HAMAMATSU F2224-31, F2224-29P, F2224-29M, F2224-24S, F2224-24P Datasheet
...
CIRCULAR MCP AND
ASSEMBLY SERIES
Information furnished by HAMAMATSU is believed to be reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed for possible inaccuracies or omissions. Specifications are
subject to change without notice. No patent rights are granted to any of the circuits described herein. ©1999 Hamamatsu Photonics K.K
Subject to local technical requirements and regulations, availability of products included in this promotional material may vary. Please consult with our sales office.
A microchannel plate (MCP) is a secondary-electron multiplier which detects and amplifies electrons in two-dimensions. The MCP is sensitive not only to electrons but to ions,
vacuum ultraviolet light, X-rays and γ-rays, making it useful in
a wide range of detection applications.
Hamamatsu has available seven types of circular MCPs,
ranging in outer diameter from 18mm to 114mm. MCP assemblies with electrode leads are also available to facilitate
use of the MCPs. These MCP assemblies offer three types
of read-out devices; a phosphor screen (optical image conversion), a multi-anode (electrical output signals responding
to the position of the incident signals), and a single-anode
(an electrical output signal within the effective area), providing a variety of readout functions to handle a range of applications. From one to three MCPs can be selected as required to provide the necessary electron gain.
These MCPs and MCP assemblies are finding wide application in fields including image intensifiers, fast time response photomultiplier tubes, and analytical instruments.
FEATURES
•
Sensitive to electrons, ions, VUV lights, X-rays and γ-rays
•
Two-dimensional image intensification
•
Fast time response
•
Immunity to magnetic fields
•
Small size and lightweight
APPLICATIONS
•
Analytical Instruments
