Page 1
DOC023.98.80052
Profibus network card
04/2011, Edition 2
User Manual
Bedienungsanleitung
Manuale dell'utente
Manuel d'utilisation
Manual del usuario
Manual do utilizador
Uživatelská příručka
Brugsanvisning
Gebruikershandleiding
Instrukcja obsługi
Bruksanvisning
Käyttäjän käsikirja
Ръководство на потребителя
Használati útmutató
Manual de utilizare
Naudotojo vadovas
Руководство пользователя
Kullanım Kılavuzu
Návod na obsluhu
Navodila za uporabo
Korisnički priručnik
Εγχειρίδιο λειτουργίας
Kasutusjuhend
Page 2

English..................................................................................................................................................................................................3
Deutsch..............................................................................................................................................................................................16
Italiano................................................................................................................................................................................................30
Français.............................................................................................................................................................................................44
Español..............................................................................................................................................................................................58
Português..........................................................................................................................................................................................72
Čeština...............................................................................................................................................................................................86
Dansk..................................................................................................................................................................................................99
Nederlands.....................................................................................................................................................................................112
Polski.................................................................................................................................................................................................126
Svenska...........................................................................................................................................................................................140
Suomi................................................................................................................................................................................................153
български.......................................................................................................................................................................................167
Magyar..............................................................................................................................................................................................181
Română...........................................................................................................................................................................................194
lietuvių kalba..................................................................................................................................................................................207
Русский............................................................................................................................................................................................221
Türkçe...............................................................................................................................................................................................235
Slovenský jazyk...........................................................................................................................................................................248
Slovenski.........................................................................................................................................................................................261
Hrvatski............................................................................................................................................................................................275
Ελληνικά..........................................................................................................................................................................................288
eesti keel.........................................................................................................................................................................................302
2
Page 3
Specifications
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
Specification Details
Profibus protocol Siemens ASIC SPC3
DP service DPV0 slave
DP/DPV1 services DPV1 class 1 and class 2 slave
I&M function
Address changing per Profibus master
Profibus baud rates 9.6k, 19.2k, 45.45k, 93.75k, 187.5k, 500k, 1.5M,
Indicators LED to display the data exchange mode
Interface type RS485
Configurable parameters Data swapping, word wise for floating points values
Dimensions (50 x 69.5 x 15.4) mm³
Operating temperature –20°C to 85 °C (–4 to 185 °F)
Operating voltage 8V–16V
Maximal power consumption 2W
Certification Class I, Division 2 groups A, B, C, D and Class I,
3M, 6M, 12M
Automatic baud rate detection
Zone 2 group IIC, T4 hazardous and ordinary
locations
General information
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special,
incidental or
in this manual. The manufacturer reserves the right to make changes in
this manual and the products it describes at any time, without notice or
obligation. Revised editions are found on the manufacturer’s website.
consequential damages resulting from any defect or omission
Safety information
Please read this entire manual before unpacking, setting up or operating
this equipment.
Pay attention to all danger and caution statements. Failure
to do so could result in serious injury to the operator or damage to the
equipment.
Make sure that the protection provided by this equipment is not impaired,
do not use or install this equipment in any manner other than that specified
in this manual.
Use of hazard information
D A N G E R
Indicates a potentially or imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will
result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially or imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that may result in minor or moderate
injury.
Indicates a situation which, if not avoided, may cause damage to the instrument.
Information that requires special emphasis.
W A R N I N G
C A U T I O N
N O T I C E
Precautionary labels
Read all labels and tags attached to the instrument. Personal injury or
damage to the instrument could occur if not observed. A symbol, if noted
on the instrument, will be included with a danger or caution statement in
the manual.
English 3
Page 4
This symbol, if noted on the instrument, references the instruction
manual for operation and/or safety information.
This symbol indicates that a risk of electrical shock and/or electrocution
exists.
This symbol indicated the presence of devices sensitive to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) and indicated that care must be taken to prevent
damage with the equipment.
Electrical equipment marked with this symbol may not be disposed of
in European public disposal systems after 12 August of 2005. In
conformity with European local and national regulations (EU Directive
2002/98/EC), European
or end-of-life equipment to the Producer for disposal at no charge to
the user.
electrical equipment users must now return old
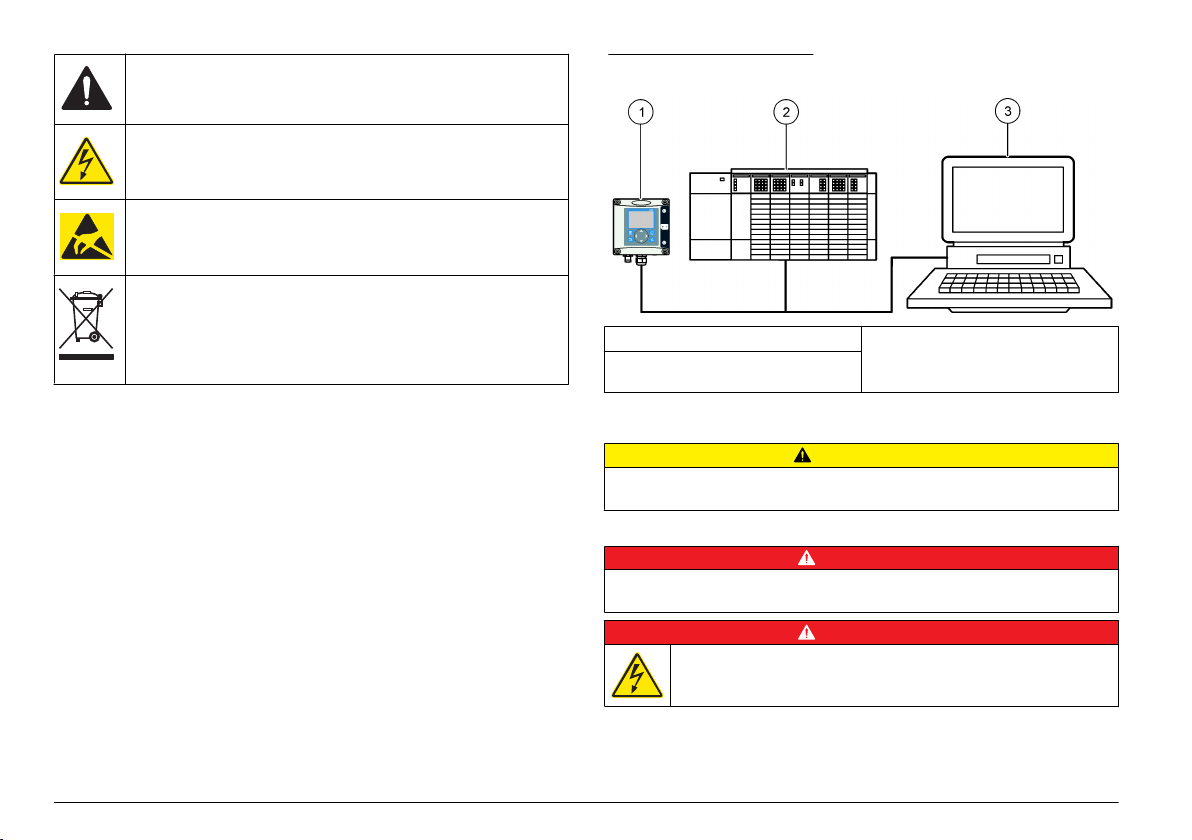
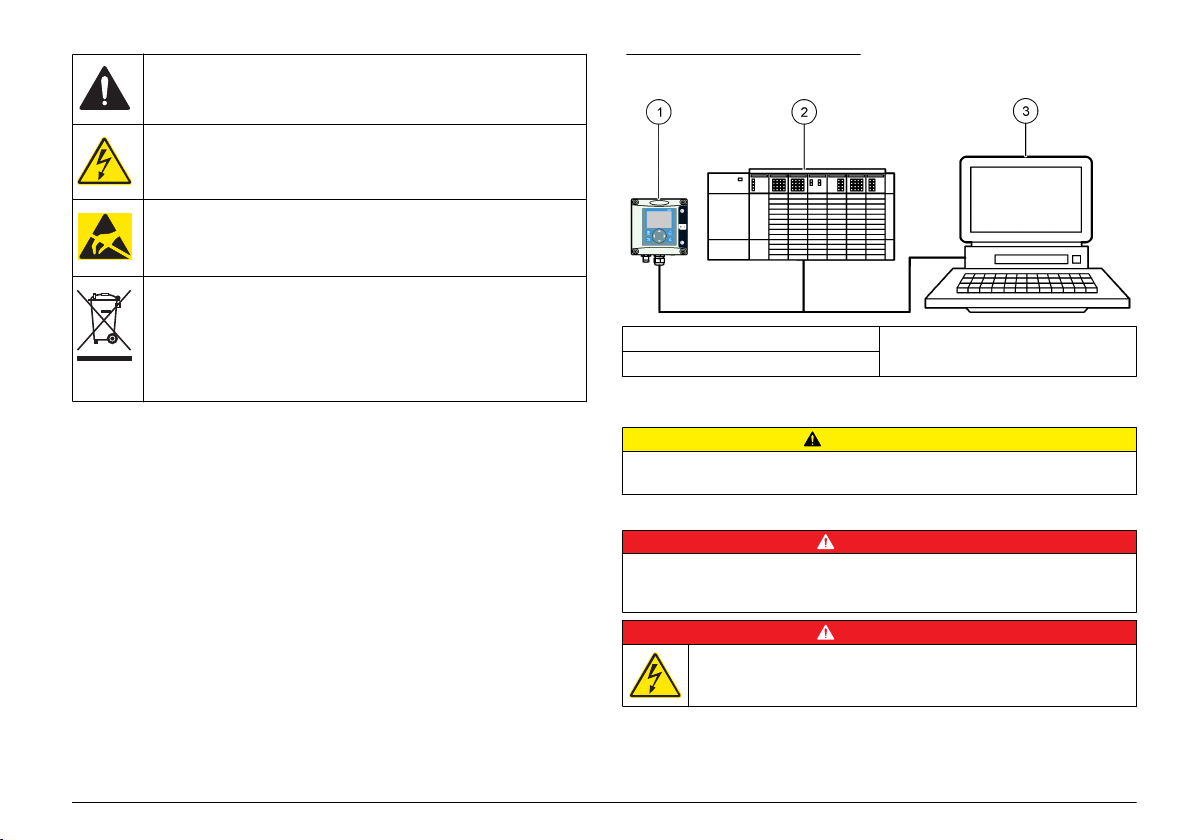
Figure 1 System overview
1 sc controller (Slave) 3 PC with software (Master class 2 e.g.
2 Programmable logic controller
(Master class 1)
PC include with CP5611 card)
Product overview
The sc controllers are the platform for all intelligent probes and analyzers.
The sc platform is a full digital communication system based on the open
Modbus standard. When a Profibus interface card is installed, the sc
controllers give the full range of standardized method values and
parameters.
The sc controllers are PNO/PTO certified Profibus DP/V1 devices. These
devices are compatible with master class 1 (PLC SCADA) and master
class 2 systems, e.g., engineering stations.
An overview of the system is shown in System overview. Profibus is
available as a factory or user installed item.
4 English
Installation
C A U T I O N
Personal injury hazard. Only qualified personnel should conduct the tasks
described in this section of the manual.
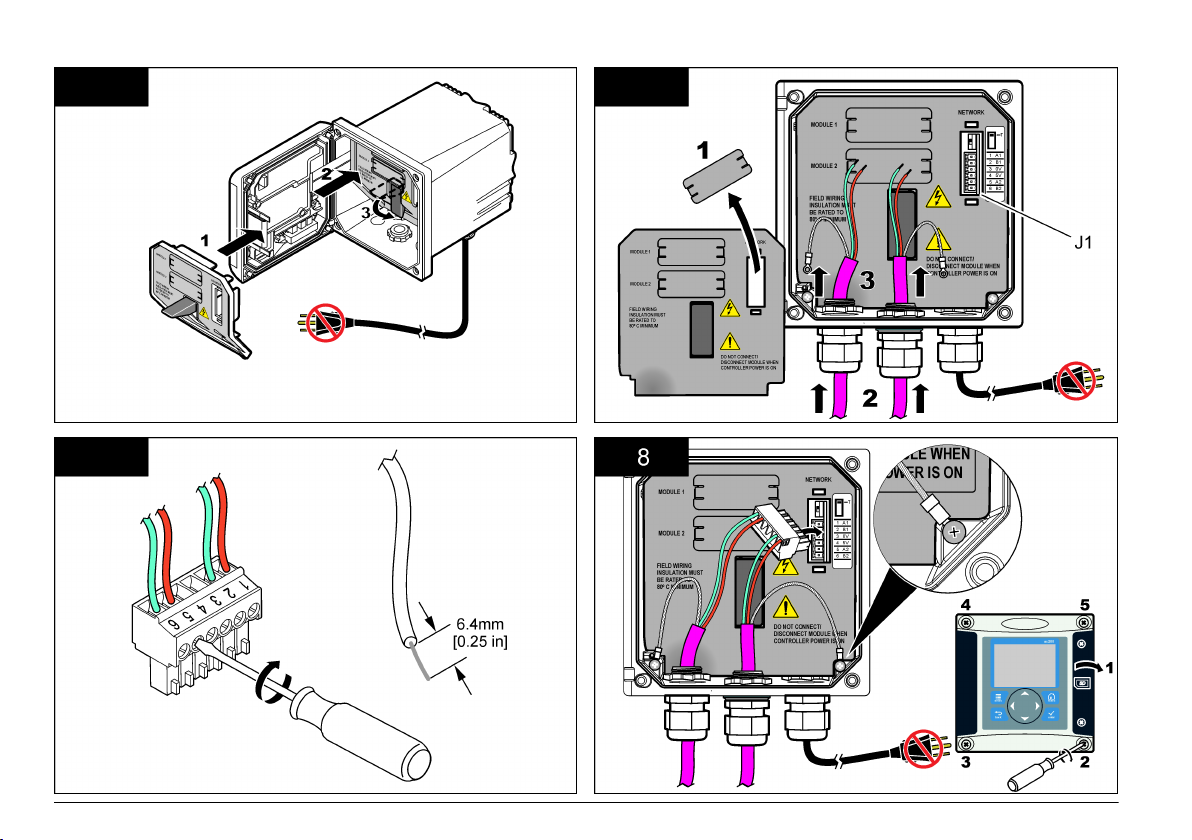
Install the module to the controller
Explosion Hazard. For the module installation in classified hazardous locations,
refer to the controller user manual for safety instructions.
Electrocution Hazard. Always remove power from the instrument before
making any electrical connections.
D A N G E R
D A N G E R
Page 5
D A N G E R
Electrocution Hazard. High voltage wiring for the controller is conducted behind the
high voltage barrier in the controller enclosure. The barrier must remain in place
except when
for power, relays or analog and network cards.
installing modules, or when a qualified installation technician is wiring
Potential Instrument Damage. Delicate internal electronic components
damaged by static electricity, resulting in degraded performance
can be
or eventual failure.
N O T I C E
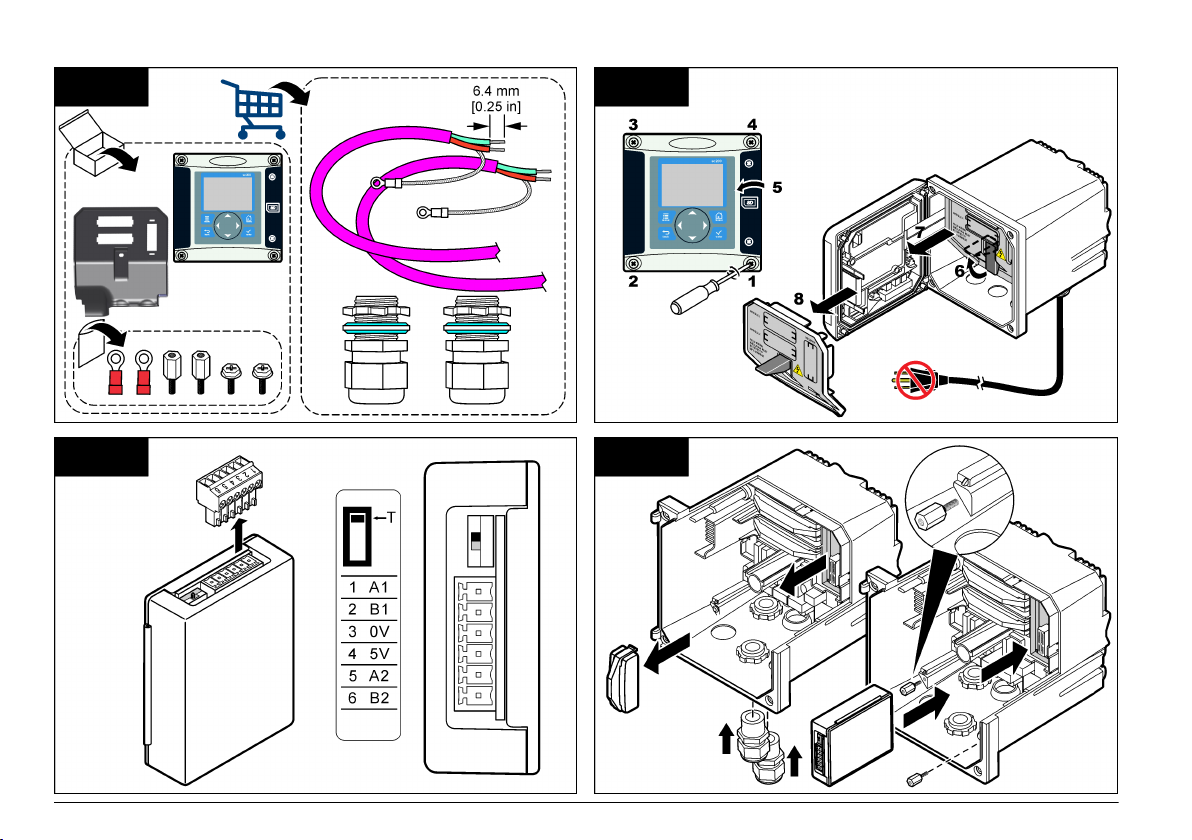
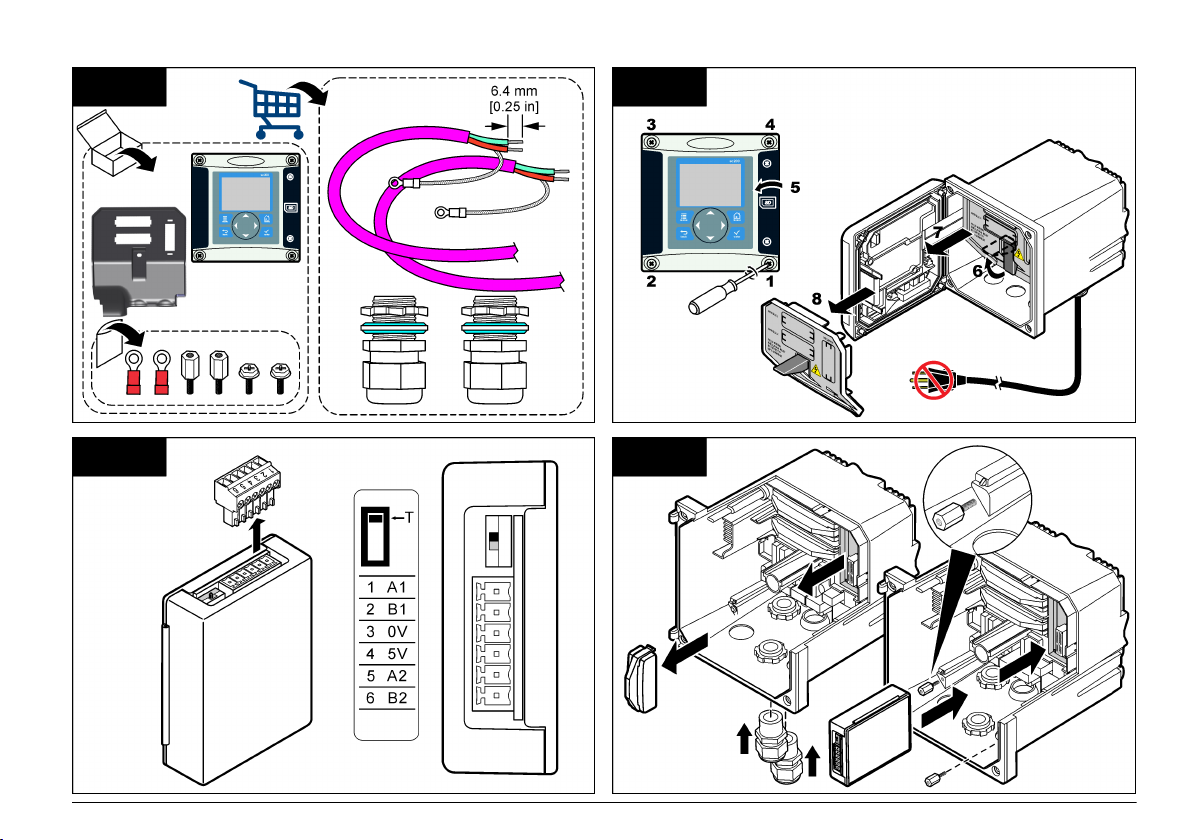
The Profibus network card supports RS485 communication. Terminal
block J1 provides the user connection to the Profibus network card. For
more wiring
details, refer to Installation Profibus and to the following steps
to install the Profibus network card.
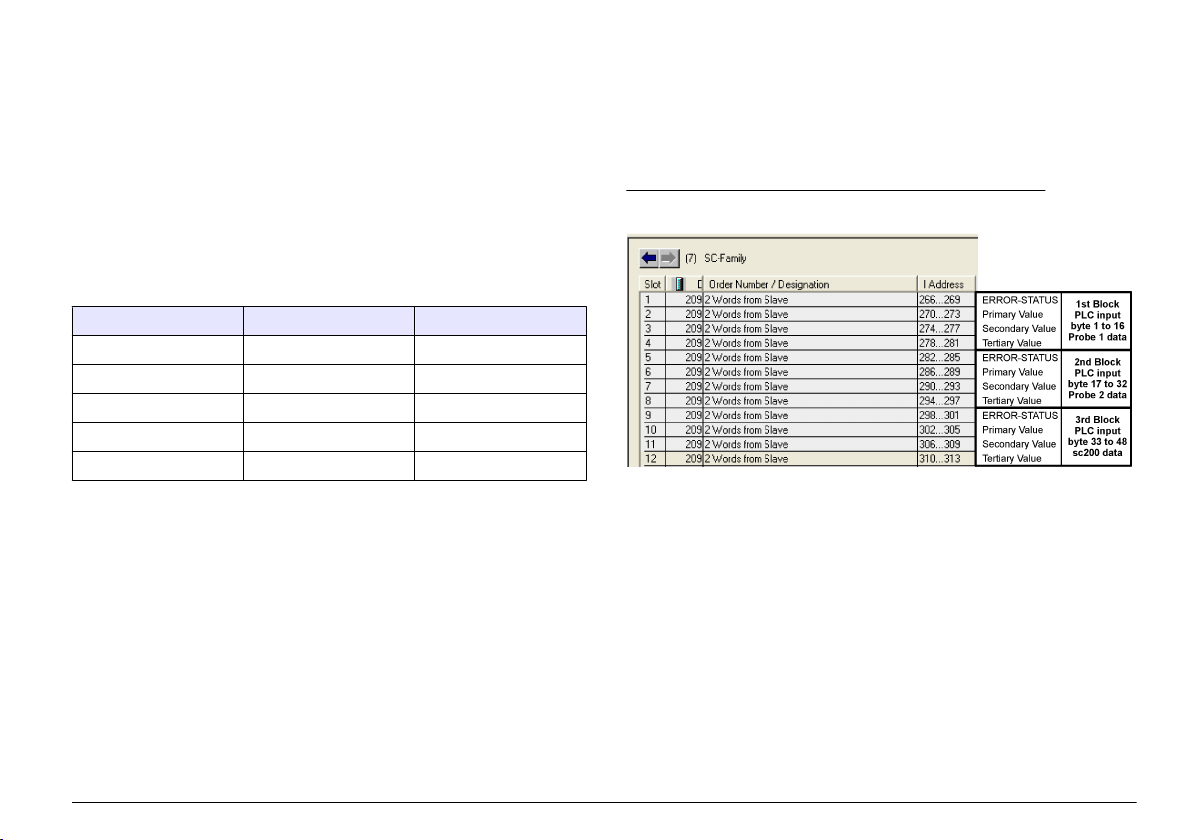
Table 1 Profibus wiring with RS485
Connector Connector
block pin
number
J1 1 A1 (Input) green Input from the
2 B1 (Input) red Input from the
3 OV — —
4 5V — —
5 A2 (Output) green Output from the
6 B2 (Output) red Output from the
Signal Cable
color
Description
network card
network card
network card
network card
English 5
Page 6
1 2
3 4
6 English
Page 7
5 6
7 8
English 7
Page 8
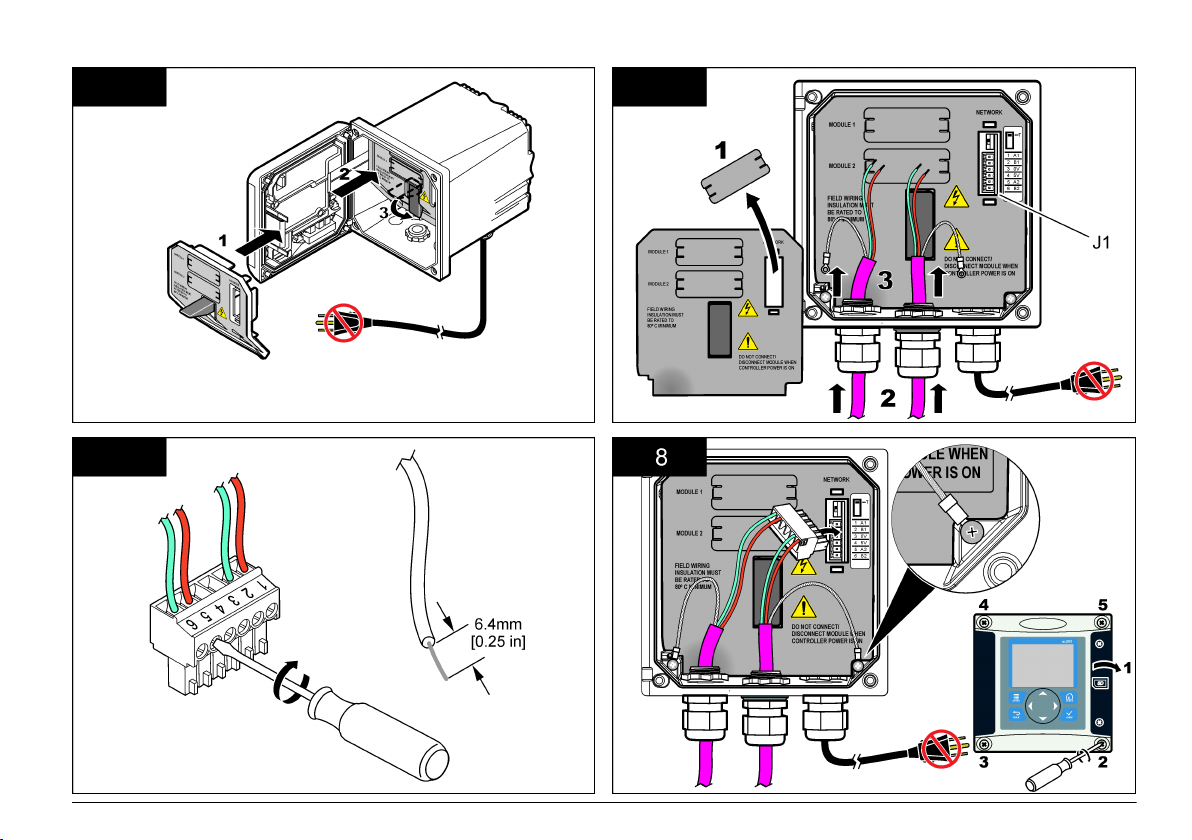
Configure the network
D A N G E R
Electrocution Hazard. Always remove power from the instrument before
making any electrical connections.
The Profibus network card provides an interface for RS485 connection.
Before use, the network card must be configured for the location in the
network. Use the switch settings on the top of the network card for
configuration (refer to the Installation section).
1. Termination switch–Termination Off. Set the switch to this position if
this is not the last slave on the bus.
2. Termination switch–Termination On ("T" position). Set the switch to
this position if this is the last or only slave device on the bus.
Operation
User navigation
Refer to the controller documentation for keypad description and
navigation information.
Setup the network
When the Profibus network card is installed, the controller requires the
correct configuration of the device and data order.
Note: Refer to
information and controller setup.
1. Select Network setup from the Settings menu.
the controller documentation for keypad description, basic navigation
2. Select, enter or change values and then push the ENTER key.
Option Description
Telegram Manages the Telegram data structure. Auto configuration:
ProfibusDPSelects one of the following options:
The Telegram is automatically configured with 16 data bytes
from each sensor and the controller. In the Auto configuration
the Telegram structure can be viewed and a new auto
configuration can be started. Manual configuration: The
Telegram is configured manually. The devices and the device
data tags included in the Telegram can be selected.
• View configuration— Views the current Telegram data
configuration
• Start Auto
which may need some sensor setup changes
• Add/Remove devices— Selects the devices included in the
Telegram
• Add/remove tags— Selects telegram data tags for each
device
• Setup telegram mode— Selects the auto configuration
(default) or the manual configuration mode.
Address— Changes the slave address
Data order— Sets the sequence of bytes when transmitting
floating point values. A floating point value consists of 4 bytes.
• Normal = IEEE Float Big Endian (Default setting)—The pairs
are not swapped. This mode fits to all known Profibus master
systems.
• Swapped = IEEE Float word wise swapped: Swaps the first
pair of bytes with the last pair.
config— Starts a new auto configuration process
8 English
Page 9

