Page 1

Instructions - Parts
Optional PrecisionSwirl Orbital
Dispenser (sold separately)
PCF Control Center
PCF Fluid Plate
™
PCF
with
™
PrecisionSwirl
3A2098S
Precision Dispense System
Electronically-controlled fluid metering system that provides precise continuous flow of
up to four single-component sealants and adhesives through closed-loop technology.
Not for use in explosive atmospheres or hazardous locations.
For professional use only.
Important Safety Instructions
Read all warnings and instructions in this
manual. Save these instructions.
EN
See page 4 for model information. See page 5 for
maximum working pressure and approvals.
IMPORTANT:
This manual does not apply to some PCF systems. See note on page 3 to verify this is the
correct manual for your PCF system.
Page 2

Contents
Related Manuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Fluid Plate Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Control Panel Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Expansion Swirl Enclosure Assemblies . . . . . . . 8
PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser Assemblies . . . 8
Automation Gateway Assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Swirl Control DGM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Integration Upgrade with Advanced Map . . . . . 10
Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
System Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Typical Installation - Single Swirl, Single Fluid Plate
13
Typical Installation - Multiple Fluid Plates, No Swirl
Dispensers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Typical Installation - Multiple Fluid Plates, Multiple
Swirl Dispensers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Fluid Plate Assembly Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Control Center Assembly Overview . . . . . . . . . 19
Key Tokens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Before Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Install Control Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Install Fluid Plate Assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Install Cable Assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Install Gateway Module Interface . . . . . . . . . . . 34
System Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configure System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Configure Control Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configure Mode Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configure Delay Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configure Flow Meter Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Configure Pressure Loop Settings . . . . . . . . . . 39
Adjust Pressure Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Configure Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Setup Maintenance Schedule/Parameters . . . . 41
Configure Valve to Swirl Association and Motor
Error Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Configure Swirl Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configure Gateway Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Setup Styles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configure Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
On/Off Delays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Load Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Maintenance Mode Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Automation Control (Normal Operation) . . . . . . 49
Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Styles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Precharge Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Typical Job Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Pressure Relief Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
USB Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
USB Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
System Configuration Settings File . . . . . . . . . . 64
Custom Language File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Download Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Upload Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Fluid Plates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Flow Meter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Fluid Regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Dispense Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Gateway Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
LED Diagnostic Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
View Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Diagnose Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Event and Error Codes and Troubleshooting . . 71
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Maintenance Schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Advanced Display Module (ADM) . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Upgrade Gateway Module Software (16K743) . 81
Upgrade Gateway Module Fieldbus Map (16N601
or 17P799) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Upgrade Fluid Control Module (FCM) Software
(16K743) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Air Filter Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Swirl Dispensers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Fluid Plate Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Control Center Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Control Centers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Control Center and Expansion Swirl Enclosure
Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Fluid Plate Assembly Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
2 3A2098S
Page 3
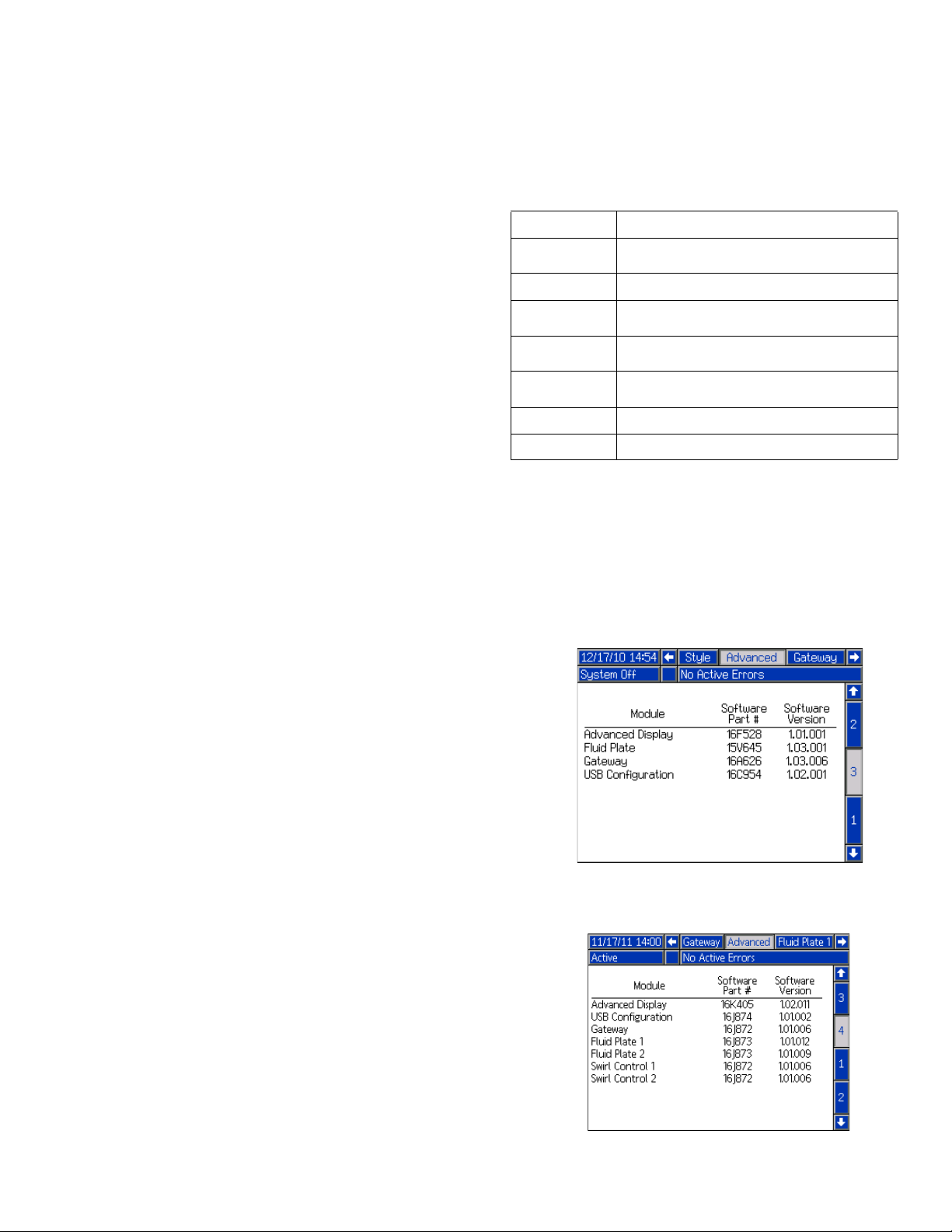
Related Manuals
ADM Software Part No. 16F528 or 15V769
(see manual 313377)
ADM Software Part No. 16K405
(use this manual)
Appendix A - Advanced Display Module (ADM) 104
Display Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Display Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Setup Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Run Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Appendix B - Discrete Gateway Module (DGM)
Connection Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
D-Sub Cable 123793 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
D-Sub Cable 123792 and Breakout Board 123783
122
DGM Digital Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
DGM Digital Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
DGM Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
DGM Analog Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Appendix C - Communications Gateway Module
(CGM) Connection Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Install Fieldbus Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
CGM I/O Data Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Appendix D - I/O Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . 146
Automation Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Automation Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Technical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Swirl Dispenser Technical Data . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Fluid Plate Assembly Technical Data . . . . . . . 149
Control Center Assembly Technical Data . . . . 149
Graco Standard Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Graco Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Related Manuals
The following is a list of component manuals written in
English. These manuals and any available translations
can be found at www.graco.com.
Manual Description
313377
309403 PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser
307517
308647
309834
3A4649 Integrated PCF Instructions
3A5295 Coriolis Flow Meter Instructions - Parts
NOTE: In the Advanced screens on your system, if the
Advanced Display software part number shown is
16F528 or 15V769 then this manual does not apply to
your system; refer to manual 313377 for your system.
Otherwise, the part number shown should be 16K405
and you should use this manual.
Original PCF Instructions - Parts
(see the note below)
Mastic Fluid Regulators Instructions-Parts
Fluid Pressure Regulators Instructions-Parts
Helical Gear Fluid Flow Meters Instructions-Parts
3A2098S 3
Page 4

Models
9902471
Certified to CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 61010-1
Conforms to
UL 61010-1
Models
Check the identification (ID) plate for the 6-digit part number of the fluid metering system. Use the following matrix to
define the construction of the system, based on the six digits. For example, Part PF1110 represents a PCF fluid
metering system (PF), a two style system (1), a fluid plate with a cartridge regulator and no meter (1), a DeviceNet
user interface (1) with a 100-240 Vac power supply (0).
NOTE: To order replacement parts, see Parts section in this manual. The digits in the matrix do not correspond to the
Ref. Nos. in the Parts drawings and lists.
™
PF 1
First and
Second Digits
PF
(Precision
Continuous
Flow)
1
Third Digit
Style/Size
Description Regulator Meter Description Description
1 2 Styles 1 Cartridge None 0 Discrete 0 100 - 240 Vac
16 Styles 2 Mastic None 1
2
3 256 Styles 3 Cartridge High
4 Mastic High
5 Heated
6 Heated Mas-
7 Cartridge Ultra High
8 Cartridge High
9 Mastic High
C Cartridge Coriolis
Fourth Digit
Fluid Plate
Mastic
tic
2
Resolution
3
Resolution
Heated
Standard Res-
olution
None 5 Not Used.
Resolution
Resolution /GB
Resolution /GB
4
6 DeviceNet
7 EtherNet I/P
1
Fifth Digit
User Interface
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
PROFIBUS
PROFINET
No ADM
No ADM
™
1 24 Vdc
™
2 100 - 240 Vac with
™
3 24 Vdc with
™
0
Sixth Digit
Voltage
Integrated Swirl
Integrated Swirl
Discrete Gateway systems do not include automation interface cables. The following Graco accessories are avail-
able for wiring to the automation system. Installers should follow Appendix B - Discrete Gateway Module
(DGM) Connection Details, page 121, for custom wiring.
For single fluid plate systems only: 50 ft (15 m) cable with flying leads (123793)
All systems: Breakout board (123783) and 50 ft (15 m) cable (123792)
NOTE: 256 styles option is not available with Discrete Gateway systems.
These fluid metering systems have ETL certification.
NOTE: Fluid metering systems with heated mastic regulators are not ETL certified.
1
This product has been tested to the requirements of CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 61010-1, second edition, including
C
Amendment 1, or a later version of the same standard incorporating the same level of testing requirements.
4 3A2098S
Page 5
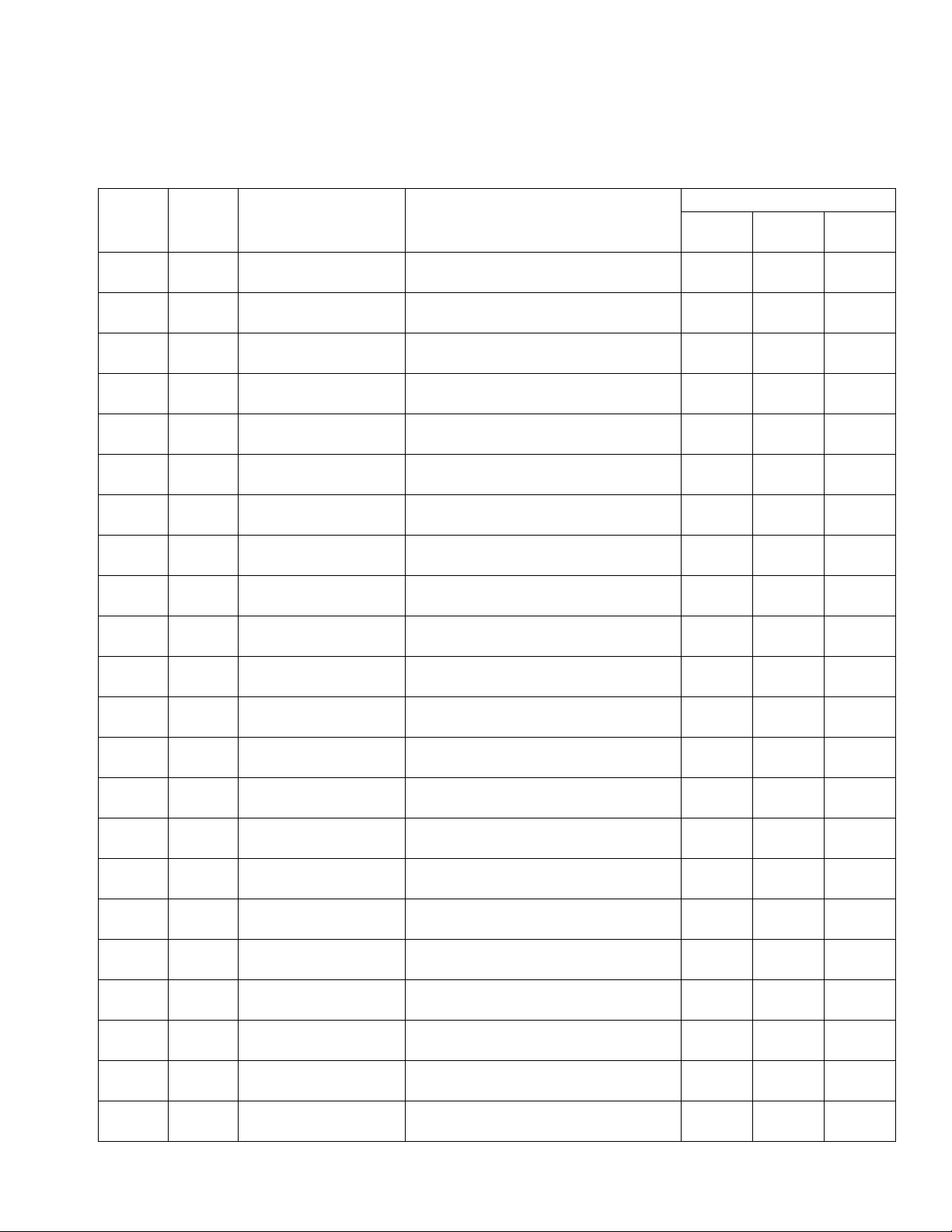
Models
Fluid Plate Kits
NOTE: The fluid plate kit numbers listed below include a CAN splitter. The fluid plate assembly included in each
PFxxxx assembly does not include a CAN splitter.
Includes:
Fluid
Plate Kit
24B958 PF13xx
24B959 PF11xx
24B960 PF14xx
24B961 PF12xx
24B962 PF15xx
24C901 PF16xx
24J873 PF17xx
24K801 PF23xx
24K802 PF21xx
24K803 PF24xx
24K804 PF22xx
24K805 PF25xx
24K806 PF26xx
24K807 PF27xx
24K808 PF33xx
24K809 PF31xx
24K810 PF34xx
24K811 PF32xx
24K812 PF35xx
24K813 PF36xx
24K814 PF37xx
24V592 PF18xx
Used by
Model
Maximum Working
Pressure
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
6000 psi
(41.4 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
Regula-
Description
Cartridge Regulator, High Resolution Flow
Meter, 2 styles
Cartridge Regulator, No Flow Meter,
2styles
Mastic Regulator, High Resolution Flow
Meter, 2 styles
Mastic Regulator, No Flow Meter, 2 styles 246642 --- 16M101
Heated Mastic Regulator, Standard Resolu-
tion Heated Flow Meter, 2 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, No Flow Meter,
2styles
Cartridge Regulator, Ultra High Resolution
Flow Meter, 2 styles
Cartridge Regulator, High Resolution Flow
Meter, 16 styles
Cartridge Regulator, No Flow Meter,
16 styles
Mastic Regulator, High Resolution Flow
Meter, 16 styles
Mastic Regulator, No Flow Meter, 16 styles 246642 --- 16M103
Heated Mastic Regulator, Standard Resolu-
tion Heated Flow Meter, 16 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, No Flow Meter,
16 styles
Cartridge Regulator, Ultra High Resolution
Flow Meter, 16 styles
Cartridge Regulator, High Resolution Flow
Meter, 256 styles
Cartridge Regulator, No Flow Meter,
256 styles
Mastic Regulator, High Resolution Flow
Meter, 256 styles
Mastic Regulator, No Flow Meter,
256 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, Standard
Resolution Heated Flow Meter, 256 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, No Flow Meter,
256 styles
Cartridge Regulator, Ultra High Resolution
Flow Meter, 256 styles
Cartridge Regulator, Glass Bead High
Resolution Flow Meter, 2 styles
tor
244734 246652 16M100
244734 --- 16M101
246642 246652 16M100
246643 246340 16M100
246643 --- 16M101
244734 16E993 16M100
244734 246652 16M102
244734 --- 16M103
246642 246652 16M102
246643 246340 16M102
246643 --- 16M103
244734 16E993 16M102
244734 246652 16M104
244734 --- 16M105
246642 246652 16M104
246642 --- 16M105
246643 246340 16M104
246643 --- 16M105
244734 16E993 16M104
244734 24P688 16M100
Flow
Meter
FCM Key
Token
3A2098S 5
Page 6
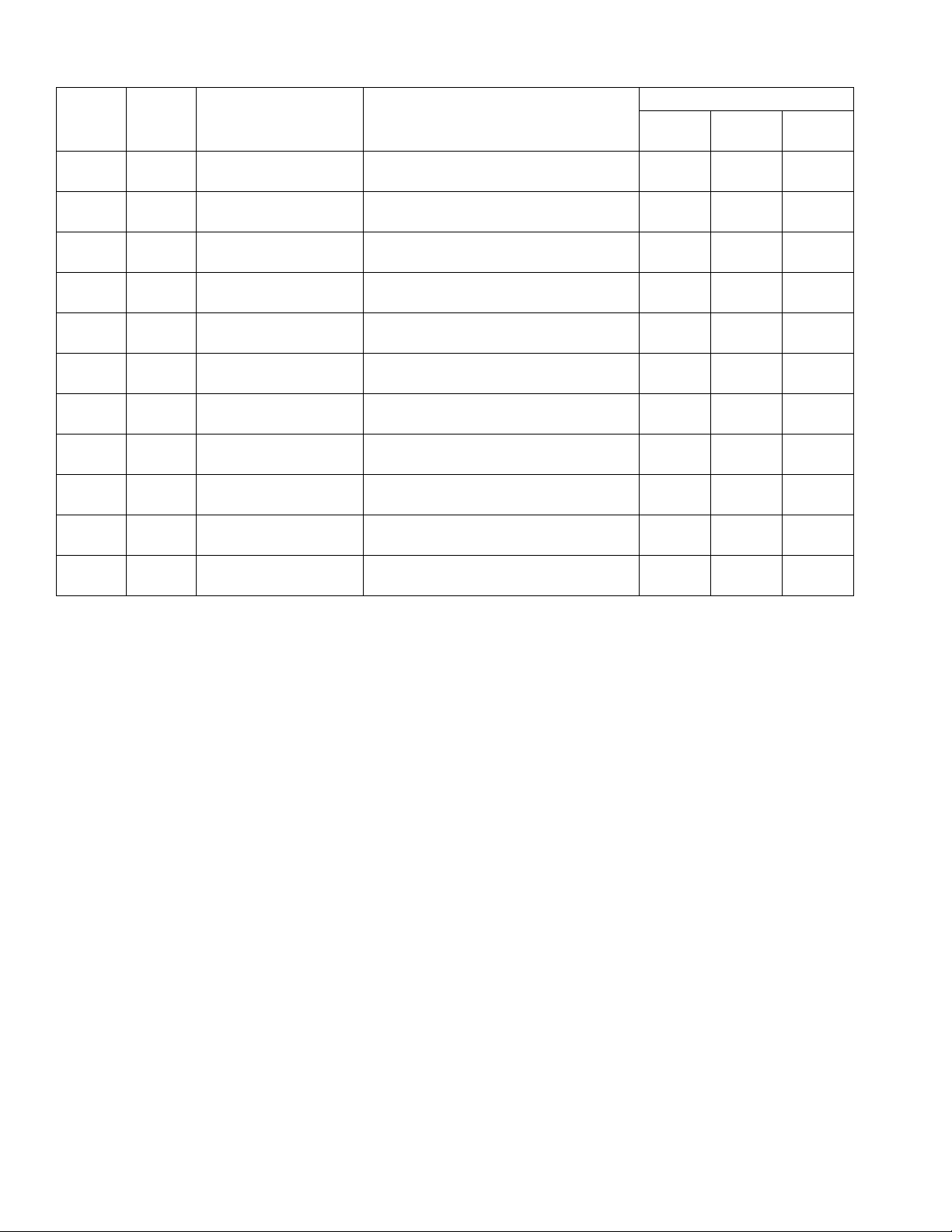
Models
Fluid
Plate Kit
24V593 PF28xx
24V594 PF38xx
24V595 PF19xx
24V596 PF29xx
24V597 PF39xx
24W201 PF15xx
24W202 PF25xx
24W203 PF35xx
25C783 PF1Cxx
25C784 PF2Cxx
25C785 PF3Cxx
Used by
Model
Maximum Working
Pressure
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
6000 psi
(41 MPa, 414 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
5000 psi
(35 MPa, 345 bar)
Description
Cartridge Regulator, Glass Bead High
Resolution Flow Meter, 16 styles
Cartridge Regulator, Glass Bead High
Resolution Flow Meter, 256 styles
Mastic Regulator, Glass Bead High
Resolution Flow Meter, 2 styles
Mastic Regulator, Glass Bead High
Resolution Flow Meter, 16 styles
Mastic Regulator, Glass Bead High
Resolution Flow Meter, 256 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, Standard
Resolution Heated Flow Meter, 2 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, Standard
Resolution Heated Flow Meter, 16 styles
Heated Mastic Regulator, Standard
Resolution Heated Flow Meter, 256 styles
Cartridge Regulator, Coriolis Flow Meter, 2
styles
Cartridge Regulator, Coriolis Flow Meter,
16 styles
Cartridge Regulator, Coriolis Flow Meter,
256 styles
Includes:
Regula-
tor
244734 24P688 16M102
244734 24P688 16M104
246642 24P688 16M100
246642 24P688 16M102
246642 24P688 16M104
246643 246340 16M100
246643 246340 16M102
246643 246340 16M104
244734 25D026 16M100
244734 25D026 16M102
244734 25D026 16M104
Flow
Meter
FCM Key
Token
6 3A2098S
Page 7

Models
Control Panel Kits
NOTE: The control kit numbers listed below are replacement control enclosures with their voltage and automation
interface listed.
Automation
Part No.
16K601 ACCESSORY SWIRL VAC
16K602 ACCESSORY SWIRL VAC
16K603 ACCESSORY SWIRL VAC
16K604 ACCESSORY SWIRL VAC
16K605 ACCESSORY SWIRL VAC IO
16K606 ACCESSORY SWIRL VDC
16K607 ACCESSORY SWIRL VDC
16K608 ACCESSORY SWIRL VDC
16K609 ACCESSORY SWIRL VDC
16K610 ACCESSORY SWIRL VDC IO
16M350 SWIRL EXPANSION VAC N/A
16M351 SWIRL EXPANSION VDC N/A
24S023 STANDARD VAC
25C590 STANDARD VAC
25C591 STANDARD VAC
25C592 STANDARD VAC
25C593 STANDARD VAC IO
24S024 STANDARD VDC
25C594 STANDARD VDC
25C595 STANDARD VDC
25C596 STANDARD VDC
25C597 STANDARD VDC IO
25C582 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VAC
25C583 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VAC
25C584 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VAC
25C585 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VAC
25C586 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VDC
25C587 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VDC
25C588 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VDC
25C589 INTEGRATED (No ADM) VDC
System Type
Voltage
Interface
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
PROFIBUS
PROFINET
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
PROFIBUS
PROFINET
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
PROFIBUS
PROFINET
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
PROFIBUS
PROFINET
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
3A2098S 7
Page 8

Models
Expansion Swirl Enclosure Assemblies
The following enclosures are ETL approved. Assemblies PFxxx2, and PFxxx3 are setup for one PrecisionSwirl Orbital
Dispenser. If you wish to have additional swirl dispensers, order one expansion PrecisionSwirl assembly below for each.
Systems with a DGM as the automation gateway can have up to two swirl dispensers total. Systems with a CGM as the
automation gateway can have up to four swirl dispensers total.
Part Description
16M350 100 - 240 Vac
16M351 24 Vdc
PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser Assemblies
See manual 309403.
Maximum
Working
Version Part, Series Coupler Offset Typical Application
Standard 243402, B 0.012 in. for narrow bead
widths
Standard 243403, B 0.028 in. for wide bead
widths
Compact 289262, A 0.012 in. for narrow bead
widths
Compact 289261, A 0.018 in. for medium bead
widths
Hem flange and after hem
Seam sealing
Hem flange and after hem
Seam sealing
Pressure
3500 psi
(24.1 MPa,
241 bar)
PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser Cable
Assemblies
Part Description
233125 6 ft (1.8 m) motor extension cable assembly
233124 9 ft (2.7 m) motor extension cable assembly
233123 15 ft (4.6 m) motor extension cable assembly
617870 55 ft (16.8 m) motor extension cable assembly
8 3A2098S
Page 9

