Page 1
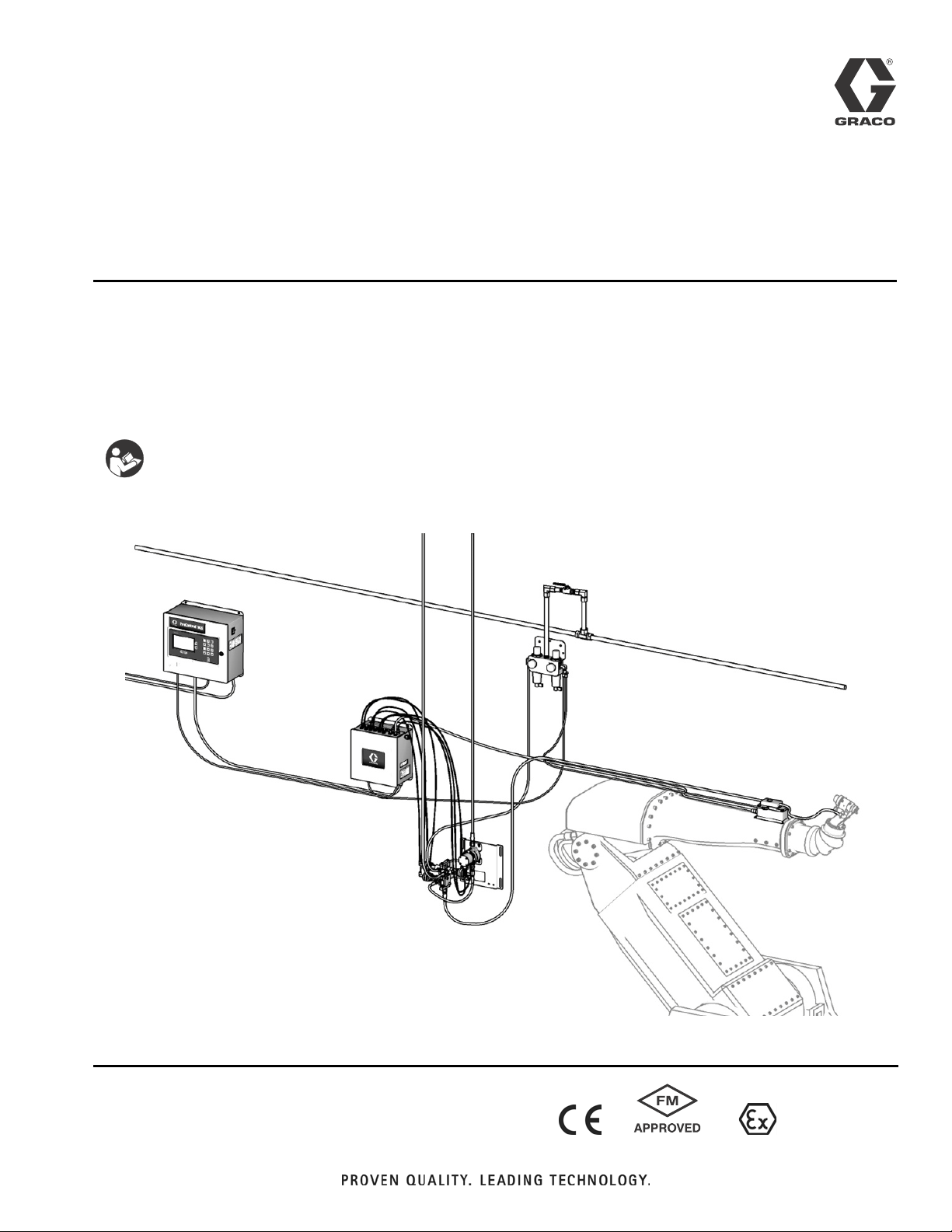
Operation
™
ProControl
Automatic system for fluid management of single component coatings. Includes flow
control, flushing, and color change. For professional use only.
Approved for use in explosive atmospheres (except the EasyKey).
Important Safety Instructions
Read all warnings and instructions in this
manual. Save these instructions.
1KS
See pages 4-5 for model information, including maximum working pressure. Equipment approval labels are
on page 3. Some components shown are not included
with all systems.
3A1080C
EN
#53
TI16328a
II 2 G
Page 2

Contents
Related Manuals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Equipment Approvals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
System Configuration and Part Numbers . . . . . . . 4
Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Important Two-Component Material Information . 9
Isocyanate Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Material Self-ignition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Keep Components A and B Separate . . . . . . . . . 9
Moisture Sensitivity of Isocyanates . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Changing Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Glossary of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Component Identification and Definition . . . . . . 12
ProControl 1KS System Components . . . . . . . . 14
EasyKey Display and Keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Keypad . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
AC Power Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
I/S Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Potlife Exceeded Audible Alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Graco Web Interface Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Ethernet Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Run Mode Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Splash Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Status Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Manual Override Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Totals Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Reset Total Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Reset Solvent Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Alarms Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Level Control Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Setup Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Password Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Set Up Home Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
System Configuration Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Option Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Advanced Setup Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Recipe Setup Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Recipe 0 Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Calibration Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics . . . . . . . . . 45
Discrete I/O vs Network Communications . . . . . 45
Discrete I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Automation Flow Charts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
System Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Operation Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Recipe (Color) Change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Flow Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Typical PLC Interaction with ProControl 1KS . . 63
General Operating Cycle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Mix Manifold Valve Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Start Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Pressure Relief Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Purging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Meter Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Color Change . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Color Change Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Color Change Sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Alarms and Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
System Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
System Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Alarm Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Schematic Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
System Pneumatic Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
System Electrical Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
EasyKey Electrical Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Technical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Graco Standard Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Graco Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
2 3A1080C
Page 3
Related Manuals
Related Manuals
Component Manuals in English
Manual Description
3A1163 ProControl 1KS Installation
3A1164 ProControl 1KS Repair-Parts
312782 Dispense Valve
312783 Color Change Valve Stacks
312787 Color Change Module Kit
312784 Gun Flush Box Kits
310745 Gun Air Shutoff Kit
312786 Dump Valve and Third Purge Valve Kits
312785 Network Communication Kits
308778 G3000/G3000HR/G250/G250HR Flow
Meter
313599 Coriolis Flow Meter
313212 Gun Flush Box Integration Kit
313290 Floor Stand Kit
313542 Beacon Kit
313386 Basic Web Interface/Advanced Web
Interface
406800 15V825 Discrete I/O Board Kit
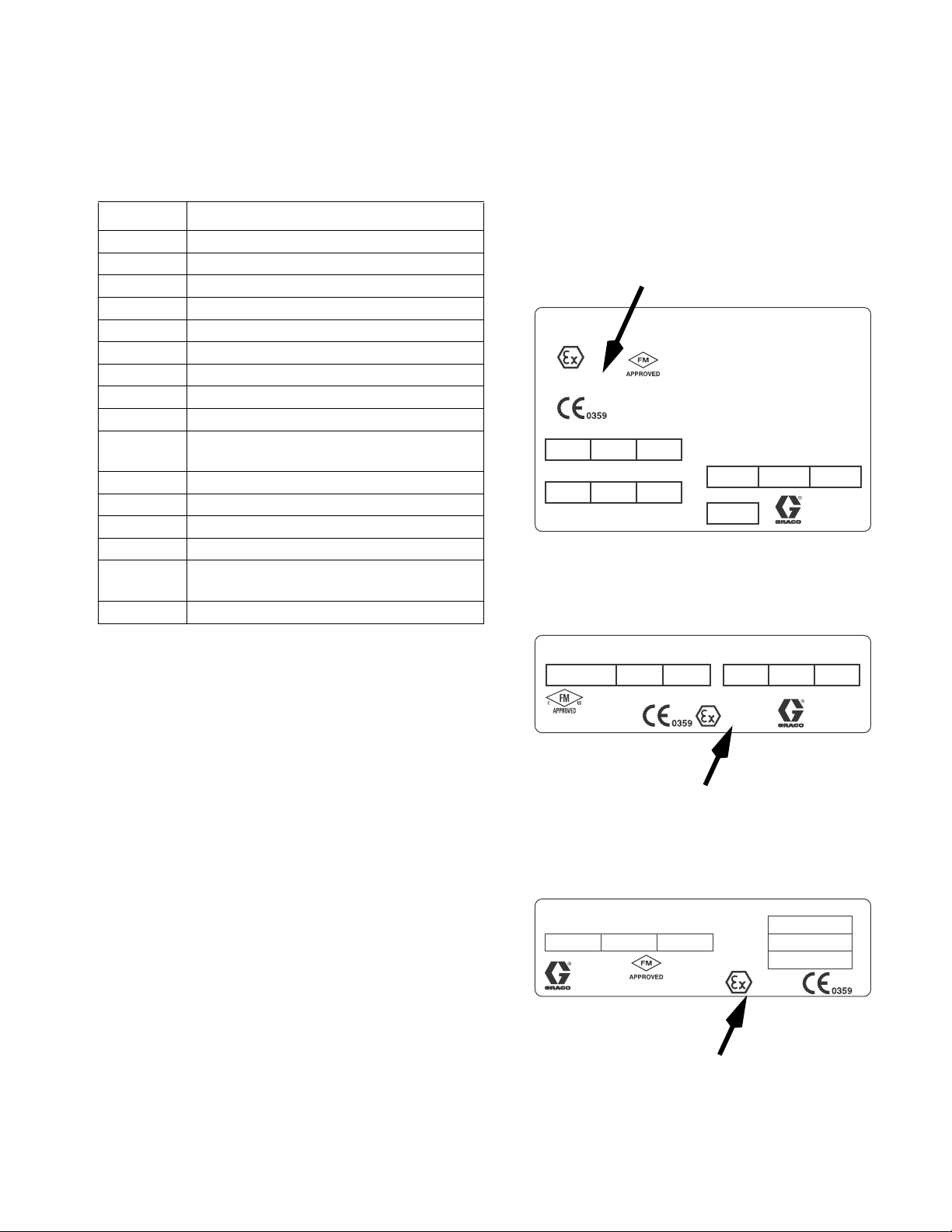
Equipment Approvals
Equipment approvals appear on the following labels
which are attached to the Fluid Station Control Box and
™
EasyKey
EasyKey and Fluid Station Control Box Label
. See FIG. 1 on page 4 for label locations.
ATEX Certificate is listed here
ProControl 1KS
Electronic Proportioner
FM08ATEX0074
II 2 G
Ex ia IIA T3
CUS
Intrinsically safe
equipment for Class I,
Div 1, Group D, T3
Ta = -20°C to 50°C
MAX AIR WPR
.7 7 100
MPa bar PSI
MAX FLUID WPR
13.1 190
1.31
MPa bar PSI
MAX TEMP 50°C (122°F)
Intrinsically Safe (IS) System. Install
per IS Control Drawing No. 289833.
EasyKey Interface IS Associated
Apparatus for use in non hazardous
location, with IS Connection to Smart
Fluid Plate IS
Apparatus for use in:
Class I, Division 1, Group D T3 C
Hazardous Locations
Read Instruction Manual
Warning: Substitution of components
may impair intrinsic safety.
PART NO. SERIES
MFG. YR.
Fluid Station Control Box Label
SERIAL
GRACO INC.
P.O. Box 1441
Minneapolis, MN
55440 U.S.A.
ProControl
PART NO. SERIES SERIAL
Intrinsically safe equipment
for Class I, Div 1, Group D, T3
Ta = -20°C to 50°C
Install per 289833
ATEX Certificate is listed here
EasyKey Label
ProControl 1KS
PART NO.
SERIES NO. MFG. YR.
277869
GRACO INC.
P.O. Box 1441
Minneapolis, MN
55440 U.S.A.
Intrinsically safe connections
for Class I, Div 1, Group D
CUS
Ta = -20°C to 50°C
Install per 289833
Um: 250 V
ATEX Certificate is listed here
FLUID PANEL
MAX AIR WPR
.7 7 100
MPa bar PSI
FM08ATEX0073
II 2 G
Ex ia IIA T3
POWER REQUIREMENTS
VOLTS
AMPS
II (2) G
[Ex ia] IIA
FM08ATEX0072
GRACO INC.
P.O. Box 1441
Minneapolis, MN
55440 U.S.A.
85-250 ~
2 AMPS MAX
50/60 Hz
3A1080C 3
Page 4
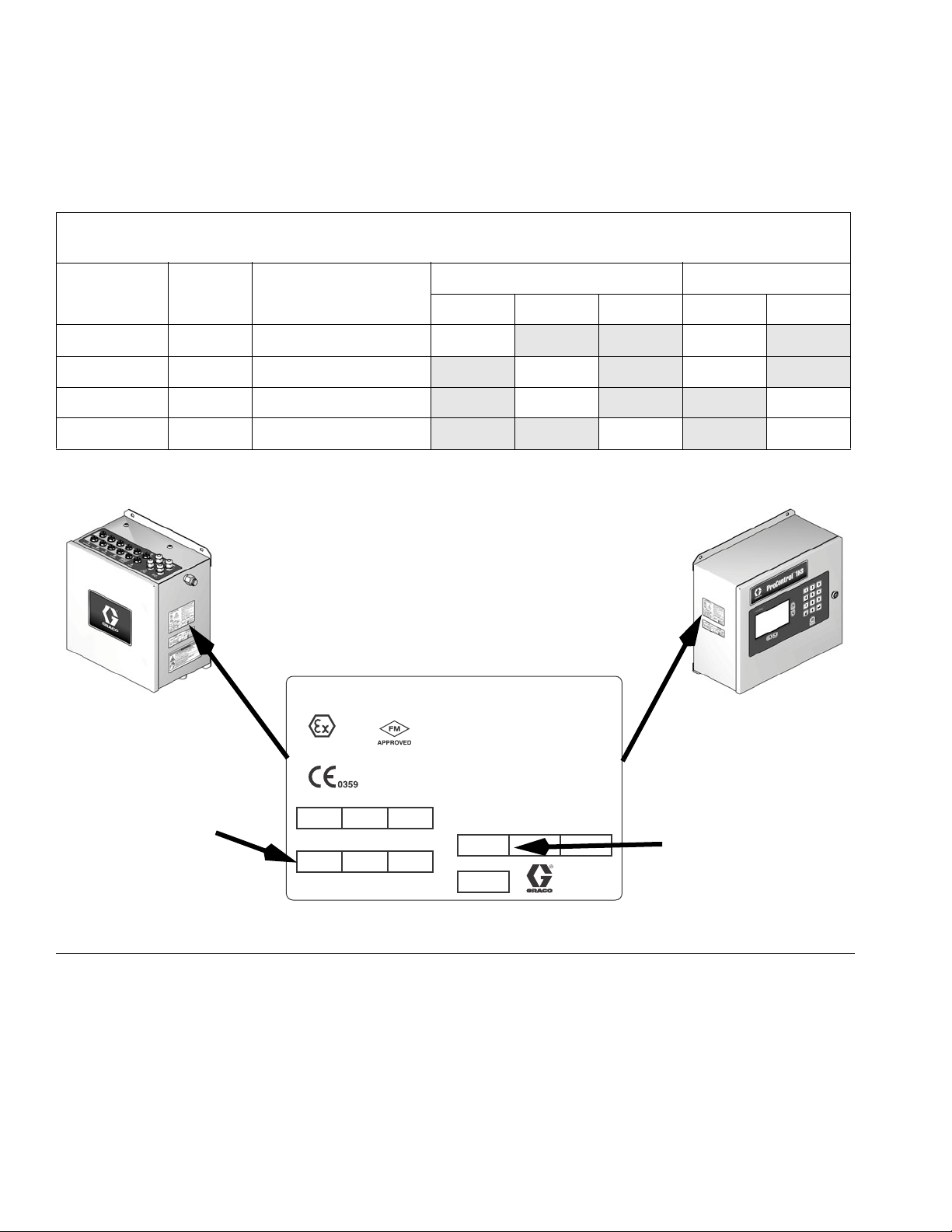
System Configuration and Part Numbers
System Configuration and Part Numbers
Models
The part number for your equipment is printed on the equipment identification labels. See FIG. 1 for
location of the identification labels.
Meter Flow Control
Part No. Series Description
262380
262381
262382
262383
Label Location
A ProControl 1KS
A ProControl 1KS
A ProControl 1KS
A ProControl 1KS
ProControl 1KS
Electronic Proportioner
on Fluid Station
Control Box
Maximum Fluid
Working Pressure
is listed here
TI15974a
FM08ATEX0074
II 2 G
Ex ia IIA T3
.7 7 100
MPa bar PSI
MAX FLUID WPR
1.31
MPa bar PSI
MAX TEMP 50°C (122°F)
CUS
Intrinsically safe
equipment for Class I,
Div 1, Group D, T3
Ta = -20°C to 50°C
MAX AIR WPR
13.1 190
None G3000 Coriolis No Yes
✔
✔
✔ ✔
✔ ✔
✔ ✔
Intrinsically Safe (IS) System. Install
per IS Control Drawing No. 289833.
EasyKey Interface IS Associated
Apparatus for use in non hazardous
location, with IS Connection to Smart
Fluid Plate IS
Apparatus for use in:
Class I, Division 1, Group D T3 C
Hazardous Locations
Read Instruction Manual
Warning: Substitution of components
may impair intrinsic safety.
PART NO. SERIES
SERIAL
Label Location
on EasyKey
TI15975a
Part Number
MFG. YR.
GRACO INC.
P.O. Box 1441
Minneapolis, MN
55440 U.S.A.
FIG. 1: Identification Label, ProControl 1KS Systems
4 3A1080C
Page 5

System Configuration and Part Numbers
Hazardous Location Approval
Models using a G3000, G3000HR, or intrinsically safe Coriolis meter are approved for installation in a Hazardous
Location - Class I, Div I, Group D, T3 or Zone I Group IIA T3.
Maximum Working Pressure
Maximum working pressure rating is dependent on the fluid component options selected. The pressure rating is
based on the rating of the lowest rated fluid component. Refer to the component pressure ratings below.
Example: Model 262383 has a maximum working pressure of 190 psi (1.31 MPa, 13.1 bar).
Check the identification label on the EasyKey or fluid station for the system maximum working pressure.
See F
IG. 1.
ProMix Fluid Components Maximum Working Pressure
Base System (no meter, no color/catalyst change option,
and no flow control [option). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4000 psi (27.58 MPa, 275.8 bar)
G3000 Meter Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4000 psi (27.58 MPa, 275.8 bar)
Coriolis Meter Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2300 psi (15.86 MPa, 158.6 bar)
Color Change Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300 psi (2.07 MPa, 20.6 bar)
Flow Control Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .190 psi (1.31 MPa 13.1 bar)
Flow Meter Fluid Flow Rate Range
G3000. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75-3800 cc/min. (0.02-1.0 gal./min.)
G3000HR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38-1900 cc/min. (0.01-0.50 gal./min.)
Coriolis Meter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20-3800 cc/min. (0.005-1.00 gal./min.)
S3000 Solvent Meter (accessory) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38-1900 cc/min. (0.01-0.50 gal./min.)
Standard Features Accessories
Feature
EasyKey with LCD
RS 485 Network Cable, 50 ft (15.25 m)
Fiber Optic and Power Cables, 50 ft (15.25 m)
Fluid Station Control Box
Discrete I/O Board
A Side Dump Valve, if color valve(s) selected
Flow Control with 15 ft (4.57 m) Cable (if selected)
Basic Web Interface
Accessory
15V536 Solvent Flow Switch Kit
15V213 Power Cable, 100 ft (30.5 m)
15G710 Fiber Optic Cable, 100 ft (30.5 m)
15G614 Flow Control Extension Cable, 40 ft (12.2 m)
15W034 Strobe Light Alarm Indicator Kit
15V331 Gateway Ethernet Communication Kit
15V963 Gateway DeviceNet Communication Kit
15V964 Gateway Profibus Communication Kit
15V337 Advanced Web Interface
3A1080C 5
Page 6
Warnings
Warnings
The following warnings are for the setup, use, grounding, maintenance, and repair of this equipment. The exclamation point symbol alerts you to a general warning and the hazard symbols refer to procedure-specific risks. When
these symbols appear in the body of this manual, refer back to these Warnings. Product-specific hazard symbols and
warnings not covered in this section may appear throughout the body of this manual where applicable.
WARNING
FIRE AND EXPLOSION HAZARD
Flammable fumes, such as solvent and paint fumes, in work area can ignite or explode. To help
prevent fire and explosion:
• Use equipment only in well ventilated area.
• Eliminate all ignition sources; such as pilot lights, cigarettes, portable electric lamps, and plastic
drop cloths (potential static arc).
• Keep work area free of debris, including solvent, rags and gasoline.
• Do not plug or unplug power cords, or turn power or light switches on or off when flammable fumes
are present.
• Ground all equipment in the work area. See Grounding instructions.
• Use only grounded hoses.
• Hold gun firmly to side of grounded pail when triggering into pail.
• If there is static sparking or you feel a shock, stop operation immediately. Do not use equipment
until you identify and correct the problem.
• Keep a working fire extinguisher in the work area.
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
This equipment must be grounded. Improper grounding, setup, or usage of the system can cause
electric shock.
• Turn off and disconnect power at main switch before disconnecting any cables and before servicing
equipment.
• Connect only to grounded power source.
• All electrical wiring must be done by a qualified electrician and comply with all local codes and
regulations.
INTRINSIC SAFETY
Intrinsically safe equipment that is installed improperly or connected to non-intrinsically safe equipment
will create a hazardous condition and can cause fire, explosion, or electric shock. Follow local
regulations and the following safety requirements.
• Only models with a G3000, G250, G3000HR, G250HR, or intrinsically safe Coriolis meter are
approved for installation in a Hazardous Location - Class I, Div I, Group D, T3 or Zone I Group IIA
T3.
• Do not install equipment approved only for a non-hazardous location in a hazardous area. See the
ID label for the intrinsic safety rating of your model.
• Do not substitute or modify system components as this may impair intrinsic safety.
6 3A1080C
Page 7
Warnings
WARNING
SKIN INJECTION HAZARD
High-pressure fluid from gun, hose leaks, or ruptured components will pierce skin. This may look like
just a cut, but it is a serious injury that can result in amputation. Get immediate surgical treatment.
• Do not spray without tip guard and trigger guard installed.
• Engage trigger lock when not spraying.
• Do not point gun at anyone or at any part of the body.
• Do not put your hand over the spray tip.
• Do not stop or deflect leaks with your hand, body, glove, or rag.
• Follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when you stop spraying and before cleaning, checking, or
servicing equipment.
• Tighten all fluid connections before operating the equipment.
• Check hoses and couplings daily. Replace worn or damaged parts immediately.
EQUIPMENT MISUSE HAZARD
Misuse can cause death or serious injury.
• Do not operate the unit when fatigued or under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
• Do not exceed the maximum working pressure or temperature rating of the lowest rated system
component. See Technical Data in all equipment manuals.
• Use fluids and solvents that are compatible with equipment wetted parts. See Technical Data in all
equipment manuals. Read fluid and solvent manufacturer’s warnings. For complete information
about your material, request MSDS from distributor or retailer.
• Do not leave the work area while equipment is energized or under pressure. Turn off all equipment
and follow the Pressure Relief Procedure when equipment is not in use.
• Check equipment daily. Repair or replace worn or damaged parts immediately with genuine
manufacturer’s replacement parts only.
• Do not alter or modify equipment.
• Use equipment only for its intended purpose. Call your distributor for information.
• Route hoses and cables away from traffic areas, sharp edges, moving parts, and hot surfaces.
• Do not kink or over bend hoses or use hoses to pull equipment.
• Keep children and animals away from work area.
• Comply with all applicable safety regulations.
3A1080C 7
Page 8

Warnings
WARNING
TOXIC FLUID OR FUMES HAZARD
Toxic fluids or fumes can cause serious injury or death if splashed in the eyes or on skin, inhaled, or
swallowed.
• Read MSDSs to know the specific hazards of the fluids you are using.
• Store hazardous fluid in approved containers, and dispose of it according to applicable guidelines.
• Always wear chemically impermeable gloves when spraying, dispensing, or cleaning equipment.
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
You must wear appropriate protective equipment when operating, servicing, or when in the operating
area of the equipment to help protect you from serious injury, including eye injury, hearing loss,
inhalation of toxic fumes, and burns. This equipment includes but is not limited to:
• Protective eyewear, and hearing protection.
• Respirators, protective clothing, and gloves as recommended by the fluid and solvent manufacturer.
8 3A1080C
Page 9
Important Two-Component Material Information
Important Two-Component Material Information
Isocyanate Conditions
Spraying or dispensing materials containing isocyanates creates potentially harmful mists, vapors, and
atomized particulates.
Read material manufacturer’s warnings and material MSDS to know specific hazards and precautions
related to isocyanates.
Prevent inhalation of isocyanate mists, vapors, and
atomized particulates by providing sufficient ventilation in the work area. If sufficient ventilation is not
available, a supplied-air respirator is required for
everyone in the work area.
To prevent contact with isocyanates, appropriate
personal protective equipment, including chemically
impermeable gloves, boots, aprons, and goggles, is
also required for everyone in the work area.
Material Self-ignition
Moisture Sensitivity of Isocyanates
Isocyanates (ISO) are catalysts used in two component
coatings. ISO will react with moisture (such as humidity)
to form small, hard, abrasive crystals, which become
suspended in the fluid. Eventually a film will form on the
surface and the ISO will begin to gel, increasing in viscosity. If used, this partially cured ISO will reduce performance and the life of all wetted parts.
NOTE: The amount of film formation and rate of crystallization varies depending on the blend of ISO, the
humidity, and the temperature.
To prevent exposing ISO to moisture:
• Always use a sealed container with a desiccant
dryer in the vent, or a nitrogen atmosphere. Never
store ISO in an open container.
• Use moisture-proof hoses specifically designed for
ISO, such as those supplied with your system.
• Never use reclaimed solvents, which may contain
moisture. Always keep solvent containers closed
when not in use.
• Never use solvent on one side if it has been contaminated from the other side.
• Always lubricate threaded parts with ISO pump oil
or grease when reassembling.
Some materials may become self-igniting if applied
too thickly. Read material manufacturer’s warnings
and material MSDS.
Keep Components A and B Separate
Cross-contamination can result in cured material in
fluid lines which could cause serious injury or damage equipment. To prevent cross-contamination of
the equipment’s wetted parts, never interchange
component A (isocyanate) and component B (resin)
parts.
3A1080C 9
Changing Materials
• When changing materials, flush the equipment multiple times to ensure it is thoroughly clean.
• Always clean the fluid inlet strainers after flushing.
• Check with your material manufacturer for chemical
compatibility.
• Most materials use ISO on the A side, but some use
ISO on the B side.
Page 10

