Page 1
D
Bedienungsanleitung
Operating manual
F
Mode d‘emploi
E
Manuel de instrucciones
Инструкция за експлоатация
Návod k použití zkoušečky
Brugsanvisning
Οδηγίες χρήσεως
H
Használati utasítás
I
Istruzioni per l’uso
Notkunarleiðbeiningar
N
Bruksanvisning
Gebruiksaanwijzing
Instrukcja obsługi
Instrucţiuni de Utilizare
Инструкция по эксплуатации
индикатора напряжения
S
Bruksanvisning
1
SRB
Upute za rukovanje
Kullanma Talimati
D D
1
2
3
4
1
000
690
400
230
0
R
AC
DC
120
50
24
V
12
analog 1000
®
5
6
7
analog
1
000
690
400
230
0
R
AC
DC
120
50
24
V
12
1
000
690
400
230
9
J
analog
8
DC
0
R
AC
120
50
24
V
12
GMC-I Messtechnik GmbH
Südwestpark 15
D-90449 Nürnberg
Telefon +49 911 8602-111
Fax +49 911 8602-777
www.gossenmetrawatt.com • info@gossenmetrawatt.com
DUSPOL
T.-Nr. 10079314.04 02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
U1
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
U202/ 2019
Page 2
D D DD
AC
DC
AC
AC
A
B
230 VAC
PE
N L
1000 VDC
E
F
C
D
230 VAC
PE
N L
230 VAC
PE
N L
DUSPOL® analog 1000
U3
DUSPOL® analog 1000
U402/ 2019
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
U5 02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
U602/ 2019
Page 3

D
Bedienungsanleitung
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Bevor Sie den Spannungsprüfer DUSPOL® analog 1000 benutzen: Lesen Sie bitte die Bedienungsanleitung und beachten
Sie unbedingt die Sicherheitshinweise!
Inhaltsverzeichnis
1. Sicherheitshinweise
2. Gerätebeschreibung
3. Funktionsprüfung vor dem Gebrauch zur Überprüfung
der Spannungsfreiheit einer Anlage
4. Überprüfung der Spannungsfreiheit einer Anlage
5. Lastzuschaltung mit Vibrationsmotor
6. Außenleiterprüfung (Phasenanzeige)
7. Drehfeldprüfung
8. Technische Daten
9. Allgemeine Wartung
10. Umweltschutz
1. Sicherheitshinweise:
- Gerät beim Benutzen nur an den isolierten Griffen L1 6
und L2 7 anfassen und die Prüfspitzen L1/- 2 und L2/+
3
nicht berühren!
- Unmittelbar vor und nach dem Benutzen, zur Überprüfung
der Spannungsfreiheit einer Anlage, den Spannungsprüfer auf Funktion prüfen! (siehe Abschnitt 3). Der Spannungsprüfer darf nicht benutzt werden, wenn die Funktion einer oder mehrerer Anzeigen ausfällt oder keine
Funktionsbereitschaft zu erkennen ist! Die Überprüfung
der Spannungsfreiheit ist dann mit einem anderen Spannungsprüfer zu wiederholen.
- Der Spannungsprüfer darf nur im angegebenen Nennspan nungs bereich und in elektrischen Anlagen bis AC/
DC 1.000 V eingesetzt werden!
- Der Spannungsprüfer darf nur in Stromkreisen der Überspan nungskategorie CAT III mit max. 1000 V oder Überspan nungs kategorie CAT IV mit max. 600 V Leiter gegen
Erde benutzt werden.
- Der Spannungsprüfer ist für die Anwendung durch Elektrofachkräfte in Verbindung mit sicheren Arbeitsverfahren
ausgelegt.
- Die LED-Stufenanzeige dient der Anzeige des Spannungsbereiches, sie ist nicht für Messzwecke bestimmt.
-
Spannungsprüfer nie länger als 30 Sekunden an Spannung
anlegen (maximal zulässige Einschalt dauer ED = 30 s)!
- Der Spannungsprüfer darf nicht zerlegt werden!
- Der Spannungsprüfer ist vor Verunreinigungen und Beschädigungen der Gehäuseoberfläche zu schüt zen.
- Als Schutz vor Verletzungen sind nach Gebrauch des
Spannungsprüfers die Prüfspit zen mit dem beiliegenden
Prüfspitzenschutz 1 zu versehen!
- Beachten Sie, dass die Impedanz (Innenwiderstand)
des Spannungsprüfers die Anzeige von Störspannungen
(kapazitiv oder induktiv eingekoppelt) beeinflusst!
Abhängig von der inneren Impedanz des Spannungs-
prüfers gibt es bei Vorhandensein von Störspannung verschiedene Möglichkeiten der Anzeige “Betriebs span nung
vorhanden” oder “Betriebsspannung nicht vorhanden“.
Niederohmiger Spannungsprüfer (Impedanz < 100 kΩ),
Störspannung wird unterdrückt bzw. herabgesetzt:
Ein Spannungsprüfer mit relativ niedriger innerer Impedanz
wird im Vergleich zum Referenzwert 100 kΩ nicht alle Störspannungen mit einem Ursprungswert oberhalb von ELV (50 V
AC/ 120 V DC) anzeigen. Bei Kontakt mit den zu prüfenden
Teilen kann der Spannungsprüfer die Störspannungen durch
Entladung vorübergehend bis zu einem Pegel unterhalb ELV
herabsetzen; nach dem Entfernen des Spannungsprüfers wird
die Störspannung ihren Ursprungswert aber wieder annehmen.
Wenn die Anzeige „Spannung vorhanden“ nicht erscheint, wird
dringend empfohlen, vor Aufnahme der Arbeiten die Erdungsvorrichtung einzulegen.
Hochohmiger Spannungsprüfer (Impedanz > 100 kΩ: Stör-
spannung wird nicht unterdrückt bzw. herabgesetzt:
Ein Spannungsprüfer mit relativ hoher innerer Impedanz wird
im Vergleich zum Referenzwert 100 kΩ bei vorhandener Störspannung „Betriebsspannung nicht vorhanden“ nicht eindeutig
anzeigen. Wenn die Anzeige „Spannung vorhanden“ bei einem Teil erscheint, der als von der Anlage getrennt gilt, wird
dringend empfohlen, mit zusätzlichen Maßnahmen (Beispiel:
Verwendung eines geeigneten Spannungsprüfers der in der
Lage ist Betriebsspannung von Störspannung unterscheiden,
Sichtprüfung der Trennstelle im elektrischen Netz, usw.) den
Zustand „Betriebsspannung nicht vorhanden“ des zu prüfenden Teils nachzuweisen und festzustellen, dass die vom Spannungsprüfer angezeigte Spannung eine Störspannung ist.
Spannungsprüfer die in der Lage sind, durch Last zu
schal tung Betriebsspannung von Störspannung zu unter
scheiden:
Ein Spannungsprüfer mit der Angabe von zwei Werten der
inneren Impedanz hat die Prüfung seiner Ausführung/ Konstruktion zur Behandlung von Störspannungen bestanden
und ist (innerhalb der technischen Grenzen) in der Lage, Betriebsspannung von Störspannung zu unterscheiden und den
vorhandenen Spannungstyp direkt oder indirekt anzuzeigen.
Elektrische Symbole auf dem Gerät:
Symbol Bedeutung
Achtung Dokumentation beachten!
Das Symbol gibt an, dass die Hinweise in der
Bedienungsanleitung zu beachten sind, um
Gefahren zu vermeiden
Gerät oder Ausrüstung zum Arbeiten unter
Spannung
Drucktaster
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
3
Page 4

D
AC Wechselspannung
DC Gleichspannung
DC/AC Gleich- und Wechselspannung
Erde (Spannung gegen Erde)
Drucktaster (handbetätigt); weist dar auf
hin, dass entsprechende Anzeigen nur bei
Betätigung beider Drucktaster erfolgen
Rechtsdrehfolge; die Drehfeldrichtung kann nur
bei 50 bzw. 60 Hz und in einem geerdeten Netz
angezeigt werden
Tauchspul-Pegelanzeige
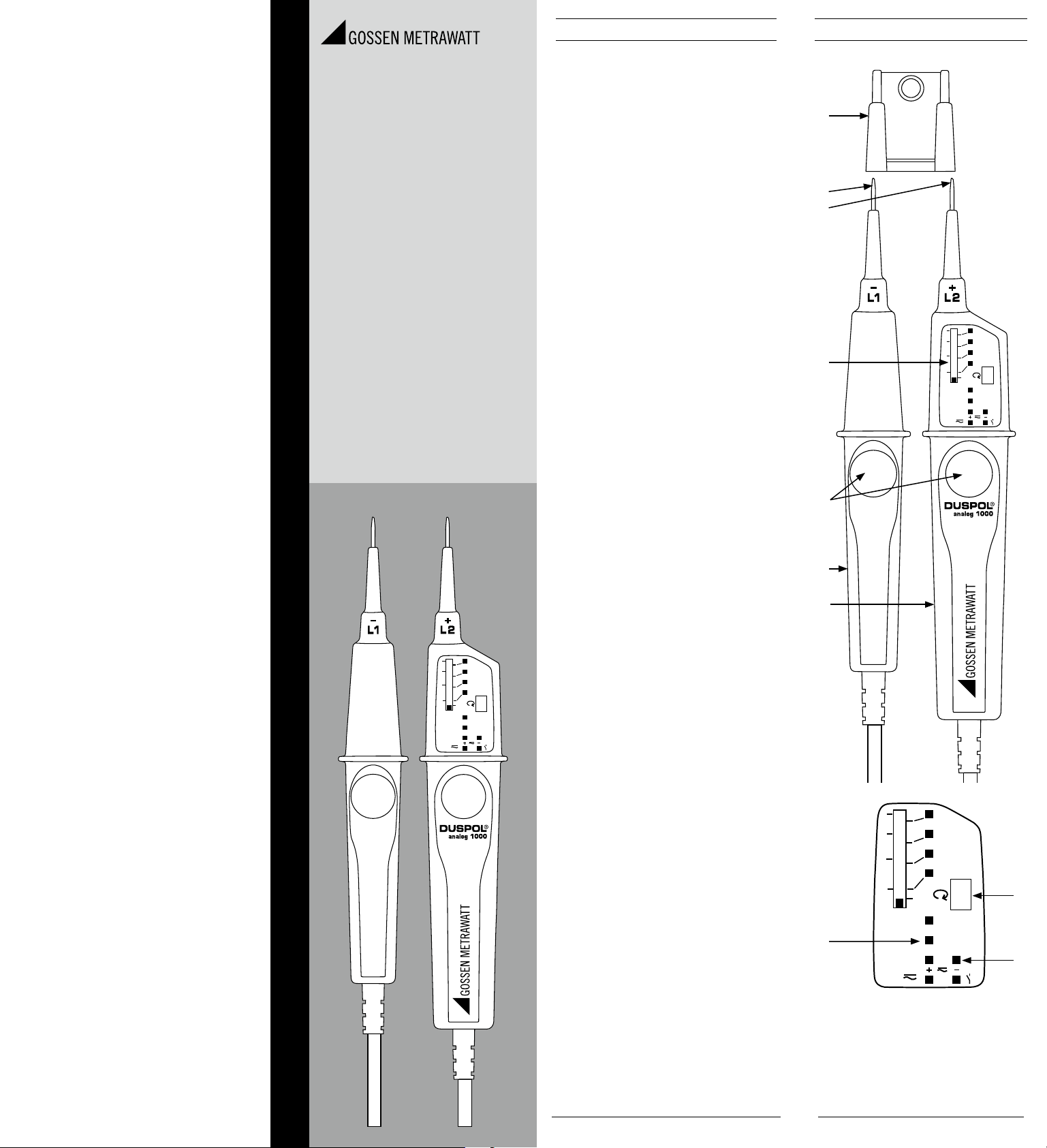
2. Gerätebeschreibung
1
Prüfspitzenschutz
2
Prüfspitze L1/-
3
Prüfspitze L2/+
4
Tauchspul-Pegelanzeige
5
Drucktaster
6
Griff L1
7
Anzeigegriff L2
8
LED-Stufenanzeige
9
LC-Display mit „R“ Symbol für Außenleiterprüfung (Pha-
senanzeige) und Drehfeldanzeige (rechts)
J
+/- LED´s der Polaritätsanzeige
3. Funktionsprüfung vor dem Gebrauch zur Überprüfung
der Spannungsfreiheit einer Anlage
- Unmittelbar vor und nach dem Benutzen den Spannungsprüfer auf Funktion prüfen!
- Testen Sie den Spannungsprüfer an bekannten Spannungsquellen z.B. an einer 230 V-Steckdose.
- Verwenden Sie den Spannungsprüfer nicht, wenn nicht
Spannungsanzeige, Phasenanzeige und Vibrationsmotor
einwandfrei funktionieren!
4. Überprüfung der Spannungsfreiheit einer Anlage
(Bild A/B)
Bei der Anlagenüberprüfung prüfen Sie die Spannungsfreiheit
der Anlage durch die Kontrolle der Spannungsanzeige,
der Phasenanzeige (Phasenanzeige funktioniert nur im
geerdeten Wechselspannungsnetz) und dem Vibrationsmotor
(Vibrationsmotor wird durch die Betätigung beider Drucktaster
aktiviert). Die Spannungsfreiheit der Anlage liegt nur vor,
wenn alle drei Prüfkreise Spannungsfreiheit signalisieren
(Spannungsanzeige, Phasenanzeige und Vibrationsmotor).
- Legen Sie die beiden Prüfspitzen L1/+ 2 und L2/- 3 an
die zu prüfenden Anlagenteile.
- Die Höhe der anliegenden Spannung wird über die LEDStufenanzeige 8 angezeigt.
- Durch Betätigung beider Drucktaster 5 wird die
Tauchspul-Pegelanzeige 4, die 12 V LED-Stufe (+/ -) und
eine interne Last im Spannungsprüfer zugeschaltet.
- Wechselspannungen (AC) werden über das gleichzeitige
Aufleuchten der + 24 V LED und der - 24 V LED angezeigt.
- Gleichspannungen (DC) werden durch das Aufleuchten
der + 24 V LED oder der - 24 V LED angezeigt. Über die
Polaritätsanzeige J wird die an der Prüfspitze L2/+ 3
anliegende Polarität + oder - angezeigt.
- Zwecks Unterscheidung von energiereichen und energiearmen Spannungen (z.B. kapazitiv eingekoppelte Störspannungen) kann durch Betätigung beider Drucktaster
eine interne Last im Spannungsprüfer zugeschaltet werden (siehe Abschnitt 5.)
5. Lastzuschaltung mit Vibrationsmotor (Bild A/B)
Beide Griffe L1 6 und L2 7 sind mit Drucktastern 5 versehen. Bei Betätigung beider Drucktaster wird auf einen geringeren Innenwiderstand geschaltet. Hierbei wird ein Vibrationsmotor (Motor mit Unwucht) an Spannung gelegt. Ab ca.
200 V wird dieser in Drehbe wegung gesetzt. Mit steigender
Spannung erhöht sich auch dessen Drehzahl und Vibration.
Die Dauer der Prüfung mit geringerem Innenwiderstand (Lastprüfung) ist abhängig von der Höhe der zu messenden Spannung. Damit das Gerät sich nicht unzulässig erwärmt, ist ein
thermischer Schutz (Rückregelung) vorgesehen. Bei dieser
Rückregelung fällt die Drehzahl des Vibrationsmotors und der
Innenwiderstand steigt an.
Die Lastzuschaltung (beide Drucktaster sind gedrückt) kann
genutzt werden um …
- Blindspannungen (induktive und kapazitive Spannungen)
zu unterdrücken
- Kondensatoren zu entladen
- 10/30 mA FI-Schutzschalter auszulösen. Die Auslösung
des FI-Schutzschalters erfolgt durch Prüfung an Außenleiter (Phasenanzeige) gegen PE (Erde). (Bild D)
6. Außenleiterprüfung (Phasenanzeige) (Bild C)
- Umfassen Sie vollflächig die Griffe L1 6 und L2 7 um
eine kapazitive Kopplung gegen Erde zu gewährleisten.
- Legen Sie die Prüfspitze L2/+ 3 an das zu prüfende Anlagenteil.
Achten Sie unbedingt darauf, dass bei der einpoligen Au-
ßenleiterprüfung (Phasenanzeige) die Prüfspitze L1/- 2
nicht berührt wird und diese kontaktfrei bleibt.
- Wenn auf dem LC-Dispay 9 ein „R“-Symbol erscheint,
liegt an diesem Anlagenteil der Außenleiter (Phase) einer
Wechselspannung.
Hinweis:
Die einpolige Außenleiterprüfung (Phasenanzeige) ist im geerdeten Netz ab 230 V, 50/60 Hz (Phase gegen Erde) möglich.
Schutzkleidung und isolierende Standortgegebenheiten kön-
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
4
Page 5
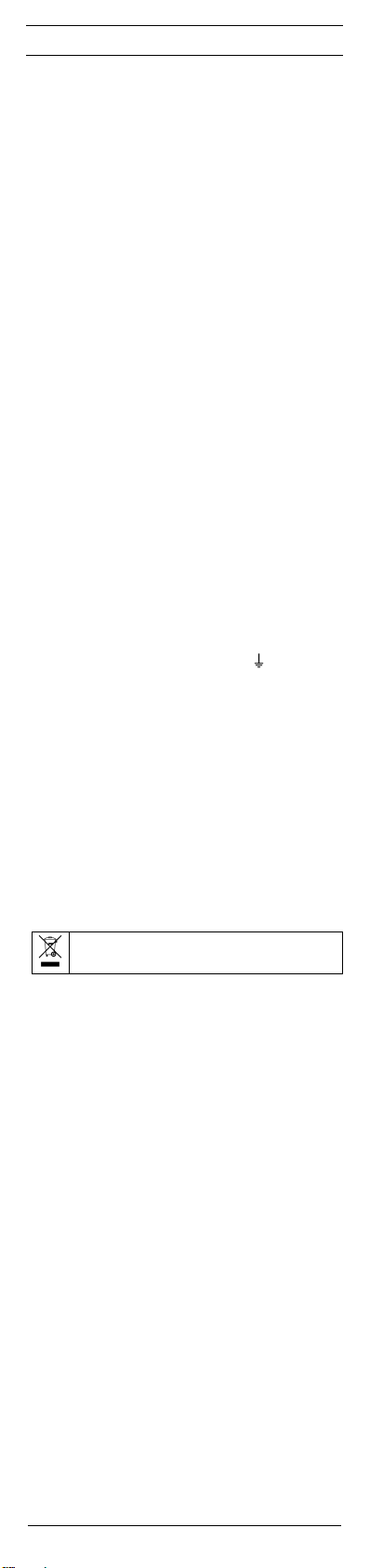
nen die Funktion beeinträchtigen.
Achtung!
Eine Spannungsfreiheit kann nur durch eine zweipolige Prüfung festgestellt werden.
7. Drehfeldprüfung (Bild E/F)
- Umfassen Sie vollflächig beide Griffe L1 6 und L2 7 um
eine kapazitive Kopplung gegen Erde zu gewährleisten.
- Legen Sie die Prüfspitzen L1/- 2 und L2/+ 3 an zwei
Außenleiter (Phasen) eines Drehstromnetzes (ohne Betätigung der Drucktaster 5) und prüfen Sie ob die Außenleiterspannung von z.B. 400 V anliegt.
- Eine Rechtsdrehfolge (Phase L1 vor Phase L2) ist gegeben, wenn auf dem LC-Display 9 ein „R“-Symbol
erscheint. Das LC-Display bleibt erloschen, wenn keine
Rechtsdrehfolge erkannt wurde.
- Die Drehfeldprüfung erfordert stets eine Gegenkontrolle!.
Zeigt das LC-Display die Rechtsdrehfolge über das „R“
Symbol an, muss bei der Gegenkontrolle mit vertauschten
Prüfspitzen L1/- 2 und L2/+ 3 das LC-Display erloschen
bleiben.
Zeigt das LC-Display in beiden Fäl len ein „R“-Symbol an,
liegt eine zu schwache Erdung vor.
Hinweis:
Die Drehfeldprüfung ist ab 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (Phase
gegen Phase) im geerdeten Drehstromnetz möglich. Schutzkleidung und isolierende Standortgegebenheiten können die
Funktion beeinträchtigen
8. Technische Daten
- Vorschrift: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Nennspannungsbereich: 12 V bis AC/DC 1.000 V
- Nennfrequenzbereich f: 0 bis 60 Hz
- Max. Anzeigefehler: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0 %, - 15 %
- Impedanz (Innenwiderstand) Messkreis/ Lastkreis:
200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Stromaufnahme Messkreis: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Stromaufnahme Lastkreis: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polaritätsanzeige: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (bei Drucktasterbetätigung)
- Außenleiterprüfung (Phasenanzeige): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/
60 Hz
- Drehfeldprüfung: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibrationsmotor, Anlauf: ≥ Un 200 V
- Überspannungskategorie: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Schutzart: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/ EN 60529)
6 - erste Kennziffer: Schutz gegen Zugang zu gefähr lichen
Teilen und Schutz gegen feste Fremdkörper, staubdicht
5 - zweite Kennziffer: Geschützt gegen Strahlwasser. Auch
bei Niederschlägen verwendbar.
-
max. zulässige Einschaltdauer:
ED = 30 s (max. 30 Sekunden), 600 s Pause
- Gewicht: ca. 250 g
- Verbindungsleitungslänge: ca. 1000 mm
- Betriebs- und Lagertemperaturbereich: - 20 °C bis + 45 °C
(Klimakategorie N)
- Relative Luftfeuchte: 20 % bis 96 % (Klimakategorie N)
- Rückregelzeiten (thermischer Schutz):
Spannung/Zeit: 230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
9. Allgemeine Wartung
Reinigen Sie das Gehäuse äußerlich mit einem sauberen trockenen Tuch.
10. Umweltschutz
Bitte führen Sie das Gerät am Ende seiner Lebensdauer den zur Verfügung ste hen den Rückgabe- und
Sammelsystemen zu.
Operating Manual
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Before using the DUSPOL® analog 1000 voltage tester, proceed as follows: Please read the operating manual and absolutely observe the safety instructions!
Table of Contents
1. Safety instructions
2. Device description
3. Functional test before use to ensure the absence of
voltage of an installation
4. Checking the absence of voltage of an installation
5. Load connection with vibration motor
6. External conductor test (phase indication)
7. Phase sequence test
8. Technical data
9. General maintenance
10. Environmental protection
1. Safety instructions:
- During use, touch the tester at the insulated handles L1 6
and L2 7 only and do not touch the probe tips L1/- 2 and
L2/+ 3!
- Check the voltage tester for correct functioning immediately before and after using it in order to ensure the absence of voltage of an installation (see section 3)! Do not
use the voltage tester, if one or more indications are not
working or if it does not seem to be ready for operation!
Please repeat the test with another voltage tester afterwards.
- The voltage tester must be used only within the stated
nominal voltage range and in electrical installations of up
to 1,000 V AC/DC!
- The voltage tester must be used only in electric circuits of
overvoltage category CAT III with max. 1,000 V or over-
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
5
Page 6
voltage category CAT IV with max. 600 V for phase-toearth measurements.
- The voltage tester is designed for being used by qualified
electricians and under safe working conditions.
- The LED step indicator is intended for indicating the voltage range. It is not intended for measuring purposes.
- Creating a voltage tester for more than 30 seconds voltage (maximum duty cycle = 30 s)!
- Do not dismantle the voltage tester!
- The voltage tester must be protected against contamination and damaging of the housing surface.
- To protect them against damaging, provide the probe tips
with the enclosed probe tip protector 1 after using the
voltage tester!
- Please observe that the impedance (internal resistance) of
the voltage tester influences the indication of interference
voltages (capacitively or inductively induced)!
Depending on the internal impedance of the voltage detector,
there will be a different capability of indicating the presence
or absence of operating voltage in case of the presence of
interference voltage.
Low-impedance voltage tester (impedance < 100 kΩ), inter-
ference voltage is suppressed or reduced:
A voltage tester of relatively low internal impedance, compared
to the reference value of 100 kΩ, will not indicate all interference voltages having an original voltage value above the ELV
level (50 V AC/ 120 V DC). When in contact with the parts
to be tested, the voltage tester may discharge temporarily the
interference voltage to a level below the ELV, but it will be back
to the original value when the voltage tester is removed.
When the indication “voltage present” does not appear, it is
highly recommended to install earthing equipment before starting work.
High-impedance voltage tester (impedance > 100 kΩ): Inter-
ference voltage will not be suppressed or reduced:
A voltage tester of relatively high internal impedance, com-
pared to the reference value of 100 kΩ, may not permit to
clearly indicate the absence of operating voltage in case of
presence of interference voltage. When the indication “voltage
present” appears on a part that is expected to be disconnected
from the installation, it is highly recommended to conrm by
another means (e.g. use of an adequate voltage tester capable
of distinguishing between operating voltages and interference
voltages, visual inspection of the disconnecting point of the
electric circuit, etc.) that there is no operating voltage on the
part to be tested and to conclude that the voltage indicated by
the voltage tester is an interference voltage.
Voltage testers capable of distinguishing between operating voltage and interference voltage by means of load
connection:
A voltage tester stating two values of internal impedance has
passed a performance test of managing interference voltages
and is (within technical limits) able to distinguish operating voltage from interference voltage and has a means to directly or
indirectly indicate which type of voltage is present.
Electrical symbols on the device:
Symbol Meaning
Important documentation!
The symbol indicates that the guide described
in the manual, to avoid any risks
Device or equipment for working under voltage
Push-button
Alternating voltage (AC)
Direct voltage (DC)
Direct and alternating voltage (DC/AC)
Earth (voltage to ground)
Push-button (manually actuated); indicates that
the respective indications are made only with
both push-buttons being actuated
Clockwise phase sequence; the phase sequence can be indicated only at 50 or 60 Hz
and in an earthed mains
Plunger coil level indicator
2. Device description
1
Probe tip protector
2
Probe tip L1/-
3
Probe tip L2/+
4
Plunger coil level indicator
5
Push-button
6
Handle L1
7
Display handle L2
8
LED step indicator
9
LC display mit "R" symbol für external conductor test
(phase indication) and phase sequence indicator (clockwise)
J +/- LEDs of the polarity indication
3. Functional test before use to ensure the absence of
voltage of an installation
- Check the voltage tester for correct functioning
immediately before and after using it!
- Test the voltage tester with familiar voltage sources, e.g.
with a 230 V socket.
- Do not use the voltage tester, if the voltage indication, the
phase indication and the vibration motor are not working
properly!
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
6
Page 7

4. Checking the absence of voltage of an installation
(figure A/B)
For checking the installation, please test the absence of voltage by checking the voltage indication, the phase indication
(the phase indication only works in an earthed AC voltage
mains) and the vibration motor (the vibration motor is activated
by actuating both push-buttons). The installation is only free
of voltage, if all three test circuits (voltage indication, phase
indication and vibration motor) are signaling the absence of
voltage.
- Apply the two probe tips L1/+ 2 and L2/- 3 to the system
parts to be tested.
- The level of voltage applied is indicated by means of the
LED step indicator 8.
- Actuate both push-buttons 5 to connect the plunger coil
level indicator 4, the 12 V LED step (+/ -) and an internal
load in the voltage tester.
- Alternating voltages (AC) are indicated by the +24 V LED
and the -24 V LED lighting up simultaneously.
- Direct voltages (DC) are indicated by the +24 V LED or the
-24 V LED lighting up. The polarity indication J shows the
polarity (+ or -) applied to the probe tip L2/+ 3.
- To differentiate between low-energy and high-energy voltages (e.g. capacitively induced interference voltages), an
internal load in the voltage tester can be connected by actuating both push-buttons (see section 5).
5. Load connection with vibration motor (gure A/B)
Both handles L1 6 and L2 7 are equipped with push-buttons
5
. Actuate both push-buttons to switch to a lower internal resistance. Here, voltage is applied to a vibration motor (motor
with unbalanced mass). From approx. 200 V on, this motor is
set in rotary motion. With the voltage increasing, the motor's
speed and vibration increases as well. The duration of the test
with a lower internal resistance (load test) depends on the level
of voltage to be measured. In order to avoid an inadmissible
warming of the device, it is provided with a thermal protection
(controlled reduction). With this controlled reduction, the speed
of the vibration motor is reduced and the internal resistance
increases.
The load connection (with both push-buttons being actuated)
can be used ...
- to suppress reactive voltages (inductive and capacitive
voltages),
- to charge capacitors,
- to trip 10 mA/ 30 mA RCD safety switches. The tripping
of the RCD safety switch is done by testing the external
conductor (phase indication) to PE (earth). (figure D)
6. External conductor test (phase indication) (gure C)
- Fully grasp the handles L1 6 and L2 7, in order to en-
sure a capacitive coupling to earth.
- Apply the probe tip L2/+ 3 to the system part to be tested.
During the single-pole external conductor test (phase in-
dication), make absolutely sure not to touch the probe tip
L1/- 2 and that it remains contactless.
- If an "R" symbol is shown on the LC display 9, the exter-
nal conductor (phase) of an AC voltage is applied to this
system part.
Note:
The single-pole external conductor test (phase indication)
can be carried out in an earthed mains from 230 V, 50/60 Hz
(phase to earth) on. Protective clothing and insulating conditions on site might impair the function.
Attention!
The absence of voltage can only be determined by means of
a two-pole test.
7. Phase sequence test (gure E/F)
- Fully grasp both handles L1 6 and L2 7, in order to en-
sure a capacitive coupling to earth.
-
Apply the probe tips L1/- 2 and L2/+ 3 to two external
conductors (phases) of a three-phase mains (without actuation the push-buttons 5) and check whether the external
conductor voltage of e.g. 400 V is applied
- A clockwise phase sequence (phase L1 before phase L2)
is given, if an "R" symbol is shown on the LC display 9.
Nothing is shown on the LC display, if no clockwise phase
sequence has been detected.
- The phase sequence test always requires a countercheck!
If the LC display shows the clockwise phase sequence by
means of the "R" symbol, the LC display must show nothing during the countercheck with the probe tips L1/- 2
and L2/+ 3 being inverted.
If the LC display shows the "R" symbol in both cases, the
earthing is too weak.
Note:
The phase sequence test can be carried out in an earthed
three-phase mains from 400 V - 900 V, 50 / 60 Hz (phase to
phase) on. Protective clothing and insulating conditions on site
might impair the function.
8. Technical data
- regulation: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- nominal voltage range: 12 V to 1,000 V AC/DC
- nominal frequency range f: 0 to 60 Hz
- max. indication error: Un ±15%, ELV Un +0% -15%
- Impedance (internal resistance) of measuring circuit/ load
circuit: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- current consumption of measuring circuit: Is < 6,0 mA
(1,000 V)
- current consumption of load circuit: Is < 550 mA (1,000 V)
- polarity indication: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (with push-buttons being actuated)
- external conductor test (phase indication): ≥ Un 230 V,
50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- phase sequence test: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- vibration motor, start: ≥ Un 200 V
.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
7
Page 8

