Page 1

Instructions - Parts
™
PGM
Precision Gear Metering
For metering and dispensing ambient or high-temperature, high-viscosity
single-component materials. For professional use only.
Not approved for use in European explosive atmosphere locations.
2500 psi (17.2 MPa, 172 bar) Maximum Working Outlet Pressure
1500 psi (10.3 MPa, 103 bar) Maximum Working Inlet Pressure
See Technical Specifications on page 102 for temperature ranges
3A5185B
EN
See page 4 for model information.
Important Safety Instructions
Read all warnings and instructions in this
manual. Save these instructions.
Page 2

Contents
Related Manuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Bulk Melt (Therm-O-Flow 20 + Therm-O-Flow 200)
and Ambient Hoses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Remote Dispense Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Fixed Dispense Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
System Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Component Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
System Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Typical Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Before Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Install Control Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Install Gear Meter Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Install Cable Assemblies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
System Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Configure Control Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Configure Mode Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Configure Delay Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Adjust Pressure Sensors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Configure Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Load Material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Maintenance Mode Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Dispense from Maintenance Screen . . . . . . . . . 25
Automation Control (Normal) Operation . . . . . . 25
Typical Automation Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Pressure Relief Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Dispense Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
View Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Diagnose Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Clear Errors and Reset Control Unit . . . . . . . . . 31
Error Codes and Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Maintenance Schedule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Gear Meter Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
PGM-6 Pump Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
PGM-20 Pump Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Gear Pump Maintenance Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Installing new heater units and RTD sensors . . 48
Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
PGM-20 Mounting Frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
PGM-20 Lower Assembly Block . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
PGM-20 Pump Heat Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
PGM Drive - 20 cc Pump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
EnDure Dispense Valve Fix Mounted . . . . . . . . 53
Gear Meter Assembly Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
PGM Back Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Remote Mount Amplifiers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
PGM Remote Dispense Valve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
PGM Ambient Transducer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
PGM-6 Mounting Frame . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
PGM-6 Drive Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
PGM-6 Lower Assembly Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
PGM-6 Pump Heat Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Schematics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Accessory Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Automation Interface Cable Assembly . . . . . . . 74
Dynamic Regulators (98****) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
EnDure Valve Nozzles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Heater Nests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Appendix A - User Interface Display . . . . . . . . . . 82
Screen Navigation Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Main Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Calibrate Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Home Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Maintenance Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Robot I/O Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Setup #1 Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Setup #2 Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Setup #3 Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Setup #4 Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Setup #5 Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Setup #6 Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Supply Pump Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Pressure Trend Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Torque Trend Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Alarm Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
2 3A5185B
Page 3

Appendix B - I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Using the PGM I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Appendix C - Theory of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Theory of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Graco Standard Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Graco Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Related Manuals
Part Description
309376
310538
334130 Therm-O-Flow 200 (P/N UH****)
311208 Therm-O-Flow 200 (P/N 98****)
313296 Warm Melt Supply Systems
309213 Therm-O-Flow Accessory Heat Zone
EnDure
Instructions-Parts List
Therm-O-Flow
Valves Instructions-Parts List
Instructions-Parts
Instructions
Instructions-Parts
Controls Instructions-Parts List
®
Automatic Dispense Valves
®
Automatic Dispense
313526 Ambient Supply Systems Operation
3A5185B 3
Page 4
Models
Models
NOTE: This manual covers a series change to the PGM system. For systems built prior to 2016, refer to manual
3A0260.
Check the identification (ID) plate for the 6-digit part number of the fluid metering system. Use the following matrix to
define the construction of the system, based on the six digits. For example, Part PG0111 represents a PGM fluid
metering system (PG), with a 6cc system (0), unheated (1), with controls/3m (1), and an EnDure snuff-back (1).
NOTE: To order replacement parts, see Parts section in this manual. The digits in the matrix do not correspond to the Ref. Nos. in the Parts drawings and lists.
PG 0
First and
Second Digits
Third Digit
Size
1
Fourth Digit
Heat
1
Fifth Digit
Controls *
2
Sixth Digit
Valve
Description Description Description Description
PG
(Precision
Gear Meter)
0
2 20cc 2 Heated 1 Controls / 3m 6 Remote mount
6cc 1 Unheated 0 No controls 1 EnDure
snuff-back
2 Controls / 6m
3 Controls / 9m
4 Controls / 15m
* PGM Control Center does not include heat controls. Heat loads are configured to be controlled by Therm-O-Flow
Controllers.
Bulk Melt (Therm-O-Flow 20 + Therm-O-Flow 200) and Ambient
Hoses
Hose Diameter
- 8
3/4 in. - 16 JIC
6 ft None 19M404
10 ft 19M402
15 ft Non None None None 109165/
Hose Length
PGM Inlet
(-16 SAE)
PGM Outlet
(3/4 in. npt)
Valve Inlet 124287 C20768 107052 124288 158256 † 190451 †
17J652
None None 124238
124286 C20595 15M863 107127 124290 † 124289 †
- 10
7/8 in. - 14 JIC
17J654
19M405
17J655
- 12
1-1/16 in. - 12
JIC
None 19M416
19M412
17J662
Fittings
124235 (90°)
1-5/16 in. - 12 JIC
- 16
17J666
19M417
17J667
124239
124243 †
124236 (90°)
Non-Heated Hoses
3/8 in. 1/2 in.
109163 626720
None 215441
685602*
None None
(1/2 in. x 5 ft)
511381*
* Indicates PTFE hose, all others Buna-N.
† Indicates swivel.
Therm-O-Flow part number 98xxxx models.
4 3A5185B
Page 5
Models
Remote Dispense Valves
Part Description
243694 Heated Dispense Valve
244951 EnDure Valve, Heated,
1/2 in. npt male outlet
244909 EnDure Valve, Heated
Fixed Dispense Valves
Part Description
244907 EnDure Valve snuff-back
Accessories
Part Description
24D824 Automation I/O Cable
24E654 Ribbon Nozzle Kit, 10 x 1.5 mm
24E655 Bead Nozzle Kit, 3 mm dia.
25A055 Dynamic Air Regulator for
Therm-O-Flow (P/N UH****)
24E575 Dynamic Air Regulator for
Therm-O-Flow (P/N 98****)
24E607 Gear Pump Seals, 6 cc
24E619 Gear Pump Seals, 20 cc
24E677 O-ring Kit, 6 cc
24E626 O-ring Kit, 20 cc
24E678 Heated Nest, Pilot
24E679 Heated Nest, Ribbon or Bead
16E242 Nozzle Heater Insert
16E256 Ported Nozzle Heater Insert
Part Description
124267 Seal Housing, 6 cc
24E826 Gear Shaft Repair Kit, 6 cc
24E827 Seal Shaft Repair Kit, 6 cc
124266 Pump Seal Housing, 20 cc
24E824 Gear Shaft Repair Kit, 20 cc
24E825 Seal Shaft Repair Kit, 20 cc
124235 Elbow Fitting, 90 degree, 3/4 in.
tube x 16 SAE
124236 Elbow Fitting, 90 degree, 1 in. tube
x 16 SAE
124237 Elbow Fitting, 90 degree, 16 SAE x
20 JIC
124238 Adapter Fitting, 3/4 in. Tube x
16 SAE
124239 Adapter Fitting, 1 in. Tube x
16 SAE
124240 Adapter Fitting, 1-1/4 in. Tube x
16 SAE
124241 Adapter Fitting, 16 SAE x
1in.NPTF
124242 Swivel, 16 SAE x 1 in. NPTF
124243 Swivel, 16 SAE x 1 in. tube
124244 Swivel, 1/2 NPTM x 10 JIC
124245 Swivel, 1/2 NPTM x 1/2 NPTF
124286 Adapter Fitting, 3/4 NPTM x 8 JICM
124287 Adapter Fitting, 1/2 NPTM x 8 JICM
124288 Adapter Fitting, 1/2 NPTM x 16
JICM
124289 Swivel Fitting, 3/4 NPTM x 1/2 NPS
124290 Swivel Fitting, 3/4 NPTM x 3/8 NPS
3A5185B 5
Page 6
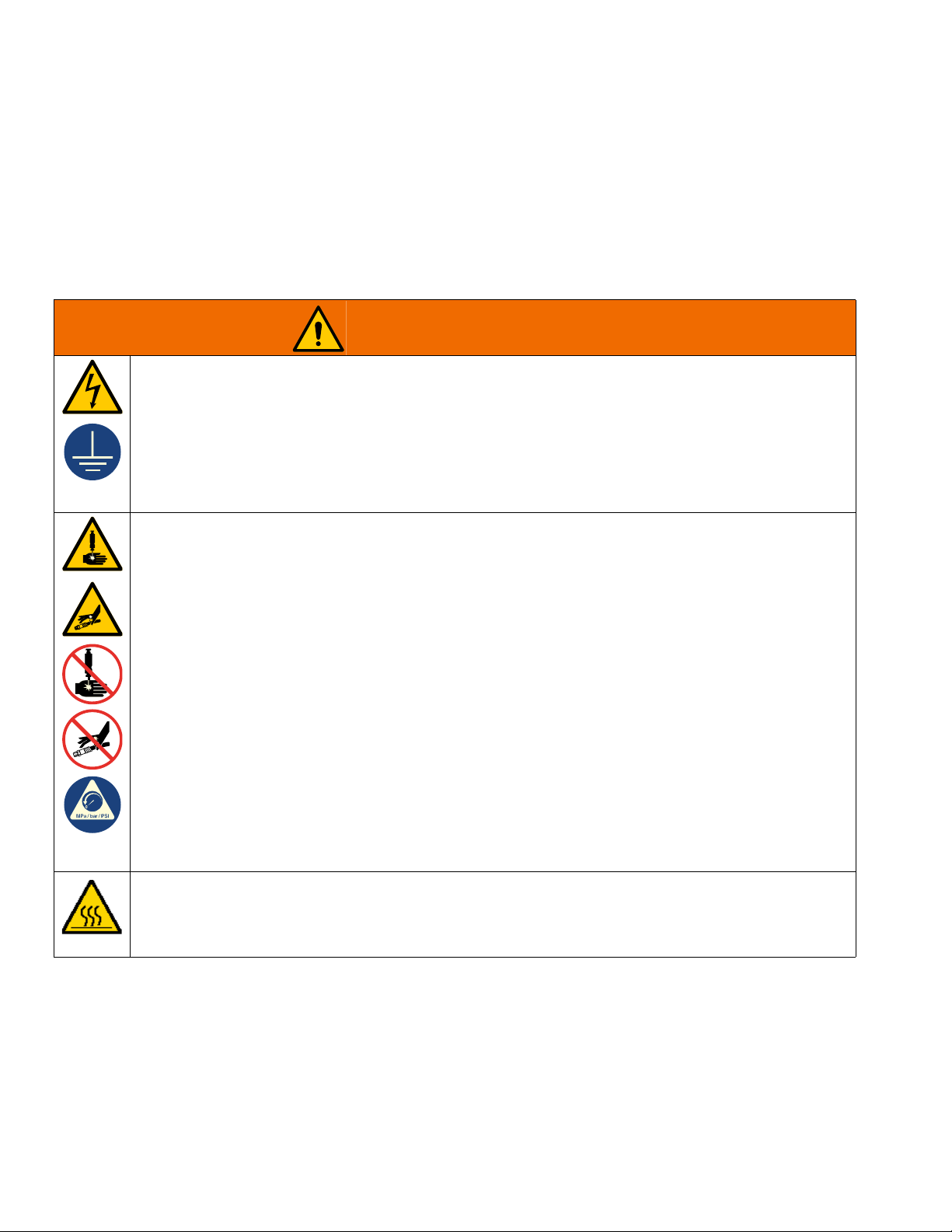
Warnings
WARNING
Warnings
The following warnings are for the setup, use, grounding, maintenance, and repair of this equipment. The exclamation point symbol alerts you to a general warning and the hazard symbols refer to procedure-specific risks. When
these symbols appear in the body of this manual or on warning labels, refer back to these Warnings. Product-specific
hazard symbols and warnings not covered in this section may appear throughout the body of this manual where
applicable.
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
This equipment must be grounded. Improper grounding, setup, or usage of the system can cause electric
shock.
• Turn off and disconnect power at main switch before disconnecting any cables and before servicing or
installing equipment.
• Connect only to grounded power source.
• All electrical wiring must be done by a qualified electrician and comply with all local codes and regulations.
SKIN INJECTION HAZARD
High-pressure fluid from dispensing device, hose leaks, or ruptured components will pierce skin. This
may look like just a cut, but it is a serious injury that can result in amputation. Get immediate surgical
treatment.
• Engage trigger lock when not dispensing.
• Do not point dispensing device at anyone or at any part of the body.
• Do not put your hand over the fluid outlet.
• Do not stop or deflect leaks with your hand, body, glove, or rag.
• Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when you stop dispensing and before cleaning, checking, or
servicing equipment.
• Tighten all fluid connections before operating the equipment.
• Check hoses and couplings daily. Replace worn or damaged parts immediately.
BURN HAZARD
Equipment surfaces and fluid that is heated can become very hot during operation. To avoid severe
burns:
• Do not touch hot fluid or equipment.
6 3A5185B
Page 7

Warnings
WARNING
FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
Flammable fumes, such as solvent and paint fumes, in work area can ignite or explode. Paint or solvent
flowing through the equipment can cause static sparking. To help prevent fire and explosion:
• Use equipment only in well-ventilated area.
• Eliminate all ignition sources; such as pilot lights, cigarettes, portable electric lamps, and plastic drop
cloths (potential static sparking).
• Ground all equipment in the work area. See Grounding instructions.
• Never spray or flush solvent at high pressure.
• Keep work area free of debris, including solvent, rags and gasoline.
• Do not plug or unplug power cords, or turn power or light switches on or off when flammable fumes are
present.
• Use only grounded hoses.
• Hold gun firmly to side of grounded pail when triggering into pail. Do not use pail liners unless they are
anti-static or conductive.
• Stop operation immediately if static sparking occurs or you feel a shock. Do not use equipment until
you identify and correct the problem.
• Keep a working fire extinguisher in the work area.
EQUIPMENT MISUSE HAZARD
Misuse can cause death or serious injury.
• Do not operate the unit when fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
• Do not exceed the maximum working pressure or temperature rating of the lowest rated system component. See Technical Specifications in all equipment manuals.
• Use fluids and solvents that are compatible with equipment wetted parts. See Technical Specifications
in all equipment manuals. Read fluid and solvent manufacturer’s warnings. For complete information
about your material, request Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) from distributor or retailer.
• Do not leave the work area while equipment is energized or under pressure.
• Turn off all equipment and follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when equipment is not in use.
• Check equipment daily. Repair or replace worn or damaged parts immediately with genuine manufacturer’s replacement parts only.
• Do not alter or modify equipment. Alterations or modifications may void agency approvals and create
safety hazards.
• Make sure all equipment is rated and approved for the environment in which you are using it.
• Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Call your distributor for information.
• Route hoses and cables away from traffic areas, sharp edges, moving parts, and hot surfaces.
• Do not kink or over bend hoses or use hoses to pull equipment.
• Keep children and animals away from work area.
• Comply with all applicable safety regulations.
TOXIC FLUID OR FUMES HAZARD
Toxic fluids or fumes can cause serious injury or death if splashed in the eyes or on skin, inhaled, or
swallowed.
• Read Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) to know the specific hazards of the fluids you are using.
• Store hazardous fluid in approved containers, and dispose of it according to applicable guidelines.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
Wear appropriate protective equipment when in the work area to help prevent serious injury, including
eye injury, hearing loss, inhalation of toxic fumes, and burns. Protective equipment includes but is not
limited to:
• Protective eyewear, and hearing protection.
• Respirators, protective clothing, and gloves as recommended by the fluid and solvent manufacturer.
3A5185B 7
Page 8
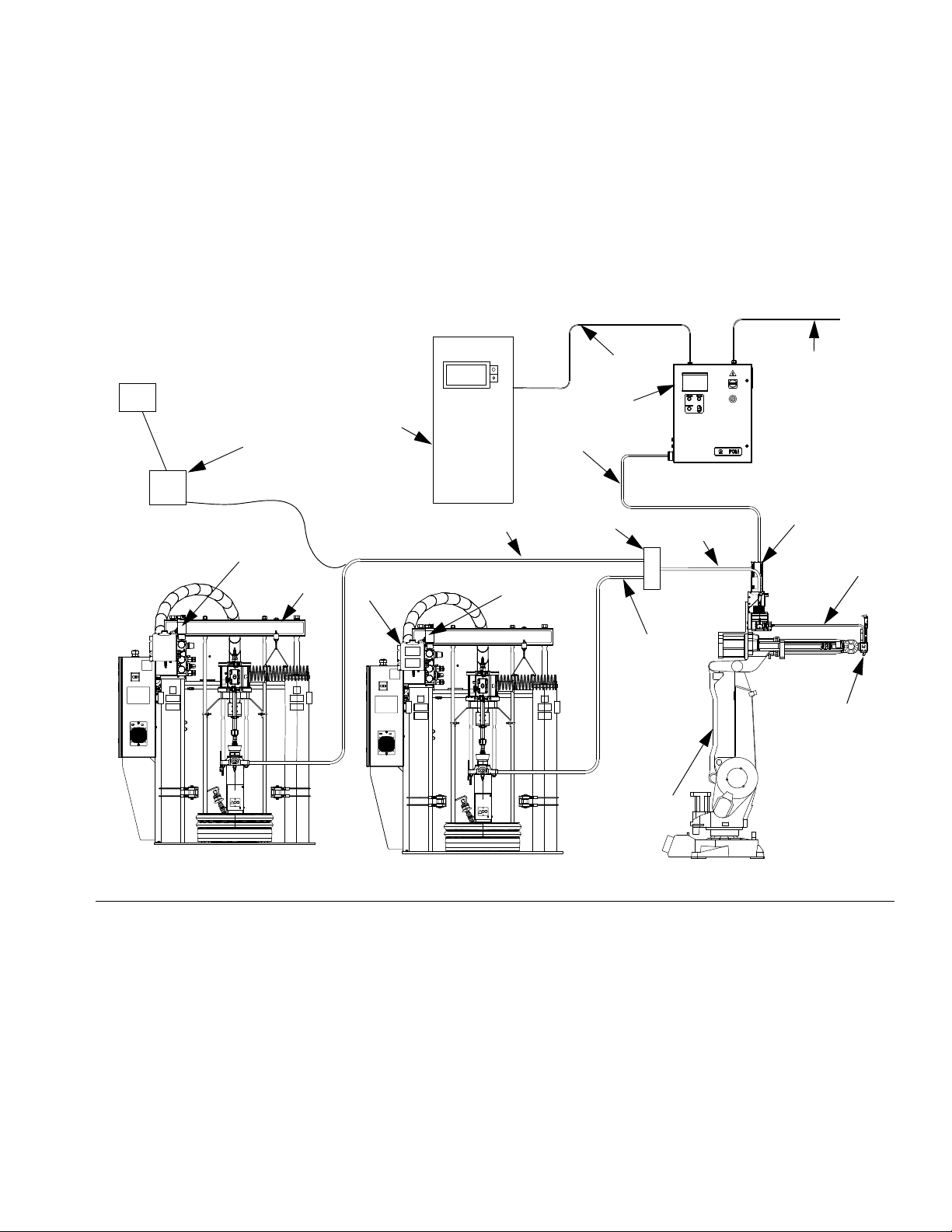
Overview
AD
AC
AH
AB*
AF*
AA*
AE
AK
AM
AG
Air Supply
Drop Site
AN
Power
AL
AJ
AH
AH
AO
AO
Overview
System Configurations
Typical Heated System Installation
F
IG. 1: Typical Heated System Installation
Key:
AA *Control Center (User Interface)
AB *Gear Meter Assembly
AC Applicator/Dispense Valve†
AD Automation Robot
AE Automation Interface Cable †
AF *Gear Meter Cables
AG Heated Fluid Supply System
AH Fluid Supply Hose
AJ Heat Control
AK Automation Controller
AL Air Filter Assembly
AM Remote Dispense Hose †
AN Heated Manifold
AO Dynamic Regulator †
*Included
† Accessory
8 3A5185B
Page 9

Typical Ambient System Installation
G
D
C*
F*
A*
E
H
J
Air Supply
Drop Site
K
Power
B*
Overview
F
IG. 2: Typical Ambient System Installation
Key:
A *Control Center (User Interface)
B *Gear Meter Assembly
C *Applicator/Dispense Valve
D Automation Robot
E Automation Interface Cable†
F *Gear Meter Cables
G Fluid Supply System
H Fluid Supply Hose
J Automation Controller
K Air Filter Assembly
* Included
† Accessory
3A5185B 9
Page 10

Overview
Key:
1 Gear Meter
2 System Controls Box
3 User-Interface Touch Display
4 External Control Interface
Connections
5 Power Input
6 Main Power Switch
7 Emergency Stop
8 Pump Fault Indicator Light
9 Control Power On/Off buttons
10 Pump Ready Light
11 Manual Purge Button
12 Dispense Valve
1
2
3
4
5
12
6
7
8
9
10
11
Component Identification
FIG. 3
10 3A5185B
Page 11
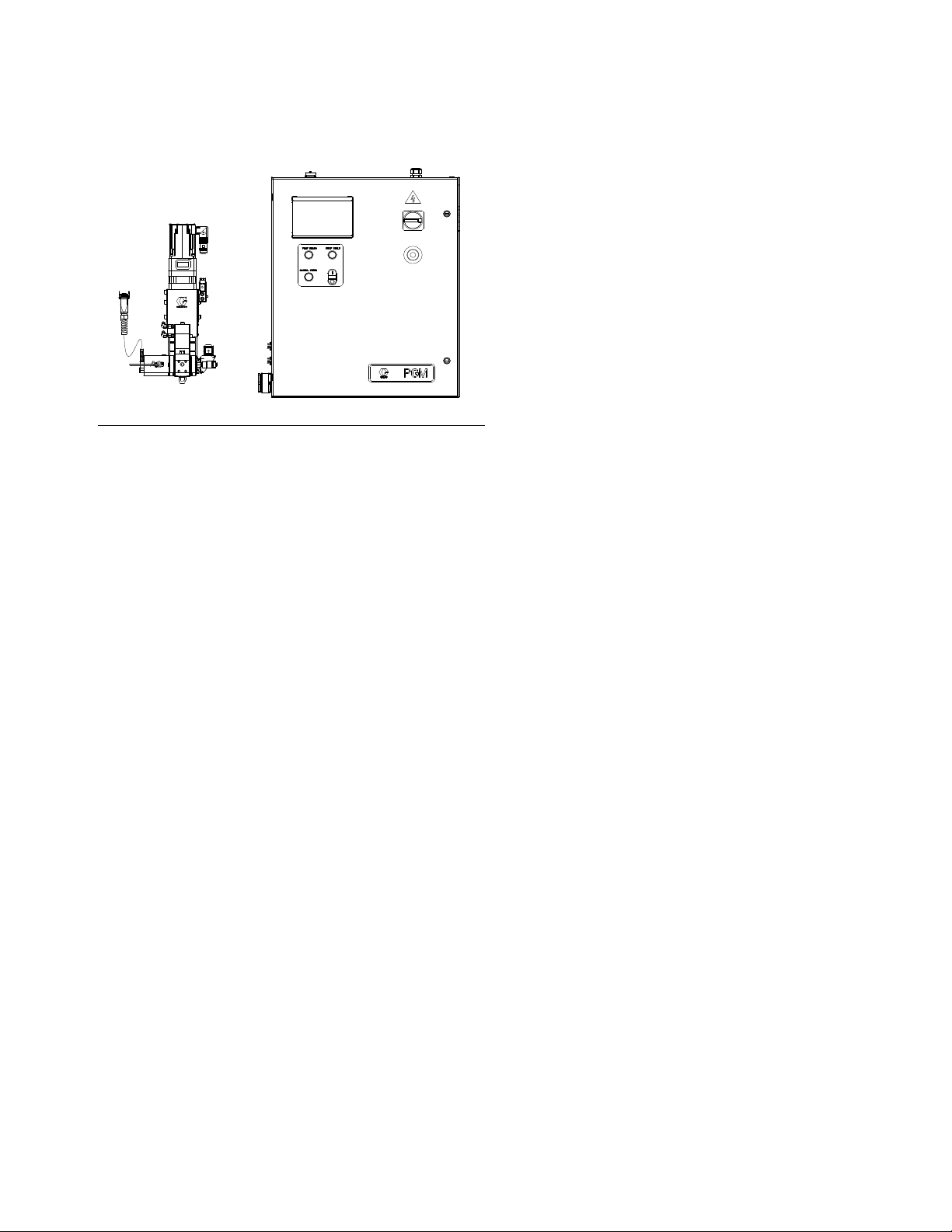
Overview
System Overview
F
IG. 4: Control Center Dimensions
The PGM system provides positive displacement metering for precision bead control. The control accepts automation signals to provide accurate and consistent output
flow. The gear meter can achieve high flow rates with
high viscosity materials.
Control Power On/Off
Typical Applications
• Solar Panel
• Perimeter Seal
• Desiccant
• Edge Seal
• Automotive Manufacturing
• Window and Door General Assembly
Control Power is the power for the signals to the gear
meter which control gear meter rotation. When Control
Power is off, the gear meter cannot rotate.
Pump Ready Light
The Pump Ready light displays when the pump is ready
for Automatic Mode dispensing. When Manual mode is
enabled, this light will not turn on.
Pump Fault Light
The Pump Fault light is illuminated whenever a pump
fault is active.
Manual Purge Button
The Manual Purge button initiates a shot.
3A5185B 11
Page 12

Installation
Installation
Before Installation
• Have all system and component documentation
available during installation.
• See component manuals for specific data on component requirements. Data presented here applies to
the PGM assemblies only.
• Be sure all accessories are adequately sized and
pressure-rated to meet system requirements.
• Use the PGM control center only with the PGM
metering assembly.
Overview
The basic steps to install a PGM system are shown
below. See the separate component manuals for
detailed information on supply systems and dispense
valves.
NOTICE
To avoid damaging the PGM system, use at least two
people to lift, move, or disconnect the system. The
system is too heavy for one person to lift or move.
Installation Steps
1. Mount control center.
2. Connect and ground control center.
3. Mount gear meter assembly.
4. Ground gear meter assembly.
5. Check ground continuity.
6. Connect fluid line between gear meter and dispense
valve. For remote mount dispense valves, connect fluid supply line and air supply to gear meter.
7. Plumb filter assembly near air drop site that will be
used for gear meter assembly.
8. Connect other fluid and air lines to additional system
components as instructed in their manuals.
9. Install cable assemblies.
12 3A5185B
Page 13
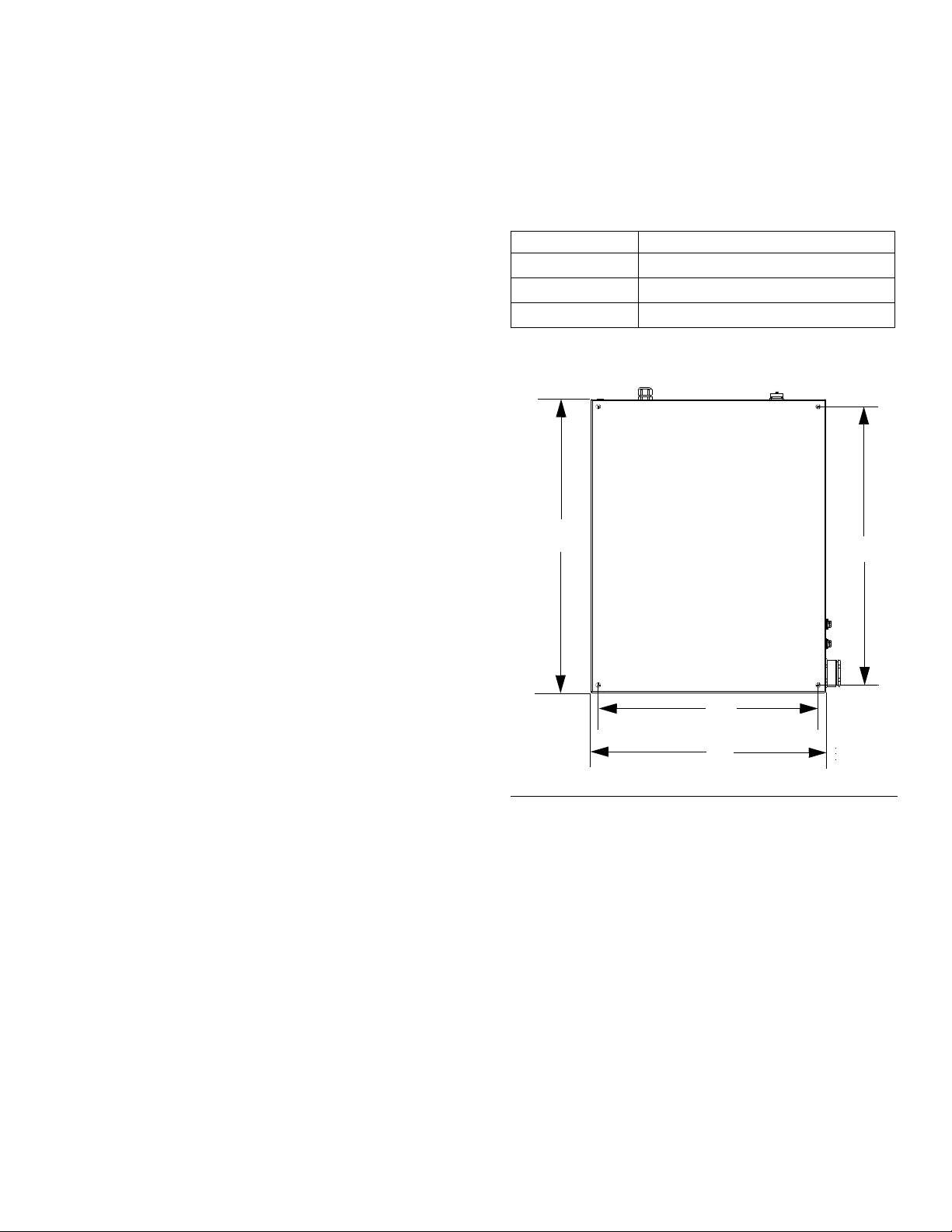
Installation
A
B
C
D
Install Control Center
Mount
Ensure the following criteria are met before mounting
the PGM control center:
• Select a location for the control center that allows
adequate space for installation, service, and use of
the equipment.
• For best viewing, the user interface should be
60-64 in. (152-163 cm) from the floor.
• Ensure there is sufficient clearance around the control unit to run cables to other components.
• Ensure there is easy access to an appropriate electrical power source. The National Electric Code
requires 3 ft. (0.91 m) of open space in front of the
control center.
• Ensure there is easy access to the power switch.
Secure the control center with appropriate size bolts
through the 0.50 in. (13 mm) diameter holes. See the
mounting dimensions in the following table and F
Control Center Assembly Measurement
A
B
C
D
24.0 in. (610 mm)
22.5 in. (572 mm)
30.0 in. (762 mm)
28.5 in. (724 mm)
IG. 5.
• Ensure the mounting surface can support the weight
of the control center and the cables attached to it.
F
IG. 5: Control Center Dimensions
3A5185B 13
Page 14
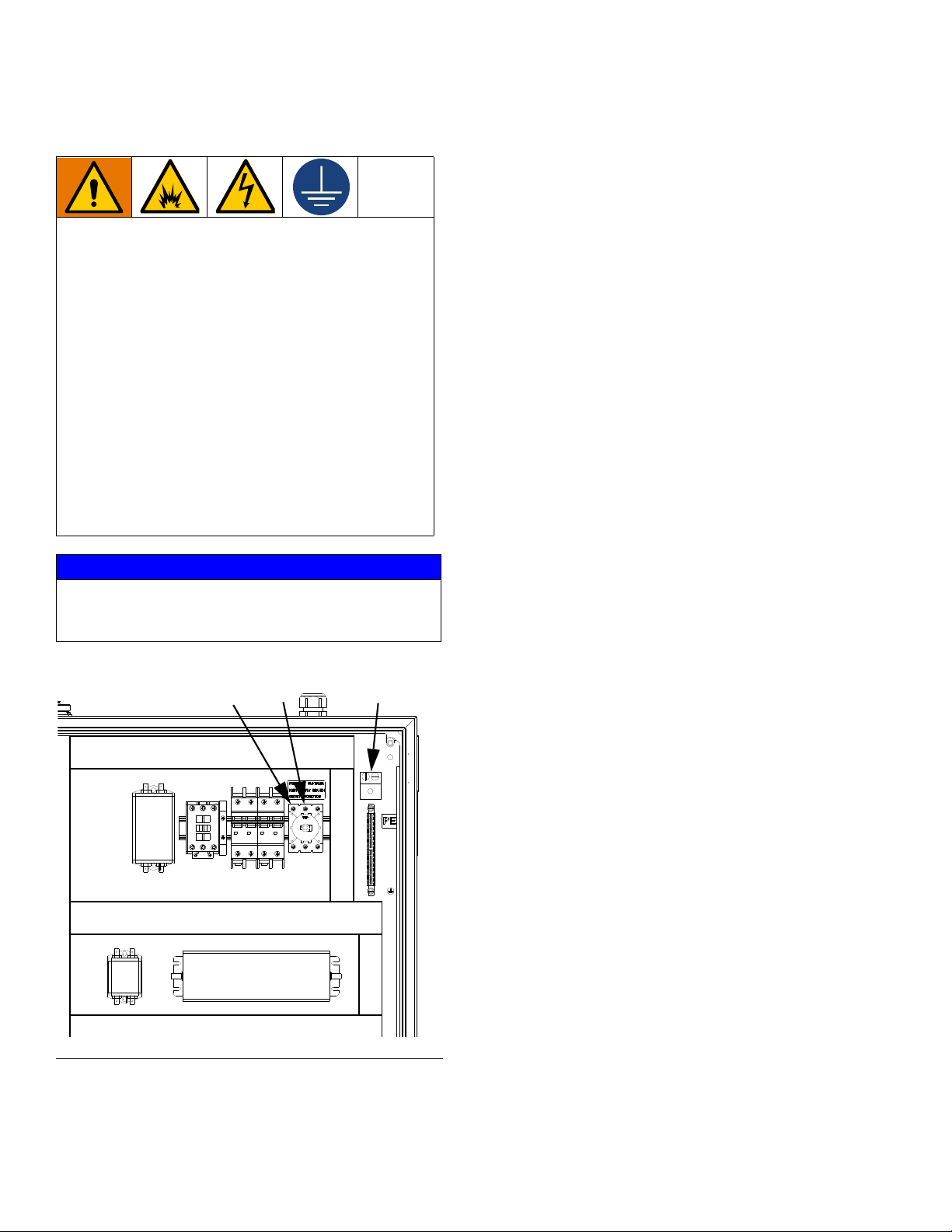
Installation
L2
L1
Ground
Electrical Connections
Follow these precautions when grounding, connecting cables, connecting to a power source or making
other electrical connections.
To reduce the risk of fire, explosion, or electric
shock:
• The control center must be electrically connected
to a true earth ground; the ground in the electrical
system may not be sufficient.
• A qualified electrician must complete all grounding and wiring connections.
• For wiring, refer to F
Refer to your local code for the requirements for a
“true earth ground” in your area.
If power and grounding connections are not done properly, the equipment will be damaged and the warranty
voided.
IG. 6.
NOTICE
Install Gear Meter Assembly
To install the PGM metering assembly:
• Mount the gear meter assembly.
• Ground gear meter assembly.
• Connect the gear meter assembly to the control cen-
ter.
• Connect fluid lines and cables.
Mount
Before Mounting Assembly
• See component manuals for specific information on
component requirements. Information presented
here pertains to the PGM gear meter assembly only.
• Have all system and subassembly documentation
available during installation.
• Be sure all accessories are adequately sized and
pressure-rated to meet the system's requirements.
• Use only the Graco PGM gear meter assembly with
the Graco PGM control center.
Mount Assembly
F
IG. 6: 240 Vac Wiring
1. Select a location for the gear meter assembly. Keep
the following in mind:
• Allow sufficient space for installing the equipment.
• Make sure all fluid lines, cables and hoses easily reach the components to which they will be
connected.
• Make sure the gear meter assembly allows the
automation unit to move freely along all axis.
• Make sure the gear meter assembly provides
easy access for servicing its components.
14 3A5185B
Page 15

