Page 1
Instruction Manual
HI 38083
Gypsum Requirement
&
Exchangeable Sodium
Test Kit
www.hannainst.com
Dear Customer,
Thank you for choosing a Hanna Product.
Please read the instruction sheet carefully before using the
test kit. It will provide you with the necessary information
for correct use of the kit. If you need additional information,
do not hesitate to e-mail us at tech@hannainst.com.
Remove the chemical test kit from the packing material and
examine it carefully to make sure that no damage has
occurred during shipping. If there is any noticeable damage, notify your Dealer or the nearest Hanna office
immediately.
Each kit is supplied with:
HI 38083A-0 Calcium Sulfate, 1 bottle (10 g);
•
Buffer Solution 10.2±0.2, 1 bottle with dropper
•
(30 mL);
HI 38083C-0 EDTA Solution, 3 bottles (3 x 100 mL);
•
Calmagite Indicator, 1 bottle with dropper (10 mL);
•
Demineralizer Bottle with filter cap for about 12 liters
•
of deionized water (depending on the hardness level
of water to be treated)
• 1 2-mm soil sieve;
1 plastic test tube (14 mL) with screw cap;
•
1 plastic test tube (50 mL) with screw cap;
•
• 1 small funnel;
• filter paper discs ∅ 80 mm (100 pcs);
• 1 brush;
• 1 calibrated plastic vessel (50 mL);
;
• 2 calibrated plastic vessels (20 mL) with cap;
1 plastic pipette (3 mL);
•
1 plastic pipette (1 mL);
•
• 1 syringe (1 mL) with tip;
2 spoons.
•
Note: Any damaged or defective item must be returned in
its original packing materials.
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONSSPECIFICATIONS
Range GR: 0 to 213 metric ton/ha
(0 to 95 ton/acre)
EES: 0 to 56.4 meq/100 g soil
Smallest Increment 3.8 metric ton/ha (1.7 ton/acre) as GR
1.95 meq/100 g soil as EES
Analysis Method Drop count titration
Sample Size 0.5 mL of soil
Number of Tests 100
Case Dimensions 235x175x115 mm (9.2x6.9x4.5")
Shipping Weight 883 g (31.1 oz.)
Note: GR is Gypsum Requirement and EES is Estimated Exchange-
able Sodium; meq/100 g is milliequivalent per 100 grams.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
SIGNIFICANCE AND USESIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Alkaline soils are characterized by a low electrical conductivity (EC), high exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) and
presence of carbonate and bicarbonate sodium salts. Hydrolysis of carbonate causes also an increase in pH, such
that it is always greater than 8.5.
The "saline-sodic" soil group, which possesses the following
peculiarities, also belongs to this alkaline group:
EC > 4 mmhos, ESP > 15, pH ≤ 8.5
High alkalinity causes impairment to plant growth since it
gives rise to an incomplete solubilization of necessary nutrients such as iron, copper and manganese. Chlorosis, for
instance, is a typical disease of leaves due to iron deficiency.
It is possible to correct soil alkalinity by adding a proper
compound (generally gypsum) that removes sodium and
decreases the pH. The exact quantity of gypsum needed for
correction can be calculated with the Hanna Gypsum Requirement Test Kit.
CHEMICAL REACTIONCHEMICAL REACTION
CHEMICAL REACTION
CHEMICAL REACTIONCHEMICAL REACTION
The extraction method is the saturated calcium sulfate method.
The Hanna Test Kit determines Gypsum Requirement by
ISTR38083 02/00 PRINTED IN ITALY
titration of Calcium. The indicator chelates with Calcium ions
to form a red colored complex. As EDTA is added, calcium
complexes with it: the reaction endpoint is indicated by a
change in color of the indicator from red to blue.
SAMPLING PROCEDURESAMPLING PROCEDURE
SAMPLING PROCEDURE
SAMPLING PROCEDURESAMPLING PROCEDURE
WHEN TO TEST YOUR SOIL
Soil should be tested not only when the plant appears to
be unhealthy (yellow leaves or stunted growth), but prior to
seeding, planting and fertilizing as well as when other
material such as manure or compost has been added.
