Page 1
GKS9
G
AS
-F
IRED
W
ARM
A
IR
F
URNACE
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated Upflow. A “Blocked Drain Kit” is available and MUST
BE USED if the furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal Right. Check the Serial/Rating Plate on the
furnace for the Kit part number.
Installer: Affix all manuals adjacent to the unit.
(T ype FSP CATEGORY IV Direct or Non Direct Vent Air Furnace)
These furnaces comply with requirements
embodied in the American National S tandard
/ National Standard of Canada ANSI
Z21.47·CSA-2.3 Gas Fired Central Furnaces.
C
®
US
RECOGNIZE THIS SYMBOL AS A SAFETY PRECAUTION.
ATTENTION INSTALLING PERSONNEL
As a professional installer you have an obligation to know the product better than the customer. This includes all safety
precautions and related items.
Prior to actual installation, thoroughly familiarize yourself with this Instruction Manual. Pay special attention to all safety
warnings. Often during installation or repair it is possible to place yourself in a position which is more hazardous than
when the unit is in operation.
Remember, it is your responsibility to install the product safely and to know it well enough to be able to instruct a
customer in its safe use.
Safety is a matter of common sense...a matter of thinking before acting. Most dealers have a list of specific good safety
practices...follow them.
The precautions listed in this Installation Manual are intended as supplemental to existing practices. However, if there is
a direct conflict between existing practices and the content of this manual, the precautions listed here take precedence.
*NOTE: Please contact your distributor or our
website for the applicable Specification Sheet
referred to in this manual.
IO-300J
12/10
Goodman Manufacturing Company , L.P.
5151 San Felipe, Suite 500, Houston, TX 77056
www.goodmanmfg.com
© 2006-2008, 2010 Goodman Manufacturing Company, L.P .
Page 2

Table of Contents
I. Component Identification ............................................................................................................................................... 5
II. Safety .............................................................................................................................................................................. 6
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) PRECAUTIONS ................................................................................................... 6
III. Product Application ...................................................................................................................................................... 6
IV . Location Requirement s & Considerations.................................................................................................................. 7
GENERAL ......................................................................................................................................................... 7
LEARANCES AND ACCESSIBILITY........................................................................................................................... 8
C
URNACE SUSPENSION ........................................................................................................................................ 8
F
XISTING FURNACE REMOVAL .............................................................................................................................. 8
E
HERMOSTAT LOCATION ....................................................................................................................................... 9
T
V. Combustion & Ventilation Air Requirements ............................................................................................................... 9
VI. Installation Positions ...................................................................................................................................................11
VII. Horizontal Applications & Considerations ................................................................................................................11
GENERAL ........................................................................................................................................................11
RAIN TRAP AND LINES .....................................................................................................................................11
D
EVELING ........................................................................................................................................................11
L
LTERNATE VENT/FLUE CONNECTION .....................................................................................................................11
A
LTERNATE ELECTRICAL AND GAS LINE CONNECTIONS ............................................................................................ 12
A
RAIN PAN ..................................................................................................................................................... 12
D
REEZE PROTECTION ........................................................................................................................................ 12
F
URNACE SUSPENSION ...................................................................................................................................... 12
F
VIII. Propane Gas /High Altitude Installations............................................................................................................... 12
IX. Vent/Flue Pipe & Combustion Air Pipe ..................................................................................................................... 12
GENERAL ....................................................................................................................................................... 12
D
UAL CERTIFICA TION : NON-DIRECT/DIRECT VENT ................................................................................................... 13
ATERIALS AND JOINING METHODS ..................................................................................................................... 13
M
ROPER VENT/FLUE AND COMBUSTION AIR PIPING PRACTICES ................................................................................. 13
P
ERMINATION LOCATIONS ................................................................................................................................... 13
T
ANADIAN VENTING REQUIREMENTS..................................................................................................................... 14
C
TANDARD FURNACE CONNECTIONS ..................................................................................................................... 14
S
LTERNATE FURNACE CONNECTIONS ..................................................................................................................... 14
A
ON-DIRECT VENT (SINGLE PIPE) PIPING ............................................................................................................ 15
N
IRECT VENT (DUAL PIPE) PIPING ...................................................................................................................... 16
D
ENT/INTAKE TERMINATIONS FOR INSTALLATION OF MULTIPLE DIRECT VENT FURNACES .................................................. 18
V
ONCENTRIC VENT TERMINATION ......................................................................................................................... 18
C
IDE WALL VENT KIT........................................................................................................................................ 18
S
X. Condensate Drain Lines & Drain Trap........................................................................................................................ 18
GENERAL ....................................................................................................................................................... 18
U
PRIGHT INST ALLATIONS ..................................................................................................................................... 18
ORIZONTAL INSTALLA TIONS ................................................................................................................................21
H
XI. Electrical Connections................................................................................................................................................ 22
WIRING HARNESS ............................................................................................................................................ 22
OLT LINE CONNECTIONS ............................................................................................................................ 23