Option Description
Simulation Simulation— Simulates two floating point values and error/
Version Software version of the Profibus network card.
status to substitute a real instrument. Select the following
options and
setting:
• Simulation: Turns the simulation on or off.
• Period: Sets the time the first floating point value needs to
• Maximum: Sets the upper limit for the first floating point
• Minimum: Sets the lower limit for the first floating point value
• Error: The value entered in this menu will be set in the first
• Status: The value entered in this menu will be set in the
• Toggle: Changes the direction of the simulated ramp.
• Test/maint:
use the arrows to enter the values or use the default
Yes: Starts a simulation
No: Stops a simulation (Default setting)
run through the whole range between MINIMUM and
MAXIMUM—2 min (Default setting)
value.—20.0 (Default setting)
—10.0 (Default setting)
simulated tag—16 (Default setting)
second simulated tag—5 (Default setting)
Enabled: Sets the TEST/MAINT bit (0x0004) of every status
register of every configured slave in the cyclic Profibus
telegram to indicate the “Service” mode.
Disabled: Normal operation mode (Default setting)
Option Description
Location Edits the location name.
Status Status— Indicates the Profibus network card status
• Please wait: is shown until the network card has found all
configured slaves or is displayed when the card is new
configured and is searching for sensor connections
• PLC configure err: is shown when the network card has
received a wrong configuration of a PLC (Programmable
logic controller). Check the GSD file.
• Ready: is
to the Profibus. Check the address and/or the wiring.
• Online: is shown when the network card is in contact with
PLC and cyclic Data is sent
shown when the network card is ready to send data
Device order
The device
order in the Profibus telegram is fixed. The first and the second
installed sensors are always on position one and two and the controller is
on position three.
When no sensor is installed, the controller will stay in position three. The
position for the uninstalled sensors will be filled with 0xFF.
If two sensors are connected (maximum allowable) and scanned at the
same time, the installation order will be based on the location where the
sensor (or sensor module) is connected. The order is as follows:
• The top analog card connector.
• The bottom analog card connector.
• The left digital sensor connector.
• The right digital sensor connector.
Standard data structure (Auto configuration)
When the auto configuration (default) is selected, the Profibus network
card supplies a pre-defined data telegram for each connected device. The
telegram contains important data about the device.
The data block structure of the Profibus messages is standardized for all
types of probes. For the data block structure, refer to Profibus data
telegram register.
English 9
Page 10
When the manual configuration is selected, the telegram data structure
can be configured by the user (refer to Setup the network on page 8).
Table 2 Profibus data telegram structure
Byte number Data Data type
1–2 Classified error Integer (2 bytes)
3–4 Classified status Integer (2 bytes)
5–8 Measurement 1 Floating (4 bytes)
9–12 Measurement 2 Floating (4 bytes)
13–16 Measurement 3 Floating (4 bytes)
Display values
The Profibus data block structure (Profibus message data block
structure) can
replace sc probes without changes in the PLC configuration.
The primary value is always the measured value.
The secondary value, if not available, is filled with zero.
The tertiary value, if not available, is filled with zero.
Figure 2 Profibus message data block structure
Process data controller block
The data
block for the sc controller is similar to the data block for sensors.
The structure of the sc controller data block is independent of the number
of connected sensors:
• sc controller_ERROR
• sc controller_STATUS
• Primary value
• Secondary value
• Tertiary value
Block 3 sc controller ERROR and Block 3 sc controller STATUS show the
data definitions for error and status 1 in the sc controller.
Table 3 Block 3 sc controller ERROR
Bit Error Note
0 Sensor 1 communication
error
1 Sensor 2 communication
error
2–15 Not used
A communication error has occurred
between the sc controller and sensor 1, the
sensor could be disconnected.
A communication error has occurred
between the sc controller and sensor 2, the
sensor could be disconnected.
Table 4 Block 3 sc controller STATUS
Bit Status1 Note
0 Sensor 1 installed First sensor has been installed to the sc controller. This
1 Sensor 2 installed Second sensor has been installed to the sc controller.
2 Relay A on
3 Relay B on
bit is set even if the sensor is disconnected after
installation.
This bit is set even if the sensor is disconnected after
installation.
10 English
Page 11
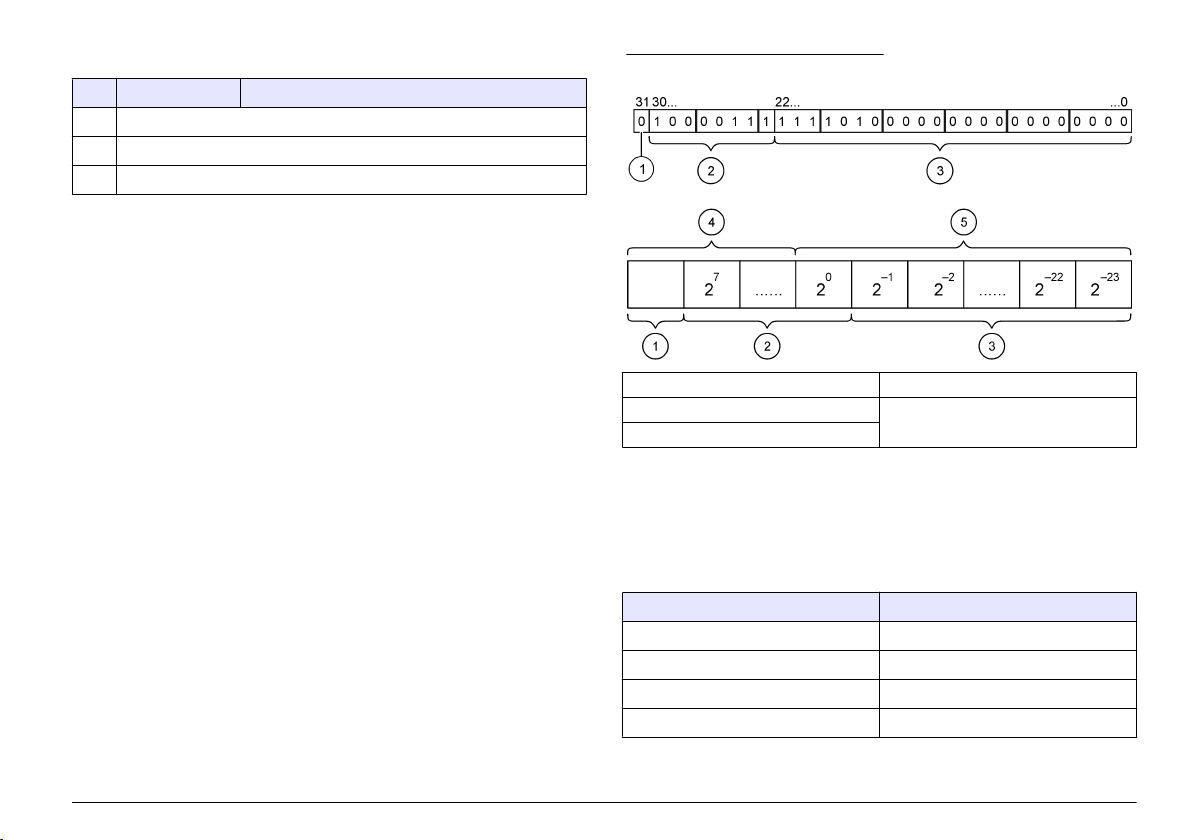
Table 4 Block 3 sc controller STATUS (continued)
Bit Status1 Note
4 Relay C on
5 Relay D on
6–15 Not used
sc controller values
The following list show the data definitions for the sc controller:
• The sc controller primary value shows the result of a calculation.
The sc controller secondary value shows the 0–20 mA or the 4–20 mA
•
output from Channel 1.
• The sc controller tertiary value shows the 0–20 mA or the 4–20 mA
output from Channel 2.
IEEE 745 floating point definition
Profibus uses 32-bit single precision IEEE floating point definition. The
definition has twenty three bits for the mantissa and eight bits for the
exponent. There is one bit for the sign of the mantissa. Refer to Floating
point definition.
Figure 3 Floating point definition
1 Sign bit 4 Exponent
2 Exponent 5 Mantissa
3 Mantissa
Word wise swapping
Byte order inside Profibus telegram shows swapped and normal byte
sequences. In word wise swapping, the third and fourth bytes are
interchanged in
order with the first and second bytes. This results in a byte
order of 3 4 1 2.
Table 5 Byte order inside Profibus telegram
sc controller swapped sc controller normal
Byte T1 value 0 x 91 Byte T1 value 0 x 3F
Byte T2 value 0 x B9 Byte T2 value 0 x 67
Byte T3 value 0 x 3F Byte T3 value 0 x 91
Byte T4 value 0 x 67 Byte T4 value 0 x B9
English 11
Page 12
Troubleshooting
W A R N I N G
Multiple hazards. Do not disassemble the instrument for maintenance or service.
If the
internal components must be cleaned or repaired, contact the manufacturer.
Error and status indicators
Error and
status words follow the same standard definition for all sc probes
and controllers.
Error messages lists bit position and error messages. Status indicator
messages lists bit position and status messages.
A bit value of zero shows the error or status condition that is not true.
A bit value of 1 shows the error or status condition that is true. For example,
if Bit 0 has the value of 1, an error has occurred during the last calibration.
Table 6 Error messages
Bit Message Indication
0 Measurement calibration
error
1 Electronic adjustment error An error has occurred during the last electronic
2 Cleaning error The last cleaning cycle failed
3 Measuring module error A failure has been detected in the Measurement
4 System re-initialization
error
5 Hardware error A general hardware error has been detected
6 Internal communication
error
7 Humidity error Excessive humidity has been detected within
8 Temperature error Temperature within the device exceeds a
An error has occurred during the last calibration
calibration
Module
Some settings are inconsistent and have been
reset to factory defaults
A communication failure within the device has
been detected
the device
specified limit
Table 6 Error messages (continued)
Bit Message Indication
9 — —
10 Sample warning Some action is required with the sample system
11 Questionable calibration
warning
12 Questionable
measurement warning
13 Safety warning A condition has been detected which may result
14 Reagent warning The reagent system requires attention
15 Maintenance required
warning
The last calibration may not be accurate
One or more of the device measurements are
out of range or are of questionable accuracy
in a safety hazard
The device requires maintenance
Table 7 Status indicator messages
Bit Message Indication
0 Calibration in progress The device is in a calibration mode.
1 Cleaning in progress The device is in a cleaning mode.
2 Service/Maintenance menu The device is in a service or maintenance
3 Common error The device has recognized an error. See Error
4 Measurement 0 Quality Bad Precision of measurement is out of specified
5 Measurement 0 Low Limit Measurement is below the specified range.
6 Measurement 0 High Limit Measurement is above the specified range.
7 Measurement 1 Quality Bad Precision of measurement is out of the
Measurements may not be valid.
Measurements may not be valid.
mode. Measurements may not be valid.
Register for Error Class.
limits.
specified limits.
12 English
Page 13
Table 7 Status indicator messages (continued)
Bit Message Indication
8 Measurement 1 Low Limit Measurement is below the specified range.
9 Measurement 1 High Limit Measurement is above the specified range.
10 Measurement 2 Quality Bad Precision of measurement is out of the
specified limits.
11 Measurement 2 Low Limit Measurement is below the specified range.
12 Measurement 2 High Limit Measurement is above the specified range.
13 Measurement 3 Quality Bad Precision of measurement is out of the
specified limits.
14 Measurement 3 Low Limit Measurement is below the specified range.
15 Measurement 3 High Limit Measurement is above the specified range.
Event Log
Refer to Event Log for diagnostic device information.
Table 8 Event log
Event Description
ADDRESS Adjusted Profibus address
DATA ORDER Indicates the data order of 2 word variables in the cyclic and
acyclic Profibus telegram
SIMULATION Indicates if the simulated data is set into the cyclic Profibus
telegram.
Table 8 Event log (continued)
Event Description
SENSOR POWER Turn-on instant of the Profibus card
SET DATE/TIME Point in time set-up of the internal timer of the Profibus card
NEW CONFIG Point in time of a new configuration
AUTO CONFIGURE Point in time of a new menu setting
CODE VERSION Point in time of a new software download (Software version)
Replacement parts and accessories
Communication network cards and accessories
Description Item number
Profibus DP kit 9173900
Profibus M12 connector kit 9178500
Profibus M12 socket Profibus 9178200
Profibus M12 T plug 9178400
Product and Article numbers may vary for some selling regions. Contact
the appropriate distributor or refer to the company website for contact
information.
English 13
Page 14
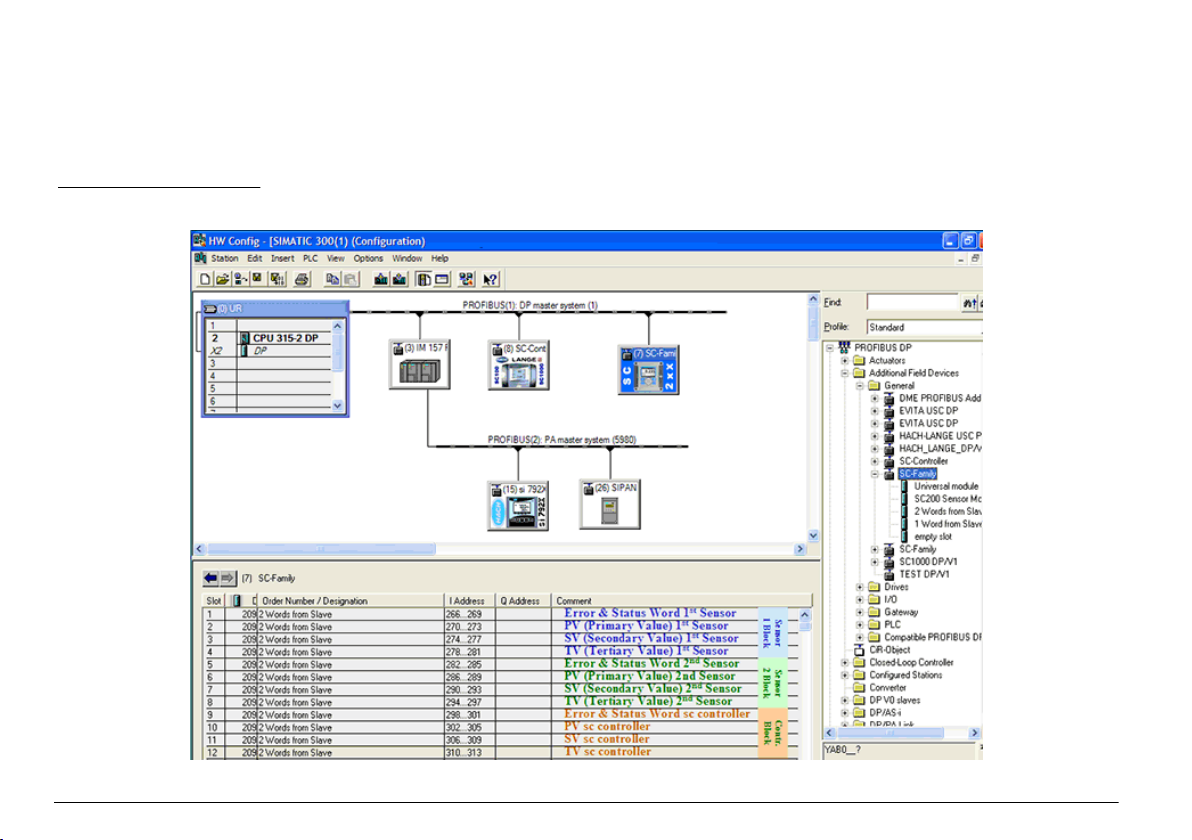
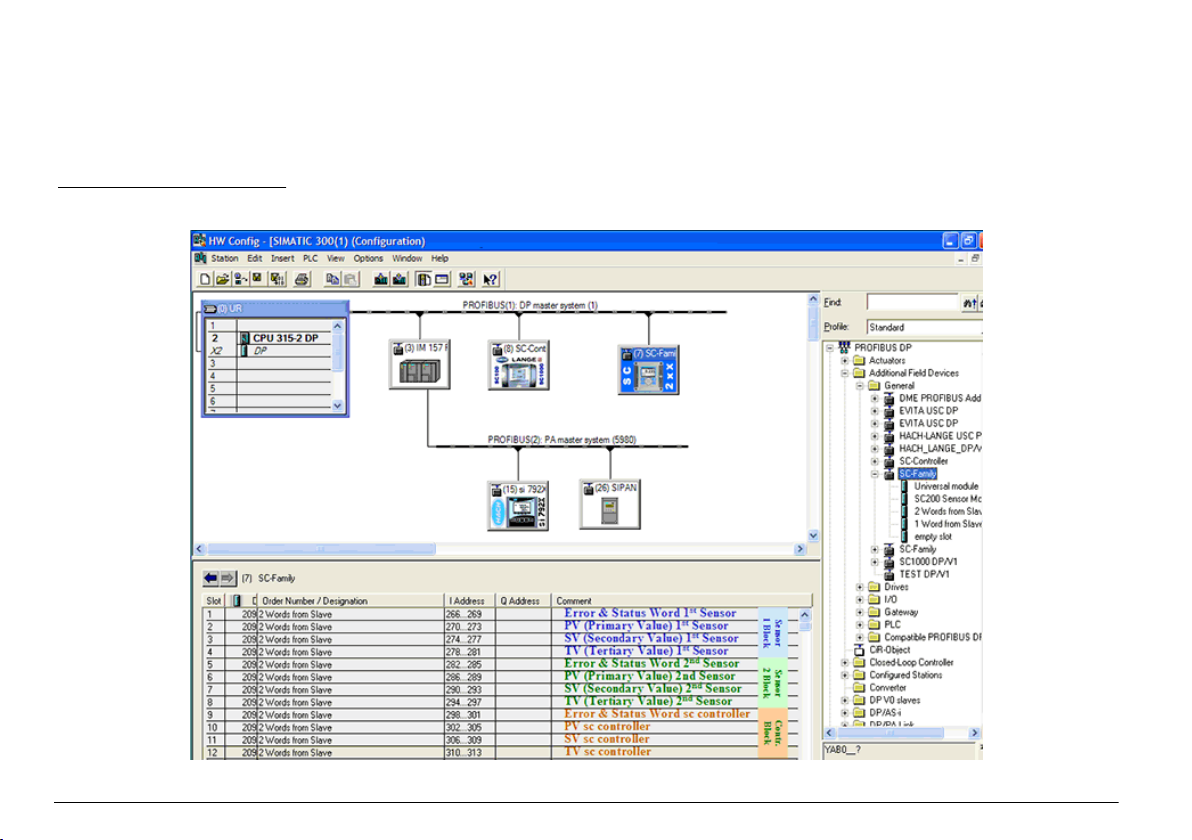
Example Simatic
When HALA09AC.GSD is imported, the slave will be located at PROFIBUS DP, ADDITIONAL FIELD DEVICES, GENERAL.
1. Select 2 Words from Slave network card.
Each module is 4 bytes of the input address range.
Figure 4 Example Simatic
14 English
Page 15

