HIKVISION DS-9564NI-ST, DS-9508NI-ST, DS-9516NI-ST, DS-9532NI-ST, DS-9508NI-RT User Manual
...Page 1

Network Video Recorder
User Manual
UD.6L0202D1182A01
Page 2

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
1
Hikvision® Network Digital Video Recorder User Manual
This manual, as well as the software described in it, is furnished under license and may be used or copied only in
accordance with the terms of such license. The content of this manual is furnished for informational use only, is
subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by Hikvision Digital Technology
Co., Ltd. (Hikvision). Hikvision assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may
appear in the book.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written
permission of Hikvision.
HIKVISION MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
REGARDING THE HIKVISION SOFTWARE. HIKVISION DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR
MAKE ANY REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE OF THE
HIKVISION SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY,
CURRENTNESS, OR OTHERWISE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE RESULTS AND PERFORMANCE OF
THE HIKVISION SOFTWARE IS ASSUMED BY YOU. THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES IS
NOT PERMITTED BY SOME STATES. THE ABOVE EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
IN NO EVENT WILL HIKVISION, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES, OR AGENTS BE LIABLE
TO YOU FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR INDIRECT DAMAGES (INCLUDING
DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS
INFORMATION, AND THE LIKE) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE HIKVISION
SOFTWARE EVEN IF HIKVISION HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR
CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Page 3

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
2
Regulatory information
FCC information
FCC compliance: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a digital device, pursuant
to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
FCC conditions
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
EU Conformity Statement
This product and - if applicable - the supplied accessories too are marked with "CE" and comply therefore with the
applicable harmonized European standards listed under the Low Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC, the EMC
Directive 2004/108/EC.
2002/96/EC (WEEE directive): Products marked with this symbol cannot be disposed of as unsorted municipal
waste in the European Union. For proper recycling, return this product to your local supplier upon the purchase of
equivalent new equipment, or dispose of it at designated collection points. For more information see:
www.recyclethis.info.
2006/66/EC (battery directive): This product contains a battery that cannot be disposed of as unsorted municipal
waste in the European Union. See the product documentation for specific battery information. The battery is
marked with this symbol, which may include lettering to indicate cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), or mercury (Hg). For
proper recycling, return the battery to your supplier or to a designated collection point. For more information see:
www.recyclethis.info.
Page 4

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
3
Preventive and Cautionary Tips
Before connecting and operating your NVR, please be advised of the following tips:
• Ensure unit is installed in a well-ventilated, dust-free environment.
• Unit is designed for indoor use only.
• Keep all liquids away from the NVR.
• Ensure environmental conditions meet factory specifications.
• Ensure unit is properly secured to a rack or shelf. Major shocks or jolts to the unit as a result of dropping it
may cause damage to the sensitive electronics within the unit.
• Use the NVR in conjunction with an UPS if possible.
• Power down the unit before connecting and disconnecting accessories and peripherals.
• A factory recommended HDD should be used for this device.
• Improper use or replacement of the battery may result in hazard of explosion. Replace with the same or
equivalent type only. Dispose of used batteries according to the instructions provided by the battery
manufacturer.
Page 5
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
4
Thank you for purchasing our product. If there is any question or request, please do not hesitate to contact dealer.
This manual is applicable to the models listed in the following table.
Series
Model
Type
9500NI-ST
DS-9508NI-ST
DS-9516NI-ST
DS-9532NI-ST
DS-9564NI-ST
Network Video Recorder
9500NI-RT
DS-9508NI-RT
DS-9516NI-RT
DS-9532NI-RT
DS-9564NI-RT
Network Video Recorder
8500NI-ST
DS-8508NI-ST
DS-8516NI-ST
DS-8532NI-ST
DS-8564NI-ST
Network Video Recorder
Page 6

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
5
Product Key Features
General
Connectable to the network cameras, network dome and encoders.
Connectable to the third-party network cameras like ACTI, Arecont, AXIS, Bosch, Brickcom, Canon,
PANASONIC, Pelco, SAMSUNG, SANYO, SONY, Vivotek and ZAVIO, and cameras that adopt
ONVIF or PSIA protocol.
Each channel supports dual-stream.
Up to 64 network cameras can be added.
Independent configuration for each channel, including resolution, frame rate, bit rate, image quality,
etc.
The quality of the input and output video is configurable.
HDD Management
Up to 8 SATA hard disks, 8 network disks (8 NAS disks, or 7 NAS disks+1 iSCSI disk) and 1 eSATA
disk can be connected, each disk with a maximum of 4TB storage capacity.
Support RAID0, RAID1, RAID5, RAID10 storage scheme. And 8 virtual disks can be
configured.(Only for DS-9500NI-RT series NVR)
Support eSATA disk for recording or backup.
Support S.M.A.R.T. and bad sector detection. (Not supported with DS-9500NI-RT series NVR.)
HDD group management.
Support HDD standby function.
HDD property: redundancy, read-only, read/write (R/W).
HDD quota management; different capacity can be assigned to different channel.
Recording and Capturing
Holiday recording schedule configuration.
Cycle and non-cycle recording mode.
Multiple recording types: manual, continuous, alarm, motion, motion | alarm, motion & alarm.
8 recording time periods with separated recording types.
Pre-record and post-record for alarm, motion detection for recording or capture, and pre-record time
for schedule and manual recording.
Searching record files and captured pictures by events (alarm input/motion detection).
Locking and unlocking record files.
Local redundant recording and capturing.
Manual capturing and continuous capturing are supported.
Backup
Support NTFS and FAT32 formatted backup devices.
Export data by USB or eSATA devices.
Management and maintenance of backup devices.
Either Normal or Hot Spare working mode is configurable to constitute an N+1 hot spare system.
Alarm and Exception
Configurable arming time of alarm input/output.
Alarm for video loss, motion detection, tampering, abnormal signal, illegal login, network
Page 7

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
6
disconnected, IP confliction, abnormal record/capture, video signal exception, resolution mismatch,
HDD error, and HDD full, etc.
Alarm triggers full screen monitoring, audio alarm, notifying surveillance center, sending email and
alarm output.
Automatic restore when system is abnormal.
Network Functions
2 self-adaptive 10M/100M/1000M network interfaces, with working modes configurable:
multi-address, load balance, network fault tolerance, etc.
IPv6 is supported.
TCP/IP protocol, PPPoE, DHCP, DNS, DDNS, NTP, SADP, SMTP, SNMP, NFS, UPnP, and iSCSI
are supported.
TCP, UDP and RTP for unicast.
Auto/Manual port mapping by UPnP.
Remote web browser access by HTTPS ensures high security.
Remote reverse playback through RTSP.
Support accessing by the platform via ONVIF.
Remote search, playback, and download, lock/unlock of record files, support breakpoint resume.
Remote parameters setup; remote import/export of device parameters.
Remote viewing of the device status, system logs and alarm status.
Remote keyboard operation.
Remote HDD formatting and program upgrading.
Remote system restart and shutdown.
RS-232, RS-485 transparent channel transmission.
Alarm and exception information can be sent to the remote host.
Remotely start/stop recording.
Remotely start/stop alarm output.
Remote PTZ control.
Remote JPEG capture.
Embedded WEB server.
Other Functions
Control via mouse, remote control and special keyboard.
Three-level user management; admin user is allowed to create many operating accounts and define
their operating permission, which includes the limit to access any channel.
Powerful recording and search for logs of operation, alarm, exceptions and information.
Import/export of device configuration files.
Development Scalability
SDK for Windows and Linux system.
Source code of application software for demo.
Development support and training for application system.
Page 8

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
7
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Product Key Features .............................................................................................................................. 5
Chapter 1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................. 10
1.1 Front Panel .................................................................................................................................... 11
1.2 Rear Panel ..................................................................................................................................... 12
1.3 Starting and Shutting Down Your NVR ......................................................................................... 13
Chapter 2 Network Parameters Configuration ........................................................................................... 14
Chapter 3 Getting Started ............................................................................................................................ 16
3.1 Plug-in Control Installation ........................................................................................................... 17
3.2 User Login ..................................................................................................................................... 18
3.3 Camera Management ..................................................................................................................... 19
3.3.1 Quick Adding of IP Cameras....................................................................................... 19
3.3.2 Manually Adding IP Cameras ..................................................................................... 19
Chapter 4 Live View ..................................................................................................................................... 21
4.1 Operations in Live View ................................................................................................................ 22
4.1.1 Start Live View ........................................................................................................... 23
4.1.2 Live View Control ....................................................................................................... 23
4.1.3 Stop Live View ............................................................................................................ 23
4.2 Image Parameters Configurations .................................................................................................. 24
Chapter 5 PTZ Control ................................................................................................................................ 25
5.1 Configuring RS-485 ...................................................................................................................... 26
5.2 PTZ Control in Live View ............................................................................................................. 27
5.2.1 PTZ Control Panel ...................................................................................................... 27
5.2.2 Setting a Preset ............................................................................................................ 27
5.2.3 Calling a Preset ........................................................................................................... 28
Chapter 6 Recoding and Capturing Settings .............................................................................................. 29
6.1 Manual Recording and Capturing .................................................................................................. 30
6.1.1 Manual Recording ....................................................................................................... 30
6.1.2 Manual Capturing ....................................................................................................... 30
6.2 Schedule Recording and Capturing ............................................................................................... 31
6.3 Holiday Recording and Capturing ................................................................................................. 33
Chapter 7 Playback ...................................................................................................................................... 34
7.1 Playing Back Record Files ............................................................................................................ 35
7.2 Video Clips .................................................................................................................................... 37
7.3 Capturing Image and Download .................................................................................................... 38
7.4 Backup ........................................................................................................................................... 39
7.4.1 One-touch Backup....................................................................................................... 39
7.4.2 Remote Backup ........................................................................................................... 39
7.5 Hot Spare Device Backup.............................................................................................................. 41
7.5.1 Setting Hot Spare Device ............................................................................................ 41
7.5.2 Setting Working Device .............................................................................................. 41
7.5.3 Managing Hot Spare System ....................................................................................... 42
Chapter 8 Alarms Settings ........................................................................................................................... 44
Page 9

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
8
8.1 Configuring Alarm Input ............................................................................................................... 45
8.2 Configuring Alarm Output............................................................................................................. 48
8.3 Configuring Motion Detection ...................................................................................................... 49
8.4 Configuring Video Loss ................................................................................................................. 51
8.5 Configuring Tamper-proof ............................................................................................................. 52
8.6 Configuring Exceptions ................................................................................................................. 53
Chapter 9 Network Configuration ................................................................................................................ 54
9.1 Basic Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 55
9.2 PPPoE Settings .............................................................................................................................. 56
9.3 DDNS Settings .............................................................................................................................. 57
9.4 NTP Settings .................................................................................................................................. 60
9.5 Email Settings ............................................................................................................................... 61
9.6 Port Settings .................................................................................................................................. 62
9.7 SNMP Settings .............................................................................................................................. 63
9.8 NAT Settings ................................................................................................................................. 64
9.8.1 UPnPTM ....................................................................................................................... 64
9.8.2 Manual Mapping ......................................................................................................... 65
9.9 HTTPS Settings ............................................................................................................................. 67
9.10 Remote Alarm Host Settings ......................................................................................................... 69
9.11 Multicast Address Settings ............................................................................................................ 70
Chapter 10 Camera Settings ......................................................................................................................... 71
10.1 Channel Display Settings .............................................................................................................. 72
10.2 Text Overlay .................................................................................................................................. 73
10.3 Privacy Mask ................................................................................................................................. 74
10.4 Video and Continuous Capture Parameter Settings ....................................................................... 75
10.4.1 Video Parameter Settings ............................................................................................ 75
10.4.2 Continuous Capture Parameters Settings .................................................................... 76
Chapter 11 RAID Configuration .................................................................................................................. 77
11.1 Configuring Array and Logical Disk ............................................................................................. 78
11.1.1 One-touch Configuration ............................................................................................ 78
11.1.2 Manually Creating Array and Logical Disk ................................................................ 80
11.2 Rebuilding Array ........................................................................................................................... 84
11.2.1 Automatically Rebuilding Array ................................................................................. 84
11.2.2 Manually Rebuilding Array ......................................................................................... 85
11.3 Repairing Logical Disk .................................................................................................................. 86
11.4 Deleting Array / Logical Disk ....................................................................................................... 87
11.4.1 Deleting the Logical Disk ........................................................................................... 87
11.4.2 Deleting the Array ....................................................................................................... 87
11.5 Upgrading RAID Adapter .............................................................................................................. 89
Chapter 12 HDD Settings .............................................................................................................................. 90
12.1 Local HDD Settings ...................................................................................................................... 91
12.1.1 Disk Initializing .......................................................................................................... 91
12.1.2 Disk Property Management ......................................................................................... 91
12.1.3 HDD Sleeping ............................................................................................................. 92
Page 10