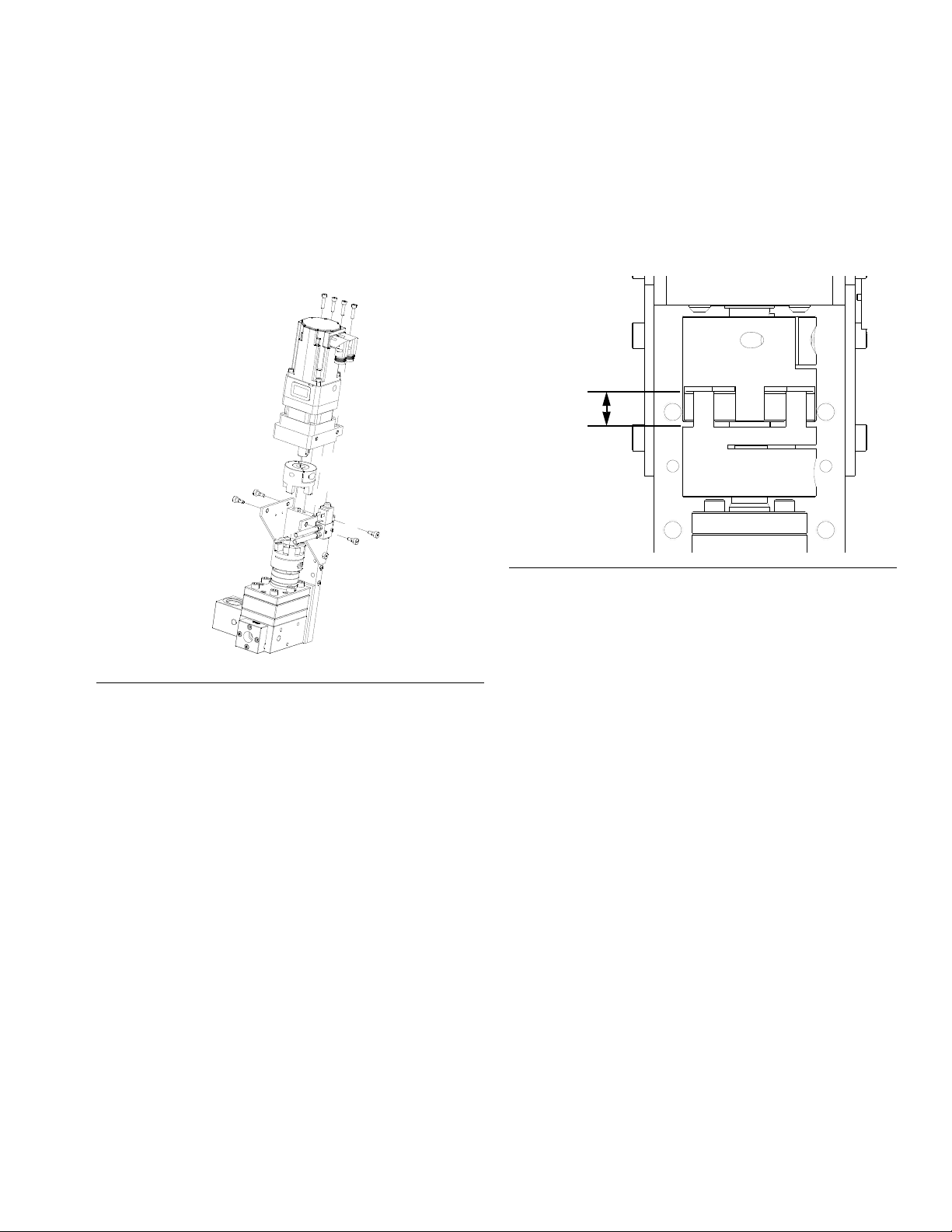
2. Mount and secure the gear meter assembly to the
C
B
6 cc Pump
20 cc Pump
A
A
D
C
B
0.238 in. (6.0 mm)
diameter
0.238 in. (6.0 mm)
diameter
automation unit (or other mounting surface) with
mounting plate. The mounting plate is tapped with
M10 x 1.5 bolts. Maximum bolt length through plate
is 0.75 in. (19 mm). See the mounting dimensions in
Table 4 and F
IG. 7.
Table 4: Gear Meter Assembly Measurement
6 cc Pump 20 cc Pump
Installation
A
B
C
D
2.00 in. (50.8 mm) 3.00 in. (76.2 mm)
5.00 in. (127 mm) 3.875 in. (98.43 mm)
2.375 in. (60.33 mm) 2.313 in. (58.75 mm)
NA 1.063 in. (27.00 mm)
F
IG. 7: Gear Meter Assembly Dimensions
3A5185B 15
Page 16
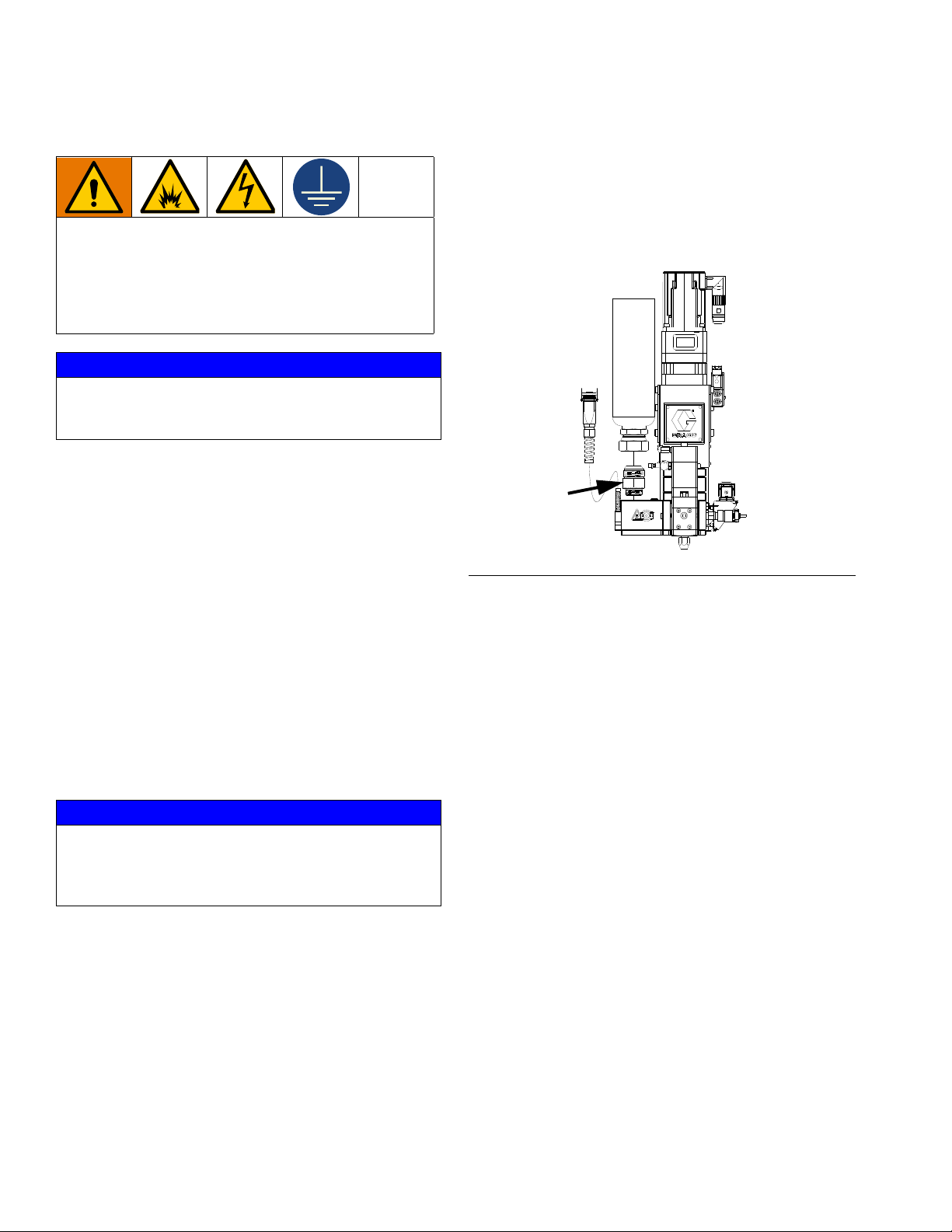
Installation
Grounding
The equipment must be grounded to reduce the risk
of static sparking and electric shock. Electric or static
sparking can cause fumes to ignite or explode.
Improper grounding can cause electric shock.
Grounding provides an escape wire for the electric
current.
NOTICE
If power and grounding connections are not done properly, the equipment will be damaged and the warranty
voided.
Gear Meter
Ground the gear meter assembly as instructed here and
in the individual component manuals. Make sure the
gear meter assembly and its components are installed
correctly to ensure proper grounding.
• For a remote mount dispense valve, connect a
fluid line between the gear meter outlet and the dispense valve. Shorter fluid lines (hoses) will provide
better fluid system response.
• See page 4 for list of inlet fittings.
FIG. 8: Inlet Fitting
Air and Fluid Hoses
For static dissipation, use only electrically conductive
hoses or ground the applicator / dispense valves.
Dispense Valve
Follow the grounding instructions in the dispense valve
manual.
Connect Fluid and Air Lines
NOTICE
Route all fluid and air lines carefully. Avoid pinching
and premature wear due to excessive flexing or rubbing. Hose life is directly related to how well they are
supported.
Follow the instructions in your separate component
manuals to connect air and fluid lines. The following are
only general guidelines.
• The PGM gear meter assembly should be installed
on the automation unit or in another appropriate
place, as close as practical to the dispense valve.
• Air must be clean and dry, between 60-100 psi
(0.41-0.68 MPa, 4.14-6.89 bar). Flush air line before
plumbing in air filter assembly (234967). Plumb in air
filter assembly near air drop site (upstream of PGM).
Adding an air regulator to this line will provide more
consistent dispense valve response times.
• Connect a 1/4 in. OD air supply line to the inlet port
on the PGM air supply inlet.
NOTE: To maximize system performance keep the
dispense hose length as short as the application
will allow.
16 3A5185B
Page 17

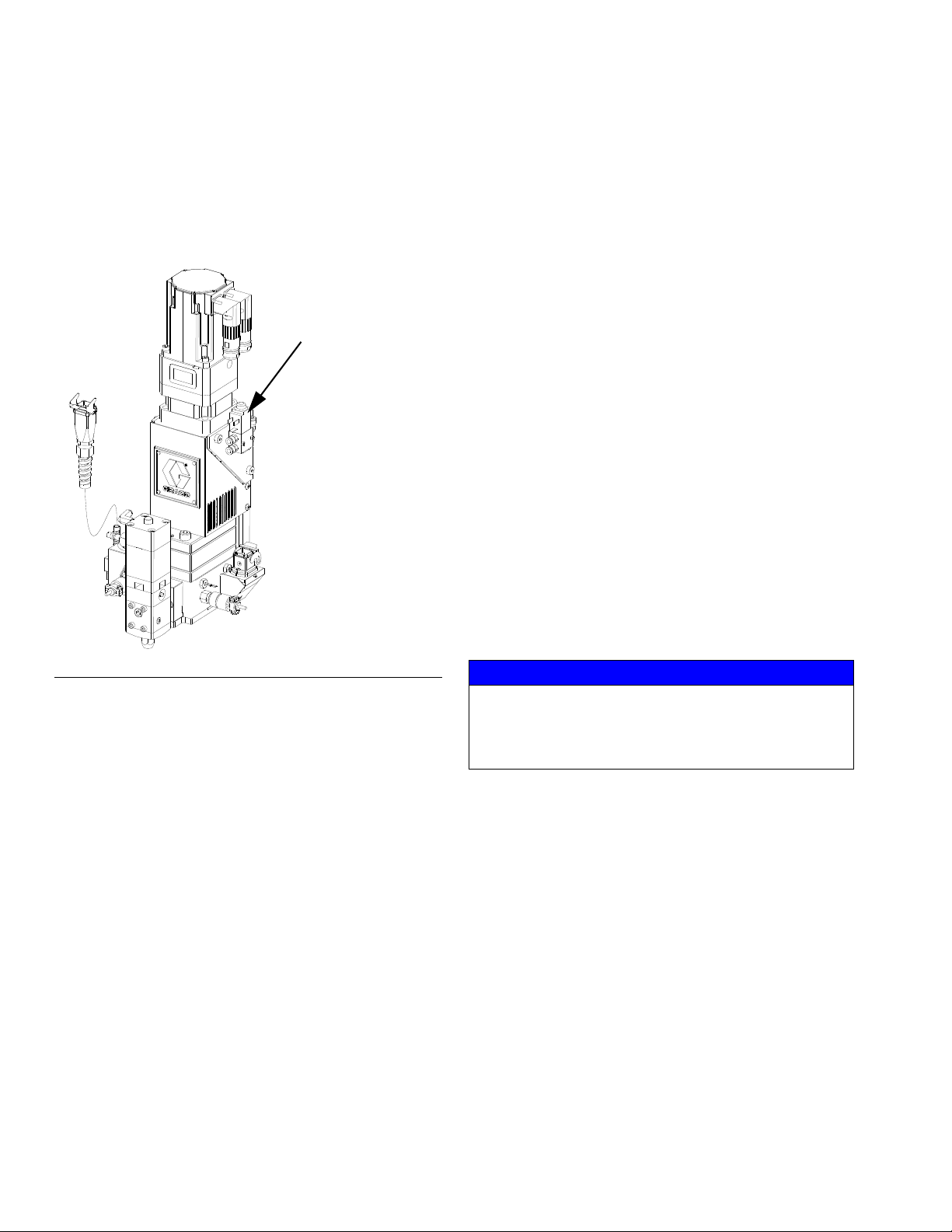
Install Cable Assemblies
NOTE: Models with
15 meter cables
include a remote
junction box to be
mounted in the field.
Installation
1. Connect servo motor power and feedback cables.
2. Connect pressure transducer cable.
3. Connect dispense valve solenoid cable.
4. Connect heat cables, if equipped, to Therm-O-Flow
controller.
F
IG. 9: Cable Installation Diagram
3A5185B 17
Page 18
System Setup
System Setup
Configure Control Settings (page 19)
Configure Mode Settings (page 19)
Configure Delay Settings (page 20)
Adjust Pressure Sensors (page 20)
Configure Errors (page 21)
End System Setup
System Setup
Overview
The PGM system compensates for temperature, flow, or
pressure fluctuations. However, if there is a hardware
change on the supply system or the dispense material is
changed, the PGM system must be setup again.
After material is loaded into the supply system, set up
the PGM system using the Setup screens. F
shows the major system setup steps. The following subsections provide instructions to complete each setup
step. Once these steps are complete the module is
ready for operation.
NOTE: See Appendix A - User Interface Display on
page 82 for detailed operating instructions for each
user interface screen.
IG. 10
F
IG. 10
18 3A5185B
Page 19

System Setup
Configure Control Settings
Set the controls for the dispense source, how dispense
commands are sent, and auto mode settings.
1. From the Home screen, select the Setup icon
.
NOTE: The Setup screens are password protected.
Enter password “PGM17
screens.
”to access the following
Configure Mode Settings
Set the dispense mode (bead or shot). The bead scale
and pre-charge are also adjustable from the Mode Settings screen.
NOTE: See Appendix A - User Interface Display on
page 82 for a description of each feature.
1. With the system in setup mode,
igate to the Mode Settings screen.
press
to nav-
F
IG. 11
2. Select Display or Remote from the Command Value
Source Options.
3. If Command Value Source is set to Remote,
enter the Remote Max Flow (cc/min) for the 10 VDC
command source.
4. Select Enable or Disable for Run Mode Bead Adjust
Options. Default is Disable.
5. Select Display or Remote for Job End Mode
Options.
6. If Job End Mode is set to Display, press Job End
Delay Display field and enter desired delay time in
seconds.
FIG. 12
2. Select Bead or Shot for the Dispense Mode.
3. If Command Value Source is set to Display, enter
the flow rate in cc/min in the Fixed Command Flow
Rate. See Configure Control Settings for instructions to set the Command Value Source value.
4. If Shot Time is displayed, enter the Shot Time in
Seconds.
NOTE: Shot Time is only displayed if Dispense
Mode is set to Shot.
3A5185B 19
Page 20
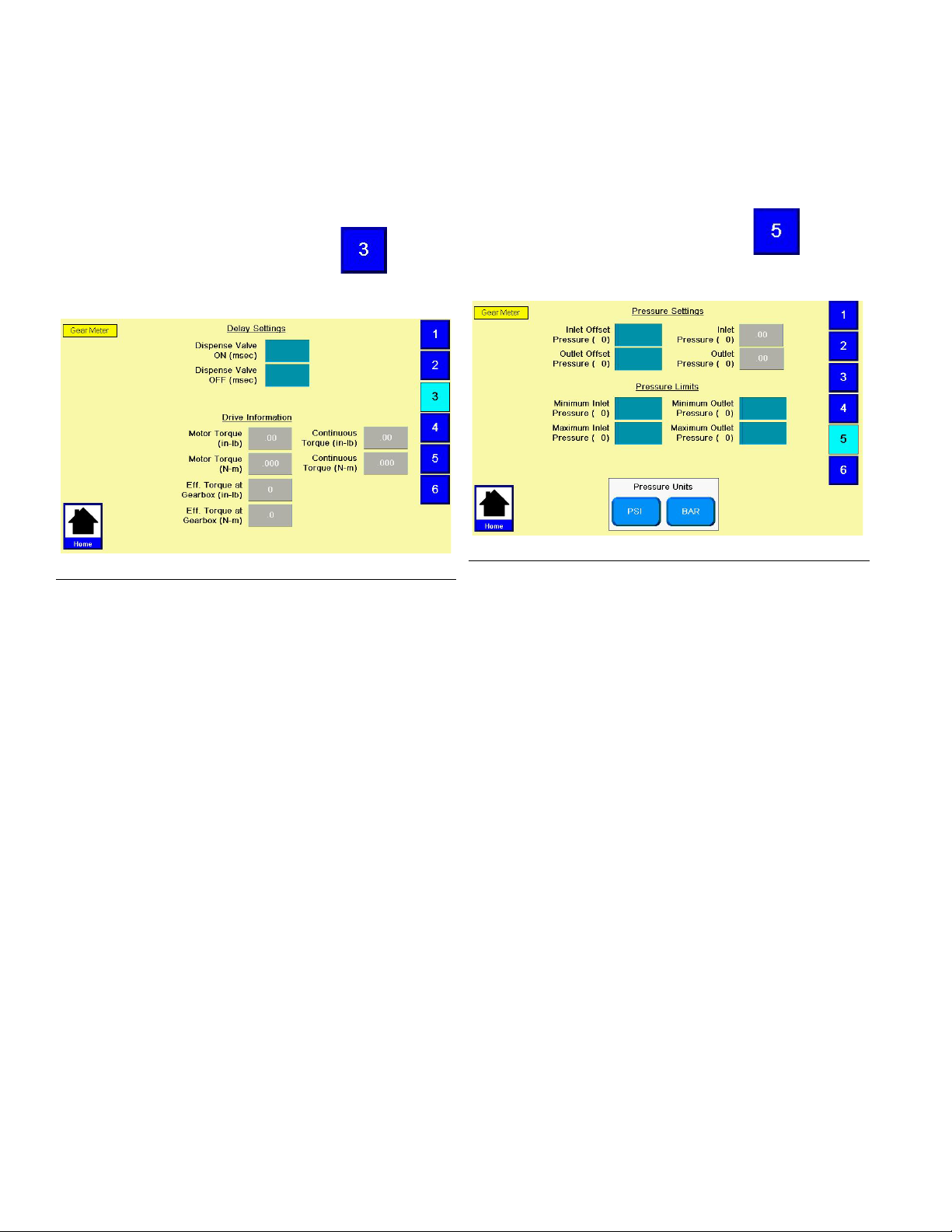
System Setup
Configure Delay Settings
Set on and off delays (in milliseconds) for the dispense
valve.
1. With the system in setup mode,
igate to the Delay Settings screen.
F
IG. 13
press
to nav-
Adjust Pressure Sensors
Set pressure offsets and pressure limits.
1. With the system in setup mode,
igate to the Pressure Sensor screen.
FIG. 14
press
to nav-
2. Press the On Delay field and enter a desired delay
value in milliseconds. Default is zero milliseconds.
3. Press the Off Delay field and enter e desired value
in milliseconds. Default is zero milliseconds.
2. Set the desired offset for the inlet and outlet pressures. Remove all pressure on the sensors, and
then adjust the offset so the measured value
reads 0.
NOTE: Offsets are set at the factory.
3. Set the desired minimum and maximum pressure
limits for the inlet and outlet.
NOTE: These values may need changed after the
system has gone through the Startup procedure.
20 3A5185B
Page 21
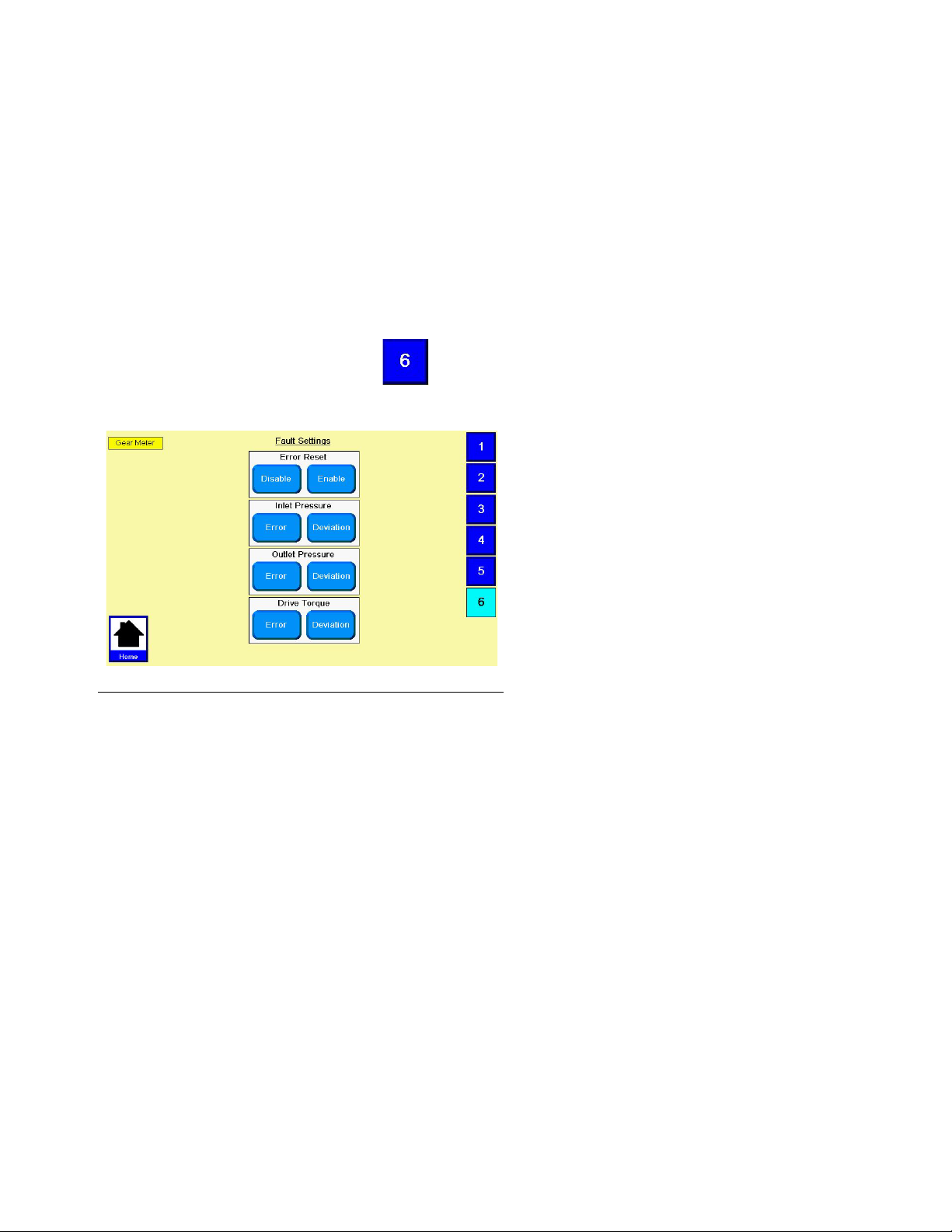
Configure Errors
Set the error type (error or deviation) that will be issued
if the pressure or drive torque goes outside the set high
and/or low limits. See Appendix A - User Interface
Display on page 82 for information on the purpose of
each error type.
NOTE: When an alarm is set to Error the machine
will be disabled when the alarm occurs.
System Setup
1. With the system in setup mode,
igate to the Errors screen.
F
IG. 15
2. Select Enable or Disable for the Error Reset.
3. Select Error or Deviation for the Inlet Pressure.
4. Select Error or Deviation for the Outlet Pressure.
press
to nav-
5. Select Error or Deviation for the Drive Torque.
3A5185B 21
Page 22

Operation
Operation
Startup
Initial Startup
1. Ensure the PGM control enclosure and all of the
proper connections to and from the control enclosure have been made. Ensure fittings are tight.
2. Read and understand the Operation and User
Interface sections of this manual along with the
related manuals.
3. Continue startup with Step 2 in Standard Startup.
Standard Startup
1. Carefully inspect the entire system for signs of leakage or wear. Replace or repair any worn or leaking
components before operating the system.
2. Press the Stop button on the control enclosure.
3. Turn on air and electrical power to the system.
4. Turn on the main power to supply power to the
PGM.
Load Material
Before using the system, material must be loaded into
the supply system.
1. If this is a new installation, follow the Initial Startup
procedure. Otherwise, follow the Standard Startup
procedure.
2. Turn on the fluid supply pressure to the fluid inlet
block for the PGM.
3. Place the dispense valve over a waste container.
4. Navigate to the Maintenance screen. See Screen
Navigation Diagram on page 82 in the Appendix
A - User Interface Display section.
5. Select Manual Control Mode .
6. Enter the minimum flow rate to prime the system.
See the following table.
Pump Size
cc / revolution
612
20 40
Min Flow Rate
cc / minute
5. Check Interface Signals: If this is a new installation, power on each system input and verify that
each input is being received. See Appendix B - I/O
on page 98.
6. For heated systems, open the dispense valve over a
waste container while the system is heating up. This
will prevent a pressure build-up caused by fluids or
gases expanding from the heat.
7. Turn on the material supply system.
22 3A5185B
7. Press and hold the manual start button .
Dispense fluid until clean, air-free fluid flows from
the dispense valve.
NOTE: The manual purge button on the user-interface panel can be used to prime the system.
8. If desired, press to navigate to the Home
screen.
Page 23
Operation
Maintenance Mode Operation
Operating from maintenance mode enables the pump to
begin dispensing when the user presses .
Dispense parameters and duration depend on the
selected control.
Verify System Operation
Use maintenance mode to manually check the operation
of the PGM system components before switching over
to automation control (normal operation).
NOTE: Perform any of the following procedures
while in maintenance mode.
Set Inlet Pressure
The inlet pressure reading should be in the range of
300 psi (2.1 MPa, 21 bar) to 1500 psi (10.3 MPa,
103 bar). The recommended inlet pressure should be
500 psi (3.4 MPa, 34 bar) lower than the outlet pressure.
Dispense Weight Verification
1. From maintenance screen, select Shot mode.
2. Enter a 10 second shot time.
3. Enter the desired flow rate.
4. Record a minimum of 5 shot weights.
5. If shot weights are inconsistent check feed pressure
or reduce flow rate and repeat shot test.
NOTE: Regular weight checks are recommended to
ensure system is performing properly.
Follow steps in the supply system manual to set the inlet
pressure.
NOTICE
Excessive inlet pressure will cause accelerated wear
on the gear meter seals and the pump feed system.
Feed System Pressure Drop
During material flow, the PGM inlet pressure decreases.
The amount the pressure decreases is the amount of
pressure lost between the feed pump and the PGM inlet.
With high viscosity fluids, long line lengths, or small
diameter line sizes this pressure decrease can be thousands of psi (hundreds of bar). This means that the
static pump pressure is set much higher than the PGM
needs at its inlet. To prevent excessive static pressure
at the inlet of the PGM, a dynamic regulator is recommended on air motor supply air. During dispense the
normal pump regulator is active. During a stalled condition the dynamic regulator is active.
3A5185B 23
Page 24