Glossary of Terms
Glossary of Terms
Air Chop - the process of mixing air and solvent
together during the flush cycle to help clean the lines
and reduce solvent usage.
Analog - relating to, or being a device in which data are
represented by continuously variable, measurable,
physical quantities, such as length, width, voltage, or
pressure.
Closed Loop Flow Control - refers to the process
when the flow rate is adjusted automatically to maintain
a constant flow.
Color/Catalyst Dump - refers to the time required to
flush the lines from the color or catalyst change module
to the mix manifold during a color or catalyst change.
Color/Catalyst Fill - refers to the time required to fill the
lines from the color or catalyst change module to the mix
manifold.
Coriolis Meter - a non-intrusive flow meter often used in
low flow applications or with light viscosity, shear sensitive, or acid catalyzed materials. This meter uses vibration to measure flow.
Digital Input and Output - a description of data which
is transmitted as a sequence of discrete symbols, most
commonly this means binary data represented using
electronic or electromagnetic signals.
Discrete I/O - refers to data that constitutes a separate
entity and has direct communication to another control.
Dose Size - the amount of resin (A) and catalyst (B) that
is dispensed into an integrator (in ProMix 2KS applications).
Dose Time Alarm - the amount of time that is allowed
for a dose to occur before an alarm occurs.
Ethernet - a method for directly connecting a computer
to a network or equipment in the same physical location.
Fill Time - the amount of time that is required to load
mix material to the applicator.
Flow Control Resolution - a settable value that allows
the flow control system to maximize its performance.
The value is based on maximum desired flow rates.
Flow Rate Analog Signal - the type of communication
signal that can be used on the ProControl module.
Flow Rate Tolerance - the settable percent of acceptable variance that the system will allow before a flow
rate warning occurs.
Flow Set Point - a predefined flow rate target.
Grand Total - a non-resettable value that shows the
total amount of material dispensed through the system.
Gun Trigger Input Signal - used to manage ratio assurance dose times and flow control processes.
Intrinsically Safe (IS) - refers to the ability to locate certain components in a hazardous location.
Idle - if the gun is not triggered for 2 minutes the system
enters Idle mode. Trigger the gun to resume operation.
Job Total - a resettable value that shows the amount of
material dispensed through the system for one job. A job
is complete when a color change or complete system
flush occurs.
K-factor - a value that refers to the amount of material
that passes through a meter. The assigned value refers
to an amount of material per pulse.
Ki - refers to the degree fluid flow over shoots its set
point.
Kp - refers to the speed in which the fluid flow reaches
its set point.
Fiber Optic Communication - the use of light to transmit communication signals.
10 3A1080C
Page 11

Glossary of Terms
Manual Mode - when the proportioning or flow control
system is controlling the inputs without any input from
an outside control.
Mix - when cross-linking of the resin (A) and catalyst (B)
occurs (in ProMix 2KS applications). In ProControl 1KS
applications, indicates the system is active.
Mix Input Signal- refers to system mode status where
system begins a dose sequence each time the mix signal is made “High”.
Modbus/TCP - a type of communication protocol used
to communicate Digital I/O signals over an ethernet.
Network Station - a means to identify a particular individual proportioning or flow control system.
Overdose Alarm - when either the resin (A) or catalyst
(B) component dispenses too much material and the
system cannot compensate for the additional material.
Potlife Time - the amount of time before a material
becomes unsprayable.
Potlife Volume - the amount of material that is required
to move through the mix manifold, hose and applicator
before the potlife timer is reset.
Purge - when all mixed material is flushed from the system.
Purge Time - the amount of time required to flush all
mixed material from the system.
Ratio Tolerance - the settable percent of acceptable
variance that the system will allow before a ratio alarm
occurs.
Sequential Color Change - the process when a color
change is initiated and the system automatically flushes
the old color and loads a new color.
Solvent Fill - the time required to fill the mixed material
line with solvent.
Standby - refers to the status of the system.
Third Purge Valve - refers to the use of three purge
valves used to flush some waterborne materials. The
valves are used to flush with water, air and solvent.
V/P - refers to the voltage to air pressure device in the
flow control module.
3A1080C 11
Page 12
Overview
Overview
Usage
The Graco ProControl 1KS is an electronic flow control and color change system, for use with most solvent and
waterborne epoxy, polyurethane, and acid-catalyzed paints. It is not for use with “quick-setting” paints (those with a
potlife of less than 15 minutes).
• Has user selectable ratio assurance and can maintain up to +/-1% accuracy, depending on materials
and operating conditions.
• Models are available to operate air spray or
air-assisted systems with a capacity of up to 3800
cc/min.
Component Identification and Definition
SeeTable 1 and FIG. 2 for the system components.
• Color change options are available for low pressure
(300 psi [2.1 MPa, 21 bar]) air spray and high pressure (3000 psi [21 MPa, 210 bar]) systems with up
to 30 color change valves and up to 4 catalyst
change valves.
NOTE: Optional accessories are available for in field
installation to achieve 30 colors.
Table 1: Component Descriptions
Component Description
EasyKey (EK)
Fluid Station
Control Box (ST)
Fluid Manifold (FM)
Flow Meters (MA,
MS)
Used to set up, display, operate, and monitor the system. The EasyKey accepts 85-250
VAC, 50/60 Hz line power and converts that power to acceptable low voltage and optical
signals used by other system components.
Includes air control solenoids. Its control board manages all fluid functions.
Includes wall mounting bracket and mountings for the fluid meter and the following valves:
• Pneumatically Operated Dose Valve for component A
• Purge Valves for solvent and air purge
Four optional flow meters are available from Graco:
• G3000 is a general purpose gear meter typically used in flow ranges of 75-3800
cc/min. (0.02–1.0 gal/min.), pressures up to 4000 psi (28 MPa, 276 bar), and viscosities of 20–3000 centipoise. The K-factor is approximately 0.119 cc/pulse.
• G3000HR is a high resolution version of the G3000 meter. It is typically used in flow
ranges of 38–1900 cc/min. (0.01–0.5 gal/min.), pressures up to 4000 psi (28 MPa,
276 bar). and viscosities of 20–3000 centipoise. The K-factor is approximately 0.061
cc/pulse.
• S3000 is a gear meter used for solvents in flow ranges of 38-1900 cc/min. (0.01–0.50
gal/min.), pressures up to 3000 psi (21 MPa, 210 bar), and viscosities of 20–50 centipoise. The K-factor is approximately 0.021 cc/pulse.
• Coriolis is a specialty meter capable of a wide range of flow rates and viscosities.
This meter is available with 1/8 in. or 3/8 in. diameter fluid passages. For detailed
information on the Coriolis meter, see manual 313599.
The K-factor is user-settable; at lower flow rates use a lower K-factor.
➜ 1/8 in. fluid passages: set K-factor to .020 or .061.
➜ 3/8 in. fluid passages: set K-factor to .061 or 0.119.
12 3A1080C
Page 13
Table 1: Component Descriptions
Component Description
Overview
Color Change
Valves (ACV) and
Color Change
Module (CCM)
Dual Fiber Optic
Cable (FO)
Fluid Station
Control Box Power
Supply Cable (PS)
Flow Control
Regulator
Assembly (FC)
An optional component. It is available as a color change valve stack for either low or high
pressure with up to 30 color change valves. Each stack includes one additional valve for
solvent to clean the fluid line between color changes.
Used to communicate between the EasyKey and Fluid Station Control Box.
Used to provide power to the Fluid Station Control Box.
Includes an air operated fluid pressure regulator, fluid pressure sensor, voltage to air
pressure transducer and circuit board. The function of this unit is to receive the flow analog signal and drive (manage) the desired flow rate.
3A1080C 13
Page 14
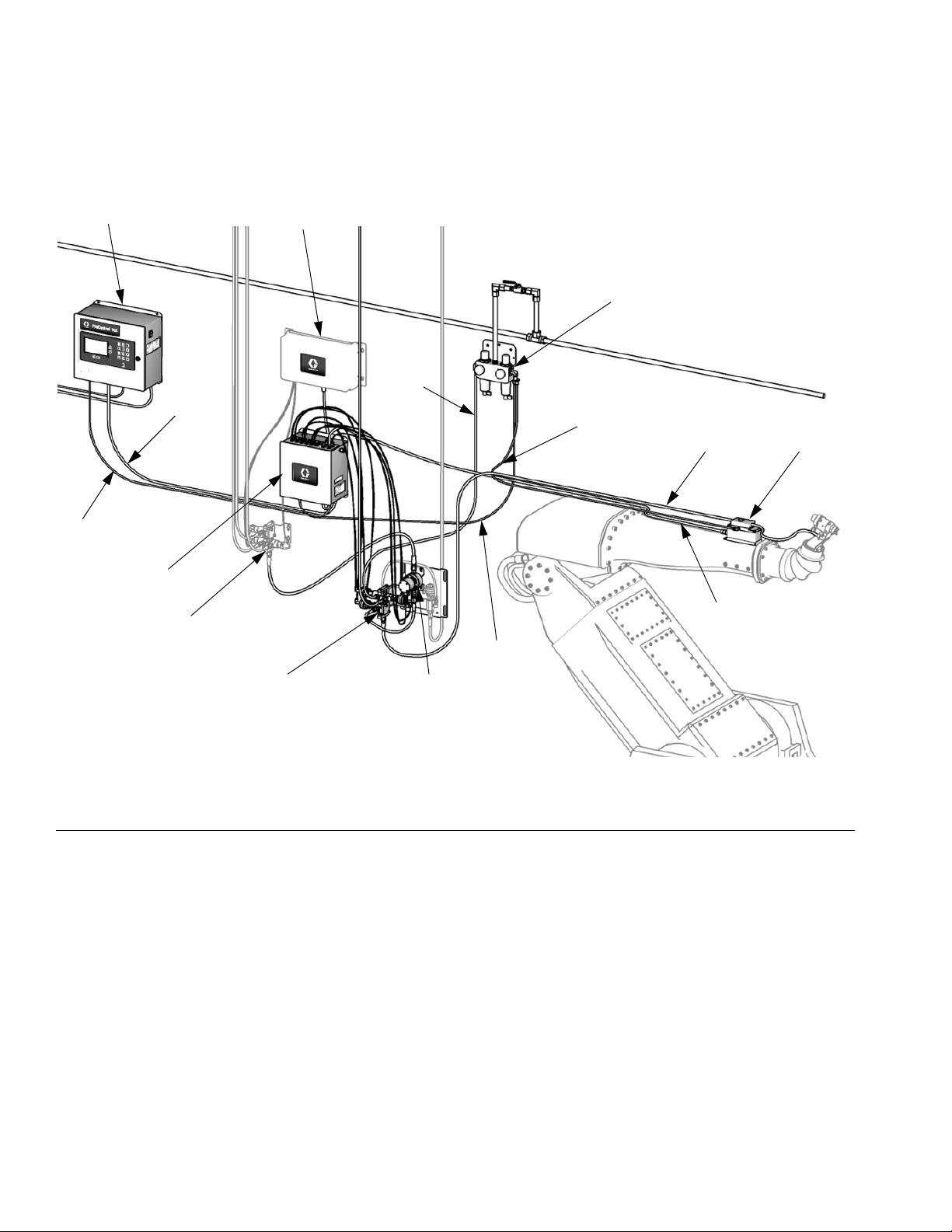
Overview
ProControl 1KS System Components
FO*
EK
ST
PS*
ACV
CCM
Purge
Air
Logic Air
Air Control
Module
Regulator
V/P Air
Fluid
FC Cable*
FC (see
F
IG. 4)
MAFM (see
F
IG. 3)
* See the ProControl 1KS
Repair-Parts manual for
optional cable lengths.
FIG. 2. ProControl 1KS System, shown with G3000 Meter, Color Change, and Flow Control
TI15961b
14 3A1080C
Page 15
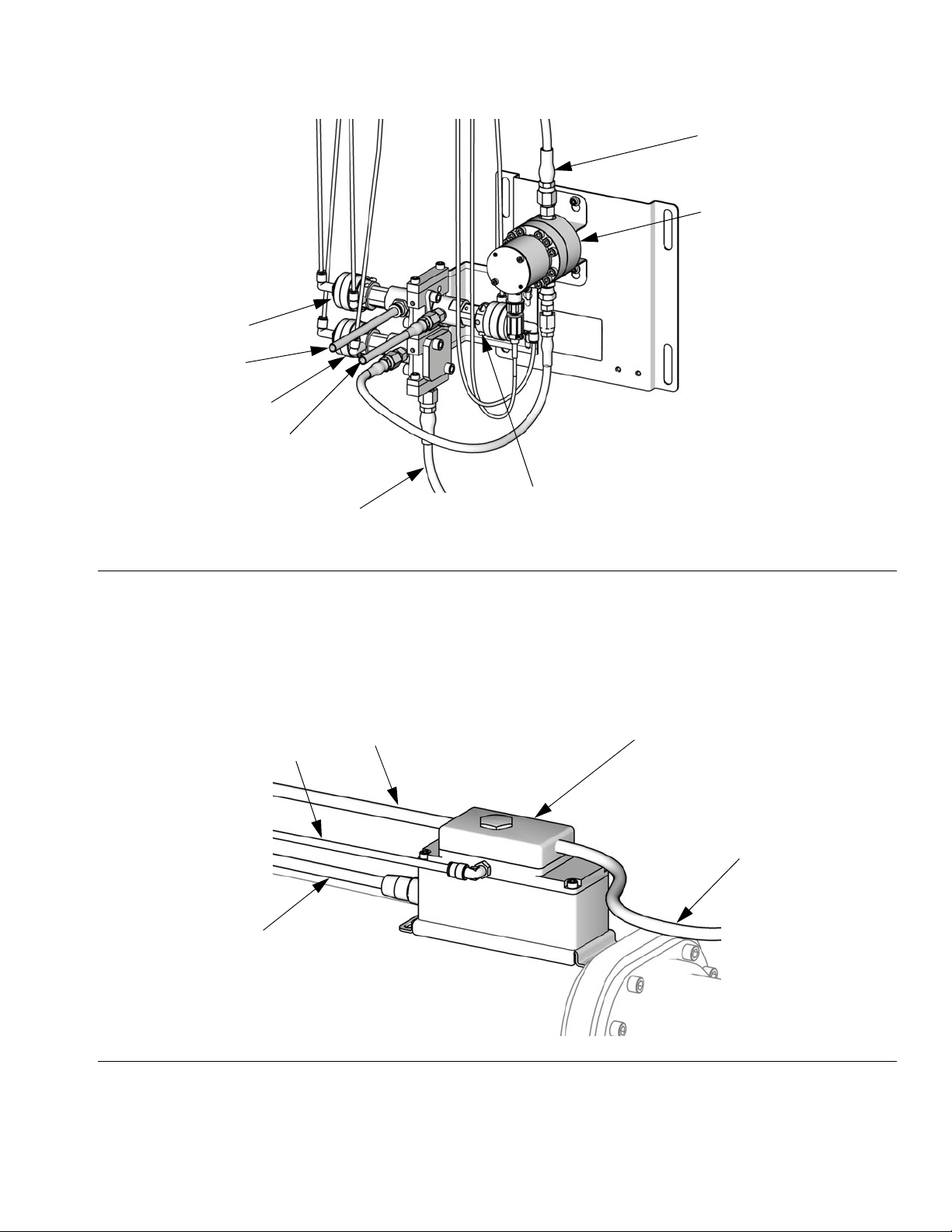
APV
AT
Overview
FIH
MA
DVA
SS
FOH
FIG. 3. Fluid Manifold
Key:
MA Component A Meter
DVA Component A Dose Valve
SPV Solvent Purge Valve
SS Solvent Purge Valve Solvent Supply Tube
Regulator
Fluid In
V/P Air
FC Cable
SPV
APV Air Purge Valve
AT Air Purge Valve Air Supply Tube
FIH Fluid Inlet Hose
FOH Fluid Outlet Hose
FC
TI15977a
Fluid Out
TI15976a
F
IG. 4. Flow Control Regulator
3A1080C 15
Page 16
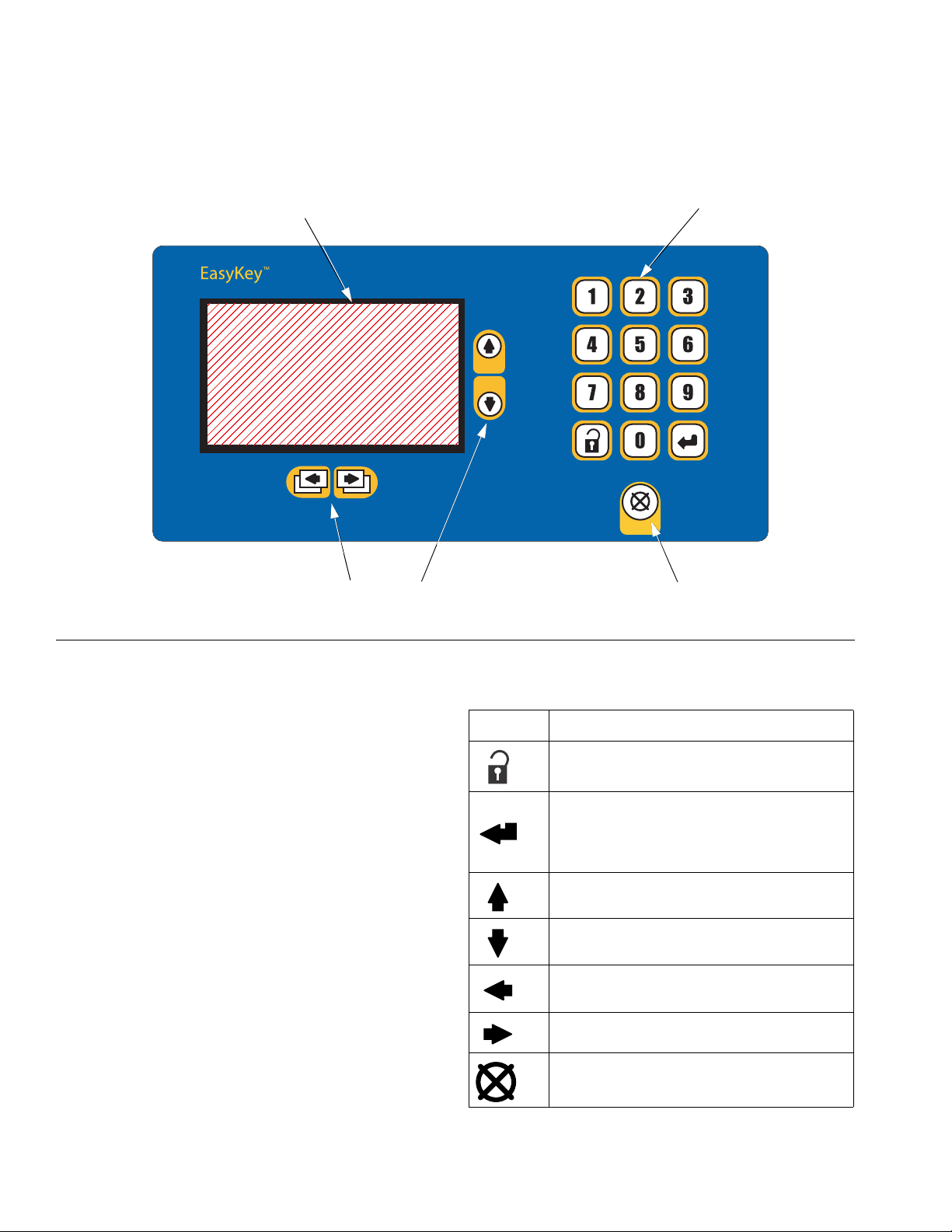
EasyKey Display and Keyboard
EasyKey Display and Keyboard
LCD Display
F
IG. 5. EasyKey Display and Keypad
Keypad
TI11630A
Navigation Keys Alarm Reset Key
Display
Shows graphical and text information related to setup
and spray operations. Back light will turn off after 10
minutes without any key press. Press any key to turn
back on.
Keypad
Used to input numerical data, enter setup screens, scroll
through screens, and select setup values.
In addition to the numbered keys on the EasyKey keypad, which are used to enter values in setup, there are
keys to navigate within a screen and between screens,
and to save entered values. See Table 2.
Table 2: EasyKey Keypad Functions (see FIG. 5)
Key Function
Setup: press to enter or exit Setup mode.
Enter: if cursor is in menu box, press Enter
key to view menu. Press Enter to save a
value either keyed in from the numerical
keypad or selected from a menu.
Up Arrow: move to previous field or menu
item, or to previous screen within a group.
Down Arrow: move to next field or menu
item, or to next screen within a group.
Left Arrow: move to previous screen group.
Right Arrow: move to next screen group.
Alarm Reset: resets alarms.
16 3A1080C
Page 17
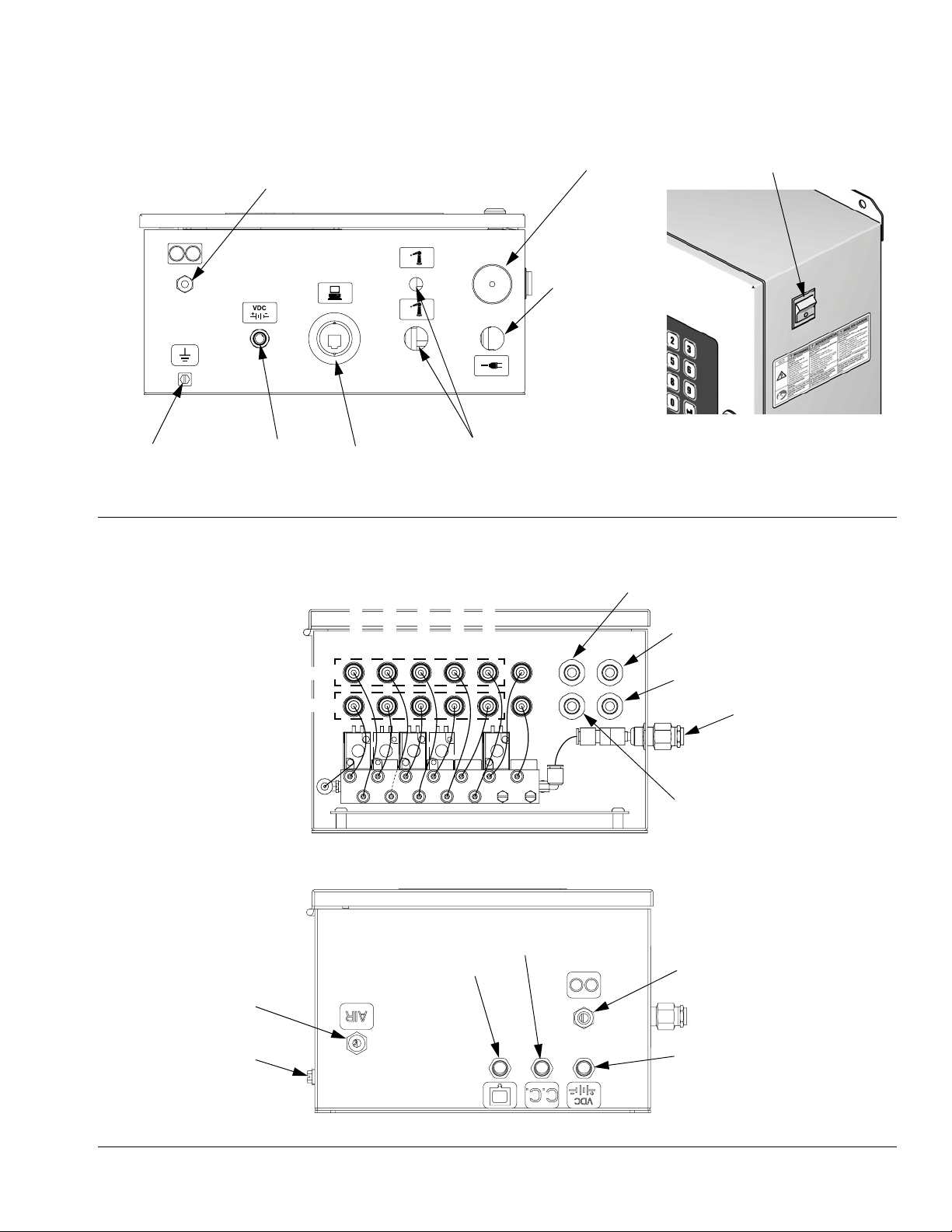
Relief Port
TOP VIEW
Ground Screw
I/S Power Discrete I/O Cable
Graco Web
Interface
Connector Ports
FIG. 6. EasyKey Connections and AC Power Switch
Audible AlarmFiber Optic Strain
Main Power
Access Port
TI12638a
EasyKey Display and Keyboard
AC Powe r
Switch
TI12657a
Logic Air Inlet
CLOSE
OPEN
A PURGE
B DOSE
A DOSE
BOTTOM VIEW
Booth Control
(Manual Systems
B PURGE
3RD PURGE
only)
Meter A
Flow Control
Gun Air
Muffler
A DUMP B DUMP
Meter B
(not used)
TI15917a
Color Change
Module
Fiber Optic Strain
Relief Port
Ground Screw
IG. 7. Fluid Station Control Box Connections
F
3A1080C 17
I/S Power
TI15919a
Page 18