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
9
12.2 Network HDD Settings .................................................................................................................. 93
12.3 Managing eSATA .......................................................................................................................... 94
Chapter 13 Local Configuration ................................................................................................................... 96
Chapter 14 Maintenance ............................................................................................................................... 98
14.1 View Device Information .............................................................................................................. 99
14.2 Time Settings ............................................................................................................................... 100
14.3 Log Search................................................................................................................................... 101
14.4 Rebooting NVR ........................................................................................................................... 102
14.5 Restoring Default Settings ........................................................................................................... 103
14.6 Upgrade Remotely ....................................................................................................................... 104
14.7 Importing/Exporting Configuration File ...................................................................................... 105
14.7.1 Importing Configuration File .................................................................................... 105
14.7.2 Exporting Configuration File .................................................................................... 105
14.8 RS-232 Configuration ................................................................................................................. 106
14.9 Account Management .................................................................................................................. 107
Appendix ..................................................................................................................................................... 109
Glossary ................................................................................................................................................. 110
Troubleshooting ................................ ................................ ................................................................ ..... 111
List of Compatible IP Cameras ................................................................................................ .............. 115
List of Hikvision IP Cameras ......................................................................................................... 115
List of Third-party IP Cameras ....................................................................................................... 118
Page 11

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
10
Chapter 1 Introduction
Page 12
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
11
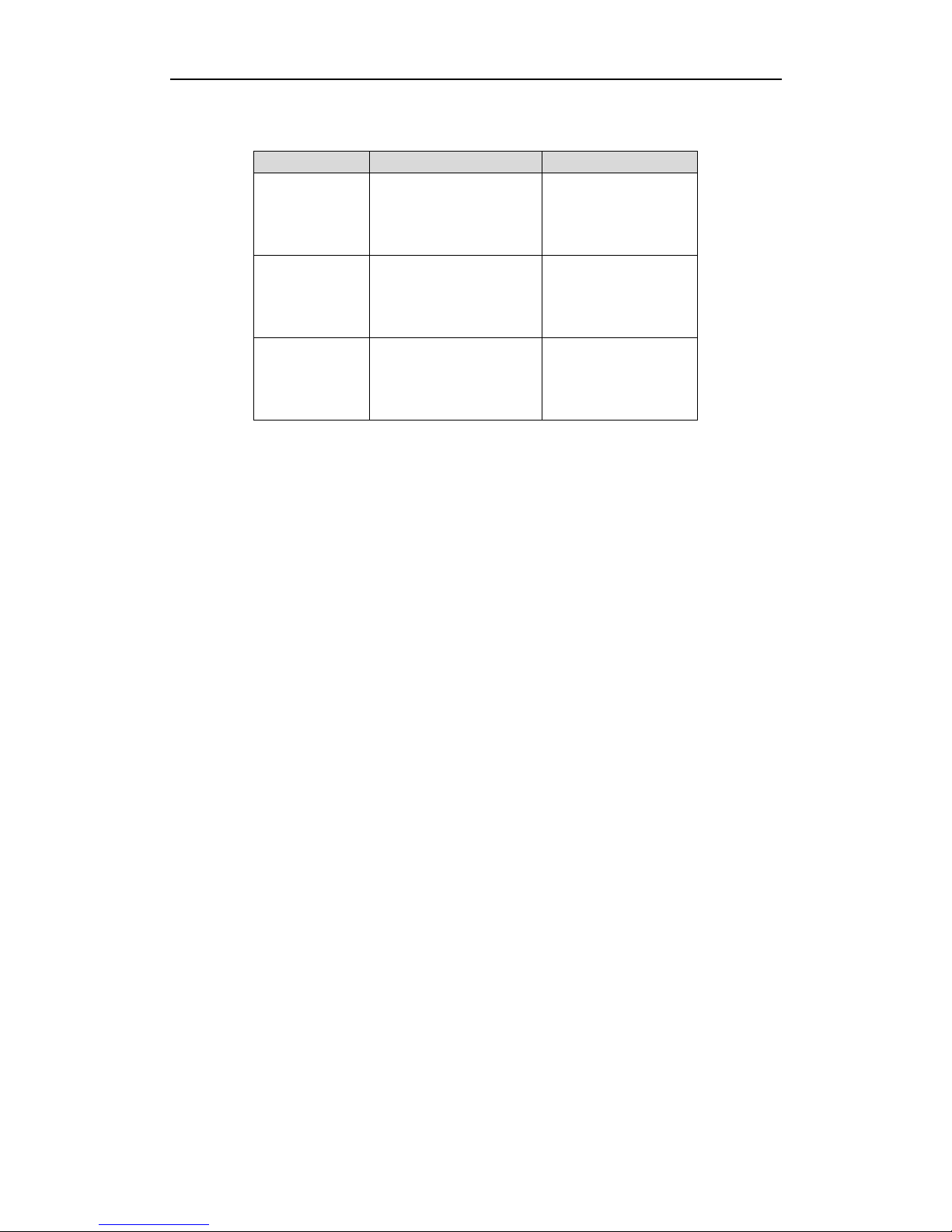
1.1 Front Panel
Figure 1. 1 DS-9500NI-ST/RT
Figure 1. 2 DS-8500NI-ST
Table 1. 1 Description of Front Panel
No.
Name
Description
1
Status
LED
Indicators
Power
Turning red indicates power is connected but the system isn’t
running; turning blue indicates power is connected and the system is
running.
Alarm
Alarm LED turns red when a sensor alarm is detected.
TX/RX
TX/RX LED flashes blue when network connection is functioning
properly.
HDD
HDD LED flashes red when data is being read from or written to
HDD.
Ready
Ready LED turns blue when NVR is functioning properly.
Backup
Backup LED flashes blue when data is being backed up.
2
Backup Button
Back up video files.
3
USB Ports
Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports for additional devices such as USB
mouse and USB Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
4
Power Button
Powers NVR on/off.
5
Channel Status Indicators
Blue indicates recording, red indicates network connection, and
purple indicates recording and network connection.
6
Front Panel Lock
(for DS-9500NI-ST&RT series)
You can lock or unlock the panel by the key.
Page 13
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
12
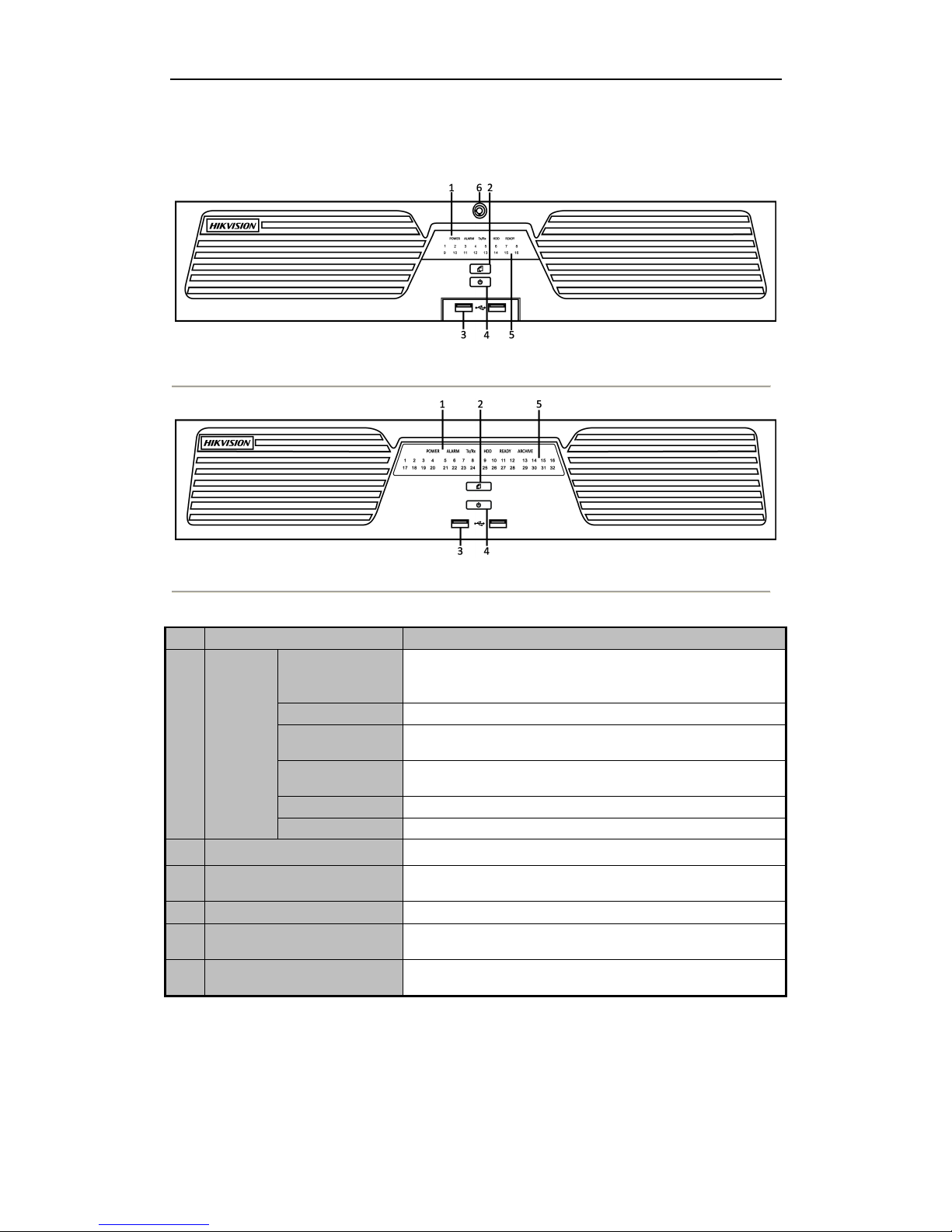
1.2 Rear Panel
Figure 1. 3 DS-9500NI-ST/RT and DS-8500NI-ST
Table 1. 2 Description of Rear Panel
No.
Item
Description
1
RS-232
Connect to RS-232 devices.
2
eSATA
Connect to external SATA HDD, DVD-R/W.
3
LAN
2 network interfaces.
4
RS-485
Connect to RS-485 devices, e.g., P/T receiver, etc. Use the T+ and T-terminals
of RS-485 interface to connect to the R+ and R- terminals of the receiver.
ALARM IN
Connector for alarm input.
ALARM OUT
Connector for alarm output.
5
GND
Grounding
6
POWER
100 ~ 240 VAC power supply
7
Power Switch
Switch for turning on/off the device.
8
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports for additional devices such as USB mouse
and USB Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
9
Termination Switch
RS-485 termination switch.
Up position is not terminated.
Down position is terminated with 120Ω resistance.
10
RESET
Press and hold it for 10 seconds to reset all parameters to factory defaults.
Note: The RS-485 interface is reserved for future use.
Page 14

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
13
1.3 Starting and Shutting Down Your NVR
Power On
If the power LED indicator on the front panel is off, please check if the power supply is plugged into an electrical
outlet and the power switch is turned on; the LED should turn red, indicating the unit is receiving power.
When the LED is red, please press the Power button on the front panel. The Power indicator will turn blue. The
unit will begin to start.
Note: When the Ready indicator turns blue, the device is powered on and works properly.
Power Off
Standard Shutdown
Press and hold the POWER button for 3 seconds, and the device will enter power-off process. When the Power
LED turns red, turn off the power switch on the rear panel.
Other Methods of Shutdown
• Shutdown with Power Switch
Please try to avoid shutting down the unit by turning off the power switch on the back panel (especially
during recording).
• Shutdown by Unplugging Power Supply
Please try to avoid shutting down the unit by unplugging power supply (especially during recording).
Note: It is highly recommended that an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) be used in conjunction with the unit.
Page 15

