Page 1

1
RocketRAID 2740/2744
SAS 6Gb/s PCI-E 2.0
Host Adapters User’s Guide
Revision: 1.0
Date: August 2010
HighPoint Technologies, Inc.
Page 2

2
Copyright
Copyright © 2010 HighPoint Technologies, Inc. This document contains materials protected by
International Copyright Laws. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted
or transcribed in any form and for any purpose without the express written permission of HighPoint
Technologies, Inc.
Trademarks
Companies and products mentioned in this manual are for identification purpose only. Product names or
brand names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their
respective owners. Backup your important data before using HighPoint's products and use at your own risk.
In no event shall HighPoint be liable for any loss of profits, or for direct, indirect, special, incidental or
consequential damages arising from any defect or error in HighPoint's products or manuals. Information in
this manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
HighPoint.
Notice
Reasonable effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate. HighPoint
assumes no liability for technical inaccuracies, typographical, or other errors contained herein.
Page 3

3
HIGHPOINT TECHNOLOGIES, INC................................................................... 5
HIGHPOINT ROCKETRAID 2740/2744 ............................................................... 6
6GB/S SASPCI-EXPRESS 2.0 X16 ......................................................................... 6
1 - Features and Specifications .................................................................................................................... 7
2 - Kit Contents ............................................................................................................................................. 8
HARDWARE – DESCRIPTION AND INSTALLATION ........................................ 9
1 - Host Adapter Descriptions and PCB Layout ........................................................................................ 9
RocketRAID 2740 Host Adapter layout ..................................................................................................... 9
RocketRAID 2744 Host Adapter layout ....................................................................................................10
ROCKETRAID BIOS UTILITY .......................................................................... 13
1 - BIOS Settings Overview ........................................................................................................................13
Using the BIOS Utility ..............................................................................................................................13
BIOS Commands.......................................................................................................................................14
2 - Creating RAID Arrays ...........................................................................................................................14
3 – Deleting Arrays ......................................................................................................................................17
4 - Add/Remove Spare Disks .......................................................................................................................18
5 - Settings ....................................................................................................................................................18
HIGHPOINT SOFTWARE CD ............................................................................ 19
Creating a driver diskette ...........................................................................................................................19
Device Driver Installation – Windows Operating Systems ......................................................................20
RocketRAID 2740/2744 Windows Driver Installation..............................................................................21
Windows XP, 2003 ....................................................................................................................................21
RocketRAID 2740/2744 Windows 7/Vista/Windows 2008 Driver Installation ........................................24
HIGHPOINT RAID MANAGEMENT UTILITIES (HRM) – WEB GUI / CLI ..... 28
Windows Operating Systems – Installing the Web GUI from the Software CD. ...................................28
Red Hat Enterprise/CentOS, Fedora Core, Open SuSE – Installing the Web-based Management utility .28
Debian/Ubuntu Linux Distributions – Installing the Web-based Management Utility ..............................29
Linux Distributions – Command Line Interface (CLI) ..............................................................................29
1 - Installing the Web GUI (v1.5.3) - Windows Operating Systems (2000, XP, 2003, Vista, 2008,
Windows 7) ...................................................................................................................................................30
Page 4

4
2 - Starting the Web GUI ............................................................................................................................35
3 - Web GUI – Icon Definitions ..................................................................................................................36
4 - Web GUI - Configuring an Array .........................................................................................................37
Initializing a new hard drive ......................................................................................................................37
Create an Array .........................................................................................................................................38
5 - Web GUI - Configuring Spare Disks ....................................................................................................40
To assign a Spare disk: ..............................................................................................................................40
6 - Web GUI - Recovering an Array ...........................................................................................................42
To Rebuild an array: ..................................................................................................................................42
7 - Web GUI - Maintaining RAID Arrays .................................................................................................44
Scheduling Tasks: ......................................................................................................................................44
Removing Tasks ........................................................................................................................................45
SHI – Storage Health Inspector .................................................................................................................46
8 - Web GUI - Safeguarding your Array ...................................................................................................47
Automatic RAID Rebuilding.....................................................................................................................47
9 - Web GUI - Event Notification ...............................................................................................................49
Configuring SMTP (E-mail) Notification .................................................................................................50
10 - Web GUI - Advanced RAID Functions (Windows VSS, OCE/ORLM) ...........................................51
VSS – Variable Sector Size .......................................................................................................................51
Online Capacity Expansion and RAID Level Migration (OCE/ORLM)...................................................56
MAC OS X DRIVER AND WEB-BASED RAID MANAGEMENT UTILITY ....... 59
1 - Overview .................................................................................................................................................59
2 - Installing the package ............................................................................................................................59
3 - Installing Web RAID Management Software ......................................................................................61
4 - Web RAID Management Interface .......................................................................................................61
5 – Uninstalling ............................................................................................................................................62
CUSTOMER SUPPORT ...................................................................................... 63
THANK YOU ...................................................................................................... 64
Contact Us ....................................................................................................................................................64
Page 5

5
HighPoint Technologies, Inc.
HighPoint Technologies, Inc. is a professional, host-based, RAID controller manufacturer. For more than
15 years, we’ve dedicated ourselves towards the manufacturing and deployment of quality, robust, cutting
edge RAID host adapters based on the latest storage interfaces delivering our field-proven products to
corporations, system builders, and individual consumers worldwide.
HighPoint Technologies is unique amongst host controller manufacturers: Our comprehensive range of
RAID and non-RAID products are designed to support the latest SAS, SATA and SSD hard disk devices
including SATA 6G.
Page 6

6
HighPoint RocketRAID 2740/2744
6Gb/s SASPCI-Express 2.0 X16
The RocketRAID 2740/2744 host adapter is a high-performance SAS RAID solution, delivering reliability
to demanding data-intensive applications such as tiered storage environments (disk-to-disk or disk-to-diskto-tape backup), security and surveillance, video editing, and digital content creation.
Support for both 6Gb/s SAS and SATA drives on the same controller maintains configuration optimization
for performance based on the characteristics of SAS and SATA drives available today.
HighPoint RAID Management HighPoint RAID Management software offers a user friendly interface to
create, manage and maintain your storage solutions. Email notification and remote are some of the advance
features that the RAID Management software has to offer.
COMPREHENSIVE OS SUPPORT
HighPoint offers the broadest range of support for all major operating systems to ensure OS and hardware
server compatibility. Device drivers are available Windows, Linux and FreeBSD.
Page 7