Automation Gateway Assemblies
Automation Gateway
(DGM or CGM)
Swirl Control DGM
Each control center comes with one automation gateway assembly. The automation gateway module is either a Discrete Gateway Module (DGM) or one of the Communications Gateway
Modules (CGM).To order a replacement, see the following table.
You will also need to order software upgrade token (16K743).
NOTE: Base and cable are not included.
Gateway
Compatible
with
Advanced
CGM Map
PCF
Model
User
Interface
Description
Part
Number
To
Order
Rotary
Switch
Position
Models
PFxx0x Discrete
(DGM)
PFxx1x
+
PFxx6x
PFxx2x
+
PFxx7x
PFxx3x
PFxx4x
DeviceNet
(CGM)
EtherNet/IP
(CGM)
PROFIBUS
(CGM)
PROFINET
(CGM)
24B681 0 No
™
15V759 Any Yes
™
15V760 Any Yes
™
15V761 Any No
™
15V762 Any No
Swirl Control DGM
The assemblies below each contain one swirl control DGM used
to control one Swirl Dispenser. To order a replacement, see the
following table. You will also need to order software upgrade
token (16K743).
Assembly
Part Number
To Order
Rotary Switch
Position
PFxxx2,
PFxxx3,
16M350,
16M351
3A2098S 9
24B681
see Swirl Control
DGM on page 22
1, 2, 3, or 4;
Page 10
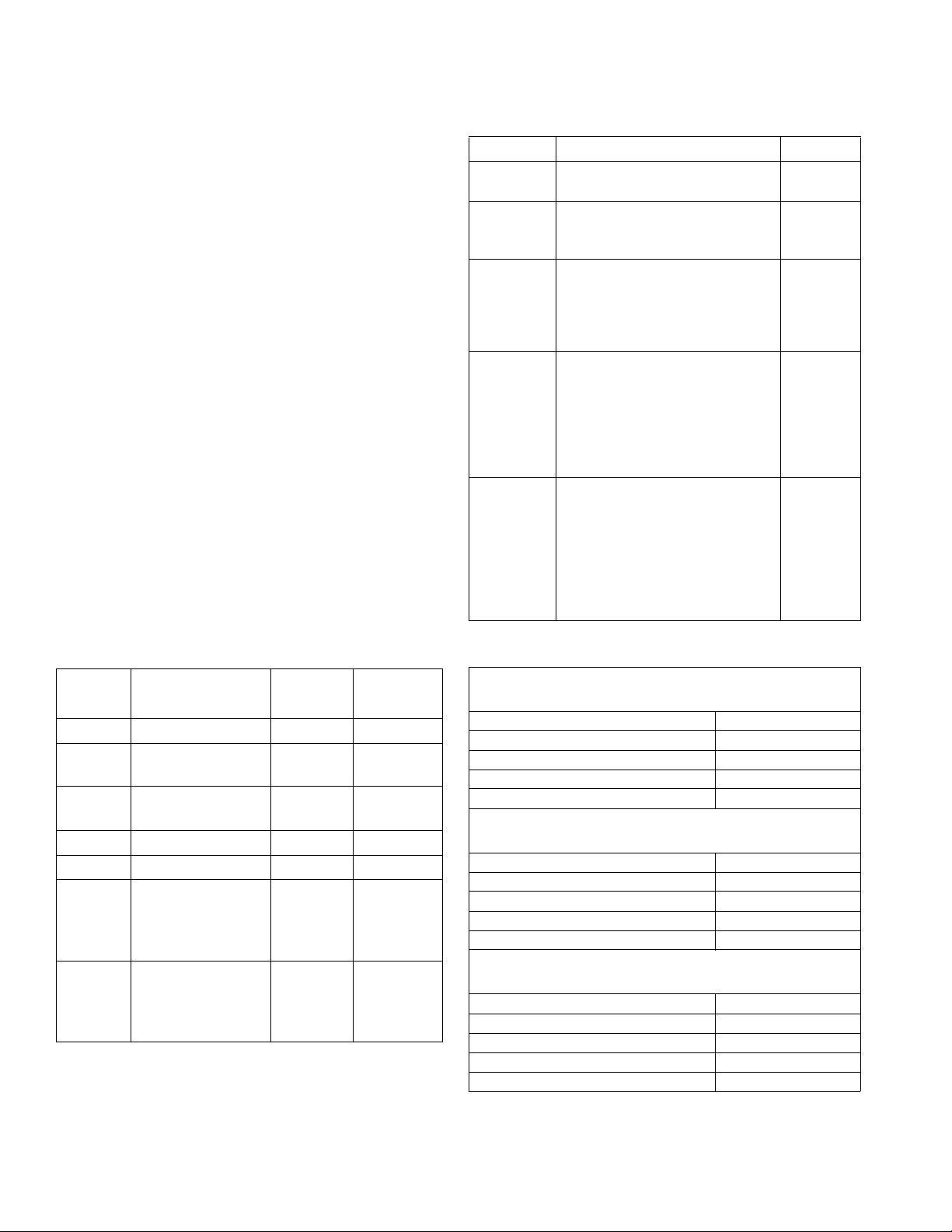
Models
Integration Upgrade with Advanced Map
NOTE: See manual 3A4649 for more information.
Graco provides an upgraded software solution for PCF
systems that came with automation communication
gateway modules (CGM). The table below shows which
systems have the ability to upgrade their system with
the update kit (25C527). This kit includes new CGM
software, as well as a larger data map.
Benefits of Upgrading:
1. Direct access to important information such as flowrates and pressures of the system (all four fluid
plates).
2. Allows for a complete integration of a Graco PCF
system, meaning an ADM is no longer necessary.
3. Much easier set up and integrate.
4. Much more supporting documentation to identify
what is important.
NOTE: Only systems with Ethernet I/P and Device Net
are capable of upgrading to use the Advanced Map.
Table 1: Software Upgrade Tokens
Part Description Contents
16K743
* 16N601 PCF Gateway map token: Installs
16T061 PCF Gateway map token: Installs
16K742 Historical PCF Gateway map
25C527 Advanced integration software kit.
Includes PCF software for the
ADM, FCM, CGM, and DGM
the CGM map starting on
page 128.
the CGM map starting on page
128.
token: Only for users that used the
original PCF with a Gateway, have
purchased a new PCF, and do not
wish to change their Gateway
setup from the old Gateway map
to the new Gateway map.
Includes the latest PCF software
for the ADM, FCM, CGM, and
DGM (16K743). It also includes
the larger Map (17P799). Both of
these must be installed for the
CGM to run, and have advanced
integration features.
System
Software
Standard
Gateway
Map
Basic
Gateway
Map (2
fluid plate),
No Swirl
Historical
Map
System
Software
and
Advanced
Map
Table 2: Fieldbus Setup Options
PCF
Model
User Interface
Description
Able to
Upgrade
Upgrade
Kit
PFxx0x Discrete (DGM) No N/A
PFxx1x Device Net
Yes 25C527
(CGM)
PFxx2x Ethernet I/P
Yes 25C527
(CGM)
PFxx3x ProfiBus (CGM) No N/A
PFxx4x ProfiNet (CGM) No N/A
PFxx6x Device Net
(CGM)
PFxx7x Ethernet I/P
(CGM)
Already
has
upgrade
installed
Already
has
upgrade
installed
Already
has
upgrade
installed
Already
has
upgrade
installed
Basic Gateway Map: 16T061
System Software: 16K743
Comm. Format: Data - SINT
Input Assembly Instance: 100
Input Instance Size: 10
Output Assembly Instance: 150
Output Instance Size: 6
Standard Gateway Map: 16N601
System Software: 16K743
Comm. Format: Data - SINT
Input Assembly Instance: 100
Input Instance Size: 26
Output Assembly Instance: 150
Output Instance Size: 42
Advanced Gateway Map: 17P799
System Software: 16K743 (newest version)
Comm. Format Data - SINT
Input Assembly Instance: 100
Input Instance Size 126
Output Assembly Instance: 150
Output Instance Size: 44
10 3A2098S
Page 11

Warnings
Warnings
The following warnings are for the setup, use, grounding, maintenance, and repair of this equipment. The exclamation point symbol alerts you to a general warning and the hazard symbols refer to procedure-specific risks. When
these symbols appear in the body of this manual, refer back to these Warnings. Product-specific hazard symbols and
warnings not covered in this section may appear throughout the body of this manual where applicable.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
This equipment must be grounded. Improper grounding, setup, or usage of the system can cause
electric shock.
• Turn off and disconnect power at main switch before disconnecting any cables and before servicing
or installing equipment.
• Connect only to grounded power source.
• All electrical wiring must be done by a qualified electrician and comply with all local codes and
regulations.
SKIN INJECTION HAZARD
High-pressure fluid from dispensing device, hose leaks, or ruptured components will pierce skin. This
may look like just a cut, but it is a serious injury that can result in amputation. Get immediate surgical
treatment.
• Do not point dispensing device at anyone or at any part of the body.
• Do not put your hand over the fluid outlet.
• Do not stop or deflect leaks with your hand, body, glove, or rag.
• Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when you stop dispensing and before cleaning, checking, or
servicing equipment.
• Tighten all fluid connections before operating the equipment.
• Check hoses and couplings daily. Replace worn or damaged parts immediately.
FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
Flammable fumes, such as solvent and paint fumes, in work area can ignite or explode. To help prevent
fire and explosion:
• Use equipment only in well ventilated area.
• Eliminate all ignition sources; such as pilot lights, cigarettes, portable electric lamps, and plastic drop
cloths (potential static arc).
• Keep work area free of debris, including solvent, rags and gasoline.
• Do not plug or unplug power cords, or turn power or light switches on or off when flammable fumes
are present.
• Ground all equipment in the work area. See Grounding instructions.
• Use only grounded hoses.
• Hold gun firmly to side of grounded pail when triggering into pail.
• If there is static sparking or you feel a shock, stop operation immediately. Do not use equipment
until you identify and correct the problem.
• Keep a working fire extinguisher in the work area.
3A2098S 11
Page 12

Warnings
WARNING
EQUIPMENT MISUSE HAZARD
Misuse can cause death or serious injury.
• Do not operate the unit when fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
• Do not exceed the maximum working pressure or temperature rating of the lowest rated system
component. See Technical Data in all equipment manuals.
• Use fluids and solvents that are compatible with equipment wetted parts. See Technical Data in all
equipment manuals. Read fluid and solvent manufacturer’s warnings. For complete information
about your material, request MSDS forms from distributor or retailer.
• Check equipment daily. Repair or replace worn or damaged parts immediately with genuine manufacturer’s replacement parts only.
• Do not alter or modify equipment.
• Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Call your distributor for information.
• Route hoses and cables away from traffic areas, sharp edges, moving parts, and hot surfaces.
• Do not kink or over bend hoses or use hoses to pull equipment.
• Keep children and animals away from work area.
• Comply with all applicable safety regulations.
BURN HAZARD
Equipment surfaces and fluid that’s heated can become very hot during operation. To avoid severe
burns:
• Do not touch hot fluid or equipment.
TOXIC FLUID OR FUMES HAZARD
Toxic fluids or fumes can cause serious injury or death if splashed in the eyes or on skin, inhaled, or
swallowed.
• Read MSDS’s to know the specific hazards of the fluids you are using.
• Store hazardous fluid in approved containers, and dispose of it according to applicable guidelines.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
You must wear appropriate protective equipment when operating, servicing, or when in the operating
area of the equipment to help protect you from serious injury, including eye injury, hearing loss, inhalation of toxic fumes, and burns. This equipment includes but is not limited to:
• Protective eyewear, and hearing protection.
• Respirators, protective clothing, and gloves as recommended by the fluid and solvent manufacturer
12 3A2098S
Page 13

System Configurations
G
D
C
B*
F*
A*
E
H
J
K*
Power In
Air Supply
Drop Site
L
M
NOTE: Shown with one fluid plate and one swirl dispenser.
F*
N
Typical Installation - Single Swirl, Single Fluid Plate
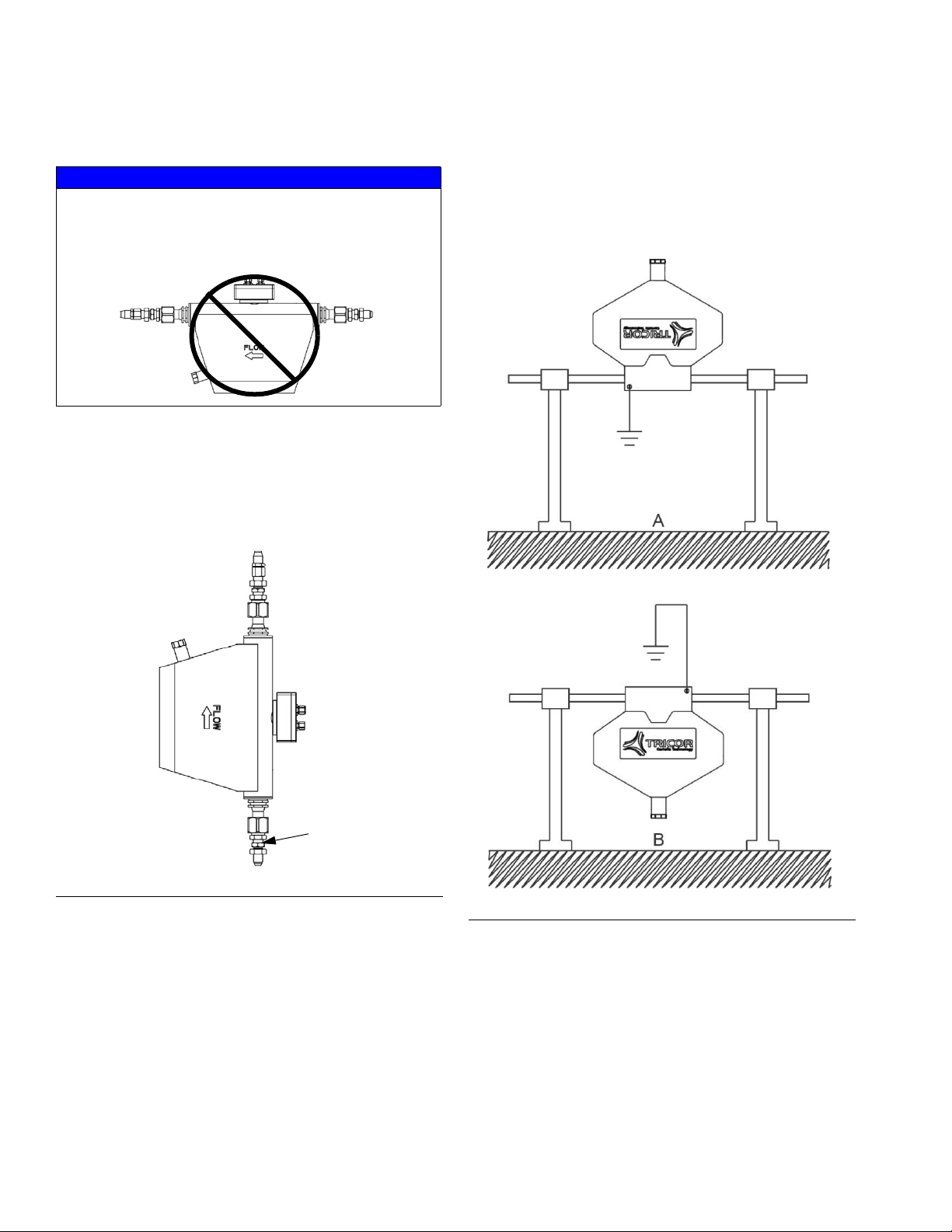
System Configurations
F
IG. 1: Typical Ambient System Installation
Key:
A *Control Center (User Interface)
B *Fluid Plate Assembly
C Applicator/Dispense Valve
DSealer Automation
E Automation Interface Cable
F *CAN Cable
G Fluid Supply System
H Fluid Supply Hose
J Automation Controller
3A2098S 13
K *Air Filter Assembly
L PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser (Swirl Dispenser)
M PrecisionSwirl Cable
N Sealer Automation Control Cable
* Included
Optional
Page 14
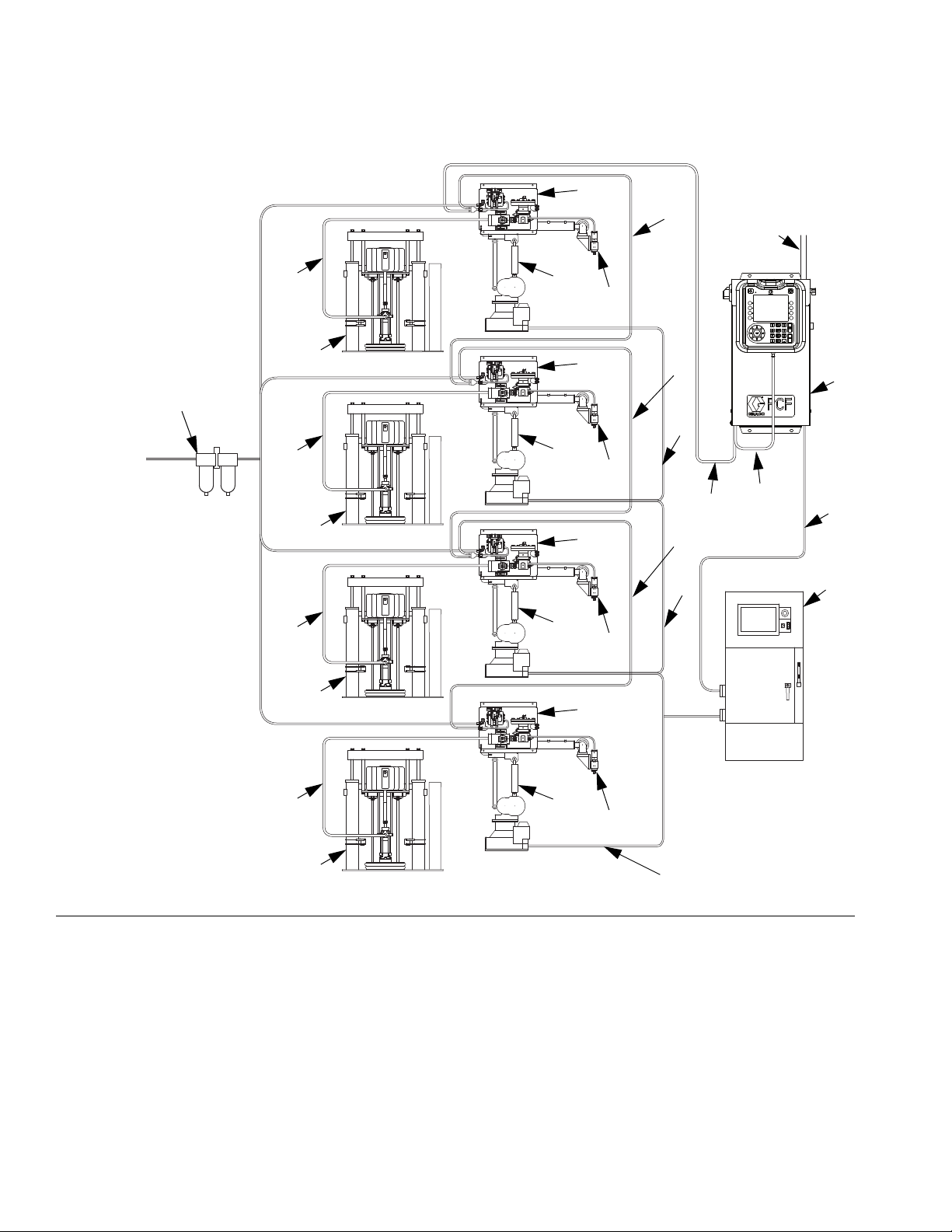
System Configurations
J
Air Supply
Drop Site
K*
H
Power In
A
E
F*
F*
F*
F*
B*
B*
B*
B*
D
C
D
C
D
C
D
C
H
H
H
G
G
G
G
F*
L
L
L
Typical Installation - Multiple Fluid Plates, No Swirl Dispensers
F
IG. 2: Typical Multiple Fluid Plate System Installation
Key:
A *Control Center (User Interface)
B *Fluid Plate Assembly
C Applicator/Dispense Valve
DSealer Automation
E Automation Interface Cable
F *CAN Cable
G Fluid Supply System
H Fluid Supply Hose
J Automation Controller
K *Air Filter Assembly
L Sealer Automation Control Cable
* Included
14 3A2098S
Page 15
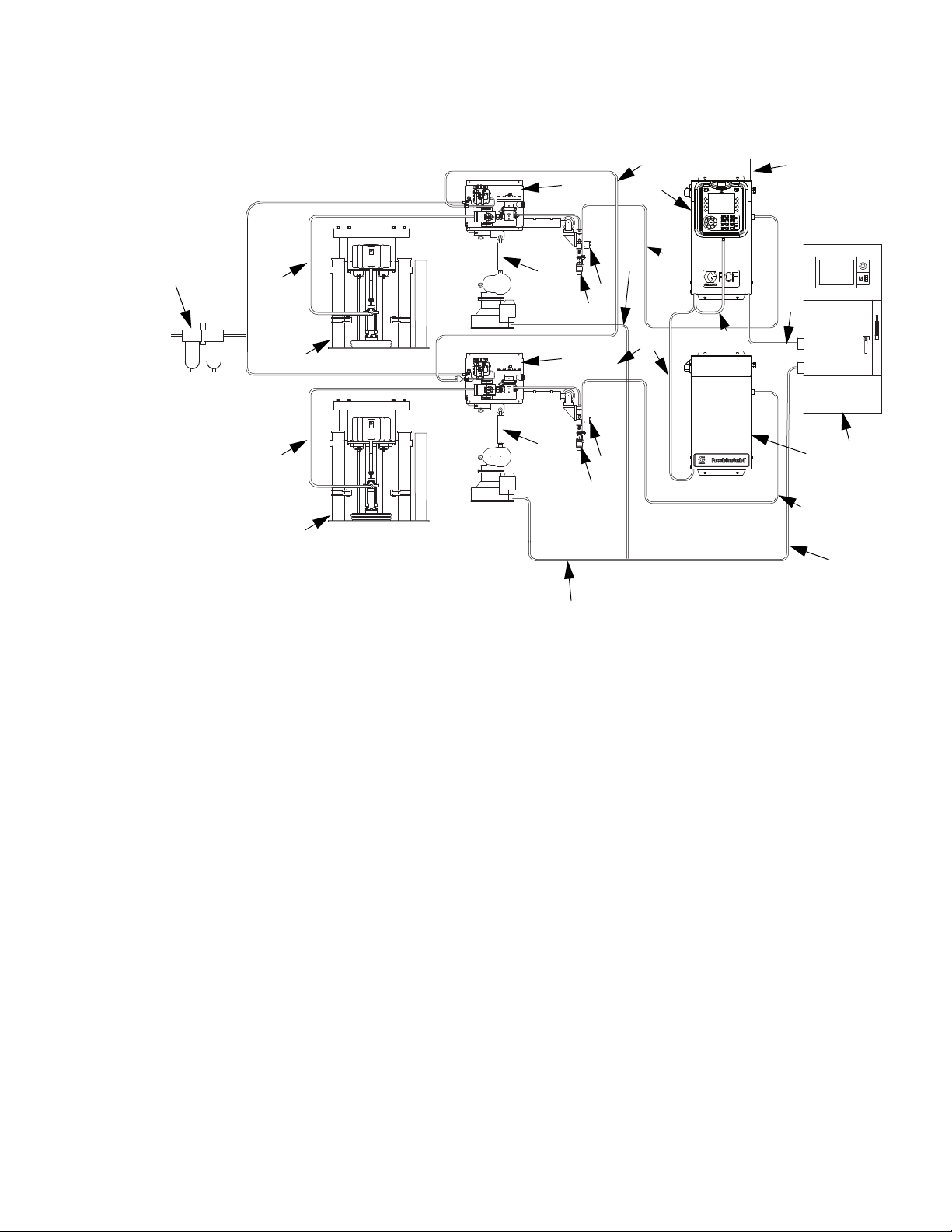
System Configurations
J
Air
Supply
Drop Site
K*
H
Power In
A
E
M
F*
F*
B*
B*
D
C
D
C
H
G
G
F*
N
L
L
M
O
O
O
Typical Installation - Multiple Fluid Plates, Multiple Swirl Dispensers
F
IG. 3: Typical Multiple Fluid Plate System Installation
Key:
A *Control Center (User Interface)
B *Fluid Plate Assembly
C Applicator/Dispense Valve
DSealer Automation
E Automation Interface Cable
F *CAN Cable
G Fluid Supply System
H Fluid Supply Hose
J Automation Controller
K *Air Filter Assembly
L PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser (Swirl Dispenser)
M PrecisionSwirl Cable
N Expansion Swirl Enclosure
O Sealer Automation Control Cable
* Included
Optional
3A2098S 15
Page 16
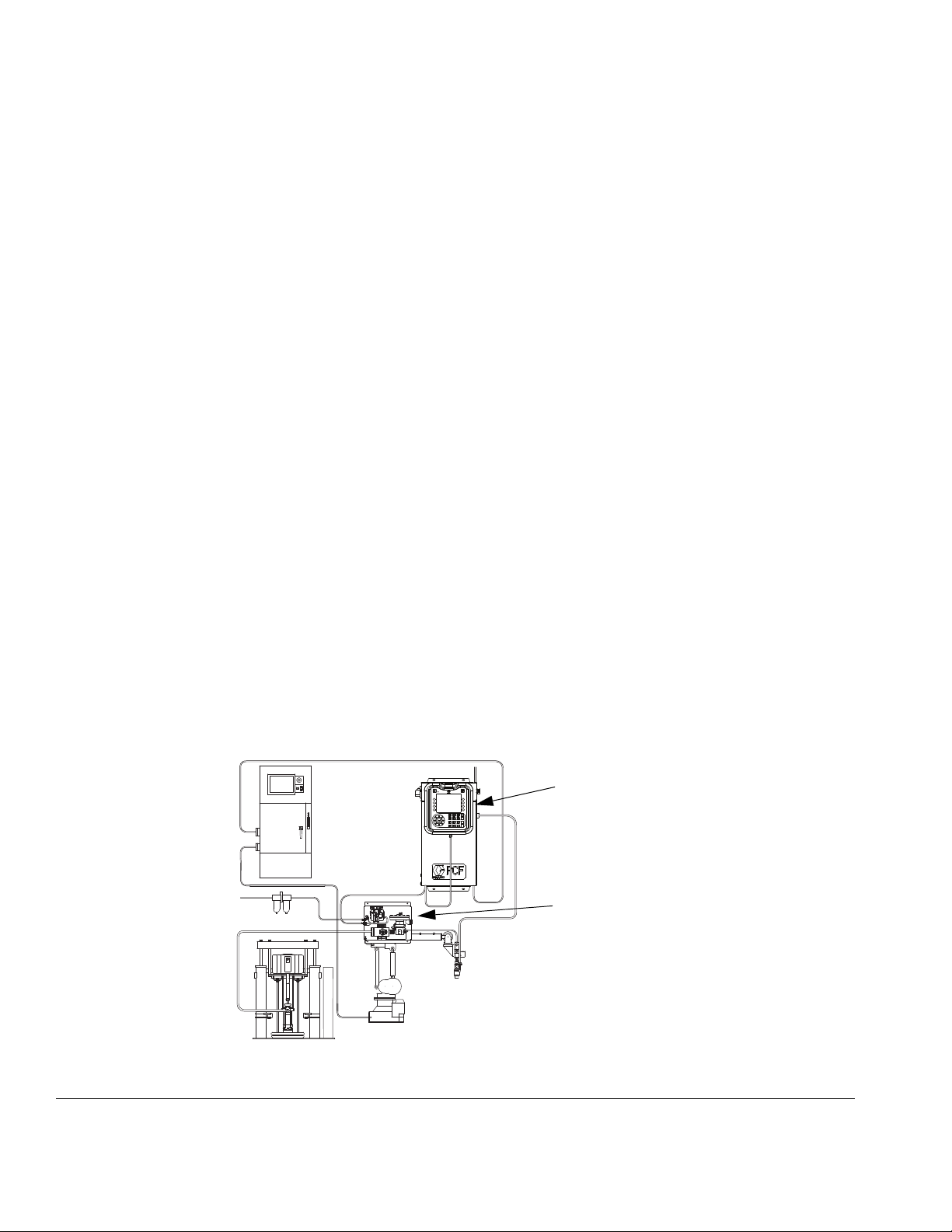
Overview
System shown with one fluid plate and one swirl dispenser
Control Center
(User Interface)
Fluid Plate Assembly
Overview
System Overview
The PCF fluid metering system combines closed-loop
pressure control with the ability to change bead profiles
quickly. When used with an optional flow meter, the
system automatically adjusts for fluctuations in the
operating environment, such as material viscosity,
temperature and tip wear, in order to maintain the
desired dispense rate. The module responds to
automation signals to provide an accurate and
consistent output flow based on a comparison of actual
to desired flow rates.
Typical Applications
• Bead dispensing
• Gasketing
• Seam sealing
• Hem flange
• Sound deadening
• Anti-flutter
• Body panel reinforcement
• Profile wrapping
• Cable filling
Control Center (User Interface)
NOTE: The control center is available with or without an
ADM, depending on the model you are using. See
Models on page 4.
The control center communicates with the PCF fluid
plate assembly to control fluid pressure and dispense
valve operation.
The control center receives input from the automation
controller, and uses these inputs to determine
communication to the fluid plate assembly.
Fluid Plate Assembly
The fluid plate assembly contains components that
control and monitor fluid dispensing. A PCF fluid
metering system can have up to four fluid plates. Each
fluid plate can control up to four dispense valves. The
system supports up to 16 dispense valves and can
simultaneously dispense from up to 10 dispense valves.
PrecisionSwirl Orbital Dispenser
(Swirl Dispenser), Sold Separately
System Components
The diagram in FIG. 4 shows an example of the PCF
module and cables.
F
IG. 4: PCF System Components
The swirl dispenser dispenses material in a circular pattern at speeds from 6600 to 24000 rpm. A PCF fluid
metering system can have up to four swirl dispensers.
See manual 309403 for detailed information.
16 3A2098S
Page 17