115 V
OLT THERMOSTAT WIRING ............................................................................................................................ 23
24 V
XII. Gas Supply and Piping.............................................................................................................................................. 23
GENERAL ....................................................................................................................................................... 23
AS PIPING CONNECTIONS ................................................................................................................................24
G
ROPANE GAS TANKS AND PIPING...................................................................................................................... 26
P
XIII. Circulating Air & Filters ............................................................................................................................................ 26
DUCTWORK - AIR FLOW ..................................................................................................................................... 26
OTTOM RETURN AIR OPENING [UPFLOW MODELS]............................................................................................... 27
B
ILTERS - READ THIS SECTION BEFORE INSTALLING THE RETURN AIR DUCTWORK ....................................................... 27
F
PRIGHT INST ALLATIONS ..................................................................................................................................... 27
U
ORIZONTAL INSTALLA TIONS ................................................................................................................................28
H
2
Page 3
Table of Contents
XIV. Startup Procedure & Adjustment............................................................................................................................. 28
HEA T ANTICIPAT OR SETTING ................................................................................................................................28
RAIN TRAP PRIMING ....................................................................................................................................... 28
D
URNACE OPERATION ......................................................................................................................................... 28
F
AS SUPPLY PRESSURE MEASUREMENT .............................................................................................................. 28
G
AS MANIFOLD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT .................................................................................. 29
G
AS INPUT RATE MEASUREMENT (NA TURAL GAS ONLY) ......................................................................................... 29
G
EMPERATURE RISE ......................................................................................................................................... 30
T
IRCULATOR BLOWER SPEEDS ........................................................................................................................... 30
C
XV. Normal Sequence of Operation................................................................................................................................ 30
POWER UP ..................................................................................................................................................... 30
EATING MODE ............................................................................................................................................... 30
H
OOLING MODE .............................................................................................................................................. 31
C
AN ONLY MODE............................................................................................................................................. 31
F
XVI. Operational Checks .................................................................................................................................................. 31
BURNER FLAME ............................................................................................................................................... 31
XVII. Safety Circuit Description ....................................................................................................................................... 31
GENERAL ....................................................................................................................................................... 31
NTEGRATED CONTROL MODULE .......................................................................................................................... 31
I
RIMARY LIMIT ................................................................................................................................................ 31
P
UXILIARY LIMIT............................................................................................................................................... 31
A
OLLOUT LIMIT ................................................................................................................................................ 31
R
RESSURE SWITCHES ........................................................................................................................................ 31
P
LAME SENSOR ............................................................................................................................................... 31
F
XVIII. Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................................... 32
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) PRECAUTIONS ................................................................................................. 32
IAGNOSTIC CHART .......................................................................................................................................... 32
D
ESETTING FROM LOCKOUT ............................................................................................................................... 32
R
XIX. Maintenance ............................................................................................................................................................. 32
ANNUAL INSPECTION .......................................................................................................................................... 32
ILTERS .......................................................................................................................................................... 32
F
URNERS ....................................................................................................................................................... 33
B
NDUCED DRAFT AND CIRCULATOR BLOWERS ......................................................................................................... 33
I
ONDENSATE TRAP AND DRAIN SYSTEM (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY)...................................................................... 33
C
LAME SENSOR (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY) ...................................................................................................... 33
F
GNITER (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY).................................................................................................................. 33
I
LUE PASSAGES (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY) ..................................................................................................... 33
F
XX. Before Leaving an Installation ................................................................................................................................. 33
XXI. Repair & Replacement Parts ................................................................................................................................... 33
APPENDIX
Troubleshooting Chart ...................................................................................................................................................... 34
GKS9 Wiring Diagram ...................................................................................................................................................... 36
WARN ING
G
OODMAN WILL NOT BE RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY INJURY OR
PROPERTY DAMAGE ARISING FROM IMPROPER SERVICE OR SERVICE
PROCEDURES
YOU ASSUME RESPONSIBILITY FOR ANY PERSONAL INJURY OR
PROPERTY DAMAGE WHICH MAY RESULT
REQUIRE A LICENSE TO INSTALL OR SERVICE HEATING AND AIR
CONDITIONING EQUIPMENT
. IF
YOU INSTALL OR PERFORM SERVICE ON THIS UNIT
. M
ANY JURISDICTIONS
.