EasyKey Display and Keyboard
AC Power Switch
Turns system AC power on or off.
I/S Power
Power circuit to Fluid Station Control Box.
Potlife Exceeded Audible Alarm
Alerts the user when a Potlife Exceeded alarm occurs.
Clear by pressing the Alarm Reset
key.
Graco Web Interface Port
Used to communicate with the ProMix from a PC to:
➜ Upgrade software
➜ View software version
➜ Download
• Job and alarm logs
• Material usage report
• Setup values (can also upload)
➜ Clear job, alarm, and material usage
reports
➜ Upload a custom language to view on
screen
➜ Restore factory defaults
➜ Restore setup password
See manual 313386 for more information.
NOTE: If using the Graco Gateway in your system, disconnect its cable from the EasyKey before updating the
ProMix 2KS/ProControl 1KS software.
Ethernet Connection
You can access data on an office or industrial network
through the internet with the proper configuration. See
manual 313386 for more information.
18 3A1080C
Page 19

Run Mode Screens
Run Mode Screens
NOTE: See FIG. 10 for a map of the Run screens.
Detailed screen descriptions follow.
Splash Screen
At power up, the Graco logo and software revision will
display for approximately 5 seconds, followed by the
Status Screen (see page 21).
F
IG. 8. Splash Screen
.
The Splash screen will also momentarily display “Establishing Communication.” If this display remains for more
than one minute, check that the fluid station control box
circuit board is powered up (LED is on) and that the fiber
optic cable is properly connected (see Installation manual).
NOTE: If the software version of the fluid plate does not
match the version of the EasyKey, the EasyKey will
update the fluid plate, and the fluid plate programming
screen will appear until the update is completed.
F
IG. 9. Fluid Plate Programming Screen
3A1080C 19
Page 20
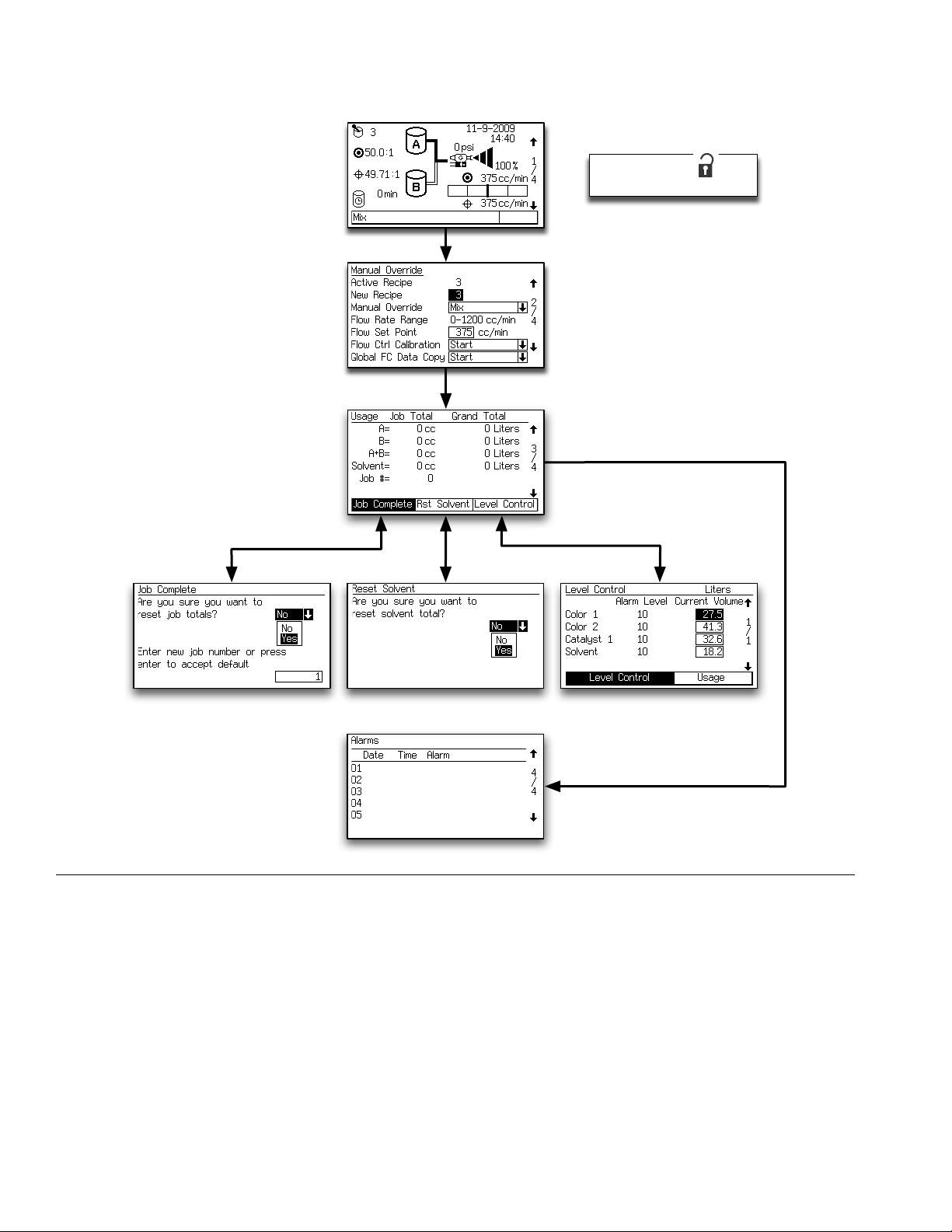
Run Mode Screens
Press the Setup key to
enter Setup mode.
TI12802a
FIG. 10. Run Screens Map
20 3A1080C
Page 21
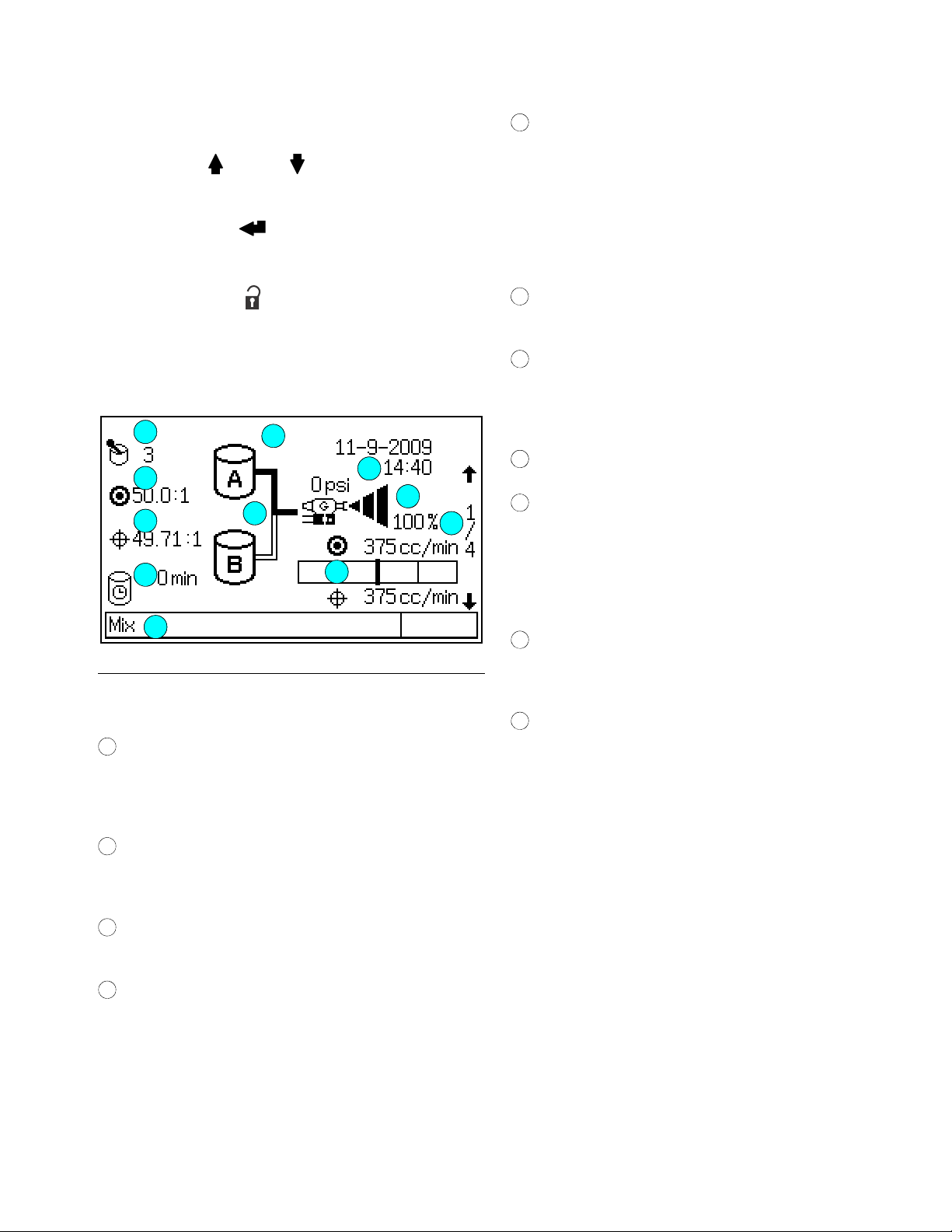
Run Mode Screens
Status Screen
• Use the Up or Down keys to scroll through the
Run screens.
• Press the Enter key to select a different fluid
station control box.
• Press the Setup key to enter the Setup screens
from the Status screen.
• The other keys have no function in this Status
screen.
1
2
3
4
11
8
10
7
9
6
5
Status Bar: shows current alarm or operation mode
(standby, mix, purge, recipe change, or the current
alarm).
NOTE: If the auto key board is removed from the
EasyKey display board, the Status Bar will read
“Auto key not found.” This indicates that the automatic mode is not operable.
6
Target Flow Rate and Current Flow Rate: in
cc/min.
7
Animation: when the gun is triggered, the gun
appears to spray and the component A or B hose
lights up, showing which component dose valve is
open.
8
Current Date and Time
9
Screen Number and Scroll Arrows: displays the
current screen number and the total number of
screens in a group. The Up and Down arrows on the
right edge of the screen indicate the scroll feature.
The total number of screens in some groups may
vary depending on system configuration selections.
5
F
IG. 11. Status Screen
Key to F
1
2
3
4
IG. 11:
Active Recipe: shows the active recipe.
NOTE: At power up the system defaults to Recipe
61, which is not a valid recipe number.
Target R atio: for the active recipe. The ratio can be
from 0.0:1–50.0:1, in 0.1 increments. For the ProControl 1KS, set the ratio at 0:1.
Actual Ratio: in hundredths, calculated after each
dose of A.
Potlife Timer: shows remaining potlife time in minutes. Two times are shown if there are two guns
(manual or semi-automatic mode only).
10
Current Flow Control Data: fluid output pressure
and percentage of analog signal range used for driving the fluid regulator V/P.
11
Lock Symbol: indicates that Setup screens are
password protected. See page 26.
3A1080C 21
Page 22
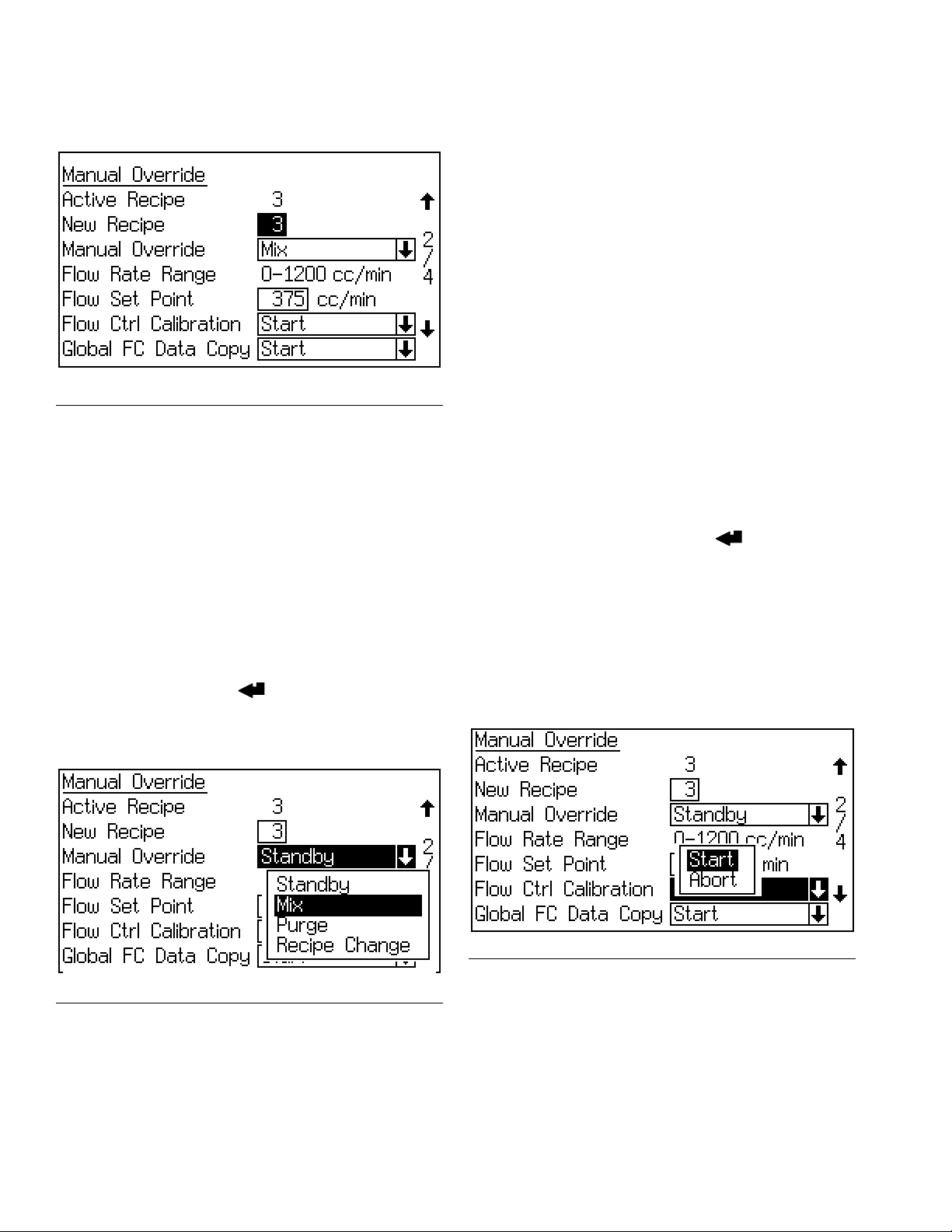
Run Mode Screens
Manual Override Screen
F
IG. 12. Manual Override Screen
This screen will appear if Manual Override is set to “On”
in Advanced Setup Screen 1 (page 35). It shows the
active recipe, new/go to recipe, and manual override
mode.
If Flow Control is set to “On” in Configure Screen 5 on
page 31, this screen will also display Flow Rate Range,
Flow Set Point, Flow Control Calibration (Start/Abort),
and Global Flow Control Data Copy (Start/Abort).
Manual Override Menu
This field allows you to set the operating mode from the
EasyKey. Press the Enter key to view the menu,
then select the desired operating mode (Standby, Mix,
Purge, or Recipe Change). See F
IG. 13.
Flow Rate Range
This screen displays the flow rate range selected on
Advanced Setup Screen 5 (see page 37).
Flow Set Point
The Flow Set Point is user settable. If Flow Control
Override is set to “Off” or “Pressure” in Advanced
Setup Screen 1 on page 35, the Flow Set Point will display as cc/min. Enter the desired flow set point within
the range.
If Flow Control Override is set to “% Open,” the Flow Set
Point will display as % Open. This percentage relates to
the flow control V/P ratio which translates to a fluid flow
rate. Set the initial percentage at 35% and increase as
necessary to reach the desired flow rate.
Flow Control Calibration
This field allows you to calibrate flow control for each
recipe. The system must be in Mix mode and receiving a
Gun Trigger signal. Press the Enter key to view the
menu, then select Start or Abort. See F
The flow rate will drop to 0, then incrementally increase
until it reaches the maximum flow rate. To view the progress, go to the Status Screen, page 21. The system will
populate the data for the current recipe. To copy this
data to all recipes, see Global Flow Control Data
Copy, page 23.
IG. 14.
FIG. 14. Flow Control Calibration
F
IG. 13. Manual Override Menu
22 3A1080C
Page 23
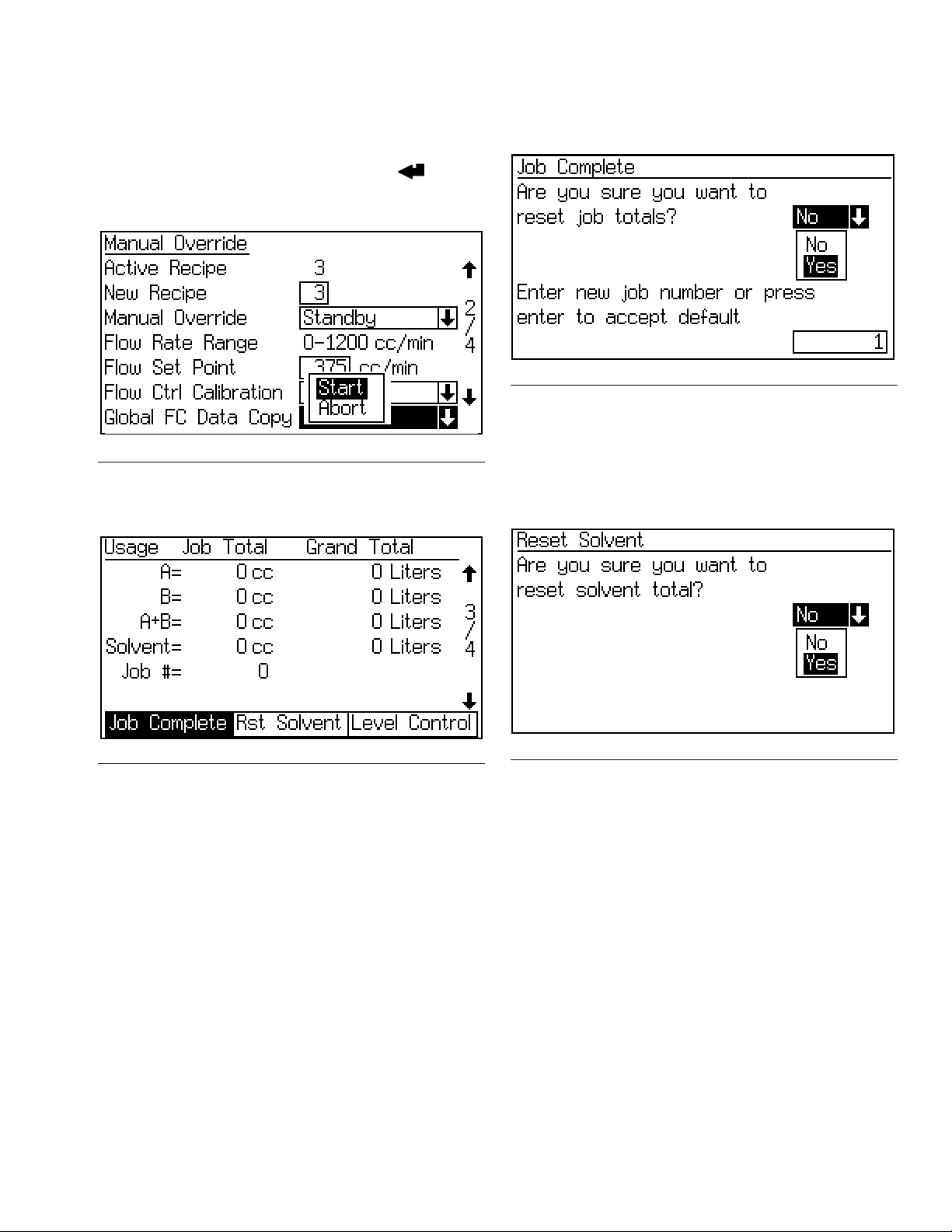
Run Mode Screens
Global Flow Control Data Copy
This field allows you to copy flow control data from the
active recipe to all recipes. Press the Enter key to
view the menu, then select Start or Abort. See F
F
IG. 15. Global FC Data Copy
IG. 15.
Totals Screen
Reset Total Screen
FIG. 17. Reset Total Screen
If job is reset, job number will increment by one for
default.
Reset Solvent Screen
F
IG. 16. Totals Screen
F
This screen shows the job totals, grand totals, and job
number. Use the tabs to reset job totals (Job Complete),
reset solvent totals (Rst Solvent), or go to Level Control
Screen, page 24.
Solvent Totals and the Rst Solvent tab only appear if
“Meter” is selected under Solvent Monitor in Configure
Screen 5 on page 31.
NOTE: Grand totals are not resettable.