F
- overvoltage category: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1,000 V
- protection category: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/ EN
60529)
6 - first index: protection against access to dangerous
parts and protection against solid impurities, dustproof
5 - second index: protected against water jets. The device
can also be used in the rain.
-
max. allowable Duty cycle: 30 s (max. 30 seconds), 600 s off
- weight: approx. 250g
- length of connecting cable: approx. 1,000 mm
- operating temperature and storage temperature range:
- 20 °C to + 45 °C (climatic category N)
- relative air humidity: 20 % to 96 % (climatic category N)
- times of controlled reduction (thermal protection):
voltage/time: 230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
9. General maintenance
Clean the exterior of the device with a clean dry cloth.
10. Environmental protection
Please lead the device at the end of its useful life to
the available return and collection systems.
Mode d'emploi
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Avant d'utiliser le contrôleur de tension DUSPOL® analog 1000
: Lisez le mode d'emploi et tenez impérativement compte des
consignes de sécurité !
Table des matières
1. Consignes de sécurité
2. Description de l’appareil
3. Contrôle de fonctionnement avant l'utilisation afin
d'assurer l'absence de tension d'une installation
4. Vérification de l'absence de tension d'une installation
5. Connexion de charge avec moteur à vibration
6.
Contrôle du conducteur extérieur ( indication de phase )
7. Test d'ordre de phases
8. Caractéristiques techniques
9. Entretien général
10. Protection de l’environnement
1. Consignes de sécurité :
- Lors de l’utilisation, ne touchez l’appareil qu’aux poignées
isolées L1 6 et L2 7 et ne touchez jamais les pointes
d'essai L1/- 2 et L2/+ 3 !
- Contrôlez toujours le bon fonctionnement du contrôleur
de tension immédiatement avant et après de l'utiliser afin
d’assurer l’absence de tension de l’installation (voir paragraphe 3)! Le contrôleur de tension ne doit être utilisé dès
lors qu'une ou plusieurs affichages ne fonctionnent plus
ou dès lors l'appareil n'est plus opérationnel ! Ensuite,
répétez ce contrôle au moyen d’un autre contrôleur de
tension.
- Le contrôleur de tension ne doit être utilisé que dans la
plage de tension nominale spécifiée et dans les installations électriques jusqu'à 1.000 V AC / DC !
- Le contrôleur de tension ne doit être utilisé que dans les
circuits électriques de la catégorie de surtension CAT III
avec un maximum de 1.000 V ou de la catégorie de surtension CAT IV avec des conducteurs de 600 V max. par
rapport à la terre.
- Le contrôleur de tension est conçu afin d'être utilisé par
des électrotechniciens en combinaison avec des procédés de travail sûrs.
- L'affichage de niveau par LED sert à indiquer la plage de
tension et n'est donc pas prévu afin d'effectuer des mesures.
- Création d'un testeur de tension pour tension de plus de
30 secondes (cycle d'utilisation maximal)
- Le contrôleur de tension ne doit être pas démonté !
- Protégez le contrôleur de tension contre les impuretés ain-
si que contre l'endommagement de la surface du boîtier.
- Comme protection contre les blessures, les pointes d'es-
sais doivent être munies du protecteur de pointe d'essai
ci-inclus 1 suite à l'utilisation du contrôleur de tension !
- Tenez compte du fait que l'impédance (résistance interne)
du contrôleur de tension influencera l'affichage de tensions parasites (couplées de façon capacitive ou induc-
tive) !
Selon l’impédance interne du contrôleur de tension, il existe
une capacité différente à indiquer la présence ou l’absence de
tension de service en présence d’une tension parasite.
Contrôleur de tension à basse impédance (impédance
< 100 kΩ), la tension parasite sera supprimée ou réduite :
Un contrôleur de tension présentant une impédance interne
relativement basse, comparée à la valeur de référence de
100 kΩ, n’indique pas toutes les tensions parasites dont la tension d’origine est supérieure au niveau de la TBT (tension très
basse, 50 V AC/ 120 V DC). Lorsque le contrôleur de tension
est en contact avec les pièces à contrôler, il peut évacuer temporairement la tension parasite à un niveau inférieur à la TBT
(tension très basse), puis revenir à la valeur d’origine suite au
retrait du contrôleur de tension.
Si l'indication « présence de tension » n'apparaît pas, il est fortement recommandé de mettre le dispositif de mise à la terre
avant de commencer le travail.
Contrôleur à haute impédance (impédance > 100 kΩ) : La
tension parasite ne sera pas supprimée ou réduite :
Un contrôleur de tension présentant une impédance interne
relativement élevée, comparée à la valeur de référence de 100
kΩ, ne peut pas clairement indiquer l’absence de tension de
service en cas de présence d'une tension parasite. Si l’indica-
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
8
Page 9
F
tion « présence de tension » apparaît sur une partie censée
être déconnectée de l’installation, il est fortement recommandé de conrmer par d’autres moyens (l'utilisation d’un contrôleur de tension approprié capable de distinguer les tensions
de service des tensions parasites, un contrôle visuel du point
de déconnexion du circuit électrique, par exemple) l’absence
de tension de service sur la pièce à tester, et conclure que la
tension indiquée par le contrôleur de tension est une tension
parasite.
Contrôleurs de tension capables de distinguer les ten-
sions de services des tensions parasites au moyen d'une
connexion de charge :
Un contrôleur de tension déclarant deux valeurs d’impédance
interne a satisfait à un essai de performances de gestion des
tensions parasites, et est en mesure de distinguer (dans les
limites techniques) la tension de service de la tension parasite,
et dispose d’un moyen d’indiquer directement ou indirectement le type de tension présente.
Symboles électriques sur l'appareil :
Symbole Signication
Des documents importants!
Le symbole indique que le guide décrit dans le
manuel, pour éviter tout risque
appareil ou équipement pour le travail sous
tension
bouton-poussoir
tension alternative (AC)
tension continue (DC)
tension continue et alternative (DC/AC)
Terre (tension à la terre)
bouton-poussoir (manuel); indique que les
indications correspondantes ne soient afchées
qu'avec les deux bouton-poussoirs actionnés
ordre de phases dans le sens horaire ; l'ordre
de phases ne peut être afché qu'à 50 ou 60 Hz
et dans un réseau mis à la terre
Afchage de niveau à bobine mobile
2. Description de l’appareil
1
Protecteur de pointe d'essai
2
Pointe d'essai L1/-
3
Pointe d'essai L2/+
4
Afchage de niveau à bobine mobile
5
Bouton-poussoir
6
Poignée L1
7
Poignée indicatrice L2
8
Afchage de niveau par LED
9
Ecran à cristaux liquides avec symbole « R » pour le
contrôle du conducteur extérieur ( indication de phase ) et
avec indication de l'ordre de phases ( sens horaire )
J
LED +/- de l'afchage de polarité
3. Contrôle de fonctionnement avant l'utilisation afin
d'assurer l'absence de tension d'une installation
- Contrôlez toujours le bon fonctionnement du contrôleur de
tension immédiatement avant et après de l'utiliser !
- Testez le contrôleur de tension sur une source de tension
connue comme par exemple sur une prise de courant de
230 V.
- Le contrôleur de tension ne doit plus être utilisé si l’indica-
tion de tension, l’indication de phase ou le moteur à vibra-
tion ne fonctionnent pas correctement !
4. Vérification de l'absence de tension d'une installation
(figures A/B)
Lors du contrôle d’une installation, assurez l’absence de
tension de l’installation en vériant l’indication de tension,
l’indication de phase ( l’indication de phase ne fonctionne que
dans un réseau de tension alternative mis à la terre ) ainsi
que le moteur à vibration ( le moteur à vibration est activé
en appuyant sur les deux bouton-poussoirs ) . L’absence
de tension n’est assurée que si tous les trois circuits de test
( l’indication de tension, l’indication de phase et le moteur à
vibration ) signalent l’absence de tension.
- Reliez les deux pointes d'essai L1/+ 2 et L2/- 3 aux
composants à contrôler.
- La valeur mesurée de la tension appliquée est affichée au
moyen de l'affichage de niveau par LED 8.
- Appuyez sur les deux bouton-poussoirs 5 afin d'activer
l'affichage de niveau à bobine mobile 4, l'affichage de
niveau par LED de 12 V (+/-) ainsi qu'une charge interne
dans le contrôleur de tension.
- Les tensions alternatives ( AC ) sont indiquées par l'allu-
mage simultané de la LED +24 V et de la LED -24 V.
- Les tensions continues ( DC ) sont indiquées par l'allu-
mage simultané de la LED +24 V ou de la LED -24 V.
L'affichage de polarité J sert à afficher la polarité ( +
ou - ) présente à la pointe d'essai L2/+ 3.
- Afin de différencier les tensions à haute énergie des
tensions à faible énergie ( par ex. les tensions parasites
induites de manière capacitive ), appuyez sur les deux
bouton-poussoirs pour connecter une charge interne dans
le contrôleur de tension ( voir paragraphe 5 ).
5. Connexion de charge avec moteur à vibration (gures
A/B)
Les deux poignées L1 6 et L2 7 sont pourvues de boutonpoussoirs 5. Appuyez sur les deux bouton-poussoirs an de
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
9
Page 10

F
commuter à une résistance interne plus faible. En faisant cela,
une tension est appliquée à un moteur à vibration ( moteur
avec masse non équilibrée ). Ce moteur est mis en marche à
partir de 200 V environ. En augmentant la tension, la vitesse
et la vibration du moteur augmentent également. La durée du
test à résistance interne plus faible ( test de charge ) dépend
de l'hauteur de la tension à mesurer. An d'éviter un chauffage
inadmissible de l'appareil, ceci est pourvu d'une protection
thermique ( réduction réglée ). Avec cette réduction réglée,
la vitesse du moteur à vibration est réduite et la résistance
interne augmente.
La connexion de charge (avec les deux bouton-poussoirs
étant actionnés) peut être utilisée an de …
- supprimer les tensions réactives (tensions inductives et
capacitives),
- décharger des condensateurs,
- déclencher un disjoncteur différentiel de 10/30 mA. Le
déclenchement du disjoncteur différentiel est effectué au
moyen d'un test du conducteur extérieur ( indication de
phase ) par rapport au conducteur de terre (PE). (figure D)
6. Contrôle du conducteur extérieur ( indication de
phase ) (figure C)
- Mettez la main complètement autour des poignées L1 6
et L2 7 afin d'assurer un couplage capacitif par rapport à
la terre.
- Reliez la pointe d'essai L2/+ 3 au composant à contrôler.
Faites attention de ne pas toucher la pointe d'essai L1/- 2
lors du contrôle monophasé du conducteur extérieur ( indi-
cation de phase ) et veillez à ce que cette pointe d'essai
reste sans contact.
- Si un symbole « R » apparaît sur l'écran à cristaux liquides
9
, le conducteur extérieur ( phase ) d'une tension alterna-
tive est appliqué à ce composant.
Remarque :
Le contrôle monophasé du conducteur extérieur ( indication
de phase ) peut être effectué dans un réseau mis à la terre à
partir de 230 V, 50/60 Hz ( phase par rapport à la terre ). Les
vêtements protecteurs ainsi que les conditions isolantes sur
site peuvent perturber le bon fonctionnement.
Attention !
L'absence de tension ne peut être déterminée que par un
contrôle biphasé.
7. Test d'ordre de phases (gure E/F)
- Mettez la main complètement autour des deux poignées
L1 6 et L2 7 afin d'assurer un couplage capacitif par
rapport à la terre.
- Reliez les pointes d'essai L1/- 2 et L2/+ 3 à deux
conducteurs extérieurs (phases) d'un réseau triphasé
(sans appuyer sur le bouton-poussoir 5) et vérifiez si une
tension composée de par ex. 400 V est appliquée.
- Il s'agit d'un ordre de phases dans le sens horaire (phase
L1 avant phase L2), si le symbole «R» apparaît sur l'écran
à cristaux liquides 9. Il n'apparaît rien sur l'écran à cris-
taux liquides, si l'appareil n'a pas détecté un ordre de
phases dans le sens horaire.
- Le test d'ordre de phases nécessite toujours d'effectuer
une contre-épreuve ! Au cas où l'écran à cristaux liquides
indiquerait un ordre de phases dans le sens horaire par le
symbole «R», l'écran ne doit afficher rien lors de la contre-
épreuve avec les pointes d'essai L1/- 2 et L2/+ 3 inver-
sées.
Si l'écran à cristaux liquides affiche le symbole «R» dans
les deux cas, la mise à la terre est trop faible.
Remarque :
Le test d'ordre de phases peut être effectué dans un réseau
triphasé mis à la terre à partir de 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz
(phase par rapport à la phase). Les vêtements protecteurs
ainsi que les conditions isolantes sur site peuvent perturber le
bon fonctionnement.
8. Caractéristiques techniques
- spécification : DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- plage de tension nominale : 12 V à 1.000 V AC / DC
- plage de fréquence nominale f : 0 à 60 Hz
- erreur d'indication max. : Un ± 15 %, «ELV» (très basse
tension) Un + 0% - 15%
- Impédance (résistance interne) du circuit de mesure / cir-
cuit de charge : 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
-
consommation de courant du circuit de mesure : Is
(1.000 V)
- consommation de courant du circuit de charge :
Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- affichage de polarité : LED + 24 V, LED - 24 V, LED + 12 V,
LED - 12 V (bouton-poussoirs actionnés)
- contrôle du conducteur extérieur ( indication de phase ) :
≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- test d'ordre de phases : ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- moteur à vibration, démarrage : ≥ Un 200 V
- catégorie de surtension : CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1.000 V
- type de protection : IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN
60529)
6 – premier indice : protection contre l'accès aux com-
posants dangereux et protection contre les impuretés
solides, étanche aux poussières
5 – second indice : protection contre les jets d'eau. L'appa-
reil peut aussi être utilisé en cas de précipitations.
- max. Cycle admissible: 30 s (max. 30 secondes), 600 s off
- poids : 250 g environ
- longueur de la ligne de raccordement : 1.000 mm environ
- température de service et de stockage : - 20 °C à + 45 °C
( catégorie climatique N )
- humidité relative de l'air : 20 % à 96 % ( catégorie clima-
tique N)
- temps de réduction réglée ( protection thermique ) :
tension/temps : 230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
< 6,0 mA
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
10
Page 11

E
9. Entretien général
Nettoyez l'extérieur du boîtier avec un chiffon propre et sec.
10. Protection de l’environnement
Jetez l‘appareil devenu inutilisable aux systèmes de
recyclage et de tri de déchets disponibles.
Instrucciones de servicio
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Antes de utilizar el Comprobador de tensión DUSPOL® analog
1000: Deberá leer estas instrucciones de servicio y observar
necesariamente las advertencias de seguridad.
Índice de contenido
1. Advertencias de seguridad
2. Descripción del aparato
3. Comprobación del funcionamiento antes del empleo
para comprobar la ausencia de tensión de una
instalación
4. Comprobación de la ausencia de tensión de una
instalación
5. Conexión de carga con motor de vibración
6. Comprobación de conductor de hilo (indicación de
fase)
7. Comprobación del campo giratorio
8. Datos técnicos
9. Mantenimiento general
10. Protección ambiental
1. Advertencias de seguridad:
- Tocar el aparato durante la utilización únicamente por los
mangos con aislamiento L1 6 y L2 7 y no rozar las pun-
tas de prueba L1/- 2 y L2/+ 3.
- Inmediatamente antes y después de su empleo, para
comprobar la ausencia de tensión de una instalación, se
deberá comprobar el funcionamiento del detector de ten-
sión. (véase el capítulo 3). El comprobador de tensión no
deberá utilizarse si fallase el funcionamiento de una o más
indicaciones o si no se puede ver que esté el aparato esté
listo para el funcionamiento. Después se deberá repetir la
comprobación con otro detector de tensión.
- El comprobador de tensión sólo deberá emplearse en el
margen de tensión nominal indicado y en instalaciones
eléctricas de hasta AC/DC 1.000 V.
- El comprobador de tensión sólo deberá emplearse en cir-
cuitos de corriente de la categoría de sobretensión CAT III
con como máx. 1000 V o categoría de sobretensión CAT
IV con como máx. 600 V conductor contra tierra.
- El comprobador de tensión ha sido diseñado para ser
empleado por electricistas con procedimientos de trabajo
seguro.
- La indicación de escalón LED está destinada a la indica-
ción del margen de tensión, no está destinada a fines de
medición.
- Creación de un comprobador de tensión durante más de
30 segundos de tensión (duración máxima admisible de
conexión ED = 30 s)!
- No está permitido desensamblar el comprobador de ten-
sión.
- Proteger el comprobador de tensión de la suciedad y el
deterioro en la superficie de la carcasa.
- Como protección contra posibles lesiones, después del
uso del comprobador de tensión deberá colocarse la
protección de puntas 1 suministrada, en las puntas de
prueba.
-
¡Tenga en cuenta que la impedancia (resistencia interna)
del detector de voltaje tiene efecto sobre la indicación de los
voltajes de interferencia! (conexión capacitiva o inductiva)
Dependiendo de la impedancia interna del detector de voltaje,
la presencia de voltajes de interferencia se muestra en diferentes indicaciones «voltaje de funcionamiento existente» o
«voltaje de funcionamiento no existente».
Detector de voltaje de baja impedancia (Impedancia
< 100 kΩ), el voltaje de interferencia será suprimido o reducido:
Un detector de voltaje con impedancia interna relativamente
baja se compara con el valor de referencia de 100 kΩ y no
mostrará todos los voltajes de interferencia con un valor inicial
por encima de ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V DC). Al entrar en contacto
con las piezas a examinar, el detector de voltaje puede reducir
los voltajes de interferencia a través de descarga transitoria
hasta un nivel por debajo del ELV; después de sacar el detector de voltaje, el voltaje de interferencia toma nuevamente
su valor original.
Cuando no aparece la indicación «voltaje existente», es muy
recomendable introducir el dispositivo de puesta a tierra antes
de empezar a trabajar.
Detector de voltaje de alta impedancia (Impedancia
> 100 kΩ): El voltaje de interferencia no se suprime ni se reduce:
Un detector de voltaje con impedancia interna relativamente
alta no mostrará claramente «voltaje de funcionamiento exis-
tente» en comparación con el valor de referencia de 100 kΩ
cuando exista voltaje de interferencia. Cuando aparece la
indicaciónl «voltaje existente» para una pieza que se considera separada de la instalación, es muy recomendable, con
medidas adicionales (ejemplo: uso de un detector de voltaje
adecuado capaz de distinguir entre voltaje de funcionamiento
y voltaje de interferencia, inspección visual del punto de separación en la red eléctrica, etc.) detectar el estado «voltaje de
funcionamiento no existente» de la pieza a examinar y determinar que el voltaje indicado por el detector de voltaje es un
voltaje de interferencia.
Detectores de voltaje capaces de distinguir, a través de
la carga, el voltaje de funcionamiento del voltaje de inter-
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
11
Page 12

E
ferencia:
Un detector de voltaje con indicación de dos valores de la impedancia interna ha superado la prueba de su diseño / construcción para el tratamiento de los voltajes de interferencia y
está en condición (dentro de los límites técnicos) de distinguir
el voltaje de funcionamiento del voltaje de interferencia y de
noticar directa o indirectamente el tipo de voltaje.
Símbolos eléctricos en el aparato:
Símbolo Signicado
Documentación Importante!
El símbolo indica que las instrucciones descri-
tas en el manual, para evitar cualquier riesgo
Aparato o equipo para trabajar bajo tensión
Pulsador
AC Tensión alterna
DC Tensión continua
DC/AC Tensión continua y alterna
Tierra (voltaje a tierra)
Pulsador (accionado a mano); indica que las
correspondientes indicaciones sólo tienen lugar al accionarse los dos pulsadores
Secuencia de giro a la derecha; el sentido del
campo giratorio sólo se puede indicar con 50 ó
60 Hz y en una red con toma de puesta a tierra
Indicación de nivel de bobina móvil
2. Descripción del aparato
1
Protección de puntas de prueba
2
Punta de prueba L1/-
3
Punta de prueba L2/+
4
Indicación de nivel de bobina móvil
5
Pulsador
6
Mango L1
7
Mango de indicación L2
8
Indicación de escalón LED
9
Display LC con símbolo „R“ para comprobación de con-
ductor de hilo (indicación de fase) e indicación de campo
giratorio (a la derecha)
J
+/- LED´s de la indicación de polaridad
3. Comprobación del funcionamiento antes del empleo
para comprobar la ausencia de tensión de una
instalación
- Inmediatamente antes y después de utilizar el comproba-
dor de tensión, comprobar el funcionamiento.
- Probar el comprobador de tensión en fuentes de tensión
conocidas p. ej. en una caja de enchufe de 230 V.
- No emplear el detector de tensión si no funcionan correc-
tamente la indicación de tensión, la indicación de fase y el
motor de vibración.
4. Comprobación de la ausencia de tensión de una
instalación (Figura A/B)
Al efectuar una comprobación de la instalación, comprobar la
ausencia de tensión de la misma controlando la indicación de
tensión, la indicación de fase (la indicación de fase sólo funciona en una red de tensión alterna con puesta a tierra) y el
motor de vibración (el motor de vibración se activa actuando
ambos pulsadores). La ausencia de tensión en la instalación
sólo existirá cuando los tres circuitos de prueba señalen que
no hay tensión (indicación de tensión, indicación de fase y motor de vibración).
- Conectar las dos puntas de prueba L1/+ 2 y L2/- 3 con
las partes de la instalación que se han de comprobar.
- En la indicación de escalón LED 8 se muestra la tensión
existente.
- Accionando ambos pulsadores 5 se conecta la indicación
de nivel de bobina móvil 4, el escalón LED (+/ -) 12 V y
una carga interna en el comprobador de tensión.
- Las tensiones alternas (AC) se indican al encenderse al
mismo tiempo el LED + 24 V y el LED - 24 V.
- Las tensiones continuas (DC) se indican al encenderse
el LED + 24 V o el LED - 24 V. Mediante la indicación de
polaridad J se muestra la polariad + ó - existente en la
punta de prueba L2/+ 3.
- Para diferenciar las tensiones con mucha energía o con
poca energía (p. je. tensiones parásistas acopladas
capacitivas) se puede conectar adicionalmente una carga
interna en el comprobador de tensión, accionando ambos
pulsadores (véase el capítulo 5).
5. Conexión de carga con motor de vibración (Figura A/B)
Ambos mangos L1 6 y L2 7 están provistos de pulsadores
5
. Al accionar ambos pulsadores se conecta una resistencia interior más baja. Para ello se pone bajo tensión un motor
vibratorio (motor con desequilibrio). A partir de aprox. 200 V
éste se pone bajo movimiento giratorio. Al aumentar la tensión
aumentará también su número de revoluciones y vibración. La
duración de la comprobación con resistencia interior más baja
(prueba con carga) dependerá del nivel de la tensión a medir.
Para que el aparato no se caliente de forma inadmisible, se
ha previsto una protección térmica (regulación hacia atrás).
En esta regulación hacia atrás desciende el número de revoluciones del motor vibratorio y la resistencia interna aumenta.
La conexión adicional de carga (ambos pulsadores están accionados) se puede emplear para …
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
12
Page 13

E
- suprimir tensiones reactivas (tensiones inductivas y capa-
citivas)
- descargar condensadores
- disparar el interruptor diferencial RCD 10 mA/ 30 mA. El
disparo del interruptor diferencial RCD tiene lugar mediante comprobación en conductor de hilo (indicación de fase)
contra PE (tierra). (Figura D)
6. Comprobación de conductor de hilo (indicación de
fase) (Figura C)
- Agarrar completamente los mangos L1 6 y L2 7 para
garantizar un acoplamiento capacitivo contra tierra.
- Poner la punta de prueba L2/+ 3 en la parte de la insta-
lación a comprobar.
Observar necesariamente que en la comprobación de
conductor de hilo unipolar (indicación de fase) no se toque la punta de prueba L1/- 2 y que permanezca libre de
contacto.
- Si en el display LC 9 aparece un símbolo „R“, se en-
cuentra en esta parte de la instalación el conductor de hilo
(fase) de una tensión alterna.
Advertencia:
La comprobación de conductor de hilo unipolar (indicación de
fase) es posible en la red puesta a tierra a partir de 230 V,
50/60 Hz (fase contra tierra). Ropa protectora y condiciones
aislantes en el lugar de emplazamiento pueden perjudicar el
funcionamiento.
¡Atención!
La no existencia de tensión sólo se puede constatar mediante
una comprobación bipolar.
7. Comprobación del campo giratorio (Figura E/F)
- Agarrar completamente los dos mangos L1 6 y L2 7
para garantizar un acoplamiento capacitivo contra tierra.
- Poner las puntas de prueba L1/- 2 y L2/+ 3 en dos
conductores de hilo (fases) de una red de corriente
trifásica (sin necesidad de pulsar el botón 5) y comprobar
si existe la tensión entre fases de p. ej. 400 V.
- Existirá una secuencia de giro a la derecha (fase L1 antes
que fase L2), cuando en el display LC 9 aparece un
símbolo „R“. El display LC permanece apagado, si no se
detecta una secuencia de giro a la derecha.
- La comprobación del campo giratorio requiere siempre un
segundo control. En el caso de que el display LC muestre
la secuencia de giro a la derecha mediante el símbolo „R“,
al efectuar el segundo control con puntas de prueba L1/-
2
y L2/+ 3 cambiadas, el display LC debe permanecer
apagado.
En el caso de que el display LC muestre en ambos casos
un símbolo „R“, la puesta a tierra será demasiado débil.
Advertencia:
La comprobación del campo giratorio es posible a partir de
400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (fase contra fase) en la red de co- V, 50/60 Hz (fase contra fase) en la red de corriente trifásica puesta a tierra. Ropa protectora y condiciones
aislantes en el lugar de emplazamiento pueden perjudicar el
funcionamiento.
8. Datos técnicos
- Norma: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Rango de tensión nominal: 12 V hasta AC/DC 1.000 V
- Rango de frecuencia nominal f: 0 hasta 60 Hz
- Error de indicación máx.: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0 % - 15 %
- Impedancia (resistencia interior) circuito de medición/ cir-
cuito de carga: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Consumo de corriente circuito de medición: Is < 6,0 mA
(1.000 V)
- Consumo de corriente circuito de carga: Is < 550 mA
(1.000 V)
- Indicación de polaridad: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V
LED, - 12 V LED (al accionar los pulsadores)
- Comprobación de conductor de hilo (indicación de fase):
≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Comprobación del campo giratorio: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/
60 Hz
- Motor vibratoro, arranque: ≥ Un 200 V
-
Categoría de sobretensión: CAT IV 600 V,
- Tipo de protección: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN
60529)
6 - primera cifra: protección contra acceso a piezas peli-
grosas y protección contra cuerpos extraños sólidos, estanco al polvo
5 - segunda cifra: protegido contra chorros de agua. Se
puede emplear también con precipitaciones.
- max. El ciclo de trabajo permitida: 30 s (máx. 30 segun-
dos), 600 s apagado
- Peso: aprox. 250 g
- Longitud de cable de conexión: aprox. 1000 mm
- Margen de temperatura de servicio y almacenamiento:
- 20 °C hasta + 45 °C (categoría climática N)
- Humedad relativa del aire: 20 % hasta 96 % (categoría
climática N)
- Tiempo de regulación hacia atrás (protección térmica):
Tensión/Tiempo:
1000 V/2 s
9. Mantenimiento general
Limpiar la carcasa por el exterior con un paño limpio y
seco.
10. Protección ambiental
Al concluir la vida útil de aparato, éste deberá deponerse en los sistemas de reciclado o recogia que
estén a disposición.
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s,
CAT III 1000 V
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
13
Page 14

Инструкция за експлоатация
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Преди използване на индикатора за напрежение DUSPOL®
analog 1000: Моля прочетете внимателно инструкцията за
експлоатация и винаги спазвайте указанията за безопасност!
Съдържание
1. Указания за безопасност
2. Описание на уреда
3. Експлоатационна проверка преди използване за
контролно изпитване за липса на напрежение на
устройство
4. Контролно изпитване за липса на напрежение на
устройство
5. Присъединяване на натоварване с вибриращ мо-
тор
6. Тестване на външен проводник (Индикация на фа-
зата)
7. Тестване на въртящо се магнитно поле
8. Технически данни
9. Основна поддръжка
10. Защита на околната среда
1. Указания за безопасност
- При използване дръжте уреда само за изолираните
ръкохватки L1 6 и L2 7 и не докосвайте измервателните сонди L1/- 2 и L2/+ 3!
- Непосредствено преди и след използване, за да из-
вършите контролно изпитване за липса на напрежение на устройството, направете експлоатационна
проверка на тестера за напрежение (виж част 3)! Индикаторът за напрежение не бива да се използва, ако
една или повече функции на дисплея са повредени
или индикаторът за напрежение не е готов за работа!
После контролното изпитване трябва да се повтори с
друг тестер за напрежение.
- Индикаторът за напрежение може да се само в рам-
ките на зададения номинален обхват на напрежение и
в електроинсталации до AC/ DC 1.000 V!
- Индикаторът за напрежение трябва да се използва
само в електрически вериги с категория на пренапрежение CAT III с макс. 1000 V или категория на пренапрежение CAT IV с макс. 600 V проводник към земя.
- Индикаторът за напрежение е конструиран с цел из-
ползване от професионални електротехници, като се
спазва безопасен режим на работа.
- LED-степенният индикатор служи за показване на об-
хвата на напрежението, той не е предназначен за измерване.
-
напрежение тестер за повече от 30 секунди, за да напрежение (максимално допустимо работно време = 30 s)!
- Не разглобявайте индикатора за напрежение!
- Пазете повърхността на корпуса на индикатора за на-
прежение от замърсявания и повреди.
- За да предотвратите повреждане, след използване на
индикатора за напрежение покрийте измервателните
сонди с предвидените предпазители 1!
- Вземете под внимание, че импедансът (вътрешното
съпротивление) на детектора на напрежение оказва
влияние на дисплея на интерференцията на напреже-
ние (свързан капацитивно или индуктивно)!
В зависимост от вътрешния импеданс на детектора на
напрежение при наличието на смущения в напрежението
съществуват различни възможни показания на дисплея
“Налично работно напрежение” или “Липса на работно
напрежение“.
Детектор на напрежение с ниска стойност на Ом (импеданс < 100 kΩ), напрежението със смущение се потиска
или намалява:
В сравнение с референтна стойност 100 kΩ детекторът
на напрежение с относително нисък вътрешен импеданс
няма да показва всички смущения в напрежението с първоначална стойност над ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V DC). При
контакт с подлежащите на проверка части детекторът на
напрежение може да намали временно смущенията в напрежението чрез изпускане до ниво под ELV; но след премахване на детектора на напрежение смущението на напрежението отново ще заеме първоначалната си стойност.
Ако на дисплея не се появи „Наличие на напрежение“, се
препоръчва спешно поставянето на устройството за заземяване преди началото на дейността.
Детектор на напрежение с висока стойност на Ом (импеданс > 100 kΩ): смущението на напрежението не се потиска или намалява:
Детектор на напрежение с относително висок вътрешен
импеданс в сравнение с референтна стойност от 100 kΩ
няма да покаже еднозначно „Липса на работно напрежение” при налично смущение на напрежението. Ако дисплеят отчете „Наличие на напрежение“ при част, която
се счита за отделена от съоръжението, се препоръчва с
допълнителни мерки спешно да се докаже и установи състоянието „Липса на работно напрежение” на подлежащата
на проверка част, че показаното напрежение е смущение в
напрежението (Пример: Използване на подходящ детектор
на напрежение, който да е в състояние да различи смущение в работното напрежение от смущение в напрежението,
проверка чрез оглед на прекъснатото място в електрическата мрежа и т.н.).
Детектор на напрежение, който е в състояние да различи работно напрежение от смущение в напрежението
чрез включване на натоварване:
Детектор на напрежение с показател на вътрешен импеданс от две стойности е положил изпитанието за изпълнение/конструкция с оглед на обработката на смущения в
напрежението и е (в рамките на техническите си граници)
в състояние да различи работно напрежение от смущение
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
14
Page 15