3
,
Page 4
WARN ING
IF
THE INFORMATION IN THESE INSTRUCTIONS IS NOT FOLLOWED
EXACTLY, A FIRE OR EXPLOSION MAY RESULT CAUSING PROPERTY
DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR LOSS OF LIFE
- D
O NOT STORE OR USE GASOLINE OR OTHER FLAMMABLE VAPORS
AND LIQUIDS IN THE VICINITY OF THIS OR ANY OTHER APPLIANCE
.
.
- WHAT T O D O IF YO U SMELL GA S:
* D
O NOT TRY TO LIGHT ANY APPLIANCE
* D
- I
NSTALLATION AND SERVICE MUST BE PERFORMED BY A QUALIFIED
INSTALLER, SERVICE AGENCY OR THE GAS SUPPLIER
O NOT TOUCH ANY ELECTRICAL SWITCH; DO NOT USE
ANY PHONE IN YOUR BUILDING
MMEDIATELY CALL YOUR GAS SUPPLIER FROM A
* I
NEIGHBORS PHONE
INSTRUCTIONS
F YOU CANNOT REACH YOUR GAS SUPPLIER, CALL THE
* I
FIRE DEPARTMENT
. F
OLLOW THE GAS SUPPLIERS
.
.
.
.
WARN ING
S
HOULD OVERHEATING OCCUR OR THE GAS SUPPLY FAIL TO SHUT
OFF, TURN OFF THE MANUAL GAS SHUTOFF VALVE EXTERNAL TO THE
FURNACE BEFORE TURNING OFF THE ELECTRICAL SUPPLY
.
CARBON MONOXIDE POI SONING HAZARD
Special Warning for Installation of Furnace or Air Handling Units in
Enclosed Areas such as Garages, Utility Rooms or Parking Areas
TO THE INSTALLER
Before installing this unit, please read this manual thoroughly to
familiarize yourself with specific items which must be adhered to,
including but not limited to: unit maximum external static pressure,
gas pressures, BTU input rating, proper electrical connections, circulating air temperature rise, minimum or maximum CFM, and motor speed connections.
TRANSPORTATION DAMAGE
All units are securely packed in shipping containers tested according to International Safe Transit Association specifications. The carton must be checked upon arrival for external damage. If damage
is found, a request for inspection by carrier’s agent must be made in
writing immediately.
The furnace must be carefully inspected on arrival for damage and
bolts or screws which may have come loose in transit. In the event
of damage the consignee should:
1. Make a notation on delivery receipt of any visible damage to
shipment or container.
2. Notify carrier promptly and request an inspection.
3. With concealed damage, carrier must be notified as soon as
possible - preferably within five days.
4. File the claim with the following support documents within a
nine month statute of limitations.
• Original or certified copy of the Bill of Lading, or indemnity
bond.
• Original paid freight bill or indemnity in lieu thereof.
• Original or certified copy of the invoice, showing trade and
other discounts or reductions.
• Copy of the inspection report issued by carrier’s
representative at the time damage is reported to carrier.
The carrier is responsible for making prompt inspection of damage
and for a thorough investigation of each claim. The distributor or
manufacturer will not accept claims from dealers for transportation
damage.
Keep this literature in a safe place for future reference.