Operation
Calibration
1. Perform Startup procedure, page 22. Verify all system components are at desired pressures and temperatures. Adjust as desired.
2. Navigate to the Calibrate screen. See Screen Navi-
gation Diagram on page 82 in the Appendix A User Interface Display section.
NOTE: PGM systems are calibrated at the factory. Per-
form calibration after pump maintenance or during troubleshooting (see page 29 for troubleshooting matrix).
3. Press the Enable Calibration button .
4. Weigh one disposable container and tare the scale.
5. Place container below dispense tip.
15. Enter the volume into the High Speed Calibration
Actual Volume input box .
16. Press the Done button .
17. If desired, press to navigate to the Main
screen.
6. Press the Start Low Speed Calibration
button .
7. Weigh the container.
8. Divide the weight of the dispensed material by the
specific gravity to determine the volume.
9. Enter the volume into the Low Speed Calibration
Actual Volume input box .
10. Weigh a second disposable container and tare the
scale.
11. Place container below dispense nozzle.
12. Press the Start High Speed Calibration
button .
13. Weigh the container.
14. Divide the weight of the dispensed material by the
specific gravity to determine the volume.
24 3A5185B
Page 25
Operation
Dispense from Maintenance Screen
1. Navigate to the Maintenance screen. See Screen
Navigation Diagram on page 82 in the Appendix
A - User Interface Display section.
2. Select Manual Control Mode .
3. Select Bead or Shot from the Manual Mode Option.
Manually Dispense Fluid
1. Press and verify the dispense valve
opens.
2. Continue to press as long as needed to
load or dispense material. Release to stop dispensing.
Automation Control (Normal) Operation
During automation control (normal operation) the PGM
automatically dispenses when it receives a command
from the automation unit.
NOTE: See Appendix B - I/O on page 98.
To enter Auto mode, select Auto (A) Control
Mode .
Typical Automation Cycle
In order for the system to run it must be in Auto mode.
Before a cycle begins the robot outputs should have the
following values:
• Job Complete: 0
• Dispense Trigger: 0
A typical cycle consists of the following dispensing
sequence.
3. If desired, press to navigate to the Home
screen.
1. The robot checks that Dispenser Ready signal is set
to On (High). If On, a cycle can begin.
2. If command source is set to Remote, robot sends
0-10 VDC Flow Rate signal.
NOTE: See Setup Screen 1 information in the
Appendix A - User Interface Display section beginning on page 82.
3. Robot turns on dispense trigger.
4. PGM turns on In Cycle.
5. Robot removes dispense trigger.
6. If Job Complete is set to Remote, robot turns on Job
Complete.
7. Robot removes Job Complete before starting the
next cycle.
NOTE: In the event of a deviation alarm, the Dispense Ready signal will remain on along with the
alarm signal. In the event of an error alarm, the Dispense Ready signal will turn off and the alarm signal
will remain on.
3A5185B 25
Page 26
Pressure Relief Procedure
Pressure Relief Procedure
Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure whenever
you see this symbol.
This equipment stays pressurized until pressure is
manually relieved. To help prevent serious injury from
pressurized fluid, such as skin injection, follow the
Pressure Relief Procedure when you stop dispensing and before cleaning, checking, or servicing the
equipment.
1. Shut off the fluid supply to the PGM inlet block.
2. If equipped, place a waste container beneath the
fluid drain valve under the filter.
3. Place a waste container beneath the dispense
valve.
4. Slowly open the drain valve at each fluid filter to
relieve fluid pressure. Close valve when pressure
gauge reads zero.
5. Navigate to the Maintenance screen. See Screen
Navigation Diagram on page 82 in the Appendix
A - User Interface Display section.
6. Perform the following steps to perform a low flow
dispense:
a. From the Mode drop-down menu, select Bead
mode.
b. Enter the minimum flow rate for your system.
For example, 12 cc/min or 40 cc/min depending
on the size of the gear meter.
c. Press or the Purge button on the
control enclosure to begin the low flow dispense.
d. Continue to dispense until the inlet pressure on
the PGM is near zero.
e. Visually locate the plug installed at the back of
the inlet block.
f. Place a container under the plug and slowly
remove the plug to relieve remaining inlet pressure.
7. In maintenance mode, select Open Dispense Valve
Control mode , which opens
the dispense valve. Press the manual dispense but-
ton until fluid flow stops.
26 3A5185B
Page 27

Pressure Relief Procedure
Dispense Valve
Air Solenoid
8. If the dispense device cannot be actuated from the
control center, refer to F
IG. 16 and perform the fol-
lowing steps to open the dispense valve and relieve
fluid pressure:
a. Manually actuate the plunger on the solenoid,
that opens the dispense valve to relieve fluid
pressure. Refer to F
IG. 16.
b. Continue actuating the plunger until all pressure
is purged from the system between the needle
and dispense valve before proceeding to the
next step.
9. If you suspect that a valve, hose, or dispense nozzle
is clogged or that pressure has not been fully
relieved:
a. Very slowly remove the dispense tip, clean the
orifice, and continue relieving pressure as
described in steps 6-8.
b. If this does not remove the obstruction, very
slowly loosen the hose end coupling to relieve
pressure gradually, then loosen the coupling
completely. Clear the valves or hose. Do not
pressurize the system until the blockage is
cleared.
10. Shut off power and air to the fluid supply system.
FIG. 16: Dispense Valve Air Solenoid
3A5185B 27
Page 28

Shutdown
Shutdown
1. Press the Stop button. See FIG. 17.
2. Shut off the material supply to the gear meter/meter.
3. Shut off heat to PGM. See related manuals section
for Therm-O-Flow manual and Accessory Heat Control.
4. For heated systems, open the dispense valve over a
waste container while the system is cooling down.
This will prevent a pressure build-up caused by fluids or gases expanding from the heat.
5. Shut off power and air to the fluid supply system.
6. Turn off the main power supply.
FIG. 17: Stop Button
28 3A5185B
Page 29

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
NOTE: Check all possible solutions in the chart
below before you disassemble the system.
Refer to Supply Systems manual for additional troubleshooting; refer to Related Manuals on page 3. Also
refer to Error Codes and Troubleshooting, page 32.
PGM Fluid Assembly
Problem Cause Solution
No Inlet Pressure No air pressure on supply system Verify supply system pressure
Leak in supply system Check supply lines and connections
False signal being sent to control Check inlet pressure sensor output;
verify that it corresponds to zero
pressure; replace sensor and/or
amplifier
Leak at PGM drive shaft Replace drive shaft seals
No Outlet Pressure Dispense motor not rotating Refer to Error code section of the
manual; Cycle power and perform
startup
Dispense Off delay set too long Verify Dispense valve delays in
setup screens
Dispense valve solenoid stuck
open
False signal being sent to control Check outlet pressure sensor out-
High Outlet Pressure Blocked dispense tip Replace dispense tip
Flow rate too high for application decrease flow rate
Dispense valve On delay set too
long
Dispense valve solenoid stuck
closed
3A5185B 29
Verify function of dispense valve
put; verify that it corresponds to zero
pressure; replace sensor and/or
amplifier
Verify Dispense valve delays in
setup screens
Verify function of dispense valve
Page 30
Troubleshooting
Dispense pattern too light Supply pressure too low Verify inlet pressure needed for flow
rate
Flow rate too high for application Perform dispense weight verifica-
tion, see Calibration procedure on
page 24; Lower flow rate and repeat
Measured flow does not match
command
Supply pressure too low Verify inlet pressure needed for flow
rate
Flow rate too high for application Perform dispense weight verifica-
tion, see Calibration procedure on
page 24; Lower flow rate and repeat
Gear meter is not calibrated Perform calibration; Perform weight
verification, see Calibration procedure on page 24
Gear meter is worn or damaged Perform weight verification, see Cal-
ibration procedure on page 24; if
weights are not repeatable repair or
replace gear meter
Dispense Valves
Problem Cause Solution
Valve not opening Air not getting to open port Verify air pressure solenoid
No Dispense Trigger signal from
automation unit
Valve not shutting off Air not getting to close port (except
AutoPlus valve)
Dispense Trigger signal from automation unit is on
Sluggish open/close Air pressure low Verify air pressure is above 60 psi
Needle/seat worn Rebuild valve; replace needle/seat
Pressurized material past the valve
shut-off is escaping
Material leaks from back of valve Shaft seal is worn Rebuild valve; replace seals
Air leaks from dispense valve Loose air connections Check air connections; tighten if
Worn piston o-ring Rebuild valve; replace piston o-ring
Check input from automation unit
Verify air pressure to solenoid
Verify solenoid operation
Verify air line routing and connections
Check input from automation unit
(0.4 MPa, 4 bar)
Reduce running pressure
Reduce nozzle length
Increase nozzle orifice size
necessary
30 3A5185B
Page 31

Errors
Access the Alarm
View screen
Errors
View Errors
Errors can be viewed from the Home screen or from the
Alarm View screen.
There are three levels of errors: alarms, deviations, and
advisories. Alarms are critical and require immediate
correction; therefore the system automatically shuts
down. Deviations are important and require attention but
not immediately. Advisories are not critical but still
require attention.
NOTE:
• Errors set the dispenser ready signal LOW.
Clear Errors and Reset Control Unit
From the Alarm View screen, perform the following
steps to clear an error before restarting the control unit:
1. Press Acknowledge All List
2. Press Clear All Alarms
NOTE: Acknowledging alarms does not clear them.
NOTE: See the Configure Errors section on page 21.
• Advisories and deviations do not set the dispenser
ready signal LOW.
Diagnose Errors
See Error Codes and Troubleshooting for valid error
codes, possible causes, and solutions.
3A5185B 31
Page 32

Errors
Error Codes and Troubleshooting
Error
No.
1 Control Power Off Control power has
2 Inlet Pressure Devia-
3 Inlet High Pressure
4 Inlet Low Pressure
5 Outlet Pressure Devi-
Error Name Error Description
PGM Control Errors
been removed
Inlet material pres-
tion
Error
Error
ation
sure outside limits
Inlet material pressure above max limit
Inlet material pressure below min limit
Outlet material pressure outside limits
Error
Type
Advisory Stop button or
Deviation Feed pressure set
Alarm Feed pressure too
Alarm Feed pressure too
Deviation Back pressure is
Cause Solution
E-stop
too high or too
low. Limits are not
set correctly
high. Limits are
not set correctly.
low. Limits are not
set correctly.
too high or too
low. Limits are not
set correctly.
Press Control Power
button
Verify pressure limits
in Setup Screen 5.
Verify supply pressures during dispense.
Verify pressure limits
in Setup Screen 5.
Verify supply pressures during dispense.
Verify pressure limits
in Setup Screen 5.
Verify supply pressures during dispense.
Verify pressure limits
in Setup Screen 5.
Verify outlet pressures during dispense.
6 Outlet High Pressure
Error
7 Outlet Low Pressure
Error
8 Inlet Max Pressure
Fault - Relieve Pressure and Cycle Power
Outlet material pressure above max limit
Outlet material pressure below min limit
Inlet material pressure exceeds max
rated pressure
Alarm Back pressure is
too high. Limits
are not set correctly.
Alarm Outlet pressure
too low. Limits are
not set correctly.
Alarm Feed system pres-
sure is set too
high. Pressure
sensor damaged.
Verify pressure limits
in Setup Screen 5.
Verify outlet pressures during dispense.
Verify pressure limits
in Setup Screen 5.
Verify outlet pressures during dispense.
Perform pressure
relief procedure.
Change inlet supply
pressure. Cycle
power; Verify Pressure sensor is working properly.
32 3A5185B
Page 33
Errors
Error
No.
9 Outlet Max Pressure
10 Drive Torque Devia-
Error Name Error Description
Outlet material presFault - Relieve Pressure and Cycle Power
sure exceeds max
rated pressure
Motor exceeds contion
tinuous rated torque
11 Drive Torque Error Motor exceeds con-
tinuous rated torque
12 Drive Peak Torque
Error - Drive disabled,
Motor exceeds peek
torque rating
Cycle Power
Error
Type
Cause Solution
Alarm Dispense valve
not opening. Flow
rate too high.
Material not at
temperature.
Deviation Flow rate too high.
Dispense Valve
not opening.
Material not at
temperature.
Alarm Flow rate too high.
Dispense Valve
not opening.
Material not at
temperature.
Alarm Flow rate too high.
Dispense Valve
not opening.
Material not at
temperature.
Perform pressure
relief procedure;
Cycle Power; Verify
Dispense valve function; Perform weight
check verification;
Reduce flow rate.
Lower flow rate;
reduce outlet pressure drop; Verify
material temperature.
Lower flow rate;
reduce outlet pressure drop; Verify
material temperature.
Cycle Power Lower
flow rate; reduce outlet pressure drop;
Verify material temperature.
13 Pre-Charge Timeout Pre-Charge Pressure
was not reached
after dispense
14 High Pressure Inter-
lock OFF
15 Dispense Valve Open
(Auto Default)
16 Calibration is enabled
complete calibration
Pressure limit is
bypassed
Dispense valve is
open
Calibration mode
enabled
procedure
17 Drive Fault, Cycle
Power
18 Calibration out of
range
Motor drive is dis-
abled
Calibration values
are out of range or
flow rate is too low
for current K factor
Advisory Pre-Charge value
not set correctly.
Advisory Pressure sensors
are disabled.
Advisory Dispense valve
open button has
been selected.
Advisory Calibration
enabled selected
from the calibrate
screen.
Alarm Various condi-
tions.
Advisory Improper calibra-
tion, flow rate too
low, or pump
wear.
Set Pre-Charge to
zero. Monitor outlet
pressure; Adjust
Pre-Charge pressure.
Contact Graco customer service.
From the Maintenance screen select
Dispense valve Auto.
Complete calibration
procedure.
Cycle Power verify
motor torque during
dispense.
Perform calibration
procedure.
3A5185B 33
Page 34

Maintenance
Maintenance
Prior to performing any maintenance procedures, follow
the Pressure Relief Procedure on page 26.
Maintenance Schedule
The following tables list the recommended maintenance procedures and frequencies to operate the equipment
safely. The maintenance is divided between mechanical and electrical tasks. Maintenance must be performed by
trained personnel per this schedule to assure safety and reliability of the equipment.
Mechanical
Operator Maintenance Person
Task Daily Weekly Monthly
Inspect system for leaks
Depressurize fluid, after opera-
tion
Remove heat from system,
after operation
Inspect filter (234967) bowls
and drain
Check hoses for wear
Check/tighten fluid connections
Check/tighten air connections
Lubricate dispense valves*
Replace gear meter seals
Rebuild dispense valve*
Replace air filter
Replace Solenoid
Replace gear meter drive shaft
Replace gear head
* Check component manual for more detailed maintenance information.
3-6
months
or
125,000
cycles
18-24
months
or
500,000
cycles
36-48
months
or
1,000,000
cycles
As
Required
Electrical
Task Weekly
Check cables for wear
Verify cable connections
Verify operation of “System Stop” button
* Check Component Manual for more detailed maintenance information.
34 3A5185B
Page 35
Repair
Repair
NOTE: Refer to Parts section beginning on page 49
for part reference number identification.
Gear Meter Assembly
This section describes how to remove and replace components on the gear meter assembly.
Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair
Replace Servo Motor or Gear Head
Replacing either the Servo Motor or Gear Head requires
the following procedure.
Remove Servo Motor and Gearhead
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
page 35.
2. Remove support gussets (9, 1106).
3. Remove bolts (1, 1103) connecting top mounting
plate (8, 1105) to vertical mounting plate (10, 1107).
4. Remove servo motor, gear head, and top plate.
Coupling (303, 1203) will separate.
5. Remove coupling half.
6. Remove 4 screws (3, 1110) that mount to plate to
gear head.
7. Remove gear head coupling covers (302a, 1202a).
8. Loosen gearhead coupling on gearhead shaft.
FIG. 18
1. Perform Pressure Relief Procedure, page 26.
2. Disconnect main power at the control box.
3. If present, remove power from the heat control.
4. Remove servo power cable and servo feed back
cable. See gear meter assembly parts; see Parts
section starting on page 49.
5. Remove heat cables.
6. Remove pressure transducer cables and dispense
valve cable.
7. Remove supply air pressure from solenoid.
8. Remove front guard.
9. Remove material hoses if necessary.
9. Remove 4 bolts connecting servo motor to gearhead.
10. Remove servo motor from gear head.
3A5185B 35
Page 36

Repair
SEE DETAIL
A
DETAIL
A
SCALE
3/2
Install Servo Motor or Gearhead
1. Remove key from motor shaft.
NOTICE
Use caution when handling servo motor to prevent
damage. Do not use tools that could cause damage.
2. Slide the gear head. bushing into the drive coupling
and align slots in drive coupling and bushing. See
IG. 19.
F
FIG. 19
3. Rotate the drive coupling to align clamping bolts
with access holes.
4. Place motor on work surface with motor shaft facing
NOTE: Orient servo motor so that the motor connections do not interfere with material inlet hose.
9. Install gussets with shoulder bolts (5, 1104).
straight up then mount the gear head. Mounting the
gear head in any other orientation will usually lead
to misalignment and excessive noise.
Remove Coupling
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
5. Pre-torque drive coupling to 0.4 N•m (4 in-lb).
6. Bolt gear head to the motor with fasteners provided.
7. Final toque drive coupling to 8.5 N•m (76 in-lb) in
three steps increasing torque each time.
8. Do not tighten coupling to gear head output shaft
page 35.
2. Remove support gussets (9, 1106).
3. Remove bolts (1, 1103) connecting top mounting
plate (8, 1105) to vertical mounting plate (10, 1107).
4. Remove servo motor, gear head, and top plate.
until drive assembly is mounted in frame.
36 3A5185B
Page 37
Repair
Gap
5. Loosen clamping bolts on each side of coupling and
remove coupling.
NOTE: Pump shaft key may fall out during coupling
removal. Secure pump shaft key until coupling is
replaced.
Install Coupling
5. Separate coupling until proper gap is created. F
21. See the following table.
Pump Size
cc / revolution Gap (mm)
618
20 20
FIG. 21
IG.
FIG. 20
1. Slide coupling onto gear head output shaft. Tighten
coupling bolt just enough to hold it’s position.
2. Align pump shaft key and slide coupling onto pump
shaft. Tighten coupling bolt just enough to hold it’s
position.
3. Attach servo motor, gear head, and top plate to
pump assembly. See F
IG. 20.
4. Slide drive coupling so it is evenly spaced between
pump and gearhead. Both sides of coupling should
slide easily on each shaft. If coupling does not slide
freely, loosen pump bolts (103, 1303) and align
pump until coupling moves freely. Tighten pump to
pump block to 430-480 in-lb (48.58-54.23 N•m).
6. Tighten coupling bolts to the following torques:
Pump Size
cc / revolution
Torque,
in-lb (N•m)
6 132 (15)
20 309 (35)
7. Install gussets with shoulder bolts (5, 1104).
3A5185B 37
Page 38
Repair
Dispense Valve
Air Solenoid
Remove Dispense Valve
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
page 35.
2. Manually actuate solenoid to ensure pressure has
been removed.
4. Connect air lines.
5. Apply air to the solenoid.
6. Manually shuttle solenoid, see F
pense valve is open when solenoid is depressed.
IG. 22. Verify dis-
Replace Solenoid
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
page 35.
2. Disconnect solenoid cable. Remove mating
screws (405) from gusset.
3. Remove the dispense valve solenoid (410) and
replace it with a new solenoid.
4. Reconnect solenoid cable.
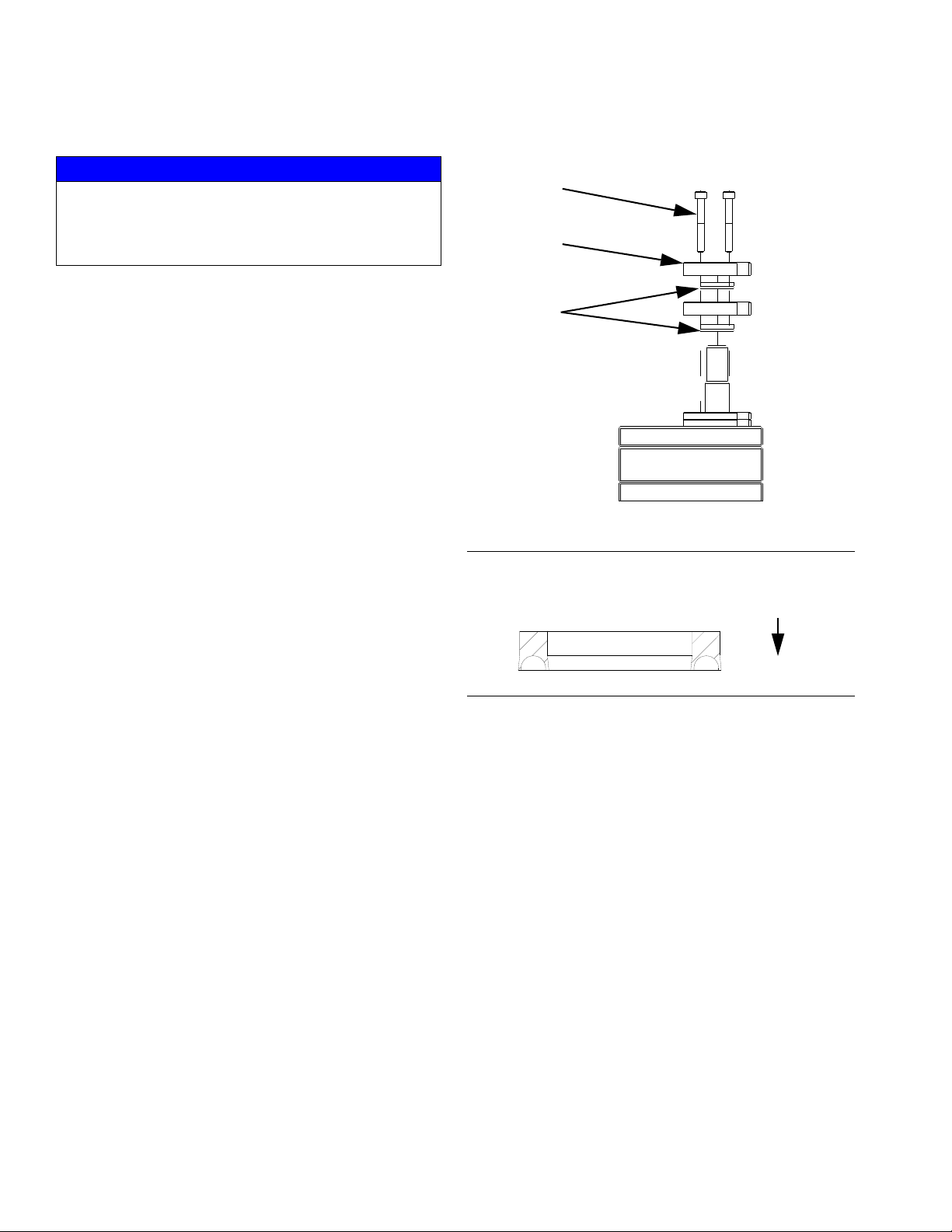
Gear Meter O-Ring Replacement
Refer to Parts section starting on page 49 for o-ring kits.
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
page 35.
FIG. 22: Dispense Valve Air Solenoid
3. Verify air supply is off.
4. Remove air lines from dispense valve.
5. Remove four dispense valve mounting bolts and
remove dispense valve.
NOTE: For remote mount dispense valves, remove
supply hose at inlet block of dispense valve.
6. Refer to dispense valve manual for complete dispense valve repair instructions; refer to Related
Manuals on page 3.
Install Dispense Valve
1. For direct mounted dispense valves, replace
o-ring (409) if necessary.
2. Align dispense valve with mounting pins on front
block.
2. Remove pump block shoulder bolts (4, 1102). See
F
IG. 23.
NOTICE
Pump section should be fully supported to prevent
damage being dropped. It is recommended that the
gear meter assembly be located on a work bench for
service.
3. Install four mounting bolts (408) torque to
50-60 in-lb (5.6-6.7 N•m).
38 3A5185B
Page 39

Repair
4, 1102
*107, 1306
105,
1305*
102, 1302
104, 1304
* Provided in o-ring kit 24E626.
103,
1303
106,
1304
109,
1308
412
407
108,
1309
3. Remove drive assembly. See FIG. 23.
12. Replace pump block o-rings (106, 104; 1304). See
F
IG. 24.
FIG. 23
4. Perform Remove Dispense Valve procedure.
5. Loosen 4 bolts (407) and remove front block (412).
6. Loosen 4 bolts and remove inlet block (110, 1302).
7. Loosen pump bolts (3, 1303) and remove
pump (108, 1309).
8. Replace front block o-ring (105, 1305).
9. Install front block (412) onto pump block (109,
1308).
10. Replace inlet block o-ring (107, 1306).
11. Install inlet block (102, 1302) onto pump block.
FIG. 24
13. Place pump (109, 1308) onto pump block. Install
bolts (103, 1303) and tighten to 430 in-lb (48.58
N•m).
14. Locate drive assembly on top of pump assembly.
15. Tighten pump block mounting shoulder bolts to
frame (4, 1102).
16. Replace all electrical connections and fluid connections before applying fluid pressure and power.
3A5185B 39
Page 40

1614
1611
1612†
1611
1612†
1613
1601
1602
1607
1608
1615
1605
1609
1604
1606
1603
1610
† Parts included in kit 24E607.
Parts included in kit 24E827.
Parts included in kit 24E826.
(P/N: 125657)
(P/N: 125656)
Repair
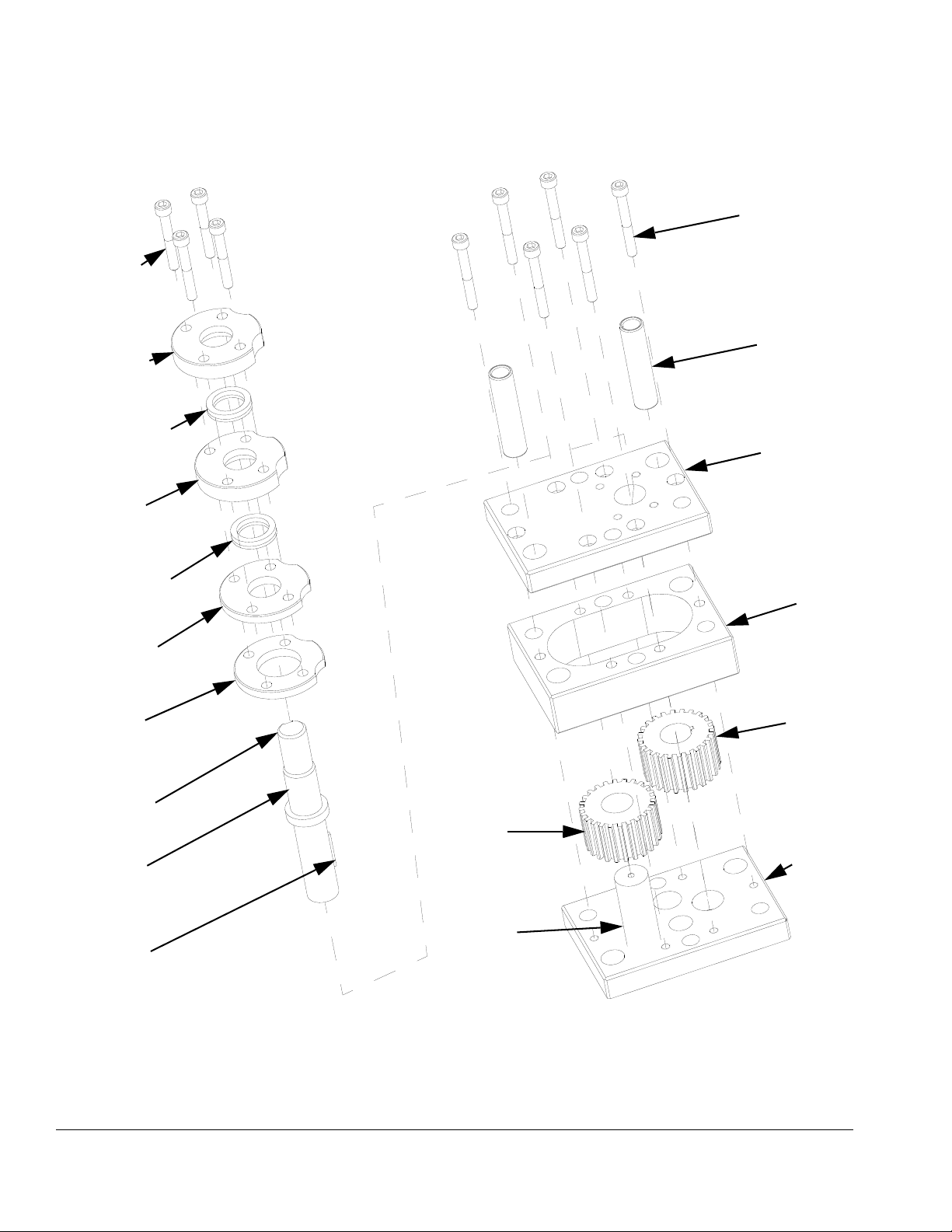
PGM-6 Pump Repair
FIG. 25: PGM-6
40 3A5185B
Page 41
Repair
PGM-6 Pump Disassembly
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
page 35.
2. Refer to Gear Pump Maintenance Guide on
page 47 for special notes regarding gear pump
repair.
3. Remove four pump block shoulder bolts (1102).
NOTICE
Pump section should be fully supported to prevent
damage being dropped. It is recommended that the
gear meter assembly be located on a work bench for
service.
4. Remove drive assembly. See F
NOTICE
IG. 23.
NOTE: Notches on the pump plates can be used to
separate the plates.
9. To remove the drive shaft (1605) from the bottom
plate (1603) press the shaft and gear from the bottom pump plate towards the coupling end.
10. To remove the drive gear (1607) from the drive shaft
(1605), support the drive gear at the lower end to
allow the shaft to be pressed through the gear from
the top or coupling end. Make sure to leave clearance for the drive key.
11. The stud (1606) for the driven gear (1608) is press
fit into the back plate (1603) and need not be
removed if not worn.
NOTICE
The PGM pump design relies on a lap fit between
components for performance and sealing. Be careful
not to drop the gears (1607, 1608) or damage the
mating surfaces of the pump plates (1601, 1603) and
gear case (1602). To prevent damage, do not use pliers or screwdrivers to remove the gears.
Thicker materials may require heating prior to disassembly. Do not expose the pump to thermal shock.
Raise temperature at a maximum rate of 180°F
(100°C) per hour. Do not exceed 400°F (204°C).
Exceeding this temperature could promote leakage in
the pump. Gradually cool the pump to room temperature.
5. Remove seal retainer fasteners (1614) and seal
retainers (1611).
6. Remove pump dowel pins (1610) using an arbor
press.
NOTICE
Do not use a hammer to remove dowel pins as this
will damage the pump.
7. Remove the pump plate screws (1613).
8. Separate the pump front plate (1601), gear case
(1602) and back plate (1603).
12. Clean all components thoroughly before reassembly. The use of an ultrasonic cleaner is recommended.
3A5185B 41
Page 42
Repair
1515,
1614
1512,
1611
*1513,
1612
Pump Body
PGM-6 Pump Assembly
NOTICE
Do not hammer or force components together or damage may occur. Parts will drop into place if properly
cleaned and aligned. Use of a compatible oil is recommended during assembly.
1. Place the back plate (1603) on a table inside facing
up.
2. Place the driven gear (1608) on its stud (1606).
3. Place gear case (1602) onto back plate (1603).
Check orientation of dowel pin holes to assure they
align with the ones in the back plate.
4. Slide drive gear (1607) onto drive shaft (1605). Verify shaft key (1609) is installed properly.
5. Install drive gear (1607) and drive shaft (1605) into
back plate (1603).
6. Position top plate (1601) over drive shaft (1605) and
place onto gear case (1602).
12. Install new seals (1612). See F
FIG. 26: Seal Locations
IG. 26 and FIG. 27.
7. Rotate the gears several times to ensure free rotation.
8. Insert the dowel pins (1610) and rotate the gears
several times to ensure free rotation.
NOTE: Dowel pins are not a press fit and may be
installed using a plastic hammer if necessary.
9. Install pump plate screws (1613) and tighten to
85-105 in-lb (9.6-11.8 N•m).
10. Rotate the gears several times to ensure free rotation.
11. Apply a heat resistant, non-evaporating lubricant to
the seal area of the drive shaft (1605).
FIG. 27: Seal Orientation
13. Install seal retainers (1611) and seal retainer
screws (1614). Tighten screws to 85-105 in-lb
(9.6-11.8 N•m).
14. Align pump shaft key and slide coupling onto pump
shaft. Tighten coupling bolt just enough to hold it’s
position.
15. Attach servo motor, gear head, and top plate to
pump assembly. See F
IG. 20.
16. Separate coupling until proper gap is created. See
F
IG. 21.
17. Tighten pump block mounting shoulder bolts to
frame (1102).
18. Replace all electrical connections and fluid connections before applying fluid pressure and power.
42 3A5185B
Page 43

