Page 1

Scaientific
Calculator
Owner’s
Manual
HP-275
[/
5ackaro
Page 2
-
A
27S
Z.8161
3,564,
5idaro
SCIENTIFIC
8084
2
_Z
4
6
—:Q
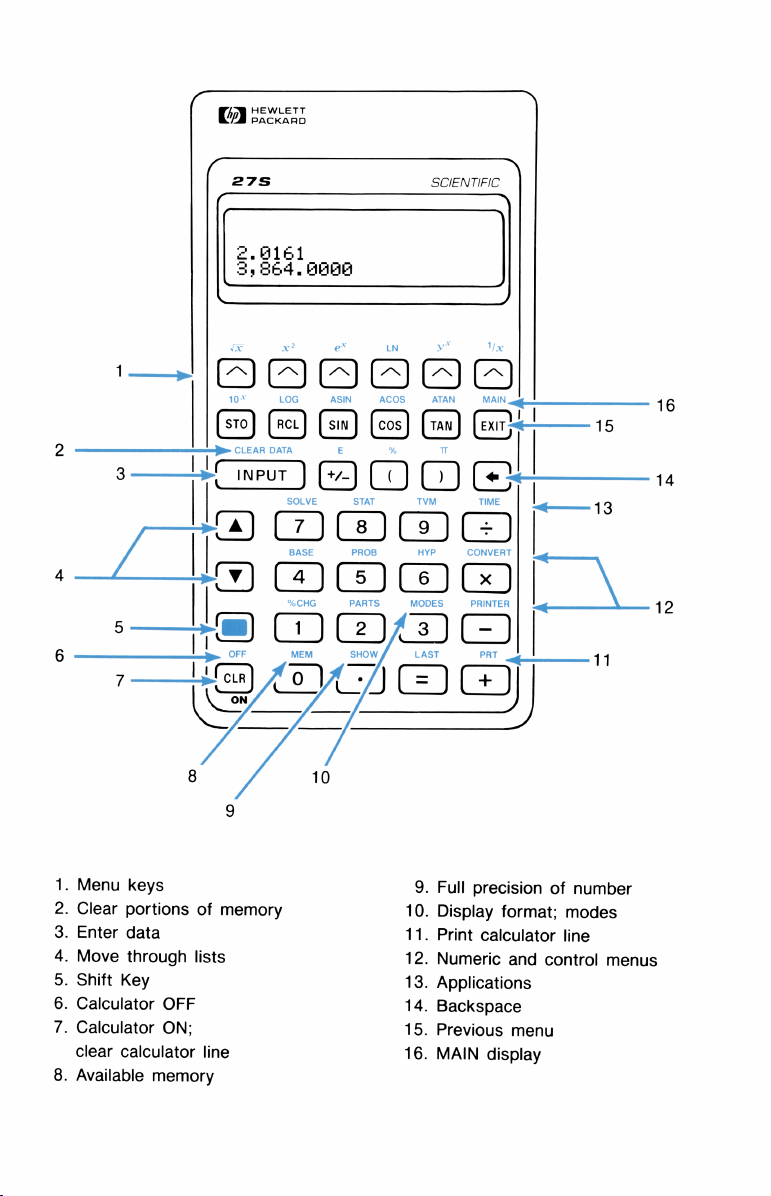
1.
Menu
2.
Clear
3.
Enter
4.
Move
5.
Shift
6.
Calculator
7.
Calculator
clear
8.
Available
—
—HGwmD)
---.-()
P
(4]
D
G
Lo
(=)
CLEAR
DATA
SOLVE
L7j[8][9jt
BASE
D
%
CHG
MEM
7_
8
9
keys
portions
data
through
Key
calculator
OFF
ON;
memory
of
lists
line
memory
()
@
10
ASIN
B
PARTS
(o)
OO
STAT
PROB
SHOW
[3
ACOS
ATAN MAIN
(]
MODES
LAST
9.
Full
10.
Display
11.
Print
12.
Numeric
13.
Applications
14.
Backspace
15.
Previous
16.
MAIN
(i
—1s
E
TIME
)
CONVERT
PRINTER
e
-JJ
precision
format;
calculator
and
menu
display
16
\
12
|
|
|
13
1 1
of
number
modes
line
control
menus
Page 3

Help
By
takingamoment
understand
them
out.
Us
your
Thank
Help
to
fill
You!
out
needs. Please
you.
this
read
card,
all
you
the
can
help
questions
HP
first,
to
then
better
fill
Model
HP-27S
Name
Address
City,
State,
Age
1.
Whatisyour
101[]Student
102[]Educator,
103[]Professional
104]Middle
2.
Whatisyour
201[Mechanical
202[]Civil
203]Electrical
204]Chemical
205[]Other
206]Surveying
207[]Data
208]Quality
3. In
what
301[]Education
302[]Banking,
303]Insurance
304]Real
305[]Business/Consulting
306]Technical
307[]Software,
308[]Construction,
309[]Mining,
4.
Where
401[]Retail
402[]Office
403]Bookstore
404]Department
406]Catalog
5.
How
501[]PreviousHPOwner
502[]AdviceofFriends,
503]MagazineorNewspaper
504]Press
Date
acquired
Zip
Phone
( )
POSITIONOROCCUPATION?
Researcher
Staff
Manager
AREAOFACTIVITYorFIELDOFWORK/STUDY?
Engineering
Engineering
Engineering
Engineering
Engineering
Processing
Control
INDUSTRYdoyou
Finance,
Investment
Estate
Consulting
Computer
Architectural
Oil
Drilling,
did
your
purchase
did
Computer
Equipment
you
Articles
Store
first
Store
hear
Store
Store
about
Collegues,
HELP
105]Top
106
107[]Field
108[]Technician
work?
Services
Services
Exploration
yourHPcalculator?
US
Manager
[_]
Owner,
Agent,
(SkipifStudentorRetired.
this
model?
Professor
Advertising
HELP
YOQU!
Business
(Please
check
only
one)
Principal,VP110]Retired
Rep
209]Purchasing,
210]Accounting,
211]Finance,
212[]General
213[]Marketing
214]Sales
215]Customer
216[]Other
310[]Chemical,
311]Agriculture,
312]Food
313[]Manufacturing
314]Manufacturing
315]Transportation
316[]Communication,
317[]Public
318[]Other
(Please
407(]Mail
408]Specialty
409]PurchasedbyCompany/School
410[]Directly
411]Other
505]Direct
506]Salesperson
507(]BrochureorIn
508[]Other
109]Independent,
111]Other
(Please
check
Scheduling,
Auditing
Investment
Administration/Management
Service,
Processing/Distribution
Admin./Government/Military
check
only
Order
Store
from
Mail
Please
Refining
Forestry,
Industrial
Consumer
Utilities
one)
HP
Store
Analysis
Maintenance
check
Livestock
Literature
___orHome
self-employed
only
one)
Inventory
Cntrl.
only
one)
Goods
Goods
___
Page 4

MAILED
POSTAGE
IF
NECESSARY
NO
THE
IN
STATES
UNITED
OR
CARD
CORVALLIS,
NO. 35
REPLY
PERMIT
CLASS
BUSINESS
FIRST
Company
ADDRESSEE
BY
PAID
BE
WILL
Hewlett-Packard
POSTAGE
Blvd.
Dept.
Circle
Inquiries
N.E.
1000
ATTN:
U.S.A.
97330,
OR
Corvallis,
Page 5

Comments
on
the
HP-27S
Owner’s
We
welcome
suggestions
Printing
Please
the
1=Strongly Agree
2=Agree
3=Neutral
®
The
®|can
®
The
®|can
®
The
®
The
®
The
®
The
®
The
®
The
1
Manual
your
evaluationofthis
helpusimprove
HP-27S
dateofthe
circlearesponse
Comments
manualiswell
find
informationinthe
easily
manual
examples
layout
illustrations
manual
chapter(s)
2 3 4
spacetoprovide
the
information|want.
understand
contains
are
and
format
are
length
and
manual.
our
publications.
Owner’s
manual
(from
for
eachofthe
4=Disagree
5=_Strongly
organized.
manualisaccurate.
enough
appropriate
are
clear
is:
appendixes|refertomost
5 6 7 8 9
Disagree
the
instructions.
examples.
and
attractive
and
helpful.
too
long
the
title
statements
additional
helpful.
and
Manual
Your
page)
opinions.
useful.
appropriate
frequently
comments
below.
12
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
A
You
2 3
2
2
2
2
2 3
2 3 4
too
are:
B
can
3
3 4
3 4
3
3
C
and
use
45
4 5
5
5
4 5
4 5
45
5
short.
D
Comments:
Name:
Address:
City/State/Zip:
Occupation:
Page 6

MAILED
POSTAGE
IF
NECESSARY
NO
THE
IN
STATES
UNITED
OR
CARD
CORVALLIS,
38
NO.
REPLY
PERMIT
CLASS
ADDRESSEE
BY
PAID
BE
WILL
Department
Division
Company
Blvd.
Circle
Computer
Documentation
N.E.
U.S.A.
97330,
OR
BUSINESS
FIRST
Hewlett-Packard
POSTAGE
Portable
ATTN:
1000
Corvallis,
Page 7

HP-27S
Scientific
Owner’s
Manual
Calculator
flf
Edition2February
Reorder
HEWLETT
PACKARD
Number
1988
00027-90028
Page 8

Notice
For
warranty
199
and
This
manual
vided
“as
Packard
this
manual
ing,
but not
and
fitness
be
liable
connection
the
keystroke
©
Hewlett-Packard
aptation,ortranslationofthis
prohibited
pany, exceptasallowed
Company
manual
The
programs
rights
are
programs
also
prohibited.
and
203.
and
is”
and
Company
or
the
limited
foraparticular
for
any
errorsorfor
with
the
programs
without
grants
in
you
this
Hewlett-Packard
that
reserved.
without
regulatory
any
are
makes
keystroke
to,
information
keystroke
subjecttochange
no
the
furnishing,
contained
Co.
1987.
prior
written
under
the
righttouse
control
your
Reproduction,
prior
written
implied
purpose.
for
this
calculator,
programs
warranty
programs
incidentalorconsequential
contained
without
of
any
kind
contained
warranties
Hewiett-Packard
herein
notice.
of
Hewlett-
with
herein,
merchantability
Co.
damages
performance,oruseofthis
herein.
All
rights
manual,
reserved.
including
Reproduction,
any
programs,
permissionofHewlett-Packard
the
copyright
any
laws.
program
Hewlett-Packard
containedinthis
calculator.
calculator
are
copyrighted
adaptation,ortranslationofthose
permissionofHewlett-Packard
see
pages
are
regard
includ-
shall
manual
Com-
and
Co.
pro-
to
not
in
or
ad-
is
all
is
Portable
1000
N.E.
Corvallis,
Computer
Circle
OR
97330,
Division
Bivd.
U.S.A.
Page 9

Printing
Edition
Edition
1
2
History
October
February
1987
1988
Mfg.
Mfg.
No.
00027-90029
No.
00027-90046
Page 10

Contents
11
ListofExamples
14
1
15
15
15
15
16
18
20
20
21
21
21
21
22
22
22
How
to
Use
Getting
Power
The
The
The
The
Display
Started
On
and
Display
Display
MAIN
Calculator
Messages
Annunciators
The
Keyboard
The@(Shift)
The
Editing
Viewing
Menu
Clearing
and
the
Keys
PortionsofMemory
This
Manual
Off
Contrast
Display
Line
Key
Key
Clearing
History
and
the
Stack
Menus
Calculator
With
With
[a]
Line
and
[V¥]
M(CLEAR
22
25
27
28
28
30
Using
Menus
Applications
Numeric
Control
Calculations
Display
Mode
Function
Menus
With
and
Menus
VariablesinMenus
FormatofNumbers
4
Contents
Page 11
31
32
32
34
34
34
35
35
36
38
40
42
42
42
43
43
45
46
46
49
51
53
53
59
60
61
62
Specifying
Places
Displaying
Scientific
(FIX
the
Mode)
the
and
Interchanging
Showing
Available
Beeper
Introducing
Typing
Editing
the
Full
Calculator
Function
the
Alphabetic
Alphabetic
Solver
SolvinganEquation
Keyboard
The
Arithmetic
Chain
Operator
Using
Reusing
Using
Numeric
General
Logarithmic
Arithmetic
Calculator
ParenthesesinCalculations
the
Registers
Line
Operators
Calculations
Priority
Previous
Functions
Functions
Functions
Trigonometric
Probability
Hyperbolic
Functions
Functions
PartsofNumbers
RangeofNumbers
Number
Full
Engineering
the
of
Displayed
PrecisionofNumbers
Notation
Period
and
Comma
Precision ofaNumber
Memory
and
the
ALPHA
Information
Information
and
Numeric
and
Result
Angle
([l[LAST))
Functions
Decimal
Menu
Functions
63
63
65
65
67
Base
Conversions
Switching
Bases
and
RepresentationofNumbers
Range
Arithmetic
of
HEX,
Operations
OCT,
and
Base
BIN
Arithmetic
Numbers
Contents
5
Page 12

4
69
70
71
72
74
74
75
76
76
79
81
85
Statistics
Entering
Entering
Viewing
CopyingaList
Naming
Switching
ClearingaList
One-Variable
Statistics
Linear
Weighted
the
STAT
Data
and
Editing
and
RenamingaList
Lists
Statistics
Operations
Regression,
Mean
Application
and
Calculating
Number
and
Creating
and
the
With
Curve
Grouped
List
to
the
Two
Fitting,
the
Running
Calculator
New
Lists
Lists
and
Standard
Total
Line
(GET)
Estimation
Deviation
87
S
89
90
91
92
93
93
94
94
95
95
Summation
The
Equation
Entering
Entering
Doing
Solver
Clearing
Viewing
Naming
Shared
Solver
Deleting
Deleting
Statistics
Solver
the
SOLVE
Equations
Calculations
Solver
and
an
the
All
Variables
Editing
Equation
Variables
Current
Equations
Application
the
Equation
Equation
and/or
and/or
Their
Its
Variables
Variables
6
Contents
Page 13

The
96
98
103
106
108
110
110
110
111
112
113
117
118
120
122
122
123
127
130
131
134
SyntaxofEquations
Solver
How
Time
Entering
Cash
TVM
Clearing
Loan
Savings
Functions
Conditional
Creating
Function)
The
Menus
Summing
Summing
the
Solver
Direct
Halting
Entering
and
and
Guesses
Outcomes
Value
the
Flow
Diagrams
Calculations
the
Calculations
Calculations
Expressions
for
Multiple
(Z)
Function
Operations
Works
Iterative
Solutions
RestartinganIterative
ofanIterative
of
Money
TVM
Application
and
TVM
Variables
Amortization
DisplayinganAmortization
PrintinganAmortization
(IF
With
Sign
Function)
Equations
STAT
Solution
Convention
Schedule
Schedule
(S
Lists
Search
136
136
137
139
139
140
140
142
143
143
Time,
Viewing
Setting
Changing
Adjusting
Appointments,
the
the
the
the
Appointments
Viewing
and
Acknowledging
Unacknowledged
Clearing
and
Time
and
Date
Time
and
Date
Time
and
Date
Clock
Setting
SettinganAppointment
an
Appointment
Appointments
Appointments
Date
Formats
Arithmetic
Contents
7
Page 14

145
145
146
147
147
8
9
148
149
149
150
150
151
152
153
154
154
154
156
158
160
163
165
166
168
171
172
176
179
181
183
186
188
Date
Arithmetic
Determining
Calculating
Calculating
Clearing
the
Day
the
Number
PastorFuture
the
Date
Arithmetic
of
Printing
Printing
Printing
Printing
Interrupting
Additional
Vector Calculations
Laws
Probability
SimulatingaTossofDice
Motionofa
The
Distance
Leasing
Interest
Finding
Moving
Chi-Squared
Calculating
Number
Speed
the
Other
Printing
Printing
Trace
Printing
and
Calculator
Information
Variables,
Descriptive
the
Printer
Examples
Adding
Angle
ProjectionofOne
Two
Between
of
Sines
Calculations
Catenary
Between
Calculations
Rate
Several
Average
Subtotals
of
Days
VectorsinPolar
and
Projectile
Equation
Conversions
Rootsofa
(x?)
the
Printer’s
Line
Lists,
Messages
Two
Vectors
VectoronAnother
Cosines
Two
Locations
Statistics
UntilaSpecial
the
Week
for
of
Days
Between
Dates
Variables
Power
(J§[PRT])
(J[PRINTER])
and
Appointments
Coordinates
Function
Day
Any
Dates
Source
Date
8
Contents
Page 15

