Page 1

DOC022.98.00743.NOV05
Piston pipette
with tip ejector system
Kolbenhubpipette
mit Spitzen-Auswurfsystem
Pipette à piston
avec dispositif d’éjection des cônes
Pipeta de émbolo
con sistema de expulsión de puntas
Pipetta a pistone
con sistema di espulsione del puntale
Page 2

Page 3

DOC022.98.00743.NOV05
Piston pipette
Kolbenhubpipette
Pipette à piston
Pipeta de émbolo
Pipetta a pistone
USER MANUAL
BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG
MODE D’EMPLOI
MANUAL DEL USUARIO
MANUALE UTENTE
November 2005, Edition 1
© Hach Company, 2005. All rights reserved. Printed in Germany
CK/SK
Page 4

2
Page 5

Table of Contents
Section 1 Description of the piston pipette ....13
1.1 Pipette tips ..................................................... 14
Section 2 Using the pipette ..............................15
2.1 Setting the volume ......................................... 15
2.2 Tip ejection ..................................................... 15
2.3 Pipetting techniques ....................................... 16
Section 3 Standard technique .........................17
Section 4 Daily check .......................................18
Section 5 Maintenance .....................................19
5.1 Opening the pipettes (0.2–1.0 mL) ................ 19
5.2 Opening the pipette (1–5 mL) ........................ 21
Section 6 Calibration ........................................22
6.1 Checking the calibration ................................. 22
Section 7 Recalibration ....................................24
Section 8 Troubleshooting ...............................25
Section 9 Warranty, liability and complaints ..26
3
Page 6

Table of Contents
4
Page 7

Inhaltsverzeichnis
Kapitel 1 Beschreibung der
Kolbenhubpipette ..............................................27
1.1 Pipettenspitzen .............................................. 28
Kapitel 2 Pipettenbedienung ...........................29
2.1 Volumeneinstellung ........................................ 29
2.2 Spitzenauswurf .............................................. 29
2.3 Pipettiertechniken .......................................... 30
Kapitel 3 Standard-Technik ..............................31
Kapitel 4 Pipettieren von Vollblut ....................32
Kapitel 5 Tägliche Prüfung ..............................33
Kapitel 6 Wartungsarbeiten .............................34
6.1 Öffnen der Pipetten (0,2–1,0 mL) .................. 34
6.2 Öffnen der Pipette (1–5 mL) .......................... 36
Kapitel 7 Kalibrierung .......................................37
7.1 Prüfen der Kalibrierung .................................. 37
Kapitel 8 Rekalibrierung ...................................39
Kapitel 9 Fehlersuche .......................................40
Kapitel 10 Gewährleistung, Haftung und
Beanstandungen ................................................41
5
Page 8

Inhaltsverzeichnis
6
Page 9

Table des matières
Section 1 Description de la pipette à piston ..43
1.1 Pointes de pipette .......................................... 44
Section 2 Utilisation de la pipette ...................45
2.1 Réglage du volume ........................................ 45
2.2 Ejection de la pointe ....................................... 45
2.3 Techniques de pipetage ................................. 46
Section 3 Technique standard .........................47
Section 4 Pipetage de sang complet ..............48
Section 5 Contrôle quotidien ...........................49
Section 6 Entretien ...........................................50
6.1 Pour ouvrir la pipette (0,2–1,0 mL) ................ 50
6.2 Pour ouvrir la pipette (1–5 mL) ...................... 52
Section 7 Etalonnage .......................................53
7.1 Vérification de l'étalonnage ............................ 53
Section 8 Recalibrage ......................................55
Section 9 Recherche de problèmes ................56
Section 10 Garantie, responsabilité et
réclamations .......................................................57
7
Page 10

Table des matières
8
Page 11

Índice
Sección 1 Descripción de la pipeta de
émbolo ................................................................59
1.1 Puntas de pipeta ............................................ 60
Sección 2 Utilización de la pipeta ...................61
2.1 Ajuste del volumen ......................................... 61
2.2 Expulsión de la punta .....................................61
2.3 Técnicas de pipeteado ................................... 62
Sección 3 Técnica estándar .............................63
Sección 4 Pipeteado de sangre completa ......64
Sección 5 Control diario ..................................65
Sección 6 Mantenimiento .................................66
6.1 Abrir las pipetas (0,2–1,0 mL) ........................ 66
6.2 Abrir la pipeta (1–5 mL) ................................. 68
Sección 7 Calibración ......................................69
7.1 Comprobación de la calibración ..................... 69
Sección 8 Recalibración ..................................71
Sección 9 Localización y resolución de
fallos ...................................................................72
Sección 10 Garantía, responsabilidad y
reclamaciones ....................................................73
9
Page 12

Índice
10
Page 13

Indice
Sezione 1 Descrizione della pipetta a pistone 75
1.1 Puntali per pipette .......................................... 76
Sezione 2 Uso della pipetta .............................77
2.1 Regolazione del volume ................................. 77
2.2 Espulsione del puntale ................................... 77
2.3 Tecniche di pipettatura ................................... 78
Sezione 3 Tecnica standard .............................79
Sezione 4 Pipettare sangue intero ..................80
Sezione 5 Controllo quotidiano .......................81
Sezione 6 Manutenzione ..................................82
6.1 Apertura delle pipette (0,2–1,0 mL) ............... 82
6.2 Apertura della pipetta (1–5 mL) ..................... 84
Sezione 7 Calibrazione .....................................85
7.1 Controllo della calibrazione ............................ 85
Sezione 8 Ricalibrazione ..................................87
Sezione 9 Diagnostica ......................................88
Sezione 10 Garanzia, responsabilità e
reclami ................................................................89
11
Page 14

Indice
12
Page 15
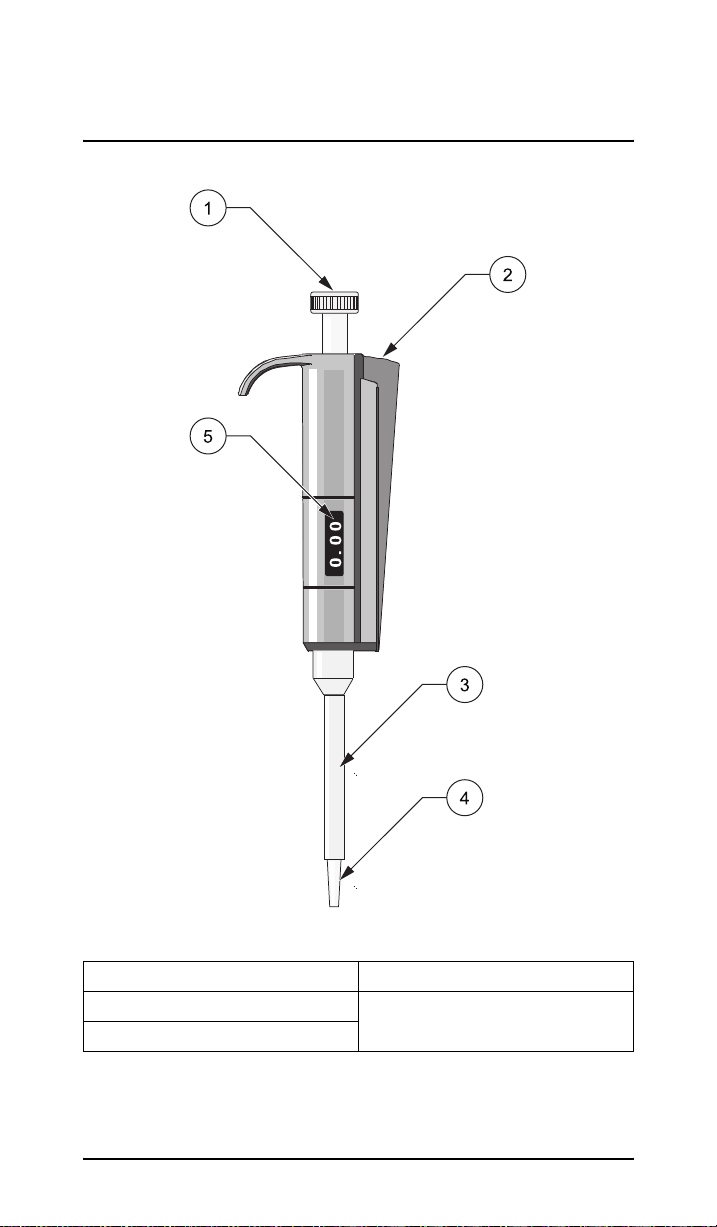
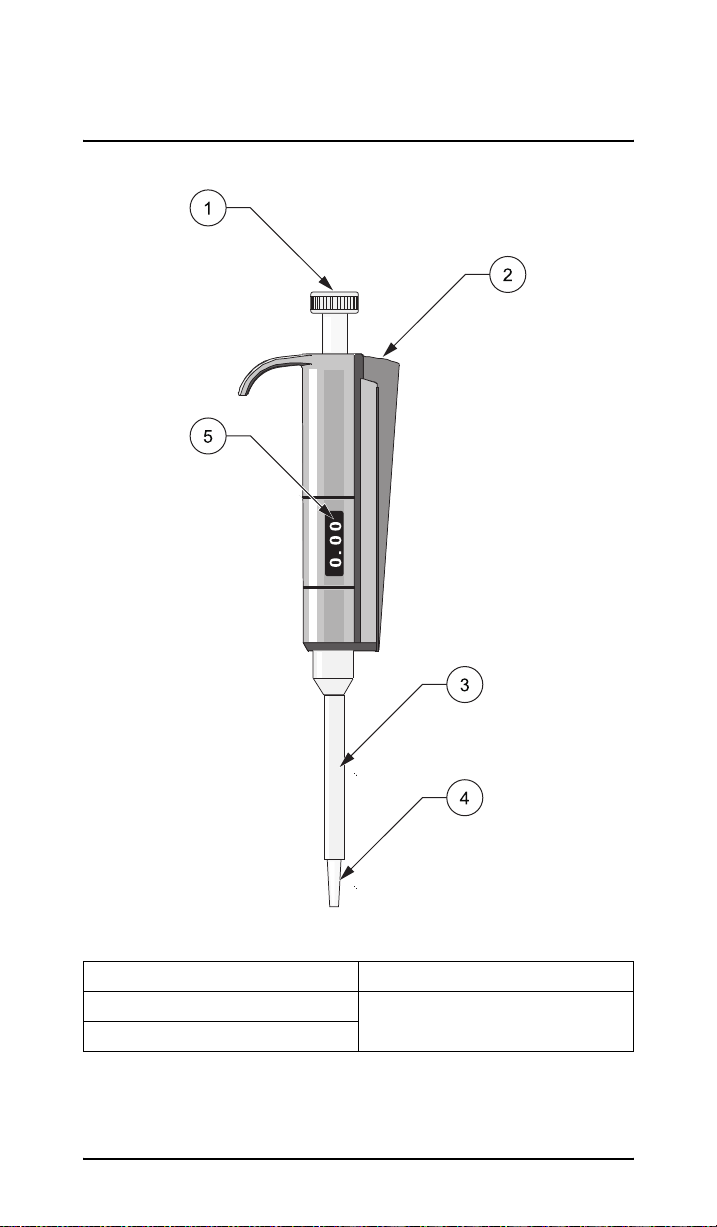
Section 1 Description of the
piston pipette
Figure 1 Description of the piston pipette
1 Push button 4 Cone
2 Ejector button 5 Volume scale
3 Tip ejector
13
Page 16