Repair
3A5185B 43
Page 44
Repair
1515
1512
1513†
1512
1513†
1511
1510
1504
1508
1516
1514
1509
1501
1502
1506
1503
1507
1505
† Parts included in kit 24E619.
Parts included in kit 24E825.
Parts included in kit 24E824.
(P/N: 125655)
(P/N: 125654)
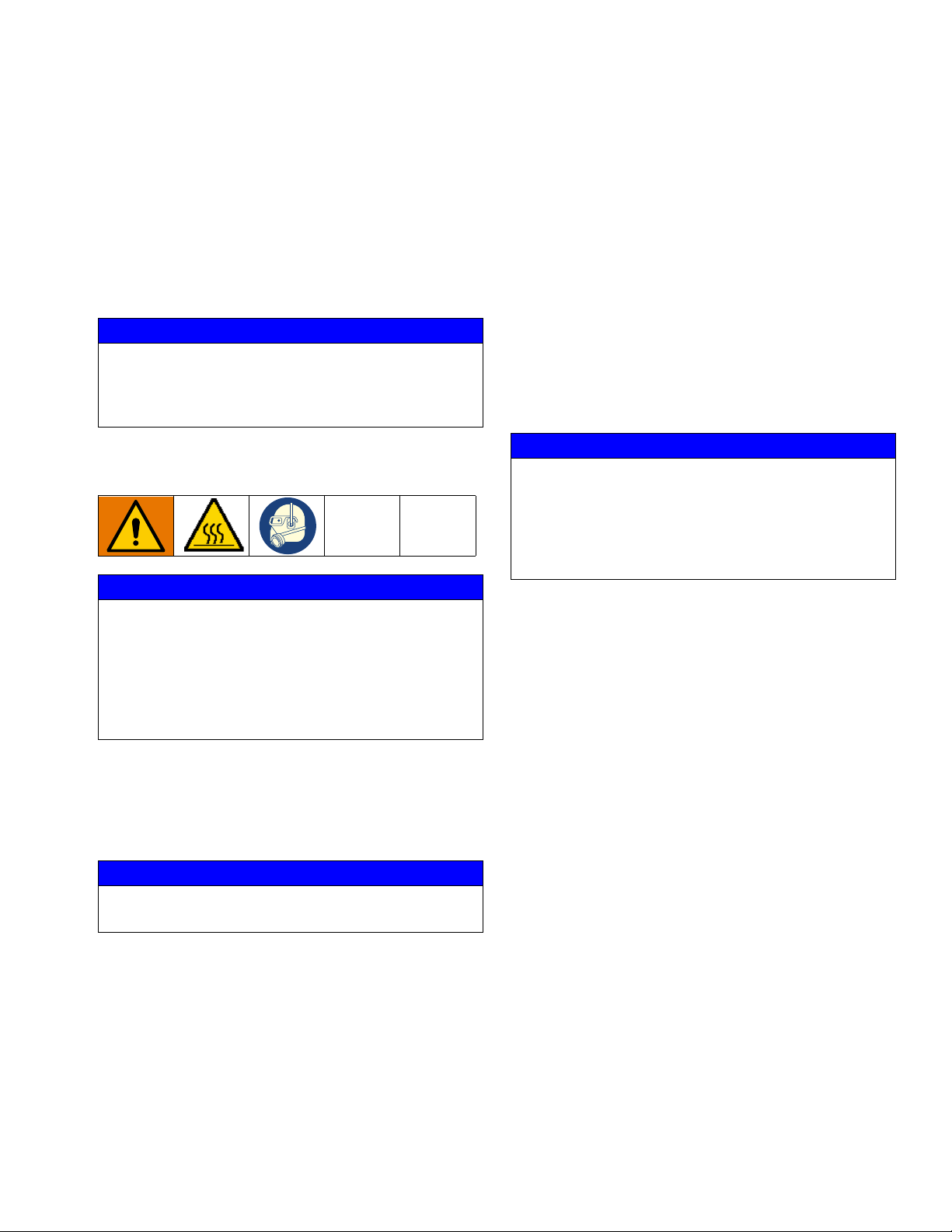
PGM-20 Pump Repair
FIG. 28: PGM-20
44 3A5185B
Page 45
Repair
PGM-20 Pump Disassembly
1. Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair,
page 35.
2. Refer to Gear Pump Maintenance Guide on
page 47 for special notes regarding gear pump
repair.
3. Remove six pump block shoulder bolts (4).
NOTICE
Pump section should be fully supported to prevent
damage being dropped. It is recommended that the
gear meter assembly be located on a work bench for
service.
4. Remove drive assembly. See F
NOTICE
IG. 23.
be needed. These will provide clearance for the
drive shaft key (1508) and the top plate (1501).
10. Support pump top plate (1501) and press drive shaft
(1504) through drive gear (1506). Stop when there
is enough clearance between the drive gear (1506)
and top plate (1501) to insert one spacer. Be sure to
allow clearance for drive key (1508).
11. Continue pressing the drive shaft (1504) and inserting spacers until the shaft is free from the drive gear
(1506).
12. The stud (1505) for the driven gear (1507) is press
fit into the back plate (1503) and need not be
removed if not worn.
NOTICE
The PGM pump design relies on a lap fit between
components for performance and sealing. Be careful
not to drop the gears (1607, 1608) or damage the
mating surfaces of the pump plates (1601, 1603) and
gear case (1602). To prevent damage, do not use pliers or screwdrivers to remove the gears.
Thicker materials may require heating prior to disassembly. Do not expose the pump to thermal shock.
Raise temperature at a maximum rate of 180°F
(100°C) per hour. Do not exceed 400°F (204°C).
Exceeding this temperature could promote leakage in
the pump. Gradually cool the pump to room temperature.
5. Remove seal retainer fasteners (1515) seal retainers (1512), spacers (1510) and (1511).
6. Remove pump dowels (1509) using an arbor press.
NOTICE
Do not use a hammer to remove dowel pins as this
will damage the pump.
7. Remove the pump plate screws (1514).
8. Separate the pump front plate (1501), gear case
(1502) and back plate (1503).
NOTE: Notches on the pump plates can be used to
separate the plates.
13. Clean all components thoroughly before reassembly. The use of an ultrasonic cleaner is recommended.
9. To remove drive shaft (1504) from the drive gear
(1506) several flat spacers 1/8 in. (3 mm) thick will
3A5185B 45
Page 46

Repair
PGM-20 Pump Assembly
NOTICE
Do not hammer or force components together, or
damage may occur. Parts will drop into place if properly cleaned and aligned. Use of a compatible oil is
recommended during assembly.
1. Place back plate (1503) on a table inside face up.
2. Install the driven gear (1507) on stud (1505).
3. Place gear case (1502) onto back plate (1503).
Check orientation of dowel pin holes to assure they
align with the ones in the back plate.
4. Place the top plate (1501) on its edge on a table.
Pass the drive shaft (1504) through the top plate
from the seal side so that the boss on the shaft rests
on the top plate.
5. Rotate the drive shaft (1504) to position the drive
key slot at the top. Insert the drive key (1508) and
driven gear (1506).
14. Align pump shaft key and slide coupling onto pump
shaft. Tighten coupling bolt just enough to hold it’s
position.
15. Attach servo motor, gear head, and top plate to
pump assembly. See F
IG. 20.
16. Separate coupling until proper gap is created. See
F
IG. 21.
17. Tighten pump block mounting shoulder bolts to
frame (4).
18. Replace all electrical connections and fluid connections before applying fluid pressure and power.
6. Grasp the top plate (1501), drive shaft (1504) and
driven gear (1506) to prevent them from separating
and carefully lower them into position onto the gear
case (1502).
7. Rotate the gears several times to ensure free rotation.
8. Insert the dowel pins (1509) and check again for
free rotation.
NOTE: Dowel pins are not a press fit and may be
installed using a plastic hammer if necessary.
9. Install pump plate screws (1514) and tighten to
85-105 in-lb (9.6-11.8 N•m).
10. Rotate the gears several times to ensure free rotation.
11. Apply a heat resistant, non-evaporating lubricant to
the seal area of the drive shaft (1504).
12. Install new seals (1513). See F
IG. 26 and FIG. 27.
13. Install spacers (1510, 1511), seal retainers, (1512)
and seal retainer screws (1515). Tighten screws to
85-105 in-lb (9.6-11.8 N•m).
46 3A5185B
Page 47

Gear Pump Maintenance Guide
Review these guidelines prior to performing any maintenance on the pumps.
• Do not run pump dry.
• Do not pull from a vacuum or negative suction head.
• Do not flush with water or other non-lubricating fluid.
• Do not pump corrosives, abrasives and/or fluids carrying particles that may harm the pump.
• Do not heat or cool pump faster than 180°F (100°C)
per hour.
• Do not drop disassembled parts on a hard surfaces
and do not let parts knock together.
• Never strike the pump parts with an iron hammer.
The parts are designed to drop in place if properly
aligned. Use arbor press to insert or remove press
fit components.
Repair
• Do not use pliers to lift the gears.
• Never use a screwdriver to pry the gears upward.
• Apply clean oil or compatible fluid during assembly.
3A5185B 47
Page 48
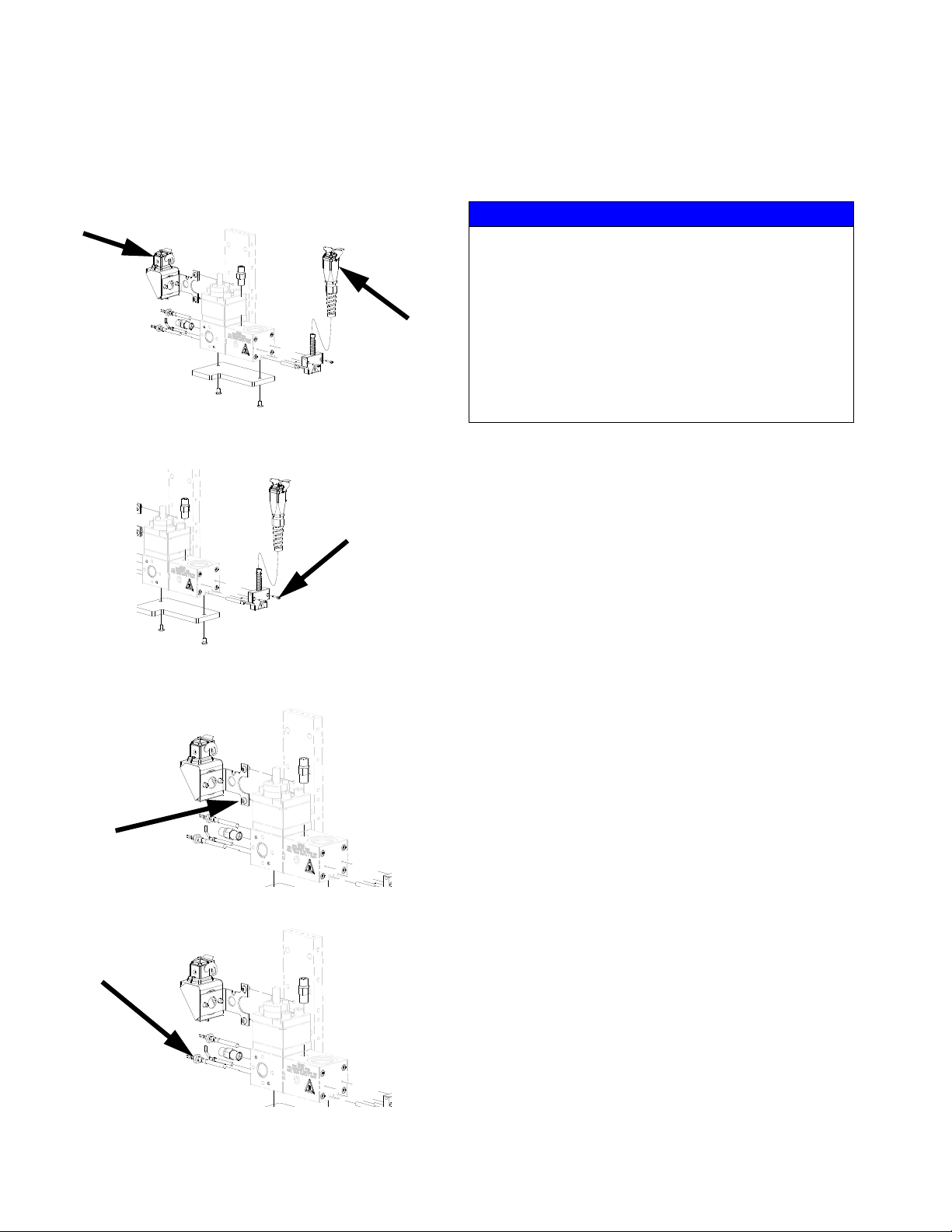
Repair
Installing new heater units and RTD sensors
1.Prepare Gear Meter Assembly for Repair, page 35.
2. Disconnect the power cables from the heaters.
3. Remove two M3 screws to remove the kit from the
inlet block.
6. Remove the heaters and sensor from the block.
NOTICE
The heaters may be difficult to remove and removal
depends on the system type. To ensure proper heat
transfer and to avoid premature heater failure,
System with through hole:
Press out the heater element using an 0.125” (3 mm)
diameter pin.
System without through hole:
Drill out the heater element using a 5mm (0.203 in.)
drill bit. Do not increase the hole diameter.
7. Clean any residue from both heater and sensor
ports.
8. Installation is the reverse of removal.
4. Remove two M6 screws to remove the kit from the
pump block.
5. Remove the two M8 heater nuts and M6 sensor nut.
48 3A5185B
Page 49

Parts
12
11
10
9
3
8
1
4
2
5
ti21285a
PGM-20 Mounting Frame
Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
1 124164 SCREW, shcs, M6-1.0 x 25 4
2 124165 SCREW, bhcs, M5-0.6 x 10 4
3 124166 SCREW, bhcs, M6-1.0 x 10 4
4 124167 SCREW, shoulder, 10x30, M8-1.25 6
5 124168 SCREW, shoulder, 8 x 6, M6-1.0 8
8 16D840 PLATE, mounting 1
9 16D841 GUSSET 2
10 16D842 PLATE 1
11 16D843 INSULATOR 1
12 16V444 GUARD, drive 1
3A5185B 49
Page 50
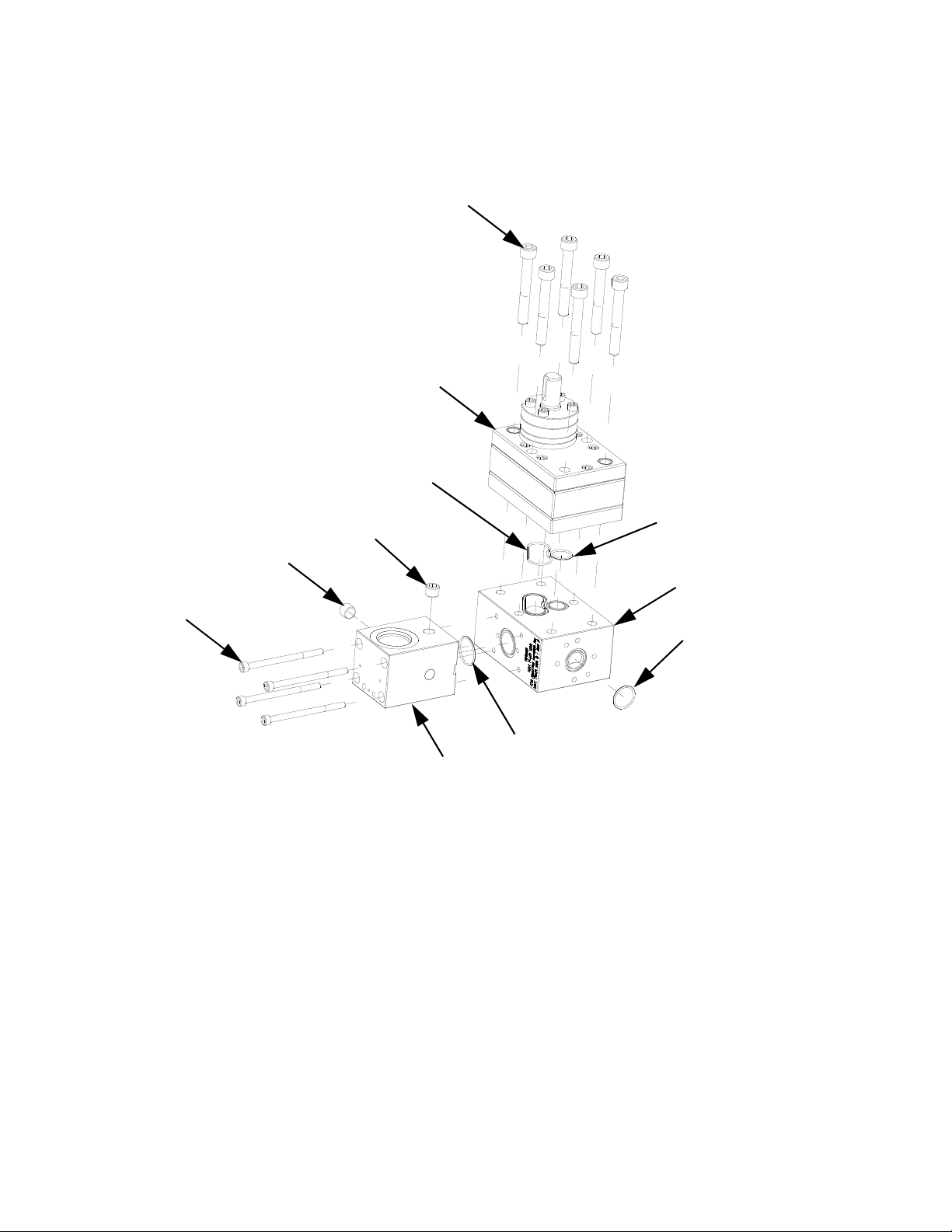
Parts
103
108
104
101
101
102
105
109
106
107
110
PGM-20 Lower Assembly Block
Ref Part Description Qty
101 101970 PLUG, pipe, headless 2
102 124173 SCREW, M6-1.0 x 90 4
103 124174 SCREW, M10-1.5 x 75 6
104† O-RING 1
105† PACKING, o-ring 1
106† PACKING, o-ring 1
107† PACKING, o-ring 1
108* 16D827 METER, gear, precision, 20cc/rev 1
109 16D915 BLOCK, pump, mounting 1
110 16D916 BLOCK, inlet, PGM 1
† Part included in o-ring kit 24E626.
* For part breakdown and repair kits, refer to PGM-20
Pump Repair, page 44.
50 3A5185B
Page 51
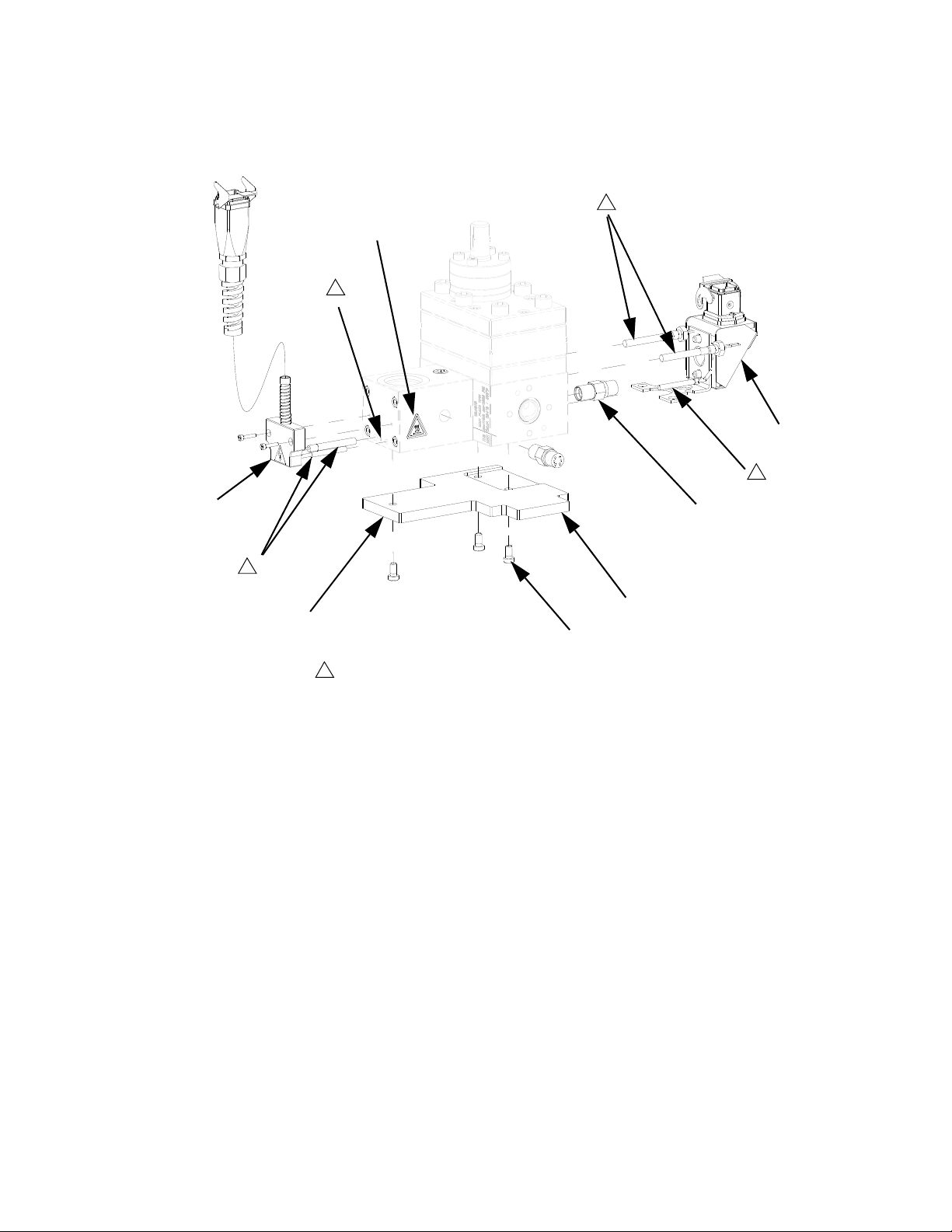
PGM-20 Pump Heat Kit
203
201
202
1
3
204
1
1
Ground location.
3
206
206
205
Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
201 117764 SENSOR, pressure 2
202 24E412 KIT, heat, pump, PGM-20 1
203 24E413 KIT, heat, PGM, inlet 1
204 125363 LABEL, heat/burn, warning 2
205 16D923 INSULATOR 1
206 124175 SCREW 3
Replacement Danger and Warning labels, tags, and
cards are available at no cost.
3A5185B 51
Page 52

Parts
301
302
303
302a
PGM Drive - 20 cc Pump
Ref Part Description Qty
301 16D947 MOTOR, PGM drive, servo, 4
frame
302 16D946 GEAR REDUCER, PGM drive,
50:1, 80mm frame
302a COVER 1
303 16D945 COUPLING, PGM drive, 18x20mm,
w/key
1
1
1
52 3A5185B
Page 53
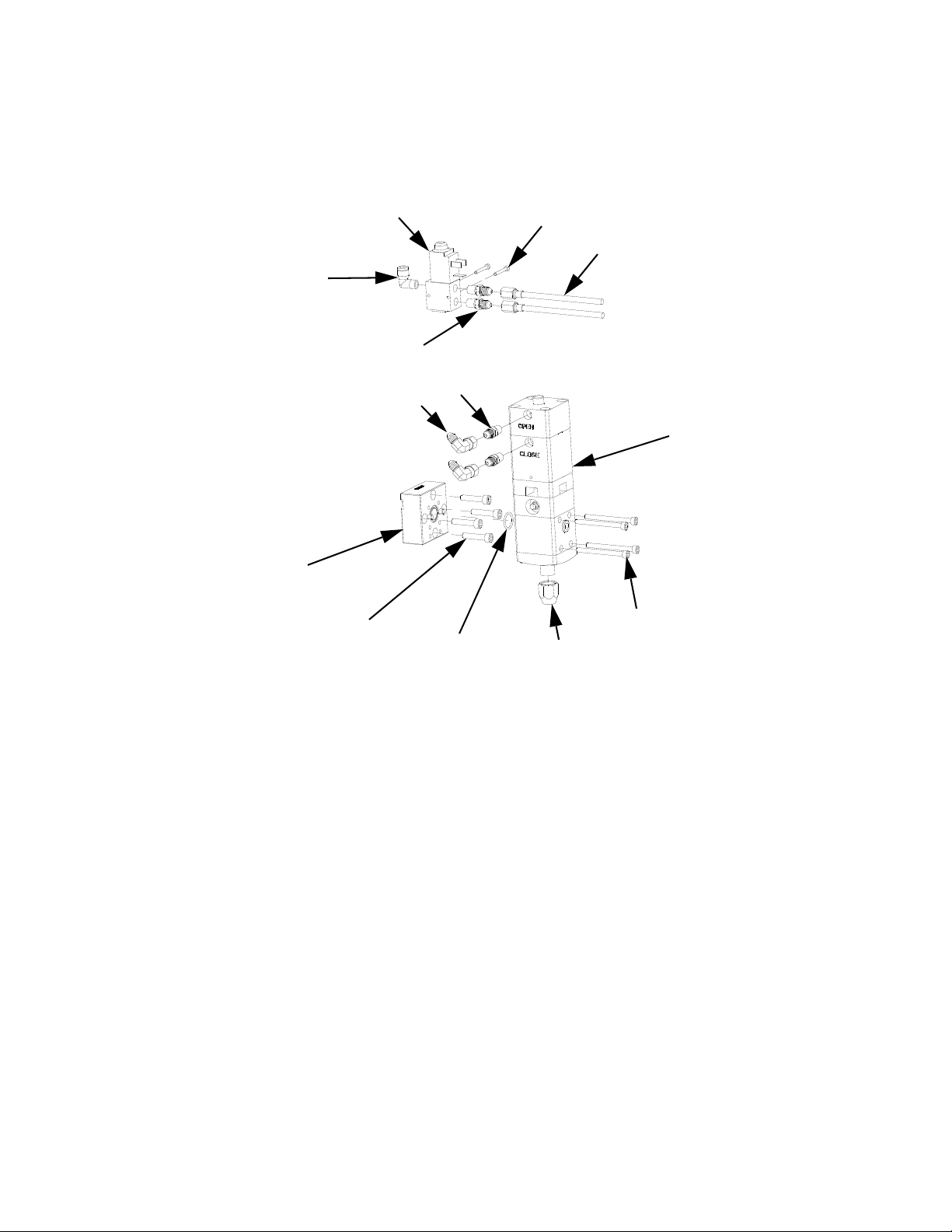
EnDure Dispense Valve Fix Mounted
410
403
405
412
404
409
411
402
406
401
408
406
407
Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
401 597151 FITTING, elbow, 1/4 tube x 1/8 NPT, male 1
402 117820 SCREW, cap, socket head, M3 2
403 124200 SCREW, socket head cap screw, M6-1.0 x 30,
stainless steel
404 124201 SCREW, socket head cap screw, M5-0.8 x 60,
stainless steel
405 116768 PACKING, o-ring 1
406 124403 FITTING, adapter, 1/8 NPTM x 03 JICM, mild steel 4
407 124405 SWIVEL, elbow, 90 deg, 03 JICF x 03 JICM, mild
408 198446 VALVE, dispense, closer 1
409 244907 VALVE, EnDure 1
410 16D943 BLOCK, mounting 1
411 16E899 HOSE, assembly, stainless steel braid, 3/16 x 12 2
412 C32089 RETAINER, seat 1
steel
4
4
2
3A5185B 53
Page 54

Parts
652
624
609
626, 612
618
622, 625
601
614
614
614
616
616
617
615
615
614
617
611, 612, 613
606
608
607
604
605
610
651
603
620
619
602
Gear Meter Assembly Panel
54 3A5185B
Page 55
Parts
Part
Ref
601
---
Description Qty
ENCLOSURE, control, gear meter
1
painted
602 25C836 MODULE, HMI, PGM 1
603 121148 HANDLE, disconnect, electric 1
604 81/2060-
BUTTON, dual, grn/red, w/pl-wht 1
P/11
605 81/2065-
BUTTON, operator, pl, red 1
R/11
606 81/2065-
BUTTON, operator, pl, green 1
G/11
607
---
LABEL, legend, panel, PGM 1
608 16D363 BUTTON, operator, pb, flush, black 1
609
---
610
---
611 81/1060-
14/25
FITTING, bulkhead, gland, 9wire 1
GRIP, cord, .35-.63, 3/4 1
CONNECTOR, sq, 14pw/key, 7a,
panel m
1
612 96/0360/99FASTENER, shc, 4-40x0.25, ms, e 12
613
---
COVER, dust, amp17 conn w/chain1
614 81/2070/11LATCH, operator 4
Part
Ref
615 81/2080-
Description Qty
CONTACT, block, no 2
1/11
616 81/2072-
LIGHT, led, white, 24vdc, latch 3
2/11
617 81/2081-
CONTACT, block, nc 2
1/11
619 81/2060-
BUTTON, mush, maint, twist, red 1
E/11
620 81/2060-
LABEL, legend, e-stop, 60mm 1
EL/11
622 126987 CABLE, communication 1
624 84/0130-
LABEL, prot earth(grnd).375x.375 1
23/11
625
---
626 81/1060-
4/25
STRAP, wrap, spiral, 1/2'', nylon 4
CONNECTOR, sq, 4p w/key, 7a,
panel m
2
651 196548 LABEL, caution 1
652 15M511 LABEL, warning,
1
english/spanish/french
Replacement Danger and Warning labels, tags, and
cards are available at no cost.
Cables
Description 3 Meter 6 Meter 9 Meter 15 Meter
Servo Power Cable 17R673 17R674 17R675 17R676
Feedback Cable 17R677 17R678 17R679 17R680
Dispense Valve 24E571 24E572 24E573 24U020
3A5185B 55
Page 56
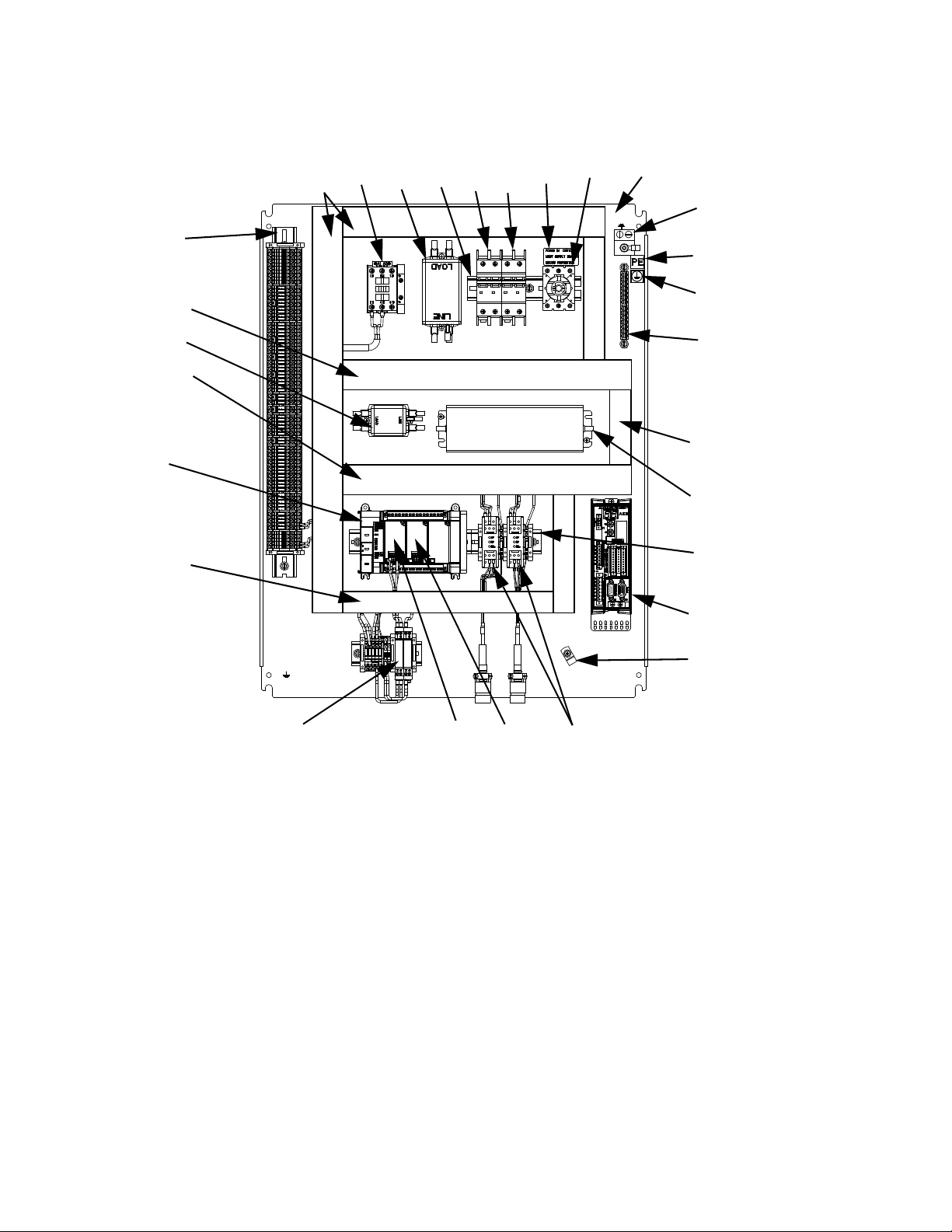
Parts
718, 720
718, 720
718, 720
716
701
704
729
728
719, 721
710, 725
727
726, 728
717
714
722*
746 713
711
705
708
709
717
706
707
731
702, 707
712
715
PGM Back Panel
Ref Part Description Qty
701
---
702 123361 SWITCH, disconnect, 32a 1
703 124228 EXTENSION, disconnect,
704 117666 TERMINAL, ground 1
705 U70077 TERMINAL, lug, ground, bus type 1
706 123298 CIRCUIT, breaker, 2p, 20a, ul489 1
707 123296 CIRCUIT, breaker, 2p, 1a, ul489 1
708 123359 RELAY, contactor, 30a, 3p, 24vdc co1
709 130185 FILTER 1
710 121808 POWER SUPPLY, 24vdc, 4.0a,
PANEL, back, for30x24 encl,
conduit
230-350mm
100w
1
1
1
Ref Part Description Qty
711 123718 FILTER, emi, 6a, spade con 1
712 25C833 MODULE, plc, 14di/10do, 24dc 1
713 129709 MODULE, analog in 1
714 U70899 MODULE, ana-out 1
715 25C834 DRIVE, indexer (PGM-06 only) 1
716
717
718
719
720
721
25C835 DRIVE, indexer (PGM-20 only) 1
---
---
---
---
---
---
STRIP, terminal, PGM, control 1
RAIL, din 1
WIREWAY, panduit, 1.5""x3.0""x6' 6
WIREWAY, panduit, 1"x3"x6' 6
COVER, panduit, 1.5""x6' 6
WIREWAY, cover, panduit, 1"x6' 6
56 3A5185B
Page 57
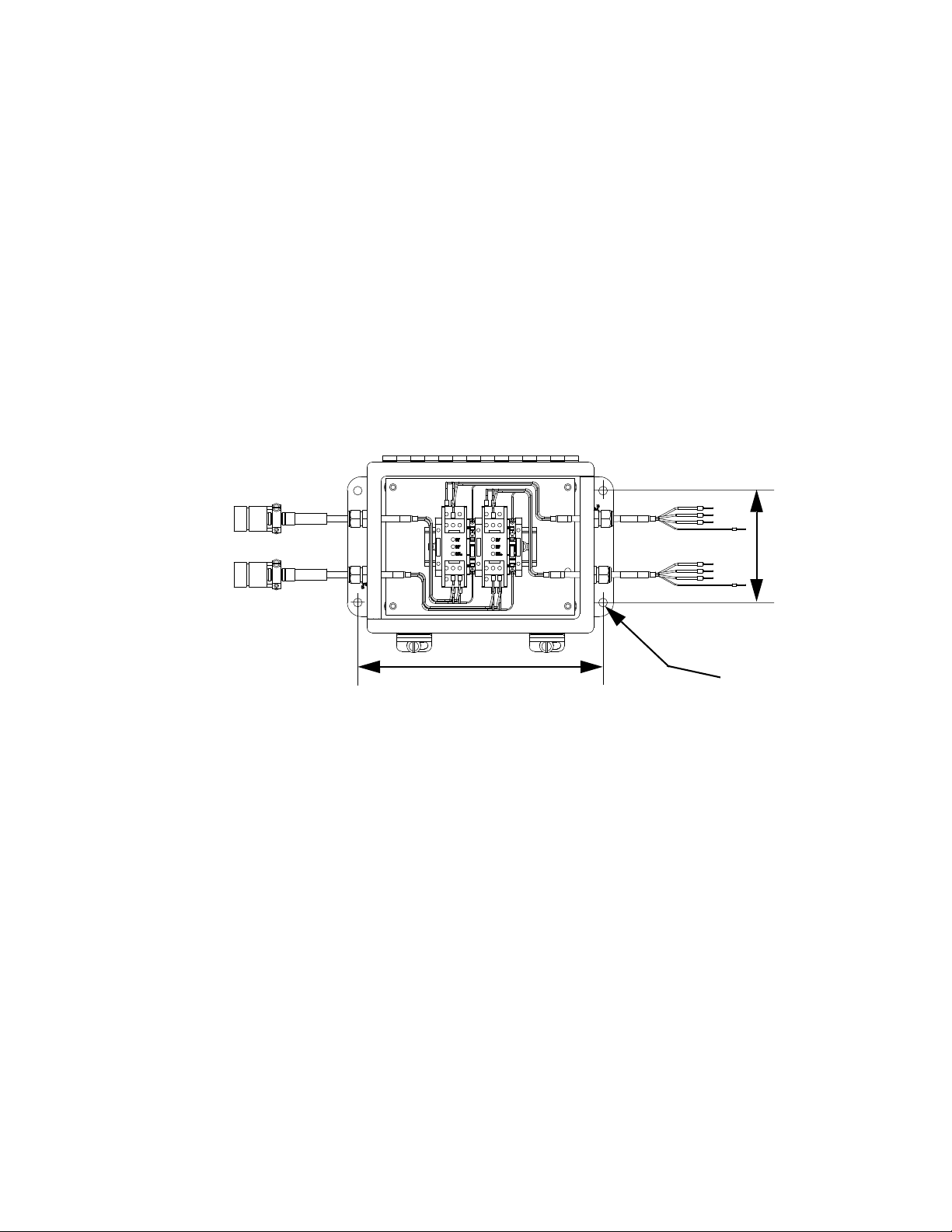
Parts
8.77 in.
(222.76 mm)
Ø .31 in.
(7.87 mm)
4.0 in.
(101.6 mm)
Ref Part Description Qty
722 129710 AMPLIFIER, signal conditioner,
PGM (3, 6, or 9 m cables)
725 120997 CABLE, turck, rs 4t-4 1
727
---
CLAMP, wire, harness, 1/4,
galvaniz
2
1
Remote Mount Amplifiers
Only for control centers with 15 m cables.
Ref Part Description Qty
728 84/0130-
23/11
729 84/0130-
26/11
746 --- MODULE, varistor 1
Replacement Danger and Warning labels, tags, and
cards are available at no cost.
LABEL, prot earth (grnd).375x.375 1
LABEL, pe 1
3A5185B 57
Page 58
Parts
809
807
808
805
804
PGM Remote Dispense Valve
Ref Part Description Qty
804 FITTING 1
805 117820 SCREW, cap, socket head, M3 2
807 124200 SCREW, shsc, M6-1.0 x 30, stain-
808 198446 VALVE, dispense, closer 1
809 16E055 BLOCK, outlet, PGM, 3/4 NPTF,
less steel
stainless steel
4
1
58 3A5185B
Page 59