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
14
Chapter 2 Network Parameters
Configuration
Page 16
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
15
DS-9500/8500NI-ST and DS-9500NI-RT Series NVR is mainly used with IPC, DVS for network video storage
and playback. Network configurations are needed before operating, including: IP address, subnet mask, gateway
and port.
The factory default IP address of DS-9500/8500NI-ST and DS-9500NI-RT series NVR is 192.0.0.64.
Steps:
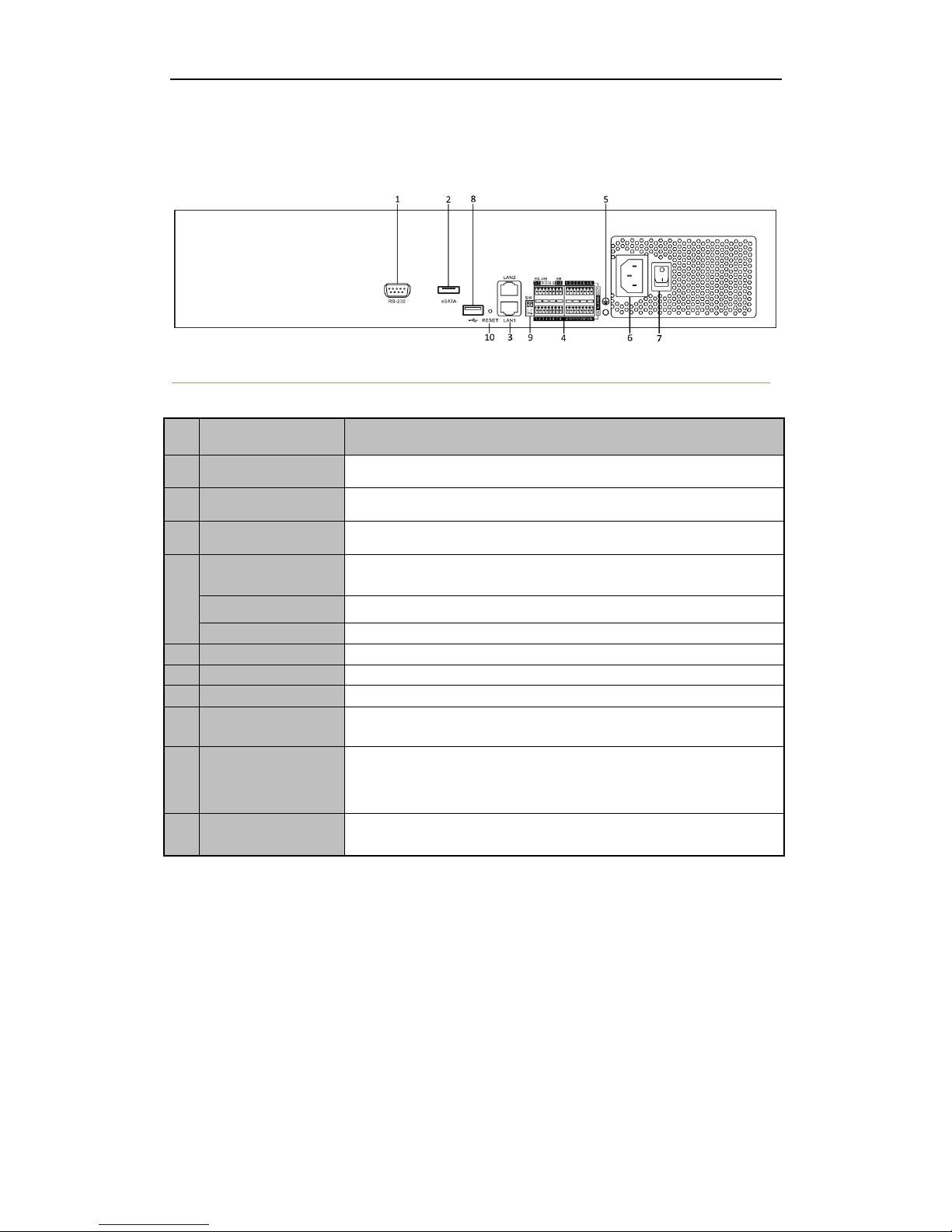
1. Open the SADP software to search online devices which in the same subnet with PC.
Start> All programms> SADP
Figure 2. 1 SADP interface
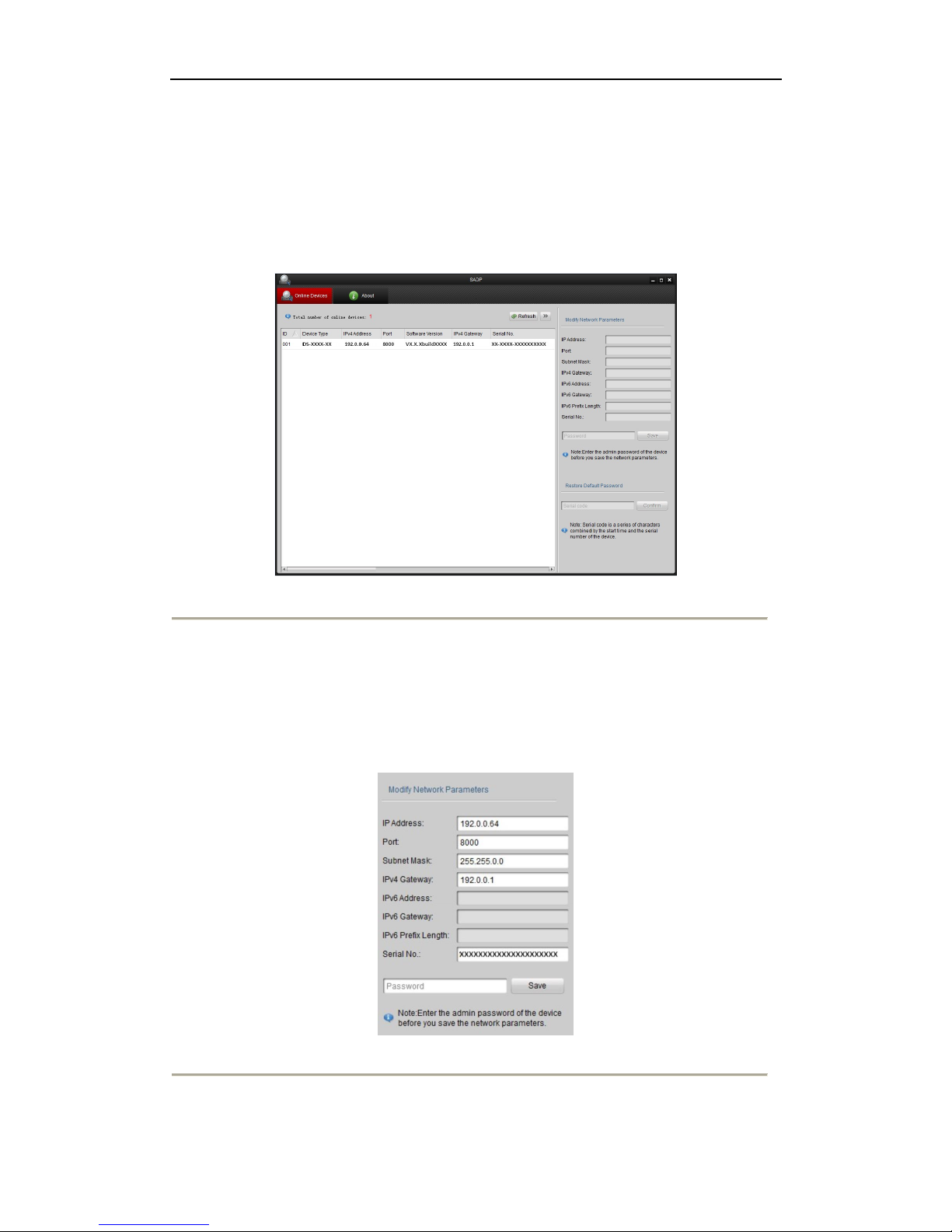
2. Edit the network parameters.
Steps:
(1) Click to select the device you want to edit.
(2) You can edit the IP Address, Port, Subnet Mask, and Gateway.
(3) Input the correct password of admin and click Save button to modify the parameters.
Note: The factory default password is 12345.
Figure 2. 2 Editing the network parameters
Page 17

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
16
Chapter 3 Getting Started
Page 18

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
17
3.1 Plug-in Control Installation
DS-8500/9500NI-ST, DS-9500NI-RT series NVR can be accessed and configured by web server. Open web
browser, input the IP address of the device and then press Enter. The system will remind you to install the Plug-in
control. After the installation, you can configure and manage the NVR remotely.
Notes:
The default IP address is 192.0.0.64.
You may use one of the following web browsers: Internet Explorer 6.0, Internet Explorer 7.0, Internet Explorer
8.0, Internet Explorer 9.0, Internet Explorer 10.0, Apple Safari, Mozilla Firefox, and Google Chrome.
The supported resolutions include 1024*768 and above.
Page 19

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
18
3.2 User Login
Steps:
1. Open web browser, input the IP address of NVR, and the web server will select the language automatically
according to the system language and maximize the web browser.
Figure 3. 1 Login Interface
On the top right corner, language is selectable between Chinese and English.
2. Input the correct user name and password, and click Login to enter live view interface, or it will pop up an
error box.
Note: The default user name is admin, and password is 12345.
Page 20

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
19
3.3 Camera Management
Purpose:
The main function of the NVR is to connect the network cameras and record the video got from it. So before you
can get a live view or record of the video, you may add the network cameras to the device. You can enter the
camera management interface by:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Management> IP Camera
Figure 3. 2 IP Camera Management Interface
3.3.1 Quick Adding of IP Cameras
DS-8500/9500NI-ST and DS-9500NI-RT series NVR provide a function of remote auto searching IP camera.
When there are supported IP cameras in the same network segment of a LAN with NVR, you may add it in one
button with default user name, password and port number.
Note: Before applying Quick Add function, please make sure that IP camera is compatible with NVR and the
default user name, password and port number are not changed.
Click Quick Add button, the online IP cameras will be listed as figure shown below:
Figure 3. 3 Quick Adding Interface
Check the checkbox of the listed cameras to select them and click the OK button to finish adding.
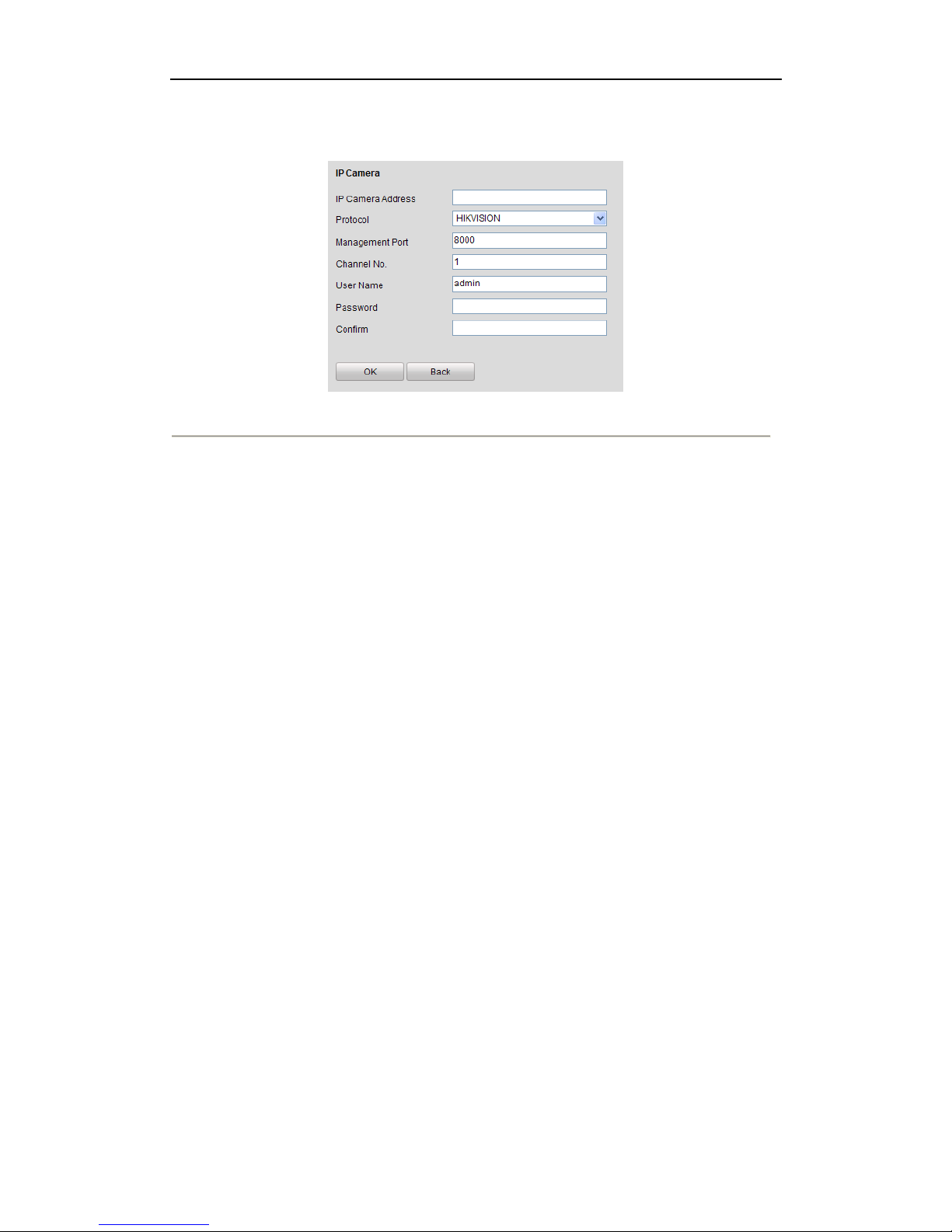
3.3.2 Manually Adding IP Cameras
Page 21
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
20
Steps:
1. Click the Add button, and the following interface will be shown:
Figure 3. 4 Manually Adding interface
2. Input the IP address or domain name of the network camera in the IP Camera Address text field, and user
name and password.
Note: Before you input the domain name of the network camera, make sure you have registered the device on
the DDNS server.
3. Click the OK button to finish adding.
And the camera and its information will be added in the list of cameras.
Page 22