в напрежението и да показва съществуващия тип напрежение директно или косвено.
Индикаторът за напрежение има маркировка с електрически символи:
Символ Значение
Важна документация!
Символ показва, че ръководството е
описано в ръководството, за да се избегнат
всякакви рискове
Уред или съоръжение за работа под
напрежение
Бутон
AC Променливо напрежение
DC Постоянно напрежение
DC/ AC Постоянно и променливо напрежение
Земята (напрежение спрямо земята)
Бутон (активира се ръчно); показва, че съответните индикации се появяват само когато
и двата бутона са натиснати
Фазова последователност в посока на въртене на часовниковата стрелка; фазовата последователност може да се индицира само
при 50 респ. 60 Hz и при заземена мрежа
Бубина за показание на нивото
2. Описание на уреда
1
Предпазители на измервателните сонди
2
Измервателна сонда L1/-
3
Измервателна сонда L2/+
4
Бубина за показание на нивото
5
Бутони
6
Ръкохватка L1
7
Ръкохватка на индикатора L2
8
LED-степенен индикатор
9
LC-дисплей със символ „R“ за тестване на външен
проводник (Индикация на фазата) и индикация за фа-
зовата последователност (по посока на часовниковата
стрелка)
J +/- LED-светодиоди за индикацията на поляритет
3. Експлоатационна проверка преди използване за
контролно изпитване за липса на напрежение на
устройство
- Непосредствено преди и след използване на индика-
тора за напрежение направете експлоатационна про-
верка!
- Проверете индикатора за напрежение посредством
познати източници на напрежение напр. контакт 230 V.
- Не използвайте тестера за напрежение, ако индикаци-
ята на напрежението, индикацията на фазата и вибри-
ращият мотор не работят безупречно!
4. Контролно изпитване за липса на напрежение на
устройство (картина A/B)
При контролно изпитване на устройството проверете за
липса на напрежение на устройството чрез проверка на
индикацията на напрежението, индикацията на фазата
(индикацията на фазата работи само в заземена мрежа с
променливо напрежение) и вибриращия мотор (вибриращият мотор се задейства чрез натискане на двата бутона). В устройството липсва напрежение само ако и трите
контролни вериги сигнализират за липса на напрежение
(индикация на напрежението, индикация на фазата и вибриращ мотор).
- Поставете двете измервателни сонди L1/+ 2 и L2/- 3
срещу съответните точки на устройството, което изпит-
вате.
- Височината на приложеното напрежение се показва на
LED-степенния индикатор 8.
- Чрез натискане на двата бутона 5 се включва бубина-
та за показание на нивото 4, 12 V LED-степен (+/ -) и
вътрешно натоварване в индикатора за напрежение.
- Променливите напрежения (AC) се индицират чрез
едновременно светване на + 24 V LED-светодиод и на
- 24 V LED-светодиод.
- Постоянните напрежения (DC) се индицират чрез свет-
ване на + 24 V LED-светодиод или на - 24 V LED-све-
тодиод. Посредством индикацията на поляритет J се
показва приложеният на измервателните сонди L2/+
3
поляритет + или -.
- За да се различават високоенергийни и нискоенергий-
ни напрежения (напр. капацитивно въведени напре-
жения на смущаващо напрежение), чрез натискане на
двата бутона може да бъде присъединено вътрешно
натоварване в индикатора за напрежение (виж част 5.)
5. Присъединяване на натоварване с вибриращ
мотор (картина A/В)
На двете ръкохватки L1 6 и L2 7 се намират бутони 5.
При натискане на двата бутона се превключва към по-ниско
вътрешно съпротивление. При това се включва вибриращ
мотор (дисбалансиран мотор). От ок. 200 V този мотор се
задвижва. С повишаване на напрежението се увеличават
оборотите и вибрацията му. Продължителността на теста
с по-ниско вътрешно съпротивление (тест на натоварване)
зависи от височината на напрежението, което ще се измерва. За да се предотврати загряване на индикатора, той е
оборудван с термична защита (обратно регулиране). Посредством обратното регулиране оборотите на вибриращия
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
15
Page 16

мотор спадат и вътрешното съпротивление се повишава.
Присъединяването на натоварване (двата бутона са натиснати) може да се използва, за да …
- се потискат реактивни напрежения (индуктивни и капа-
цитивни напрежения)
- се разредят кондензаторите
-
се задейства 10/30 mA предпазителя. Задействането на
предпазителя става чрез тестване на външен провод-
ник (Индикация на фазата) към PE (земя). (картина D)
6. Тестване на външен проводник (Индикация на фа-
зата) (картина C)
- Хванете ръкохватките L1 6 и L2 7, като обвиете с
длан цялата повърхност, за да осигурите капацитивна
връзка към земята.
- Сложете измервателната сонда L2/+ 3 на съответна-
та точка на устройството, което ще изпитвате.
Обърнете специално внимание на това, при еднопо-
люсното тестване на външен проводник (Индикация
на фазата) измервателната сонда L1/- 2 да не бъде
докосвана и да остане безконтактна.
- Ако върху LC-дисплея 9 се появи символът „R“, в тази
част на съоръжението външният проводник (фаза) е
поставен под променливо напрежение.
Указание:
Еднополюсното тестване на външен проводник (Индикация на фазата) е възможно в заземена мрежа от 230 V,
50/60 Hz (фаза към земя). Защитно облекло и някои изолиращи особености на участъка могат да попречат на
функцията.
Внимание!
Липсата на напрежение може да бъде установена само с
двуполюсно тестване.
7.
Тестване на въртящо се магнитно поле (картина E/F)
- Хванете ръкохватките L1 6 и L2 7, като обвиете с
длани цялата повърхност, за да осигурите капацитив-
на връзка към земята.
- Сложете измервателните сонди L1/- 2 и L2/+ 3 до
два външни проводника (фази) на мрежа за трифазен
ток и проверете дали e приложено напрежение на
външния проводник от напр. 400 V.
- Фазова последователност в посока на въртене на
часовниковата стрелка (фаза L1 преди фаза L2) е за-
дадена, когато върху LC-дисплея 9 се появи символ
„R“. LC-дисплеят остава изгасен, ако не е разпозната
фазова последователност в посока на въртене на ча-
совниковата стрелка.
- Тестването на въртящото се магнитно поле винаги
изисква кръстосана проверка! Ако LC-дисплеят показ-
ва фазова последователност в посока на въртене на
часовниковата стрелка чрез символа „R“, при кръсто-
саната проверка с разменени измервателни сонди L1/-
2
и L2/+ 3 LC-дисплеят трябва да остане угаснал.
Ако LC-дисплеят и в двата случая показва символа
„R“, заземяването е прекалено слабо.
Указание:
Тестването на въртящо се магнитно поле е възможно в заземена мрежа от 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (фаза към фаза).
Защитно облекло и някои изолиращи особености на участъка могат да попречат на функцията.
8. Технически данни
- Стандарт: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Номинален обхват на напрежение: 12 V до AC/ DC
1.000 V
- Номинален обхват на честота f: 0 до 60 Hz
- Макс. грешка на индикация : Un ±15 %, ELV Un + 0%,
-15%
- Импеданс (вътрешно съпротивление), измервателна
верига/ товарна верига: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Консумация на ток, измервателна верига: Is < 6,0 mA
(1.000 V)
- Консумация на ток, товарна верига: Is < 550 mA
(1.000 V)
- Индикация на поляритет: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V
LED, - 12 V LED (при натискане на бутона)
- Тестване на външен проводник (Индикация на фаза-
та): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Тестване на въртящо се магнитно поле: ≥ Un 400 V,
50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Вибриращ мотор, пускане: ≥ Un 200 V
- Категория на пренапрежение: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III
1000 V
- Клас на защита: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/ EN 60529)
6 – първа цифра: Защита от достъп до опасни части и
места, както и защита от проникване на твърди части-
ци, прахоустойчивост
5 – втора цифра: Защита от напръскване. Може да
бъде използван и при валеж.
- макс.допустимо Работен цикъл: 30 s (макс. 30 секун-
ди), 600 s на разстояние
- Тегло: ок. 250g
- Дължина на присъединителните кабели: ок. 1000 mm
- Температурен обхват на работа и съхранение: - 20 °C
до + 45 °C (климатична категория N)
- Относителна влажност на въздуха: 20 % до 96 % (кли-
матична категория N)
- Време на обратно регулиране (термична защита):
Напрежение/Време: 230V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s,
1000 V/2s
9. Основна поддръжка
Почиствайте корпуса от външната страна с чиста суха
кърпа.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
16
Page 17

10. Защита на околната среда
Моля, оловни батерии и устройството в края на
полезния си живот наличната Връщане и системи
за събиране.
Návod k použití
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Před použitím zkoušečky napětí DUSPOL® analog 1000: Přečtěte si návod k použití a bezpodmínečně dodržujte bezpeč-
nostní pokyny!
Obsah
1. Bezpečnostní pokyny
2. Popis přístroje
3. Funkční zkouška před použitím zkoušečky ke kontrole
absence napětí zařízení
4. Kontrola absence napětí zařízení
5. Připojení zátěže s vibračním motorem
6. Zkouška vnějších vodičů (zobrazení fází)
7. Zkouška otáčivého pole
8. Technické parametry
9. Všeobecná údržba
10. Ochrana životního prostředí
1. Bezpečnostní pokyny:
- Přístroje se při používání dotýkat pouze za izolované ru-
kojeti L1 6 a L2 7 a nedotýkejte se měřicích hrotů L1/-
2
a L2/+ 3!
- Zkontrolovat funkčnost zkoušečky napětí bezprostředně
před a po jejím použití, ke kontrole absence napětí zaříze-
ní (viz část 3)! Zkoušečku napětí nesmíte používat, pokud
vypadne funkce jednoho nebo několika ukazatelů nebo
není detekována připravenost k použití! Tuto kontrolu je
nutno zopakovat pomocí jiné zkoušečky napětí.
- Zkoušečku napětí můžete používat jen v uvedeném roz-
sahu jmenovitého napětí a v elektrických zařízeních do
AC/DC 1.000 V!
- Zkoušečka napětí může být používána jen v proudových
okruzích kategorie přepětí CAT III s max. 1000 V nebo ka-
tegorie přepětí CAT IV s max. 600 V s uzemněnými vodiči.
-
Zkoušečka napětí je dimenzována pro použití kvalifikovanými
elektrikáři ve spojení s bezpečnými pracovními postupy.
- Stupňová indikace LED slouží k zobrazení napěťového
rozsahu, který není určen k účelům měření.
- Vytvoření napětí tester pro více než 30 sekund napětí
(maximálně přípustná doba zapnutí ED = 30 s)!
- Zkoušečku napětí nesmíte nikdy rozebírat!
- Zkoušečku napětí je třeba chránit před znečištěním a po-
škozením povrchu krytu.
- Jako ochrana před poškozením je třeba po použití zkou-
šečky napětí opatřit měřicí hroty přiloženou ochranou 1!
- Vezměte prosím na vědomí, že impedance (vnitřní odpor)
zkoušečky napětí ovlivňuje zobrazení rušivých (přivede-
ných kapacitních nebo indukčních) napětí!
V závislosti na vnitřní impedanci zkoušečky napětí se při přítomnosti rušivého napětí mohou zobrazovat indikace „Provozní napětí přítomno“ nebo „Provozní napětí nepřítomno“.
Nízkoohmová zkoušečka napětí (impedance < 100 kΩ), rušivé napětí se potlačí resp. sníží:
Zkoušečka napětí s relativně nízkou vnitřní impedancí nezobrazí ve srovnání s referenční hodnotou 100 kΩ všechna rušivá
napětí s původní hodnotou nad ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V DC). Při
kontaktu se zkoušenými díly může zkoušečka napětí přechodně snížit rušivá napětí v důsledku vybití až na hladinu nižší než
ELV; po odebrání zkoušečky napětí nabyde rušivé napětí opět
původní hodnoty.
Jestliže se nezobrazí indikace „Napětí přítomno“, důrazně doporučujeme, abyste před zahájením prací zajistili řádné připojení zemnícího zařízení.
Vysokoohmová zkoušečka napětí (impedance > 100 kΩ):
Rušivé napětí se nepotlačí resp. nesníží:
Zkoušečka napětí s relativně vysokou vnitřní impedancí nezobrazí při přítomnosti rušivého napětí ve srovnání s referenční hodnotou 100 kΩ jednoznačně „Provozní napětí nepřítomno“. Jestliže se u některého dílu, který je považován
za odpojený od zařízení, zobrazí indikace „Napětí přítomno“,
důrazně doporučujeme, abyste dalšími opatřeními (například
použitím vhodné zkoušečky napětí, která je schopna rozlišovat
provozní napětí od rušivého, vizuální kontrolou místa odpojení
v elektrické síti apod.) zkontrolovali stav „Provozní napětí nepřítomno“ zkoušeného dílu a zjistili tak, že napětí zobrazované
zkoušečkou napětí je rušivým napětím.
Zkoušečky napětí, které jsou schopny připojením zátěže
rozlišovat provozní napětí od rušivého:
Zkoušečka napětí s uvedením dvou hodnot vnitřní impedance
obstála ve zkoušce svého provedení/konstrukce při ošetření
rušivých napětí a je (uvnitř technických mezí) schopna rozlišovat provozní napětí od rušivého a zobrazit příslušný přítomný
typ napětí přímo nebo nepřímo.
Elektrické symboly na přístroji:
Symbol Význam
Důležité dokumentace!
Symbol znamená, že příručka je popsáno v pří-
ručce, aby se zabránilo vzniku rizik
Přístroj nebo vybavení k práci pod napětím
Tlačítko
Střídavé napětí AC
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
17
Page 18

Stejnosměrné napětí DC
Stejnosměrné a střídavé napětí DC/AC
Země (napětí proti zemi)
Tlačítko (ručně ovládané); dbejte na to, aby se
odpovídající symboly objevily pouze po stisknu-
tí obou tlačítek
Otáčení doprava; směr otáčivého pole může
být zobrazen jen při 50 popř. 60 Hz a při uzemnění sítě
Ukazatel úrovně ponorné cívky
2. Popis přístroje
1
Ochrana zkušebních hrotů
2
Měřicí hrot L1/-
3
Měřicí hrot L2/+
4
Ukazatel úrovně ponorné cívky
5
Tlačítko
6
Rukojeť L1
7
Rukojeť s indikacemi L2
8
Stupňová indikace LED
9
Displej LC se symbolem „R“ pro zkoušku vnějších vodičů
(zobrazení fází) a indikace otáčivého pole (vpravo)
J
+/- LED indikace polarity
3. Funkční zkouška před použitím zkoušečky ke kontrole
absence napětí zařízení
- Bezprostředně před a po použití zkontrolujte funkci zkou-
šečky napětí!
- Zkoušečku napětí zkontrolujte v rámci známých napěťo-
vých zdrojů, např. na zásuvce 230 V.
- Nepoužívejte zkoušečku napětí, pokud zobrazení napětí,
fází a vibrační motor správně nefungují!
4. Kontrola absence napětí zařízení (obrázek A/B)
Při kontrole zařízení kontrolujete absenci napětí zařízení pomocí kontroly zobrazení napětí, zobrazení fází (zobrazení fází
funguje pouze v uzemněné síti se střídavým napětím) a vibrační motor (vibrační motor se aktivuje zmáčknutím obou tlačítek). Absence napětí zařízení je zaručena pouze v případě,
že všechny tři zkušební obvody signalizují tuto absenci napětí
(zobrazení napětí, fází a vibrační motor).
- Oba měřicí hroty L1/+ 2 a L2/- 3 přiložte k měřeným
dílům zařízení.
- Velikost přiloženého napětí se zobrazí na stupňové indika-
ci LED 8.
- Po stisknutí obou tlačítek 5 se zapojí ukazatel úrovně
ponorné cívky 4, stupeň LED 12 V (+/ -) a interní zatížení
ve zkoušečce napětí.
- Střídavá napětí (AC) jsou indikována současným rozsví-
cením LED +24 V a LED -24 V.
- Stejnosměrná napětí (DC) jsou indikována rozsvícením
LED +24 V nebo LED -24 V. Ukazatelem polarity J je
indikována polarita + nebo - na měřicím hrotu L2/+ 3.
- Za účelem rozlišení vysoko a nízkoenergetických napětí
(např. kapacitně navazující rušivá napětí) může být stisk-
nutím obou tlačítek připojeno interní zatížení ve zkoušeč-
ce napětí (viz část 5.)
5. Připojení zátěže s vibračním motorem (obrázek A/B)
Obě rukojeti L1 6 a L2 7 jsou opatřeny tlačítky 5. Při použití
obou tlačítek dojde k přepnutí na malý vnitřní odpor. Přitom je
vibrační motor (motor s nevyvážením) přiložen k napětí. Asi
od 200 V se motor začne otáčet. Se stoupajícím napětím se
zvyšují i jeho otáčky a vibrace. Doba trvání měření s malým
vnitřním odporem (kontrola zatížení) je závislá na velikosti měřeného napětí. Aby nedocházelo k nepřípustnému zahřívání
přístroje, je instalována tepelná ochrana (zpětná regulace).
Při této zpětné regulaci dochází k poklesu otáček vibračního
motorku a zvýšení vnitřního odporu.
Zátěžové připojení (obě tlačítka jsou stisknutá) může být použito, aby …
-
byla potlačena jalová napětí (induktivní a kapacitní napětí),
- byly vybity kondenzátory,
- byl inicializován ochranný spínač poruchového proudu
10/30 mA. Ochranný spínač poruchového proudu se inici-
alizuje zkouškou vnějších vodičů (zobrazení fází) vůči PE
(zemi). (obrázek D)
6. Zkouška vnějších vodičů (zobrazení fází) (obrázek C)
- K zajištění kapacitního spojení vůči zemi uchopte rukojeti
L1 6 a L2 7 po celé ploše.
- Měřicí hrot L2/+ 3 přiložte k měřené části zařízení.
Bezpodmínečně dbejte, abyste se při jednopólovém zkou-
šení vnějších vodičů (zobrazení fází) nedotýkali měřicího
hrotu L1/- 2, a aby hrot zůstal bez kontaktu.
- Pokud se na displeji LC 9 objeví symbol „R“, je k této čás-
ti zařízení přiložen vnější vodič (fáze) střídavého napětí.
Upozornění:
Jednopólová zkouška vnějších vodičů (zobrazení fází) je
možná v uzemněné síti od 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fáze vůči zemi).
Ochranný oděv a izolační podmínky na stanovišti mohou negativně ovlivnit funkci.
Pozor!
Beznapěťový stav je možné stanovit pouze dvoupólovým měřením.
7. Zkouška otáčivého pole (obrázek E/F)
- K zajištění kapacitního spojení vůči zemi uchopte obě ru-
kojeti L1 6 a L2 7 po celé ploše.
- Měřicí hroty L1/- 2 a L2/+ 3 přiložte ke dvěma vnějším
vodičům (fáze) trojfázové sítě a zkontrolujte, zda je přilo-
ženo napětí vnějšího vodiče např. 400 V.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
18
Page 19
- Otáčení doprava (fáze L1 před fází L2) je stanoveno, když
se na displeji LC 9 objeví symbol „R“. Na displeji LC se
neobjeví žádný symbol, pokud nebylo detekováno otáčení
doprava.
- Zkouška otáčivého pole vyžaduje stálou kontrolu!. Pokud
displej LC indikuje otáčení doprava symbolem „R“, nesmí
se při kontrole se zaměněnými měřicími hroty L1/- 2 a
L2/+ 3 na displeji LC objevit nějaký symbol.
Pokud se na displeji LC v obou případech objeví symbol
„R“, je uzemnění příliš slabé.
Upozornění:
Zkouška otáčivého pole je možná od 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz
(fáze proti fázi) v uzemněné trojfázové síti. Ochranný oděv
a izolační podmínky na stanovišti mohou negativně ovlivnit
funkci.
8. Technické parametry
- Norma: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Rozsah jmenovitého napětí: 12 V až AC/DC 1.000 V
- Rozsah jmenovité frekvence pro: 0 až 60 Hz
- Max. odchylka ukazatele: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0 % - 15 %
- Impedance (vnitřní odpor), měřicí obvod/ zátěžový obvod:
200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Příkon, měřicí obvod: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Příkon, zátěžový obvod: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Ukazatel polarity: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (u stisknutého tlačítka)
- Zkouška vnějších vodičů (zobrazení fází): ≥ Un 230 V,
50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Zkouška otáčivého pole: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibrační motorek, rozběh: ≥ Un 200 V
- Kategorie přepětí: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Krytí: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - první číslice: Ochrana proti vniknutí nebezpečných
částí a ochrana proti pevným cizím tělesům, prachotěsná
5 - druhá číslice: Ochrana proti stříkající vodě. Lze použít
i za deště.
- max. přípustná Pracovní cyklus: 30 s (max. 30 sekund),
600 s vypnuto
- Hmotnost: asi 250 g
- Délka spojovacího vedení: asi 1000 mm
- Rozsah teploty při provozu a skladování: - 20 °C až
+ 45 °C (klim. kategorie N)
-
Relativní vlhkost vzduchu: 20 % až 96 % (klim. kategorie N)
- Doby zpětné regulace (tepelná ochrana):
Napětí/čas:
9. Všeobecná údržba
Kryt zevně utírejte čistou a vlhkou utěrkou.
10. Ochrana životního prostředí
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Přístroj na konci jeho životnosti zavezte k recyklaci na
dostupná sběrná místa.
Brugsanvisning
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Før De bruger spændingsviseren DUSPOL® analog 1000: Læs
venligst hele brugsanvisningen og vær under alle omstændigheder opmærksom på sikkerhedshenvisningerne!
Indholdsfortegnelse
1. Sikkerhedshenvisninger
2. Instrumentbeskrivelse
3. Funktionsprøvning til prøvning af anlægget for spæn-
dingsfrihed før brug
4. Prøvning af anlægget for spændingsfrihed
5. Belastningstilslutning med vibrationsmotor
6. Prøvning af faseledning (fasevisning)
7. Drejefeltprøvning
8. Tekniske data
9. Almindelig vedligeholdelse
10. Miljøbeskyttelse
1. Sikkerhedshenvisninger:
- Under anvendelsen må apparatet kun holdes på de isole-
rede håndtag L1 6 og L2 7 og prøvespidserne L1/- 2
og L2/+ 3 må ikke berøres!
- Spændingsviseren prøves for funktion umiddelbart før og
efter anvendelse til prøvning af anlægget for spændings-
frihed (se afsnit 3)! Spændingsviseren må ikke bruges ved
funktionssvigt af en eller flere indikatorer, eller hvis der
ikke kan ses nogen funktionsdygtighed! Prøvning skal så
gentages med en anden spændingsviser.
- Spændingsviseren må kun anvendes inden for det anførte
mærkespændingsområde og i elektriske anlæg op til AC/
DC 1.000 V!
-
Spændingsviseren må kun bruges i strømkredse i over-
spændingskategori CAT III med maks. 1000 V eller i over-
spændingskategori CAT IV med maks. 600 V leder mod jord.
- Spændingsviseren er beregnet til at blive anvendt af en
faglært elektriker i forbindelse med en sikker arbejdsme-
tode.
- LED-trinvisningen tjener til visning af spændingsområdet,
den er ikke bestemt til måleformål.
- Oprettelse af en spændingstester i mere end 30 sekun-
der spænding (maksimalt tilladt indkoblingsvarighed ED =
30 s)
- Spændingsviseren må ikke adskilles!
- Spændingsviseren skal beskyttes, således at forureninger
og beskadigelser på kabinettets overflade undgås.
- Som beskyttelse mod personskader skal prøvespidserne,
efter brug af spændingsviseren, forsynes med den ved-
lagte prøvespidsbeskyttelse 1!
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
19
Page 20
- Bemærk at testerens impedans (indre modstand) påvirker
visningen af støjspændingen (kapacitiv eller induktiv kob-
let)!
Afhængig af den interne impedans af spændingstesteren, er
der i tilfælde af støjspænding forskellige måder for visning af
”driftsspænding tilgængelig” eller ”driftsspænding ikke tilgængelig”.
Lav impedans spændingstester (impedans < 100 kΩ), Støj-
spændingen undertrykkes d.v.s. reduceres:
En spændingstester med relativt lav intern impedans vil i
sammenligning med referenceværdien 100 kΩ ikke vise alle
støjspændinger med en oprindelig værdi over ELV (50 V AC/
120 V DC). Ved kontakt med de dele, der skal testes, kan
spændingstesteren midlertidigt reducere støjspændingen ved
udladning til et niveau under ELV. Efter fjernelse af spændingsdetektoren vil støjspændingen dog antage sin oprindelige
værdi igen.
Når ”spænding tilgængelig” ikke vises, anbefales det kraftigst,
at sørge for at jordforbindelsen oprettes inden arbejdet påbegyndes.
Høj impedans spændingstester (impedans > 100 kΩ): Støj-
spændingen bliver ikke undertrykt eller reduceret:
En spændingstester med relativt høj intern impedans, vil i
forhold til referenceværdien på 100 kΩ ved eksisterende støjspænding ”driftsspænding ikke tilgængelig” ikke vise en entydig værdi. Når ”spænding tilgængelig” vises, på en del, der be-
nder sig separat i forhold til anlægget, anbefales det stærkt,
at fortsætte med yderligere foranstaltninger (For eksempel:
Ved hjælp af en passende spændingsdetektor, som er i stand
til at differentiere mellem driftsspænding og støjspænding, visuel inspektion af adskillelsespunktet i det elektriske netværk,
etc.) At efterprøve tilstanden ”Ingen driftsspænding” af den
del, der skal inspiceres, sådan at spændingen der angives af
spændingstesteren er en støjspænding.
Spændingstestere som er i stand til at skelne mellem
driftsspændinger og støjspændinger:
En spændingstester med angivelse af to værdier af den interne impedans har bestået testen af sit design/ konstruktion til
behandling af interferens spændinger og er (inden for de tekniske grænser) i stand til at differentiere mellem driftspænding
og støjspænding og kan vise den eksisterende spændingstype
direkte eller indirekte.
Elektriske symboler på apparatet:
Symbol Betydning
Vigtigt dokumentation! Symbolet angiver, at
vejledningen er beskrevet i manualen, for at
undgå enhver risiko
Apparat eller udstyr til arbejder under spænding
Trykknap
AC Vekselspænding
DC Jævnspænding
DC/ AC Jævn- og vekselspænding
Jorden (spænding til jord)
Trykknap (håndbetjent): henviser til, at tilsvarende visning kun sker ved betjening af begge
trykknapper
Højredrejende følge: Drejefelt-retning kan kun
vises ved 50 hhv. 60 Hz og i et net med jordforbindelse
Dykføler-niveauindikering
2. Instrumentbeskrivelse
1
Prøvespidsbeskyttelse
2
Prøvespids L1/-
3
Prøvespids L2/+
4
Dykføler-niveauindikering
5
Trykknap
6
Håndtag L1
7
Indikatorhåndtag L2
8
LED-trinvisning
9
LC-display med „R“-symbol for prøvning af faseledning
(fasevisning) og drejefeltvisning (højre)
J
+/- lysdioder for polaritetsvisning
3. Funktionsprøvning til prøvning af anlægget for spæn-
dingsfrihed før brug
- Umiddelbart før og efter brug skal spændingsviseren prø-
ves for korrekt funktion!
- Test spændingsviseren på kendte spændingskilder, f. eks.
på en 230 V-stikkontakt.
- Anvend spændingsviseren ikke, hvis spændingsvisning,
fasevisning og vibrationsmotor ikke fungerer upåklageligt!
4.
Prøvning af anlægget for spændingsfrihed (billede A/B)
Ved prøvning af anlægget skal anlægget prøves for spændingsfrihed ved at kontrollere spændingsvisning, fasevisning
(fasevisning fungerer kun i et jordforbundet vekselspændingsnet) og vibrationsmotor (aktivering af vibrationsmotor sker ved
at betjene begge trykknapper). Anlæggets spændingsfrihed er
kun sikret, hvis alle tre prøvekredse signalerer spændingsfrihed (spændingsvisning, fasevisning og vibrationsmotor).
- Læg begge prøvespidser L1/+ 2 og L2/- 3 på de an-
lægsdele, der skal prøves.
- Størrelsen på den påførte spænding vises via LED-trinvis-
ning 8.
- Ved betjening af begge trykknapper 5 tilkobles visningen
for dykføler-niveauindikering 4, 12 V LED-trin (+/ -) og en
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
20
Page 21

intern belastning i spændingsviseren.
- Vekselspændinger (AC) vises ved, at + 24 V LED og -
24 V LED begynder at lyse samtidig.
- Jævnspændinger (DC) vises ved, at + 24 V LED eller -
24 V LED begynder at lyse samtidig. Via polaritetsvisning
J
vises den på prøvespids L2/+ 3 påførte polaritet +
eller -.
- For at kunne skelne mellem energirig og energifattig
spænding (f. eks. forstyrrende, kapacitivt indkoblede
spændinger), kan der, ved betjening af begge trykknap-
per, tilkobles en intern belastning i spændingsviseren (se
afsnit 5.)
5.
Belastningstilslutning med vibrationsmotor (billede A/B)
Begge håndtag L1 6 og L2 7 er forsynet med trykknapper
5
. Ved betjening af begge trykknapper skiftes der til en lavere indvendig modstand. Herved påføres en vibrationsmotor
spænding (motor med ubalance). Fra ca. 200 V vil denne
sættes i en drejebevægelse. Stigende spænding vil også øge
dens omdrejningstal og vibration. Varigheden af en prøvning
med en lavere indvendig modstand (belastningprøvning) er
afhængig af størrelsen af den spænding, der skal måles. For
at forhindre en ikke-tilladelig opvarmning af apparatet, er der
anbragt en termisk beskyttelse (returregulering). Ved hjælp af
denne returregulering vil vibrationsmotorens omdrejningstal
falde og den indvendige modstand vil stige.
Belastningstilslutningen (begge trykknapper trykket) kan bruges, for at …
- undertrykke blindspændinger (induktive og kapacitive
spændinger),
- aflade kondensatorerne
- udløse en 10/ 30 mA RCD-beskyttelsesafbryder. Udløs-
ning af RCD-beskyttelsesafbryderen sker ved prøvning på
faseledningen (fasevisning) mod PE (jord) - (billede D).
6. Prøvning af faseledning (fasevisning) (billede C)
- Grib fat i hele fladen af håndtagene L1 6 og L2 7, for at
sikre en kapacitiv kobling mod jorden.
- Læg prøvespidsen L2/+ 3 på den anlægsdel, der skal
prøves.
Vær under alle omstændigheder opmærksom på, at
prøvespidsen L1/- 2, ved 1-polet prøvning af faseledning
(fasevisning), ikke berøres samt at den forbliver kontaktfrit.
- Hvis der fremkommer et „R“-symbol på LC-display 9,
ligger der en faseledning (fase) af en vekselspænding på
denne anlægsdel.
Henvisning:
1-polet prøvning af faseledning (fasevisning) er mulig i et net
med jordforbindelse fra 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fase mod jord). Beskyttelsestøj og isolerende forhold på opstillingsstedet kan
påvirke funktionen.
OBS!
Spændingsfrihed kan kun fastslås ved hjælp af 2-polet prøvning.
7. Drejefeltprøvning (billede E/F)
- Grib fat i hele fladen af begge håndtag L1 6 og L2 7, for
at sikre kapacitiv kobling mod jorden.
- Læg prøvespidserne L1/- 2 og L2/+ 3 på to faselednin-
ger (faser) af et trefaset net og prøv, om der er påført en
faseledningsspænding på f. eks. 400 V.
- En højredrejende følge (fase L1 før fase L2) er givet, hvis
der fremkommer et „R“-symbol på LC-displayet 9. LCdisplayet bliver slukket, hvis der ikke kunne registreres en
højredrejende følge.
- Drejefeltprøvning kræver altid en modkontrol! Hvis LC-dis-
playet viser følgen med højredrejninger via „R“-symbolet,
skal LC-displayet forblive i slukket tilstand ved modkontrol
med ombyttede prøvespidser L1/- 2 og L2/+ 3.
Hvis LC-displayet indikerer et „R“-symbol i begge tilfælde,
foreligger der en for svag jording.
Henvisning:
Drejefeltprøvning er mulig fra 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (fase
mod fase) i et trefaset net med jordforbindelse. Beskyttelsestøj
og isolerende forhold på opstillingsstedet kan påvirke funktionen.
8. Tekniske data
- Forskrift: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Mærkespændingsområde: 12 V til AC/ DC 1.000 V
- Mærkefrekvensområde f: 0 til 60 Hz
- Maks. visningsfejl: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0% - 15%
- Impedans (indvendig modstand) målekreds/ belastnings-
kreds: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Strømoptagelse målekreds: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Strømoptagelse belastningskreds: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polaritetsvisning: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (ved trykknapbetjening)
- Prøvning af faseledning (fasevisning): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/
60 Hz
- Prøvning af drejefelt: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibrationsmotor, opstart: ≥ Un 200 V
- Overspændingskategori: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Beskyttelsesart: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - første kodetal: Beskyttelse mod tilgang til farlige dele
og beskyttelse mod faste fremmedlegemer, støvtæt
5 - andet kodetal: Beskyttet mod strålevand. Kan også an-
vendes ved nedbør.
-
max. tilladelige Duty cycle: 30 s (maks. 30 sekunder), 600 s off
- Vægt: ca. 250g
- Længde af forbindelsesledning: ca. 1000 mm
- Drifts- og lagertemperaturområde: - 20 °C til + 45 °C (kli-
makategori N)
- Relativ luftfugtighed: 20 % til 96 % (klimakategori N)
- Returreguleringstider (termisk beskyttelse):
Spænding/ tid: 230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
21
Page 22