PGM Ambient Transducer
901901901
20 cc Pump 6 cc Pump
901
Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
901 124517 SENSOR, pressure 2
NOTE: Ambient sensors are used on models PGx1xx
(unheated). See technical page for ambient operating
temperature range.
3A5185B 59
Page 60
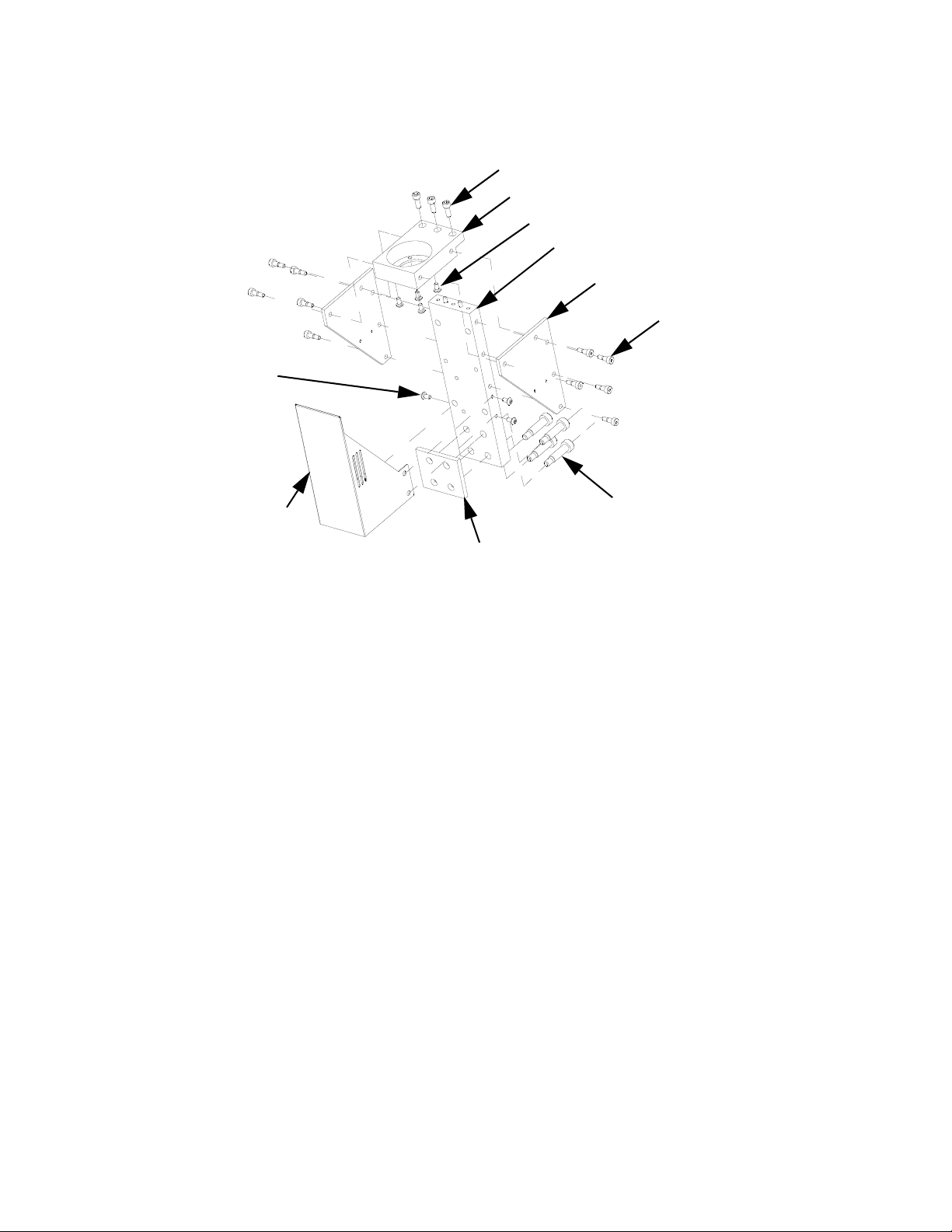
Parts
1107
1103
1105
1106
1104
1102
1108
1109
1101
1101
PGM-6 Mounting Frame
Ref Part Description Qty
1101 124165 SCREW, bhcs, M5-0.8 x 10, stain-
less steel
1102 124167 SCREW, shoulder, 10 x 30,
M8-1.25, stainless steel
1103 124313 SCREW, shcs, M6-1 x 16 mm,
stainless steel
1104 124314 SCREW, shoulder, 6 x 8, M5 - 0.8,
carbon steel
1105 16E327 PLATE, mounting, drive, PGM-6 1
1106 16E328 GUSSET, drive, PGM-6 2
1107 16E329 PLATE, mounting, pump, PGM-6 1
1108 16E330 INSULATOR, pump, PGM-6 1
1109 16E331 GUARD, drive, PGM-6 1
7
4
3
8
60 3A5185B
Page 61
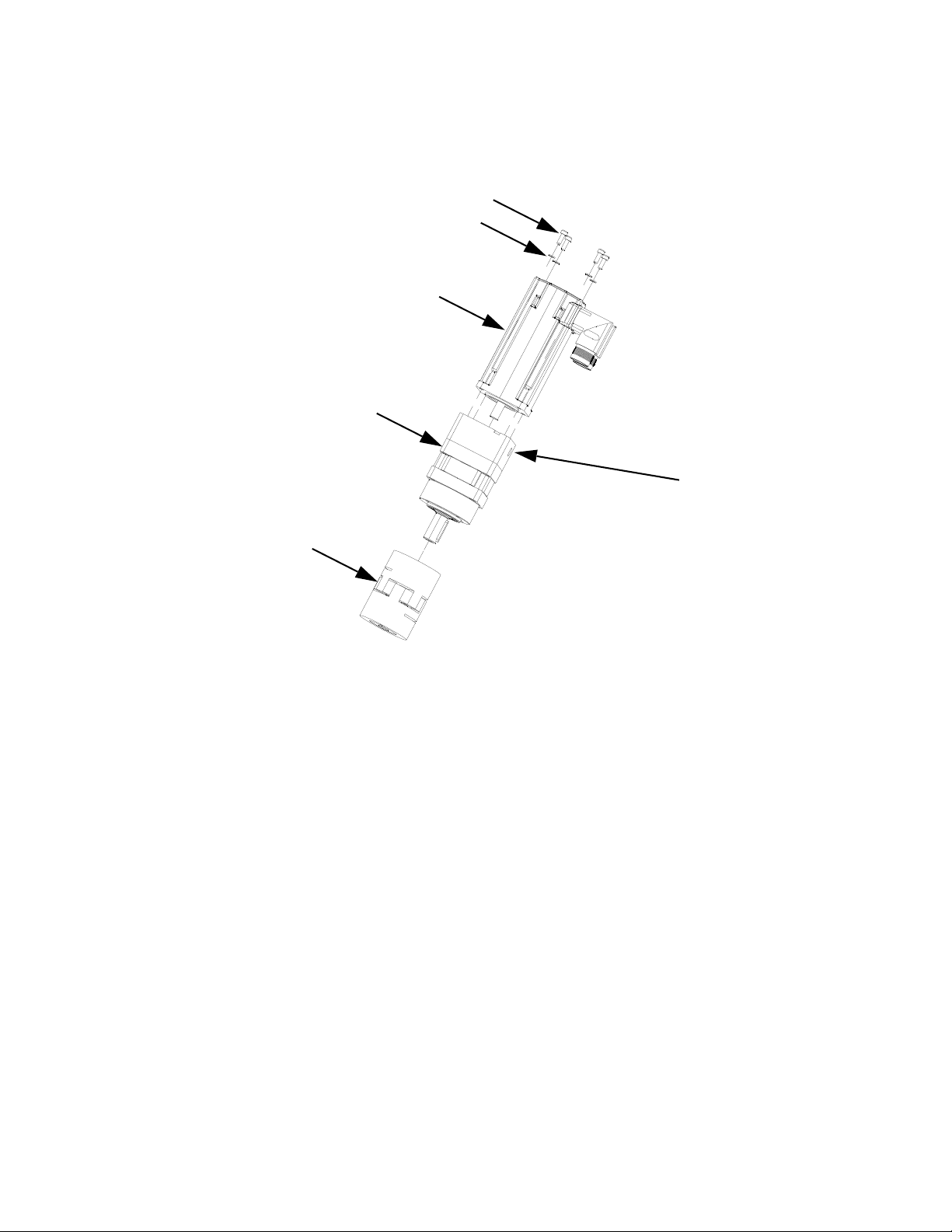
PGM-6 Drive Kit
1203a
1203b
1203
1202
1201
1202a
Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
1201 16E367 COUPLING, PGM drive, 12 mm x
14 mm, with key
1202 16E368 GEAR REDUCER, PGM drive,
50:1, 60 mm frame
1202a COVER 1
1203 16E369 MOTOR, PGM drive, frame 1
1203a SCREW 4
1203b WASHER 4
1
1
3A5185B 61
Page 62
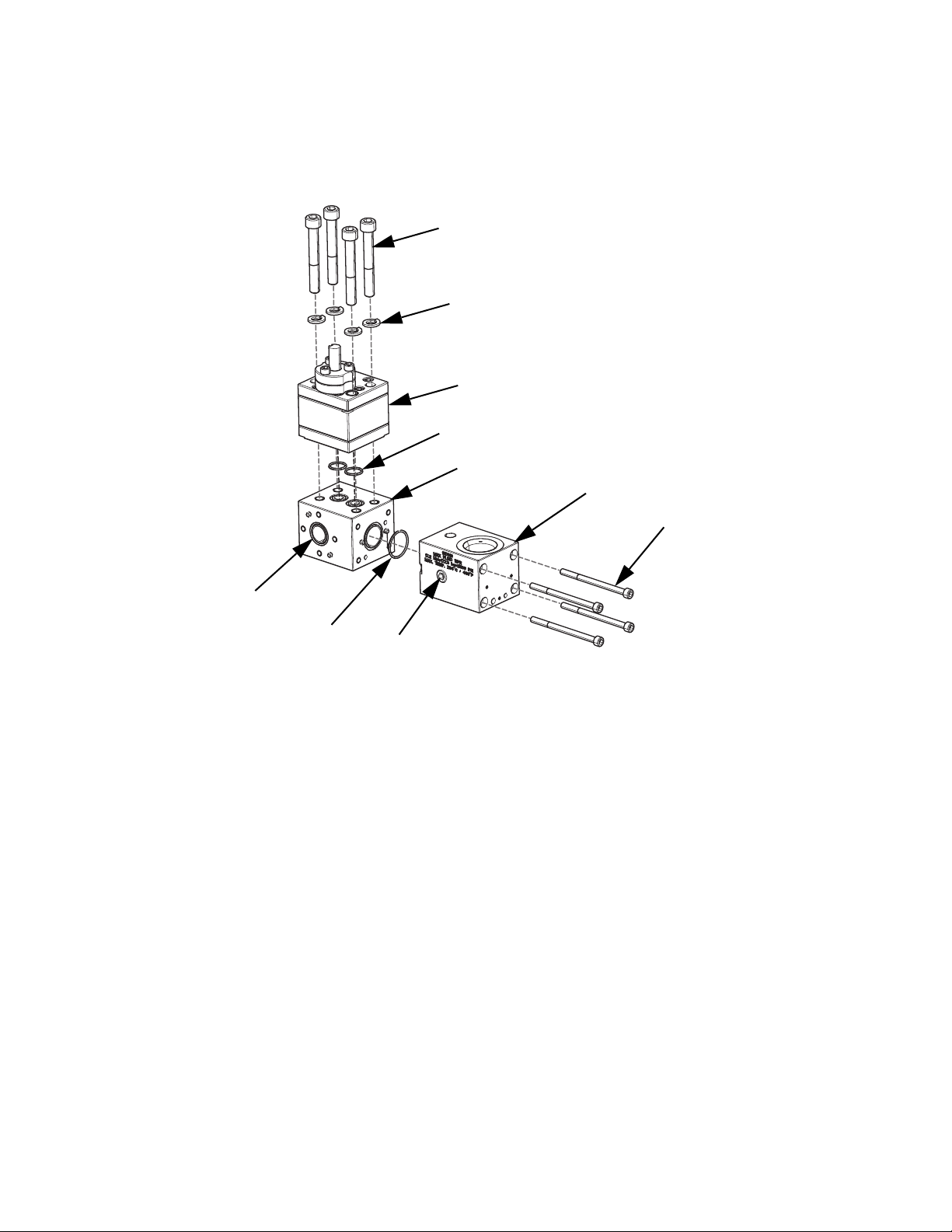
Parts
1303
1309
1304
1308
1302
1307
1310
1305
1306
1301
PGM-6 Lower Assembly Block
Ref Part Description Qty
1301 101970 PLUG, pipe, headless 2
1302 124173 SCREW, shcs, M6-1.0 x 90, stain-
less steel
1303 124174 SCREW, shcs, M10- 1.5 x 75,
stainless steel
1304† --- PACKING, o-ring 2
1305† --- O-RING 1
1306† --- PACKING, o-ring 1
1307 16D916 BLOCK, inlet, PGM 1
1308 16E340 BLOCK, pump mounting, PGM-6 1
1309* 24E832 METER, gear, precision, 6cc/rev 1
1310 16K738 WASHER, split, lock, M10, sst 4
† Parts are available in o-ring kit 24E677.
* For part breakdown and repair kits, refer to PGM-6
Pump Repair, page 40.
62 3A5185B
4
4
Page 63
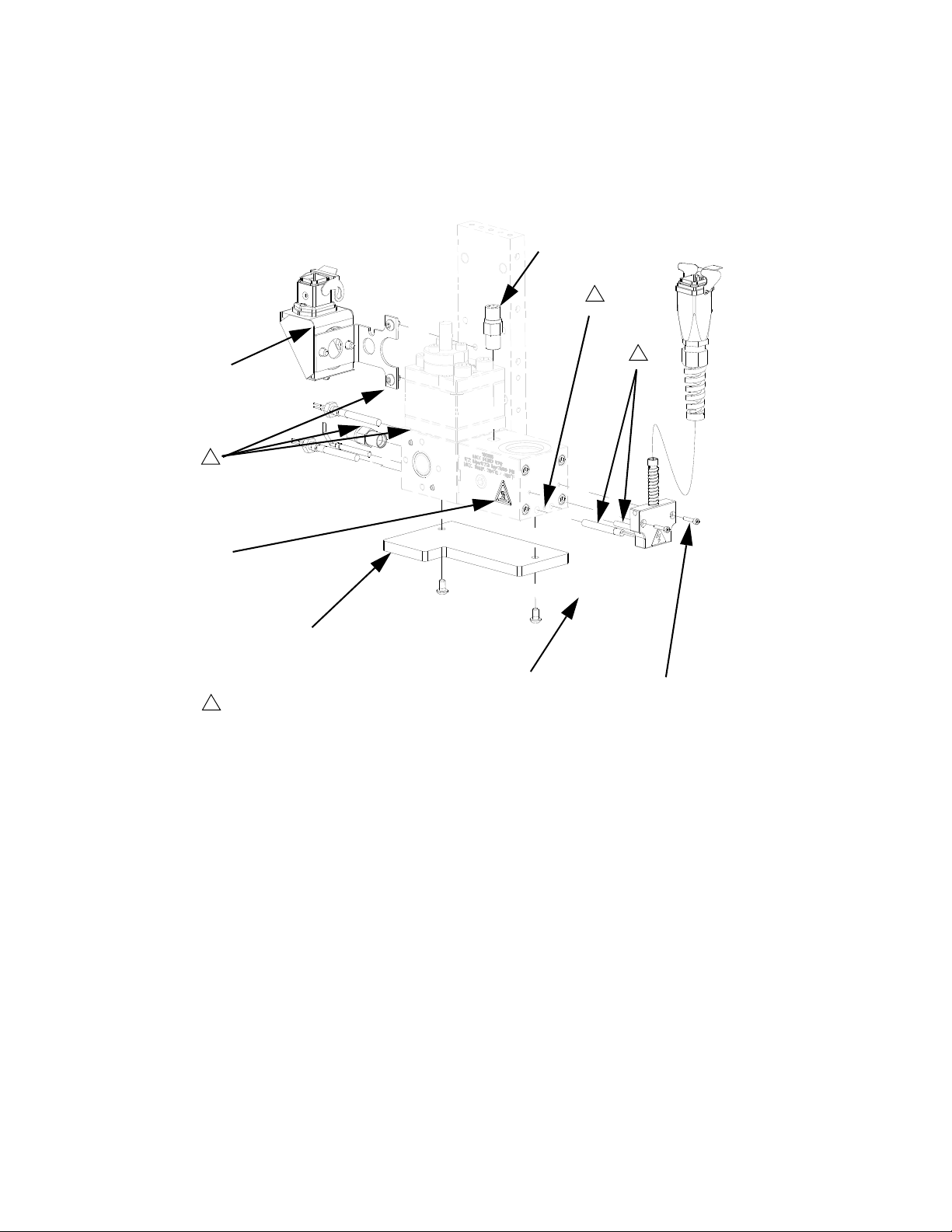
PGM-6 Pump Heat Kit
1
3
1401
1405
1402
Ground location.
3
1406
1403
1
1404
Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
1401 117764 SENSOR, pressure 2
1402 24E732 KIT, heat, pump, PGM-6 1
1403 24E413 KIT, heat, PGM, inlet 1
1404125363 LABEL, heat, warning 2
1405 16E366 INSULATOR 1
1406 124166 SCREW 2
Replacement Danger and Warning labels, tags, and
3A5185B 63
cards are available at no cost.
Page 64

Schematics
CUSTOMER MUST SUPPLY BRANCH CIRCUIT PROTECTION
50-60HZ
1PH/
230V/
DISC-1
L21L2
L11L1
GND
1L1
CB5
1L1
1L21L2
1L1
CB1A
1L1
1L21L2
20A
5A
110
111
100
101
GND
FIL-1
LOAD
LINE
102
103
GND
FIL-2
LOAD
LINE
112
113
X3
AC
POWER
GND
-RB
-DC
+RB
L1
L2
L3
PE
PS-1
N
24V DC
L
FG
V-
V+
130
125
104
105
HARNESS
10 AWG
10 AWG
12 AWG
16 AWG
DC COM
2
PG-PS1
3
PG-PS1
HARNESS 120997
1
PG-PS1
12 AWG
CABLE FROM PS-1
P
N
P
N
P
N
P
N
17S930
104
105
HARNESS
17S895
DVS-1
DVS-2
14 AWG
14 AWG
105
104
140
149
147
145
142
110
138
136
134
132
130
128
126
124
122
120
118
114
116
112
108
106
104
102
100
141
148
144
146
143
111
139
137
135
133
131
129
127
125
123
121
119
115
117
113
109
107
105
103
101
CRM
12
CRM
34
4
3
2
1
7
6
5
BRN
BLU
WHT
BLU
BRN
Schematics
FIG. 29: Schematics, Page 1 of 10
64 3A5185B
Page 65
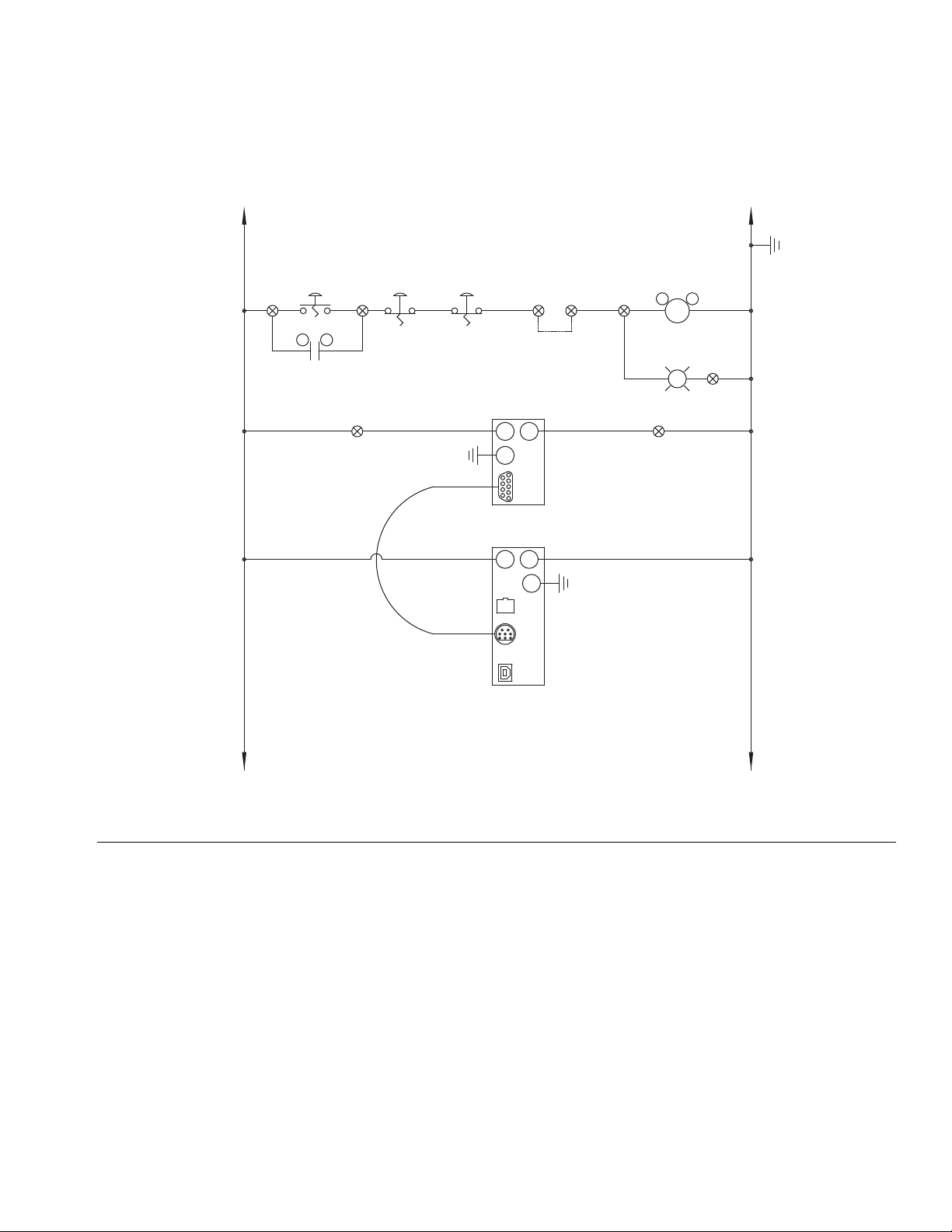
Schematics
CRM
A1 A2
5
9
3
8
7
4
1
6
2
0X
I
PB-1
125
CONTROL POWER
140
CONTROL_PWR
ON
PL-3
130
0
PB-1A
XO
24
VDC
REMOTE STOP
125
125
130
130
130
141
142
143
143
DC COM
PB-2
XO
E-STOP
HMI1
PE
+
_
RS232
PORT
125
130
CAB-1
126987
PLC1
FG
+24 COM
RS232
PORT
125
130
USB PORTPROGRAMMING
ETHERNET
PORT
190
199
197
195
192
160
188
186
184
182
180
178
176
174
172
170
168
164
166
162
158
156
154
152
150
191
198
194
196
193
161
189
187
185
183
181
179
177
175
173
171
169
165
167
163
159
157
155
153
151
W
125 130
125 130
CRM
56
FIG. 30: Schematics, Page 2 of 10
3A5185B 65
Page 66

Schematics
0X
PB-3
MANL-PURGE
24
VDC
130
CONTROL POWER
1
2
5
125
DC COM
PG-IO
PG-IO
PG-IO
125
320
14
PG-IO
310
ONBOARD DIGITAL
INPUTS
I-04
I-05
I-06
I-07
COM
0
PLC-1
AUTOMATION
START
AUTOMATION
JOB COMPLETE
MANUAL START
X8
125
DRIVE-1
FAULT
24VDC+
12524VDC+
DRIVE-1
RUN
CONNECTOR
SPARE
I-00
I-01
I-02
I-03
SPARE
HARNESS
17R672
DRIVE-1 I/O
X7
CONNECTOR
HARNESS
17R671
DRIVE-1 I/O
125 130
XXX XXX
240
249
247
245
242
210
238
236
234
232
230
228
226
224
222
220
218
214
216
212
208
206
204
202
200
241
248
244
246
243
211
239
237
235
233
231
229
227
225
223
221
219
215
217
213
209
207
205
203
201
125
125
1
2
5
6
ORG
ORG
ORG
310
212
210
208
206
204
202
200
FIG. 31: Schematics, Page 3 of 10
66 3A5185B
Page 67