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
21
Chapter 4 Live View
Page 23
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
22
4.1 Operations in Live View
Note: We take the operation of DS-9500NI-RT as the example, and other models may be different depending on
their functions.
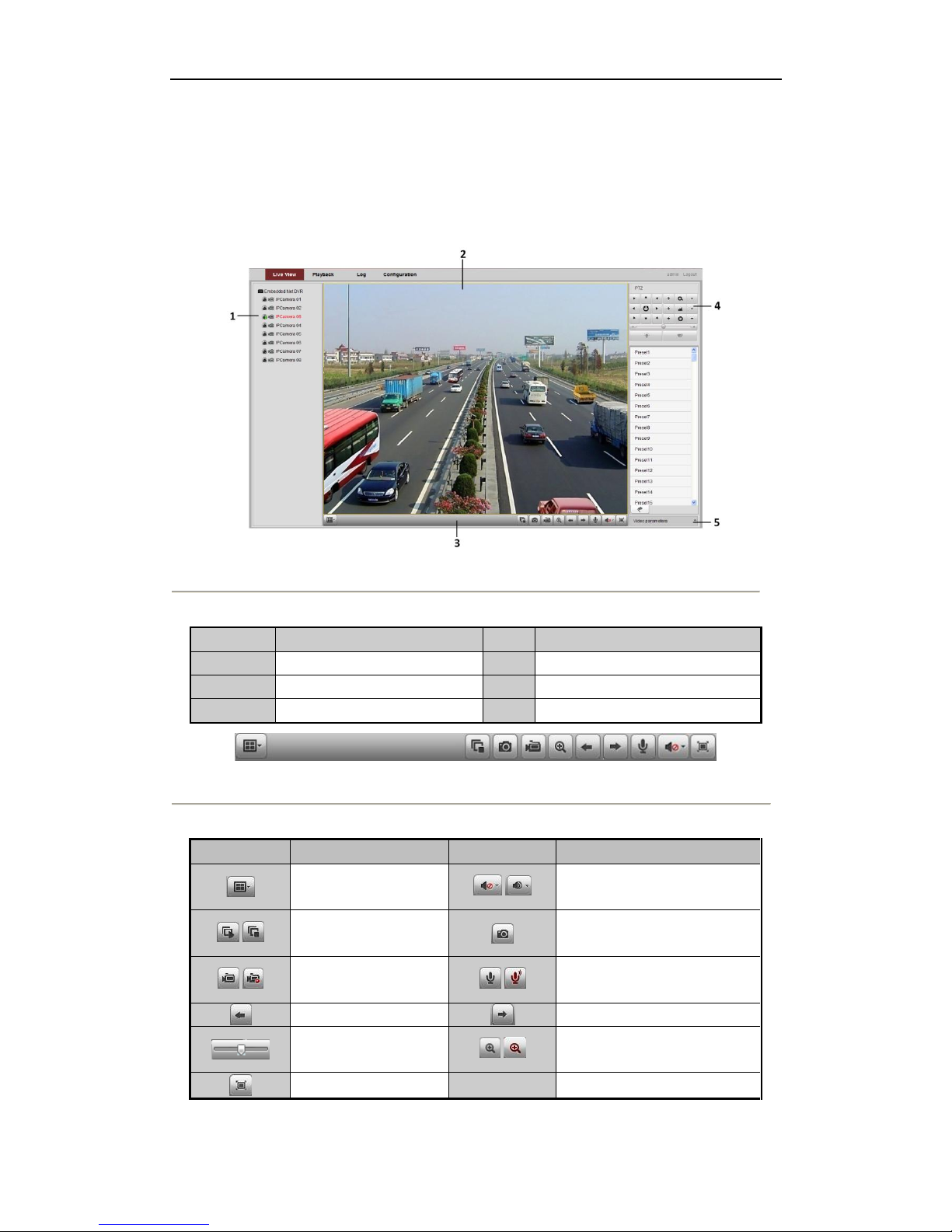
After login, the live view interface will display, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 4. 1 Live View Interface
Table 4. 1 Live View Interface Descriptions
Area
Description
Area
Description
1
Channel list
2
Live view
3
Play control
4
PTZ control
5
Video parameters configuration
Figure 4. 2 Live View Control Bar
Table 4. 2 Play Control Buttons Descriptions
Button
Description
Button
Description
Window division mode
/
Open/Close audio
/
Start/Stop all live view
Capture
/
Start/Stop all recording
/
Start/Stop two-way Audio
Previous page
Next page
Adjust volume
/
Enable/Disable digital zoom
Full Screen
Page 24

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
23
4.1.1 Start Live View
Live View by channel:
Select one window, and click on channel list or double-click the camera name to view the current camera. If
live view successful, the icon will become .
Click to switch to the next page, click to view the previous page.
Or just click and to start live view by page.
4.1.2 Live View Control
Multi-window Division
In live view mode, the windows division can be selected by clicking the button on play control area.
It supports 1, 4, 9 and 16 windows-division modes: .
The change between different windows-division modes will not stop the current live view, and the window still can
be operated.
Full-screen live view
Double click the selected window or click the button to maximize the window to full screen. Press Esc
button on your keyboard or double click again to resume.
Open/Close audio
When live view is on, select the channel, and click to open audio, and the status changes to . Drag
to adjust the audio volume.
When audio is open, click to close audio and the status will resume to .
Note: When live view with web browser, only the audio of one camera can be opened at one time.
Digital Zoom
When live view is on, click to activate digital zoom, the status will be .
Drag and draw a red rectangle to select the target area. Click the image to resume.
Click to disable digital zoom and the status will be resume to .
4.1.3 Stop Live View
Click on the playlist to stop live view, and the icon changes to .
Click to stop live view of all channels.
Page 25

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
24
4.2 Image Parameters Configurations
The Video parameters tab is folded by default; you may click to extend it. Then select the live view channel, and
adjust the Brightness, Contrast, Saturation and Hue for it.
You can click button to resume the default values.
Figure 4. 3 Video Parameters Configuration
Page 26

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
25
Chapter 5 PTZ Control
Page 27
User Manual of Network Video Recorder
26
In live view mode, you are allowed to use the PTZ control buttons to realize pan/tilt/zoom control of the camera.
Note: To realize PTZ control, the camera connected to the network must support the PTZ function or a pan/tilt
device is connected to the camera.
5.1 Configuring RS-485
Purpose:
Follow the procedure to set the parameters for PTZ. Configure the PTZ parameters should be done before you
control the PTZ camera.
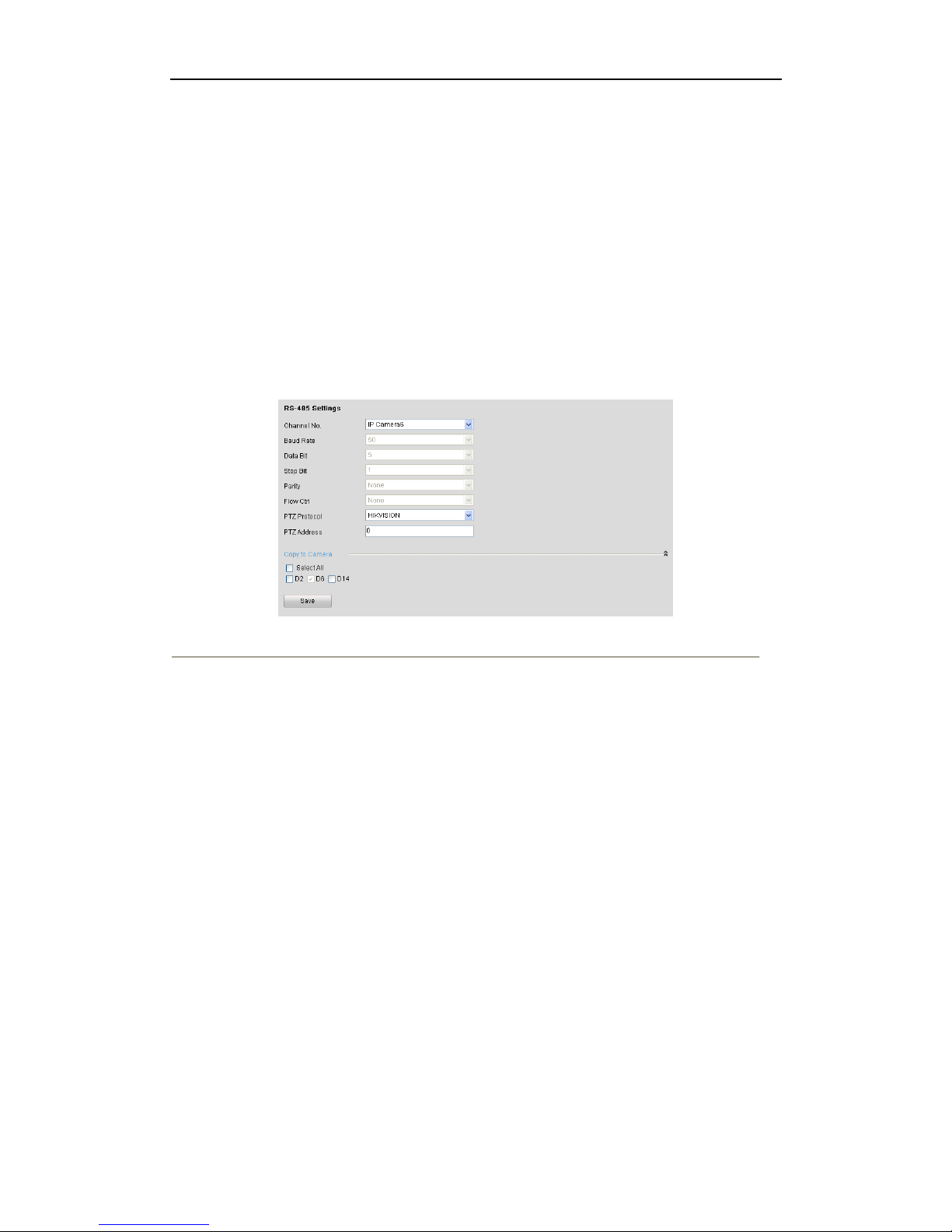
Steps:
1. Enter the RS-485 Settings interface.
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Serial Port Settings> 485 Serial Port
Figure 5. 1 RS-485 Settings Interface
2. Choose the camera for PTZ setting in the drop-down list.
3. Edit the parameters of the PTZ camera.
Note: Only PTZ protocol and PTZ address can be configured, and the parameters should be exactly the same as
the PTZ camera parameters.
4. Click Save to save the settings.
Page 28

