Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 3810
Dissolved Oxygen
Test Kit
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product. Please read the
instructions carefully before using the chemical test kit. It
will provide you with the necessary information for correct
use of the kit.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office
immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
• Manganous Sulphate Solution, 1 bottle with dropper
(30 mL);
• Alkali-Azide Reagent, 1 bottle with dropper (30 mL);
• Sulphuric Acid Solution, 2 bottles with dropper (60
mL);
• Starch Indicator, 1 bottle with dropper (10 mL);
• HI3810-0 Reagent Titrant Solution, 1 bottle (120 mL);
• 1 glass stoppered bottle;
• 1 calibrated vessel (10 mL);
• 1 calibrated syringe with tip.
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
Range 0 to 10 mg/L (ppm) O
Smallest Increment 0.1 mg/L (ppm) O
Analysis Method Azide Modification Titration
Sample Size 5 mL
Number of Tests 110 (average)
Case Dimensions 260x120x60 mm (10.2x4.7x2.4")
Shipping Weight 910 g (34.0 oz.)
SPECIFICATIONS
its original packing materials.
SPECIFICATIONS
2
2
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The concentration of dissolved oxygen in water is extremely
important in nature as well in man’s environment. In the
oceans, lakes, rivers, and other surface water bodies, dissolved
oxygen is essential to the growth and development of aquatic
life. Without oxygen, the water can become toxic due to the
anaerobic decaying of organic matter. In man’s environment,
water must contain at least 2 mg/L of oxygen to protect water
pipes from corrosion. However, boiler system water, in many
cases, cannot contain greater than 10 mg/L oxygen.
The Hanna Dissolved Oxygen Test Kit can determine the
oxygen concentration in water quickly and easily. The kit is
portable and can be used in the field as well in the
laboratory.
Note: mg/L is equivalent to ppm (parts per million).
CHEMICAL REACTION
A modified Winkler method is used. Manganous ions react
with oxygen in the presence of potassium hydroxide to form
a manganese oxide precipitate (Step 1). An azide is present
to prevent any nitrite ions from interfering with the test. On
addition of acid, manganese oxide hydroxide oxidizes the
iodide to iodine (Step 2). Since the amount of iodine generated is equivalent to the oxygen in the sample, the
concentration of iodine is calculated by titration of thiosulfate ions that reduce the iodine back to iodide ions.
Step 1: 2Mn
Step 2: MnO(OH)2 + 2I– + 4H
Step 3: I2 + 2S2O
2+
+ O2+ 4OH– →2MnO(OH)
+
2–
→ 2I– + S4O
3
→Mn
2+
2–
6
INSTRUCTIONS
READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE TEST KIT
LOOK AT THE BACK PAGE FOR THE ILLUSTRATED PROCEDURE
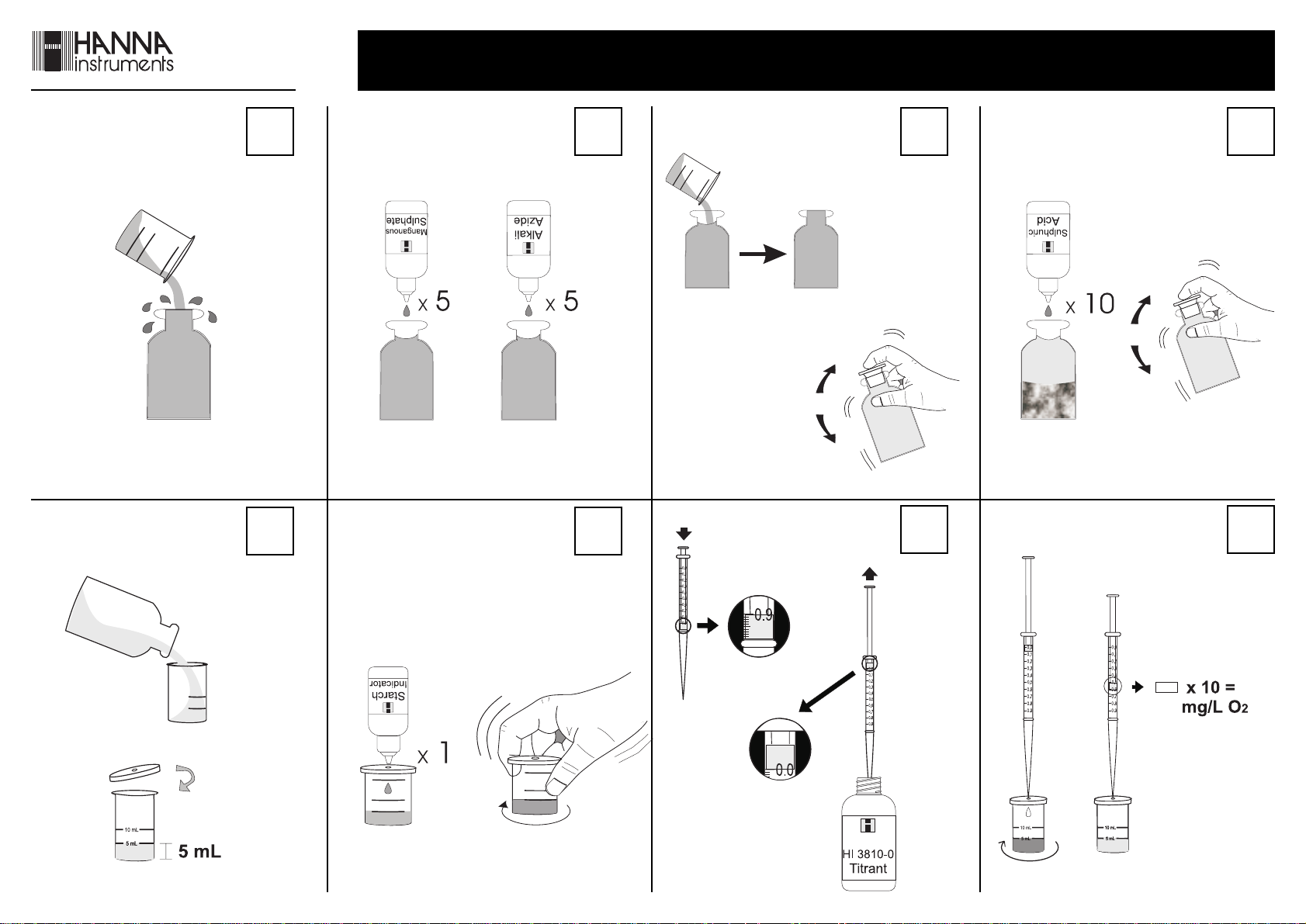
• Rinse the glass bottle 3 times with water sample and fill
