKD Reagent syringe 713-1059
SV 4 2-way HB-11-X0193 Open 24 V DC CKD Incubation bath water intake 713-1379
SV 5 2-way HB-11-X0193 Open 24 V DC CKD
SV 6 2-way HB-11-X0193 Open 24 V DC CKD
SV 8 2-way HB-11-X0193 Open 24 V DC CKD
SV 9 2-way HB-11-X0193 Open 24 V DC CKD
SV 10 2-way HB-11-X0193 Open 24 V DC CKD
SV 11 3-way A2-5619 – 24 V DC CKD
SV 12 2-way NTV-2-HN Open 24 V DC Takasago
SV 13 2-way NTV-2-HN Open 24 V DC Takasago
SV 14 3-way NRV – 24 V DC Takasago Vacuum tank (evacuation) 713-0332
SV 15 2-way A2-5618 Open 24 V DC CKD
SV 16 2-way MTV-21-SM6M Open 24 V DC Takasago ISE syringe 713-0317
SV 17 2-way MTV-21-SM6M Open 24 V DC Takasago ISE sample discharge 713-0324
SV 18 2-way MTV-21-SM6M Open 24 V DC Takasago ISE and REF aspiration 713-0325
2-way/
3-way
Type
Open/Close
When
Energized
Voltage Maker Application Part No.
Stirring and washing water
supply
Reagent probe outside
washing water supply
Sample probe outside
washing water supply
Rinsing and nozzle tip
washing water supply
Rinsing and cell blank water
supply
Rinsing and cell washing
water supply
Waste solution discharge
(low concentration)
Waste solution discharge
(high concentration)
Incubation bath water
discharge
713-1379
713-1379
713-1379
713-1379
713-1379
707-0290
713-0331
713-0331
713-0320
SPV 1 Pinch
valve
SD10BA-2A-00T Open 24 V DC Advance ISE aspiration 707-0327
3 - 1
Page 94

SV4
SV10
SV9
SV6
SY2
SY3
SY16
SV5
SV8
3 - 2
Page 95

3.3 Flow Rate at Each Location
Location
S probe Outside
washing
Inside
washing
R probe Outside
washing
Inside
washing
Stirring and washing
Rinsing High
concentration
waste solution
probe
Low
concentration
waste solution
probe
Cell blank washing
Nozzle tip washing
Incubation bath flow
rate
Returning from water
supply pump
Flow rate through lamp 0.30 or more
Flow Rate
mL/min
270 ± 30
35 ± 5
270 ± 30
120 ± 20
320 ± 30
90 ± 10
90 ± 10
450 ±150
(µL/0.8 sec)
140 ± 15
3.7 ± 0.2
(L/min)
(L/min)
Remarks
SV unit restrictor ø1.5/tube L = 80, restrictor ø1.0/tube L = 650
Tube = Tygon ø3.17 × ø6.35
SV unit restrictor ø1.5/tube L = 80, restrictor ø1.0/tube L =820
Tube = Tygon ø3.17 × ø6.35
SV unit restrictor ø1.5/tube L = 80, restrictor ø1.15/tube L =
1000 Tube = Tygon ø3.17 × ø6.35
SV11/branch tube/tube L = 395/high
concentration waste solution probe
Tube = Tygon ø2.38 × ø3.96
Same as above
SV unit restrictor ø1.5/tube A = 580, specials/tube B = 500
Tube A = Tygon ø3.17 × ø6.35, tube B = Silastic tube ø1.0 ×
ø3.0
SV unit restrictor ø1.5/tube L = 1080
Tube = Tygon ø2.38 × ø3.96
After pouring water into the incubation bath with cells set, flow
velocity on water surface should be measured with cells
removed (in sec/circumference).
Measure with the lamp coolant tube disconnected at the lamp
inlet.
Restrictor ø1.0
3 - 3
Page 96

3.4 WASH
3.4.1 Details of WASH Processing
START
1)
Operator's
judgment
2)
Made
Abnormal
Unnecessary
Maintenance
screen
WASH necessary?
Necessary
"Execution" input
WASH
"STOP" input
Operation check
Normal
Function : Washing of each mechanism
Necessary : WASH (cell) 15 min 20 sec
WASH (ISE) 5 min 44 sec
WASH (All) 20 min 20 sec
3)
Alarm indication
4)
FD (alarm logging)
END
Step No. Contents of Processing Reference Document
1) Start from MAINTENANCE screen Screen specifications
2) See next page
3)
4)
When mechanism operates, its operation is checked. If abnormal,
alarm is indicated.
Alarm will be saved into the alarm FD.
Screen specifications
Alarm code table
FD specifications
Remarks: (1) Start method and resulting action
(a) Specify DAILY.
All cells, probes (S and R), stirrer and ISE mechanism are washed.
(b) Specify reaction cell.
(c) Specify ISE.
The ISE mechanism is washed.
NOTE: Specification of ISE for WASH
when without ISE mechanism...............Input cannot be made from the screen.
Specification of all mechanisms
when without ISE mechanism...............Operation is carried out according to "cell"
specification.
3 - 4
Page 97