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
27
5.2 PTZ Control in Live View
5.2.1 PTZ Control Panel
Click on the direction buttons to control the pan/tilt movements.
Figure 5. 2 PTZ Control Panel
Click the zoom/iris/focus buttons to realize lens control.
Notes:
There will be 8 direction arrows ( , , , , , , , ) in the live view window when you
click and drag the mouse in the relative positions.
For the cameras which support lens movement only, the direction buttons are invalid.
Table 5. 1 Descriptions of PTZ Control Panel
Button
Description
Zoom in/out
Focus near/far
Iris open/close
Light on/off
Wiper on/off
Adjust speed of pan/tilt movements
5.2.2 Setting a Preset
Steps:
1. In live view mode, select a preset number from the preset list.
Page 29

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
28
Figure 5. 3 Preset List
2. Use the PTZ control buttons to move the lens to the desired position.
• Pan the camera to the right or left.
• Tilt the camera up or down.
• Zoom in or out.
• Refocus the lens.
3. Click to finish the setting of the current preset.
Note: Up to 256 presets can be configured.
5.2.3 Calling a Preset
Purpose: This feature enables the camera to point to a specified preset scene when an event takes place.
For the defined preset, you can call it at any time to the desired preset scene.
In live view mode, select a defined preset from the list and click to call a preset.
Note: You can set Pattern and Patrol mode in the iVMS-4200 client software. Please refer to the User Manual of
iVMS-4200 Client Software for detailed information.
Page 30

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
29
Chapter 6 Recoding and Capturing
Settings
Page 31

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
30
6.1 Manual Recording and Capturing
Before you start:
The channel for recording and capturing should be in the live view mode.
Note: When the live view of the current channel is stopped, the recording or the capturing of this channel will be
stopped as well.
6.1.1 Manual Recording
Click icon to start recording of this channel, if the icon does not change to , it will pop up note message
“Recording failed”. When the recording is on, click to stop recording.
When multiple channels are in live view mode, you may click to start recording for all the channels, or click
to stop recording for all the channels.
Note: If the free disk space is less than 500M, the web server will stop recording automatically.
You can refer to Chapter 13 Local Configuration to edit the recording saving directory.
6.1.2 Manual Capturing
Select a live view window, click to capture image.
Note: If the free space of the saving file disk is less than 500M, capture image will be failed.
You can refer to Chapter 13 Local Configuration to edit the capture image saving directory.
Page 32

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
31
6.2 Schedule Recording and Capturing
Note: In this section, we take the record schedule procedure as an example, and the same procedure can be
applied to configuring schedule for both recording and capture. To schedule the automatic capture, you need
to choose the Capture tab in the Schedule interface.
Steps:
1. Enter Schedule Settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuraion> Camera Settings> Schedule Settings
2. Select the camera to configure the record schedule.
3. Check the checkbox of Enable Record Schedule.
Note: When NVR succeeds to connect to IP camera, it will start schedule recording which means recording
for 24*7 hours by default.
Figure 6. 1 Schedule Recording Configuration
4. Click Edit button to enter setup page.
Figure 6. 2 Schedule Editing Interface
1) Choose the day in a week to configure scheduled recording.
Page 33

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
32
2) Configure All Day or Customize Record:
If you want to configure the all-day recording, please check the All Day checkbox.
If you want to record in different time sections, check the Customize checkbox. Set the Start Time and
End Time.
Note: Up to 8 segments can be configured and each segment cannot be overlapped.
3) Select a Record Type. The record type can be Normal, Motion, Alarm, Motion & Alarm, and Motion |
Alarm.
Note: There five recording types supported, including “Normal”, “Motion Detection”, “Alarm”,
“Motion detection & Alarm”, “Motion detection | Alarm”. “&” means recording is triggered when two
situations happened together and “|” means recording is triggered when one of the situations happened.
4) Check the checkbox of Select All and click Copy to copy settings of this day to the whole week. You
can also check any of the checkboxes before the date and click Copy.
5) Click OK to save the settings and exit the Edit Schedule interface.
5. Click Advanced to configure advanced record parameters.
Configure the supported parameters which are listed below, and click OK button to save and return to the
previous interface.
Figure 6. 3 Advanced Parameters Configuration
• Enable ANR: Enable the ANR function to save the recording files in the IP camera when the
network is disconnected, and synchronize the files to the NVR when the network is resumed.
• Pre-record: The time you set to record before the scheduled time or event. For example, when an
alarm triggered the recording at 10:00, if you set the pre-record time as 5 seconds, the camera
records it at 9:59:55.
• Post-record: The time you set to record after the event or the scheduled time. For example, when
an alarm triggered the recording ends at 11:00, if you set the post-record time as 5 seconds, it
records till 11:00:05.
• Stream Type: Select the stream type of recording, Main Stream and Sub Stream are selectable.
• Record Audio: Select in the drop-down list to enable or disable audio recording.
• Expired Time: The expired time is the longest time for a record file to be kept in the HDD, if the
deadline is reached, the file will be deleted. You can set the expired time to 0, and then the file will
not be deleted. The actual keeping time for the file should be determined by the capacity of the
HDD.
6. Click Save to validate the above settings.
Page 34

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
33
6.3 Holiday Recording and Capturing
Steps:
1. Enter Holiday Settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Settings> Holiday Settings
Figure 6. 4 Holiday Settings Interface
2. Click to enter the parameters settings interface.
Figure 6. 5 Holiday Editing
3. Check the checkbox of Enable Holiday and modify the corresponding parameters, including Holiday Name, Type,
Start Date and End Date.
4. Click OK to save and exit the settings.
Page 35

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
34
Chapter 7 Playback
Page 36

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
35
7.1 Playing Back Record Files
Note: Playing back by time is only supported playing back function when you success and configure the device by
web browser. You can refer to the User Manual of iVMS-4200 to get more information of playing back by other
ways. And only single-screen playback is supported.
Steps:
1. Click Playback tab to enter playback interface.
Figure 7. 1 Playback Interface
Table 7. 1 Playback interface description
Area
Description
Area
Description
1
Channel list
2
Playback video
3
Playback Control
4
Time Line
5
Playback Status
6
Calendar
Figure 7. 2 Playback Control Bar
Table 7. 2 Playback control buttons description
Button
Description
Button
Description
/
Play/Pause Stop
Slow down
Speed up
Play by single frame
Capture
Stop All Playback
Download
Page 37

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
36
/
Video Clip
/
Open/Close audio
Full screen
2. Select a channel on the channel list. (Channel 1 is the default.)
Figure 7. 3 Channel List
3. Select a date in calendar. The date with recording files is marked as .
Figure 7. 4 Calendar
4. Click the Search button to search the matched recorded files. If there are search results, then they will be
shown in the time bar area.
Figure 7. 5 Time Bar
You can drag the time bar to select the specific time, or input the time in and click
to locate the playback point. This will start the file playback from the specified time.
Different file types are indicated with different colors.
Figure 7. 6 Video Type
5. After searching file, click to play.
When playback, the the channel number and status is displayed.
Figure 7. 7 Playback Status
Note: More types of playback are supported in iVMS-4200 client software; please refer to the User Manual of
iVMS-4200 for detailed information.
Page 38

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
37
7.2 Video Clips
Click the button on the play control bar to start video clipping, and the button will become .
Click to stop clipping. There will be note of clip succeed, and the video clips will be saved in the default
saving path. You can refer to Chapter 13 Local Configuration to configure the saving path.
Page 39

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
38
7.3 Capturing Image and Download
When playback, click to capture image.
When playback, click to pop up saving file window.
Figure 7. 8 Download Files Interface
Check the checkbox of the files and click Download to download the selected file(s). There will display the
progress of downloading ratio.
Page 40

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
39
7.4 Backup
DS-9500/8500NI-ST and DS-9500NI-RT support local one-touch backup function, and can also support backup to
USB or eSATA storage devices remotely.
7.4.1 One-touch Backup
Steps:
1. Connect the backup device to the NVR.
2. Press the BACKUP button on the front panel and the device will start to search the recording files in the
recent 24 hours, and then back up them to the default backup device.
If the size of the searched files is larger than the free space of backup device, the more recent files will be
backed up preferentially.
The backup indicator blinks when backup is on.
Note: A player will be copied to the backup device together with the backup record files.
7.4.2 Remote Backup
Note: This function is only supported by the iVMS-4200 client software.
1. Enter the File Backup interface:
Device Management> Remote Configuration> File
Figure 7. 9 File Search Interface
Page 41

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
40
2. Select Camera and Property in the drop-down menu; modify Start Time and End Time. Then click Search
button.
3. Check the checkbox in front of file name and click the Backup button.
Figure 7. 10 Backup Window
4. Select backup device in the drop-down menu, and you can check the checkbox of Backup Player.
5. Click the Start button to start backup.
Figure 7. 11 Backup in process
6. The backup ratio will display in process bar. You can click the Stop button to stop backup.
Note: If the backup device cannot be detected, please try to connect again. If it still cannot be detected, this may be
because of the compatible problem between NVR and backup device.
Page 42

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
41
7.5 Hot Spare Device Backup
Purpose:
Several devices which run on the same basis can form an N+1 hot spare system. The system consists of several
working devices and a hot spare device; when the working device fails, the hot spare device switches into
operation, thus increasing the reliability of the system.
Before you start:
At least 2 devices are online.
Note: This function is only supported by the iVMS-4200 client software.
7.5.1 Setting Hot Spare Device
Notes:
The camera connection will be disabled when the device works in the hot spare mode.
It’s highly recommended to restore the defaults of the device to ensure the normal operation afterwards after
switching the working mode of the hot spare device to normal mode.
Steps:
1. Enter the HDD settings interface.
Device Management> Remote Configuration> HDD
2. Click the N+1 Configuration button to set the hot spare function.
3. Set the Working Mode as Hot Spare Mode, click the Yes button in the pop-up message box.
Figure 7. 12 Reboot Attention
The device reboots automatically to make the change take effect.
7.5.2 Setting Working Device
Steps:
1. Enter the HDD settings interface.
Device Management> Remote Configuration> HDD
2. Click the N+1 Configuration button to set the hot spare function.
Page 43

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
42
Figure 7. 13 N+1 Configuration Interface
3. Set the Work Mode as Normal Mode (default).
4. Select the Operation type as Add Spare Device in the drop-down list and enter the IP address and password
of hot spare device.
5. Check the checkbox of Enable to enable the hot spare function.
6. Click the Yes button to save the settings.
If the working device connects to the hot spare device successfully, you can see the working status in the
N+1 configuration interface.
Figure 7. 14 Hot Spare Information
7.5.3 Managing Hot Spare System
Steps:
1. Enter the Hot Spare Settings interface of the hot spare device.
Figure 7. 15 Add Working Device
2. Select the Operation Type as Add Work Device, input the IP address in the text filed and click the Yes button
Page 44

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
43
to link the working device to the hot spare device.
You can also select the Operation Type as Delete Work Device, and
Note: A hot spare device can connect up to 32 working devices.
3. You can view the working status of the hot spare device on the Working Device Status list.
When the working device works properly, the working status of the hot spare device is displayed as Stop
Sparing.
Figure 7. 16 No Recording
When the working device gets offline, the hot spare device will record the video of the IP Camera connected
to the working device for backup, and the working status of the hot spare device is displayed as Sparing.
Figure 7. 17 Backing up
When the working device comes online, the lost video files will be restored by the record synchronization
function.
Note: The record synchronization function can be enabled for up to 1 working device at a time.
Page 45

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
44
Chapter 8 Alarms Settings
Page 46

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
45
8.1 Configuring Alarm Input
Steps:
1. Enter Alarm Input Settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Alarm Settings> Alarm Input
Figure 8. 1 Alarm Input Settings
2. Select the alarm input number and alarm type, “NO” or “NC”.
Note: “NO” is the default type. The settings will become effective after rebooting.
If you are using IP camera that is not from our manufacturer, please set this function by using its own
software.
3. Check the checkbox of Enable to enable the alarm input channel.
4. Set arming schedule.
steps:
(1) Click Arming Schedule tab to enter arm schedule settings interface.
(2) Click Edit button to set recording schedule.
Page 47

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
46
Figure 8. 2 Schedule Editing
(3) Choose the day you want to set the arming schedule.
(4) Click to set the time period for the arming schedule.
(5) (Optional) After you set the arming schedule, you can copy the schedule to other days.
(6) Click OK button to save the settings.
5. Click Linkage Method tab to set alarm actions.
Check the checkbox to select the linkage method. Full screen monitoring, audible warning, notify surveillance
center, send email, trigger channel, trigger alarm output, and PTZ linking are selectable.
Figure 8. 3 Linkage Method
Table 8. 1 Linkage Method Description
Parameters
Description
Full Screen Monitoring
Pop the image to full-screen when the event occurs.
Page 48