189
189
189
191
191
192
194
195
196
196
197
197
198
199
199
200
200
201
201
201
202
202
202
203
203
203
Assistance,
Obtaining
Answers
Power
and
Low-Power
Installing
Managing
Resetting
Erasing
Clock
Accuracy
Environmental
Batteries,
HelpinOperating
to
Common
Batteries
Indications
Batteries
Calculator
the
Calculator
Continuous
Limits
DeterminingIfthe
Confirming
Limited
What
What
Consumer
If
the
Obtaining
Service
Shipping
Warranty
Service
Regulatory
Radio
Air
Calculator
One-Year
Is
Covered
Is
Not
Transactionsinthe
Calculator
Service
Charge
Instructions
on
Agreements
Information
Frequency
Safety
Notice
Covered
Service
Memory,
Questions
Memory
Memory
Calculator
Operation—The
Warranty
Requires
Interference
(U.S.A.)
the
Requires
Service
and
Service
Calculator
Service
Self-Test
United
Kingdom
Contents
9
Page 16

B
C
D
204
204
207
207
209
211
215
222
224
225
226
226
228
229
230
231
232
More
About
Direct
Iterative
Equations
SOLVE
Statistics
Curve
TVM
Numeric
Menu
Solutions
Solutions
How
the
Solver
The
Solver’s
Cases
and
Case2Solutions
Case
Case
Round-off
WhereARootisDisplayed
1b)
3:
Bad
4:
When
Used
Fitting
Function
Maps
The
Solver
FindsaRoot
AbilitytoFindaRoot
Guesses
a
Error
and
Solution
by
HP-27S
Menus
Tables
Isn’t
Menus
Iteratively
(Cases
Found
la
238
243
10
Contents
Error
Index
Messages
Page 17

List
The
only
of
following
the
examples
Examples
list
groups
that
the
requireamoderate
examplesbychapter.
1 StartingtoUse
28
29
30
36
37
39
40
3
64
67
4
73
77
83
85
87
Calculating
Numbers
Calculating
Using
WritingaSolver
Typing
Editing
Carbon-14
Base
Converting
ArithmeticinHEX, OCT,
the
NEW
the
%CHG
the
Radioactive
the
Radioactive
Dating
Conversions
Between
Statistics
UpdatingaCheckbook
One-Variable
Curve
Weighted
Grouped
Summation
Fitting
Statistics
Mean
Data
Statistics
the
Percent
in
Menu
Equation
and
and
number
HP-27S
Change
the
%CHG
inaChain
for
Decay
Decay
and
Base
Bases
and
Calculations
Estimation
Standard
The
list
of
steps.
Between
Menu
Calculation
Radioactive
Equation
Equation
Arithmetic
BIN
Bases
Calculations
Deviation
of
shows
Two
Decay
ListofExamples
11
Page 18

The
Equation
89
94
105
107
109
113
6
123
124
125
127
129
132
134
7
139
144
146
The
EquationofMotion
Temperature
NestedIFFunctions
Unit
Conversions
A
Series
Entering
Time
Value
A
Car
Loan
A
Home
A
Mortgage
A
Savings
An
Individual
DisplayinganAmortization
PrintinganAmortization
Time,
Setting
Setting
Appointments,
the
and
Calculating
Solver
for
Conversions
Using
Expansion
Guesses
of
Money
Mortgage
WithaBalloon
Account
Retirement
Account
Schedule
Schedule
and
Date
Date
and
Time
ClearinganAppointment
the
Number
of
Days
Free-Fall
Shared
Payment
Arithmetic
Between
Variables
Two
Dates
147
DeterminingaFuture
Date
8
12
Printing
152
ListofExamples
Trace
PrintinganArithmetic
Calculation
Page 19

Additional
154
156
158
160
162
163
165
166
168
171
172
174
Adding
Angle
ProjectionofOne
Law
of
Law
of
Probability
SimulatingaTossofDice
Motionofa
The
Catenary
Distance
CalculatingaLease
Present
Advanced
176
179
181
183
186
188
Interest
Finding
Moving
Chi-Squared
Calculating
NumberofDays
More
212
212
214
216
218
220
221
222
A
Case1Solution
A
Case1Solution
A
Discontinuous
A
Case2aSolution
A
Case
A
Case
A
Function
A
Case3Situation
Examples
Two
VectorsinPolar
Between
Two
Sines
Cosines
Calculations
Projectile
Equation
Between
(Capitalized)
Payments
Rate
Conversions
Several
Rootsofa
Average
(x?)
Subtotals
About
2b
Solution
2c¢
Solution
the
Dippingtothe
Coordinates
Vectors
VectoronAnother
Two
Locations
Payment
Value
of a
and
OptiontoBuy
Function
Statistics
UntilaSpecial
Solver
With
One
Root
With
Two
Roots
Function
(Relative
Minimum)
X-Axis
Lease
Day
With
ListofExamples
13
Page 20

How
The
you
joy
people
each
the
We
to
Use
HP-27Sisdesignedtominimize
enjoy
reading
immersing
don’t
paragraph.
calculator
have
some
manuals
yourselfinthis
wanttoput
So,
we’ve
while
you
suggestions
This
Manual
your
needtouse
cover-to-cover,wehope
one.
However,
aside
written
use
it.
for
whatever
the
using
they’ve
manualtohelp
the
manual
that
we
know
been
doingtosavor
you
effectively:
the
you
manual.
will
that
learn
If
en-
most
about
B Read
chapter1foranoverviewofhow
duces terms
B
The
HP-27S
are
unfamiliar
read
pages43through
calculations.
B
There
are
the
subject
B
B
pendix
Before
lator
For
Browse
stroke
ideas
D.
doing
uses
this
example
for
and
concepts
does
keyboard
with
this
several
waystolocate
index,
the
time-value-of-money
positive
information,
through
putting
and
refertopage
the
examplesinchapter9.You
you
can
the
the
used
throughout
arithmetic
wayofdoing
using
arithmetic
45inchapter2before
information:
listofexamples,
and
problems,
negative
numbers
120.
use.
Justasimportant,
HP-27S
to
work
for
HP-27S
the
manual.
algebraic
calculations,
you
the
tableofcontents,
the
menu
learn
in
financial
you
you.
works.Itintro-
logic.Ifyou
please
do
multi-step
maps
in
how
the
calcu-
calculations.
may
seeakey-
may
find
some
ap-
14
How
to
Use
This
Manual
Page 21

Getting
Power
The
HP-27Sispowered
shipped
To
the@(shift)
Memory,
To
stop
If
play,
instructionsonpage
The
The
To
or
with
turnonthe
turningitoff
conserve
using
you
see the
you
Display
Display
adjust
[-].
Started
On
and
batteries
calculator,
key,
energy,
it.
low-battery
should
Contrast
the
display
then
replace
Off
by
installed.
press
[CLR].
does
the
calculator
the
192.
contrast,
three
mercury
[CLR].Toturn
Since
not
affect
turns
annunciator
batteriesassoonaspossible,
hold
batteries.
the
the
calculator
the
information
itself
off10minutes
(§&==J)atthe
down
The
calculator
has
while
calculator
off,
Continuous
you’ve
stored.
after
topofthe
using
you
press
is
press
you
dis-
the
1:
Getting
Started
15
Page 22
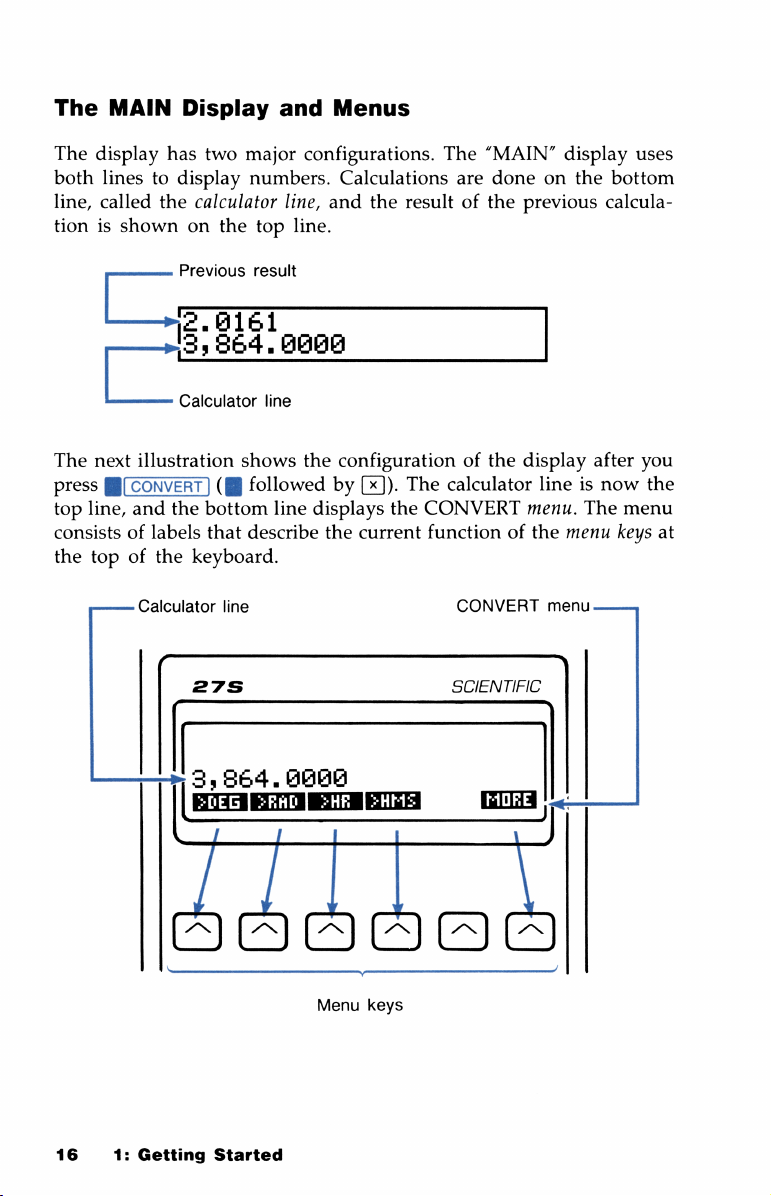
The
MAIN
The
display
both
linestodisplay
line,
called
tionisshown
Display
has
two
the
calculator
on
major
numbers.
the
top
and
Menus
configurations.
Calculations
line,
and
the
line.
The
“MAIN”
are
done
resultofthe
display
on
the
previous
uses
bottom
calcula-
Previous
|2
—
The
next
press[CONVERT
top
line,
consistsoflabels
the
topofthe
3y
Calculator
illustration
and
the
keyboard.
Calculator
(
27S
3,
mmmm
)
result
8161
864.B08H
line
shows
([}
bottom
that
line
864.08680
the
followedby[x]).
line
describe
configurationofthe
The
calculator
displays
the
the
current
CONVERT
functionofthe
CONVERT
SCIENTIFIC
GG
=
display
lineisnow
menu.
The
menu
menu
)
|
after
menu
keys
you
the
at
rAHL]fi(—]
Menu
keys
16
1:
Getting
Started
Page 23
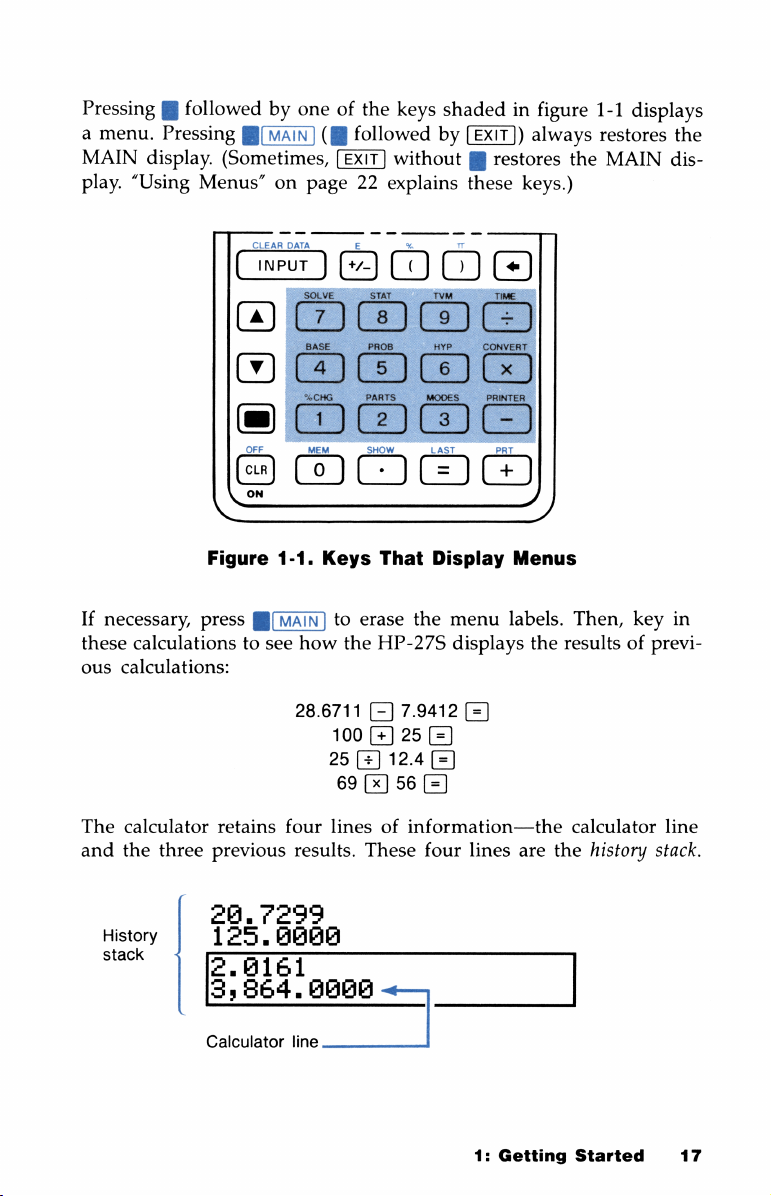
Pressing[lfollowedbyoneofthe
a
menu.
MAIN
play.
Pressing[vAIN]
display.
“Using
(Sometimes,
Menus”
([l
followedby(ExIT])
on
page22explains
keys
shadedinfigure
always
without[restores
these
keys.)
1-1
restores
the
displays
MAIN
the
dis-
If
necessary,
these
calculationstosee
ous
calculations:
CLEAR
Con)
OFF
Figure
press
1-1.
J[MAIN]toerase
DATA
(A
MEM
Keys
how
the
28.6711
100
25
69
E
Yo
(0
SHOW
That
the
HP-27S
(=]
7.9412
25
(3]
12.4
[x]56(=)
s
)
LAST
Display
menu
displays
[=]
[5)
[5)
&
PRT
Menus
labels.
Then,
the
resultsofprevi-
key
in
The
and
isory
stac
calculator
the
three
retains
previous
2@,
7299
125,
Z.0161
3,
864.
Calculator
four
linesofinformation—the
results.
These
8089
0080
line
<—
four
lines
1:
Getting
are
calculator
the
history
Started
line
stack.
17
Page 24