3A1080C 23
IG. 18. Reset Solvent Total Screen
The screen will ask if you want to reset solvent total.
Select Yes or No.
Page 24
Run Mode Screens
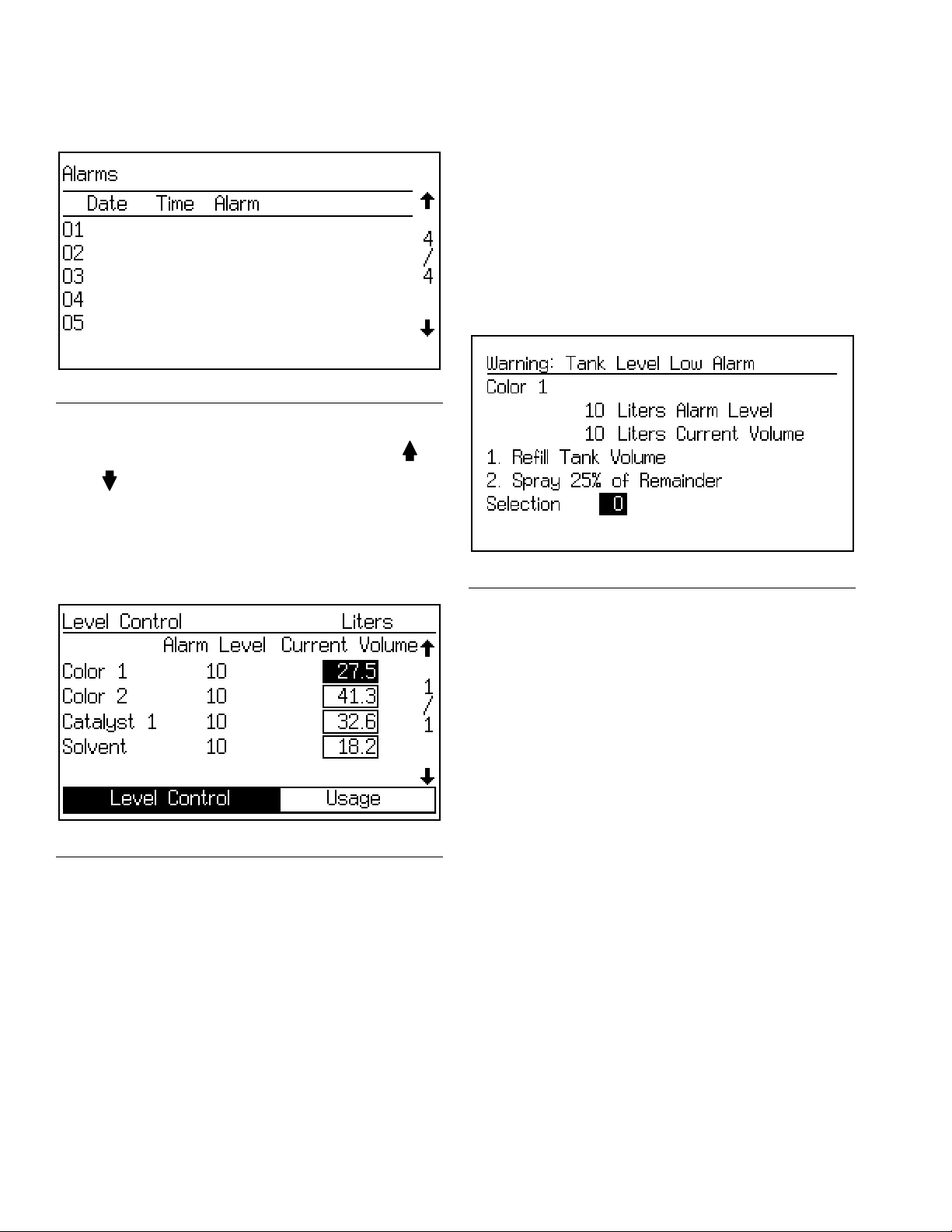
Alarms Screen
F
IG. 19. Alarms Screen
Two screens show the last 10 alarms. Use the Up or
See F
IG. 21. If the tank volume reaches the low-level
threshold, the EasyKey screen will display the Tank
Level Low alarm and prompt the user to do one of the
following:
1. Refill tank volume to clear the alarm.
2. Resume mixing by selecting “Spray 25% of Remainder.” If this selection is chosen, a second alarm will
occur after 25% of the remaining volume is mixed.
Refill tank volume to clear the alarm.
Down
See Table 13 on page 90 for a list of alarm codes.
keys to scroll between the two screens.
Level Control Screen
IG. 20. Level Control Screen
F
This screen shows the current volume for each fluid.
Adjust the actual volumes on this screen, or use the tab
to go to Usage (Totals Screen, page 23).
FIG. 21. Tank Level Low Screen (Tank A Shown)
24 3A1080C
Page 25
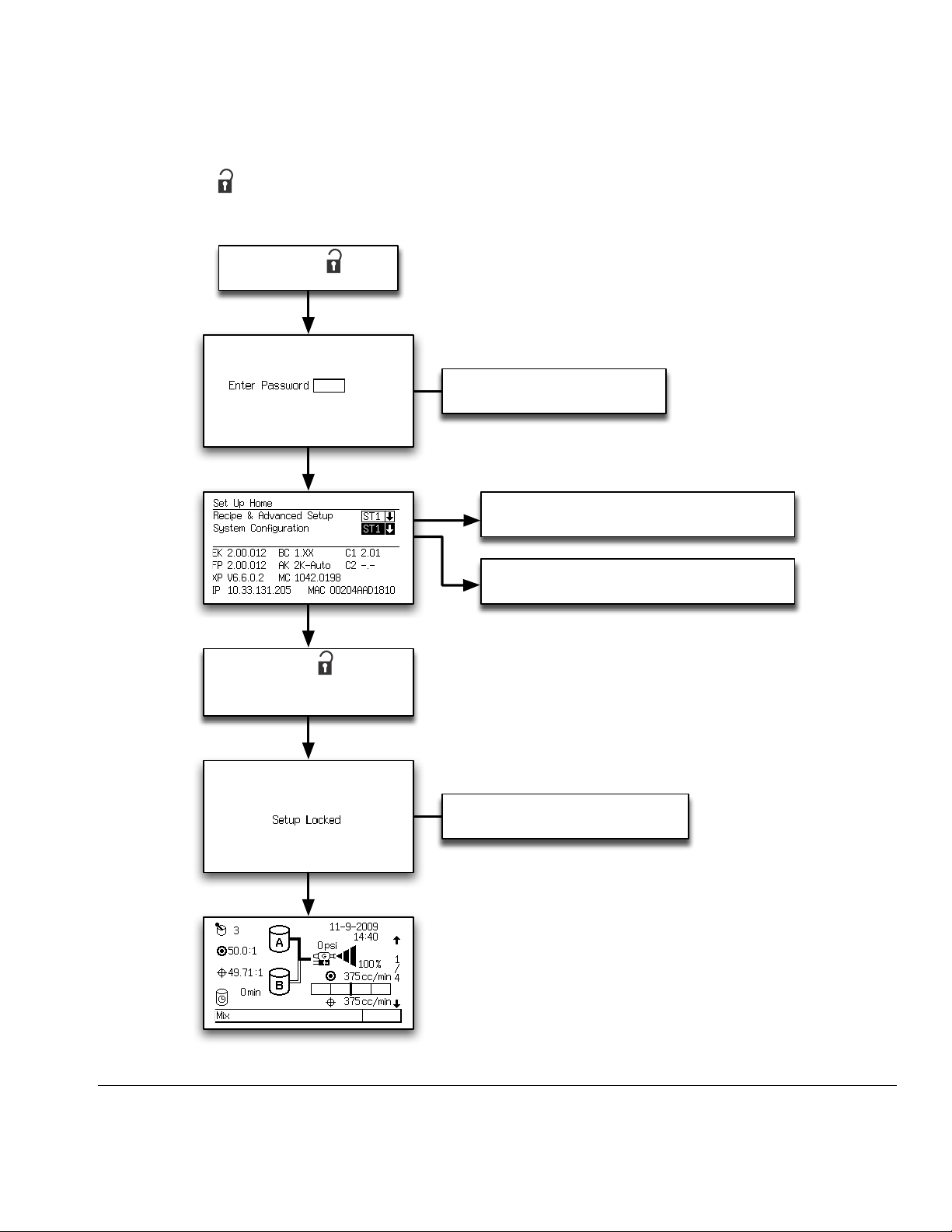
Setup Mode
Setup Mode
Press the Setup key to enter Setup mode.
Press the Setup key to
enter Setup mode.
NOTE: See F
IG. 22 for a map of the Setup screens.
Detailed screen descriptions follow.
This screen appears only if a
password is activated.
To access Advanced Setup Screens, page
34 and Recipe Setup Screens, page 39.
To access System Configuration Screens,
page 28.
Press the Setup key to exit
Setup mode and return to the Status
FIG. 22. Setup Screens Map
screen.
This screen appears momentarily
if a password is activated.
TI12803a
3A1080C 25
Page 26
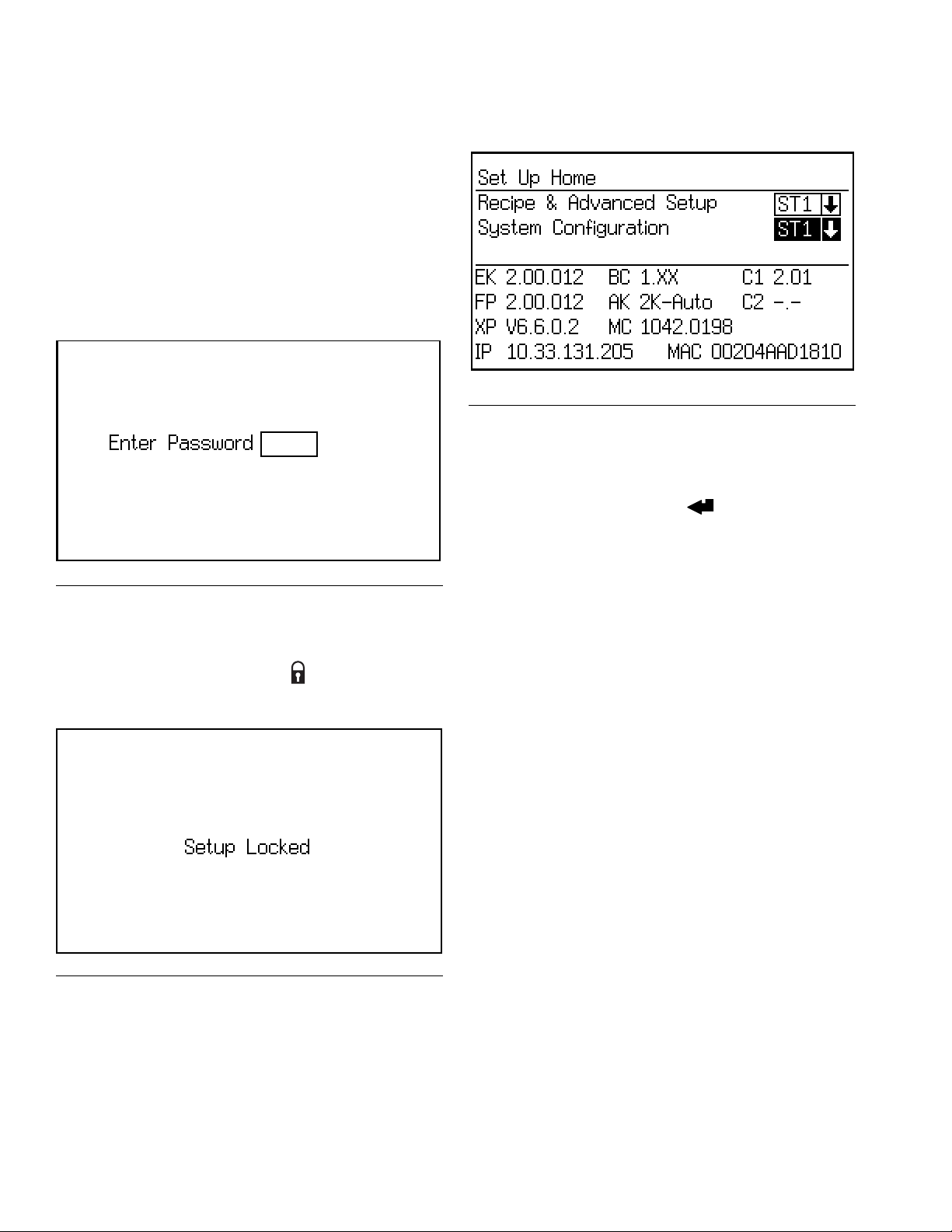
Setup Mode
Password Screen
If a password has been activated (see Configure
Screen 1, page 29), the Password screen will appear.
You must enter the password to access the Set Up
Home Screen. Entering the wrong password returns the
display to the Status Screen.
NOTE: If you forget the password, you can reset the
password (to 0), using the ProMix Web Interface (see
manual 313386).
F
IG. 23. Password Screen
NOTE: If a password is activated, Setup Locked dis-
plays momentarily after exiting Setup mode and returning to the Status Screen. A lock symbol appears
Set Up Home Screen
FIG. 25. Set Up Home Screen
This screen displays when you enter Setup mode. From
it you can go to Recipe and Advanced Setup Screens
(pages 34-42) or System Configuration Screens
(pages 28-33). Press the Enter key to go to the
selected screen set.
The screen also displays software versions and internet
addresses of various components. The values shown in
F
IG. 25 are only examples and may vary on your screen.
See Table 3 for further information.
on the Status Screen.
IG. 24. Setup Locked Screen
F
26 3A1080C
Page 27
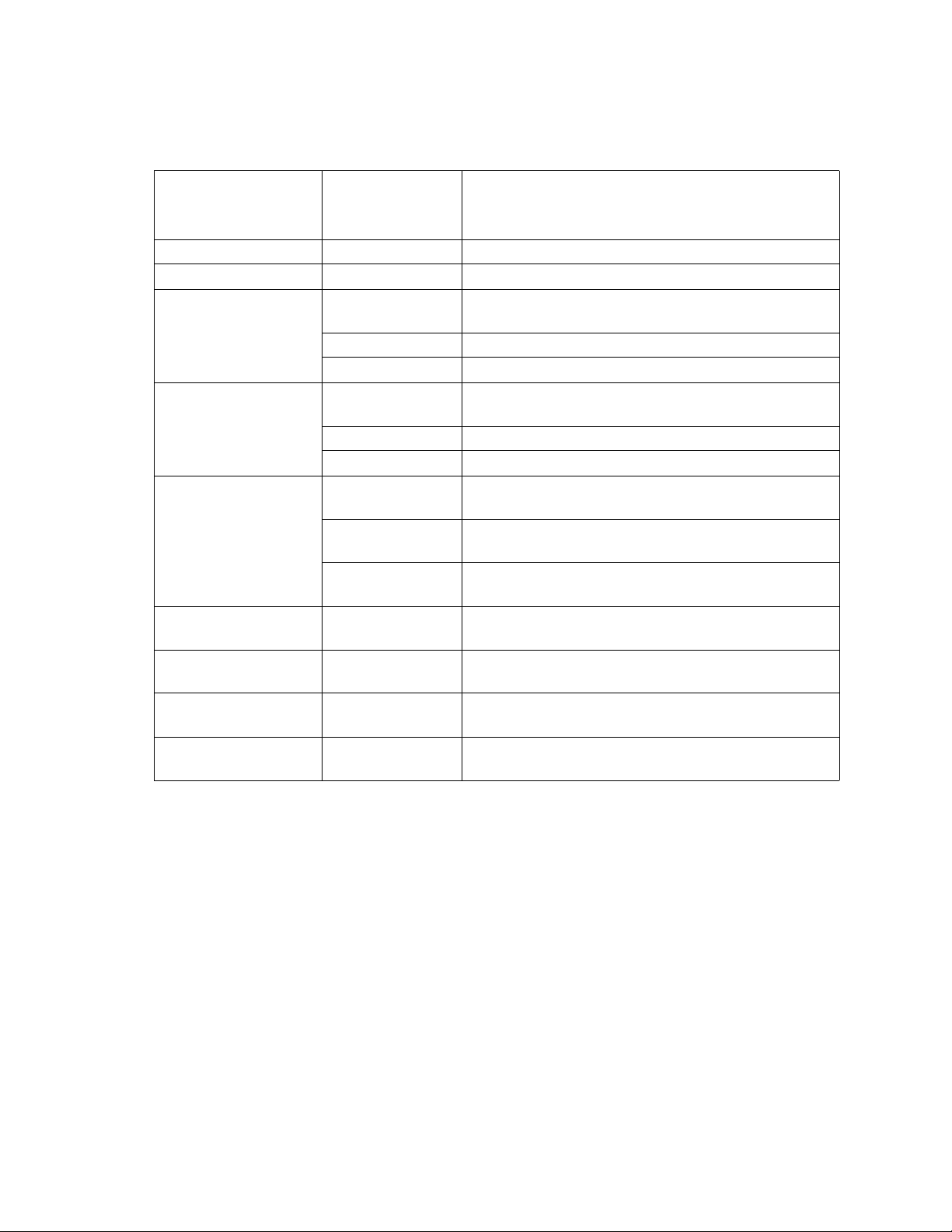
Setup Mode
Table 3: Component Software Versions
Display (may vary
from examples
Component
shown) Description
EK (EasyKey) 2.00.012 EasyKey software version.
FP (Fluid Plate) 2.00.012 Fluid Plate software version.
BC (Booth Control) -.- Booth Control not installed, not detected, or not oper-
ational.
1.XX Booth Control software version 1.00 or 1.01.
2.XX Booth Control software version 2.XX.
C1/C2 (Color Change
Modules 1 and 2)
-.- Color Change Module 1/2 not installed, not detected,
or not operational.
1.XX Color Change Module software version 1.00 or 1.01.
2.XX Color Change Module software version 2.XX.
AK (Autokey) 2K-Manual No AutoKey installed or detected. System operates in
2K Manual Mode only
2K-Auto 2K AutoKey detected. System can operate in 2K Man-
ual, Semi-automatic, or Automatic Mode.
3K-Auto 3K AutoKey detected. System can operate in 3K Man-
ual, Semi-automatic, or Automatic Mode.
XP (XPORT) V6.6.0.2 Example of XPORT network module software version.
Other versions are acceptable.
MC (Micro Controller) 1042.0198 Example of fluid plate micro controller version. Other
versions are acceptable.
IP (Internet Address) 192.168.178.5 Example of the address EasyKey is set to for basic
and advanced web interface reporting.
MAC (MAC address) 00204AAD1810 Example of internet MAC address. Each EasyKey will
have a different value in this format.
3A1080C 27
Page 28
Setup Mode
System Configuration Screens
NOTE: See FIG. 26 for a map of the System Configura-
tion Screens. Detailed screen descriptions follow.
NOTE: Each screen displays the current screen number
and the total number of screens in the group.
TI12804a
F
IG. 26. System Configuration and Option Screens Map
28 3A1080C
Page 29
Setup Mode
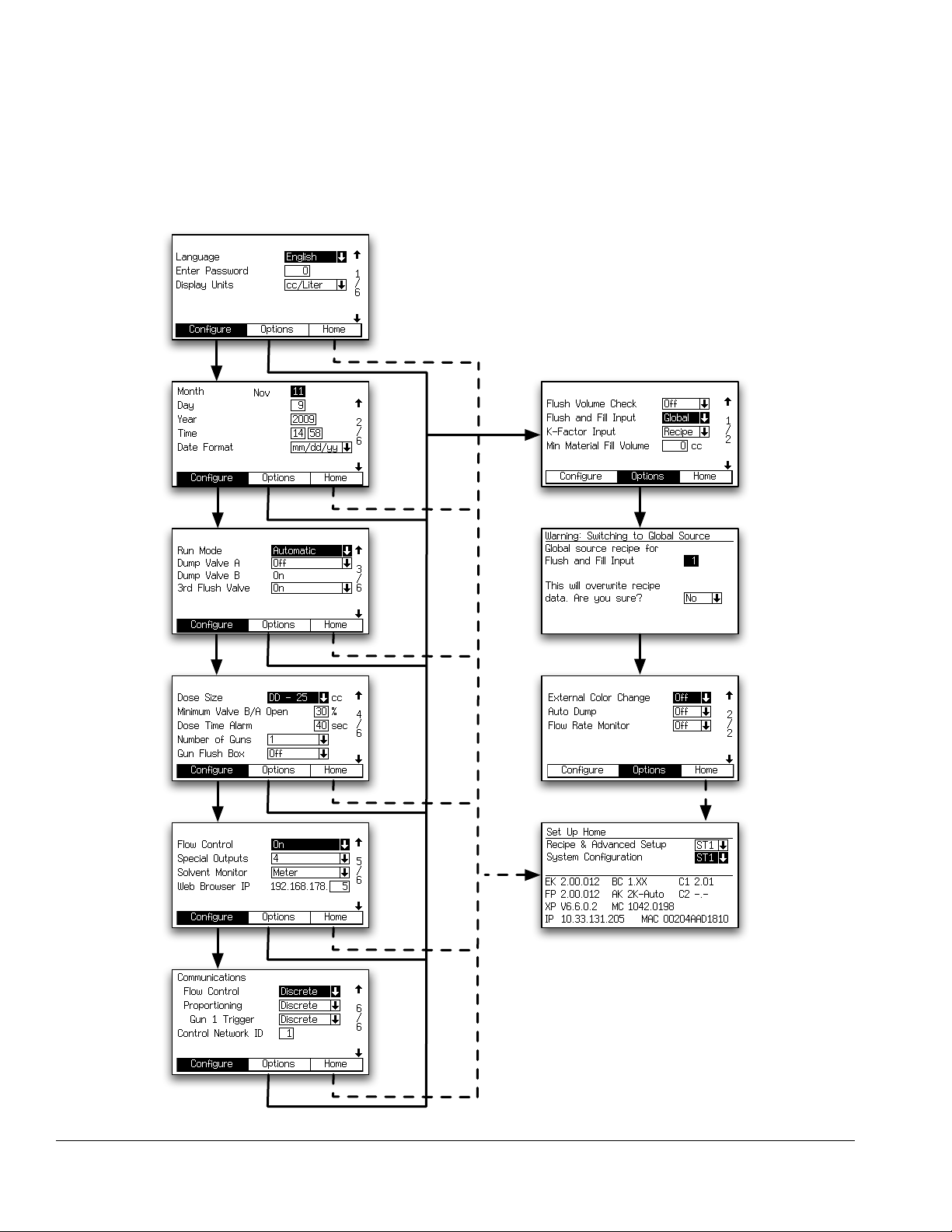
Configure Screen 1
F
IG. 27. Configure Screen 1
Language
Defines the language of the screen text. Select English
(default), Spanish, French, German, Italian, Dutch, Japanese (Kanji), Korean, and Chinese (Simplified).
Password
The password is only used to enter Setup mode. The
default is 0, which means no password is required to
enter Setup. If a password is desired, enter a number
from 1 to 9999.
Configure Screen 2
FIG. 28. Configure Screen 2
Month
Enter current month.
Day
Enter current day.
Year
Enter current year (four digits).
Time
NOTE: Be sure to write down the password and keep it
in a secure location.
Display Units
Select the desired display units:
• cc/liter (default)
• cc/gallon
Enter current time in hours (24 hour clock) and minutes.
Seconds are not adjustable.
Date Format
Select mm/dd/yy or dd/mm/yy.
3A1080C 29
Page 30
Setup Mode
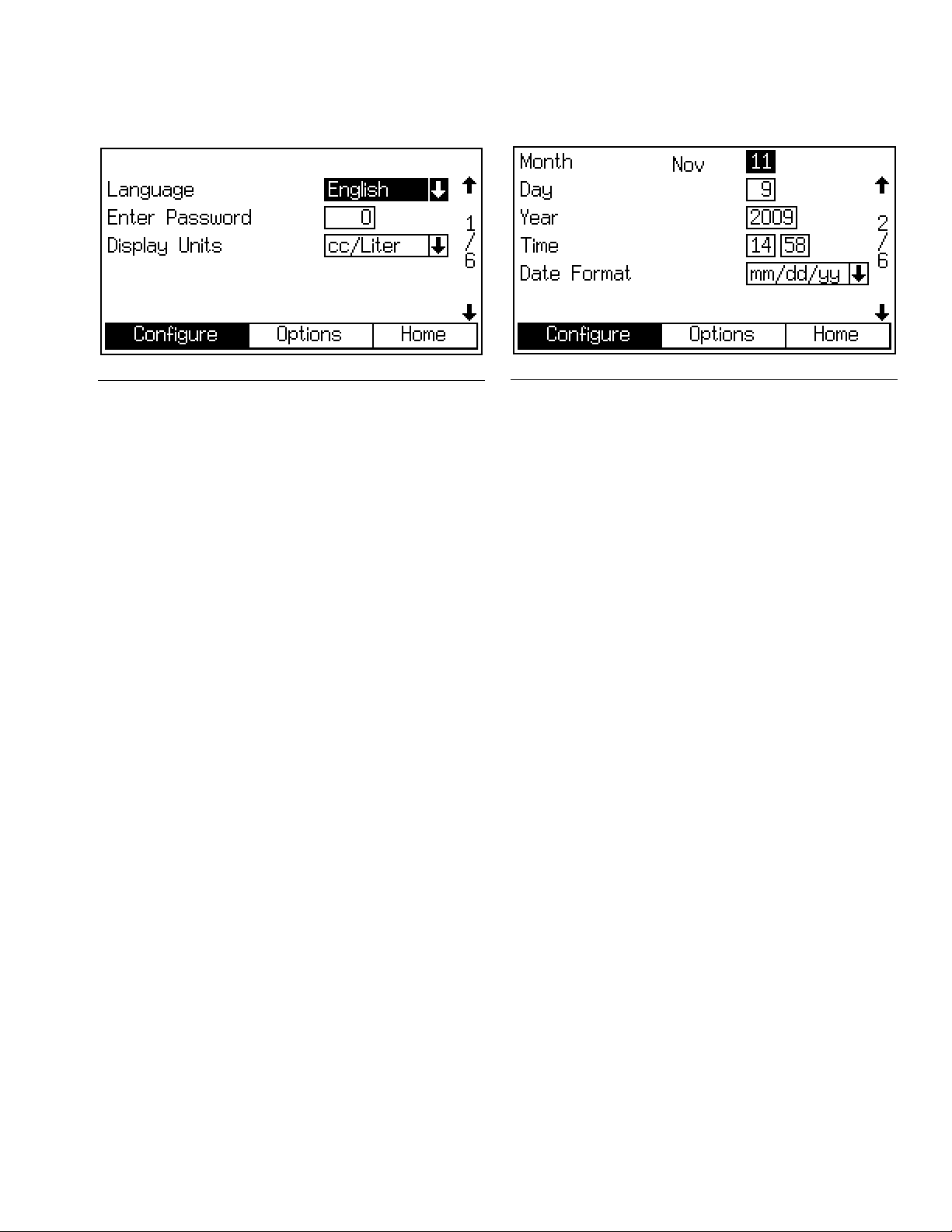
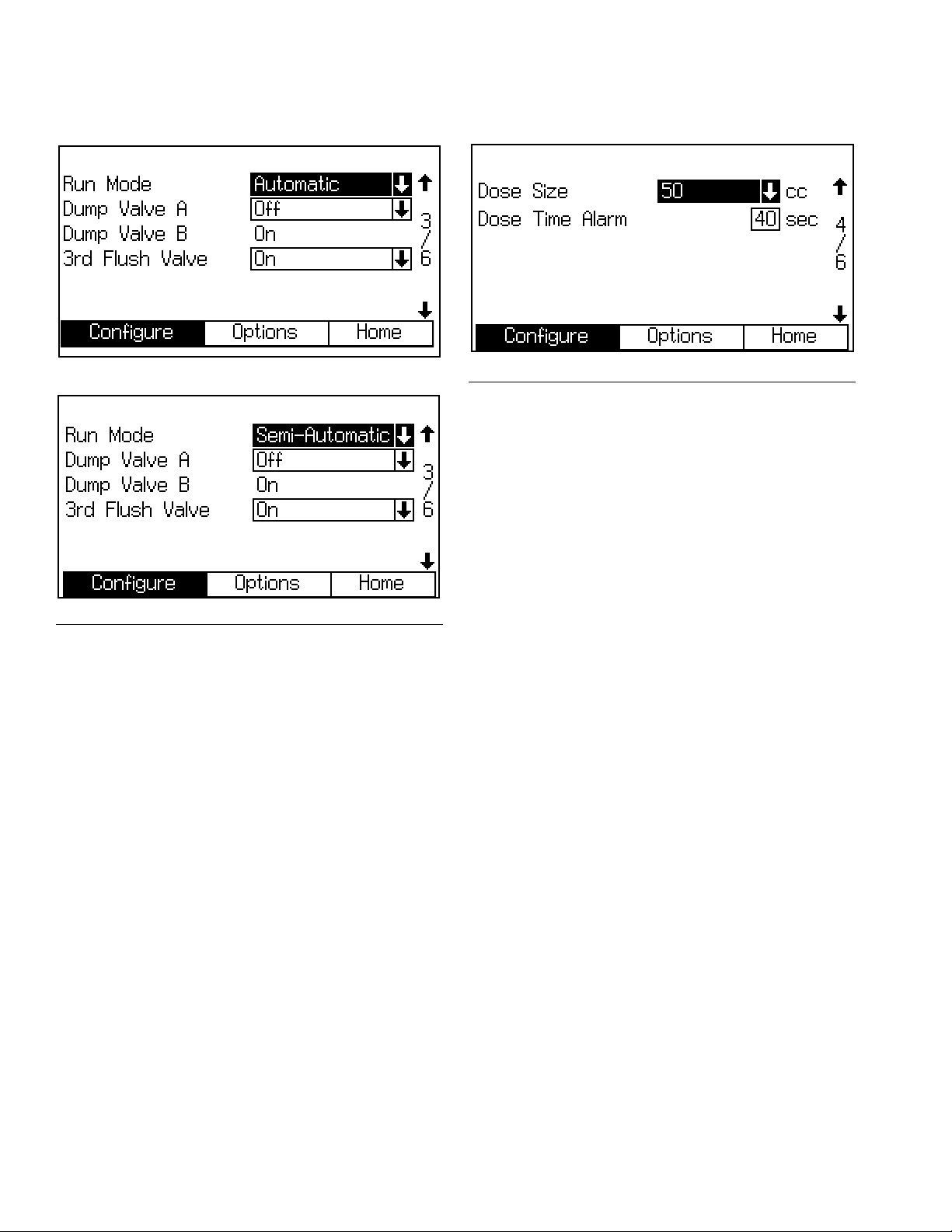
Configure Screen 3
F
IG. 29. Configure Screen 3
OR
Configure Screen 4
FIG. 30. Configure Screen 4
Dose Size
Select the total dose size (cc) from the pulldown menu:
100, 50, 25, or 10. The DD selection (dynamic dosing) is
not used with the ProControl 1KS.
Dose Time Alarm
Enter the dose time (1 to 99 seconds). This is the
amount of time allowed for a dose to occur before a
dose time alarm occurs.
Number of Guns
Run Mode
Select the Run mode application from the pulldown
menu: Automatic (default), Semi-Automatic (uses a
manual spray gun), or Manual.
Dump Valve A
This field only appears if the system includes an optional
dump valve A. If dump valve A is included, set to On.
Dump Valve B
This field only appears if the catalyst change option is
detected from the cc board, meaning that dump valve B
is present. On is the only setting.
3rd Flush Valve
Off is default. If optional 3rd flush valve is used, set to
On.
Enter the number of spray guns (1 or 2).
NOTE: Only 1 gun is used in automatic mode.
Gun Flush Box (manual or semi-automatic mode)
Enter the number of gun flush boxes (Off, 1, or 2).
30 3A1080C
Page 31