Schematics
24
VDC
130
DC
COM
DRIVE-1
I-08
COM
01
ONBOARD DIGITAL
INPUTS
PLC-1
HARNESS
17R671
X7
12524VDC+
CONNECTOR
DRIVE-1 I/O
DIGITAL-OUT1
I-09
I-10
I-11
I-12
I-13
RESERVED
SPARE
SPARE
SPARE
SPARE
125 130
125 130
258
265
263
260
256
254
252
250
259
266
262
264
261
257
255
253
251
267
268
279
298
296
294
292
290
287
283
285
281
277
275
273
271
269
280
299
297
295
293
291
289
284
286
282
278
276
274
272
270
288
125
7
8
214
.
.
.
.
.
FIG. 32: Schematics, Page 4 of 10
3A5185B 67
Page 68
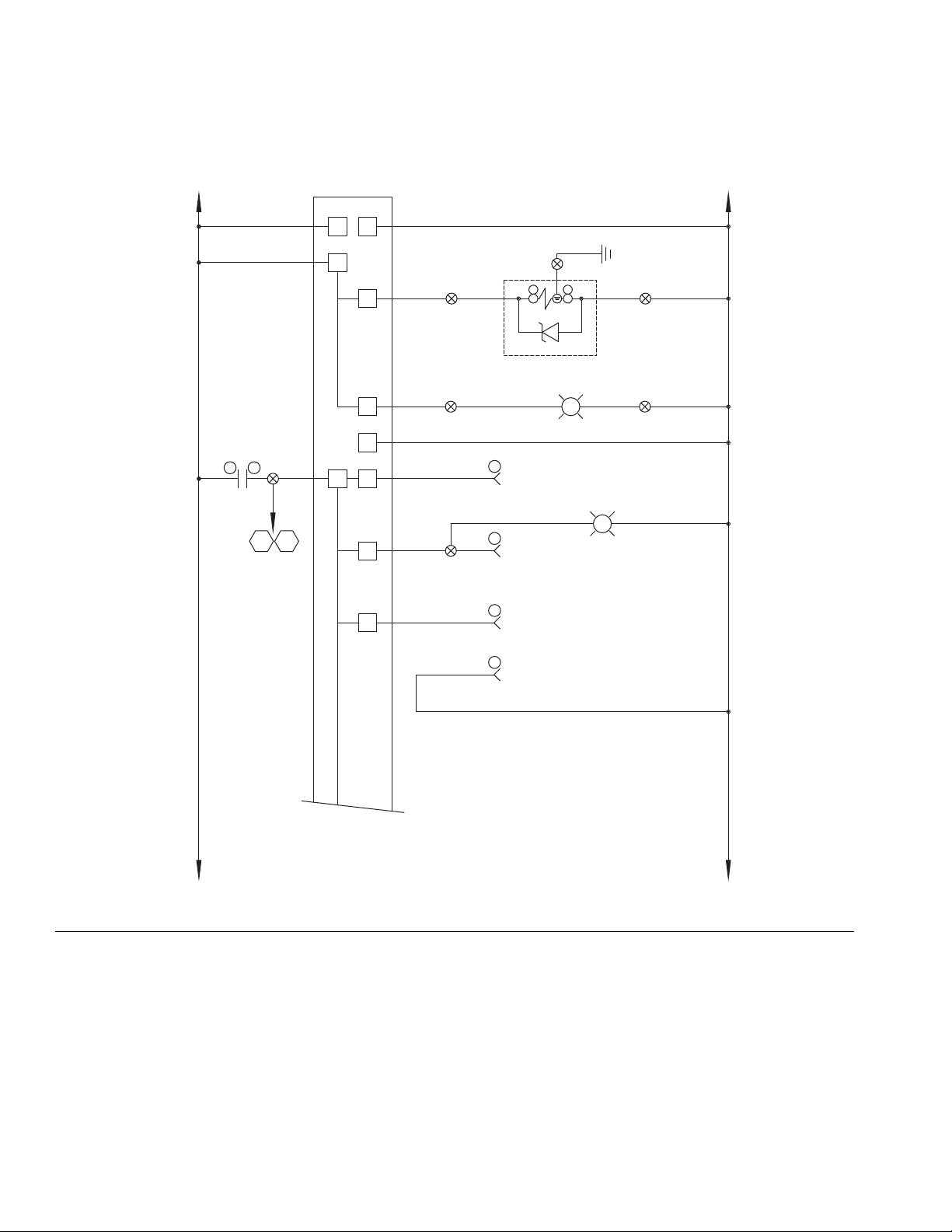
Schematics
125
24VDC
130
130
DC
COM
R
FAULT
PL-2
DISPENSE
VALVE
OPEN
130
SOL-DV
+
1
RED
-
2
WHT
BLK
DC
ONBOARD DIGITAL
OUTPUTS
+24
+
CM0
+
CM1
DC
-24
O
00
O
01
-
CM0
0
02
PLC-1
125
130
125
310
GEARMETER
FAULT
GEARMETER
FAULT
IN CYCLE
GEARMETER
11
12
6
130
24VDC
COMMON
PG-IO
PG-IO
PG-IO
0
03
0
04
249
508
READY TO
DISPENSE
GEARMETER
10
PG-IO
G
READY
PL-1
130
125 130
125 130
310
319
317
315
312
308
306
304
302
300
311
318
314
316
313
309
307
305
303
301
329
336
334
331
326
324
322
320
330
337
333
335
332
328
325
323
321
327
348
346
344
342
340
338
349
347
345
343
341
339
CRM
13 14
306
308
300
304
302
302
FIG. 33: Schematics, Page 5 of 10
68 3A5185B
Page 69
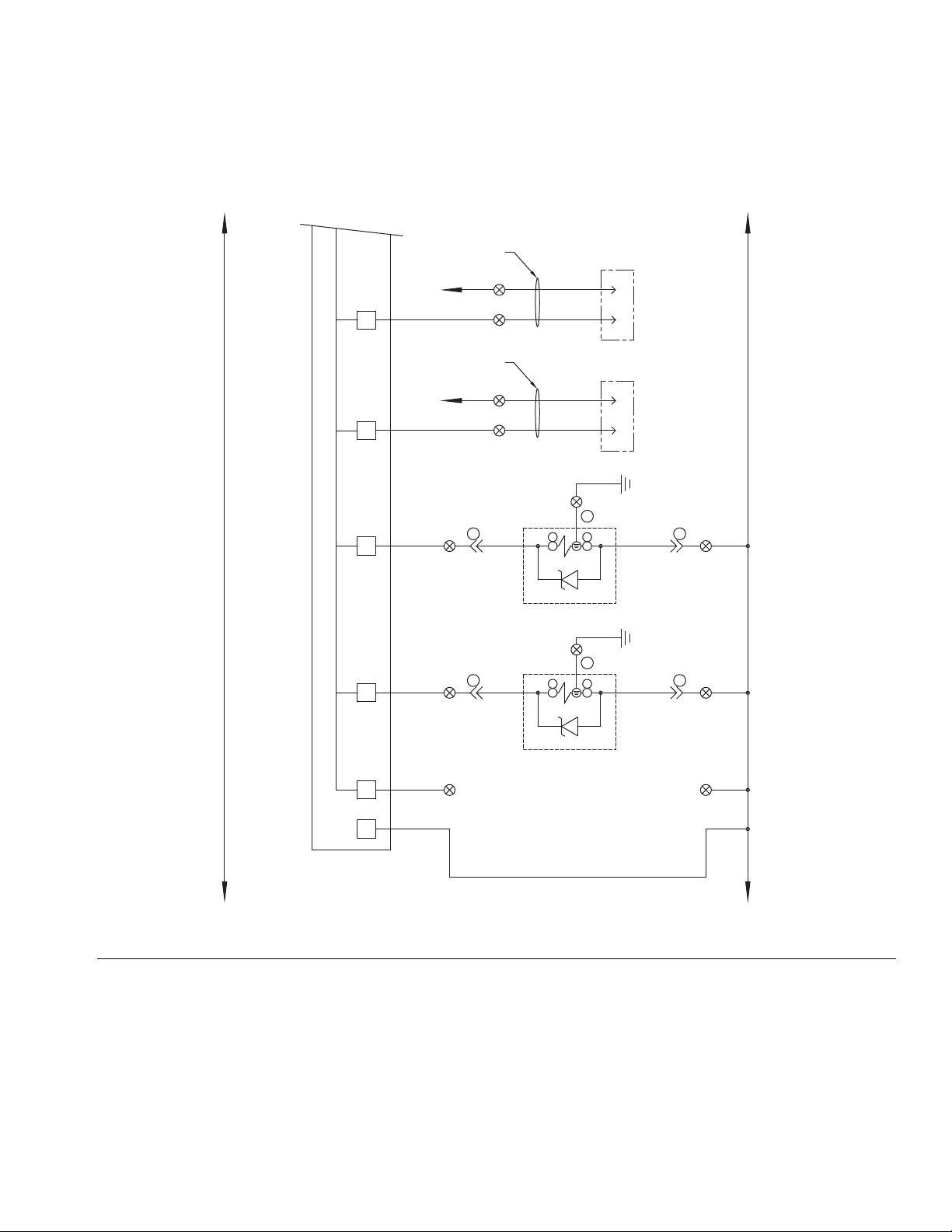
Schematics
RESERVED
24VDC
DC
COM
X8
CONNECTOR
130
312
DC COM
HARNESS
17R672
DRIVE-1 I/O
DRIVE-1
ENABLE
PRIMARY A
DYNAMIC REGULATOR
130
130
SOL-B
BLK
+
1
RED
-
2
WHT
PG-B
2
PG-B
1
3
TANDEM B
130
SOL-A
BLK
+
1
RED
-
2
WHT
PG-A
2
PG-A
1
3
130
DYNAMIC REGULATOR
0
05
0
06
0
07
0
08
ONBOARD DIGITAL
OUTPUTS
PLC-1
0
09
-
CM1
X7
CONNECTOR
130
314
DC COM
HARNESS
17R671
DRIVE-1 I/O
DRIVE-1
DIGITAL-IN3
130
125 130
125 130
378
387
385
383
380
376
374
372
370
368
366
364
362
360
358
356
352
354
350
379
386
382
384
381
377
375
373
371
369
367
365
363
361
359
357
353
355
351
391
398
396
393
389
392
399
395
397
394
390
388
130
4
3
4
1
318
314
316
312
320
130
FIG. 34: Schematics, Page 6 of 10
3A5185B 69
Page 70
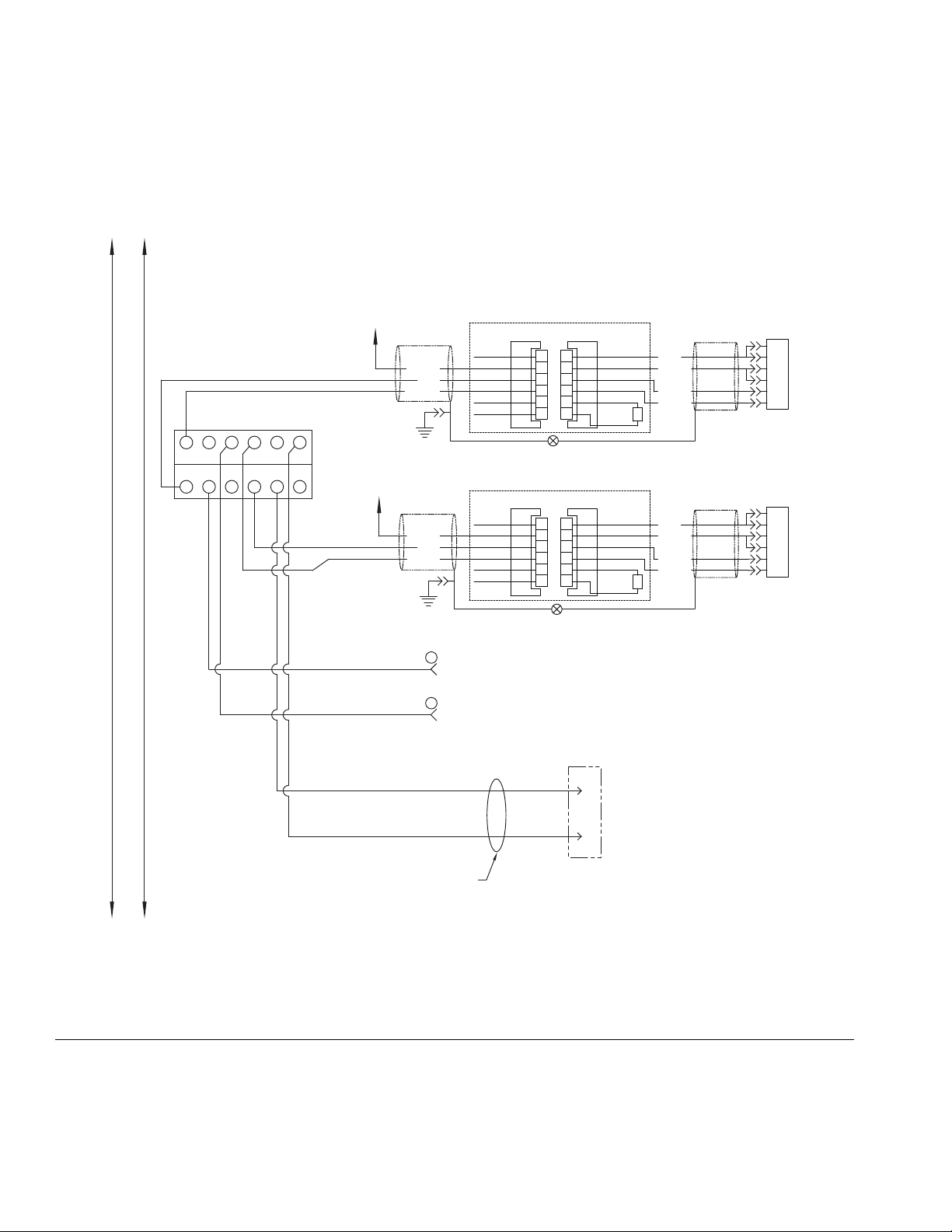
Schematics
+EXCITATION
-EXCITATION
-SIGNAL
+SIGNAL
POWER TRANSDUCER
WHITE
GREEN
BLACK
RED
WHITE
RED
BLACK
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
-SHUNT
+SUPPLY
-SUPPLY
+OUTPUT
-OUTPUT
+SHUNT
+EXCITATION
-EXCITATION
.
POWER TRANSDUCER
BLACK
RED
WHITE
RED
BLACK
RES A
RES B
.
.
.
.
.
.
-SHUNT
+SUPPLY
-SUPPLY
+OUTPUT
-OUTPUT
+SHUNT
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
RES A
RES B
A
B
C
D
E
F
-SIGNAL
+SIGNAL
WHITE
GREEN
A
B
C
D
E
F
400
130
24VDC
COM
DC
INLET
PRESURE
TRANSDUCER
402
130
24VDC
OUTLET
PRESURE
TRANSDUCER
404
7
130
8
0-10 VDC
ANALOG FLOW COMMAND
ANALOG COM
FROM AUTOMATION
PG-IO
PG-IO
X8
CONNECTOR
408
HARNESS
17R672
DRIVE-1 I/O
ANALOG-OUT +
PLC ANALOG IN MODULE
DRIVE-1
A GND
DRIVE-1
24VDC
130
406
404
402
405
403
400
401
442
449
447
444
411
440
438
436
434
432
430
428
426
424
422
419
415
417
413
409
407
443
446
448
445
412
441
439
437
435
433
431
429
427
425
423
421
416
418
414
410
408
420
125 130
125
125 130
125
7
8
ORG
ORG
COM
VI-0
CI-2
COM
COM
VI-1
VI-3
CI-1
CI-3
COM
VI-2
CI-0
B3 B4 B6B1 B2 B5
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
INLET AMP
OUTLET AMP
FIG. 35: Schematics, Page 7 of 10
70 3A5185B
Page 71
Schematics
24VDC
COM
DC
HARNESS
17R672
DRIVE-1 I/O
ANALOG OUT
0-10 VDC
COMMANDED
FLOW TO DRIVE
PLC ANALOG OUT MODULE #1
412
410
DRIVE-1
ANALOG-IN COM
ANALOG-IN +
X8
CONNECTOR
410
412
RESERVED
451
450
461
468
466
463
458
456
454
452
462
469
465
467
464
460
457
455
453
459
474
471
470
473
472
475
486
498
496
494
490
492
488
484
482
480
478
476
487
499
497
495
491
493
489
485
483
481
479
477
125 130
125 130
10
9
B1
VO-0
COM
CO-0
COM
VO-1
COM
CO-1
COM
B2 B3 B4
A1 A2 A3 A4
FIG. 36: Schematics, Page 8 of 10
3A5185B 71
Page 72
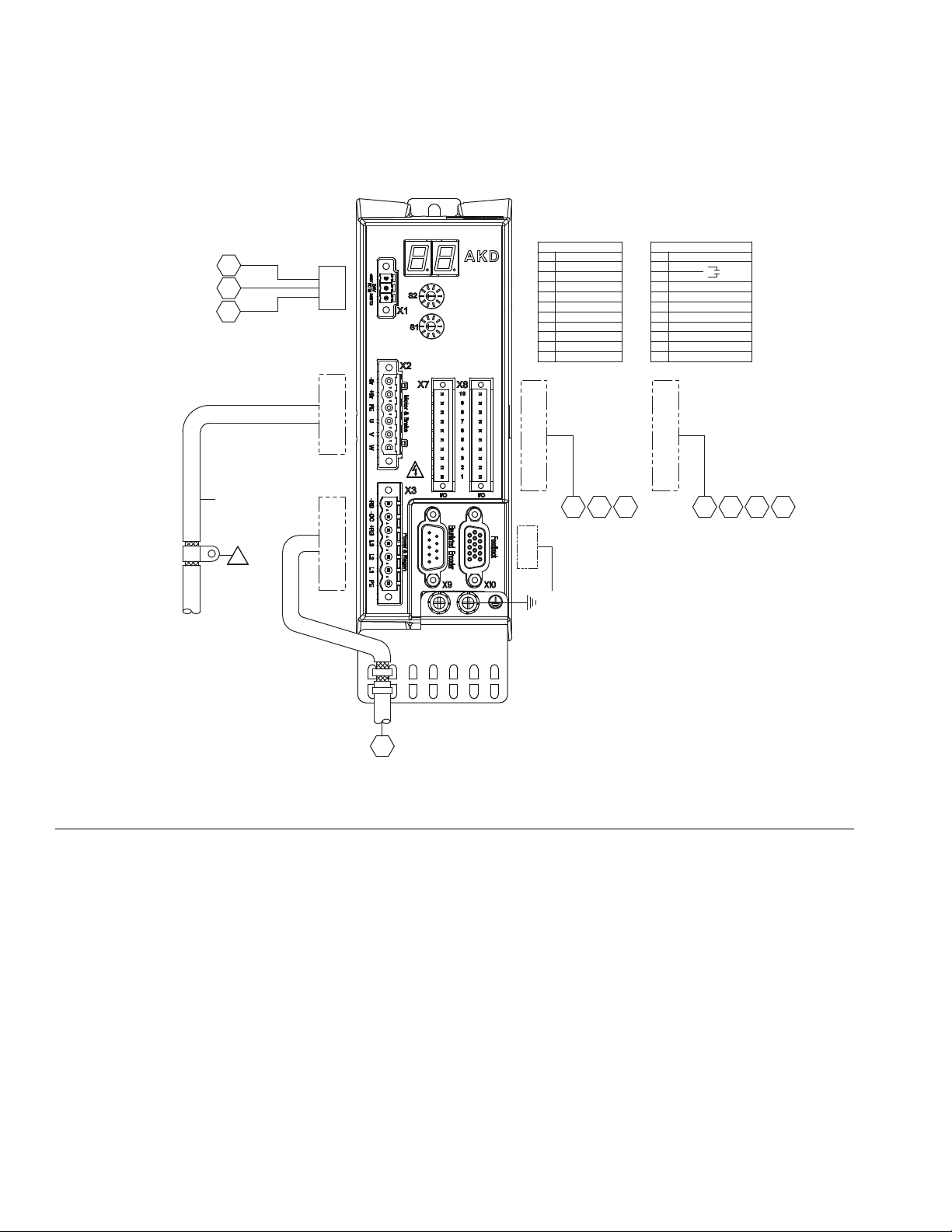
Schematics
6
POWER
CABLE
FEEDBACK
CABLE
MOTOR
X10
X2
X3
X7
223
HARNESS
17R671
X8
215
HARNESS
17R672
DRIVE
I/0
DRIVE
I/0
DRIVE
PWR
259
355 440
X1
24VDC
PWR
320
HARNESS
17S161
130
125
24VSTO
-24V
+24V
310
130
125
X7
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 DC COM
2 IN 7
3 IN 4
4 IN 3
5 OUT 26 OUT 2+
7 OUT 18 OUT 1+
9 IN 2
10 IN 1
X8
PIN DESCRIPTION
1FAULT
2FAULT
3 DC COM
4 ENABLE
5 IN 6
6 IN 5
7 A GND
8 ANALOG OUT +
9 ANALOG IN 10 ANALOG IN +
365 458
110
HARNESS
17S930
516
525
523
521
518
514
512
510
508
506
504
502
500
517
524
520
522
519
515
513
511
509
507
505
503
501
534
541
539
536
532
530
528
526
535
542
538
540
537
533
531
529
527
543
544
549
547
545
548
546
DRIVE-1
FIG. 37: Schematics, Page 9 of 10
72 3A5185B
Page 73
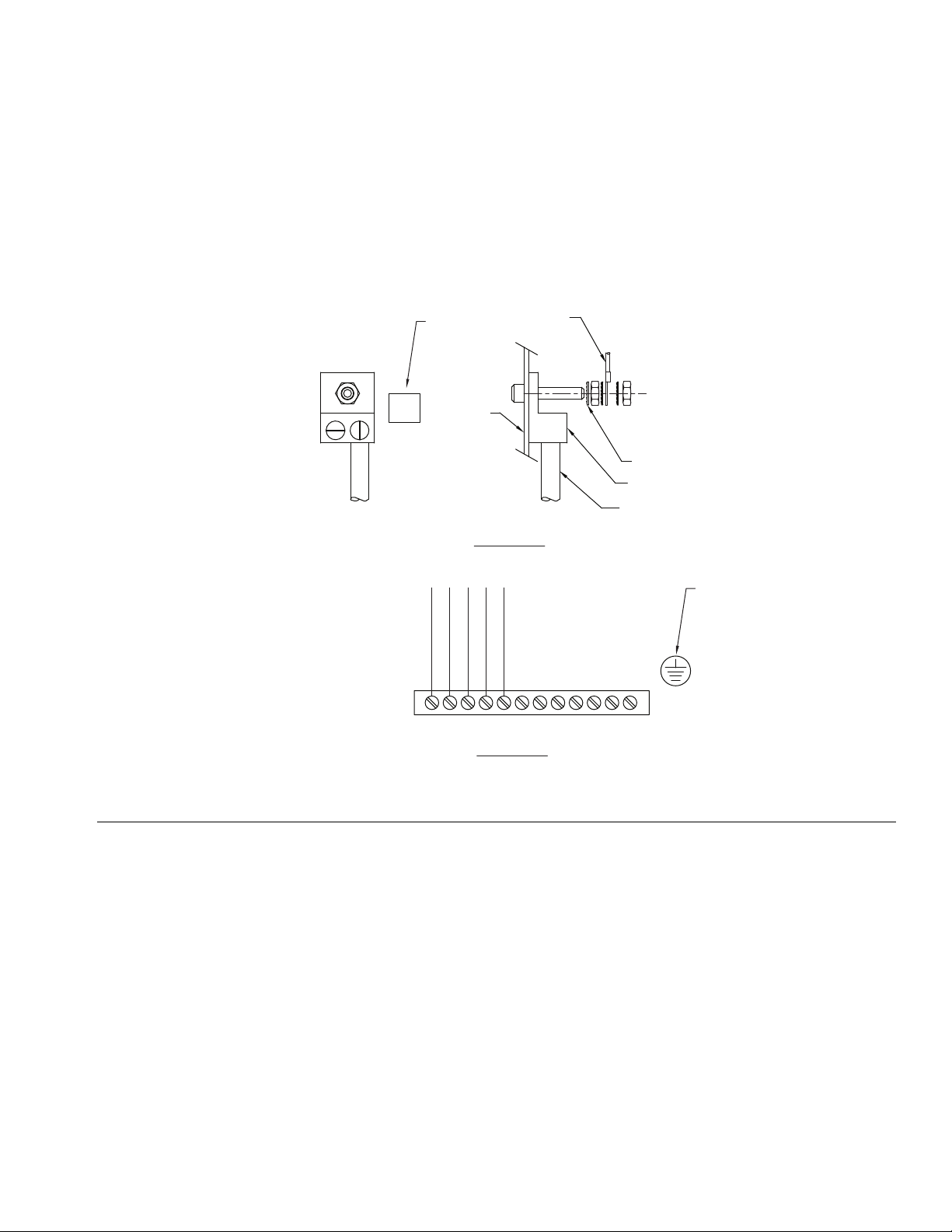
Schematics
TO GROUND
DIST. BAR #1
STAR WASHER
GROUND LUG
INCOMING GROUND
PROTECTIVE EARTH
SUBPLATE
PE GROUND STUD GRN/YEL
DRIVE-1 PE
DRIVE-1 X3-1
PLACE NEAR
GROUND DIST BAR
GROUNDING NOTES:
1. GROUND ALL DISTRIBUTION BARS.
2. GROUND ALL DOORS.
3. DO NOT JUMPER GROUND WIRES.
PE
PLACE NEAR
GROUND LUG
FIL-2
FIL-1
585
595
593
591
587
555
583
581
579
577
575
573
571
569
567
565
563
559
561
557
553
551
586
594
589
592
588
556
584
582
580
578
576
574
572
570
568
566
564
560
562
558
554
552
550
598
596
599
597
590
GROUND DIST. BAR
FIGURE 2
NTS
FIGURE 1
NTS
FIG. 38: Schematics, Page 10 of 10
3A5185B 73
Page 74
Accessory Parts
Accessory Parts
Automation Interface Cable Assembly
The cable length of automation interface cable assembly 24D824 is 40 ft (12.2 m). This figure shows the cable and
identifies the cable interface signals. See Appendix B - I/O on page 98 for wiring details. See Appendix C - Theory
of Operation on page 101.
Pin # Wire # Color Description
1 208 Black Dispense Start
2 210 Red Job Complete
3 SPARE White N/C
4 SPARE White/Black N/C
5 125 Orange 24 VDC from PGM
6 130 Blue 24 VDC common
7 404 Red/Black Analog flow command
8 130 Green Analog common
9 SPARE Green/Black N/C
10 302 Blue/Black Dispenser ready
11 300 Red/White Fault present
12 304 Orange/Black In cycle
13 SPARE Green/White N/C
14 310 Blue/White 24 VDC thru E-stop
74 3A5185B
Page 75
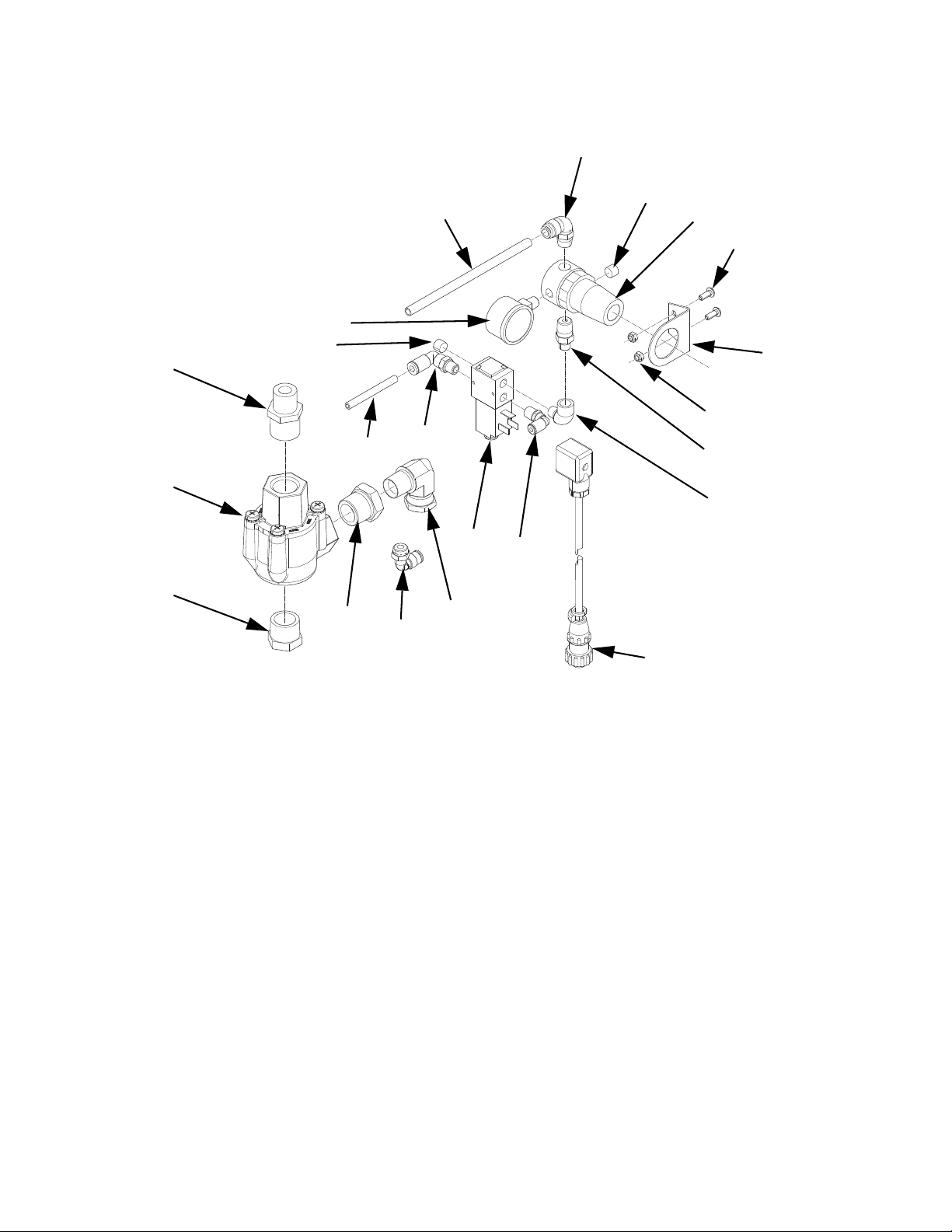
Dynamic Regulators (98****)
1011
1004
1008
1006
1010
1013
1001
1005
1004
1004
1014
1016
1003
1002
1012
1007
1009
1018
1017
1021
1020
1019
NOTE: This kit is intended for Therm-O-Flow units built prior to 2016, which includes part numbers
that start with 98xxxx. See Accessories on page 5 for the latest version of the Therm-O-Flow
which includes part number UHxxxx.
Kit 24E575
Accessory Parts
Ref Part Description Qty
1001 112699 TUBE, 1/4 OD 2
1002 C20466 FITTING, nipple, hex 1
1003 112307 FITTING, elbow, street 1
1004 100139 PLUG, pipe 2
1005 112781 FITTING, elbow, swivel 1
1006 054776 TUBE, nylon, round, 5/16 in/ 8 mm 2
1007 110321 BRACKET, mounting 1
1008 297612 SCREW, cap, button head 2
1009 110318 REGULATOR, air, 1/4 in. npt 1
1010 110319 GAUGE, pressure, air, 1/8 npt 1
1011 115948 FITTING, elbow, 1/4 nptM, 5/16T OD 1
1012 107110 NUT, lock 2
1013 121022 FITTING, elbow, male, 1/4 npt 1
1014 198171 FITTING, elbow 1
1015 198446 VALVE, dispense, closer 1
1016 24E574 CABLE, feed regulator, PGM, 9 meter 1
1017 080226 VALVE, quick exhaust, 3/4 in. nptf 1
1018 C20461 FITTING, nipple, reducing, hex 1
1019 125466 FITTING, swivel, elbow, 1/2 nptf 1
1020 100896 FITTING, bushing, pipe 1
1021 111530 MUFFLER 1
3A5185B 75
Page 76

Accessory Parts
Dynamic Regulator Setup and Installation
(P/N 98****) 24E575
1. Remove air pressure from Therm-O-Flow supply
system. See Pressure Relief Procedure in manual
311208.
2. Install dynamic regulator kit. See F
page 77.
3. Apply air to the Therm-O-Flow supply. Check for air
leaks.
4. Set the secondary regulator for a low operating
pressure, for example 20-25 psi.
5. Adjust the panel mount Therm-O-Flow regulator to
zero psi.
6. Connect the dynamic regulator cable from the
Therm-O-Flow to the PGM control box.
7. Navigate to the Supply Pump screen. See Appen-
dix A - User Interface Display starting on page 82
for Supply Pump screen information.
8. Select ON mode for the Primary or Tandem Pump
drop-down menu.
9. Set the appropriate press for the panel mount regulator on the Therm-O-Flow. For example, 30-40 psi.
10. Select AUTO mode for the Primary or Tandem
Pump drop-down menu.
IG. 39 on
11. Verify operation of the new regulator and adjust
pressure as needed to achieve a maximum static
pressure of 1500 psi (103 bar) when the system is
not dispensing.
76 3A5185B
Page 77
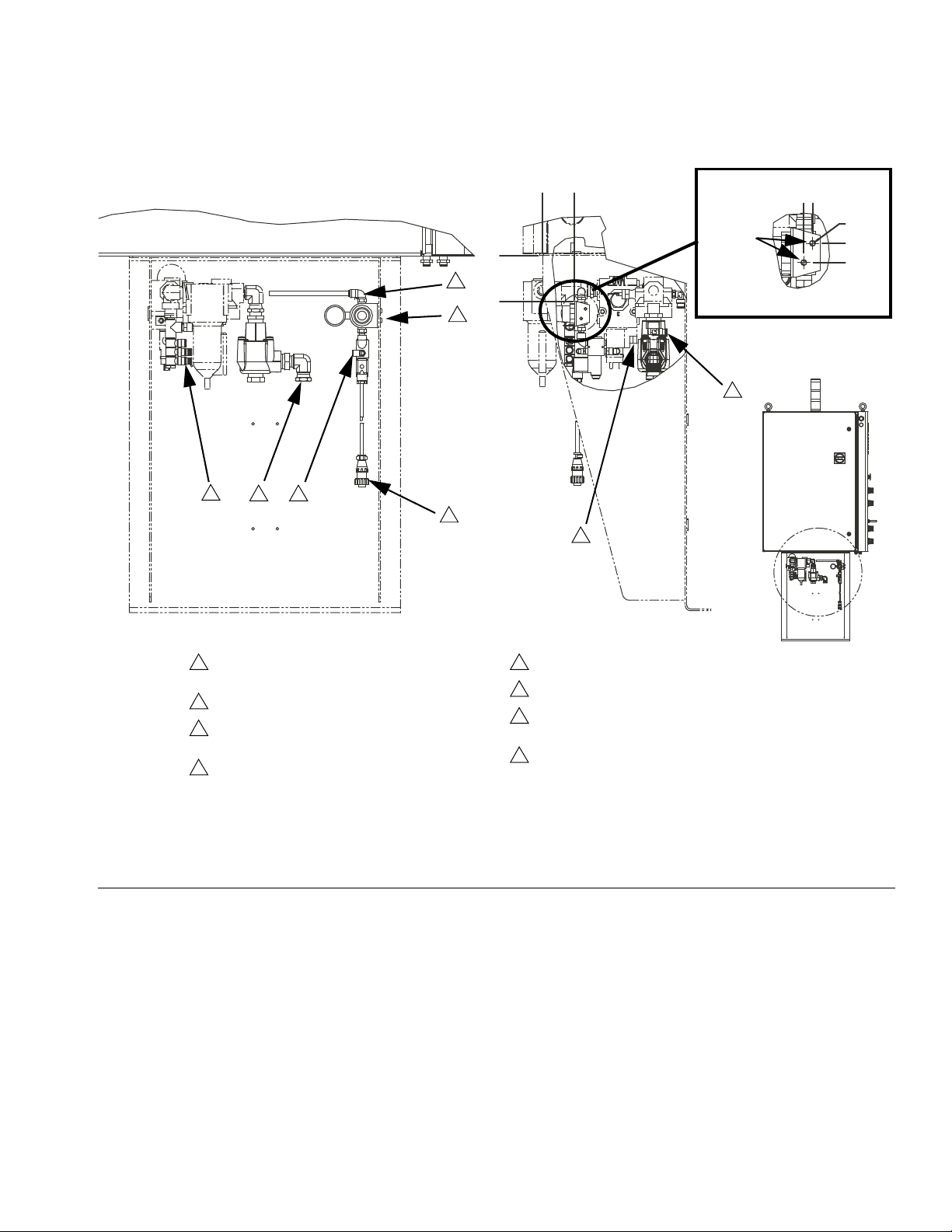
Dynamic Regulator Installation 24E575
Detail A
3
1
6
2
4
11/16 in.
7/32 in.
5
diameter
7
8
Remove plug and attach supplied tubing to
regulator inlet.
Holes required for mounting. See detail A.
5/32 in. tubing removed from Therm-O-Flow
regulator to be attached here.
Regulator pilot port will have an existing 5/32 in.
air line. This air line and its fitting are to be
removed from the regulator and replaced with
the fitting supplied with dynamic regulator.
The existing pilot tube will be connected to the
5/32 fitting on the diverting valve supplied with
24E575.
To Therm-O-Flow regulator pilot port.
Regulator inlet.
Thread existing air line with 1/2 in. npt coupling
to 90° swivel fitting.
Attach to PGM control panel.
1234567
8
5/16 in.
Accessory Parts
F
IG. 39
The dynamic regulator kit is used to control the static
pressure of a Therm-O-Flow (98****). The PGM has a
maximum inlet pressure of 1500 psi. During dispense
the dynamic regulator kit will activate the normal regulator located on the front panel of the Therm-O-Flow.
When the system is idle the secondary regulator will
control static pressure.
3A5185B 77
Page 78
Accessory Parts
1001
1002
1003
1004
1005
1006
1018
1007
1016
1017
1009
1012
1014
1014
1015
1003
1013
1012
1011
1010
1009
1018
1008
NOTE: This kit is for the current series of Therm-O-Flow which contains part number UHxxxx.
Kit 25A055
Dynamic Regulators (UH****)
Ref Part Description Qty
1001 158491 FITTING, nipple 1
1002 120435 REGULATOR, remote piloted 1
1003 121022 FITTING, elbow, male, 1/4 npt 2
1004 C20461 FITTING, nipple, reducing, hex 1
1005 080226 VALVE, quick exhaust, 3/4” nptf 1
1006 111530 MUFFLER 1
1007 121282 FITTING, swivel, straight, 1/2 fx3/4 m 1
1008 24E574 CABLE, feed regulator, pgm, 9 mtr 1
1009 112781 ELBOW, swivel, 90 deg 2
1010 112307 FITTING, street elbow 1
1011 C20466 FITTING, nipple, hex 1
1012 100139 PLUG, pipe 2
1013 110318 REGULATOR, air, 1/4” npt 1
1014 123257 FITTING, nipple, hex, 1/4 npt, brs 2
1015 113264 CROSS, pipe 1
1016 110319 GUAGE, press, air, 1/8” npt 1
1017 198446 VALVE, dispense, closer 1
1018 054130 TUBE, plyeth .250 od 3
78 3A5185B
Page 79