The
Calculator
The
following
Arithmetic
Line
examples
calculations
use
the
calculator
are
coveredingreater
line
for
simple
detailinchapter
calculations.
2.
Keys:
24.715
62.471
[+]
(=)
Display:
24,715+
87.1860
Whenacalculation
number
19(x]12.68
If
ous
(+]
(=)
Math
key
startsanew
(=]
you
pressanoperator
result
remainsinthe
1155
functions involving
24@.9200
240
356.4200
right.
3.57
B=
(=]
2.36
2.5700+5.5696
9.1396
has
been
calculation.
key
calculator
,92088+115.5
one
Description:
Adds
completed
(by
pressing
Calculates19x
after
completingacalculation,
line.
Completes
calculation.
number
use
the
number
Calculates
Completes
calculation.
24.715
and
[=]),
the
furthesttothe
2.362.
the
62.471.
pressing
12.68.
the
previ-
a
You
6.9
918
18
can
do
(x]5.35(+]
(=)
1:
Getting
“chain”
36.9158<
48,2124
Started
calculations
without
using
(=]
Pressing
intermediate
after
[+]
each
step.
displays
answer.
the
Page 25
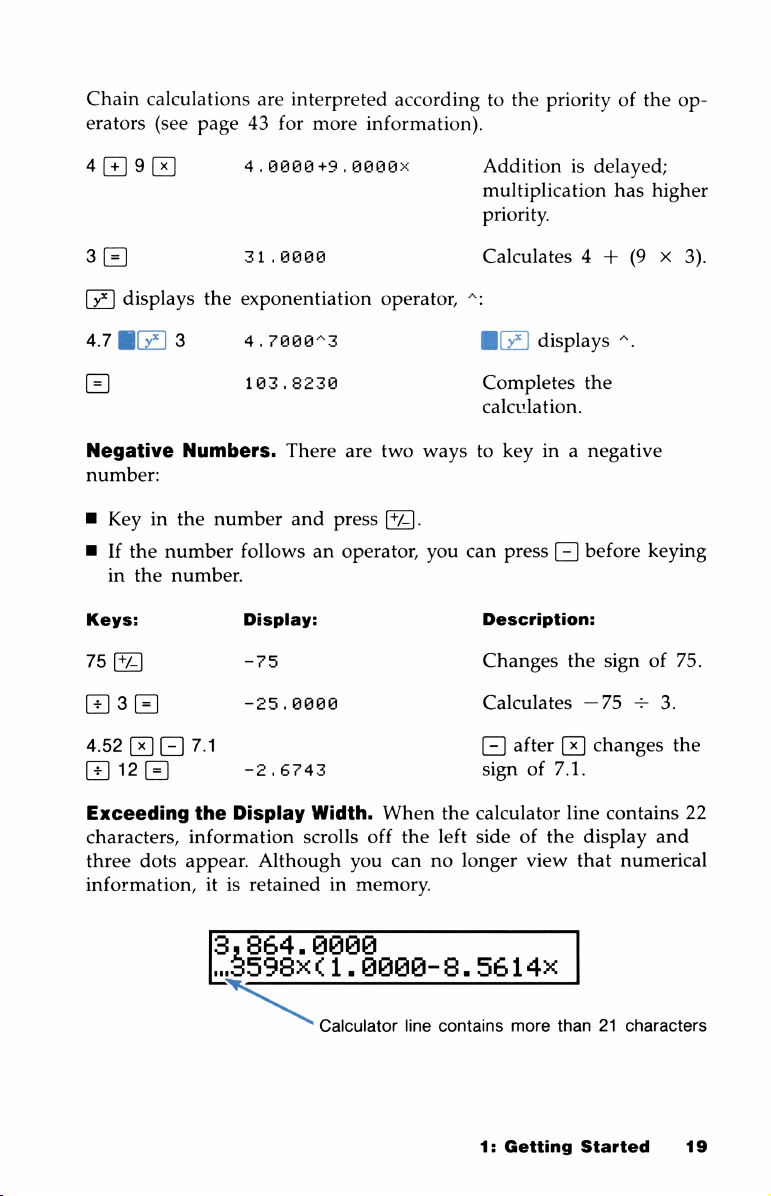
Chain
erators
calculations
(see
page
43
are
interpreted
for
more
accordingtothe
information).
priorityofthe
op-
4 9
3
(=)
displays
478
(=)
Negative
number:
B
Keyinthe
B[fthe
in
the
Keys:
75
(+]3(=)
452
()12
(=]
the
3
Numbers.
number
number.
(x][=]
7.1
4.,0000+9,0000x
31.0000
exponentiation
4,7800"3
183.8230
There
number
and
are
press
followsanoperator,
Display:
-75
-25.00008
-2.6743
operator,
two
ways
[*4].
you
Additionisdelayed;
multiplication
priority.
has
Calculates4+
*:
B
(7]
Completes
calculation.
to
keyina
can
press
Description:
Changes
Calculates
(-]
after
displays
(-]
the
negative
before
the
signof75.
—75
changes
~.
signof7.1.
higher
(9x3).
keying
=+
3.
the
Exceeding
characters,
three
dots
information,
the
Display
information
appear.
itisretained
3
864.88680
5535%¢1.0PPP-5.
TN
Width.
scrolls
Although
Calculator
in
When
off
you
memory.
the
can
line
the
left
no
longer
contains
calculator
sideofthe
view
5614%
more
than
1:
Getting
line
display
that
21
Started
contains
and
numerical
characters
22
19
Page 26
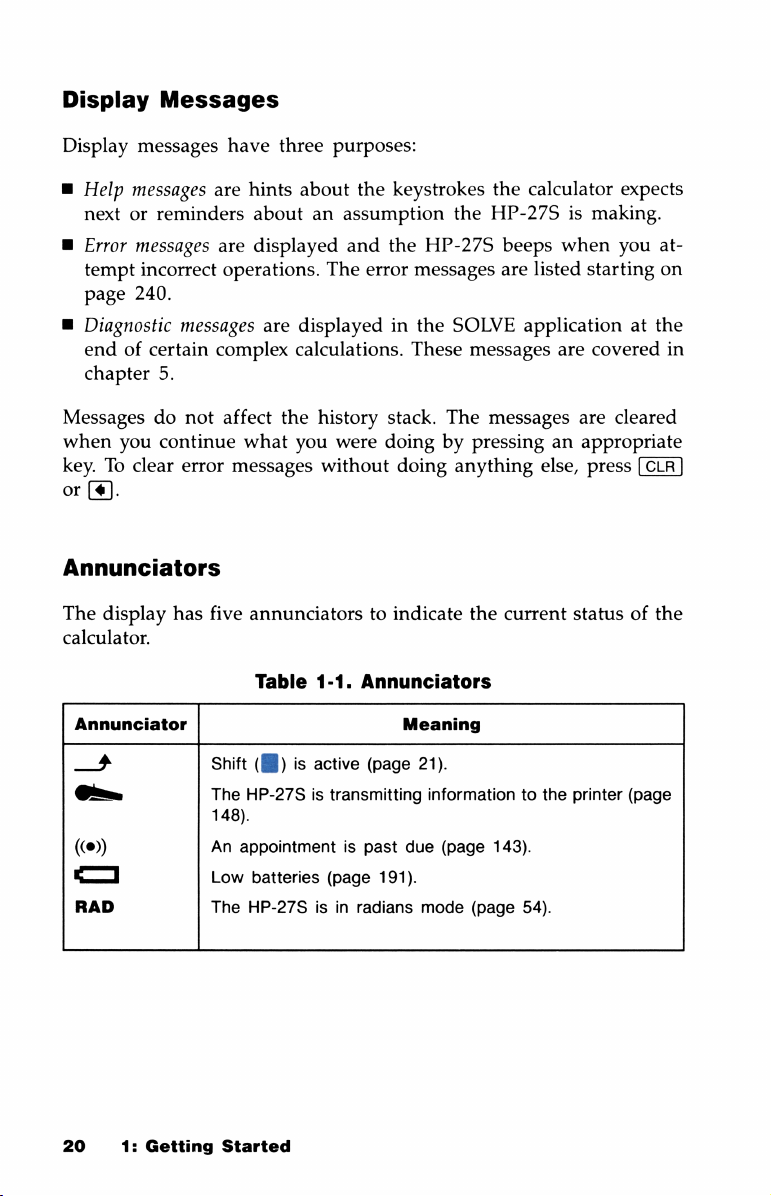
Display
Messages
Display
W
B
B
Messages
when
key.Toclear
or
Annunciators
The
calculator.
Annunciator
4
O,
((®)
1
RAD
messages
Help
messages
nextorreminders
Error
messages
tempt
incorrect
page
240.
Diagnostic
endofcertain
chapter
you
(¢].
display
messages
5.
do
not
continue
error
has
have
three
purposes:
are
hints
about
the
aboutanassumption
are
displayed
operations.
are
complex
affect
the
what
messages
five
annunciatorstoindicate
Table
shift()is
The
HP-27Sistransmitting
148).
An
appointmentispast
Low
batteries
The
HP-27S
and
The
error
displayedinthe
calculations.
history
you
were
without
1-1.
Annunciators
active
(page
(page
191).
isinradians
keystrokes
the
HP-27S
messages
These
stack.
doingbypressinganappropriate
doing
Meaning
21).
informationtothe
due
mode
the
calculator
the
HP-27Sismaking.
beeps
are
listed
SOLVE
The
anything
(page
applicationatthe
messages
messages
else,
the
current
143).
(page
54).
expects
when
you
starting
are
covered
are
cleared
press
statusofthe
printer
(page
at-
on
in
20
1:
Getting
Started
Page 27

The
Keyboard
The[(Shift)
Most
keys
haveasecond
blue
shift
key
press
and
release[}to
press
the
key.
B(OFF])
If
annunciator.
turns
you
accidentally
The
The
into
memory.
calculations.
manual.
Editing
When
you
furthesttothe
and
the cursorisvisible,(](backspace)
keyed
in.
Key
accesses
For
example,
the
Key
keyisusedincertain
You
Using
Clearing
When
right.
function
these
turn
pressing[lfollowed
calculator
press[,press@againtoturn
can
also
is
the
cursorisnot
printedinblue
operations.Todoa“shifted”
on
the
shift
annunciator
by
off.
applicationstoenter
use
covered
the
in
placeof(=]inarithmetic
whereitis
Calculator
deletes
visible,
(4]
above
off
used
Line
the
deletes
the
key.
operation,
(__4).
throughout
last
Then,
(also
written
the
shift
information
character
the
number
The
the
Pressing
line.
When
and
restores
an
the
when
the
calculatorison
error
messageisdisplayed,
original
contentsofthe
usually
calculator
1:
clears
erases
Getting
the
line.
Started
calculator
the
message
21
Page 28

Viewing
(a]
and
history
line.
In
tional
the
stack
STAT
stored
the
[v]
roll
when
and
information.
History
the
history
thereisan
SOLVE
Stack
stackupand
applications,
With
incomplete
(ao]
and
down.
calculationinthe
(o]
and
[¥]
You
let
(V]
cannot
you
view
roll
the
calculator
addi-
Menu
The
increase
cause
The
changeasyou
use
Clearing
B
three
data
sociated
discussionsofthose
Using
Pressing
menu.
change)
Keys
six
keysatthe
they
menu
these
CLEAR
previous
associated
For
menu:
the
number
change
keys
have
switch
functions
Portions
clears
results.Incertain
with
with
menus
Menus
oneofthe
example,
topofthe
of
functionasyou
shifted
menus.
without
the
that
is
menus.
shifted
pressingB[%CHG
keyboard
operations
functions—\/x,
When
pressing
of
Memory
history
menu.
covered
Using[[CLEAR
keys
are
menu
available
switch
menu
.
from
menus.
labels
With[CLEAR
stack—the
menus,[CLEAR
throughout
labeled
calculator
the
with
displays
x?,
bold
keys.
the
etc,
are
manual
letters
the
%CHG
The
menu
keyboard
thatdonot
absent,
to
line
also
clear
in
you
and
clears
data
the
displays
(percent
keys
be-
can
the
as-
a
6.
8884
KNLR
S
Percent
22
1:
Getting
Started
change
IEE
menu
Page 29

The
menu
Here,
percent
menu
The
The
B
oLp
change.
and
keys
that
tableisdivided
Applications.
menus.
that
Pressinganapplication
application.
youtoaccess
pressing@TIME
the
TIME
menu.
B
Numeric
numeric
B
(°:CHG]
calculations.
B
Control
to
Some
key
menus.
control
menus
switches
keys
are
now
,
HNEW,and
Pressing[MAIN]
restores
the
display
accordingtothe
Eachofthe
Menus
all
the
displays
application.
functions.
functions
displays
the
Control
the
optional
contain
between
labeledbythe
%cH
(or,inthis
MAIN
menus
display.
are
describedintable
four
applications
key
“branching”
functionalityinthe
the
TIME
Each
keyinthe
Numeric
available
numeric
menus
function
from
the
function
allow
printer.
more
than
six
labels.Inthose
the
“pages”ofthe
bottom
are
variables
three
typesofmenus:
displays
from
the
application.
menu—the
TIME
menus
keyboard.
menu
youtoset
menu.
lineofthe
usedtocalculate
case,
[(EXIT])
1-2onpage
consistsofa
the
top-level
top-level
menu
For
top-level
menu
displays
extend
For
for
the
example,
percent
certain
menus,
display.
erases
group
menu
example,
menu
another
number
change
modes
a
the
24.
of
in
allow
in
of
and
MORE
1:
Getting
Started
23
Page 30
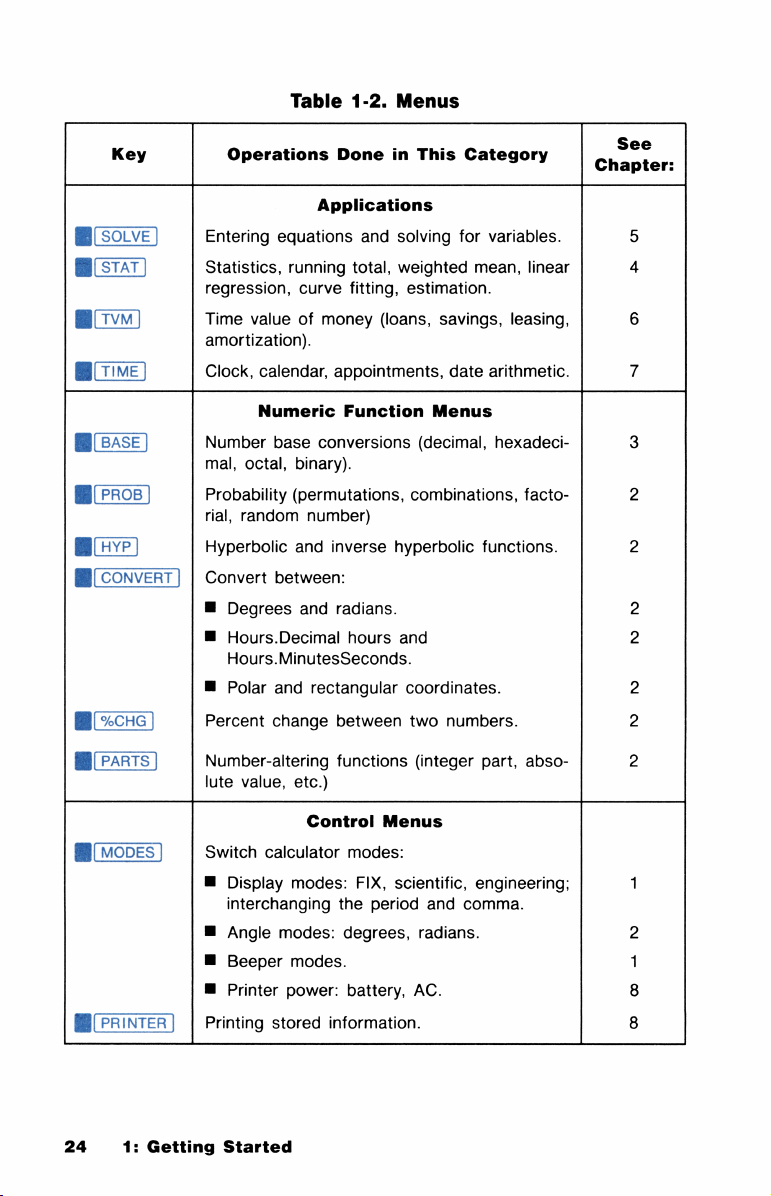
Table
1-2.
Menus
Key
B(soLvE])
B
(sTAT]
Bvv]
B(TvE)
B
(BAsSE]
B(ProB]
B(HvyrP)
B[
CONVERT]
B
(sCHG)
Operations
Applications
Entering
Statistics,
regression,
Time
amortization).
Clock,
Number
mal,
Probability
rial,
Hyperbolic
Convert
B
B
B
Percent
equations
running
curve
valueofmoney
calendar,
Numeric
base
conversions
octal,
binary).
(permutations,
random
Degrees
Hours.Decimal
Hours.MinutesSeconds.
Polar
number)
and
inverse
between:
and
and
rectangular
change
Done
in
This
and
solving
total,
weighted
fitting,
estimation.
(loans,
savings,
appointments,
Function
radians.
hours
between
Menus
(decimal,
combinations,
hyperbolic
and
coordinates.
two
numbers.
Category
for
variables.
mean,
date
arithmetic.
hexadeci-
functions.
linear
leasing,
facto-
Ch:‘:t!er:
6
7
3
2
2
2
2
B
(PARTS]
B
(MODES
@(PRINTER]
24
1:
Number-altering
lute
value,
Switch
B
B
B
B
Printing
calculator
Display
interchanging
Angle
Beeper
Printer
stored
Getting
Started
etc.)
Control
modes:
modes:
modes.
power:
information.
functions
Menus
modes:
FIX,
scientific,
the
period
degrees,
battery,
(integer
engineering;
and
comma.
radians.
AC.
part,
abso-
2
1
2
1
8
8
Page 31

Applications
Figure
top-level
CALC
shows
m
B
1-2
illustrates
STAT
menu
menu
(displayed
th
e
functionofseveral
Use
ofanapplication
Use[MAIN]toleave
to
display
A
T11||11
STAT
menu
B(vAN]
CALC
menu
two
menu
(displayed
when
the
previous
restores
the
application
CALC
|
TOTAL
levelsinthe
when
you
press
other
menu.
the
MAIN
B(sTAT)
INSR
I
MEAN MEDN
|
MIN
you
keys:
display.
and
MAIN
DELET
MAX
STAT
press
[[STAT])
€AL&).The
Exiting
restore
Display
NAME
| |
STDEV
| |
SORT
application—the
and
illustration
from
the
top
the
MAIN
GET
display.
TOTAL
]
RANG
MORE
]
FRCST
MORE
the
level
Figure
1-2.
An
Application
Menu
1:
Map
Getting
Started
25
Page 32

Figure
do
1-3
not
needtopress@[MAIN]toswitch
application
exit
from
the
of
the
new
STAT
Menu
illustrates
key
(for
switching
example,
previous
application.
from
[[STAT])
application,
MAIN
Display
one
applicationtoanother.
applications;
and
performs
entry
into
two
the
B(sTAT]
You
pressing
an
operations—an
top-level
menu
TIME
Menu
CALC
INSR
DELET.
NAME
GET
TOTAL
‘
CALC
APPT
I
ADJST
B(sTAT]
CALC
Menu Menu
TOTAL
MEAN
MEDN
STDEV
‘
RANG
MORE
‘
APT
1
APT
’
APTBI
2
APT
B(sTAT)
APT
MSG
Menu
‘
RPT
Figure
1-3.
Switching
DATE
TIME
Applications
‘
A/PM
l
SET
APPT
|
)
APT
5
3
HELP
l
MORE
4
26
1:
Getting
Started
Page 33