Description of the piston pipette
The piston pipette is a handy, general-purpose microliter
pipette for transferring exact volumes of liquid. It operates on
the principle of air expulsion, making use of disposable tips.
The volume that is to be pipetted is shown in a clearly visible
display on the pipette handle. All piston pipettes are fitted with
a mechanical tip ejector system.
1.1 Pipette tips
We recommend the use of original HACH pipette tips when
working with the piston pipette. The pipette tips are made of
polypropylene and can be autoclaved at 121 °C/250 °F.
14
Page 17

Section 2 Using the pipette
2.1 Setting the volume
(only for variable piston pipettes)
The pipette volume is set with the push button at the end of the
handle. Turn the button anticlockwise to increase the volume
and clockwise to decrease it. Make sure that the volume
setting is correct (clicks into place) and the volume shown in
the display is completely visible.
Figure 2 Setting the volume
Important Note: The given precision and accuracy only apply
for the volume range specified on the pipette. Do not set the
volume to a value outside of this range. Do not use force to
turn the push button to a volume that is outside of the specified
range. This could damage the pipette.
2.2 Tip ejection
Each piston pipette is fitted with a tip ejection system to
prevent possible contamination. Press thumb down on ejector
button and remove tip from tip cone.
15
Page 18

Using the pipette
2.3 Pipetting techniques
The pipette is operated by means of the push button at the
end of the handle.
Maximum accuracy can be achieved by carrying out the
following steps:
1. Move the piston up or down slowly and evenly. (especially
when pipetting highly viscous liquids)
2. Do not allow the push button to spring back into its original
position.
3. Use light pressure to fit a new tip to the cone, turning the
tip slightly as you do so.
4. Make sure that the tip is firmly in position on the tip cone
and there are no foreign bodies between the tip and the
cone.
5. Wet the tips with the liquid by repeatedly filling and
emptying them.
6. Hold the pipette almost vertical (no more than 10° from the
vertical) while liquid is being drawn into the tip.
7. The temperature of the pipette and the tip should match
that of the liquid.
16
Page 19
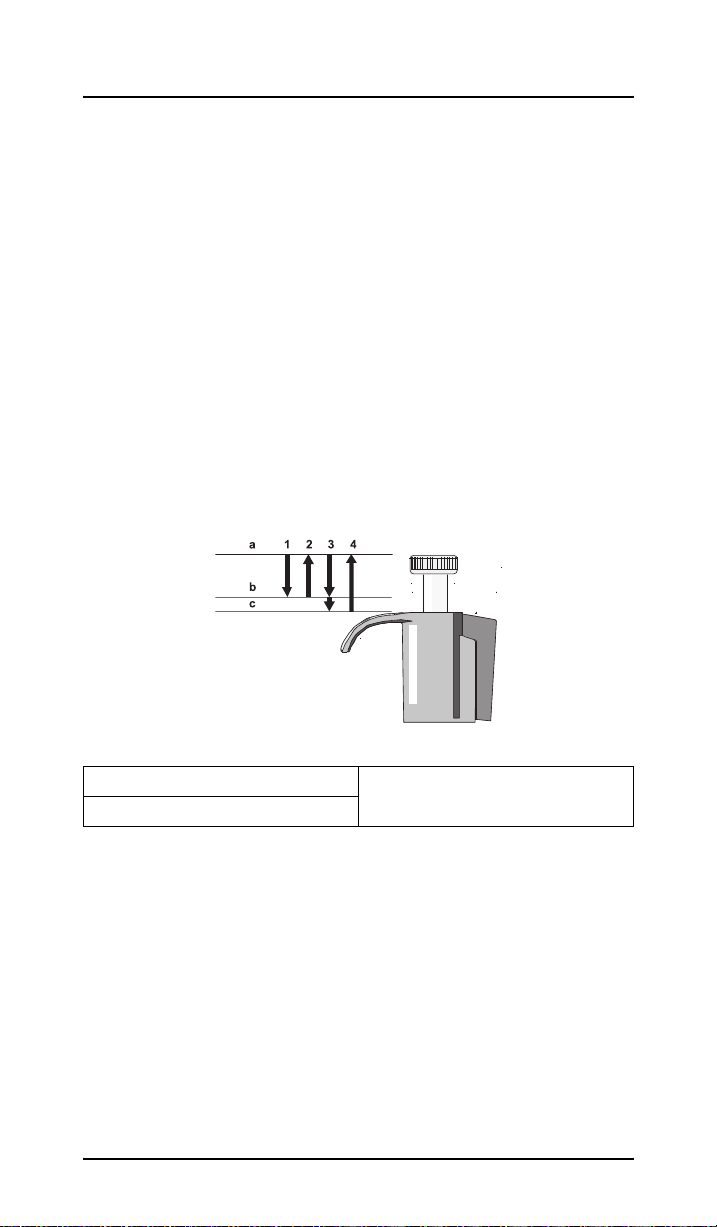
Section 3 Standard technique
1. Press the push button to the first pressure point.
2. Dip the pipette tip under the surface of the liquid (2–3 mm)
and slowly release the push button. Take the tip out of the
liquid and touch it against the inside wall of the vessel to
remove excess liquid.
3. Place the tip against the inside wall of the vessel and
press lightly and evenly on the push button until the first
pressure point is reached. Hold the pipette in this position.
After about one second, press the push button until the
second pressure point is reached. This completely
empties the tip.
4. Allow the push button to return to its rest position.
Figure 3 Standard technique
a Rest position c Second pressure point
b First pressure point
Important Note: After use change pipette tip!
17
Page 20

Section 4 Daily check
Check the pipette daily for dust and external soiling before
starting work or after finishing work. Pay special attention to
the tip cone. Clean the pipette with 70% alcohol. Do not use
any other solvents to clean the pipette.
18
Page 21
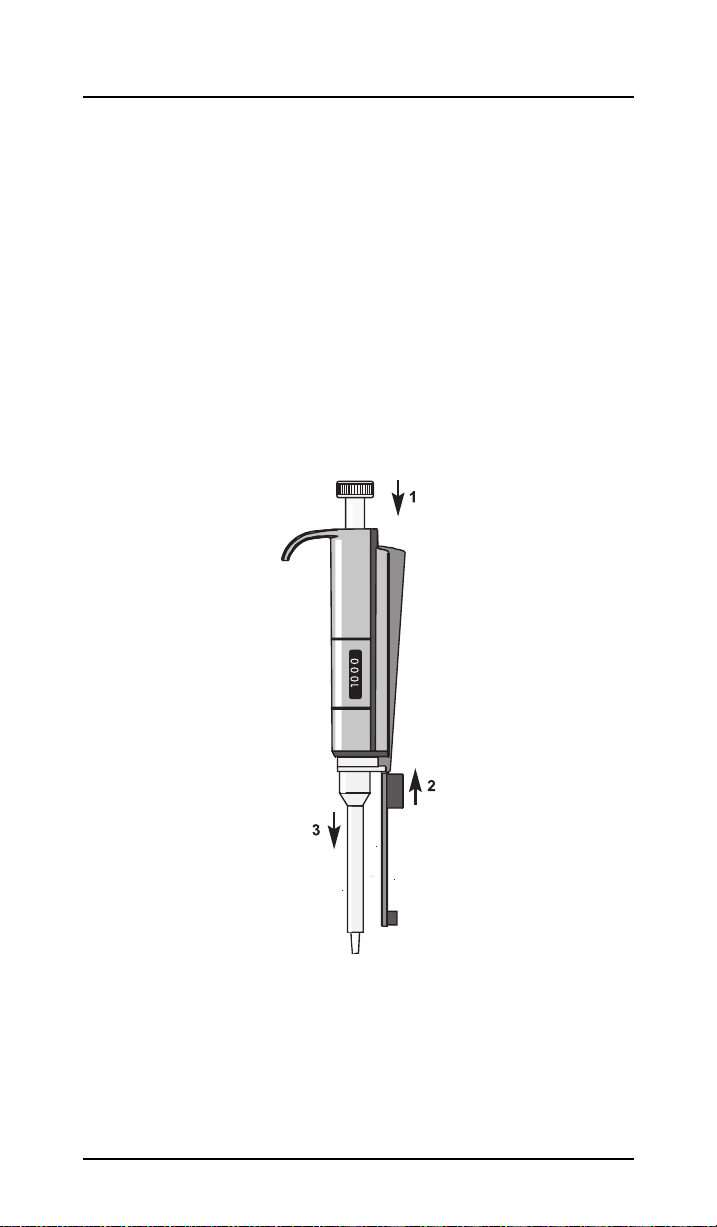
Section 5 Maintenance
If the pipette is used each day, maintenance should be carried
out at least twice each year. Maintenance can be carried out
in your laboratory. Carry out the steps described below:
5.1 Opening the pipettes (0.2–1.0 mL)
1. Press the ejector button.
2. Insert the tip of the opening tool into the opening at the
end of the ejector button.
3. Pull out the ejector button and the tip ejector piston.
Figure 4 Opening the pipettes
19
Page 22