Overview
U
R
P
T
S
Fluid Plate Assembly Overview
Fluid Plate Components
The fluid plate assembly in FIG. 5 can be attached to an
automation arm or mounted on a pedestal. The main
components of the fluid plate assembly include:
• Fluid regulator (cartridge, ambient mastic, or heated
mastic) (P).
• Flow meter (R) (optional) precisely measures the
flow rate of fluid dispensed.
• Solenoid air valve (S) controls the dispense valve.
• Voltage to Pressure Transducer (T), abbreviated V/P
transducer, adjusts the air pressure to the fluid regulator (P).
• Fluid Control Module (FCM) (U) receives pulse readings from the flow meter (R) and pressure readings
from the regulator. It also controls the fluid regulator
(P) and solenoid air valve (S).
The PCF fluid regulator is electrically controlled by the
PCF fluid control module. Consistent material flow is
assured by a closed-loop pressure or closed-loop flow
control design. The module responds to automation-supplied signals to provide an accurate and consistent output flow based on a comparison of actual to
desired flow rates. The fluid regulator uses air pressure
to control fluid pressure and to provide fast response to
electronic commands and ensure a precisely controlled,
continuous flow of material.
The fluid plate assembly is available in two versions:
ambient and heated.
Ambient Fluid Plate Assembly
There are five ambient versions available:
• cartridge regulator without a flow meter
• ambient mastic regulator without a flow meter
• cartridge regulator with a high resolution meter
• ambient mastic regulator with a high resolution
meter
• cartridge regulator with an ultra high resolution
flow meter
• cartridge regulator with Coriolis flow meter
Heated Fluid Plate Assembly
There are two heated versions available:
• heated mastic fluid regulator with a heated flow
meter
• heated mastic fluid regulator without a flow
meter
F
IG. 5: Fluid Plate Components
3A2098S 17
Page 18
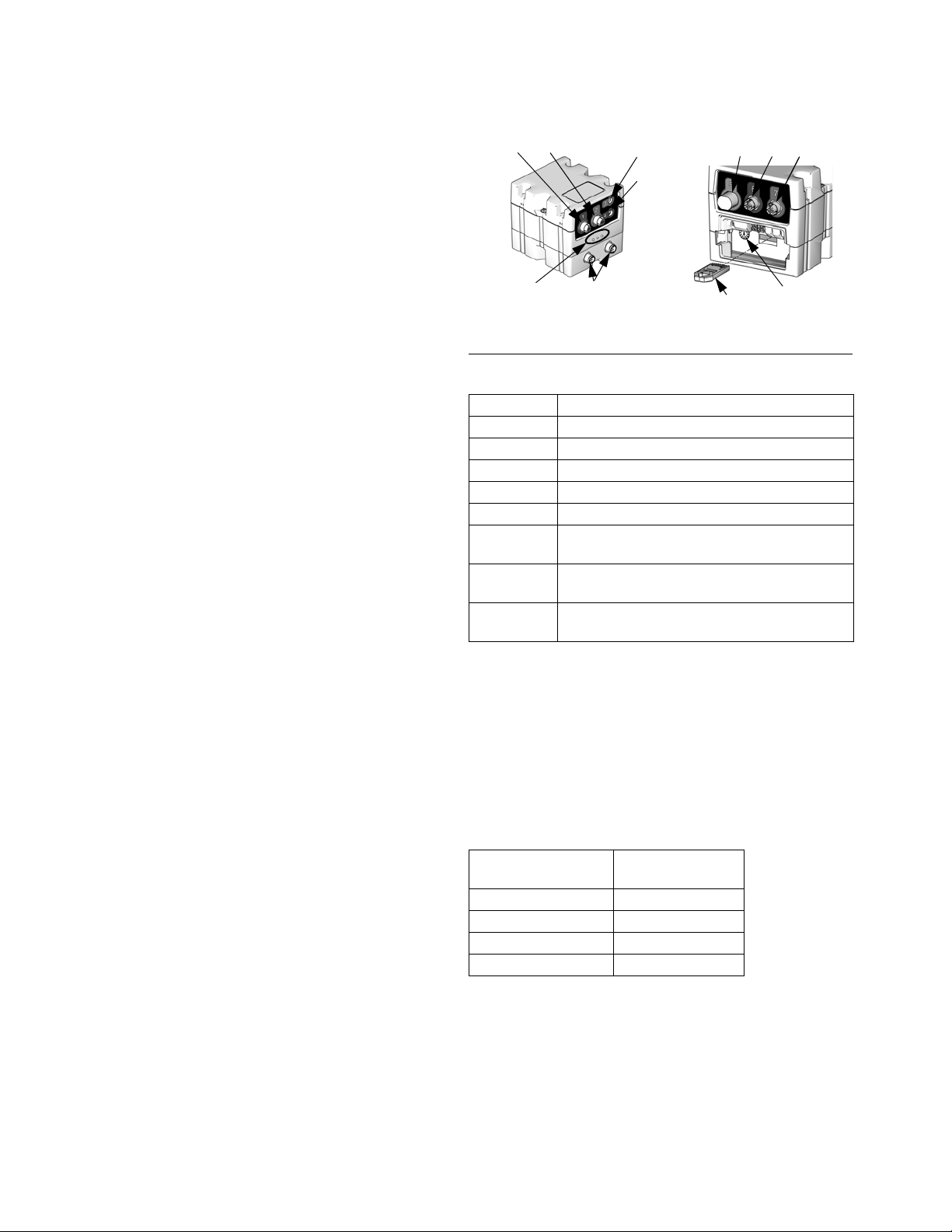
Overview
3
4
5
CAN
Connectors
6
7
Status
LEDs
1
2
Key
token
Rotary
Switch
Fluid Regulator
There are three fluid regulator options:
•cartridge
• ambient mastic
• heated mastic
All of the fluid regulator options use air pressure to control fluid pressure, provide fast response to electronic
commands, and ensure a precisely controlled, continuous flow of material.
Cartridge
The cartridge regulator (244734) is ideal for low to
medium viscosity sealants and adhesives.
Ambient Mastic
The ambient mastic regulator (246642) is ideal for
medium to high viscosity sealants and adhesives.
Heated Mastic
The heated mastic regulator (246643) is ideal for low to
high viscosity warm-melt and hot-melt sealants or adhesives.
Fluid Control Module (FCM)
F
IG. 6: FCM Sensor Connections
Connection Sensor Description
1 Dispense solenoid
2Flow meter
3 Outlet pressure sensor (heated systems only)
4 Voltage to Pressure (V/P) Transducer
5 Command cable (optional accessory kit)
6 Inlet pressure sensor (non-heated systems
7 Outlet pressure sensor (non-heated systems
CAN
Connectors
Table 3: FCM Sensor Connections
only)
only)
---
Rotary Switch on FCM
The rotary switch on the FCM, see F
IG. 6, must be set to
a valid position and each FCM must have a unique
rotary switch position. The FCM rotary switch position
determines which number to assign to that fluid plate.
The settings, including defined styles, for each fluid
plate are stored in each FCM so changing the rotary
switch position causes the settings to be shown under
the new number on the ADM.
Rotary Switch
Item
Fluid Plate 1 0 or 1
Fluid Plate 2 2
Fluid Plate 3 3
Fluid Plate 4 4
Position
NOTE: See LED Diagnostic Information, page 69, for
signal definitions.
18 3A2098S
Page 19

Control Center Assembly Overview
Front View Side View
ADM
Gateway
Module
Front View
Swirl Board
Swirl Control
DGM
100-240 Vac Assembly
CAN Splitter
- To Fluid Plate
- To ADM
Overview
F
IG. 7: Control Center Components
The control center includes the following components:
• Advanced Display Module (ADM) with USB; see
page 20 for details.
• USB enables users to download job, event, and
data logs; save and restore system settings; and
customize the language. See USB Data on
page 63.
• 24 Vdc and 100-240 Vac customer-wired options
available.
• If system has a swirl dispenser: Swirl Control DGM
(the module on the left) and Swirl Board.
• Automation Gateway Module (the module on the
right), which can be one of the following five types:
• Discrete (supports up to 2 Fluid Plates)
• DeviceNet (supports up to 4 Fluid Plates)
• EtherNet/IP (supports up to 4 Fluid Plates)
• PROFIBUS (supports up to 4 Fluid Plates)
• PROFINET (supports up to 4 Fluid Plates)
Expansion Swirl Enclosure
If more than one swirl dispenser is installed, the system will have one Expansion Swirl Enclosure for each additional
swirl dispenser. The Expansion Swirl Enclosure is similar to the primary control center, but it does not include the
ADM or the Automation Gateway module.
3A2098S 19
Page 20
Overview
TI12362a
BA
BB
BC
BE
BH
BG
BF
BD
r_24E451_3B9900_1a
BJ
BR
BP
BN
BM
BL
BK
BS
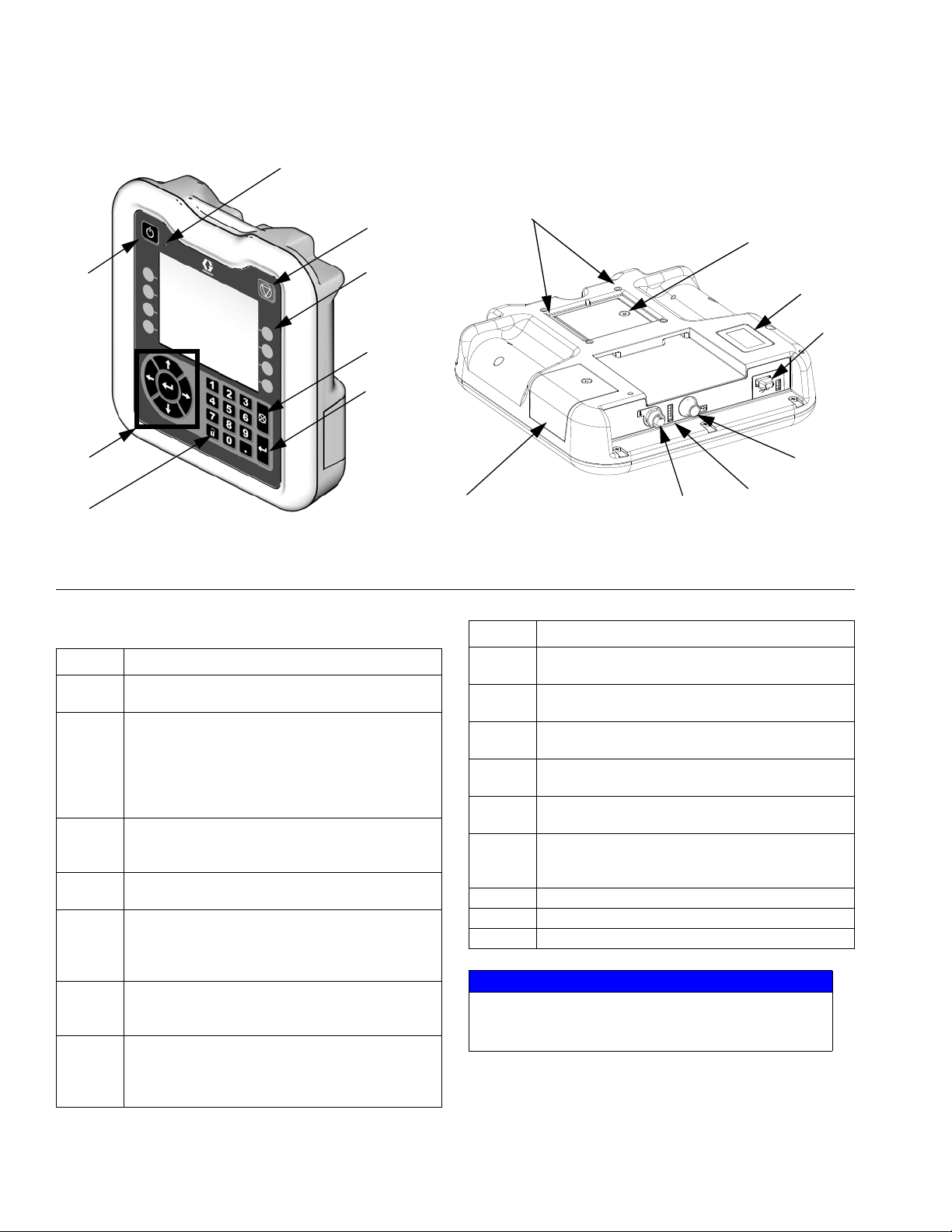
Advanced Display Module (ADM)
F
IG. 8: Advanced Display Module Component Identification
KEY:
Callout Function
BA Power On/Off Button
Enables/disables system.
BB System Status Indicator LED
Displays system status. Green LED indicates the
system is active. Orange LED indicates the system is off. Solid LEDs (green or orange) indicate
the system is in Run mode. Flashing LEDs (green
or orange) indicate the system is in Setup mode.
BC Stop Button
Stops all system processes. However, it is not a
safety or emergency stop.
BD Soft Keys
Functions vary depending on the screen.
BE Cancel Button
Clears system errors and cancels a selection or
number entry while in the process of entering a
number or making a selection.
BF Enter Button
Acknowledge changing a value or making a
selection.
BG Lock/Setup
Toggle between run and setup screens. If setup
screens are password protected, button toggles
between run and password entry screens.
Callout Function
BH Navigation Buttons
Navigate within a screen or to a new screen.
BJ Flat Panel Mount
Mounts to control center bracket (optional).
BK Model Number Tag
Model number.
BL USB Module Interface
USB port and USB indicator LEDs.
BM CAN Connector
Power connection.
BN Module Status LEDs
BP Battery Cover
BR Token Access Cover
BS Digital I/O Port for Light Tower
See LED Diagnostic Information, page 69, for
signal definitions.
NOTICE
To prevent damage to the soft key buttons, do not
press the buttons with sharp objects such as pens,
plastic cards, or fingernails.
20 3A2098S
Page 21
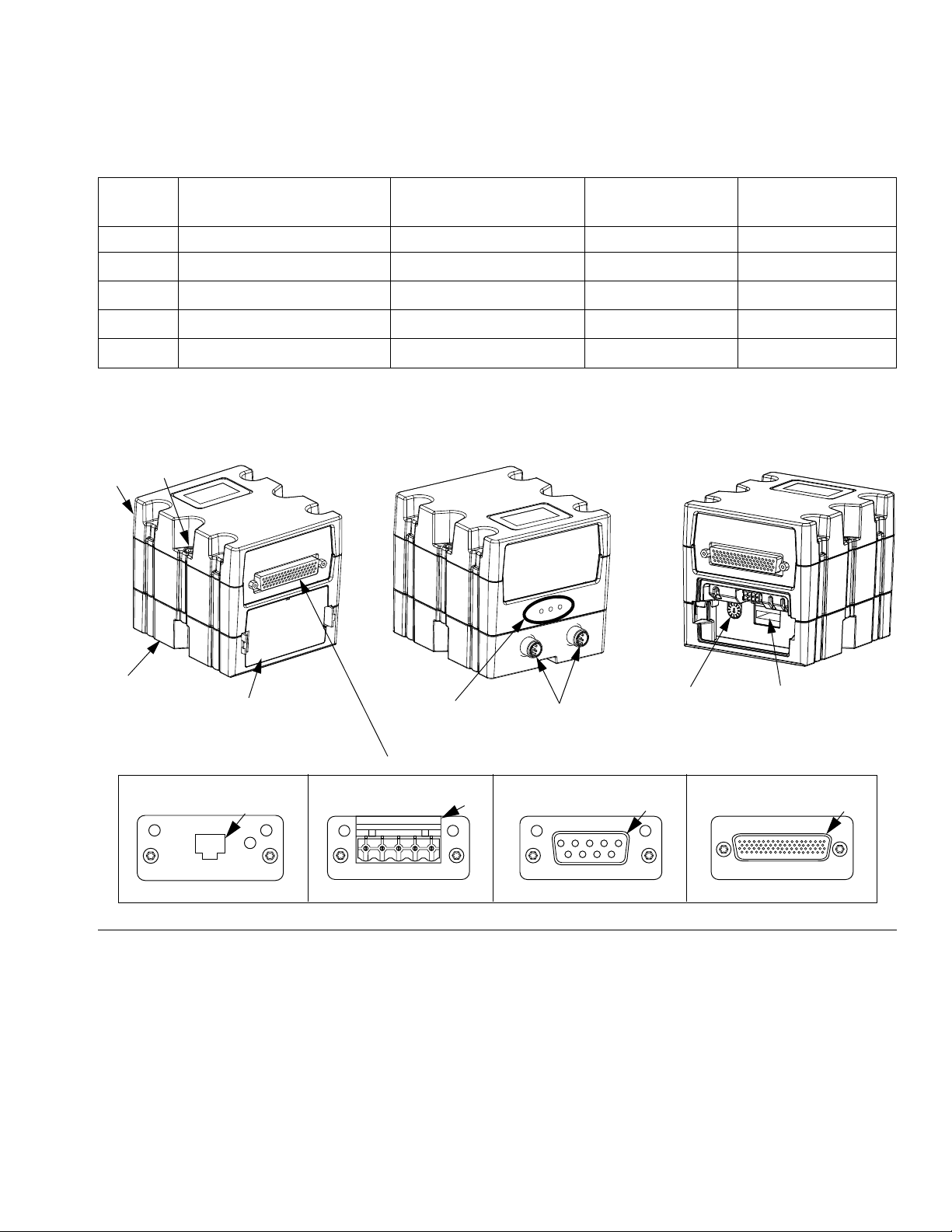
Automation Gateway Module
TI11816A
PROFIBUS
Discrete
CG
CC
TI11814A
TI11815A
CA
CD
Gateway Module Connectors
CB
PROFINET or EtherNet/IP
DeviceNet
CE
CF
CH
Front Back
CC
CC
Rotary
Switch
Software
Token Slot
Front
(Access Cover Removed)
See the following table for the appropriate rotary switch position for your automation gateway module.
Overview
PCF
Model User Interface Description
Gateway Part Number
To Order
Rotary Switch
Position
Max Number of
Fluid Plates
PFxx0x Discrete (DGM) 24B681 0 2
PFxx1x
PFxx2x
PFxx3x
PFxx4x
DeviceNet
EtherNet/IP
PROFIBUS
PROFINET
™
(CGM)
™
(CGM)
™
(CGM)
™
(CGM)
15V759 Any 4
15V760 Any 4
15V761 Any 4
15V762 Any 4
NOTE: See Control Center Assembly Overview on page 19 for automation and swirl control DGM identification.
IG. 9: Automation Gateway Module Components
F
Key:
CA Gateway Module
CB Base
CC Fieldbus Connector (see Appendix C - Communi-
cations Gateway Module (CGM) Connection
Details, page 128, for more information)
CD Module Connection Screws
CE Access Cover
CF Module Status LEDs (see LED Diagnostic Infor-
mation, page 69)
3A2098S 21
CG D-Subminiature (D-Sub) Connector (see Appendix
CH CAN Connectors
B - Discrete Gateway Module (DGM) Connection
Details, page 121, for pinout details)
Page 22
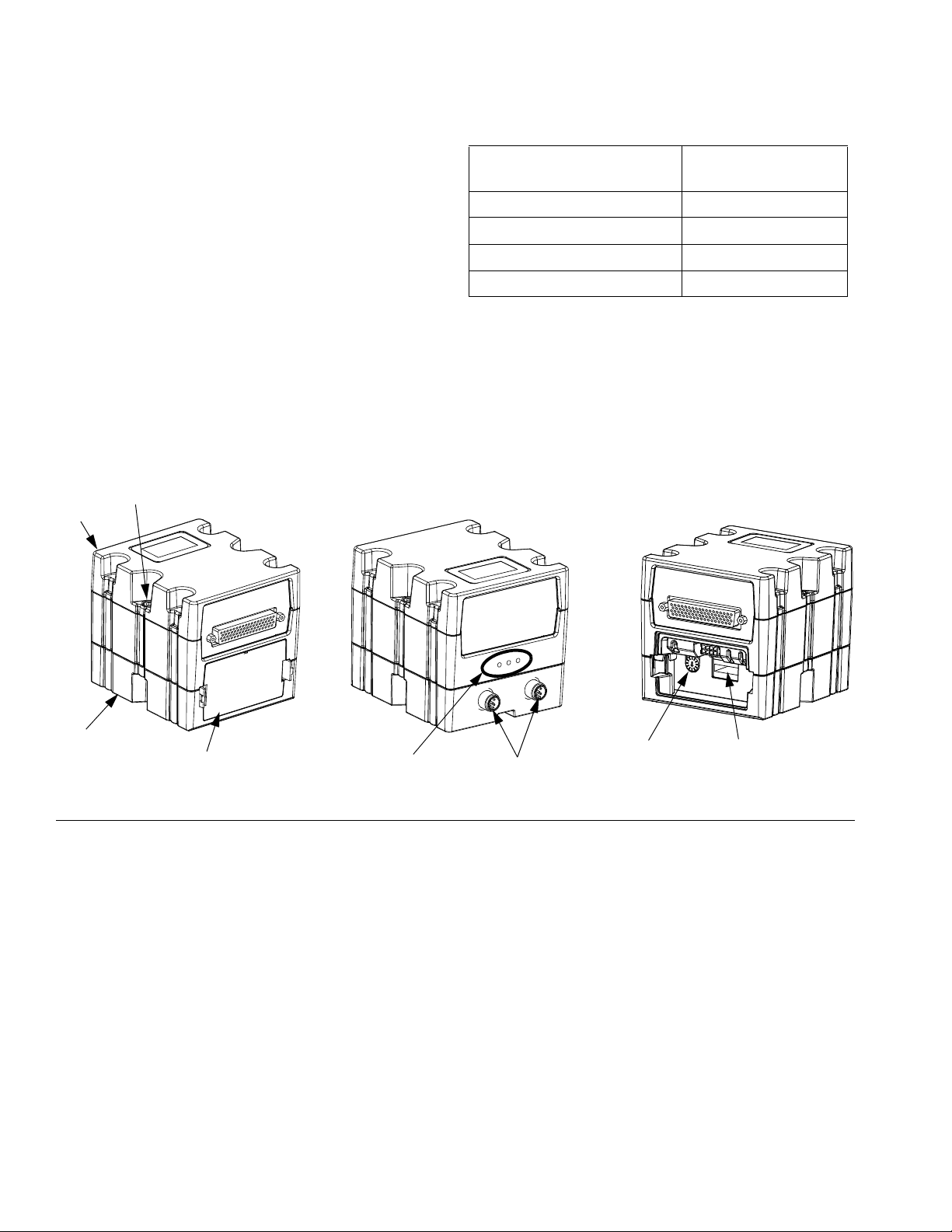
Overview
CA
CD
CB
CE
CF
CH
Front
Back
Rotary
Switch
Software
Token Slot
Front
(Access Cover Removed)
Swirl Control DGM
One swirl control DGM is included in the integrated Swirl
control center, and in each expansion swirl enclosure.
Each Swirl control DGM controls one swirl orbiter.
Each swirl control DGM must have a unique rotary
switch position. The rotary switch position determines
the number assigned to the swirl dispenser attached to
that DGM. If the rotary switch position must be changed,
do so with the power off.
Each integrated swirl control center and swirl enclosure
comes with a pre-installed cable between the swirl control DGM and the swirl board. The customer does not
need to make any external connections with the swirl
control DGM.
DGM Function
Swirl Control 1 1
Swirl Control 2 2
Swirl Control 3 3
Swirl Control 4 4
Rotary Switch
Position
FIG. 10: Swirl Control DGM
22 3A2098S
Page 23