Dynamic Regulator Setup and Installation
(P/N UH****) 25A055
1. Remove air pressure from Therm-O-Flow supply
system. See Pressure Relief Procedure in manual
334130.
Accessory Parts
2. Install dynamic regulator kit. See F
page 80.
3. Apply air to the Therm-O-Flow supply. Check for air
leaks.
4. Set the secondary regulator for a low operating
pressure, for example 20-25 psi.
5. Adjust the air motor regulator at the top of the air
tree to zero psi.
6. Connect the dynamic regulator cable from the
Therm-O-Flow to the PGM control box.
7. Navigate to the Supply Pump screen. See Appen-
dix A - User Interface Display starting on page 82
for Supply Pump screen information.
8. Select ON mode for the Primary or Tandem Pump
drop-down menu.
9. Set the appropriate pressure for the air motor regulator at the top of the air tree on the Therm-O-Flow.
For example, 30-40 psi.
IG. 40 on
10. Select AUTO mode for the Primary or Tandem
Pump drop-down menu.
11. Verify operation of the new regulator and adjust
pressure as needed to achieve a maximum static
pressure of 1500 psi (103 bar) when the system is
not dispensing.
3A5185B 79
Page 80

Accessory Parts
5
7
1
4
3
6
2
Disconnect red airline from air tree.
Remove pressure relief safety valve from air
tree.
Screw in the cross with adjustable air pressure
regulator into the pressure relief safety valve
hole.
Attach the dynamic regulator assembly to the
hose connection on the air tree.
Attach the red air hose to the dynamic regulator
assembly.
Attach the pressure relief safety valve to open
port on the cross fitting.
Attach to PGM control panel.
12345
6
7
Dynamic Regulator Installation
F
IG. 40
The dynamic regulator kit is used to control the static
pressure of a Therm-O-Flow (UH****). The PGM has a
maximum inlet pressure of 1500 psi. During dispense
the dynamic regulator kit will activate the normal regulator located on the front panel of the Therm-O-Flow.
When the system is idle, the secondary regulator will
control static pressure.
80 3A5185B
Page 81

EnDure Valve Nozzles Heater Nests
Accessory Parts
Part Description
24E654 10 x 1.5 mm Ribbon Nozzle
24E655 1/8 in. Bead Nozzle
Part Description
24E678 Heater Nest with Blank Insert
24E679 Heater Nest with Ported Insert
3A5185B 81
Page 82
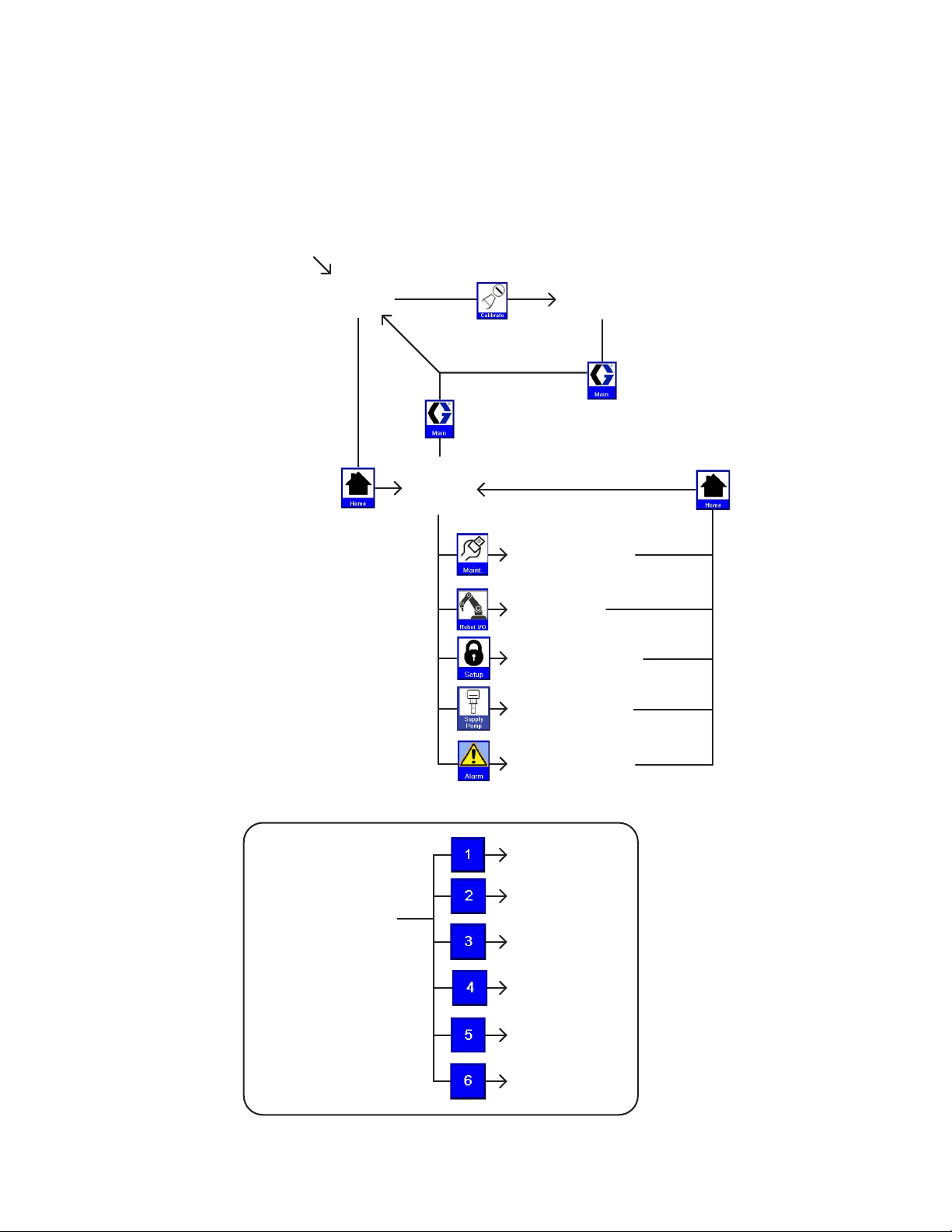
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Screen #1
Current Setup
Screen
Screen #2
Screen #3
Screen #4
Screen #5
Main
START MACHINE
Maintenance
Home
Calibrate
Robot I/O
Setup Screens Flow
Supply Pump
Setup Screens
Alarm Screen
Screen #6
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Screen Navigation Diagram
82 3A5185B
Page 83
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Key:
A Navigate to the Home screen
B Navigate to the Calibrate screen
A
B
Main Screen
Press the appropriate button to navigate to either the Home or Calibration screen. To access the Calibration screen,
select the login button and enter user “setup
.
” and password “PGM17”.
3A5185B 83
Page 84
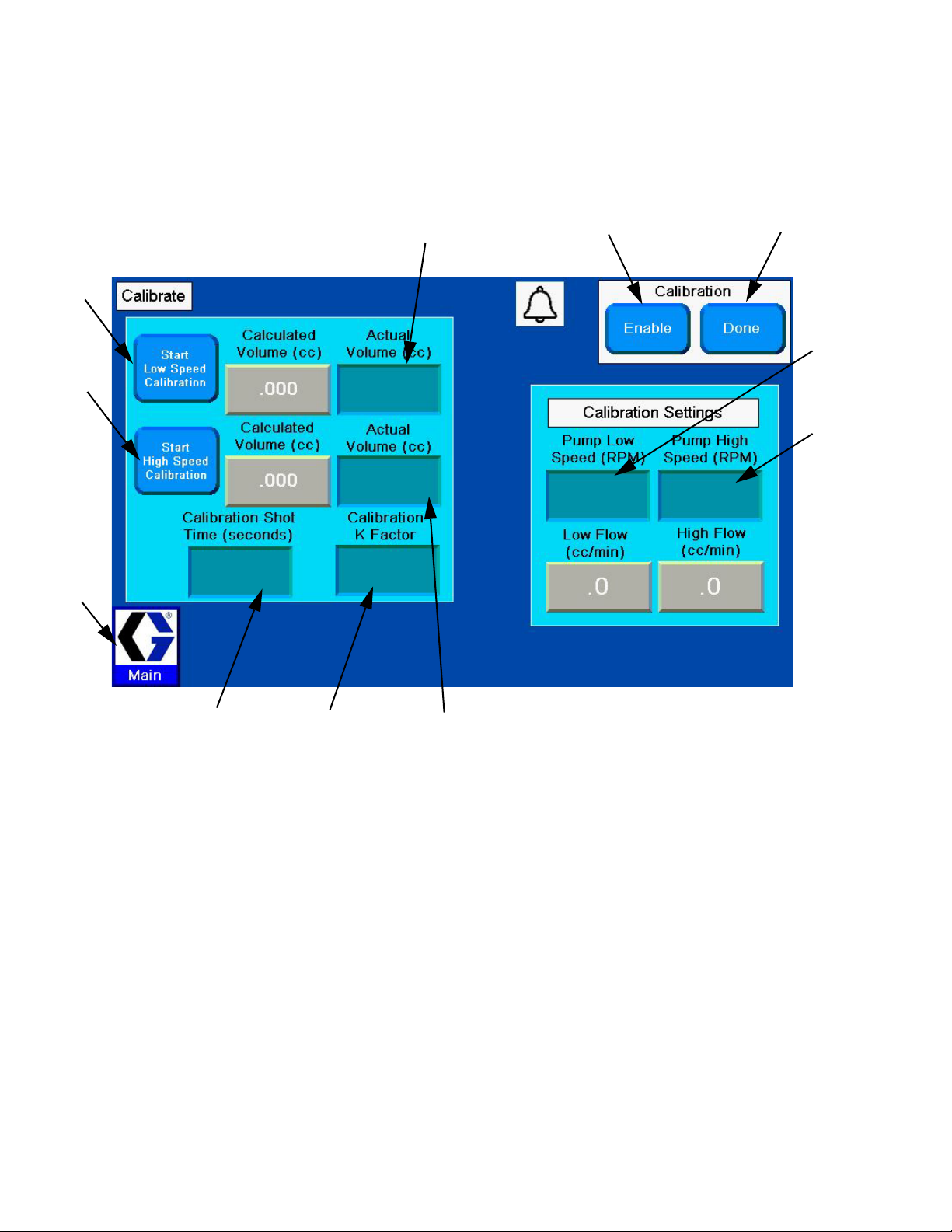
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Key:
C Enable Calibration button (Begin
Calibration)
D Done button (Finish Calibration)\
E Calibration Shot Time Input Box
F Calibration K Factor (Automatically
Calculated)
G Start Low Speed Calibration button
H Low Speed Calibration Shot Volume Input
Box
J Start High Speed Calibration button
K High Speed Calibration Shot Volume Input
Box
L Navigate to Main Screen
M Pump RPM during low speed calibration
N Pump RPM during high speed calibration
K
F
E
L
J
G
H
C
D
N
M
Calibrate Screen
NOTE: See Calibration procedure on page 24.
84 3A5185B
Page 85
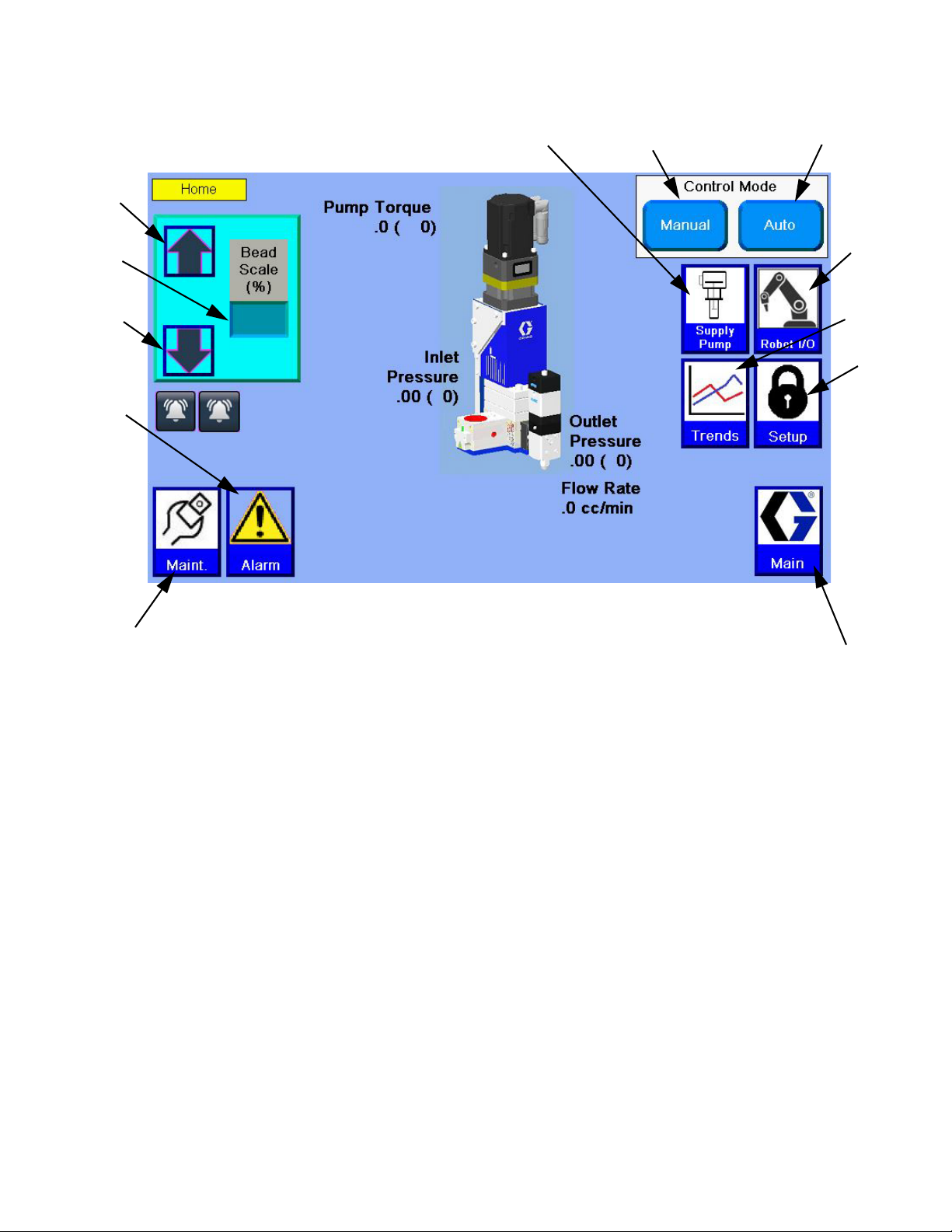
Home Screen
Key:
O Enable Manual mode
P Enable Automatic mode
R Increase Bead Scale
S Decrease Bead Scale
T Current Bead Scale setting
U Navigate to Maintenance Screen
V Navigate to Robot I/O Screen
W Navigate to Setup Screens
X Navigate to Main Screen
Y Navigate to Alarm Screen
Z Navigate to Supply Pump Screen
AA Navigate to Trend Screen
R
T
S
Y
U
X
W
AA
V
Z
O
P
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Manual Mode
In Manual Mode, the machine only accepts signals from
the User Interface touch screen and the physical buttons
on the machine. All signals from an External Control
Interface to initiate a shot will be ignored.
Automatic Mode
In Automatic Mode, the machine only accepts initiate
shot signals from an external machine. All signals to initiate a shot using the User Interface touch screen or the
physical buttons on the machine will be ignored.
The primary purpose of the bead scale is to be able to
quickly adjust volume dispensed to be able to find that
actual desired volume. Once the correct volume is found,
the flow rate should be adjusted accordingly.
Screens Navigation
Access to the Setup screens requires the setup password.
Flow Rate Display
The Home screen will display the commanded Flow Rate
from 1 of 3 sources:
Bead Scale
The bead scale function adjusts the quantity dispensed
by the scale percent value shown. For example, if the
system is setup to dispense 100 cc/min and the bead
scale setting is 110 then the machine will dispense
100 cc/min x 110% scale =110 cc/min.
3A5185B 85
• 1 - Maintenance Flow Rate (see Maintenance
Screen on page 86)
• 2 - Auto Mode Display Flow (see Setup #2 Screen
on page 89)
• 3 - Remote 0-10 VDC Command Flow (see Appen-
dix B - I/O on page 98)
Page 86
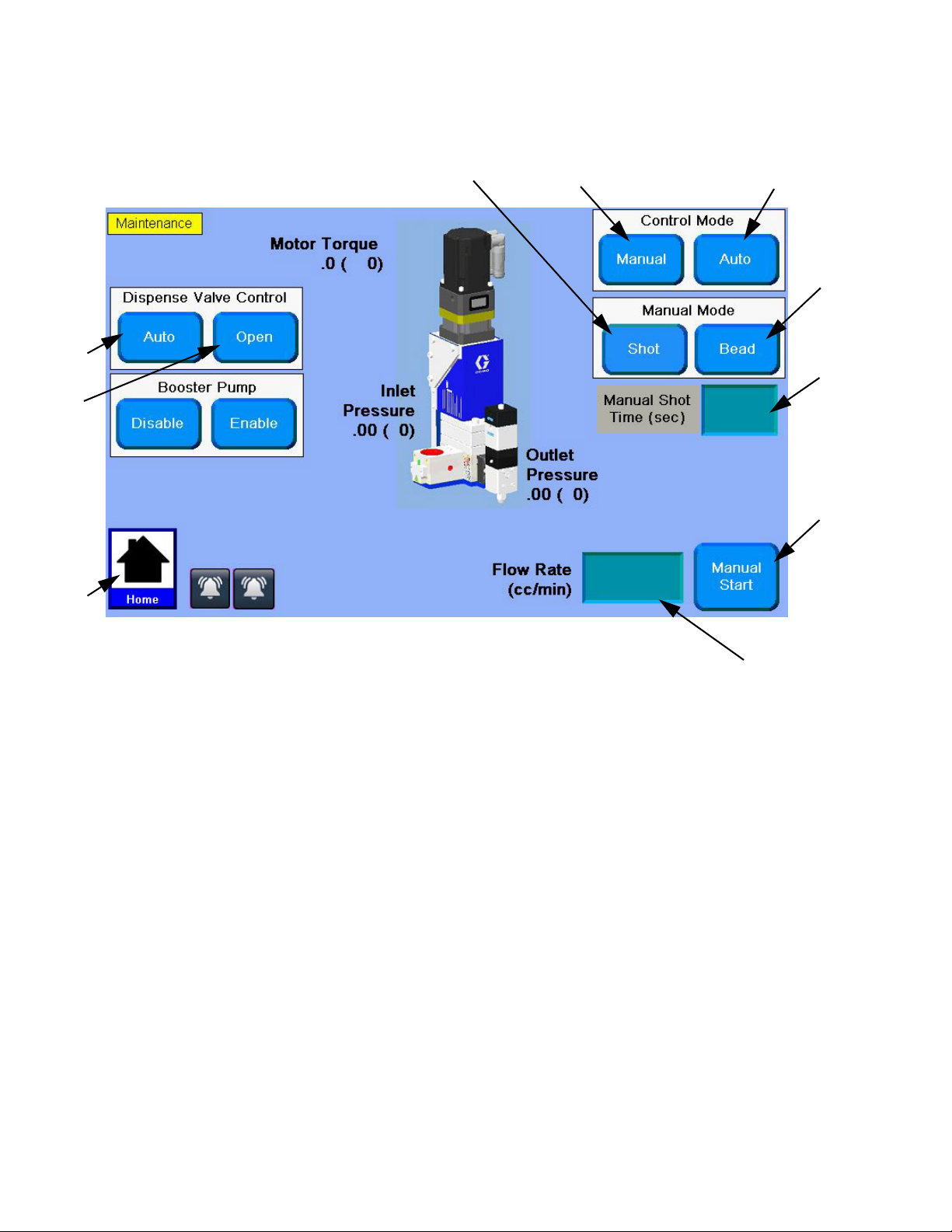
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Key:
AB Enable Automatic Dispense Valve
Control
AC Open the Dispense Valve, Disable
Automatic Dispense Valve Control
AD Enable Bead Manual Mode
AE Enable Shot Manual Mode
AF Dispense Duration Input Box
AG Flow Rate Input Box
AH Manual Start Dispense
A
AC
AB
AG
AD
AF
AH
Q
AE
P
Maintenance Screen
Dispense Valve Control
Dispense Duration: This is the amount of time the
machine will dispense at the given flow rate. This value
When Automatic Dispense Valve Control is enabled, the
is only used in Shot Mode.
dispense valve will open and close as needed to dispense material.
Flow Rate: This is the rate at which the machine will
dispense for the given dispense duration.
When Open the Dispense Valve is selected, the dispense valve will open and remain open until Automatic
Dispense Valve Control is enabled.
Manual Start Dispense
After adjusting the settings, the user can press the Man-
Dispense Settings
Dispense Mode: Options include Bead and Shot.
• In Bead mode, dispensing begins when the initiate
shot button is pressed and dispensing ends when
the initiate shot button is released.
ual Start Dispense button (AH) to dispense material
using the current settings.
NOTE: This button performs the same function as the
manual purge button located on the control panel.
• In Shot mode, dispensing begins when the initiate
shot button is pressed and released. Dispensing
ends when the Dispense Duration (AF) elapses.
86 3A5185B
Page 87

Robot I/O Screen
A
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Overview
This screen is for settings related to an external
machine setup to control the dispense operation of this
system. See Appendix B - I/O on page 98 for more
information.
Robot Outputs
These are signals sent by the external machine when
the related action should occur. The Job Complete signal is sent to stop the In Cycle signal. The Dispense
Trigger is sent to begin dispensing. The Command Voltage is a display of the voltage of the command cable
and is for troubleshooting only. See Appendix B - I/O
on page 98 for more information.
Robot Inputs
These are signals sent to the external machine to notify
it of system conditions. The Dispense Ready signal tells
the external machine that the system is ready to dispense and a dispense can be initiated. The No Alarm
signal tells the machine that there are currently no active
alarms. The In Cycle signal tells the external machine
that the system is currently busy so dispensing cannot
be initiated.
NOTE: Dispense Ready remains on while in Auto Mode.
If a deviation alarm occurs the Dispense Ready and
Alarm signal will remain ON. If an error alarm occurs the
Dispense Ready will be removed.
3A5185B 87
Page 88
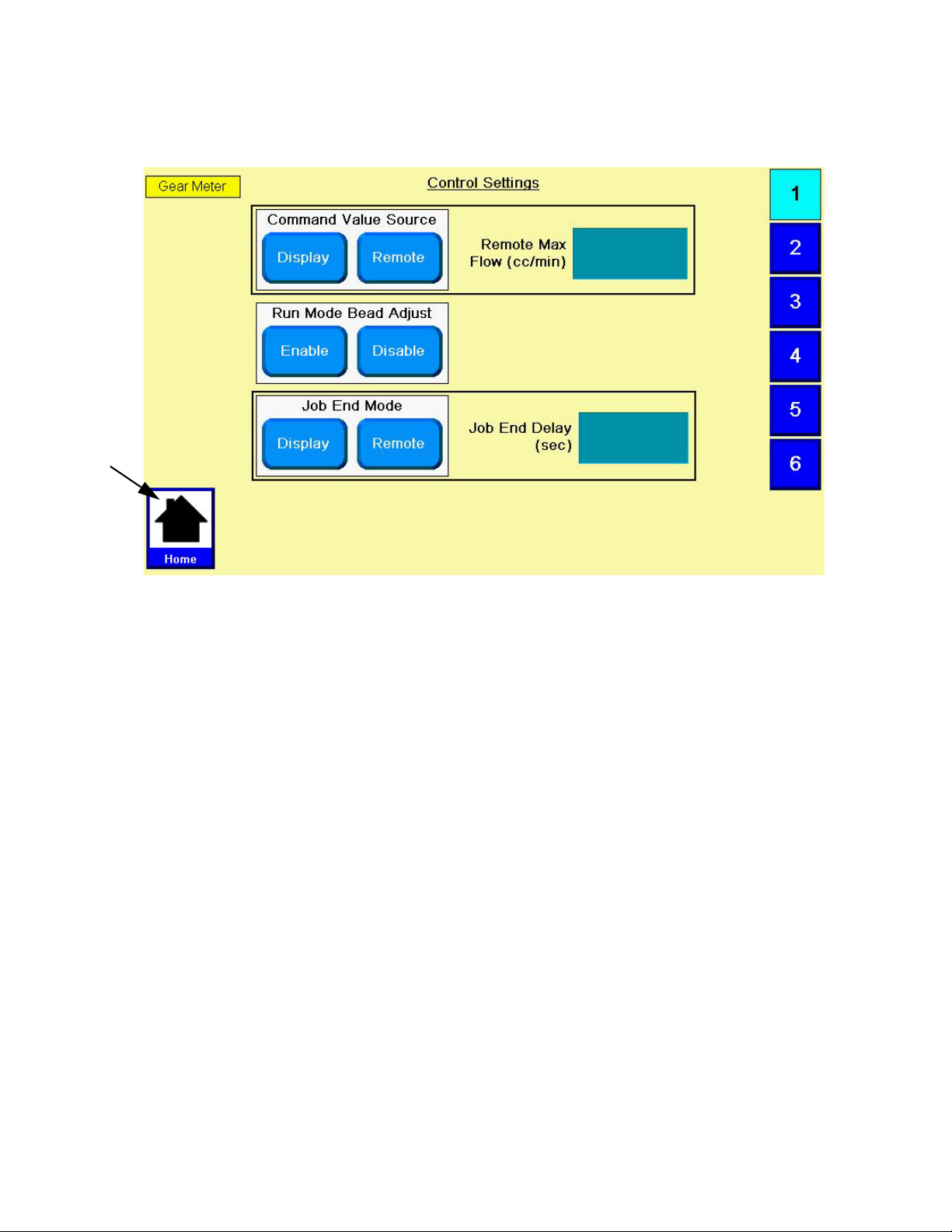
Appendix A - User Interface Display
A
Setup #1 Screen
#1 to #6 Buttons
Press to navigate to the Setup Screen with that number.
For example, press #3 to navigate to Setup Screen #3.
Command Value Source
Command Values can be controlled by the user-interface touch screen or by an external machine connected
to the system via the External Control Interface.
Run Mode Bead Adjust
When this option is enabled the Bead Scale function
appears on the Home Screen. See the Home Screen
on page 85 for more information.
Job End Mode
The In Cycle signal can be dropped when the dispense
trigger is removed when Display is selected.
If Remote is selected the Job Complete signal is
required to remove the In Cycle signal.
Job End Delay (sec)
When Job End mode is set to Display the In Cycle signal
is removed after the time in this field.
88 3A5185B
Page 89
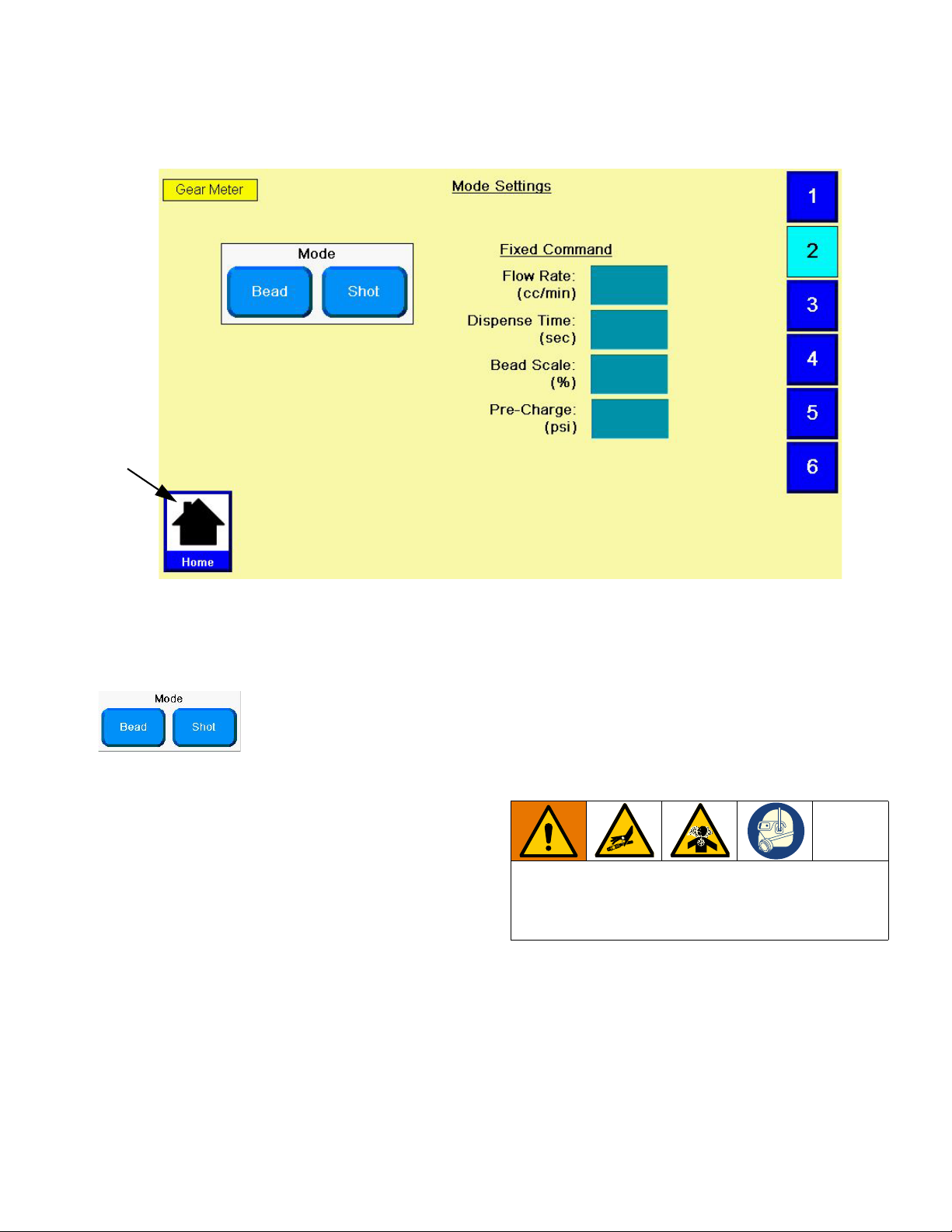
Setup #2 Screen
A
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Overview
The Dispense Mode, Flow Rate, and Dispense Duration
settings apply to Automatic Control Mode
only. Values changed on this
screen independent of changes made on the Maintenance screen.
The Bead Scale value is a duplicate to the Bead Scale
setting on the Home Screen, which can be enabled or
disabled from the Setup #1 screen. See Setup #1
Screen on page 88 for more information.
Fixed Command cc/min
Flow rate can be entered here. This field is only used
when command value source is set to Display on Setup
Screen 1. See Setup #1 Screen on page 88 for more
information.
Pre-Charge
This is the pressure between the meter and the dispense valve when the dispense valve is closed. If the
pre-charge setting is non-zero then, immediately after
dispensing, the gear meter will continue to rotate after
the dispense valve closes until the pre-charge pressure
value is achieved. The maximum Pre-Charge value is
2500 psi (17.2 MPa, 172 bar).
Larger values for the On Delay setting lead to larger
pressures in the system. If a value too large is input,
the machine could over-pressurize leading to ruptured components and serious injury.
#1 to #6 Buttons
Press to navigate to the Setup Screen with that number.
For example, press #3 to navigate to Setup Screen #3.
3A5185B 89
Page 90
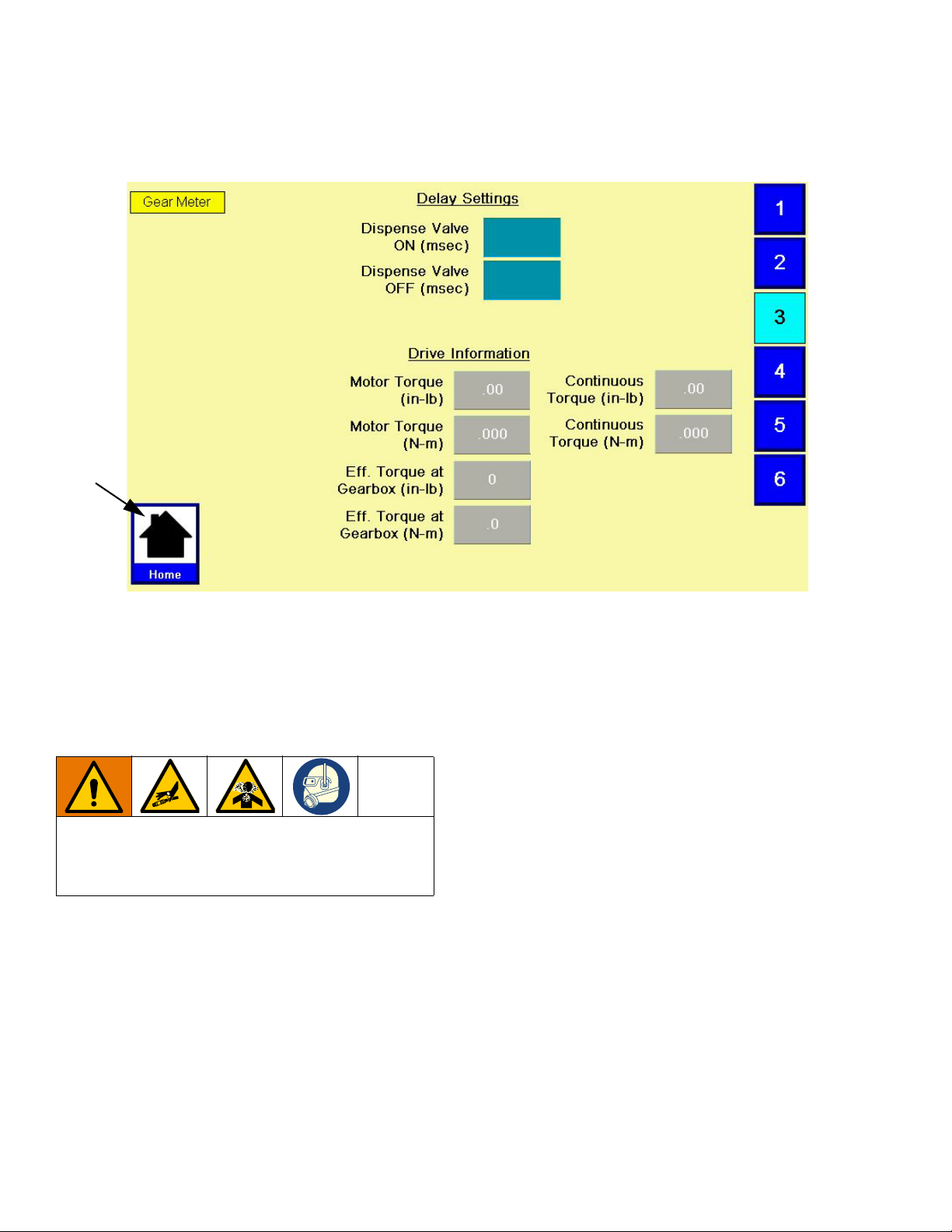
Appendix A - User Interface Display
A
Setup #3 Screen
#1 to #6 Buttons
Press to navigate to the Setup Screen with that number.
For example, press #3 to navigate to Setup Screen #3.
Delay Settings
Larger values for the On Delay setting lead to larger
pressures in the system. If a value too large is input,
the machine could over-pressurize leading to ruptured components and serious injury.
The Delay Settings affect the timing of the Dispense
Valve opening and closing when a shot is initiated.
The On Delay is the amount of time, in milliseconds,
between a shot being initiated and the dispense valve
opening. If the On Delay is set to 100 the machine will
wait 100 milliseconds after a shot is initiated before
opening the dispense valve. This will lead to a pressure
build up between the meter and dispense valve until the
dispense valve opens.
The Off Delay is the amount of time, in milliseconds,
between a shot completing and the dispense valve closing. If the Off Delay is set to 100 the machine will wait
100 milliseconds after a shot is complete before closing
the dispense valve.
Drive Information
Motor Torque
Display motor torque during dispense. If motor torque
climbs above continuous torque an alarm is issued. See
Errors on page 31.
Cont. Torque
Continuous torque rating of the motor.
NOTE: The motor torque display is a good way to determine the maximum flow rate with a given viscosity.
90 3A5185B
Page 91