Maintenance
4. Remove the tip cone by turning it anticlockwise with the
enclosed tool.
5. Pull out the piston.
6. Remove the O-rings from the tip cone.
7. Clean the piston, the piston spring and the O-rings with a
clean, dry cloth.
8. Check the cylinder for foreign substances. Remember that
the cylinder does not have to be greased.
9. Grease the cleaned parts lightly with the accompanying
grease.
10. Reassemble the pipette.
20
Page 23
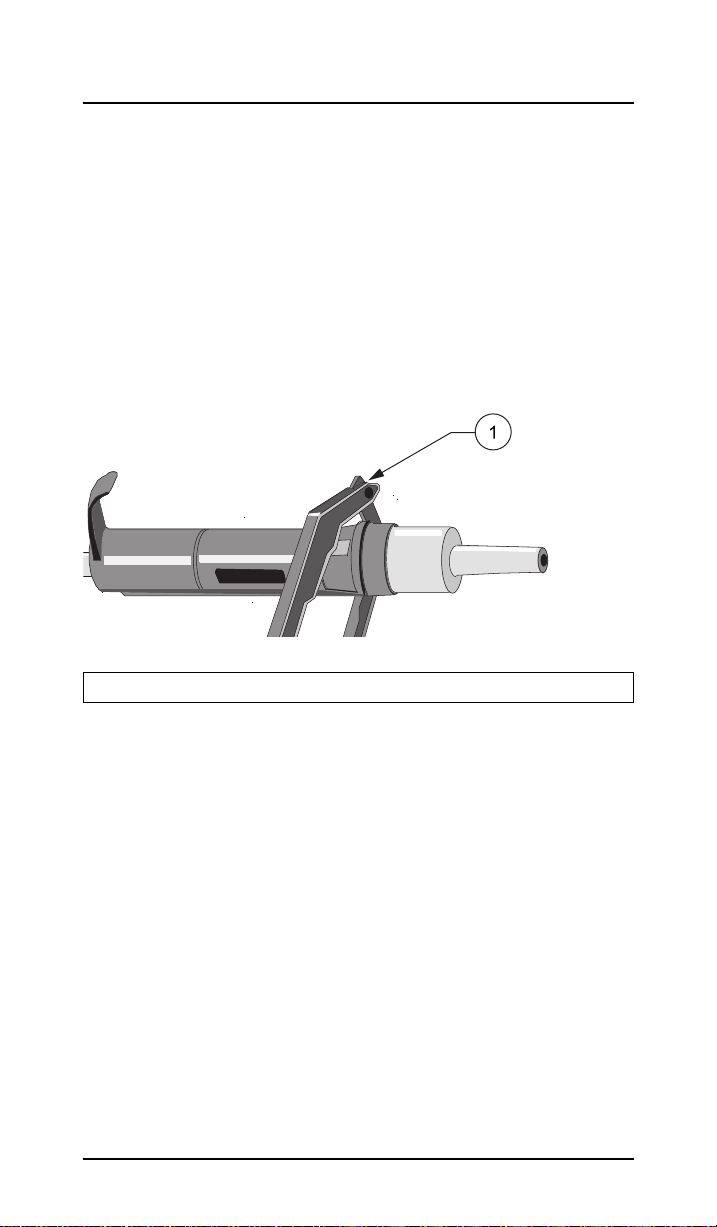
Maintenance
5.2 Opening the pipette (1–5 mL)
1. Remove ejector button and tip ejector as described above
(for 0.2–1.0 mL pipettes) section 5.1 on page 19.
2. Remove cover.
3. Remove cone and cylinder with the help of the tool by
pressing the two projections together. While pressing the
projections, push the tool towards the cone.
Figure 5 Opening the pipette
1 Service tool to open the pipette
4. Take apart, clean and grease as described above (for
0.2–1.0 mL pipettes) section 5.1 on page 19.
5. Reassemble in reverse sequence.
21
Page 24

Section 6 Calibration
The pipette is calibrated in the factory with distilled water at
22 °C/72 °F. No recalibration is needed for routine use. The
pipette can, however, be recalibrated for other temperatures
and solutions of different viscosities. An appropriately
sensitive analytical balance, a small beaker and distilled water
are needed to carry out the calibration.
Important Note: If either the handle or the piston is replaced,
the pipette must be recalibrated. If the O-rings or the tip cone
are replaced, the calibration should be checked.
6.1 Checking the calibration
1. Set the pipette volume as follows in Table 1 Checking the
calibration:
Table 1 Checking the calibration
Pipette
(µL)
10 10 9.8–10.2
20 20 19.8–20.2
50 50 49.5–50.5
100 100 99.2–100.8
200 200 198.7–201.3
500 500 497.0–503.0
1000 1000 994.0–1006.0
2000 2000 1990.0–2010.0
200–1000 300 298–302
1000–5000 2000 1990–2010
Volume setting
permissible
weight range
(mg)
22
Page 25

Calibration
2. Use light pressure to place a tip on the tip cone, turning
the tip slightly.
3. Pipette distilled water into previously weighed beaker at
least five times. Determine each weight in mg to the first
decimal place and compare this with the weight shown
above. If the weight is not within this range, recalibrate the
pipette.
23
Page 26

Section 7 Recalibration
The calibration is carried out with the supplied calibration key.
1. Place the calibration key in the holes of the calibration
groove at the top end of the handle.
2. Increase the volume by turning in clockwise direction or
reduce it by turning in anticlockwise direction.
Figure 6 Recalibration
1 Calibration key
3. Afterwards check the volume as described above
Section 6 Calibration on page 22.
Important Note: The pipette can only be calibrated within the
limits of the volume range for which it is meant to be used.
24
Page 27
Section 8 Troubleshooting
The following table is intended to help you to identify and
eliminate errors:
Table 2 Troubleshooting
Error Possible cause Response
Leakage
Inaccurate
pipetting
Tip not attached
properly
Foreign bodies
between cone and
tip
Foreign bodies
between O-ring and
piston
Insufficient grease
on the O-rings and
the piston
Defective O-rings Replace O-rings
Incorrect operation
Tip not firmly
attached
Calibration has
changed, e.g. due to
faulty operation
Fix tip firmly in place
Clean the cone and
attach a new tip
Clean and grease
the O-rings and the
piston in the cylinder.
Use the supplied
grease
Grease adequately
Use pipette as
described in the
manual
Attach tip firmly
Recalibrate
25
Page 28

Section 9 Warranty, liability
and complaints
The manufacturer warrants that the product supplied is free of
material and manufacturing defects and undertakes the
obligation to repair or replace any defective parts at zero cost.
The warranty period for these pipettes is 24 months.
With the exclusion of the further claims, the supplier is liable
for defects including the lack of assured properties as follows:
all those parts that can be demonstrated to have become
unusable or that can only be used with significant limitations
due to a situation present prior to the transfer of risk, in
particular due to incorrect design, poor materials or
inadequate finish will be improved or replaced, at the
supplier's discretion. The identification of such defects must be
notified to the supplier in writing without delay, however at the
latest 7 days after the identification of the fault. If the customer
fails to notify the supplier, the product is considered approved
despite the defect. Further liability for any direct or indirect
damages is not accepted.
If specific maintenance work defined by the supplier is to be
performed within the warranty period by the customer
(maintenance) and these requirements are not met, claims for
damages due to the failure to comply with the requirements
are rendered void.
Any further claims, in particular claims for consequential
damages cannot be made.
Consumables and damage caused by improper handling, poor
installation or incorrect use are excluded from this clause.
26
Page 29
Kapitel 1 Beschreibung der
Kolbenhubpipette
Abbildung 1 Pipettenbeschreibung
1 Kolbenknopf 4 Konus
2 Auswurftaste 5 Volumenanzeige
3 Spitzenabwerfer
27
Page 30

Beschreibung der Kolbenhubpipette
Die Kolbenhubpipette ist eine handliche, allgemein
verwendbare Mikroliterpipette zum Aufnehmen und Dosieren
von exakten Flüssigkeitsvolumina. Sie arbeitet nach dem
Prinzip der Luftverdrängung (Volumenhub) mit aufsetzbaren
Einmalspitzen. Das einstellbare Pipettiervolumen wird in einer
gut sichbaren Digitalanzeige am Pipettengriff dargestellt. Alle
Kolbenhubpipetten sind mit einem mechanischen
Spitzenabwurf-System ausgestattet.
1.1 Pipettenspitzen
Es wird empfohlen, nur Original HACH Pipettenspitzen bei der
Arbeit mit der Kolbenhubpipette einzusetzen. Die
Pipettenspitzen sind aus Polypropylen hergestellt und bei
121 °C autoklavierbar.
28
Page 31

Kapitel 2 Pipettenbedienung
2.1 Volumeneinstellung
(nur für variable Kolbenhubpipetten)
Das Pipettiervolumen wird über den Kolbenknopf am Griffende
eingestellt. Zur Vergrößerung des Volumens drehen Sie den
Kolbenknopf entgegen dem Uhrzeigersinn. Ein geringeres
Volumen stellen Sie durch Drehen des Kolbenknopfes im
Uhrzeigersinn ein. Stellen Sie sicher, dass das eingestellte
Volumen einrastet und die Zahlen der Volumenangabe an der
Digitalanzeige voll sichtbar sind.
Abbildung 2 Volumeneinstellung
Wichtiger Hinweis: Die angegebene Präzision und
Genauigkeit gilt nur für den auf der Pipette angegebenen
Volumenbereich. Stellen Sie keine Volumina außerhalb dieses
Bereiches ein. Drehen Sie die Volumeneinstellung nicht unter
Kraftanwendung über den angegebenen Bereich hinaus. Die
Pipette kann dadurch mechanisch zerstört werden.
2.2 Spitzenauswurf
Jede Kolbenhubpipette ist mit einem Spitzenauswurf-System
ausgestattet, um eine mögliche Kontamination zu verhindern.
Drücken Sie die Auswurftaste mit dem Daumen nach unten
und entfernen Sie die Spitze von dem Pipettenkonus.
29
Page 32