9. Almindelig vedligeholdelse
Den udvendige del af kabinettet renses en ren og tør klud.
10. Miljøbeskyttelse
I slutningen af dets levetid skal apparatet aeveres
til de dertil beregnede indsamlings- og retursystemer.
Οδηγίες χρήσεως
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Πριν να χρησιμοποιήσετε τον ανιχνευτή τάσης DUSPOL®
analog 1000: Να διαβάζετε τις οδηγίες χρήσεως και να λαμβάνετε οπωσδήποτε υπόψη σας τις υποδείξεις ασφαλείας,
παρακαλώ!
Πίνακας περιεχομένων
1. Υποδείξεις ασφαλείας
2. Περιγραφή συσκευής
3. Λειτουργικός έλεγχος πριν την μεταχείριση για την
εξέταση της ανυπαρξίας τάσης μιας εγκατάστασης
4. Έλεγχος της ανυπαρξίας τάσης μιας εγκατάστασης
5. Χειρισμός υπό φορτίο με κινητήρα δόνησης
6. Έλεγχος (Ένδειξη φάσης)
7. Δοκιμή περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου
8. Τεχνικά στοιχεία
9. Γενική συντήρηση
10. Προστασία περιβάλλοντος
1. Υποδείξεις ασφαλείας:
- Να πιάνετε τη συσκευή από τις μονωμένες λαβές L1 6 και
L2 7 και να μην αγγίζετε τις ακίδες L1/- 2 και L2/+ 3!
- Να ελέγχετε τον ανιχνευτή τάσης ως προς λειτουργία, άμε-
σα πριν και μετά την χρήση, για τον έλεγχο της εγκατάστασης ως προς την ανυπαρξία τάσης (βλέπε παράγραφο 3)!
Ο ανιχνευτής τάσης δεν επιτρέπεται να χρησιμοποιείται,
όταν μία /ή περισσότερες ενδείξεις δεν λειτουργούν ή δεν
διακρίνεται ετοιμότητα λειτουργίας! Στη συνέχεια, ο έλεγχος πρέπει να επαναληφθεί με ένα άλλο ανιχνευτή τάσης.
- Ο ανιχνευτής τάσης επιτρέπεται να χρησιμοποιείται μόνο
στο εύρος της αναφερόμενης ονομαστικής τάσης και σε
ηλεκτρικές εγκαταστάσεις έως AC/DC 1.000 V!
- Ο ανιχνευτής τάσης επιτρέπεται να χρησιμοποιείται μόνο
σε ηλεκτρικά κυκλώματα της κατηγορίας υπέρτασης CAT
III με μάξιμουμ 1000 V ή της κατηγορίας υπέρτασης CAT
IV με μάξιμουμ 600 V αγωγού ως προς τη γη.
- Ο ανιχνευτής τάσης έχει σχεδιαστεί για τη χρήση από ηλε-
κτροτεχνίτες σε συνδυασμό με ασφαλείς μεθόδους εργασίας.
- Η βαθμιδωτή ένδειξη φωτοδιόδων εξυπηρετεί στην ένδει-
ξη του εύρους τάσεως, αυτή δεν προορίζεται για μέτρηση.
- Δημιουργώντας μια τάση tester για περισσότερο από 30
δευτερόλεπτα τάσης (μέγιστη κύκλος)
- Ο ανιχνευτής τάσης δεν επιτρέπεται να αποσυναρμολογεί-
ται!
- Ο ανιχνευτής τάσης πρέπει να προφυλάσσεται από ακα-
θαρσίες και φθορές της επιφάνειας περιβλήματος.
- Μετά από τη χρήση πρέπει να εφοδιάζονται οι ακίδες του
ανιχνευτή τάσης με το εσώκλειστο προστατευτικό ακίδων
1
, ως προστασία από φθορές!
- Σημειώστε ότι η σύνθετη αντίσταση (εσωτερική αντίσταση)
του ελεγκτή τάσης επηρεάζει την ένδειξη τάσεων θορύβου
(ενσωμάτωση χωρητικά ή επαγωγικά)!
Ανάλογα με την εσωτερική σύνθετη αντίσταση του ελεγκτή τάσης, υπάρχουν για την περίπτωση παρουσίας τάσης θορύβου
διάφορες δυνατότητες για την ένδειξη "υπάρχει τάση λειτουργίας" ή " δεν υπάρχει τάση λειτουργίας».
Ελεγκτής τάσης χαμηλής σύνθετης αντίστασης (Σύνθετη
αντίσταση < 100 kΩ), η τάση θορύβου περιορίζεται ή μειώνεται:
Ένας ελεγκτής τάσης με σχετικά χαμηλή εσωτερική σύνθετη
αντίσταση δεν θα εμφανίζει σε σύγκριση με την τιμή αναφοράς
των 100 kΩ όλες τις τάσεις θορύβου με αρχική τιμή άνω του
ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V DC). Κατά την επαφή με τα προς έλεγχο
μέρη, ο ελεγκτής τάσης μπορεί, μέσω εκκένωσης, να μειώσει
προσωρινά την τάση θορύβου κάτω από το επίπεδο του ELV.
Όταν δεν εμφανίζεται η ένδειξη "υπάρχει τάση", συνιστάται η
άμεση τοποθέτηση διάταξης πριν από την έναρξη των εργασιών.
Ελεγκτής τάσης υψηλής σύνθετης αντίστασης (Σύνθετη
αντίσταση > 100 kΩ): Η τάση θορύβου δεν περιορίζεται και
δεν μειώνεται:
Σε περίπτωση ύπαρξης τάσης θορύβου, ένας ελεγκτής τάσης
με σχετικά υψηλή εσωτερική σύνθετη αντίσταση δεν θα εμφανίζει σαφώς την ένδειξη «δεν υπάρχει τάση λειτουργίας», σε
σχέση με την τιμή αναφοράς των 100 kΩ. Όταν εμφανίζεται
σε ένα αντικείμενο, το οποίο θεωρείται αποζευγμένο από την
εγκατάσταση, η ένδειξη "Υπάρχει τάση", συνιστάται οπωσδήποτε η λήψη πρόσθετων μέτρων (παράδειγμα: Χρησιμοποίηση ενός κατάλληλου ελεγκτή τάσης, ο οποίος είναι σε θέση να
διακρίνει την τάση λειτουργίας από την τάση θορύβου, οπτική
επιθεώρηση του σημείου διαχωρισμού στο ηλεκτρικό δίκτυο,
κλπ) για την ανίχνευση και τον καθορισμό της κατάστασης "Δεν
υπάρχει τάση λειτουργίας" του αντικειμένου που πρόκειται να
δοκιμαστεί, έτσι ώστε να βεβαιωθείτε ότι τάση που εμφανίζει ο
ελεγκτής τάσης είναι πράγματι τάση θορύβου.
Ελεγκτές τάσης που είναι σε θέση να διακρίνουν μέσω
εφαρμογής πρόσθετου φορτίου, την τάση λειτουργίας
από την τάση θορύβου:
Ένας ελεγκτής τάσης με ένδειξη δύο τιμών για την εσωτερική
σύνθετη αντίσταση έχει περάσει τον έλεγχο έκδοσης/ κατασκευής για την καταλληλότητα χειρισμού τάσεων θορύβου και
είναι σε θέση να διακρίνει (εντός των τεχνικών ορίων) την τάση
λειτουργίας από την τάση θορύβου και να εμφανίζει άμεσα ή
έμμεσα τον υφιστάμενο τύπο της τάσης.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
22
Page 23

Ηλεκτρικά σύμβολα πάνω στο όργανο:
Σύμβολο Σημασία
Σημαντικά έγγραφα!
Το σύμβολο αυτό υποδεικνύει ότι ο οδηγός που
περιγράφεται στο εγχειρίδιο, για να αποφευχθούν οι κίνδυνοι
Συσκευή ή εξοπλισμός για την εργασία υπό
τάση
Πιεζοστατικός διακόπτης
AC Εναλλασσόμενη τάση
DC Συνεχής τάση
DC/ AC Συνεχής και εναλλασσόμενη τάση
Γη (τάση προς τη γη)
Πιεζοστατικός διακόπτης (χειροκίνητος)· υποδεικνύει ότι οι αντίστοιχες ενδείξεις γίνονται
μόνο κατά την ενεργοποίηση και των δύο πιεζοστατικών διακοπτών
Δεξιόστροφη διαδοχή· η κατεύθυνσης του περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου εμφανίζεται μόνο στα 50 ή
60 Hz και σε ένα γειωμένο δίκτυο ηλεκτρισμού
Ένδειξη στάθμης κινητού πηνίου
2. Περιγραφή συσκευής
1
Προστατευτικό ακίδων ανιχνευτή
2
Ακίδα L1/-
3
Ακίδα L2/+
4
Ένδειξη στάθμης κινητού πηνίου
5
Πιεζοστατικός διακόπτης
6
Χειρολαβή L1
7
Χειρολαβή με ένδειξη L2
8
Βαθμιδωτή ένδειξη φωτοδιόδων
9
Οθόνη υγρών κρυστάλλων με σύμβολο „R“ για έλεγχο
(Ένδειξη φάσης) και ένδειξη περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου (δε-
ξιά)
J
+/- Φωτοδίοδοι της ένδειξης πολικότητας
3. Λειτουργικός έλεγχος πριν την μεταχείριση για την
εξέταση της ανυπαρξίας τάσης μιας εγκατάστασης
- Να ελέγχετε αν λειτουργεί ο ανιχνευτής τάσης πριν και
μετά από τη χρήση!
- Δοκιμάστε τον ανιχνευτή τάσης σε γνωστές πηγές τάσης,
π.χ. σε μια πρίζα 230 V.
- Μην χρησιμοποιείτε τον ανιχνευτή τάσης, εάν δεν λειτουρ-
γούν άψογα η ένδειξη τάσης, η ένδειξη φάσης και ο κινη-
τήρας δόνησης!
4. Έλεγχος της ανυπαρξίας τάσης μιας εγκατάστασης
(εικόνα A/B)
Κατά τον έλεγχο της εγκατάστασης ελέγξτε την ανυπαρξία
τάσης της εγκατάστασης με έλεγχο της ένδειξης τάσης, της
ένδειξης φάσης (η ένδειξη φάσης λειτουργεί μόνο σε γειωμένο
δίκτυο εναλλασσόμενης τάσης) και του κινητήρα δόνησης ( ο
κινητήρας δόνησης ενεργοποιείται με το πάτημα και των δυο
κομβίων). Η ανυπαρξία τάσης της εγκατάστασης υφίσταται,
εάν όλα τα τρία κυκλώματα ελέγχου σηματοδοτούν ανυπαρξία
τάσης ( Ένδειξη τάσης, ένδειξη φάσης και κινητήρας δόνησης).
- Θέστε τις δύο ακίδες L1/+ 2 και L2/- 3 στα προς έλεγχο
τμήματα της εγκατάστασης.
- Το μέγεθος της προσκείμενης τάσης γνωστοποιείται μέσω
της βαθμιδωτής ένδειξης φωτοδιόδων 8.
- Πιέζοντας και τους δύο πιεζοστατικούς διακόπτες 5, εμ-
φανίζεται στον ανιχνευτή τάσης η ένδειξη στάθμης κινητού
πηνίου 4, η βαθμίδα φωτοδιόδων (+/-) 12 V και ένα εσω-
τερικό φορτίο.
- Η ενδείξεις εναλλασσόμενης τάσης (AC) γίνονται μέσω
ανάμματος των φωτοδιόδων + 24 V και των φωτοδιόδων
- 24 V.
- Η ενδείξεις συνεχούς τάσης (DC) γίνονται μέσω ανάμμα-
τος των φωτοδιόδων + 24 V ή των φωτοδιόδων - 24 V.
Μέσω της ένδειξης πολικότητας J γνωστοποιείται η προ-
σκείμενη στην ακίδα L2/+ 3 πολικότητα + ή -.
- Με σκοπό τη διάκριση ανάμεσα σε χαμηλές και υψηλές
τάσεις (π.χ. χωρητικά συζευγμένες παρασιτικές τάσεις) και
πιέζοντας και τους δύο πιεζοστατικούς διακόπτες, μπορεί
να ενεργοποιηθεί στον ανιχνευτή τάσης ένα εσωτερικό
φορτίο (βλέπε παράγραφο 5).
5. Χειρισμός υπό φορτίο με κινητήρα δόνησης (εικόνα
A/B)
Οι δύο χειρολαβές L1 6 και L2 7 είναι εφοδιασμένες με
πιεζοστατικούς διακόπτες 5. Πιέζοντας και τους δύο πιεζοστατικούς διακόπτες, ενεργοποιείται μια ελάχιστη εσωτερική αντίσταση. Σ' αυτή την περίπτωση τίθεται υπό τάση ένας
κινητήρας ταλαντώσεων (κινητήρας με φορτίο εκτός θέσεως
ισορροπίας). Από τα 200 V περίπου τίθεται αυτός σε περιστροφική κίνηση. Με αυξανόμενη τάση αυξάνεται επίσης ο αριθμός
στροφών και οι ταλαντώσεις του. Η διάρκεια της δοκιμής με
ελάχιστη εσωτερική αντίσταση (δοκιμή φορτίου) εξαρτάται από
το μέγεθος της προς μέτρηση τάσης. Για να μην υπερθερμαίνεται το όργανο, έχει προβλεφτεί μια θερμική προστασία (περιορισμός ρεύματος). Κατά τον περιορισμό ρεύματος μειώνεται
ο αριθμός στροφών του κινητήρα ταλαντώσεων και αυξάνεται
η εσωτερική αντίσταση.
Η ενεργοποίηση φορτίου (πιέζονται και οι δύο πιεζοστατικοί
διακόπτες) μπορεί να χρησιμοποιείται …
- για την καταστολή άεργων τάσεων (επαγωγικές και χωρη-
τικές τάσεις)
- για την εκφόρτιση πυκνωτών
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
23
Page 24

- για την απασφάλιση προστατευτικού διακόπτη RCD
10 mA/ 30 mA. Η απασφάλιση του προστατευτικού δια-
κόπτη RCD πραγματοποιείται μέσω ελέγχου των (Ένδειξη
φάσης) ως προς την αντιτασική προστασία (γη). (εικόνα
D)
6. Έλεγχος (Ένδειξη φάσης) (εικόνα C)
- Περιβάλτε ολόκληρη την επιφάνεια των χειρολαβών L1 6
και L2 7 με την παλάμη σας, για να εξασφαλίσετε μια
χωρητική σύζευξη ως προς τη γη.
- Θέστε την ακίδα L2/+ 3 στο προς έλεγχο τμήμα της εγκα-
τάστασης.
Δώστε προσοχή, ώστε κατά τον έλεγχο της μονοπολικής
(Ένδειξη φάσης) να μην αγγίζεται και να παραμένει άνευ
επαφής η ακίδα L1/- 2.
- Εάν εμφανιστεί στην οθόνη υγρών κρυστάλλων 9 το
σύμβολο „R“, τότε υπάρχει στο τμήμα εγκατάστασης της
φάσης εναλλασσόμενη τάση.
Υπόδειξη:
Ο έλεγχος της μονοπολικής (Ένδειξη φάσης) είναι δυνητικός
σε γειωμένο δίκτυο ηλεκτρισμού με τουλ. 230 V, 50/60 Hz
(φάση ως προς τη γη). Προστατευτικός ρουχισμός και ηλεκτρομονωτικές συνθήκες στη θέση εγκατάστασης μπορούν να
επηρεάζουν τη λειτουργία.
Προσοχή!
Το εάν υπάρχει τάση ή όχι, εξακριβώνεται μόνο με μια δοκιμή
και των δύο πόλων.
7. Έλεγχος περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου (εικόνα E/F)
- Περιβάλτε ολόκληρη την επιφάνεια των δύο χειρολαβών
L1 6 και L2 7 με την παλάμη σας, για να εξασφαλίσετε
μια χωρητική σύζευξη ως προς τη γη.
- Θέστε τις ακίδες L1/- 2 και L2/+ 3 σε δύο φάσεις ενός
τριφασικού δικτύου ηλεκτρισμού και ελέγξτε αν είναι η
τάση φάσεως π.χ. 400 V.
- Μια δεξιόστροφη διαδοχή (φάση L1 πριν από τη φάση
L2) είναι δεδομένη, όταν εμφανιστεί στην οθόνη υγρών
κρυστάλλων 9 το σύμβολο „R“. Εάν δεν ανιχνευτεί καμία
δεξιόστροφη διαδοχή, τότε παραμένει η οθόνη υγρών κρυ-
στάλλων σβηστή.
- Η δοκιμή περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου προϋποθέτει πάντα
έναν αντιέλεγχο! Δείχνει η οθόνη υγρών κρυστάλλων τη
δεξιόστροφη διαδοχή μέσω του συμβόλου „R“, τότε πρέ-
πει να παραμένει η οθόνη υγρών κρυστάλλων κατά τον
αντιέλεγχο με ανταλλαγή των ακίδων L1/- 2 και L2/+ 3
σβηστή.
Δείχνει η οθόνη υγρών κρυστάλλων και στις δύο περιπτώ-
σεις το σύμβολο „R“, τότε υπάρχει μια πολύ ασθενή γείω-
ση.
Υπόδειξη:
Η δοκιμή περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου είναι δυνητική σε γειωμένο
τριφασικό δίκτυο ηλεκτρισμού με τουλ. 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz
(φάση ως προς τη φάση). Προστατευτικός ρουχισμός και ηλεκτρομονωτικές συνθήκες στη θέση εγκατάστασης μπορούν να
επηρεάζουν τη λειτουργία.
8. Τεχνικά στοιχεία
- Προδιαγραφή: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Εύρος ονομαστικής τάσης: 12 V έως AC/DC 1.000 V
- Φάσμα ονομαστικής συχνότητας f: 0 έως 60 Hz
- Μεγ. λάθος ένδειξης: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0 % - 15 %
- Σύνθετη αντίσταση (εσωτερική αντίσταση) κύκλωμα με-
τρήσεων/ κύκλωμα φορτίου: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Απαίτηση σε ηλεκτρικό ρεύμα Κύκλωμα μετρήσεων:
Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Απαίτηση σε ηλεκτρικό ρεύμα Κύκλωμα φορτίου:
Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Ένδειξη πολικότητας: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V
LED, - 12 V LED (με ενεργοποιημένους πιεζοστατικούς
διακόπτες)
- Δοκιμή εξωτερικού αγωγού (Ένδειξη φάσης): ≥ Un 230 V,
50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Δοκιμή περιστρεφόμενου πεδίου: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Κινητήρας ταλαντώσεων, εκκίνηση: ≥ Un 230 V
- Κατηγορία υπέρτασης: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Είδος προστασίας: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN
60529)
6 - πρώτος κωδικός αναγνώρισης: προστασία έναντι πρό-
σβασης σε επικίνδυνα τμήματα και προστασία έναντι στε-
ρεών ξένων σωμάτων, στεγανότητα σκόνης
5 - δεύτερος κωδικός αναγνώρισης: προστασία έναντι πί-
δακα νερού. Μπορεί να χρησιμοποιείται και στη βροχή.
- max. επιτρεπόμενη Κύκλος: 30 s (έως 30 δευτερόλεπτα),
600 s off
- Βάρος: 250 γρ. περίπου
- Μήκος καλωδίου σύνδεσης: 1000 χιλ. περίπου
- Διακύμανση θερμοκρασίας λειτουργίας και αποθήκευσης:
- 20 °C έως + 45 °C (κατηγορία κλίματος N)
- Σχετική υγρασία ατμόσφαιρας: 20 % έως 96 % (κατηγορία
κλίματος N)
- Χρόνος περιορισμού ρεύματος (θερμική προστασία):
τάση/χρόνος:
9. Γενική συντήρηση
Καθαρίζετε το περίβλημα μόνο με ένα καθαρό, στεγνό πανί.
10. Προστασία περιβάλλοντος
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Παρακαλώ παραδώστε τη συσκευή μετά το τέλος του
κύκλου ζωής της στα ευρισκόμενα στη διάθεσή σας
συστήματα συλλογής και επιστροφής.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
24
Page 25

H
DUSPOL® analog 1000
használati utasítás
Mielőtt megkezdené a DUSPOL® analog 1000 feszültségvizs-
gáló használatát: olvassa el a használati utasítást és okvetlenül tartsa a biztonsági tudnivalókat!
Tartalomjegyzék
1. Biztonsági tudnivalók
2. A készülék leírása
3. A használatba vétel előtti felülvizsgálat során a beren-
dezés árammentességének vizsgálata
4. A berendezés árammentességének vizsgálata
5. Terhelés csatlakozó vibrációs motorral
6. Fáziskijelzőellenőrzés
7. Fázissorrendellenőrzés
8. Műszaki adatok
9. Általános karbantartás
10. Környezetvédelem
1. Biztonsági tudnivalók:
- A készüléket a használat során csak a 6 L1 és 7 L2
markolatoknál fogva tartsa és ne érintse meg a 2 L1/- és
a 3 L2/+ mérőtüskéket!
-
Közvetlenül a használatbavétel előtt, majd azt követően, a
berendezés árammentességének ellenőrzése érdekében
vizsgáljuk meg, működik-e a feszültségmérő (ld. a 3 feje-
zetet)! A feszültségvizsgálót nem szabad használni, ha egy
vagy több kijelzés működése hiányzik vagy nincs látható
működőképesség! A vizsgálatot ezután egy másik feszült-
ségmérővel is meg kell ismételni.
- A feszültségvizsgálót csak a megadott névleges feszült-
ségtartományban és max. 1000 V -os egyen és váltakozó
áramú elektromos berendezéseknél szabad alkalmazni!
- A feszültségvizsgálót csak max. 1000 V-os CAT III túl-
feszültség-kategóriás vagy 600 V-os CAT IV túlfeszült-
ség-kategóriás áramkörök vezetékeinél szabad a földdel
szemben használni.
- A feszültségvizsgáló villamos szakemberek által történő
alkalmazásra biztonságos munkavégzési eljárásokhoz
van kialakítva.
- A LED-fokozatjelző a feszültségtartomány kijelzésére
szolgál, s nem szolgál mérési célokra .
- Létrehozása feszültségvizsgáló több, mint 30 másodper-
cig feszültség (max. megengedett bekapcsolási időtartam
ED = 30 s)!
- A feszültségvizsgálót nem szabad szétszerelni!
- A feszültségvizsgáló óvni kell szennyeződésektől és a ké-
szülékház felületének sérüléseitől.
- Sérülések elleni védelemként a feszültségvizsgáló hasz-
nálata után a mérőtüskéket a mellékelt 1 csúcsvédővel
kell ellátni!
- Vegye figyelembe, hogy a feszültség-ellenőrző impedan-
ciája (belső ellenállás) befolyásolja a zavarófeszültségek
kijelzését (kapacitív vagy induktív bekerítéssel)!
A feszültség-ellenőrző belső impedanciájától függően zavarófeszültségek fellépése esetén különböző kijelzési lehetőségek
vannak, "Üzemi feszültség fennáll" vagy "Üzemi feszültség
nem áll fenn".
Alacsony ellenállású feszültségellenőrző (impedancia
< 100 kΩ) zavarófeszültség el lesz nyomva ill. le lesz csökkentve:
Egy relatív alacsony belső impedanciájú feszültség-ellenőrző
a 100 kΩ referencia-értékhez képest nem fog minden zavaró-
feszültséget kijelezni ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V DC) feletti eredeti
érték esetén. Az ellenőrzendő alkatrészekkel való érintkezés
esetén a feszültség-ellenőrző kisülés miatt átmenetileg az ELV
alatti szintig csökkenhet; a feszültség-ellenőrző eltávolítása
után a zavarófeszültség vissza fogja venni az eredeti értékét.
Ha nem jelenik meg a "Feszültség van" kijelzés, akkor haladéktalanul érdemes a munka felvétele előtt a földelő berendezést behelyezni.
Nagy ellenállású feszültségellenőrző (impedancia
> 100 kΩ): A zavarfeszültség nem lesz elnyomva ill. csökkentve:
Egy relatív magas belső impedanciájú feszültség-ellenőrző a
100 kΩ referencia-értékhez képest meglévő zavarófeszültség
esetén - "Üzemi feszültség nincs" - nem fog egyértelműen
kijelezni. Ha a "Feszültség van" kijelzés egy résznél megje-
lenik, amely a berendezéstől leválasztottnak minősül, akkor
haladéktalanul érdemes kiegészítő intézkedésekkel (például:
alkalmas feszültség-ellenőrző használata, amely képes kü-
lönbséget tenni az üzemi feszültség és a zavarófeszültség
között, a megszakító hely szemrevételezése az elektromos
hálózatban stb.) az ellenőrzendő alkatrész esetén az "Üzemi
feszültség nincs" állapotot igazolni és megállapítani, hogy a
feszültség-ellenőrző által kijelzett feszültség zavarófeszültség.
Azok feszültségellenőrzők, amelyek képesek teherhozzákapcsolással megkülönböztetni az üzemi feszültséget a
zavarófeszültségtől:
Olyan feszültség-ellenőrző, amely a belső impedancia két értékét adja meg, megfelelt a zavarófeszültségek kezelésével
kapcsolatban a kivitelezése / szerkezete vizsgálatának, és (a
műszaki határokon belül) képes különbséget tenni az üzemi
feszültség és a zavarófeszültség között, valamint a meglévő
feszültségtípust közvetlenül vagy közvetetten megjeleníteni.
A készüléken található elektromos piktogramok
Ikon Jelentés
Fontos dokumentációt!
A szimbólum azt jelzi, hogy az útmutatóban leírt
kézikönyv, a kockázatok elkerülése érdekében
Készülék vagy felszerelés feszültség alatti
munkához
Nyomógomb
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
25
Page 26

H
AC váltakozó feszültség
DC egyenfeszültség
DC/AC egyen- és váltakozó feszültség
Föld (feszültség a földhöz)
Nyomógomb (kézi); arra gyelmeztet, hogy az
adott kijelzések csak mindkét nyomógomb mű-
ködtetésére történnek meg
Jobbos fázissorrend; a fázis-forgásirányt csak
50 ill. 60 Hz és földelt hálózat esetén lehet kijelezni
Lengőtekercses szintkijelző
2. A készülék leírása
1
Mérőtüske-védő
2
L1/- mérőtüske
3
L2/+ mérőtüske
4
Lengőtekercses szintkijelző
5
Nyomógombok
6
L1 markolat
7
L2 kijelzős markolat
8
LED-es fokozatkijelző
9
Folyadékkristályos display „R“ ikonnal a fáziskijelző-vizs-
gálat és a fázissorrend -kijelzéshez (R=jobbraforgó)
J
A Polaritás-kijelzés +/- LED-jei
3. A használatba vétel előtti felülvizsgálat során a beren-
dezés árammentességének vizsgálata
- Közvetlenül a használat előtt és után ellenőrizze le a fe-
szültségvizsgáló működését!
- Ellenőrizze le a feszültségvizsgálót ismert feszültségforrá-
sokon, pl. egy 230 V-os dugaljon.
- A használatba vétel előtti felülvizsgálat során a berende-
zés árammentességének vizsgálata
4.
A berendezés árammentességének vizsgálata (A/B kép)
A berendezés felülvizsgálatakor vizsgálja meg, hogy a
berendezés árammentes-e: ellenőrizze a feszültségmutatót,
a fáziskijelzőt (a fáziskijelző kizárólag földelt váltóáramos
hálózatban működik) és a vibrációs motort (a vibrációs motor
mindkét nyomókapcsoló gomb egyidejű megnyomásával
aktiválható). A berendezés kizárólag abban az esetben
árammentes, ha mindhárom vizsgálati kör árammentességet
jelez (a feszültségmutató, a fáziskijelző és a vibrációs motor
egyaránt).
- Tegye rá a 2 L1/+ és a 3 L2/- mérőtüskét a vizsgálandó
berendezés-részekre.
- A rajtuk lévő feszültséget a 8 LED-fokozatkijelző mutatja.
- A két 5 nyomógomb megnyomására bekapcsolódik a 4
lengőtekercses szintkijelző, a 12 V-os LED-fokozat (+/ -),
valamint egy belső terhelés a feszültségvizsgálóban.
- A váltakozó feszültségek (AC) kijelzése a + 24 V LED és
a - 24 V LED egyidejű világításával történik.
- Az egyenfeszültségek (DC) kijelzése vagy a + 24 V LED
vagy - 24 V LED világításával történik. A J polaritás-kijel-
ző útján történik a 3 L2/+ mérőtüskén lévő + vagy - pola-
ritás kijelzése.
- Az energiagazdag és energiaszegény feszültségek (pl.
kapacitíve bekapcsolódott zavarfeszültségek) megkülön-
böztetése céljából mindkét nyomógomb megnyomásával
egy feszültségvizsgálón belüli terhelést lehet rákapcsolni
(lásd 5. fejezet)
5. Terhelés csatlakozó vibrációs motorral (A/B kép)
A két 6 L1 és 7 L2 markolat egy-egy 5 nyomógombbal van
ellátva. A két nyomógomb megnyomására egy kis belső ellenállára kapcsolunk. Ugyanekkor feszültséget adunk egy rezgő-
motorra (kiegyensúlyozatlan röpsúlyos motor). Kb. 200 V-tól
kezdve ez forgásba jön. Növekvő feszültséggel növekszik
ennek fordulatszáma és rezgése is. A kis belső ellenállással
történő vizsgálat (terheléses vizsgálat) időtartama a mérendő
feszültség nagyságától függ. A készülék meg nem engedett
melegedésének elkerülésére egy hővédelem (visszaszabályozás) szolgál. E visszaszabályozás során a rezgőmotor fordulatszám csökken, a belső ellenállás pedig megnő.
A terheléses kapcsolás (mindkét nyomógomb megnyomva) a
következőkre használható:
- Reaktív feszültségek (induktív és kapacitív feszültségek)
elnyomására
- kondenzátorok kisütésére
- 10/30 mA-es hibaáram-védőkapcsolók kioldására. A hiba-
áram-védőkapcsolók kioldása a fáziskijelző földdel (PE)
szembeni vizsgálatával történik. (D kép)
6. Fáziskijelző vizsgálat (C kép)
- Fogja át teljes felületén a 6 L1 és 7 L2 markolatokat
hogy kapacitív csatolást biztosítson a földdel szemben.
- Tegye rá a 3 L2/+mérőtüskét a vizsgálandó berendezés-
részre.
Okvetlenül ügyeljen arra, hogy egypólusos fáziskijelző-
vizsgálat esetén a 2 L1/- mérőtüskét ne érintse és ez
kontaktusmentes maradjon.
- Ha a 9 folyadékkristályos kijelző egy „R“ ikon jelenik
meg, a fázisvezeték ezen berendezésrészén váltakozó
feszültség van.
Megjegyzés:
Az egypólusos fáziskijelző-vizsgálat földelt hálózatban 230 V,
50/60 Hz (fázis a földdel szemben) feszültségtől lehetséges.
Védőburkolat ás szigetelő helyi adottságok hátrányosan befo-
lyásolhatják a funkciót.
Figyelem!
Feszültségmentességet csak kétpólusos vizsgálattal lehet
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
26
Page 27