SAMPLING
1) Soil Sample Extraction
– Within a large homogeneous area, take 1 or 2 samples
per 1000 m
– Even for smaller areas, 2 samples are recommended
(the more samples, the better the end-results, because the end sample is more representative).
– For a small garden or plot, 1 sample is sufficient.
2) Avoid extracting samples from soil presenting obvious
anomalies and from border areas (near ditches and roads).
3) Sample quantity:
Take the same quantity of soil for each sample. For example, use bags with similar dimensions (1 bag per
sample).
4) Depth of extraction:
General: dig and discard 5 cm (2") of topsoil
For lawns: take the sample at a depth of 5 to 15 cm (from
2" to 6").
For other plants (flowers, vegetables, shrubs): from 20 to
40 cm of depth (8" to 16").
For trees: Samples from 20 to 60 cm of depth (8" to 24'’).
5) Mix all the samples together to obtain a homogeneous
mixture of soil, discarding stones and vegetable residues.
6) From this mixture, take the quantity of soil that you
need for the analysis.
7) Crumble the large chunks and distribute the soil sample
on paper or plastic to air dry it.
8) Use a small bar to crush the air dried sample and pass it
through the 2-mm soil sieve.
2
(0.25 acre).
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS
INSTRUCTIONSINSTRUCTIONS
READ THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING THE KIT
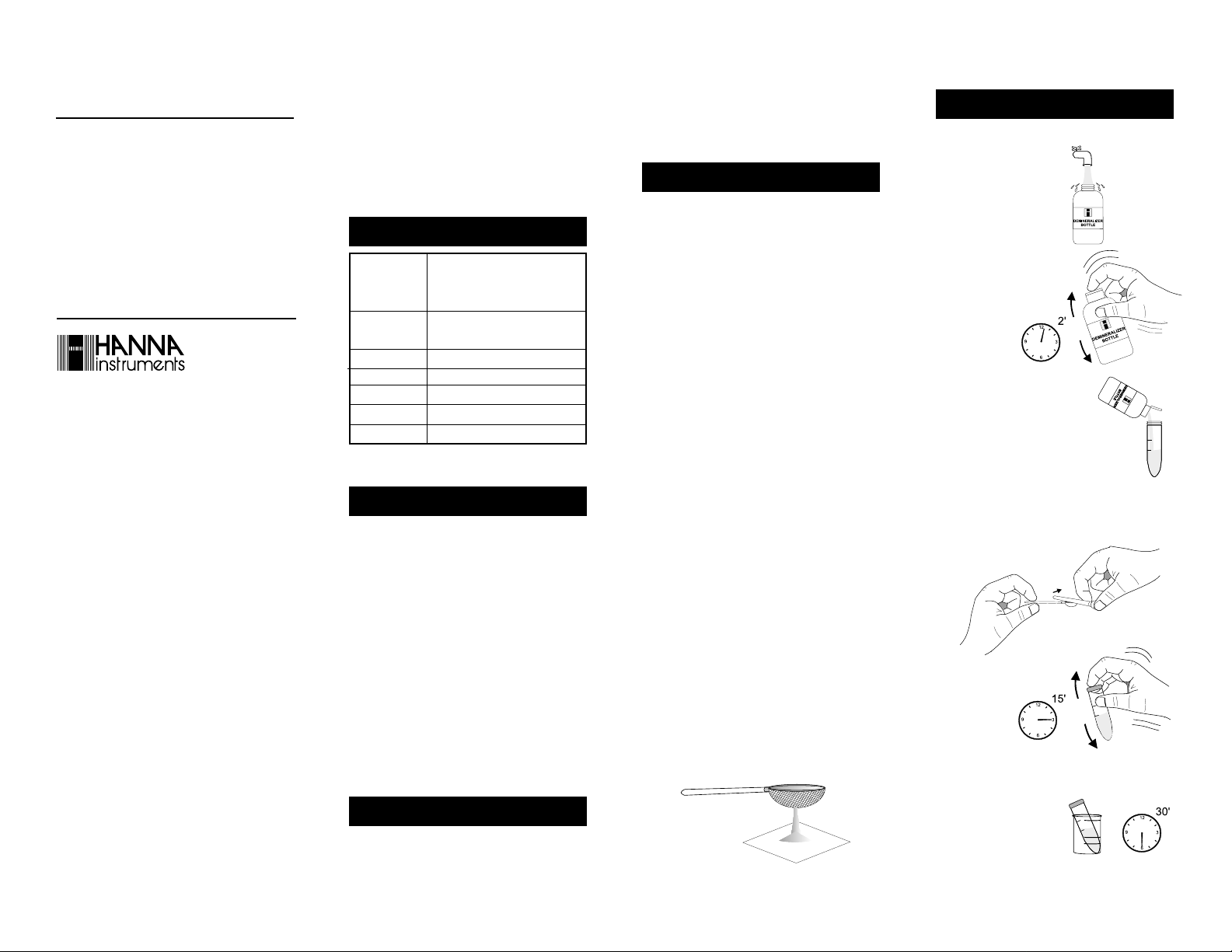
• Remove the cap and fill
the Demineralizer Bottle
with tap water.