to overflow. Insert stopper and ensure that a small
part of the sample spills over.
ISTR3810R2 03/02 PRINTED IN ITALY
2
+ I2 + 3H2O
• Remove the stopper and add 5 drops each of Manganous
Sulphate Solution and Alkali-Azide Reagent.
• Add some more sample to fill the bottle completely.
Carefully stopper the bottle again and ensure that a
part of the sample spills over. This is to make sure that
no air bubbles have been trapped inside, which would
corrupt the reading.
• Invert several times the
bottle. The sample
becomes orange-yellow
and a flocculent
precipitate will form if
oxygen is present.
• Let the sample stand and the
flocculent precipitate will start to
settle.
• After approximately 2 minutes,
when the upper half of the bottle
becomes limpid, add 10 drops of
Sulphuric Acid Solution.
• Again stopper the bottle and invert it until all particulate
material is dissolved. The sample is ready for measurement
when it is yellow and completely limpid.
• Remove the cap from the plastic
vessel. Rinse the plastic vessel with
the solution in the bottle, fill to the
5 mL mark and replace the cap.
• Add 1 drop of Starch Indicator through the cap port
and mix by carefully swirling the vessel in tight circles.
The solution will turn a violet to blue color.
• Push and twist pipet tip onto tapered
end of syringe ensuring an air tight-fit.
Take the titration syringe and push the
plunger completely into the syringe.
Insert tip into HI 3810-0 Titrant Solution
and pull the plunger out until the
lower edge of the plunger seal is on the
0 mL mark of the syringe.
• Place the syringe tip into the cap port
of the plastic vessel and slowly add the
titration solution dropwise, swirling to
mix after each drop. Continue adding
titration solution until the solution in
the plastic vessel changes from blue to
colorless.
• Read off the milliliters of titration solution
from the syringe scale and multiply by 10
to obtain mg/L (ppm) oxygen.
x 10 = mg/L O
• If results are lower than 5
mg/L, the precision of the
test can be improved as
follows. Add an amount of
unused sample in the glass
bottle to the 10 mL mark of
the plastic vessel.
• Proceed with the test as described before and multiply the
values on the syringe scale by 5 to obtain mg/L oxygen
x 5 = mg/L O
in the sample.
1987 Annual Book of ASTM Standard, Volume 11.01
Water (1), pages 629-638.
Official Methods of Analysis, A.O.A.C., 14th Edition, 1984,
pages 620-621.
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 16th Edition, 1985.
REFERENCES
HEALTH & SAFETY DATA
The chemicals contained in this test kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read Health and Safety Data Sheets
before performing the test.
2
2
Page 2
Rinse x 3
HI 3810 DISSOLVED OXYGEN TEST KIT
2 3 41
5 mL sample
5
6
7 8
 Loading...
Loading...