I
megállapítani.
7. Fázissorrendvizsgálat (E/F kép)
- Fogja át teljes felületén a 6 L1 és 7 L2 markolatokat
hogy kapacitív csatolást biztosítson a földdel szemben.
- Tegye a 2 L1/- és a 3 L2/+ mérőtüskét egy váltakozó
áramú hálózat két fázisára és ellenőrizze, hogy megvan-e
a kb. 400 V-os vonalfeszültség.
- Jobbos (azaz L1 fázis az L2 fázis előtt) fázissorrend van
akkor, ha a 9 folyadékkristályos kijelzőn egy „R“ ikon jele-
nik meg. A folyadékkristályos kijelző sötét marad, ha nem
lehetett jobbos fázissorrendet érzékelni.
- A fázissorrend-vizsgálatnál mindig ellenpróbát kell végez-
ni! Ha a 9 folyadékkristályos kijelző jobbos fázissorrendet
jelez az „R“ ikon útján, akkor a felcserélt 2 L1/- és 3
L2/+mérőtüskékkel végzett ellenpróbánál a folyadékkris-
tályos kijelzőnek sötéten kell maradnia.
Amennyiben a folyadékkristályos kijelző mindkét esetben
„R“-ikont mutat, akkor túl gyenge a földelés.
Megjegyzés:
A fázissorrend-vizsgálat földelt hálózatban 400 V - 900 V,
50/60 Hz (fázis a földdel szemben) feszültségtől lehetséges.
Védőburkolat ás szigetelő helyi adottságok hátrányosan befo-
lyásolhatják a funkciót.
8. Műszaki adatok
- Előírás: DIN EN 61243 -2: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Névleges feszültségtartomány: 12 V - AC/DC 1.000 V
- Névleges frekvenciatartomány f: 0 - 60 Hz
- Max. kijelzési hiba: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0 % - 15 %
- Mérőkör/ terheléskör, impedancia (belső ellenállása):
200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Mérőkör áramfelvétele: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Terheléskör áramfelvétele: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polaritás-kijelzés: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (nyomógomb-lenyomás esetén)
- Fáziskijelző: ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Fázissorrend vizsgálat: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Rezgőmotor, indulás: ≥ Un 200 V
- Túlfeszültség-kategória: CAT IV. 600 V, CAT III. 1000 V
- Védelmi fokozat: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - os első jelzőszám: Védelem veszélyes részekhez valló
hozzáférés ellen és védelem szilárd idegen testek ellen,
portömör.
5 - ös második jelzőszám: Védett vízsugár ellen. Csapa-
dék esetén is használható.
- max. megengedett Terhelhetőség: 30 s (max. 30 másod-
perc), 600 s off
- Tömeg: kb. 250 g
- Összekötő vezeték hossz: kb. 1.000 mm
- Üzemi és raktározási hőmérséklettartomány: - 20 °C -
+ 45 °C (N klímakategória)
- Relatív légnedvesség: 20% - 96% (N klímakategória)
- Visszaszabályozási idők (hővédelem):
feszültség/ idő:
9. Általános karbantartás
Tiszta, száraz kendővel tisztogassa kívül a készülékházat.
10. Környezetvédelem
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Kérjük vigye a készüléket élettartamának végén a
rendelkezésre álló visszavételi és gyűjtőrendszerekbe.
Istruzioni per l‘uso
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Prima di utilizzare l’indicatore di tensione DUSPOL® analog
1000, si prega di leggere attentamente le istruzioni per l’uso e
di osservare assolutamente le indicazioni di sicurezza!
Indice
1. Indicazioni di sicurezza
2. Descrizione dell’apparecchio
3. Prova di funzionamento prima dell'uso per verificare
l'assenza di tensione di un impianto
4. Verifica dell'assenza di tensione di un impianto
5. Connessione addizionale di carica con motore a
vibrazione
6. Controllo della indicatore di fase
7. Controllo del campo rotante
8. Dati tecnici
9. Manutenzione generale
10. Protezione dell’ambiente
1. Indicazioni di sicurezza:
- In occasione dell’esecuzione dell’uso afferrare l’apparec-
chio tenendolo esclusivamente per le impugnature isolate
L1 6 e L2 7 e non toccare mai le punte di controllo L1/-
2
e L2/+ 3!
-
Immediatamente prima e dopo l’uso, per verificare se l’im-
pianto è privo di tensione, controllare il buon funzionamen-
to del controllore di tensione! (vedi capitolo 3)! L’indicatore
di tensione non può essere utilizzato quando uno o più
indicatori non funzionano oppure quando non è possibile
constatare la perfetta funzionalità dell’apparecchio! Il con-
trollo deve poi essere ripetuto con un altro controllore di
tensione.
- Questo indicatore di tensione può essere impiegato esclu-
sivamente nel settore di tensione nominale indicato e per
impianti elettrici fino a AC/DC 1.000 V!
- Questo indicatore di tensione può essere utilizzato esclu-
sivamente in circuiti elettrici della categoria di sovratensio-
ne CAT III con al massimo 1000 V oppure in circuiti elettrici
della categoria di sovratensione CAT IV con al massimo
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
27
Page 28

I
600 V – conduttore verso terra.
- Questo indicatore di tensione è stato progettato per esse-
re impiegato da parte di elettricisti specializzati, nell’ambi-
to di procedure di lavoro che garantiscono la sicurezza.
- L’indicatore LED con livelli serve ad indicare il settore di
tensione e non è utilizzabile per scopi di misurazione.
- Creazione di un tester di tensione per più di 30 secondi di
tensione (duty cycle massimo)
- L’indicatore di tensione non può essere disassemblato!
- L’indicatore di tensione deve essere protetto dalle impurità
e dai danneggiamenti alla superficie del suo involucro.
- A scopo protezione dagli infortuni, dopo l’impiego dell’indi-
catore di tensione, sulle punte di controllo deve essere ap-
plicata l’apposita protezione 1 compresa nella fornitura!
- Si prega di tener presente che l'impedenza (resistenza
interna) del voltmetro influenza il valore visualizzato sul
display a causa di tensioni di disturbo (accoppiamento ca-
pacitivo o induttivo)!
In presenza di tensioni di disturbo, a seconda dell'impedenza
interna del voltmetro, può indicare "Tensione di esercizio presente" o "Tensione di esercizio non presente".
Voltmetro bassa resistenza (Impedenza < 100 kΩ), la tensio-
ne di disturbo viene soppressa o ridotta:
Un voltmetro con impedenza interna relativamente bassa ri-
spetto al valore di riferimento di 100 kΩ, non visualizza tutte
le tensioni di disturbo con un valore originario al di sopra di
ELV (50 V CA/ 120 V CC). A contatto con le parti da testare il
voltmetro può ridurre le tensioni di disturbo scaricando no a
un livello inferiore di ELV; dopo aver staccato il voltmetro viene
di nuovo rilevata la tensione di disturbo del valore originale.
Se non viene visualizzata la scritta "tensione presente", si consiglia di inserire il dispositivo di messa a terra prima di iniziare
il lavoro.
Voltmetro alta resistenza (Impedenza > 100 kΩ): La tensione
di disturbo non viene soppressa nè ridotta:
Un voltmetro con impedenza interna relativamente alta ri-
spetto al valore di riferimento di 100 kΩ, chiaramente non
visualizza, in caso di tensione di disturbo, la scritta "Tensione di esercizio non presente". Se il display mostra "tensione
presente" riferendosi ad un componente separato dal sistema,
si consiglia vivamente, con ulteriori provvedimenti (esempio:
Usare un voltmetro adatto in grado di distinguere tra tensione
di esercizio e tensione di disturbo, controllare visivamente i
punti di sconnessione nella rete elettrica, ecc.) di vericare lo
stato "tensione di esercizio non presente" della parte da testare, in modo che la tensione visualizzata dal voltmetro sia una
tensione di disturbo.
Voltmetro in grado di distinguere fra la tensione applicata
al carico e la tensione di disturbo:
Il voltmetro con indicazione di due valori dell'impedenza interna ha superato la prova per il trattamento di tensioni di disturbo
ed è in grado (entro i limiti tecnici) di distinguere tra tensione di
esercizio e tensione di disturbo e di visualizzare direttamente
o indirettamente il tipo di tensione esistente.
Simboli elettrici sull‘apparecchio:
simbolo signicato
Documentazione Importante!
Il simbolo indica che la guida descritta nel
manuale, per evitare qualsiasi rischio
apparecchio o equipaggiamento per lavori sotto
tensione
pulsante
AC – tensione alternata
DC – tensione continua
DC/AC – tensione continua e tensione alternata
Terra (tensione a massa)
Indicazione della direzione del campo rotante:
la direzione del campo rotante può essere indicata solo in presenza di 50 - 60 Hz ed in una
rete collegata a massa
Indicatore di livello con bobina mobile
2. Descrizione dell‘apparecchio
1
Protezione per le punte di controllo
2
Punta di controllo L1/-
3
Punta di controllo L2/+
4
Indicatore di livello con bobina mobile
5
Pulsante
6
Impugnatura L1
7
Impugnatura con display L2
8
Indicatore LED con livelli
9
Display LC con simbolo “R” per il controllo della indicatore
di fase e l’indicazione del campo rotante (destrorso)
J
+/- LED dell’indicatore di polarità
3. Prova di funzionamento prima dell’uso per verificare
l’assenza di tensione di un impianto
- Verificare la funzionalità dell’indicatore di tensione imme-
diatamente prima e dopo averlo impiegato!
- Eseguire il test di controllo del funzionamento presso sor-
genti di tensione conosciute, per esempio una presa di
corrente da 230 V
- Non usare il controllore di tensione se l’indicatore di ten-
sione, l’indicatore di fase e il motore a vibrazione non fun-
zionano correttamente!
4. Verifica dell'assenza di tensione di un impianto (Figura
A/B)
In occasione del controllo dell'impianto, controllare l'assenza
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
28
Page 29

I
di tensione dell'impianto controllando l'indicatore di tensione,
l'indicatore di fase (l'indicatore di fase funziona solo nella
rete a corrente alternata a terra) e il motore a vibrazione (il
motore di vibrazione si attiva premendo entrambi i pulsanti).
L'impianto è privo di tensione solo quando tutti e tre i circuiti
di prova indicano assenza di tensione (indicatore di tensione,
indicatore di fase e motore a vibrazione).
- Collegare entrambe le punte di controllo L1/+ 2 e L2/- 3
alle parti dell’impianto che devono essere controllate
- L’entità della tensione esistente viene indicata per mezzo
dell’indicatore LED con livelli 8.
- Premendo entrambi i pulsanti 5 vengono azionati anche
l’indicatore di livello con bobina mobile 4 ed il livello LED
da 12 V (+/-) e può inoltre essere connesso un carico in-
terno nell’indicatore di tensione.
- Le tensioni alternate (AC) vengono visualizzate per mezzo
dell’illuminazione contemporanea del LED + 24 V e del
LED - 24 V.
- Le tensioni continue (DC) vengono visualizzate per mezzo
dell’illuminazione del LED + 24 V oppure del LED - 24 V.
Per mezzo dell’indicatore di polarità J viene indicata la
polarità + oppure - esistente presso la punta di controllo
L2/+ 3.
- Allo scopo di distinguere fra tensioni ricche e povere di
energia (per esempio tensioni di disturbo provocate da ac-
coppiamenti capacitivi), premendo contemporaneamente
i due pulsanti. è possibile connettere un carico interno
nell’indicatore di tensione (vedi punto 5)
5. Connessione addizionale di carica con motore a vibra-
zione (Figura A/B)
Entrambe le impugnature L1 6 e L2 7 sono equipaggiate
con pulsanti 5. Premendo entrambi i pulsanti viene commutata una resistenza interna ridotta. In quest’occasione viene
applicata tensione su di motore vibrante (vibrodina). A partire
da una tensione di circa 200 V questo motore inizia a ruotare.
Quando la tensione aumenta, aumentano anche il regime e le
vibrazioni del motore. La durata del controllo con resistenza
interna ridotta (controllo del carico) dipende dall’entità della
tensione da misurare. Afnchè l’apparecchio non si surriscaldi
in misura maggiore rispetto ai valori consentiti, è stata progettata una protezione termica (regolazione di ritorno). Grazie a
questa regolazione di ritorno il regime del motore vibrante si
riduce e la resistenza interna aumenta.
La connessione di carico (entrambi i pulsanti sono premuti)
può essere utilizzata per:
- eliminare le tensioni reattive (tensioni induttive e capaciti-
ve)
- scaricare condensatori
- azionare interruttori di sicurezza per correnti di guasto da
10/30 mA. L’azionamento dell’interruttore di sicurezza per
correnti di guasto avviene per mezzo del controllo della
indicatore di fase verso PE (massa). (figura D)
6. Controllo della indicatore di fase (Figura C)
- Afferrare le impugnature L1 6 e L2 7 in corrispondenza
della loro superficie complessiva allo scopo di garantire un
accoppiamento capacitivo verso massa.
- Applicare la punta di controllo L2/+ 3 alla parte dell’im-
pianto da controllare. In quest’occasione assicurarsi as-
solutamente che nel corso del controllo unipolare della
indicatore di fase la punta di controllo L1/- 2 non venga
toccata e che essa rimanga quindi priva di contatto.
- Quando sul display LC 9 viene visualizzato un simbolo
“R“, significa che in questa parte dell’impianto è presente
la fase di una tensione alternata.
Indicazione:
Il controllo unipolare della indicatore di fase è possibile in una
rete collegata a massa a partire da 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fase verso terra). Gli indumenti protettivi ed i dispositivi di isolamento
installati nel luogo in cui avviene il controllo possono pregiudicare questa funzione.
Attenzione!
Un’eventuale assenza di tensione può essere constatata
esclusivamente per mezzo di un controllo bipolare.
7. Controllo del campo rotante (Figura E/F)
- Afferrare le impugnature L1 6 e L2 7 in corrispondenza
della loro superficie complessiva allo scopo di garantire un
accoppiamento capacitivo verso massa.
- Applicare le punte di controllo L1/- 2 e L2/+ 3 presso
due fasi di una rete a corrente trifase e verificare se esiste
una tensione di fase, per esempio di 400 V.
- Una sequenza di rotazione destrorsa (fase L1 prima della
fase L2) esiste quando sul display LC 9 viene visualizza-
to un simbolo “R”. Il display LC resta spento quanto non è
stata riconosciuta l’esistenza di alcuna sequenza di rota-
zione destrorsa.
- Il controllo del campo rotante richiede sempre l’esecuzio-
ne di una controprova! Quando il display LC segnala l’esi-
stenza di una sequenza di rotazione destrorsa per mezzo
del simbolo “R”, in occasione della controprova eseguita
con le punte di controllo L1/- 2 e L2/+ 3 scambiate, il
display LC deve rimanere spento.
Quando sul display LC viene visualizzato in entrambi i casi
un simbolo “R”, il collegamento a massa è troppo debole.
Indicazione:
Il controllo del campo rotante è possibile in una rete trifase
collegata a massa a partire da 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (fase
verso fase). Gli indumenti protettivi ed i dispositivi di isolamento installati nel luogo in cui avviene il controllo possono pregiudicare questa funzione.
8. Dati tecnici
- Prescrizioni: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Settore di tensione nominale: 12 V fino a AC/DC 1.000 V
- Settore di frequenza nominale f: 0 - 60 Hz
-
Errore d’indicazione massimo: Un ±15 %, ELV Un +0% -15%
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
29
Page 30

N
- Impedenza (resistenza interna), circuito di misurazione/
circuito di carico: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Circuito di misurazione corrente assorbita: Is < 6,0 mA
(1.000 V)
- Circuto di carico potenza assorbita: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Indicazione della polarità: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V
LED, - 12 V LED (quando i pulsanti sono premuti)
- Controllo della indicatore di fase: ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Controllo del campo rotante: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Avviamento del motore vibrante: ≥ Un 200 V
- Categoria di sovratensione: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III
1000 V
- Tipo di protezione: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 – prima cifra indicativa: protezione contro l’accesso a
parti pericolose e protezione contro corpi estranei solidi,
impermeabile alla polvere.
5 – seconda cifra indicativa: protetto dai getti d’acqua. Uti-
lizzabile anche in caso di precipitazioni.
-
max. Duty ammissibile ciclo: 30 s (max. 30 secondi), 240 s off
- Durata massima di attivazione in caso di azionamento dei
pulsanti:
ED = 30 s (max. 30 secondi), 240 s di pausa
- Peso: ca. 250 g
- Lunghezza delle linee di collegamento: ca. 1000 mm
- Settore della temperatura di esercizio e di immagazzina-
mento: da - 20 °C a + 45 °C (categoria climatica N)
- Umidità relativa dell’aria: dal 20 % al 96 % (categoria cli-
matica)
- Tempi della regolazione di ritorno (protezione termica):
tensione/tempo: 230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
9. Manutenzione generale
Pulire l’involucro all’esterno per pezzo di un panno pulito ed
asciutto.
10. Protezione dell’ambiente
Alla ne del periodo di durata utile dell’apparecchio
si prega di portarlo presso i centri di restituzione e
raccolta esistenti.
Bruksanvisning
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Før du tar spenningsindikatoren DUSPOL® analog 1000 i bruk:
Les bruksanvisningen, og alle sikkerhetsanvisningene!
Innholdsfortegnelse
1. Sikkerhetsanvisninger
2. Apparatbeskrivelse
3. Funksjonstest før bruk for å teste at det ikke er noen
spenning i anlegget
4. Funksjonstest for å teste at det ikke er noen spenning
i systemet
5. Driftstilkobling med vibrasjonsmotor
6. Ytterledertesting (faseindikator)
7. Dreifelttesting
8. Tekniske data
9. Generelt vedlikehold
10. Miljøvern
1. Sikkerhetsanvisninger:
- Hold alltid apparatet i de isolerte håndtakene L1 6 og L2
7
under bruken, og ikke berør testspissene L1/- 2 og
L2/+ 3!
- Umiddelbart før bruk må man bruke spenningsmåleren for
å kontrollere spenningen i systemet, og fravær av spen-
ning etter bruk (se avsnitt 3)! Spenningsindikatoren må
ikke brukes hvis en eller flere av visningene ikke fungerer,
eller det ikke kan fastlegges at apparatet er klart til bruk.
Kontrollen gjentas da med en annen spenningsmåler.
- Spenningsindikatoren må kun brukes innenfor det angitte
merkespenningsområdet og i elektriske anlegg på opp til
AC/DC 1.000!
- Spenningsindikatoren må kun brukes i strømkretser med
overspenningskategori CAT III med maks. 1000 V eller
overspenningskategori CAT IV med maks 600 V jordleder.
- Spenningsindikatoren er beregnet på bruk av faglærte
elektrikere, og under overholdelse av regler for sikre ar-
beidsmetoder.
- LED-nivåvisningene brukes til å vise spenningsområdet,
og er ikke ment for målingsformål.
- Opprette en spenning tester for mer enn 30 sekunder
spenning (maksimal innkoblingsvarighet = 30 s)
- Spenningsindikatoren må ikke tas fra hverandre!
- Beskytt spenningsindikatoren mot smuss og skader på
overflaten.
- Sett på den medfølgende testpissbeskytteren 1 på test-
spissen etter bruk av spenningsindikatoren, for å beskytte
mot personskader!
- Vær oppmerksom på påvirkende impedans (indre mot-
stand) av spenningstesteren som viser interferensspen-
ning (kapasitivt eller induktivt koplet)!
Avhengig av den interne impedansen til spenningstesteren,
nnes det i nærvær av støyspenning ulike alternativer som viser «driftsspenning tilstede» eller «driftsspenning nnes ikke».
Spenningstestere for lav impedans (Impedans < 100 kΩ),
forstyrrelsespenning er undertrykt eller redusert:
En spenningstester med forholdsvis lav indre impedans blir
sammenlignet med referanseverdien 100 kΩ, og viser ikke alle
støyspenninger med ett startverdi over ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V
DC). Ved kontakt med de delene som skal testes kan spenningstesteren temporært redusere interferensspenning ved
utladning til et nivå under ELV; etter fjernelse av spenningstestere vil interferensspenning anta dens opprinnelige verdi igjen.
Når «spenning til stede» ikke vises, er det sterkt anbefalt at du
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
30
Page 31

N
setter jordingsenheten før du starter arbeidet.
Spenningtestere for høy impedans (Impedans > 100 kΩ):
Forstyrrelsespenning er ikke undertrykt eller redusert:
En spenningstester med relativt høy indre impedans vises
ikke klart i forhold til referanseverdien på 100 kΩ eksisterende
forstyrrelsespenning «driftsspenning til stede». Når «spenning
til stede» vises på en del som gjelder separat i anlegget, er
det sterkt anbefalt med ytterligere tiltak (eksempel: Ved hjelp
av en passende spenningstester av stand til driftsspenning
for forstyrrelser for spenning er forskjellig, visuell inspeksjon
av separasjonspunkt i det elektriske nettverket, etc.) «Ingen
driftsspenning» av den del som skal testes for å påvise og bestemme at spenningen som indikeres av spenningstesteren er
en interferensspenningstilstand.
Spenningstestere som er i stand til å skille av lasten, som
opererer spenning for forstyrrelsespenning:
En spenningstester med angivelse av de to verdiene i den
indre impedansen har bestått testen av utformingen/ konstruksjon av behandlingen av støyspenninger, og må skilles
(innenfor de tekniske begrensninger) i stand til driftsspenning
for interferensspenning og fremvise den eksisterende spenningstypen direkte eller indirekte.
Elektriske symboler på apparatet:
Symbol Betydning
Viktig dokumentasjon!
Symbolet angir at guiden er beskrevet i
håndboken, for å unngå eventuelle risikoer
Apparat eller utstyr under spenning under ar-
beidet
Trykknapp
AC vekselstrøm
DC likestrøm
DC/AC likestrøm og vekselstrøm
Earth (spenning til jord)
Trykknapp (betjenes manuelt). Henviser til at
de tilhørende visningene kun vises når man
trykker på begge trykknappene
Dreieretning. Dreiefeltretningen kan kun vises i
et jordet nett på 50/60 Hz
Svingspolenivåvisning
2. Apparatbeskrivelse
1
Testspissbeskyttelse
2
Testspiss L1/-
3
Testspiss L2/+
4
Svingspolenivåvisning
5
Trykknapp
6
Håndtak L1
7
Visningshåndtak L2
8
LED-nivåvisning
9
LCD-display med «R»-symbol for ytterledertesting (fasein-
dikator) og dreifeltvisning (høyre)
J
+/- LED-er for polaritetsvisning
3. Funksjonstest før bruk for å teste at det ikke er noen
spenning i anlegget
- Kontroller spenningsindikatorens funksjon umiddelbart før
og etter bruk!
- Test spenningsindikatoren på kjente spenningskilder,
f.eks. en 230 V stikkontakt.
- Ikke bruk spenningsmåleren når ikke spenningsindikato-
ren, faseindikatoren og vibrasjonsmotoren ikke virker.
4. Funksjonstest for å teste at det ikke er noen spenning
i systemet (bilde A/B)
Ved målingskontrollen tester du at det ikke er noen spenning
i systemet ved å kontrollere indikatorene for spenning,
fase (faseindikatoren virker bare i vekselstrømnett som er
jordet) og vibrasjonsmotoren (vibrasjonsmotoren aktiveres
ved å trykke på begge knappene). Det er ingen spenning i
systemet bare når alle de tre kretsene som testes ikke viser
noe spenningssignal (spenningsindikator, faseindikator og
vibrasjonsmotor).
- Plasser de to testspissene L1/+ 2 og L2/- 3 på anleggs-
delen som skal testes.
- Spenningsverdien vises i LED-nivåvisningen 8.
- Når man trykker på begge trykknappene 5 kobles svings-
polenivåvisningen 4, 12 V LED-nivået (+/-) og en intern
last i spenningsindikatoren inn.
- Vekselstrøm (AC) vises ved at + 24 V LED og - 24 V LED
begynner å lyse samtidig.
- Likestrøm (DC) vises ved at enten + 24 V LED eller - 24 V
LED begynner å lyse. Med polaritetsvisningen J vises
polariteten + eller - på L2/+ 3.
- For å undersøke energirike og energifattige spenninger
(f.eks. kapasitivt innkoblede støyspenninger) kan man ved
å rykke på begge trykktastene koble inn en intern last i
spenningsindikatoren (se avsnitt 5).
5. Driftstilkobling med vibrasjonsmotor (bilde A/B)
Begge håndtakene L1 6 og L2 7 har trykktaster 5. Når
man trykker på begge tastene kobles det om til en lav innvendig motstand, Dermed settes en vibrasjonsmotor (motor
med ubalanse) under spenning. Fra ca. 200 V settes denne
i gang i en rotasjonsbevegelse. Når spenningen øker, øker
også omdreiningstallet vibrasjonen for motoren. Testvarigheten med lav innvendig motstand (lasttest), avhenger av hvor
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
31
Page 32

høy spenningen som skal måles er. For at apparatet ikke skal
overopphetes. har den en termisk beskyttelse (termisk tilbakekobling). Denne tilbakekoblingen reduseres omdreiningstallet
på vibrasjonsmotoren, og den innvendige motstanden stiger.
Lastilkoblingen (begge trykknappene er trykket inn) kan brukes til å …
- undertrykke reaktansspenninger (induktive og kapasitive
spenninger)
- lade ut kondensatorer
- løse ut jordfeilbryter 10/30 mA. Jordfeilbryteren løses ut
ved å teste ytterleder (faseindikator) mot PE (jordleder).
(Bilde D)
6. Ytterledertesting (faseindikator) (bilde C)
- Bruk hele overflaten på håndtakene L1 6 og L2 7 for å
sikre en kapasitiv kobling mot jord.
- Plasser testspissene L2/+ 3 på anleggsdelen som skal
testes.
Forsikre deg om at testspissen L1/- 2 ikke berøres under
enpolet ytterledertesting (faseindikator), og at den er kon-
taktfri.
- Hvis det vises et «R»-symbol i LCD-displayet 9, forelig-
ger det vekselstrøm på denne anleggsdelen på ytterlede-
ren (fase).
Merk:
Enpolet ytterledertesting (faseindikator) er mulig i jordede nett
fra 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fase mot jord). Verneklær og isolerende
foranstaltninger på bruksstedet kan virke inn på funksjonen.
NB!
Spenningsfrihet kan kun fastslås med topolet testing.
7. Dreiefelttesting (bilde E/ F)
- Bruk hele overflaten på begge håndtakene L1 6 og L2 7
for å sikre en kapasitiv kobling mot jord.
- Plasser testspissene L1/- 2 og L2/+ 3 på to ytterledere
(faser) i et trefasenett og test om ytterlederspenningen er
på f.eks. 400 V.
- Høyredreining (fase L1 før fase L2) foreligger hvis det
vises et «R»-symbol i LCD-displayet 9. LCD-displayet
begynner ikke å lyse hvis en høyredreining kunne regis-
treres.
- Dreiefelttestingen må alltid kryssjekkes!. Hvis LDC-dis-
playet viser høyredreining med «R»-symbolet, skal LCD-
displayet ikke begynne å lyse, når man kryssjekker ved å
bytte om testspissene L1/- 2 og L2/+ 3.
Hvis LCD-display viser et «R»-symbol i begge tilfeller, er
jordingen for svak.
Merk:
Dreiefelttesting er mulig i jordede nett fra 400 V - 900 V,
50/60 Hz (fase mot fase). Verneklær og isolerende foranstaltninger på bruksstedet kan virke inn på funksjonen
8. Tekniske data
- Forskrift: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Merkespenningsområde: 12 V til AC/DC 1.000 V
- Merkefrevensområde: 0 til 60 Hz
- Maks. visningsfeil: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0% - 15 %
- Impedans (indre motstand) målesløyfe/ lastkrets: 200 kΩ/
5 kΩ
- Strømopptak målesløyfe: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Strømopptak lastkrets: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polaritetsvisning: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (når trykktaster trykkes inn)
- Ytterledertesting (faseindikator): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Dreiefelttesting: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibrasjonsmotor, start: ≥ Un 200 V
- Overspenningskategori: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Kapslingsgrad: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 – Første kodetall: Beskyttelse om inntrenging av farlige
gjenstander og beskyttelse mot faste fremmedlegemer,
støvtett
5 – Andre kodetall: Beskytter mot vannsprut. Kan også
brukes når det er nedbør.
-
maks. tillatte Driftssyklus: 30 s (maks. 30 sekunder), 240 s off
- Vekt: ca. 250g
- Ledningslengde: ca. 1000 mm
- Drifts- og oppbevaringstemperaturområde: - 20 °C til
+ 45 °C (Klimakategori N)
- Relativ luftfuktighet: 20 % til 96 % (Klimakategori N)
- Tilbakekoblingstid (termisk beskyttelse):
Spenning/tid:
9. Generelt vedlikehold
Rengjør kapslingen utvendig med en ren klut.
10. Miljøvern
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Bruk tilgjengelige avfallsinnsamlingssystemer og resirkuleringsordninger, når apparatet er uttjent og skal
kastes.
Bedieningshandleiding
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Voordat u de spanningstester DUSPOL® analog 1000 gebruikt:
Lees de bedieningshandleiding en neem in ieder geval de veiligheidsinstructies in acht!
Inhoudsopgave
1. Veiligheidsinstructies
2. Apparaatbeschrijving
3. Functiecontrole voor het gebruik ter controle van de
spanningloosheid van de installatie
4. Controle van de installatie op spanningloosheid
5. Vermogeninschakeling met vibratiemotor
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
32
Page 33