Setup Mode
Configure Screen 5
F
IG. 31. Configure Screen 5 FIG. 32. Configure Screen 6 (Automatic mode shown)
Flow Control
This field only appears if Run Mode is set to “Automatic”
in Configure Screen 3, page 30. Select On or Off.
If set to “On,” Advanced Setup Screen 5, page 37 is
added.
Special Outputs
Configure Screen 6
Flow Control
This field only appears if Run Mode is set to “Automatic”
in Configure Screen 3, page 30. Select “Discrete” or
“Network.”
Proportioning
Select “Discrete” or “Network.”
Select special outputs (0-4). Each output has two different start times and durations.
Solvent Monitor
Select solvent monitor (Off, Flow Switch, or Meter).
Web Browser IP
The default web browser IP address prefix is
192.168.178.__ Assign a unique number for each
EasyKey in your system (1-99) and enter it here.
Gun 1 Trigger
Displays AFS if Run Mode is set to “Semi-automatic” in
Configure Screen 3, page 30.
Select “Discrete” or “Network” if Run Mode is set to
“Automatic” in Configure Screen 3, page 30.
Gun 2 Trigger
Displays AFS if Number of Guns is set to “2” in Config-
ure Screen 4, page 30.
Control Network ID
Used for the Graco Gateway network system. See
Graco Gateway manual 312785 for further information
3A1080C 31
Page 32

Setup Mode
Option Screens
NOTE: See FIG. 26 on page 28 for a map of the Option
Screens. Detailed screen descriptions follow.
NOTE: Each screen displays the current screen number
and the total number of screens in the group.
Option Screen 1
F
IG. 33. Option Screen 1
Verification Screen
FIG. 34. Verification Screen
Verification
This screen appears if Flush and Fill Input or K-Factor
Input are changed from “Recipe” to “Global” in Option
Screen 1.
Flush Volume Check
This field only appears if Solvent Monitor is set to
“Meter” in Configure Screen 5, page 31.
If set to “On”, Minimum Flush Volume will appear in Rec-
ipe Setup Screen 2, page 40.
Flush and Fill Input
If set to “Global”, Color/Catalyst Purge and Color/Catalyst Fill are added to Advanced Setup Screen 1, page
35. Advanced Setup Screen 2 and 3 are added. See
pages 36-38.
If set to “Recipe”, Color/Catalyst Purge and Color/Catalyst Fill are added to Recipe Setup Screen 2, page 40.
Recipe Setup Screen 3, 4, and 7 are added. See
pages 41-42.
K-Factor Input
If set to “Global,” Advanced Setup Screen 4, page 37 is
added.
If set to “Recipe,” Recipe Setup Screen 5, page 42, is
added.
Minimum Material Fill Volume
Enter 0-9999 cc.
32 3A1080C
Page 33

Option Screen 2
F
IG. 35. Option Screen 2
External Color Change
If set to “Off”, Color/Catalyst Purge Time and Color/Catalyst Fill Time appear in Advanced Setup Screen 1,
page 35 or Recipe Setup Screen 2, page 40 (depending on whether Flush and Fill Inputs are set to “Global”
or “Recipe”).
Setup Mode
If set to “On”, these fields are removed from the screens.
Auto Dump
If the auto dump feature is being used, set to “On”. Once
the auto dump is enabled, the gun flush box is enabled
and the potlife alarm is active for 2 minutes, the system
will automatically flush out the old material.
Flow Rate Monitor
This field only appears if Flow Control is set to “Off” in
Configure Screen 5, page 31.
If set to “On,” Recipe Setup Screen 6 on page 42 is
added, enabling setting of high and low flow limits.
If set to “Off,” flow rate monitoring is disabled and Rec-
ipe Setup Screen 6 on page 42 will not appear.
3A1080C 33
Page 34

Setup Mode
Advanced Setup Screens
NOTE: See FIG. 36 for a map of the Advanced Setup Screens. Detailed screen descriptions follow.
Advanced Setup screens 2, 3,
4, and 8 appear depending on
selections made in Option
screens 1 and 2. Screen 5
appears if Flow Control is set
to “On” in Configure screen 5.
TI12805a
F
IG. 36. Advanced Setup Screens Map
34 3A1080C
Page 35

Setup Mode
NOTE: Each screen displays the current screen number
and the total number of screens in the group. The total
number of screens in a group and the fields displayed
on each screen may vary depending on selections
made in the System Configuration Screens and
Option Screens.
Advanced Setup Screen 1
F
IG. 37. Advanced Setup Screen 1
Flow Control Override
This field only appears if Flow Control is set to “On” in
Configure Screen 5 on page 31. The selections made
will affect the display in Manual Override Screen on
page 22. Choose the desired selection as defined
below:
Selection Description
Off Normal operation
% Open Flow control regulator is opened to a
desired percentage.
Pressure Flow control regulator is opened to a
calibrated pressure.
Manual Override
This field only appears if Run Mode is set to “Automatic”
or “Semi-automatic” in Configure Screen 3, page 30.
Set to “On” to override all outside control. If selected, the
Manual Override Screen (page 22) will be added.
Gun 1/Gun2 Potlife Volume
Enter the potlife volume (1 to 1999 cc) for each gun.
This is the amount of material required to move through
the mix manifold, hose and applicator/gun before the
potlife timer is reset.
Use the following information to determine approximate
pot life volume (PLV) in cc:
Hose ID (inches) Volume (cc/foot)*
3/16 5.43
1/4 9.648
3/8 21.71
Integrator manifold and mixer volume = 75 cc
Spray Gun Volume = 20 cc
(Hose Volume* x Feet of Hose) + 75 + 20 = PLV
Color/Catalyst Purge
NOTE: ProControl 1KS uses Color only.
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module and Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Global” in Option Screen 1, page 32. Enter the purge
time (0 to 99 seconds). It refers to the amount of time
required to flush the lines from the color or catalyst module to the dose valve or dump valve.
Color/Catalyst Fill
NOTE: ProControl 1KS uses Color only.
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module and Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Global” in Option Screen 1, page 32. Enter the fill time
(0 to 99 seconds). It refers to the time required to fill the
lines from the color or catalyst module to the dose valve
or dump valve.
3A1080C 35
Page 36

Setup Mode
Advanced Setup Screen 2
F
IG. 38. Advanced Setup Screen 2
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Global” in Option Screen 1, page 32.
First Purge Source
Select “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30).
Chop Type
Select “Air/Solvent” or “Air/3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30). This refers to the process of mixing air and solvent (or air and 3rd flush fluid) together
during the flush cycle, to help clean the lines and reduce
solvent usage.
Final Purge Source
Select “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30).
Air Chop Time
Advanced Setup Screen 3
FIG. 39. Advanced Setup Screen 3
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Global” in Option Screen 1, page 32.
If Number of Guns is set to “2” in Configure Screen 4,
page 30, a Gun 2 column will appear in this screen.
First Purge Time
Enter the first purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
Total Chop Time
Enter the total chop time (0 to 999 seconds).
Final Purge Time
Enter the final purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
Mixed Material Fill Time
Enter the mixed material fill time (0 to 999 seconds). It
refers to the amount of material that is required to fill
from the dose valves to the applicator/gun.
Enter the air chop time (0.0 to 99.9 seconds).
Solvent Chop Time/3rd Flush Valve Chop Time
Enter the solvent or 3rd flush valve chop time (0.0 to
99.9 seconds).
36 3A1080C
Page 37

Setup Mode
Advanced Setup Screen 4
F
IG. 40. Advanced Setup Screen 4
This screen appears only if K-Factor Input is set to
“Global” in Option Screen 1, page 32.
K-factor A Meter
Enter the k-factor (cc/pulse) for flow meter A. This is the
amount of material that passes through the flow meter
per pulse (electrical pulse signal).
K-factor B Meter
NOTE: Not used with ProControl 1KS.
Enter the k-factor (cc/pulse) for flow meter B.
K-factor Solvent Meter
This field only appears if Solvent Monitor in Configure
Screen 5, page 31, is set to “Meter.” Enter the k-factor
(cc/pulse) for the solvent flow meter.
Advanced Setup Screen 5
FIG. 41. Advanced Setup Screen 5 (Automatic Mode
with Flow Control Only)
This screen appears only if Flow Control is set to “On” in
Configure Screen 5, page 31.
Flow Rate Range
Enter the flow rate range (0-300, 0-600, or 0-1200). This
determines the flow control PID loop resolution.
Flow Rate Tolerance
Enter the flow rate tolerance (1 to 99%). This is the percentage of variance that the system will allow before a
flow rate warning/alarm occurs.
Flow Rate Ki
Enter the flow rate Ki (flow control PID loop integral
value). This refers to the degree that fluid flow overshoots its set point.
Flow Rate Kp
Enter the flow rate Kp (flow control PID loop gain value).
This refers to the speed at which the fluid flow reaches
its set point.
Flow Rate Alarm Time
Enter the flow rate alarm time (1 to 99 seconds).
3A1080C 37
Page 38

Setup Mode
Advanced Setup Screen 6
F
IG. 42. Advanced Setup Screen 6
This screen shows the status of recipe analog inputs
and digital outputs. If box is shaded the input recipe is
active.
Advanced Setup Screen 7
Advanced Setup Screen 8
FIG. 44. Advanced Setup Screen 8
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Global” in Option Screen 1, page 32 and Special Outputs is set to 1, 2, 3, or 4 in Configure Screen 5, page
31. The I/O board has four programmable outputs.
F
IG. 43. Advanced Setup Screen 7
This screen shows the status of digital inputs and digital
outputs. If box is shaded the input is active. If not, input
is off.
38 3A1080C
Page 39

Recipe Setup Screens
NOTE: See FIG. 45 for a map of the Recipe screens. Detailed screen descriptions follow.
Recipe 0 Screens
Setup Mode
Recipe screens 3, 4, 5, 6,
and 7 appear depending on
selections made in Option
screens 1 and 2
TI12806a
F
IG. 45: Recipe Screens Map
3A1080C 39
Page 40

Setup Mode
NOTE: Each screen displays the current screen number
and the total number of screens in the group. The total
number of screens in a group and the fields displayed
on each screen may vary depending on selections
made in the System Configuration Screens and
Option Screens.
Recipe Setup Screen 1
F
IG. 46. Recipe Setup Screen 1
Ratio
Enter the mix ratio of component A over component B
(0.0:1 to 50:1). Set to 0:1 for ProControl 1KS.
Recipe Setup Screen 2
FIG. 47. Recipe Setup Screen 2
Minimum Flush Volume
This field only appears if Flush Volume Check is set to
“On” in Option Screen 1 on page 32. Enter the minimum flush volume (0 to 999 cc). Entering 0 disables this
function.
Potlife Time
Enter the potlife time (0 to 999 minutes). Entering 0 disables this function.
Color/Catalyst Purge
Ratio Tolerance
Enter the ratio tolerance (1 to 99%). This refers to the
percent of acceptable variance that the system will allow
before a ratio alarm occurs.
Component A (Color) Valve (if present)
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module. Enter the color valve number (1 to 30).
Component B (Catalyst) Valve (if present)
NOTE: Not used with ProControl 1KS.
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module. Enter the catalyst valve number (1 to
4).
NOTE: ProControl 1KS uses Color only.
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module and Flush and Fill Input is set to “Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32. Enter the purge time
(0 to 99 seconds). It refers to the amount of time
required to flush the lines from the color or catalyst module to the dose valve or dump valve.
Color/Catalyst Fill
NOTE: ProControl 1KS uses Color only.
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module and Flush and Fill Input is set to “Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32. Enter the fill time (0
to 99 seconds). It refers to the time required to fill the
lines from the color or catalyst module to the dose valve
or dump valve.
40 3A1080C
Page 41

Setup Mode
Recipe Setup Screen 3
F
IG. 48. Recipe Setup Screen 3
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32.
First Purge Source
Select “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30).
Chop Type
Select “Air/Solvent” or “Air/3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30). This refers to the process of mixing air and solvent (or air and 3rd flush fluid) together
during the flush cycle, to help clean the lines and reduce
solvent usage.
Final Purge Source
Select “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30).
Recipe Setup Screen 4
FIG. 49. Recipe Setup Screen 4
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32.
If Number of Guns is set to “2” in Configure Screen 4,
page 30, a Gun 2 column will appear in this screen.
First Purge Time
Enter the first purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
Total Chop Time
Enter the total chop time (0 to 999 seconds).
Final Purge Time
Enter the final purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
Mixed Material Fill Time
Enter the mixed material fill time (0 to 999 seconds). It
refers to the amount of material that is required to fill
from the dose valves to the applicator/gun.
Air Chop Time
Enter the air chop time (0.0 to 99.9 seconds).
Solvent Chop Time/3rd Flush Valve Chop Time
Enter the solvent or 3rd flush valve chop time (0.0 to
99.9 seconds).
3A1080C 41
Page 42

Setup Mode
Recipe Setup Screen 5
F
IG. 50. Recipe Setup Screen 5
This screen appears only if K-Factor Input is set to “Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32.
K-factor A Meter
Enter the k-factor (cc/pulse) for flow meter A. This is the
amount of material that passes through the flow meter
per pulse (electrical pulse signal).
Recipe Setup Screen 6
FIG. 51. Recipe Setup Screen 6
This screen appears only if Flow Rate Monitor is set to
“On” in Option Screen 2 on page 33.
Flow Rate Monitor
Select the desired flow rate monitoring (Off, Warning, or
Alarm).
Low Flow Limit
K-factor B Meter
NOTE: Not used with ProControl 1KS.
Enter the k-factor (cc/pulse) for flow meter B.
K-factor Solvent Meter
This field only appears if Solvent Monitor is set to
“Meter” in Configure Screen 5, page 31. Enter the
k-factor (cc/pulse) for the solvent flow meter.
Enter the low flow rate limit (1 to 3999 cc/min).
High Flow Limit
Enter the high flow rate limit (1 to 3999 cc/min).
Recipe Setup Screen 7
F
IG. 52. Recipe Screen 7
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32 and Special Outputs is set to 1, 2, 3, or 4 in Configure Screen 5, page
31. The I/O board has four programmable outputs.
42 3A1080C
Page 43

Recipe 0 Screens
Setup Mode
NOTE: See FIG. 45 on page 39 for a map of the Recipe
0 screens. Detailed screen descriptions follow.
Recipe 0 is typically used in multiple color systems to
purge out material lines without loading a new color
NOTE: Each screen displays the current screen number
and the total number of screens in the group. The total
number of screens in a group and the fields displayed
on each screen may vary depending on selections
made in the System Configuration Screens and
Option Screens.
Recipe 0 Screen 1
Final Purge Source
Select “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30).
Air Chop Time
Enter the air chop time (0.0 to 99.9 seconds).
Solvent Chop Time/3rd Flush Valve Chop Time
Enter the solvent or 3rd flush valve chop time (0.0 to
99.9 seconds).
Recipe 0 Screen 2
F
IG. 53. Recipe 0 Screen 1
First Purge Source
Select “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30).
Chop Type
Select “Air/Solvent” or “Air/3rd Flush Valve” (available
only if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure
Screen 3 on page 30). This refers to the process of mixing air and solvent (or air and 3rd flush fluid) together
during the flush cycle, to help clean the lines and reduce
solvent usage.
FIG. 54. Recipe 0 Screen 2
If Number of Guns is set to “2” in Configure Screen 4,
page 30, a Gun 2 column will appear in this screen.
Color/Catalyst Purge Time
NOTE: ProControl 1KS uses Color only.
This field only appears if the system includes a color
change module. Enter the purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
First Purge Time
Enter the first purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
Total Chop Time
Enter the total chop time (0 to 999 seconds).
Final Purge Time
Enter the final purge time (0 to 999 seconds).
3A1080C 43
Page 44

Setup Mode
Recipe 0 Screen 3
F
IG. 55. Recipe 0 Screen 3
This screen only appears if Solvent Monitor is set to
“Meter” in Configure Screen 5, page 31 and Flush Vol-
ume Check is set to “On” in Option Screen 1, page 32
or 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in Configure Screen 3
on page 30.
Recipe 0 Screen 4
FIG. 56. Recipe 0 Screen 4
This screen appears only if Flush and Fill Input is set to
“Recipe” in Option Screen 1, page 32 and Special Outputs is set to 1, 2, 3, or 4 in Configure Screen 5, page
31. The I/O board has four programmable outputs.
Calibration Screen
Minimum Flush Volume
This field only appears if Flush Volume Check is set to
“On” in Option Screen 1 on page 32. Enter the minimum flush volume (0 to 999 cc).
Exiting Fill Source
This field only appears if 3rd Flush Valve is set to “On” in
Configure Screen 3 on page 30. Select “Off,” “Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Valve.”
Exiting Fill Time
This field only appears if Exiting Fill Source is set to
“Air,” “Solvent,” or “3rd Valve.” Enter the time in seconds.
F
IG. 57. Calibration Screen
Use this screen to calibrate a meter. Set to “Meter A,”
“Meter B,” or “Solvent Meter” (available if Solvent Monitor in Configure Screen 5, page 31, is set to “Meter”).
• Start - start calibration
• Abort - stop calibration
• Purge - purge sampling valves after calibration
See Meter Calibration, page 76, for when and how to
calibrate meter.
44 3A1080C
Page 45

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Discrete I/O vs Network Communications
The ProControl 1KS system does not use a Booth Control. Instead, it uses Discrete I/O or Network Communications to drive the system. Each method can be used
exclusively, or both at the same time.
In Automatic mode, the following fields can be set to
“Discrete” or “Network” (see Configure Screen 6 on
page 31):
• Flow Control
• Proportioning
• Gun 1 Trigger
NOTE: In Semi-automatic mode, only the Proportioning
field is available,
NOTE: The Manual Override function enables you to
operate the system before the automation (PLC) is available. Manual Override still requires some communication through Discrete I/O or Network Communications.
Although Manual Override is not intended to be the main
mode of control, it can be used if proper Gun Trigger
Input is provided.
Discrete I/O
Discrete I/O requires a 24 Vdc power supply which must
be supplied on site. The ProControl 1KS does not supply power for Discrete I/O.
See Table 4 on page 49, F
8 on page 59 for inputs and outputs. Understanding
these inputs and outputs is necessary to properly integrate the ProControl 1KS to the automation.
Input and output connections are made at the Discrete
I/O terminal strips (F
(F
IG. 61) inside the EasyKey. Also see the System
Electrical Schematic on page 102.
Review the Color Change Charts (F
understanding of the color change sequence is necessary to properly drive the inputs and monitor the outputs.
See Advanced Setup Screen 7, page 38. This screen
shows the actual status of all inputs and outputs. It is
important to ensure that each input from local automation (PLC) is received by the EasyKey and to verify that
the ProControl 1KS is sending outputs to the automation.
IG. 67 on page 58, and Table
IG. 60) and the discrete I/O board
IG. 78-FIG. 95). A full
Display Board Barrier Board
F
IG. 58: EasyKey Control Boards
The following paragraphs describe each discrete I/O
function in detail.
Terminal Strips
(see F
IG. 60)
Discrete I/O Board (see FIG. 61)
TI12496a
3A1080C 45
Page 46

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Multiple Station
GND
A
B
A
B
GND
TI12923a
Integration Control
RT1
FIG. 59: 255767 EasyKey Display Board
Analog In Common
Analog In Signal
Reset Alarm
Remote Stop
Potlife Alarm
Output Common
General Alarm
Gun Trigger
Input Common
Flow Control Calibrate
TI12924a
46 3A1080C
Page 47

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Digital Inputs
See Automation Flow Charts, pages 50-54.
Mix Start: This is a maintained input. When High, the
ProControl 1KS will attempt to enter Mix mode. This Mix
Start input should not be attempted unless the
Mix_Ready output is recognized. This ensures that
there are no alarms and that the Mix Start input is
appropriate.
This input stays High at all times when mixing on
demand is required. When Low, the intent is to stop mixing material and perform a purge or recipe change.
Do not toggle this input to set the unit to Standby mode
during short work stoppages. The ProControl 1KS will
automatically go into Idle mode after 2 minutes of inactivity. When a Gun Trigger input is seen, the ProControl
1KS will automatically leave Idle mode and resume mixing material where it left off.
Purge Start: This is a maintained input. When recog-
nized by the ProControl 1KS, the Purge Sequence will
start, using the Purge Time from the active recipe. This
will also include the Solvent Fill Time. Proper monitoring
of the Purge/Color Change Output is required to ensure
this function has begun. Once this output is removed,
the system will immediately go to Standby mode.
Gun Trigger: When High, this input signals the ProControl 1KS that the gun is actually triggered. It should be
sent every time the gun is triggered. This input provides
timing for alarm functions and also drives the flow control functions. Without it, no flow control functions will
start.
Job Complete: This is a momentary input, 100 msec
minimum. When recognized by the ProControl 1KS, the
Job totals are cleared and a time/date stamp is added
for retrieval.
Remote Stop: Use this input when external equipment
is used to stop the system. Clear any alarms before
using this input. For more information about when this
input is needed, contact your Graco distributor.
Alarm Reset: This is a momentary input, 100 msec
minimum. When recognized by the ProControl 1KS it
clears any active alarms and allows the automation to
take the next step.
Common: This is not an input, but the ProControl 1KS
expects to have the COM side of the 24 Vdc supply connected as shown in Table 8. This ensures proper opera-
tion of each input and output.
I/O Terminal Strip Detail
Color Change Start: This is a momentary input, 100
msec minimum. When recognized by the ProControl
1KS, the Color Change sequence will begin, starting at
the Color/Catalyst Dump.
NOTE: If the new recipe has the same color as the
active recipe, then the Color/Catalyst Dump and
Color/Catalyst Fill times are skipped and the Color
Change Sequence starts with the Purge. Also, the recipe bit configuration for the Color Change must be
loaded at least 100 msec before the Color Change Start
input is turned on. The recipe bit configuration must
remain on while the Color Change Start input is
removed. Graco recommends the recipe bits stay active
and do not change until a new color is required. The
PLC should monitor the Purge/Color Change Output as
well as the Fill Active Output to ensure the process happens as required. A complete color change without
errors (resulting in a Mix Ready Output state) is a completed color change.
NOTE: This also applies if using the Modbus Registers
(see the Modbus Map table in manual 312785).
Pin 1
Pin 1
F
IG. 60: EasyKey Terminal Strips
RS485 Integration A
RS485 Integration B
RS485 Integration Ground
RS485 Network A
RS485 Network B
RS485 Network Ground
Flow Control Calibrate
Gun Trigger
Digital Common
Remote Stop
Alarm Reset
General Alarm
Digital Common
Potlife Alarm
Flow Rate Analog In
Flow Rate Analog Common
INPUTS
OUTPUTS
TI12958a
3A1080C 47
Page 48