Read data
For usual data sequence, use L PED at the module starting address to
read a floating point object. There is no need for more conversions.
Note: PEW/PED is the SIMATIC or German code mnemonic. Use PIW/PID for IEC
or English.
1. Read ERROR or STATUS words.
2. Use the L PEW instruction.
English 15
Page 16
Technische Daten
Änderungen vorbehalten.
Technische Daten Details
Profibus-Protokoll Siemens ASIC SPC3
DP-Dienst DPV0-Slave
DP/DPV1-Dienste DPV1-Slave Klasse 1 und Klasse 2
I&M-Funktion
Adressänderung per Profibus-Master
Profibus-Baudraten 9,6 k, 19,2 k, 45,45 k, 93,75 k, 187,5 k, 500 k, 1,5
Anzeigen LED zur Anzeige des Datenaustauschmodus
Schnittstellentyp RS485
Konfigurierbare Parameter Datenfolge, Wortblocktausch für Gleitpunktwerte
Abmessungen (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Betriebstemperatur -20 °C bis 85 °C (-4 ° bis 185 °F)
Betriebsspannung 8 V– 16 V
Maximale
Leistungsaufnahme
Zertifizierung Klasse I, Abschnitt 2 Gruppen A, B, C, D und
M, 3 M, 6 M, 12 M
Automatische Baudratenerkennung
2 W
Klasse I, Zone 2 Gruppe IIC, T4 gefährliche und
normale Standorte
Allgemeine Informationen
Der Hersteller
oder Folgeschäden, die aus Fehlern oder Unterlassungen in diesem
Handbuch entstanden. Der Hersteller behält sich jederzeit und ohne
vorherige Ankündigung oder Verpflichtung das Recht auf Verbesserungen
ist nicht verantwortlich für direkte, indirekte, versehentliche
an diesem Handbuch und den hierin beschriebenen Produkten vor.
Überarbeitete Ausgaben sind auf der Hersteller-Webseite erhältlich.
Sicherheitshinweise
Bitte lesen Sie dieses Handbuch komplett durch, bevor Sie dieses Gerät
auspacken, aufstellen oder bedienen. Beachten Sie alle Gefahren- und
Warnhinweise. Nichtbeachtung kann zu schweren Verletzungen des
Bedieners oder Schäden am Gerät führen.
Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Sicherheitseinrichtung dieses Messgerätes
nicht beeinträchtigt wird. Verwenden bzw. installieren Sie das
Messsystem nur auf solche Art und Weise, wie sie in diesem Handbuch
beschrieben wird.
Verwendung der Gefahrenhinweise
G E F A H R
Kennzeichnet eine mögliche oder drohende Gefahrensituation, die, wenn sie nicht
vermieden wird, zum Tod oder zu schweren Verletzungen führen kann.
W A R N H I N W E I S
Kennzeichnet eine mögliche oder drohende Gefahrensituation, die, wenn sie nicht
vermieden wird, zum Tod oder zu schweren Verletzungen führen kann.
Kennzeichnet eine mögliche Gefahrensituation, die zu geringeren oder moderaten
Verletzungen führen kann.
Kennzeichnet eine Situation, die, wenn sie nicht vermieden wird, das Gerät
beschädigen kann. Informationen, die besonders beachtet werden müssen.
V O R S I C H T
H I N W E I S
Warnhinweise
Lesen Sie alle am Gerät angebrachten Aufkleber und Hinweise.
Nichtbeachtung
Verletzungen oder Beschädigungen des Geräts zur
kann
Folge haben. Auf ein am Gerät angebrachtes Symbol wird im Handbuch
durch einen Hinweis GEFAHR oder ACHTUNG verwiesen.
16 Deutsch
Page 17
Dieses Symbol kann am Gerät angebracht sein und verweist auf
Betriebs- und/oder Sicherheitshinweise in der Bedienungsanleitung.
Dieses Symbol weist auf die Gefahr eines elektrischen Schlages hin,
der tödlich sein kann.
Diese Symbol kennzeichnet das Vorhandensein von Geräten, die
empfindlich auf elektrostatische Entladung (ESD) reagieren und zeigt
an, dass Vorsicht erforderlich ist, um Schäden an diesem Gerät zu
vermeiden.
Elektrische Geräte, die mit diesem Symbol gekennzeichnet sind,
dürfen in Europa seit dem 12. August 2005 nicht mehr über das
öffentliche Entsorgungssystem entsorgt werden. Gemäß europäischer
lokal und national geltender Bestimmungen (EU-Richtlinie 2002/98/
EC) müssen europäische Verbraucher alte oder ausgediente Elektround Elektronikgeräte an die Hersteller zurückgeben, die diese für den
Verbraucher kostenlos entsorgen
Produktübersicht
Die sc Controller stellen die Plattform für alle intelligenten Sonden und
Analyzer dar. Bei der sc Plattform handelt es sich um ein vollständig
digitales Kommunikationssystem, welches auf dem offenen ModbusStandard basiert. Mit eingebauter Profibus-Schnittstellenkarte liefert der
sc Controller die gesamte Bandbreite der Standard-Verfahrenswerte und
-parameter.
Die sc Controller sind PNO/PTO zertifizierte Profibus DP/V1-Bausteine.
Diese Bausteine sind kompatibel mit den Master Class 1 (SPS SCADA)
und Master Class 2 Systemen, z.B. Engineering Tools (PDM).
Eine Übersicht
Profibus ist als werks- oder anwenderinstallierte Einheit erhältlich.
des Systems wird unten System overview dargestellt. Der
Abbildung 1 Systemübersicht
1 sc Controller (Slave) 3 PC mit Software (Master Klasse 2, z.
2 SPS (Master Klasse 1)
B. PC mit CP5611-Karte)
Installation
V O R S I C H T
Verletzungsgefahr. Nur qualifiziertes Personal sollte die in diesem Kapitel der
Bedienungsanleitung beschriebenen Aufgaben durchführen.
Einbau des Moduls im Controller
Explosionsgefahr. Sicherheitsanweisungen für die Installation des Moduls in als
gefährlich eingestuften Standorten finden Sie im Benutzerhandbuch für den
Controller.
Gefahr durch elektrischen Schlag. Trennen Sie das Gerät immer von
der Spannungsversorgung, bevor Sie elektrische Anschlüsse
herstellen.
G E F A H R
G E F A H R
Deutsch 17
Page 18
G E F A H R
Gefahr durch elektrischen Schlag. Die Hochspannungsleitungen für die Steuerung
verlaufen hinter der Hochspannungssperre im Steuerungsgehäuse. Die Sperre
muss eingebaut bleiben, außer bei der Installation von Modulen oder wenn ein
qualifizierter Installationstechniker die Stromversorgung, Relais oder Netzkarten
anschließt.
Möglicher Geräteschaden Empfindliche interne elektronische Bauteile
können durch
Gerät mit verminderter Leistung funktioniert oder schließlich ganz
ausfällt.
statische Elektrizität beschädigt werden, wobei dann das
H I N W E I S
Die Profibus-Netzwerkkarte unterstützt die RS485-Kommunikation. Die
Klemmenleiste J1 stellt einen Benutzeranschluss für die ProfibusNetzwerkkarte zur Verfügung. Details zur Verdrahtung entnehmen Sie
bitte Installation Profibus und den folgenden Schritten zur Installation der
Profibus-Netzwerkkarte.
Tabelle 1 Profibus-Verdrahtung mit RS485
Stecker Pinnummer des
Steckerblocks
J1 1 A1 (Eingang) grün Eingang von der
2 B1 (Eingang) rot Eingang von der
3 OV — —
4 5 V — —
5 A2 (Ausgang) grün Ausgang von der
6 B2 (Ausgang) rot Ausgang von der
Signal Kabelfarbe Beschreibung
Netzwerkkarte
Netzwerkkarte
Netzwerkkarte
Netzwerkkarte
18 Deutsch
Page 19
1 2
3 4
Deutsch 19
Page 20
5 6
7 8
20 Deutsch
Page 21
Konfigurieren des Netzwerks
G E F A H R
Gefahr durch elektrischen Schlag. Trennen Sie das Gerät immer von
der Spannungsversorgung, bevor Sie elektrische Anschlüsse
herstellen.
Die Profibus-Netzwerkkarte stellt einen Schnittstelle zum RS485-Bus
bereit. Bevor die Netzwerkkarte eingesetzt werden kann, muss sie
entsprechend ihrer Position im Netzwerk konfiguriert werden.
Konfigurieren Sie das Modul mit den Schaltern oben auf der
Netzwerkkarte (siehe Kapitel Installation).
1. Terminierungsschalter–Terminierung Aus. Stellen Sie den Schalter
auf diese Position, wenn dies nicht der letzte Slave auf dem Bus ist.
2. Terminierungsschalter–Terminierung Ein ("T"-Position). Stellen Sie
den Schalter auf diese Position, wenn dies der letzte oder einzige
Slave auf dem Bus ist.
Vorgang
Benutzernavigation
Eine Beschreibung der Tastatur und Informationen zur Navigation
entnehmen Sie bitte der Controller-Dokumentation.
Netzwerkeinrichtung
Nachdem die Profibus Netzwerkkarte installiert wurde, fordert der
Controller die korrekte Gerätekonfiguration und Datenreihenfolge.
Hinweis: Eine Beschreibung der Tastatur und Informationen zur allgemeinen
Navigation sowie
Dokumentation.
1. Wählen Sie NETZWERK-SETUP aus dem Menü „Einstellungen“.
zur Einrichtung des Controllers entnehmen Sie bitte der Controller-
2. Wählen Sie
die Werte, ändern Sie diese oder geben Sie diese ein und
drücken Sie dann ENTER.
Optionen Beschreibung
Telegramm Verwaltet die Telegramm-Datenstruktur Automatische
Profibus DP Wählt eine der folgenden Optionen:
Konfiguration: Das Telegramm wird automatisch mit 16
Datenbytes von
Bei automatischer Konfiguration können die Telegrammstruktur
angezeigt und eine neue automatische Konfiguration gestartet
werden. Manuelle Konfiguration: Das Telegramm wird
manuell konfiguriert. Die Geräte und die Gerätedatenregister,
die im Telegramm enthalten sind, können ausgewählt werden.
• View configuration— (Konfiguration anzeigen) Zeigt die
aktuelle Konfiguration der Telegrammdaten an
• Start Auto config— (Automatische Konfiguration starten)
Startet einen neuen automatischen Konfigurationsprozess,
dessen Sensoreinrichtungen möglicherweise geändert
werden müssen
• Add/Remove devices— (Geräte hinzufügen/entfernen)
Wählt die im Telegramm enthaltenen Geräte aus
• Add/remove tags— (Register hinzufügen/entfernen) Wählt
die Telegrammdatenregister für jedes Gerät aus
• Setup telegram mode— (Telegrammmodus einrichten)
Wählt die automatische Konfiguration (Standard) oder die
manuelle Konfiguration aus.
Adresse— Ändert die Salve-Adresse
Datenfolge— Legt die Reihenfolge der Bytes für die
Übertragung der Gleitpunktwerte fest. Ein Gleitpunktwert
besteht aus 4 Byte.
• Normal = IEEE Float Big Endian (Standardeinstellung)— Die
Bytepaare sind nicht getauscht. Dieser Modus ist für alle
bekannten Profibus-Mastersysteme passend.
• Getauscht = IEEE Float Wortblocktausch: Erstes und letztes
Bytepaar sind getauscht.
jedem Sensor und dem Controller konfiguriert.
Deutsch 21
Page 22

Optionen Beschreibung
Simulation Simulation— Simuliert zwei Gleitpunktwerte und Fehler/
Status zum Ersatz eines echten Instruments. Wählen Sie die
folgenden Optionen und geben Sie die Werte ein oder
verwenden Sie die Standardeinstellung:
• Simulation: Schaltet die Simulation ein oder aus.
Ja: Startet eine Simulation
Nein: Stoppt eine Simulation (Standardeinstellung)
• Dauer:Bestimmt die Zeit, die der erste Gleitpunktwert
benötigt, um durch den gesamten Bereich zwischen
MINIMUM und MAXIMUM zu laufen— 2 min
(Standardeinstellung).
• Maximum: Legt die Obergrenze für den ersten
Gleitpunktwert fest.— 20,0 (Standardeinstellung)
• Minimum: Legt die Untergrenze für den ersten
Gleitpunktwert fest— 10,0 (Standardeinstellung)
• Fehler: Der in dieses Menü eingegebene Wert wird in das
erste simulierte Register gesetzt)— 16
(Standardeinstellung)
• Status: Der in dieses Menü eingegebene Wert wird in das
zweite simulierte Register gesetzt)— 5
(Standardeinstellung)
• Toggle: Ändert die Richtung der simulierten Rampe.
• Service:
Aktiviert: Setzt das SERVICE-Bit (0x0004) jedes
Statusregisters jedes konfigurierten Slaves im zyklischen
Profibus-Telegramm, um den „Service“-Modus anzuzeigen.
Deaktiviert: Normaler Betrieb (Standardeinstellung)
Version Software-Version der Profibus-Netzwerkkarte.
Optionen Beschreibung
Standort Ändert den Namen des Messorts.
Status Status— Gibt den Status der Profibus-Netzwerkkarte an
• Bitte warten: wird angezeigt, bis die Netzwerkkarte alle
konfigurierten Slaves
konfiguriert wurde und nach angeschlossenen Sensoren
sucht.
• SPS Konfig.-Fehler wird angezeigt, wenn die
Netzwerkkarte eine falsche Konfiguration von der SPS
(Speicherprogrammierbare Steuerung) empfangen hat.
Überprüfen Sie die GSD-Datei.
• Bereit: wird angezeigt, wenn die Netzwerkkarte bereit ist,
Daten an den Profibus zu senden. Überprüfen Sie die
Adresse und/oder die Verdrahtung.
• Online: wird angezeigt, wenn die Netzwerkkarte mit der SPS
verbunden ist und zyklische Nachrichten ausgetauscht
werden.
gefunden hat oder wenn die Karte neu
Gerätereihenfolge
Die Reihenfolge der Geräte im Profibus-Telegramm ist fest vorgegeben.
Die ersten und zweiten installierten Sensoren befinden sich immer an
Position eins und zwei, der Controller immer an Position drei.
Auch wenn kein Sensor installiert ist, bleibt der Sensor an Position drei.
Die freien Sensorposition werden mit 0xFF gefüllt.
Wenn im
Vollausbau zwei Sensoren angeschlossen sind und gleichzeitig
gemessen werden, hängt die Reihenfolge der Sensoren von der
physischen Position ab, an der der Sensor (oder das Sensormodul)
angeschlossen ist. Die Reihenfolge ist:
• Der obere Analogkartenanschluss.
• Der untere Analogkartenanschluss.
• Der linke Digitalsensoranschluss.
• Der rechte Digitalsensoranschluss.
22 Deutsch
Page 23
Standard-Datenstruktur (Automatische Konfiguration)
Wenn „Automatische Konfiguration" (Standard) ausgewählt wurde, stellt
die Profibus-Netzwerkkarte für jedes angeschlossene Gerät ein
vordefiniertes Datentelegramm bereit. Das Telegramm enthält wichtige
Daten über das Gerät.
Die Datenblockstruktur
der Profibus-Nachrichten ist für alle Sondentypen
standardisiert. Die Datenblockstruktur ist in Profibus data telegram
register gezeigt.
Wenn „Manuelle Konfiguration“ ausgewählt wird, kann die
Telegrammdatenstruktur vom Benutzer konfiguriert werden (siehe
Netzwerkeinrichtung auf Seite 21).
Tabelle 2 Struktur des Profibus-Datentelegramms
Byte-Nummer Daten Datentyp
1–2 Klassifizierter Fehler Integer (2 Byte)
3– 4 Klassifizierter Status Integer (2 Byte)
5–8 Messung 1 Gleitend (4 Byte)
9– 12 Messung 2 Gleitend (4 Byte)
13– 16 Messung 3 Gleitend (4 Byte)
Anzeigenwerte
Die Profibus-Datenblockstruktur (Profibus message data block structure)
kann sc Sonden ohne Änderungen der PLC-Konfiguration austauschen.
Der Erstwert ist immer der Messwert.
Der Zweitwert wird, wenn dieser nicht verfügbar ist, mit Null angegeben.
Der Drittwert wird, wenn dieser nicht verfügbar ist, mit Null angegeben.
Abbildung 2 Profibus Nachrichten-Datenblockstruktur
Prozessdatenblock des Controllers
Der Datenblock für den sc Controller ähnelt dem Datenblock für die
Sensoren. Die Struktur des Controller-Prozessdatenblocks ist von der
Anzahl der angeschlossenen Sensoren unabhängig:
•
sc Controller_FEHLER
sc Controller_STATUS
•
• Erstwert
• Zweitwert
• Drittwert
Block 3 sc controller ERROR und Block 3 sc controller STATUS zeigen
die Datendefinition für Fehler und Status 1 im sc Controller.
Deutsch 23
Page 24
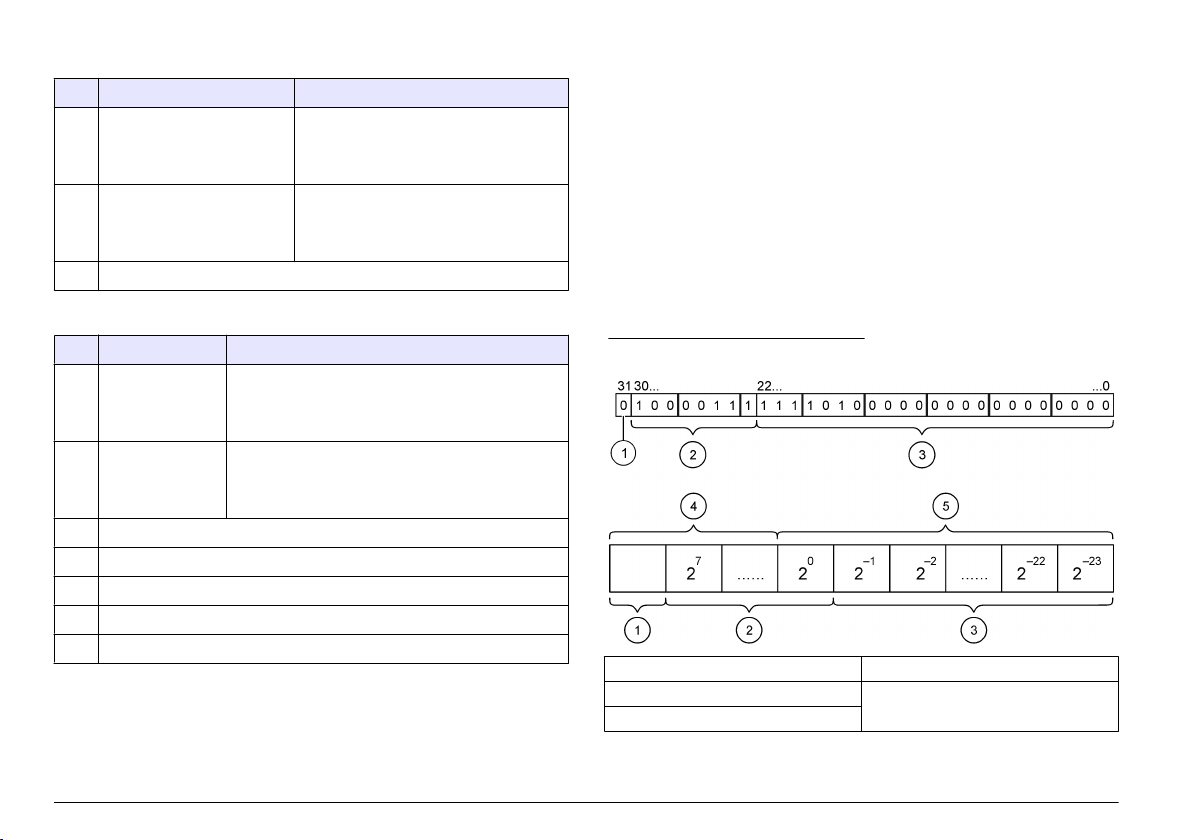
Tabelle 3 Block 3 sc Controller-FEHLER
Bit Fehler Hinweis
0 Sensor 1
Kommunikationsfehler
1 Sensor 2
Kommunikationsfehler
2–15 Nicht belegt
Zwischen dem sc Controller und dem
Sensor 1 ist ein Kommunikationsfehler
aufgetreten, der Sensor ist eventuell nicht
mehr angeschlossen.
Zwischen dem sc Controller und dem
Sensor 2 ist ein Kommunikationsfehler
aufgetreten, der Sensor ist eventuell nicht
mehr angeschlossen.
Tabelle 4 Block 3 sc Controller-STATUS
Bit Status1 Hinweis
0 Sensor 1 installiert Der erste Sensor wurde am sc Controller
1 Sensor 2 installiert Der zweite Sensor wurde am sc Controller
2 Relais A ein
3 Relais B ein
4 Relais C ein
5 Relais D ein
6–15 Nicht belegt
angeschlossen. Dieses
Sensor nach der Installation vom Controller getrennt
wurde.
angeschlossen. Dieses Bit ist gesetzt, selbst wenn der
Sensor nach der Installation vom Controller getrennt
wurde.
Bit ist gesetzt, selbst wenn der
sc Controller-Werte
Die folgende Liste gibt eine Aufstellung der Datendefinitionen für den sc
Controller:
• Der sc Controller-Erstwert gibt das Ergebnis einer Berechnung an.
Der sc Controller-Zweitwert gibt das 0– 20 mA- der das 4– 20 mA
•
Ausgangssignal von Kanal 1 an.
• Der sc Controller-Drittwert gibt das 0– 20 mA- der das 4– 20 mA
Ausgangssignal von Kanal 2 an.
IEEE 745-Gleitpunktdefinition
Profibus verwendet 32-Bit-Gleitpunktwerte mit einfacher Genauigkeit
nach IEEE-Definition. Die Definition sieht dreiundzwanzig Bit für die
Mantisse und acht Bit für den Exponenten vor. Das Vorzeichen der
Mantisse verwendet ein Bit. Siehe Floating point definition.
Abbildung 3 Gleitpunktdefinition
1 Vorzeichenbit 4 Exponent
2 Exponent 5 Mantisse
3 Mantisse
24 Deutsch
Page 25
Wortblocktausch
Byte order inside Profibus telegram zeigt getauschte und normale Byte-
Reihenfolgen. Bei einem Wortblocktausch werden das dritte und vierte
der Reihenfolge mit dem ersten und zweiten Byte getauscht. Dies
Byte in
führt zu einer Byte-Reihenfolge von 3 4 1 2.
Tabelle 5 Byte-Reihenfolge im Profibus-Telegramm
sc Controller getauscht sc Controller normal
Byte T1 Wert 0 x 91 Byte T1 Wert 0 x 3F
Byte T2 Wert 0 x B9 Byte T2 Wert 0 x 67
Byte T3 Wert 0 x 3F Byte T3 Wert 0 x 91
Byte T4 Wert 0 x 67 Byte T4 Wert 0 x B9
Fehlersuche und -behebung
W A R N H I N W E I S
Mehrere Gefahren. Nehmen Sie das Gerät nicht zur Wartung auseinander. Falls
eine Reinigung oder Instandsetzung von externen Bauteilen erforderlich ist,
wenden Sie sich an den Hersteller.
Fehler- und Statusanzeigen
Die Fehler- und Statuswörter unterliegen den gleichen
Standarddefinitionen für alle sc Sonden und Controller.
Error messages
Status indicator messages listet die Bit-Positionen und deren
Statusnachrichten auf.
Ein Bit-Wert von Null zeigt an, dass der Fehler- oder Statuszustand nicht
Wahr ist.
Ein Bit-Wert von 1 zeigt an, dass der Fehler- oder Statuszustand Wahr ist.
Wenn zum Beispiel Bit 0 den Wert 1 hat, ist bei der letzten Kalibrierung ist
ein Fehler aufgetreten.
listet die Bit-Positionen und deren Fehlernachrichten auf.
Tabelle 6 Fehlermeldungen
Bit Meldung Erklärung
0 Kalibrierungsfehler Messung Bei der letzten Kalibrierung ist ein Fehler
1 Elektronischer
Justierungsfehler
2 Reinigungsfehler Der letzte Reinigungszyklus ist
3 Messmodulfehler Im Messmodul wurde ein Fehler entdeckt
4 Systemfehler bei Neustart Einige Einstellungen waren nicht
5 Hardware-Fehler Ein allgemeiner Hardware-Fehler wurde
6 Interner
Kommunikationsfehler
7 Feuchtigkeitsfehler Im Gerät wurde übermäßige Feuchtigkeit
8 Temperaturfehler Die Temperaturen im Gerät überschreiten die
9 — —
10 Probenwarnung Bitte überprüfen Sie das Probensystem
11 Warnung: zweifelhafte
Kalibrierung
12 Warnung: zweifelhafte
Messung
13 Sicherheitswarnung Es wurde ein Zustand entdeckt, der zu einer
aufgetreten
Bei der letzten elektronischen Kalibrierung ist
ein Fehler aufgetreten
fehlgeschlagen
durchgängig und wurden auf die
Standardwerte zurückgesetzt
entdeckt
Innerhalb des Geräts wurde ein
Kommunikationsfehler entdeckt
entdeckt
festgelegten Grenzwerte
Die letzte Kalibrierung war möglicherweise
ungenau
Eine oder mehrere Messung(en) des Geräts
lagen außerhalb des Toleranzbereichs oder
waren möglicherweise nicht genau
Gefahrensituation führen kann
Deutsch 25
Page 26
Tabelle 6 Fehlermeldungen (fortgesetzt)
Bit Meldung Erklärung
14 Reagenswarnung Bitte überprüfen Sie das Reagenssystem
15 Warnung: Instandhaltung
erforderlich
Das Gerät benötigt eine Instandhaltung.
Tabelle 7 Nachrichten Statusanzeige
Bit Meldung Erklärung
0 Kalibrierungsablauf Das Gerät wurde in den
1 Reinigungsablauf Das Gerät wurde in den Reinigungsmodus
2 Service- /
Instandhaltungsmenü
3 Allgemeiner Fehler Das Gerät hat einen Fehler erkannt. Siehe
4 Messung 0 Qualität schlecht Die Genauigkeit der Messung liegt
5 Messung 0 Untergrenze Messung liegt unterhalb des
6 Messung 0 Obergrenze Messung liegt oberhalb des
7 Messung 1 Qualität schlecht Die Genauigkeit der Messung liegt
8 Messung 1 Untergrenze Messung liegt unterhalb des
9 Messung 1 Obergrenze Messung liegt oberhalb des
Kalibrierungsmodus versetzt. Die
Messungen sind möglicherweise ungültig.
versetzt. Die Messungen sind
möglicherweise ungültig.
Das Gerät ist im Service- oder
Instandhaltungsmodus. Die Messungen
sind möglicherweise ungültig.
Fehlerliste für Fehlerklasse.
außerhalb des Toleranzbereichs.
Toleranzbereichs.
Toleranzbereichs.
außerhalb des Toleranzbereichs.
Toleranzbereichs.
Toleranzbereichs.
Tabelle 7 Nachrichten Statusanzeige (fortgesetzt)
Bit Meldung Erklärung
10 Messung 2 Qualität schlecht Die Genauigkeit der Messung liegt
außerhalb des Toleranzbereichs.
11 Messung 2 Untergrenze Messung liegt unterhalb des
Toleranzbereichs.
12 Messung 2 Obergrenze Messung liegt oberhalb des
Toleranzbereichs.
13 Messung 3 Qualität schlecht Die Genauigkeit der Messung liegt
außerhalb des Toleranzbereichs.
14 Messung 3 Untergrenze Messung liegt unterhalb des
Toleranzbereichs.
15 Messung 3 Obergrenze Die Messung liegt über dem
Toleranzbereich.
Event Log
Für Gerätediagnose-Informationen siehe Event Log.
Tabelle 8 Ereignisprotokoll
Ereignis Beschreibung
ADRESSE Die eingestellte Profibus-Adresse
DATENREIHENFOLGE Gibt die Datenfolge der 2 Words langen Variablen in
zyklischen und azyklischen Profibus-Telegrammen an.
SIMULATION Gibt an, ob das zyklische Profibus-Telegramm
simulierte Daten enthält.
SENSOR STROM Zeitpunkt, zu dem die Profibus-Karte eingeschaltet
wurde.
DATUM/ZEIT Zeitpunkt, zu dem der interne Timer der Profibus-Karte
eingestellt wurde.
NEUE KONFIG Zeitpunkt einer neuen Konfiguration
26 Deutsch
Page 27
Tabelle 8 Ereignisprotokoll (fortgesetzt)
Ereignis Beschreibung
AUTO KONFIG. Zeitpunkt einer neuen Menüeinstellung
SOFTWARE-VERS Zeitpunkt eines neuen Software-Downloads (Software-
Version)
Ersatzteile und Zubehör
Netzwerkkarten und Zubehör
Beschreibung Artikelnummer
Profibus DP-Satz 9173900
Profibus M12-Steckersatz 9178500
Beschreibung Artikelnummer
Profibus M12-Buchse Profibus 9178200
Profibus M12-T-Stecker 9178400
Produkt- und Artikelnummern können für einige Verkaufsgebiete
abweichen. Wenden
Sie sich an den zuständigen Händler oder schlagen
Sie die Kontaktinformationen auf der Webseite des Unternehmens nach.
Deutsch 27
Page 28
Beispiel Simatic
Nach dem Import von HALA09AC.GSD steht der Slave unter PROFIBUS DP, WEITERE FELDGERÄTE, ALLGEMEIN.
1. Wählen Sie die Netzwerkkarte 2 Words from Slave.
Jedes Modul umfasst 4 Byte des Eingangsadressbereiches.
Abbildung 4 Beispiel Simatic
28 Deutsch
Page 29