• Replace the cap
and shake gently for at least
2 minutes. The
demineralized
water is now
ready.
• Flip open the top of the Demineralizer Bottle cap. By gently
squeezing the bottle, add demineralized water to the large (50
mL) test tube up to the 25 mL
mark.
• Add 1 spoon of HI 38083A-0 Calcium Sulfate (discard
the excess soil by using the handle of the other spoon).
• Place the cap
on the tube
and shake it
several times
during a 15
minute period.
• Place the tube into the
large (50 mL) vessel and
wait for 30 minutes. The
saturated calcium sulfate
extractant solution is
ready.
25 mL
Page 2
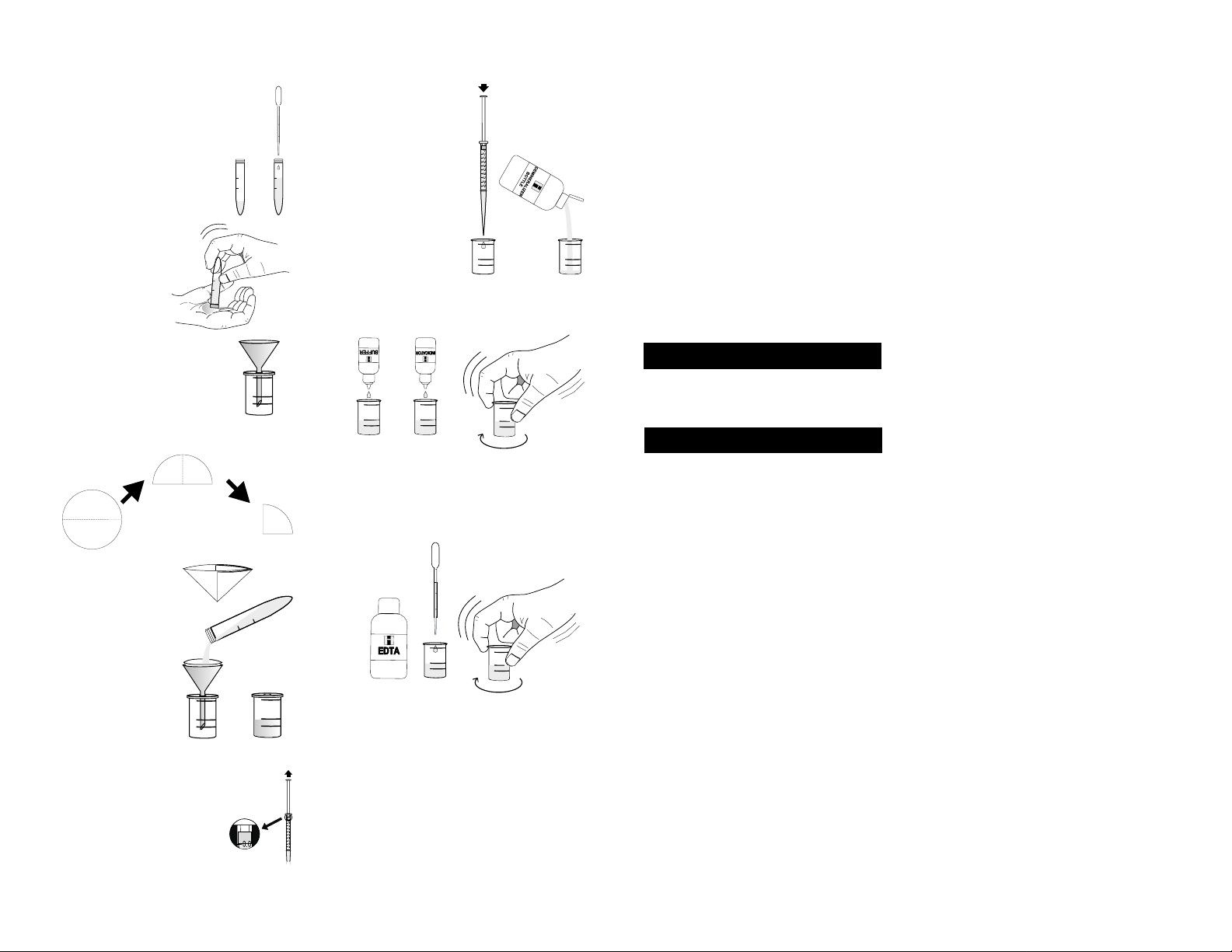
• To obtain the soil extract measure in the small (14 mL)
test tube 0.5 mL of the prepared soil and add with the
3 mL pipette the saturated
calcium sulfate extractant solution up to the 11 mL mark.
• Replace the cap and
shake vigorously by
striking the tube
against the palm of
your hand, to completely suspend the
soil. Shake the tube
three times for 1
minute at 10 minute
intervals.
• Place the cap on one of the small (20
mL) calibrated vessels and insert the
funnel into the cap hole.
• Fold a filter paper disc twice as shown in the figure.
0.5 mL
of soil
11 mL
• Insert the syringe into
the other small plastic
vessel and push the
plunger out until the
lower edge of the seal
is on the 1.0 mL mark.
Add to the vessel demineralized water from
the Demineralizer Bottle
up to the 10 mL mark.
• Add 4 drops of Buffer Solution 10.2±0.2, 1 drop of
Calmagite Indicator and swirl to mix.
x 4
• Using the
EDTA Solution, swirling after each drop, while keeping