Numeric
The
major
tion
menus
®
Numeric
branching
B
Numeric
the
%
CHG
’
OLD
Function
differences
are:
function
from
functions
application.
menu
|
NEW
‘
%CH
Menus
between
menus
these
menus.
canbeused
W[7CHG
I
have
numeric
only
within
CALC
TOTAL
function
one
applications
level;
STAT
menus
there
arenomenus
without
application
and
applica-
| |
’
INSRT
|
I
MEAN‘STDEV‘MORE
NAME
DELET
MEDN
GET
|
RANG
leaving
|
TOTAL
|
Figure
Numeric
ample,ifyou
menu,
1-4.
function
UsingaNumeric
menus
display
does
replace
the
%CHG
not
returntothe
Function
one
another
menu
%CHG
and
Menu
then
menu.
1:
inanApplication
(see
figure
1-5).
switchtothe
Getting
Started
For
ex-
HYP
27
Page 34

B
(~CHG]
MAIN
application
Display
menu
or
(EXIT]
%CHG
NEW
oLD
Control
Each
plays
operation
data,
Calculations
Many
a
setofvariables
menu
%CH
Figure
1-5.
Menus
control
the
menu
menu
has
you
performedissetting
the
exit
occurs
With
application
and
accessedbymenu
locationincalculator
bers
into
the
known
Example:
Numbers.
the
%CHG
Calculating
Calculate
menu.
.m
Switching
one
were
level.
viewing
Numeric
Exitingacontrol
the
automatically.
Variables
numeric
memory.
variables
the
the
You
andtosolve
Percent
percent
function
change
COSH
SINH
Function
previously.
display
formatorprinting
in
Menus
menus
keys.
The
use
the
menu
for
Change
between
HYP
menu
ASNH
TANH
Menus
menu
When
the
do
calculations
variables
keystostore
the
unknown
Between
37.5
and
‘
ATNH
ACOSH
always
dis-
control
stored
using
areanamed
num-
variable.
Two
55.6
using
Press@[%CHG]
variables
keystrokes
28
1:
OLD,
for
Getting
to
display
NEW,
doing
Started
the
and
%CH.
the
calculation.
%CHG
The
menu,
following
which
consistsofthe
illustration
shows
the
Page 35

Keys:
Display:
Keys:
Display:
Keys:
Display:
55.6
37.5
:
™1
%CH_
NEMW
OLD
NEW
%
CH
Calculator
Memory
Example:
number
variables:
Keys:
Display:
Keys:
Display:ilDi=2%
Keys:
Display:
The
B
15%
15
HEHEE=~
&
25.85
NEW
HEW=Z1,
rules
To
storeavalue,
If
the
calculator
the
expressionisevaluated
stored.Tostore
pressing
calculator
just
keyed
Calculating
less
than
EIROH
15
OLD
&an
275
for
using
line
only
the
menu
line
that
in).
NEW
in
the
25.85.
This
calculation
menu
variables
keyinthe
containsanexpression
the
rightmost
key.
Also
was
previously
number
and
use
are:
the
%CHG
calculated
and
result
number,
to
Menu.
NEW
press
(for
(in
storeanumber
Calculate
uses
the
same
|
%CH
the
menu
example,2[x]
this
case,
press
(one
that
you
the
three
|
Calculator
Memory
key.
58),
100)
is
before
on
the
haven’t
1:
Getting
Started
29
Page 36

B
To
calculateavalue,
number.Inother
another,
message
the
second key
CALCULATING.
®Torecallapreviously
lowed
by
the
menu
valueinOLD.
BToclear
all
the
variablesina
menuisdisplayed.
B
Certain
variables
pressamenu
words,
storedorcalculated
key.
The
are
store-only
mapsinappendixDindicate
key
without
when
you
press
two
doesacalculation.
..isbriefly
For
example,
menu,
history
stackisalso
these
displayed.
pressiCLEAR
or
calculate-only.
variables.
menu
During
value,
gLo
cleared.
first
keying
keys
one
after
calculations,
press
displays
while
The
menu
in a
the
fol-
the
the
Example:
the
percent
is
usedtostore
Keys:
45
B(:CcHG)
.95
STO oLD
25
NEW
%CH
(=)
Display
When
played
The
The
you
with
display
MODES
Using
the
change
Display:
42.7500+
16
42.75680+16,80800
42
42.7500+56,2500
99.0000
Mode
turnonthe
four
decimal
mode
controls
menu
%CHG
between
only
.75808+25,80800
and
16
the
rightmost
Format
Menu
HP-27S
places
how
is
usedtochange
inaChain
and
25tothe
productof45x.95.
number
Description:
Calculates
Stores16in
Stores25in
Calculates
Completes
calculation.
of
Numbers
for
the
first
time,
andaperiodasthe
numbers
are
formattedinthe
the
display
Calculation.
on
the
calculator
the
%CH.
the
numbers
decimal
mode.
product.
OLD.
NEW.
are
display.
Add
line.
dis-
point.
30
1:
Getting
Started
Page 37

Decimal
ELEI:T
mmmm
point,
digit
separator
DI
SPLHH\FDRMHT
/
Scientific
Select
0—11
Regardlessofthe
12-digit
mantissa
display
withasigned,
pressing@[-]inFIX4mode
is
storedas3.14159265359
Specifying
(FIX
Mode)
To
specify
1.
Press[MODES].
2.
Press
from0to
the
Number
the
number
of
F1®.Keyinthe
11)
and
press
\
notation
decimal
mode,
places
each
three-digit
displays
x
10000,
of
displayed
number
[INPUT].
Full
calculator
Engineering
notation
numberisstoredasa
exponent.*
3.1416.
Displayed
decimal
of
decimal
Internally,
Decimal
places:
precision
For
places
example,
the
number
Places
(an
signed,
integer
*
During
results.
complex
internal
calculations,
the
HP-27S
uses
15-digit
1:
Getting
precision
for
Started
intermediate
31
Page 38

Keys:
Display:
Description:
45.6
(=]
@
FIX
.1256
3.7274
(VODES
3
5.727
@8
(voDEs
FI&"
6
5.727360
@
(vODES
FIR
4
5.7274
Whenanumberistoo
mat,itis
Displaying
To
display
digits,
displayedinscientific
the
Full
numbers
as
press[MODES]
Initially,4decimal
places.
Displays3decimal
places.
Displays6decimal
places.
Restores
places.
largeortoo
smalltobe
notation.
Precision
of
Numbers
preciselyaspossibleuptoamaximum
ALL
four
decimal
displayedinFIX
of
for-
12
Scientific
Scientific
mantissa
10
32
with
raisedtoa
1:
Getting
and
Notation.
one
digittothe
power.
Sign
of
mantissa
Started
Engineering
Scientific
leftofthe
Digits
decimal
-1.234567232012E-5
e
Mantissa
Notation
notation
after
point
(12
expressesanumber
decimal
digits
point,
Sign
of
exponent
maximum)
multiplied
Power
of
as a
by
10
Page 39

To
1.
2.
specify
scientific
Press
@(voDES],
Keyinthe
11)
and
number
press
notation:
then
of
[INPUT].
8E1
decimal
placesinthe
mantissa(0through
Engineering
a
mantissa
point,
To
multipliedby10
specify
1.
Press[voDES],then
2.
Keyinthe
first
Keying
play
mode,
by
an
exponent:
1.
Keyinthe
change
2.
Press
3.Ifthe
4.
Keyinthe
Notation.
with
Sign
mantissa Mantissa
engineering
digit
in
Numbers
you
the
(E]
exponentisnegative,
Engineering
one,
two,
or three
raisedtoa
c?ilgirt"sflg?tne:r
first
digit
[
-12.3456789012E-12
L
of
notation:
ENG
numberofsignificant
and
press
(INPUT].
With
Exponents.
can
always
mantissa.Ifthe
keyina
mantissaisnegative,
sign.
to
start
the
exponent.
press
exponent.
notation
expressesanumber
digitstothe
power
divisible
Sign
exponent
/
(12
digits
maximum)
digitstobe
Regardlessofthe
number
asamantissa
[-].
leftofthe
evenlyby3.
of
Powerof10
(multiplesof3)
displayed
use
decimal
after
current
followed
as
the
dis-
to
1:
Getting
Started
33
Page 40

Keys:
478
B[]
13
()8
M(E]
25
(=]
2.36
[*~)
M(E]
(=]15[x]12([=)
Display:
5.9750E-13
-2.8320E-14
Description:
4.78x1013=8x10?5
equals
5.9750x10713,
—236x10715x12
=
—2.832x10714,
Interchanging
You
can
interchange
separator.
To
interchange
then
For
1,080,00808,.080080
.-,
Showing
To
temporarily
lator
line,
press@and
two
numbers
Release
in
Available
The
HP-27S
use.[lMEM]
displayed
has
displays
until
the
the
characters
example,
the
the
view
one
decimal
Full
the
full
then
the
calculator
to
restore
Calculator
approximately
the
you
release
Period
million
point
and
usedasthe
canbedisplayed:
or
and
digit
Precision
12-digit
hold
the
precisionofthe
down
line,
only
calculator
[SHOW].Ifthere
the
line.
Memory
6,900
bytesofmemory
amountofunused
[MEM].
Comma
decimal
1.800,.0080,08008
separator,
of
rightmost
memory.
press [l
a
Number
numberinthe
number
available
The
point
and
MODES
are
more
is
shown.
for
information
digit
|,
calcu-
than
your
is
AVYAILABLE
6,883 BYTES
34
1:
Getting
Started
HMEMORY:
864
Page 41

If
you
attemptanoperation
rently
have
available,
the
that
HP-27S
requires
displays:
more
memory
than
you
cur-
You
must
eraseaportionofyour
proceeding
tional
information).
stored
(see
Beeper
Ordinarily,
tone
when
come
due.
ling
when
1.
Press[lMODES
2.
Press
HP-27S
B
BEEPER
an
B
BEEPER
B
BEEPER
due
3.
Press
INSUFFICIENT
(see
“Managing
You
“Erasing
Continuous
Function
the
beeperison,
error
messages
However,
the
BEEP
displays
appointment
and
[EXIT].
the
beeper
oneormore
ON:
OFF.
ON.
when
The
previously
Calculator
can
also
Memory”
erase
Memory”
and
the
calculator
are
displayed
HP-27S
has
three
sounds.Tochange
MORE
timestochange
the
appropriate
APPTS
comes
The
beeper
beeper
error
messages
ONLY.
due.
message:
The
does
sounds
are
MEMORY
stored
all
the
on
and
beeper
the
beeper
not
sound.
when
displayed.
information
on
page
194
information
page
196).
sounds
when
beeper
the
an
appointments
modes
for
mode:
mode,
sounds
an appointment
for
you've
audible
control-
until
only
before
addi-
the
when
comes
Introducing
The
SOLVE
and
create
menus
isabrief
alphabetic
and
introductiontothe
characters,
other
characters
the
application,orSolver,
consistingofthe
this
not
eredindetailinchapter
Solver
and
lets
variablesinthose
Solver.
section
Because
also
presentonthe
5.
the
you
enter
equations
explains
keyboard.
1:
ALPHA
your
how
The
Getting
Menu
own
equations
equations.
usually
to
Started
contain
type
letters
Solveriscov-
This
35
Page 42

Example:
equation
where:
WritingaSolver
for
computing
Equation
the
rateofdecayofradioactive
—kt
=
lnl
for
Radioactive
N
0
Decay.
substances
The
is:
t=elapsed
k=the
rate
substance.
Ny,=the
N
=
The
Typing
The
menu,
amount
the
amount
equation
Alphabetic
ALPHA
andatother
ters.Itallows
®
Uppercase
B
Space.
B
Various
other
letters.
time.
constant
for
the
Variablestandkmust
of
the
substance
of
the
substance
must
be
writtenina
Optional
-KXT
Solver
Information
menuisdisplayed
times
when
youtotype
lettersAthrough
characters,
the
characters
including
decay,
characteristicofthe
use
presentatt=0.
presentattime
form
spaces
=
LNCN+N@>
——
function
when
you
you
needtoenter
that
Z.
punctuation
the
the
press
are
same
¢.
Solver
HEW
alphabetic
notonthe
and
particular
time
units.
can
interpret:
in
the
keyboard:
non-English
SOLVE
charac-
The
lettersAthroughZare
example,Ais
restores
displayedbypressing
the
ALPHA
character.
36
1:
Getting
menu,
Started
displayedbypressing
so
you
ABEBE
are
"A
readytotype
two
.
Pressing
menu
the
keys;
next
for
A
Page 43

|
ABCDE
l
<
—_—
lG|LTI
>#space
FGHI
|
l
|
space
$
¥,.
———
|
JKLM
OTLER
|/
I
NOPQ
FE
AOUg?
-
|
RSTUV
l
1
L’J \I/
.,
J
WXYZ
OTlER
AAoON,;
y
l
Alph
mgni
Letters,
space
OTHER
characters
AC&°A
e’
Each
letter
menu
~!@"
\
has
%
.
J
an
thanAthroughZ.Pressing
same
setoffive
through
The
seven
letter
includeaspace
The
following
can
use
(4]tocorrect
further
editing,
characters
setsofcharacters.
menus
with
only
character
keystrokes
typing
refertothe
( )-
enter
tion.”
Example:
keystrokestoenter
Typing
the
Radioactive
the
equation
Solver:
Keys:
@
(SoLvE
B
[NEMW
S
-
OTHER
OTHER
plus
four
mistakes
next
I
.
key
for
in
any
MGRE,which
letters
the
(for
radioactive
discovered
section,
“Editing
Decay
—KXT
J
accessing
letter
characters
menu
allows
displays
youtopage
example,Nthrough
decay
equation.
right
away.Todo
Alphabetic
Equation.
=
LN(N-+NO0)
Display:
ALPHA
-
Use
into
menu
other
the
Q)
You
Informa-
these
the
JKLM
RSTUWY
WXYZ
(=)
K
-K
~Kx
T
-KXT
-KxT
-KxT
1:
Getting
(space)
=
Started
37
Page 44

ABCDE OTHER
to
displayaspace)
B(LN]
(typing
JKLM
NOP@R
(=]
NOP@Q
(0]
(“zero”
key)
i
H
H
aid)
or
HOPQ
(another
H
way
-KxT
—KxT
-KxT
~KXT
-KXT
-KxT
=
(space)
=
LHN¢
=
LNCN
LN(M:
=
=
LNC(N=N
=
LN(N+N®B
—KxT=LNCN+N@)
Enters
memory.
the
equation
into
@(L\]isatyping
lists
the
other
typing
etc.)
are
not
active
Editing
The
ALPHA
Alphabetic
menu
whichisdisplayed
you
press
EDIT
monu
T
ALPHA-edit
menu
T
ALPHA
menu
aid
during
aids.)
when
alphabetic
The
the
ALPHA
Information
hasacompanion
when
you
in
the
SOLVE
|
CALC
[
DEL
| l
<<—
|
ABCDE
entry.
application
menu
menu,
exit
from
menu.*
|
EDIT
<—
|
FGHI
JKLM
the
|
(Table
keys
is
the
ALPHA
I l
—_>
NOPQ
5-3onpage
(B[
SOLVE|,BI[STAT],
displayed.
ALPHA-edit
menu
or
|
DELETE
—=>
|
RSTUV
]
ALPHA
|
menu,
when
|
NEW
]
WXYZ
98
*
38
The
ple,
ALPHA
ALPHA-edit
when
you
menu
1:
Getting
menuis“skipped
press
NEW
before
typing
Started
any
in
the
over”
whenitmakesnosensetodisplay
SOLVE
characters.
menu, and
when
you
press
it—for
in
examthe
Page 45

Table
1-2
describes
insert
keyisnecessary—characters
the
keys
for
editing
alphabetic
are
insertedatthe
information.
cursor
position.
No
Key
DEL
(L=~
==
o)
i
ALPHA
(&)
CLR
Example:
dioactive
are
separated
the
Editing
decay
usedtoidentify
fromitbyacolon.)
equal
sign.
Table
Deletes
Moves
the
again,
moves
Moves
the
Moves
the
Moves
the
again,
moves
Displays
Backspace;
Clears
the
equation
1-2.
Alphabetic
ALPHA-Edit
the
characteratthe
cursortothe
the
cursor
cursor
one
positiontothe
cursor
one
positiontothe
cursortothe
the
cursor
the
ALPHA
erases
calculator
the
Radioactive
equations.
menu.
Keyboard
the
charactertothe
line.
enteredonpages37and38DECAY.
They
Also
Editing
Description
cursor
left
sideofthe
one
display
right
sideofthe
one
display
Decay
precede
delete
Menu
position.
widthtothe
widthtothe
Keys
Equation.
the
Keys
display;
left.
right.
display;
leftofthe
the
equation
spaces
when
left.
when
right.
cursor.
Name
before
pressed
pressed
the
(Names
and
and
ra-
are
after
Keys:
EDIT
ABCDE
ABCDE
ABCDE
ALFHA
D
E
c
Display:
-KxT
D-KxT
DE-K=T
DEC-K=T
1:
=
LHCN+N@2
=
LHCH+H&>
=
=
Getting
LHCH+=HA2>
LMCH+N@>
Started
39
Page 46