Daten lesen
Für die übliche Datenreihenfolge verwenden Sie L PED an der ModulStartadresse zum Lesen des Gleitpunktobjekts. Weitere Umwandlungen
sind nicht notwendig.
Hinweis: PEW/PED ist der SIMATIC oder deutsche Code-Mnemonik. Verwenden
Sie PIW/PID für IEC oder Englisch.
1. Lesen Sie die ERROR- oder STATUS-Wörter
2. Befolgen Sie die L PEW Anleitung.
Deutsch 29
Page 30
Dati tecnici
I dati tecnici sono soggetti a modifica senza preavviso.
Dato tecnico Dettagli
Protocollo Profibus Siemens ASIC SPC3
Servizio DP Slave DPV0
Servizi DP/DPV1 Slave DPV1 classe 1 e classe 2
Funzione I&M
Indirizzo diverso in base al master Profibus
Baud rate Profibus 9.6k, 19.2k, 45.45k, 93.75k, 187.5k, 500k, 1.5M,
Indicatori LED per visualizzazione delle modalità di scambio
Tipo di interfaccia RS485
Parametri configurabili Scambio dati, basato su parole per valori in virgola
Dimensioni (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Temperatura di
funzionamento
Tensione operativa 8V–16V
Consumo di potenza
massimo
Certificazione Classe I, Divisione 2 Gruppi A, B, C, D e Classe I,
3M, 6M, 12M
Rilevamento automatico baud rate
dati
mobile
da –20 a 85 °C (da –4 a 185 °F)
2 W
Zona 2
Gruppo IIC, T4 Aree pericolose e ordinarie
Informazioni generali
In nessun
danni diretti, indiretti, particolari, causali o consequenziali per qualsiasi
caso, il produttore potrà essere ritenuto responsabile in caso di
difetto o omissione relativa al presente manuale. Il produttore si riserva il
diritto di apportare eventuali modifiche al presente manuale e ai prodotti
ivi descritti in qualsiasi momento senza alcuna notifica o obbligo. Le
edizioni riviste sono presenti nel sito Web del produttore.
Informazioni sulla sicurezza
Prima di disimballare, installare o utilizzare l’apparecchio, si prega di
leggere l’intero manuale. Si raccomanda di leggere con attenzione e
rispettare le istruzioni riguardanti possibili pericoli o note cautelative. La
non osservanza di tali indicazioni potrebbe comportare lesioni gravi
dell'operatore o danni all'apparecchio.
Assicurarsi che la protezione fornita da questa apparecchiatura non sia
danneggia. Non utilizzare o installare questa apparecchiatura in modo
diverso da quanto specificato nel presente manuale.
Utilizzo dei segnali di avvertimento
P E R I C O L O
Indica una situazione di pericolo potenziale o imminente che, se non evitata,
potrebbe causare lesioni gravi o la morte.
A V V E R T E N Z A
Indica una situazione di pericolo potenziale o imminente che, se non evitata,
potrebbe comportare lesioni gravi, anche mortali.
A T T E N Z I O N E
Indica una situazione di pericolo potenziale che potrebbe comportare lesioni lievi
o moderate.
Indica una situazione che, se non evitata, può danneggiare lo strumento.
Informazioni che richiedono particolare attenzione da parte dell'utente.
A V V I S O
Etichette di avvertimento
Leggere tutte le etichette presenti sullo strumento. La mancata
osservanza delle stesse può causare lesioni personali o danni allo
strumento. A ogni simbolo riportato sullo strumento corrisponde
un'indicazione di pericolo o di avvertenza nel manuale.
30 Italiano
Page 31

Tale simbolo, se apposto sullo strumento, intende fare riferimento al
manuale delle istruzioni d’uso per informazioni riguardanti l’esercizio
e/o la sicurezza.
Questo simbolo indica il rischio di potenziali scosse e/o scariche
elettriche.
Questo simbolo indica la presenza di apparecchi particolarmente
sensibili alle cariche elettrostatiche (ESD) e segnala la necessità di
applicare le necessarie misure per prevenire danni all’apparecchiatura.
Gli apparecchi elettrici contrassegnati da questo simbolo potrebbero
non essere smaltiti nei sistemi di smaltimento pubblici europei dopo il
12 agosto
(a norma della direttiva UE 2002/98/CE), gli utenti dovranno restituire
le apparecchiature vecchie o non più utilizzabili al produttore, il quale
è tenuto a provvedere allo smaltimento gratuito.
2005. In conformità ai regolamenti europei locali e nazionali
Figura 1 Panoramica del prodotto
1 controller sc (Slave) 3 PC con software (master classe 2,
2 Programmable logic
master classe 1)
controller (PLC,
ad es. il PC comprende la scheda
CP5611)
Descrizione del prodotto
I controller sc sono la piattaforma per tutte le sonde e gli analizzatori
intelligenti. La piattaforma sc è un sistema di comunicazione
completamente digitale basato internamente sullo standard Modbus
aperto. Quando una scheda di interfaccia Profibus è installata, i controller
sc offrono l'intera gamma di valori e parametri di metodi standardizzati.
I controller sc sono dispositivi Profibus DP/V1 certificati PNO/PTO. Questi
dispositivi sono compatibili con sistemi di classe 1 master (PLC SCADA)
e di classe 2 master, ad es., stazioni ingegneristiche.
La System overview fornisce una panoramica del sistema. Profibus è
disponibile come elemento installato in fabbrica o dall'utente.
Installazione
A T T E N Z I O N E
Pericolo di lesioni personali. Le operazioni riportate in questa sezione del manuale
devono essere eseguite esclusivamente da personale qualificato.
Installare il modulo sul controller
Pericolo di esplosione. Per l'installazione del modulo in aree classificate come
pericolose, fare riferimento alle istruzioni sulla sicurezza riportate nel manuale
dell'utente del controller.
Rischio di scossa elettrica. Scollegare sempre l'alimentazione dallo
strumento prima di eseguire collegamenti elettrici.
P E R I C O L O
P E R I C O L O
Italiano 31
Page 32

P E R I C O L O
Rischio di scossa elettrica. Il cablaggio ad alta tensione per il controller viene
trasmesso attraverso la protezione per l'alta tensione nell'alloggiamento del
controller. La barriera deve rimanere in posizione tranne quando si installano i
moduli oppure
l'alimentazione, i relè o le schede di rete e analogiche.
quando un addetto all'installazione qualificato esegue i cablaggi per
Danno potenziale allo strumento. Componenti elettronici interni delicati
possono essere danneggiati dall'elettricità statica, compromettendo le
prestazioni o provocando guasti.
A V V I S O
La scheda di rete Profibus supporta la comunicazione RS485. Il blocco
terminale J1 offre all'utente la connessione alla scheda di rete Profibus.
Per ulteriori informazioni sulle connessioni, fare riferimento a Installation
Profibus e ai seguenti passaggi per installare la scheda di rete Profibus.
Tabella 1 Cablaggio Profibus con RS485
Connettore Numero pin
blocco
connettore
J1 1 A1 (ingresso) verde Ingresso dalla
2 B1 (ingresso) rosso Ingresso dalla
3 OV — —
4 5 V — —
5 A2 (uscita) verde Uscita dalla scheda
6 B2 (uscita) rosso Uscita dalla scheda
Segnale Colore
cavo
Descrizione
scheda di rete
scheda di rete
di rete
di rete
32 Italiano
Page 33

1 2
3 4
Italiano 33
Page 34

5 6
7 8
34 Italiano
Page 35

Configurare la rete
P E R I C O L O
Rischio di scossa elettrica. Scollegare sempre l'alimentazione dallo
strumento prima di eseguire collegamenti elettrici.
La scheda di rete Profibus presenta un'interfaccia per la connessione
RS485. Prima dell'uso, è necessario configurare la scheda di rete per la
posizione nella rete. Per la configurazione, utilizzare le impostazioni
dell'interruttore sulla
parte superiore della scheda di rete (fare riferimento
alla sezione Installazione).
1. Interruttore di terminazione - Terminazione Off. Impostare l'interruttore
in questa posizione se non è l'ultimo slave sul bus.
2. Interruttore di terminazione - Terminazione On (posizione "a T").
Impostare l'interruttore in questa posizione se è l'ultimo o l'unico
dispositivo slave sul bus.
Funzionamento
Navigazione dell'utente
Per la descrizione del tastierino e le informazioni sulla navigazione., fare
riferimento alla documentazione del controller.
Configurare la rete
Quando la scheda di rete Profibus è installata, il controller necessita della
configurazione del dispositivo e dell'ordine dei dati corretto.
Nota: Fare riferimento alla documentazione sul controller per la descrizione del
tastierino, le informazioni di base sulla navigazione e la configurazione del controller.
1. Selezionare Configurazione rete dal menu Impostazioni.
2. Selezionare, inserire o modificare i valori e quindi premere il tasto
INVIO.
Opzione Descrizione
Telegram
(Telegramma)
Gestisce la struttura dei dati del telegramma. Auto
configuration (Configurazione automatica): il telegramma
viene configurato automaticamente con dati 16 byte da
ciascun sensore e dal controller. Nella configurazione
automatica, è possibile visualizzare la struttura del
telegramma e
Manual configuration (Configurazione manuale): il
telegramma viene configurato manualmente. È possibile
selezionare i dispositivi e i tag dati dei dispositivi inclusi nel
telegramma.
• View configuration (Visualizza configurazione):
consente di visualizzare la configurazione dei dati del
telegramma corrente.
• Start Auto config (Avvia configurazione auto): avvia un
nuovo processo di configurazione automatica che può
richiedere di modificare la configurazione del sensore.
• Add/Remove devices (Aggiungi/Rimuovi dispositivi):
consente di selezionare i dispositivi inclusi nel
telegramma.
• Add/remove tags (Aggiungi/Rimuovi tag): consente di
selezionare i tag dati del telegramma per ciascun
dispositivo.
• Setup telegram mode (Configura modalità telegramma):
consente di selezionare la configurazione automatica
(predefinita) oppure la configurazione manuale.
avviare una nuova configurazione automatica.
Italiano 35
Page 36

Opzione Descrizione
Profibus DP Seleziona una delle opzioni seguenti:
Address (Indirizzo): modifica l'indirizzo slave
Data order (Ordine dati): imposta la sequenza di byte
quando si
in virgola mobile è composto da 4 byte.
• Normal = IEEE Float Big Endian (impostazione
• Swapped = IEEE Float word wise swapped: scambia la
trasmettono dei valori in virgola mobile. Un valore
predefinita): le coppie non sono scambiate. Questo modo
è compatibile con tutti i sistemi principali Profibus
conosciuti.
prima coppia di byte con l'ultima coppia.
Opzione Descrizione
Simulation
(Simulazione)
Simulation: simula due valori in virgola mobile ed errore/
stato per sostituire un dispositivo reale. Selezionare le
seguenti opzioni
l'impostazione predefinita:
• Simulation: attiva o disattiva la simulazione.
YES: avvia una simulazione
NO: interrompe una simulazione (impostazione
predefinita)
• Period (Periodo): imposta il tempo richiesto dal primo
valore in virgola mobile per l'esecuzione sull'intero
intervallo tra MINIMUM (MINIMO) e MAXIMUM
(MASSIMO).
• Maximum: imposta il limite superiore per il primo valore
in virgola mobile.—20.0 (impostazione predefinita)
• Minimum: imposta il limite inferiore per il primo valore in
virgola mobile—10.0 (impostazione predefinita)
• Error: (Errore) il valore immesso in questo menu verrà
impostato nel primo tag simulato—16 (impostazione
predefinita)
• Status: (Stato) il valore immesso in questo menu verrà
impostato nel secondo tag simulato—5 (impostazione
predefinita)
• Toggle: (Scambia) modifica la direzione della rampa
simulata.
• Test/maint:
Enabled (attivato): imposta il bit TEST/MAINT (TEST/
MANUT) (0 x 0004) di ogni registro di stato di ciascuna
unità slave configurata nel telegramma Profibus per
indicare la modalità "Service" (Assistenza).
Disabled (disattivato): modalità di funzionamento normale
(impostazione predefinita)
e usare le frecce per inserire i valori o usare
36 Italiano
Version
(Versione)
Versione del software della scheda di rete Profibus.
Page 37

Opzione Descrizione
Location
(Ubicazione)
Status Status (Stato): indica lo stato della scheda di rete Profibus
Modifica il nome dell'ubicazione.
• Please wait (Attendere):
scheda di rete non ha rilevato tutti gli slave configurati o
è visualizzato quando la scheda è di nuova
configurazione e sta cercando le connessioni dei sensori
• PLC configure err (Err. config. PLC) viene mostrato
quando la scheda di rete ha ricevuto una configurazione
non corretta di un PLC (Programmable logico controller).
Consultare il file GSD.
• Ready (Pronto): viene mostrato quando la scheda di rete
è pronta a inviare dati al Profibus. Verificare l'indirizzo e/
o il cablaggio.
• Online: è mostrato quando la scheda di rete è in contatto
con il PLC e vengono inviati dati ciclici
viene mostrato fino a quando la
Ordine dispositivo
L'ordine del
dispositivo nel telegramma Profibus è fisso. I primi due sensori
installati sono sempre in posizione uno e due e il controller è in posizione
tre.
Quando non è installato alcun sensore, il controller sarà in posizione tre.
La posizione dei sensori non installati sarà riempita con 0xFF.
Se sono collegati due sensori (numero massimo consentito) acquisiti
contemporaneamente, l'ordine di installazione sarà basato sulla posizione
di collegamento del sensore (o del modulo del sensore). L'ordine è il
seguente:
• Il connettore della scheda analogica superiore
• Il connettore della scheda analogica inferiore
• Il connettore del sensore digitale sinistro
• Il connettore del sensore digitale destro
Struttura standard dei dati (configurazione automatica)
Se viene selezionata la configurazione automatica (predefinita), la scheda
di rete Profibus fornisce un telegramma dati predefinito per ciascun
dispositivo collegato. Il telegramma contiene dati importanti sul
dispositivo.
La struttura di blocco dati dei messaggi Profibus è standardizzata per tutti
i tipi di sonde. Per la struttura del blocco dati, fare riferimento a Profibus
data telegram register.
Se viene invece selezionata la configurazione manuale, la struttura dati
del telegramma può essere configurata dall'utente (fare riferimento a
Configurare la rete a pagina 35).
Tabella 2 Struttura del telegramma di dati Profibus
Numero byte Dati Tipo dati
1–2 Errore classificato Intero (2 byte)
3–4 Stato classificato Intero (2 byte)
5–8 Misurazione 1 In virgola mobile (4 byte)
9–12 Misurazione 2 In virgola mobile (4 byte)
13–16 Misurazione 3 In virgola mobile (4 byte)
Italiano 37
Page 38

Visualizzazione valori
La struttura del blocco dati Profibus (Profibus message data block
structure) può sostituire sonde pc senza modificare la configurazione del
PLC.
Il valore primario è sempre il valore misurato.
Il valore secondario, se non disponibile, è riempito con zero.
Il valore terziario, se non disponibile, è riempito con zero.
Figura 2 Struttura del blocco dati dei messaggi Profibus
Blocco dati controller
Il blocco dati per il controller sc è simile al blocco dati per i sensori. La
struttura del blocco dati del controller sc è indipendente dal numero di
sensori collegati:
•
sc controller_ERROR
sc controller_STATUS
•
• Valore primario
• Valore secondario
• Valore terziario
Block 3 sc controller ERROR e Block 3 sc controller STATUS mostrano le
definizioni dei dati per errore e stato 1 nel controller sc.
Tabella 3 ERRORE controller sc Blocco 3
Bit Errore Nota
0 Errore di comunicazione
Sensore 1
1 Errore di comunicazione
Sensore 2
2–15 Non usato
Si è verificato un errore di comunicazione tra
il controller sc e il sensore 1; il sensore
potrebbe essere scollegato.
Si è verificato un errore di comunicazione tra
il controller sc e il sensore 2; il sensore
potrebbe essere scollegato.
Tabella 4 STATO controller sc Blocco 3
Bit Status 1 Nota
0 Sensore 1 installato Il primo sensore è stato installato sul controller sc.
1 Sensore 2 installato Il secondo sensore è stato installato sul controller sc.
2 Relè A ON
3 Relè B ON
4 Relè C ON
5 Relè D ON
6–15 Non usato
Questo bit è impostato anche se il sensore viene
scollegato dopo l'installazione.
Questo bit è impostato anche se il sensore viene
scollegato dopo l'installazione.
valori controller sc
L'elenco seguente mostra le definizioni dei dati per il controller sc.
• Il valore primario del controller sc mostra il risultato di un calcolo.
Il valore secondario del controller sc mostra l'output da 0-20 mA o 4-20
•
mA dal Canale 1.
• Il valore terziario del controller sc mostra l'output da 0-20 mA o 4-20 mA
dal Canale 2.
38 Italiano
Page 39

Definizione in virgola mobile IEEE 745
Profibus utilizza una definizione in virgola mobile IEEE a precisione
singola a
32 bit. La definizione ha ventitrè bit per la mantissa e otto bit per
l'esponente. C'è un bit per il segno della mantissa. Fare riferimento a
Floating point definition.
Figura 3 Definizione in virgola mobile
1 Bit per il segno 4 Esponente
2 Esponente 5 Mantissa
3 Mantissa
Scambio basato su parole
Byte order
inside Profibus telegram mostra le sequenze di byte normali e
scambiate. Nello scambio basato su parole (word wise), il terzo e il quarto
byte sono scambiati in ordine con il primo e il secondo byte. Il risultato è
un ordine di byte di 3 4 1 2.
Tabella 5 Ordine dei byte nel telegramma Profibus
controller sc scambiato controller sc normale
Valore byte T1 0 x 91 Valore byte T1 0 x 3F
Valore byte T2 0 x B9 Valore byte T2 0 x 67
Valore byte T3 0 x 3F Valore byte T3 0 x 91
Valore byte T4 0 x 67 Valore byte T4 0 x B9
Individuazione ed eliminazione dei guasti
A V V E R T E N Z A
Rischi multipli. Non smontare lo strumento per operazioni di manutenzione o
assistenza. Se è necessario pulire o riparare i componenti interni, contattare il
produttore.
Indicatori di stato ed errori
Le parole errore e stato hanno la stessa definizione standard per tutte le
sonde sc e i controller.
Error messages elenca la posizione in bit e i messaggi di errore. Status
indicator messages elenca la posizione in bit e i messaggi di stato.
Un valore di bit pari a zero mostra una condizione di errore o stato non
vera.
Un valore di bit pari a 1 mostra una condizione di errore o stato vera. Ad
esempio, se Bit 0 ha un valore pari a 1, si è verificato un errore durante
l'ultima calibrazione.
Italiano 39
Page 40

Tabella 6 Messaggi di errore
Bit Messaggio Indicazione
0 Errore di calibrazione misura Si è verificato un errore durante l'ultima
1 Errore di regolazione
elettronico
2 Errore di eliminazione L'ultimo ciclo di eliminazione ha avuto esito
3 Errore modulo di misura È stato rilevato un errore nel modulo di misura
4 Errore di reinizializzazione
del sistema
5 Errore hardware È stato rilevato un errore di hardware
6 Errore di comunicazione
interna
7 Errore umidità È stata rilevata umidità eccessiva nel
8 Errore di temperatura La temperatura nell'apparecchio supera il
9 — —
10 Avviso campione Sono richieste alcune azioni con il sistema
11 Avviso calibrazione da
verificare
12 Avviso misura da verificare Una o più misurazioni del dispositivo sono
13 Avviso sicurezza È stata rilevata una condizione che potrebbe
calibrazione
Si è verificato un errore durante l'ultima
calibrazione elettronica
negativo
Alcune impostazioni sono incoerenti e sono
state riportate ai valori predefiniti di fabbrica
generale
È stato rilevato un errore di comunicazione
nell'apparecchio
dispositivo
limite specificato
campione
L'ultima calibrazione potrebbe non essere
accurata
fuori intervallo o di precisione dubbia
causare un pericolo per la sicurezza
Tabella 6 Messaggi di errore (continua)
Bit Messaggio Indicazione
14 Avviso reagente Il sistema del reagenti ha bisogno di
15 Avviso richiesta
manutenzione
attenzione
Il dispositivo necessita di manutenzione
Tabella 7 Messaggi indicatori di stato
Bit Messaggio Indicazione
0 Calibrazione in corso L'apparecchio è in modalità di calibrazione. Le
1 Pulizia in corso L'apparecchio è in modalità di pulizia. Le
2 Menu Servizio/
Manutenzione
3 Errore comune Il dispositivo ha riconosciuto un errore. Vedere
4 Misura 0 Qualità scarsa La precisione della misura è fuori dai limiti
5 Misura 0 limite basso La misura è al di sotto del limite specificato.
6 Misura 0 limite alto La misura è al di sopra del limite specificato.
7 Misura 1 Qualità scarsa La precisione della misura è fuori dai limiti
8 Misura 1 limite basso La misura è al di sotto del limite specificato.
9 Misura 1 limite alto La misura è al di sopra del limite specificato.
10 Misura 2 Qualità scarsa La precisione della misura è fuori dai limiti
11 Misura 2 limite basso La misura è al di sotto del limite specificato.
12 Misura 2 limite alto La misura è al di sopra del limite specificato.
misurazioni potrebbero non essere valide.
misurazioni potrebbero non essere valide.
L'apparecchio è in modalità di servizio o
manutenzione. Le misurazioni potrebbero non
essere valide.
il Registro
specificati.
specificati.
specificati.
degli errori per la Classe dell'errore.
40 Italiano
Page 41