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
JLS
Digital Output
Special Output #4
Special Output #3
Common/Power
Special Output #2
Digital Output
Special Output #1
Common/Power
Digital Output Common/Power
Flow Rate Alarm Output
Flow Control Calibrate Active
Fill Active
Mix Ready Output
Mix Active Output
Purge/Recipe Change Active Output
Digital Output Common/Power
Recipe Change Input
Recipe Bit 5 Input
Recipe Bit 4 Input
FIG. 61: 255766 Discrete I/O Board
Mix Input
Purge Input
Job Complete Input
Recipe Bit 3 Input
Recipe Bit 2 Input
Recipe Bit 1 Input
Recipe Bit 0 Input
Digital Input Common
Spare
Digital Input Common
External Color Change Ready
48 3A1080C
Page 49

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Digital Outputs
See Automation Flow Charts, pages 50-54.
Purge_CC_Active: This output will remain High during
the manual Purge or Color Change purge sequence.
See the Color Change Charts (F
ther information.
Fill_Active: This output will remain High while the ProControl 1KS is in the Mixed Material Fill at the end of a
typical color change sequence.
Mix_Active: This output will remain High while the ProControl 1KS is in Mix mode. There may be alarm outputs while this output is High; these are typically
High/Low Flow Warnings. Always monitor this output
and the alarm outputs to provide feedback of the actual
status of the ProControl 1KS. (See the Modbus charts in
the Graco Gateway manual 312785.)
Mix_Ready: This output will remain High while there are
no alarms and the ProControl 1KS is ready to go to Mix
mode.
General Alarm: This output will remain High when any
alarm is active. See Table 13 on page 90 for a complete
list of alarms.
IG. 78-FIG. 95) for fur-
Analog Inputs
Flow Command: This is the positive side of the 0 – 10
Vdc signal. (See Common under Digital Inputs, page
47.) This input corresponds to the Flow Range setting in
Advanced Setup Screen 5, page 37. For example, if
the setting is 0 – 300 cc/min, the 0 Vdc analog input is 0
cc/min, therefore the 10 Vdc analog input is 300 cc/min.
Table 4: Sourcing/Sinking Inputs and Outputs
Inputs (Automation Sourcing)
1 Flow Control Calibration Black +
2 Gun Trigger White +
3 Digital In Common Red -
4 Remote Stop Green +
5 Alarm Reset Brown +
Outputs (Automation Sourcing)
6 Alarm Output Blue +
7 Digital Out Common Orange -
8 Pot Life Yellow +
Outputs (Automation Sinking)
NOTE: It is important to monitor this output along with
Mix_Active to understand the alarm’s true meaning.
Alarm_Potlife: This output will remain High along with
the Alarm output when the potlife time has been
reached for the active recipe. The Mix_Active output will
drop Low, even if the Mix_Start input is High. This output
will remain High until the potlife volume is dispensed or
the ProControl 1KS completes a Purge or a Color
Change. The Alarm Reset input will not stop this output
but will silence the audible alarm on the EasyKey.
NOTE: The Alarm Reset
audible alarm.
To dispense the potlife volume, the ProControl 1KS
Mix_Start input must be turned Off then back to High to
spray material. At this point, Mix_Active, Alarm, and
Alarm_Potlife outputs will be High until the potlife volume is sprayed.
Digital Out Supply: This is the supply for the digital outputs. It is the same supply for the digital inputs. (See
Common under Digital Inputs, page 47.)
key will also reset the
6 Alarm Output Blue -
7 +24 Volts Orange +
8 Pot Life Yellow -
Automation
9 Flow Rate Analog In Purple +
10 Flow Rate Analog Common Gray -
3A1080C 49
Page 50

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Automation Flow Charts
Start Mix Mode Process
See FIG. 62, Table 5, and Table 6.
Start Mix
Mode Process
Must be Alarm Condi-
tion or Active Recipe
61. See Alarm Pro-
cessing on page 54,
or Startup from Recipe
61 (see NOTE below)
NOTE: At power up the system
defaults to Recipe 61, which is
not a valid recipe number. Initiate
a color change to Recipe 0 or a
valid recipe number (1-60).
Is Mix Ready
bit = 1?
NO
YESNO
Set Mix bit = 1
Is Mix Active
bit = 1?
YES
ProControl 1KS in Mix
Mode (Complete).
Mix Active = 1 while
the ProControl 1KS is
in Mix mode
F
IG. 62. Start Mix Mode Process Flow Chart
50 3A1080C
Page 51

Mixing Mode Process
See FIG. 63, Table 5, and Table 6.
ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Mixing Mode
Process
Mixing Mode is desired.
PLC is polling to ensure
Mixing Mode is main-
tained.
Check Alarm
Condition: is Alarm_
General bit = 1?
YES
NO
Is Mix Active
bit = 1?
YESNO
Mixing Process active
Go to Start Mix Mode
Process, page 50
Go to Alarm Process-
ing, page 54
IG. 63. Mixing Mode Process Flow Chart
F
3A1080C 51
Page 52

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Purge Mode Process
See FIG. 64, Table 5, and Table 6.
Start
Must be Alarm
Condition or Active
Recipe 61. See
Alarm Processing
on page 54, or
Startup from Recipe
61 (see NOTE below).
Is Mix Ready
bit = 1?
NO
YESNO
Set Purge bit = 1?
YES
Is Purge_CC_Active
bit = 1?
NO
NOTE: At power up the system
defaults to Recipe 61, which is
not a valid recipe number. Initiate
a color change to Recipe 0 or a
valid recipe number (1-60).
F
IG. 64. Purge Mode Process Flow Chart
52 3A1080C
(Wait for Mix Ready)
Is Mix Ready
bit = 1?
YES
ProControl 1KS in
Purge_CC Mode
(Process Started)
ProControl 1KS Purge
Process (Complete)
Page 53

Color Change Mode Process
See FIG. 65, Table 5, and Table 6.
ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Color Change
Process
(basic)
Do nothing.
Spraying at
desired recipe.
Ensure ColorChange bit is seen
by ProControl 1KS
YES NO
NO
Is Active Recipe =
to desired recipe?
(Register 40005).
Is
Purge_CC_Active
bit = 1?
YES
Load ccNewRecipe
(Register 40046) with
recipe number to Color
Change to (0 through
60 is valid).
Set ColorChange (CC)
bit = 1.
Clear ColorChange (CC)
bit (momentary input).
CC process started.
NO
NO
F
IG. 65. Color Change Mode Process Flow Chart
3A1080C 53
Check Alarm
Condition: is Alarm_
General bit = 1?
YES
(Wait for Mix Ready)
Is Mix Ready
bit = 1?
YES
Process Alarm. See
Alarm Processing,
ProControl 1KS Color
Change Process
(Complete)
page 54.
Page 54

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Alarm Processing
See FIG. 66, Table 5, Table 6, and Table 7.
Alarm Processing
An Alarm Condition
has been found
previously.
Alarm_General = 1.
Determine the exact alarm
from Table 7 on page 57
and solve what caused the
alarm, as required.
Reset the alarm.
Reset_Alarm = 1.
NO YES
Is Mix Ready
bit = 1?
Check if Potlife
Alarm: is Alarm_
Potlife bit = 1?
YESNO
Two options:
• Purge or Color Change to remove
mixed material in the line.
• Place in Mix mode and spray the
Potlife Volume set in the ProControl
1KS.
NOTE: The Reset key only silences
the alarm. To clear the alarm you must
use one of these two options.
Go to next process,
as desired.
IG. 66. Alarm Processing Flow Chart
F
54 3A1080C
Page 55

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Table 5: ProControl 1KS Digital Inputs (Modbus Register 40040)
Bit Digital Input Binary Name Details
0:5 0000000000XXXXXXRecipe Binary bits for viewing discrete inputs only.
6 000000000
1000000Color Change
Set bit to “1” to initiate Color Change (momentary)
(CC)
7 00000000
8 0000000
10000000Mix Set bit initiate Mix mode (maintain)
100000000Purge Set bit to “1” to initiate Purge sequence (maintained)
9 0000001000000000Job_Complete Set bit to “1” to initiate Job Complete input (momen-
tary)
10 0000010000000000External CC
Ready
Set bit to “1” to initiate External Color Change
(momentary)
11 0000100000000000Not Used
12 0001000000000000FC _Calibrate Set bit to “1” to initiate a Flow Control Calibrate input
(momentary)
13 0010000000000000Gun_Trigger Set bit to “1” to indicate the gun is actually triggered
(maintain while gun is triggered, remove when gun is
closed)
14 0
100000000000000Reset_Alarm Set bit to “1” to clear an active Alarm (momentary)
15 1000000000000000Remote Stop Set bit to remotely stop unit (momentary)
NOTE: Shaded cells relate to the flow charts on pages 50-54.
3A1080C 55
Page 56

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Table 6: ProControl 1KS Digital Outputs (Modbus Register 40041)
Bit Digital Input Binary Name Details
0 000000000000000
1 Purge_CC_Active “1” indicates Purge or Color Change is in prog-
ress
1 00000000000000
2 0000000000000
10Mix_Active “1” indicates Mix is in progress
100Mix_Ready “1” indicates No Alarms and OK to Mix
3 0000000000001000CC_Fill_Active “1” indicates the Fill portion of a Color Change is
in progress
4 0000000000010000FCalActive “1” indicates the Flow Control Calibrate routine is
in progress
5 0000000000100000Flow_Rate_Alarm “1” indicates the Flow Rate Alarm/Warning is
active
6 0000000001000000Special_1 “1” indicates the Special_1 output is on (monitor
only)
7 0000000010000000Special_2 “1” indicates the Special_2 output is on (monitor
only)
8 0000000100000000Special_3 “1” indicates the Special_3 output is on (monitor
only)
9 0000001000000000Special_4 “1” indicates the Special_4 output is on (monitor
only)
10 0000010000000000Not Used
11 0000100000000000Not Used
12 0 0 0
1000000000000Alarm_General “1” indicates a General Alarm is in process. (If
Mix_Active is still High, then a Warning only.) See
the Modbus charts in the Graco Gateway manual
312785 for details on type.
13 0010000000000000Alarm_Potlife “1” indicates a Potlife Alarm is in process.
NOTE: Shaded cells relate to the flow charts on pages 50-54.
56 3A1080C
Page 57

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Table 7: ProControl 1KS Active Alarms (Modbus Register 40010)
Bit Digital Input Binary Name Details
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0000 No Bits Set No Active Alarms
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0001 Comm_Error
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0010 Potlife_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0100 Ratio_High_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 1000 Ratio_Low_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0001 0000 Overdose_A_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0010 0000 Overdose_B_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 0100 0000 Dose_Time_A_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0000 1000 0000 Dose_Time_B_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0001 0000 0000 Mix_In_Setup_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0010 0000 0000 Remote_Stop_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 0100 0000 0000 Purge_Volume_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0000 1000 0000 0000 CAN_Comm_Error_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0001 0000 0000 0000 High_Flow_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0010 0000 0000 0000 Low_Flow_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 0100 0000 0000 0000 System_Idle_Alarm
Low Byte: 0 1000 0000 0000 0000 Setup_Change_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0001 Power_On_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0010 Defaults_Loaded_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 0100 IO_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0000 1000 Purge_Initiate_Error
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0001 0000 Material_Fill_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0010 0000 Tank_A_Low_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 0100 0000 Tank_B_Low_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0000 1000 0000 Tank_S_Low_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0001 0000 0000 Auto_Dump_Complete
High Byte: 0 0000 0010 0000 0000 Color/Catalyst_Purge_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 0100 0000 0000 Color/Catalyst_Fill_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0000 1000 0000 0000 Num_Alarm_Desc
High Byte: 0 0001 0000 0000 0000 Spare3_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0010 0000 0000 0000 Spare2_Alarm
High Byte: 0 0100 0000 0000 0000 Spare1_Alarm
High Byte: 0 1000 0000 0000 0000 Potlife_Buzzer
3A1080C 57
Page 58

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
ProControl 1KS
PLC Output
EasyKey Digital Input
(Sourcing)
Input
Common
ProControl 1KS EasyKey
Digital Output
Output
Common
24
Vdc
Output
CommonInput
24
Vdc
PLC Input
Input
(Sinking)
ProControl 1KS
EasyKey Digital Output
Output
Common
Output
FIG. 67. Automation 24 Vdc Sourcing Input Diagram
24
Vdc
CommonOutput
PLC Input
(Sourcing)
Input
Common
58 3A1080C
Page 59

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Table 8: Discrete I/O Terminal Connections
Terminal Terminal Location Name Details (also see pages 55 and 56)
Digital Inputs
1 J2, Remote I/O Board Mix Set Bit to Initiate Mix Mode (maintain)
2 J2, Remote I/O Board Purge Set Bit to “1” to initiate Purge Sequence
(maintained)
3 J2, Remote I/O Board Job_Complete Set Bit to “1” to initiate Job Complete Input
(momentary)
4 J2, Remote I/O Board External CC Ready Set Bit to “1” to initiate External Color
Change (maintained)
5 J2, Remote I/O Board Spare
6* J2, Remote I/O Board Digital Input Common
1* J3, Remote I/O Board Digital Input Common
2 J3, Remote I/O Board Recipe Bit 0 Set Binary Bits for Recipe to Change To (hold
until changing again)
3 J3, Remote I/O Board Recipe Bit 1 Set Binary Bits for Recipe to Change To (hold
until changing again)
4 J3, Remote I/O Board Recipe Bit 2 Set Binary Bits for Recipe to Change To (hold
until changing again)
5 J3, Remote I/O Board Recipe Bit 3 Set Binary Bits for Recipe to Change To (hold
until changing again)
6 J3, Remote I/O Board Recipe Bit 4 Set Binary Bits for Recipe to Change To (hold
until changing again)
7 J3, Remote I/O Board Recipe Bit 5 Set Binary Bits for Recipe to Change To (hold
until changing again)
8 J3, Remote I/O Board Color Change (CC) Set Bit to “1” to initiate Color Change
(momentary)
1 10 Pin Terminal Block Flow Control Calibrate Set Bit to “1” to initiate Flow Control Calibrate
(momentary)
2 10 Pin Terminal Block Gun Trigger Set Bit to “1” to indicate Gun is Triggered
(fluid flow expected)
3† 10 Pin Terminal Block Digital Input Common
4 10 Pin Terminal Block Remote Stop Set Bit to “1” to initiate a Remote Stop
(momentary)
5 10 Pin Terminal Block Reset_Alarm Set Bit to “1” to Clear an Active Alarm
(momentary)
* Digital inputs tied together on the I/O board (see F
† Digital inputs tied together on the EasyKey Display Board (see F
IG. 61).
IG. 59).
Multiple connection points for convenience.
3A1080C 59
Page 60

ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
Table 8: Discrete I/O Terminal Connections
Terminal Terminal Location Name Details (also see pages 55 and 56)
Digital Outputs
1★ J4, Remote I/O Board Digital Output Common/Power
2 J4, Remote I/O Board Purge_CC Active “1” Indicates Purge or Color Change is in
progress
3 J4, Remote I/O Board Mix_Active “1” Indicates Mix is in progress
4 J4, Remote I/O Board Mix_Ready “1” Indicates No Alarms and OK to Mix
5 J4, Remote I/O Board CC_Fill_Active “1” Indicates the Fill Portion of a Color
Change is in progress
6 J4, Remote I/O Board FCalActive “1” Indicates the Flow Control Calibrate rou-
tine is in progress
7 J4, Remote I/O Board Flow_Rate “1” Indicates the Flow Rate Alarm/Warning is
active
8★ J4, Remote I/O Board Digital Output Common/Power
1★ J5, Remote I/O Board Digital Output Common/Power
2 J5, Remote I/O Board Special_1 “1” Indicates the Special_1 Output is on
3 J5, Remote I/O Board Special_2 “1” Indicates the Special_2 Output is on
4 J5, Remote I/O Board Special_3 “1” Indicates the Special_3 Output is on
5 J5, Remote I/O Board Special_4 “1” Indicates the Special_4 Output is on
6★ J5, Remote I/O Board Digital Output Common/Power
6 10 Pin Terminal Block General Alarm Output “1” Indicates the General Alarm Output is on
7◆ 10 Pin Terminal Block Digital Output Common/Power
8 10 Pin Terminal Block Potlife Alarm “1” Indicates the Potlife Alarm Output is on
9 10 Pin Terminal Block Flow Rate Analog In (0-10
VDC)
0 - 10VDC input for Flow Setpoint relative to
flow range set in 2KS Flow Range Screen
10 10 Pin Terminal Block Flow Rate Common to Pin 9 Common side of Flow Setpoint from Terminal
9
Communications
1 6 Pin Terminal Block RS485 Integration A
2 6 Pin Terminal Block RS485 Integration B
Communication to External PLC/Controller
3 6 Pin Terminal Block RS485 Integration
Shield/Ground
4 6 Pin Terminal Block RS485 Network A
Communication to Multiple EasyKeys only5 6 Pin Terminal Block RS485 Network B
6 6 Pin Terminal Block RS485 Network Shield/Ground
★ Digital outputs tied together on the I/O board (see F
◆ Digital outputs tied together on the EasyKey Display Board (see F
IG. 61).
IG. 59).
Multiple connection points for convenience.
60 3A1080C
Page 61

Table 9: ProControl 1KS Recipe Bits
Recipe Bits Number Recipe Bits Number
543210 543210
000000 0 100001 33
000001 1 100010 34
000010 2 100011 35
000011 3 100100 36
000100 4 100101 37
000101 5 100110 38
000110 6 100111 39
000111 7 101000 40
001000 8 101001 41
001001 9 101010 42
001010 10 101011 43
001011 11 101100 44
001100 12 101101 45
001101 13 101110 46
001110 14 101111 47
001111 15 110000 48
010000 16 110001 49
010001 17 110010 50
010010 18 110011 51
010011 19 110100 52
010100 20 110101 53
010101 21 110110 54
010110 22 110111 55
010111 23 111000 56
011000 24 111001 57
011001 25 111010 58
011010 26 111011 59
011011 27 111100 60
011100 28
011101 29
011110 30
011111 31
100000 32
ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics
3A1080C 61
Page 62

System Operation
System Operation
Operation Modes
Mix
System mixes and dispenses material (apply Mix input).
Standby
Stops the system (remove Mix input).
Purge
Purges the system, using air and solvent (apply Purge
input).
Recipe (Color) Change
The process when the system automatically flushes out
the old color and loads a new color. See pages 78-89.
Flow Control
NOTE: Flow control is not available with dynamic dos-
ing.
Flow control is an optional feature of the ProControl 1KS
automatic system. Flow control regulates the flow of
material to a manual or automatic air spray gun, to help
ensure adequate coverage and avoid sags or runs in the
finish coat. It is not for use with air-assisted or airless
spray guns.
See F
IG. 68. The flow regulator (FC) is required to use
flow control in your system. Connect the fluid inlet and
outlet lines, air line, and cable as shown.
Set Flow Control to “On” in Configure Screen 5 on
page 31. Make the desired selections in Advanced
Setup Screen 5, page 37.
See the Graco Gateway manual 312785 for Flow Control Modbus addresses.
Fluid Inlet from
Fluid Manifold
Cable from
Fluid Station
Control Box
FIG. 68. Flow Control Regulator
Air Line from
Air Control
FC
Fluid Outlet to Gun
TI13656a
62 3A1080C
Page 63

System Operation
Typical PLC Interaction with ProControl 1KS
This section describes a typical interaction when a local
PLC is directly connected to the Discrete I/O connections of the ProControl 1KS.
See ProControl 1KS Integration Specifics on page 45
for a detailed explanation of inputs and outputs.
NOTE: Communications fields of Configure Screen 6
must be set to DISCRETE (see page 31).
Start Mixing
To start the mix process, the PLC will monitor and
ensure the Mix_Ready output is High. This provides
assurance it is ready to mix. PLC will drive High the
Mix_Start input, keep it High and monitor the Mix_Active
output to ensure the ProControl 1KS followed through
on the request.
Stop Mixing
To stop mixing (to perform a purge or color change),
remove the Mix_Start input (the status bar on the
EasyKey will show STANDBY). Monitor the Mix_Ready
output to ensure the Mix_Active output goes Low.
Color Change
To perform a color change, ensure there are no alarms
(except the Potlife Alarm). If alarms are present, the
Alarm_Reset input should be sent momentarily to clear
the alarm (>100 msec).
During the short On state, the recipe will be read from
this binary sequence and the status bar of the EasyKey
will display COLOR CHANGE XX. The
Purge_CC_Active output will be High for the duration of
the color change purge process. During the Mixed Material Load portion at the end of the Color Change
sequence, the Fill_Active output will be on, indicating
that portion of the color change. These will not be on at
the same time. Once the Mix_Ready output goes High
with no alarms, then the PLC has assurance that the
requested color change has taken place with the
requested recipe being the current active recipe. If any
error occurs during the process, the requested recipe
will not be loaded, and the old recipe will remain active.
NOTE: It is not possible to read the active recipe
through Discrete I/O alone. Only by monitoring networked registers through the Gateway is it possible to
view the active recipe. Proper management of the alarm
status outputs during the color change process will
ensure the active recipe is what is expected.
Purge
To start a Purge (no color change), drive the
Purge_Start input High (maintained) while ensuring
Mix_Ready output is High (ensuring no active alarms).
An exception is Potlife alarm (see Color Change above
if alarms are present.) The Purge_CC_Active output is
High for the entire Purge process. Ensure there are no
alarms during this process. Fill_Active is High when Mix
is on. When complete, Mix _Ready output will be High,
indicating a completed purge.
NOTE: No change is made to the active recipe.
NOTE: Alarm_Reset will not reset a Potlife alarm. Only
dispensing the Potlife Volume or a complete
Purge/Color Change will reset a Potlife alarm.
The Alarm Reset Input will silence the audible alarm.
Turn the Color_Change_Start input on momentarily
(>100 msec) while the proper sequence of recipe bits
are set.
NOTE: The Recipe Bits must be presented at least 100
msec before the Color Change Start input is turned on
and remain until a new recipe is required.
3A1080C 63
Gun Trigger Input
This input is sent and expected every time the gun is
actually triggered, and this input is turned off when the
gun is not triggered. Never tie this input with any other
signal. Without this input, some critical mixing alarms
are eliminated. This input should be provided through
Discrete I/O only for flow control applications to ensure
fast coordination with the flow control process. Applications without integrated flow control can use Gun Trigger
input through Network Communications or Discrete I/O.
NOTE: This has the same effect as the air flow switch
used on manual ProControl 1KS systems.
Page 64