7
1 - Features and Specifications
Host Adapter Architecture
PCI-Express x16 (Gen2)
Support up to 16 SAS/SATA drives
Internal Mini-SAS Connectors (SFF-8087) – RR2740
External Mini-SAS Connectors (SFF-8088) – RR2744
NVRAM for write journaling
Hot Swap and hot plug
RoHS complaint
Advanced RAID Features
Supports RAID 0, 1, 5, 10 , 50 and JBOD
NCQ (Native Command Queuing)
Auto detect of unplug/plug SAS/SATA hard drive for RAID auto rebuild
Staggered drive spin up
Support bad sector repair feature
Support Disk Scrubbing
BIOS Booting (INT13) to RAID array for better redundancy
64bit LBA for RAID arrays greater than 2TB single partition
Array Monitors, Alerts and Indicators
Hard Drive LED Indicators (Activity and Failed)
SMTP email notification for events and error reporting
Alarm/Buzzer alerts for drive/array failure
SAF-TE (I2C) and SGPIO enclosure management
SHI – Storage Health Inspector (S.M.A.R.T. and disk maintenance)
RAID Management
Online Capacity Expansion (OCE) and Online RAID Level Migration (ORLM) for
Windows/Linux/FreeBSD/Mac OS X (RR2744)
Quick and Background initialization for instant RAID access
Online array roaming
Page 8
8
HighPoint RAID Management (HRM)
PCI-E
3.3V
12V
Power
10W max
20W max
Hot key (ctrl-h) boot-up RAID manager via BIOS
Web browser-base RAID management software (Web GUI)
Command Line Interface (CLI) – FreeBSD/Linux
Operating System Support
Windows XP, 2003, Windows Vista, Windows 2008, Windows 7 (32 and 64-bit versions)
Linux (Fedora Core, Red Hat Enterprise / CentOS, SuSE, Debian Ubuntu)
FreeBSD
Mac OS X (RR2744 only)
PHYSICAL SPECIFICATIONS (RR2740)
Size: 220.0mm X 68.0mm
EMI: FCC Part 15 Class B and CE
PHYSICAL SPECIFICATIONS (RR2744)
Size: 107.0 mm×140 mm×1.6mm
EMI: FCC Part 15 Class B and CE
Thermal and Atmospheric Characteristics:
Work Temperature Range: +5 C ~+ 55 C
Relative Humidity Range: 5% ~ 60% non-condensing
Storage Temperature: -20 ~ +80 C
MTBF: 920,585 Hours
Electrical Characteristics:
2 - Kit Contents
RocketRAID Host Adapter
Quick Install Guide
HighPoint RAID Management and software CD
Low profile bracket
Page 9
9
Hardware – Description and Installation
Pin Number
Pin 1
Pin 2
Pin3
Pin4
A1
Channel 1
Channel 2
Channel 3
Channel 4
A2
Channel 5
Channel 6
Channel 7
Channel 8
A3
Channel 9
Channel 10