Tabella 7 Messaggi indicatori di stato (continua)
Bit Messaggio Indicazione
13 Misura 3 Qualità scarsa La precisione della misura è fuori dai limiti
specificati.
14 Misura 3 limite basso La misura è al di sotto del limite specificato.
15 Misura 3 limite alto La misura è al di sopra del limite specificato.
Tabella 8 Memoria eventi (continua)
Evento Descrizione
AUTO CONFIGURE
(CONFIGURAZIONE
AUTOMATICA)
CODE VERSION (VERSIONE
CODICE)
Punto nel tempo di una nuova impostazione
di menu
Punto nel tempo di un nuovo download del
software (Versione software)
Memoria eventi
Per informazioni
sul dispositivo diagnostico, fare riferimento a Event Log.
Tabella 8 Memoria eventi
Evento Descrizione
ADDRESS (INDIRIZZO) Indirizzo Profibus regolato
DATA ORDER (ORDINE DATI) Indica l'ordine dei dati di variabili a 2 parole
SIMULATION (SIMULAZIONE) Indica se i dati simulati sono impostati nel
SENSOR POWER (POTENZA
SENSORE)
SET DATE/TIME
(IMPOSTAZIONE DATA/ORA)
NEW CONFIG (NUOVA CONFIG.) Punto nel tempo di una nuova configurazione
nel telegramma Profibus ciclico e aciclico
telegramma Ciclico di Profibus.
Istante di accensione della scheda Profibus
Punto dell'impostazione dell'ora del timer
interno della scheda Profibus
Parti di ricambio e accessori
Schede di rete di comunicazione e accessori
Descrizione Codice prodotto
Kit Profibus DP 9173900
Kit connettore Profibus M12 9178500
Presa Profibus M12 9178200
Spina a T Profibus M12 9178400
Numeri di Prodotti e Articoli possono variare per alcune regioni di vendita.
Contattare il distributore appropriato o fare riferimento al sito Web
dell'azienda per dati di contatto.
Italiano 41
Page 42

Esempio Simatic
Quando viene importato HALA09AC.GSD, lo slave si troverà in PROFIBUS DP, ADDITIONAL FIELD DEVICES, GENERAL (PROFIBUS DP,
DISPOSITIVI AGGIUNTIVI, GENERALE).
1. Selezionare la scheda di rete 2 Words from Slave (2 parole da slave).
Ogni modulo è 4 byte del range dell'indirizzo di input.
Figura 4 Esempio Simatic
42 Italiano
Page 43

Dati reali
sequenza di dati solita, utilizzare L PED nell'indirizzo di avvio del
Per una
modulo per leggere un oggetto in virgola mobile. Non sono necessarie
ulteriori conversioni.
Nota: PEW/PED è il codice parlante SIMATIC o tedesco. Utilizzare PIW/PID per IEC
o inglese.
1. Leggere le parole di ERRORE o STATO.
2. Utilizzare le istruzioni L PEW.
Italiano 43
Page 44

Caractéristiques
Les caractéristiques techniques peuvent être modifiées sans préavis.
Caractéristique Détails
Protocole Profibus Siemens ASIC SPC3
Service DP Esclave DPV0
Services DP/DPV1 Esclave DPV1 classe 1 et classe 2
Fonction I&M
Modification d'adresse par le maître Profibus
Débit en bauds Profibus 9,6k, 19,2k, 45,45k, 93,75k, 187,5k, 500k, 1.5M,
Indicateurs Voyant LED pour afficher le mode d'échange de
Type d'interface RS485
Paramètres configurables Échange de données mot pour mot pour les
Dimensions (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Température de
fonctionnement
Tension de fonctionnement 8 V–16 V
Consommation électrique
maximale
Certification Classe I, Division 2, groupes A, B, C, D et
3M, 6M, 12M
Détection automatique du débit en bauds
données
valeurs en virgule flottante
–20°C à 85 °C (–4 à 185 °F)
2 W
Classe I,
Zone 2, groupe IIC, T4 sites dangereux
et normaux
Généralités
En aucun
directs, indirects, spéciaux, accessoires ou consécutifs résultant d'un
cas le constructeur ne saurait être responsable des dommages
défaut ou d'une omission dans ce manuel. Le constructeur se réserve le
droit d'apporter des modifications à ce manuel et aux produits décrits à
tout moment, sans avertissement ni obligation. Les éditions révisées se
trouvent sur le site Internet du fabricant.
Consignes de sécurité
Veuillez lire
l'ensemble du manuel avant le déballage, la configuration ou
la mise en fonctionnement de cet appareil. Respectez toutes les
déclarations de prudence et d'attention. Le non-respect de cette
procédure peut conduire à des blessures graves de l'opérateur ou à des
dégâts sur le matériel.
Assurez-vous que la protection fournie avec cet appareil ne soit pas
compromise, n'utilisez pas ou n'installez pas cet appareil d'une autre façon
que celle décrite dans ce manuel.
Interprétation des indications de risques
D A N G E R
Indique une situation de danger potentiel ou imminent qui, si elle n'est pas évitée,
entraîne des blessures graves, voire mortelles.
A V E R T I S S E M E N T
Indique une situation de danger potentiel ou imminent qui, si elle n'est pas évitée,
peut entraîner des blessures graves, voire mortelles.
Indique une situation de danger potentiel qui peut entraîner des blessures
mineures ou légères.
Indique une situation qui, si elle n'est pas évitée, peut occasionner
l'endommagement du
matériel. Informations nécessitant une attention particulière.
A T T E N T I O N
A V I S
Etiquettes de mise en garde
Lisez toutes les étiquettes et tous les repères apposés sur l’instrument.
Des
personnes
peuvent se blesser et le matériel peut être endommagé si
ces instructions ne sont pas respectées. Les symboles apposés sur
l'appareil sont complétés par un paragraphe Danger ou Attention dans le
manuel.
44 Français
Page 45

Lorsque ce symbole est présent sur l’instrument, reportez-vous au
manuel d’instructions pour obtenir des informations relatives au
fonctionnement et/ou à la sécurité.
Ce symbole indique qu'il existe un risque de choc électrique et/ou
d'électrocution.
Ce symbole indique la présence de dispositifs sensibles aux décharges
électrostatiques (ESD) et indique que des précautions doivent être
prises pour éviter les dommages avec l'équipement.
L’équipement électrique portant ce symbole ne peut être mis au rebut
systèmes de mise au rebut publics européens après le 12 août
dans les
2005. Conformément aux règlements nationaux et européens
(Directive 2002/98/EC), les appareils électriques doivent, depuis le 12
août 2005, ne pas être mis au rebut dans les décharges traditionnelles,
mais être, à la fin de leur service, renvoyés par les utilisateurs
européens au fabricant, qui se chargera de les éliminer à ses frais.
Figure 1 Vue d'ensemble du sytème
1 Automate sc (esclave) 3 PC avec logiciel (maître classe 2,
2 Automate programmable (maître
classe 1)
c'est-à-dire PC avec carte CP5611)
Aperçu général du produit
Les contrôleurs sc sont les plateformes standard de toutes les sondes et
analyseurs intelligents. La plateforme sc est un système de
communication entièrement numérique fondé sur le standard Modbus
ouvert. Lorsqu'une carte d'interface Profibus est installée, les
transmetteurs sc fournissent l'étendue complète de la méthode standard
des valeurs et des paramètres.
Les automates sc sont des appareils Profibus DP/V1 certifiés PNO/PTO.
Ces appareils sont compatibles avec les systèmes maîtres de classe 1 et
les systèmes maîtres de classe 2, par exemple, les stations d'ingénierie.
Une vue d'ensemble du système est fournie à la System overview. Le
Profibus peut être installé à l'usine ou par l'utilisateur.
Installation
A T T E N T I O N
Risque de blessures corporelles Seul le personnel qualifié est autorisé à
entreprendre les opérations décrites dans cette section du manuel.
Mise en place du module dans le transmetteur
Risque d'explosion Si vous souhaitez installer le module dans un environnement
classé comme
des raisons de sécurité.
dangereux, reportez-vous au manuel d'utilisation du contrôleur pour
Risque d'électrocution Débranchez systématiquement l'alimentation de
l'appareil avant tout branchement électrique.
D A N G E R
D A N G E R
Français 45
Page 46

D A N G E R
Risque d'électrocution Le câblage à haute tension du contrôleur est effectué
derrière la barrière de protection à haute tension du boîtier du contrôleur. L'écran
de protection doit rester en place, sauf lors de l'installation de modules ou
l'installation par un technicien qualifié du câblage d'alimentation, de relais ou de
cartes analogiques et réseau.
Dégât potentiel sur l'appareil Les composants électroniques internes
de l'appareil peuvent être endommagés par l'électricité statique, qui
risque d'altérer ses performances et son fonctionnement.
A V I S
La carte réseau Profibus assure la prise en charge de la communication
RS485. Le bornier J1 assure la connexion utilisateur à la carte réseau
Profibus. Pour plus de détails de câblage, consultez Installation Profibus
procédure ci-dessous pour mettre en place la carte réseau Profibus.
et la
Tableau 1 Câblage Profibus avec RS485
Connecteur Numéro de
broche du
bornier
J1 1 A1 (Entrée) vert Entrée de la carte
2 B1 (Entrée) rouge Entrée de la carte
3 OV — —
4 5 V — —
5 A2 (Sortie) vert Sortie de la carte
6 B2 (Sortie) rouge Sortie de la carte
Signal Couleur de
câble
Description
réseau
réseau
réseau
réseau
46 Français
Page 47

1 2
3 4
Français 47
Page 48

5 6
7 8
48 Français
Page 49

Configuration du réseau
D A N G E R
Risque d'électrocution Débranchez systématiquement l'alimentation de
l'appareil avant tout branchement électrique.
La carte réseau Profibus assure une interface de connexion RS485. Avant
utilisation, la
carte réseau doit être configurée pour son emplacement sur
le réseau. Utilisez les réglages de commutateur en haut de la carte réseau
pour la configuration (consultez la section Installation).
1. Interrupteur de fin de ligne - interrupteur inactif. Réglez le commutateur
sur cette position s'il n'est le dernier esclave sur le bus.
2. Commutateur de terminaison – Terminaison activée (position "T").
Réglez l'interrupteur sur cette position si l'appareil est le dernier ou le
seul esclave sur le bus.
Fonctionnement
Navigation utilisateur
Consultez la documentation du transmetteur pour une description du
clavier et des informations de navigation.
Configuration du réseau
Lorsque la carte de réseau Profibus est installée, le transmetteur requiert
une configuration correcte de l'appareil et de l'ordre des données.
Remarque : Consultez la documentation du transmetteur pour la description du
clavier, les informations de navigation de base et la configuration du transmetteur.
1. Sélectionnez Configuration réseau sur le menu Paramètres.
2. Choisissez la saisie ou la modification de valeurs et appuyez sur la
touche ENTER.
Option Description
Télégramme Gère la structure de données du télégramme. Configuration
Profibus DP Sélectionnez une des options suivantes :
automatique : Le télégramme est configuré
automatiquement avec 16 bits de données provenant de
chaque capteur et du transmetteur. En configuration
automatique, il est possible de visualiser la structure du
télégramme et de lancer une nouvelle configuration
automatique. Configuration manuelle : Le télégramme est
configuré manuellement. Les périphériques et les étiquettes
de données de périphérique inclus dans le télégramme
peuvent être sélectionnés.
• Afficher la configuration— Affiche la configuration
actuelle des données du télégramme
• Lancer la configuration automatique— Démarre un
nouveau processus
nécessiter des modifications dans le paramétrage du
capteur
• Ajouter/Supprimer des périphériques— Sélectionne les
périphériques inclus dans le télégramme
• Ajouter/Supprimer des étiquettes— Sélectionne des
étiquettes de données de télégramme pour chaque
périphérique
• Paramétrer le mode du télégramme— Sélectionne le
mode de configuration automatique (par défaut) ou
manuelle.
Adresse — Modifie l'adresse d'esclave
Ordre de données — Définit la séquence d'octets pour la
transmission des valeurs en virgule flottante. Une valeur en
virgule flottante comprend 4 octets.
• Normal = IEEE virgule flottante gros boutiste (réglage par
défaut) — Les paires ne sont pas échangées. Ce mode
convient à tous les systèmes Profibus maîtres connus.
• Échangé = IEEE en virgule flottant échangé mot pour mot :
échange la première paire d'octets avec la dernière paire.
de configuration automatique qui peut
Français 49
Page 50

Option Description
Simulation Simulation — Simule deux valeurs en virgule flottante et
Version Version du logiciel de la carte réseau Profibus.
erreur/statut pour
les options ci-dessous et utilisez les flèches pour entrer les
valeurs en ms ou utilisez le réglage par défaut :
• Simulation : Active ou désactive la simulation.
OUI : Démarre une simulation
Non : Arrête une simulation (par défaut)
• Période :Configure le temps pendant lequel la première
valeur de la virgule flottante doit fonctionner à l'aide de
toute l'intervalle entre le MINIMUM et le MAXIMUM — 2
min (par défaut).
• Maximum : Configure la limite supérieure pour la première
valeur de la virgule flottante.— 20,0 (par défaut)
• Minimum : Configure la limite inférieure pour la première
valeur de la virgule flottante — 10,0 (par défaut)
• Erreur : La valeur entrée dans le menu sera configurée
dans la première balise simulée — 16 (par défaut).
• Statut : La valeur entrée dans le menu sera configurée
dans la deuxième balise simulée — 5 (par défaut).
• Bascule : Change le sens de la rampe simulée.
• Test/maint :
Activé : active le bit TEST/MAINT (0x0004) de chaque
registre d'état de chaque esclave configuré dans le
télégramme cyclique Profibus pour indiqué le mode
"Service".
Désactivé : Mode de fonctionnement normal (réglage par
défaut)
remplacer un instrument réel. Sélectionnez
Option Description
Emplacement Modifie le nom d'emplacement.
Statut Statut — Indique le statut de la carte réseau Profibus
• Please wait : apparaît jusqu'à ce que la carte ait trouvé
tous les
esclaves configurés ou quand la carte vient d'être
configurée et recherche des connexions réseau
• PLC configure err : apparaît quand la carte réseau a reçu
une configuration erronée depuis un automate (automate
programmable). Vérifiez le fichier GSD.
• Ready : apparaît quand la carte réseau est prête à envoyer
des données sur le Profibus. Vérifiez l'adresse et/ou le
câblage.
• Online : apparaît quand la carte réseau est en contact
avec l'automate programmable et que des données
cycliques sont envoyées
Ordre de l'appareil
L'ordre des
périphériques dans le télégramme Profibus est fixe. Le premier
et le deuxième capteurs installés sont toujours en position un et deux et
le contrôleur en position trois.
Quand aucun capteur n'est installé, le contrôleur doit rester en position
trois. La position des capteurs non installés sera remplie de 0xFF.
Si deux capteurs sont connectés (maximum autorisé) et scrutés en même
temps, l'ordre d'installation se basera sur l'emplacement auquel le capteur
(ou le module capteur) est connecté. L'ordre est le suivant :
• Connecteur supérieur de carte analogique.
• Connecteur inférieur de carte analogique.
• Connecteur gauche de capteur numérique.
• Connecteur droit de capteur numérique.
50 Français
Structure de données standard (configuration automatique)
Lorsque la configuration automatique (par défaut) est sélectionnée, la
carte réseau Profibus génère un télégramme de données prédéfini pour
chaque périphérique connecté. Le télégramme contient des données
importantes sur le périphérique.
Page 51

La structure d'un bloc de données des messages du Profibus est
commune à tous les types de sondes. Pour la structure du bloc de
données, consultez Profibus data telegram register.
Lorsque la configuration manuelle est sélectionnée, l'utilisateur peut
configurer la structure de données du télégramme (reportez-vous à la
section Configuration du réseau à la page 49).
Tableau 2 Structure du télégramme de données Profibus
Numéro d'octet Données Type de données
1–2 Erreur classifiée Entier (2 octets)
3–4 État classé Entier (2 octets)
5–8 Mesure 1 Flottant (4 octets)
9–12 Mesure 2 Flottant (4 octets)
13–16 Mesure 3 Flottant (4 octets)
Valeurs affichées
La structure du bloc de données Profibus (Profibus message data block
structure) peut remplacer les sondes sc sans modification de la
configuration de l'automate programmable.
La valeur principale est toujours la valeur mesurée.
La valeur secondaire, si elle n'est pas disponible, sera égale à zéro.
La valeur tertiaire, si elle n'est pas disponible, est égale à zéro.
Figure 2 Structure du bloc de données du message du Profibus
Traitement du bloc de données du contrôleur
Le bloc de données pour le transmetteur sc est similaire au bloc de
données
les capteurs. La structure du bloc de données du contrôleur
pour
sc est indépendante du nombre de capteurs connectés :
• sc controller_ERROR
• sc controller_STATUS
• Valeur primaire
• Valeur secondaire
• Valeur tertiaire
Les Block 3 sc controller ERROR et Block 3 sc controller STATUS
présentent les définitions de données des bits d'erreur et d'état dans le
contrôleur sc.
Français 51
Page 52

Tableau 3 Bloc 3 ERROR de l'automate sc
Bit Erreur Remarque
0 Erreur de communication du
capteur 1
1 Erreur de communication du
capteur 2
2–15 Non utilisé
Une erreur de communication est survenue
entre le
contrôleur et le capteur 1, le capteur
est peut-être déconnecté.
Une erreur de communication est survenue
entre le contrôleur et le capteur 2, le capteur
est peut-être déconnecté.
Tableau 4 Bloc 3 STATUS du contrôleur sc
Bit Status1 Remarque
0 Capteur 1 installé Le premier capteur a été installé sur le contrôleur sc.
1 Capteur 2 installé Le deuxième capteur a été installé sur le contrôleur sc.
2 Relai A activé
3 Relai B activé
4 Relai C activé
5 Relai D activé
6–15 Non utilisé
Ce bit est activé même si le capteur est débranché
après l'installation.
Ce bit est activé même si le capteur est débranché
après l'installation.
Définition de la virgule flottante IEEE
Le Profibus utilise une définition de point flottant IEEE d'une précision
unique de 32 bit. La définition a 23 bits pour la mantisse et 8 bits pour
l'exposant. Le signe de la mantisse a un bit. Référez-vous à Floating point
definition.
Figure 3 Définition du point flottant
1 Signe du bit 4 Exposant
2 Exposant 5 Mantisse
3 Mantisse
Valeurs d'automate sc
Vous trouverez
ci-dessous les définitions de données pour l'automate sc :
• La valeur primaire de l'automate sc indique le résultat d'un calcul.
• La valeur secondaire de l'automate sc affiche la sortie 0–20 mA ou 4–
20 mA du canal 1.
• La valeur tertiaire de l'automate sc affiche la sortie 0–20 mA ou 4–20
mA du canal 2.
52 Français
Page 53

Échange de Mots
Byte order inside Profibus telegram indique les séquences d'octets
échangés ou
normales. En Échange de Mots, le troisième et le quatrième
sont échangés avec le premier et le deuxième octets. Ceci a pour résultat
un ordre d'octet de 3 4 1 2.
Tableau 5 Ordre des octets à l'intérieur d'un télégramme Profibus
Automate sc échangé Automate sc normal
Valeur d'octet T1 0 x 91 Valeur d'octet T1 0 x 3F
Valeur d'octet T2 0 x B9 Valeur d'octet T2 0 x 67
Valeur d'octet T3 0 x 3F Valeur d'octet T3 0 x 91
Valeur d'octet T4 0 x 67 Valeur d'octet T4 0 x B9
Dépannage
A V E R T I S S E M E N T
Dangers multiples. Ne démontez pas l'appareil pour l'entretien. Si les composants
internes doivent être nettoyés ou réparés, contactez le fabricant.
Indicateurs d'erreur et de statut
Les mots erreur et statut suivent les même définitions standards pour
toutes les sondes et contrôleurs SC.
Error messages donne
Status indicator messages donne la liste des positions et messages d'état.
Une valeur de bit de zéro indique que la condition d'erreur ou de statut
n'est pas vraie.
Une valeur de bit de 1 indique que la condition d'erreur ou de statut est
vraie. Par exemple, si le bit 0 a la valeur 1, une erreur est survenue lors
du dernier étalonnage.
la liste des positions de bit et messages d'erreur.
Tableau 6 Messages d’erreur
Bit Message Indication
0 Erreur d'étalonnage de la
mesure
1 Erreur de réglage
électronique
2 Erreur de nettoyage Le dernier cycle de nettoyage a échoué
3 Erreur de module de
mesure
4 Erreur de ré-initialisation du
système
5 Erreur de hardware Une erreur de hardware générale a été
6 Erreur de communication
interne
7 Erreur d'humidité Un excès d'humidité a été détecté dans
8 Erreur de température La température dans l'appareil dépasse une
9 — —
10 Erreur d'échantillon Il est nécessaire de vérifier le système
11 Alerte d'étalonnage
douteux
12 Alerte de mesure douteuse Une des mesures de l'appareil ou plus est hors
13 Alerte de sécurité Une condition a été détectée qui pourra causer
Une erreur a eu lieu pendant le dernier
étalonnage
Une erreur a eu lieu pendant le dernier
étalonnage électronique
Une panne a été détectée dans le Module de
Mesure
Certaines configurations manquent de
cohérence et ont été réinitialisées selon des
paramètres d'usine par défaut
détectée
Un panne de communication a été détectée
dans l'appareil
l'appareil
limite spécifiée
d'échantillonnage
Il est possible que le dernier étalonnage ne soit
pas exact
plage ou est d'une précision douteuse
une situation dangereuse
Français 53
Page 54

Tableau 6 Messages d’erreur (suite)
Bit Message Indication
14 Alerte de réactif Il est nécessaire de prêter attention au système
15 Alerte d'entretien requis L'appareil a besoin d'être entretenu
des réactifs
Tableau 7 Messages d'indicateur de statut
Bit Message Indication
0 Etalonnage en cours L'appareil est en mode d'étalonnage. Il se
1 Nettoyage en cours L'appareil est en mode de nettoyage. Il se
2 Menu Entretien /
Maintenance
3 Erreur commune L'appareil a reconnu un erreur. Voir le
4 Mauvaise qualité de la
Mesure 0
5 Limite basse de la Mesure 0 La mesure est en dessous de la plage
6 Limite haute de la Mesure 0 La mesure est au-dessus de la plage
7 Mauvaise qualité de la
Mesure 1
8 Limite basse de la Mesure 1 La mesure est en dessous de la plage
9 Limite haute de la Mesure 1 La mesure est au-dessus de la plage
10 Mauvaise qualité de la
Mesure 2
peut que les mesures ne soient pas valides.
peut que les mesures ne soient pas valides.
L'appareil est en mode Entretien ou
Maintenance. Il se peut que les mesures ne
soient pas valides.
Registre des Erreurs pour le Type d'Erreur.
La précision de la mesure est en dehors des
limites spécifiées.
spécifiée.
spécifiée.
La précision de la mesure est en dehors des
limites spécifiées.
spécifiée.
spécifiée.
La précision de la mesure est en dehors des
limites spécifiées.
Tableau 7 Messages d'indicateur de statut (suite)
Bit Message Indication
11 Limite basse de la Mesure 2 La mesure est en dessous de la plage
12 Limite haute de la Mesure 2 La mesure est au-dessus de la plage
13 Mauvaise qualité de la
Mesure 3
14 Limite basse de la Mesure 3 La mesure est en dessous de la plage
15 Limite haute de la Mesure 3 La mesure est au-dessus de la plage
spécifiée.
spécifiée.
La précision de la mesure est en dehors des
limites spécifiées.
spécifiée.
spécifiée.
Journal des évènements
Voir la Event Log pour des informations de diagnostic sur l'appareil.
Tableau 8 Journal des évènements
Evénement Description
ADRESSE Adresse Profibus ajustée
DATA ORDER Indique l'ordre des données des variables à 2 mots du
SIMULATION Indique si les données simulées sont définies dans le
SENSOR POWER Instant d'activation de la carte Profibus
RÉGLER DATE/HEURE Instant de configuration de la temporisation interne de
NEW CONFIG Instant de nouvelle configuration
AUTO CONFIGURE Instant de nouveau réglage de menu
VERSION CODE Instant de nouveau téléchargement de logiciel (version
télégramme Profibus cyclique et acyclique
télégramme Profibus cyclique.
la carte Profibus
de logiciel)
54 Français
Page 55

Pièces et accessoires de rechange
Cartes de communication réseau et accessoires
Description Article numéro
Kit Profibus DP 9173900
Kit de connecteur Profibus M12 9178500
Description Article numéro
Profibus M12 prise Profibus 9178200
Profibus M12 fiche en T 9178400
Les numéros de référence de produit et d'article peuvent dépendre des
régions de commercialisation. Prenez contact avec le distributeur
approprié ou consultez le site web de la société pour les informations de
contact.
Français 55
Page 56