System Operation
Alarm Monitoring/Reset (Discrete I/O)
Anytime an alarm occurs, the Alarm Reset input will
reset the alarms and allow for processing of the next
step by automation, except for the following condi-
tions:
• Potlife Alarms cannot be reset by the Alarm Reset
input or through the EasyKey Alarm Reset
key. Only a Purge/Color Change or spraying the Pot-
life volume will reset a Potlife alarm. (See
Alarm_Potlife output information on page 49.)
• When Flow Control is turned on (see Configure
Screen 5 on page 31), the Flow_Rate_Alarm output
will be High when the instantaneous flow rate is
above or below the Flow Rate tolerance setting.
(High Flow or Low Flow will be the condition, indicating in the status bar of the EasyKey.) This output will
be High along with the Mix_Active output. The PLC
should monitor the amount of time this condition
exists and take action at a predetermined time. With
Flow Control there will be times (for example during
flow rate changes) where the general alarm as
described here will be High (typically momentarily).
The PLC must read this Alarm output (i.e. general
alarm), see if Mix_Active is still High, and if so, start
a timer. A typical example would be to ensure all
parts are sprayed within a specific flow rate range. A
maximum predetermined time would be set to allow
a Low or High flow condition to exist continuously.
• Shutdown or go to Standby after the flow rate alarm
time expires.
Job_Complete Input
For Applications with Dump Valves (for quick
purges/color changes at or near the gun):
ProControl 1KS has four specials that can each be
turned off and on twice throughout a color change
sequence. See Advanced Setup Screen 8 on page 38
or Recipe Setup Screen 7 on page 42.
For example, a dump valve at a gun on a robot could be
opened at the appropriate times to facilitate fast color
changes. Another output could be used to automatically
drive an air-operated fluid regulator High during the
Purge or Color Change process.
NOTE: With integrated Flow Control, the flow control
regulator automatically is driven High. See Advanced
Setup Screen 5 on page 37 for specifics on setting up
these values. Each of the specials can be monitored, but
can only be controlled through the times entered within
the setup screens of the EasyKey or by managing the
proper registers on the network.
The following ProControl 1KS inputs should never be on
(High) at the same time:
•Mix_Start
• Purge_Start
• Color_Change_Start
The Recipe Bits (0-6) are always on at the same time.
The only time these bits are recognized is when the
Color_Change_Start input is High. The Recipe Bits
should be loaded and stay loaded for the current recipe. Do not change the Recipe Bits until a color change
is required again. Inconsistent results are possible if this
is not followed.
Every time a momentary Job_Complete input is seen by
the ProControl 1KS, a job log will be recorded, logging
the A meter volume (cc) with a time and date stamp. The
volume will then be reset to 0. (Volume totals are accumulated since the last reset.)
NOTE: A Color Change accomplishes the same Job
Complete Reset functions. The Job_Complete input is
commonly used to record material usage for a specific
set of parts. These volumes are sprayed material volumes.
64 3A1080C
Page 65

System Operation
General Operating Cycle
1. The system enters and loads the desired color.
2. The system enters Mix mode to begin operation.
3. The ProControl 1KS controller sends signals to activate the solenoid valves. The solenoid valves activate Dose Valve A. Fluid flow begins when the Gun
Trigger input is seen.
4. Dose Valve A (DVA) opens, and fluid flows to the
gun.
5. Flow Meter A (MA) monitors the fluid volume dispensed and sends electrical pulses to the ProControl 1KS controller. The controller monitors these
pulses and signals.
6. When the target volume dispenses, Dose Valve A
closes.
NOTE: The dispense volume of component A is
based on the mix ratio and dose size set by the user
and calculated by the ProControl 1KS controller.
7. Component A is fed to the gun as long as the Gun
Trigger input is seen.
8. If the Gun Trigger input is not seen for two minutes,
the system switches to Idle mode, which closes off
the mix manifold dose valve.
9. When the Gun Trigger input is seen again, the ProControl 1KS continues the process where it left off.
NOTE: Operation can be stopped at any time by
going to Standby mode (remove Mix input).
FIH
APV
AT
DVA
SS
FOH
Key:
MA Component A Meter
DVA Component A Dose Valve
SPV Solvent Purge Valve
SS Solvent Purge Valve Solvent Supply Tube
MA
SPV
APV Air Purge Valve
AT Air Purge Valve Air Supply Tube
FIH Fluid Inlet Hose
FOH Fluid Outlet Hose
TI15977a
F
IG. 69. Fluid Manifold
3A1080C 65
Page 66

System Operation
Mix Manifold Valve Settings
To open dose or purge valves, turn hex nut (E) counterclockwise. To close, turn clockwise. See Table 10 and
F
IG. 70.
Table 10: Mix Manifold Valve Settings
F
IG. 70. Valve Adjustment
E
TI11581a
Valve Setting Function
Dose (see
F
IG. 70)
Purge (see
F
IG. 70)
Hex nut (E) 1-1/4 turns out
from fully closed
Hex nut (E) 1-1/4 turns out
from fully closed
Limits maximum fluid flow rate into integrator
and minimizes valve response time.
Limits maximum fluid flow rate into integrator
and minimizes valve response time.
66 3A1080C
Page 67

System Operation
Start Up
1. Go through the Pre-Operation Checklist in Table 11.
Table 11: Pre-Operation Checklist
✓ Checklist
System grounded
Verify all grounding connections were made. See
the Installation manual.
All connections tight and correct
Verify all electrical, fluid, air, and system connections are tight and installed according to the
Installation manual.
Fluid supply containers filled
Check component A and solvent supply containers.
Mix manifold valves set
Check that mix manifold valves are set correctly.
Start with the settings recommended in Mix Mani-
fold Valve Settings, page 66, then adjust as
needed.
Fluid supply valves open and pressure set
Solenoid pressure set
➜ In bottom left corner, the system status displays,
which can be Standby, Mix, Purge, or an alarm
notification.
FIG. 72. Status Screen
3. Verify that the EasyKey is working. The active recipe
number and Standby mode should be displayed.
4. If this is the first time starting up the system, purge it
as instructed in Purging Fluid Supply System,
page 74. The equipment was tested with lightweight
oil, which should be flushed out to avoid contaminating your material.
75-100 psi inlet air supply (0.5-0.7 MPa, 5.2-7 bar)
2. Turn the AC Power Switch ON (I = ON, 0 = OFF).
I = ON
TI12656a
F
IG. 71. Power Switch
➜ Graco logo, software revision, and “Establishing
Communication” will display, followed by Status
screen. See page 19.
➜ At power up the system defaults to Recipe 61,
which is not a valid recipe number. Initiate a
color change to Recipe 0 or a valid recipe number (1-60).
5. Make sure that the EasyKey is in Standby (remove
Mix input).
6. Adjust component A fluid supply as
needed for your application. Use lowest
pressure possible.
7. Do not exceed the maximum rated working pressure shown on the system identification
label or the lowest rated component in the system.
8. Open the fluid supply valves to the
system.
9. Adjust the air pressure. Most applications require about 80 psi (552
kPa, 5.5 bar) air pressure to operate properly. Do
not use less than 75 psi (517 kPa, 5.2 bar).
3A1080C 67
Page 68

System Operation
10. Purge air from the fluid lines.
a. Shut off air to the gun by clos-
ing the air regulator or shutoff
valve for the gun atomizing air.
b. Trigger the gun (man-
ual or automatic) into
Manual
gun shown
a grounded metal pail.
c. Go to Mix mode.
d. If the flow meters over-run because of air in the
system, an alarm will occur and operation stops.
Press the Alarm Reset
key to clear
alarm.
e. Go to Mix mode.
11. Adjust the flow rate.
Watch the fluid flow rate displayed on the Status
screen while the gun is fully open.
If the fluid flow rate is too low: increase air pressure to the fluid supply or increase the regulated
fluid pressure.
If the fluid flow rate is too high: reduce the air
pressure, close the fluid manifold dose valves further, or adjust the fluid pressure regulator.
NOTE: Pressure adjustments of each component will
vary with fluid viscosity. Adjust as needed.
12. Turn on atomizing air to the gun. Check the spray
pattern as instructed in your spray gun manual.
NOTE: Do not allow a fluid supply tank to run empty. It is
possible for air flow in the supply line to turn gear meters
in the same manner as fluid. This can lead to the mixing
of fluid and air that meets the ratio and tolerance settings of the equipment.
The fluid flow rate is shown on the EasyKey Status
screen. The fluid supply lines on the screen highlight when the dose valve is open.
F
IG. 73. Status Screen Flow Rate Display
68 3A1080C
Page 69

System Operation
Shutdown
Overnight Shutdown
1. Leave the power on.
2. Run Recipe 0 to purge solvent through meters and
gun.
Service Shutdown
1. Follow Pressure Relief Procedure on page 69.
2. Close main air shutoff valve on air supply line and
on ProControl 1KS.
3. Shut off ProControl 1KS power (0 position). F
4. If servicing EasyKey, also shut off power at main circuit breaker.
IG. 74.
0 = OFF
Pressure Relief Procedure
NOTE: The following procedures relieve all fluid and air
pressure in the ProControl 1KS system. Use the procedure appropriate for your system configuration.
Relieve pressure when you stop spraying, before
changing spray tips, and before cleaning, checking, or
servicing equipment.
Single Color Systems
1. While in Mix mode (gun triggered), shut off the fluid
supply pumps/pressure pots. Close all fluid shutoff
valves at the pump outlets.
2. With the gun triggered, push the manual override on
the A dose valve solenoid to relieve pressure. See
F
IG. 75.
NOTE: If a Dose Time alarm (E-7, E-8) occurs, clear
the alarm.
F
IG. 74. Power Switch
TI12657a
3. Do a complete system purge, following the instructions under Purging Using Recipe 0, page 74.
4. Shut off the fluid supply to the solvent purge valve
(SPV) and the air supply to the air purge valve
(APV), F
5. With the gun triggered, push the manual override on
the A purge valve solenoid to relieve air and solvent
pressure. See F
is reduced to 0.
NOTE: If a Purge Volume alarm (E-11) occurs, clear
the alarm.
IG. 77.
IG. 75. Verify that solvent pressure
3A1080C 69
Page 70

System Operation
Systems with Color Change and Dump
Valves
NOTE: This procedure relieves pressure through the
dump valves.
1. Complete all steps under Single Color Systems,
page 69.
2. Shut off all color and catalyst supplies to the valve
stacks.
3. Press and hold the dump valve A solenoid override,
F
IG. 75.
4. See F
IG. 76. Open the color change module. Using
the solenoid identification labels as a guide, press
and hold the override button on each color solenoid
until flow from dump valve A stops.
5. Press and hold the dump valve A solenoid override,
F
IG. 75.
6. Press and hold the A side (color) solvent solenoid
override until clean solvent comes from the dump
valve, then release.
7. Shutoff the solvent supply to the color/catalyst
change stack solvent valves.
8. Press and hold the A solvent solenoid override and
dump valve override until solvent flow from the
dump valve stops.
70 3A1080C
Page 71

Dose Valve A
Solenoid
Purge Valve A
Solenoid
System Operation
Purge Valve B
Solenoid
Dose Valve B
Solenoid
J14
J15
J8
CAN
CAN
J1J12J3J9
Power
Fiber
Optic
TI15916a
FIG. 75. Fluid Solenoids
3A1080C 71
Page 72

System Operation
Solenoid
Identification
Label
Color Catalyst
Solenoid
Identification
Label
Color
TI12826a
FIG. 76: Color Change Solenoids
APV
AT
DVA
Solvent Solenoid
Overrides
FIH
MA
Key:
MA Component A Meter
DVA Component A Dose
Valve
SPV Solvent Purge Valve
SS Solvent Purge Valve
Solvent Supply Tube
APV Air Purge Valve
AT Air Purge Valve Air
Supply Tube
FIH Fluid Inlet Hose
FOH Fluid Outlet Hose
SS
FOH
SPV
TI15977a
FIG. 77. Fluid Manifold
72 3A1080C
Page 73

System Operation
Purging
Read Warnings, page 6. Follow the Grounding
instructions in your system Installation manual.
To avoid splashing fluid in the eyes, wear eye protection.
There are 4 purging procedures in this manual:
• Purging Mixed Material (below)
• Purging Using Recipe 0 (page 74)
• Purging Fluid Supply System (page 74)
Use the criteria listed in each procedure to determine
which procedure to use.
Purging Mixed Material
There are times when you only want to purge the fluid
manifold, such as:
2. Set the solvent supply pressure regulator at a pressure high enough to completely purge the system in
a reasonable amount of time but low enough to
avoid splashing or an injection injury. Generally, a
setting of 100 psi (0.7 MPa, 7 bar) is sufficient.
3. If using a gun flush box, place the gun into the box
and close the lid. Go to Purge mode. The purge
sequence automatically starts.
If the gun flush box is not used, trigger the gun (manual or automatic)
into a grounded metal pail until the
purge sequence is complete.
When done purging, the EasyKey automatically
switches to Standby mode.
4. If the system is not completely clean, repeat step 3.
NOTE: If necessary, adjust purge sequence so only
one cycle is required.
• end of potlife
• breaks in spraying that exceed the potlife
• overnight shutdown
• before servicing the fluid manifold assembly, hose or
gun.
1. Go to Standby mode (remove Mix input).
Trigger the gun to relieve pressure.
If you are using a high pressure gun, engage the trigger lock. Remove spray tip and clean tip separately.
If using an electrostatic gun shut off the electrostatics
before flushing the gun.
Trigger the gun to relieve pressure. Engage trigger
lock.
5. If spray tip was removed, reinstall it.
6. Adjust the solvent supply regulator back to its normal operating pressure.
3A1080C 73
Page 74

System Operation
Purging Using Recipe 0
Recipe 0 is typically used in multiple color systems to
purge out material lines without loading a new color.
To setup Recipe 0, go to Advanced Setup. Select the
Recipe tab and change the Recipe to 0. The Recipe 0
Setup Screen appears. Set the chop times from 0-999
seconds in increments of 1 second.
1. Go to Standby mode (remove Mix input).
Trigger the gun to relieve pressure.
If you are using a high pressure gun, engage the trigger lock. Remove spray tip and clean tip separately.
Purging Fluid Supply System
Follow this procedure before:
• the first time material is loaded into equipment*
• servicing
• shutting down equipment for an extended period of
time
• putting equipment into storage
* Some steps are not necessary for initial flush-
ing, as no material has been loaded into the
system yet.
1. Go to Standby mode (remove Mix input).
Trigger the gun to relieve pressure.
If you are using a high pressure gun, engage the trigger lock. Remove spray tip and clean tip separately.
If using an electrostatic gun shut off the electrostatics
before flushing the gun.
2. If using a gun flush box, place the gun into the box
and close the lid.
3. Select Recipe 0 and press Enter .
4. If a gun flush box is not used, trigger
the gun (manual or automatic) into a
grounded metal pail until the purge
sequence is complete.
5. The color change LED blinks while Recipe 0 runs
and turns solid after purge sequence is complete.
6. If the system is not completely clean, you can
repeat Recipe 0 by pressing Enter
.
If using an electrostatic gun, shut off the electrostatics
before flushing the gun.
2. Attach solvent supply lines as follows:
• Single color systems: disconnect the fluid
supply at the flow meter inlet, and connect regulated solvent supply lines.
• Multiple color systems: disconnect the fluid
supply at the flow meter inlet and connect a regulated solvent supply line.
74 3A1080C
Page 75

3. Adjust the solvent fluid supply pressure. Use the
lowest possible pressure to avoid splashing.
4. Remove the Fluid Station Control Box cover to
access the solenoid valves. See F
IG. 75 on page 71.
5. Purge as follows:
• Single color systems: Press the manual over-
ride on the Dose Valve A solenoid valve and
trigger the gun into a grounded metal pail until
clean solvent flows from the gun.
• Multiple color systems: Select Recipe 0 and
press Enter . The color change LED blinks
while Recipe 0 runs and turns solid after purge
sequence is complete.
6. Reinstall the Fluid Station Control Box cover.
7. Shut off the solvent fluid supply.
System Operation
8. Disconnect the solvent supply lines and reconnect
the fluid supply.
9. See page 67 for Start Up procedure.
3A1080C 75
Page 76

Meter Calibration
Meter Calibration
Calibrate the meter:
• The first time the system is operated.
• Whenever new materials are used in the system,
especially if the materials have viscosities that differ
significantly.
• At least once per month as part of regular maintenance.
• Whenever a flow meter is serviced or replaced.
NOTE:
• K-Factors on the Calibration Screen are
updated automatically after the calibration procedure is completed.
4. On the EasyKey, press the Setup key to access
setup screens.
5. Press the Right Arrow key to select the Cali-
bration Screen. Press
Dose Valve A. Press the Down Arrow
select Start from the menu. Start only one at a time.
the Enter key to select
key and
• K-Factor values on the screen are viewable
only. If needed, you can manually edit the
K-Factors in Advanced Setup Screen 4 (see
page 37) or Recipe Setup Screen 5 (page 42).
• All values on this screen are in cc, independent
of the units set in Configure Screen 1.
• The controller will use the active recipe
K-factors for meter calibration. The active recipe
must be recipe 1 to recipe 60. Recipes 0 and 61
do not have K-factor values.
1. Before calibrating meter A, prime the system with
material. For a color change system, make sure the
color valve is open.
2. Shut off all spray or dispense devices connected to
the ProControl 1KS.
3. Place the beaker (minimum size - 250 cc) to capture
fluid from the gun.
6. Dispense a minimum of 250 cc into beaker; make
sure enough material is dispensed to accurately
read the volume with your beaker.
7. The volume that the ProControl 1KS measured displays on the EasyKey.
76 3A1080C
Page 77

8. Compare the amounts on the EasyKey to the
amount in the beaker.
NOTE: For maximum accuracy, use a gravimetric
(mass) method to determine the actual volume dispensed.
9. If the screen and actual volume are different, enter
the actual dispensed volume in cc for A or Solvent
Volume field, and press the Enter key
.
If the value was substantially different, repeat the
calibration process.
NOTE: If the screen and actual volume is the same
or if for any reason you want to cancel the calibration procedure, scroll to Abort on the Calibration
Screen menu and press the Enter key
.
10. After the volume for A or Solvent is entered, the ProControl 1KS controller calculates the new flow meter
K-Factor and shows it on the Calibration Screen.
Meter Calibration
NOTE: K-Factor values on the screen are viewable
only. If needed, you can manually edit the K-Factors
in Advanced Setup Screen 4 (page 37) or Recipe
Setup Screen 5 (page 42).
11. Before you begin production, clear the system of
solvent and prime it with material.
a. Go to Mix mode.
b. Trigger the gun into a grounded metal pail until
mixed material flows from the gun nozzle.
c. To begin operation, see Start Up, page 67.
3A1080C 77
Page 78

Color Change
Color Change
Color Change Procedures
Multiple Color Systems
1. Shut off air to the gun.
2. Place the gun in the gun flush box if used, and close
the lid.
3. Go to Standby
4. Select the new recipe. Begin the color change
sequence.
5. If a gun flush box is not used, trigger
the gun (manual or automatic) into a
grounded metal pail until the color
change sequence is complete.
NOTE: The color change timer does not start until a
Gun Trigger input is seen and fluid flow is detected.
If no flow is detected within 2 minutes, the color
change operation aborts. The system enters
Standby mode (remove Mix input) at the previ-
ous color.
6. When you are ready to spray, remove the gun from
the gun flush box if used, and close its door (manual
and semi-automatic systems only).
NOTE: The gun flush box door must be closed for
the atomizing air valve to open.
mode (remove Mix input).
Color Change Sequences
FIG. 78 through FIG. 95 illustrate various color change
sequences. See Table 12 to determine which figure to
reference, based on the recipe change and system configuration. The time sequences are detailed in the following paragraphs.
NOTE: See Setup Mode on page 25 to select purge
sources and set desired purge, chop, and fill times.
NOTES:
• The system uses old recipe data for the purge cycle.
However, it opens the new color valve based on the
new recipe data.
• The system uses the new recipe data for the fill
cycle.
• For the one gun flush box (GFB) option, the spray
gun must be inserted in the GFB during the entire
color change cycle (purge and fill). The GFB trigger
output will be on during the recipe change cycle.
• For the two gun flush box (GFB) option, both spray
guns must be inserted in the GFBs during the entire
color change cycle (purge and fill). The system will
turn each GFB trigger output on and off based on
the preset time for each gun.
• For Special Outputs options, the system will turn
each output on and off based on the preset times.
Each Special Output has two different start times
and durations.
7. Enter Mix mode to start spraying.
• For systems without dump valves, the First Purge
begins after the Color Change steps are completed.
Single Color Systems
1. Follow procedure for Purging Fluid Supply System, page 74.
2. Load the new color. See Start Up, page 67.
3. Enter Mix mode to start spraying.
78 3A1080C
• When going from Recipe X to Recipe 0, only the
purge cycle data from Recipe 0 is used.
• When going from Recipe 0 to Recipe X, only the fill
cycle data from Recipe X is used.
Page 79

Color Change
Color Purge/Dump
Step P0-P1
• This sequence flushes out the color with solvent,
from the color valve to the Dump A valve.
• The color change solvent valve and the Dump A
valve open during the Purge Time.
• The color change solvent valve closes when the
Purge Time expires.
Color Fill
Step P1-P2
• This sequence fills the line with the new color all the
way to the Dump A valve.
• The new color valve and the Dump A valve open
during the Fill Time.
• The new color valve and the Dump A valve close
when the Fill Time expires.
First Purge
Step M0-M1
Select the First Purge Source (air, solvent, or 3rd valve)
and First Purge Time. For most applications, air is
selected.
Final Purge
Step M2-M3
Select the Final Purge Source (air, solvent, or 3rd valve)
and Final Purge Time. For most applications, solvent is
selected.
The system fills the line with solvent from the dose
valves to the gun, using only the selected purge media
(usually solvent). The selected purge valve opens during
the Final Purge Time and closes when the time expires.
Fill
Step M3-M4
This sequence fills the line from the dose valves to the
gun, and is also referred to as the mixed material fill.
The system begins dispensing component A until the Fill
Time expires.
Purge Active
Step M0-M3
The system turns on the Purge/Recipe Change Purge
Active output during steps M0-M3.
Fill Active
Step M3-M4
The system turns on the Recipe Change Fill Active output during step M3-M4.
The system purges the old material from the dose
valves to the gun, using only the selected purge media
(usually air). The selected purge valve opens during the
First Purge Time and closes when the time expires.
Chop Cycle
Step M1-M2
Select the Chop Type (air/solvent or air/3rd valve) and
Chop Times.
The air purge valve opens only during the air chop cycle,
and the solvent (or 3rd valve) opens only during the solvent chop cycle. The number of chop cycles is determined by dividing the Total Chop Time by the sum of the
Air and Solvent Chop Times.
3A1080C 79
Page 80

Color Change
Table 12: Color Change Chart Reference
Number of
Starting
Recipe
Ending
Recipe
Color
Change
Catalyst
Change
Dump
Valves
3rd Purge
Valve
Gun Flush
Boxes Refer to Fig.
X X Ye s Ye s Ye s Ye s 0 FIG. 79
X X Ye s Ye s Ye s No 0 FIG. 78
X X Ye s No No No 0 FIG. 81
X X Ye s No Ye s No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 80
X X No Ye s Ye s No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 82
X X No No No No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 92
X X Ye s Ye s Ye s N o 1 F
X X YesNoNoNo 1F
X X Ye s Ye s Ye s No 2 FIG. 83
X X Ye s No No No 2 FIG. 85
X 0 Yes Ye s Ye s N o 0 , 1 , o r 2 F
X 0 Yes No Yes No 0, 1, or 2 F
X 0 YesNoNoNo0, 1, or 2F
X 0 No Yes Yes No 0, 1, or 2 F
X 0 No No No No 0, 1, or 2 F
0 or 61 X Ye s Ye s Ye s No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 88*
0 or 61 X Ye s No Ye s No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 88*
0 or 61 X Ye s No No No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 90**
0 or 61 X No Ye s Ye s No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 88*
0 or 61 X No No No No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 90**
0 0 Ye s Ye s Ye s N o 0 , 1 , o r 2 F
0 0 Yes No Yes No 0, 1, or 2 F
0 0 YesNoNoNo0, 1, or 2F
0 0 No Yes Yes No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 87*
0 0 No No No No 0, 1, or 2 F
61 0 Ye s o r No Yes o r No Yes o r No No 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 87*
0 X Yes Yes Yes Yes 0, 1, or 2 FIG. 94
0 X Ye s N o Ye s Ye s 0, 1, o r 2 F
0 X Yes No No Yes 0, 1, or 2 F
0 X No Yes Yes Ye s 0, 1, o r 2 F IG. 94
0 X No No No Yes 0, 1, or 2 F
IG. 84
IG. 86
IG. 87*
IG. 87*
IG. 89**
IG. 87*
IG. 89**
IG. 87*
IG. 87*
IG. 89**
IG. 89**
IG. 94
IG. 95
IG. 95
NOTES:
* F
IG. 87 and FIG. 88 show both color and catalyst change. If the color or catalyst is not changing, disregard that
portion of the chart.
** F
IG. 89 and FIG. 90 show color change. If the color is not changing, disregard that portion of the chart.
F
IG. 91 (page 87) shows a recipe change with Special Outputs.
F
IG. 93 (page 88) shows an External Color Change.
80 3A1080C
Page 81

V
Dump A
V
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Color Fill Time P1->P2
Catalyst Purge Time P2->P3
Catalyst Fill Time P3->P4
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time M0->M1
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Mixed Fill Time M3->M4
FIG. 78: Color Change Chart 1
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 1: A1 to A2, B1 to B2 with Dump Valves
A
A
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4
B
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
B
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of Mixed Material Purge Timers. This
line defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins.
Color Change
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
*Two Second Initial Purge Time M0->M1
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M2->M3
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
*Applies to ALL charts when 3rd Flush Valve is ON
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Color Fill Time P1->P2
Catalyst Purge Time P2->P3
Catalyst Fill Time P3->P4
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
*Two Second Solvent Purge
First Purge Time M1->M2
Final Purge Time M3->M4
Mixed Fill Time M4->M5
FIG. 79: Color Change Chart 2
Chart 2: A1 to A2, B1 to B2 with Dump Valves and 3rd Flush Valve
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4 M5
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
A
A
B
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
B
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of Mixed Material Purge Timers. This
line defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins.
3A1080C 81
Page 82