Overview
FCMADM
Key Tokens
The ADM and FCM must each have a key token
installed in order to operate. If the incorrect key token is
installed, the module will not operate. The DGM does
not require a key token.
F
IG. 11
NOTE: There is one FCM located on each fluid plate.
If a new ADM or FCM is installed, follow the instructions
on page 81 to upgrade the software in the new module
and to install the key token from the old module in the
new module.
The following is a list of key token part numbers. If you
lose your key token be sure to order the correct item to
ensure proper system operation.
NOTE: The key tokens for the ADM and FCM look alike
but only work in one module or the other. If the key
tokens for the ADM and FCM become mixed, locate the
part number on each token then refer to the following
table to determine which module each token applies to.
Part Description
16M100 FCM Key Token, 2 styles, Flow Meter,
ADM required
16M101 FCM Key Token, 2 styles, No Flow Meter,
ADM required
16M102 FCM Key Token, 16 styles, Flow Meter,
Integrator Mode Enabled, ADM not
required
16M103 FCM Key Token, 16 styles, No Flow
Meter, Integrator Mode Enabled, ADM not
required
16M104 FCM Key Token, 256 styles, Flow Meter,
Integrator Mode Enabled, ADM not
required
16M105 FCM Key Token, 256 styles, No Flow
Meter, Integrator Mode Enabled, ADM not
required
16M217 ADM Key Token, Standard PCF
3A2098S 23
Page 24

Installation
Installation
Before Installation
• Have all system and component documentation
available during installation.
• See component manuals for specific data on component requirements. Data presented here applies to
the PCF assemblies only.
• Be sure all accessories are adequately sized and
pressure-rated to meet system requirements.
• Use the PCF control center only with the PCF fluid
plate assembly.
Overview
The basic steps to install a PCF system are shown
below. See the separate component manuals for
detailed information.
To avoid injury and damage to equipment, use at
least two people to lift, move, or disconnect the system. The system is too heavy for one person to lift or
move.
10. For systems with swirl dispensers, install each swirl
dispenser onto outlet of a dispense valve.
11. Connect other fluid and air lines to additional system
components as instructed in their manuals.
12. Install fluid plate, swirl, and gateway cable assemblies, page 32.
13. Install Gateway interface, page 34.
Installation Steps
1. Mount control center, page 25.
2. For systems with multiple swirl dispensers, mount
expansion Swirl enclosures, page 25.
3. Connect and ground control center and expansion
Swirl enclosures, page 26.
4. Mount each fluid plate assembly, page 27.
5. If using a Coriolis flow meter system, mount the flow
meter, page 149.
6. Ground each fluid plate assembly, page 31.
7. Check ground continuity.
8. Connect fluid lines between each fluid plate and
applicator. Connect fluid supply line and air supply
to module. See page 31.
9. Plumb air filter assembly near air supply drop site
that will be used for fluid plate assembly.
24 3A2098S
Page 25
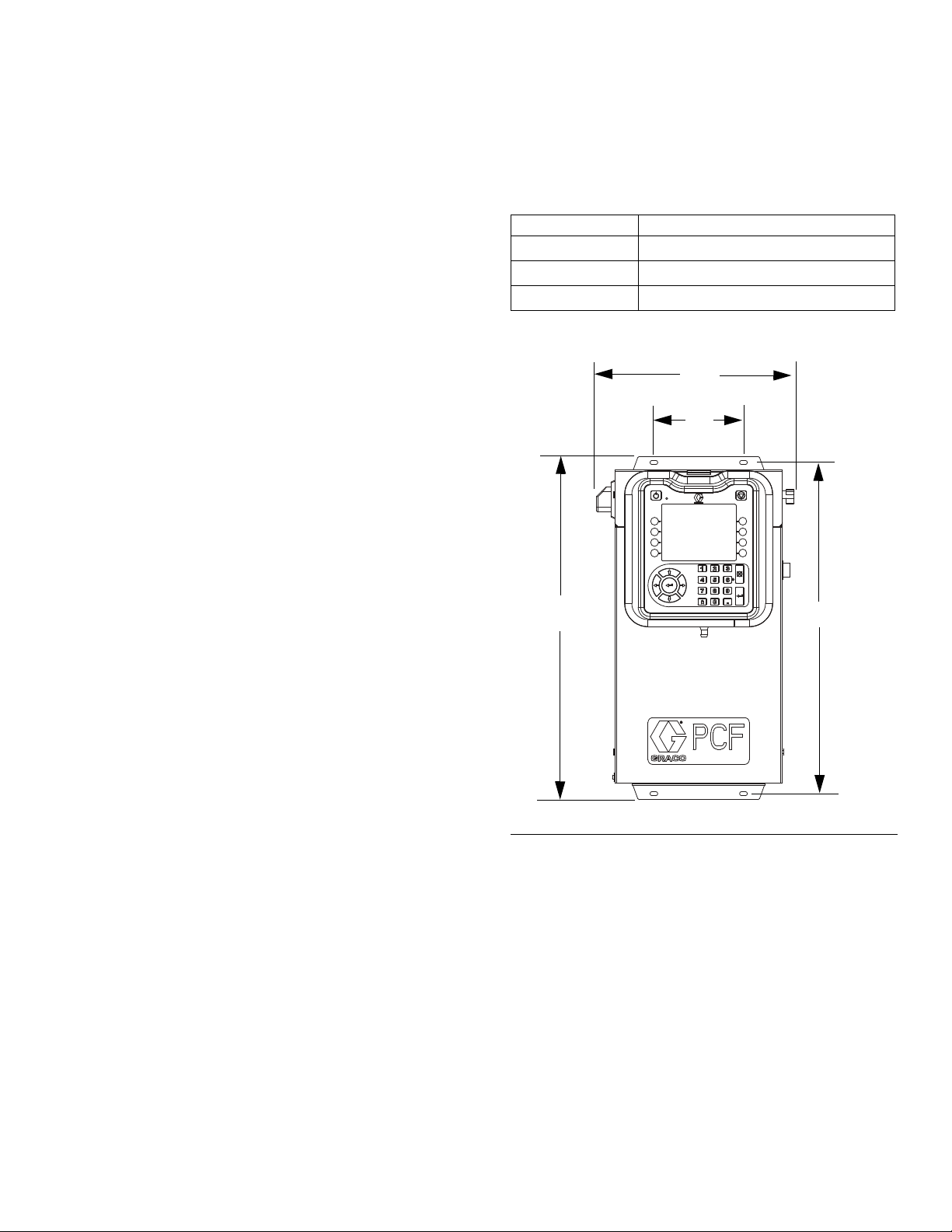
Installation
A
B
C
D
Install Control Center
NOTE: This section applies to both the primary control
center and the expansion Swirl enclosures.
Mount
Ensure the following criteria are met before mounting
the PCF control center:
• Select a location for the control center that allows
adequate space for installation, service, and use of
the equipment.
• For best viewing, the ADM should be 60-64 in.
(152-163 cm) from the floor.
• Ensure there is sufficient clearance around the control unit to run cables to other components.
• Ensure there is safe and easy access to an appropriate electrical power source. The National Electric
Code requires 3 ft (0.91 m) of open space in front of
the control center.
Secure the control center with appropriate size bolts
through the 0.27 in. (7 mm) diameter holes in the mounting tabs. See the following mounting dimensions.
Table 4: Control Center Assembly Measurement
A
B
C
D
10.50 in. (267 mm)
5.75 in. (146 mm)
22.00 in. (559 mm)
21.25 in. (540 mm)
• Ensure there is easy access to the power switch.
• Ensure the mounting surface can support the weight
of the control center and the cables attached to it.
F
IG. 12: Control Center Dimensions
3A2098S 25
Page 26

Installation
+
-
Ground
Ground
N
L
Electrical Connections
This product must be grounded. In the event of an
electrical short circuit, grounding reduces the risk of
electric shock by providing an escape wire for the
electric current.
• The control center must be electrically connected
to a true earth ground; the ground in the electrical
system may not be sufficient. Refer to your local
code for the requirements for a “true earth ground”
in your area.
• All wires used for grounding must be 18 AWG
minimum.
• All electrical wiring must be done by a qualified
electrician and comply with all local codes and
regulations.
FIG. 14: 100-240 Vac Wiring
• For 24 Vdc wiring refer to F
• For 100-240 Vac wiring refer to F
• Incoming power wiring must be guarded from the
enclosure. Use a protective grommet where the
power wiring enters the enclosure to prevent
wear.
NOTICE
If power and grounding connections are not done
properly, the equipment will be damaged and the
warranty voided.
IG. 13.
IG. 14.
Connect Light Tower Accessory
NOTE: A light tower is not included on models that do
not have an ADM. See Models on page 4.
1. Order the 255468 Light Tower Accessory as a
diagnostic indicator for the PCF system.
2. Connect the cable from the light tower to the digital
I/O port (BS) on the ADM.
See Table 3 for a description of light tower signals.
Table 5: Light Tower Signals
Signal Description
Green No errors.
Yellow An advisory exists.
Yellow flashing A deviation exists.
Red solid An alarm exists. One or more fluid
plates may be shutdown.
NOTE: See Errors, page 70, for error definitions.
F
IG. 13: 24 Vdc Wiring
26 3A2098S
Page 27

Installation
D
A
B
C
Inlet
Outlet
CAN
Connector
Dispense
Valve to
Gun Open
Dispense
Valve to
Gun Close
Install Fluid Plate Assemblies
To install the PCF fluid plate assemblies:
• Mount the fluid plate assemblies, page 27
• Ground fluid plate assemblies, page 31
• Connect one fluid plate assembly to the control
center. See Install Cable Assemblies on page 32.
• If multiple fluid plates, connect the fluid plates
together. See Install Cable Assemblies on
page 32.
• Connect fluid lines, air lines, and cables; page 31
Mount
Before Mounting Assembly
• See component manuals for specific information on
component requirements. Information presented
here pertains to the PCF fluid plate assembly only.
2. Mount and secure the fluid plate assembly to the
automation unit (or other mounting surface) with
appropriate size bolts through the 0.397 in. (10 mm)
diameter holes in the base plate. See the mounting
dimensions in Table 4 and F
IG. 15.
Table 4: Fluid Plate Assembly Measurement
A
B
C
D
16.5 in. (419 mm)
14.0 in. (356 mm)
14.4 in. (366 mm)
13.4 in. (340 mm)
• Have all system and subassembly documentation
available during installation.
• Be sure all accessories are adequately sized and
pressure-rated to meet the system's requirements.
• Use only the Graco PCF fluid plate assembly with
IG. 15: Fluid Plate Assembly Dimensions
F
the Graco PCF control center.
Mount Assembly
1. Select a location for the fluid plate assembly. Keep
the following in mind:
• Allow sufficient space for installing the equipment.
• Make sure all fluid lines, cables and hoses easily reach the components to which they will be
connected.
• Make sure the fluid plate assembly allows the
automation unit to move freely along all axis.
• Make sure the fluid plate assembly provides
easy access for servicing its components.
3A2098S 27
Page 28
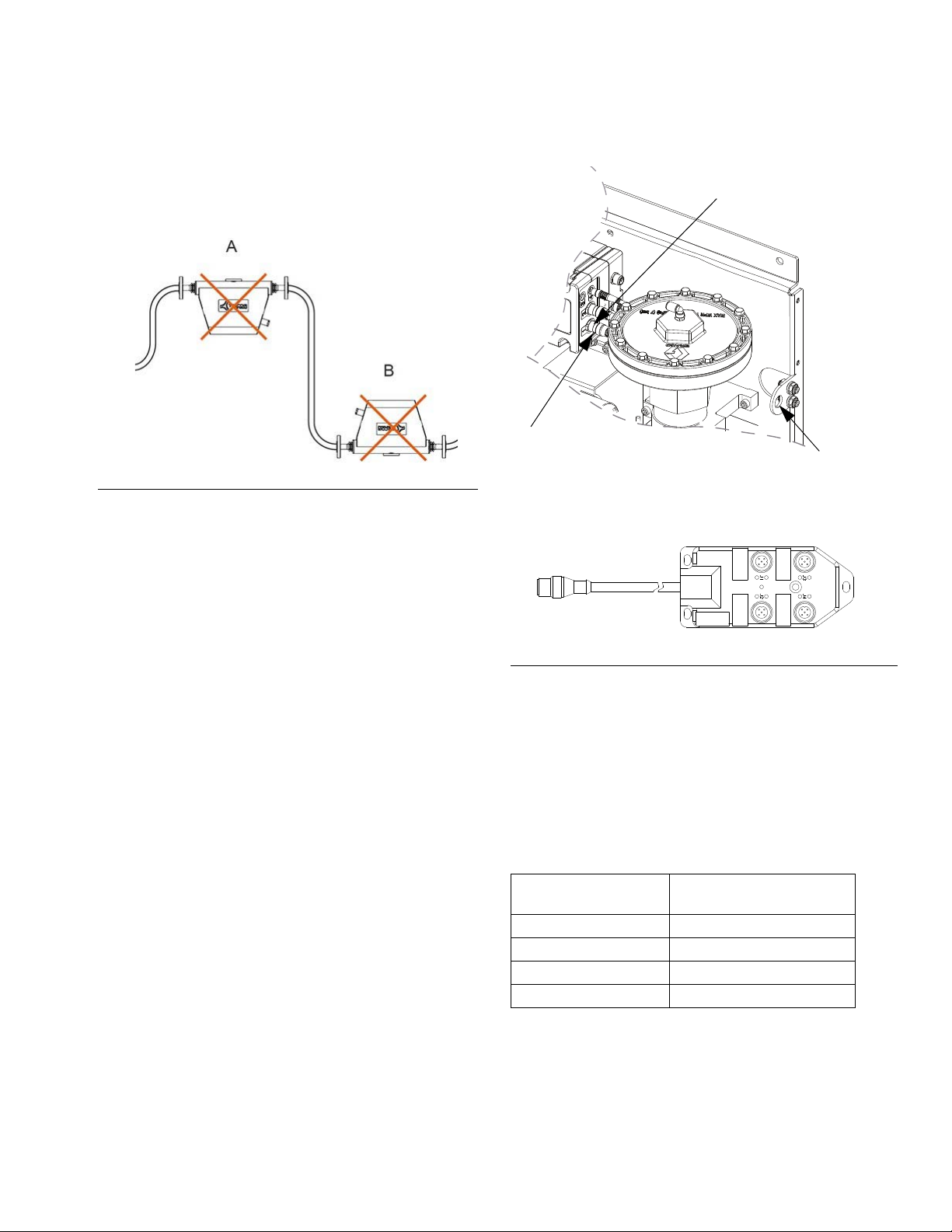
Installation
check valve
Mount Coriolis Flow Meter
NOTE: A Coriolis flow meter only comes with PFxCxx
assemblies.
NOTICE
See Fluid Plate Assembly Technical Data on page
149 for the weight of your meter. The meter is heavy
and must be properly supported to avoid stress on the
fluid connections.
Fluid Flow Upward
Mounting so fluid flow is upward through the meter is
preferred as this allows solids to settle out and air to rise
away from metering tube. See F
IG. 16.
Horizontal Installation
The horizontal installation is the recommended installation.
If the medium might contain solid particles, mount the
meter as shown in position A, in all other cases as
shown in position B.
F
IG. 16. Fluid Flow Upward
FIG. 17.
28 3A2098S
Page 29
Installation
GCA Cable
Splitter Assembly
Hole for bulkhead fitting
Connection 1
J1 J3
J2 J4
Critical Installations
The meters must be mounted at the highest point of the
tubing (A), if gas bubbles are to be expected, or at the
lowest point (B), if solid particles are to be expected, as
in both cases also the right orientation might not help.
F
IG. 18.
Mount Four-Valve Breakout Kit 24B693
PCF is capable of controlling up to four separate
dispense valves from port 1 on the FCM. A four-valve
breakout kit (24B693) is available to split the dispense
solenoid connector (port 1 on the FCM) into four
separate dispense solenoid connectors. For each
additional dispense valve, order one dispense valve
solenoid (258334) and one solenoid cable (121806).
2. Install bulkhead fitting (included in the kit) into the
empty hole on the fluid plate.
FIG. 19: Mount Breakout Kit
Follow this procedure if using the four-valve breakout
kit.
1. Remove the existing dispense solenoid and cable
from the fluid plate.
3. Connect one end of the extension cables (included
in the kit) to connection 1 on the FCM and the other
end of the cable to the bulkhead fitting.
4. Connect the splitter assembly to the bulkhead fitting.
5. Connect the dispense valve cable(s) to the
connections on the splitter assembly.
Connects to Splitter
Cable for:
Dispense Valve 1 J1
Dispense Valve 2 J2
Dispense Valve 3 J3
Dispense Valve 4 J4
Connection Labeled:
6. Mount splitter assembly and dispense valves, and
connect air lines as necessary for application.
3A2098S 29
Page 30
Installation
Custom Breakout Cable
If desired, the following connector pinout information
may be used to build a custom breakout cable:
Pinout of FCM Port 1
Pin 1: Dispense Solenoid 4
Pin 2: Dispense Solenoid 2
Pin 3: Voltage - (common for all solenoids)
Pin 4: Dispense Solenoid 1
Pin 5: Dispense Solenoid 3
Dispense solenoid outputs are 24 Vdc. Dispense
solenoid outputs are capable of sourcing up to 0.5A
each (maximum 12W coil).
Install Command Cable Kit 24B694
Follow this procedure if using the command cable kit.
1. Install bulkhead fitting (included in the kit) into the
empty hole on the fluid plate. See F
IG. 19 on
page 29.
2. Connect one end of the extension cable (included in
the kit) to connection 5 on the FCM and the other
end of the cable to the bulkhead fitting.
3. Connect command cable to bulkhead fitting and
wire to automation controller per the following pinout
table.
Function
FCM
Port
Pin #
Command
Cable Wire
Color
1 White Command voltage (0-10 Vdc) Command voltage (0-10 Vdc)
2 Brown No connection Valve 3 dispense trigger (*sourc-
3 Green Dispense trigger (*sourcing input) Valve 1 dispense trigger (*sourc-
4 Yellow No connection Valve 2 dispense trigger (*sourc-
5 Gray Dispense trigger ground Dispense trigger ground
6 Pink No connection No connection
7 Blue Command signal ground Command signal ground
8 Red No connection No connection
Dispense Trigger Source:
‘Command Cable’ or
‘Combined’
Dispense Trigger Source:
‘Command Cable 3x’
ing input)
ing input)
ing input)
NOTE: Command cable inputs are not isolated from
PCF 24 Vdc power.
* To turn on the dispense trigger, connect the
dispense trigger pin to the dispense trigger ground
pin (pin 5).
30 3A2098S
Page 31

Installation
Ground
This product must be grounded. In the event of an
electrical short circuit, grounding reduces the risk of
electric shock by providing an escape wire for the
electric current.
• The control center must be electrically connected
to a true earth ground; the ground in the electrical
system may not be sufficient. Refer to your local
code for the requirements for a “true earth ground”
in your area.
• All wires used for grounding must be 18 AWG
minimum.
• A qualified electrician must complete all grounding
and wiring connections.
• For 24 Vdc wiring refer to F
• For 100-240 Vac wiring refer to F
• Incoming power wiring must be guarded from the
enclosure. Use a protective grommet where the
power wiring enters the enclosure to prevent
wear.
IG. 13.
IG. 14.
Solvent Pails Used When Flushing
Follow local code. Use only conductive metal pails,
placed on a grounded surface. Do not place the pail on
a non-conductive surface, such as paper or cardboard,
which interrupts grounding continuity.
Connect Fluid and Air Lines
NOTICE
Route all fluid and air lines carefully. Avoid pinching
and premature wear due to excessive flexing or
rubbing. Hose life is directly related to how well they
are supported.
Follow the instructions in your separate component
manuals to connect air and fluid lines. The following are
only general guidelines.
• The PCF fluid plate assembly should be installed on
the automation unit or in another appropriate place,
as close as practical to the dispense valve.
• Connect a fluid line between the fluid plate outlet and
the dispense valve. Smaller diameter and shorter
fluid lines (hoses) will provide better fluid system
response.
NOTICE
If power and grounding connections are not done
properly, the equipment will be damaged and the
warranty voided.
Ground the fluid plate assembly as instructed here and
in the individual component manuals. Make sure the
fluid plate assembly and its components are installed
correctly to ensure proper grounding.
Air and Fluid Hoses
For static dissipation, use only electrically conductive
hoses or ground the applicator / dispense valves.
Dispense Valve
Follow the grounding instructions in the dispense valve
manual.
Fluid Supply Container
Follow local code.
• Connect a fluid line to the flow meter fluid inlet or to
the regulator inlet if your system does not have a
flow meter.
• Air must be clean and dry, between 60-120 psi
(0.41-0.82 MPa, 4.14-8.27 bar). Flush air line before
plumbing in air filter assembly (234967). Plumb in air
filter assembly near air drop site (upstream of fluid
plate module). Adding an air regulator to this line will
provide more consistent dispense valve response
times.
• Connect an air supply line to the 1/4 npt inlet port on
the fluid plate(s) air supply inlet.
• Connect 5/32 in. or 4 mm OD air lines from the
applicator's solenoid valve to the applicator. Plug any
unused solenoid ports.
NOTE: To maximize system performance keep the
dispense hose length and ID as small as the application
will allow.
3A2098S 31
Page 32