Channel 11
Channel 12
A4
Channel 13
Channel 14
Channel 15
Channel 16
F1
Channel 1
Channel 2
Channel 3
Channel 4
F2
Channel 5
Channel 6
Channel 7
Channel 8
F3
Channel 9
Channel 10
Channel 11
Channel 12
F4
Channel 13
Channel 14
Channel 15
Channel 16
Connections
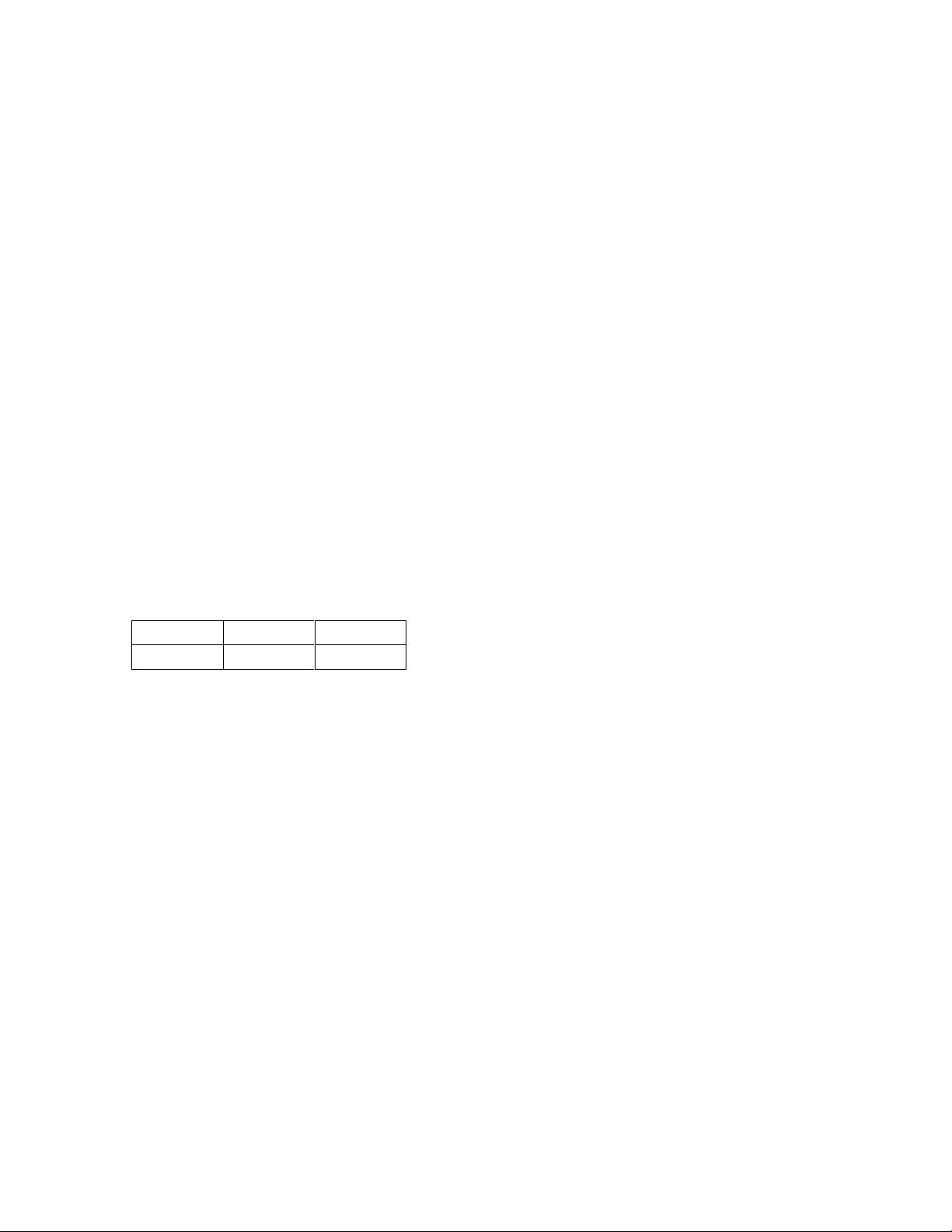
1 - Host Adapter Descriptions and PCB Layout
RocketRAID 2740 Host Adapter layout
Port1-Port4
These represent the RocketRAID 2740/2744’s four Internal Mini-SAS ports. Each port can support up
to 4 SATA/SAS hard disks.
LED Connections
LED connectors (Drive-activity/Drive-failure): The RocketRAID 2740/2744 host adapter has 16 LED
connectors that are used to indicate the activity and failure status of hard drives attached to the card’s 16
SATA/SAS channels.
A1-A4, F1-F4
A1-A4 provide LED support for Drive Activity, while F1-F4 supports Drive Failure.
Pin Connections represent SATA/SAS channel/port
Page 10
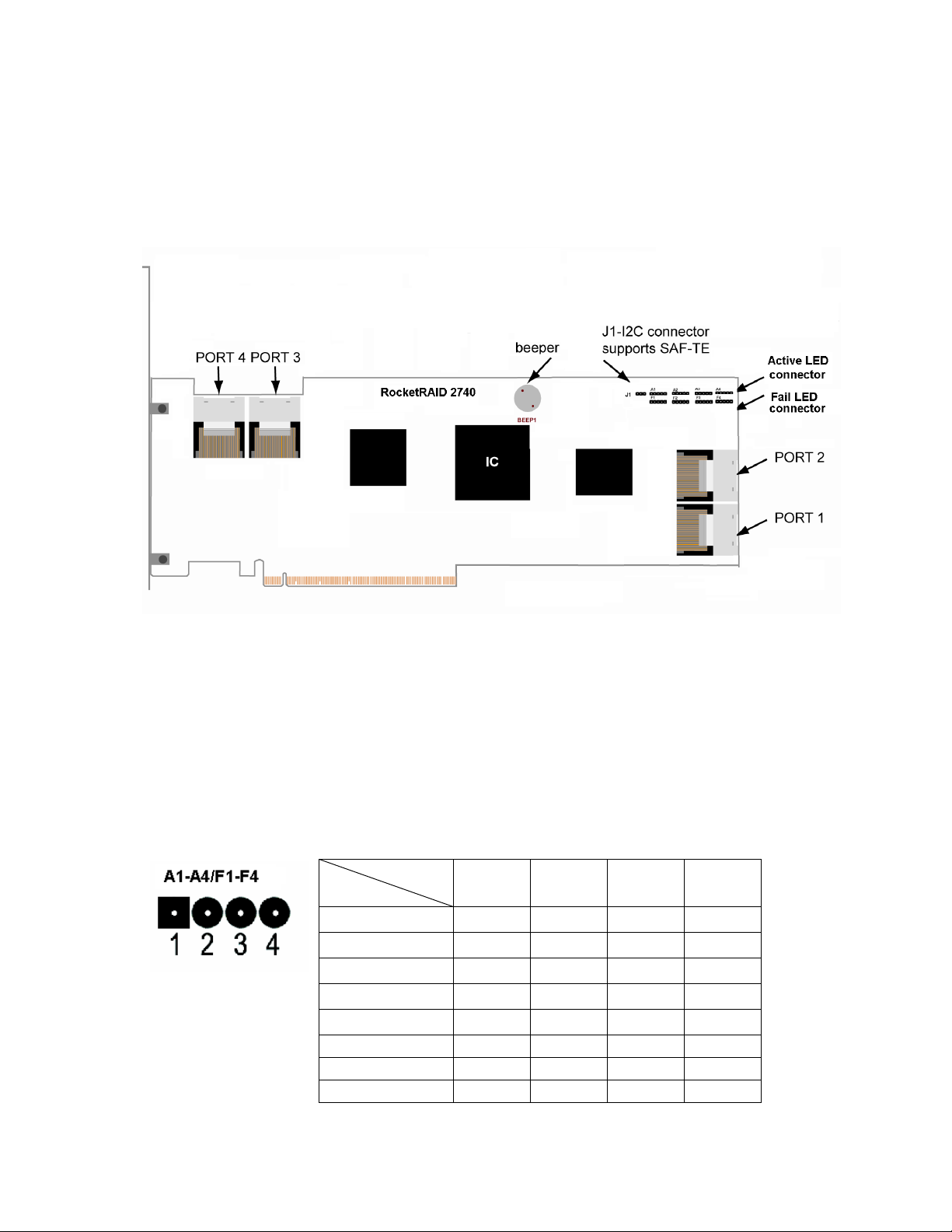
10
BEEP1-Speaker
Pin Number
PIN description
Pin1
SCL
Pin2
GND
Pin3
SDA
Alarm (speaker): the speaker emits and audible alarm in the case of Drive/array failure.
J1
This jumper supports SAF-TE interface (I2C).
RocketRAID 2744 Host Adapter layout
Port1-Port4
These represent the RocketRAID 2744’s 4 external Mini-SAS ports. Each port can direct
connect up to 4 SATA/SAS hard disks.
BEEP1-Speaker
Alarm (speaker): the speaker emits and audible alarm in the case of Drive/array failure.
Page 11
11
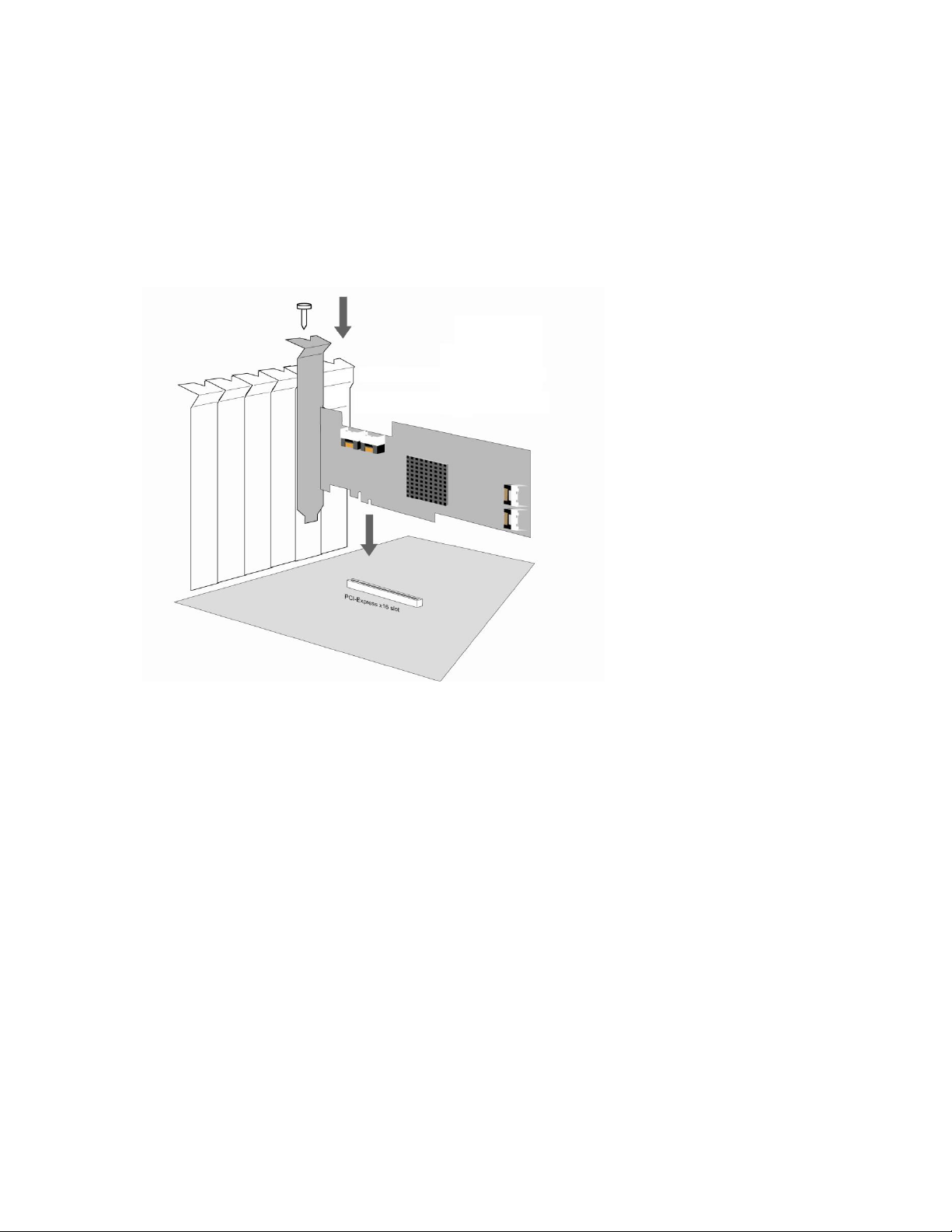
2 - Installing the RocketRAID Host Adapter
Note: Make sure the system is powered-off before installing the RocketRAID host adapter. Illustration
below shows the RR2740.
1. Open the system chassis and locate an unused PCI-Express x16.
2. Remove the PCI slot/bracket cover.
3. Gently insert the RocketRAID card into the PCI-Express slot, and secure the bracket to the system
chassis.
4. After installing the adapter, attach hard drives to the host adapter using the appropriate data cable.
Note: Many server-level chassis include hard-drive hot-swap bays. For these system chassis, cables are
attached to the chassis backplane, rather than directly to each individual hard drive. Consult the chassis
manual for proper installation procedures.
5. Close and secure the system chassis.
Page 12