Color Change
V
V
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Color Fill Time P1->P2
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time M0->M1
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Mixed Fill Time M3->M4
FIG. 80: Color Change Chart 3
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 3: A1 to A2, same B with Dump Valves
A
A
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of Mixed Material Purge Timers. This
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4
line defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins.
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B Air Chop Time B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) 3->4
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
Color Purge Time 0->1
Color Fill Time 1->2
First Purge Time 2->3
Final Purge Time 4->5
Mixed Fill Time 5->6
FIG. 81: Color Change Chart 4
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 4: A1-A2, same B without Dump Valves
Solvent Chop Time
012 3 4 5 6
82 3A1080C
Page 83

V
Dump A
V
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
Catalyst Purge Time P0->P1
Catalyst Fill Time P1->P2
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time M0->M1
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Mixed Fill Time M3->M4
FIG. 82: Color Change Chart 5
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 5: B1 to B2, same A with Dump Valves
B
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4
B
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of Mixed Material Purge Timers. This
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
line defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins.
Color Change
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Flush Box Output #1
Gun Flush Box Output #2
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Color Fill Time P1->P2
Catalyst Purge Time P2->P3
Catalyst Fill Time P3->P4
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time M0->M1
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Mixed Fill Time M3->M4
FIG. 83: Color Change Chart 6
Chart 6: A1 to A2, B1 to B2 with Dump Valves, 2 GFBs
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
A
A
B
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
B
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of System Purge Timers. This line
defines when the System Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the System Fill Time
begins.
3A1080C 83
Page 84

Color Change
V
V
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Flush Box Output #1
Gun Flush Box Output #2
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Color Fill Time P1->P2
Catalyst Purge Time P2->P3
Catalyst Fill Time P3->P4
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time M0->M1
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Mixed Fill Time M3->M4
FIG. 84: Color Change Chart 7
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 7: A1 to A2, B1 to B2 with Dump Valves, 1 GFB
A
A
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4
B
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
B
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of Mixed Material Purge Timers. This
line defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins.
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B Air Chop Time B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Flush Box Output #1
Gun Flush Box Output #2
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) 3->4
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
Color Purge Time 0->1
Color Fill Time 1->2
First Purge Time 2->3
Final Purge Time 4->5
Mixed Fill Time 5->6
FIG. 85: Color Change Chart 8
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 8: A1-A2, same B without Dump Valves, 2 GFBs
Solvent Chop Time
012 3 4 5 6
84 3A1080C
Page 85

Color Change
V
V
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 9: A1-A2, same B without Dump Valves, 1 GFB
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B Air Chop Time B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
Dispense A A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Flush Box Output #1
Gun Flush Box Output #2
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) 3->4
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
012 3 4 5 6
Color Purge Time 0->1
Color Fill Time 1->2
First Purge Time 2->3
Final Purge Time 4->5
Mixed Fill Time 5->6
Solvent Chop Time
FIG. 86: Color Change Chart 9
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A
Catalyst Change B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A
Dispense B
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Notes:
All timing from Recipe 0
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Catalyst Purge Time P1->P2
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time M0->M1
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Chart 10: Recipe X, 0, OR 61 to Recipe 0 with Dump Valves
P0 P1 P2
M0 M1 M2 M3
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
A
B
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
Color/Catalyst Purge Timers are
independent of Mixed Material Purge
Timers.
FIG. 87: Color Change Chart 10
3A1080C 85
Page 86

Color Change
V
V
Dump A A
Dump B B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A A A
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
FIG. 88: Color Change Chart 11
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A
Catalyst Change B Air Chop Time
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
alve Time-Sequence
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
Chart 11: Recipe 0 OR 61 to Recipe X with Dump Valves
alve Time-Sequence
Color Fill Time 0->1
Catalyst Fill Time 1->2
Mixed Fill Time 2->3
Chart 12: Recipe X, 0, OR 61 to Recipe 0 without Dump Valves
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
012 3
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Solvent Chop Time
Dispense A A
Dispense B
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Color Purge Time 0->1
First Purge Time 1->2
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) 2->3
Notes:
All timing from Recipe 0
Final Purge Time 3->4
FIG. 89: Color Change Chart 12
01 2 3 4
86 3A1080C
Page 87

Color Change
V
V
FIG. 90: Color Change Chart 13
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Valve
alve Time-Sequence
Color Purge Time P0->P1
Color Fill Time P1->P2
Catalyst Purge Time P2->P3
Catalyst Fill Time P3->P4
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
Chart 13: Recipe 0 OR 61 to Recipe X without Dump Valves
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A A A A
Dispense B B B
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
P0 P1 P2 P3 P4
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
01 2
Color Fill Time 0->1
Mixed Fill Time 1->2
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 14: A1 to A2, B1 to B2 with All
A
A
B
Air Chop Time
Solvent Chop Time
B
CC Purge/Fill Timers are independent
of Mixed Material Purge Timers. This
line defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins. The longer of the two timers
defines when the Mixed Fill Time
begins.
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
M0 M1 M2 M3 M4
First Purge Time M0->M1
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) M1->M2
Final Purge Time M2->M3
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
Special Output #1
Special Output #2
Special Output #3
Special Output #4
Recipe Change Purge Active Output
Recipe Change Fill Active Output
Mixed Fill Time M3->M4
1st On/Start 1st On Length/Duration 2nd On/Start 2nd On Length
FIG. 91: Color Change Chart 14
3A1080C 87
Page 88

Color Change
V
V
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A
Catalyst Change B Air Chop Time B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) 1->2
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
alve Time-Sequence
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time 0->1
Final Purge Time 2->3
Mixed Fill Time 3->4
FIG. 92: Color Change Chart 15
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 15: Same A, Same B
Solvent Chop Time
01 23 4
Dump A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A
Catalyst Change B Air Chop Time
Air Purge
Solvent Purge Final Purge (one of these)
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A AA
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Chop Time (air/solvent or air/3rd flush) 1->2
Wait for External Color Change Ready signal
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Purge from old recipe
Fill from new recipe
Recipe Change Purge Active Output
Recipe Change Fill Active Output
alve Time-Sequence
First Purge (one of these) 3rd Flush Chop Time
First Purge Time 0->1
Final Purge Time 2->3
(before advance to step 4) 3->4
Mixed Fill Time 4->5
FIG. 93: Color Change Chart 16
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Chart 16: External Color Change Option
Solvent Chop Time
01 234 5
88 3A1080C
Page 89

Color Change
V
V
Dump A A
Dump B B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B B B
Air Purge
Solvent Purge
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A A A
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Mixed Material Purge Timers from old recipe
CC Purge/Fill Timers and Mixed Fill Time f rom new recipe
*Exiting Fill Source and Length are Programmable
FIG. 94: Color Change Chart 17
Dump A A
Dump B
Color Change Solvent
Catalyst Change Solvent
Color Change A A A
Catalyst Change B
Chart 17: Recipe 0 OR 61 to Recipe X with Dump Valves and 3rd Flush Valve
alve Time-Sequence
*Exiting Fill Time 0->2
Color Fill Time 0->1
Catalyst Fill Time 1->2
Mixed Fill Time 2->3
Chart 18: Recipe 0 OR 61 to Recipe X without Dump Valves and 3rd Flush Valve
alve Time-Sequence
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
*Exiting Fill
012 3
ProMix 2KS Recipe Change
Mixed Fill Time does not
begin until the Exiting Fill
Time and Color/Catalyst Fill
Time is complete.
Air Purge
Solvent Purge
3rd Flush Purge
Dispense A A A A
Dispense B BB
Gun Trigger(s) by Operator
Notes: Load tables from new recipe
Mixed Material Purge Timers from old recipe
CC Purge/Fill Timers and Mixed Fill Time f rom new recipe
*Exiting Fill Source and Length are Programmable
FIG. 95: Color Change Chart 18
*Exiting Fill
012 3
*Exiting Fill Time 0->1
Color Fill Time 1->2
Mixed Fill Time 2->3
3A1080C 89
Page 90

Alarms and Warnings
Alarms and Warnings
NOTE: Do not use the fluid in the line that was dis-
pensed off ratio as it may not cure properly.
System Alarms
System alarms alert you of a problem and help prevent
off-ratio spraying. If an alarm occurs, operation stops
and the following occurs:
• Alarm sounds.
• Status bar on the EasyKey shows the alarm E-Code
with a description (see Table 13).
System Warnings
Table 13 lists the System Warning Codes. Warnings do
not stop operation or sound an alarm. They are saved in
the date/time stamped log, which can be viewed on a
PC, using the Web Interface (see manual 313386).
To Reset Alarm and Restart
NOTE: When an alarm occurs be sure to determine the
E-Code before resetting it. See Table 13. If you forget
which E-Code occurred, use the Alarms Screen (page
24) to view the last 10 alarms, with date and time
stamps.
To reset alarms, see Table 14. Many alarms can be
cleared by simply pressing the Alarm Reset
key.
Table 13: System Alarm/Warning Codes
Code Description Details
E-1 Communication Error Alarm Page 91
E-2 Potlife Alarm Page 91
E-3 Ratio High Alarm Page 92
E-4 Ratio Low Alarm Page 93
E-5 Overdose A/B Dose Too Short
Alarm
E-6 Overdose B/A Dose Too Short
Alarm
E-7 Dose Time A Alarm Page 95
E-8 Dose Time B Alarm Page 95
E-9 Mix in Setup Alarm Page 96
E-10 Remote Stop Alarm Page 96
E-11 Purge Volume Alarm Page 96
E-12 CAN Network Communication Error
Alarm
E-13 High Flow Alarm Page 96
E-14 Low Flow Alarm Page 96
E-15 System Idle Warning Page 97
E-16 Setup Change Warning Page 97
E-17 Power On Warning Page 97
E-18 Defaults Loaded Warning Page 97
E-19 I/O Alarm Page 98
E-20 Purge Initiate Alarm Page 99
E-21 Material Fill Alarm Page 99
E-22 Tank A Low Alarm Page 99
E-23 Tank B Low Alarm Page 99
E-24 Tank S Low Alarm Page 99
E-25 Auto Dump Complete Alarm Page 100
E-26 Color/Catalyst Purge Alarm Page 100
E-27 Color/Catalyst Fill Alarm Page 100
Page 94
Page 94
Page 96
90 3A1080C
Page 91

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-1: COMM_ERROR
Cause Solution
No power to the EasyKey. Connect power to EasyKey.
Alarm Troubleshooting
No power to Fluid Station Control Box. The intrinsically
safe power cable between the EasyKey and Fluid Station
Control Box is not connected.
No power to Fluid Station Control Box. The fluid control
board fuse is blown.
The fiber optic cable between the EasyKey and Fluid
Station Control Box is not connected.
The fiber optic cable is cut or bent. Verify that the cable has not been cut or bent at a radius
Dirty fiber optic cable ends. Disconnect fiber optic cable ends and clean with a
A communication cable or connector failed. Replace cable.
E-2: POTLIFE_ALARM
Cause Solution
The potlife time has been exceeded for the mixed material.
NOTICE
To prevent mixed material from curing in the equipment, do not shut off power. Follow one of the solutions at right.
Verify that the cable is correctly connected. See Installation manual.
Verify condition of fuse and replace if necessary. See
Repair-Parts manual.
Verify that the cable is correctly connected. See Installation manual.
smaller than 1.6 in. (40 mm).
lint-free cloth.
Press the Alarm Reset
alarm. Purge the system with solvent, fresh mixed mate-
rial, or a new color:
• Solvent Purge - See Purging Mixed Material on
page 73. The system purges until the preset purge
time is complete.
key to stop the audible
• New Mixed Material Purge - Go to Mix mode and
spray the required volume to restart the timer.
• Color Change - Perform a color change, see page
78.
3A1080C 91
Page 92

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-3: RATIO_HIGH_ALARM
The mix ratio is higher than the set tolerance on the previous dose cycle.
Cause Solution
There is too little restriction in the system. • Check that the system is fully loaded with material.
• Check that the supply pump’s cycle rate is set properly.
• Check that the spray tip/nozzle is properly sized for
the flow and application, and that it is not worn.
• Check that the fluid regulator is set properly.
If the alarm occurs during start up, after purging, the flow
rate was probably too high.
If the alarm occurred after you were spraying for some
time, the pressures from the fluid supply could be too
Restrict gun needle travel to slow down the initial fluid
delivery rate until fluid hoses are loaded with material.
Adjust fluid supply regulator pressure. Verify that component A dose valve is operating properly.
high.
Slow actuation of the component A valve. This can be
caused by:
Manually operate the Dispense A solenoid valves as
instructed in the ProControl 1KS Repair-Parts manual to
check operation.
• Air pressure to the valve actuator is too low. • Increase air pressure. Air pressure must be 75-120
psi (0.52-0.84 MPa, 5.2-8.4 bar); 120 psi is recommended.
• Something is restricting the solenoid or tubing and
interrupting valve actuation air.
• There may be dirt or moisture in the air supply. Filter
appropriately.
• A dose valve is turned in too far. • Refer to Table 10: Mix Manifold Valve Settings,
page 67, for adjustment guidelines.
• Fluid pressure is high and air pressure is low. • Adjust air and fluid pressure. See recommended air
pressure above.
92 3A1080C
Page 93

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-4: RATIO_LOW_ALARM
The mix ratio is lower than the set tolerance on the previous dose cycle.
Cause Solution
There is too much restriction in the system. • Check that the system is fully loaded with material.
• Check that the supply pump’s cycle rate is set properly.
• Check that the spray tip/nozzle is properly sized for
the flow and application, and that it is not clogged.
• Check that the fluid regulator is set properly.
If the alarm occurs during start up, after purging, the flow
rate was probably too high.
If the alarm occurred after you were spraying for some
time, the pressure from the fluid supply could be too low.
Slow actuation of the component A valve. This can be
caused by:
Restrict gun needle travel to slow down the initial fluid
delivery rate until fluid hoses are loaded with material.
Adjust fluid supply regulator pressure. Verify that component A dose valve is operating properly.
Manually operate the Dispense A solenoid valves as
instructed in the ProControl 1KS Repair-Parts manual to
check operation.
• Air pressure to the valve actuator is too low. • Increase air pressure. Air pressure must be 75-120
psi (0.52-0.84 MPa, 5.2-8.4 bar); 120 psi is recommended.
• Something is restricting the solenoid or tubing and
interrupting valve actuation air.
• There may be dirt or moisture in the air supply. Filter
appropriately.
• A dose valve is turned in too far. • Refer to Table 10: Mix Manifold Valve Settings,
page 67, for adjustment guidelines.
• Fluid pressure is high and air pressure is low. • Adjust air and fluid pressure. See recommended air
pressure above.
3A1080C 93
Page 94

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-5: OVERDOSE_A/B_DOSE_TOO_SHORT_ALARM and
E-6: OVERDOSE_B/A_DOSE_TOO_SHORT_ALARM
E-5: the A dose overshoots and, when combined with B, is too large for the mix chamber capacity.
E-6: the B dose overshoots and forces an A side dose that, when combined with B, is too large for the mix chamber
capacity.
Cause Solution
Valve seal or needle/seat are leaking. Check F
IG. 16
Repair the valve (see valve manual 312782).
Totals Screen on page 23. I
Sampling valve is leaking. Tighten or replace valve.
Flow meter fluctuations caused by pressure pulsations. Check for pressure pulsations:
1. Close all the manifold valves.
2. Turn on the circulating pumps and all the booth
equipment (such as fans and conveyors).
3. Check if the ProControl 1KS is reading any fluid flow.
4. If the ProControl 1KS shows there is fluid flow and
there are no leaks from the gun or any other seals or
fittings, the flow meters are probably being affected
by pressure pulsations.
5. Close the fluid shutoff valve between the fluid supply
system and the flow meter. The flow indication
should stop.
6. If necessary, install pressure regulators or a surge
tank on the fluid inlets to the ProControl 1KS to
reduce the fluid supply pressure. Contact your Graco
distributor for information.
Slow actuation of component A valve. See E-3: RATIO_HIGH_ALARM and E-4:
RATIO_LOW_ALARM, pages 92-93.
Running a high mix ratio and a high flow rate. It may be necessary to restrict the flow rate through the
component B dose valve by adjusting its hex nut (E). See
page 66.
94 3A1080C
Page 95

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-7: DOSE_TIME_A_ALARM and E-8: DOSE_TIME_B_ALARM
E-7: gun trigger input is active (AFS or Integration) and no A meter pulses are detected during the dose time
selected.
E-8: gun trigger input is active (AFS or Integration) and no B meter pulses are detected during the dose time
selected.
Cause Solution
System is in Mix mode and gun is only partially triggered,
Fully trigger the gun.
allowing air but no fluid to pass through gun.
Fluid flow rate is too low. Increase flow rate.
Dose time setting is too short for the current flow rate. Increase the dose time setting.
Flow meter or cable failed or flow meter clogged. To check meter sensor operation, remove meter cap to
expose sensor. Pass a ferrous metal tool in front of the
sensor.
TI12792a
If there is a meter or cable failure, you will see a large difference between the amount of fluid dispensed and the
flow meter volume displayed by the EasyKey. Clean or
repair meter as necessary. Also see meter manual
308778.
Follow Meter Calibration procedure, page 76.
Slow actuation of component A valve. See E-3: RATIO_HIGH_ALARM and E-4:
RATIO_LOW_ALARM, pages 92-93.
The supply pump is not turned on. Turn on the supply pump.
System is in Mix mode with 0 volume entered for Min
Material Fill Volume (see Option Screen 1, page 32),
Verify condition of fuse and replace if necessary. See
Repair-Parts manual.
and Fuse F1 is blown.
3A1080C 95
Page 96

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-9: MIX_IN_SETUP_ALARM
Cause Solution
Attempt to operate system while in Setup mode. System must be in Standby to change current recipe,
and cannot be operated.
E-10: REMOTE_STOP_ALARM
Cause Solution
Automation has requested that the system abort all oper-
Abort operations. Troubleshoot automation system.
ations.
E-11: PURGE_VOLUME_ALARM
Cause Solution
ProControl 1KS solvent flow switch is not activated while
purging.
Verify that the gun is not shut off and that the solvent flow
switch is activated while purge is taking place.
Minimum flush volume is set too high. Increase solvent supply or decrease minimum volume
setting.
No meter pulses during Color/Catalyst Dump. Color change solvent supply not set up or functional.
Check Color Change setup.
E-12: CAN_COMM_ERROR_ALARM
Cause Solution
Communication between the Color Change Module and
Verify that the cable is correctly connected.
the Fluid Station Control Box is interrupted.
Communication between the Color Change Module and
the Fluid Station Control Box is interrupted. The fluid
Verify condition of fuse and replace if necessary. See
Repair-Parts manual.
control board fuse is blown.
E-13: HIGH_FLOW_ALARM or E-14: LOW_FLOW_ALARM (may also be set as Warnings)
Cause Solution
Fluid system is producing too much or too little flow. Troubleshoot fluid system for restrictions, leaks,
exhausted fluid supply, incorrect settings, etc. Increase
or decrease flow rate, as required.
96 3A1080C
Page 97

E-15: SYSTEM_IDLE_WARNING
Cause Solution
Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
Mix input is high, but the gun has not been triggered for 2
If not painting, clear alarm and resume operation.
minutes.
If painting, shut down and inspect fluid meter.
E-16: SETUP_CHANGE_WARNING
Cause Solution
The system setup parameters have been changed. No action required. See Event Log available through
advanced web interface.
E-17: POWER_ON_WARNING
Cause Solution
The power to the system has been cycled. No action required. See Event Log available through
advanced web interface.
E-18: DEFAULTS_LOADED_WARNING
Cause Solution
The factory defaults have been installed on the system. No action required. See Event Log available through
advanced web interface.
3A1080C 97
Page 98

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-19: I/O_ALARM
Cause Solution
The Mix and Purge digital inputs are on at the same time. Ensure that only one input is on at a time. At least 1 sec
delay is required when switching from Mix to Purge or
vice versa.
NOTE: The I/O alarm incorporates several sub-alarms relating to internal data issues, as detailed below. These
alarms may not apply to all software versions.
Fluid Plate Reboot (FP Reboot): Occurs if the system
detects a fluid plate control board reboot or power cycle
not triggered from the EasyKey. The system reverts to
Recipe 61, and mixed material may be in the lines.
Autokey Lost: Occurs if the Autokey is lost or changed
after having been detected. (A short term loss of the
Autokey will not be registered.) Some system functions
may become unavailable. For example, an automatic
system will not respond to PLC or robot control.
Illegal Source: Occurs if a recipe outside of the range
1-60 is detected as the source data for global recipe data
copies. This is possible if an invalid configuration file is
sent to the EasyKey.
2K/3K Error: Occurs if the recipe data is incompatible
with the current Autokey setting (2K or 3K). This is possible if the Autokey is changed or an invalid configuration
file is sent to the EasyKey.
Init Error: Occurs if the recipe data codes specifying the
type of machine they were made on are not what is
expected. For example, a 3KS machine receives a configuration file originally made on a 2KS machine.
Config Error: Occurs if a configuration file sent to the
EasyKey specifies a different hardware setup than what
exists. For example, the configuration file specifies 2
color change boards but only 1 is present.
Flush the system or perform a color change. If possible,
identify the origin of the reboot or power cycle.
Reinstall the Autokey, or verify that the Autokey is set
properly.
Verify that the source data is from a valid recipe (1-60).
Verify that the Autokey is set properly or that the configuration file is valid.
Verify that the configuration file is valid.
Verify that the configuration file specifications and the
hardware conform.
Range Error: Occurs if a valve used in a recipe is not
present in the current hardware setup. For example, a
Verify that the recipe specifications and the hardware
conform.
recipe calls for valve 30 but the system has only 12
valves.
Level Control (LC) Error: Occurs if level control data is
Verify that the Autokey is set properly.
received by the EasyKey, and the current Autokey setting
(2K or 3K) has changed since the level control data was
originally initialized.
Level Control (LC) Range Error: Occurs if level control
Set level control data correctly.
data includes a valve range exceeding the capability of
the machine.
Modbus (MB) Overflow: Occurs if the Modbus connec-
Verify the Modbus protocol to the EasyKey.
tion to a PLC experiences data overflow.
98 3A1080C
Page 99

E-20: PURGE_INITIATE_ALARM
Cause Solution
Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
System detects atomizing air to the gun when purge is
Shut off gun air.
selected.
For systems with a gun flush box, gun is not in the box
when purge is selected.
For systems with auto dump on, gun is not in the box
when auto dump is initiated.
Place gun in gun flush box. Verify that gun flush box is
operating properly.
Place gun in gun flush box. Verify that gun flush box is
operating properly.
For systems with a gun flush box, Fuse F2 is blown. Verify condition of fuse and replace if necessary. See
Repair-Parts manual.
E-21: MATERIAL_FILL_ALARM
Cause Solution
For systems with minimum mixed material fill volume
Check for restrictions or leaks in the fluid supply system.
entered, the system detects that fill volume is not
achieved during mixed material fill time.
Check if the fill volume is properly configured:
• Adjust fill volume.
• Adjust fill time.
For systems without color change and with minimum
mixed material fill volume entered, Fuse F1 is blown.
Verify condition of fuse and replace if necessary. See
Repair-Parts manual.
E-22: TANK_A_LOW_ALARM, E-23: TANK_B_LOW_ALARM, or E-24: TANK_S_LOW_ALARM
Cause Solution
The tank volume reaches the low-level threshold. The EasyKey screen will display the alarm and prompt
the user to do one of the following:
• Refill tank volume to clear the alarm.
• Resume mixing by selecting “Spray 25% of remaining volume.” If this selection is chosen, a second
alarm will occur after 25% of the remaining volume is
mixed. Refill tank volume to clear the alarm.
3A1080C 99
Page 100

Alarm Troubleshooting
Table 14. Alarm Troubleshooting
E-25: AUTO_DUMP_COMPLETE_ALARM
Cause Solution
A potlife alarm is active for more than 2 minutes, the gun
Be sure to spray all mixed material before potlife expires.
flush box is enabled and gun is in the gun flush box, and
an auto dump flush sequence is complete.
E-26: COLOR/CATALYST_PURGE_ALARM
Cause Solution
System detects no meter pulses, or a disruption in meter
Check that meter cable is connected.
pulses lasting longer than 1 second throughout the Color
purge time duration.
Clean or repair meter.
E-27: COLOR/CATALYST_FILL_ALARM
Cause Solution
System detects no meter pulses, or system must detect
Check that meter cable is connected.
at least 10cc of material from each side throughout the
Color fill time duration.
Gun, dump valve, or correct color/catalyst valve not
Clean or repair meter.
Open the valve.
open.
Exhausted fluid supply. Check fluid level and refill if necessary.
Fuse F1, F2, or both are blown. Verify condition of fuses and replace if necessary. See
Repair-Parts manual.
100 3A1080C
 Loading...
Loading...