Installation
Install Cable Assemblies
NOTE: To prevent system errors, only connect cables
with the power off.
NOTE: See F
1. For systems with more than one swirl dispenser:
Use a CAN cable to connect the control center to
one swirl expansion enclosure. Use additional CAN
cables to connect any remaining expansion swirl
enclosures together in sequence.
2. For systems with one or more swirl dispensers, use
motor cable to connect each swirl dispenser to an
expansion swirl enclosure or to the control center.
3. Connect a CAN cable from the control center to one
fluid plate assembly.
4. For multiple fluid plate systems, use CAN cables to
connect each fluid plate to one other fluid plate
Repeat until all fluid plates are connected to one
other fluid plate.
NOTE: Use the connections on the CAN splitter on the
left side of each fluid plate to connect the fluid plates
together. There will be a CAN splitter on all but one fluid
plate.
IG. 20 on page 33.
NOTE: The control center, expansion swirl enclosures,
and fluid plates may be connected in any order as long
as each is connected to another system component with
a CAN cable. See the example shown in F
page 33.
5. Use the automation interface cable (not provided) to
connect the Gateway module to the automation
controller.
IG. 20 on
32 3A2098S
Page 33

Installation
ti30855a
Multiple Fluid Plate and Multiple Swirl System shown
4
5
4
4
3
1
1
2
2
2
2
1
FIG. 20: Cable Installation Diagram
3A2098S 33
Page 34

Installation
Install Gateway Module Interface
NOTE: Systems with swirl dispensers will have two gateway modules in the control center. The gateway module on
the left is the swirl control DGM module, and does not need any setup or modification. The gateway module on the
right is the automation Gateway module. This section covers the automation Gateway module.
Fieldbus Communications Gateway Module
Module Description
The Communications Gateway Module (CGM) provides
a control link between the PCF system and a selected
fieldbus. This provides the means for remote monitoring
and control by external automation systems.
See Automation Control (Normal Operation), page
49, for details on controlling the PCF system through the
Gateway module.
Data Exchange
Data is available by block transfer, cyclic transfer,
change of state triggered, and explicit access to
individual attributes as defined by the fieldbus
specification. Refer to Appendix C - Communications
Gateway Module (CGM) Connection Details, page
146, for details about PCF/fieldbus data map.
NOTE: The following system network configuration files
are available at www.graco.com
• EDS file: DeviceNet or EtherNet/IP fieldbus networks
• GSD file: PROFIBUS fieldbus networks
• SDML: PROFINET fieldbus networks
CGM Status LED Signals
Installation
NOTE: The following installation instructions assume
the person implementing the PCF fieldbus connection
fully comprehends the fieldbus being used. Ensure the
installer understands the automation controller
communication architecture and the fieldbus being
used.
NOTE: An Integrated PCF (without ADM) has a CGM
that must be configured through an ADM. A single ADM
may be used to set up multiple machines.
1. Install interface cables between the PCF system
and the automation controller per the fieldbus
standards. Refer to Appendix C -
Communications Gateway Module (CGM)
Connection Details, page 128, for details.
2. Turn on system power. Navigate to the Gateway
setup screens and ensure the data map name is:
PCF 4FP. Refer to Appendix A - Advanced
Display Module (ADM), page 104, for details about
the data map.
3. Set the PCF Gateway configuration values as
required to interface with automation controller.
Refer to Appendix A - Advanced Display Module
(ADM), page 104, for details about the configuration
settings.
Signal Description
Green on System is powered up
Yellow Internal communication in progress
Red
Solid
*Red
(7 flashes)
*The red LED (CF) will flash a code, pause, then repeat.
34 3A2098S
CGM hardware failure
Data map load failure
Incorrect data map for fieldbus type
No data map loaded
4. Retrieve the appropriate fieldbus configuration file
for the fieldbus being used from www.graco.com.
5. Install the configuration file on the automation
controller (fieldbus master). Configure it for
communication with the PCF Gateway (fieldbus
slave).
6. Establish communication between the automation
controller and the PCF Gateway to confirm the
successful configuration of the hardware and data.
NOTE: Use the ADM screens for troubleshooting fieldbus data communication problems. Refer to Appendix
A - Advanced Display Module (ADM), page 104, for
details. Also, use the LED status indicators on the PCF
Gateway module for fieldbus status information. Refer to
Appendix C - Communications Gateway Module
(CGM) Connection Details, page 128, for details.
Page 35

Installation
r_24B681_2B9904_2b
CG
Discrete Gateway Module
Module Description
The Discrete Gateway Module (DGM) provides a control
link between the PCF system and an automation
controller through discrete input and output connections.
This provides the means for remote monitoring and
control by external automation systems.
See Automation Control (Normal Operation), page
49, for details on controlling the PCF system through the
Gateway module.
Connect D-Sub Cable
The DGM provides all I/O through the D-Sub cable.
Graco offers two options for connecting a D-Sub cable
to the D-Sub connector (CG). Both options are
accessories and must be ordered separately.
• For single fluid plate systems only: D-Sub to
flying leads cable (123793). See Appendix B -
Discrete Gateway Module (DGM) Connection
Details, page 121, for details and cable
interface signals.
DGM Rotary Switch Position
The Discrete Gateway Module (DGM) rotary switch
must be in position 0 for Automation Gateway DGMs
and positions 1-4 for Swirl Control DGMs in order for the
DGM to operate. See Automation Gateway Module on
page 21 and Swirl Control DGM on page 22.
• For multiple fluid plate systems: D-Sub cable
(123972) and 78-pin breakout board (123783).
See Appendix B - Discrete Gateway Module
(DGM) Connection Details, page 121, for
details and pin assignments.
F
IG. 21: Connect D-Sub Cable
DGM Status LED Signals
See LED Diagnostic Information, page 69, for signal
definitions.
3A2098S 35
Page 36

System Setup
System Setup
Overview
The PCF system compensates for temperature, flow, or
pressure fluctuations. However, if there is a hardware
change on the supply system or the dispense material is
changed, the PCF system must be set up again.
After material is loaded into the supply system, set up
the PCF system using the Setup screens. The following
procedure outlines the major system setup steps. The
following subsections provide instructions to complete
each setup step. Once these steps are complete the
module is ready for operation.
NOTE: See the Advanced Display Module (ADM)
section, page 20, and Appendix A - Advanced Display
Module (ADM), page 104, for detailed operating
instructions for the display keypad and each screen.
NOTE: If configuring an Integrated PCF (without ADM),
at least one ADM must be purchased to allow for setup
and troubleshooting.
1. Configure System, page 36.
Configure System
Define the number of installed fluid plates (called
“Dispenser” on this screen) and number of installed swirl
dispensers. If a fluid plate is listed as “Uninstalled” the
screens for that fluid plate will not appear in the run or
setup screens.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the
System screen.
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
3. Use the arrow keys to navigate to the desired field.
4. Press to open the drop-down list, and select
the desired setting. Press to accept the
selection.
5. Repeat for the other Dispensers and Swirl
Dispensers.
6. Press to exit edit mode.
2. Configure Control Settings, page 37.
3. Configure Mode Settings, page 38.
4. Configure Delay Settings, page 38.
5. Configure Flow Meter Settings, page 39.
6. Configure Pressure Loop Settings, page 39.
7. Adjust Pressure Sensors, page 40.
8. Configure Errors, page 40.
9. Setup Maintenance Schedule/Parameters, page 41.
10. For systems with swirl dispensers only:
a. Configure Swirl to valve association and error
type, page 41.
b. Configure Swirl settings, page 42.
11. Configure Gateway Settings, page 42.
12. Setup Styles, page 42.
F
IG. 22
13. Configure Advanced Settings, page 42.
36 3A2098S
Page 37

System Setup
Configure Control Settings
Set the controls for the dispense source, how dispense
commands are sent, and job settings.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to Fluid
Plate x, screen 1 (Control Settings).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
7. Press to move to the Job End Delay field. Enter
the desired delay time (in seconds). Press to
enter the value.
8. Press to move to the Run Mode Bead Adjust
field. Press to open the drop-down list, and
select Enable or Disable. Press to enter the
value.
9. Press to move to the End Job on Alarm Check
Box. Press to enable or disable.
10. Press to move to the Display Control Password
field. Press to enter the value.
11. Press to exit edit mode.
12. If multiple fluid plates are installed, repeat this
procedure for the other Fluid Plates.
IG. 23
F
3. Press to open the Dispense Trigger Source
drop-down list, and select Gateway, Command
Cable, Command Cable 3x, or Combined. If
Command Cable is selected, users can enable the
valves. Press to finalize the selection.
4. If the dispense trigger source is set to Command
Cable, press to move to the Enable Valves field.
Press and to enable valves.
5. Press to move to the Command Value Source
field. Press to open the drop-down list, and
select Gateway, Command Cable, or Display. Press
to enter the value.
6. Press to move to the Job End Mode field. Press
to open the drop-down list, and select Timer or
Gateway. Press to enter the value.
3A2098S 37
Page 38

System Setup
Configure Mode Settings
Set valve commands, including the dispense mode
(pressure, bead, shot, or full open) and flow rate or
pressure for each valve. The bead scale is also
adjustable from this screen.
NOTE: For a description of each dispense mode, see
Dispense Control Modes, page 118.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the Fluid
Plate x, screen 2 (Mode Settings).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
5. Press to move to the Bead Scale field. Enter a
scale value between 50% and 150%. Press to
enter the value.
6. Press to exit edit mode.
Configure Delay Settings
Set on and off delays (in milliseconds) for each valve
and the regulator. For an explanation of the on and off
delays, refer to the On/Off Delays section on page 43.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the Fluid
Plate x, screen 3 (Delay Settings).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
IG. 24
F
3. Press and to set the mode for each
valve that will be used to Pressure, Bead, Shot, or
Full Open. Press to enter each selection.
4. Use the four arrow buttons to navigate to each
Fixed Command field. Enter the desired value for
each valve that will be used. Press to enter
each value.
NOTE: The ability to dispense from multiple valves
simultaneously is only allowed in either of the following
scenarios.
• Each valve is set to Pressure mode and has
identical Fixed Command values.
• Each valve is set to Full Open mode.
Attempting to dispense from multiple valves
simultaneously using any other combination will cause
an Incompatible Valves Settings alarm.
FIG. 25
3. Use the four arrow buttons to navigate to each On
and Off field. Enter a desired delay value (in
milliseconds) for each valve that will be used and
the regulator. Press to enter each value.
4. Press to exit edit mode.
38 3A2098S
Page 39

System Setup
Configure Flow Meter Settings
The accuracy of the PCF volume reporting depends on
precise adjustment of the K-factor(s). The fluid plate
uses the K-factor(s) to calculate the volume dispensed.
If the set value is not correct, the system still delivers
repeatable flow rates; however, the reported value may
not be correct. See Verify Flow Meter Calibration,
page 46, for additional K-factor information.
Table 5: Flow Meter K-Factors
Part Description K-Factor
246652 High Resolution Helical
Gear Meter
246340 Heated Helical Gear
Meter
16E993 Ultra High Flow Meter 33000
25D026 Coriolis Flow Meter 1176
Set Flow Meter K-Factor
NOTE: In systems without a flow meter, the flow meter
settings will be grayed out.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the Fluid
Plate x, screen 4 (Pressure Loop and Flowmeter
Settings).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
7000
3500
3. Press to open the Meter Type drop-down list,
and select the meter type used by the system.
Select Volume for volumetric flow meters or Mass
for mass flow meters. Press to enter the
selection.
4. Press to move to the K-Factor field. Key in the
K-factor value. See Table 5: Flow Meter K-Factors
for values. Press to enter the value.
5. Press to exit edit mode.
NOTE: If necessary, verify flow meter calibration. See
Verify Flow Meter Calibration, page 46, for
instructions.
Configure Pressure Loop Settings
The PCF system uses variables (Kp, Ki, and Kd) in the
software calculations to accurately and precisely control
the fluid pressure.
NOTE: It is recommended that these values are not
changed from the factory defaults of 32.00 for Kp,
128.00 for Ki, and 0.00 for Kd. However, if the values
need to be adjusted, see Manually Adjust Control
Loop Parameters on page 47.
F
IG. 26
3A2098S 39
Page 40

System Setup
Adjust Pressure Sensors
Set pressure offsets and pressure limits.
NOTE: Inlet sensor settings will be grayed out on this
screen for systems with heated fluid plates.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the Fluid
Plate x, screen 5 (Pressure Sensors).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
F
IG. 27
Configure Errors
Set the error type (alarm, deviation, or none) that will be
issued if the pressure, flow rate, volume, or computed
target goes outside the tolerance settings of the active
style. When an alarm occurs, the system stops
dispensing. When a deviation occurs, the system will
continue dispensing. See Fluid Plate x, Screen 6
(Error Type) on page 113 for more information.
NOTE: Only the low/high pressure errors will be
enabled for systems without a flow meter.
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to Fluid
Plate x, screen 6 (Error Type).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
NOTE: For the following steps, press and
to navigate through each field, and to open
drop-down menus and enter changes or selections.
3. Set the desired offset for the inlet and outlet
pressures between 0 and 100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7.0
bar). Remove all pressure on the sensors, and then
adjust the offset so the measured value reads 0.
NOTE: It is recommended that offsets should not be
changed from the factory defaults of 0.
4. Set the desired minimum and maximum pressure
limits for the inlet, and the desired maximum
pressure limit for the outlet.
5. Set the error type (alarm or deviation) that will be
issued:
• If the minimum inlet pressure decreases below
the setting.
• If the maximum inlet pressure increases above
the setting.
• If the maximum outlet pressure increases above
the setting.
FIG. 28
3. Press to open the Low Pressure drop-down
list, and select either Alarm or Deviation for the error
type. Press to enter the selection.
4. Press to move to the next field. Repeat Step 4
for each field.
5. Press to exit edit mode.
6. Press to exit edit mode.
40 3A2098S
Page 41

System Setup
Setup Maintenance Schedule/Parameters
Set the volume (or hours) limit that will trigger a
maintenance advisory for the fluid supply, Voltage to
Pressure (V/P) Transducer, fluid regulator, flow meter,
and all four valves.
NOTE: Hours is shown instead of Volume for fluid plates
without a flow meter.
The Volume (or Hours) column displays the current
totalizer value. If this value exceeds the set limit, the
value will turn red and a maintenance advisory is issued.
See Fluid Plate x, Screen 7 (Maintenance Advisory
Limits), page 113, for more information about
maintenance totalizers.
To set limits:
1. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the Fluid
Plate x, screen 7 (Maintenance Advisory Limits).
2. Press to access the fields to make changes.
To reset a totalizer value:
1. Follow Steps 1-3 of To set limits: to make changes
in
Fluid Plate x, screen 7 (Maintenance Advisory
Limits)
.
2. Press to scroll to the system component to
reset.
3. Press to reset the value.
Configure Valve to Swirl Association and Motor Error Type
Define which Swirl number is installed on which
dispense valve.
Set the error type (alarm or deviation) that will be issued
if a motor fault occurs. When an alarm occurs, the fluid
plate stops dispensing. When a deviation occurs, the
fluid plate will continue dispensing.
F
IG. 29
3. Enter the desired limit for the air supply and press
to enter the selection.
4. Press to move to the next field. Repeat Step 4
for each field.
5. Press to exit edit mode.
3A2098S 41
FIG. 30
Page 42

System Setup
Configure Swirl Settings
NOTE: This applies only to systems with swirl
dispensers.
Set the individual Swirl settings for each installed Swirl.
F
IG. 31
Configure Gateway Settings
Gateway settings differ for each system. See
Automation Gateway Setup Screens, page 107, for
guidelines on configuring each type of Gateway
interface.
Setup Styles
The PCF system can store up to 256 styles. See Styles,
page 50, for more information about styles and
instructions on setting up styles. Style 0 is always the
purge style.
Configure Advanced Settings
Use the advanced settings to set or change the format
and display units, such as the language, date format,
and pressure units, for all PCF screens. See Setup
Mode, page 106, for advanced setting guidelines.
42 3A2098S
Page 43

On/Off Delays
D
C
A
B
Dispense Valve
Signal
Fluid
Regulator
Valve Open
Command
Valve Actually
Open
E
F
The PCF fluid regulator can physically respond faster
than the dispense device and its solenoid. As a result,
the fluid regulator can supply material to the dispense
device before the device has time to open. Supplying
material to a closed device can create trapped-pressure.
At the end of a cycle, the dispense device can shut off
before the pressure has dissipated. This can cause a
dispense of an excess of material at the beginning of the
next cycle.
To eliminate these two problems, change the delay time
associated with the opening of the fluid
regulator/dispense and/or the closing of the dispense
device, see Table 5: On/Off Delay Variables. For
instructions setting on/off delays, see Configure Delay
Settings, page 38.
NOTE: On/Off delay can be set for each dispense
device.
In general, delays should be adjusted so the outlet
pressure during “no flow” is slightly below the outlet
pressure during dispense.
Table 5: On/Off Delay Variables
Variable: Sets the Amount of Time:
System Setup
F
IG. 32 and Table 6: Delay On/Off Timing show delay
ON and OFF timing.
Table 6: Delay On/Off Timing
A Regulator ON
delay
The user sets the fluid
regulator ON delay timing.
B Valve ON delay Usually set to zero. Can be
used to change the starting
point of a bead.
C Valve OFF Delay Usually set to zero. Higher
values will lower the trapped
pressure.
D Regulator OFF
delay
The user sets the regulator
OFF delay timing. Zero or
small values will lower the
trapped pressure.
E Valve Open
Reaction Time
Time delay for valve to
physically open. Delay
varies based on pneumatic
hose length and valve air
volume.
F Valve Close
Reaction Time
Time delay for valve to
physically close. Delay
varies based on pneumatic
hose length and valve air
volume.
Valve ON Sets time from Dispense Valve High
Regulator
ON
Valve OFF Sets time from Dispense Valve Low
Regulator
OFF
FIG. 32: Timing Delay
to Valve Open command
Sets time from Dispense Valve High
to Regulator ON
to Valve Close command
Sets time from Dispense Valve Low
to Regulator OFF
3A2098S 43
Page 44

Operation
Operation
Pressure control may degrade at low output pressures.
It is not recommended to dispense at outlet pressures
less than 500 psi (3.4 MPa, 34 bar).
Startup
Initial Startup
1. Ensure the PCF control center is installed and all of
the proper connections to and from the control
center have been made. Ensure fittings are tight.
2. Read and understand the Operation (page 44) and
Advanced Display Module (ADM) (page 20)
sections of this manual.
3. Continue startup with step 2 in Standard Startup.
Standard Startup
1. Carefully inspect the entire system for signs of leakage or wear. Replace or repair any worn or leaking
components before operating the system.
Load Material
Before using the system material must be loaded into
the supply system.
1. If this is a new installation, follow the Initial Startup
procedure. Otherwise, follow the Standard Startup
procedure. See page 44.
2. Turn on the fluid supply pressure to the fluid plate
assembly.
3. Place the valve(s) over a waste container.
4. Enter the maintenance screen. See Dispense
From Maintenance Screen, page 47.
5. Select a control mode. See Dispense From Main-
tenance Screen, page 47.
6. If the system status indicator LED (BB) is orange,
press to turn the system on.
2. Press the Stop button (BC). See F
3. Turn on air.
4. Turn on electrical power to the system.
5. Turn on the main power to supply power to the PCF.
6. Check Interface Signals: If this is a new
installation, power on each system input and verify
that each input is being received.
7. Turn on the material supply system.
IG. 8 on page 20.
7. Press and hold . Dispense fluid until clean,
air-free fluid flows from the valve.
8. Press to exit maintenance screen.
44 3A2098S
Page 45

Operation
Fluid Plate
Maintenance Screen
Swirl
Maintenance Screen
Maintenance Mode Operation
Operating from maintenance mode enables manual
dispensing ( ) and manually starting the swirl
dispenser ( ).
The system begins dispensing when the user presses
. Dispense parameters and duration depend on the
selected control. Dispensing continues for as long
as is pressed.
Follow steps in the supply system manual to set the inlet
pressure.
NOTICE
Inlet pressure beyond the recommended range
above will cause accelerated wear on the regulating
valve and the pump feed system.
Feed System Pressure Drop
During material flow, the regulator inlet pressure
decreases. The amount the pressure decreases is the
amount of pressure lost between the feed pump and the
regulator inlet.
With high viscosity fluids, long line lengths, or small
diameter line sizes this pressure decrease can be
thousands of psi (hundreds of bar). This means that the
static pump pressure is set much higher than the
regulator needs at its inlet. To prevent excessive control
regulator wear or surging, a mastic fluid pressure
regulator is recommended on the feed line close to the
control regulator. The mastic regulator will suppress the
static feed pressure at the control regulator inlet.
The system starts the swirl dispenser when the user
presses . The swirl dispenser continues to run until
is pressed again.
There is one maintenance screen for each installed fluid
plate and each installed Swirl. The maintenance
controls for the Swirl are shown on both the Swirl
maintenance screen and on the Fluid Plate
maintenance screen for the fluid plate where the swirl
dispenser is installed.
Verify System Operation
Use maintenance mode to manually check the operation
of the PCF system components before switching over to
automation control (normal operation). See Dispense
From Maintenance Screen, page 47, for instructions
on operating from maintenance mode.
NOTE: Perform the following procedures while in
maintenance mode.
Set Inlet Pressure
The inlet pressure reading should be in the range of
300 psi (2.1 MPa, 21 bar) to 500 psi (3.4 MPa, 34 bar)
above the outlet pressure reading under your highest
flow condition.
3A2098S 45
Page 46

Operation
fluid mass (g)
density (g/cc)
= measure volume (cc)
K-Factor (new) =
displayed volume (cc) x K-Factor (old)
measured volume (cc)
Dispense from Each Valve
Dispense from each valve that will be used in normal
operation to confirm that the entire system is installed
correctly and is capable of delivering desired results.
Follow the steps outlined in Dispense From
Maintenance Screen, page 47, to perform each of the
following applicable system verification checks.
NOTE: Each fluid plate controls only the dispense
valves connected to it.
• For each valve that will be used during normal
operation, dispense at each pressure or flow rate
that will be used during normal operation. This
verification check confirms that the system is
capable of delivering material at your maximum
desired operating point.
• For systems that will operate multiple valves in
pressure mode at the same time, dispense from
each valve at the same time. This verification check
confirms that the system is capable of delivering
material at your maximum desired operating point.
• For each valve operating in bead mode, perform an
initial teaching process. Follow this procedure after
significant system and/or material characteristic
changes.
a. For each flow rate that will be used during
Verify Flow Meter Calibration
Most sealant and adhesive materials are compressible.
Since the flow meter measures the material under high
pressure, the actual volume of material dispensed may
vary slightly from the measured volume, due to this
compressibility. If the K-factor is not correct, the
displayed volume will not be accurate.
Follow either of the following methods to calibrate the
flow meter during initial setup and on a routine basis to
check for flow meter wear.
Method 1. Using a gram scale
1. Record the flow meter k-factor shown on Fluid Plate
x, screen 4 (Flowmeter Settings). See F
IG. 26 on
page 39.
2. Use a 500 cc or larger beaker. Measure the mass of
the empty beaker.
3. Manually dispense material into the beaker. Hold
the beaker so that the stream of material is
submerged in the captured material to minimize air
entrapment in the container.
4. Record the volume dispensed on Fluid Plate x,
screen 1. See F
IG. 33 on page 47.
5. Calculate the actual volume dispensed:
normal operation, press until PCF
achieves the flow rate setpoint.
NOTE: During the initial system operation verification, it
may take four to five seconds for the system to learn
system characteristics.
b. Continue to press for several seconds
after the desire flow rate is reached to confirm
that the system is capable of maintaining the
desired flow rate.
c. Repeat Steps a and b for a range of flow rates
to confirm that the system responds quickly to
achieve setpoint when is pressed.
6. Calculate the new flow meter K-factor:
7. Enter new K-factor.
8. Repeat the procedure to verify the new K-factor.
Method 2. Without using a gram scale, visual measurement
1. Record the flow meter k-factor shown on Fluid
Plate x, screen 4 (Flowmeter Settings). See F
IG. 26
on page 39.
2. Use a 500 cc or larger beaker.
46 3A2098S
Page 47