• Electron Beam Measuring System (EBMS)
• FIM, AP-FIM
• ESCA
• Mass Spectrometer (MS)
• TOF-MS
• LEED, MEED, etc.
•
Electron Tube
• Image Intensifier
• Fast Time Response PMT
• Streak Camera
•
Cosmic Measurement
• Detection of Plasma Ions, Soft X-rays and VUV lights
•
High Energy Physics
• Detection of Ions, Electrons, Positrons, High Energy
Particles and X-rays
CIRCULAR MCP SERIES
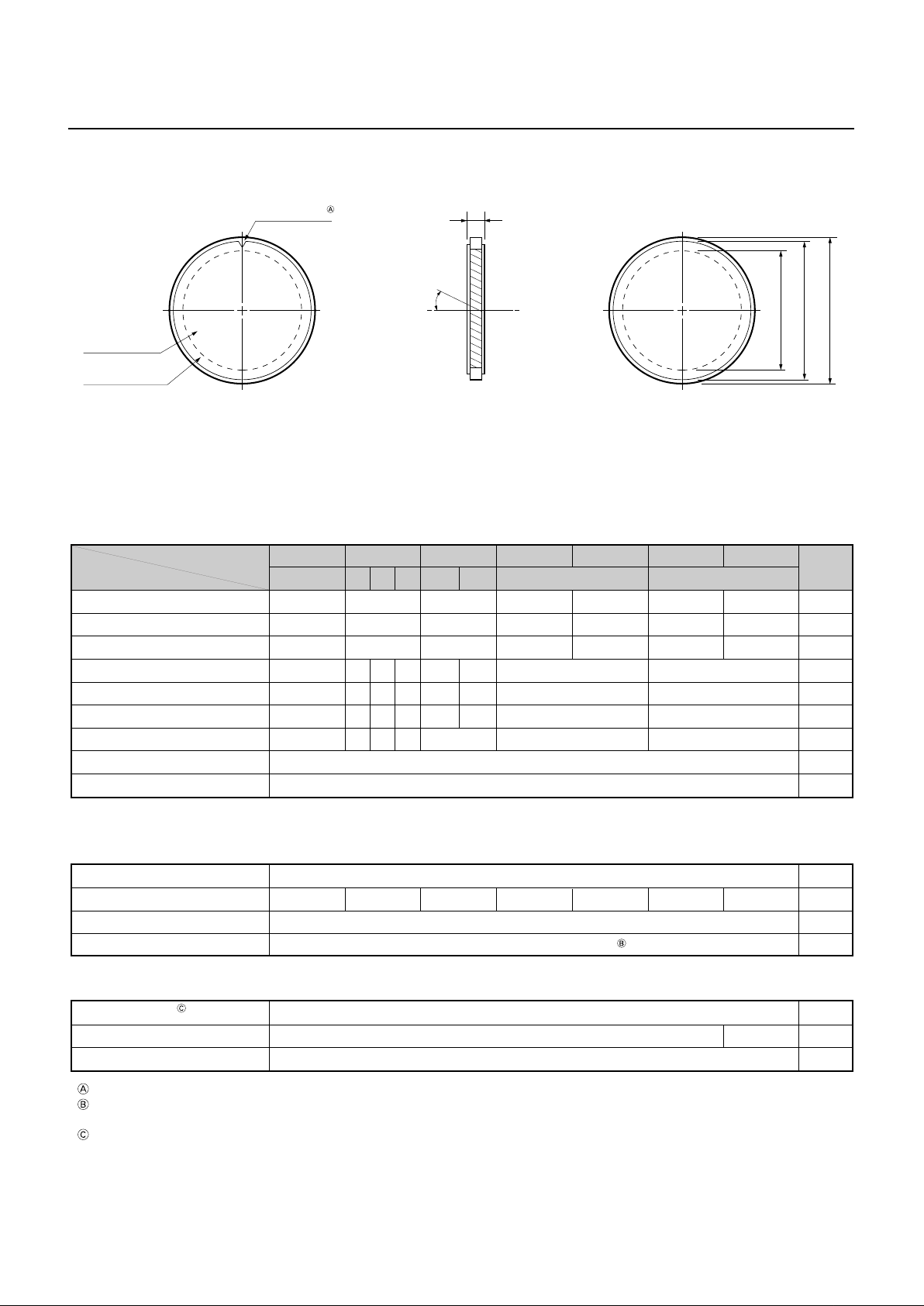
MCP DIMENSIONAL OUTLINES (Unit: mm)
A
B
C
INDICATOR
EFFECTIVE
AREA
INPUT SIDE OUTPUT SIDE
ELECTRODE
D
θ
TMCPA0025EB
Outer Diameter
Electrode Diameter
Effective Diameter
Thickness
Channel Diameter
Channel Pitch
Bias Angle
Open Area Ratio
Electrode Material
Parameter
Type No.
17.9
17
14.5
0.48
12
15
8
24.8
23.9
20
0.41
10
12
5,15
32.8
31.8
27
8,12
38.5
36.5
32
60
Inconel
49.9
49
42
0.24
6
7.5
13
0.48
12
15
5,8,15
0.41
10
12
0.48
12
15
0.48
12
15
8
86.7
84.7
77
114
112
105
mm
mm
mm
mm
µm
µm
degrees
%
—
—
MΩ
A/cm
3
—
V
°C
°C
F2395
Unit
F1942
-04
F1217F1208
-01
F1552F1094
-09
F1551
-01 -07 -01 -09 -01
1.00
25
31
8
A
B
C
D
θ
Gain
Plate Resistance
Dark Current
Max. Linear Output Signal
100 to 700 50 to 500 30 to 300
More than 10
4
20 to 200
Less than 5 × 10
-13
Up to 7% of the strip current
10 to 200 10 to 100 5 to 50
Supply Voltage
Ambient Temperature
Baking Temperature
1000 (Channel Diameter: 6µm, 10µm, 12µm): 1200 (Channel Diameter: 25µm)
-50 to +70
400
-50 to +30
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Supply Voltage: 1000V, Vacuum: 1.3 × 10-4 Pa (1 × 10-6 Torr), Ambient Temperature: +25°C)
MAXIMUM RATINGS
This indicator shows the MCP input side and the direction of channel bias.
The strip current is the current which flows along the channel wall when a voltage is applied between the MCP input and output and is given by applied
voltage/plate resistance.
At a vacuum of 1.3 × 10
-4
Pa (1 × 10-6 Torr) or less.
Consult us for more details on MCP dimensions and tolerances.