Pipettenbedienung
2.3 Pipettiertechniken
Die Bedienung der Pipette erfolgt über den Kolbenknopf am
Griffende.
Ein Maximum an Genauigkeit wird durch das Einhalten der
nachfolgenden Schritte erreicht:
1. Heben und Senken Sie den Kolbenknopf langsam und in
der gleichen Geschwindigkeit (besonders beim Pipettieren
von hochviskosen Flüssigkeiten).
2. Lassen Sie den Kolbenknopf nicht zurückschnappen.
3. Setzen Sie eine neue Spitze unter leichtem Druck und
einer leichten Drehung auf den Konus der
Kolbenhubpipette.
4. Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Pipettenspitze fest auf dem
Spitzenkonus sitzt und sich keine Fremdkörper zwischen
der Spitze und dem Konus befinden.
5. Durch mehrmaliges Füllen und Leeren der Spitzen mit der
jeweiligen Flüssigkeit die Spitzen benetzen.
6. Halten Sie die Pipette während der Flüssigkeitsaufnahme
nahezu senkrecht (maximal 10° entfernt von der
Senkrechten).
7. Die Temperatur der Pipetten und der Spitzen sollte mit der
Flüssigkeitstemperatur übereinstimmen.
30
Page 33

Kapitel 3 Standard-Technik
1. Drücken Sie den Kolbenknopf bis zum ersten Druckpunkt.
2. Die Pipettenspitze unter die Flüssigkeitsoberfläche
eintauchen (2–3 mm) und den Kolbenknopf langsam
loslassen. Nehmen Sie die Spitze aus der Flüssigkeit und
berühren Sie dabei den Rand des Gefäßes zum
Abstreifen von der überschüssigen Flüssigkeit.
3. Berühren Sie die Gefäßinnenseite mit der Spitze und
pipettieren Sie die Flüssigkeit durch leichtes,
gleichmäßiges Drücken des Kolbenknopfes bis zum
ersten Druckpunkt. Halten Sie die Pipette in dieser
Position. Nach ca. einer Sekunde drücken Sie den
Kolbenknopf bis zum zweiten Druckpunkt. Dadurch wird
die Spitze vollständig entleert.
4. Lassen Sie den Bedienungsknopf bis zur Grundstellung
zurückgehen.
Abbildung 3 Standard-Technik
a Grundstellung c zweiter Druckpunkt
b erster Druckpunkt
Wichtiger Hinweis: Nach Gebrauch Pipettenspitze wechseln!
31
Page 34

Kapitel 4 Pipettieren von
Vollblut
1. Tauchen Sie die Spitze in die Probe und drücken Sie den
Kolbenknopf bis zum ersten Druckpunkt. Stellen Sie
sicher, dass sich die Spitze unter der Oberfläche befindet.
2. Lassen Sie den Kolbenknopf langsam los, bis er sich in
der Ausgangsposition befindet. Die Spitze ist jetzt mit der
Probe gefüllt. Nehmen Sie die Spitze nicht aus der Probe.
3. Drücken Sie den Kolbenknopf bis zum ersten Druckpunkt
und lassen Sie ihn langsam wieder los. Wiederholen Sie
diesen Vorgang bis die Spitzenwand frei von Blut ist.
4. Drücken Sie den Kolbenknopf bis zum zweiten
Druckpunkt und entleeren Sie die Spitze vollständig.
Abbildung 4 Pipettieren von Vollblut
a Grundstellung c zweiter Druckpunkt
b erster Druckpunkt
32
Page 35

Kapitel 5 Tägliche Prüfung
Prüfen Sie die Pipette täglich vor Arbeitsbeginn oder nach
Arbeitsende auf Staub und äußere Verschmutzungen. Achten
Sie dabei besonders auf den Spitzenkonus. Reinigen Sie die
Pipette mit 70%-igem Alkohol. Setzten Sie zum Reinigen der
Pipette keine anderen Lösungsmittel ein.
33
Page 36

Kapitel 6 Wartungsarbeiten
Wird die Pipette täglich benutzt, ist mindestens zweimal pro
Jahr eine Wartung erforderlich. Die Wartung kann von Ihnen
im Labor durchgeführt werden oder senden Sie die Pipette an
HACH LANGE. Führen Sie die im folgenden beschriebenen
Arbeiten durch:
6.1 Öffnen der Pipetten (0,2–1,0 mL)
1. Drücken Sie die Auswurftaste nach unten.
2. Setzen Sie die Spitze des Öffnungs-Werkzeuges in die
Öffnung am Ende der Auswurftaste.
3. Ziehen Sie die Auswurftaste und den
Spitzenauswurfkolben ab.
34
Abbildung 5 Öffnen der Pipetten
Page 37

Wartungsarbeiten
4. Entfernen Sie den Spitzenkonus durch Drehen entgegen
dem Uhrzeigersinn mit dem beigefügten Werkzeug.
5. Ziehen Sie den Kolben heraus.
6. Entfernen Sie die O-Ringe von dem Spitzenkonus.
7. Reinigen Sie den Kolben, die Kolbenfeder und die
O-Ringe mit einem trockenen, sauberen Tuch.
8. Überprüfen Sie den Zylinder auf Fremdstoffe. Beachten
Sie, dass der Zylinder nicht gefettet werden muss.
9. Fetten Sie die gereinigten Teile leicht mit dem
beiliegenden Fett.
10. Setzen Sie die Teile wieder zusammen.
35
Page 38

Wartungsarbeiten
6.2 Öffnen der Pipette (1–5 mL)
1. Auswurftaste und Spitzenauswerfer wie für Pipette
0,2–1,0 mL Kapitel 6.1 auf Seite 34 beschrieben
entfernen.
2. Abdeckung entfernen.
3. Konus mit Zylinder durch Zusammendrucken der zwei
Haltenasen mit Hilfe des Werkzeuges entfernen. Beim
Zusammendrucken gleichzeitig das Werkzeug in Richtung
Konus schieben.
Abbildung 6 Öffnen der Pipetten
1 Werkzeug zum Öffnen der Pipette
4. Auseinandernehmen, Reinigen und Fetten wie für
Pipetten 0,2–1,0 mL Kapitel 6.1 auf Seite 34 beschrieben.
5. Zusammenbau in umgekehrter Reihenfolge.
36
Page 39

Kapitel 7 Kalibrierung
Die Pipette wurde werkseitig mit destilliertem Wasser bei
22 °C kalibriert. Für den Routinegebrauch ist keine
Rekalibrierung erforderlich. Die Pipette ist jedoch mit einer
Kalibriermöglichkeit zur Einstellung auf andere Temperaturen
und Lösungen verschiedener Viskositäten ausgestattet. Zur
Durchführung der Kalibrierung sind eine Analysenwaage mit
geeigneter Empfindlichkeit, ein kleines Becherglas und
destilliertes Wasser erforderlich.
Wichtiger Hinweis: Wurden der Handgriff oder der Kolben
gewechselt, muss die Pipette rekalibriert werden. Bei dem
Wechsel der O-Ringe oder des Spitzenkonus sollte die
Kalibrierung überprüft werden.
7.1 Prüfen der Kalibrierung
1. Stellen Sie das Volumen der Pipette wie in Tabelle 1
Pipettenkalibrierung beschrieben ein:
Tabelle 1 Pipettenkalibrierung
Pipette
(µL)
10 10 9,8–10,2
20 20 19,8–20,2
50 50 49,5–50,5
100 100 99,2–100,8
200 200 198,7–201,3
500 500 497,0–503,0
1000 1000 994,0–1006,0
2000 2000 1990,0–2010,0
200–1000 300 298–302
1000–5000 2000 1990–2010
Vol umen-
einstellung
erlaubter
Gewichtsbereich
(mg)
37
Page 40

Kalibrierung
2. Setzen Sie eine Spitze mit leichtem Druck und leichter
Drehung auf den Spitzenkonus.
3. Pipettieren Sie destilliertes Wasser in das vorher
gewogene Becherglas wenigstens fünf mal. Ermittlen Sie
jedes Gewicht mit einer Stelle nach dem Komma in mg
und vergleichen Sie dieses mit dem oben angegebenen
Wert. Liegt ein Wert nicht innerhalb des Bereiches, sollte
die Pipette rekalibriert werden.
38
Page 41

Kapitel 8 Rekalibrierung
Die Kalibrierung wird mit dem mitgelieferten Kalibrierschlüssel
durchgeführt.
1. Setzen Sie den Kalibrierschlüssel in die Löcher der
Kalibrierungsnute am oberen Ende des Handgriffes.
2. Erhöhen Sie das Volumen durch Drehen im Uhrzeigersinn
oder verringern Sie es durch Drehen entgegen dem
Uhrzeigersinn.
Abbildung 7 Rekalibrierung
1 Kalibrierschlüssel
3. Überprüfen Sie nach dem Einstellen das Volumen wie in
Kapitel 7 Kalibrierung auf Seite 37 beschrieben.
Wichtiger Hinweis: Die Pipette kann nur in dem für sie
vorgesehenen Volumenbereich kalibriert werden.
39
Page 42

Kapitel 9 Fehlersuche
Die folgende Tabelle gibt Ihnen Hinweise zu möglichen
Fehlern und deren Abhilfe
Tabelle 2 Fehlerbeschreibung
Fehler Möglicher Grund Lösung
:
Undichtigkeit
Ungenaues
pipettieren
Spitze nicht fest
aufgesetzt
Fremdkörper
zwischen Konus und
Spitze
Fremdkörper
zwischen O-Ring
und Kolben
Ungenügende
Fettung an den
O-Ringen und dem
Kolben
O-Ringe defekt O-Ringe wechseln
Falsche Bedienung
Spitze nicht fest
aufgesetzt
Kalibrierung hat sich
geändert z.B. durch
falsche Bedienung
Spitze fest aufsetzen
Reinigen des Konus
und aufsetzen einer
neuen Spitze
Reinigen und Fetten
der O-Ringe und des
Kolbens im Zylinder.
Verwenden Sie das
mitgelieferte Fett
Ausreichend fetten
Der Anleitung
gemäß arbeiten
Spitze fest aufsetzen
Rekalibrieren
40
Page 43