12
3 - Verifying Installation
Once the host adapter and hard drives have been installed into the chassis, boot-up the system to verify that
the hardware is properly recognized.
1. Power on the system. If the system detects the presence of the adapter, the RocketRAID BIOS Utility
will be displayed during boot up.
2. Press Ctrl+H to access the RocketRAID adapter’s BIOS Utility.
The BIOS Utility will display information about hard drives attached to the adapter.
Make sure all attached drives are detected by this utility. If any of the hard drives are not detected, powerdown the system and check the power and cable connections.
Page 13
13
RocketRAID BIOS Utility
The RocketRAID 2740/2744 card will display its BIOS screen during the system's boot process.
Press Control + H when prompted, to access the BIOS settings Menu.
1 - BIOS Settings Overview
The RocketRAID 2740/2744 BIOS utility is an interface that provides management commands and
controller related settings.
Using the BIOS Utility
The following keys utilized by the RocketRAID 2740/2744 BIOS utility:
Alt – press Alt to highlight the tool bar.
Arrow keys – use these to move between different menu items, and to browse through the device list (the
menu will display 8 disks/ports at once)
Enter – Open the selected toolbar command/execute the selected command.
Esc – move back to the previous menu, cancel the selected operation, or exit the BIOS Utility.
Page 14
14
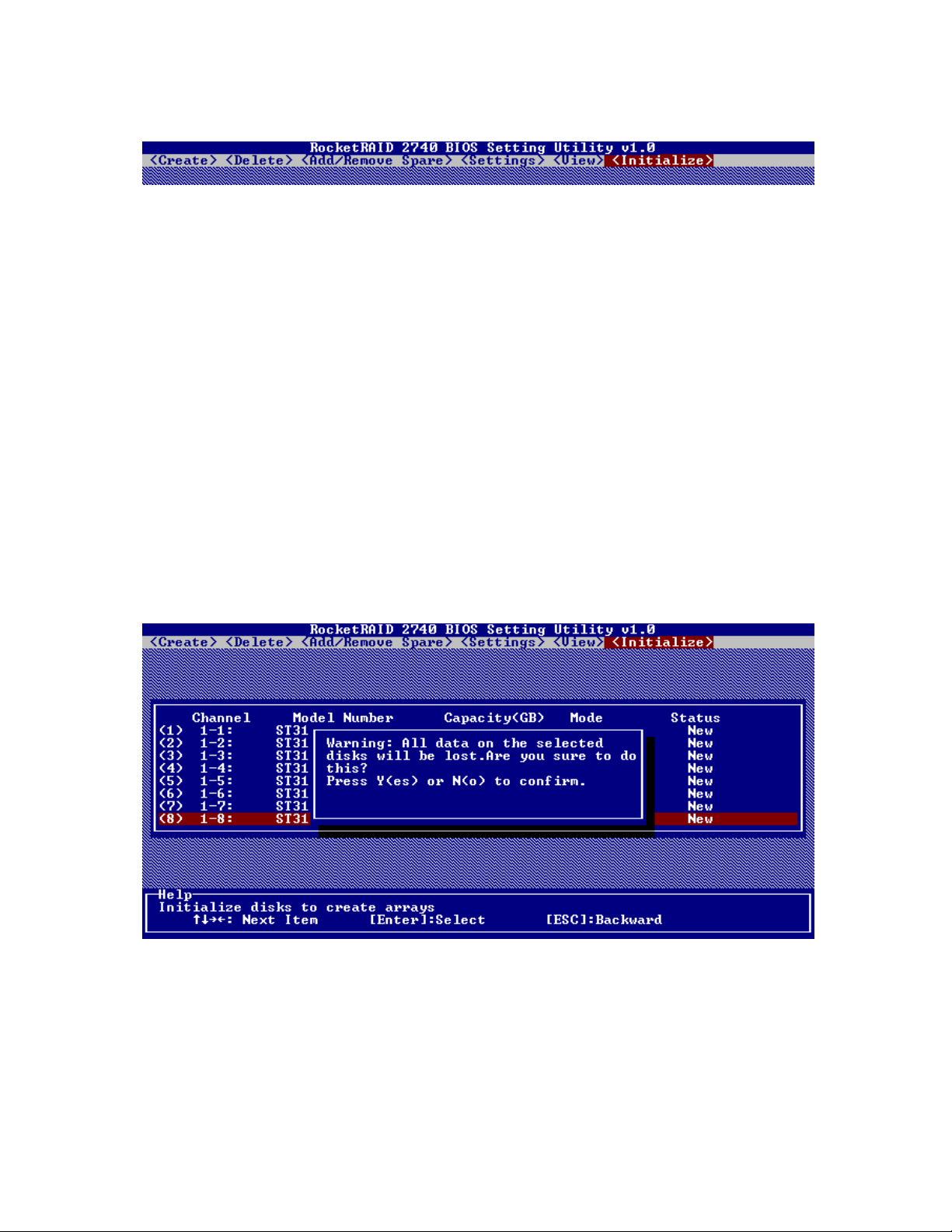
BIOS Commands
Create - this command is used to open the RAID Creation menu.
Delete - this command will delete the selected RAID array.
Add/Remove Spare - this command is used to assign hard disks to function as spare disks. The controller
is capable of using spare disks to automatically rebuild broken or faulted RAID arrays.
Settings - this command opens the settings menu (selecting the boot disk/array, staggered drive spinup)
View – this command is used to select between two views: Devices (HARD DISKS), and Arrays
(configured RAID arrays).
Initialize - this command is used to prepare disks for use with RAID arrays. Disks must be initialized
before they can be used to create arrays.
2 - Creating RAID Arrays
Initializing Disks:
Before creating a RAID array, the disks must be initialized. Disk initialization writes necessary RAID
configuration information to the hard disks. Select the Initialize command from the toolbar, and press
ENTER.
Highlight the target disks using the arrow keys, then select using Enter. You can use the arrow keys to
select from the next set of disks (the screen will display 8 ports at a time. A numeral will be displayed
before each selected disk. Once all target disks have been selected, press ESC. The utility will display a
warning, and ask you to press Y (yes) to initialize, or N (no) to cancel. Once initialized, these disks can be
used to create RAID arrays.
Warning: Initialization will destroy all pre- existing data on the selected hard disks. Only initialize
disks that do not contain critical data.
Page 15
15
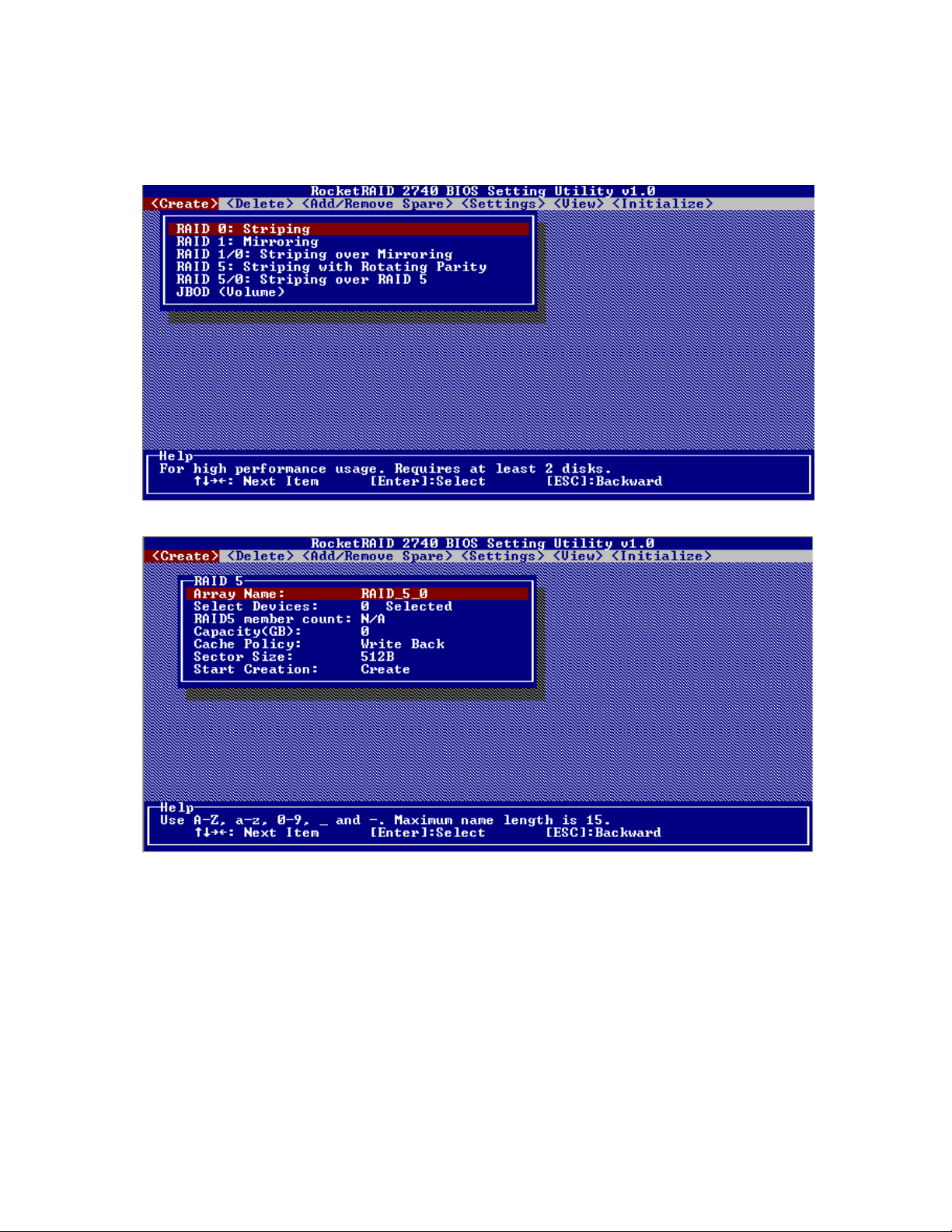
Creating Arrays:
Select Create from the toolbar and press Enter.
1. Use the arrow keys to select the RAID level and press ENTER.
2. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Array Name option and press Enter. The array name dialogue box
will appear. Use the keyboard to input a new Array Name, and press the Enter key.
Note: the Array Name command is optional – it is not necessary to name the array. The array can be named
at a later time, and the name of the array can be changed at any time.
Page 16
16
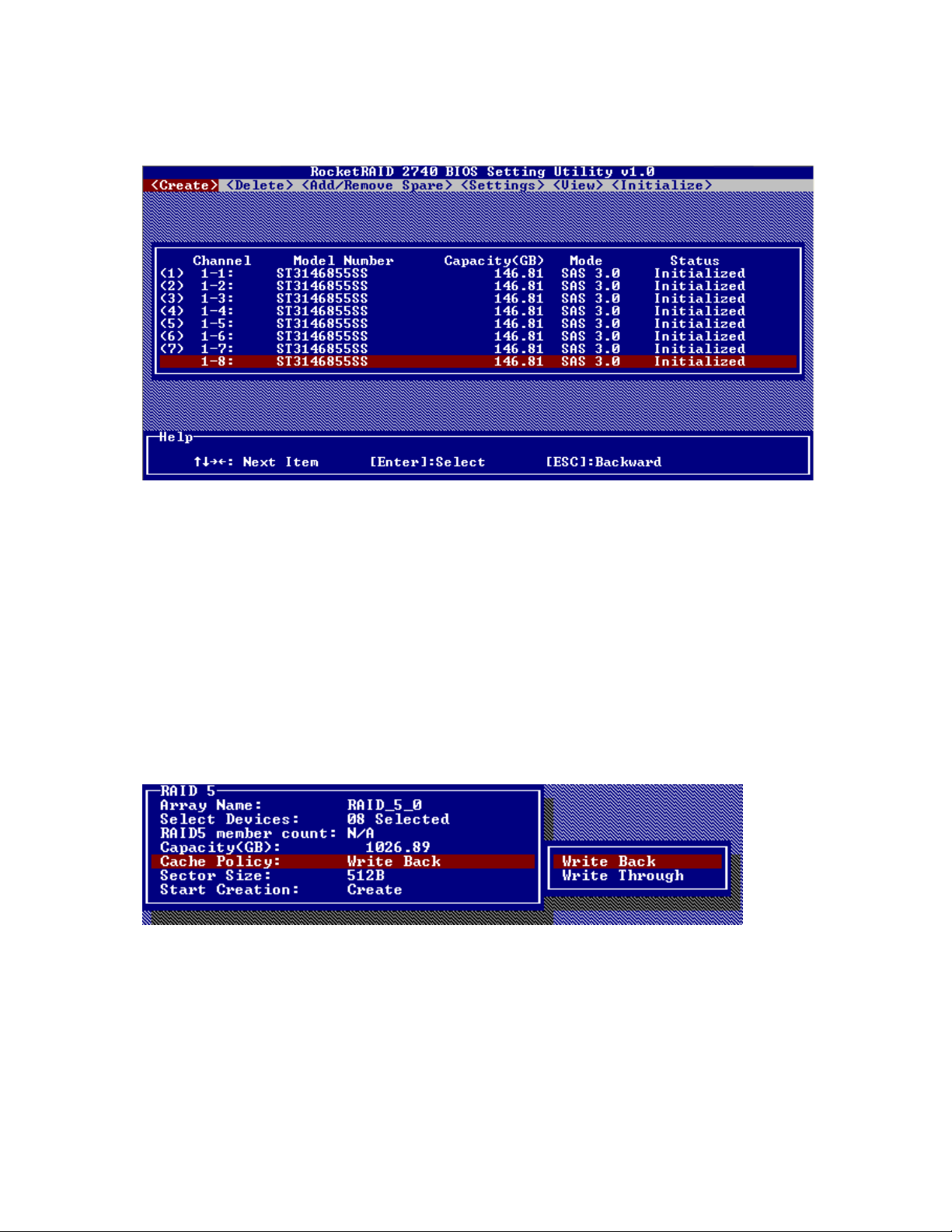
3. On the Create menu, use the arrow keys to highlight the Select Devices item and press Enter. A device
list will appear, and display all available hard disk drives.
4. Highlight the target disks that you want to use, and press Enter to select them. You can use the arrow
keys to select from the next set of disks (the screen will display 8 ports at a time. A numeral will be
displayed before each selected disk. This number designates disk order. After all of the disks have
been selected and press the ESC key to return to the Create Menu.
5. Next, Use the ↓ arrow key to highlight the Capacity (GB) option and press Enter. The total available
capacity will be displayed. Press ENTER if you wish to use all available space. If you wish to reserve
disk space for additional arrays/single disks, use the keyboard to input the amount of space (in GB)
you wish to set aside for this particular array, and press Enter.
Note: Multiple arrays can be created using the same set of hard disk drives.
The Capacity option allows you to set aside disk space that be used to create another array, set as a spare
disk, or partitioned to act as a single disk (by the operating system).
6. For redundant RAID arrays (RAID 1, 5, 10), select the Cache Policy:
Write Back – utilizes disk cache (higher performing)
Write Through – writes directly to the disks (may reduce the risk of data loss during a critical failure, but
at the cost of lower performance).
Page 17