Setup #4 Screen
A
Appendix A - User Interface Display
#1 to #6 Buttons
Press to navigate to the Setup Screen with that number.
For example, press #3 to navigate to Setup Screen #3.
Pump Settings
Snuff Back: This enables the gear meter to rotate in
reverse, immediately following dispensing, to pull material back from the dispense valve to minimize or eliminate material drooling. The Snuff Back Time and Snuff
Back Pump RPM are the settings used when Snuff Back
is enabled. These settings should be adjusted to work
best for your material.
NOTE: Not recommended for very viscous materials.
Pump Hour Totalizer: This field will record the total dis-
pense time on the machine in hours. This field is
non-resettable.
Pump Hour Meter: This field displays total dispense
time in hours. This field is resettable.
3A5185B 91
Page 92
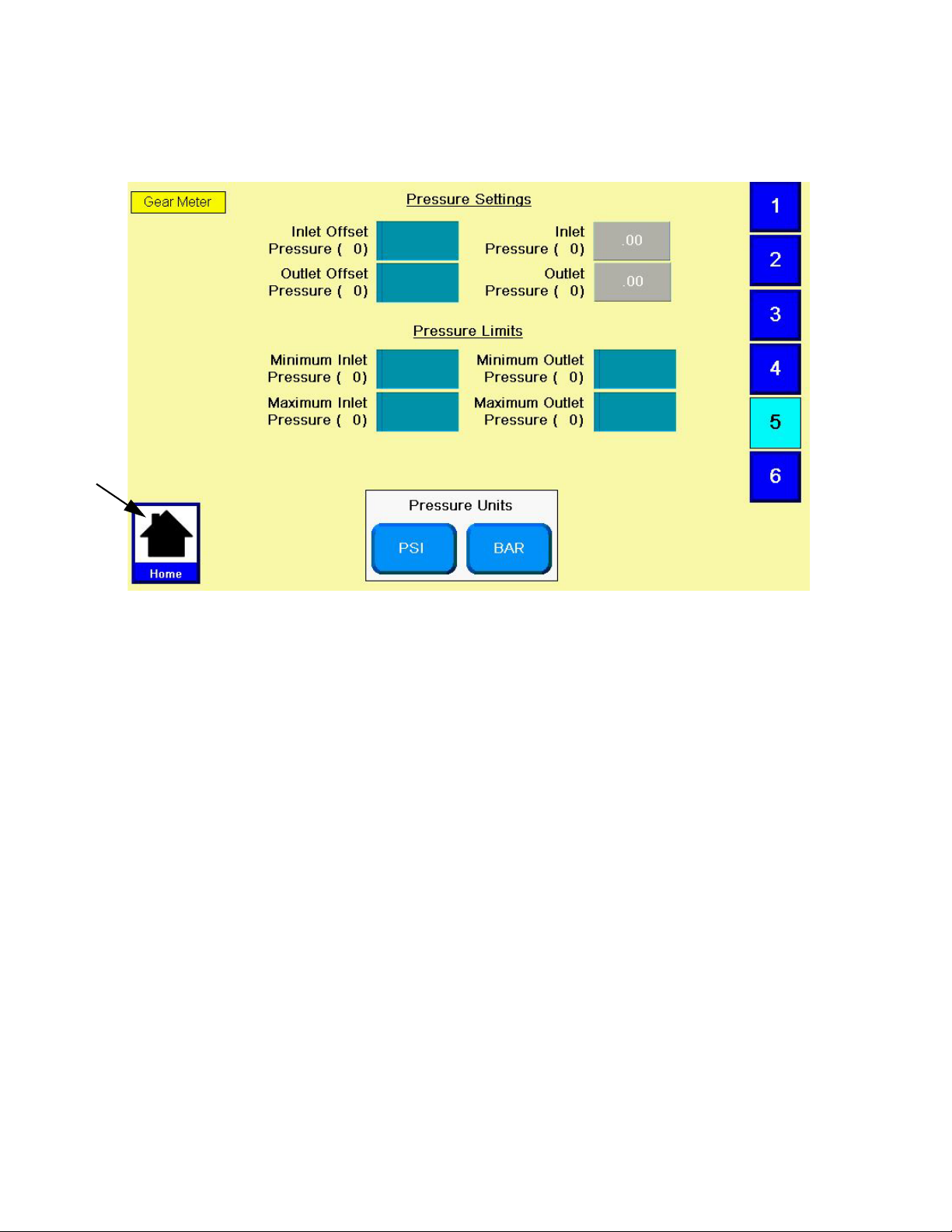
Appendix A - User Interface Display
A
Setup #5 Screen
Overview
This screen controls settings for the pressure sensors.
These values are used for triggering errors.
#1 to #6 Buttons
Press to navigate to the Setup Screen with that number.
For example, press #3 to navigate to Setup Screen #3.
Inlet, Outlet Offset
The inlet, outlet offset values are used to tune the pressure transducer. If the pressure transducers do not register zero pressure when there is no material in the
system, enter a value to shift the pressure value to zero.
For example, if 15 psi is shown, enter -15 psi to shift the
value to 0.
Min/Max Inlet/Outlet Limits
These limit values are used to set the acceptable range
of values for dispensing. If values are outside of this
range during dispensing the machine will issue an
alarm. See Errors on page 31.
PSI, BAR
Set the unit of measure for pressure system-wide.
92 3A5185B
Page 93
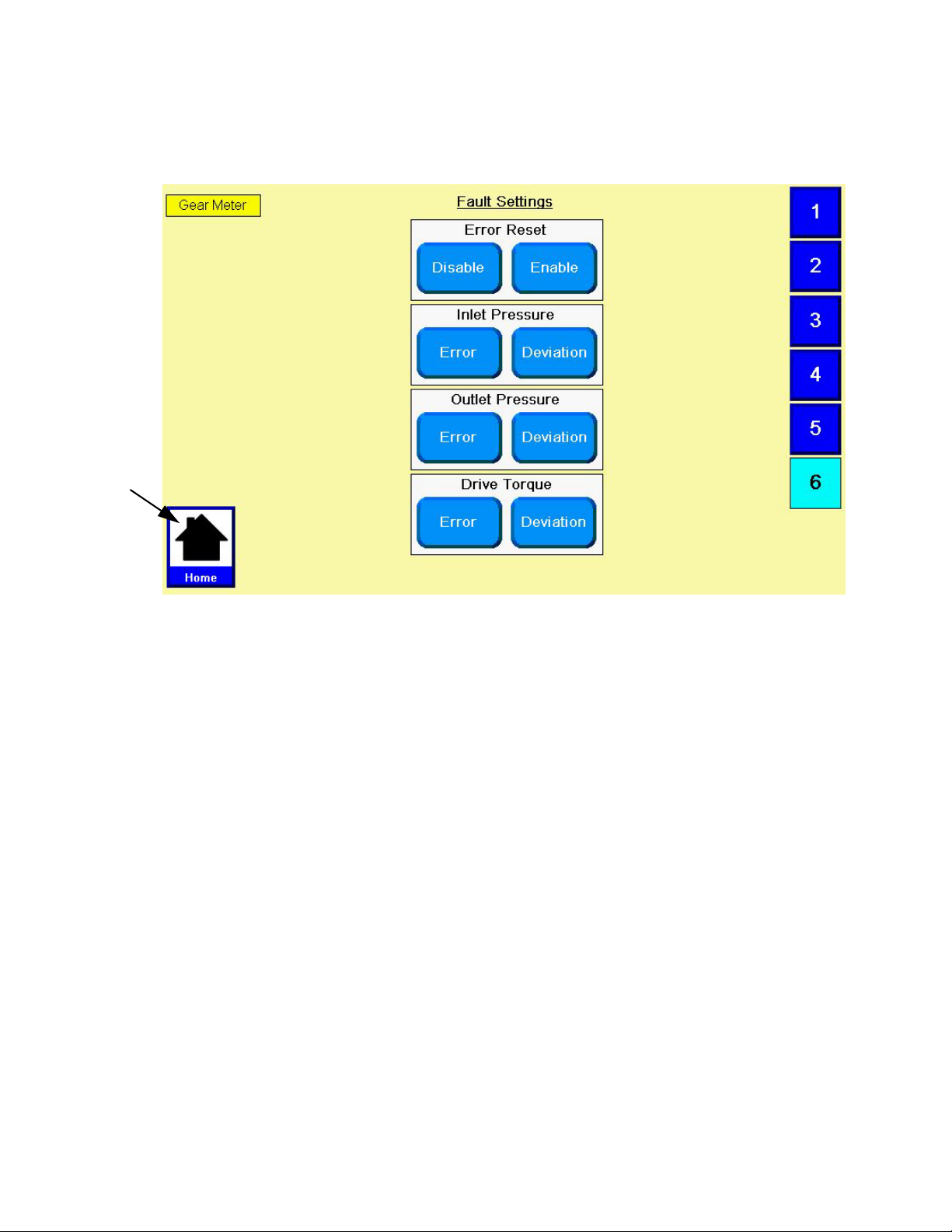
Setup #6 Screen
A
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Fault Settings
Error Reset: If set to Disable, errors cannot be reset. If
set to Enable, errors can be reset.
Inlet/Outlet Pressure, Drive Torque: If set to Error, an
error will be generated when the out-of-limit condition
occurs. The machine will be disabled until the error is
reset. If set to deviation, an error will be generated when
the out-of-limit condition occurs. The machine will not be
disabled until the error is reset.
If set to Deviation, an error will be generated when the
out-of-limit condition occurs. The machine will not be
disabled. See Errors on page 31.
3A5185B 93
Page 94
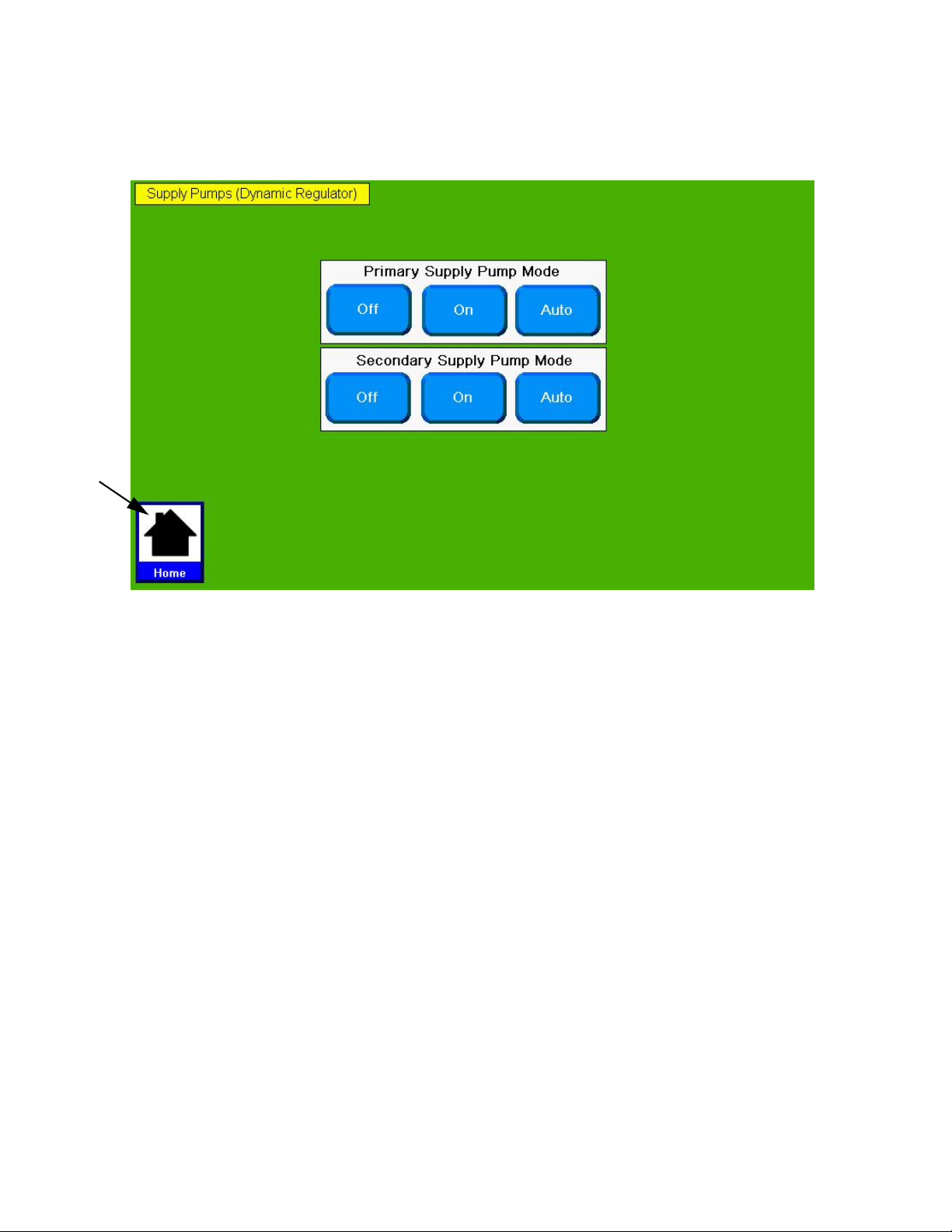
Appendix A - User Interface Display
A
Supply Pump Screen
NOTE: This screen is used to control the optional
dynamic regulator kit for a Therm-O-Flow. See
Accessory Parts section on page 74 for additional
information on the dynamic regulator kit option.
Supply Pumps (Dynamic Analog Regulator)
Primary Supply Pump Mode
• Auto Mode: During normal operation this mode will
activate the dynamic regulator solenoid when the
dispense valve solenoid is activated.
• On Mode: This will activate the dynamic regulator
solenoid.
• Off Mode: The dynamic regulator option is disabled.
Secondary Supply Pump Mode
• Same control features as primary pump.
94 3A5185B
Page 95
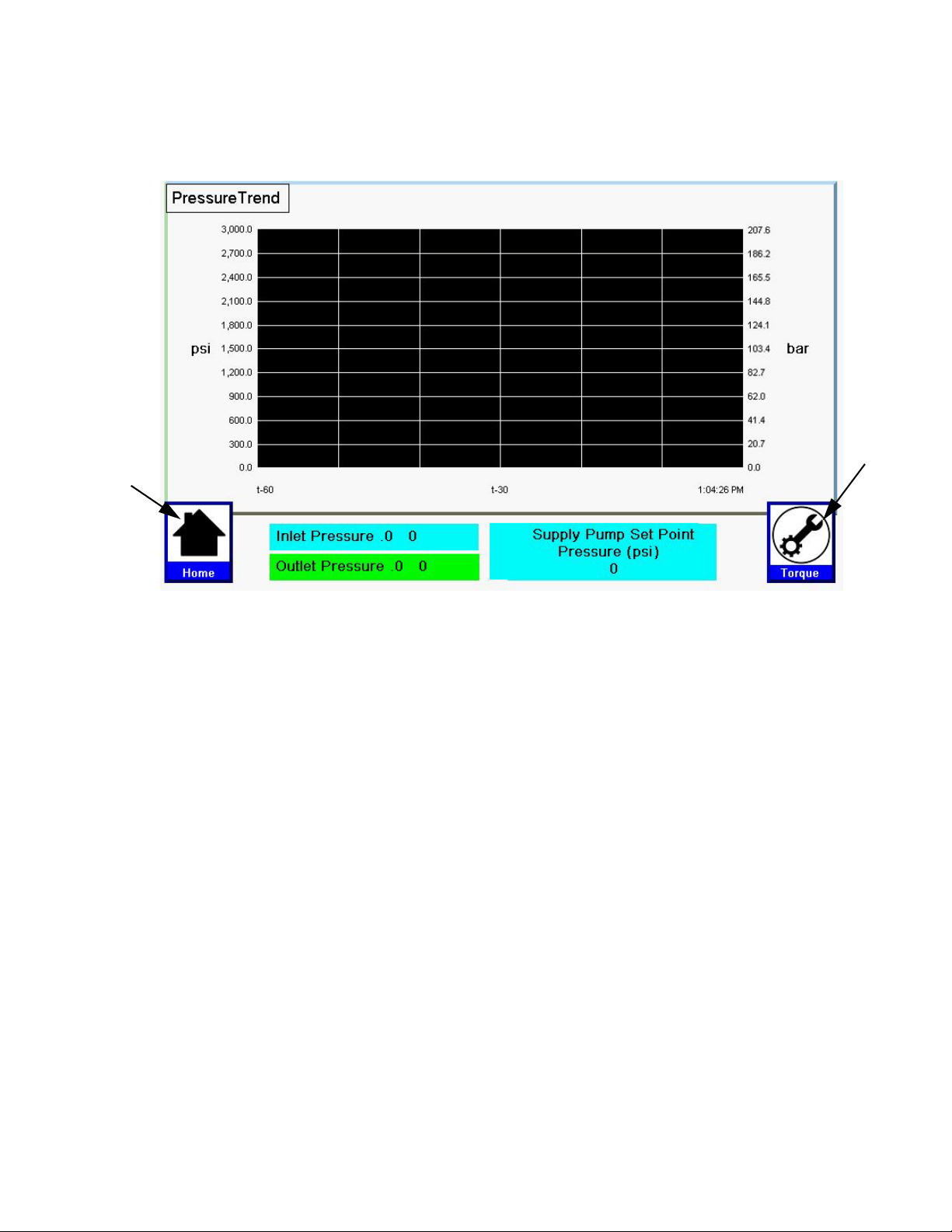
Pressure Trend Screen
Key:
AI Navigate to the Torque Trend
screen.
A
AI
Appendix A - User Interface Display
Overview
The Pressure Trend screen allows the user to view both
inlet and outlet pressures in real time. The pressures
displayed on this screen are the same values shown on
the Home and Maintenance screens.
3A5185B 95
Page 96

Appendix A - User Interface Display
Key:
AJ Navigate to the Pressure Trend
screen.
A
AJ
Torque Trend Screen
Overview
The Torque Trend screen allows the user to view the
pump torque and motor torque in real time.
Pump Torque
The Pump Torque shows the effective torque on the
pump during operation.
Motor Torque
The Motor Torque shows the torque on the motor during
operation and is measured in in/lbs.
96 3A5185B
Page 97

Appendix A - User Interface Display
A
Alarm Screen
Refer to Error Codes and Troubleshooting on page 32 for information on possible errors.
Acknowledge All List
When pressed, the Acknowledge All List button
acknowledges all errors listed on the Alarm Screen and
adds to the screen the time when the errors were
acknowledged. This button must be pressed prior to
pressing the Clear All Alarms button.
NOTE: Acknowledging alarms does not clear them.
Clear All Alarms
When pressed, the Clear All Alarms button will remove
all errors listed on the Alarm Screen. Before pressing
the Clear All Alarms button, all alarms must be acknowledged.
NOTE: The Clear All Alarms button can only be pressed
if Error Reset is Enabled (see Configure Errors on
page 21).
3A5185B 97
Page 98
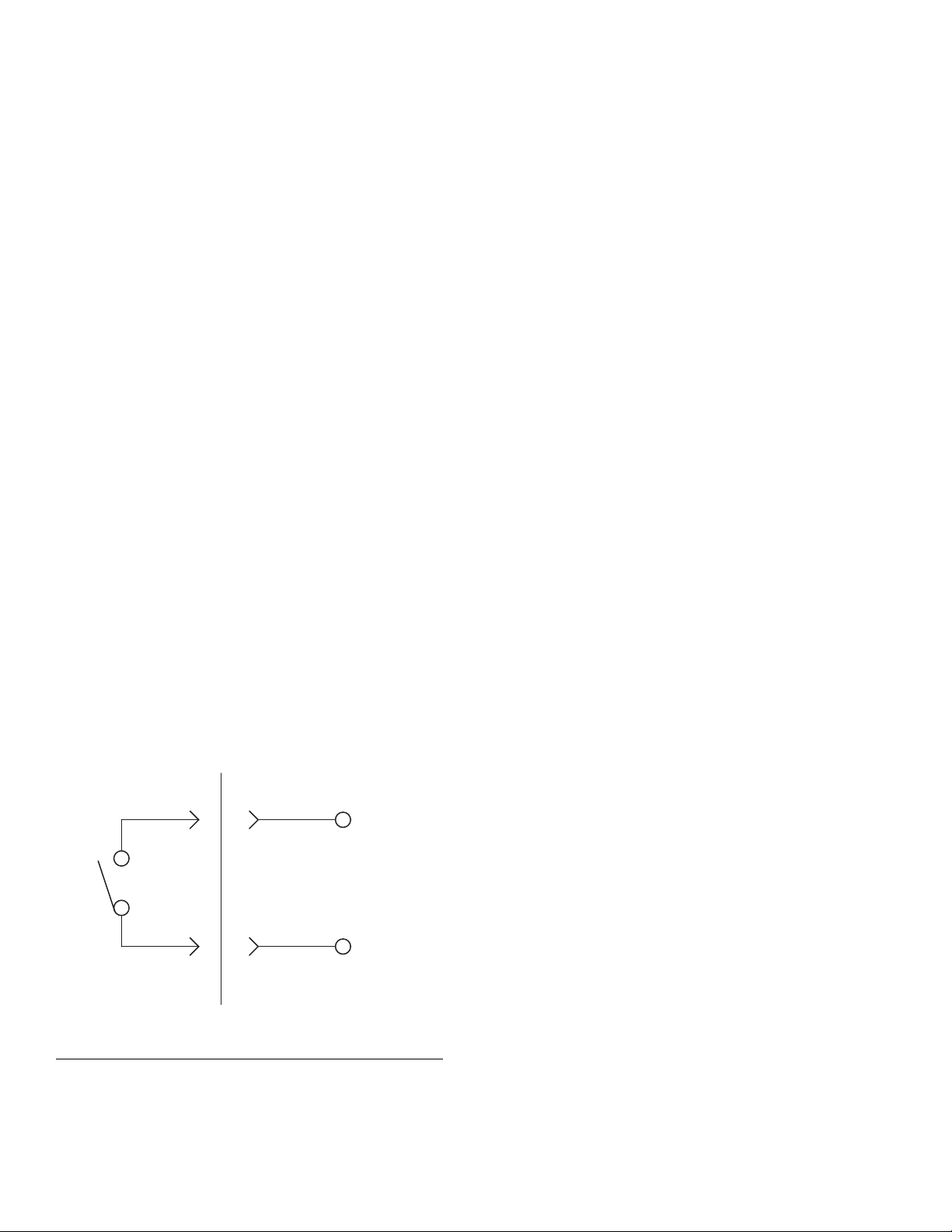
Appendix B - I/O
Automation PGM Control
Input Circuit
24VDC
Relay
Contact
Input
Pin 1 or 2
5
Appendix B - I/O
Using the PGM I/O
The gear meter uses several I/O signals to communicate with plant automation controllers. There are two digital
inputs, three digital outputs, and one analog input. All of these signals are routed to the I/O connector on the top of
the controller.
Other pins on the I/O connector include 24 VDC power, 24 VDC common, analog common, and a signal which is 24
VDC power only when the controller E-Stop switch is latched in. None of the signals are isolated; all are referenced
to the ground plane of the control box. The following paragraphs describe typical connection methods for the automation controller signals.
Digital Inputs
The two digital inputs are Dispense Start and Job Complete. These inputs require a 24 VDC current sourcing
output from the automation controller. See F
IG. 41.
If the automation controller uses relay contacts to activate I/O signals, the 24 VDC available at the gear meter
I/O connector (pin 5) should be used to drive the inputs.
If the automation controller uses high-side switching of
24 VDC, the automation outputs can be directly connected to the inputs as long as the 24 VDC common
(pin 6) of the gear meter is able to be connected to the
automation controller common. If the automation controller outputs are low-side switching (open collector) or
a voltage other than 24 VDC, relays must be used as
shown in F
IG. 41.
FIG. 41
98 3A5185B
Page 99
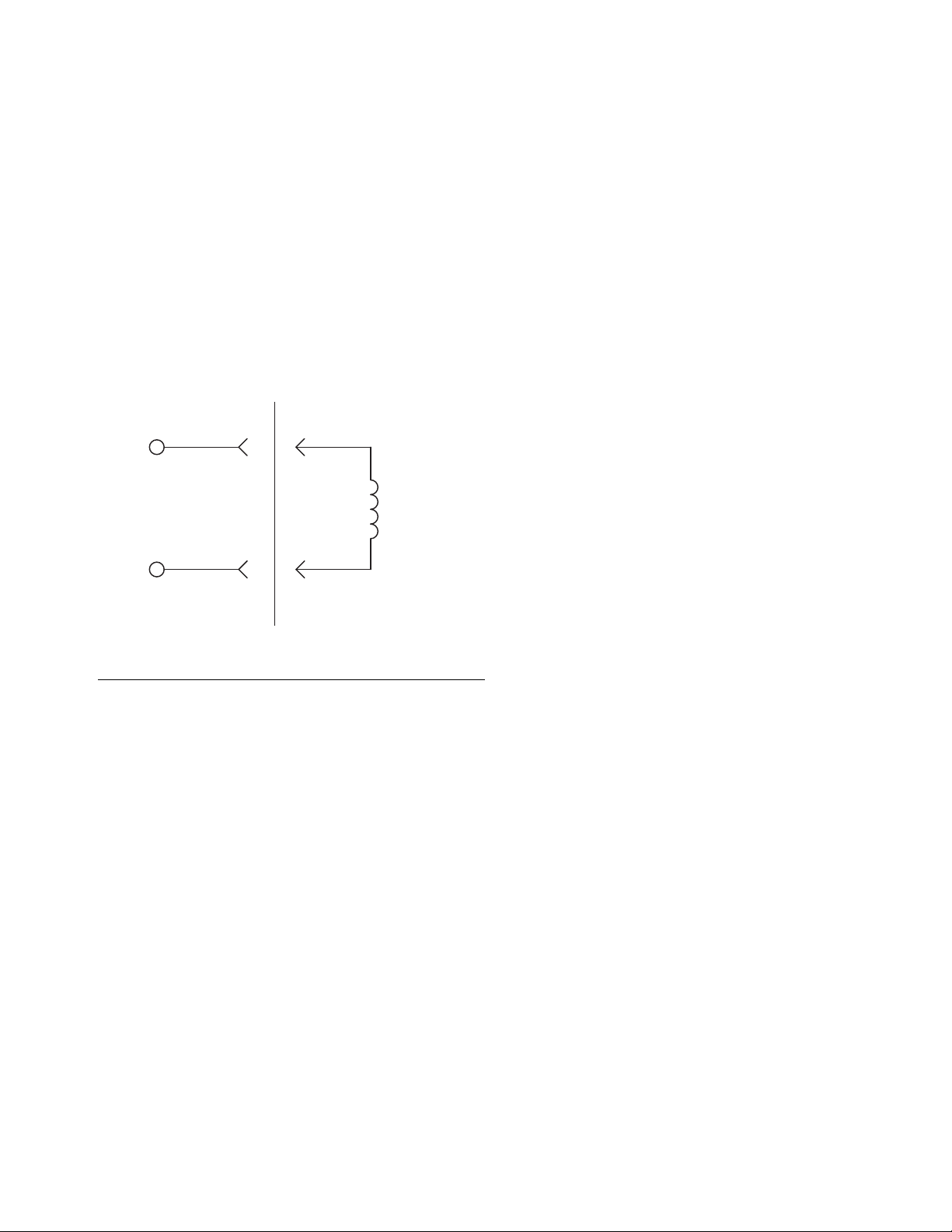
Digital Outputs
AutomationPGM Control
Output Circuit
Load
(750 mA max)
Pins 10, 11, 12
DC Common
6
The three digital outputs are Dispenser Ready, Fault
Present and In Cycle. These outputs perform high-side
switching of 24 VDC and require a 24 VDC current sinking input at the automation controller. See F
automation controller uses 24 VDC relay coils to receive
I/O signals, the signals should be connected as shown
in F
IG. 42.
If the automation controller inputs are current sourcing
or use a voltage other than 24 VDC, relays with 24 VDC
coils must be used as shown in F
IG. 42.
IG. 42. If the
Appendix B - I/O
IG. 42
F
3A5185B 99
Page 100
Appendix B - I/O
+24 VDC
E-Stop Switch
Pin 14
Analog Inputs
The PGM receives a flow rate analog command from
the automation. The 0 to 10 VDC analog input is referenced to analog common on the control. See F
The reference for the automation controller analog output must be connected to the PGM analog reference
(pin 8) for this signal to function properly.
AutomationPGM Control
0 to 10 VDC
Pin 7
Pin 8
Analog Input
F
IG. 43
_
+
-
IG. 43.
Voltage
Relays
If the use of relays is required to condition the digital I/O
signals, these are some examples of part numbers that
could be used.
For 24 VDC Coils:
• Relay: Phoenix Contact Part Number: 2966171
For 120 VAC Coils:
• Relay: Phoenix Contact Part Number: 2966197
24 VDC From E-Stop
The PGM provides a signal that can be used by the
automation controller to monitor the emergency stop
switch position of the PGM controller. See F
F
IG. 44
IG. 44.
100 3A5185B
 Loading...
Loading...