Kapitel 10 Gewährleistung,
Haftung und
Beanstandungen
Der Hersteller gewährleistet, dass das gelieferte Produkt frei
von Material- und Verarbeitungsfehlern ist und verpflichtet
sich, etwaige fehlerhafte Teile kostenlos instandzusetzen oder
auszutauschen.
Die Verjährungsfrist für Mängelansprüche beträgt bei diesen
Pipetten 24 Monate.
Für Mängel, zu denen auch das Fehlen zugesicherter
Eigenschaften zählt, haftet der Lieferer unter Ausschluss
weiterer Ansprüche wie folgt: Alle diejenigen Teile sind nach
Wahl des Lieferers unentgeltlich auszubessern oder neu zu
liefern, die innerhalb der Verjährungsfrist vom Tage des
Gefahrenüberganges an gerechnet, nachweisbar infolge eines
vor dem Gefahrenübergang liegenden Umstandes,
insbesondere wegen fehlerhafter Bauart, schlechter Baustoffe
oder mangelhafter Ausführung unbrauchbar werden oder
deren Brauchbarkeit erheblich beeinträchtigt wurde. Die
Feststellung solcher Mängel muss dem Lieferer unverzüglich,
jedoch spätestens 7 Tage nach Feststellung des Fehlers,
schriftlich gemeldet werden. Unterlässt der Kunde diese
Anzeige, gilt die Leistung trotz Mangels als genehmigt. Eine
darüber hinausgehende Haftung für irgendwelchen
unmittelbaren oder mittelbaren Schaden besteht nicht.
Sind vom Lieferer vorgegebene spezifische Wartungsarbeiten
innerhalb der Verjährungsfrist durch den Kunden selbst
durchzuführen (Wartung) und werden diese Vorgaben nicht
ausgeführt, so erlischt der Anspruch für die Schäden, die
durch die Nichtbeachtung der Vorgaben entstanden sind.
Weitergehende Ansprüche, insbesondere auf Ersatz von
Folgeschäden, können nicht geltend gemacht werden.
Verschleißteile und Beschädigungen, die durch
unsachgemäße Handhabung, unsichere Montage oder nicht
bestimmungsgerechten Einsatz entstehen, sind von dieser
Regelung ausgeschlossen.
41
Page 44

Gewährleistung, Haftung und Beanstandungen
42
Page 45

Section 1 Description de la
pipette à piston
Figure 1 Description de la pipette à piston
1 Bouton du piston 4 Cône
2 Bouton d'éjection 5 Indication du volume
3 Ejecteur de la pointe
43
Page 46

Description de la pipette à piston
La pipette à piston est une pipette à microlitre manuelle, à
usage multiple, destinée au prélèvement et au dosage de
volumes exacts de liquides. Elle fonctionne suivant le principe
du pistonnement à l'aide de pointes démontables à usage
unique. Le volume de pipetage réglable apparaît sur un
affichage bien visible, sur la poignée de la pipette. Toutes les
pipettes à piston sont équipées d'un système mécanique
d'éjection de la pointe.
1.1 Pointes de pipette
Nous conseillons de n'utiliser que des pointes de pipette
HACH d'origine sur la pipette à piston. Elles sont fabriquées
en polypropylène et résistent à 121 °C/250 °F en autoclave.
44
Page 47

Section 2 Utilisation de la
pipette
2.1 Réglage du volume
(uniquement pour les pipettes à piston variables)
Le volume de pipetage se règle par l'intermédiaire du bouton
du piston, sur l'extrémité de la poignée. Pour augmenter le
volume, tournez dans le sens anti-horlogique. A l'inverse, pour
diminuer le volume, tournez dans le sens horlogique.
Assurez-vous que le volume choisi est bien mémorisé et que
les chiffres qui l'indiquent apparaissent bien sur l'affichage
numérique..
Figure 2 Réglage du volume
Remarque importante : Pour que le dosage soit précis et
exact, il faut choisir un volume dans la gamme de volumes
propre à la pipette en question. Ne sélectionnez pas de
volume qui se situe en dehors de cette fourchette de valeurs.
Ne forcez pas le réglage du volume au-delà de la gamme de
volumes donnée ; vous risqueriez d'endommager le
mécanisme de la pipette.
2.2 Ejection de la pointe
Toute pipette à piston est pourvue d'un système d'éjection de
la pointe destiné à prévenir une éventuelle contamination.
Avec le pouce, enfoncez le bouton d'éjection et retirez la
pointe du cône de la pipette.
45
Page 48

Utilisation de la pipette
2.3 Techniques de pipetage
Pour contrôler la pipette, utilisez le bouton du piston situé à
l'extrémité de la poignée.
Pour un maximum de précision, respectez les consignes
suivantes :
1. Levez et abaissez le bouton du piston lentement et à
vitesse régulière (surtout si vous pipetez des liquides très
visqueux).
2. Ne laissez pas "sauter" le bouton du piston.
3. Placez une pointe neuve en appuyant et en tournant
légèrement le cône de la pipette à piston.
4. Assurez-vous que la pointe est solidement fixée dans le
cône et qu'il n'y a aucun corps étranger entre eux.
5. Amorcez les pointes en les remplissant et les vidant
plusieurs fois de suite avec le liquide concerné.
6. Durant le prélèvement, tenez la pipette le plus
verticalement possible (pas plus de 10° par rapport à la
verticale).
7. La pipette et la pointe doivent être à la même température
que le liquide.
46
Page 49

Section 3 Technique standard
1. Enfoncez le bouton jusqu'au premier point de poussée.
2. Plongez la pointe de la pipette sous la surface du liquide
(2–3 mm) et relâchez lentement le bouton du piston.
Retirez la pointe du liquide et effleurez le bord du récipient
pour ôter l'excédent le liquide.
3. Posez la pointe contre la paroi interne du récipient et
pipetez le liquide en appuyant légèrement et
régulièrement sur le bouton du piston jusqu'au premier
point de poussée. Maintenez la pipette dans cette
position. Après une seconde environ, enfoncez le bouton
jusqu'au second point de poussée pour vider
complètement la pointe.
4. Laissez revenir le bouton de commande en position
initiale.
Figure 3 Technique standard
a Position initiale c Second point de poussée
b Premier point de poussée
Remarque importante : Après usage, remplacez la pointe!
47
Page 50

Section 4 Pipetage de sang
complet
1. Plongez la pointe dans le réactif et enfoncez le bouton du
piston jusqu'au premier point de poussée. Assurez-vous
que la pointe de la pointe se trouve bien sous la surface.
2. Laissez remonter lentement le bouton du piston jusqu'à sa
position initiale. La pointe est à présent remplie de réactif.
Ne la retirez pas encore du réactif.
3. Enfoncez le bouton du piston jusqu'au premier point de
poussée et relâchez-le à nouveau lentement. Répétez
cette manoeuvre jusqu'à ce qu'il n'y ait plus de sang sur la
paroi de la pointe.
4. Enfoncez le bouton du piston jusqu'au second point de
poussée et videz complètement la pointe.
Figure 4 Pipetage de sang complet
a Position initiale c Second point de poussée
b Premier point de poussée
48
Page 51

Section 5 Contrôle quotidien
Contrôlez la pipette chaque jour avant le début du travail ou en
fin de journée. Vérifiez qu'elle ne porte ni poussières, ni
salissures extérieures. Faites tout particulièrement attention
au cône d'adaptation de la pointe. Nettoyez la pipette avec de
l'alcool à 70%. N'utilisez pas d'autre solvant.
49
Page 52

Section 6 Entretien
Si la pipette sert quotidiennement, elle doit être entretenue au
moins deux fois par an. Vous pouvez l'entretenir vousmême,
au laboratoire. Procédez par étapes, comme suit :
6.1 Pour ouvrir la pipette (0,2–1,0 mL)
1. Enfoncez le bouton d'éjection.
2. Introduisez la pointe de l'outil d'ouverture dans l'orifice
situé à l'extrémité du bouton d'éjection.
3. Otez le bouton et le piston d'éjection de la pointe.
50
Figure 5 Pour ouvrir la pipette
Page 53

Entretien
4. Retirez le cône d'adaptation de la pointe en le faisant
tourner dans le sens anti-horlogique, à l'aide de l'outil
fourni.
5. Retirez le piston.
6. Otez les joints toriques du cône d'adaptation de la pointe.
7. Nettoyez le piston, les ressorts de piston et les joints
toriques à l'aide d'un chiffon sec et propre.
8. Vérifiez qu'il n'y a pas de substance étrangère dans le
cylindre. Attention! le cylindre ne doit pas être graissé.
9. Graissez les parties nettoyées avec la graisse fournie.
10. Remontez les différentes pièces.
51
Page 54

Entretien
6.2 Pour ouvrir la pipette (1–5 mL)
1. Retirez le bouton d'éjection et l'éjecteur de la pointe
comme décrit pour la pipette 0,2–1,0 mL Section 6.1 a la
page 50.
2. Otez le couvercle.
3. Retirez le cône et le cylindre en pressant l'un vers l'autre
les deux ergots de butée à l'aide de l'outil. Tout en
pressant, faites glisser l'outil en direction du cône.
Figure 6 Pour ouvrir la pipette
1 L’outil pour ouvrir la pipette
4. Démontez, nettoyez et graissez comme expliqué pour la
pipette 0,2–1,0 mL Section 6.1 a la page 50.
5. Remontez en suivant les étapes dans l'ordre inverse.
52
Page 55

Section 7 Etalonnage
La pipette a été étalonnée en usine avec de l'eau distillée à
22 °C/72 °F. Un usage courant ne nécessite pas de
recalibrage. La pipette dispose toutefois d'une possibilité
d'adaptation à d'autres températures et viscosités. Pour
étalonner la pipette, il faut une balance de laboratoire de
sensibilité adéquate, un petit bécher et de l'eau distillée.
Remarque importante : En cas de remplacement de la
poignée ou du piston, il faut recalibrer la pipette. En cas de
remplacement des joints toriques ou du cône, il faut vérifier
l'étalonnage.
7.1 Vérification de l'étalonnage
1. Réglez le volume de la pipette comme expliqué
ci-dessous Tableau 1 Vérification de l'étalonnage :
Tableau 1 Vérification de l'étalonnage
Pipette
(µL)
10 10 9,8–10,2
20 20 19,8–20,2
50 50 49,5–50,5
100 100 99,2–100,8
200 200 198,7–201,3
500 500 497,0–503,0
1000 1000 994,0–1006,0
2000 2000 1990,0–2010,0
200–1000 300 298–302
1000–5000 2000 1990–2010
Réglage
du volume
Gamme
de masse autorisée
(mg)
53
Page 56