Operation
K-Factor (new) =
displayed volume (cc) x K-Factor (old)
dispensed volume (cc)
3. Manually dispense material into the beaker. Hold the
beaker so that the stream of material is submerged
in the captured material to minimize air entrapment
in the container.
4. Record the volume dispensed on Fluid Plate x,
screen 1. See F
IG. 33 on page 47.
5. Settle the material into the beaker and view the
actual volume dispensed.
6. Calculate the new flow meter K-factor:
7. Enter new K-factor.
8. Repeat the procedure to verify the new K-factor.
Manually Adjust Control Loop Parameters
NOTE: It is recommended that these values not be
changed from the factory defaults of 32.00 for Kp, 128.00
for Ki, and 0.00 for Kd.
6. Optional: To fine tune the step response in pressure
mode, gradually increase the Kd value.
NOTE: Increasing Kd (pressure only) is typically not necessary but it may improve step response. However setting Kd too high may cause the system to oscillate.
7. Stop dispensing.
Dispense From Maintenance Screen
1. Navigate to Fluid Plate x, screen 1 for the desired
fluid plate.
If the system is not maintaining the desired setpoint while
in pressure or bead control mode, manually change the
Kp and Ki values:
NOTE: Pressure parameters should be adjusted first,
even if you typically operate in bead control mode.
1. Begin dispensing material.
NOTE: Begin a new dispense each time control
parameters are changed.
2. If the regulator outlet pressure does not closely
follow the desired pressure, set Ki to zero then
increase Kp until the proper pressure control is
achieved.
3. If the regulator outlet pressure oscillates rapidly
above and below the commanded pressure,
decrease Kp by 10%. Continue to decrease the Kp
value in 10% increments until the outlet pressure is
stable.
4. Set Ki value to 2 then increase the Ki value until the
system oscillates.
5. Decrease Ki until oscillation stops.
FIG. 33
2. Press to enter maintenance screen.
IG. 34
F
3. Press to open the Control Mode drop-down list,
and select the preferred control mode. Press
again to exit the drop-down list.
3A2098S 47
Page 48

Operation
4. Press to move to the target fields. Enter the
target pressure, flow rate, or volume (dependent on
control mode) and press to save.
5. Press to move to the valve check boxes. Press
to select the desired valves.
6. Follow step 2 - 4 of Manually Dispense Fluid, page
48.
Manually Dispense Fluid
1. From Fluid Plate x, screen 1, press to enter
maintenance screen.
2. Press and verify that the valve opens.
3. Continue to press as long as needed to load or
dispense material.
2. Press to enter maintenance screen.
FIG. 36
3. To change the RPM, use the arrow keys to navigate
to the RPM box then enter the desired RPM.
4. Press again to exit maintenance screen.
Operate Swirl Dispenser From Maintenance
Screen
1. Navigate to the Swirl x screen for the desired Swirl
Dispenser. If the Swirl Dispenser is installed on
Fluid Plate x, you may also navigate to Fluid Plate x,
screen 1.
4. Press and verify that the Swirl Dispenser
begins rotating. Press again to stop the Swirl
Dispenser.
5. Press again to exit maintenance screen.
F
IG. 35
48 3A2098S
Page 49

Operation
Automation Control (Normal Operation)
During automation control (normal operation), the
system can dispense or change dispense parameters
when it receives a command from the automation unit.
The automation control operates using the concept of
jobs and styles. For a detailed explanation of jobs and
how they work within the PCF system, see Jobs on
page 49. For a detailed explanation of styles and how
they work within the PCF system, see Styles on
page 50.
Jobs
NOTE: See Appendix D - I/O Signal Descriptions,
page 146, for automation input and output signal
descriptions.
A job is an automation sequence in which material can
be dispensed. The amount of material specified for a job
varies by application. In some applications, a job may be
the amount of material dispensed on a part. Other
applications may define a job to be the amount of
material dispensed on a number of parts or dispensed
over a period of time.
A job is initiated when the automation sends a Style
Strobe signal to the PCF. Once the job is initiated, the
PCF will start tracking the amount of volume requested
by the automation and the amount of material that is
actually dispensed. These volumes will be tracked until
the job is completed. At the end of the job, error
calculations are made and the volumes are stored on
the PCF system (Job Log).
The PCF system monitors two things to determine when
a job is complete. Either the Dispense Complete signal
is sent by the automation or the job complete timer
expires. The type of job end signal is configured to
Timer or Gateway in Fluid Plate x, screen 1 (Control
Settings). If the timer method is used, the timer begins
counting every time the dispense valve is turned off. If
the valve stays off for more than the preset timer value,
the job is considered complete.
Once the job is complete, the job information is stored to
memory. The most recent jobs can be viewed on the
Job screen. The information stored with each job is as
follows. See Job Report Screens, page 120, for
instructions on how to view job reports.
Actual (Measured) Volume - The amount of material
measured by the flow meter during a job.
Requested Volume - The amount of material that the
automation tries to dispense during a job. In Bead
mode, the requested volume is calculated as the
requested flow rate multiplied by the duration of the dispense. In all other modes, the requested volume is
same as the target volume.
Target Volume - The amount of material a job should
have. This is defined in the Style.
Jobs in Bead Mode
In Bead Mode, all of the previously mentioned volumes
are monitored. The High Volume, Low Volume, and
Computed Target errors are evaluated at the end of the
job. The volume alarms compare the measured volume
to the requested volume and the computed target alarm
compares the requested volume to the target volume.
Jobs in Pressure Mode
In Pressure Mode, the requested volume is not
measured. In this mode, the automation command
voltage corresponds to a pressure instead of flow rate.
For this reason the requested volume is not available
(as well as the Computed Target error). The high and
low volume alarms compare the measured volume to
the target volume for pressure mode.
Jobs in Shot Mode
In Shot Mode, the job is started the same as a normal
job, but when the gun is triggered it dispenses until the
target volume is reached. After the shot is done, the
Dispense in Process bit goes low and you can check the
Volume OK bit to see if the shot was within tolerance. If
the Job End Mode is set to Timer, the shot times out
after the specified amount of time and sends an
advisory, even if target volume is not reached.
Continuously Running Applications
In some cases the target volume for a job is not known.
An example of a case where the target volume is
unknown is a continuously running system. This would
be a system that does not run jobs, but runs continuously over a day or a shift. In this case, the flow rate
becomes more important than the amount of volume
dispensed in a job. The way to handle this situation is to
set the target volume to a value of zero. This effectively
disables the Computed Target error. The controls will
still maintain the desired flow rate and report errors corresponding to the tolerance set for the running style.
3A2098S 49
Page 50

Operation
Styles
The PCF system has the ability to handle up to 256
styles, depending on the selected option.
NOTE: The number of available styles depends on the
fluid plate configuration. See Models on page 4. Style 0
is specified for purging only.
For each style, an independent target volume and
tolerance can be configured. This allows for job-related
errors and logs to be evaluated for each style. The style
is read at the beginning of a job and cannot be changed
until the next job.
PCF reads in the styles via the Gateway interface. For
detailed interface information, see Appendix B - Dis-
crete Gateway Module (DGM) Connection Details on
page 121, and Appendix C - Communications Gate-
way Module (CGM) Connection Details on page 128,
as applicable.
To setup a style:
1. Navigate to Fluid Plate x, screen 8.
3. Enter the style number in the Style field.
4. Enter Style Name:
a. Press while in the Style Name field to
display the Keyboard screen.
FIG. 38
2. Press to access the style setup fields.
F
IG. 37
b. Use the arrow buttons on the ADM to scroll
through each letter. Press to enter a letter
in the style name field. See Keyboard Screen,
page 114, for further details.
c. Press to accept the new value.
5. Enter the target volume in the Volume field, and the
tolerance percentages in the Low and High
Tolerance fields.
6. Enter precharge mode and parameters. See
Precharge Modes beginning on page 51.
7. Press to exit edit mode.
50 3A2098S
Page 51

Operation
Precharge Modes
NOTE: See the diagram on the following page.
Static Precharge Mode
Display
When Display precharge mode is selected, a static
precharge pressure can be defined. When a job is active
and all dispense valves are closed, the regulator will
maintain the defined precharge pressure.
Gateway
NOTE: Gateway precharge mode is only available for
systems containing CGMs.
When “Gateway” precharge mode is selected, the outlet
pressure will be set according to the current
pressure/flow command using the scaling set for
dispense valve(s) selected through the gateway
interface.
Dynamic Precharge Modes
Dynamic precharge control allows the system to better
prepare for the upcoming dispense. The pressure/flow
command is used to actively set the outlet pressure to
the ideal pressure while all dispense valves are closed
and provide a boost while the valve is opening to help
accelerate material.
The “Closed” scaling will be applied when all dispense
valves are closed and the “Opening” scaling will be
applied immediately after a dispense valve starts to
open and continue for the user-specified duration (in
milliseconds). The precharge scaling values modify the
control signals that are necessary to obtain the desired
pressure/flow. The precharge pressure can be changed
dynamically throughout the job by varying the pressure/flow command value.
Valve 1
When the “Valve 1” precharge mode is selected, the
outlet pressure will be set according to the current
pressure/flow command using Valve 1 scaling values.
3A2098S 51
Page 52

Operation
Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction
Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction
Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction
Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction Dispense Application Direction
-Controls outlet pressure based on desired command while valves are closed.
-Ideal value is typically less than 100% due to the minimal pressure losses within the system when fluid is not
flowing.
-Provides a boost upon valve opening to accelerate material.
-Ideal value is typically greater than 100%.
-The duration for which the valve opening scaling is application before the command is no longer scaled.
-Controls timing of transition from valve “closed” precharge to valve “opening” precharge and regular dispense.
-This delay should approximate the time it takes a dispense to open.
Closed Precharge Scaling Value
Opening Precharge Scaling Value
Opening Precharge Duration Value
Regulator On Delay Value
Value Too Low Ideal Value Value Too High
Value Too Low Ideal Value
Value Too High
Value Too Low Ideal Value Value Too High
Value Too Low Ideal Value Value Too High
52 3A2098S
Page 53

Operation
Typical Job Cycle
In order for the system to run it must be in the active
state (status LED next to on the ADM is green).
Before a job begins the automation controller outputs
should have the following values:
• Style Strobe: 0
• Dispense Complete: 0
• Dispense Valve x On: all should be 0
• Style: Any value is acceptable
A typical job cycle consists of the following dispensing
sequence. See Typical Job Cycle Chart, page 54.
NOTE: Each job cycle can apply to only one fluid plate.
1. The automation controller checks that Dispenser
(Fluid Plate) Ready signal is set to 1. If it is set to 1,
a job can begin.
2. The automation controller sets the Style to the next
desired style value.
NOTE: Each fluid plate has a unique set of styles. For
example, Style 2 for Fluid Plate 1 is different from Style
2 for Fluid Plate 2.
3. The automation controller sets the Style Strobe to 1.
7. PCF sets the following signals based on the results
of the job.
• Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
• Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
• Dispense Volume OK
•Error
• Dispensed Volume
NOTE: The automation controller should not read the
Dispense Volume OK or Dispense Volume signals until
after the system clears the Dispense In Process signal.
8. PCF sets Dispense In Process to 0 to indicate the
job is complete. At this time the signals from step 7
should be read.
9. The automation controller must clear Dispense
Complete and Style Strobe (either can be cleared
first) before the next job can start.
Jobs with Command Cable Dispense
Trigger
With the Dispense Trigger Source configured to
Command Cable or Command Cable 3x, users only
need to trigger the dispense applicator to start a job.
This configuration is useful for less demanding
applications that do not require a full automation
interface.
4. PCF reads the Style bits to select the new style. The
system then starts a new job and sets Dispense In
Process to 1.
5. The automation controller begins dispensing. The
automation controller sets and clears Dispense
Valve x On bits as desired throughout the course of
the job.
6. When the dispense is complete the automation
controller sets Dispense Complete to 1.
The following limitations apply when starting a job with
this configuration:
• The selected style defaults to Style 1.
• There can be up to a 100 ms delay before
dispensing while PCF prepares for the new job
cycle.
• The job end mode timer must be used to end a
job.
3A2098S 53
Page 54

Operation
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) In Process
Volume OK
Style Bits
Style Strobe
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
Dispense Valve X On
Dispense Complete
Regulator Active (Precharge = 0)
PCF State
Dispense Valve X Open
Dispense Ready
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
First Job
Second Job
Typical Job Cycle Chart
NOTE: Swirl can be turned on at any point inside of or
outside of a job. Allow time for the swirl to reach desired
RPM. If possible, verify Swirl speed through the
automation interface prior to opening the dispense
valve.
NOTE: A 50ms delay is suggested between each
signal.
NOTE: Dispense Complete must be strobed, not held
high in order to avoid an advisory.
54 3A2098S
Page 55

Control Charts
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Volume OK
Dispense Ready
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispense In Process
Purge In Process
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
Style Bits
Style Strobe
Dispense Valve X On
Dispense Complete
Dispense Valve X Open
PCF State
Purge Using Style 0
Purge Using Purge Bit
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense Ready
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispense In Process
Purge In Process
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
Remote Start / Purge
Dispense Valve X On
PCF State
Dispense Valve X Open
Operation
3A2098S 55
Page 56

Operation
Remote Start
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) Ready
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) Remote Start/Purge in Process
Remote Start/Purge
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm / Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
Error Reset
Error Reset
Rising Edge Only
Cancel Job
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense In Process
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
Error Reset
Control Charts (continued)
56 3A2098S
Page 57

Control Charts (continued)
Precharge* - Gateway Mode
Precharge* - Display Mode
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense Ready
* Precharge: After starting a job and prior to opening the dispense valve, the fluid pres-
sure is increased to try to match the dispensing pressure. This helps the consistency
of the dispense.
Shaded areas indicate the precharge is active.
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispense In Process
Volume OK
Style Bits
Style Strobe
Dispense Valve X On
Dispense Complete
Regulator Active
Dispense Valve X Open
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
PCF State
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense Ready
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispense In Process
Volume OK
Style Bits
Style Strobe
Precharge Valve X On†
Command Signal Valid‡
Regulator Active
Dispense Valve X Open
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
PCF State
Dispense Valve X On
Dispense Complete
* Precharge: After starting a job and prior to opening the dispense valve, the fluid pres-
sure is increased to try to match the dispensing pressure. This helps the consistency of
the dispense.
Shaded areas indicate the precharge is active.
† The “Precharge Valve X On” bits are only available through a fieldbus interface. This
precharge method is not valid for DGM systems.
‡ Only applies to command signals when either “Command Cable” or “gateway” is
selected as “Command Value Source”.
Operation
3A2098S 57
Page 58

Operation
Precharge* - Valve 1 Mode
* Precharge: After starting a job and prior to opening the dispense valve, the fluid pressure is
increased to try to match the dispensing pressure. This helps the consistency of the dispense.
Shaded areas indicate the precharge is active.
† Only applies to command signals when either “Command Cable” or “gateway” is selected as “Com-
mand Value Source”. In systems containing an automation gateway DGM, when “Digital” is
selected as the “Command Value Type”, the “Digital CMD 1” and “Digital CMD 2” inputs set the
command.
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense Ready
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Alarm
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) No Error
Dispense In Process
Volume OK
Style Bits
Style Strobe
Command Signal Valid†
Regulator Active
Dispense Valve X Open
Automation Outputs (PCF Inputs)
PCF State
Dispense Valve X On
Dispense Complete
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense In Process
Automation Outputs (PCF Gateway Inputs)
Dispense Valve 1 Trigger
PCF State
Regulator Active (Precharge = 0)
Dispense Valve 2 Trigger
Dispense Valve 3 Trigger
Dispense Valve 1 Open
Dispense Valve 2 Open
Dispense Valve 3 Open
Trigger Using Command Cable 3x
Control Charts (continued)
58 3A2098S
Page 59

Control Charts (continued)
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense In Process
Automation Outputs (PCF Gateway Inputs)
Dispense Valve X On
PCF State
Regulator Active (Precharge = 0)
Trigger Using Command Cable and Gateway (Combined)
Dispense Valve Y On
Dispense Valve X On
Dispense Valve Y On
Command Cable
Dispense Trigger
Trigger Using Command Cable
* Dispense Valve X Open determined by Enable Valves check
boxes on Fluid Plate x, screen 1(Control Settings).
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense In Process
Command Cable
Dispense Trigger
PCF State
Regulator Active (Precharge = 0)
Dispense Valve X Open*
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispense In Process
Automation Outputs (PCF Gateway Inputs)
Dispense Valve 1 On
PCF State
Regulator Active (Precharge = 0)
Trigger Using Gateway
Dispense Valve 2 On
Dispense Valve 3 On
Dispense Valve 4 On
Dispense Valve 1 On
Dispense Valve 2 On
Dispense Valve 3 On
Dispense Valve 4 On
Operation
3A2098S 59
Page 60

Operation
Automation Inputs (PCF Outputs)
Dispenser (Fluid Plate) Ready
Automation Outputs (PCF Gateway Inputs)
Swirl X Actual Speed - RPM (32 bits)
PCF State
Swirl X On
Enable Swirl Dispenser
Swirl X Speed Command (12 bits)
NOTE: Swirl orbiter may take a few seconds to reach full speed.
Swirl X Enable
Speeding Up
Command Value Set
Actual Speed Value Valid
Full Speed
Control Charts (continued)
60 3A2098S
Page 61

Pressure Relief Procedure
Dispense Valve Air Solenoid
The equipment stays pressurized until pressure is
manually relieved. To help prevent serious injury from
pressurized fluid such as skin injection, splashing
fluid and moving parts, follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when you stop dispensing and before cleaning, checking or servicing the equipment.
Pressure Relief Procedure
b. Continue actuating the plunger until all pressure
is purged from the system between the needle
and the dispense valves attached to this fluid
plate before proceeding to the next step.
5. For systems with multiple fluid plates, repeat
previous steps for other fluid plates.
6. Shut off air to the fluid plate.
1. Shut off the fluid supply to the fluid plate assembly.
2. Place a waste container beneath the dispense
valve.
3. In maintenance mode, select Full Open Dispense
Mode, which opens the regulator and dispense
valve. Press the manual dispense button until
the fluid flow stops.
4. If the dispense valve cannot be actuated from the
control center, refer to F
following steps to open the dispense valve and
relieve fluid pressure:
a. Manually actuate the plunger on the solenoid to
open all dispense valves attached to this fluid
plate and relieve fluid pressure. See F
IG. 39 and perform the
IG. 39.
7. Place a waste container below the air filter
assembly then open drain valve on the air filter
assembly. Close drain valve once air is relieved.
8. Turn main power switch on control panel to the OFF
position.
9. If you have followed the previous steps and suspect
that a valve, hose, or dispense nozzle is clogged or
that pressure has not been fully relieved, very slowly
remove the dispense tip, clean the orifice, and
continue relieving pressure.
10. If this does not remove the clog, cover the hose end
coupling with a rag then very slowly loosen the hose
end coupling to relieve pressure gradually, then
loosen the coupling completely. Clear the valves or
hose. Do not pressurize the system until the blockage is cleared.
F
IG. 39: Dispense Valve Air Solenoid
3A2098S 61
Page 62

Shutdown
BC
TI12362a
Shutdown
1. Press the Stop button (BC).
FIG. 40: ADM - Stop Button
2. Shut off the material supply to the fluid plate/meter.
3. Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure on page 61.
4. Turn off the PCF system's compressed air supply.
5. Turn main power switch on control panel to the OFF
position.
F
IG. 41: Control Center Main Power Switch
62 3A2098S
Page 63

USB Data
USB Data
NOTE: USB data is not available on models that do not
have an ADM. See Models on page 4.
All files downloaded from the USB are put in a DOWNLOAD folder on the drive. For example:
“E:\GRACO\12345678\DOWNLOAD\”
The 8-digit numeric folder name matches the 8-digit
ADM serial number. When downloading from multiple
ADMs, there will be one sub-folder in the GRACO folder
for each ADM.
USB Logs
F
IG. 42: ADM USB Port
During operation, PCF stores system and performance
related information to memory in the form of log files.
PCF maintains three types of log files: a job log, an
event log, and dispense data logs. Follow the Down-
load Procedure, page 65, to retrieve log files.
Event Log
• Job number (sequential number)
• Dispenser (Fluid Plate) Number
•Style number
• Target volume (in the units shown in the volume
units column)
• Requested volume (in the units shown in the
volume units column)
• Actual dispensed volume (in the units shown in
the volume units column)
• Volume units
• Error percentage between actual dispensed volume and requested volume (maximum of
100%)
• Minimum inlet pressure during job (measured in
bar, heated systems will always read 0)
• Average inlet pressure during job (measured in
bar, heated systems will always read 0)
• Maximum inlet pressure during job (measured
in bar, heated systems will always read 0)
• Minimum outlet pressure during job (measured
in bar)
• Average outlet pressure during job (measured
in bar)
• Maximum outlet pressure during job (measured
in bar)
• Minimum flow rate during job (measured in
cc/min, systems with no flow meter will read 0)
• Average flow rate during job (measured in
cc/min, systems with no flow meter will read 0)
• Maximum flow rate during job (measured in
cc/min, systems with no flow meter will read 0)
• Elapsed time (mS)
The event log file name is 1-EVENT.CSV and is stored
in the DOWNLOAD folder.
The event log maintains a record of the last 1,000
events. Each event record in the log file contains the
date and time the event occurred, the event type, event
code, and event description.
Job Log
The job log file name is 2-JOB.CSV and is stored in the
DOWNLOAD folder.
The job log maintains a record of the last 10,000 jobs. At
the completion of each job the following data is stored in
the log file:
• Job completion date
• Job completion time
3A2098S 63
Dispense Data Log
The dispense data log file name is 3-DATAx.CSV and is
stored in the DOWNLOAD folder. There is one dispense
data log file for each installed fluid plate, so there can be
up to four data logs.
The dispense data log maintains a record of system inlet
pressure (heated systems will always read 0), system
outlet pressure, system flow rate (systems without flow
meters will always read 0), and active dispense valves.
This data is recorded at one second intervals when a job
cycle is in process. Each dispense data log is capable of
storing up to two hours of data.
Page 64

USB Data
System Configuration Settings File
The system configuration settings file name is
SETTINGS.TXT and is stored in the DOWNLOAD
folder.
A system configuration settings file automatically
downloads each time a USB flash drive is inserted. Use
this file to back up system settings for future recovery or
to easily replicate settings across multiple PCF systems.
Refer to the Upload Procedure, page 65, for
instructions on how to use this file.
It is recommended to retrieve the SETTINGS.TXT file
after all system settings are set as desired. Store the file
for future use as a backup in case the settings are
changed and need to be quickly changed back to the
desired setup.
NOTE: System settings may not be compatible between
different versions of the PCF software.
NOTE: Do not modify the contents of this file.
Custom Language File
The custom language file name is DISPTEXT.TXT and
is stored in the DOWNLOAD folder.
A custom language file automatically downloads each
time a USB flash drive is inserted. If desired, use this file
to create a user-defined set of custom language strings
to be displayed within the ADM.
The PCF system is able to display the following Unicode
characters. For characters outside of this set, the
system will display the Unicode replacement character,
which appears as a white question mark inside of a
black diamond.
• U+0020 - U+007E (Basic Latin)
• U+00A1 - U+00FF (Latin-1 Supplement)
• U+0100 - U+017F (Latin Extended-A)
• U+0386 - U+03CE (Greek)
• U+0400 - U+045F (Cyrillic)
Create Custom Language Strings
The custom language file is a tab-delimited text file that
contains two columns. The first column consists of a list
of strings in the language selected at the time of
download. The second column can be used to enter the
custom language strings. If a custom language was
previously installed, this column contains the custom
strings. Otherwise the second column is blank.
Modify the second column of the custom language file
as needed and then follow the Upload Procedure,
page 65, to install the file.
The format of the custom language file is critical. The
following rules must be followed in order for the
installation process to succeed.
• The file name must be DISPTEXT.TXT.
• The file format must be a tab-delimited text file
using Unicode (UTF-16) character
representation.
• The file must contain only two columns, with
columns separated by a single tab character.
• Do not add or remove rows to the file.
• Do not change the order of the rows.
• Define a custom string for each row in the
second column.
64 3A2098S
Page 65

USB Data
Download Procedure
1. Insert USB flash drive into USB port (BL). See FIG.
42 on page 63.
2. The menu bar and USB indicator lights indicate that
the USB is downloading files. Wait for USB activity
to complete. A pop-up will be present until the
transfer is complete if it is not acknowledged.
3. Remove USB flash drive from USB port (BL).
4. Insert USB flash drive into USB port of computer.
5. The USB flash drive window automatically opens. If
it does not, open USB flash drive from within
Windows
6. Open Graco folder.
7. Open system folder. If downloading data from more
than one system, there will be more than one folder.
Each folder is labeled with the corresponding serial
number of the ADM (The serial number is on the
back of the ADM.)
®
Explorer.
Upload Procedure
Use this procedure to install a system configuration file
and/or a custom language file.
1. If necessary, follow the Download Procedure,
page 65, to automatically generate the proper folder
structure on the USB flash drive.
2. Insert USB flash drive into USB port of computer.
3. The USB flash drive window automatically opens. If
it does not, open USB flash drive from within Windows Explorer.
4. Open Graco folder.
5. Open system folder. If working with more than one
system, there will be more than one folder within the
Graco folder. Each folder is labeled with the
corresponding serial number of the ADM. (The
serial number is on the back of the module.)
6. If installing the system configuration settings file,
place SETTINGS.TXT file into UPLOAD folder.
8. Open DOWNLOAD folder.
9. Open LOG FILES folder labeled with the highest
number. The highest number indicates the most
recent data download.
10. Open log file. Log files open in Microsoft
default as long as the program is installed. However, they can also be opened in any text editor or
Microsoft
NOTE: All USB logs are saved in Unicode (UTF-16)
format. If opening the log file in Microsoft Word, select
Unicode encoding.
®
Word.
®
Excel® by
7. If installing the custom language file, place
DISPTEXT.TXT file into UPLOAD folder.
8. Remove USB flash drive from computer.
9. Install USB flash drive into PCF system USB port.
10. The menu bar and USB indicator lights indicate that
the USB is downloading files. Wait for USB activity
to complete.
11. Remove USB flash drive from USB port.
NOTE: If the custom language file was installed, users
can now select the new language from the Language
drop-down menu in the Advanced Setup Screen 1.
3A2098S 65
Page 66