6. Buitengeleider testen (faseweergave)
7. Draaiveld testen
8. Technische gegevens
9. Algemeen onderhoud
10. Milieubescherming
1. Veiligheidsinstructies:
- Het apparaat mag bij het gebruik alleen worden vastge-
nomen aan de geïsoleerde handgrepen L1 6 en L2 7
en de teststaven L1/- 2 en L2/+ 3 mogen niet worden
aangeraakt!
- Controleer vlak voor en na het gebruik ter controle van de
spanningloosheid van de installatie de spanningszoeker
ten aanzien van zijn functionaliteit (zie hoofdstuk 3)! De
spanningstester mag niet worden gebruikt, wanneer de
functie van één of meerdere indicators uitvalt of wanneer
er geen gebruiksklare toestand kan worden vastgesteld!
De controle dient dan met een andere spanningszoeker te
worden herhaald.
- De spanningstester mag alleen binnen het aangegeven
nominale spanningsbereik en in elektrische installaties tot
AC/DC 1.000 V worden gebruikt!
- De spanningstester mag alleen worden gebruikt in stroom-
circuits van overspanningscategorie CAT III met maximum
1000 V of overspanningscategorie CAT IV met maximum
600 V geleider tegen aarde.
- De spanningstester is voorzien voor gebruik door gespe-
cialiseerde elektrotechnici in combinatie met veilige werk-
methoden.
- De graduele LED-indicator dient om het spanningsbereik
weer te geven en is niet bestemd voor meetdoeleinden.
- Het creëren van een spanningstester voor meer dan 30
seconden spanning (maximaal toegestane inschakelduur
ID = 30 seconden)
- De spanningstester mag niet worden gedemonteerd!
- De spanningstester moet worden beschermd tegen ver-
ontreinigingen en beschadigingen van het behuizingop-
pervlak.
- Als bescherming tegen lichamelijke letsels moet na ge-
bruik van de spanningstester de meegeleverde teststaaf-
bescherming 1 worden aangebracht op de teststaven!
- Merk op dat de impedantie (inwendige weerstand) van de
spanningstester de weergave van stoorspanningen (capa-
citief of inductief gekoppeld) beïnvloedt!
Afhankelijk van de inwendige impedantie van de spanningstester zijn er, in aanwezigheid van stoorspanning, verschillende mogelijkheden voor de weergave "bedrijfsspanning
aanwezig" of "bedrijfsspanning niet aanwezig".
Laagohmige spanningstester (impedantie < 100 kΩ), stoor-
spanning wordt onderdrukt of verlaagd:
Een spanningstester met relatief lage inwendige impedantie
zal in vergelijking met de referentiewaarde 100 kΩ niet alle
stoorspanningen weergeven met een oorsprongwaarde boven
ELV (50 V AC/120 V DC). Bij contact met de te testen delen
kan de spanningstester de stoorspanningen door ontlading tijdelijk tot een niveau onder ELV verlagen; na het verwijderen
van de spanningstester zal de stoorspanning echter weer haar
oorspronkelijke waarde aannemen.
Wanneer de indicatie "spanning aanwezig" niet verschijnt, is
het ten stelligste aan te bevelen de aardingsinrichting in te leggen voor met de werken wordt begonnen.
Hoogohmige spanningstester (impedantie > 100 kΩ): Stoor-
spanning wordt niet onderdrukt of verlaagd:
Een spanningstester met relatief hoge inwendige impedan-
tie zal in vergelijking met de referentiewaarde 100 kΩ bij
aanwezige stoorspanning "bedrijfsspanning niet aanwezig"
niet eenduidig aangeven. Wanneer de aanduiding "spanning
aanwezig" verschijnt bij een component die als gescheiden
van de installatie geldt, is het dringend aan te bevelen met
bijkomende maatregelen (bijvoorbeeld: gebruik van een geschikte spanningstester die een onderscheid kan maken tussen bedrijfsspanning en stoorspanning, visuele controle van
het scheidingspunt in het elektrisch net, enz.) de toestand
"bedrijfsspanning niet aanwezig" van het te testen onderdeel
aan te tonen en vast te stellen dat de door de spanningstester
aangegeven spanning een stoorspanning is.
Spanningstesters die door belastingsbijschakeling een
onderscheid kunnen maken tussen bedrijfsspanning en
stoorspanning:
Een spanningstester met vermelding van twee waarden van
de inwendige impedantie, is geslaagd in de test van zijn uitvoering/constructie voor de behandeling van stoorspanningen
en is (binnen de technische grenzen) in staat een onderscheid
te maken tussen bedrijfsspanning en stoorspanning en het
aanwezige spanningstype direct of indirect weer te geven.
Elektrische symbolen op het apparaat:
Symbool Betekenis
Belangrijke documentatie!
Het symbool geeft aan dat de gids beschreven
in de handleiding, om risico's te vermijden
Apparaat of uitrusting voor het werken onder
spanning
Drukschakelaar
AC wisselspanning
DC gelijkspanning
DC/ AC gelijk- en wisselspanning
Aarde (spanning naar aarde)
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
33
Page 34

Drukschakelaar (handbediening); wijst er
op,dat de desbetreffende indicaties alleen
plaatsvinden bij bediening van de beide drukschakelaars
Rechts draaiveld; de draaiveldrichting kan alleen bij 50 of 60 Hz en in een geaard netwerk
worden weergegeven
Draaispoelindicatie
2. Apparaatbeschrijving
1
Teststaafbescherming
2
Teststaaf L1/-
3
Teststaaf L2/+
4
Draaispoelindicatie
5
Drukschakelaar
6
Handgreep L1
7
Indicatorgreep L2
8
Graduele LED-indicator
9
LC-display met „R“ symbool voor het testen van de buiten-
geleider (faseweergave) en de draaiveldindicatie (rechts)
J
+/- LED´s van de polariteitsindicatie
3. Functiecontrole voor het gebruik ter controle van de
spanningloosheid van de installatie
- Onmiddellijk voor en na het gebruik moet de spannings-
tester worden gecontroleerd op zijn werking!
- Test de spanningstester op bekende spanningsbronnen
bijv. op een 230 V-contactdoos.
- Gebruik de spanningstester niet, wanneer spanningsindi-
cator, fase-indicator en vibratiemotor niet correct functio-
neren!
4. Controle van de installatie op spanningloosheid (af-
beelding A/B)
Bij de installatiecontrole dient u de spanningloosheid van de
installatie te controleren door de spanningsindicator, de faseindicator (fase-indicator functioneert alleen in het geaarde
wisselspanningsnet) en de vibratiemotor (vibratiemotor wordt
door bediening van beide druktoetsen geactiveer) te controleren. Van spanningloosheid van de installatie is alleen sprake,
wanneer alle drie testkringen spanningloosheid aangeven
(spanningsindicator, fase-indicator en vibratiemotor).
- Leg de beide teststaven L1/+ 2 en L2/- 3 tegen de te
testen installatieonderdelen.
- De omvang van de aanwezige spanning wordt weergege-
ven via de graduele LED-indicator 8.
- Door bediening van de beide drukschakelaars 5 worden
de draaispoelindicatie 4, de 12 V LED-indicator (+/-) en
een interne last in de spanningstester ingeschakeld.
-
Wisselspanningen (AC) worden weergegeven door het ge-
lijktijdig oplichten van de + 24 V LED en van de - 24 V LED.
- Gelijkspanningen (DC) worden weergegeven door het
oplichten van de + 24 V LED of van de - 24 V LED. Via
de polariteitsindicatie J wordt de op de teststaaf L2/+ 3
aanwezige polariteit + of - weergegeven.
- Om een onderscheid te maken tussen energierijke en
energiearme spanningen (bijv. capacitief ingekoppelde
stoorspanningen) kan door bediening van de beide druk-
schakelaars een interne last in de spanningstester worden
ingeschakeld. (zie hoofdstuk 5.)
5. Vermogeninschakeling met vibratiemotor (afbeelding
A/B)
De beide handgrepen L1 6 en L2 7 zijn voorzien van drukschakelaars 5. Bij bediening van de beide drukschakelaars
wordt er op een lagere inwendige weerstand geschakeld. Hierbij wordt een vibratiemotor (motor met onbalans) onder spanning gezet. Vanaf ca. 200 V wordt deze in een draaibeweging
gebracht. Naarmate de spanning stijgt, verhogen ook het toerental en de vibratie. De duur van de test met een lagere inwendige weerstand (lasttest) is afhankelijk van de omvang van de
te meten spanning. Om ervoor te zorgen dat het apparaat niet
ontoelaatbaar wordt verhit, is er een thermische beveiliging (terugregeling) voorzien. Bij deze terugregeling daalt het toerental
van de vibratiemotor en stijgt de inwendige weerstand.
De lastinschakeling (beide drukschakelaars zijn ingedrukt) kan
worden gebruikt om …
- blinde spanningen (inductieve en capacitieve spanningen)
te onderdrukken
- condensatoren te ontladen
- een 10/30 mA aardlekschakelaar te activeren. De active-
ring van de aardlekschakelaar vindt plaats door middel
van een test aan de buitengeleider (faseweergave) tegen
PE (aarde). (afbeelding D)
6. Buitengeleider testen (faseweergave) (afbeelding C)
- Neem de beide handgrepen L1 6 en L2 7 over het vol-
ledige oppervlak vast om een capacitieve koppeling tegen
aarde te garanderen.
- Leg de teststaaf L2/+ 3 tegen het te testen installatieon-
derdeel.
Zorg er daarbij in ieder geval voor dat bij de eenpolige bui-
tengeleidertest (faseweergave) de teststaaf L1/- 2 niet
wordt aangeraakt en deze contactvrij blijft.
- Wanneer op het LC-display 9 een „R”-symbool ver-
schijnt, dan ligt op dit installatieonderdeel de buitengelei-
der (fase) van een wisselspanning.
Opmerking:
De eenpolige buitengeleidertest (faseweergave) is mogelijk in
het geaarde netwerk vanaf 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fase tegen aarde).
Beschermende kleding en isolerende lokale omstandigheden
kunnen de werking negatief beïnvloeden.
Let op!
Een spanningsvrijheid kan alleen worden vastgesteld door een
tweepolige test.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
34
Page 35

7. Draaiveld testen (afbeelding E/F)
- Neem de beide handgrepen L1 6 en L2 7 over het vol-
ledige oppervlak vast om een capacitieve koppeling tegen
aarde te garanderen.
- Leg de teststaven L1/- 2 en L2/+ 3 tegen twee buitenge-
leiders (fasen) van een draaistroomnet (zonder bediening
de drukschakelaars 5) en controleer of er een buitenge-
leiderspanning van bijv. 400 V aanwezig is.
- Een rechts draaiveld (fase L1 voor fase L2) is aanwezig,
wanneer op het LC-display 9 een „R“-symbool verschijnt.
Het LC-display blijft zwart, wanneer er geen rechts draai-
veld werd gedetecteerd.
- Bij het testen van het draaiveld is steeds een tegencon-
trole vereist!. Wanneer het LC-display bijv. het rechtse
draaiveld aangeeft via het „R”-symbool, dan moet het LC-
display bij de tegencontrole met verwisselde teststaven
L1/- 2 en L2/+ 3 zwart blijven.
Wanneer het LC-display in beide gevallen een „R”-symbool
weergeeft, dan is er een te zwakke aarding aanwezig.
Opmerking:
Het testen van het draaiveld is vanaf 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz
(fase tegen fase) in het geaarde draaistroomnet mogelijk.
Beschermende kleding en isolerende lokale omstandigheden
kunnen de werking negatief beïnvloeden
8. Technische gegevens
- Voorschriften: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Nominaal spanningsbereik: 12 V tot AC/DC 1.000 V
- Nominaal frequentiebereik: 0 tot 60 Hz
- Maximale indicatiefout: Un ±15 %, ELV Un +0% -15%
- Impedantie (inwendige weerstand) meetcircuit/ lastcircuit:
200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Stroomopname meetcircuit: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Stroomopname lastcircuit: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polariteitsindicatie: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (bij bediening van de drukschakelaars)
- Testen van de buitengeleider (faseweergave): ≥ Un 230 V,
50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Testen van het draaiveld: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibratiemotor, start: ≥ Un 200 V
- Overspanningscategorie: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Beschermingsgraad: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN
60529)
6 - eerste kengetal: Bescherming tegen toegang tot ge-
vaarlijke onderdelen en bescherming tegen vaste vreem-
de voorwerpen, stofdicht
5 - tweede kengetal: Beschermd tegen straalwater. Ook te
gebruiken bij neerslag.
- max. toegestane Inschakelduur: 30 s (max. 30 seconden),
240 s uit
- Gewicht: ca. 250g
- Lengte van de verbindingsleiding: ca. 1000 mm
- Temperatuurbereik voor werking en opslag: - 20 °C tot
+ 45 °C (klimaatcategorie N)
- Relatieve luchtvochtigheid: 20 % tot 96 % (klimaatcatego-
rie N)
- Terugregeltijden (thermische beveiliging):
Spanning/tijd:
9. Algemeen onderhoud
Reinig de behuizing aan de buitenkant met een schone, droge
doek.
10. Milieubescherming
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Lever het apparaat aan het einde van zijn levensduur
in bij de beschikbare recycling- en inzamelsystemen.
Instrukcja obsługi
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Przed użyciem próbnika napięcia DUSPOL® analog 1000 należy: przeczytać instrukcję obsługi i koniecznie przestrzegać
wskazówek bezpieczeństwa!
Spis treści
1. Wskazówki bezpieczeństwa
2. Opis urządzenia
3. Sprawdzenie prawidłowości działania przed użyciem
do kontroli braku napięcia w urządzeniu
4. Sprawdzenie braku napięcia w urządzeniu
5. Włączenie obciążenia silnikiem wibracyjnym
6. Sprawdzenie przewodu zewnętrznego (wskaźnik faz)
7. Sprawdzenie pola wirującego
8. Dane techniczne
9. Konserwacja ogólna
10. Ochrona środowiska naturalnego
1. Wskazówki bezpieczeństwa:
- Przy używaniu urządzenia trzymać za izolowane chwyty
L1 6 i L2 7 nie dotykając końcówek L1/- 2 oraz L2/+
3
!
- Próbnik napięcia sprawdzić na prawidłowość działania
bezpośrednio przed użyciem oraz po użyciu go do kontroli
braku napięcia w urządzeniu (zobacz ustęp 3)! Próbni-
ka napięcia nie można używać, jeśli funkcja jednego za
wskaźników lub wielu wskaźników nie działa lub jest nie-
rozpoznawalna! Następnie sprawdzenie powtórzyć przy
pomocy innego próbnika napięcia.
- Z próbnika napięcia można korzystać tylko w podanym
zakresie napięcia znamionowego oraz w urządzeniach
elektrycznych do AC/DC 1.000 V!
- Próbnik napięcia może być użyty tylko w obwodach prą-
dowych kategorii przepięcia CAT III do max. 1000 V lub
kategorii przepięcia CAT IV do max. 600 V przewodu
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
35
Page 36
względem ziemi.
- Próbnik napięcia przeznaczony jest do użytkowania przez
wysoko wykwalifikowanych elektryków cechującymi się
niezawodną metodą pracy.
- Świecąca dioda zakresów służy do wyświetlania zakresu
napięcia, ale nie jest przewidziana do celów pomiaru.
- Tworzenie testerem napięcia przez ponad 30 sekund na-
pięcia (maksymakny czas włączenia ED = 30 s)
- Próbnika napięcia nie wolno rozmontowywać!
- Powierzchnię zewnętrzną obudowy próbnika napięcia na-
leży chronić przed zanieczyszczeniami i uszkodzeniami.
- Aby po użyciu próbnika napięcia zabezpieczyć się przed
skaleczeniem należy na jego ostre końcówki nałożyć do
tego celu przewidziane ochraniacze 1 !
- Należy pamiętać, że impedancja (rezystancja wewnętrz-
na) wskaźnika napięcia wpływa na wskazanie wartości
napięcia zakłócającego (podłączenie pojemnościowe lub
indukcyjne)!
W zależności od wewnętrznej impedancji wskaźnika napięcia,
w razie wystąpienia napięcia zakłócającego istnieją różne
możliwości wskazania statusu „występuje napięcie robocze”
lub „nie występuje napięcie robocze”.
Małooporowy wskaźnik napięcia (impedancja < 100 kΩ),
napięcie zakłócające jest tłumione lub obniżane:
W porównaniu z wartością referencyjną 100 kΩ wskaźnik napięcia ze stosunkowo niską impedancją wewnętrzną nie wskaże wszystkich wartości napięcia zakłócającego przy wartości
pierwotnej powyżej ELV (50 V AC/ 120 V DC). Przy kontakcie
z kontrolowanymi elementami wskaźnik napięcia może tymczasowo obniżyć wartości napięcia zakłócającego poprzez
rozładowanie do poziomu poniżej ELV; jednak po usunięciu
wskaźnika napięcie zakłócające ponownie wzrośnie do pierwotnej wartości.
Jeśli nie pojawia się wskazanie „występuje napięcie“, zdecydowanie zaleca się zastosowanie urządzenia uziemiającego
przed rozpoczęciem prac.
Wielkooporowy wskaźnik napięcia (impedancja > 100 kΩ):
napięcie zakłócające nie jest tłumione lub obniżane:
W porównaniu z wartością referencyjną 100 kΩ wskaźnik
napięcia ze stosunkowo wysoką impedancją wewnętrzną nie
wskaże jednoznacznie przy występowaniu napięcia zakłócającego statusu „nie występuje napięcie robocze”. Jeśli wskazanie „występuje napięcie” pojawia się przy elemencie, który
jest odłączony od instalacji, zdecydowanie zaleca się poprzez
wykonanie dodatkowych czynności (np.: zastosowanie odpowiedniego wskaźnika napięcia, który umożliwia rozróżnienie napięcia roboczego od napięcia zakłócającego, kontrola
wzrokowa miejsca odłączenia w sieci elektrycznej itp.) potwierdzenie statusu „nie występuje napięcie robocze” kontrolowanego elementu i stwierdzenie, że napięcie wskazywane przez
wskaźnik jest napięciem zakłócającym.
Wskaźniki napięcia, które umożliwiają rozróżnienie napięcia roboczego od napięcia zakłócającego:
Wskaźnik napięcia z opcją wskazania dwóch wartości wewnętrznej impedancji uzyskał pozytywny wynik kontroli wykonania/ konstrukcji w zakresie obsługi napięcia zakłócającego i
umożliwia (w ramach granic technicznych) rozróżnienie napięcia roboczego i napięcia zakłócającego oraz bezpośrednie lub
pośrednie sprawdzenie typu występującego napięcia.
Elektryczne Symbole na urządzeniu:
Symbol Znaczenie
Ważna dokumentacja!
Symbol wskazuje, że podręcznik z instrukcją,
aby uniknąć ryzyka
Urządzenie lub wyposażenie do pracy pod na-
pięciem
Klawisz
AC napięcie przemienne
DC napięcie stałe
DC/AC napięcie stałe/przemienne
Ziemia (napięcie do masy)
Klawisz (uruchamiany ręcznie); oznacza to, że
odpowiednie wskazania nastąpią dopiero po
uruchomieniu obu klawiszy
Kierunek obrotu w prawo; kierunek wirowania
pola może być pokazywany tylko przy 50 lub 60
Hz i uziemionej sieci
Elektromagnetyczny wskaźnik napięcia
2. Opis urządzenia
1
Ochraniacze końcówek
2
Końcówka próbnika L1/-
3
Końcówka próbnika L2/+
4
Elektromagnetyczny wskaźnik napięcia
5
Klawisz
6
Chwyt L1
7
Chwyt wskaźnika L2
8
Świecąca dioda zakresów
9
Wyświetlacz ciekłokrystaliczny z symbolem „R“ do kontroli
przewodów zewnętrznych (wskaźnik faz) oraz wskaźnika
kierunku wirowania pola (w prawo)
J
+/- Dioda wskaźnika biegunowości
3. Sprawdzenie prawidłowości działania przed użyciem
do kontroli braku napięcia w urządzeniu
- Bezpośrednio przed jak też po użyciu próbnika napięcia
sprawdzić jego działanie!
- Proszę sprawdzić próbnik napięcia na znanych źródłach
napięcia, np. na gniazdku wtyczkowym 230 V.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
36
Page 37

- Próbnika napięcia nie należy używać, gdy wskaźnik na-
pięcia, wskaźnik faz oraz silnik wibracyjny nie funkcjonują
prawidłowo!
4. Sprawdzenie braku napięcia w urządzeniu (rysunek
A/B)
Sprawdzenie urządzenia na brak napięcia następuje poprzez
kontrolę wskaźnika napięcia, wskaźnika faz (wskaźnik faz
funkcjonuje tylko w uziemionej sieci prądu zmiennego) oraz
silnika wibracyjnego (silnik wibracyjny należy uruchomić poprzez nacisk na oba przyciski). Brak napięcia w urządzeniu
możemy stwierdzić tylko wtedy, gdy wszystkie trzy sprawdzane obwody sygnalizują brak napięcia (wskaźnik napięcia,
wskaźnik faz oraz silnik wibracyjny).
- Przyłożyć obydwie końcówki próbnika L1/+ 2 oraz L2/-
3
do sprawdzanych części urządzenia.
- Wysokość załączonego napięcia będzie pokazywana na
świecącej diodzie zakresów 8.
- Poprzez nacisk na oba klawisze 5 zostanie włączony
elektromagnetyczny wskaźnik napięcia 4, 12 V dioda
zakresów (+/-) oraz wewnętrzne obciążenie w próbniku
napięcia.
- Napięcie przemienne (AC) pokazywane będzie poprzez
równoczesne zabłyśnięcie diody + 24 V oraz diody - 24 V.
- Napięcie stałe (DC) będzie pokazywane poprzez za-
błyśnięcie diody + 24 V LED albo diody - 24 V. Poprzez
wskaźnik biegunowości J pokazywana będzie występu-
jąca na L2/+ 3 biegunowość + albo -.
- Celem rozróżnienia między bogatymi a ubogimi energe-
tycznie napięciami (np. pojemnościowo sprzężone napię-
cia zakłócające) może poprzez nacisk obu klawiszy zostać
dołączone wewnętrzne obciążenie w próbniku napięcia
(zobacz ustęp 5).
5. Włączenie obciążenia silnikiem wibracyjnym (rysunek
A/B)
Oba chwyty L1 6 oraz L2 7 posiadają klawisze naciskowe 5. Poprzez nacisk na oba klawisze zostanie włączony
niewielki opór wewnętrzny. Przy tym do silnika wibracyjnego
(silnik niewyważony) zostanie podłączone napięcie. Przy napięciu ok. 200 V zostanie on wprawiony w ruch obrotowy. Ze
zwiększeniem napięcia wzrosną jego obroty oraz wibracja.
Czas kontroli przy niewielkim oporze wewnętrznym (kontrola pod obciążeniem) jest zależny od wielkości mierzonego
napięcia. Aby nie doszło do niedopuszczalnego przegrzania
urządzenie zaopatrzone jest w ochronę termiczną (regulacja
odwrotna). Przy regulacji odwrotnej spada ilość obrotów silnika wibracyjnego a wzrasta opór wewnętrzny.
Włączania obciążenia (oba klawisze są naciśnięte) można
używać w następujących przypadkach …
- do stłumienia napięcia biernego (napięcia indukcyjnego
oraz pojemnościowego)
- do rozładowania kondensatorów
-
do wyzwolenia wyłącznika zabezpieczającego RCD 10 mA/
30 mA. Wyzwolenie wyłącznika zabezpieczającego RCD
następuje poprzez sprawdzenie przewodu zewnętrznego
(wskaźnik faz) względem PE (uziemienia). (rysunek D)
6. Sprawdzenie przewodu zewnętrznego (wskaźnik faz)
(rysunek C)
- Proszę objąć całą powierzchnią chwyty L1 6 oraz L2 7,
aby uzyskać pojemnościowe sprzężenie względem ziemi.
- Proszę przyłożyć końcówki próbnika L2/+ 3 do części
sprawdzanego urządzenia.
Proszę koniecznie zwrócić uwagę na to, aby przy spraw-
dzaniu jednobiegunowego przewodu zewnętrznego
(wskaźnik faz) końcówka L1/- 2 nie była dotykana i pozo-
stawała bezstykowo.
- Jeśli na wyświetlaczu 9 pojawi się symbol „R“, to na tą
część urządzenia, na przewód zewnętrzny (fazę) dopro-
wadzane jest napięcie przemienne.
Wskazówka :
Sprawdzanie jednobiegunowego przewodu zewnętrznego
(wskaźnik faz) w uziemionej sieci od 230 V, 50/60 Hz (faza
względem ziemi) jest możliwe. Odzież ochronna oraz izolacyjne warunki lokalizacji mogą mieć wpływ na tą funkcję.
Uwaga!
Brak napięcia można stwierdzić tylko przy pomocy dwubiegunowej kontroli.
7. Sprawdzenie pola wirującego (rysunek E/ F)
- Proszę objąć całą powierzchnią chwyty L1 6 oraz L2 7,
aby uzyskać pojemnościowe sprzężenie względem ziemi.
- Proszę przyłożyć końcówki L1/- 2 oraz L2/+ 3 do dwóch
przewodów zewnętrznych (faz) sieci prądu trójfazowego
i sprawdzić (bez nacisku przycisku 5), czy przewód ze-
wnętrzny znajduje się pod napięciem np. 400 V.
- Kierunek obrotu w prawo (faza L1 przed fazą L2) nastą-
pi wtedy, jeśli na wyświetlaczu 9 pojawi się symbol „R“.
Wyświetlacz pozostaje wygaszony, jeśli kierunek obrotu w
prawo nie zostanie rozpoznany.
- Kontrola pola wirującego wymaga stale dalszej kontroli!
Jeśli wyświetlacz poprzez symbol „R“ pokazuje kierunek
obrotu w prawo, to przy dalszej kontroli po zamianie koń-
cówek L1/- 2 z L2/+ 3 wyświetlacz powinien być wyga-
szony.
Jeśli w obydwu przypadkach wyświetlacz pokazuje sym-
bol „R“, to znaczy, że mamy do czynienia ze zbyt słabym
uziemieniem.
Wskazówka:
Kontrola pola wirującego w uziemionej sieci prądu trójfazowego (faza względem fazy) jest możliwa od 400 V - 900 V,
50/60 Hz. Odzież ochronna oraz izolacyjne warunki lokalizacji
mogą mieć wpływ na tą funkcję.
8. Dane techniczne
- Przepisy: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Zakres napięcia znamionowego: 12 V do AC/DC 1.000 V
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
37
Page 38

- Zakres częstotliwości znamionowej f: 0 do 60 Hz
- Maksymalny błąd wskazań: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0% - 15%
- Impedancja (rezystancja wewnętrzna) obwodu pomiaro-
wego/ obciążającego: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Prąd pobierany obwodu pomiarowego: Is < 6,0 mA
(1.000 V)
-
Prąd pobierany obwodu obciążającego: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Wskaźnik biegunowości: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V
LED, - 12 V LED (przy naciśniętym klawiszu)
- Przewód zewnętrzny (wskaźnik faz): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/
60 Hz
- Kontrola pola wirującego: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Silnik wibracyjny, rozruch: ≥ Un 200 V
- Kategoria przepięcia: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Rodzaj ochrony: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - pierwszy wskaźnik: zabezpieczenie przed dostępem
do niebezpiecznych części oraz ochrona przed stałymi
ciałami obcymi, pyłoszczelne
5 – drugi wskaźnik: ochrona przed strumieniem wodnym.
Również przy opadach.
- max. dopuszczalne Cykl pracy: 30 s (maks. 30 sekund),
240 s off
- ciężar: ok. 250g
- długość kabla przyłączeniowego ok. 1000 mm
- zakres temperatury pracy oraz składowania: - 20 °C do
+ 45 °C (kategoria klimatu N)
- względna wilgotność powietrza: 20 % do 96 % (kategoria
klimatu N)
- czasy regulacji odwrotnej (ochrona termiczna):
napięcie/czas:
9. Konserwacja ogólna
Proszę zewnętrzną część obudowy czyścić czystą oraz suchą
ściereczką.
10. Ochrona środowiska naturalnego
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Po osiągnięciu końca żywotności urządzenia należy
je oddać w punkcie przeznaczonym do utylizacji zużytych narzędzi oraz urządzeń.
Instrucţiuni de utilizare
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Înainte de utilizarea testerului de tensiune DUSPOL® analog
1000: citiţi cu atenţie instrucţiunile de utilizare şi respectaţi neapărat indicaţiile privind siguranţa!
Cuprins
1. instrucţiuni de siguranţă
2. descrierea aparatului
3. Test de funcţionare înainte de utilizare, pentru a verifi-
ca absenţa tensiunii unui dispozitiv
4. Verificarea lipsei tensiunii unui dispozitiv
5. Conexiune de sarcină cu motor de vibraţii
6. verificare ecran de fază
7. Verificare sens de rotaţie (succesiunea fazelor)
8. date tehnice
9. întreţinere generală
10. protecţia mediului înconjurător
1. instrucţiuni de siguranţă
- în timpul utilizării se vor apuca mânerele izolate L1 6 şi
L2 7 ; nu se vor atinge vârfurile metalice de testare L1/-
2
şi L2 + 3!
- Imediat înainte şi după utilizare, a se verifica funcţionarea
testerului de tensiune, pentru a verifica absenţa tensiunii
(a se vedea 3.)! Este interzisă întrebuinţarea testerului de
tensiune dacă unul sau mai multe elemente indicatoare nu
afişează sau nu se poate stabili funcţionalitatea sa! Revi-
zuirea trebuie să fie repetată după aceea cu un tester de
tensiune diferit.
- Testerul de tensiune trebuie întrebuinţat numai în plaja de
tensiune nominală dată şi în instalaţii cu până la AC/DC
1000 V!
- Testerul de tensiune poate fi întrebuinţat în categoriile de
tensiune de tip CAT III cu maximum de 1000 V sau CAT IV
cu maximum 600 V, între conductor şi împământare.
-
Testerul de tensiune va fi întrebuinţat numai de personal
calificat şi numai sub condiţii de siguranţă în timpul lucrului.
- Indicatorii LED pentru trepte de tensiune servesc numai
pentru ilustrarea plajei de tensiune şi nu în scopul efectu-
ării de măsurători.
- Crearea unui tester de tensiune pentru mai mult de 30
secunde de tensiune (timpul maxim pentru ţinere sub ten-
siune după comutare, ED = 30 s)
- este interzisă demontarea testerului de tensiune!
- Se vor evita murdărirea şi stricarea carcasei testerului de
tensiune.
- Pentru evitarea rănirilor, după întrebuinţare, pe vârfurile
metalice de testare ale aparatului se vor monta elemente-
le de protecţie existente 1.
- Ţineţi cont că impedanţa testerului de tensiune (rezistenţa
internă) influenţează indicarea tensiunilor perturbatoare
(cuplate capacitiv sau inductiv)!
În caz de tensiuni perturbatoare, în funcţie de impedanţa internă a testerului de tensiune, există diverse posibilităţi de aşare, precum „Tensiune de exploatare existentă” sau „Tensiune
de exploatare inexistentă”.
Tester de tensiune cu impedanţă mică (impedanţa
< 100 kΩ): tensiunea perturbatoare este suprimată, respectiv
diminuată:
Un tester de tensiune cu impedanță internă relativ mică nu indică, în comparaţie cu valoarea de referinţă de 100 kΩ, toate
tensiunile perturbatoare cu o valoare iniţială peste tensiunea
ELV (50 V c.a./ 120 V c.c.). La contactul cu elementele de
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
38
Page 39
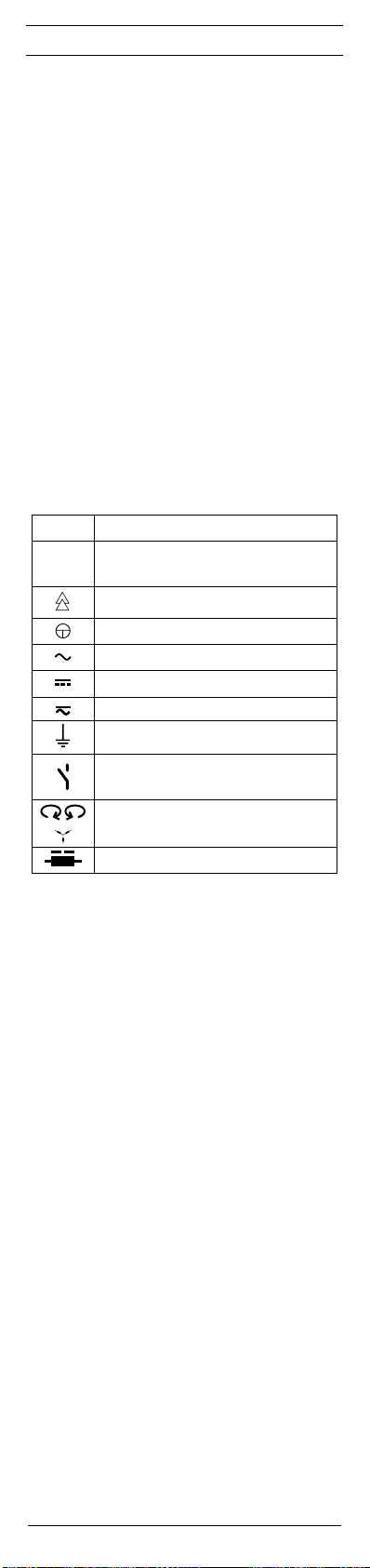
vericat, testerul de tensiune poate să diminueze tensiunile
perturbatoare prin descărcare tranzitorie până la un nivel sub
limita ELV; după îndepărtarea testerului, tensiunea perturbatoare revine însă la valoarea sa iniţială.
Dacă aşajul „Tensiune existentă” nu apare, se impune să
introduceţi dispozitivul de împământare înainte de a proceda
la lucru.
Tester de tensiune cu impedanţă mare (impedanţa
> 100 kΩ): tensiunea perturbatoare nu este suprimată, respectiv diminuată:
Un tester de tensiune cu impedanţă internă relativ mare este
posibil să nu indice explicit, în comparaţie cu valoarea de referinţă de 100 kΩ, „Tensiune de exploatare inexistentă” în caz
de tensiuni perturbatoare. Dacă aşajul „Tensiune existentă”
apare la o componentă cu posibilitate de deconectare din sistem, se recomandă imperios ca prin alte mijloace (de exemplu:
utilizarea unui tester de tensiune adaptat care să deosebească
tensiunea de exploatare de tensiunea perturbatoare, exami-
narea vizuală a punctului de deconectare în reţeaua electrică
etc.) să vericaţi şi să stabiliţi starea „Tensiune de exploatare
inexistentă“ a componentei de vericat, respectiv că tensiunea
indicată de tester este o tensiune perturbatoare.
Testere de tensiune capabile să deosebească tensiunea
de exploatare de tensiunea perturbatoare la conectarea
sub sarcină:
Un tester de tensiune cu specicaţia a două valori pentru impedanţa internă a fost testat în materie de execuţie/ construcţie pentru procesarea de tensiuni perturbatoare şi este capabil
(în limite tehnice) să deosebească tensiunea de exploatare de
tensiunea perturbatoare şi să aşeze tipul de tensiune aplicată
direct sau indirect.
Simboluri electrice aate pe aparat:
Simbol însemnătate
Important documentație!
Simbolul indică faptul că ghidul este descrisă în
manualul, pentru a evita orice riscuri
aparat sau echipament pentru lucru sub tensi-
une
buton-întrerupător
AC tensiune alternativă
DC tensiune continuă
DC/AC tensiune continuă şi alternativă
Pământ (tensiunea la masă)
Butonul-întrerupător (apăsat manual); arată că
aşarea are loc numai la acţionarea ambelor
butoane
Secvenţa de rotaţie către dreapta a câmpului
rotitor este vizibilă numai la 50 sau 60 de Hz şi
numai într-o o reţea cu împământare
bobina magnetică - indicatorul de nivel
2. Descrierea aparatului
1
elemente de protecţie a vârfurile metalice de testare
2
vârf de vericare L1/-
3
vârf de vericare L2/+
4
bobina magnetică - indicatorul de nivel
5
butoane-întrerupător
6
mâner L1
7
mâner cu aşaj L2
8
LED-uri indicatoare de trepte valorice
9
Display- LC cu simbol „R” pentru vericare de ecran de
fază şi aşaj rotire câmp fază (dreapta)
J
+/- al indicatorului de polaritate
3. Test de funcţionare înainte de utilizare, pentru a verifi-
ca absenţa tensiunii unui dispozitiv
- Funcţionarea testerul de tensiune se va controla obligato-
riu de fiecare dată imediat înainte şi după folosirea sa!
- Se poate verifica testerul de tensiune la surse de tensiune
cunoscute, de exemplu la o priză de 230 de volţi.
- Nu folosiţi testerul de tensiune, în cazul în care nu se afi-
şează tensiunea şi în cazul în care indicatorul de fază şi
funcţia motorului cu vibraţie nu funcţionează în mod cores-
punzător/ ireproşabil!
4. Verificarea lipsei tensiunii unui dispozitiv (figura A/B)
La vericarea instalaţiei a se verica absenţa tensiunii dispozitivului, controlând ecranul de tensiune, aşajul fazei (aşajul
fazei funcţionează doar în curent alternativ cu împământare)
şi motorul de vibraţii (motorul de vibraţii este activat prin apă-
sarea ambelor butoane). Lipsa de tensiune a sistemului este
disponibilă numai atunci când toate cele trei circuite de test
semnalizează absenţa de tensiune (aşare tensiune, indicator
de fază şi motor cu vibraţie).
- Aduceţi vârfurile metalice de testare L1 /+ 2 şi L2/- 3 pe
elementele de verificat.
- Mărimea tensiunii la locul respectiv va fi indicată prin indi-
catorul LED cu trepte valorice 8.
- Prin apăsarea concomitentă a celor două butoane-între-
rupător 5, se comută pe pornit: bobina - magnetică -
indicatorul de nivel, 4, LED-ul pentru indicatorul de 12 V
pentru trepte (+/-), precum şi o încărcare internă.
- Tensiunile alternative (AC) se vizualizează, prin aprinde-
rea simultană a LED-ului de + 24 V şi a celui de – 24 V.
- Tensiunile continue (DC) se vizualizează, prin lumina
LED-ului de + 24 V sau a celui de – 24 V. Prin afişajul de
polaritate J, se va indica la vârful de verificare L2/+, 3,
polaritatea + sau -.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
39
Page 40