17
7. Sector Size – Also known as “Variable Sector Size”. Use this option if you are using an older 32-bit
Windows operating system. This allows older operating systems to support volumes over 2TB in
size. Do not use if the operating system already supports large volumes (such as GPT).
8. To complete the creation procedure, use the arrow key to highlight the Start Creation item and
press Enter. Press the Y (yes) key to create the array, or N (no) key to cancel the creation process.
3 – Deleting Arrays
Highlight the Delete command from the toolbar, and press Enter.
The BIOS utility will display a list of available RAID arrays. Select the array you wish to delete, and press
Enter.
The utility will display a warning message. Press Y (yes) to delete the array, or select N (no) to cancel.
Warning: all data stored on the array will be lost – do not delete if the array contains critical data.
Page 18
18
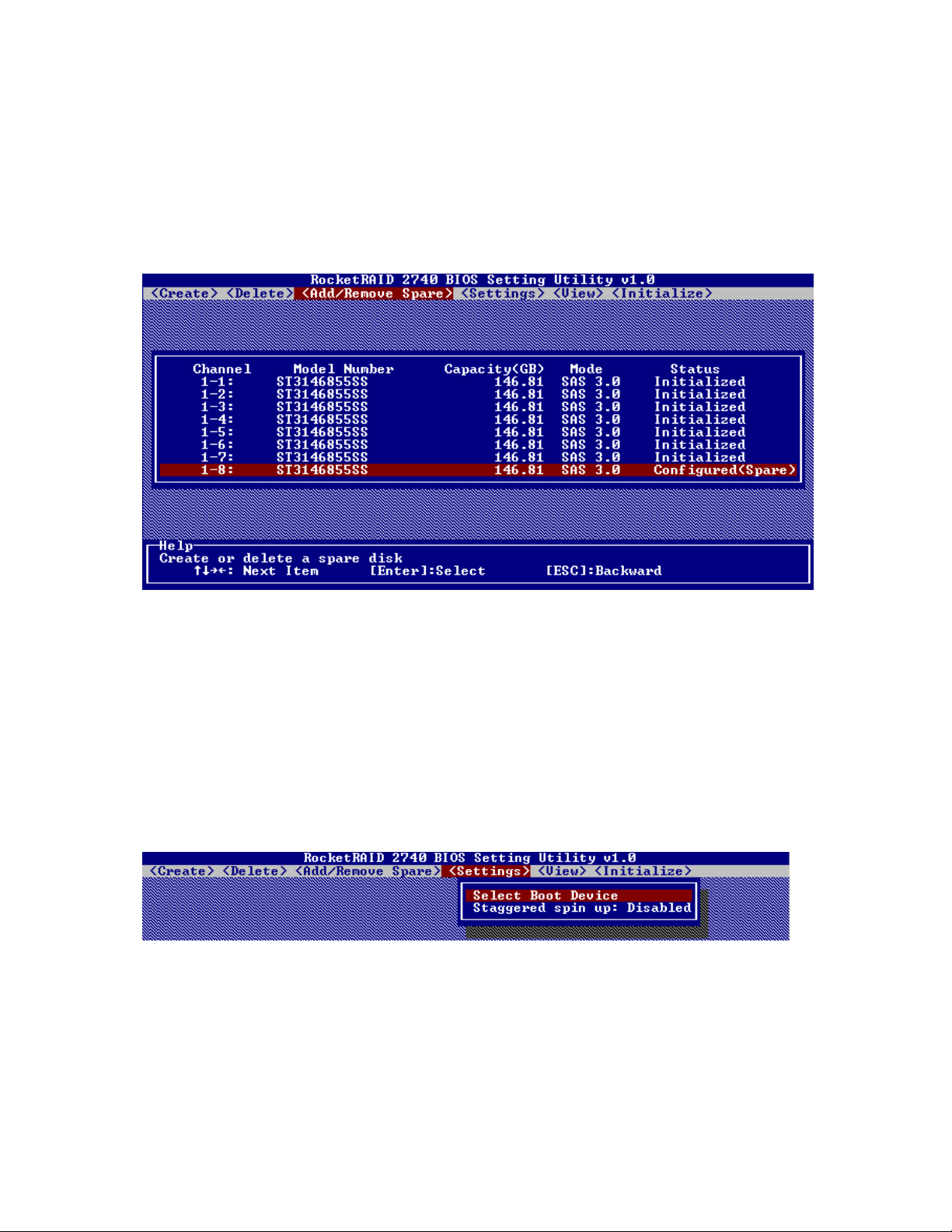
4 - Add/Remove Spare Disks
This Add/Remove Spare command is used to assign a hard disk to act as a Spare Disk. Spare Disks are
used to automatically rebuild Redundant RAID arrays (RAID 1, 5, 10, 50) in the case of disk failure. As
with creating RAID arrays, disks must be initialized before they can be used as spares. To set a hard disk
to act as a Spare Disk, use the arrow keys to select the target disk from the list of initialized disks, and press
Enter. To remove the Spare Disk setting from a hard disk, highlight the spare disk, and press Enter.
Generally, single disks are designated to act as spares (disks that are not configured into RAID arrays).
However, in some instances, disks that are members of RAID arrays may also be designated to act as a
spare. If the disks in question are part of a RAID array that did not utilize the full available capacity at the
time of creation, these disks may be used as spares. For example: a RAID 0 array was created between two
200GB hard disks, but only 200GB of space (out of a grand total of 400GB), was assigned to that array. In
this example, 200GB of disk space remains unallocated. This unallocated space would allow these disks to
be set as spares for a separate redundant array that falls into the same capacity range (200GB).
5 - Settings
To access the Settings menu, highlight the Settings command from the toolbar, and press Enter.
Select Boot Device – select which disk or array will act as the boot disk, if the motherboard BIOS instructs
the card to act as the boot device.
Staggered Drive Spinup – This option is disabled by default. Enabling this setting will instruct the card to
power up the hard disks, sequentially (one disk approximately every 2 seconds). Not all disk support this
setting – consult the disk documentation for more information.
Warning: Western Digital hard disks do not support this setting. Enabling this setting is not
recommended. If enabled, these disks may not be detected by non-RAID controllers.
Page 19
19
HighPoint Software CD
Each retail box includes a copy of the HighPoint Products Software CD.
This CD can be used to generate driver diskettes, and install the HighPoint RAID Management Utility Suite
for a variety of operating systems.
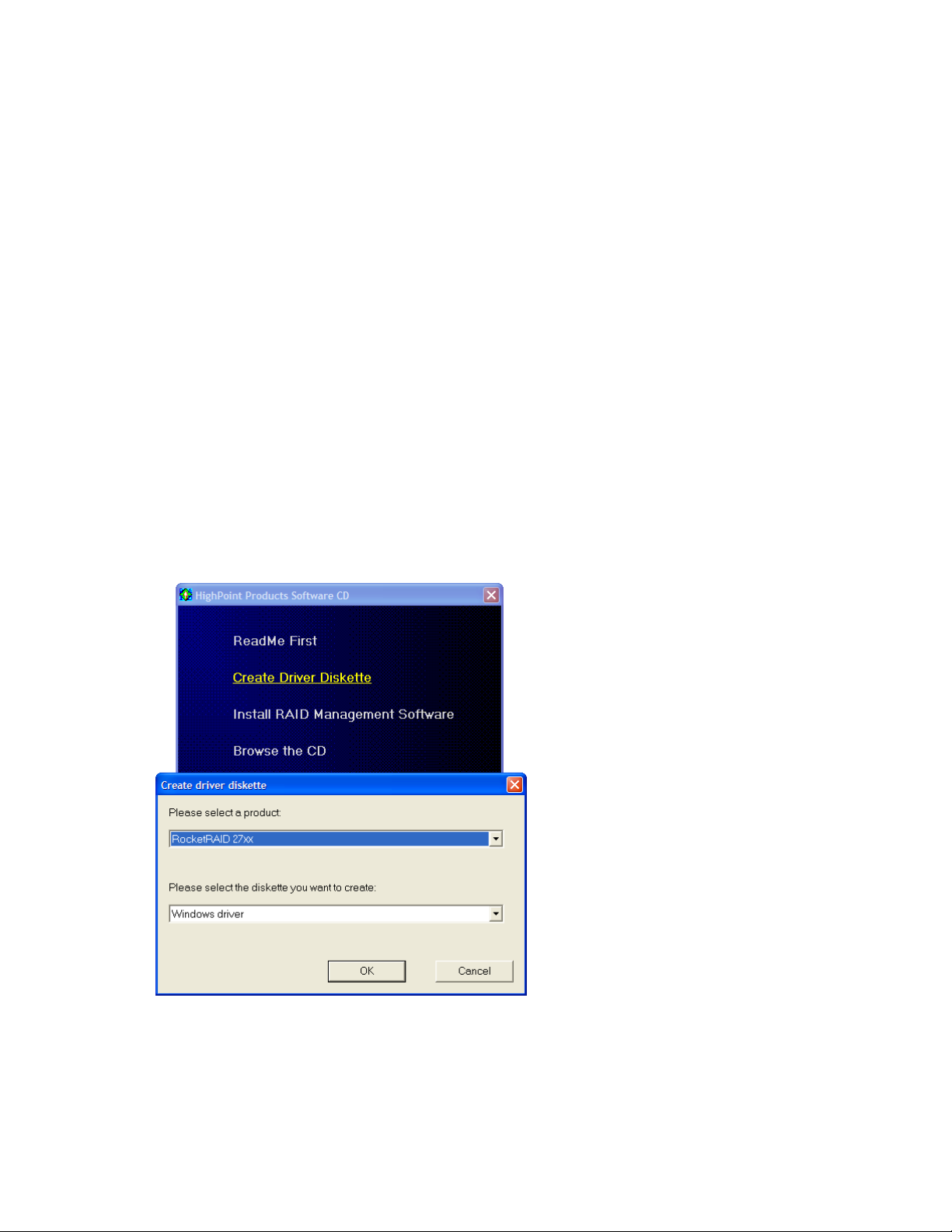
Creating a driver diskette
Windows XP, 2003 and several distributions of Linux and FreeBSD require driver diskettes when
installing the operating system directly to a disk or array hosted by the Rocket RAID host adapter.
To create a driver floppy diskette:
1. Insert the CD into the system’s CD/DVD drive. The program should start automatically.
2. Insert a blank floppy diskette into the system’s floppy drive.
3. Click on “Create Driver Diskette”.
4. Click on the “Please Select a Product” drop-down button, and select the appropriate host adapter model
from the list.
5. Click on the “Please Select the Diskette you want to create” drop-down button, and select the desired
operating system from the list.
6. Click on the “OK” button to create the driver diskette.
Page 20