an accurate count of the number of drops being added
to the solution.
x 1
1 mL plastic pipette, add drops of HI 38083C-0
10 mL
• Calculate the Gypsum Requirement as follows:
GR (meq/100 grams of soil) = 56 - drops added
GR (ton/acre) = (meq/100 g) x 1.7
GR (metric ton/ha) = (meq/100 g) x 3.81
Note: if more than 56 drops need to be added, there is no
Gypsum Requirement.
• Calculate the Estimated Exchangeable Sodium as follows:
EES (meq/100 grams of soil) = 0.99 x GR (meq/100 g) + 0.96
REFERENCESREFERENCES
REFERENCES
REFERENCESREFERENCES
P. Sequi, Chimica del suolo, Patron Editore, Ed. 1991
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETY
HEALTH AND SAFETYHEALTH AND SAFETY
The chemicals contained in this kit may be hazardous if
improperly handled. Read the relevant Health and Safety
Data Sheet before performing this test.
• Separate one side from
the other three to form a
cone.
• Place the folded filter disc
into the funnel and filter
the sample by pouring the
soil extract into the cone.
The extracted sample in
the beaker is now ready
for analysis.
DETERMINATION OF GYPSUM REQUIREMENT
• Take the syringe and push the
plunger completely down into the
syringe. Insert tip into sample and
pull the plunger out until the lower
edge of the seal is on the 0.0 mL
mark of the syringe.
• Continue adding EDTA Solution until the solution in the
vessel changes from red-violet to pure blue. If necessary
refill the pipette with EDTA Solution, while keeping
count of the drops being added. Record the number of
drops needed to obtain the final color change (from
wine red to pure blue).
 Loading...
Loading...