ABCDE
WXYZ
A
¥
DECA-KXT
DECAY-KXT
=
LNC(N+N@>
=
LN{(N+NB&>
ABCDE
EXIT
Solving
Press
cay
Example:
sequoia
of
of
gramofcarbon.
OTHER
->
€ALE
equation
tree
this
woodis15.3
wood
from
!
=
(four
times)
DEL
an
Equation
to
display
enteredonpages37and
8.
868y
KTN
Carbon-14
Dating.
exchanges carbon with
counts
the
centerofthe
The
rate
1C,is1.20x10~%How
Keys:
Display:
the
menu
per
constant
oldisthe
DEL
of
N0
Wood
its
minute
tree
for
DECRY
:-KXT
DECAY:-KxXT
DECAY:-KXT=LN{(H+N@>
Enters
variables
the
for
edited
the
38.
on
the
outer
environment.
per
gramofcarbon.Asample
yields
the
radioactive
tree?
Whatisthe
10.9
counts
Description:
=
LNC(N+N@&>
=
LN(N+N@&>
equation.
radioactive
surface
The
of a
giant
radioactivity
per
minute
formofcarbon,
half-lifeof14C?
de-
per
1.28(E](=)
K
10.9
153
H
NB
T
40
1:
Getting
4
K=.080801
N=18.9086
NB=15.3000
T=2,825.7583
Started
Stores
rate
Stores
activityattime
Stores
initial
Calculates
in
years.
constant.
activity.
age
of the
T.
tree
Page 47

Calculate
the
material
1
H
2
No
the
half-life
(t.,)of14C,
presenttodecay.
N=1.8600
NB=2.0000
that
is,
the
N=1
ratio
t=tl/z.
Stores
time
is
N/Ny,
required
derived
=
Nj.
from
%2
for
when
half
the
¥
T=5,776.2265
Calculates
Displays
menu.
half-life.
the
SOLVE
1:
Getting
Started
41
Page 48

2
Keyboard
Numeric
The
The
lineofthe
when
Calculator
The
as
erases
Calculator
calculator
menu
MAIN
16.2785
25.800808
calculator
MEAN=124,68.
the
2
[=]
MAIN
line
label
would
Arithmetic
Functions
lineisalmost
display,
labels
are
displa
Py
line
can
Pressing
and
continues
calculate
Line
always
and
present.
B7crc)
>
-
B(VAIN]
contain
an
124.60
and
present.Itoccupies
moves
messages
the
to
the
top
25.
8888
OLD
NEW
and
labeled
operatorornumeric
calculation.
plus
2.
For
the
lineofthe
Calculator
/
=CH
%
numbers,
function
example,
bottom
display
CHG
menu
such
key
pressing
line
Arithmetic
The
following
42
2:
Keyboard
Operators
keystrokes
Arithmetic
illustrate
and
simple
Numeric
arithmetic
Functions
operations.
Page 49

Keys:
Display:
Description:
54.69
=)
750
(]
5
B4
360
28.33
12(=]
(=]
(=)
53,0200
9,000.0000
25.0000
625.0000
BVAIN]6()
3
(=]
Chain
Chain
after
Calculations
calculationsdoa
each
operation.
systemofoperator
Keys:
216.0000
Display:
sequenceofoperations
Chain
calculations
priority
describedinthe
Addition.
Multiplication;
number
startsanew
Division;
erator
continues
Exponentiation.
B
before
essaryinthe
display.
without
evaluate
expressions
next
section.
Description:
pressing
key
after
calculation.
pressinganop-
key
after
(=]
the
calculation.
is
unnec-
MAIN
pressing
using
a
(=]
=]
the
750
360
12(+]
(=]
Operator
Some
chain
For
example,9+
9,000.0000-
25.0000
Priority
calculations
12+3
12
9+—=
2:
Keyboard
=
3
Calculates
value.
Completes
calculation.
mightbeinterpreted
has
two
interpretations:
and
9+
Numeric
13
Arithmetic
several
3
intermediate
the
different
_
Functions
ways.
43
Page 50

The
sions:
HP-27S
usesasystemofoperator
prioritytoevaluate
expres-
The
HP-27S
you
keyinhas
Calculate
9+13—2
Keys:
9(+]12(+]
3(=]
Calculate4x
4[x]7
3
5
B
(+]
(exponentiation)
(=]
=]
calculatesanintermediate
lowerorequal
:
Display:
9.0000+12,.
13,0000
73
plus5x
4.00808x7,8888"
1,372.0000+
1,372.0000+5,0000x%
priority.
0000+
72
plus
6.
Highest
Lowest
result
Description:
Pressing
9+12;
priority
(7]
than
Calculates4x
(x]
than
priority
priority
when
the
than
has
(x].
has
higher
(+].
[+]
[+]
higher
next
does
has
[+].
priority
operator
not
add
higher
priority
73.
78]
6
Ifacalculation
tent
(=]
with
2
requires
operator
multiplication),
44
2:
Keyboard
~B0BA+5,
7.00880"2
1,617
1,623.0000
priority
use
parentheses.
Arithmetic
BEOAX
.0060+
that
operationsbedoneinan
(for
example,
and
addition
Numeric
(%]
has
than
[x].
Adds5x
Completes
calculation.
order
before
Functions
higher
priority
72to1,372.
the
inconsis-
Page 51

Using
Use
they
Parentheses
parenthesestogroup
are
performed.*
in
Calculations
operations
andtospecify
the
orderinwhich
Calculate
Keys:
9+
(J9(+]12))]
(]3[=]
Calculate
__30
85—12
30(+]((J85(-]
12
(J16.9(-]8()]
B
(=]
:
Display:
21.0608
7.0000
X
\V16.9—8
:
30.0PPBB+(85.0080-
30.0000+73.0000
@.4110x
®©.4118x8,9000
@.41109%2.9833
1.2260
Description:
evaluates
parentheses.
Parenthesis
viding30by
evaluates
parentheses.
Calculates
evaluates
30
parentheses.
Calculates
Completes
calculation.
\/8.9.
the
contents
prevents
85.
inside
=
73.
contents
of
di-
of
of
*
Closing
25+
parenthesesatthe
(3x(9+12
(=]isequivalentto25+(3x(9+12))
2:
Keyboard
endofthe
Arithmetic
expression
canbeomitted.
[=].
and
Numeric
For
example,
Functions
45
Page 52

Reusing
B
LAST
the
copies the
processofdoing.
Previous
previous
The
following
Result
result
intoacalculation
keystrokes
(7]
use[LAST
0821x(18+273.1)=?
2x.0821x(18+273.1)=?
3x.0821x(18+273.1)=?
LAST])
you
areinthe
to
calculate:
Keys:
.0821
2731
2
(x]BLAST]
(=]
CLR
3
B[
LAsT)
=)
Using
The
They
u
number
beriscopied
u
displayedinthe
Registers
HP-27S
are
accessed
n,
wherenisaninteger0through9,copies
in
n
copies
Display:
18
()]J(=]
23.8993
2.8000x23,8993
47,7986
0.0000
71.6979
has10registers
using
the
calculator
with
full
precision.
the
contentsofR,tothe
current
display format.
for
storing
and
[RCL].
linetothe
Description:
First
Second
Clears
prevents
becoming
Third
numbers—R,
designated
calculator
answer.
answer.
calculator
47.7986
last.
answer.
through
the
register.
line.
The
line;
from
Rq.
rightmost
The
num-
number
is
To
The
46
cancel
storeorrecall
following
2:
Keyboard
keystrokes
(27.1+35.6)x1.0823
Arithmetic
after
you've
pressed
useR;andR,to
(27.1+35.6)1.0823
and
Numeric
or [RCL],
calculate:
Functions
press
(¢].
Page 53

Keys:
Display:
Description:
27.1
35.6
=)
STO
1
1.0823
2
]
RCL
1
B
(ReL]
2
(=)
Clearing
to
cleararegister
vious
accessedbyany
Registers.Tocleararegister,
value
with
B2,
78008
5TO
62,7808
62
.7808x1,8823
67
8682+
RCL
_
&7.BE6B2+62.,70084
Mo
2+e2.7A808
0
&
=M
oD@
=J™0
)
My
O
—
=
store0in
before
the
storingavalue,
new
value.
since
Furthermore,
applicationsorfunctions.
Calculator
awaits
register
number.
Stores
Stores
Calculator
62.7inR;.
1.0823inR,.
awaits
register
number.
Recalls
Recalls
contentsofRj.
contentsofR,.
Exponentiationisdone
before
division.
it.Itis
n
the
registers
unnecessary
replaces
the
are
pre-
not
ArithmeticinRegisters.
tions
that
canbeperformed
Table
(sTO](=]n
(sTO](+]
2:
Keys
B
(%]
Keybnard
2-1.
n
n
n
n
Table
2-1
describes
on
numbers
Arithmetic
New
Number
old
number+displayed
old
number—displayed
old
numberxdisplayed
old
number+displayed
old
number~displayed
Arithmetic
and
the
arithmetic
storedinregisters.
in
Registers
in
Register
number
number
number
number
number
Numeric
Functions
opera-
Page 54

The
following
keystrokes
use
two
registers
to calculate:
Keys:
1.097
0
25.6671
1
(=]
0
(x]10(sTO][+]
1
1
(=]
1.097
1.097
Display:
x
x
25.6671
35.6671
1.09780
1.8970%x25.6671
28.1568
1.8970
sSTO+_
1.8970x10.0000
1.8978x%x35.6671
39.1268
=
?
?
Description:
Stores
Stores
First
Recalls
and
tion.
1.097inR,.
25.6671inR;.
answer.
contentsofR
startsanew
Calculator
number.
Adds
10tocontents
R;.
ContentsofR;
rightmost
Second
answer.
awaits
replace
number.
calcula-
register
of
You
can
example,
rent
contentsofOLD
48
2:
also
do
2
Keyboard
arithmetic
oLD
by2and
Arithmetic
with
(in
the
the
%CHG
stores
and
values
the
Numeric
stored
menu)
in
variables.
multiplies
productinOLD.
Functions
the
For
cur-
Page 55

Numeric
Many
of
the
ample,
menus
This
follows:
B
B
®
B
®
B
(see
section
General
Logarithmic
Trigonometric
B
Degrees/radians
u
T
®m
SIN,
B
Angle
Hours.Decimal
coordinates
Probability
mutations
Hyperbolic
Number-altering
parts,
rounding
Functions
numeric
(sine),@[Loc
figure
describes
functions:
functions:
and
COS,
TAN,
and
coordinate
(CONVERT
functions:
(PROB
and
functions
are
(base10logarithm).
2-1onpage
eachofthe
\/;
angle
angle
ASIN,
50).
x?,
1/x,%,and
LN,
e¥,
functions:
modes.
ACOS,
numeric
LOG,
conversions:
hours/Hours.Minutes
menu).
factorial,
menu).
inverse
functions:
(PARTS
random
hyperbolic
absolute
menu).
visibleonthe
Others
functions,
%CHG
10*.
ATAN.
degrees/radians,
Seconds,
number,
functions
value,
integer
keyboard—for
areinfunction
categorized
(percent
change).
polar/rectangular
combinations,
(HYP
menu).
and
fractional
ex-
as
per-
Base
conversions
2:
are
coveredinchapter
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
3.
Numeric
Functions
49
Page 56

OLD
°/o
NEW
1D
BASE
)
)
[_][_J[j
HG
PARTS
=
L
Cunfaales
OFF
ME!
SHOW
()
FP
Figure
RND
ABS
2-1.
Numeric
XCORD
Function
| |
SINHlTANH
COSH
—
TVM
‘ACOSH'
ASNH
“TIME
_JL)
YP
CONVERT
W
MODES
N
LAST
>DEG
| |
YCORD
>RAD
Menus
PRINTER
R
>HR
l
A
—
>HMS
l
D/R
ATNH
MORE
I
MORE
50
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Functions
Page 57

General
Functions
@],
lator
Keys:
B[z,
line.
45@=)
SWi/x[+]
B/
(=]
125@y*]
3W/sE]
B(vAIN]
(=?]
Percent.
B
When
operator
B
B
When
rightmost
number
and@[1/x]
You
do
not
Display:
6.7082
4
B.3333+0.2500
8.5833
5.00
5.9
34.8100
The
[}(%]function
thereisonly
preceding
divides
+
the
or—precedes
number
preceding
actonthe
rightmost
needtopress[}when
performs
one
number
the
rightmost
rightmost
the
asapercentage,
the+or
in
the
numberisanything
number
rightmost
and
—.
number
menu
Description:
\V45.
Calculates1=~
Calculates
125.
No
needtouse
(x?]inMAIN
two
different
calculator
by
100.
number,
returns
in
labels
are
cube
display.
operations:
line,orwhen
but+or
[j[<
interprets
that
percentofthe
the
calcu-
absent.
3,1=4.
root of
[§j
before
the
the
—,
Keys:
85.3
B
(=]
200
B
(=)
(x]
(-]
25
27
Display:
85.3000x0.,2700
22.8310
200
.0000-50.0000
156,
0008
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
Description:
Divides27by
Calculates
Calculates
Completes
calculation.
and
Numeric
27%
25%
the
Functions
100.
of
of
85.3
200.
51
Page 58

Percent
percent
change
ables—OLD,
additional
change.
between
NEW,
information
The%CHG
two
and
%CH.
about
menu
numbers.
If
necessary,
using
does
calculations
The
menu
contains
refertopage
variablesinmenus.
based
three
29
on
for
the
vari-
Calculate
Keys:
B
(>:CHG]
291.7
316.8
Todoa
tion,
menu
OLD
NEW
%CH
percent
you
variablesonpage
12Xthe
65
12
80
[(sT0]
oLD
45
(sT0]
%CH
NEW
the
must
number
[x]
percent
difference
Display:
OLD=291.70086
NEW=316.800808
#“CHANGE=8.60847
change
use
calculationinthe
with
29).
45%
larger
The
780.0000x
780.0000%x580.0000
750.0000x45,
780.0000%x116.0000
between
the
menu
following
than
0000
80.
291.7
and
Description:
Displays
Stores
Stores
Calculates
change.
middleofa
key
(see
keystrokes
Stores80in
Stores45in
116is45%
80.
316.8.
%CHG
OLD.
NEW.
percent
chain
the
rules
calculate65X
OLD.
%CH.
larger
menu.
calcula-
for
using
than
(=]
52
2:
Keyboard
90,480.0000
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Completes
calculation.
Functions
the
Page 59

Logarithmic
The
logarithmic
line.
You
do
labels
are
absent.
Functions
functions
not
needtopress[before
use
the
rightmost
number
and
in
when
the
calculator
the
menu
Table
Natural
Natural
multiplying
Show
Keys:
47.5
(=)
47.5
(=]
Keys
@]
@[N]
@[N]
68.3
B
that
@(LN]
68.3
Trigonometric
Trigonometric
Radians—determine
trigonometric
assumes
Degrees.MinutesSeconds).InRadians
in
radians.
that
and
all
2-2.
Logarithmic
Function
antilogarithm.@[10*]
logarithm.
numbersisequivalenttoadding
Display:
3.8687
3.8687+4,2239
3,244,2508
3,244
Mode.
angles
,2500
and
Angle
The
how
numbers
coordinate
are
measuredindecimal
two
conversion
Keys
@
Functions
trigonometric
are
Functions
Base10antilogarithm.
L0oG]
Base10logarithm.
Description:
Natural
Natural
Natural
the
Compare
result.
interpreted
functions.
mode,
Function
logof47.5.
logof68.3.
antilogarithm
sum.
to
modes—Degrees
when
Degrees
degrees
all
angles
are
logarithms.
previous
and
using
the
mode
(rather
than
measured
of
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Functions
53
Page 60

The
radians
trigonometic
stackorin
To
change
1.
2.
3.
the
PressB[MODES
Press
annunciator.
Press
[(EXIT].
annunciator
mode
does
variables.
trigonometric
],
bsR.Check
then
RAD
not
for
indicates
change
mode:
HORE
the
Radians
numbers
presenceorabsenceofthe
mode.
storedinthe
Changing
history
radians
the
Thereisa
7.
Pressing
rent
Find
display
the
surface
second
B[~
format.
area=4xr?):
Keys:
4
[x)
B~
45
B+
(=]
Trigonometric
rightmost
imal
numberinthe
degreesorradians,
Keys
SIN
coS
TAN
bR
keyinthe
returns
areaofa
Display:
the
sphere
12-digit
4.8000x%3.1416
12.5664%20,
254.,4690
Functions.
Table
2-3.
The
calculator
depending
Trigonometric
Function
sine
cosine
tangent
CONVERT
valueof=,
with
radius=4.5
2500
trigonometric
line.
Angles
on
the
Functions
Keys
B(AsIN
B
Acos]
BI[ATAN]
menu.
displayedinthe
Description:
Displays
Surface
inches.
current
.
areainsquare
functions
are
interpretedindec-
angle
Function
arc
sine
arc
cosine
arc
tangent
inches
use
mode.
cur-
(surface
the
54
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and Numeric
Functions
Page 61