- În scopul deosebirii tensiunilor bogate sau sărace în ener-
gie (de exemplu energii capacitive de perturbare) este
posibil, ca prin apăsarea simultană a butoanelor-întreru-
pător, să se comute pe pornit, o tensiune de sarcină. (a se
vedea partea 5.)
5. Conexiune de sarcină cu motor de vibraţii (gura A/B)
Pe ambele mânere, L1 6 şi L2 7, se aă butoane-întrerupă-
tor 5. La apăsarea celor 2 butoane se comută pe o rezistenţă
internă ceva mai redusă. În acest scop este ataşat la tensiune
un motor vibrator (cu excentric). Începând de la circa 200 V
acesta se pune în mişcare. O dată cu creşterea tensiunii, cresc
şi viteza de rotaţie şi vibraţia. Durata măsurării la rezistenţă internă mică (test de încărcare) depinde de mărimea tensiunii de
măsurat. Pentru ca aparatul să nu se încălzească inutil, a fost
prevăzut în acest scop un sistem de ocrotire(reglare inversă).
Prin această reglare inversă se reduce numărul de rotaţii al
motorului cu vibraţii şi creşte rezistenţa internă.
Conexiunea de încărcare, (amândouă butoanele sunt apăsate) poate folosită
- pentru a reduce tensiuni oarbe (tensiuni inductive şi capa-
citive)
- a descărca condensatori
- a porni întrerupătoare de protecţie de 10/30 mA. Comu-
tarea unui întrerupător de protecţie are loc prin legarea la
ecran de fază şi la PE (pământ) (Figura D)
6. Verificarea ecran de fază (gura C)
- Apucaţi complet mânerele L1 6 şi L2 7 pentru a asigura
o legătură capacitivă la pământ.
- Aduceţi vârful de verificare L2/+ 3 pe locul de măsurat.
Atenţie neapărat, ca la verificarea unipolară (ecran de
fază), vârful de verificare L1/- 2 să nu atingă nimic, deci
să fie liber de orice contact.
- atunci când pe display-ul LC 9, apare simbolul „R”, este
vorba de o parte a instalaţiei ce se află conectată la faza
unei tensiuni alternative.
Indicaţie:
Vericarea ecran de fază este posibilă în reţea împământată,
începând de la 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fază contra pământ). Îmbrăcămintea de protecţie şi condiţiile locale de izolare, pot inuenţa
această funcţiune.
Atenţie!
Lipsa de tensiune poate constatată numai prin măsurare
bipolară.
7. Verificarea sensului de rotire al câmpului –
succesiunea fazelor – (gura E/F)
- Apucaţi complet mânerele L1 6 şi L2 7 pentru a asigura
o legătură capacitivă la pământ.
- Aduceţi vârfurile metalice de testare L1/- 2 şi L2/+ 3 la
două faze ale unei reţele trifazate şi verificaţi dacă tensiu-
nea fazei este, de exemplu, 400 V.
- Există o rotaţie spre dreapta faza L1 înaintea fazei L2),
dacă pe display-ul LC 9, apare un simbol „R”. Dacă dis-
play-ul LC rămâne întunecat, nu a fost recunoscută rotirea
de faze spre dreapta.
- Verificarea rotirii trifazice necesită mereu un control supli-
mentar! Dacă display-ul arată sensul de rotire spre dreap-
ta, prin simbolul „R”, la controlul suplimentar cu vârfurile
metalice de testare schimbate între ele, la conectarea
L1/- 2 şi L2/+ 3 display-ul trebuie să rămână întunecat.
Dacă display-ul arată în ambele cazuri un simbol „R”, cau-
za este o împâmântare slabă.
Indicaţie:
Vericarea fazei este posibilă în reţea împământată, începând
de la 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (fază contra fază). Îmbrăcă-400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz (fază contra fază). Îmbrăcă- V, 50/60 Hz (fază contra fază). Îmbrăcămintea de protecţie şi condiţiile locale de izolare, pot inuenţa
această funcţiune.
8. Date tehnice
- prescripţii: IEC 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- plaja de tensiune nominală: 12 V până la AC/DC 1000V
- plaja de frecvenţă: 0 până la 60 de HZ
- max. greşeli de afişaj: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0% – 15%
- Impedanţa (rezistenta interioară) circuit de măsură/ circuit
de sarcină: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- preluare de curent, circuit de măsură: ls < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- preluare curent, circuit de sarcină: Is < 550 mA (1000 V)
- afişarea polarităţii: + 24 V LED, -24V LED, +12 LED,
- 12 V LED (la apăsarea butoanelor)
- ecran de fază: ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- verificarea rotaţiei la trifazic: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- motor cu vibraţii, pornire ≥ Un 200V
- categoria pentru depăşirea de tensiune CAT IV 600V,
CAT III 1000 V
- felul protecţiei: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 – prima cifră: protecţie împotriva accesului la componen-
te periculoase şi protecţie împotriva impurităţilor solide,
impermeabil la praf
5 – a doua cifră :protecţie contra stropirii cu jet de apă,
poate fi întrebuinţat şi pe ploaie
-
max. Ciclu de admisibilă: 30 s (max. 30 secunde), 240 s off
- greutate: circa 250 g
- lungime conductor de legătură: circa 1000 mm
- marja temperaturii de lucru şi de depozitare: - 20°C până
la + 45 °C (categoria de climă N)
-
umiditate relativă: 20 % până la 96 % (categoria de climă N)
- reprogramare reglaje (protecţie termică) :
tensiune/timp:
9. Întreţinere
Se va curăţa carcasa, în exterior, cu un şervet curat şi uscat.
10. Protecţia mediului înconjurător
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
La expirarea duratei de viaţă a aparatului, acesta să
e depus în locuri special amenajate şi în sistemul de
colectare a deşeurilor.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
40
Page 41

Инструкция по эксплуатации
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Перед использованием индикатора напряжения DUSPOL®
analog 1000: прочитайте, пожалуйста, инструкцию по эксплуатации и обязательно соблюдайте указания по технике
безопасности!
Содержание
1. Указания по технике безопасности
2. Описание прибора
3. Контроль функционирования перед использова-
нием для контроля отсутствия напряжения какой
либо установки
4. Контроль отсутствия напряжения какойлибо уста-
новки
5. Подключение нагрузки с вибрационным двигате-
лем
6. Контроль фазового провода
7. Контроль направления вращения магнитного поля
8. Технические данные
9. Общее техническое обслуживание
10. Охрана окружающей среды
1. Указания по технике безопасности
- При использовании брать в руки прибор за изолиро-
ванные ручки L1 6 и L2 7 и не прикасаться к испыта-
тельным щупам L1/- 2 и L2/+ 3!
- Непосредственно перед и после использования при-
бора, необходимо для контроля отсутствия напряже-
ния на установке, проверить индикатор напряжения
на его функционирование (см. раздел 3)! Индикатор
напряжения не разрешается использовать, если функ-
ция одной или нескольких индикаций не действует или
прибор выглядит неработоспособным. Контроль сле-
дует, затем повторить с другим прибором индикатора
напряжения.
- Индикатор напряжения разрешается использовать
только для указанных интервалов напряжения и на
электрических установках с напряжением переменно-
го или постоянного тока до 1000 В!
- Индикатор напряжения разрешается использовать
только в электрических цепях категории перенапря-
жения CAT III с не более, чем 1000 В или категории
перенапряжения CAT IV с не более, чем 600 В фазы
относительно земли.
- Индикатор напряжения предназначен для примене-
ния профессиональными электриками с соблюдением
правил безопасной работы.
- Светодиодная ступенчатая индикация служит для ука-
зания интервала напряжения, она не служит для из-
мерения.
- Создание тестер напряжения более чем на 30 секунд
напряжение (максимально допустимое время включе-
ния ED = 30 с)!
- Индикатор напряжения не разрешается разбирать!
- Поверхность корпуса индикатора напряжения необхо-
димо защищать от загрязнения и повреждений.
- В качестве защиты от ранения необходимо после ис-
пользования индикатора напряжения надеть защит-
ные колпачки на измерительные щупы 1!
- Необходимо учитывать, что полное (внутреннее) со-
противление индикатора напряжения влияет на инди-
кацию напряжения помех (емкостная или индуктивная
наводка)!
В зависимости от внутреннего сопротивления индикатора
напряжения при наличии напряжения помех существуют
разные варианты индикации «Рабочее напряжение имеется» или «Рабочее напряжение отсутствует».
Низкоомный индикатор напряжения (внутреннее сопротивление < 100 кОм), напряжение помех подавляется/
снижается.
Индикатор напряжения с относительно низким внутренним сопротивлением по сравнению с эталонным значением 100 кОм не будет отображать все напряжения помех
с исходным значением выше сверхнизкого напряжения
(ELV, 50 В перем. тока / 120 В пост. тока). При контакте
с проверяемыми деталями индикатор напряжения может
временно подавлять напряжения помех до уровня ниже
сверхнизкого напряжения (ELV); после удаления индикатора напряжения напряжение помех восстанавливается до
исходного значения.
Если индикация «Напряжение имеется» не появляется,
настоятельно рекомендуется перед началом работ установить заземляющее устройство.
Высокоомный индикатор напряжения (внутреннее сопротивление > 100 кОм): напряжение помех не подавляется/снижается.
Индикатор напряжения с относительно высоким внутренним сопротивлением по сравнению с эталонным значением 100 кОм не будет однозначно отображать «Рабочее
напряжение отсутствует» при наличии напряжения помех.
Если индикация «Напряжение имеется» появляется на
детали, которая считается отсоединенной от установки,
настоятельно рекомендуется с помощью дополнительных
мер (например, использование подходящего индикатора
напряжения, способного отличить рабочее напряжение от
напряжения помех, визуальная проверка места соединения в электросети и пр.) подтвердить состояние «Напряжение отсутствует» на проверяемой детали и удостоверить,
что отображаемое индикатором напряжение является напряжением помех.
Индикаторы напряжения, способные посредством
подключения нагрузки отличить рабочее напряжение
от напряжения помех:
Индикатор напряжения с указанием двух значений внутреннего сопротивления прошел проектные/ конструктивные испытания для работы с напряжениями помех и (в
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
41
Page 42

предельном техническом диапазоне) способен отличать
рабочее напряжение от напряжения помех и обеспечивать
прямое или опосредованное отображение имеющегося
вида напряжения.
Электрические символы на приборе:
Символ Значение
Важная документация!
Этот символ указывает, что в руководстве
описано в руководстве, чтобы избежать
любого риска
Прибор или оборудование для работы под
напряжением
Клавиша
AC переменное напряжение
DC постоянное напряжение
DC/AC постоянное и переменное напряжение
Земля (напряжение относительно земли)
Клавиша (приводимая в действие вручную);
символ указывает на то, что соответствующая индикация производится только при нажатии обеих клавиш
Правое поле вращения: направление вращения магнитного поля может быть показано только в заземленной сети с частотой 50
или 60 Гц
Индикация уровня на базе подвижной
катушки
2. Описание прибора
1
Защитный колпачок щупов
2
Испытательный щуп L1/-
3
Испытательный щуп L2/+
4
Индикация уровня на базе подвижной катушки
5
Клавиша
6
Ручка L1
7
Ручка с дисплеем L2
8
Светодиоды индикации уровня
9
Жидкокристаллический дисплей с символом „R“ для
контроля фазового провода и указания вращения маг-
нитного поля (направо)
J
Светодиоды +/- индикации полярности
3. Контроль функционирования перед использова-
нием для контроля отсутствия напряжения какой
либо установки
- Непосредственно перед использованием и после ис-
пользования индикатора напряжения проверить рабо-
тоспособность!
- Проверьте индикатор напряжения на известном источ-
нике напряжения, например, в розетке 230 В.
- Не используйте индикатор напряжения, если индика-
ция напряжения, индикация фаз, либо вибрационный
двигатель не функционируют безупречно!
4. Контроль отсутствия напряжения какойлибо уста-
новки (Рис. A/B)
При контроле установки проверьте отсутствие напряжения установки контролем индикацией напряжения, индикацией фаз (индикация фаз действует только в заземленных
сетях переменного тока) и с вибрационным двигателем
(вибрационный двигатель активируется нажимом на обе
клавиши). Отсутствие напряжения установки имеется
только в том случае, если все три контрольные цепи сигнализируют отсутствие напряжения (индикация напряжения,
индикация фаз и вибрационный двигатель).
- Приложите оба испытательных щупа L1/+ 2 и L2/- 3
к подлежащим контролю частям электроустановки.
-
Величина имеющегося напряжения указывается с по-
мощью светодиодов индикации уровня напряжения 8.
- Посредством нажима двух клавиш 5 подключается
индикация уровня с подвижной катушкой 4, уровень
светодиодов 12 В (+/-) и внутренняя нагрузка в индика-
торе напряжения.
- Индикация переменных напряжений (AC) произво-
дится одновременным свечением светодиода + 24 В и
светодиода - 24 В.
- Индикация постоянных напряжений (DC) производит-
ся свечением светодиода + 24 В или светодиода - 24 В.
С помощью индикации полярности J производится
индикация полярности + или - напряжения на щупе
L2/+ 3.
- C целью различия энергоемких и не энергоемких на-
пряжений (например, подключенных емкостных напря-
жений помех) можно путем нажатия обеих клавишей
подключать внутреннюю нагрузку (см. раздел 5.)
5. Подключение нагрузки с вибрационным двигате-
лем (Рис. A/B)
Обе ручки L1 6 и L2 7 оснащены клавишами 5. При нажиме обеих клавиш производится переключение на меньшее внутреннее сопротивление. При этом подается напряжение на вибрационный двигатель (несбалансированный
двигатель). При напряжении более 200 В он приводится во
вращательное движение. С увеличением напряжения он
вращается быстрее и увеличивается его вибрация. Длительность проверки с меньшим внутренним сопротивлением (контроль нагрузки) зависит от величины измеряемого
напряжения. Для предотвращения недопустимого нагрева
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
42
Page 43

S
прибора предусмотрена термическая защита (обратная
регулировка). При этой обратной регулировке уменьшается число оборотов вибрационного двигателя, а внутреннее сопротивление повышается.
Подключение нагрузки (обе клавиши нажаты) может
использоваться для ...
- подавления реактивного напряжения (индуктивные
или емкостные напряжения)
- разряда конденсаторов
- срабатывания RCD-выключателя 10/30 мA. Срабаты-
вание RCD-выключателя производится путем контро-
ля внешнего провода (Индикация фаз) относительно
защитного провода (рис. D)
6.
Проверка внешнего провода (Индикация фаз) (рис. C)
- Обхватите по всей поверхности ручки L1 6 и L2 7,
чтобы обеспечить емкостное соединение с землей.
- Приложите испытательный щуп L2/+ 3 к проверяемой
части электроустановки.
Обязательно обратите внимание на то, чтобы при од-
нополюсной проверке внешнего провода (Индикация
фаз) испытательный щуп L1/- 2 не имел контакта и
ничего не касался.
- Если на жидкокристаллическом дисплее 9 появляет-
ся символ „R“, то на этой части установки находится
внешний провод (фаза) переменного напряжения.
Указание:
Однополюсная проверка внешнего провода (Индикация
фаз) возможна в заземленной сети напряжением боле
230 В, 50/60 Гц (фаза относительно земли). Спецодежда и
условия изоляции местоположения могут нарушить функцию.
Внимание!
Отсутствие напряжения может быть определено только
двухполюсным контролем.
7. Проверка направления вращения магнитного поля
(рис. E/ F)
- Полностью обхватите ручки L1 6 и L2 7, чтобы обе-
спечить емкостное соединение с землей.
- Приложите испытательные щупы L1/- 2 и L2/+ 3 к
двумя внешним проводами (фазы) трехфазной сети и
проверьте, имеется ли например напряжение 400 В на
внешних проводах.
- Правое вращение магнитного поля (фаза L1 перед фа-
зой L2) имеется тогда,
когда на жидкокристаллической дисплее 9 появля-
ется символ „R“. Жидкокристаллический дисплей не
светится, если не обнаружено правое вращение маг-
нитного поля.
- Проверка вращения магнитного поля всегда требует
контрольной проверки! При индикации на жидкокри-
сталлическом дисплее правого вращения магнитного
поля символом „R“, при контрольной проверке путем
перестановки испытательных щупов L1/- 2 и L2/+ 3
жидкокристаллический дисплей не должен светиться.
Если на жидкокристаллическом дисплее в обоих случа-
ях имеется символ „R“, то имеется слабое заземление
Указание:
Проверка вращения магнитного поля возможна в трехфазных сетях с напряжением более 400 B - 900 В, 50/60 Гц
(фаза относительно фазы). Спецодежда и условия изоляции местоположения могут нарушить функцию.
8. Технические данные
- Правила: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Интервалы номинального напряжения: 12 В - AC/DC
1000 В
- Интервал номинальной частоты f: 0 - 60 Гц
-
Макс. погрешность индикации: Uн ± 15 %, ELV Uн + 0% - 15 %
- Полное (внутреннее) сопротивление, измерительная
цепь/ цепь нагрузки: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Потребление тока, измерительная цепь: Is < 6,0 мA
(1.000 B)
- Потребление тока, цепь нагрузки: Is < 550 мA (1.000 В)
- Индикация полярности: + 24 В светодиод, - 24 В свето-
диод, + 12 В светодиод - 12 В светодиод (при нажатии
клавиши)
- Проверка внешнего провода: ≥ Uн 230 В, 50 Гц/ 60 Гц
- Проверка вращения магнитного поля: ≥ Uн 400 В,
50 Гц/ 60 Гц
- Вибрационный двигатель, срабатывание при: ≥ Uн
200 В
- Категория перенапряжения: CAT IV 600 В, CAT III
1000 В
- Тип защиты: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - первый показатель: защита против доступа к опас-
ным частям и защита против инородных тел, пылене-
проницаемый
5 - второй показатель: защищен от брызг воды. Может
применяться при осадках.
- максимум допустимая нагрузка: 30 с (макс. 30 секунд),
240 с выкл
- Масса: около 250 г
- Длина соединительного кабеля: около 1000 мм
- Интервал рабочих температур и температур хранения:
- 20 °C - + 45 °C (категория климата N)
- Относительная влажность: 20 % - 96 % (категория кли-
мата N)
-
Время обратного регулирования (термическая защита):
напряжение/время: 230 В/30 с, 400 В/9 с, 690 B/5 c,
1000 B/2 c
9. Общее техническое обслуживание
Очищайте прибор снаружи чистой и сухой тряпкой.
.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
43
Page 44

S
10. Защита окружающей среды
По окончанию срока службы сдайте прибор в имеющиеся пункты утилизации.
Bruksanvisning
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Läs noga igenom bruksanvisningen och säkerhetsanvisningarna innan du använder spänningsprovaren DUSPOL® analog
1000.
Innehållsförteckning
1. Säkerhetsanvisningar
2. Funktionsbeskrivning
3. Spänningsprovaren skall funktionstestas innan den
får användas för kontroll av spänningsfriheten
4. Kontroll av spänningsfriheten
5. Lasttillkoppling med vibrationsmotor
6. Provning av ytterledaren (fasindikering)
7. Fasföljdsprovning
8. Tekniska data
9. Allmän skötsel
10. Miljöinformation
1. Säkerhetsanvisningar
- Håll alltid spänningsprovaren i de isolerade handtagen L1
6
och L2 7 under mätningen. Vidrör EJ någon av prov-
spetsarna L1/- 2 och L2/+ 3!
- Spänningsprovaren skall funktionstestas både direkt före
och direkt efter användning (se punkt 3)! Spänningspro-
varen får inte användas om minst en av indikeringarna
inte visar något värde eller om funktionen uteblir helt. En
annan spänningsprovare skall då användas för att testa
spänningsprovaren.
- Spänningsprovaren får endast användas inom specifice-
rat märkspänningsområde och på elsystem upp till AC/DC
1000 V.
- Spänningsprovaren får endast användas i strömkretsar
enligt överspänningskategori CAT III med max. 1 000 V el-
ler överspänningskategori CAT IV med en ledare på max.
600 V mot jord.
-
Spänningsprovaren är avsedd att användas av elinstallatö-
rer som vet hur man handskas med den på ett säkert sätt.
- Lysdioderna (LED) visar endast spänningsområdet och är
inte till för mätningsändamål.
- Skapa en spänningsprovare för mer än 30 sekunder spän-
ning (max. tillåten inkopplingstid ED = 30 s)!
- Spänningsprovaren får inte tas isär.
- Spänningsprovarens hölje skall skyddas mot skador och
smuts.
-
För att man inte skall kunna skada sig på provspetsarna
skall dessa förses med bifogade skyddshättor 1 när spän-
ningsprovaren inte skall användas under en längre tid.
- Observera att impedansen (inre motståndet) i testaren
påverkas av störningsspänningar (kopplad kapacitivt eller
induktivt)!
Beroende på den inre impedansen i spänningstestaren nns
det på grund av närvaro av störningsspänning olika alternativ som visar ”driftspänning tillgänglig” eller ”driftspänning inte
tillgänglig”.
Spänningstestare för låg impedans (Impedans < 100 kΩ),
spänningsstörningar undertrycks eller minskas
En spänningstestare med relativt låg inre impedans som
jämförs med referensvärdet 100 kΩ visar inte alla störningsspänningar med ett begynnelsevärde över ELV (50 V AC/
120 VDC). Vid kontakt med de delar som ska testas kan spänningstestaren minska störningsspänningen genom tillfällig
urladdning till en nivå under ELV; men efter avlägsnande av
spänningsdetektorn antar störningsspänningen sitt ursprungliga värde på nytt.
När ”spänning tillgänglig” inte visas är det starkt rekommenderat att införa den jordade enheten innan arbetet påbörjas.
Spänningstestare för hög impedans (Impedans > 100 kΩ):
Störningsspänning undertrycks eller minskas inte:
En spänningsprovare med relativt hög inre impedans visas
inte tydligt i förhållande till referensvärdet på 100 kΩ bentlig
störningsspänning ”driftspänning”. När ”spänning tillgänglig”
visas gällande en separat del i anläggningen rekommenderas starkt ytterligare åtgärder (till exempel: Med hjälp av en
lämplig spänningsdetektor kunna mäta om driftspänning och
störningsspänningen är annorlunda, visuell kontroll av separationspunkten i elnätet, mm.) och tillståndet ”driftspänning
inte tillgänglig” av den del som skall testas för att bevisa och
bestämma om den spänning som anges av spänningstestaren
är en interferensspänning.
Spänningsdetektorerna kan skilja av belastningen, som
verkar som spänning hos interferensspänningen:
En spänningstestare med två värden angivna på den inre impedansen har klarat testet av utformningen / konstruktionen
för behandling av störningsspänningar och måste särskiljas
(inom tekniska gränser) med förmågan för driftspänning och
störningsspänning och måste visa den bentliga spänningstypen direkt eller indirekt.
Elektriska symboler på spänningsprovaren:
Symbol Betydelse
Viktig dokumentation!
Symbolen visar att guiden som beskrivs i
handboken, för att undvika risker
Instrument eller utrustning för arbete under
spänning
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
44
Page 45

S
Tryckknapp
Växelspänning (AC)
Likspänning (DC)
Lik- och växelspänning (DC/AC)
Jord (spänning till jord)
Tryckknapp (handmanövrerad): hänvisar till att
värdena endast visas när båda tryckknapparna
trycks in
Högerrotation: rotationsfältets riktning kan bara
visas vid 50 resp. 60 Hz i jordat nät
Dykspole
2. Funktionsbeskrivning
1
Skyddshättor
2
Provspets L1/-
3
Provspets L2/+
4
Dykspole
5
Tryckknapp
6
Handtag L1
7
Displayhandtag L2
8
Spänningsindikering (LED)
9
LC-display med "R"-symbol för provning av fasindikering
och fasföljdsvisning (högerrotation)
J
+/- LED-dioder för polaritetsvisning
3. Spänningsprovaren skall funktionstestas innan den
får användas för kontroll av spänningsfriheten
- Spänningsprovaren skall funktionstestas både direkt före
och direkt efter användning.
- Testa alla funktioner på kända spänningskällor, t.ex. på ett
230 V vägguttag
- Spänningsprovaren får inte användas om spänningsindi-
keringen, fasindikeringen eller vibrationsmotorn inte fung-
erar felfritt!
4. Kontroll av spänningsfriheten (bild A/ B)
Kontrollera att systemet är spänningsfritt genom att läsa av
spänningsindikeringen, fasindikeringen (fasindikeringen fungerar endast i jordat växelspänningsnät) och vibrationsmotorn
(vibrationsmotorn aktiveras med båda tryckknapparna). Systemet är endast spänningsfritt när alla tre mätkretsarna visar
spänningsfrihet (spänningsindikeringen, fasindikeringen och
vibrationsmotorn).
- Anslut båda provspetsarna L1/+ 2 och L2/- 3 till den
anläggningsdel som skall provas.
- Den aktuella spänningen visas med lysdioderna på spän-
ningsindikeringen 8.
- När man trycker in båda tryckknapparna 5 tillkopplas
dykspolen 4, lysdioden för 12 V (+/-) och en intern last
i spänningsprovaren.
- Växelspänningar (AC) visas genom att lysdiod + 24 V och
lysdiod - 24 V blinkar till samtidigt.
- Likspänningar (DC) visas genom att lysdiod + 24 Veller
lysdiod - 24 V blinkar till. Polaritetsindikeringen J visar
polariteten +/- för provspets L2/+ 3.
- För att kunna särskilja energirika och energifattiga spän-
ningar åt (t.ex. kapacitivt inkopplade brusspänningar) kan
man tillkoppla en intern last i spänningsprovaren genom
att trycka in båda tryckknapparna (se punkt 5).
5. Lasttillkoppling med vibrationsmotor (bild A/B)
Båda handtagen L1 6 och L2 7 är försedda med tryckknappar 5. När båda knapparna trycks in kopplas spänningsprovaren om till en lägre ingångsresistans. I och med detta läggs
en vibrationsmotor (motor med obalans) under spänning. Vid
cirka 200 V börjar motorn rotera, och i takt med att spänningen
stiger ökar även motorns varvtal och vibration. Tiden för mätningen med lägre ingångsresistans (lasttest) är beroende av
den spänning som skall mätas. För att spänningsprovaren
inte skall bli för varm har den ett inbyggt termiskt skydd. När
skyddet aktiveras sjunker vibrationsmotorns varvtal medan ingångsresistansen ökar.
Lasttillkoppling (med båda tryckknapparna intryckta) kan utnyttjas för att
- förhindra kapacitiva och induktiva spänningarna
- ladda ur kondensatorer
- utlösa jordfelsbrytare 10/30 mA. Jordfelsbrytaren utlöses
genom test på fasindikering mot jord (bild D).
6. Provning av fasindikering (bild C)
- Greppa helt om handtagen L1 6 och L2 7 för att garan-
tera kapacitiv koppling mot jord.
- Anslut provspets L2/+ 3 till den anläggningsdel som skall
provas.
Var noga med att inte vidröra provspetsen L1/- 2 under
mätningen!
- När "R"-symbolen lyser på LCD-dispayen 9 har denna
anläggningsdel en fasledare med växelspänning.
OBS!
Den enpoliga provningen av fasindikering kan utföras först vid
minst 230 V, 50/60 Hz (fas mot jord) i jordade nät. Funktionen
kan påverkas av skyddsklädsel och av isolationsförhållandena
på mätplatsen.
Obs!
Det går endast att fastställa om systemet är spänningsfritt genom att göra en tvåpolig provning.
7. Fasföljdsprovning (bild E/F)
- Greppa helt om handtagen L1 6 och L2 7 för att garan-
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
45
Page 46