20
Device Driver Installation – Windows Operating Systems
We recommend visiting the RocketRAID product pages for the latest Windows Device Driver updates:
http://highpoint-tech.com
Drivers are posted in .zip archive format. Most Windows operating systems will recognize this archive
format, natively. Double click the driver download to view and extract their contents. Drivers can be
extracted and/or copied to various media.
Page 21

21
RocketRAID 2740/2744 Windows Driver Installation
Windows XP, 2003
Installing the RocketRAID driver for an existing Windows system
After the operating system has booted, the Hardware Wizard will detected the card and request that the
Device Driver be installed.
1. When the “Found New Hardware Wizard” window appears and asks to search online, select “No, not
this time”.
2. Select “Install from a list or specific location (Advanced)”, and click Next to continue.
Page 22

22
3. Click on the “Include this location in the search” option, and click “Browse”.
Browse to the location of the driver and click Next.
4. Windows will display a warning message that states the driver has “not been signed”. Select “Continue
Anyway”.
Page 23

23
5. Windows will repeat this process 4 times – you will not need to specify the location of the driver.
Allow Windows to locate the driver automatically.
6. After the driver has been installed for the last time, Windows will display a new prompt. Click finish
when prompted, and allow Windows to reboot.
Installing the RocketRAID driver during a fresh Windows installation
1. After booting from the Windows CD or DVD-ROM, when the Windows Setup
blue screen appears, look towards the bottom of the screen. Windows will
prompt you to press the F6 key if you want to install a third party SCSI or RAID
driver. Press the F6 key at this time.
2. The setup procedure will continue, and will later instruct you to press the “S” key
to specify additional adapters. Press the “S” key as instructed.
3. Next, the setup program will prompt for the insertion of the driver diskette. Please
insert the driver diskette, and then press ENTER to continue.
4. The next window will display several driver options. Please select the driver for
the corresponding operating system, and press ENTER to continue.
Page 24

24
RocketRAID 2740/2744 Windows 7/Vista/Windows 2008 Driver Installation
Installing the driver for an existing Windows 7, Vista and 2008 system
1. Install the RocketRAID host adapter into the PC, then boot up Windows
Vista.
2. Windows should automatically detect the card, and display the “Found New
Hardware” wizard pop-up window. Select “Locate and install driver software”.
When Windows asks: “Windows needs your permission to continue”, select
“continue”.
3. When asked to search online select “Don’t Search Online”.
Page 25

25
4. Select “I don’t have disc, show me other options”.
5. Select “Browse my computer for driver software”.
.
Page 26

26
6. Browse to the location of the driver and click “Next”.
7. When asked: “Would you like to install this driver software?” select “Install”.
Page 27

27
8. Reboot the system when prompted. The RocketRAID host adapter will be ready for use after Windows
reboots.
Installing the driver during a fresh Windows 7, 2008, Vista installation
1. Boot from the Windows Installation DVD.
2. When the screen “where do you want to install Windows” appears, click “Load
driver” and browse for the driver location. Windows can install drivers from several media types: floppy
diskette, USB flash disk or CD.
3. Select the RocketRAID 2740/2744 controller driver, and click “Next”.
4. The driver is now installed – the disk or array will be recognized as available disk space. Windows setup
will then proceed normally.
Linux and FreeBSD Device Driver installation
Binary and source driver updates are routinely posted for a variety of older Linux operating systems
including past versions of Red Hat Enterprise, CentOS, Open SuSE, Ubuntu, Debian and Fedora Core.
Drivers are also available for several FreeBSD revisions, and are available from the card’s Product page.
Several driver sets are included with the RocketRAID Software CD.
Each binary driver and source package includes an installation guide (.pdf format).
Page 28

28
HighPoint RAID Management Utilities (HRM) – Web GUI /
CLI
The HighPoint RAID Management Utility Suite, also known as “HRM”, includes several user interface
options. The latest version of the Web Management utility user manual, is available from our website.
Windows Operating Systems – Installing the Web GUI from the Software CD.
Click on “Install RAID Management Software”.
Select the desired software from the drop down menu, and click on the “OK” button.
Red Hat Enterprise/CentOS, Fedora Core, Open SuSE – Installing the Web-based
Management utility
Linux operating systems that support .rpm packages, allow you to double-click the HighPoint Web RAID
Management .rpm file to start the installation process.
1. Copy the Web RAID Management package from the RR2740/2744 Software CD, to the desktop of the
Linux operating system. The .rpm file is located in HighPoint RAID Management Software –
\HighPoint RAID Management Software\WebGUI\RR2xxx_3xxx_None-OBM\Linux\WebGui-
Linux.tbz.
2. Extract the .tbz file to the desktop, and browse to the appropriate .rpm file (there are 32 and 64-bit
options).
1. Double click the .rpm file – this should open the operating systems software installer. Enter the
Administrative password when prompted and proceed with installation.
2. The package can also be installed manually, using a terminal. Log on in as “root”, open a terminal, and
browse to the location of the .rpm file. Run the following command:
3. # rpm -i hptsvr-https-1.4-10.i386.rpm (or hptsvr-https-1.4-10.x86_64.rpm)
Note: The i386 rpm package can also work on 64-bit systems if you have 32-bit runtime libraries installed.
If you use the x86_64 rpm package, please make sure the controller driver has 64-bit ioctl support.
Page 29

29
Debian/Ubuntu Linux Distributions – Installing the Web-based Management Utility
For Debian/Ubuntu Linux distributions, you can use alien to convert the rpm packages to a .deb package,
then use "dpkg -i" command to install each package. Some script files may be lost during the conversion
process from rpm to .deb, so you may need to make manual corrections. .
The following files will be installed/configured:
/usr/bin/hptsvr - service program
/etc/hptcfg - service config file
/etc/rc.d/init.d/hptdaemon - service control script
/usr/share/hpt/webguiroot - data files
If there is no /etc/hptcfg present, you can add it manually using by using the “echo” command on the
driver file name to /etc/hptcfg.
For example:
# echo hptiop.ko >/etc/hptcfg
Uninstalling the Utility
Open a terminal, and use the following command:
# rpm -e hptsvr-https
Linux Distributions – Command Line Interface (CLI)
Command Line interface versions of the RocketRAID management utilities are available for Linux and
FreeBSD operating systems.
These packages are posted on the HighPoint Technologies, Inc. website, under RR2700 Product page
(downloads).
Page 30

30
1 - Installing the Web GUI (v1.5.3) - Windows Operating Systems (2000, XP, 2003,
Vista, 2008, Windows 7)
1) After downloading the Web GUI, double-click the zip file to view the contents. Double-click “Setup”
to start installation. If you are running a 64-bit version of Windows 7, 2008 or Vista, you may need to
right-click the icon, and select “Run as Administrator.”
2)
Click “Run” to continue:
Page 31

31
2) The HighPoint Web RAID Management Service install screen will display. Click Next to continue:
3) Click Yes to install the Management utility:
Page 32

32
4) Specify the Destination folder and click Next:
Confirm the install location, and click Next:
Page 33

33
5) Select the SAF-TE configuration file for the system’s chassis. If the system does not support SAF-TE,
select the default option “Skip and Configure Later”.
6) Specify the listening port. 7402 is the default setting, and recommended for most systems.
Page 34

34
7) Choose to enable or disable Remote Access. Remote access allows the card to be managed via a Web
browser from a separate system.
8) Click OK to complete the installation procedure:
Page 35

35
2 - Starting the Web GUI
1) Double-click the “HighPoint Web RAID Management” Icon on the Desktop to start the Web GUI. The
system’s default Web Browser will open the following page:
2) Type in the default username and password to start the Web GUI:
Username: RAID
Password: hpt
Note: The password can be changed using the “Settings” menu from the toolbar.
3) Click Login. The Manage – Array screen will be displayed:
Page 36

36
3 - Web GUI – Icon Definitions
The Rocket RAID Web GUI uses a variety of Icons to represent various states or functions. The
following is a list of common icons, and their definitions.
1. :“Critical-broken” status. Fault-tolerance is disabled. The array requires a replacement disk in
order to rebuild parity.
2. :“Verifying” status. The controller is checking the consistency of RAID data.
3. :“Rebuilding” status. The controller is rebuilding the array.
4. :“Critical” status (may also be listed as “degraded”). If displayed above an Array: the array needs
to be rebuilt. If displayed above a Device (disk): this device is a member of the array that needs to be
rebuilt.
5. :“Disabled” status. An array or device marked as “disabled” has experienced a major hardware or
parity error, and is hidden from the operating system.
6. :This icon is shown when an array is being initialized. There are two types of RAID initialization:
The first is known as “foreground” – the controller will write “0’s” to the array disks. The array cannot
be used until this procedure is complete. The second is “background” – the card will rebuild the parity
data, while enabling access to the array.
7. :“Uninitialized” status. If displayed above an Array, this Array requires initialization (see number 6,
above). If it appears above a Device ( ), the disk is considered new – it must be initialized before
it can be used to create an array.
8. :This shows that Array is performing an OCE/ORLM procedure.
9. :This shows the OCE/ORLM procedure has been stopped or paused.
10. :This icon is displayed above ”Legacy Disks” – non-RAID disks ( ). The controller will
assign this status to disks that contain valid partition tables and/or useable data.
11. :This icon is displayed above “spare” ( ) disks。The controller will use spare disks to
automatically rebuild a critical array.
Page 37