3 - 5
Page 98

3.5 Carry-over Evasion Function
(1) Outline
The carry-over evasion function is provided to prevent occurrence of inaccurate data due
to sample carry-over in photometry assay and ISE tests.
This function works on routine samples alone and does not work on calibrator and control
samples. Carry-over is evaded by changing the measuring sequence among the reagents
or samples, which may cause carry-over, or by execution of washing. The kinds of
evasion/washing are listed below.
(a) Evasion of reagent carry-over due to reagent probe and washing for evasion
(b) Evasion of carry-over between reagents due to cell and washing for evasion
(c) Evasion of sample carry-over due to sample probe and washing for evasion
(a) Evasion of reagent carry-over due to reagent probe and washing for evasion
(I) Condition for carry-over evasion
When the evasion of reagent carry-over due to reagent probe is set, it is
attempted at first by changing the reagent sampling sequence (test sequence).
If this method is unusable, carry-over evasion by washing is executed. That is,
when the sequence of pipetting reagents (R1 to R3) with the reagent probe
matches the specified pattern, carry-over is prevented by (i) to (iii) below. In (ii)
and (iii), throughput is degraded.
(i) For avoiding the relevant pattern, channel registration is changed for a
different test within the test sequence of the same sample.
(ii) When step (i) cannot be taken, a channel is registered after reagent probe
washing cycle.
(iii) Cell is made blank and the system waits till deviation from the specified
pattern.
(II) Method of carry-over evasion
The reagent probe is washed by aspirating detergent (detergent 1 or 2) or
system water (distilled water for washing the inside of probe) and discharging it
into a cell. At this time, the stirring rod is also washed in that cell.
(III) Carry-over evasion-specified pattern
The patterns, for which the evasion of carry-over between reagent types is
specified, are listed below.
"→ ALL" indicates that evasion is required in all types of R1, R2 and R3.
ALL represents 3 reagent types for 3-reagent system, and 2 reagent types for 2reagent system.
R3 → R3, R3 → R2, R3 → R1,
R2 → R3, R2 → R2, R2 → R1,
R1 → R3, R1 → R2, R1 → R1
(IV) Registration of carry-over evasion-specified pattern
Up to 40 kinds of patterns, for which the evasion of carry-over due to the
reagent probe is specified, can be registered.
3 - 6
Page 99

(V) Probe washing cycle
350
µ
L)
Probe washing employs one (1) machine cycle.
Within one machine cycle, the specified detergent (system water) placed on the
reagent disk is aspirated in the specified volume and discharged into the cell at
the same timing as for reagent aspiration and discharge.
(VI) Measure for ISE
Of the reagents for ISE, the internal standard solution and diluent are applicable
to carry-over evasion. Carry-over evasion cannot be specified for reference
electrode solution.
(VII) Specification from screen
From the screen, the following need be specified; a carry-over giving test and
its reagent type (R1, R2, R3), a carry-over receiving test and its reagent type
(R1, R2, R3), detergent set position on the reagent disk and detergent volume.
An example of specification is shown below.
[GPT] [1] [LDH] [4] [38] [350]
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
Carryover
giving test
(CH1 to 36)
Reagent
type
(1:R1
2:R2
3:R3)
Carryover
receiving
test
(CH1 to
Reagent
type
(1:R1
2:R2
3:R3)
36, ISE
Detergent set position
(1 to 39...ISE excluded
1 to 36,39...ISE
allowed
W1..........System
water)
ALL)
Detergent
discharge
volume
(50 µL to
(VIII) Examples of evading procedure
Examples of carry-over evading procedure are shown below.
A to C represent tests, and W stands for washing.
Example of Carry-over
Evasion-specified Pattern
A
A
A
R3
R3
R3
B
R2
B
R3
B
R1
A
R3
A
R3
A
R3
Example of Evading Procedure
C
(example of succeeding in evasion by
R2
change in channel registration)
W B
W B
R3
R1
3 - 7
Page 100

(b) Evasion of carry-over between reagents due to cell and washing for evasion
(I) Condition for carry-over evasion
The cell used for analysis of the specified test is not used for analysis in the
next round (after 48 cycles). Instead, it is washed for prevention of carry-over.
(II) Method of carry-over evasion
Cell is washed by aspirating detergent (detergent 1 or 2) or system water and
discharging it into a cell. At this time, washing is facilitated by stirring.
Carry-over evasion of cell is also effected during S. Stop. After completion of
washing all cells, auto stop occurs.
When stop status is set for any cause other than auto stop, cell washing for
evading carry-over due to the previous operation will not be resumed in start
from the standby status.
Execution of cell washing degrades throughput.
(III) Registration of carry-over evasion-specified pattern
Up to 10 kinds of patterns, for which the evasion of carry-over due to cell is
specified, can be registered.
(IV) Specification from screen
From the screen, the following need be specified; a carry-over giving test,
detergent set position on the reagent disk and detergent volume.
An example of specification is shown below.
[TG] [38] [350]
↑ ↑ ↑
Carryover
giving test
(CH1 to 36)
Detergent set position
(1 to 39...ISE excluded
1 to 36,39...ISE allowed
W1…System water)
Detergent discharge
volume
(50 µL to 350 µL)
(V) Cell washing cycle
When detergent discharge volume exceeds 350 µL, detergent is discharged by
using 2 timings among the 3 timings (R1, R2, R3) for reagent aspiration and
discharge in one cycle.
(VI) Example of evading procedure
An example of carry-over evading procedure is shown below.
A to E represent tests, and W stands for washing.
Carry-over Evasion-specified Test
A
a-th cycle............ B A C.......
(a -1)th cycle....... D W E.......
Example of Evading Procedure
3 - 8
 Loading...
Loading...