Exemple Simatic
Lorsque le
1. Sélectionnez la carte réseau 2 Words from Slave.
Figure 4 Exemple Simatic
HALA09AC.GSD est importé, l'esclave se trouve sousPROFIBUS DP>APPAREILS SUR LE TERRAIN SUPPLEMENTAIRES>GENERAL.
Chaque module a 4 octets de la plage de l'adresse de l'entrée.
56 Français
Page 57

Lecture de données
Pour les séquence de données habituelles, utilisezL PED à l'adresse de
démarrage du module pour lire un objet de point flottant. Aucune
conversion n'est nécessaire.
Remarque
PIW/PID pour l'IEC ou l'anglais.
: PEW/PED
1. Mots d'ERREUR ou de STATUT de lecture
2. Utilisez les instructions L PEW.
est le SIMATIC ou code mnémotechnique allemand. Utilisez
Français 57
Page 58

Especificaciones
Las especificaciones están sujetas a cambios sin previo aviso.
Especificación Detalles
Protocolo de Profibus Siemens ASIC SPC3
Servicio DP Esclavo DPV0
Servicios DP/DPV1 Esclavo DPV1 clase 1 y clase 2
Función de instalación y mantenimiento
La dirección cambia según el maestro Profibus
Tasas de baudio de Profibus 9,6k, 19,2k, 45,45k, 93,75k, 187,5k, 500k, 1,5M,
Indicadores LED para mostrar el modo de intercambio de
Tipo de interfaz RS485
Parámetros configurables Intercambio de datos, palabra acertada para los
Dimensiones (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Temperatura de
funcionamiento
Voltaje de funcionamiento 8 V - 16 V
Máximo consumo de energía 2 W
Certificación Clase I, División 2 (grupos A, B, C, D), Zona 2
3M, 6M, 12M
Detección automática de la tasa de baudios
datos
valores de coma flotante
–20°C a + 85°C [–4° a 185°F]
(grupo IIC), ubicaciones normales y peligrosas
T4
Información general
En ningún caso el fabricante será responsable de ningún daño directo,
indirecto, especial,
accidental o resultante de un defecto u omisión en este
manual. El fabricante se reserva el derecho a modificar este manual y los
productos que describen en cualquier momento, sin aviso ni obligación.
Las ediciones revisadas se encuentran en el sitio Web del fabricante.
Información de seguridad
Lea todo el manual antes de desembalar, instalar o trabajar con este
equipo. Ponga atención a todas las advertencias y avisos de peligro. El
no hacerlo puede provocar heridas graves al usuario o daños al equipo.
Para garantizar
que no disminuya la protección que ofrece este producto,
no use o instale el equipo de manera diferente a la especificada en este
manual.
Utilización de la información sobre riesgos
P E L I G R O
Indica una situación potencial o de riesgo inminente que, de no evitarse, provocará
la muerte o lesiones graves.
A D V E R T E N C I A
Indica una situación potencial o inminentemente peligrosa que, de no evitarse,
podría provocar la muerte o lesiones graves.
P R E C A U C I Ó N
Indica una situación potencialmente peligrosa que podría provocar una lesión
menor o moderada.
Indica una situación que, si no se evita, puede provocar daños en el instrumento.
Información que requiere especial énfasis.
A V I S O
Etiquetas de precaución
Lea todas las etiquetas y rótulos adheridos al instrumento. En caso
contrario, podrían producirse heridas personales o daños en el
instrumento. Se incluye un símbolo, en caso de estar rotulado en el
equipo, con una indicación de peligro o de advertencia en el manual.
58 Español
Page 59

Este símbolo (en caso de estar colocado en el equipo) refiere a las
instrucciones de operación o bien la información de seguridad.
Este símbolo indica que hay riesgo de descarga eléctrica y/o
electrocución.
Este símbolo indica la presencia de dispositivos sensibles a descargas
electrostáticas y que se deben tomar precauciones para evitar daños
en el equipo.
El equipo eléctrico marcado con este símbolo no se podrá desechar
por medio de los sistemas europeos públicos de eliminación después
del 12 de agosto de 2005. En cumplimiento de las reglamentaciones
nacionales y locales (directiva europea 2002/98/CE), los usuarios de
equipos eléctricos deben devolver los equipos viejos o los que han
alcanzado el término de su vida útil al fabricante para su eliminación
gratuita.
Figura 1 Generalidades del sistema
1 Controlador sc (esclavo) 3 PC con software (Clase maestra 2,
2 Controlador lógico programable
(Clase maestra 1)
por ej., PC con tarjeta CP5611)
Generalidades del producto
Los controladores sc son la plataforma de todos los analizadores y sondas
inteligentes. La plataforma sc es un sistema completo de comunicación
digital basado en el Modbus abierto estándar. Al instalar una tarjeta de
interfaz Profibus, los controladores sc brindan la escala completa de
valores y parámetros del método estandarizado.
Los controladores sc son dispositivos Profibus DP/V1 certificados por
PNO/PTO. Estos dispositivos son compatibles con los sistemas clase
maestra 1 (PLC SCADA) y clase maestra 2, por ej., las estaciones de
ingeniería.
En la System overview se muestra una visión general del sistema.
Profibus viene disponible como un artículo instalado de fábrica o por el
usuario.
Instalación
P R E C A U C I Ó N
Peligro de lesión personal. Las tareas descritas en esta sección del manual solo
deben ser realizadas por personal cualificado.
Instalación del módulo para el controlador
Peligro de explosión Para obtener información sobre las instrucciones de
seguridad relativas a la instalación del módulo en ubicaciones clasificadas como
peligrosas, consulte el manual de usuario del controlador.
Peligro de electrocución. Desconecte siempre la alimentación del
instrumento antes de hacer conexiones eléctricas.
P E L I G R O
P E L I G R O
Español 59
Page 60

P E L I G R O
Peligro de electrocución. El cableado de alto voltaje para el controlador se realiza
detrás de
permanecer en su lugar excepto durante la instalación de módulos o cuando un
técnico de instalación cualificado esté realizando el cableado de alimentación, de
los relés o de las tarjetas analógicas y de red.
la barrera de alto voltaje en la carcasa del controlador. La barrera debe
Daño potencial al instrumento. Los delicados componentes
electrónicos internos pueden sufrir daños debido a la electricidad
estática, lo que acarrea una disminución del rendimiento del
instrumento y posibles fallos.
A V I S O
La tarjeta de red Profibus es compatible con la comunicación RS485. El
bloque de
terminales J1 proporciona la conexión del usuario con la tarjeta
de red Profibus. Para obtener más información sobre el cableado,
consulte la Installation Profibus y los siguientes pasos para instalar la
tarjeta de red Profibus.
Tabla 1 Cableado del Profibus con RS485
Conector Número de
patillas del
bloque del
conector
J1 1 A1 (entrada) verde Entrada de la tarjeta de
2 B1 (entrada) rojo Entrada de la tarjeta de
3 OV — —
4 5V — —
5 A2 (salida) verde Salida de la tarjeta de
6 B2 (salida) rojo Salida de la tarjeta de
Señal Color del
cable
Descripción
red
red
red
red
60 Español
Page 61

1 2
3 4
Español 61
Page 62

5 6
7 8
62 Español
Page 63

Configuración de la red
P E L I G R O
Peligro de electrocución. Desconecte siempre la alimentación del
instrumento antes de hacer conexiones eléctricas.
La tarjeta de red Profibus brinda una interfaz para la conexión del RS485.
Antes de utilizarse, la tarjeta de red se debe configurar para la ubicación
en la red. Utilice los ajustes del conmutador situado en la parte superior
de la
tarjeta de red para la configuración (consulte la sección Instalación).
1. Interruptor de la terminación: OFF (apagado). Ponga el interruptor en
esta posición en caso que éste no sea el último esclavo de la barra
colectora.
2. Interruptor de la terminación: ON (encendido - posición en "T"). Ponga
el interruptor en esta posición en caso que éste sea el último o el único
esclavo de la barra colectora.
Operación
Desplazamiento del usuario
Consulte la documentación del controlador para ver la descripción del
teclado e información sobre cómo desplazarse.
Configuración de la red
Al instalar la tarjeta de red Profibus, el controlador requiere la
configuración correcta del dispositivo y el correcto orden de los datos.
Nota: Consulte la documentación del controlador para ver la descripción del teclado,
información básica sobre el desplazamiento y la configuración del controlador.
1. Seleccione la opción Montar red en el menú de configuración.
2. Seleccione, ingrese o cambie los valores y pulse la tecla ENTER.
Opción Descripción
Telegrama Gestiona la estructura de datos del Telegrama. Configuración
Profibus DP Selecciona una de las siguientes opciones:
automática: El Telegrama se configura de forma automática
con 16 bytes de datos de cada sensor y el controlador. En la
configuración automática,
Telegrama e iniciar una configuración automática nueva.
Configuración manual: El Telegrama se configura de forma
manual. Se pueden seleccionar los dispositivos y las etiquetas
de datos de dispositivos incluidas en el Telegrama.
• View configuration (Ver configuración): Se visualiza la
configuración actual de datos del Telegrama
• Start Auto config (Iniciar configuración automática):
Inicia un proceso nuevo de configuración automática que
puede requerir algunos cambios en la configuración del
sensor
• Add/Remove devices (Añadir/quitar dispositivos):
Selecciona los dispositivos incluidos en el Telegrama
• Add/remove tags (Añadir/quitar etiquetas): Selecciona
las etiquetas de datos del telegrama para cada dispositivo
• Setup telegram mode (Establecer modo de telegrama):
Selecciona la configuración automática (predeterminada) o
el modo de configuración manual.
Dirección: cambia la dirección esclava
Orden de los datos: configura la secuencia de bytes al
transmitir valores de coma flotante. Un valor de coma flotante
consiste de 4 bytes.
• Normal = Byte más significativo primero de IEEE punto
flotante (configuración predeterminada): los pares no se
intercambian. Este modo se ajusta a todos los sistemas
maestros Profibus conocidos.
• Intercambiados = Palabra de IEEE punto flotante
intercambiada de manera acertada: intercambia el primer
par de bytes con el último.
se puede visualizar la estructura del
Español 63
Page 64

Opción Descripción
Simulación Simulación: simula
para sustituir un instrumento real. Seleccione las siguientes
opciones y utilice las flechas para introducir los valores o utilice
la configuración predeterminada:
• Simulación: activa o desactiva la simulación.
Sí: inicia la simulación
No: detiene la simulación (configuración predeterminada)
• Período: configura el tiempo que el primer valor de coma
flotante necesita para desplazarse a través del rango
completo entre MÍNIMO y MÁXIMO (configuración
predeterminada: 2 min)
• Máximo: configura el límite superior para el primer valor de
coma flotante.(configuración predeterminada: 20,0)
• Mínimo: configura el límite inferior para el primer valor de
coma flotante (configuración predeterminada: 10,0)
• Error: el valor ingresado en este menú se configurará en la
primera etiqueta simulada (configuración predeterminada:
16).
• Estado: el valor ingresado en este menú se configurará en
la segunda etiqueta simulada (configuración
predeterminada: 5).
• Conmutador: Cambia la dirección de la rampa simulada.
• Prueba/mant:
Habilitado: configura el bit PRUEBA/MANT (0x0004) de
todos los registros de estado de todos los esclavos
configurados en el telegrama de Profibus para indicar el
modo "Servicio".
Deshabilitado: Modo de operación normal (configuración
predeterminada)
Versión Versión de software de la tarjeta de red Profibus.
dos valores de coma flotante y error/estado
Opción Descripción
Lugar Edita el nombre del lugar.
Estado Estado: indica el estado de la tarjeta de red Profibus
• Espere: aparece
encuentre todos los esclavos configurados y aparece
cuando la tarjeta tiene una nueva configuración y está
buscando las conexiones del sensor
• Error config PLC: aparece cuando la tarjeta de red recibe
una configuración errónea de un PLC (controlador lógico
programable). Controle el archivo GSD.
• Listo: aparece cuando la tarjeta de red está lista para enviar
datos al Profibus. Controle la dirección y/o el cableado.
• En línea: aparece cuando la tarjeta de red está en contacto
con el PLC y se envían datos cíclicos
hasta el momento en que la tarjeta de red
Disposición del dispositivo
La disposición
del dispositivo en el telegrama Profibus es inalterable. Los
sensores que se instalaron en primer y en segundo lugar están siempre
en las posiciones uno y dos y el controlador en la posición tres.
Cuando no se instale ningún sensor, el controlador permanecerá en la
posición tres. Las posiciones de los sensores no instalados se
completarán con 0xFF.
En caso que se conecten dos sensores (máximo permitido) y se escaneen
al mismo tiempo, el orden de instalación se basará en el lugar donde se
conecte el sensor (o el módulo del sensor). El orden es el siguiente:
• El conector superior de la tarjeta analógica.
• El conector inferior de la tarjeta analógica.
• El conector digital izquierdo del sensor.
• El conector digital derecho del sensor.
64 Español
Estructura de datos estándar (Configuración automática)
Al seleccionar la configuración automática (predeterminada), la tarjeta de
red Profibus proporciona un telegrama de datos predefinido para cada
dispositivo conectado. El telegrama contiene datos importantes sobre el
dispositivo.
Page 65

La estructura del bloque de datos de los mensajes de Profibus se
encuentra estandarizada
para todos los tipos de sonda. Para la estructura
del bloque de datos, consulte la Profibus data telegram register.
Al seleccionar la configuración manual, el usuario puede configurar la
estructura de datos del telegrama (consulte Configuración de la red
en la página 63).
Tabla 2 Estructura del telegrama de datos de Profibus
Nº de byte Dato Tipo de dato
1-2 Error clasificado Entero (2 bytes)
3-4 Estado clasificado Entero (2 bytes)
5-8 Medición 1 Flotante (4 bytes)
9-12 Medición 2 Flotante (4 bytes)
13-16 Medición 3 Flotante (4 bytes)
Valores en pantalla
La estructura de bloques de datos de Profibus (Profibus message data
block structure) puede reemplazar a las sondas sc sin cambiar la
configuración del controlador lógico programable.
El valor principal siempre es el valor de la medición.
En caso de no disponer de un valor secundario, completar con cero.
En caso de no disponer de un valor terciario, completar con cero.
Figura 2 Estructura de bloques de datos de mensaje de Profibus
Bloque del controlador de datos del proceso
El bloque de datos del controlador sc es similar al de los sensores. La
estructura del bloque de datos del controlador sc es independiente de la
cantidad de sensores conectados:
•
sc controller_ERROR
sc controller_STATUS
•
• Valor principal
• Valor secundario
• Valor terciario
La Block 3 sc controller ERROR y la Block 3 sc controller STATUS
muestran las definiciones de los datos de error y estado 1 en el controlador
sc.
Español 65
Page 66

Tabla 3 Errores del bloque 3 del controlador sc
Bit Error Nota
0 Error de comunicación del
sensor 1
1 Error de comunicación del
sensor 2
2–15 No se usa
Se produjo un error de comunicación entre
el controlador
el sensor no esté conectado.
Se produjo un error de comunicación entre
el controlador sc y el sensor 2, es posible que
el sensor no esté conectado.
sc y el sensor 1, es posible que
Tabla 4 ESTADO del bloque 3 del controlador sc
Bit Estado 1 Nota
0 Sensor 1 instalado Se instaló el primer sensor en el controlador sc. Este
1 Sensor 2 instalado Se instaló el segundo sensor en el controlador sc.
2 Relé A encendido
3 Relé B encendido
4 Relé C encendido
5 Relé D encendido
6–15 No se usa
bit se configura incluso cuando el sensor no esté
conectado después de la instalación.
Este bit
se configura incluso cuando el sensor no esté
conectado después de la instalación.
Definición de la coma flotante IEEE 745
Profibus utiliza una definición de coma flotante IEEE de precisión simple
de 32 bits. La definición tiene veintitrés bits para la mantisa y ocho bits
para el exponente. Hay un bit para el signo de la mantisa. Consulte la
Floating point definition.
Figura 3 Definición de la coma flotante
1 Bit de signo 4 Exponente
2 Exponente 5 Mantisa
3 Mantisa
Valores del controlador sc
La siguiente
lista muestra las definiciones de los datos para el controlador
sc:
• El valor primario del controlador sc muestra el resultado de un cálculo.
• El valor secundario muestra la salida de 0–20 mA o 4–20 mA del Canal
1.
• El valor terciario muestra la salida de 0–20 mA o 4–20 mA del Canal 2.
66 Español
Page 67

Intercambio acertado de palabras
Byte order inside Profibus telegram muestra las secuencias de bytes
normales e intercambiadas. En el intercambio acertado de palabras, el
cuarto y quinto byte intercambian el orden con el primero y el segundo.
Esto da por resultado un orden de bytes de 3 4 1 2.
Tabla 5 Orden de los bytes dentro del telegrama de Profibus
Controlador sc intercambiado Controlador sc normal
Valor del Byte T1 0 x 91 Valor del Byte T1 0 x 3F
Valor del Byte T2 0 x B9 Valor del Byte T2 0 x 67
Valor del Byte T3 0 x 3F Valor del Byte T3 0 x 91
Valor del Byte T4 0 x 67 Valor del Byte T4 0 x B9
Solución de problemas
A D V E R T E N C I A
Peligros diversos. No desmonte el instrumento para su mantenimiento o
reparación. Si es necesario limpiar o reparar los componentes internos, póngase
en contacto con el fabricante.
Indicadores de error y estado
Las palabras de error y estado siguen la misma definición estándar para
todos los controladores y sondas sc.
Error messages enumera la posición binaria y los mensajes de error.
Status indicator
estado.
Un valor binario igual a cero muestra el error o la condición del estado que
no es real.
Un valor binario igual a 1 muestra el error o la condición del estado real.
Por ejemplo, si el bit 0 tiene el valor 1, significa que hubo un error durante
la última calibración.
messages enumera la posición binaria y los mensajes de
Tabla 6 Mensajes de error
Bit Mensaje Indicación
0 Error de calibración de
medición
1 Error de ajuste electrónico Se ha producido un error durante la última
2 Error de limpieza Falló el último ciclo de limpieza
3 Error del módulo de
medición
4 Error de reinicialización del
sistema
5 Error de hardware Se ha detectado un error general de hardware
6 Error de comunicación
interna
7 Error de humedad Se ha detectado demasiada humedad dentro
8 Error de temperatura La temperatura dentro del dispositivo excede
9 — —
10 Advertencia de muestra Se necesita alguna acción con el sistema de
11 Advertencia de calibración
cuestionable
12 Advertencia de medición
cuestionable
13 Advertencia de seguridad Se ha detectado una condición que puede
Se ha producido un error durante la última
calibración
calibración electrónica
Se ha detectado un error en el módulo de
medición
Algunas configuraciones son incoherentes y
se han restablecido a las configuraciones
predeterminadas de fábrica
Se ha detectado un error en la comunicación
dentro del dispositivo
del dispositivo
el límite especificado
muestra
Es posible que la última calibración no sea
precisa
Una o más de las mediciones del dispositivo se
encuentran fuera de rango o su precisión es
cuestionable
resultar en un peligro de seguridad
Español 67
Page 68

Tabla 6 Mensajes de error (continúa)
Bit Mensaje Indicación
14 Advertencia de reactivo El sistema de reagentes activos requiere
15 Advertencia de
mantenimiento requerido
atención
El dispositivo requiere mantenimiento
Tabla 7 Mensajes indicadores del estado
Bit Mensaje Indicación
0 Calibración en progreso El dispositivo se encuentra en el modo de
1 Limpieza en progreso El dispositivo se encuentra en el modo de
2 Menú Servicio/
Mantenimiento
3 Error común El dispositivo ha reconocido un error. Consulte
4 Medición 0, mala calidad La precisión de la medición se encuentra fuera
5 Medición 0, límite bajo La medición es inferior al rango especificado.
6 Medición 0, límite alto La medición es superior al rango especificado.
7 Medición 1, mala calidad La precisión de la medición se encuentra fuera
8 Medición 1, límite bajo La medición es inferior al rango especificado.
9 Medición 1, límite alto La medición es superior al rango especificado.
10 Medición 2, mala calidad La precisión de la medición se encuentra fuera
calibración Es posible que las mediciones no
sean válidas
limpieza Es
válidas
El dispositivo se encuentra en el modo de
servicio o mantenimiento Es posible que las
mediciones no sean válidas
el Registro de errores para ver la Clase de
error.
de los límites especificados.
de los límites especificados.
de los límites especificados.
posible que las mediciones no sean
Tabla 7 Mensajes indicadores del estado (continúa)
Bit Mensaje Indicación
11 Medición 2, límite bajo La medición es inferior al rango especificado.
12 Medición 2, límite alto La medición es superior al rango especificado.
13 Medición 3, mala calidad La precisión de la medición se encuentra fuera
14 Medición 3, límite bajo La medición es inferior al rango especificado.
15 Medición 3, límite alto La medición es superior al rango especificado.
de los límites especificados.
Registro de eventos
Consulte la Event
Log para ver información del dispositivo de diagnóstico.
Tabla 8 Registro de eventos
Evento Descripción
DIRECCIÓN Dirección de Profibus ajustada
ORDEN DE DATOS Indica el orden de los datos de dos variables de palabras
SIMULACIÓN Indica si los datos simulados se configuraron dentro del
ENER DEL SENSOR Encendido instantáneo de la tarjeta Profibus
FECHA/HORA Punto en la configuración del tiempo del temporizador
CONFIG NUEVA Punto en el tiempo para una configuración nueva
CONFIG AUTO Punto en el tiempo para una configuración nueva del menú
VERSIÓN CÓDIGO Punto en el tiempo para una nueva descarga del software
en el telegrama cíclico y acíclico de Profibus
telegrama cíclico de Profibus.
interno de la tarjeta Profibus
(versión de Software)
68 Español
Page 69

Piezas de repuesto y accesorios
Tarjetas de red y accesorios para comunicaciones
Descripción Nº de artículo
Kit Profibus DP 9173900
Kit de conectores Profibus M12 9178500
Descripción Nº de artículo
Tomacorriente Profibus M12 9178200
Clavija Profibus M12 T 9178400
Los números de producto y artículo pueden variar para algunas regiones
de venta.
Comuníquese con el distribuidor correspondiente o visite el sitio
Web de la compañía para obtener la información de contacto.
Español 69
Page 70

Ejemplo Simatic
Al importar HALA09AC.GSD, el esclavo se ubicará en PROFIBUS DP, DISPOSITIVOS DE CAMPO ADICIONALES, GENERAL.
1. Seleccione 2 palabras de la tarjeta de red esclava.
Cada uno de los módulos es equivalente a 4 bytes de la escala de dirección de entrada.
Figura 4 Ejemplo Simatic
70 Español
Page 71

Lectura de datos
Para la secuencia habitual de los datos, utilice L PED en la dirección de
inicio del módulo para leer un objeto de coma flotante. No es necesario
realizar ninguna otra conversión.
Nota: PEW/PED
IEC o inglés.
1. Lea las palabras de ERROR o de ESTADO.
2. Utilice la instrucción L PEW.
el código nemónico alemán o de SIMATIC. Utilice PIW/PID para
es
Español 71
Page 72

Especificações
As especificações podem ser alteradas sem aviso prévio.
Especificação Detalhes
Protocolo Profibus Siemens ASIC SPC3
Serviço DP Slave DPV0
Serviços DP/DPV1 Slave DPV1 classe 1 e classe 2
Função I&M
O endereço muda conforme o master Profibus
Taxas baud do Profibus 9.6k, 19.2k, 45.45k, 93.75k, 187.5k, 500k, 1.5M,
Indicadores LED para visualizar o modo de intercâmbio de
Tipo de interface RS485
Parâmetros configuráveis Troca de dados, a nível das palavras para
Dimensões (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Temperatura de funcionamento –20° C a 85 °C
Tensão de funcionamento 8V–16V
Consumo de energia máximo 2W
Certificação Classe I, Divisão 2 grupos A, B, C, D e Classe I,
3M, 6M, 12M
Detecção da taxa baud automática
dados
valores de pontos flutuantes
Zona 2
grupp IIC, T4 locias perigosos e normais
Informação geral
Em caso algum o fabricante será responsável por quaisquer danos
directos, indirectos, especiais, acidentais ou consequenciais resultantes
de qualquer
-se o direito de, a qualquer altura, efectuar alterações neste manual ou no
incorrecção ou omissão deste manual. O fabricante reserva-
produto nele descrito, sem necessidade de o comunicar ou quaisquer
outras obrigações. As edições revistas encontram-se disponíveis no
website do fabricante.
Informações de segurança
Por favor,
ler o manual na sua totalidade antes de desembalar, configurar,
ou operar este equipamento. Preste atenção ao todas as indicações de
perigo e cuidado. Caso as ignore poderá resultar em lesões ao operador
ou em danos no equipamento.
Certifique-se que a protecção fornecida por este equipamento não é
prejudicada, não utilize ou instale o mesmo de maneira diferente daquela
especificada neste manual.
Significado da Informação de Risco
P E R I G O
Indica uma situação de risco potencial ou eminente que, se não for evitada,
resultará em morte ou lesão grave.
A D V E R T Ê N C I A
Indica uma situação de perigo potencial ou eminente que, caso não seja evitada,
poderá resultar na morte ou em ferimentos graves.
Indica uma situação de risco potencial, que pode resultar em lesão ligeira a
moderada.
Indica uma situação que, caso não seja evitada, poderá causar danos no
instrumento. Informação que requer ênfase especial.
A V I S O
A T E N Ç Ã O
Avisos de precaução
Leia todas as etiquetas presentes no aparelho. A sua não observação
pode resultar em lesões para as pessoas ou em danos para o aparelho.
Qualquer
afixado no aparelho poderá ser encontrado no manual
símbolo
com a respectiva indicação de perigo ou precaução .
72 Português
Page 73