37
4 - Web GUI - Configuring an Array
This guide assumes that the hard disks have already been installed into the external chassis, and attached to
the card. These hard disks must be initialized before they can be configured as arrays.
Initializing a new hard drive
Use the Initialize Devices option to prepare hard disks for use (creating arrays, rebuilding arrays, expanding
arrays, Spare disks).
1. Open the Web GUI interface, log-on, and select “Manage”, then “Device” from the toolbar:
2. Click the “Initialize Devices” button towards the top of the screen:
3. This will open a small menu. Check the box before the disk you wish to initialize and press “Submit”.
The initialized disk can now be added to the array.
Note: initializing disks will delete all data from the selected disks.
Page 38

38
Create an Array
To create an array, select Manage – Array from the Web RAID Management Utility’s toolbar. This will
open the Manage Array menu:
To create an array:
1) Select the desired RAID level from the Array Type drop down menu:
2) Name the array – enter a name for the array, using the Array Name filed (optional).
3) When creating a Redundant Array (RAID 1, 5, 10, 50), specify an initialization method. Select
Background of Foreground from the drop down menu:
No Initialization: Not recommended for most configurations. This option will not build parity.
Select this when testing storage. The array must be verified manually if this option is selected
Page 39

39
Foreground: The RAID initialization process will be set as high priority. The array cannot be utilized
this procedure is complete, but the build process will take considerably less time, as the host adapter
will dedicate its resources to completing this task. This is most secure option.
Background: This option lowers the priority of RAID initialization. This option will start to build
parity like the Foreground option, but at a lesser rate of speed. This option allows the array to be
accessed immediately. However, as a result, protection against data loss is much lower compared to
the Foreground option.
4) If you are creating a Redundant Array (RAID 1, 5, 10, 50), specify the array’s Cache Policy. If you
are creating a JBOD or RAID 0 array, skip to step 6. Select Write-Back or Write-Through from the
drop down menu:
Write Back – this setting is best for optimal transfer rates, and fully utilizes the available memory to
enhance read and write performance. However, this option raises the risk of data loss in the event of
hardware failure.
Write Through – this option raises the level of data security. Data is written directly to disk when this
Cache Policy is enabled.
However, this lowers the overall performance of the array, when compared to Write Back.
5) Assign hard disks to the array. To add a hard disk to the array, check the box displayed before
each disk’s entry. You can also use the “Select All” button to quickly select all disks attached to
the host adapter.
6) Specify the capacity. Manually enter the desired RAID capacity (in MB). If you wish to use all
available hard disk capacity, leave the “Maximum” entry in place, and proceed to the next space.
If you choose to specify the capacity, make a note that the remaining capacity (unused space) can
be used to configure additional arrays, or set to act as a “spare” disk.
7) Once all of the RAID parameters have been specified click the “Create” button to create the array.
The utility will display a brief summary after successfully creating the array:
Page 40

40
5 - Web GUI - Configuring Spare Disks
The term “Spare Disk” refers to a hard disk, or dedicated disk space, that is used to rebuild a RAID array in
the case of hard disk failure. If free ports/channels are available, spare disks are ideal for minimizing g
downtime – the administrator does not have to work directly with the storage devices, nor install or remove
any additional hardware in order to rebuild parity.
Spare disks can be created from available hard disks (disks that have been initialized) or free disk space
(unallocated space on a set of RAID disks – leftover space not assigned to an active array).
To configure Spare Disks, select Manage – Spare from the utility tool bar:
To assign a Spare disk:
1) Click on the box displayed before the target disk entry, under the Available Disks section, and
click the “Add Spare” button:
Page 41

41
2) Click “OK” when the pop-up window is displayed. This will add the disk to the Spare Pool.
3) To remove a Spare Disk from the Spare pool, click the box before the target Spare Disk, and click
the “Remove Spare” button:
The disk will be moved o the “Available Disk” Section
Page 42

42
6 - Web GUI - Recovering an Array
When a redundant array’s status is ”Critical”, fault tolerance is disabled. The array is can be used in this
format, but should be rebuild as soon as possible. If a Spare disk was configured, the RocketRAID
2740/2744 will use this disk to automatically rebuild the array. If a spare is not available, the array can be
rebuilt manually.
If Auto-Rebuild is enabled, simply install a new disk – the RocketRAID 2740/2744 will initialize the drive,
and initiate the rebuild process. If the setting is not enabled, follow the steps below.
To Rebuild an array:
1) Click “Maintenance” towards the right of the target array.
Page 43

43
2) Click “Add Disk”.
3) Select the desired drive and click “submit.
4) The Web GUI will initiate the rebuild procedure, and display a progress bar.
Page 44

44
7 - Web GUI - Maintaining RAID Arrays
Regular scheduled RAID Maintenance is essential to data security. We recommend routine RAID
verification sessions to ensure the parity of redundant arrays is properly synchronized. Unsynchronized
arrays face an elevated risk of data loss in the event of hardware failure, even if the array itself is left intact.
To schedule maintenance sessions, or “Tasks”, select the “Task” option from the utility toolbar.
This will open the Tasks List and Health Inspector Scheduler page:
Scheduling Tasks:
1) Enter a name for the task in the “Task Name” field.
2) Specify the frequency of this task. Click the open circle before the desired frequency (Daily, Weekly,
Bi-Weekly or Monthly).
3) Specify the time. Select the day from the drop-down menu, then enter the desired time in the provided
fields. Note: the Health Inspector Scheduler works from a 24-hr clock (3PM is represented as hour
“15”, for example).
4) Once the task has been named and scheduled, click the “Submit” button to add the task to the Task
List.
Page 45

45
Removing Tasks
1) From the task List, Check the box before the target Task and click “Delete”.
Page 46

46
SHI – Storage Health Inspector
The Storage Health Inspector section provides real-time device related information including temperature
readings, bad sector counts, and access to SMART data.
Click “SMART” besides each disk to see its SMART attribute status.
SMART attributes vary based on the disk model and manufacturer. This information is reported by the
drives themselves – SHI simply displays and organizes this data. If any attribute is reported to have
failed, or generated an error, we would recommend contacting the disk manufacturers for additional
technical support, and service recommendations.
Page 47

47
8 - Web GUI - Safeguarding your Array
The RocketRAID Host Adapter provides a number of innovative maintenance and notification features
designed to help streamline the administration of critical data storage, and minimize downtime in the case
of a major hardware failure. To access these features, select Settings – System from the utility toolbar:
Automatic RAID Rebuilding
Automatic RAID rebuilding can save an administrator considerable time when servicing a failed redundant
array, virtually eliminating downtime.
This feature instructs the Host Adapter to automatically initiate a rebuild procedure for a failed redundant
array, when the Administrator inserts a new hard disk, using the card’s Hot Swap (Rescan) options.
Simply inset the new hard disk and click “Rescan” from the Manage – Array page.
The host adapter will handle the rest.
Click on the drop down menu provided for “Auto Rebuild”. Select “Enabled” and click on the “Submit”
button.
Page 48

48
Enable Audible Alarm – enable or disable the card’s alarm. The alarm will sound if the disk or array stops
responding.
Event Log Path – Use this to select the location of the Web GUI’s event log.
Enable Continue to Rebuild on Error – this setting is disabled by default. We do not recommend using
unless replacement disks are unavailable, or if recommended by a Customer Support technician.
Set Rebuild Priority – The default setting is Medium. Alter this setting to lower or raise the priority of an
Initialization, Rebuild or Verification session. A lower setting devotes resources to other systems tasks. A
higher setting prioritizes the RAID maintenance session
Power Saving – Spin-down of idle disks (MAID)
This feature allows the card to safely power down RAID arrays when not in use.
Allowing idle disks to spin down minimizes the power consumption of the system’s storage devices.
In addition to saving energy, spinning down unused disks reduces mechanical wear and the buildup of
waste heat, which in turn, can greatly prolong the life of the system’s storage hardware, over the long-term.
Click on the drop down menu provided for “Spin down idle disk (minutes)”, and select a time (in
minutes). This determines when Host Adapter will power down idle hard disks.
Click the “Submit” button to activate this feature.
SAF-TE – This setting is related to the system chassis. The RR2740/2744 models do not support this
option.
Listening Port – This item is the card’s port address. 7402 is the default setting.
Password – Use this feature to change the Administrator’s password. The default password is “hpt”.
Page 49

49
9 - Web GUI - Event Notification
The RocketRAID 2740/2744 host adapter will record Administrator activity or RAID related errors to the
Web GUI’s Event Log. Data recorded to the event log is classified as an “event”. From the toolbar, click
“Event”.
The Event Log records and presents three types of “Events”:
Information: Information data includes all general user/administrator activity (creating/deleting
arrays, configuring spares, rebuilding arrays, configuring event notification and maintenance tasks, etc.).
Warning: Warning data includes alerts issued by the Host Adapter (SMART/SHI warnings including
temperature and sector alerts, unresponsive hard disks, unsynchronized parity due to a verification failure,
etc.)
Error: Error data includes instances of hardware related problems, such as hard disk failure, broken
arrays, card related problems (BBU, memory failure).
Note: Press the Clear button to delete the current event log
Page 50