Etalonnage
2. Placez une pointe sur le cône en appuyant et en tournant
légèrement.
3. Pipetez de l'eau distillée au moins cinq fois dans le
bécher préalablement pesé. Notez chaque masse en mg,
en prenant une décimale, et comparez avec la valeur
précitée. Si une des valeurs se situe en dehors de la
fourchette de valeurs, la pipette doit être recalibrée.
54
Page 57

Section 8 Recalibrage
Pour l'étalonnage, utilisez la clef d'étalonnage fournie.
1. Introduisez la clef d'étalonnage dans les orifices des
rainures d'étalonnage situés à l'extrémité supérieure de la
poignée.
2. Augmentez le volume en tournant dans le sens horlogique
ou diminuez-le en tournant dans l'autre sens..
Figure 7 Recalibrage
1 Clef d'étalonnage
3. Vérifiez le réglage du volume de la manière expliquée
précédemment. Section 7 Etalonnage a la page 53
Remarque importante : La pipette ne peut être étalonnée
que dans la gamme de volumes qui lui est propre.
55
Page 58

Section 9 Recherche de
problèmes
Le tableau qui suit vous donne des indications sur les
problèmes possibles et la manière de les résoudre :
Tableau 2 Description de problèmes
Problème Cause possible Solution
Fixez la pointe
correctement
Nettoyez le cône et
placez une nouvelle
pointe
Nettoyez et graissez
les joints toriques et
le piston dans le
cylindre. Employez
la graisse fournie
Graissez
suffisamment
Remplacez les joints
toriques
Suivez le mode
d'emploi
Fixez la pointe
correctement
Recalibrez
Fuite
Pipetage incorrect
Pointe mal fixée
Corps étranger entre
le cône et la pointe
Corps étranger entre
le joint torique et le
piston
Graissage insuffisant
des joints toriques et
du piston
Joints toriques
défectueux
Mauvaise
manoeuvre
Pointe mal fixée
L'étalonnage s'est
modifié à cause, par
exemple, d'une
mauvaise
manoeuvre
56
Page 59

Section 10 Garantie,
responsabilité et
réclamations
Votre fabricant garantit que le produit livré est exempt de vices
de matériaux et d’usinage et s’engage à réparer ou à
remplacer gratuitement les éventuelles pièces erronées.
Le délai de prescription pour les réclamations concernant les
pipettes achetés est de 24 mois.
Le fournisseur est responsable des vices, comprenant
également l’absence de propriétés garanties, à l’exclusion de
toute autre demande, de la manière suivante : Le fournisseur
choisit de réparer gratuitement ou de remplacer toutes les
pièces qui, pendant la garantie à compter du jour du transfert
des risques, sont indubitablement inutilisables ou dont l’utilité
est nettement compromise à la suite d’un événement situé
avant le transfert des risques, notamment en raison de vices
de construction, de matériaux ou de finition. Le client est tenu
de notifier immédiatement par écrit au fournisseur la
constatation de tels vices, toutefois sept jours au plus tard
après la constatation du défaut. Dans le cas contraire, la
prestation est considérée comme acceptée en dépit du vice
constaté. Il n’existe pas de responsabilité supplémentaire pour
tout dommage direct ou indirect.
Si, pendant la garantie, conformément aux consignes
prescrites par le fournisseur, certains travaux de maintenance
spécifiques à la pipette sont à effectuer par le client
(maintenance) et que ces travaux ne sont pas effectués, le
client perdra tout droit à réparation des dommages dus au
non-respect de ces prescriptions.
Il est impossible de faire valoir des droits supplémentaires,
notamment des droits à réparation des dommages
consécutifs.
Les pièces d’usure et les dommages causés par une
manipulation, un montage ou une application non conformes,
sont exclus de cette clause.
57
Page 60

Garantie, responsabilité et réclamations
58
Page 61

Sección 1 Descripción de la
pipeta de émbolo
Figura 1 Descripción de la pipeta de émbolo
1 Disco de empuje 4 Cono
2 Pulsador de expulsión 5 Indicación del volumen
3 Expulsor de la punta
59
Page 62

Descripción de la pipeta de émbolo
La pipeta de émbolo es una pipeta de microlitro fácil de
manejar, de uso general, destinada a la toma y dosificación de
volúmenes exactos de líquido. Funciona según el principio de
la expulsión de aire y utiliza puntas desechables. El volumen
que se ha de pipetear aparece en un display bien visible, en el
mango de la pipeta. Todas las pipetas de émbolo están
equipadas con un sistema mecánico de expulsión de la punta.
1.1 Puntas de pipeta
Recomendamos utilizar únicamente puntas de pipeta HACH
originales al trabajar con la pipeta de émbolo. Las puntas de
pipeta son de polipropileno y pueden ser tratadas en
autoclave a 121 °C/250 °F.
60
Page 63

Sección 2 Utilización de la
pipeta
2.1 Ajuste del volumen
(solamente para las pipetas de émbolo variables)
El volumen a pipetear se fija con el disco de empuje situado
en el extremo del mango. Para aumentar el volumen, gire el
disco en sentido antihorario y, para reducirlo, gírelo en sentido
horario. Cerciórese de que el volumen seleccionado es
correcto (queda fijado en su sitio con un clic) y de que los
números que lo indican se ven bien en el display.
Figura 2 Ajuste del volumen
Nota importante: La precisión y exactitud especificadas son
únicamente válidas para el rango de volumen especificado en
la pipeta. No seleccionar un volumen que se encuentre fuera
de este rango. No girar con fuerza el disco de empuje para
fijar un volumen que se encuentra fuera del rango
especificado, ya que se podría estropear el mecanismo de la
pipeta.
2.2 Expulsión de la punta
Todas las pipetas de émbolo están equipadas con un sistema
de expulsión de la punta para impedir una posible
contaminación. Presione el pulsador de expulsión con el dedo
pulgar y retire la punta del cono.
61
Page 64

Utilización de la pipeta
2.3 Técnicas de pipeteado
Para manejar la pipeta utilice el disco de empuje que tiene en
el extremo del mango.
Para obtener la máxima precisión siga las siguientes
recomendaciones:
1. Suba y baje el disco de empuje lentamente y a una
velocidad uniforme (sobre todo al pipetear líquidos muy
viscosos).
2. No deje que el disco de empuje "salte" y vuelva a su
posición inicial.
3. Para colocar una punta nueva en el cono, presione
ligeramente y gire un poco la punta.
4. Cerciórese de que la punta está firmemente colocada en
el cono y de que no existen cuerpos extraños entre
ambos.
5. Humedezca las puntas llenándolas y vaciándolas varias
veces seguidas con el líquido en cuestión.
6. Mantenga la pipeta en posición casi vertical (no más de
10° respecto de la vertical) mientras el líquido está
entrando en la punta.
7. La temperatura de la pipeta y de la punta debe ser igual a
la del líquido.
62
Page 65

Sección 3 Técnica estándar
1. Presione el disco de empuje hasta el primer punto de
presión.
2. Introduzca la punta de la pipeta en el líquido (a una
profundidad de 2 ó 3 mm) y suelte lentamente el disco de
empuje. Saque la punta del líquido y toque con ella la
pared interior del recipiente para eliminar el exceso de
líquido.
3. Ponga la punta contra la pared interior del recipiente y
presione uniforme y ligeramente el disco de empuje hasta
alcanzar el primer punto de presión. Mantenga la pipeta
en esta posición. Al cabo de aprox. un segundo, presione
el disco de empuje hasta el segundo punto de presión; así
se habrá vaciado totalmente la punta.
4. Deje que el disco de empuje vuelva a su posición inicial.
Figura 3 Técnica estándar
a Posición inicial c Segundo punto de presión
b Primer punto de presión
Nota importante: ¡Cambiar la punta después del uso!
63
Page 66

Sección 4 Pipeteado de
sangre completa
1. Introduzca la punta en la muestra y presione el disco de
empuje hasta el primer punto de presión. Cerciórese de
que la punta está debajo de la superficie.
2. Suelte lentamente el disco de empuje hasta que se
encuentre en la posición inicial. La punta estará entonces
llena de muestra; no la saque de la muestra.
3. Presione el disco de empuje hasta el primer punto de
presión y, lentamente, vuelva a soltarlo. Repita esta
operación hasta que no quede sangre en la pared de la
punta.
4. Presione el disco de empuje hasta el segundo punto de
presión y vacíe totalmente la punta.
Figura 4 Pipeteado de sangre completa
a Posición inicial c Segundo punto de presión
b Primer punto de presión
64
Page 67

Sección 5 Control diario
Compruebe la pipeta cada día, antes de empezar a trabajar o
después de finalizado el trabajo, para verificar la posible
presencia de polvo y suciedad exterior. Preste especial
atención al cono de la punta. Limpie la pipeta con alcohol al
70%. No utilice ningún otro solvente.
65
Page 68

Sección 6 Mantenimiento
Si se utiliza la pipeta todos los días, el mantenimiento deberá
realizarse por lo menos dos veces al año; lo puede llevar a
cabo Usted mismo, en el laboratorio. Proceda de la manera
que se describe a continuación:
6.1 Abrir las pipetas (0,2–1,0 mL)
1. Presione el pulsador de expulsión.
2. Introduzca la punta de la herramienta de apertura en el
orificio situado en el extremo del pulsador de expulsión.
3. Saque el pulsador de expulsión y el émbolo de expulsión
de la punta.
66
Figura 5 Cómo abrir las pipetas
Page 69

Mantenimiento
4. Retire el cono de la punta girándolo en sentido antihorario
con la herramienta suministrada.
5. Saque el émbolo.
6. Retire las juntas tóricas del cono de la punta.
7. Limpie el émbolo, el muelle del émbolo y las juntas tóricas
con un paño seco y limpio.
8. Compruebe que no existen sustancias extrañas en el
cilindro. Tenga en cuenta que no hay que engrasar el
cilindro.
9. Engrase las partes limpias ligeramente con la grasa
suministrada.
10. Vuelva a ensamblar la pipeta.
67
Page 70