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
NOTE: Check all possible solutions in the chart below
before you disassemble the system.
Troubleshooting for individual fluid regulators and flow
meters is also discussed in their separate manuals;
refer to Related Manuals on page 3. Also refer to Event
and Error Codes and Troubleshooting, page 71, for
detailed information on how error codes are
communicated.
Fluid Plates
Problem Cause Solution
No outlet pressure Air pressure low Verify air pressure is above 60 psi
(410 kPa, 4.1 bar)
No “Valve On” signal from automation unit
No air signal to air diaphragm Check for loose/disconnected
False signal being sent to control Check outlet pressure sensor output;
High outlet pressure Fluid regulator needle/seat is worn Rebuild fluid regulator; replace
Air leaks from fluid plate Loose air connections Check air connections; tighten if
Worn gaskets Check/replace gaskets on Voltage to
Check output and wiring from
automation unit
connector to Voltage to Pressure
(V/P) Transducer; tighten
verify that it corresponds to zero
pressure; replace sensor and/or
amplifier
needle/ seat
necessary
Pressure (V/P) Transducer and
solenoid valve
66 3A2098S
Page 67

Troubleshooting
Flow Meter
Problem Cause Solution
No flow measurement Flow meter pick-up sensor loose Tighten flow meter pick-up sensor
Flow too low Verify flow rate is above minimum
for the installed flow meter
Loose wiring Verify connection from flow meter to
FCM
Damaged flow meter pick-up sensor Replace pick-up sensor
False measurement Flow meter not calibrated Calibrate flow meter, page 46
System not grounded properly Verify system ground
Noisy power source Verify clean power supply power to
main enclosure
Flow reported is not correct or
inconsistent
Flow meter not calibrated Calibrate flow meter, page 46
Flow meter is worn Replace flow meter
Fluid Regulator
Problem Cause Solution
No pressure regulation Damaged diaphragm Replace diaphragm
Leaking or dirty seat Replace cartridge, or clean seat
No fluid flow Damaged valve actuator Replace valve actuator
Pressure creeps above setting Metal chip or contamination
between ball and seat
Damaged diaphragm Replace diaphragm
Damaged o-ring or improper seal Replace the o-ring under the seat
Damaged or clogged air regulator or
line
Leaking or dirty seat Replace cartridge, or clean seat
Large change in inlet pressure Stabilize regulator inlet pressure
Pressure drops below setting Empty/clogged supply line Fill/flush supply line
Damaged or clogged air regulator or
line
Using valve beyond its rated flow
capacity
Large change in inlet air or fluid
pressure
Fluid leaks from spring housing Loose fluid housing Tighten the four cap screws
Damaged diaphragm Replace diaphragm
Chatter
Excessive pressure differential be
tween pump and valve
Excessive flow rate
Replace cartridge, or clean seat
area
Clear obstruction in line. Service
regulator if necessary
Clear obstruction in line. Service
regulator if necessary
Install valve for each spray valve or
dispensing valve
Stabilize air and fluid regulator inlet
pressures
Reduce pump pressure to not more
than 2000 psi (14 MPa, 138 bar)
greater than required valve pressure.
Reduce fluid flow through regulator.
Connect only one spray gun or dispense valve to each fluid regulator
3A2098S 67
Page 68

Troubleshooting
Dispense Valves
Problem Cause Solution
Valve not opening Air not getting to the open port Verify air pressure to solenoid
No “Valve On” signal from automation unit
Valve not shutting off Air not getting to the close port
(except AutoPlus valve)
“Valve On” signal from automation
unit is on
Sluggish open/close Air pressure low Verify air pressure is above 60 psi
Needle/seat worn Rebuild valve; replace needle/seat
Pressurized material past the valve
shut-off is escaping
Faulty solenoid valve Replace solenoid valve
Solenoid valve muffler restricted Clean or replace muffler
Material leaks from back of valve Shaft seal is worn Rebuild valve; replace seals
Air leaks from dispense valve Loose air connections Check air connections; tighten if
Worn piston o-ring Rebuild valve; replace piston o-ring
Check input from automation unit
Verify air pressure to solenoid
Verify solenoid operation
Verify air line routing and connections
Check input from automation unit
(410 kPa, 4.1 bar)
Reduce running pressure
Reduce nozzle length
Increase nozzle orifice size
necessary
Swirl Dispenser
Problem Cause Solution
Motor not running (motor fault alarm
active)
Motor not running (motor fault alarm
not active)
Cable disconnected Verify cable connections to swirl
board, swirl motor cable, and swirl
orbiter
CAN cable was re-connected with
system power on (amber LED on
swirl board will be on, this indicates
circuit protection was triggered)
Shorted motor cable (amber LED on
swirl board will be on, this indicates
circuit protection was triggered)
Faulty swirl orbiter Replace swirl orbiter
Cable disconnected
No “Swirl Enable” signal from automation unit
Swirl not installed
Cycle system power
Replace swirl motor cable (55 ft)
then cycle power
Verify cable connections to swirl
board, swirl board power cable, and
swirl control DGM
Check input from automation unit
Verify that the proper swirl orbiter is
installed in the system setup screen
68 3A2098S
Page 69

Troubleshooting
Motor not responding to change in
speed command
No “Swirl Speed Command” signal
from automation unit
Swirl speed source incorrectly set Verify Speed Command Source in
Check input from automation unit
Swirl Setup screen
Gateway Module
Problem Cause Solution
No communication Incorrect wiring Check wiring per fieldbus standard. Refer to PCF Gateway
LED status indicators and Appendix C - Communications
Gateway Module (CGM) Connection Details, page 128.
Incorrect fieldbus settings Confirm fieldbus settings at automation controller (fieldbus
master) and PCF Gateway (fieldbus slave). Refer to Appen-
dix A - Advanced Display Module (ADM), page 104, for
information on PCF Gateway configuration settings.
Incorrect data
Incorrect fieldbus configuration file installed on
automation controller
(fieldbus master)
Incorrect map installed on
PCF Gateway
Download PCF fieldbus configuration file from
www.graco.com, and install on automation controller (fieldbus
master).
Confirm correct PCF data map is installed on PCF Gateway.
Refer to Appendix A - Advanced Display Module (ADM),
page 104, for information on how to determine installed data
map. If necessary, install a new Gateway data map. Refer to
Upgrade Gateway Module Fieldbus Map (16N601 or
17P799), page 82, for instructions, and Control Center and
Expansion Swirl Enclosure Parts, page 96, for map token
part number.
LED Diagnostic Information
The following LED signals, diagnosis, and solutions apply to the Advanced Display Module, Fluid Control Module,
and Gateway module.
Module Status LED Signal Diagnosis Solution
Green on System is powered up -
Yellow Internal communication in progress -
Red solid Hardware failure Replace module
Red flashing fast Uploading software -
Red flashing slow Token error Remove token and upload software
token again.
Red flashes three times, pauses,
then repeats
Invalid rotary switch position (FCM
and DGM only)
Change rotary switch position to a
valid position then restart the system.
See page 18.
3A2098S 69
Page 70

Errors
Error
Errors
View Errors
When an error occurs, an error pop-up is displayed that
takes up the entire screen until the error is
acknowledged by pressing . Errors can also be
acknowledged over the gateway. Active errors are
displayed in the menu bar.
F
IG. 43: Error Pop-Up
The previous 200 errors are displayed on the error
report screens. See Run Mode, page 116, for
instructions on navigating to and through the error report
screens.
Diagnose Errors
See Event and Error Codes and Troubleshooting on
page 71 for error codes, possible causes, and solutions.
There are three levels of errors: alarms, deviations, and
advisories. Alarms cause the system to shut down.
Deviations and advisories do not shut down the system.
NOTE:
• Alarms set the dispenser (fluid plate) ready signal
LOW.
• Advisories and deviations do not set the dispenser
(fluid plate) ready signal LOW.
Errors can be viewed through a CGM on models that do
not have an ADM. See Appendix C, page 128, Output
bits 0x0DB. The Error codes are described by a 4 digit
ASCII string. For example: the first event code in the
manual is EC0X and is represented using an ASCII
table:
E = 0x45
C = 0x43
0 = 0x00
X = 0x58
70 3A2098S
Page 71

Errors
Event and Error Codes and Troubleshooting
Error codes are stored in the events log and are displayed on the error report screens. Gateway error numbers are
reported over the Gateway interface.
Error codes shown as XYZ_ represent error codes XYZ1, XYZ2, XYZ3, XYZ4, where the last digit represents the
number of the fluid plate to which the error applies. Error codes in the following table are sorted by gateway error
number, then by event code.
NOTE: The following error list is available in the PCF
Integration package at www.graco.com.
System Events and Errors
Event
Code
--- 0 No Active Errors No errors --- --- No action necessary
EC0X --- Setup Values
EL0X --- Power Up Control box power up Record only --- No action necessary
EM0X --- Power Down Control box power
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
Changed
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
System Events and Errors
Setup change notification
down
Record only A setup value was
changed on the display
Record only --- ---
No action necessary if
changes were desired
Control Center Events and Errors
Event
Code
EVUX --- USB Disabled USB download
MMUX --- USB Log 90%
V1G0 --- DGM Unpowered The Discrete Gateway
WSG0 --- Gateway Setup
EAUX --- Download to
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
Full
Error
USB in Process
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Control Center Events and Errors
attempted, however,
USB activity is disabled.
One or more USB log is
90% full.
Module does not have
logic power supplied to
it.
System settings are
incompatible with Discrete Gateway Module.
Information is currently
being downloaded to
USB
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Advisory Data in the jobs or
Advisory 24 Vdc has not been
Advisory Fluid plate 1 is not
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Transfers are disabled in Advanced
Setup screen 2.
events log has not
been downloaded
recently and logs are
nearly full.
connected to the
power pins.
installed. Or Fluid
plate 3 or fluid plate 4
is installed.
Swirl 1 is not installed.
Or Swirl 3 or Swirl 4 is
installed.
--- No action necessary
Clears when drive is
removed.
Download the data or
disable USB errors.
Connect power according to Appendix B -
Discrete Gateway
Module (DGM) Connection Details on
page 121.
Install fluid plate 1,
uninstall fluid plates 3
and 4.
Install Swirl 1, uninstall
swirls 3 and 4.
3A2098S 71
Page 72

Errors
Event
Code
EBUX --- Download to
WSU0 --- USB configura-
WNC0 32 ADM Key Token
WNG0 --- Gateway Map
CBG0 --- Gateway Reset Gateway reset Advisory
WMG0 --- Gateway Error
CBD_ --- Fluid Plate Com-
CCG_ --- Fieldbus Com-
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
USB Complete
tion error
Error
Error
Detected
munication Error
munication Error
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Control Center Events and Errors
Download to the USB is
complete
USB configuration error Advisory USB configuration
Missing or invalid key
token
Missing or invalid map Advisory Missing or invalid
Gateway error
detected; includes any
error not covered by
another more specific
error
Fluid Plate Communication Error with ADM
Fieldbus Communication Error
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Alarm An ADM key token is
(self-clearing)
Alarm --- ---
Alarm The ADM lost commu-
Alarm The automation gate-
--- No action necessary
Reinstall system soft-
invalid or not present
required to run the
system
Gateway map
Gateway setting(s)
changed
nications with the
FCM.
way lost communication with the
automation controller.
ware on display
Verify the key token is
installed
Verify the key token
part number is correct
for the PCF ADM
Install PCF map in
Gateway
Wait for reset to complete before attempting automation control
Restore communication.
Restore communications.
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Event
Code
CAC_ --- CGM Communi-
CAD_ --- Fluid Plate Com-
B7C_ 30 Style Out of
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
cation Error
munication Error
Range
Communication lost
between CGM and
Fluid Plate
FCM lost communication with the ADM
Style is out of range Alarm Style requested by
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Advisory Fluid Plate and CGM
are no longer communicating
CGM is not functioning Replace the CGM if the
Alarm ADM is not communi-
cating
ADM is not functioning Replace FCM if red
ADM does not contain
appropriate key token
automation controller
exceeds number of
styles available on the
fluid plate
Reconnect or replace
CAN cable
red status LED is solid
Reconnect or replace
CAN cable
status LED is solid
Verify intended ADM
key token is properly
inserted
Use a style number
that is in range
Increase number of
styles in PCF; purchase accessory key
token
72 3A2098S
Page 73

Errors
Event
Code
B30_
B40_
B10_
B20_
B1C_
B2C_
B3C_
B4C_
WND_ 51 Fluid Plate Key
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
31 High Material Material dispensed
32 Low Material Material dispensed
33 Low Computed
Target
34 High Computed
Target
Token Error
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
during last dispense
cycle was above
amount requested plus
the allowed tolerance
during last dispense
cycle below amount
requested minus the
allowed tolerance
Requested volume/
mass differs from
entered process target
by more than entered
tolerance for style
requested
Requested volume/
mass differs from
entered process target
by more than entered
tolerance for style
requested
Missing or invalid key
token
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm FCM key token is
PCF regulator is not
regulating correctly
Incorrect style target
volume or tolerance
Partially plugged tip or
supply system
Insufficient flow to
PCF regulator inlet
PCF regulator is not
regulating correctly
Check regulator;
repair if necessary
Entered process target
incorrectly
Entered tolerance
incorrectly
Requested volume
incorrectly
Automation problem Verify automation is
Entered process target
incorrectly
Entered tolerance
incorrectly
Requested volume
incorrectly
Automation problem Verify automation is
required to run system
Check regulator and
repair if necessary
Enter correct values or
set tolerance to 0% to
disable error
Clean tip and/or supply
system
Increase flow rate to
regulator inlet
Incorrect style target
volume or tolerance
setting
Enter correct process
target
Enter correct tolerance
Check automation program
correct
Enter correct process
target
Enter correct tolerance
Check automation program
correct
Verify FCM key token
is installed
Verify FCM key token
is correct part number
P6D_ 52 Outlet Pressure
Transducer Error
P6F_ 53 Inlet Pressure
Transducer Error
F6D_ 54 Flow Meter Error Flow Meter error Alarm Problem detected with
3A2098S 73
Outlet pressure transducer error
Inlet pressure transducer error
Alarm Problem detected with
outlet pressure transducer
Advisory Problem detected with
inlet pressure transducer
flow meter
Verify outlet pressure
transducer is installed
and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Verify inlet pressure
transducer is installed
and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Verify flow meter is
installed and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Page 74

Errors
Event
Code
WED_ 55 V/P Error Voltage to Pressure
WJ1_ 56 Dispense Valve 1
WJ2_ 57 Dispense Valve 2
WJ3_ 58 Dispense Valve 3
WJ4_ 59 Dispense Valve 4
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
Error
Error
Error
Error
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Transducer error
Dispense valve 1 error Alarm Problem detected with
Dispense valve 2 error Alarm Problem detected with
Dispense valve 3 error Alarm Problem detected with
Dispense valve 4 error Alarm Problem detected with
Alarm Problem detected with
V/P
dispense valve 1
dispense valve 2
dispense valve 3
dispense valve 4
Verify outlet pressure
transducer is installed
and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Verify dispense valve 1
is installed and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Verify dispense valve 2
is installed and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Verify dispense valve 3
is installed and/or connected correctly
Replace if necessary
Verify dispense valve 4
is installed and/or connected correctly
WSD_ 60 Incompatible
Valve Settings
WSD5 60 Incompatible
Valve Settings
F7D_ 61 Closed Valve
Flow
V2D_ 62 Low Analog Command cable ana-
Incompatible settings
for multiple valve operation; attempted to dispense
Incompatible settings
for multiple valve operation; attempted to dispense
System reading flow
meter pulses with
valve(s) closed
log command dropped
below minimum value
of 1 V while dispensing
Replace if necessary
Alarm Attempted to dis-
pense simultaneously
from multiple valves
on the same fluid plate
with different pressure
settings
Alarm Attempted to dis-
pense simultaneously
from multiple valves
on the same fluid plate
with different pressure
settings
Alarm Dispense hose leak Check hose; replace if
Flow meter providing
false pulses
Dispense valve not
operating correctly
Deviation Bad or loose com-
mand cable connection
Entered command
mode incorrectly
Automation program
error
Check settings shown
on Fluid Plate x,
screen 2 (Mode Settings)
Verify automation programming
In the Discrete Gateway screens, change
the settings of the
simultaneously dispensing valves to the
same pressure
Verify automation programming
needed
Replace flow meter
sensor or calibrate
meter
Repair dispense valve
Check command cable
and connection
Enter correct command code
Verify correct automation program
74 3A2098S
Page 75

Errors
Event
Code
WFD_
WFG_
EJD_ 64 Job Cycle Time
WXD_ 65 Fluid Plate Error
P3F_
P4F_
P3D_
P4D_
P1F_
P2F_
P1C_
P2C_
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
63 Flow Meter
Required
Out
Detected
66 Maximum Inlet
Pressure
67 Maximum Outlet
Pressure
68 Minimum Inlet
Pressure
69 Low Pressure Measured outlet pres-
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Operating mode
requires flow meter.
Advisory is issued if
fluid plate settings
require a flow meter but
meter is not present.
Alarm is issued if dispense is attempted in
mode that requires a
flow meter but meter is
not present.
Job cycle time out Alarm Automation signals did
Fluid plate error
detected; includes any
error not covered by
another more specific
error
Inlet pressure to regulator is above upper limit
set for operation
Outlet pressure of regulator is above upper
limit set for operation
Inlet pressure to regulator is below lower limit
set for operation
sure less than desired
outlet pressure minus
tolerance
Alarm or
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Alarm Analog voltage applied
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user selectable)
Selected valve mode
settings require flow
meter
FCM key token missing or invalid
not properly end job
cycle
to pin 1 of the command cable exceeds
10 Vdc.
Failed FCM Replace FCM if neces-
Incorrect set limit Verify limit is set cor-
Material supply pressure is too high
Failed transducer Check transducer;
Incorrect set limit Verify limit is set cor-
Material supply pressure is too high
Failed transducer Check transducer;
Incorrect set limit Verify limit is set cor-
Material supply pressure is too low
Failed transducer Check transducer;
Incorrect limit set Verify limit is set cor-
No or insufficient
material flow
Dispense valve needle
is stuck closed
Dispense valve leaking
Regulator not operating correctly
Pump wink passed
through outlet
Failed transducer Check transducer;
Check valve mode settings
Purchase meter
enabled token for FCM
and install flow meter
Check for FCM key
token error
Check automation programming per job
operating instruction
Limit signal on pin 1 of
command cable to the
range of 0-10 Vdc.
sary
rectly
Decrease material supply pressure
replace if necessary
rectly
Decrease material supply pressure
replace if necessary
rectly
Increase crease material supply pressure
replace if necessary
rectly
Increase material flow
rate
Dislodge and inspect
needle
Repair dispense valve
Repair regulator
Increase pump pressure
replace if failed
3A2098S 75
Page 76

Errors
Event
Code
P3C_
P4C_
F1D_
F2D_
F3D_
F4D_
EKD_ 73 Shot Terminated
EHD_ 74 Purge Timer
EAC_ 75 Maintenance
EBC_ 76 Maintenance
MHD_ 77 Maintenance
MFD_ 78 Maintenance
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
70 High Pressure Measured outlet pres-
71 Low Flow Rate Measured flow rate less
72 High Flow Rate Measured flow rate
by Job Timer
Expired
Mode Entered
Mode Exited
Due - Regulator
Due - Flow Meter
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Alarm or
sure greater than
desired outlet pressure
plus tolerance
than desired flow rate
minus tolerance
greater than desired
flow rate plus tolerance
Shot dispense cycle
terminated by job timer
Purge timer expired Advisory PCF purge timer (style
Maintenance mode
entered
Maintenance mode
exited
Maintenance due for
regulator
Maintenance due for
flow meter
Deviation
(user select-
able)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user select-
able)
Alarm or
Deviation
(user select-
able)
Advisory Job end timer was
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
Incorrect limit set Verify limit is set cor-
rectly
Dispense hose/device
plugged
Failed transducer Check transducer;
Regulator is not closing completely when it
should
Fluid supply too low to
achieve desired flow
rate
Tip plugged Clean/replace tip
No air pressure to
solenoid valves
No flow meter signal Check cable and sen-
No material supply Replace drum or turn
Incorrect flow tolerance of flow error time
Operating below minimum regulator operating pressure
Regulator worn or not
operating correctly
Flow meter providing
false pulses
Incorrect flow error tolerance or flow error
time
used to stop shot dispense
0) has expired
Entered maintenance
dispense mode
Exited maintenance
dispense mode
limit setting
limit setting
Clean/replace
hose/device
replace if failed
Repair regulator
Increase fluid supply
pressure or check for
clogged filter
Turn on air to solenoid
valves
sor
on pumps
Enter correct tolerance or flow error time
Increase fluid pressure above regulator
minimum
Repair regulator
Replace flow meter
sensor
Enter correct tolerance or flow error time
No action required if
timed shot is desired
Automation control
requests purge
No action required
No action required
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
76 3A2098S
Page 77

Errors
Event
Code
MED_ 79 Maintenance
MCD_ 80 Maintenance
MD1_ 81 Maintenance
MD2_ 82 Maintenance
MD3_ 83 Maintenance
MD4_ 84 Maintenance
CCD_ 85 Duplicate Module Duplicate Fluid Control
EAD_
WFC_
CR1_
CR2_
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
Due - V/P
Due - Supply
Due - Valve 1
Due - Valve 2
Due - Valve 3
Due - Valve 4
86 Swirl Mainte-
nance Mode
Entered
87 Shot No-Flow
Timeout
88 Valve 1 Swirl
Communication
Error
89 Valve 2 Swirl
Communication
Error
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Maintenance due for
Voltage to Pressure
Transducer
Maintenance due for
supply system
Maintenance due for
valve 1
Maintenance due for
valve 2
Maintenance due for
valve 3
Maintenance due for
valve 4
Module Detected
Swirl maintenance
mode entered
No flow detected for
five seconds on valve
activated in shot mode
Fluid plate communication error with swirl
Fluid plate communication error with swirl
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
limit setting
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
limit setting
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
limit setting
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
limit setting
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
limit setting
Advisory Totalizer exceeded
limit setting
Alarm Two or more FCMs
have the same rotary
switch setting
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Alarm Dispense valve not
Alarm The fluid plate lost
Alarm The fluid plate lost
Swirl zone that is
associated with this
fluid plate entered
maintenance mode
operating properly
Fluid leak Check fluid connec-
communication with
the swirl zone associated with this valve
and fluid plate
communication with
the swirl zone associated with this valve
and fluid plate
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Verify that all FCMs
have proper rotary
switch settings. Reset
module after changing
rotary switch setting.
Refer to Fluid Plate
Assembly Overview
section, page 17
No action required
Check dispense valve
for correct operation
and/or clogging
tions
Restore communications.
Restore communications.
3A2098S 77
Page 78

Errors
Event
Code
CR3_ 90 Valve 3 Swirl
CR4_
WD1_
WD2_ 93 Valve 2 Swirl
WD3_ 94 Valve 3 Swirl
WD4_
MB1_ 96 Maintenance due
MB2_
MB3_
MB4_
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
Communication
Error
91 Valve 4 Swirl
Communication
Error
92 Valve 1 Swirl
Fault
Fault
Fault
95 Valve 4 Swirl
Fault
- V1 Orbiter
97 Maintenance due
- V2 Orbiter
98 Maintenance due
- V3 Orbiter
99 Maintenance due
- V4 Orbiter
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Fluid Plate Events and Errors
Fluid plate communication error with swirl
Fluid plate communication error with swirl
Swirl motor fault Alarm or
Swirl motor fault Alarm or
Swirl motor fault Alarm or
Swirl motor fault Alarm or
Maintenance due on
valve 1 swirl orbiter
Maintenance due on
valve 2 swirl orbiter
Maintenance due on
valve 3 swirl orbiter
Maintenance due on
valve 4 swirl orbiter
Alarm The fluid plate lost
communication with
the swirl zone associated with this valve
and fluid plate
Alarm The fluid plate lost
communication with
the swirl zone associated with this valve
and fluid plate
The swirl zone associDeviation
(user-selectable)
Deviation
(user-selectable)
Deviation
(user-selectable)
Deviation
(user-selectable)
Advisory The active time total-
Advisory The active time total-
Advisory The active time total-
Advisory The active time total-
ated with this valve
and fluid plate caused
a fault
The swirl zone associ-
ated with this valve
and fluid plate caused
a fault
The swirl zone associ-
ated with this valve
and fluid plate caused
a fault
The swirl zone associ-
ated with this valve
and fluid plate caused
a fault
izer for the swirl dis-
penser associated
with this valve and
fluid plate exceeded
limit setting
izer for the swirl dis-
penser associated
with this valve and
fluid plate exceeded
limit setting
izer for the swirl dis-
penser associated
with this valve and
fluid plate exceeded
limit setting
izer for the swirl dis-
penser associated
with this valve and
fluid plate exceeded
limit setting
Restore communications.
Restore communications.
Resolve swirl motor
fault (see error WBDX
for possible solutions)
Resolve swirl motor
fault (see error WBDX
for possible solutions)
Resolve swirl motor
fault (see error WBDX
for possible solutions)
Resolve swirl motor
fault (see error WBDX
for possible solutions)
Service Component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service Component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service Component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
Service Component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
78 3A2098S
Page 79