Quando encontrar este símbolo no instrumento, isto significa que
deverá consultar
o funcionamento do instrumento e/ou de segurança.
Este símbolo indica que existe um risco de choque eléctrico e/ou
electrocussão.
Este símbolo indica a presença de dispositivos sensíveis à Descarga
Electrostática (ESD) e que é necessário ter cuidado de modo a evitar
danificar o equipamento.
Desde 12 de Agosto de 2005, os equipamentos eléctricos marcados
com este símbolo não poderão ser depositados nos sistemas
europeus públicos de recolha de resíduos. Em conformidade com a
legislação europeia e nacional (Directiva europeia 2002/98/EC), os
utilizadores europeus de equipamento eléctrico deverão devolver os
equipamentos usados
à sua eliminação sem quaisquer custos para o utilizador.
o manual de instruções para obter informações sobre
ou em fim de vida ao Fabricante, que procederá
Figura 1 Visão geral do sistema
1 Controlador sc (slave) 3 PC com software (master classe 2,
2 Controlador lógico programável
(master classe 1)
ex.: PC com placa CP5611)
Vista geral do produto
Os controladores sc são a plataforma para todas as sondas e analisadores
inteligentes. A plataforma sc é um sistema de comunicação digital
completo baseado no padrão Modbus aberto. Quando existe uma placa
de interface Profibus instalada, os controladores sc disponibilizam a gama
completa de parâmetros e valores de métodos padronizados.
Os controladores sc são dispositivos Profibus DP/V1 com certificação
PNO/PTO. Estes dispositivos são compatíveis com os sistemas master
de classe 1 (PLC SCADA) e master de classe 2, como por exemplo,
estações de engenharia.
A System overview apresenta uma visão geral do sistema. O Profibus está
disponível como item fornecido de fábrica ou instalado pelo utilizador.
Instalação
A V I S O
Perigo de danos pessoais. As tarefas descritas neste capítulo do manual devem
ser efectuadas apenas por pessoal qualificado.
Instalar o módulo no controlador
Perigo de explosão. Para instalar o módulo em locais considerados perigosos,
consulte as instruções de segurança no manual do utilizador do controlador.
Perigo de electrocussão. Retire sempre a potência do instrumento
antes de efectuar quaisquer ligações eléctricas.
P E R I G O
P E R I G O
Português 73
Page 74

P E R I G O
Perigo de electrocussão. A ligação de fios de alta voltagem para o controlador é
conduzida atrás da barreira de alta voltagem na embalagem do controlador. A
barreira deve permanecer no local excepto quando instalar módulos, ou quando
um técnico
rede ou analógicos.
de instalação qualificado estiver a ligar a potência, relés ou cartões de
Danos no instrumento potencial. Os componentes electrónicos
internos delicados podem ser danificados através da electricidade
estática, provocando
A T E N Ç Ã O
um desempenho reduzido ou uma eventual falha.
A placa de rede Profibus suporta comunicações RS485. O bloco terminal
J1 fornece ao utilizador a ligação à placa de rede Profibus. Para
informações mais
detalhadas, consulte a Installation Profibus e os passos
seguintes para instalar a placa de rede Profibus.
Tabela 1 Ligação de fios do Profibus com RS485
Conector Número de
pinos do
bloco
conector
J1 1 A1 (entrada) verde Entrada a partir da
2 B1 (entrada) vermelho Entrada a partir da
3 OV — —
4 5V — —
5 A2 (saída) verde Saída a partir da
6 B2 (saída) vermelho Saída a partir da
Sinal Côr do cabo Descrição
placa de rede
placa de rede
placa de rede
placa de rede
74 Português
Page 75

1 2
3 4
Português 75
Page 76

5 6
7 8
76 Português
Page 77

Configurar a rede
P E R I G O
Perigo de electrocussão. Retire sempre a potência do instrumento
antes de efectuar quaisquer ligações eléctricas.
A placa de rede Profibus fornece uma interface para a ligação RS485.
Antes da utilização, a placa de rede tem de ser configurada para a
localização na
rede. Use as definições do interruptor na parte superior da
placa de rede para a configuração (consulte a secção Instalação).
1. Botão de terminação–Terminação desligada. Coloque o botão nesta
posição se este não for o último dispositivo slave no bus.
2. Botão de terminação–Terminação ligada (posição "T"). Coloque o
botão nesta posição se este for o último ou o único dispositivo slave
no bus.
Funcionamento
Navegação do utilizador
Consulte a documentação do controlador para obter uma descrição do
teclado e informações de navegação.
Instalar a rede
Quando a placa de rede Profibus é instalada, o controlador requer a
configuração correcta do dispositivo e da ordem de dados.
Nota: Consulte a documentação do controlador para obter uma descrição do
teclado, informações de navegação básicas e de configuração do controlador.
1. Seleccione Configuração da rede no menu Definições.
2. Seleccione, introduza
ou altere os valores e depois carregue na tecla
ENTER.
Opção Descrição
Telegrama Efectua a gestão da Estrutura de dados do telegrama. Auto
Profibus DP Seleccione uma das seguintes opções:
configuration (Configuração automática): o Telegrama é
configurado automaticamente
sensor e do controlador. Na Configuração automática, é
possível visualizar a estrutura de Telegrama e pode ser iniciada
uma nova configuração automática. Manual configuration
(Configuração manual): o telegrama é configurado
manualmente. Os dispositivos e as etiquetas de dados do
dispositivo incluidas no telegrama podem ser seleccionados.
• View configuration (Ver configuração)— vizualização da
configuração de dados actual do telegrama
• Start Auto config (Iniciar configuração automática)—
inicia um novo processo de configuração que pode
necessitar de algumas alterações de configuração do
sensor
• Add/Remove devices (Adicionar/remover dispositivos)
— selecciona os dispositivos incluidos no telegrama
• Add/remove tags (Adicionar/remover etiquetas)—
selecciona etiquetas de dados de telegrama para cada
dispositivo
• Setup telegram mode (Configuração do modo de
telegrama)— selecciona a configuração automática
(padrão) ou o modo de configura~çao manual.
Endereço— altera o endereço do slave
Ordem dados— define a sequência de bytes durante a
transmissão de valores de pontos flutuantes. Um valor de ponto
flutuante consiste de 4 bytes.
• Normal = Big Endian flutuante IEEE (predefinição)—os
pares não são trocados. Este modo ajusta-se a todos os
sistemas master Profibus.
• Trocado = troca a nível da palavra de flutuante IEEE: troca
o primeiro par de bytes pelo último par.
com 16 bytes de dados de cada
Português 77
Page 78

Opção Descrição
Simulação Simulação— simula dois valores de pontos flutuantes e erro/
Versão Versão do software da placa de rede Profibus.
estado para substituir um instrumento real. Seleccione as
opções seguintes e use as setas para introduzir os valores ou
use a predefinição:
• Simulação: activa ou desactiva a simulação.
Sim: inicia uma simulação
Não: pára uma simulação (predefinição)
• Período: define a altura em que o primeiro valor do ponto
flutuante precisa de passar pelo intervalo completo entre
MÍNIMO e MÁXIMO—2 min (predefinição)
• Máximo: define
flutuante.—20,0 (predefinição)
• Mínimo: define o limite inferior do primeiro valor do ponto
flutuante—10,0 (predefinição)
• Erro: o valor introduzido neste menu será definido na
primeira etiqueta simulada—16 (predefinição)
• Estado: o valor introduzido neste menu será definido na
segunda etiqueta simulada—5 (predefinição)
• Toggle (Alternar): muda a direcção da rampa simulada.
• Teste/manut:
Habilitado: define o bit TESTE/MANUT (0x0004) de cada
registo de estado de cada slave configurado no telegrama
Profibus cíclico para indicar o modo “Serviço”.
Desabilitado: modo de funcionamento normal (predefinição)
o limite superior do primeiro valor do ponto
Opção Descrição
Localização Edita o nome da localização.
Estado Estado— Indica o estado da placa de rede Profibus
• Aguarde: é apresentado até que a placa de rede tenha
encontrado todos os slaves configurados ou aparece
quando a placa é configurada novamente e está a procurar
as ligações do sensor
• PLC configure err (Erro config. PLC): é apresentado
quando a
um PLC (controlador lógico programável). Verifique o
ficheiro GSD.
• Ready (Pronta): é apresentado quando a placa de rede está
pronta para enviar dados para o Profibus. Verifique o
endereço e/ou os fios.
• Online: é apresentado quando a placa de rede está em
contacto com o PLC e são enviados Dados cíclicos
placa de rede recebe uma configuração errada de
Ordem dos dispositivos
A ordem dos dispositivos no telegrama Profibus é fixa. O primeiro e o
segundo sensores instalados estão sempre na posição um e dois e o
controlador encontra-se na posição três.
houver um sensor instalado, o controlador permanece na posição
Se não
três. As posições dos sensores desinstalados são preenchidas com 0xFF.
Se forem ligados e digitalizados dois sensores (máximo permitido) em
simultâneo, a ordem de instalação basear-se-á na localização onde o
sensor (ou módulo do sensor) está ligado. A ordem é a seguinte:
• O conector da placa analógica superior.
• O conector da placa analógica inferior.
• O conector do sensor digital da esquerda.
• O conector do sensor digital da direita.
78 Português
Estrutura de dados padrão (Configuração automática)
Quando está seleccionada a configuração automática (padrão), a placa
de rede do Profibus fornece um telegrama de dados predefinido para cada
Page 79

dispositivo conectado. O telegrama contém dados importantes acerca do
dispositivo.
A estrutura de bloco de dados das mensagens Profibus é padronizada
para todos os tipos de sondas. Para a estrutura de bloco de dados,
consulte Profibus data telegram register.
Quando está seleccionada a configuração manual, a estrutura de dados
do telegrama pode ser configurada pelo utilizador (consultarInstalar a
rede na página 77).
Tabela 2 Estrutura do telegrama de dados Profibus
Número de bytes Dados Tipo de dados
1–2 Erro classificado Inteiro (2 bytes)
3–4 Estado classificado Inteiro (2 bytes)
5–8 Medição 1 Flutuante (4 bytes)
9–12 Medição 2 Flutuante (4 bytes)
13–16 Medição 3 Flutuante (4 bytes)
Visualizar os valores
A estrutura de bloco de dados Profibus (Profibus message data block
structure) pode substituir as sondas sc sem alterações na configuração
PLC.
O valor primário é sempre o valor medido.
O valor secundário, se não estiver disponível, é preenchido com zero.
O valor terciário, se não estiver disponível, é preenchido com zero.
Figura 2 Estrutura de bloco de dados de mensagens Profibus
Processar bloco do controlador de dados
O
de dados do controlador sc é semelhante ao bloco de dados dos
bloco
sensores. A estrutura do bloco de dados do controlador sc é independente
do número de sensores ligados:
• sc controller_ERROR
• sc controller_STATUS
• Valor primário
• Valor secundário
• Valor terciário
A Block 3 sc controller ERROR e a Block 3 sc controller STATUS mostram
as definições de dados para o erro e estado 1 no controlador sc.
Português 79
Page 80

Tabela 3 Controlador sc do bloco 3 - ERRO
Bit Erro Nota
0 Erro de comunicação do
sensor 1
1 Erro de comunicação do
sensor 2
2–15 Não utilizado
Ocorreu um erro de comunicação entre o
controlador sc e o sensor 1; o sensor pode
estar desligado.
Ocorreu um erro de comunicação entre o
controlador sc e o sensor 2; o sensor pode
estar desligado.
Tabela 4 Controlador sc do bloco 3 - STATUS
Bit Status1 Nota
0 Sensor 1 instalado O primeiro sensor foi instalado no controlador sc. Este
1 Sensor 2 instalado O segundo sensor foi instalado no controlador sc.
2 Relé A activo
3 Relé B activo
4 Relé C activo
5 Relé D activo
6–15 Não utilizado
bit é definido mesmo se o sensor for desligado após
a instalação.
Este bit é definido mesmo se o sensor for desligado
após a instalação.
Valores do controlador sc
A seguinte lista mostra as definições de dados do controlador sc:
• O valor primário do controlador sc mostra o resultado de um cálculo.
O valor secundário do controlador sc mostra a saída de 0–20 mA ou 4–
•
20 mA do Canal 1.
• O valor terciário do controlador sc mostra a saída de 0–20 mA ou 4–20
mA do Canal 2.
Definição de ponto flututante IEEE 745
O Profibus utiliza a definição de ponto flutuante IEEE de precisão única
(32 bits). A definição tem 23 bits para a mantissa e 8 bits para o expoente.
Existe 1 bit para o sinal da mantissa. Consulte o Floating point definition.
Figura 3 Definição de ponto flutuante
1 Bit de sinal 4 Expoente
2 Expoente 5 Mantissa
3 Mantissa
80 Português
Page 81

Troca a nível das palavras
A Byte order inside Profibus telegram mostra as sequências de bytes
normais e trocadas. Na troca a nível das palavras, o terceiro e o quarto
bytes são intercambiados pelo primeiro e segundo bytes. Isto resulta
numa ordem de bytes de 3 4 1 2.
Tabela 5 Ordem de bytes dentro do telegrama Profibus
controlador sc trocado controlador sc normal
Byte T1 valor 0 x 91 Byte T1 valor 0 x 3F
Byte T2 valor 0 x B9 Byte T2 valor 0 x 67
Byte T3 valor 0 x 3F Byte T3 valor 0 x 91
Byte T4 valor 0 x 67 Byte T4 valor 0 x B9
Resolução de problemas
A D V E R T Ê N C I A
Vários perigos. Não desmonte o instrumento para proceder à manutenção ou
reparação. Se
o fabricante.
Indicadores de erro e de estado
As palavras
os controladores e sondas sc.
A Error messages lista as mensagens de erro e a posição dos bits. A
Status indicator messages lista as mensagens de estado e a posição dos
bits.
Um valor de bit de zero mostra a condição de erro ou estado não
verdadeira.
Um valor de bit de 1 mostra a condição de erro ou estado verdadeira. Por
exemplo, se Bit 0 tiver o valor de 1, ocorreu um erro durante a última
calibração.
for necessário limpar ou reparar os componentes internos, contacte
de erro e estado seguem a mesma definição padrão de todos
Tabela 6 Mensagens de erro
Bit Mensagem Indicação
0 Measurement calibration error
(Erro de calibração da medição)
1 Electronic adjustment error (Erro
de ajuste electrónico)
2 Cleaning error (Erro na limpeza) O último ciclo de limpeza falhou.
3 Measuring module error (Erro no
módulo de medição)
4 System re-initialization error (Erro
na reinicialização do sistema)
5 Hardware error (Erro de hardware) Foi detectado um erro de hardware
6 Internal communication error (Erro
de comunicação interna)
7 Humidity error (Erro de humidade) Foi detectada humidade excessiva no
8 Temperature error (Erro de
temperatura)
9 — —
10 Sample warning (Aviso de
amostra)
11 Questionable calibration warning
(Aviso de calibração questionável)
12 Questionable measurement
warning (Aviso de medição
questionável)
13 Safety warning (Aviso de
segurança)
Ocorreu um erro durante a última
calibração.
Ocorreu um erro durante a última
calibração electrónica.
Foi detectada uma falha no Módulo de
Medição.
Algumas definições são inconsistentes
e foram repostas com os valores
predefinidos de fábrica.
geral.
Foi detectada uma falha de
comunicação no dispositivo.
dispositivo
A temperatura do dispositivo excede
um limite especificado.
É necessária alguma acção no sistema
de amostras.
A última calibração pode não ser
precisa.
Uma ou mais das medições do
dispositivo estão
de precisão questionável
Foi detectada uma condição que pode
resultar num risco de segurança.
fora do alcance ou são
Português 81
Page 82

Tabela 6 Mensagens de erro (continuação)
Bit Mensagem Indicação
14 Reagent warning (Aviso de
reagente)
15 Maintenance required warning
(Aviso de manutenção necessária)
O sistema de reagentes requer
atenção.
O dispositivo requer manutenção.
Tabela 7 Mensagens do indicador de estado
Bit Mensagem Indicação
0 Calibration in progress (Calibração
em curso)
1 Cleaning in progress (Limpeza em
curso)
2 Service/Maintenance menu (Menu
de assistência/manutenção)
3 Common error (Erro comum) O dispositivo reconheceu um erro. Ver
4 Measurement 0 Quality Bad
(Medição 0 Má qualidade)
5 Measurement 0 Low Limit
(Medição 0 Limite baixo)
6 Measurement 0 High Limit
(Medição 0 Limite elevado)
7 Measurement 1 Quality Bad
(Medição 1 Má qualidade)
8 Measurement 1 Low Limit
(Medição 1 Limite baixo)
O dispositivo está num modo de
calibração. As
válidas.
O dispositivo está num modo de
limpeza. As medições podem não ser
válidas.
O dispositivo está num modo de
assistência ou manutenção. As
medições podem não ser válidas.
o Registo de erros para informações
sobre a Classe do erro.
A precisão da medição está fora dos
limites especificados.
A medição é inferior ao intervalo
especificado.
A medição é superior ao intervalo
especificado.
A precisão da medição está fora dos
limites especificados.
A medição é inferior ao intervalo
especificado.
medições podem não ser
Tabela 7 Mensagens do indicador de estado (continuação)
Bit Mensagem Indicação
9 Measurement 1 High Limit
(Medição 1 Limite elevado)
10 Measurement 2 Quality Bad
(Medição 2 Má qualidade)
11 Measurement 2 Low Limit
(Medição 2 Limite baixo)
12 Measurement 2 High Limit
(Medição 2 Limite elevado)
13 Measurement 3 Quality Bad
(Medição 3 Má qualidade)
14 Measurement 3 Low Limit
(Medição 3 Limite baixo)
15 Measurement 3 High Limit
(Medição 3 Limite elevado)
A medição é superior ao intervalo
especificado.
A precisão da medição está fora dos
limites especificados.
A medição é inferior ao intervalo
especificado.
A medição é superior ao intervalo
especificado.
A precisão da medição está fora dos
limites especificados.
A medição é inferior ao intervalo
especificado.
A medição é superior ao intervalo
especificado.
Registo de eventos
Consulte a Event Log para obter informações de diagnóstico do
dispositivo.
Tabela 8 Registo de eventos
Evento Descrição
ADDRESS (Endereço) Endereço Profibus ajustado
ORDEM DADOS Indica a ordem dos dados de variáveis de 2
SIMULAÇÃO Indica se os dados simulados estão configurados
ALIM SENSOR Ligação imediata da placa Profibus
CFG DATA/HORA Configuração programada do temporizador interno
palavras no telegrama Profibus cíclico e acíclico
no telegrama Profibus cíclico
da placa Profibus
82 Português
Page 83

Tabela 8 Registo de eventos (continuação)
Evento Descrição
NEW CONFIG (Nova
configuração)
CFG AUTOMÁTICA Ponto temporal de uma nova definição do menu
VERSÃO DO CÓDIGO Ponto temporal de uma nova transferência de
Ponto temporal de uma nova configuração
software (versão do software)
Acessórios e peças de substituição
Placas de rede de comunicações e acessórios
Descrição Número do item
Kit Profibus DP 9173900
Kit de conectores Profibus M12 9178500
Descrição Número do item
Tomada Profibus M12 9178200
Ficha T Profibus M12 9178400
Os números de Produtos e Artigos podem variar em algumas regiões
comerciais. Contacte o distribuidor apropriado ou consulte o website da
empresa para obter informações de contacto.
Português 83
Page 84

Exemplo de Simatic
Quando o HALA09AC.GSD é importado, o dispositivo slave encontrar-se-á em PROFIBUS DP, ADDITIONAL FIELD DEVICES, GENERAL (Profibus
DP, Dispositivos de campo adicionais, Geral).
1. Seleccione a placa de rede 2 Words from Slave.
Cada módulo é 4 bytes do intervalo de endereços de entrada.
Figura 4 Exemplo de Simatic
84 Português
Page 85

Ler os dados
Para uma sequência de dados normal, utilize L PED no endereço inicial
do módulo para ler um objecto de ponto flutuante. Não há necessidade
de fazer outras conversões.
Nota: PEW/PED é o código mnemónico alemão ou SIMATIC. Use PIW/PID para o
idioma inglês ou IEC.
1. Leia as palavras ERROR (Erro) ou STATUS (Estado).
2. Use a instrução L PEW.
Português 85
Page 86

Technické údaje
Technické údaje podléhají změnám bez předchozího upozornění.
Technické parametry Podrobnosti
Protokol Profibus Siemens ASIC SPC3
Služba DP DPV0 slave
Služby DP/DPV1 DPV1 třída 1 a třída 2 slave
Funkce I&M
Změna adresy podle zařízení Profibus master
Přenosové rychlosti sběrnice
Profibus (v baudech)
Indikátory LED k zobrazení režimu výměny dat
Typ rozhraní RS485
Konfigurovatelné parametry Záměna hodnot word v hodnotách s pohyblivou
Rozměry (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Provozní teplota -20 až 85 °C (-4 až 185 °F)
Provozní napětí 8 – 16 V
Maximální příkon 2 W
Certifikace Třída I, Část 2 skupina A, B, C, D a Třída I, zóna
9,6k, 19,2k, 45,45k, 93,75k, 187,5k, 500k,
1,5M, 3M, 6M, 12M
Automatická detekce přenosové rychlosti
řádovou čárkou
2 skupina IIC, T4 riziková a běžná umístění
Obecné informace
Výrobce není v žádném případě zodpovědný za nepřímé, zvláštní,
náhodné či následné škody, které jsou výsledkem jakékoli chyby nebo
opomenutí v této příručce. Výrobce si vyhrazuje právo provádět v této
příručce a výrobcích v ní popisovaných změny, a to kdykoliv, bez
předchozích oznámení či jakýchkoli následných závazků. Revidovaná
vydání jsou dostupná na internetových stránkách výrobce.
Bezpečnostní informace
Před vybalením, montáží a uvedením přístroje do provozu si prosím
pozorně přečtěte celý tento návod. Zvláštní pozornost věnujte všem
upozorněním na
možná nebezpečí a výstražným informacím. V opačném
případě může dojít k vážným poraněním obsluhy a poškození přístroje.
Zajistěte, aby nedošlo k oslabení ochrany poskytované tímto vybavením
a nepoužívejte je způsobem, který by byl v rozporu s pokyny v této
příručce.
Informace o možném nebezpečí
N E B E Z P E Č Í
Označuje možnou nebo bezprostředně rizikovou situaci, jež může v případě, že jí
nezabráníte, vést k usmrcení nebo vážnému zranění.
Upozorňuje na možné nebo skryté nebezpečné situace, jež by bez vhodných
preventivních opatření mohly vést k úmrtí nebo vážnému poranění.
Upozorňuje na možnou nebezpečnou situaci, jež by mohla mít za následek menší
nebo mírné poranění.
U P O Z O R N Ě N Í
Označuje situaci, která může způsobit poškození přístroje, pokud se nezabrání
jejímu vzniku. Upozorňuje na informace vyžadující zvláštní pozornost.
R E A G .
P O Z O R
Výstražné symboly
Věnujte pozornost všem nálepkám a štítkům umístěným na zařízení. V
opačném případě může dojít k poranění osob nebo poškození přístroje.
Symbol, uvedený na přístroji, odkazuje na informaci o nebezpečí nebo
nutnosti zachovávat opatrnost uvedenou v této příručce.
86 Čeština
Page 87

Tento symbol, pokud je uveden na zařízení, odkazuje na provozní a/
nebo bezpečnostní informace uvedené v uživatelské příručce.
Symbol upozorňuje na možnost úrazu nebo usmrcení elektrickým
proudem.
Tento symbol označuje přítomnost součástí citlivých na výboj
elektrostatické elektřiny a upozorňuje na nutnost zvýšené opatrnosti,
aby nedošlo k jejich poškození.
Elektrické zařízení označené tímto symbolem se po 12. srpnu 2005
nesmí likvidovat prostřednictvím evropských systémů veřejného
odpadu. V souladu s evropskými místními a národními předpisy
(Směrnice EU 2002/98/ES) musí evropští uživatelé elektrických
zařízení vrátit
k likvidaci, a to zdarma.
staré zařízení nebo zařízení s prošlou životností výrobci
Obr. 1 Přehled systému
1 Kontrolér sc (slave) 3 Počítač se softwarem (master, třída
2 Jednotka PLC (master, třída 1)
2, např. počítač s kartou CP5611)
Celkový přehled
Kontroléry sc představují platformu pro všechny inteligentní sondy a
analyzátory. Platforma sc je plně digitální komunikační systém založený
na otevřeném standardu Modbus. Po instalaci karty s rozhraním Profibus
poskytují řadiče sc kompletní rozsah hodnot a parametrů pro
standardizované metody.
Kontroléry sc jsou zařízení Profibus DP/V1 s certifikací PNO/PTO. Tato
zařízení jsou kompatibilní se systémy master třídy 1 (PLC SCADA) a
master třídy 2, např. tzv. engineering stations.
Přehled systému znázorňuje System overview. Sběrnice Profibus je
k dispozici instalovaná již ve výrobě nebo uživatelem.
Instalace
P O Z O R
Nebezpečí poranění osob. Práce uvedené v této kapitole smí provádět pouze
dostatečně kvalifikovaný personál.
Instalace modulu k řadiči
Nebezpečí výbuchu. Bezpečnostní pokyny pro instalaci modulu do klasifikovaných
rizikových umístění najdete v uživatelské příručce kontroléru.
Nebezpečí poranění elektrickým proudem. Před jakýmikoli pracemi na
elektrickém zapojení odpojte přístroj od zdroje napájení.
N E B E Z P E Č Í
N E B E Z P E Č Í
Čeština 87
Page 88