If
@
the
RAD
voDES]
annunciatorison
MORE
DOs,R
to
(indicating
set
Degrees
Radians
mode.
mode),
press
Keys:
15
1
60
(=)
.35
[[ACOS
(-]
.62
B(Acos)
(=]
Angle
in
lator
the
Menu
>DEG
>RAD
>HMS
and
CONVERT
line.
>HR
Hour
Table
Key
Display:
B.2588
2.7321
69.5127-51.6839
17.8288
Conversions.
menu.
2-4.
To
degrees;
decimal
To
radians;
to
its
To
hours;
seconds-decimal
to
decimal
To
hours-minutes-seconds;
hours
mal
They
Angle
seconds
and
converts
degree
converts
radian
equivalent.
converts
hours
(or
degrees)tohours(degrees)-minutes-seconds-deci-
format
The
use
the
Hour
the
equivalent.
the
numberafrom
the
number
seconds
(or
degrees)
(H.MMSSss
angle
rightmost
Conversion
Function
number
from
format
format.
converts
or
Description:
Sineof15°.
Calculates1+
Arc
cosineof.35
arc
cosine
and
fromaradian
hours(degrees)-minutes-
(H.MMSSss
the
D.MMSSss).
of
.62.
hour
conversion
numberinthe
Functions
valuetoits
decimal
number
degree
or
D.MMSSss)
from
tan
minus
calcu-
value
decimal
60°.
are
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Functions
55
Page 62

Angle
radians
in
Keys:
1.79
B-(=
@(CONVERT]
>DEG
90.2015
>HR
>DEG
Angleindecimal
degrees
>HMS
Angle
D.MMSSss
format format
Display:
5.6235
28,3375
(D.d)
in
>RAD
>HR
Decimal
7HMS
hours
(H.h)
Hours
H.MMSSss
Description:
in
SHR
Calculates
Converts
to
degrees.
1.797
Converts90degrees,
minutes,15seconds
decimal
degrees.
1.79.
radians
20
to
25.2589
>HMS
@
(SHow]
56
2:
Keyboard
25.1532
FULL
25.153284
Arithmetic
PRECISION
and
IS:
Numeric
Converts
format.
25
32.04
Exits
to
D.MMSSss
degrees,15minutes,
seconds.
the
CONVERT
menu.
Functions
Page 63

Polar
and
pageofthe
ing
between
Rectangular
CONVERT
polar
and
Coordinate
menu
providesasetofvariables
rectangular
Conversions.
coordinates.
The
second
for
convert-
The
angleisinterpreted
mal
degreesorradians.
between
MODES
Degrees
menu;
Store
and
Store
and
and
see
XCOORD
YCOORD
R
A
<
accordingtothe
The
menu
Radians
page
53.)
R/y
\
%
wno—>
modes.
(x-coordinate,
current
contains
(The
Displays
[Displays
B,R
same
Displays
Displays
y-coordinate)
angle
mode—deci-
for
key
appearsinthe
R*
A.*
xcooao*l
YCOORD'
switching
*
Calculates
T
Calculates
bothRandA.
both
XCOORD
2:
Keyboard
and
YCOORD.
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Functions
57
Page 64

Convert
the
rectangular
coordinates
(10,—15)topolar
coordinates.
Keys:
Display:
B(CONVERT]
MORE
If
the
RAD
annunciatorison,
10
XCORD
15
Todocoordinate
¥CORD
R
&
in
conjunction
12.734+9.231+the
12.734
9.231
25
R
45
£
XCOORD=18,080808
YCOORD=-15.00800
RADIUS=18.8278
£=-56.,3893
conversionsinthe
21.9650+
21.9650+25,
21.9650+45.0000
press
with
the
menu
x-coordinateofthe
0004
Description:
Displays
polar
version
O/R
Stores
Stores
Calculates
Calculates
middleofa
key.
The
following
vector(r=
Stores
Stores
the
/rectangular
variables.
to
set
Degrees
x-coordinate.
y-coordinate.
chain
R.
angle.
con-
mode.
R.
the
angle.
calculation,
keystrokes
25,A=
use
add
45°):
XCORD
(=]
58
2:
Keyboard
21.9650+17.6777
39.6427
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Calculates
Completes
calculation.
Exits
the
CONVERT
menu.
Functions
x-coordinate.
the
Page 65

Probability
The
PROB
menu
and
generates
Functions
calculates
sequencesofrandom
combinations,
permutations
numbers.
and
factorials,
Combinations
objects
y
more
items
The
items
number
taken yata
that
than
are
and
canbetaken
onceinthe
not
counted
of
permutationsofx
numberofdifferent
larger
group
of x
items.Noitems
rangement,
and
different
separately.
Store
X
e
Keys:
Display:
Permutations.
time
(C,)is
fromalarger
setofy
items,
The
the
numberofdifferent
groupofx
and
different
separately.
objects
takenyatatime
arrangementsofy items
can
occur
ordersofthe
X,
Y
¢
\
XJY
P
same
CombinationsofX
takenYatatime
PermutationsofX
takenYatatime
numberofcombinationsofx
sets
containing
items.Noitem
ordersofthe
that
canbetaken
more
than
y items
onceinan
are
counted
objects
occurs
same
(P,)is
from
the
ar-
objects
Description:
y
a
W(PrOB]
5
X
3
Y
C
Ri¥
P
RN
2:
X=5.,0000
¥=3.0000
C
X,Y=18.0000
P
¥.Y=60.0000
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
Displays
Stores
Stores
Calculates
Calculates
Exits
the
Numeric
PROB
the
x.
y.
combinations.
permutations.
PROB
Functions
menu.
menu.
59
Page 66

Random
Number.
range0< RAN#
Pressing
<
1.*
RAN#
displaysarandom numberinthe
When
clocktogenerateaseed—a
dom
system
number)
can
RAN#ispressed
for
the
number
numbers.
Pressing
0
clock.Tospecifyaparticular
and
press
RAN#
repeatarandom number
first
time,
the
HP-27S
that
initiates
RAN#
usesanew
seed,
keyinthe
to
display
the
random
sequencebystoring
seed.
Factorial.
the
calculator
through
Hyperbolic
The
HYP
the
rightmost
Menu
SINH
COSH
TANH
253.
Key
M!
menu
calculates
line.
The
Functions
provides
number
Table
Function
Hyperbolic
Hyperbolic
Hyperbolic
number
the
in
the
2-5.
sine
cosine
tangent
the
factorialofthe
must
hyperbolic
calculator
Hyperbolic
Menu
ASNH
ACOSH
ATNH
rightmost
beanintegerinthe
functions.
line.
Functions
Key
Inverse
Inverse
cosine
Inverse
tangent
uses
the
the
sequenceofran-
seed
from
seed(anon-zero
number.
the
same
number
The
functions
Function
hyperbolic
hyperbolic
hyperbolic
system
the
You
non-zero
on
range
0
use
sine
Keys:
B(HYP]
SINH
540.25
*
The
sequence
son
60
5
ACOSH
numberispart ofasequenceofuniformly
passes
Wesley,
1981).
2:
Keyboard
the
Display:
74,2832
£.985
spectral
Arithmetic
test
[
(D.
Knuth,
and
distributed
Seminumerical
Numeric
Description:
Hyperbolic
Inverse
cosine.
Exits
Algorithms,
hyperbolic
the
pseudo-random
Vol.2,London:
Functions
HYP
sine.
numbers.
menu.
This
Addi-
Page 67

Parts
The
calculator
of
functionsinthe
Numbers
line.
PARTS
menu
use
the
rightmost
number
on
the
Menu
Keys:
12.3456789
&
B(PARTS]
B
Key
IP
FP
RMD
ABS
RND
(sHow]
Integer
Fractional
part).
Rounds
fiedinthe
rounding
Absolute
(=]
Table
partofthe
the
occursinALL
valueofthe
Display:
12.3457
FULL
12.3456789
FULL
12.3457
2-6.
The
number.
partofthe
number
current
PRECISION
FIX,
PRECISION
PARTS
Function
number
internallytothe
SCI, or
mode).
number.
Menu
(the
ENG
Description:
Entersanine-digit
number.
IS:
Displays
number.
Number
internally.
IS:
number
without
numberofdigits
display
mode
full
is
rounded
its
integer
speci-
(no
precision
of
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
Exits
Numeric
the
Functions
PARTS
menu.
61
Page 68

Range
of
Numbers
Figure
2-2
Underflow
warning
Overflow
N
—9.99999999999
illustrates
the
displaysawarning,
and
the
largest
x
10499
—1
x
Figure
rangeofnumbers
followedby0.
positiveornegative
Underflow
~
=
10749
2-2.
Range
0
1x1049
of
Numbers
the
HP-27S
Overflow
number
9.99999999999
can
displays
possible.
Overflow
St
store.
x
10499
a
62
2:
Keyboard
Arithmetic
and
Numeric
Functions
Page 69

Base
Conversions
and
Base
The
BASE
bases—DEC
nary).
and
performs
the
four
When
highlighted
Arithmetic
menu
(decimal),
The
BASE
the
bases.
you
press[lBAse|,DEC
menu
B8.
[/DEC
Decimal
Switching
Press
oneofthe
base.
The
menu
the
calculator
base
displays
throughF.Exiting
Bases
key
line
the
([EASE|)
HEX
menu
converts
arithmetic
key.
860084
IEFENNEECE
baseisactive
menu
keysinthe
for
the
are
convertedtothe
HEX
menu,
the
HEX
does
operations
(hexadecimal),
numbers
operations
[+],
with
OCT
from
(-],
four
number
(octal),
one
(x],
and
basetoanother
and
[+]inany
baseisactive,asindicatedbythe
BASE
menu
to
switchtoa
new
baseishighlighted,
new
which
menu
allows
restores
base.
youtokeyinletters
DEC
and
SwitchingtoHEX
base.
BIN
numbers
(bi-
of
new
in
A
When
you
switch
from
DEC
numberisdisplayedinthe
sentationofthe
to
DEC
base,
current
only
BIN
display
when
base.
they
decimal
the
full
format.
are
3:
numberispreserved.
decimal
Numbers
usedinan
Base
to
any
other
base,
new
base.
Internally,
numberisdisplayed,
are
truncatedtointegers
arithmetic
Conversions
operationinHEX,
and
the
When
Base
integer
the
partofthe
12-digit
you
switch
roundedtothe
internally
Arithmetic
repre-
OCT,
back
or
63
Page 70

Ifabinary
rightmost
down
significant
numberislonger
(least
significant)20characters.
to
view
digitsonthe
than21characters,
the
entire
top
line.
number
the
Press§and
in
two
lines
display
then
with
shows
hold
the
the
most
Example:
Converting
doaseriesofbase
Convert
Keys:
125
BIN
oCcT
HEX
Convert
HEX
24
125,
J(BASE)
24FF;¢tobinary
F
F
to
Between
conversions.
binary,
Display:
125.0000
1111181
173
7D
125.00800
octal,
24FF
base:
Bases.
and
hexadecimal
The
following
keystrokes
numbers:
Description:
Displays
menu.
active.
Converts
the
BASE
DEC
base
1257,tobinary
base.
Sets
OCT
base.
1754.
Sets
HEX
base.
1755
7Dq6.
Restores
Sets
HEX
DEC
base.
base.
Keysinhexadecimal
number.
is
125,
=
=
(ExiT)
64
3:
BIN
Base
1p810811111111
9,471.0000
Conversions
and
Base
Converts
base.
Exits
stores
Arithmetic
24FF,,toBIN
BASE
menu;
DEC
base.
re-
Page 71

Representation
of
Numbers
Decimal
digit
HEX,
asa36-bit,
sign
Negative
of
Keys:
B[
BASE
HEX®
e
Range
The
representedinHEX,
numbers
numbers
exponent.
OCT,orBIN
bit;itis
numbers
the
positive
8738
36-bit
that
Whenanumberisconverted
binary
set
(1)
binary
Display:
2222
FFFFFODDE
-3,7358.08000
of
HEX,
word
size
can
are
stored
base,
number.
for
are
internally
the
integer
The
negative
represented
number.
OCT,
determines
OCT, and
be
convertedtoother
as a 12-digit
partofthe
leftmost
numbers.
and
the
BIN
(most
internallyasthe
BIN
rangeofnumbers
bases,
and
bases.
mantissa
from
its
decimal
numberisrepresented
significant)
2’s
Description:
Converts
hexadecimal
2’s
Negative
number.
8,738,
Complement.
decimal
with
value
bitisthe
Complement
base.
Numbers
that
the
rangeofdecimal
to
can
3to
be
Table
Base
DEC
HEX
OCT
BIN
3-1.
Largest
34,359,738,367
7FFFFFFFF
377777777777 400000000000
1111111111111
111111111111111111
Range
Positive
3:
Base
of
Numbers
Integer
11
Conversions
for
Base
Conversions
Largest
—34,359,738,368
800000000
100000000000000000
000000000000000000
Negative
and
Base
Arithmetic
Integer
65
Page 72

When
haltsifyou
you
keyinnumbers
attempttokeyintoo
attempttokeyina
the
HP-27S
If
the
table
TOOBIG.
3-1,
beeps
calculator
line
switchingtoHEX,
in
HEX,
10-digit
after
hexadecimal
the
ninth
containsadecimal
OCT,orBIN
OCT,
many
digit.
or
BIN
digits.
number,
number
base
base,
For
example,ifyou
digit
entry
outside
displays
digit
halts
the
the
entry
and
range
message
in
Keys:
B
(MODES
SCI
0
(INPUT]
W(BASE]
1
@(E]
20
ocCT
DEC
3@E
1123
BE)8
HEX
BVAN)
CLR
B(MODES
FIx
If
the
be
lowedbythe
4
resultofan
representedin36
Display:
TOOBIG
1.E28
TOOBIG-11E1R3088
3.E11-3.E8
B.0000
arithmetic
bits,
largest
(or
operationinHEX,
the
HP-27S
smallest)
number
displays
possible.
Description:
Sets
scientific
1x10720
converted
Restores
3E11
cannot
to
HEX
Exits
BASE
DEC
base.
Clears
cannot
to
OCT
DEC
be
base.
menu,
calculator
displaytofour
places.
OCT,orBIN
the
overflow warning,
format.
base.
base.
converted
restores
line;
decimal
base
be
sets
cannot
fol-
66
3:
Base
Conversions
and
Base
Arithmetic
Page 73

Arithmetic
The
arithmetic
in
anyofthe
arithmetic.
only.
Operations
Operations
operations
four
bases.
with
(+], (=], (xJ,
All
operations
HEX, OCT,
(#],
use
or
and
2’s
BIN
canbeperformed
Complement
bases
use
integers
When
only
Example:
12F16
Keys:
a
the
+
W(BAsE]
HEX
12F
Calculate
7760
(=)
Calculate
E9A
ocT
(-]
divisioninHEX,
integer
E9A16:
portionofthe
Arithmetic
Display:
(=]
FC39
7760g—43264:
4,041
771l
4326
3432
100g+5g:
OCT,
in
HEX,
,.00800
or
BIN
number
OCT,
base
producesaremainder,
is
retained.
and
BIN
Description:
Sets
Adds
numbers.
Exits
switchestoDEC
(FC916
Switches
(4041,
Bases.
HEX
base.
hexadecimal
HEX
menu,
==
404110)
to
=
7711y).
Calculate
base
OCT
base
100
(=]5(=]
14
Integer
3:
Base
Conversions
and
partofresult.
Base
Arithmetic
67
Page 74

Compare
the
previous
resulttothe
decimal
division
shown
below:
100
(5]
5
DEC
=]
ocT
Add
5A0;4
HEX
5A0
EXIT
BIN
(+)
1001100
Arithmetic
overflow
number:
HEX
warning
SAAAAAAAA
[J4
(=]
&4
plus
1001100,.
2RO
=)
results
.0080+5.08000
12.8000
14
1811010080080
1611116811068
that
cannotberepresentedin36
and
the
largest
SEC
positiveorsmallest
OVERFLOW
7FFFFFFFF
Converts
decimal
Displays
of
operands
base.
integer
12.8;7inOCT
KeysinHEX
number.
Switches
Calculates
base.
to
bits
Switches
Largest
to
positive
to
portion
base.
base
BIN
base.
resultinBIN
display
negative
HEX
base.
number.
an
EBBBBBBBB
(=]
6CCCCCCCC
=]
68
3:
Base
OVERFLOW
88080B0OB0O
Conversions
and
Base
Smallest
number.
Arithmetic
negative
Page 75