50
Configuring SMTP (E-mail) Notification
The Web GUI provides an SMTP notification system – this feature can be used to instruct the Web GUI to
send Event data to an Email address. This feature is useful for remote maintenance sessions.
To configure E-mail notification, select Settings – Email from the utility toolbar:
1) Enable event notification – click on the box provided before “Enable Event Notification”.
2) Enter the E-mail Server Address.
3) Specify the E-mail “From” address.
4) Specify the user login name.
5) Specify the user’s password (this is required by some E-mail servers – consult your IT department
or E-mail service for more information).
6) Specify the SMTP port (25 is default).
7) Click the “Submit” button to save the SMTP settings.
8) Enter the recipient addresses under “Add Recipient”, and click the “Submit” button to save these
settings.
Additional options:
Test Recipient - You can test a recipient’s address using this option – this will send a default test message
to the selected E-mail address, and display a Pass/Fail message. If it is unable to send a message (Fail)
double- check the SMTP and recipient settings.
Delete recipient – to remove an E-mail recipient, check the box provided before the target E-mail address
and click the “Delete” button.
Page 51

51
10 - Web GUI - Advanced RAID Functions (Windows VSS, OCE/ORLM)
Sector Size
Capacity
512B
2TB
1K
2-4TB
2K
4-8TB
4K
8-16TB
VSS – Variable Sector Size
Variable Sector size allows you specify the sector size when creating a RAID array.
This feature allows older, 32-bit versions of Windows 2000 and XP to support volumes over 2TB. This
feature is limited to data volumes – boot volumes are still limited to 2TB in size. In addition, some types of
data management or backup software may not recognize the array properly, as they were designed to work
with the default Window’s sector size of 512B.
Using VSS
1. The VSS option is provided towards the bottom of the Create Array menu. In this example a 4-disk
RAID 0 array was created, using 1TB hard disks. A sector size of 1K is required for array with a
capacity of 1-4TB.
Page 52

52
2. After selecting the block size, the Web GUI will display a warning message:
Select OK to continue. Click the “Create” button once more to create the array.
3. The Web GUI will notify you that the array has been successfully created. Click OK to confirm.
4. After creating the array, access the Windows Disk Management utility. Click the “Start” button and
select “Control Panel”.
Page 53

53
5. Double-click “Administrative Tools”.
6. Double-Click “Computer Management”.
7. Under “Storage”, click on the folder icon labeled “Disk Management”. Disk Management should open
the Disk Wizard. Click “Next” to initialize the new volume.
Page 54

54
Disk Management
8. Click “Next” to continue
Page 55

55
9. Click “Finish” to continue.
10. Right-click the “Unallocated” box and select “New Partition”.
11. Partition and format the array as desired.
Page 56

56
Online Capacity Expansion and RAID Level Migration (OCE/ORLM)
OCE/ORLM allows you to add hard disks to an existing RAID array, and/or convert the array to another
RAID level. Data stored on the array is not lost during this procedure. The procedure described below
documents the expansion of a 3-disk 2TB RAID 5 array to a 4-disk, 3TB RAID 5 array.
1. Start the Web GUI and logon. Click “Maintenance” to the right of the target array.
2. Select the desired RAID level from the drop down menu (select the existing RAID level if you only
want to add hard disks to the array). Click the OCE/ORLM button.
3. The Web GUI will display the “Array Transforming” menu (similar to the create array menu).
Array transform/transforming Menu
Page 57

57
a) Target Name – The GUI will ask that you enter a “new” name for reference (the previous
RAID configuration will be displayed until the procedure is complete). The array's name can
be changed after the expansion/migration process is complete.
b) Specify the Cache policy (Write Back is default).
c) Specify the block size (note: not available for all controller models – check the product
documentation).
d) Select the existing RAID disks, and the disks you wish to add to the array.
e) Specify the capacity. Maximum (all available space assigned to the array) is default.
f) Click “Create” to start the expansion/migration process.
Page 58

58
4. The Web GUI will notify you when the process starts. A progress bar will be displayed under the Status
column of the Manage-Array menu.
5. After the expansion/migration process is complete, Disk Management should recognize the additional
capacity. You are free to create a second partition, or expand the existing partition.
Notes:
Bootable volumes should not be expanded beyond 2TB – Windows will not recognize the
additional capacity.
Older 32-bit versions of Windows (2000, XP) limit capacity to 2TB, unless the VSS option is used.
If the VSS option is not already enabled, do not use the OCE/ORLM function – the operating
system will not recognize the additional space. You will need to start from scratch – backup the
data on the current array and create a new array using the VSS option.
Make sure to enable “GPT” when initializing/partitioning arrays for use with Windows 2003, Vista,
2008 and, using the Windows Disk Management utility. This feature supports volumes over 2TB
in size, and allows for future capacity upgrades.
Page 59

59
Mac OS X Driver and Web-based RAID Management Utility
1 - Overview
The RocketRAID 2744 is compatible with Mac OS X. The OS X software package includes the driver and
Web GUI management utility.
Please check http://www.hptmac.com for the latest software/driver packages.
Driver updates are posted on the card’s product page, under the “Download Center” section.
The latest package is posted towards the right-hand side of the page, under “Mac Driver”. On the left-hand
side of the page, there is a section devoted to user documentation. The latest versions of the Product and
Web-based RAID Management Manuals are posted here.
2 - Installing the package
1) Double click the package named RR2744.mpkg to start the installer. Click Continue.
Page 60

60
2) You will be prompted that click the install button. This will install the RocketRAID 2744 driver. Click
Install.
3) You will be prompted that a reboot is needed to install the software. Click “Continue Installation”.
Page 61

61
4) The driver will be installed to system. Click “Restart” to restart the system.
After the system is restarted, you can use a web browser to configure the controller and setup
RAID arrays, and use MacOS X Disk Utility to create partitions on the RAID arrays.
3 - Installing Web RAID Management Software
HighPoint Web RAID Management Software is used to configure and keep track of your
hard disks and RAID arrays attached to the controller. Installation of the web management
software is optional but recommended.
Please refer to HighPoint Web RAID Controller Management Software documents for more
information.
4 - Web RAID Management Interface
Note: To use the web-based RAID management interface, a web browser with XML support
is required, e.g. Safari 2.0, Internet Explorer 6.0, Mozilla or FireFox.
To run the management interface, start your browser and enter the following URL address:
https://localhost:7402
If you are managing a remote system please change "localhost" to the server’s host name or
IP address. If you can't connect to local system, please check if a process named raidman-httpsd is
running on the system. If it is not running, you can start it manually by running the command
“SystemStarter start raidman” from terminal.
If you can't connect to a remote system, check if raidman-httpsd is running on that system
Page 62

62
and you can access the remote system via TCP/IP connection. If you have firewall configured,
make sure TCP port 7402 is not blocked.
5 – Uninstalling
To uninstall the driver you can simply remove the files copied to your system. Drag
/System/Library/Extensions/rr2744.kext to the trash and reboot to uninstall driver. You can
also run uninstall.command script in installation package to uninstall driver.
Page 63

63
Customer Support
If you encounter any problems while utilizing the RocketRAID host adapter, or have any questions about
HighPoint Technologies, Inc. products, please contact our Customer Support or Department.
Troubleshooting Checklist
Before contacting our Customer Support department:
Make sure the latest BIOS, driver and HighPoint RAID Management software has been installed
for the host adapter. The latest updates are available from our website.
Prepare a list of the computer system’s hardware and software (motherboard, CPU,
memory, other PCI-E devices/host adapters, operating system, applications)
Contact Information
HighPoint USA
Web Support: http://www.highoint-tech.com/websupport
E-mail address: support@highpoint-tech.com
Phone: 408-942-5800
9:00AM-5:00PM, Pacific Standard Time
Page 64

64
Thank You
Thank you for purchasing the RocketRAID 2740/2744 SAS/SATA RAID Host adapter. We appreciate
your support, and welcome any questions, comments or product suggestions you may have.
Contact Us
HighPoint Corporate Headquarters USA
Address 1161 Cadillac Ct.
Milpitas, CA, 95035
Website: http://www.highpoint-tech.com
Phone: 1-408-942-5800 (9 am ~ 6 pm PST, M-F)
Fax: 1-408-942-5801
Sales E-mail: sales@highpoint-tech.com
Support E-mail: support@highpoint-tech.com
Web Support: http://www.highpoint-tech.com/websupport/
Support Phone: 1-408-942-5800, request Support (9 am ~ 5 pm PST, M-F)
HighPoint Taiwan
5F., No.3, Swei Lane , Jhongjheng Rd.
Sindian City, Taipei County 231, Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Website: http://www.highpoint-tech.com/Taiwan/indextw.htm
Phone: + 886-2-2218-3435 (9 am ~ 6 pm)
Fax: + 886-2-2218-3436
E-mail: sales@highpoint-tech.com
Support: support@highpoint-tech.com
HighPoint China
4th Floor Kehaifulin Building, N0. 12
Zhong Guan Cun South Rd.
Haidian District Beijing, China 100081
Website: http://www.highpoint-tech.cn/
Phone: + 86-10-6213-0920 (9 am ~ 6 pm)
Fax: + 86-10-6897-5074
Sales E-mail: sales@highpoint-tech.cn
Support E-mail: support @highpoint-tech.cn
Page 65

65
FCC Part 15 Class B Radio Frequency Interference statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment under FCC rules.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
European Union Compliance Statement
This Information Technologies Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the following
European directives:
European Standard EN55022 (1998) Class B
European Standard EN55024 (1998)
 Loading...
Loading...