N E B E Z P E Č Í
Nebezpečí poranění elektrickým proudem. Vedení vysokého napětí pro napájení
kontroléru je umístěno za vysokonapěťovou zábranou uvnitř skříně kontroléru.
Bariéra musí
napájení, relé či analogových nebo síťových karet kvalifikovaným instalačním
technikem.
zůstat na místě s výjimkou případů instalace modulů nebo vedení pro
U P O Z O R N Ě N Í
Instalujte zařízení v místech a polohách, které umožňují snadný přístup
pro odpojení
může dojít k poškození citlivých vnitřních elektronických součástí a
snížení výkonnosti či selhání.
zařízení a pro jeho obsluhu. Působením statické elektřiny
Síťová karta Profibus podporuje komunikaci podle standardu RS485.
Připojení k síťové kartě uživateli umožňuje konektorový blok J1. Další
podrobnosti k zapojení uvádí Installation Profibus a následující postup
instalace síťové karty Profibus.
Tabulka 1 Zapojení sběrnice Profibus s rozhraním RS485
Konektor Číslo pinu
v konektoru
J1 1 A1 (vstup) zelená Vstup ze síťové karty
2 B1 (vstup) červená Vstup ze síťové karty
3 0 V — —
4 5 V — —
5 A2 (výstup) zelená Výstup ze síťové karty
6 B2 (výstup) červená Výstup ze síťové karty
Signál Barva
kabelu
Charakteristika
88 Čeština
Page 89

1 2
3 4
Čeština 89
Page 90

5 6
7 8
90 Čeština
Page 91

Konfigurace sítě
N E B E Z P E Č Í
Nebezpečí poranění elektrickým proudem. Před jakýmikoli pracemi na
elektrickém zapojení odpojte přístroj od zdroje napájení.
Síťová karta Profibus je vybavena rozhraním pro připojení podle
standardu RS485. Před použitím je třeba kartu nakonfigurovat pro dané
umístění v síti. Ke konfiguraci použijte přepínač na horní straně síťové
karty (další informace naleznete v části Instalace).
1. Zakončovací přepínač
– Zakončení vypnuto. Přepínač nastavte do této
pozice, není-li toto zařízení posledním zařízením slave připojeným na
sběrnici.
2. Zakončovací přepínač – Zakončení zapnuto (poloha „T“). Přepínač
nastavte do této pozice, je-li toto zařízení posledním nebo jediným
zařízením slave připojeným na sběrnici.
Provoz
Navigace uživatele
Další informace o popisu klávesnice a navigaci naleznete v dokumentaci
k řadiči.
Nastavení sítě
Při instalaci síťové karty Profibus vyžaduje kontrolér správnou konfiguraci
zařízení a uspořádání dat.
Poznámka: Popis klávesnice, základní informace k navigaci a nastavení řadiče
naleznete v dokumentaci ke kontroléru.
1. V nabídce Settings (Nastavení) zvolte položku Network setup
(Nastavení sítě).
2. Vyberte, zadejte nebo upravte potřebné hodnoty a stiskněte tlačítko
ENTER.
Volba Charakteristika
Telegram Řídí strukturu dat zprávy. Automatická konfigurace: Zpráva
Profibus DP Nabízí tyto možnosti:
je automaticky konfigurována se 16 byty dat od každého
senzoru kontroléru. Při automatické konfiguraci lze sledovat
strukturu zprávy a může začít nová automatická konfigurace.
Manuální konfigurace: zprávy je konfigurován manuálně.
Značky přístroje a dat přístroje zahrnuté do zprávy mohou být
zvoleny.
• View configuration (Přehled konfigurace)— Přehled
aktuální konfigurace dat zprávy
• Start Auto config (Zahájení automatické konfigurace)—
Zahájí proces nové automatické konfigurace, což bude
možná vyžadovat některé změny nastavení senzoru
• Add/Remove devices
přístroje zahrnuté do zprávy
• Add/remove tags (Přidat/odebrat značky)—Vybere
značky dat zprávy pro každý přístroj
• Setup telegram mode (Nastavení režimu telegramu)—
Vybere režim automatické konfigurace (výchozí) nebo
manuální konfigurace.
Address (Adresa) – změna adresy zařízení slave.
Data order (Uspořádání dat) – nastavení pořadí dat při
přenosu hodnot v pohyblivé řádové čárce. Hodnota v pohyblivé
řádové čárce je tvořena 4 byty.
• Normal (Normální) – IEEE Float Big Endian (výchozí
nastavení). Dvojice nejsou zaměněny. Tento režim vyhovuje
všem známým systémům Profibus v režimu master.
• Swapped (Záměna) – IEEE Float se zaměněnými hodnotami
word. Provádí záměnu prvního a druhého páru bytů.
(Přidat/odebrat přístroje)— Vybere
Čeština 91
Page 92

Volba Charakteristika
Simulation
(Simulace)
Version
(Verze)
Simulation – provádí
čárce a chybových nebo stavových hlášení namísto skutečného
zařízení. Vyberte následující položky a pomocí šipek zadejte
hodnoty nebo použijte výchozí nastavení.
• Simulation: Zapne či vypne simulaci.
Yes (Ano): Spustí simulaci.
No (Ne): Zastaví simulaci (výchozí nastavení).
• Period (Doba): Nastaví dobu, kterou potřebuje první
hodnota v pohyblivé řádové čárce k průchodu celým
rozsahem mezi minimem a maximem – 2 minuty (výchozí
nastavení).
• Maximum: Nastaví horní mez pro první hodnotu v pohyblivé
řádové čárce – 20,0 (výchozí nastavení).
• Minimum: Nastaví dolní mez pro první hodnotu v pohyblivé
řádové čárce – 10,0 (výchozí nastavení).
• Error (Chyba): Hodnota zadaná v této nabídce bude
nastavena v první simulované značce – 16 (výchozí
nastavení).
• Status (Stav): Hodnota zadaná v této nabídce bude
nastavena v druhé simulované značce – 5 (výchozí
nastavení).
• Toggle (Přepnutí): Změní směr simulovaného náběhu.
• Test/main (Test/údržba):
Enabled (Zapnuto): V cyklickém telegramu Profibus nastaví
ve všech stavových registrech všech nakonfigurovaných
zařízení slave bit TEST/MAINT (0x0004) oznamující
„servisní“ režim.
Disabled (Vypnuto): Normální provozní režim (výchozí
nastavení).
Verze softwaru síťové karty Profibus.
simulaci dvou hodnot v pohyblivé řádové
Volba Charakteristika
Umístění Úprava názvu umístění.
Status
(Stav)
Status – udává stav síťové karty Profibus.
• Please wait (Vyčkejte): Zobrazuje se, dokud síťová karta
nevyhledá všechna
nové konfiguraci karty a vyhledávání připojených senzorů.
• PLC configure err (Chyba konfigurace PLC): Zobrazí se,
když síťová karta obdrží chybnou konfiguraci jednotky PLC
(Programmable logic controller). Zkontrolujte soubor GSD.
• Ready (Připravena): Zobrazí se, když je síťová karta
připravena k odesílání dat po sběrnici Profibus. Zkontrolujte
adresu a zapojení.
• Online: Zobrazuje se, když síťová karta navázala
komunikaci s jednotkou PLC a odesílá cyklická data.
nakonfigurovaná zařízení slave, nebo při
Pořadí zařízení
Pořadí zařízení v telegramu Profibus je stanoveno pevně. První a druhý
nainstalovaný senzor se vždy nacházejí na pozicích 1 a 2 a kontrolér na
pozici 3.
I když není nainstalován žádný senzor, zůstává kontrolér na třetí pozici.
Pozice nenainstalovaných senzorů budou vyplněny hodnotou 0xFF.
Při současném
připojení a vyhledání dvou (maximálního možného počtu)
senzorů bude pořadí instalace záviset na místě připojení senzoru, resp.
senzorového modulu. Toto pořadí vypadá následovně:
• horní konektor pro analogovou kartu,
• spodní konektor pro analogovou kartu,
• levý konektor pro digitální senzor,
• pravý konektor pro digitální senzor.
Standardní struktura dat (Automatická konfigurace)
Je-li zvolena automatická konfigurace (výchozí), pak síťová karta Profibus
dodává předem definovanou zprávu dat pro jednotlivé připojené přístroje.
Ten obsahuje důležité údaje o zařízení.
92 Čeština
Page 93

Struktura datových bloků ve zprávách Profibus je standardizována pro
všechny typy sond. Strukturu datových bloků popisuje Profibus data
telegram register.
Je-li zvolena manuáoní konfigurace, může být struktura dat zprávy
konfigurována uživatelem (viz Nastavení sítě Část na straně 91).
Tabulka 2 Struktura datového telegramu Profibus
Číslo bytu Data Datový typ
1–2 Klasifikovaná chyba Integer (2 byty)
3–4 Klasifikovaný stav Integer (2 byty)
5–8 Měření 1 Floating (4 byty)
9–12 Měření 2 Floating (4 byty)
13–16 Měření 3 Floating (4 byty)
Zobrazované hodnoty
Struktura datových
bloků sběrnice Profibus (Profibus message data block
structure) dokáže nahradit sondy sc beze změn v konfiguraci jednotky
PLC.
Primární hodnotou je vždy naměřená hodnota.
Jako sekundární hodnota, není-li k dispozici, se použije 0.
Jako terciární hodnota, není-li k dispozici, se použije 0.
Obr. 2 Struktura datového bloku zprávy Profibus
Blok procesních dat pro řadič
Datový blok pro kontrolér sc je podobný datovému bloku pro senzory.
Struktura datového bloku pro kontrolér sc nezávisí na počtu připojených
senzorů:
•
kontrolér sc_CHYBA,
kontrolér sc_STAV,
•
• primární hodnota,
• sekundární hodnota,
• terciární hodnota.
Block 3 sc controller ERROR a Block 3 sc controller STATUS ukazují
definice dat pro chyby a stav 1 v kontroléru sc.
Čeština 93
Page 94

Tabulka 3 Blok 3 – kontrolér sc – CHYBA
Bit Chyba Poznámka
0 Chyba komunikace senzoru1V komunikaci mezi kontrolérem sc a
1 Chyba komunikace senzoru2V komunikaci mezi kontrolérem sc a
2–15 Nepoužito
senzorem 1
být odpojen.
senzorem 2 se vyskytla chyba. Senzor může
být odpojen.
se vyskytla chyba. Senzor může
Tabulka 4 Blok 3 – kontrolér sc – STAV
Bit Stav 1 Poznámka
0 Senzor 1 nainstalován Do kontroléru sc byl nainstalován první senzor.
1 Senzor 2 nainstalován Do kontroléru sc byl nainstalován druhý senzor.
2 Relé A zapnuto
3 Relé B zapnuto
4 Relé C zapnuto
5 Relé D zapnuto
6–15 Nepoužito
Tento bit
je nastaven i v případě, že byl senzor po
instalaci odpojen.
Tento bit je nastaven i v případě, že byl senzor po
instalaci odpojen.
Hodnoty pro kontrolér sc
Následující seznam uvádí definice dat pro kontrolér sc:
• Primární hodnota pro kontrolér sc obsahuje výsledek výpočtu.
Sekundární hodnota pro kontrolér sc obsahuje výstup z kanálu 1
•
v rozsahu 0 – 20 nebo 4 – 20 mA.
• Terciární hodnota pro kontrolér sc obsahuje výstup z kanálu 2 v rozsahu
0 – 20 nebo 4 – 20 mA.
Definice hodnot v pohyblivé řádové čárce podle standardu IEEE 745
Sběrnice Profibus pracuje s 32bitovými hodnotami v pohyblivé řádové
čárce s jednoduchou přesností podle standardu IEEE. Definice používá
23 bitů pro mantisu a 8 bitů pro exponent. Jeden bit je vyhrazen pro
znaménko mantisy. Viz Floating point definition.
Obr. 3 Definice hodnot s pohyblivou řádovou čárkou
1 Znaménkový bit 4 Exponent
2 Exponent 5 Mantisa
3 Mantisa
94 Čeština
Page 95

Swapování
Byte order inside Profibus telegram porovnává normální a swapowané
pořadí bytů.
Při swapování dojde k výměně třetího a čtvrtého bytu s prvním
a druhým bytem. Výsledkem jsou byty v pořadí 3 4 1 2.
Tabulka 5 Pořadí bytů v telegramu Profibus
Řadič sc – záměna Řadič sc – normální
Byte T1 – hodnota 0x91 Byte T1 – hodnota 0x3F
Byte T2 – hodnota 0xB9 Byte T2 – hodnota 0x67
Byte T3 – hodnota 0x3F Byte T3 – hodnota 0x91
Byte T4 – hodnota 0x67 Byte T4 – hodnota 0xB9
Poruchy, jejich příčiny a odstraňování
R E A G .
Různá nebezpečí. Při údržbě nebo opravách přístroj nerozebírejte. Pokud je nutné
vyčistit nebo opravit vnitřní součásti, obraťte se na výrobce.
Chybové a stavové indikátory
Chybové a stavové hlášky odpovídají stejným standardním definicím pro
všechny sondy a kontroléry sc.
Error messages uvádí pozice bitů a chybová hlášení. Status indicator
messages uvádí pozice bitů a stavová hlášení.
Hodnota bitu 0 znamená, že chyba nebo stavová podmínka jsou
nepravdivé.
Hodnota bitu
1 znamená, že chyba nebo stavová podmínka jsou pravdivé.
Má-li například bit 0 hodnotu 1, vyskytla se při poslední kalibraci chyba.
Tabulka 6 Chybová hlášení
Bit Hlášení Význam
0 Chyba kalibrace měření Při poslední kalibraci došlo k chybě.
1 Chyba elektronického
nastavení
Při poslední elektronické kalibraci došlo k
chybě.
Tabulka 6 Chybová hlášení (pokračování)
Bit Hlášení Význam
2 Chyba čištění Poslední čisticí cyklus se nezdařil.
3 Chyba měřicího modulu Byla zjištěna chyba u měřicího modulu.
4 Chyba opětovné inicializace
systému
5 Chyba hardwaru Byla zjištěna obecná chyba hardwaru.
6 Chyba vnitřní komunikace Byla zjištěna porucha komunikace uvnitř
7 Chyba vlhkosti vzduchu V zařízení byla zjištěna nadměrná vlhkost
8 Chyba teploty Teplota v zařízení přesáhla stanovenou mez.
9 — —
10 Varování vzorku Ve vzorkovém systému je zapotřebí provést
11 Varování sporné kalibrace Poslední kalibrace nemusí být přesná
12 Varování sporného měření Jedno či více měření v zařízení leží mimo
13 Bezpečnostní varování Byl zjištěn stav, který může mít za následek
14 Varování činidla Systém činidel vyžaduje pozornost.
15 Varování při potřebě údržby Zařízení vyžaduje údržbu.
Některá nastavení nejsou konzistentní a byla
obnovena na výchozí hodnoty.
zařízení.
vzduchu.
některé kroky.
rozsah nebo je jejich přesnost sporná
vznik bezpečnostního rizika.
Tabulka 7 Hlášení stavového indikátoru
Bit Hlášení Význam
0 Probíhá kalibrace Zařízení je v režimu kalibrace Měření nemusí být
1 Probíhá čištění Zařízení je v režimu čištění Měření nemusí být
platná.
platná.
Čeština 95
Page 96

Tabulka 7 Hlášení stavového indikátoru (pokračování)
Bit Hlášení Význam
2 Nabídka servis/údržba Zařízení je v režimu servisu nebo údržby Měření
nemusí být platná.
3 Společ. chyba Zařízení zaregistrovalo chybu. Třídu chyby
naleznete v chybovém registru.
4 Měření 0 Špatná kvalita Přesnost měření je mimo stanovené rozmezí.
5 Měření 0 Dolní limit Výsledek měření je pod stanoveným rozsahem.
6 Měření 0 Horní limit Výsledek měření je nad stanoveným rozsahem.
7 Měření 1 Špatná kvalita Přesnost měření je mimo stanovené rozmezí.
8 Měření 1 Dolní limit Výsledek měření je pod stanoveným rozsahem.
9 Měření 1 Horní limit Výsledek měření je nad stanoveným rozsahem.
10 Měření 2 Špatná kvalita Přesnost měření je mimo stanovené rozmezí.
11 Měření 2 Dolní limit Výsledek měření je pod stanoveným rozsahem.
12 Měření 2 Horní limit Výsledek měření je nad stanoveným rozsahem.
13 Měření 3 Špatná kvalita Přesnost měření je mimo stanovené rozmezí.
14 Měření 3 Dolní limit Výsledek měření je pod stanoveným rozsahem.
15 Měření 3 Horní limit Výsledek měření je nad stanoveným rozsahem.
Tabulka 8 Protokol událostí (pokračování)
Událost Popis
SIMULATION Udává, zda jsou v cyklickém telegramu Profibus uváděna
simulovaná data.
SENSOR POWER Čas spuštění karty Profibus
SET DATE/TIME Nastavení času v interním časovači karty Profibus
NEW CONFIG Čas nové konfigurace
AUTO CONFIGURE Čas nového nastavení v nabídce
CODE VERSION Čas stažení nového softwaru (verze softwaru)
Náhradní díly a příslušenství
Síťové komunikační karty a příslušenství
Charakteristika Číslo položky
Sada Profibus DP 9173900
Konektorová sada Profibus M12 9178500
Zásuvka Profibus M12 9178200
T-konektor Profibus M12 9178400
Log událostí
Diagnostické informace o zařízení popisuje Event Log.
Tabulka 8 Protokol událostí
Událost Popis
ADDRESS Upravená adresa Profibus
DATA ORDER Udává uspořádání dat v proměnných se dvěma slovy
v cyklickém a acyklickém telegramu Profibus
96 Čeština
Čísla produktů a položek se mohou v některých prodejních oblastech lišit.
Obraťte se
na příslušného distributora, kontaktní informace nalezenete na
webových stránkách společnosti.
Page 97

Příklad – Simatic
Po importu souboru HALA09AC.GSD se bude zařízení slave nacházet v umístění PROFIBUS DP, ADDITIONAL FIELD DEVICES, GENERAL.
1. Vyberte 2 slova ze zařízení slave síťové karty.
Každý modul představuje 4 byty ze vstupního adresového rozsahu.
Obr. 4 Příklad – Simatic
Čeština 97
Page 98

Čtení dat
Při obvyklém pořadí dat použijte ke čtení hodnoty objektu v pohyblivé
řádové čárce
nejsou třeba.
Poznámka: PEW/PED je kód používaný v němčině a v systémech SIMATIC. Pro
angličtinu nebo IEC použijte PIW/PID.
1. Načtěte slova ERROR a STATUS.
2. Použijte instrukci L PEW.
instrukci L PED na počáteční adrese modulu. Další konverze
98 Čeština
Page 99

Specifikationer
Specifikationerne kan ændres uden varsel.
Specifikation Detaljer
Profibus-protokol Siemens ASIC SPC3
DP-service DPV0-slave
DP-/DPV1-service DPV1-klasse 1 og klasse 2-slave
I&M-funktion
Adresseændring pr. Profibus-master
Profibus- og baudrater 9,6 k, 19,2 k, 45,45 k, 93,75 k, 187,5 k, 500 k, 1,5 M,
Indikatorer LED til at vise dataudvekslingsmodusen
Interfacetype RS485
Konfigurerbare parametre Databytte, ordvist for flydende punktværdier
Dimensioner (50 x 69,5 x 15,4) mm³
Driftstemperatur –20°C til 85 °C (–4 til 185 °F)
Driftsspænding 8V–16V
Maksimalt strømforbrug 2 W
Certificering Klasse I, Division 2 grupperne A, B, C og D og Klasse
3 M, 6 M, 12 M
Automatisk baudratedetektering
I, Zone 2 gruppe IIC, T4 farlige og almindelige
omgivelser
Generelle oplysninger
Producenten kan under ingen omstændigheder holdes ansvarlig for
direkte, indirekte, specielle, hændelige eller følgeskader der opstår på
baggrund af en defekt eller udeladelse i denne vejledning. Producenten
forbeholder sig
ret til når som helst at foretage ændringer i denne manual
og de beskrevne produkter uden varsel eller forpligtelser. Reviderede
udgaver kan findes på producentens webside.
Oplysninger vedr. sikkerhed
Læs hele manualen, inden udpakning, installation eller betjening af dette
udstyr. Overhold
alle farehenvisninger og advarsler. Undladelse heraf kan
medføre, at brugeren kommer alvorligt til skade eller beskadigelse af
apparatet.
Kontroller, at den beskyttelse, som dette udstyr giver, ikke forringes. Du
må ikke bruge eller installere dette udstyr på nogen anden måde end den,
der er angivet i denne manual.
Sikkerhedshenvisninger
F A R E
Angiver en eventuel eller overhængende farlig situation, der vil medføre dødsfald
eller alvorlige kvæstelser, hvis den ikke undgås.
Angiver en potentiel eller umiddelbart farlig situation, som kan resultere i død eller
alvorlig tilskadekomst, hvis den ikke undgås.
Indikerer en potentiel farlig situation, der kan resultere i mindre eller moderat
tilskadekomst.
B E M Æ R K N I N G
Angiver en situation, der kan medføre skade på instrumentet, hvis ikke den undgås.
Oplysninger, der er særligt vigtige.
A D V A R S E L
F O R S I G T I G
Sikkerhedsmærkater
Læs
skilte og mærkater, som er placeret på apparatet. Der kan opstå
alle
person- eller instrumentskade, hvis forholdsreglerne ikke respekteres.
Hvis der er placeret et symbol på apparatet, kan det findes i
brugermanualen sammen med fare- eller forsigtighedsanvisningerne.
Dansk 99
Page 100

Hvis dette symbol findes på instrumentet, henviser det til
instruktionsmanualen vedrørende drifts- og/eller
sikkerhedsoplysninger.
Dette symbol angiver, at der er risiko for elektrisk stød og/eller dødsfald
pga. elektrisk stød.
Dette symbol angiver tilstedeværelsen af enheder, der er følsomme
over for elektrostatisk afladning (ESD), og det viser, at der skal udvises
forsigtighed for at undgå beskadigelse af udstyret.
Elektrisk udstyr markeret med dette symbol må ikke bortskaffes i det
offentlige europæiske renovationssystem efter den 12. august 2005. I
overensstemmelse med europæiske lokale og nationale forordninger
(EU-direktiv 2002/98/EF) skal brugere af elektrisk udstyr nu returnere
gammelt eller udtjent udstyr til producenten til bortskaffelse. Dette
koster ikke brugeren noget.
Figur 1 Systemoversigt
1 sc-kontrolenhed (slave) 3 PC med software (Mesterklasse 2,
2 Programmerbar logisk kontrolenhed
(Mesterklasse 1)
f.eks. pc inkluderet med CP5611kort).
Produktoversigt
sc-kontrolenhederne er platformen for alle intelligente sonder og
analysatorer. sc-platformen er et fuldt digitalt kommunikationssystem,
baseret på den åbne Modbus-standard. Hvis der installeres et Profibusinterfacekort, giver sc-kontrolenhederne det fulde område af
standardiserede metodeværdier og parametre.
sc-kontrolenhederne er PNO-/PTO-certificerede Profibus DP-/V1enheder. Disse enheder er kompatible med mesteklasse 1- (PLC SCADA)
og mesterklasse 2-systemer, f.eks. tekniske stationer.
Der vises en oversigt over systemet i System overview. Profibus er
tilgængelig som fabriks- eller brugerinstalleret emne.
100 Dansk
Installation
F O R S I G T I G
Risiko for personskade. Kun kvalificeret personale må udføre de opgaver, som er
beskrevet i dette afsnit i brugervejledningen.
Installér modulet til styringen
Eksplosionsfare. Se sikkerhedsvejledningerne i brugermanualen til controlleren
ved installation af modul på klassificerede farlige steder.
Stødfare. Slå altid strømmen fra instrumentet før der udføres nogen
elektriske tilslutninger.
F A R E
F A R E
 Loading...
Loading...