Statistics
The
STAT
application
tions
using
setsofdata
intoalist,
entered,
B
Calculate
mum,
list.
B
Sort
The
B
Curve
(linear
®
Weighted
®
Summation
The
the
the
you
and/or
the
following
fitting
regression),
number
amount
HP-27S
can:
the
list
mean
of
of
does
one-
called
displays
mean,
range
from
calculations
and
median,
(largest
smallesttolargest
use
estimation
exponential,
and
grouped
statistics—Zx,
lists
you
can
available
memory.
and
number
the
running
standard
minus
smallest)ofthe
two
number
calculations
logarithmic,
standard
Zx2,
2y,
store
and
two-variable
statistics
lists.Asnumbers
total.
Oncealist
deviation,
maximum,
number.
lists:
with
four
and
power.
deviation.
Zy?,
and
Zxy.
their
sizes
are
4
calcula-
are
entered
has
been
mini-
numbersinthe
models—Ilinear
limited
only
by
4:
Statistics
69
Page 76

Entering
To
enter
the
STAT
STAT
menu.
Menu
When
itemina
there
“prompts”
Keys
CALC
INSR
DELET
NAME
GET
TOTAL
you
enter
particular
arenolistsinmemory,
you
the
application,
Table
Displays
Inserts
Deletes
Names
Switches
Erases
lator
line.
the
STAT
number
for
the
STAT
4-1.
the
numbers
numbers
or
renames
from
the
STAT
application,
first
Application
press[}STAT].
The
STAT
Description
CALC
menu
into
the
list.
from
the
the
list.
one
listtoanother
menu
and
you
list.
This
the
current
item:
Table
Menu
for
doing
statistical
list.
and
displays
listiscalled
listisempty
are
the
viewing
4-1
describes
calculations.
creates
totalinthe
the
the
current
and
new
first
the
the
lists.
calcu-
empty
list.
HP-27S
If
If
there
are
worked
For
When
TOTAL
the
70
with
example,ifthe
the
erases
STAT
4:
lists
most
STAT
menu,
Statistics
ITEMC1O="
alreadyinmemory,
recently.
current
menu
the
menu
press
You
list
ITEM(S512="?
is
displayed,
and
[EXIT].
the
current
willbeviewing
contained50numbers,
pressingadigit
displays
the
list is
the
calculator
the
one
bottomofthe
you
would
key,
[INPUT],
line.Torestore
you
list.
see:
or
Page 77

Entering
Total
Data
and
Calculating
the
Running
Generally,anew
list
already
ways:
B
Clear
76
B
Createanew,
for
To
enter
1.
2.
contains
the
current
for
additional
additional
data
Keyinthe
During
menu.
Press
an
uated
the
number
(You
expression
and
running
setofdataisstored
data,
you
can
listbypressingB[CLEAR
information).
empty
information).
intoanempty
first
listbypressing
number
entry,
can
restore
list:
or
the
the
¢1r=7?
AAx7S
to
enter
the
(for
example,2.8888x75),
the
resultisentered
total
andaprompt
intoanempty
make
an
empty
ITGET
expression
calculator
STAT
line
menu
/
number.Ifthe
into
the
for
the
list
"%NEW
(for
example,
replaces
by
pressing
Prompt
Calculator
list.
for
calculator
the
The
next
list.Ifthe
availableintwo
[I¥ES
(see
(see
2
the
STAT
[EXIT].)
current
page
page
75).
75
ITEM(1)
line
line
contains
expressioniseval-
HP-27S
item.
displays
ITEMC
TOTAL
=7
Ira
156,
BEE9
\
Running
totalincalculator
4:
Statistics
line
71
Page 78

3.
Repeat
nizes
4.
Press
Viewing
(a]
and
beginning
affect
the
steps1and2to
the
endofa
to
and
[¥]
move
up
and
endofthe
valueofthe
list
restore
the
Editing
and
down
list.
running
enter
when
STAT
Moving
all
an
the
the
list.
total.
the
data.
itemisleft
menu.
List
[i(a]
and
up
and
down
The
calculator
blank.
@(V]
the
display
list
does
recog-
the
not
Changing
1.
2.
InsertingaNumber.
a
Number.
Use
the
arrow
Keyinthe
correct
1.Ifnecessary,
2,
Use
the
arrow
For
example,toinsertanumber
display
3.
Press
4.
Key
DeletingaNumber.
ITEM(7).
INSR
in
the
value
1.Ifnecessary,
2.
Use
the
arrow
3.
Press
'DELET
To
changeanumber
keystolocate
value
To
insertanitem:
press
keystolocate
to
insertanew
for
the
To
deleteanumber:
press
keystolocate
.
and
to
restore
item
to
restore
and
press
and
item,
and
and
in
the
display
the
(INPUT].
the
STAT
menu.
display
between
the
placeofinsertion.
ITEM(6)
whichisinitially
press
[INPUT].
the
STAT
menu.
display
the
itemtobe
list:
incorrect
and
setto0.
value.
ITEM(7),
deleted.
72
4:
Statistics
Page 79

Example:
balance
are:
Date
5/31
6/1
6/1
6/2
UpdatingaCheckbook.
was
$267.82.
Transaction
Balance
Deposit
Check
Check
The
Amount
—368.23
transactions
Date
267.82
837.42
—45.36
6/3
6/7
6/10
On
May
for
the
Transaction
Check
Check
Deposit
31,achecking
first10daysinJune
account
Amount
—128.90
—65.35
55.67
Update
Keys:
@B
the
(MODES
FIX
2
B(sTAT]
If
you
wanttopreserve
name
the
list
B(CLEARDATA]
YES
267.82
837.42
checkbook
Display:
and
then
ITEMC1>="
ITEMC(2)="7
TOTAL=267.82
ITEM¢(3)>="
TOTAL=1,1085.24
by
calculating
the
current
press
["GET
the
list,
¥NEW
running
Description:
display
Sets
mal
places.
Enters
application.
skip
the
Clears
Enters
balance.
Enters
balance.
deci-
two
to
STAT
the
next
step.
Instead,
the
list.
beginning
depositon6/1.
4:
Statistics
73
Page 80

wNo
=z
O
8.
_L__h_
Nzl
=z
([
O
5.67
|
.
(Y]
w
Ol
ut
w|o
0
N
w
2
c
Enters
transactions.
remaining
X
c
=
©
.
(6,1
S
uT
i
ITEM(S)=?
TOTAL=553.87
EXIT
MODES
FIX
Copying
4
a
ITEM(GY»="
List
Line
To
copyanumber
and
press
Naming
Naming
must
To
1.
2.
3.
lists
be
named
name
or
Press
Type
(or
eredonpages36through
Press
from
(INPUT).
and
allows
or
rename
HAME
edit)
[INPUT].
Number
the
listtothe
Renaming
youtohave
cleared
the
the
before
current
name.
more
you
list:
(Typing
40).
Restores
Restores
places.
to
the
calculator
a
List
than
one
can
switchtoa
alphabetic
the
STAT
menu.
four
decimal
Calculator
line,
display
listinmemory.Alist
informationiscov-
the
different
item
list.
74
4:
Statistics
Page 81

List
names
anyofthe
space.”
others)
For
example,ifmemory
canbeupto22
following
The
first
becomeamenu
CHECKBOOK,
To
view
the
(ExiT).
Switching
(GET)
To
switch
toadifferent
threetofive
pressing
SELECT
¥MEL{|
name
without
Lists
characters
characters:+,—,
characters
label
when
contains
RATEHREA
and
listorcreateanew
6ET
A
MAME
making
three
displays:
CHEC
any
Creating
long
x, =,),(,<,
(some
you
press
lists
named
changes,
and
letters
GET
New
list:
should
>,%,:,=,and
are
to
RATE,
press
NAME,then
Lists
not
contain
wider
switch
AREA,
than
lists.
and
1.Ifyou
2.
Display
tainsamenu
3.
Press
list.
Figure
and
FEBCHECKS,
*
NAME
characters
functions.
haven't
the
STAT
label
the
appropriate
4-1
illustrates
creatinganew
will
accept
cannotbeusedasthe
names
already
menu
for
menu
switching
containing
listname
done
so,
and
press
each
named
key.
between
list,
these
parameterinthe
name
6ET.The
*NEW
two
and
characters.
the
current
list,
plus
displaysanew,
lists
named
naming
However,
Solver
4:
GET
%NEMW
that
names
SIZES
Statistics
list.
menu
con-
empty
JANCHECKS
list.
containing
and
ITEM
these
75
Page 82

—_—
e
GET
FEEBCH
GET
JAHC
GET
¥NEW
>
do!
e
New
List
(unnamed)
.
—————
<
Can’t
Figure
Clearing
a
Clearinganumber
list
becomes
To
clear
is
named,
name
by
Pressing
retains
available
the
current
the
HP-27S
displaying:
¥E§
the
name,
One-Variable
eh
RERCH
4-1.
Switching
List
list
erases
for
list,
lets
ALSO
displaysanempty,
and
you
Statistics
all
the
other
information.
press[CLEAR
you
choose
CLEAR
willbeviewing
MARCHECKS
Between
data.
Number
The
DATA],
then
memory
whetherornottoclear
LIST
NAME?
nameless
the
list.
empty,
MARCHECK
Lists
usedbythe
¥E§.If
Pressing
named
MAME
the
NO
list.
S
list
the
Press
4-2.
76
All
4:
€ALE
the
Statistics
to
menu
display
keys
the
CALC
except
menu,
'FREST
whichisdescribedintable
use
the
current
list.
Page 83

Menu
TOTAL
MEAN
MEDN
STDEV
RANG
Key
Table
Calculates
Calculates
the
Calculates
Calculates
viationisa
the
Calculates the
number.
4-2.
the
the
list.
the
the
measureofhow
mean.
The
STAT
sumofthe
arithmetic
median.
sample
standard
difference
MORE
CALC
Description
numbersinthe
mean
(average)ofthe
deviation.*
dispersed
between
the
Menu
the
largest
list.
The
numbers
and
numbers
standard
are
smallest
in
de-
about
MIN
MAX
~
SORT
FRCST
*
The
HP-27S
a
samplingofa
population
placing
that
the
list,
new
mean
Example:
pervisor
takes.
She
out
the
Displays
Displays
Sorts
Displaysaseriesofmenus
number
grouped
calculates
larger,
standard
value
you
process,
into
must
delete
into
the
One-Variable
May
Kitt
randomly
the
smallest
the
largest
the
list
from
smallesttolargest
lists
(curve
fitting,
standard
the
sample
complete
deviation
the
list,
the
listinorder
canbecomputedbycalculating
old
deviation,
standard
set of data.Ifthe
and
then
calculating
mean
from
to calculate
Statistics
wantstodetermine
picks
ten
people,
and
records
155
125
9.25
12.0
the
100
numberinthe
numberinthe
for
calculations
estimation,
summation
deviation,
which
lististhe
the
the
the
standard
list,
calculateanew
new
true
Calculations.
how
observes
number
of
14.75
85
13.0
list.
list.
number.
based
weighted
statistics).
assumes
entire
the
meanofthe
deviation.Ifyou
population
mean
the
listofnumbers
setofdata,
mean,
and
standard
Production
longacertain
each
oneasthey
minutes
required:
11.25
12.25
on
two
and
the
true
original
later
enter
deviation.
su-
process
carry
is
list,
edit
the
4:
Statistics
77
Page 84

Calculate
display
the
the
longest
mean,
range,
time.
and
Also
standard
name
deviationofthe
the
list
TASK.
times,
and
Keys:
B(s1AT]
If
you
wanttopreserve
name
the
B(CLEAR
YES
15.5
9.25
10
14.75
11.25
12.5
12
8.5
13
12.25
[INPUT]
list
Display:
and
then
ITEMC1)="
ITEM(2)="?
TOTAL=15.5800
ITEM(3)>="
TOTAL=24,7508
ITEMC11)>="
TOTAL=119,008848
the
press
current
GET
list,
*¥NEW
Description:
Enters
application.
skip
the
next
Clears
Enters
Enters
Enters
data.
the
STAT
the
list.
the
first
the
second
the
remaining
step.
Instead,
time.
time.
MEAN
STDEV
RANG
MORE
MAX
78
CALC
4:
Statistics
119.0000
MEAN=11.95000
STDEV=2.2460
RANGE=7.0000
MAX=15,50800
Displays
menu.
Calculates
Calculates
deviation.
Calculates
smallest
Displays
number.
largest
the
CALC
mean.
standard
largest
minus
number.
Page 85

ITEMC11)="7
Displays
STAT
menu.
MAME
TASK
Statistics
These
statistics
FRCST
B
®
B
When
viously
variable.
describes
*Noerror
menu:
Curve
models.
Summation
Mean
and
grouped
you
created
The
Calculation
Curve
fitting
tion,
summation
Weighted
Grouped
deviation
occurs
dard
deviationisnot
fitting
standard
press
the
mean
standard
ITEMC11>="
Operations
operations
for
the
statistics—Zx,
standard
'FREST,the
lists—one
two
lists
contentsofthese
Table
and
estima-
statistics
use
linear,
deviation
deviation).
for
must
4-3.
Contents
List
the
x-values
Numbers
Numbers
for
non-integer
meaningful.
frequencies,
With
two
logarithmic,
Zx2,
2y,
for
HP-27S
the
x-variable
have
the
lists.
Two-List
Designated
X-Variable
butinmost
lists,
Zy?,
grouped
requires
same
Operations
of
the
Names
Two
and
exponential,
the
Lists
are
availableinthe
Zxy.
data
(weighted
youtospecify
and
one
number
of
items.
Contents
List
Designated
the
Y-Variable
y-values
Weightsofnumbers
frequencies
the
numbers
gerornon-integer).
Frequency
numbers
only*).
occur
cases
the
calculated
for
with
list
and
the
with
occur
grouped
TASK.
power
mean
two
y-
Table
of
the
which
(inte-
which
(integer
and
pre-
4-3
or
the
stan-
4:
Statistics
79
Page 86

Table
list
calculations
4-4
describes
in
the
more
FRCST
detail.
menu.
The
next
sections
describe
two-
Menu
x-variable
y-variable
CORR
B
MODL
W.MN
G.SD
SIZE
Table
Key
Used
for
vice
versa.*
*
Displays the
is@numberinthe
closely
the
catesaperfect
negative
a
poor
fit.
*
DisplaysM.For
*
DisplaysB.For
Displaysachoiceofthe
Calculates
uesasweights
Calculates
ues)
occurring
values).
Displays
4-4.
The
FRCST
Description
estimation
correlation
data
correlation.Avalue
the
the
the
fits
positive
the
the
weighted
(or
standard
with
number
calculations.
coefficient.
range
—1
the
calculated
correlation,—1indicatesaperfect
linear
linear
MORE
four
meanofthe
frequencies).
deviationofa
the
specified
of
itemsineach
through
closeto0
model,
model,
curve
Menu
Storexand
The
+1
curve.Avalueof+1
thisisthe
thisisthe
fitting
x-values
setofnumbers
integer
list.
calculateyor
correlation
that
measures
indicates
slope.
y-intercept.
models.
using
frequencies
coefficient
the
curve
the
how
indi-
is
y-val-
(x-val-
(y-
¥
Y
X2
Yz
XY
*
Calculated
models
80
4:
Calculates
Calculates the
Calculates
Calculates
Calculates the
using the
(see
Statistics
table
transformed
4-5onpage
l
the
sum
sum
the
sumofthe
the
sumofthe
sumofthe
equations
82).
MORE
(total)ofthe
(total)ofthe
squaresofthe
squaresofthe
productsofthex-and
for
the
exponential,
x-values.
y-values.
logarithmic,
x-values.
y-values.
y-values.
and
power
Page 87

Linear
Curve
fittingisa
two
variables—x
els
(see
the
correlation
vice
versa.
y
Regression,
statistical
andy.You
figure
4-2).
coefficient.
Linear
Curve
LIN
For
each model,
Fit
Curve
method
can
You
Fitting,
select
can
and
Estimation
for
finding
oneoffour
the
also
a relationship
curve-fitting
HP-27S
estimateyforagivenxand
computes
Exponential
TERP
y
between
M,Band
Curve
mod-
Fit
y=B+Mx
7
Logarithmic
y y
y=B+M
LOG
In
Curve
x
Fit
Figure
4-2.
Curve
y
=BeM~
X X
Power
Curve
Fit
TPUHR
y
=BxM
X X
Fitting
Models
4:
Statistics
81
Page 88