Swirl Events and Errors
Errors
Event
Code
CBR_
CDR_
EAD_
EBD_ --- Maintenance
MBD_ --- Maintenance
WBD_
Gateway
Error No. Event Name
--- Swirl Communication Error
--- Duplicate Module Duplicate Swirl Control
--- Maintenance
Mode Entered
Mode Exited
Due - Orbiter
--- Swirl Motor Fault Motor speed is outside
Event
Description Event Type Cause Solution
Swirl Events and Errors
Swirl communication
error with ADM
DGM Detected
Maintenance mode
entered
Maintenance mode
exited
Maintenance due on
swirl orbiter
the +/- 50% tolerance
range for at least 5 seconds while operating
Alarm The ADM lost commu-
nication with the Swirl
Control DGM
Alarm Two or more Swirl
Control DGMs have
the same rotary switch
setting
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Advisory
(self-clearing)
Advisory Swirl active time total-
Alarm Cable disconnected Verify cable connec-
Swirl maintenance
mode entered
Swirl maintenance
mode exited
izer exceeded limit setting
Shorted motor cable
(amber LED on swirl
board will be on)
Orbiter bearing failure Replace bearing
Motor defective Replace swirl orbiter
Restore communications
Verify that all Swirl
Control DGMs have
proper rotary switch
settings. Reset module after changing
rotary switch setting.
Refer to Swirl Control
DGM section, page 22.
No action required
No action required
Service Component
If necessary, reset
totalizer
tions to swirl board,
swirl motor cable, and
swirl orbiter
Replace swirl motor
cable (55 ft)
3A2098S 79
Page 80

Maintenance
Maintenance
Prior to performing any maintenance procedures, follow
the Pressure Relief Procedure on page 61.
Maintenance Schedule
The following tables list the recommended maintenance procedures and frequencies to operate the equipment
safely. The maintenance is divided between mechanical and electrical tasks. Maintenance must be performed by
trained personnel per this schedule to assure safety and reliability of the equipment.
Mechanical
Operator Maintenance Person
Task Daily Weekly Monthly
Inspect system for leaks
Depressurize fluid, after opera-
tion
Remove heat from system,
after operation
Inspect filter (234967) bowls
and drain
Check hoses for wear
Check/tighten fluid connections
Check/tighten air connections
Lubricate dispense valves*
Rebuild regulator*
Rebuild dispense valve*
Replace air filter
Replace Solenoid
Replace Voltage to Pressure
(V/P) Transducer
* Check component manual for more detailed maintenance information.
3-6
months
or
125,000
cycles
18-24
months
or
500,000
cycles
36-48
months
or
1,000,000
cycles
7000
hours
Electrical
Task Weekly
Check cables for wear
Verify cable connections
Verify operation of “System Stop” button
* Check Component Manual for more detailed maintenance information.
80 3A2098S
Page 81

Maintenance
r_24E451_3B9900_3a
Access Panel
Token
BL
r_24E451_3B9900_4a
TI12319A
Access
Cover
TI12320A
CK
Token
Press Button
Advanced Display Module (ADM)
Upgrade Software (16K743)
NOTE: Back up the custom language file (if installed)
before upgrading software. See USB Data, page 63, for
more information.
1. Turn off power to the system.
2. Remove token access panel, and then remove the
key token (do not discard token).
Upgrade Gateway Module Software (16K743)
NOTE: The Gateway module connection to the system
is temporarily disabled during the use of upgrade
tokens. The following instructions apply to all Gateway
modules.
1. Turn off power to the system.
2. Remove the access cover.
IG. 44: Remove Access Panel
F
3. Insert and press software token firmly into slot.
NOTE: There is no preferred orientation of token.
IG. 45: Insert Token
F
4. Turn on power to the system. The red indicator light
(BL) will flash until new software is completely
loaded.
5. After the red indicator light shuts off, turn off power
to the system.
6. Remove software token.
7. Reinstall blue key token, and replace token access
panel.
FIG. 46: Remove Access Cover
3. Insert and press token firmly into slot.
NOTE: There is no preferred orientation of token.
4. Press and hold the button shown in F
second, then release. The red indicator light (CK)
will flash until new software is completely loaded.
IG. 47: Insert Token
F
5. After the red indicator light shuts off, turn off power
to the system.
6. Remove token.
IG. 47 for ~1
Cleaning
7. Replace access cover.
Use any alcohol-based household cleaner, such as
glass cleaner, to clean the display.
3A2098S 81
Page 82

Maintenance
Access
Cover
TI12319A
Token
TI12320A
Push Button
CK
Upgrade Gateway Module Fieldbus Map (16N601 or 17P799)
NOTE: The fieldbus connection is temporarily disabled
during the use of a map token. The following instructions
apply to all Gateway modules.
1. Perform Upgrade Gateway Module Software
(16K743). Software must be upgraded before
upgrading the fieldbus map.
2. Remove the access cover.
4. Press and hold the push button for three seconds
and then release. The red indicator light (CK) will
flash twice, pause, and then once after the data
map is uploaded.
FIG. 49: Insert Token
5. Remove map token (CC) when software has
successfully uploaded.
F
IG. 48: Remove Access Cover
3. Insert and press map token firmly into slot.
NOTE: There is no preferred orientation of the token.
6. Replace access cover.
82 3A2098S
Page 83

Maintenance
TI12334A
Access
Cover
CK
Token
TI12335A
Press Button
Upgrade Fluid Control Module (FCM) Software (16K743)
NOTE: The FCM connection is temporarily disabled
during the use of the upgrade token.
1. Turn off power to the system.
2. Remove access cover then remove key token (do
not discard token).
7. Reinstall blue key token, and replace access cover.
Air Filter Maintenance
To prevent filter element damage, replace air filter every
two years or when pressure drop becomes 100 kPa
(1.0 bar, 14.5 psi) or greater; which ever occurs first.
Replacement Air Filters for Dual Filter
Assembly (234967)
Part Description
123091 5 micron air filter
123092 0.3 micron air filter
Swirl Dispensers
See manual 309403 for maintenance schedule.
F
IG. 50: Remove Access Cover
3. Insert and press software token firmly into slot.
NOTE: There is no preferred orientation of token.
4. Press and hold the button shown in F
second, then release. The red indicator light (CK)
will flash until new software is completely loaded.
F
IG. 51: Insert Token
IG. 51 for ~1
5. After the red indicator light shuts off, turn off power
to the system.
6. Remove software token.
3A2098S 83
Page 84

Repair
129
108
101
124
125, 126, 127
109
131
103
r_pf0000_313377_18a
Repair
Fluid Plate Assembly
This section describes how to remove and replace components on the fluid plate assembly.
Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for
Repair
1. Disconnect the CAN cable from the fluid plate.
2. Perform Pressure Relief Procedure on page 61.
3. Remove the fluid plate assembly shroud. See Fluid
Plate Assembly Parts, page 98.
Repair Flow Meter
For complete flow meter (129) repair instructions refer to
the maintenance and repair section of manual 309834.
NOTE: The Coriolis flow meter is not field repairable.
Remove Flow Meter from Mounting Plate
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Disconnect the flow meter cable (131) from the flow
meter sensor. See F
3. Disconnect the material hose.
4. Disconnect the swivel fitting (109) from the
regulator.
5. Loosen the four screws (127) and washers (125,
126); remove the bracket (124) and flow meter
(129).
6. The flow meter weighs approximately 15 lbs. (6.75
kg). Carefully lift it off the mounting plate (101).
IG. 52.
FIG. 52: Fluid Plate Assembly
84 3A2098S
Page 85

Repair
r_pf0000_313377_34a
129
108
125
124
126
127
109
137
132
118
r_pf0000_313377_33a
122
121
118
r_pf0000_313377_31a
Install Flow Meter on Mounting Plate
NOTE: The Coriolis flow meter does not mount to the
fluid plate.
1. Rest the flow meter (129) and bracket (124) on the
fluid plate while threading the swivel fitting (109)
onto the regulator material inlet. See F
2. Tighten the swivel fitting to the regulator material
inlet.
3. Tighten the four screws (127) and washers (125,
126) to hold the bracket and flow meter in place.
IG. 52.
4. Remove the dispense valve solenoid (132) and
replace it with a new solenoid.
FIG. 54
5. Secure the new solenoid to the bracket with screws.
6. Reconnect the FCM cable and all three air tubes.
F
IG. 53
4. Check that the flow meter and regulator (108) are
still aligned.
5. Connect the material hose.
6. Connect the flow meter cable (131).
Replace Solenoid
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair,
page 84.
2. Disconnect FCM cable and all three air tubes.
Replace Voltage to Pressure (V/P)
Transducer
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Disconnect the FCM cable and both air tubes.
3. Remove both transducer screws (122) from
transducer bracket (118).
4. Remove the V/P transducer (121) and replace it
with a new V/P transducer.
3. Remove both screws (137) from transducer
bracket (118).
IG. 55
F
3A2098S 85
Page 86

Repair
128
121
118
132
r_pf0000_313377_30a
102
103
106
105
103
102
5. Secure the new V/P transducer to the bracket with
screws.
6. Reconnect the FCM cable and both air tubes.
Replace Fluid Control Module
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Remove the four screws (128) from the transducer
bracket (118), and remove the bracket. (Leave the
dispense valve solenoid (132) and V/P transducer
(121) attached to the transducer bracket.)
Replace Fluid Control Module Base
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Remove the FCM (103); follow Replace Fluid
Control Module. (Leave the cables attached to the
FCM.)
3. Remove the power supply cable from the base
(102).
4. Remove the four screws (105) and ground screw
(106) from the base and replace it with a new base.
F
IG. 56
3. Remove the following cables from FCM:
• dispense valve solenoid cable
• meter sensor cable
• both V/P cables
• I/O cable
• inlet pressure transducer cable (ambient
models only)
• outlet pressure transducer cable
4. Remove the two screws from FCM (103) and
replace with a new FCM.
5. Secure the new FCM to the base (102) with screws.
6. Reconnect the cables listed in step 3.
7. Reattach the transducer bracket using screws.
FIG. 57
5. Secure the base to the fluid plate (101) with screws.
6. Reconnect the power supply cable.
7. Reattach the FCM; follow Replace Fluid Control
Module.
86 3A2098S
Page 87

Replace Transducer O-Rings
117
108
r_pf0000_313377_16a
120
CH
CG
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Remove the fluid outlet pressure sensor (117) from
the regulator (108).
Repair
F
IG. 58
3. Press the transducer (CG) out of the retainer nut
(CH).
4. Remove the faulty o-ring (120) and replace with
new.
IG. 59
F
5. Press the transducer back into the retainer nut.
6. Reconnect the fluid outlet pressure sensor to the
regulator.
3A2098S 87
Page 88

Repair
diaphragm
and valve
actuator
subassembly
cartridge
assembly
Torque Sequence for Regulator
Base Housing Screws (CF)
4
2
3
1
CD
CE
CC
Cartridge Regulator 244734 Shown
CF
Repair Fluid Regulator
For complete cartridge fluid regulator repair refer to
instruction manual 308647. For complete mastic fluid
regulator repair refer to instruction manual 307517.
See F
IG. 60 and perform the following steps.
NOTICE
Carefully handle the hard carbide ball, valve actuator, and valve seat to avoid damaging them.
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair,
page 84.
2. Remove the cartridge assembly by loosening the
valve housing (CE) with a 6 mm hex wrench and
pulling the cartridge assembly out of the base
housing (CD).
NOTE: The retaining nut (CC) often loosens when
removing the cartridge assembly from the base housing.
Be sure to re-torque as described in step 4.
3. Inspect and clean the internal walls of the base
housing (CD).
NOTE: Be careful to not scrape or gouge the internal
walls of the base housing. They are a sealing surface.
4. Re-torque the retaining nut (CC) to 140-160 in-lb
(16-18 N•m).
NOTE: You must re-torque the retaining nut before you
install it in the base housing during step 5.
5. Install the new cartridge assembly in the base
housing (CD), and torque the valve housing (CE) to
30-35 ft-lb (41-48 N•m).
NOTE: The valve seat is double sided and may be
reversed for extended life. The o-ring and ball must be
replaced. See instruction manual 308647.
FIG. 60: Replace Cartridge Assembly
88 3A2098S
Page 89

Repair
117
116
Screw
Power Output Cable
Replace Amplifier
(Heated fluid plates only)
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Disconnect pressure sensor cable (117) and power
output cable.
F
IG. 61: Replace Amplifier
Adjust Display Settings
3. With the system in setup mode, navigate to the
Advanced screens.
4. Press to scroll to Advanced screen 2.
5. Press to access the fields to make changes.
6. Press to move the Pressure Units field. Press
to open the drop-down list, and select psi.
Press to enter the new units.
3. Loosen four screws on amplifier (116) cover, and
then remove cover.
4. Remove four screws (105) securing amplifier to
bracket.
5. Remove amplifier and replace with a new amplifier.
6. Secure new amplifier to bracket with four screws.
7. Replace amplifier cover and tighten screws.
8. Reconnect pressure sensor cable (117) and power
output cable.
Calibrate Amplifier
(Heated fluid plates only)
1. Prepare Fluid Plate Assembly for Repair, page
84.
2. Remove outlet pressure sensor from outlet fitting to
ensure there is no pressure applied to the sensor.
7. Press to exit edit mode.
8. With the system still in setup mode, navigate to
Fluid Plate x, screen 5 (Pressure Sensors).
9. Press to access the fields to make changes.
10. Press to move the Outlet Offset field. Set the
psi to 0. Press to enter the new setting.
3A2098S 89
11. Press to exit edit mode.
Page 90

Repair
Shunt Calibration Pressure = (Shunt Cal Factor /
Calibration Factor) * 5000 psi
Excitation Selector
Coarse Zero
Fine Zero
Fine Gain
Coarse Gain
Panel mounting holes.
Use #6 or #8 screws.
To Transducer
To Readout
Adjust Amplifier Settings
12. Remove cover from amplifier (116). See Replace
Amplifier, page 89.
13. Ensure the EXCITATION SELECTOR jumper is in
the middle position (5 Vdc). See F
IG. 62 on page 90.
14. Ensure the COARSE GAIN dipswitch 1 is set to ON.
All others should be set to OFF.
15. Adjust the FINE ZERO potentiometer until the outlet
pressure on the display reads 0.
16. Use a small piece of jumper wire or a paper clip to
connect the SHUNT CAL and ENABLE terminals.
EXCITATION MODULE
(+)SUPPLY
(-)OUTPUT
SUPPLY RETURN
(+)OUTPUT
SHUNT CAL
ENABLE
1
2
3
4
5
6
17. Use the data from the certificate of calibration for
the pressure sensor (included with PCF
documentation or the replacement pressure sensor)
to calculate the Shunt Calibration Pressure using
the following formula:
18. Adjust the FINE GAIN potentiometer until the Outlet
Pressure on Fluid Plate x, screen 5 (Pressure
Sensors) matches the calculated Shunt Calibration
Pressure.
19. Remove the jumper wire or paper clip from the
SHUNT CAL and ENABLE terminals.
20. Repeat steps 15 - 19 at least one additional time to
ensure proper calibration.
TRANSDUCERPOWER
A
B
C
D
E
F
(+)EXCITATION
(-)EXCITATION
(+)SIGNAL
(-)SIGNAL
SHUNT CAL
RESISTOR
EX SEL
10 VDC
5 VDC
3 VDC
FIG. 62: Amplifier Settings
21. Replace the amplifier cover. See Replace
Amplifier, page 89.
22. Reconnect the outlet pressure sensor cable if it was
removed.
23. If desired, change pressure units to desired setting
on Advanced screen 2.
ZERO
COARSE
SPAN
12345678
FINE
FINE
ON
COARSE
90 3A2098S
Page 91

Repair
5
3
1
16
19
3
12
5
4
6
Control Center Assembly
Prepare Control Center for Repair
1. Power off the display.
2. Disconnect main power to the control center
assembly.
3. Remove the control center assembly front cover
(20).
Replace Gateway Module
1. Prepare Control Center for Repair, page 91.
2. Remove the automation communications cable
(AE).
3. Remove the two screws holding the Gateway
module (5) to the base (3), and remove the module.
Replace Gateway Module Base
1. Prepare Control Center for Repair, page 91.
2. Remove the Gateway module (5); follow Replace
Gateway Module. (Leave automation
communications cable (AE) attached to Gateway
module.)
3. Disconnect the CAN cable (19) and power supply
cable (6) from the base (3).
4. Remove the four screws (16) and grounding
screw (12) from the base and replace it with a new
base.
FIG. 64
5. Secure the new base to rear cover (1) using the five
screws.
6. Reattach Gateway module; follow Replace Gate-
FIG. 63
4. Attach a new Gateway module to the base using
two screws.
5. Reconnect the automation interface cable.
6. Upgrade software, page 81, then upgrade fieldbus
map, page 82.
3A2098S 91
way Module.
Page 92

Repair
a
b
c
18
11, 14, 24
2
21
Replace Swirl Board 16K570:
1. Prepare Control Center for Repair, page 91.
2. Remove screw (a) from swirl board cover. Open
swirl board cover.
3. Remove cable connectors (b) from swirl board.
4. Remove the four screws (c) from the swirl board.
Replace with new board and secure using the four
screws (c).
5. Insert cable connectors (b) into the new board.
6. Reassemble the swirl board cover using screw (a).
Replace Advanced Display Module
1. Prepare Control Center for Repair, page 91.
2. Disconnect the CAN cable (18) from the ADM (2).
FIG. 66
3. Remove the ADM by snapping it out of the mounting
bracket.
4. On old ADM, remove token access panel then
remove key token. Do not discard token.
5. Connect the CAN cable to the new ADM.
F
IG. 65
6. Upgrade new ADM software, page 81.
7. Insert key token into new ADM. Replace token
access panel.
8. Install the new ADM by snapping it into the mounting bracket.
92 3A2098S
Page 93

Repair
2
26
20
21
25
22
28
7
Replace Advanced Display Module Bracket
1. Prepare Control Center for Repair, page 91.
2. Remove the ADM (2); follow Replace Advanced
Display Module. (Leave the CAN cable attached to
the ADM.)
3. Remove the speed clips (25) and rivets (26) from
the mounting bracket (21).
Replace DIN Rail Assembly
1. Prepare Control Center for Repair, page 91.
2. Remove both screws (22) and washers (28) from
the line voltage assembly cover (7). Remove the
cover.
FIG. 68
F
IG. 67
3. Disconnect all wiring from the din rail module and
filter.
4. Remove the mounting bracket from the front cover
(20) and replace with a new bracket.
4. Remove the four screws (40) from the din rail and
filter.
5. Secure the new bracket to the front cover with
speed clips and rivets.
5. Disconnect wires from rocker/rotary switch. Take
note of wire positions for easy connection in Step 7.
6. Reinstall the ADM.
3A2098S 93
Page 94

Repair
40
40
40
r_pf0000_313377_10a
1
Fuses
r_pf0000_313377_10a
6. Remove the din rail, filter, and rocker switch (snaps
into place). Replace with new components. Secure
din rail and filter to the rear control center assembly.
cover (1) using the four screws (40). Snap
rocker/rotary switch into position.
F
IG. 69: 24 Vdc Din Rail Assembly
7. Reconnect all wiring to the din rail module, filter, and
rocker/rotary switch.
8. Reassemble the line voltage assembly cover using
the screws and washers.
Replace Fuses
Replace fuses on the din rail assembly.
• For 24 Vdc control centers: see Technical Data
on page 148 for fuse specifications.
• For 100-240 Vac control centers: Order fuse
115805.
IG. 70: Fuse Location
F
94 3A2098S
Page 95

Parts
Control Centers
Software Upgrade Tokens
Refer to the Software Upgrade Tokens table on page
10.
Control Center Key Token Part Numbers
See Key Tokens on page 23 for more information about
key tokens.
Part Description
16M217 ADM Key Token, Standard PCF
Gateway Module Part Numbers
Parts
User
PCF
Model
PFxx0x Discrete 24B681
PFxx1x
PFxx2x Ether-
PFxx3x PROFI-
PFxx4x
Parts included with 24 Vdc Module kit 24B929.
* Fieldbus Gateway modules do not have a
PCF-specific map installed. Use map token (16N601) to
install map before use.
Interface
Description
DeviceNet
™
Net/IP
™
BUS
PROFINET
Gateway Part
™
™
Number To
Order
15V759
15V760
15V761
15V762
3A2098S 95
Page 96

Parts
50
13
15
22
40
28
7
9
44
24
1
3
16
12
4
5 or 43
20
26
241114
21
25
2
6,10
38
23,27
18
13
19
24 VDC units only: 15,36
100-240 VAC units only: 6,36
43
3,4,12,16
6;
Ground/
Green
6;
Neutral/
Blue
6;
Line/
Brown
37
1
Add ferrite (36) to cable. Locate
as close to cable connector as
possible.
Included in swirl models only
(both control centers and
expansion swirl enclosures).
Control centers only. Not included
in expansion swirl enclosures.
100-240 Vac models only.
1
13
14
15
26
49
22
28
45
25
22
25
47
22
48
44
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
13
50
13
13
13
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
14
15
Control Center and Expansion Swirl Enclosure Parts
96 3A2098S
Page 97

Control Center Assembly Parts
Parts
Qty
Ref. Part Description
1 --- COVER, rear 1
2 24E451 DISPLAY, with USB 1
3 289697 BASE, cube 1
4 277674 ENCLOSURE, cube door 1
5 --- MODULE, Gateway; see table on
page 95 for part number
6‡ --- SUPPLY, power 1
7‡ --- COVER, line voltage 1
8‡ --- GROMMET 1
9‡ 196548 LABEL, warning, electric shock 1
10‡ --- SCREW, cap, socket hd; m4 x 6 4
11 --- WASHER, lock 1
12 121820 SCREW, mach, pan hd; m4 x 35 1
13 121807 CONNECTOR, splitter 1
14 110755 WASHER, plain 1
15‡ --- MODULE, line voltage 1
16 195875 SCREW, mach, pan hd 4
18 121001 CABLE, CAN, female / female 1.0m 1
19 125789 CABLE, CAN, female / female 0.5m 1
20 --- COVER, front 1
21 --- BRACKET, mounting 1
22‡ --- SCREW, mach, pan hd 2
23 120143 GUIDE, strain relief 2
24 121253 KNOB, display 2
25 --- CLIP, speed, tubular 2
26 --- RIVET, aluminum 1
27 112925 SCREW, cap 2
28 100020 WASHER, lock 2
36 121901 SUPPRESSOR, box snap, ferrite 2
37 124654 CONNECTOR, splitter 1
Ref. Part Description
.
38 --- LABEL 1
40 110637 SCREW, mach, pan hd 4
43 24B681 MODULE, DGM 1
44 --- GUARD, edging 1
45 16K570 BOARD, circuit, swirl 1
1
46 --- BRACKET, display pivot 1
47 --- COVER, swirl, hinge side 1
48 --- COVER, swirl, latch side 1
49 --- COVER, swirl, lid 1
50 24K455 CABLE, swirl board, panel mount 1
51 24K458 CABLE, SWIRL-DGM 1
52 121597 CABLE, CAN, 90 female/90 female 1
Replacement Danger and Warning labels, tags, and
cards are available at no cost.
‡ Parts included with 100-240 Vac Module kit 24B928.
Parts included with 24 Vdc Module kit 24B929.
Parts included with Display Mounting Bracket kit
24B930.
Base electronic components do not have
PCF-specific software installed. Use software
upgrade token (16K743) to install software before
use.
* Fieldbus Gateway modules do not have a
PCF-specific map installed. Use map token
(16N601) to install map before use.
--- Not for sale.
Qty
.
3A2098S 97
Page 98

Parts
S
101
143
142
152
131
153
151
135, 136
199
117, 120
Fluid Plate Assembly Parts
98 3A2098S
Page 99

Fluid Plate Assembly Parts (continued)
105
103
106
105
102
104
141
141
118
122
141
122
141
128
133
128
137
141
132
128
121
137
125
126
129
124
127
126
125
109
110
126
130
155
127
128
Parts
3A2098S 99
Page 100

Parts
111
141
113
112
113
112
127
127
114
108
115
117
108
105, 116
Fluid Plate 24B962
149
140, 141, 150
158
139
107
148
145
Shown
159
160
199
ti19262a
119
Fluid Plate Assembly Parts (continued)
100 3A2098S
 Loading...
Loading...