Carbon monoxid e producing devices (such as an automobile, space
heater, gas water heater, etc.) should not be operated in enclosed areas
such as unventilated garages, utility rooms or parking areas because of
the danger of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning resulting from the exhaust
emissions. If a furnace or air handler is installed in an enclosed area such
as a garage, utility room or parking area and a carbon monoxide producing
device is operated therein, there must be adequate, direct outside
ventilation.
This ventilation is necessary to avoid the danger of CO poisoning which
can occur if a carbon monoxide producing device continues to operate in
the enclosed area. Carbon monoxide emissions can be (re)circulated
throughout the structure if the furnace or air handler is operating in any
mode.
CO can cause serious illness including permanent brain damage or death.
-
B10259-216
4
Page 5
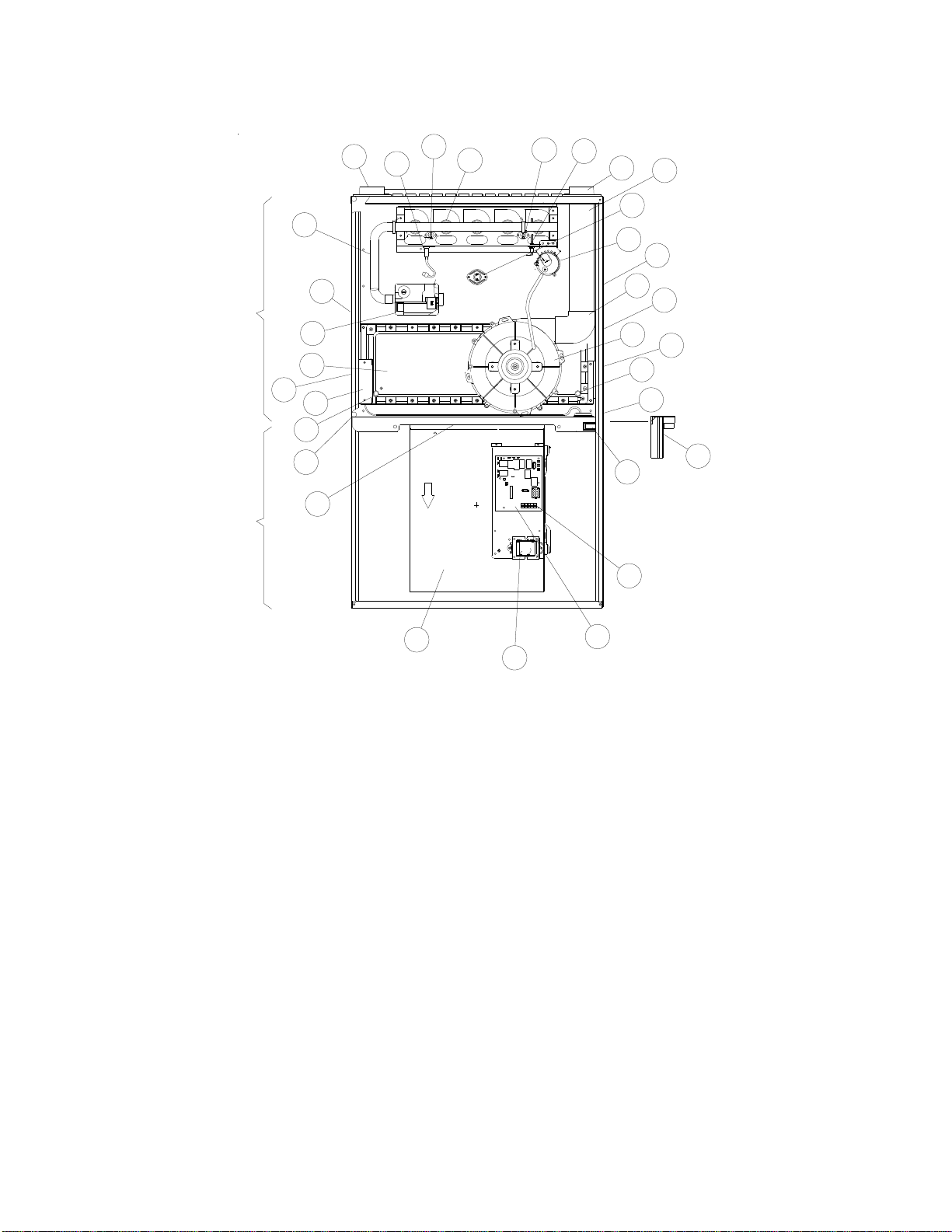
I. COMPONENT IDENTIFICATION
29
25
18
17
27
26
1
24
3
2
6
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
28
19
20
BLOWER COMPARTMENT BURNER COMPARTMENT
1 Gas Valve
2 Gas Line Entrance (Alternate)
3 Combustion Air Intake Connection / “Coupling”
4 Hot Surface Igniter
5 Burners
6 Rollout Limit
7 Flame Sensor
8 Flue Pipe Connection / “Coupling”
9 Flue Pipe (Internal)
10 Primary Limit
11 Pressure Switch
12 Gas Line Entrance
13 Rubber Elbow
14 Flue Pipe Connection (Alternate)
15 Induced Draft Blower
23
22
Upflow/Horizontal
16 Electrical Connection Inlets (Alternate)
17 Coil Front Cover Drain Port
18 Drain Line Penetrations
19 Blower Door Interlock Switch
20 24-Volt Thermostat Connections
21 Integrated Control Module
22 Transformer (40 VA)
23 Circulator Blower
24 Auxiliary Limit
25 Gas Manifold
26 Junction Box
27 Coil Front Cover
28 Drain Trap
29 Electrical Connection Inlets
21
(with fuse and diagnostic LED)
5
Page 6
II. SAFETY
Please adhere to the following warnings and cautions when installing, adjusting, altering, servicing, or operating the furnace.