Table
4-5
describes
the
linear
model,
tions
for
the
exponential,
transformations
regression.
Model
Linear
Logarithmic
Exponentialy=
Power
To
do
1'
Enter
for
same
names.
avoids
From
Press
variable,
unnamed,
Select
displays
If
pressamenu
To
and/or
To
curve
1.
2,
fitting
the
data
the
y-values.
item
(Youdonot
possible
the
[FREST'todisplayamenu
press
the
the
you
needtochange
display
B
do
estimation
Keyinthe
Press
the
modelsinmore
the
calculationiscalled
logarithmic,
that
allow
the
datatobe
Table
4-5.
Curve
Equation
y=B+Mx
y
=B
+
Be
Mx
y=BxM
MInx
Transformation
None
|y
=B
y
versusInx.
Iny=InB+Mx
Inyversus
Iny=InB+Minx
Iny
and
estimation:
into
two
STAT
lists—one
The
two
itemsinan
number
STAT
pressing
y-variablebypressing
FRCST
the
the
in
each
list.
needtoname
confusion
menu,
the
appropriate
[¥EURR"
keytoselectamodel.
curve
calculations:
known
menu
press
menu
models,
fitting
value
key
later.)
BEALEY,
selects
and
results,
for
the
detail.
and power
Fitting
+
MInx
versusInx
Give
the
of
list
menu
it.)
another
the
current
press
HGREY
press
and
press
unknown.
When
curve
fitting
linear
regression.
models
fittedbystandard
Models
x.
use
Constraints
None
x>0
y
>0
x>0,y>0
for
the
x-values
x,y
pair
must
have
both
lists
meaningful
current
then
key.
[HORE
names.
(If
menu
model.
HEGRRY,
its
menu
list,
but
To
the
current
key.
WHODL",
naming
select
The
IR,
key.
uses
Calcula-
linear
and
one
the
the
list
HP-27S
and
then
it
x-
is
4:
Statistics
Page 89

Example:
a
certain
chemical.
Curve
chemical
When
Fitting
reaction
the
concentrationofthe
X
Concentration
(moles
Y
Rate
(moles per
per
liter-
seconds)
and
dependsonthe
reactionisrun
chemical,
.050
liter)
.00620
Estimation
repeatedly,
the
following
.075
.00941
Calculations.
initial
concentrationofone
varying
rates
are
.10
.0140
.125
.0146
The
only
the
observed:
.20
.0230
rate
of
initial
Assuming
and
slopeofthe
reaction
Keys:
M(sTAT]
If
you
wanttopreserve
name
the
B
(CLEAR
YES
.05
.075
1
125
2
EXIT
NAME
CONC
[INPUT]
PRRY
*NEW
a linear
when
list
relationship,
line.
Use
the
concentration
Display:
and
then
ITEMC1D>="
ITEMCE)
TOTAL=6.55080
ITEM(E)="
ITEMC1)>=?
linear
the
press
=7
calculate
the
correlation
estimationtocalculate
equals
0.09
moles/liter.
Description:
Displays
current
[HGET™
list,
F¥NEW"
skip
the
.
Clears
Enters
data.
Displays
Names
Switchestoa
list.
coefficient
the
rateofthe
STAT
the
next
step.
the
current
the
concentration
the
STAT
the
list
new,
menu.
Instead,
list.
menu.
CONC.
empty
4:
Statistics
83
Page 90

.0062
00941
014
0146
.023
[INPUT]
ITEM(E)=?
TOTAL=0.8672
Enters
the
rate
data.
RATE
Do
[INPUT]
the
following
ITEM(E)>=7
ITEM(E)="
SELECT
SELECT
model
stepifthe
CORR=8.9898
M=0.1893
CONC=08.8908
X
VARIABLE
¥
VARIABLE
current
Displays
Names
Specifies
ing the
Specifies
ing
the
modelisnot
Selects
Calculates
coefficient.
Calculates
Stores
tion
calculation.
the
STAT
the
list
the
list
x-values.
the
list
y-values.
linear:
the
linear
the
the
CONC
menu.
RATE.
contain-
contain-
model.
correlation
slope.
for
estima-
RATE=8.86113
84
4:
Statistics
Calculates
rate.
the
estimated
Page 91

Weighted
The
following
standard
...X,
Xy,
Mean
procedure
deviation.
occurring
integerorinteger
standard
integer
To
1.
deviationofdata
frequencies
calculate
Enter
one
weighted
the
for
data
the
(frequency)
both
lists
meaningful
rent
list,
but
From
the
STAT
Press
[/FREST".Designate
x-variablebypressing
listisunnamed,
Designate
the
variablebypressing
message
Press|MORE
To
grouped
indicating
calculate
standard
and
Grouped
The
with
values
fi,
f,,
mean
into
calculates
weighted
weights
(frequencies).
points
...fu.
and/or
two
the
meanisthe
w,,
w,,
x;,
grouped
STAT
lists—one
..w,.
Grouped
x,,
weightsorfrequencies.
must
have
the
same
item
naming
menu,
list
the
names.
it
pressing
containing
the
the
weighted
deviation,
(Youdonot
avoids
press
the
list
the
appropriate
'¥CURR
the
appropriate
current
mean,
press[6.8D0
possible
€ALE,then|HORE
containing
weightsorfrequenciesasthe
model.
press[MN.To
Standard
weighted
Deviation
mean
and
meanofdata
The
weights
standard
...x;,
occurringatnon-negative
standard
for
The
number
number
can
deviationisthe
deviation:
the
numbers
and
in
each
needtoname
confusion
menu
selects
menu
it.)
key.
later.)
the
numbersasthe
key.
(If
the
Ignore
calculate
.
grouped
points
be non-
its
weight
list.
the
current
the
x;,
and
Give
cur-
y-
the
Example:
Data.
Weighted
Your
timesayear.
Mean
manufacturing
Last
year’s
Price/Part
Number
of
Parts
and
Standard
company
purchases
$4.25
250
Deviation
purchasesacertain
were:
$4.60
800
$4.70
900
$4.10
1000
4:
Statistics
of
part
Grouped
four
85
Page 92

The
price
and
number
occurred.
the
grouped
of parts
Therefore,
standard
for
each
priceisthe
you
can
deviation.
frequency
calculate
both
with
the
which
weighted
each
mean
Keys:
B(sTAT)
If
you
name
B
(CLEAR
YES
4.25
4.6
4.7
4.1
EXIT
NAME
PRICE
GET
¥NENW
250
800
900
1000
[INPUT]
Display:
wanttopreserve
the
list
and
then
ITEMC1>="
ITEM(S)="?
TOTAL=17.6500
(INPUT]
ITEM(S)>=7?
ITEMC(1>="
ITEM(S)>="?
TOTAL=2,950.0000
the
press
current
GET=|
list,
¥NEW
Description:
Displays
skip
the
next
.
Clears
Enters
Displays
Names
the
the
the
the
Switchestoa
list.
Enters
the
(frequencies).
the
STAT
step.
current
numbers.
STAT
list
new,
weights
menu.
Instead,
list.
menu.
PRICE.
empty
NAME
WEIGHT
CALC
MORE
FRCST
86
4:
Statistics
ITEM(S5)="
ITEM(S5)>="
SELECT
X
VARIABLE
Displays
Names
the
the
STAT
list
menu.
WEIGHT.
Page 93

PRICE
SELECT
Y
VARIABLE
Specifies
the
prices.
list
containing
WEIG
MORE
W.MN
G.SD
Summation
The
FRCST
2Zxy.Zxand
calculations
nated
thex-and
Example:
lowing
Keys:
W(STAT]
If
you
name
Summation
valuesofx:
wanttopreserve
the
list
model
W.MN=4.4314
G.5D=0.2641
Statistics
menu
includes
2y
are
involving
y-variable
Display:
and
then
keys
for
equivalenttothe
only
one
variable,
(see
the
Statistics.
2.345, 3.456,
the
press
4.567.
current
GET
Specifies
the
frequencies.
Calculates
mean.
Calculates
dard
deviation.
calculating
total
following
CalculateZxand
Zx,
(TOTAL)ofeach
the
same
example).
Description:
Displays
list,
skip
the
*NEW
list
containing
weighted
grouped
2y,
Zx2,
list
canbedesig-
Zx2
for
STAT
the
next
step.
stan-
Zy?,
and
list.
For
the
fol-
menu.
Instead,
B
CLEARDATA]
YES
2.345
3.456
4.567
MORE
FRCST
CALC
ITEMCL1>="
ITEMC(4)=7
TOTAL=18.36580
SELECT
X
VARIABLE
Clears
Enters
the
data.
4:
Statistics
current
list.
87
Page 94

Selects
and
y-variables.
current
listasx-
ZX=10.36889
Zx2=38,30085
Calculates
previous
Calculates
total
TOTAL).
Zx2.
(same
as
4:
Statistics
Page 95

S
The
The
each
by
are
in
motion
and
ity),orTIME
The
in
The
the
98.
Example:
object
500
1.
2.
3.
Equation
SOLVE
equation
creatingamenu
stored
chapter1(see
solve
number
each
complexityofequations
availabilityofthe
meters?
Press
Type
sary,
Press
application, or
for
any
and
calculated
page
for
free-fall:
DISTRAHCE=YA=TIME-
for
DISTANCE,
when
of
equations
equation
fallin5
DISTAHCE=WExTIME-.,S=G«TIME~Z
see
are
The
Equation
seconds?
(The
[SOLVE],
page36for
€ALE,then
Solver
Solver,
variable.
consisting of
using
29).
For
V0
(velocityatt=0),G(accelerationofgrav-
three
values
you
limited
numeric
of
How
accelerationofgravityis9.8067
then
instructionsonusing
do
these
lets
you
The
Solver
the
the
example,
are
can
store
onlybythe
the
Solver
functionsintable
Motion
long
HEW
keystrokes:
simplifies
variablesinthe
rules
for
you
S=G=TINE™Z
known.
and
amountofavaiable
can
for
Free-Fall.
doesittake
store
equations
menu
can
enter
the
number
interpretisincreased
5-3
foranobjecttofall
and
equation-solving
equation.
variables
the
startingonpage
How
meters/second?.)
(UNPUT].*
the
ALPHA
Values
covered
equation
of
variables
memory.
far
does
(If
menu.)
solve
of
by
an
neces-
*To
type*,prese
W[*].
5:
The
Equation
Soiver
89
Page 96

Keys:
Display:
Description:
9.8067I&
0
ve
5
TIME
DISTA
How
long
500
DISTA
TIME
During
the
estimates.
solutions.
Entering
To
enter
the
ory,
the
HP-27S
G=9.8067
Yo=0.0000
TIME=5.0000
DISTANCE=-122.5838
doesittake
DISTANCE=-500.0000
TIME=108.8981
iterative
See
solution
page
the
Solver,
press([SOLVE|.If
displays
for
110
for
SOLVE
the
objecttofall
for
TIME,
additional
Application
the
SOLVE
Stores
Stores
Stores
Calculates
meters
Stores
Iterative
500
the
V0.
TIME.
the
meters?
DISTANCE.
solution
TIME.
the
Solver
information
there
menu
displaysaseries
about
arenoequationsinmem-
andamessage:
constant.
the
number
object
iterative
of
falls.
for
of
{MEW>
90
5:
The
Equation
AR
SOLVE
Solver
FOR
NEW
RILTTYR
menu
EQUATION
Typeanew
equation
Page 97

If
the
plays
equation
the
current
>
list
Current
contains
equation.
equation
oneormore
DISTANCE=YBXTIME-
equations,
.
SXG..
/L
the
HP-27S
dis-
Equationislonger
To
designate
until
Menu
CALC
EDlY.
that
another
equationisdisplayed.
Key
Entering
To
enteranequation:
equationasthe
Table
Verifies
variables.
Displays
rent
equation;
whenitis
Deletes
Displays
equationisinserted
5-1.
the
current
the
ALPHA-edit
longer
the
current
the
ALPHA
also
than22characters.
Equations
than22characters
The
Description
equation
allows
equation
menu
below
current
SOLVE
menu
equation,
Menu
and
displays
and
youtoview
and/or
for
enteringanew
the
previous
cursor
the
its
press
the
menu
for
editing
entire
variables.
equation.
current
(a]or(V]
of
the
equation
equation.
cur-
The
1.
Press
[S0LVE].
2.Ifthe
3.
listisempty,orif
important,goto
place,
use
the
new
bottomofthe
Press
the
step3.To
(a]or[¥]todisplay
equation.
¥todisplay
Pressing
list.
the
locationofthe
insert
the
equationata
the
equation
(4]
or
(Y]
ALPHA
menu.
5:
The
new
that
moves
Equation
equation
willbeabove
to
Solver
isn’t
particular
the
top
or
91
Page 98

4.
Type
menu
equation
formation
5.
Press
Doing
the
equation.Ifnecessary,
to
correct
that
[INPUT]toenter
Solver
typographical
have
scrolled
about
the
Calculations
ALPHA
the
use
errors
off
the
and
equation.
[¢]
and
andtoview
display.
(See
ALPHA-edit
the
ALPHA-edit
portionsofthe
page36for
menus.)
in-
Press
its
During
ators,
names,
the
If
INVALID
positioned
To
€ALE
variables.
-
verification,
unmatched
etc.Ifthe
menu
of
the
equation
ERUATION
where
solve
foravariable:
1.
Storeavalueinall
keyinthe
2.
Optional:
or
two
value
and
TIME
page
112
3.
To
start
the
Solver
lator
line.
to
verify
the
current
1.
6060
{bI:TH]W[TIME]
Menu
of
variables
DISTANCE=VOXTIME-.SXGXTIME"2
the
Solver
parentheses,
equation
variables.
breaks
number
After
guesses
press
20
for
the
The
any
syntax
and
then
an
error
was
but
and
entering
for
the
the
menu
['TIME"
enters0and
additional
calculation,
findsasolution,
equation
G
for
the equation:
looks
misspelled
passes
valueofnew
oneofthe
verification,
rules,
displays
first
press
all
the
answer.Toenter
key
information
press
the
the
and
display
the
for
syntax
detected.
variables.Tostore
the
appropriate
known
for
the
20asguesses
menu
answerisdisplayedonthe
errors—missing
functions,
variablesissetto0.
the
HP-27S
the
equation
the
illegal
HP-27S
briefly
with
each
menu
values
unknown.
about
each
guesses).
key
for
(step
guess,
For
for
the
1),
example,
TIME
unknown.
the cursor
key.
enter
keyinthe
menu
oper-
variable
displays
displays
value,
one
(see
calcu-
of
0
If
92
5:
The
Equation
Solver
Page 99

In
most
cases,
deal
withawide
certain
necessary,
).
sionofthe
Works”
calculations,
you
The
Solver
calculationtohelp
(see
page
playedbythe
Clearing
To
clear
the
menu
to
of
variablesisdisplayed.
0.
the
Solver
displaysananswer.
varietyofcomplex
the
Solver
can
halt
these
may
also
display
110)
explains
Solver.
Solver
variablesinan
mathematical
displays
setsofchanging
calculationsbypressing
additional
you
analyze
how
informationatthe
the
to
interpret
Variables
equation,
press[CLEAR
Clearing
variables
However,
conditions.
result.
information
sets
the
any
“How
Solver
During
numbers.
key
conclu-
the
while
them
equal
can
(If
except
Solver
dis-
the
Variables
Viewing
Press
use
sary,
(see
the
use
page
are
¥todisplay
cursor
the
36
cleared
and
movement
ALPHA-edit
for
additional
editing).
If
you've
of
the
without
edited
equation
changing
the equation,
with
the
Editinganequation
*
The
HP-27S
helps
without
equation.
pressing (INPUT],
prevent
when
Editing
the
keystoscroll
and
the
edited
stored
clears
its
lossofan
the
HP-27S
the
equationisedited.
the
Equation
ALPHA-edit
ALPHA
information
press
menu
through
menus
about
to
the
replace
version.Toreturntothe
equation,
press
[EXIT].*
variables.
edited
equation.Ifyou
gives
you
another
make
opportunitytosave
and
cursor.
You
equation.Ifneces-
to
make
any
changes
alpha
entry
and
the
old version
SOLVE
changes
and
press
the edited
can
menu
5:
The
Equation
Solver
93
Page 100

Naming
an
Equation
Naming
equation
be
<,
enter
an
equation
andisseparated
any
length
and
>,",:;,=,and
the
equation,orit
Equation
e,
FREEFALL:DISTANCE=VAX..,
CALCEDIT
Shared
Ifavariable
is
shared
variable
or
until
affect
No
sharing
containedinmenus
Solver
application.
Solver
appearsinmore
among
remainsinmemory
the
variableisclearedordeleted.
the
stored
occurs
equationisnot
helps
from
can
include
space.
The
canbeadded
name
Variables
those
equations.Avalue
value.
between
outside
shared
you
identify
the
equationbya
any
characters
name
[DELET]
NEL
than
one
untilanew
Solver
the
variables
Solver.
with
it.
The
name
precedes
colon.
except+,—,
canbetypedinas
later
using
TEDIT
Names
X,
you
.
Solver
For
the
equation,
that
storedorcalculated
valueisstoredorcalculated,
Switching
and
menus
built-in
variables
example,avariableNin
variableNin
the
TVM
the
can
+,),
(,
initially
variable
for
that
does
not
a
Example:
Variables.
whereF,C,
1.
Press
2.
Type
3.
Press
4.
Press
display
94
5:
The
Temperature
Convert
F=9xC+5+32
andKare
Conversions
350°Ftodegrees
degrees
M[SOLVE]toenter
the
equation
['NEW
[A]
['€ALEtodesignate
its
menu
Equation
F-C:F=9xC+5+32
and
type
of
variables.
Solver
and
Fahrenheit,
the
Solver
the
equation
Using
Kelvin,
K=C+273.16
Celsius,
application,
[(INPUT].
K-C:K=C+273.
F-Casthe
Shared
using
current
the
equations:
and
Kelvin.
then
equation
[INEWT
16
[INPUT].
.
and
 Loading...
Loading...