RELATIVE OUTPUT
ACCUMULATED CHARGE OF OUTPUT SIGNAL (C / cm2)
SUPPLY VOLTAGE: 1000V
OUTPUT CURRENT DENSITY: 50nA/ 15mm
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
0.5
0
1.0
600
10
2
10
3
10
4
10
5
800 1000
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
GAIN
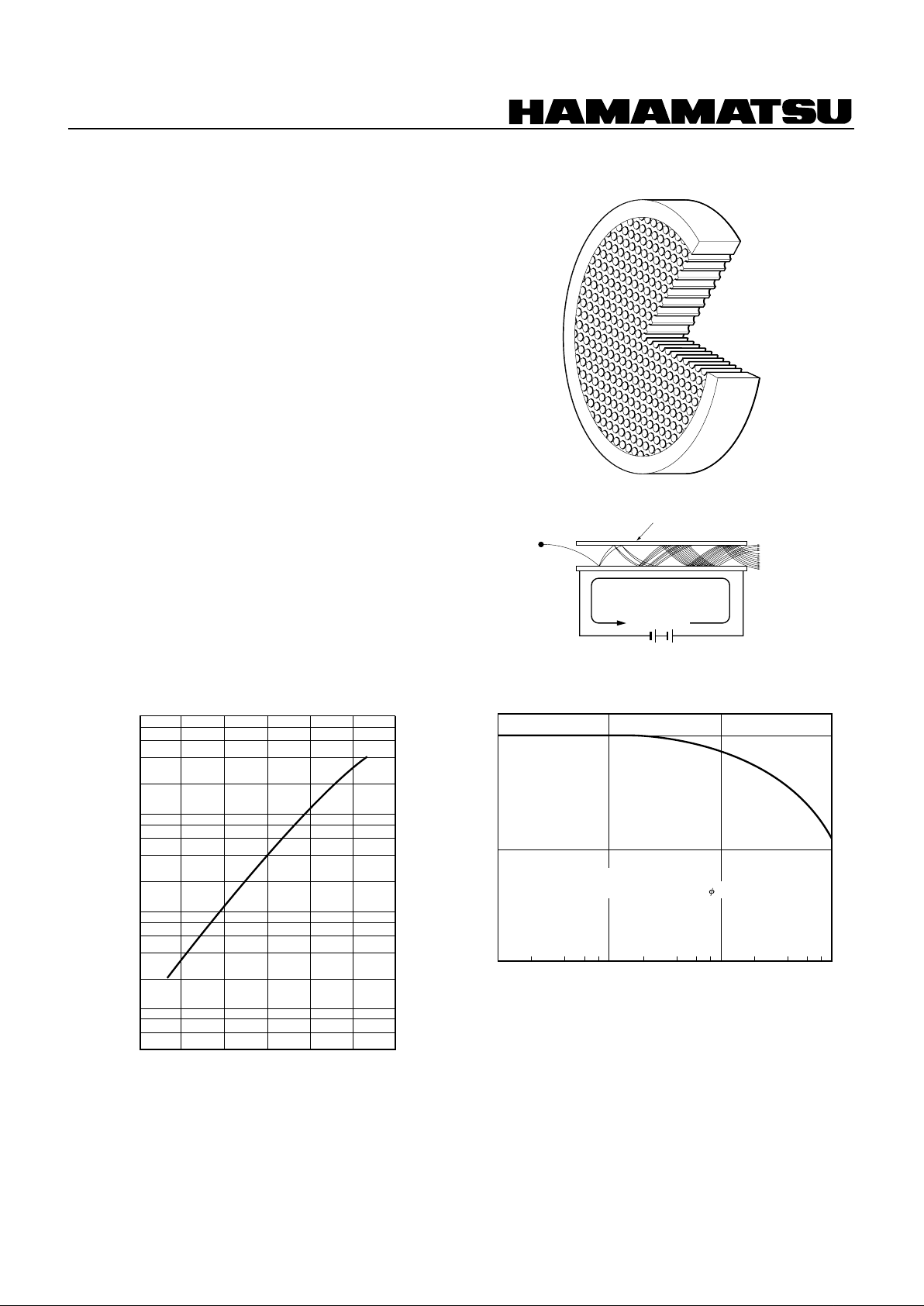
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
As shown in the figure, when a voltage VD is applied across
the input-side and output-side electrodes of the MCP, a potential gradient is built up along the channel direction. If an
incident electron strikes an inner wall on the input side, a
number of secondary electrons are emitted. These secondary electrons are accelerated by the potential gradient and
travel along a parabolic path determined by the initial velocity. They then collide with the opposing wall surface, causing
secondary electrons to be emitted again. In this manner, the
electrons collide repeatedly within the channel as they pass
towards the output side. The result is a large multiplication of
the incident electron.
MCP CONFIGURATION
CHANNEL WALL
STRIP CURRENT
V
D
OUTPUT
ELECTRONS
PRIMARY
ELECTRON
TMCPC0002EC
GAIN AND LIFE CHARACTERISTICS
• Gain vs. Supply Voltage • Life
TMCPB0031EB
TMCPB0030EC
 Loading...
Loading...