Mantenimiento
6.2 Abrir la pipeta (1–5 mL)
1. Retire el pulsador de expulsión y el expulsor de la punta
según lo descrito para las pipetas de 0,2–1,0 ml en la
Sección 6.1 en la página 66.
2. Retire la cubierta.
3. Retire el cono y el cilindro utilizando la herramienta,
apretando las dos guías. Al tiempo que presiona las
guías, deslice la herramienta hacia el cono.
Figura 6 Cómo abrir la pipeta
1 Herramienta para abrir la pipeta
4. Proceda a desmontar, limpiar y engrasar según lo descrito
para las pipetas de 0,2–1,0 ml en la Sección 6.1 en la
página 66.
5. Reensamblar en el orden inverso.
68
Page 71

Sección 7 Calibración
La pipeta se ha calibrado en fábrica con agua destilada a
22 °C/72 °F. Para el uso de rutina no se requiere recalibración.
No obstante, existe la posibilidad de recalibrar la pipeta para
otras temperaturas y soluciones de diferentes viscosidades.
Para realizar la calibración se necesitan una balanza analítica
con una sensibilidad adecuada, un vaso pequeño y agua
destilada.
Nota importante: En el caso de que se cambien el mango o
el émbolo, se deberá recalibrar la pipeta. Si se cambian las
juntas tóricas o el cono, se deberá verificar la calibración.
7.1 Comprobación de la calibración
1. Prefije el volumen de la pipeta según lo indicado en la
Tabla 1 Comprobación de la calibración:
Tabla 1 Comprobación de la calibración
Pipeta
(µL)
10 10 9,8–10,2
20 20 19,8–20,2
50 50 49,5–50,5
100 100 99,2–100,8
200 200 198,7–201,3
500 500 497,0–503,0
1000 1000 994,0–1006,0
2000 2000 1990,0–2010,0
200–1000 300 298–302
1000–5000 2000 1990–2010
Ajuste del volumen
Rango de peso
admisible
(mg)
69
Page 72

Calibración
2. Coloque una punta en el cono, presionando ligeramente y
girando un poco la punta.
3. Proceda a pipetear agua destilada, por lo menos cinco
veces, en el vaso previamente pesado. Determine cada
peso en mg, con una posición decimal, y compárelo con el
peso anteriormente citado. Si el peso está fuera del rango
de valores se deberá recalibrar la pipeta.
70
Page 73

Sección 8 Recalibración
La calibración se lleva a cabo con la llave de calibración
suministrada.
1. Coloque la llave en los agujeros de la ranura de
calibración situada en el extremo superior del mango.
2. Aumente el volumen girando en sentido horario o
redúzcalo girando en sentido antihorario.
Figura 7 Recalibración
1 Llave de calibración
3. Compruebe el ajuste del volumen de la forma descrita en
la Sección 7 Calibración en la página 69.
Nota importante: La pipeta solamente se puede calibrar
dentro de los límites del rango de volúmenes para el que está
prevista.
71
Page 74

Sección 9 Localización y
resolución de
fallos
La Tabla siguiente está prevista para ayudarle a identificar y
eliminar posibles fallos:
Tabla 2 Localización y resolución de fallos
Error Posible causa Solución
Fuga
Pipeteado
incorrecto
La punta no está
correctamente
colocada
Cuerpos extraños
entre el cono y la
punta
Cuerpos extraños
entre la junta tórica y
el émbolo
Grasa insuficiente
en las juntas tóricas
y el émbolo
Juntas tóricas
defectuosas
Funcionamiento
incorrecto
La punta no está
firmemente colocada
La calibración ha
cambiado, p.ej.
debido a un manejo
incorrecto
Fijar la punta
firmemente en su
sitio
Limpiar el cono y
colocar una punta
nueva
Limpiar y engrasar
las juntas tóricas y el
émbolo en el
cilindro. Utilizar la
grasa suministrada.
Engrasar
adecuadamente
Cambiar las juntas
tóricas
Utilizar la pipeta de
la forma descrita en
el manual
Fijar la punta
correctamente
Recalibrar
72
Page 75

Sección 10 Garantía,
responsabilidad y
reclamaciones
El fabricante garantiza que el producto suministrado se
encuentra libre de fallas de material y de fabricación y se
obliga a reparar o bien reemplazar gratuitamente las piezas
defectuosas.
El plazo prescriptivo para reclamos de falla en estos pipetas
es de 24 meses.
Para los defectos a los cuales pertenece también la ausencia
de las características aseguradas, el proveedor asume la
garantía del siguiente modo, bajo exclusión de mayores
responsabilidades: A opción del proveedor se han de reparar
o suministrar nuevamente sin coste alguno todas aquellas
piezas que se han vuelto inutilizables o cuya utilizabilidad se
ha perjudicado considerablemente y en forma comprobada a
causa de una circunstancia previa al traspaso de riesgo,
particularmente a causa de una falla de construcción, mala
calidad del material de construcción o bien un diseño
defectuoso, dentro del período de garantía y a partir del
momento de traspaso de riesgo. La determinación de tales
defectos debe notificarse por escrito en forma inmediata al
proveedor, a más tardar dentro de 7 días posteriores a la
detección del defecto. En caso que el cliente no proceda con
este aviso, se considera la prestación de servicio como
autorizada, sin considerar el defecto. No se aplica una
responsabilidad que supere los daños directos e indirectos.
En caso que el fabricante prescribiera dentro del período de
garantía la ejecución de trabajos de mantenimiento
específicos por parte del cliente y no se cumplieran estas
prescripciones, se termina la pretensión de garantía para
daños derivados por la no observación de las prescripciones.
No pueden reclamarse mayores pretensiones,
particularmente por daños consecutivos.
De esta regulación se consideran excluidas las piezas de
desgaste y los daños causados por un manejo inapropiado,
un montaje inseguro o bien una aplicación fuera del uso
previsto.
73
Page 76

Garantía, responsabilidad y reclamaciones
74
Page 77

Sezione 1 Descrizione della
pipetta a pistone
Figura 1 Descrizione della pipetta a pistone
1 Pulsante 4 Cono
2 Pulsante espulsore 5 Scala volume
3 Espulsore del puntale
75
Page 78

Descrizione della pipetta a pistone
La pipetta a pistone è una pipetta a microlitro estremamente
comoda ed universale concepita per eseguire il trasferimento
di volumi di liquido esatti. Essa funziona secondo il principio
dell’espulsione d’aria ed utilizza puntali monouso. Il volume da
pipettare è indicato su un visore chiaramente visibile posto
sull’impugnatura della pipetta. Tutte le pipette a pistone sono
dotate di un sistema meccanico per l’espulsione del puntale.
1.1 Puntali per pipette
Raccomandiamo di usare puntali per pipette HACH quando si
lavora con la pipetta a pistone. I puntali per pipette sono
fabbricati in polipropilene e possono essere autoclavati a
121 °C.
76
Page 79

Sezione 2 Uso della pipetta
2.1 Regolazione del volume
(solo per le pipette a pistone variabili)
Il volume della pipetta è regolato mediante il pulsante posto
sull’estremità dell’impugnatura. Girare il pulsante in senso
antiorario per aumentare il volume ed in senso orario per
ridurlo. Accertarsi che la regolazione del volume sia corretta
(clicca in posizione) e che il volume indicato sul visore sia
completamente visibile.
Figura 2 Regolazione del volume
Nota importante: la precisione ed accuratezza indicate si
riferiscono soltanto all'intervallo di volume specificato sulla
pipetta. Non regolare il volume su un valore esterno a tale
intervallo. Non usare la forza per girare il pulsante su un
volume esterno all'intervallo specificato. Così facendo infatti si
può danneggiare la pipetta.
2.2 Espulsione del puntale
Ogni pipetta a pistone è dotata di un sistema di espulsione del
puntale atto a prevenire eventuali contaminazioni. Con il
pollice premere il pulsante espulsore e rimuovere il puntale
dall’apposito cono.
77
Page 80

Uso della pipetta
2.3 Tecniche di pipettatura
La pipetta viene fatta funzionare con il pulsante posto
sull’estremità dell’impugnatura.
La massima accuratezza si ottiene eseguendo i seguenti
punti:
1. Muovere il pistone su e giù in maniera lenta e uniforme.
(soprattutto quando si pipettano liquidi altamente viscosi)
2. Non lasciare che il pulsante scatti indietro sulla posizione
originale.
3. Inserire un nuovo puntale nel cono esercitando una
leggera pressione e girando leggermente il puntale.
4. Accertarsi che il puntale sia saldamente posizionato nel
cono e che tra il puntale ed il cono non sia presente alcun
corpo estraneo.
5. Inumidire i puntali con il liquido riempiendoli e svuotandoli
ripetutamente.
6. Tenere la pipetta in posizione quasi verticale (a non più di
10° dalla verticale) mentre il liquido è aspirato nel puntale.
7. La temperatura della pipetta e del puntale deve
corrispondere a quella del liquido.
78
Page 81

Sezione 3 Tecnica standard
1. Premere il pulsante sul primo punto di pressione.
2. Immergere il puntale della pipetta sotto la superficie del
liquido (2–3 mm) e rilasciare lentamente il pulsante.
Estrarre il puntale dal liquido e con esso toccare la parete
interna del contenitore in modo da rimuovere il liquido in
eccesso.
3. Posizionare il puntale contro la parete interna del
contenitore e premere il pulsante in maniera leggera ed
uniforme fino a raggiungere il primo punto di pressione.
Tenere la pipetta in tale posizione. Dopo circa un secondo,
premere il pulsante fino a raggiungere il secondo punto di
pressione. Così facendo il puntale si svuota
completamente.
4. Lasciare che il pulsante torni sulla posizione di riposo.
Figura 3 Tecnica standard
a Posizione di riposo c Secondo punto di pressione
b Primo punto di pressione
Nota importante: dopo l’uso sostituire il puntale della pipetta!
79
Page 82

Sezione 4 Pipettare sangue
intero
1. Immergere il puntale nel campione e premere il pulsante
fino a raggiungere il primo punto di pressione. Accertarsi
che il puntale si trovi sotto la superficie.
2. Rilasciare lentamente il pulsante finché è nella posizione
iniziale. Il puntale è ora pieno di campione. Non togliere il
puntale dal campione.
3. Premere il pulsante fino a raggiungere il primo punto di
pressione e quindi rilasciarlo di nuovo lentamente.
Ripetere finché la parete del puntale è priva di sangue.
4. Premere il pulsante fino a raggiungere il secondo punto di
pressione e svuotare completamente il puntale.
Figura 4 Pipettare sangue intero
a Posizione di riposo c Secondo punto di pressione
b Primo punto di pressione
80
Page 83