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
47
Parameters
Description
Audible Warning
Trigger the audible warning in the NVR locally.
Notify Surveillance Center
Send an exception or alarm signal to remote management software when an
event occurs.
Send Email
Send an email with alarm information to a user or users when an event
occurs.
Trigger Channel
The video will be recorded when the motion is detected.
Trigger Alarm Output
Trigger one or more external alarm outputs when an event occurs. Be sure
the alarm output is configured. Please refer to chapter 8.2 configuring
alarm output for detailed information.
PTZ Linking
Execute a specific PTZ action when an event occurs. Make sure you have
configured the PTZ settings. Please refer to chapter 5.1 Configuring
RS-485 for detailed information.
Page 49

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
48
8.2 Configuring Alarm Output
Steps:
1. Enter Alarm Output Settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Alarm Settings> Alarm Output
Figure 8. 4 Alarm Output Settings
2. Select alarm output number in the drop-down list.
3. Set delay time and alarm name.
4. Set arming schedule. Please refer to step 3 of Chapter 8.1 Configuring Alarm Input for detailed information.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings.
Page 50

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
49
8.3 Configuring Motion Detection
Purpose:
Follow the steps to set the motion detection parameters. In the live view mode, once a motion detection event takes
place, the NVR can analyze it and perform many actions to handle it. Enabling motion detection function can
trigger certain channels to start recording, or trigger full screen monitoring, audible warning, notify the
surveillance center and so on. In this chapter, you can follow the steps to schedule a record which triggered by the
detected motion.
Steps:
1. Enter Schedule Settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuraion> Camera Settings> Motion Detection
2. Set Motion Detection parameters.
Figure 8. 5 Enable Motion Detection Interface
Steps:
(1) Select Channel No. for motion detection recording.
(2) Check the checkbox of Enable Motion Detection.
(3) (Optional) Check the checkbox of Enable Dynamic Analysis for Motion if you want the detected
moving object got marked with rectangle in the live view.
(4) Click button to draw area, you can click it again to stop drawing. Click button if you want to
clear all areas.
(5) Drag bar to adjust the sensitivity.
Notes:
Up to 8 areas can be configured.
If you are using IP camera that from third-party manufacturer, please set this function by using its own
software.
3. Set Arming Schedule.
Page 51

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
50
Please refer to step 3 of Chapter 8.1 Configuring Alarm Input for detailed information.
4. Click tab Linkage Method to edit linkage method.
Check the checkbox to activate the linkage method; you may refer to Table 8. 1 for details of linkage
methods.
Page 52

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
51
8.4 Configuring Video Loss
Steps:
1. Enter video loss settings interface
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Settings> Video Loss
Figure 8. 6 Video Loss Settings
2. Select the channel number for video loss.
3. Check the checkbox to enable video loss detection.
4. Click Edit button to edit arming schedule. Please refer to step 3 of Chapter 8.1 Configuring Alarm Input.
5. Click tab Linkage Method to edit linkage method.
Figure 8. 7 Video Loss Linkage Method Settings
Check the checkbox to activate the linkage method; you may refer to Table 8. 1 for details of linkage
methods.
Note: This function is only available on IP cameras from our manufacturer.
Page 53

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
52
8.5 Configuring Tamper-proof
Purpose:
Trigger alarm when the lens is covered and take alarm response action(s).
Steps:
1. Enter Tamper-proof settings interface
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Settings> Tamper-proof
Figure 8. 8 Tamper-proof
2. Select the channel number for tamper-proof.
3. Check the checkbox of Enable Tamper-proof.
4. Click button to draw a detecting area, click it again to stop drawing. Click button if you want to
clear the area.
5. Drag bar to adjust the sensitivity.
6. Please refer to step 3 of Chapter 8.1 Configuring Alarm Input to set arming schedule.
7. Please refer to step 5 of Chapter 8.4 Configuring Video Loss to set linkage method.
Page 54

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
53
8.6 Configuring Exceptions
Purpose:
Exception parameters are for the alarm handling of abnormal event, which include “HDD Full”, “HDD Error”
(HDD errors or HDD not initialization), “Network Disconnected”, “IP Address Conflicted”, “Illegal Login” (user
name or password wrong), “Record / Capture Exception” and “Resolution Mismatch”.
Steps:
1. Enter exception configuration interface
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Exception
Figure 8. 9 Exceptions
Table 8. 2 Exception Parameter Descriptions
Parameter
Description
HDD Full
The HDD is full.
HDD Error
Writing HDD error or unformatted HDD.
Network Disconnected
Disconnected network cable.
IP Address Conflicted
Duplicated IP address.
Illegal Login
Incorrect user ID or password.
Record/Capture Exception
No space for saving recorded files or captured pictures.
Resolution Mismatch
The configured video input standard mismatches with the video
output of the camera.
2. Select the exception type in the drop-down list and set linkage method.
3. Click the Save button to save the settings.
Page 55

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
54
Chapter 9 Network Configuration
Page 56

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
55
9.1 Basic Configuration
Steps:
1. Enter basic configuration interface
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> TCP/IP
Figure 9. 1 Network Settings Interface
2. In the General Settings interface, you can configure the following settings: Working Mode, NIC Type, IPv4
Address, IPv4 Gateway, MTU and DNS Server.
If the DHCP server is available, you can click the checkbox of DHCP to automatically obtain an IP address
and other network settings from that server.
Note: The valid value range of MTU is 500 ~ 9676.
3. After having configured the general settings, click Save to save the settings.
Working Mode
There are two 10M/100M/1000M NIC cards provided by the NVR, and it allows the device to work in the
Multi-address, Load Balance and Net-fault Tolerance modes.
Multi-address Mode:The parameters of the two NIC cards can be configured independently. You can select
LAN1 or LAN2 in the NIC type field for parameter settings.
You can select one NIC card as default route. And then the system is connecting with the extranet and the data will
be forwarded through the default route.
Net-fault Tolerance Mode: The two NIC cards use the same IP address, and you can select the Main NIC to
LAN1 or LAN2. By this way, in case of one NIC card failure, the device will automatically enable the other
standby NIC card so as to ensure the normal running of the whole system.
Load Balance Mode: By using the same IP address and two NIC cards share the load of the total bandwidth,
which enables the system to provide two Gigabit network capacity.
Page 57

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
56
9.2 PPPoE Settings
Steps:
1. Enter PPPoE setting interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> PPPoE Settings
Figure 9. 2 PPPoE Settings
2. Check the checkbox to enable PPPoE.
3. Input the user name, password and confirm password.
4. Click Save to save the changes and reboot the device to make the parameters become effective.
If dial succeeded, the current IP address will be displayed in the blank “Dynamic IP”.
Page 58

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
57
9.3 DDNS Settings
Purpose:
Adopting DDNS function can solve the problems caused by dynamic IP.
Steps:
1. Enter DDNS settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> DDNS
Figure 9. 3 DDNS Settings
2. Check the Enable DDNS checkbox to enable this feature.
3. Select DDNS Type. Five different DDNS types are selectable: IPServer, DynDNS, PeanutHull, NO-IP and
HiDDNS.
• IPServer: Enter Server Address for IPServer.
• DynDNS:
1) Enter Server Address for DynDNS (i.e. members.dyndns.org).
2) In the NVR Domain Name text field, enter the domain obtained from the DynDNS website.
3) Enter the User Name and Password registered in the DynDNS website.
• PeanutHull: Enter the User Name and Password obtained from the PeanutHull website.
• HiDDNS:
1) The Server Address of the HiDDNS server appears as www.hik-online.com by default.
2) Enter the Device Domain Name. You can use the alias you registered in the HiDDNS server or
define a new device domain name. If a new alias of the device domain name is defined in the
NVR, it will replace the old one registered on the server. You can register the alias of the device
domain name in the HiDDNS server first and then enter the alias to the Device Domain Name in
the NVR; you can also enter the domain name directly on the NVR to create a new one.
Register the device on the HiDDNS server.
1) Go to the HiDDNS website: www.hik-online.com.
2) Click to register an account if you do not have one and use the account to
log in.
Page 59

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
58
Figure 9. 4 Register an Account
3) In the Device Management interface, click to register the device.
Figure 9. 5 Register the Device
Note: The device name can only contain the lower-case English letter, numeric and ‘-’; and it
must start with the lower-case English letter and cannot end with ‘-’.
Access the Device via Web Browser or Client Software
After having successfully registered the device on the HiDDNS server, you can access your
device via web browser or Client Software with the Device Domain Name (Device Name).
Task 1: Access the Device via Web Browser
Open a web browser, and enter http://www.hik-online.com/alias in the address bar. Alias refers to
the Device Domain Name on the device or the Device Name on the HiDDNS server.
Example: http://www. hik-online.com/nvr
Note: If you mapped the HTTP port on your router and changed it to port No. except 80, you
have to enter http://www. hik-online.com/alias:HTTP port in the address bar to access the device.
You can refer to Chapter 9.8 for the mapped HTTP port No.
Task 2: Access the devices via iVMS4200
For iVMS-4200, in the Add Device window, select and then edit the device
information.
Nickname: Edit a name for the device as you want.
Server Address: www. hik-online.com
Device Domain Name: It refers to the Device Domain Name on the device or the Device Name
on the HiDDNS server you created.
User Name: Enter the user name of the device. By default it is admin.
Password: Enter the password of the device. By default it is 12345.
Page 60

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
59
Figure 9. 6 Access Device via iVMS4200
4. Click the Save button to save and exit the interface.
Page 61

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
60
9.4 NTP Settings
Purpose:
A Network Time Protocol (NTP) Server can be configured on your NVR to ensure the accuracy of system
date/time.
Steps:
1. Enter the Network Settings interface.
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Device Parameters> Time Settings
2. Select the NTP tab to enter the NTP Settings interface, as shown in Figure 9. 7
Figure 9. 7 NTP Settings Interface
3. Check the Enable NTP checkbox to enable this feature.
4. Configure the following NTP settings:
• Interval: Time interval between the two synchronizing actions with NTP server. The unit is minute.
• NTP Server: IP address of NTP server.
• NTP Port: Port of NTP server.
5. Click Save to save the settings.
Note: The time synchronization interval can be set from1 to 10080 minutes, and the default value is 60 minutes. If
the NVR is connected to a public network, you can use a NTP server that has a time synchronization function, such
as the server at the National Time Center (IP Address: 210.72.145.44). If the NVR is setup in a private network,
NTP software can be used to establish a NTP server for time synchronization.
Page 62

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
61
9.5 Email Settings
Purpose:
The system can be configured to send an Email notification to all designated users if an alarm event is detected,
etc., an alarm or motion event is detected or the administrator password is changed.
Before configuring the Email settings, the NVR must be connected to a local area network (LAN) that maintains
an SMTP mail server. The network must also be connected to either an intranet or the Internet depending on the
location of the e-mail accounts to which you want to send notification.
Steps:
1. Enter Email settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> Email
Figure 9. 8 Email Settings
2. Configure the following Email settings:
Enable Server Authentication (optional): Check the checkbox to enable the server authentication feature.
User Name: The user account of sender’s Email for SMTP server authentication.
Password: The password of sender’s Email for SMTP server authentication.
Confirm: Repeat the password you input before.
SMTP Server: The SMTP Server IP address or host name (e.g., smtp.263xmail.com).
SMTP Port No.: The SMTP port. The default TCP/IP port used for SMTP is 25.
Enable SSL (optional): Click the checkbox to enable SSL if required by the SMTP server.
Interval: The interval refers to the time between two actions of sending attached pictures.
Attached Image(optional): Check the checkbox to enable the function of attaching image when send email.
Sender: The name of sender.
Sender’s Address: The Email address of sender.
Select Receivers: Select the receiver. Up to 3 receivers can be configured.
Receiver: The name of user to be notified. Up to 3 receivers can be modified.
Receiver’s Address: The Email address of user to be notified.
3. Click Save button to save the settings.
Page 63

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
62
9.6 Port Settings
Purpose:
The HTTP port is used for remote web browser access.
The RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol) is a network control protocol designed for use in communication
systems to control streaming media servers.
For details of HTTPS, please refer to Chapter 9.9 HTTPS Settings.
The Server port is used for the remote client software access.
Steps:
1. Enter Port settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> Port
Figure 9. 9 Port Settings
2. Edit the port number it according to the actual demand.
3. Click Save to save the settings.
Page 64