WARN ING
TO
PREVENT PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH DUE TO IMPROPER
INSTALLATION, ADJUSTMENT, ALTERATION, SERVICE OR
MAINTENANCE, REFER TO THIS MANUAL
ASSISTANCE OR INFORMATION, CONSULT A QUALIFIED INSTALLER
SERVICE AGENCY OR THE GAS SUPPLIER
T
HIS PRODUCT CONTAINS OR PRODUCES A CHEMICAL OR CHEMICALS
WHICH MAY CAUSE SERIOUS ILLNESS OR DEATH AND WHICH ARE
KNOWN TO THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA TO CAUSE CANCER, BIRTH
DEFECTS OR OTHER REPRODUCTIVE HARM
. FOR
.
.
ADDITIONAL
,
WARN ING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
O AVOID PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR
T
DEATH DUE TO ELECTRICAL SHOCK, THE FURNACE MUST
BE LOCATED TO PROTECT THE ELECTRICAL
COMPONENTS FROM WATER
.
WARN ING
DO
NOT UTILIZE THE HEATING UNIT WITHOUT REASONABLE ROUTINE
INSPECTION, MAINTENANCE AND SUPERVISION
BUILDING THAT IS OR WILL BE VACANT, CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN TO
ROUTINELY INSPECT, MAINTAIN AND MONITOR THE UNIT
EVENT THAT THE BUILDING MAY BE EXPOSED TO FREEZING
TEMPERATURES AND WILL BE VACANT, DRAIN ALL WATER-BEARING
PIPES, PROPERLY WINTERIZE THE BUILDING, AND TURN OFF ALL
WATER SOURCES
FREEZING TEMPERATURES AND IS VACANT, ANY HYDRONIC COIL
UNITS SHOULD ALSO BE DRAINED AND AN ALTERNATIVE HEAT
SOURCES UTILIZED
. IN
THE EVENT THAT THE BUILDING IS EXPOSED TO
.
. IF
THE UNIT IS IN A
. IN
THE
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) PRECAUTIONS
NOTE: Discharge static electricity accumulated in the body before
touching the unit. An electrostatic discharge can adversely affect
electrical components.
Use the following precautions during furnace installation and servicing to protect the integrated control module from damage. By
putting the furnace, the control, and the person at the same electrostatic potential, these steps will help avoid exposing the integrated
control module to electrostatic discharge. This procedure is applicable to both installed and non-installed (ungrounded) furnaces.