1
SRB
tera kapacitiv koppling mot jord.
- Anslut provspetsarna L1/- 2 och L2/+ 3 mot två fasle-
dare i ett trefasnät och testa om fasledarna har en spän-
ning på t.ex. 400 V.
- Om fasledarna är anslutna för högerrotation (fas L1 före
fas L2) lyser "R"-symbolen på LCD-displayen 9. Om fas-
ledarna inte är anslutna för högerrotation lyser inte LCD-
displayen.
- Fasföljdsprovning kräver alltid en motkontroll. Visar LCD-
displayen högerrotation med "R"-symbolen måste prov-
spetsarna L1/- 2 och L2/+ 3 byta plats under motkon-
trollen och LCD-displayen vara släckt.
Om LCD-displayen visar en "R"-symbol i båda fallen före-
ligger dålig jordning.
Obs!
Fasföljdsprovningen kan utföras vid minst 400 V - 900 V,
50/60 Hz (fas mot jord) i jordade nät. Funktionen kan påverkas
av skyddsklädsel och av isolationsförhållandena på mätplatsen.
8. Tekniska data
- Standard: SS-EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Märkspänningsområde: 12 V till AC/DC 1000 V
- Märkfrekvensområde f: 0 till 60 Hz
- Max. visningsfel: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0% - 15 %
- Impedans (ingångsresistans), mätkrets/ lastkrets: 200 kΩ/
5 kΩ
- Strömförbrukning, mätkrets: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Strömförbrukning, lastkrets: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polaritetsvisning: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (med tryckknappsmanövrering)
- fasindikering: ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- fasföljdsprovning: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibrationsmotor, startspänning: ≥ Un 200 V
- Överspänningskategori: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1 000 V
- Kapslingsklass: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - första siffran: skydd mot beröring av farliga delar och
skydd mot fasta föremål, dammtäta
5 - andra siffran: skydd mot droppar från alla håll. Kan
även användas i regnväder.
- max. tillåtna Kapacitet: 30 s (max. 30 sekunder), 240 s av
- Vikt: ca 250 g
- Förbindningskabelns längd: ca 1000 mm
- Drift- och lagringstemperatur: - 20 °C till + 45 °C (klimatka-
tegori N)
- Relativ luftfuktighet: 20 % till 96 % (klimatkategori N)
- Återställningstider (termiskt skydd):
spänning/tid:
9. Allmän skötsel
Rengör höljet med en ren och torr trasa.
10. Miljöinformation
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Förbrukad produkt skall lämnas in på lämplig återvinningsstation.
Upute za rukovanje
DUSPOL® analog 1000
Prije nego što počnete upotrebljavati ispitivač napona
DUSPOL® analog 1000: Pročitajte Upute za rukovanje i
obavezno se pridržavajte uputa o sigurnosti !
Sadržaj
1. Upute o bezbednosti
2. Opis uređaja
3. Provera funkcije pre upotrebe u svrhu provere
nepostojanja napona nekog postrojenja
4. Provera nepostojanja napona nekog postrojenja
5. Priključak sa vibracionim motorom
6. Ispitivanje vanjskog vodiča (prikaz faze)
7. Provera polja okretanja
8. Tehnički podaci
9. Opšte održavanje
10. Zaštita okoline
1. Upute o bezbednosti:
- Uređaj kod upotrebe dirati samo na izoliranim ručkama L1
6
i L2 7, NE dirati vrhove ispitivača L1/- 2 i L2/+ 3!
- Neposredno pre i posle korištenja u svrhu provere
nepostojanja napona postrojenja proveriti funkciju
kontrolora napona (vidi tačku 3)! Ispitivač napona ne sme
se koristiti ako ne radi funkcija jednog ili više pokazivača
ili ako ispitivač nije spreman za rad – ne pokazuje funkcije
rada! Proveru onda treba ponoviti sa kontrolorom napona.
- Ispitivač napona se koristi samo u navedenom području
nazivnog napona i unutar električnih sistema do AC/DC
1.000 V!
- Ispitivač napona se isključivo koristi u strujnim krugovima
kategorije nadnapona CAT III sa maks. 1000 V ili kategorije
nadnapona CAT IV sa maks. 600 V vodič u zemlju.
- Ispitivač napona je namenjen za korištenje od strane
kvalifikovanih električara, u sklopu postupka sigurnog
rada.
- LED lampice sa stupnjevima služe prikazu raspona
napona, one ne služe merenju.
Ispitivač napona nakon pritiska tastera ne smemo
nikada duže od 30 sekundi staviti na napon (maksimalno
dopušteno vreme uključivanja VU(ED) = 30 sek)!
- Ispitivač napona ne sme se rastavljati!
- Ispitivač napona treba čuvati od onečišćenja i oštećenja
na površini kučišta.
- Radi zaštite od ozlede, nakon korištenja ispitivača napona,
vrhove ispitivača pokriti sa priloženom zaštitom za vrhove
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
46
Page 47

1
SRB
1
!
- Imajte na umu da impedansa (unutrašnji otpor)
detektora napona utiče na pokazivanje smetnji u naponu
(kapacitivnih ili induktivnih povezano)!
U zavisnosti od unutrašnje impedanse detektora napona, kod
održavanja smetnji u naponu postoje različite mogućnosti
pokazivanja "Radni napon postoji" ili " Radni napon ne postoji"
Niski detektor napona (impedansa < 100 kΩ), smetnje u
naponu su potisnute ili smanjene:
Detektor napona sa relativno niskom unutrašnjom
impedansom u poređenju sa referentnom vrednosti 100 kΩ
ne pokazuje sve smetnje u naponu sa početnom vrednosti
iznad GVE (50 V AC / 120 V DC). Pri kontaktu sa delovima
koji se proveravaju detektor napona može privremeno smanjiti
smetnje u naponu usled pražnjenja na nivo ispod GVE; nakon
uklanjanja detektora napona, smetnje u naponu će ponovo
postići svoju prvobitnu vrednost.
Kada se ne pojavi znak " Napon prisutan ", preporučuje se da
pre otpočinjanja rada hitno uključite uzemljenje uređaja.
Visoki detektor napona (impedansa > 100 kΩ): smetnja u
naponu nije potisnuta odn. smanjena:
Detektor napona sa relativno visokom unutrašnjom
impedansom u poređenju sa referentnom vrednosti 100 kΩ pri
postojećeoj smetnji napona " Radni napon nije prisutan " neće
biti jasno pokazan. Kada se oznaka " Napon prisutan" pojavi
na jednom delu, koji se smatra odvojenim od uređaja, hitno se
preporučuje, da se dodatnim merama (na primer: korišćenjem
odgovarajućeg detektora napona koji je u mogućnosti da
razlikuje radni napon od smetnje u naponu, vizeulna provera
razdvajanja u električnoj mreži, itd) status "Radni napon ne
postoji" dela koji se proverava, dokaže i utvrdi da je od strane
detektora napona pokazani otpor smetnja u naponu.
Detektori napona koji su u stanju da putem veze punjenja
razlikuju radni napon od smetnje u naponu:
Detektor napona sa naznakom dve vrednosti unutrašnje
impedanse je prošao test svoje izvedbe / konstrukcije za
tretman smetnji u naponu i u prilici je da (u okviru tehničkih
ograničenja) razlikuje radni napon od smetnji u naponu i da
postojeći tip napona pokaže direktno ili indirektno.
Električni simboli na uređaju:
Simbol Značenje
Важно документација!
Симбол означава да употребу описан у
приручнику, да би избегли било какве ризике
Uređaj ili oprema za rad pod naponom
Taster
AC izmenični napon
DC istosmerni napon
DC/AC istosmerni i naizmenični napon
Земља (напон на масу)
Taster (ručno aktiviran); ovo nam kaže da se
određeni prikazi dobivaju tek nakon pritiska oba
tastera
Okretanje udesno; pravac polja okretanja
se prikazuje samo kod 50 odnosno 60 Hz i u
uzemljenoj mreži
Pokazivač sa integrisanom špulom
2. Opis uređaja
1
Zaštita vrhova ispitivača
2
Vrh ispitivača L1/-
3
Vrh ispitivača L2/+
4
Pokazivač sa integrisanom špulom
5
Taster
6
Ručka L1
7
Ručka ekrana L2
8
LED-lampice prikaza stupnjeva
9
LC-displej sa simbolom „R“ za ispitivanje vanjskog vodiča
(prikaz faze) i prikaz polja okretanja (desno)
J
+/- LED-ovi prikaza polariteta
3. Provera funkcije pre upotrebe u svrhu provere
nepostojanja napona nekog postrojenja
- Neposredno prije i nakon korištenja ispitivača napona,
proveriti ga na funkciju !
- Ispitivač napona testirajte na poznatim izvorima napona ,
na primer u 230 V utičnici.
- Nemojte upotrebiti kontrolora napona, ukoliko prikaz
napona, prikaz faza i vibracijskog motora ne funkcionišu
besprekorno!
4.
Provera nepostojanja napona nekog postrojenja (slika A/B)
Kod provere postrojenja proverite nepostojanja napona
postrojenja sa kontrolom prikaza napona, prikaza faza
(prikaz faza funkcioniše samo u ozemljenoj mreži izmeničnog
napona) i vibracionog motora (vibracioni motor aktivira se
pritiskivanjem obadve pritisne dirke). Nepostojanje napona
postrojenja postoji samo onda, kada nepostojanje napona
signaliziraju sva tri kruga proveravanja (prikaz napona, prikaz
faza i vibracioni motor).
- Postavite oba ispitna vrha L1/+ 2 i L2/- 3 na delove
sistema – postrojenja koje želite ispitati.
- Visina izmerenog napona prikazuje se na LED lampicama
stupnjeva 8 .
- Pritiskom na oba tastera 5 uključuje se merna špula
s pokazivačem 4, 12 V LED-stupanj (+/ -) i interno
opterećenje u ispitivaču napona .
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
47
Page 48

1
SRB
- Izmenični naponi (AC) prikazuju se istovremenim
uključivanjem (svetle) + 24 V LED i - 24 V LED.
- Istosmerni naponi (DC) prikazuju se uključivanjem + 24 V
LED ili - 24 V LED. Preko indikatora polariteta J prikazuje
nam se polaritet + ili – na vrhu ispitivača L2/+ 3 .
- Da bismo razlikovali napone bogatije ili siromašnije
energijom (na primer kapacitativno povezane smetnje u
naponu), pritiskom na oba tastera uključujemo interno
opterećenje u samom ispitivaču napona (vidi tačku 5).
5. Priključak sa vibracionim motorom (slika A/B)
Obe ručke L1 6 i L2 7 opremljene su sa tasterima 5.
Pritiskom na oba tastera uređaj prebacujemo na manji
interni otpor. Pri tom se pod napon stavlja vibracioni motor
(necentrisani motor). Od ca. 200 V ovaj se motor uključuje
u rotaciju. Povećanjem napona povećava se broj okretaja i
vibracije. Trajanje ispitivanja sa smanjenim unutarnjim otporom
(ispitivanje opterećenja) ovisi o visini izmerenog napona. Da
ne bi došlo do neželjenog zagrijavanja uređaja, predviđena je
termička zaštita (regulaciona). Ova regulacija smanjuje broj
okretaja vibracionog motora i unutarnji otpor opet raste.
Dodavanje opterećenja (oba tastera pritisnuta) možemo
koristiti da bismo......
- suzbili slepe napone (induktivne i kapacitativne)
- ispraznili kondenzatore
- aktivirali 10/30 mA RCD-zaštitne prekidače. Aktiviranje
RCD-zaštitnog prekidača vrši se ispitivanjem na vanjskom
vodiču (prikaz faze) prema PE (uzemljenje) (slika D)
6. Ispitivanje vanjskog vodiča (prikaz faze) (slika C)
- Uhvatite u celosti ručke L1 6 i L2 7 da biste osigurali
kapacitativnu vezu sa tlom.
- Postavite vrh ispitivača L2/+ 3 na deo sistema koji
ispitujete .
Uvek paziti na to da kod jednopolnog vanjskog vodiča
(prikaz faze) ne dođe do kontakta sa vrhom ispitivača L1/-
2
i da ovaj ostane bez kontakta.
- Ako nam se na LC-displeju 9 pojavi simbol „R“, tada se
na tom delu sistema/postrojenja nalazi vanjski vodič (faza)
izmeničnog napona.
Napomena:
Ispitivanje jednopolnog vanjskog vodiča (prikaz faze) moguće
je u uzemljenoj mreži od 230 V, 50/60 Hz (faza prema
uzemljenju). Zaštitna odeća i izolacije na mestu ispitivanja
mogu delovati na funkciju.
Pažnja!
Nepostojanje napona se može ustvrditi samo dvopolnim
ispitivanjem.
7. Ispitivanje polja okretanja (slika E/F)
- Uhvatite u celosti ručke L1 6 i L2 7 da biste osigurali
kapacitativnu vezu sa tlom.
-
Postavite vrhove ispitivača L1/- 2 i L2/+ 3 na dva vanjska
vodiča (faze) jedne mreže rotacione struje i proverite da
vanjski vodiči imaju napon od na primer 400 V.
- Okretaj udesno (faza L1 prije faze L2) imamo kada se
na LC-displeju 9 pojavi simbol „R“. LC displej ostaje
isključen ako ispitivač nije prepoznao okretanje udesno.
- Ispitivanje polja okretaja uvek zahteva i dodatnu kontrolu !
Ako LC-displej pokazuje desno okretanje sa „R“ simbolom,
tada kod dodatne provere za zamenjenim vrhovima
ispitivača L1/- 2 i L2/+ 3 LC-displej ostaje isključen.
Ako bi LC-displej u oba slučaja prikazivao „R“ simbol, tada
imamo preslabo uzemljenje.
Napomena:
Ispitivanje polja okretaja moguće je od 400 V - 900 V, 50/60 Hz
(faza na fazu) kod uzemljene visokonaponske strujne mreže.
Zaštitna odeća i izolacije na mestu ispitivanja mogu delovati
na funkciju.
8. Tehnička specifikacija
- Propisi: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Područje nazivnog napona: 12 V do AC/DC 1.000 V
- Područje nazivne frekvencije f: 0 do 60 Hz
- Maks. greška u prikazu: Un ± 15 %, ELV Un + 0 % - 15 %
- Impedansa (unutarnjeg otpora), merni krug/ kruga
opterećenja: 200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Preuzimanje struje merni krug: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
-
Preuzimanje struje kruga opterećenja : Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Prikaz polariteta: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (kod aktiviranog tastera)
- Vanjski vodič (prikaz faze): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Ispitivanje okretajnog kruga: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibracioni motor, pokretanje : ≥ Un 200 V
- Kategorija nadnapona : CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Zaštita: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 – kao prvi broj : Zaštita pristupa opasnim delovima i
zaštita od čvrstih stranih tela, zaštićeno od prašine
5 – kao drugi broj: Zaštićeno od mlaza vode. Može se
koristiti i kod kiše i padalina.
- maksimalno trajanje rada kod aktiviranja tastera:
VU (ED) = 30 sek (maks. 30 sekundi), 600 sek pauze
- Težina: ca. 250 g
- Dužina spojnog kabela: ca. 1000 mm
- Temperature rada i skladištenja : - 20 °C do + 45 °C
(klimatska kategorija N)
- Relativna vlažnost zraka: 20 % bis 96 % (klimatska
kategorija N)
- Vreme regulacije rada (termička zaštita):
Napon/vreme:
9. Opšte održavanje
Kučište uređaja izvana prebrisati suhom, čistom krpom.
10. Zaštita okoline
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Molimo da uređaj nakon isteka životnog veka zbrinete
na odgovarajući, zakonom propisani način.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
48
Page 49

DUSPOL® analog 1000
Kullanım Kılavuzu
DUSPOL® analog 1000 voltaj test cihazını kullanmadan önce:
Kullanma kılavuzunu dikkatlice okuyarak burada bulunan güvenlik bilgi notlarına uyunuz!
İçindekiler
1. Emniyet bilgileri
2. Cihaz açıklaması
3. Bir tesisin gerilim içermediğine dair kontrolün kullan-
madan öne yapılması
4.
Bir tesisin gerilim içerip içermediğinin kontrol edilmesi
5. Vibrasyon motorlu yük devrelemesi
6. Harici iletken testi (faz göstergesi)
7. Faz alanı testi
8. Teknik Veriler
9. Genel bakım
10. Çevre koruması
1. Emniyet bilgisi:
- Kullanım sırasında cihazı sadece izolasyonlu yerlerinden
L1 6 ve L2 7 tutup test uçlarına L1/- 2 ve L2/+ 3 ke-
sinlikle dokunmayınız!
- Hemen kullanmadan önce ve kullandıktan sonra tesiste
elektrik olup olmadığını kontrol etmek için gerilim kontrol
aletinin çalışıp çalışmadığını kontrol ediniz (bakınız Bölüm
3)! Bir veya birden fazla göstergenin devre dışı kalması
veya fonksiyona hazır olmadığı görüldüğü takdirde voltaj
test cihazı kullanılamaz! Kontrol işlemi daha sonra başka
bir gerilim ölçüm aletiyle yinelenmelidir.
- Voltaj test cihazı sadece belirtilen nominal gerilim alanında
AC/DC 1.000 V elektrik tesisatlarında kullanılabilir!
-
Gerilim test cihazı sadece Maks.1000 V düzeyindeki CAT III
yüksek voltaj kategorisi ile Maks.600 V iletken CAT IV yük-
sek voltaj kategorisinde topraklanmış halde kullanılabilir.
- Voltaj test cihazı elektrik uzmanları tarafından güvenli ça-
lışma yöntemine uygun biçimde kullanılmak üzere tasar-
lanmıştır.
- LED kademe göstergesi voltaj aralığının ekrana getirilme-
sine yarar ve ölçüm yapmak için düzenlenmemiştir.
- 30 saniyeden daha fazla gerilim bir gerilim test cihazı
(maksimum izin verilen açma süresi ED = 30s) oluşturma!
- Voltaj test cihazı kesinlikle sökülmemelidir!
- Voltaj test cihazı kirden ve kasa üst yüzeyinin hasar gör-
mesinden korunmalıdır.
- Yaralanmalardan korunmak amacı ile voltaj test cihazı
kullanıldıktan sonra test uçlarına pakette bulunan test ucu
koruma çubuğu 1 takılmalıdır!
- Gerilim test cihazının empedansının (iç direnç), girişim
gerilimlerinin göstergesini (kapasitif veya endüktif bağlı)
etkilediğini dikkate alın!
Gerilim test cihazının iç empedansına bağlı olarak girişim
gerilimi mevcut olduğunda, "İşletme gerilimi mevcut" veya "İşletme gerilimi mevcut değil" göstergesi için farklı seçenekler
mümkündür.
Düşük ohm'lu gerilim test cihazı (Empedans < 100 kΩ), girişim gerilimi bastırılır veya düşürülür:
Düşük iç empedansa sahip bir gerilim test cihazı, 100 kΩ referans değerine göre başlangıç değeri ELV'nin (50 V AC/ 120 V
DC) üzerinde olan tüm girişim gerilimlerini göstermez. Test edilecek olan parçalarla temas halinde gerilim test cihazı, girişim
gerilimlerini deşarj ederek geçici olarak ELV'nin altına kadar bir
seviyeye düşürülebilir; ancak gerilim test cihazı çıkarıldıktan
sonra, girişim gerilimi tekrar başlangıç değerine döner.
"Gerilim mevcut" göstergesi gösterilmezse, çalışmalara başlamadan önce bir topraklama tertibatının takılması mutlaka
önerilir.
Yüksek ohm'lu gerilim test cihazı (Empedans > 100 kΩ):
Girişim gerilimi bastırılmaz veya düşürülmez:
Yüksek iç empedansa sahip bir gerilim test cihazı, 100 kΩ referans değerine göre girişim gerilimi mevcut olduğunda "İşletme
gerilimi mevcut değil" durumunu belirgin bir şekilde göstermez.
"Gerilim mevcut" göstergesi, tesisten ayrılmış olan bir parçada
gösterilirse, ek önlem alarak (Örnek: işletme gerilimini girişim
geriliminden ayırabilen uygun bir gerilim test cihazının kullanımı, elektrik şebekesinde ayırma yerinin gözle kontrolü vs.) test
edilecek olan parçanın "İşletme gerilimi mevcut değil" durumunun kanıtlanması ve gerilim test cihazı tarafından gösterilen
gerilimin bir girişim gerilimi olduğunun tespit edilmesi mutlaka
önerilir.
Yük uygulamasının yapılmasıyla işletme gerilimini girişim
geriliminden ayırabilen gerilim test cihazı:
İki iç empedans değeri belirten bir gerilim test cihazı, girişim
gerilimleri işlemlerine yönelik olarak model / konstrüksiyon testinde başarılı oldu ve (teknik sınırlar içerisinde) işletme gerilimini girişim geriliminden ayırabilmekte ve mevcut gerilim tipini
doğrudan veya dolaylı olarak gösterebilmektedir.
Cihaz üzerindeki elektrik sembolleri:
Sembol Anlam
Önemli belgeleri!
Sembol kılavuzda herhangi risklerden kaçın-
mak için, kılavuzda açıklanan belirtir
Voltaj altında çalışmaya izin veren cihaz veya
donanım
Basma tuşu
AC alternatif akım
DC sabit akım
DC/AC sabit ve alternatif akım
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
49
Page 50

Toprak (toprak gerilim)
Buton (el kumandalı); tür görüntüler sadece butonlar hem basarak belirtir
Sağ dönüş sırası, döner yönü sadece 50 veya
60 Hz ve topraklı sistemde görüntülenmez ola-
bilir
Daldırma makara seviye göstergesi
2. Cihaz açıklaması
1
Test ucu koruma çubuğu
2
Test ucu L1/-
3
Test ucu L2/+
4
Daldırma makara seviye göstergesi
5
Basmalı tuş
6
Tutacak L1
7
Gösterge tutacağı L2
8
LED kademe göstergesi
9
Harici iletken testi (faz göstergesi) ve faz alanı göstergesi
(sağ) için "R" sembollü LC ekran
J
+/- Polarite gösterge LED'leri
3. Bir tesisin gerilim içermediğine dair kontrolün kullan-
madan öne yapılması
- Kullanımın hemen öncesinde ve sonrasında voltaj test ci-
hazının işlerliğini teste edin!
- Voltaj test cihazını bildiğiniz voltaj kaynaklarında, örneğin
230 voltluk prizlerde deneyebilirsiniz.
- Gerilim göstergesi, faz göstergesi ve vibrasyon motoru
sorunsuz bir şekilde çalışmadığı takdirde gerilim kontrol
aletini kullanmayınız!
4. Bir tesisin gerilim içerip içermediğinin kontrol edilme-
si (Resim A/B)
Tesis kontrolü sırasında tesisin gerilim içermediğini gerilim
göstergesi, faz göstergesi (faz göstergesi yalnızca topraklanmış alternatif gerilim şebekesinde çalışır) ve vibrasyon motoru
(vibrasyon motoru her iki butona basılarak etkinleşir) aracılığıyla kontrol ediniz. Tesisin gerilim içermediği durumu yalnızca
üç kontrol fazının hepsi gerilimsizlik durumu sinyalize ettiğinde
mevcuttur (Gerilim göstergesi, faz göstergesi ve vibrasyon
motoru).
- Her iki test ucunu L1/+ 2 ve L2/- 3'ü test edilecek cihaza
takınız.
- Bağlanan voltajın düzeyi LED kademe göstergesi 8 ile
ekrana getirilir.
- Her iki basmalı tuşa 5 dokunulduğunda daldırma makara
düzey göstergesi 4, 12 V LED kademesi (+/-) ve voltaj
test cihazındaki dahili yük devreye girer.
- Alternatif akımlar (AC) + 24 V LED ve - 24 V LED'in eş
zamanlı olarak yanması ile ekrana getirilir.
- Sabit akımlar (AC) + 24 V LED veya - 24 V LED'in yanması
ile ekrana getirilir. Polarite göstergesi J ile test uçlarında
L2/+ 3 polarite + veya - gösterilir.
- Enerji yüklü veya enerjisi düşük voltajları (örneğin kapasi-
tif bağlantılı parazit voltajlar) birbirinden ayırmak amacı ile
her iki basmalı tuşu basılarak voltaj test cihazında dahili
yük beslemesi sağlanabilir (bakınız Bölüm 5.)
5. Vibrasyon motorlu yük devrelemesi (Resim A/B)
Her iki tutma yeri L1 6 ve L2 7 basmalı tuş 5 ile donatılmış-
tır. Her iki basmalı tuşa basıldığında daha düşü bir iç direnç
devreye girer. Burada bir vibrasyon motoru (balanssız motor)
voltaja bağlanır. Yaklaşık 200 V'tan itibaren dönüş hareketi
başlar. Gerilim arttıkça devir sayısı ve vibrasyon da artar. Testin düşük iç direnç ile sürdürülmesi (yük testi) ölçülecek voltajın
düzeyine bağlıdır. Cihazın izin verilenin ötesinde ısınmaması
için termik koruma (geri besleme) mevcuttur. Bu tür geri besle-
mede vibrasyon motorunun devir sayısı düşer ve dahili direnç
ise artar.
Yük fazlası (her iki basmalı tuşa basılır) ....
- Kör voltajı (indüktif ve kapasitif voltaj) bastırmak
- Kondansatörleri deşarj etmek
-
10 mA/ 30 mA RCD koruma şalterini devreye sokmak ama-
cı ile kullanılır. RCD koruma şalterinin devreye sokulması
harici iletkende (faz göstergesi) PE (toprak) yapılan set ile
sağlanır. (Resim D)
6. Harici iletken testi (faz göstergesi) (Resim C)
- Toprağa karşı kapasitif bağlantıyı sağlamak amacı ile L1
6
ve L2 7 tutma yerlerini komple kavrayınız.
- Test uçlarını L2/+ 3 test edilecek cihaz parçasına bağla-
yınız.
Bunu yaparken tek kutuplu harici iletken testinde (faz gös-
tergesi) test ucunun L1/- 2 temas etmemesine ve temas-
sız kalmasına özen gösteriniz.
- LC ekranda 9 bir „R“ sembolü çıktığında, cihazın bu kıs-
mına alternatif akımın bir harici iletkeni (faz) bağlıdır.
Bilgi:
Tek kutuplu harici iletken testi (faz göstergesi) topraklı şebekede 230 V, 50/60 Hz'den itibaren (toprağa karşı faz) mümkündür. Koruma giysileri ve izolasyonlu ortama bağlı özel durumlar
bu fonksiyona kısıtlama getirebilir.
Dikkat!
Voltaj olmadığı ancak iki kutuplu test ile saptanabilir.
7. Faz alanı testi (Resim E/ F)
- Toprağa karşı kapasitif bağlantıyı sağlamak amacı ile L1
6
ve L2 7 tutma yerlerini komple kavrayınız.
- Test uçlarını L1/- 2 ve L2/+ 3 alternatif akım ağının iki
harici iletkenine (faz) bağlayıp harici iletken geriliminde
400 V olup olmadığını test ediniz.
- LC ekranda 9 bir „R“ sembolü çıktığında, sağa doğru dö-
nüş dizisi (faz L2'den önce L1) söz konusudur. Sağa doğ-
ru dönüş dizisi saptanamadığı takdirde, LC ekran karanlık
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
50
Page 51
kalır.
- Faz alanı testi her zaman karşı kontrolü gerektirir!. LC ek-
ranın „R“ sembolü ile sağa dönüş dizisini gösterdiği takdir-
de, değiştirilmiş test uçları L1/- 2 ve L2/+ 3 ile yapılan
karşı kontrolde LC ekranın kapalı kalması gerekir.
LC ekranın her iki durumda da „R“ sembolü göstermesi
durumunda, topraklama zayıf demektir.
Bilgi:
Faz alanı testi topraklı alternatif akım ağında 400 V - 900 V,
50/60 Hz'den itibaren (faza karşı faz) mümkündür. Koruma giysileri ve izolasyonlu ortama bağlı özel durumlar bu fonksiyona
kısıtlama getirebilir.
8. Teknik Veriler
- Yönerge: DIN EN 61243-3: 2015, IEC 61243-3: 2014
- Nominal gerilim aralığı: 12 V ila AC/DC 1.000 V
- Nominal frekans aralığı f: 0 ila 60 Hz arası
-
Maksimum gösterge hatası: Un ± % 15, ELV Un + 0 % - % 15
- Empedans (iç direnç), ölçüm çemberi/ yük döngüsü:
200 kΩ/ 5 kΩ
- Ölçüm çemberi voltaj girişi: Is < 6,0 mA (1.000 V)
- Yük döngüsü voltaj girişi: Is < 550 mA (1.000 V)
- Polarite göstergesi: + 24 V LED, - 24 V LED, + 12 V LED,
- 12 V LED (basmalı tuşa basılı halde)
- Harici iletken (faz göstergesi): ≥ Un 230 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Faz alanı testi: ≥ Un 400 V, 50 Hz/ 60 Hz
- Vibrasyon motoru, hareket: ≥ Un 200 V
- Aşırı voltaj kategorisi: CAT IV 600 V, CAT III 1000 V
- Koruma türü: IP 65 (DIN VDE 0470-1 IEC/EN 60529)
6 - ilk kod: Tehlikeli parça veya erişim koruması ve sabit
yabancı cisimlere karşı koruma, toz geçirmez
5 - ikinci kod: Püskürtme suya karşı koruma. Yağmur altın-
da da kullanılabilir.
- maks. izin Görev döngüsü: 30 s (maks. 30 saniye), 600 s
kapalı
- Ağırlık: Yakl. 250 g
- Bağlantı hattı uzunluğu: Yakl. 1000 mm
- İşletim ve depolama ısı aralığı: - 20 °C ila + 45 °C (iklim
kategorisi N)
- Göreli hava nemi: % 20 ila % 96 (iklim kategorisi N)
- Geri besleme süreleri (termik koruma):
Voltaj/Zaman:
9. Genel bakım
Kasayı dıştan temiz ve kuru bir bezle siliniz.
10. Çevre koruması
230 V/30 s, 400 V/9 s, 690 V/5 s, 1000 V/2 s
Lütfen cihazı kullanım ömrünü tamamladıktan sonra
ait olduğu iade ve toplama sistemine dahil ediniz.
02/ 2019
DUSPOL® analog 1000
51
 Loading...
Loading...