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
63
9.7 SNMP Settings
Purpose:
You can use SNMP protocol to get device status and parameters related information. By setting the Trap Address,
the device is allowed to send the alarm event and exception message to the surveillance center.
Before you start:
Please download the SNMP software and manage to receive the device information via SNMP port.
Steps:
1. Enter SNMP settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> SNMP
Figure 9. 10 SNMP Settings
2. Check the Enable SNMP v2c checkbox to enable this feature.
3. Configure the following SNMP settings:
Trap Address: IP Address of SNMP host.
Trap Port: Port of SNMP host.
4. Click to save the settings.
Page 65

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
64
9.8 NAT Settings
Purpose:
Two ways are provided for port mapping to realize the remote access via the cross-segment network, UPnP™ and
manual mapping.
9.8.1 UPnPTM
UPnP™ can permit the device seamlessly discover the presence of other network devices on the network and
establish functional network services for data sharing, communications, etc. If you want to use the UPnP™
function to enable the fast connection of the device to the WAN via a router, you should configure the UPnP™
parameters of the device.
Before you start:
To enable the UPnP™ function of the device, you must enable the UPnP™ function of the router to which your
device is connected. When the network working mode of the device is set as multi-address, the default route
address of the device should be in the same network segment as that of the LAN IP address of the router.
Steps:
1. Enter the NAT Settings interface.
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> NAT
Figure 9. 11 UPnP™ Settings Interface
2. Check the checkbox to enable UPnP™.
3. Select the Port Mapping Mode in the drop-down list, as Manual and Auto are selectable.
Task1: Auto
If you select Auto, the Port Mapping items are read-only, and the external ports are set by the router
automatically.
Task2: Manual
If you select Manual as the mapping mode, you can edit the external port on your demand.
Page 66

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
65
Figure 9. 12 Editing Port Number
Steps:
1) Click on the External Port area of the corresponding port type, and edit the port number.
2) Click other place to finish editing.
Notes:
You can use the default port No., or change it according to actual requirements.
External Port indicates the port No. for port mapping in the router.
The value of the RTSP port No. should be 554 or between 1024 and 65535, while the value of the other
ports should be between 1 and 65535 and the value must be different from each other. If multiple devices
are configured for the UPnP™ settings under the same router, the value of the port No. for each device
should be unique.
4. Click Save to save the settings.
When the port mapping succeeded, the UPnP Status will change from Not Valid to Valid.
9.8.2 Manual Mapping
If your router does not support the UPnPTM function, perform the following steps to map the port manually in an
easy way.
Before you start:
Make sure the router support the configuration of internal port and external port in the interface of Forwarding.
Steps:
1. Enter the NAT Settings interface.
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> NAT
2. Leave the Enable UPnP checkbox unchecked.
3. Edit the external port number.
Steps:
1) Click on the External Port area of the corresponding port type, and edit the port number.
2) Click other place to finish editing.
Note: The value of the RTSP port No. should be 554 or between 1024 and 65535, while the value of the
other ports should be between 1 and 65535 and the value must be different from each other. If multiple
devices are configured for the UPnP™ settings under the same router, the value of the port No. for each
device should be unique.
4. Click Save to save the settings.
Page 67

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
66
5. Enter the virtual server setting page of router; fill in the blank of Internal Source Port with the internal port
value, the blank of External Source Port with the external port value, and other required contents.
Note: Each item should be corresponding with the device port, including server port, http port, RTSP port
and https port.
Figure 9. 13 Setting Virtual Server Item
Note: The above virtual server setting interface is for reference only, it may be different due to different router
manufactures. Please contact the manufacture of router if you have any problems with setting virtual server.
Page 68

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
67
9.9 HTTPS Settings
Purpose:
HTTPS provides authentication of the web site and associated web server that one is communicating with, which
protects against Man-in-the-middle attacks. Perform the following steps to set the port number of https.
Example:
If you set the port number as 443 and the IP address is 192.0.0.64, you may access the device by inputting
https://192.0.0.64:443 via the web browser.
Steps:
1. Enter the HTTPS settings interface.
Configuration > Remote Configuration > Network Settings > HTTPS
2. Create the self-signed certificate or authorized certificate.
Figure 9. 14 HTTPS Settings
OPTION 1: Create the self-signed certificate
(1) Click the Create button to create the following dialog box.
Figure 9. 15 Create Self-signed Certificate
(2) Enter the country, host name/IP, validity and other information.
(3) Click OK to save the settings.
OPTION 2: Create the authorized certificate
(1) Click the Create button to create the certificate request.
Page 69

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
68
(2) Download the certificate request and submit it to the trusted certificate authority for signature.
(3) After receiving the signed valid certificate, import the certificate to the device.
3. There will be the certificate information after you successfully create and install the certificate.
Figure 9. 16 Installed Certificate Property
4. Check the checkbox to activate the HTTPS function.
5. Click the Save button to save the settings.
Page 70

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
69
9.10 Remote Alarm Host Settings
Purpose:
With a remote alarm host configured, the NVR will send the alarm event or exception message to the host when an
alarm is triggered. The remote alarm host must have the Network Video Surveillance software installed.
Steps:
1. Enter the Advanced settings interface.
Configuration > Remote Configuration > Network Settings > Advanced
Figure 9. 17 Advanced Settings Interface
2. Input Alarm Host IP and Alarm Host Port in the text fields.
The Alarm Host IP refers to the IP address of the remote PC on which the Network Video Surveillance
Software (e.g., iVMS-4200) is installed, and the Alarm Host Port must be the same as the alarm monitoring
port configured in the software.
3. Click the Save button to save the settings.
Page 71

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
70
9.11 Multicast Address Settings
Purpose:
The multicast can be configured to realize live view for more than 128 connections through network for the device.
A multicast address spans the Class-D IP range of 224.0.0.0 to239.255.255.255. It is recommended to use the IP
address ranging from 239.252.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
Steps:
1. Enter the Advanced settings interface, as shown in the Figure 9. 17.
Configuration > Remote Configuration > Network Settings > Advanced
2. Set Multicast IP. When adding a device to client software, the multicast address must be the same as the one
of NVR.
3. Click the Save button to save and exit the interface.
Note: The multicast function should be supported by the network switch to which the NVR is connected.
Page 72

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
71
Chapter 10 Camera Settings
Page 73

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
72
10.1 Channel Display Settings
Note: This function is only supported by IP cameras from certain manufacturers.
Steps:
1. Enter OSD settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Settings> Display Settings
Figure 10. 1 Display Settings Interface
2. Select the channel No. for Display Settings, and you can configure the Camera Name.
3. Check the corresponding checkbox to enable the function.
4. Select the Date Format, Time Format and Display Mode.
You can use the mouse to click and drag the text frame on the live view window to adjust the OSD position
5. You can check the corresponding checkbox to copy the settings to other camera(s).
6. Click Save button to save the settings.
Page 74

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
73
10.2 Text Overlay
Purpose:
You can customize the text overlay to display on the selected channel.
Steps:
1. Enter text overlay configuration inteface:
Configuration> Remote Configuraion> Camera Settings> Text Overlay
Figure 10. 2 Text Overlay Settings
2. Check the checkbox to enable the text overlay.
3. Enter the content in the textfiled.
You can use mouse to click and drag the text frame on the live view window to adjust the position.
You can check the corresponding checkbox to copy the settings to other camera.
4. Click Save button to save the settings.
Page 75

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
74
10.3 Privacy Mask
Steps:
1. Enter Privacy Mask interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Settings> Privacy Mask
Figure 10. 3 Privacy Settings
2. Select the channel number for privacy mask.
3. Check the checkbox to enable privacy mask function.
4. Click button to draw area, click it again to stop drawing. Click button to clear all areas.
5. Click Save button to save the settings.
Note:Up to 4 areas can be added.
Page 76

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
75
10.4 Video and Continuous Capture Parameter
Settings
10.4.1 Video Parameter Settings
Steps:
1. Enter Video Encoding Configuration interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuraion> Camera Settings> Video Settings
Figure 10. 4 Video Settings Interface
2. Edit the parameters and click the Save button to save the settings.
Table 10. 1 Video Parameter Settings
Items
Descriptions
Stream Type
Main Stream (Normal): Usually used for the local recording without any
event happens.
Main Stream (Event): Usually used for the local recording when the event
happens.
Sub-stream: For the remote monitoring.
Transcoding Stream: For the remote monitoring through mobile devices or
when the network bandwidth is narrow.
Video Type
Video Stream and Video & Audio
Resolution
Recording Resolution
Bitrate Type
Variable and Constant
Video Quality
Highest, Higher, Medium, Low, Lower, Lowest
Frame Rate
The number of frames per second
Page 77

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
76
10.4.2 Continuous Capture Parameters Settings
Steps:
1. Enter continuous capture settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Camera Settings> Snapshot
Figure 10. 5 Capture Settings
2. Select a channel number in the drop-down list of Channel No..
3. Edit the parameters of the corresponding channel.
Note: The interval is the time period between two capturing actions.
4. Click the Save button to save the settings.
Page 78

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
77
Chapter 11 RAID Configuration
Page 79

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
78
Notes:
This chapter is supported by DS-9500NI-RT series only.
The RAID Configuration interface is only provided in iVMS-4200 client software.
11.1 Configuring Array and Logical Disk
Purpose:
The DS-9500NI-RT is capable of realizing Redundant Array of Independent Disk, supporting RAID0, RAID1,
RAID5 and RAID10.
Before you start:
Please install the HDD(s) properly and it is recommended to use the same enterprise-level HDDs (including model
and capacity) for array creation and configuration so as to maintain reliable and stable running of the disks.
Introduction:
The DS-9500NI-RT series can store the data (such as record, picture, log information) in the HDD only after you
have created the logical disk or you have configured network HDD (refer to Chapter 11.2 Managing Network
HDD). Our device provides two ways for creating the logical disk, including one-touch configuration and manual
configuration. The following flow chart shows the process of creating logical disk.
Figure 11. 1 RAID Working Flow
11.1.1 One-touch Configuration
Purpose:
By one-touch configuration, you can quickly create the disk array and logical disk. By default, the array type to be
Page 80

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
79
created is RAID 5.
Steps:
1. Enter the HDD Management interface.
Device Management> Remote Configuration> HDD
Figure 11. 2 HDD Management Interface
2. Click the Array Configuration button to enter Array Configuration interface.
Figure 11. 3 Array Configuration Interface
You can see information of physical disks.
3. Click One-key Configuration to enter the One-key Array Configuration interface.
Note: As the default array type is RAID 5, at least 3 HDDs must be installed on you device.
Page 81

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
80
Figure 11. 4 One-key Array Configuration
4. Edit the array name in the Array text filed and click Yes button to start configuring array.
Note: If you install 4 HDDs or above for one-touch configuration, a hot spare disk will be set by default. It is
recommended to set hot spare disk for automatically rebuilding the array when the array is abnormal.
There will be note if the operation is completed.
5. You can click Array tab to view the information of the successfully created array.
Note: By default, one-key configuration creates an array and a logical disk.
Figure 11. 5 Array Settings Interface
6. Click Logical Disk tab to view the automatically created logical disk.
Note: By default, one-touch configuration adopts background initialization to initialize the RAID. By using
background initialization, the logical disk can be used immediately.
Figure 11. 6 Logical Disk Settings Interface
7. You can see the information of the logical disk in the HDD Information interface.
Note: For configuring hot spare disk manually, please refer to steps 12-14 of Chapter 11.1.2 Manually
Creating Array and Logical Disk.
11.1.2 Manually Creating Array and Logical Disk
Purpose:
You can manually create the array of RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 and RAID 10.
Note: In this section, we take RAID 5 as an example to describe the manual configuration of array and logical
disk.
Page 82

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
81
Steps:
1. Enter the HDD Management interface.
Device Management> Remote Configuration> HDD
2. Click Create Array button to enter the Create Array interface.
Figure 11. 7 Create Array Interface
3. Edit the array name in the text filed of Array; set the RAID Type to RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 10;
select the Physical Disk that you want to configure array.
Notes:
If you choose RAID 0, at least 2 HDDs must be installed.
If you choose RAID 1, 2 HDDs need to be configured for RAID 1.
If you choose RAID 5, at least 3 HDDs must be installed.
If you choose RAID 10, 4/6/8 HDDs need to be configured for RAID 10.
4. Click Yes button to create array.
Note: If the number of HDDs you select is not compatible with the requirement of the RAID level, the error
message will pop up.
5. You can click Array tab to view the successfully created array.
6. Click to select an array and click Create Logical Disk to enter the logical disk creating interface.
Note: The device supports creating at most 8 logical disks.
Page 83