1. Disconnect all power to the furnace. Do not touch the
integrated control module or any wire connected to the control
prior to discharging your body’s electrostatic charge to
ground.
2. Firmly touch a clean, unpainted, metal surface of the
furnaces near the control. Any tools held in a person’s
hand during grounding will be discharged.
3. Service integrated control module or connecting wiring
following the discharge process in step 2. Use caution not
to recharge your body with static electricity; (i.e., do not move
or shuffle your feet, do not touch ungrounded objects, etc.).
If you come in contact with an ungrounded object, repeat
step 2 before touching control or wires.
4. Discharge your body to ground before removing a new
control from its container. Follow steps 1 through 3 if
installing the control on a furnace. Return any old or new
controls to their containers before touching any ungrounded
object.
III. PRODUCT APPLICA TION
This furnace is primarily designed for residential home-heating
applications. It is NOT designed or certified for use in mobile
homes, trailers or recreational vehicles. This unit is NOT designed
or certified for outdoor applications. The furnace must be installed
indoors (i.e., attic space, crawl space, or garage area provided the
garage area is enclosed with an operating door).
This furnace can be used in the following non-industrial commercial applications:
Schools, Office buildings, Churches, Retail stores
Nursing homes, Hotels/motels, Common or office areas
In such applications , the furnace must be installed with the following stipulations:
• It must be installed per the installation instructions
provided and per local and national codes.
• It must be installed indoors in a building constructed on
site.
• It must be part of a ducted system and not used in a free
air delivery application.
• It must not be used as a “make-up” air unit.
• It must be installed with two-pipe systems for combustion
air, especially if VOC’s or other contaminants are present
in the conditioned space.
• All other warranty exclusions and restrictions apply This
furnace is an ETL dual-certified appliance and is
appropriate for use with natural or propane gas (NOTE: If
using propane, a propane conversion kit is required).
Dual certification means that the combustion air inlet pipe is optional and the furnace can be vented as a:
Non-direct vent (single pipe) central forced air furnace in
which combustion air is taken from the installation area
or from air ducted from the outside or,
Direct vent (dual pipe) central forced air furnace in which
all combustion air supplied directly to the furnace burners
through a special air intake system outlined in these
instructions.
This furnace may be used as a construction site heater ONLY if the
following conditions are met:
• The vent system is permanently installed per these
installation instructions.
• A room thermostat is used to control the furnace. Fixed
jumpers that provide continuous heating CANNOT be
used.
• Return air ducts are provided and sealed to the furnace.
• A return air temperature range between 60ºF (16ºC) and
80ºF (27ºC) is maintained.
• Air filters are installed in the system and maintained
during construction, replaced as appropriate during
construction, and upon completion of construction are
replaced.
• The input rate and temperature rise are set per the furnace
rating plate.
• 100% outside air is provided for combustion air
requirements during construction. Temporary ducting can
be used.
6
Page 7
NOTE: Do not connect the temporary duct directly to the
furnace. The duct must be sized according to the
instructions under Section V, Combustion and Ventilation
Air Requirements, Section 5.3.3.
• The furnace heat exchanger, components, duct system,
air filters and evaporator coils are thoroughly cleaned
following final construction clean up.
• All furnace operating conditions (including ignition, input
rate, temperature rise and venting) are verified according
to these installation instructions.
NOTE: The Commonwealth of Massachusetts requires that the
following additional requirements must also be met:
• Gas furnaces must be installed by a licensed plumber or
gas fitter.
• A T-handle gas cock must be used.
• If the unit is to be installed in an attic, the passageway to
and the service area around the unit must have flooring.
To ensure proper installation and operation, thoroughly read this
manual for specifics pertaining to the installation and application
of this product.
WARN ING
P
OSSIBLE PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH DUE TO
FIRE, EXPLOSION, SMOKE, SOOT, CONDENSATION, ELECTRICAL
SHOCK OR CARBON MONOXIDE MAY RESULT FROM IMPROPER
INSTALLATION, REPAIR, OPERATION, OR MAINTENANCE OF THIS
PRODUCT
.