Sezione 5 Controllo quotidiano
Controllare quotidianamente che la pipetta non presenti tracce
di polvere o sporco esterno prima di iniziare o finire il lavoro,
facendo particolare attenzione al cono del puntale. Pulire la
pipetta con alcool al 70%. Non usare alcun altro solvente per
pulire la pipetta.
81
Page 84

Sezione 6 Manutenzione
Se la pipetta è usata ogni giorno, la manutenzione deve
essere eseguita almeno due volte all’anno. La manutenzione
può essere eseguita nel proprio laboratorio. Eseguire le fasi
descritte qui di seguito:
6.1 Apertura delle pipette (0,2–1,0 mL)
1. Premere il pulsante espulsore.
2. Inserire la punta dello strumento apertore nell’apertura
sull’estremità del pulsante espulsore.
3. Tirare fuori il pulsante espulsore ed il pistone espulsore
del puntale.
82
Figura 5 Apertura delle pipette
Page 85

Manutenzione
4. Rimuovere il cono del puntale girandolo in senso
antiorario con lo strumento fornito a corredo.
5. Tirare fuori il pistone.
6. Togliere gli O-ring dal cono del puntale.
7. Pulire il pistone, la molla del pistone e gli O-ring con un
panno asciutto e pulito.
8. Controllare che sul cilindro non siano presenti sostanze
estranee. Ricordarsi che il cilindro non deve essere
ingrassato.
9. Ingrassare leggermente le parti pulite con il grasso fornito
a corredo.
10. Riassemblare la pipetta.
83
Page 86

Manutenzione
6.2 Apertura della pipetta (1–5 mL)
1. Rimuovere il pulsante espulsore e l’espulsore del puntale
come precedentemente descritto (per le pipette da
0,2–1,0 mL) sezione 6.1 a pagina 82.
2. Rimuovere il coperchio.
3. Rimuovere il cono ed il cilindro con l’aiuto dell’utensile
premendo le due sporgenze una verso l’altra. Premendo
le sporgenze, spingere l’utensile verso il cono.
Figure 6 Apertura della pipetta
1 Utensile di assistenza per l’apertura della pipetta
4. Smontare, pulire ed ingrassare come precedente descritto
(per le pipette da 0,2–1,0 mL) sezione 6.1 a pagina 82.
5. Riassemblare in sequenza inversa.
84
Page 87

Sezione 7 Calibrazione
La pipetta è calibrata in fabbrica con acqua distillata a 22 °C.
Per l’impiego di routine non è richiesta alcuna ricalibrazione.
La pipetta può tuttavia essere ricalibrata per altre temperature
e soluzioni di diversa viscosità. Per eseguire la calibrazione
sono necessari una bilancia analitica di sensibilità appropriata,
un piccolo bicchiere ed acqua distillata.
Nota importante: se vengono sostituiti l’impugnatura o il
pistone, la pipetta deve essere ricalibrata. Se vengono
sostituiti gli O-ring o il cono del puntale, la calibrazione deve
essere verificata.
7.1 Controllo della calibrazione
1. Impostare il volume della pipetta come segue in Tabella 1
Controllo della calibrazione:
Tabella 1 Controllo della calibrazione
Pipetta
(µL)
10 10 9,8–10,2
20 20 19,8–20,2
50 50 49,5–50,5
100 100 99,2–100,8
200 200 198,7–201,3
500 500 497,0–503,0
1000 1000 994,0–1006,0
2000 2000 1990,0–2010,0
200–1000 300 298–302
1000–5000 2000 1990–2010
Regolazione del
volume
Intervallo di peso
ammesso
(mg)
85
Page 88

Calibrazione
2. Posizionare il puntale sul rispettivo cono esercitando una
leggera pressione e ruotando leggermente il puntale.
3. Pipettare l’acqua distillata nel bicchiere precedentemente
pesato per almeno cinque volte. Determinare ciascun
peso in mg alla prima posizione decimale e confrontarlo
con il peso su indicato. Se il peso non rientra in questo
intervallo, ricalibrare la pipetta.
86
Page 89

Sezione 8 Ricalibrazione
La calibrazione è eseguita con la chiave di calibrazione fornita
a corredo.
1. Mettere la chiave di calibrazione nei fori della scanalatura
di calibrazione posta sull’estremità superiore
dell’impugnatura.
2. Aumentare il volume girando il senso orario o ridurlo
girando il senso antiorario.
Figura 7 Ricalibrazione
1 Chiave di calibrazione
3. Quindi controllare il volume come precedentemente
descritto Sezione 7 Calibrazione a pagina 85.
Nota importante: la pipetta può essere calibrata soltanto
entro i limiti dell’intervallo di volume a cui è destinata.
87
Page 90

Sezione 9 Diagnostica
La tabella seguente è concepita per aiutare ad identificare ed
eliminare eventuali errori:
Tabella 2 Diagnostica
Errore Causa possibile Risposta
Perdita
Pipettatura
inaccurata
Puntale non
correttamente
attaccato
Corpi estranei tra
cono e puntale
Corpi estranei tra
O-ring e pistone
Grasso insufficiente
sugli O-ring ed il
pistone
O-ring guasti Sostituire gli O-ring
Funzionamento
incorretto
Puntale non
saldamente
attaccato
La calibrazione è
cambiata, ad es. a
causa di un
funzionamento
difettoso
Fissare il puntale
saldamente in
posizione
Pulire il cono ed
attaccare un nuovo
puntale
Pulire ed ingrassare
gli O-ring ed il
pistone nel cilindro
usando il grasso
fornito
Ingrassare
adeguatamente
Usare la pipetta
come indicato nel
manuale
Attaccare
saldamente il
puntale
Ricalibrare
88
Page 91

Sezione 10 Garanzia,
responsabilità e
reclami
Il produttore garantisce che il prodotto fornito non presenta
difetti di materiale o di lavorazione e si impegna a riparare o a
sostituire gratuitamente eventuali componenti difettosi.
Il periodo di prescrizione per rivendicazioni dovute a reclami
corrisponde a 24 mesi per tutte le pipetta.
Il fornitore è responsabile per eventuali difetti, tra i quali rientra
la mancanza delle caratteristiche assicurate, fatta esclusione
di altre rivendicazioni: il fornitore è tenuto a riparare
gratuitamente o a sostituire – a sua scelta – tutti i componenti
che, entro il periodo di prescrizione, calcolato a partire dal
giorno del trapasso del rischio, risultino inutilizzabili o
utilizzabili solo con notevoli limiti e tale inutilizzabilità sia
imputabile a condizioni precedenti il trapasso del rischio, in
particolar modo struttura costruttiva difettosa, materiali
scadenti o produzione difettosa. Il fornitore va
immediatamente informato per iscritto del fato che si siano
rilevati tali difetti, comunque entro i 7 giorni successivi alla
constatazione del difetto. Se il cliente non esegue tale
comunicazione, la prestazione commerciale effettuata sarà
ritenuta accettata, nonostante la presenza di difetti. Si esclude
un'eventuale ulteriore responsabilità per danni potenziali o
imminenti.
Se, durante il periodo di prescrizione, il fornitore prescrive
operazioni di manutenzione da eseguirsi da parte del cliente
stesso (manutenzione) e tali operazioni non siano state
effettuate, decade il diritto di rivendicazione per i danni derivati
dalla non osservanza delle suddette prescrizioni.
Non sono rivendicabili ulteriori reclami, in particolari i reclami
inerenti il risarcimento per danni indiretti.
Le parti soggette ad usura ed eventuali guasti causati da un
utilizzo improprio, da montaggio inadeguato o da un uso non
corretto, sono esclusi dalle condizioni sopra riportate.
89
Page 92

Garanzia, responsabilità e reclami
90
Page 93

Page 94

Page 95

Page 96

Hach Company
PO Box 389
Loveland, CO 80539
Phone: 970/669-3050
Fax: 970/669-2932
orders@hach.com
www.hach.com
Great Britain
Hach Lange LTD
Pacific Way
Salford
Manchester, M50 1DL
Tel. +44 (0)161 872 14 87
Fax +44 (0)161 848 73 24
info@hach-lange.co.uk
www.hach-lange.co.uk
Austria
Dr. Bruno Lange Ges. MBH
Industriestraße 12
A-3200 Obergrafendorf
Tel. +43 (0)27 47 74 12
Fax +43 (0)27 47 42 18
info@hach-lange.at
www.hach-lange.at
France
Hach Lange
Hach SAS
33 Rue du Ballon
F-93165 Noisy Le Grand
Tél. +33 (0)1 48 15 68 70
Fax +33 (0)1 48 15 80 00
info@hach-lange.fr
www.hach-lange.fr
Spain
Hach Lange S.L.U.
C/Araba, 45. Apdo. 220
E-20800 Zarautz/Guipúzcoa
Tel. +34 9 43 89 43 79
Fax +34 9 43 13 02 41
info@hach-lange.es
www.hach-lange.es
Germany
Hach Lange GmbH
Willstätterstr. 11
D-40549 Düsseldorf
Tel. +49 (0)2 11 52 88-0
Fax +49 (0)2 11 52 88-143
info@hach-lange.de
www.hach-lange.de
Switzerland
Dr. Bruno Lange AG
Juchstrasse 1
CH-8604 Hegnau
Tel. +41(0)44 9 45 66 10
Fax +41(0)44 9 45 66 76
info@hach-lange.ch
www.hach-lange.ch
Belgium
Hach Lange SA
Motstraat 54
B-2800 Mechelen
Tél. +32 (0)15 42 35 00
Fax +32 (0)15 41 61 20
info@hach-lange.be
www.hach-lange.be
Portugal
Hach Lange LDA
Rua dos Malhões
Edif. D. Pedro I
P-2770-071 Paço D'Arcos
Tel. +351 210 00 1750
Fax +351 210 00 8140
info@hach-lange.pt
www.hach-lange.pt
Italy
Hach Lange S.R.L.
Via Riccione, 14
I-20156 Milano
Tel. +39 02 39 23 14-1
Fax +33 02 39 23 14-39
info@hach-lange.it
www.hach-lange.it
1508010
 Loading...
Loading...