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
82
Figure 11. 8 Create Logical Disk Interface
7. Edit the name of the logical disk, set the capacity for the logical disk and select the initialization type for the
logical disk.
Notes:
The remaining capacity of the array displays as a logical disk of which the status is Not Distributed.
It is recommended to create one logical disk of an array.
At least 100GB capacity must be configured for each logical disk.
There are three initialization types, including Background, Foreground and Quick.
Quick (Not Recommended): The fast initialization usually takes a short time and only initializes part of the
data of the logical disk, and cannot detect the bad sector.
Foreground (Recommended): By using foreground initialization, the logical disk will be initialized totally
and the bad sector of the hard disks can be detected and repaired. The logical disk can be used only after the
initialization is complete.
Background: The background initialization can synchronize the disks, and detect and repair the bad sector
of the disks. During the background initialization, the logical disk is allowed to be used. You can set the
speed of background initialization in the RAID adapter interface by clicking the RAID Adapter tab.
8. Click Create button to create the logical or click Cancel button to return to Array Settings interface.
9. Click Logical Disk tab to enter the Logical Disk interface. The successfully created logical disk will be listed
on the interface.
Figure 11. 9 Logical Disk Interface
10. Enter the HDD Management interface (Device Management> Remote Configuration> HDD) and the logical
Page 84

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
83
disk appears. For operation guide of initializing the logical disk, please refer to Chapter 12.1 Local HDD
Settings.
Note: When the logical disk is created in the Quick or Background type, the initialization will be done
automatically.
Figure 11. 10 HDD Information Interface
11. After the logical disk has been initialized, the status will change to Normal.
12. Enter the Physical Disk Settings interface to configure the hot standby disk.
Figure 11. 11 Physical Disk Settings Interface
13. Select a disk and click Set Hot Standby to enter hot standby interface.
Figure 11. 12 Hot Standby Interface
14. Click Yes button to finish the settings.
Page 85

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
84
11.2 Rebuilding Array
Purpose:
The working status of array includes Functional, Degraded and Offline. By viewing the array status, you can take
immediate and proper maintenance for the disks so as to ensure the high security and reliability of the data stored
in the disk array.
When there is no disk loss in the array, the working status of array will change to Normal; when the number of lost
disks has exceeded the limit, the working status of array will change to Offline; in other conditions, the working
status is Disk Loss.
When the logical disk is in Degrade status, you can restore it to Normal by array rebuilding.
11.2.1 Automatically Rebuilding Array
Purpose:
When the logical disk is in Degraded status, the device can start rebuilding the array automatically with the hot
spare disk to ensure the high security and reliability of the data.
Note: The Auto Recreation function is enabled by default.
Steps:
1. Enter the Array Settings interface. The status of the array is HDD Loss. Since the hot spare disk is configured
and Auto-rebuild function is enabled. The hot spare disk will be automatically used for array rebuilding.
Device Management> Remote Management> HDD >Array Configuration> Array
Figure 11. 13 Array Settings Interface
2. Enter the Logical Disk interface to view the rebuilding status of the logical disk.
Device Management> Remote Management> HDD >Array Configuration >Logical Disk
Figure 11. 14 Logical Disk Settings Interface
Note: If there is no hot spare disk after rebuilding, it is recommended to install a HDD into the device and set
is as a hot spare disk to ensure the high security and reliability of the array. For detailed operation guide,
please refer to steps 12-14 of Chapter 11.1.2 Manually Creating Array and Logical Disk.
Page 86

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
85
11.2.2 Manually Rebuilding Array
Purpose:
If the hot spare disk has not been configured, you can rebuild the array manually to restore the array when the
array is in the HDD Loss status.
Steps:
1. Enter the Array Settings interface. The disk 5 is lost.
Device Management> Remote Management> HDD >Array Configuration >Array
Figure 11. 15 Array Settings Interface
2. Enter the Logical Disk interface to check the status of the logical disk. The logical disk is in Degrade status.
Figure 11. 16 Logical Disk Interface
3. Click Array tab to back to the Array Settings interface and click Recreate button to configure the array
rebuilding.
Note: At least one physical disk should be available for rebuilding the array.
Figure 11. 17 Rebuild Array Interface
4. Select the available physical disk and click Yes to confirm to rebuild the array.
You can enter the Array Settings interface and Logical Disk interface to view the rebuilding status.
5. After rebuilding, the status of array and logical disk will restore to Normal.
Note: It is recommended to set the hot spare disk for automatically rebuilding the array.
Page 87

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
86
11.3 Repairing Logical Disk
Purpose:
When the disk cannot display in the HDD Information interface while the logical disk can still show in the Array
Settings interface, you have to repair the logical disk.
Note: If the logical disk is in foreground initialization status, the repairing cannot be done.
Steps:
1. Enter the Logical Disk interface.
Device Management> Remote Management> HDD >Array Configuration > Logical Disk
Figure 11. 18 Logical Disk Interface
2. Click the Repair button to repair the logical disk. After successfully repairing, there will be note on the
lower-right side.
Figure 11. 19 Repairing Logical Disk Successfully
3. The disk shows again in the HDD Information interface (Device Management> Remote Management>
HDD).
Page 88

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
87
11.4 Deleting Array / Logical Disk
Note: Before deleting the array, the logical disk(s) existing under this array must be deleted first. Deleting array
and logical disk will delete all the data saved in the disk.
11.4.1 Deleting the Logical Disk
Steps:
1. Enter the Logical Disk interface.
Device Management> Remote Management> HDD >Array Configuration> Logical Disk
Figure 11. 20 Logical Disk Interface
2. Select a logical disk and click Delete button to delete the logical disk.
Figure 11. 21 Confirm Logical Disk Deletion
3. In the pop-up message box, click the Yes button to confirm the logical disk deletion.
Note: Deleting logical disk will delete all the data saved in the disk.
11.4.2 Deleting the Array
Note: You can delete the array only after all the logical disks under that array have been deleted.
Steps:
1. Enter the Array Settings interface.
Device Management> Remote Management> HDD >Array Configuration> Array
Page 89

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
88
Figure 11. 22 Array Settings Interface
2. Select an array and click the Delete button to delete the array.
Figure 11. 23 Confirm Array Deletion
3. In the pop-up message box, click the Yes button to confirm the array deletion.
Page 90

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
89
11.5 Upgrading RAID Adapter
Purpose:
You can view the information of the adapter and upgrade the adapter.
Steps:
1. Enter the RAID Adapter interface to check the information of the adapter.
Figure 11. 24 Firmware Interface
2. Click to extend the directory window of your computer and select an upgrade file.
3. Click the Upgrade button to upgrade.
Note: Please contact the dealer immediately if the device cannot work properly after upgrading.
Page 91

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
90
Chapter 12 HDD Settings
Page 92

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
91
12.1 Local HDD Settings
12.1.1 Disk Initializing
Steps:
1. Enter HDD Management Settings interface.
Configuration> HDD Management > Basic Settings
Figure 12. 1 Local Disk Management(1)
2. Check the checkbox of HDD No..
3. Click the Format button to initialize the disk.
Note: Initializing the HDD will erase all the data saved on it, please backup the data before formatting hard disk
if necessary.
4. The status changes from Uninitialized to Normal.
Figure 12. 2 Local Disk Management(2)
12.1.2 Disk Property Management
Purpose:
Multiple HDDs can be managed in groups. Video from specified channels can be recorded onto a particular HDD
group through HDD settings. You can refer to the User Manual of iVMS-4200 for detailed information.
Before you start:
Make sure you have set the storage mode to Group before configuring the HDD property. You may refer to the
User Manual of iVMS-4200 for detailed information.
Page 93

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
92
Steps:
1. Check the checkbox of disk.
2. Configure its property by selecting R/W, Read-Only or Redundancy from drop-down menu.
3. Click the Set button to save the settings.
Table 12. 1 Disk Property Description
Parameter
Description
R/W
Writing in and reading from this disk is allowed when selecting this option.
Read-Only
Unable to write in this disk to protect existed recordings from being overwritten
when selecting this option.
Redundancy
Redundant recording in this disk is allowed when selecting this option to double
secure the data.
Note: Multiple HDDs can be managed in groups. Video from specified channels can be recorded onto a particular
HDD group through HDD settings. You can refer to the User Manual of iVMS-4200 for detailed information.
12.1.3 HDD Sleeping
Purpose:
The HDD sleeping function can switch the HDD into sleeping status to reducing the consumption when there is no
need to read or write.
Steps:
1. Enter HDD Advanced Settings interface.
Configuration> HDD Management > Advanced
Figure 12. 3 HDD Sleeping Setting
2. Check the checkbox of Enable HDD Sleeping and click the Save button.
Page 94

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
93
12.2 Network HDD Settings
By Net Disk Settings, recorded data can be saved to the network storage disk provided by NAS or IP SAN server.
Steps:
1. Enter the Net Disk settings interface:
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Network Settings> NetHDD
Figure 12. 4 Network HDD Settings
2. Searching directory is provided if you do not know the created directory in the NetHDD.
Select the Type in the drop-down list and input the IP address of NetHDD, and click Search button.
Figure 12. 5 Searching Directory
3. Input Server Address, File Path and select NetHDD Type in the drop-down list on the upper text field.
4. Click Save button to save the settings.
5. Repeat steps of Chapter 12.1.1 Disk Formatting to initialize the added net HDD.
Page 95

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
94
12.3 Managing eSATA
Purpose:
When there is an eSATA device connected to NVR, you can configure the eSATA to record and capture directly on
the eSATA disk or you can configure it for export the record data on the local HDD for backup, and the
management interface is provided in the NVR.
Note: The eSATA configuration interface is only provided in the iVMS-4200 Client Software.
Steps:
1. Enter the HDD Information interface.
Device Management> Remote Configuration> HDD
2. Click the button.
3. Select the eSATA number in drop-down list of eSATA, and click to select type to Export or Record/Snapshot.
Export: use the eSATA for backup. Refer to Chapter 7.4 Backup for operating instructions.
Record/Snapshot: use the eSATA for record/capture. Refer to the following steps for operating instructions.
Figure 12. 6 Set eSATA Mode
4. When the eSATA type is selected to Record/Capture, the eSATA device will be displayed in the HDD list, as
shown in the figure below.
Note: Two storage modes can be configured for the eSATA when it is used for Record/Capture. Please refer
to chapter12. 1 Local HDD Settings for details.
Page 96

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
95
Figure 12. 7 eSATA Information
Page 97

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
96
Chapter 13 Local Configuration
Page 98

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
97
Purpose:
Local parameters configuration refers to the configuration for the NVR and not the connected remote devices to
the NVR.
Click the Configuration button in the menu bar and enter parameters setup menu, which displays local
configuration by default.
Figure 13. 1 Local Configuration Interface
Table 13. 1 Local Parameters Descriptions
Parameters
Descriptions
Protocol
Select network transmission protocol: TCP or UDP.
Stream Type
Main Stream for recording.
Sub-stream for viewing live images.
Image Size
Set the size of image. Auto-fill, 4:3, 16:9 are selectable.
Record File Size
Set the size of recordings.
Live View Performance
Set the live view performance to Shortest Delay, Real
Time, Balanced or Best Fluency.
Path of saving record files to
Select a folder to save the recordings
Path of saving snapshots in live view
Select a folder to save the pictures captured while live
view
Path of saving snapshots when
playback
Select a folder to save the pictures captured while
playback
Path of saving clips
Select a folder to save the clips while playback
Path of saving downloaded files
Select a folder to save downloaded recordings
Page 99

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
98
Chapter 14 Maintenance
Page 100

User Manual of Network Video Recorder
99
14.1 View Device Information
Steps:
1. Enter device information interface
Configuration> Remote Configuration> Device Parameters> Device Information
Figure 14. 1 Device Information
2. You can modify Device Name and Device No., and other fields are read-only.
Device No.: Edit the device number of NVR, it can be set in the range of 1 to 255, and the default number is
255. The number is used for the remote and keyboard control.
3. Click Save to save the settings.
 Loading...
Loading...