WARN ING
TO
PREVENT PERSONAL INJURY, PROPERTY DAMAGE OR DEATH DUE
TO FIRE, DO NOT INSTALL THIS FURNACE IN A MOBILE HOME
TRAILER OR RECREATIONAL VEHICLE
.
,
To ensure proper furnace operation, install, operate and maintain
the furnace in accordance with these installation and operation
instructions, all local building codes and ordinances. In their absence, follow the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code
ANSI Z223.1, and/or CAN/CSA B149.1-05 Installation Codes, local
plumbing or waste water codes, and other applicable codes.
A copy of the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1 can be obt ained
from any of the following:
American National Standards Institute
1430 Broadway
New York, NY 10018
National Fire Protection Association
1 Batterymarch Park
Quincy, MA 02269
CSA International
8501 East Pleasant Valley
Cleveland, OH 44131
A copy of the CAN/CSA B149.1-05 Installation Codes can also be
obtained from:
CSA International
178 Rexdale Boulevard
Etobicoke, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3
The rated heating capacity of the furnace should be greater than or
equal to the total heat loss of the area to be heated. The total heat
loss should be calculated by an approved method or in accordance with “ASHRAE Guide” or “Manual J-Load Calculations” published by the Air Conditioning Contractors of America.
IV . LOCATION REQUIREMENTS & CONSIDERA TIONS
GENERAL
WARNING
TO
PREVENT POSSIBLE EQUIPMENT DAMAGE, PROPERTY DAMAGE
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH, THE FOLLOWING BULLET POINTS MUST
BE OBSERVED WHEN INSTALLING THE UNIT
Follow the instructions listed below when selecting a furnace location. Refer also to the guidelines provided in Section V, Combus-
tion and Ventilation Air Requirements.
• Centrally locate the furnace with respect to the proposed
or existing air distribution system.
• Ensure the temperature of the return air entering the
furnace is between 55°F and 100°F when the furnace is
heating.
• Provide provisions for venting combustion products
outdoors through a proper venting system. Special
consideration should be given to vent/flue pipe routing
and combustion air intake pipe when applicable. Refer
to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion Air Pipe -
Termination Locations for appropriate termination
locations and to determine if the piping system from
furnace to termination can be accomplished within the
guidelines given. NOTE: The length of flue and/or
combustion air piping can be a limiting factor in the
location of the furnace.
• Locate the furnace so condensate flows downwards to
the drain. Do not locate the furnace or its condensate
drainage system in any area subject to below freezing
temperatures without proper freeze protection. Refer to
Section X, Condensate Drain Lines and Trap for further
details.
• Ensure adequate combustion air is available for the
furnace. Improper or insufficient combustion air can
expose building occupants to gas combustion products
that could include carbon monoxide. Refer to Section V,
Combustion and Ventilation Air Requirements.
• Set the furnace on a level floor to enable proper
condensate drainage. If the floor becomes wet or damp
at times, place the furnace above the floor on a concrete
base sized approximately 1-1/2" larger than the base of
the furnace. Refer to the Section VII, Horizontal
Applications and Considerations for leveling of horizontal
furnaces.
• Ensure upflow or horizontal furnaces are not installed
directly on carpeting, or any other combustible material.
The only combustible material allowed is wood.
• Exposure to contaminated combustion air will result in
safety and performance-related problems. Do not install
the furnace where the combustion air is exposed to the
following substances:
chlorinated waxes or cleaners
chlorine-based swimming pool chemicals
water softening chemicals
deicing salts or chemicals
carbon tetrachloride
halogen type refrigerants
cleaning solutions (such as perchloroethylene)
printing inks
paint removers
varnishes
hydrochloric acid
7
.
,
Page 8
cements and glues
antistatic fabric softeners for clothes dryers
and masonry acid washing materials
• Seal off a non-direct vent furnace if it is installed near an
area frequently contaminated by any of the above
substances. This protects the non-direct vent furnace
from airborne contaminants. To ensure that the
enclosed non-direct vent furnace has an adequate supply
of combustion air, vent from a nearby uncontaminated
room or from outdoors. Refer to the Section V,
Combustion and Ventilation Air Requirements for details.
• If the furnace is used in connection with a cooling unit,
install the furnace upstream or in parallel with the cooling
unit. Premature heat exchanger failure will result if the
cooling unit is placed ahead of the furnace.
• If the furnace is installed in a residential garage, position
the furnace so that the burners and ignition source are
located not less than 18 inches (457 mm) above the floor.
Protect the furnace from physical damage by vehicles.
• If the furnace is installed horizontally, the furnace access
doors must be vertical so that the burners fire horizontally
into the heat exchanger. Do not install the unit with the
access doors on the “up/top” or “down/bottom” side of
the furnace.
CLEARANCES AND ACCESSIBILITY
Installations must adhere to the clearances to combustible materials to which this furnace has been design certified. The minimum clearance information for this furnace is provided on the unit’s
clearance label. These clearances must be permanently maintained. Clearances must also accommodate an installation’s gas,
electrical, and drain trap and drain line connections. If the alternate
vent/flue connections are used additional clearance must be provided to accommodate these connections. Refer to Section IX,
Vent Flue Pipe and Combustion Air Pipe for details. NOTE: In
addition to the required clearances to combustible materials, a
minimum of 24 inches service clearance must be available in front
of the unit.
TOP
SIDE SIDE
BOTTOM
Upflow Horizontal
A furnace installed in a confined space (i.e., a closet or utility room)
must have two ventilation openings with a total minimum free area
of 0.25 square inches per 1,000 BTU/hr of furnace input rating.
Refer to the Specification Sheet applicable to your model* for minimum clearances to combustible surfaces. One of the ventilation
openings must be within 12 inches of the top; the other opening
must be within 12 inches of the bottom of the confined space. In a
typical construction, the clearance between the door and door frame
is usually adequate to satisfy this ventilation requirement.
FURNACE SUSPENSION
If suspending the furnace from rafters or joists, use 3/8" threaded
rod and 2”x2”x1/8” angle iron as shown below. The length of rod
will depend on the application and the clearances necessary.
PROVIDE 8" MINMUM CLEARANCE BETWEEN
CENTER ROD AND FURNACE CABINET
TO ALLOW FOR CIRCULATOR BLOWER REMOVAL
3/8" DIAMETER
THREADED ROD
(6 PLACES)
HOLD DOWN
NUTS
SUPPORT
NUTS
2"X2"X1/8" ANGLE IRON
(3 PLACES)
POSITION AS CLOSE AS POSSIBLE
TO BLOWER DECK TO ALLOW FOR
CIRCULATOR BLOWER REMVOAL
ASSURE FURNACE IS LEVEL FROM
END TO END AND HAS A SLIGHT
FORWARD TILT WITH THE FRONT
OF THE FURNACE 0"-3/4"
BELOW THE BACK OF THE FURNACE
TILT OUTWARD TO ALLOW FOR
DOOR AND CIRCULATOR BLOWER
REMOVAL
Suspended Furnace
EXISTING FURNACE REMOVAL
NOTE: When an existing furnace is removed from a venting system
serving other appliances, the venting system may be too large to
properly vent the remaining attached appliances.
The following vent testing procedure is reproduced from the American
National Standard/National Standard of Canada for Gas-Fired Central Furnaces ANSI Z21.47·CSA-2.3 Section 1.23.1.
The following steps shall be followed with each appliance connected to the
venting system placed in operation, while any other appliances connected to the venting system are not in operation:
a. Seal any unused openings in the venting system;
b. Inspect the venting system for proper size and horizontal pitch, as
required by the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 or the CSA
B149.1-05 Installation Codes and these instructions. Determine that
there is no blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion and other deficiencies which could cause an unsafe condition;
c. In so far as practical, close all building doors and windows and all
doors between the space in which the appliance(s) connected to the
venting system are located and other spaces of the building. Turn on
clothes dryers and any appliance not connected to the venting system. Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range hoods and bathroom
exhausts, so they shall operate at maximum speed. Do not operate a
summer exhaust fan. Close fireplace dampers;
d. Follow the lighting instructions. Place the appliance being inspected
in operation. Adjust thermostat so appliance shall operate continuously;
e. Test for draft hood equipped spillage at the draft hood relief opening
after 5 minutes of main burner operation. Use the flame of a match
or candle;
f. After it has been determined that each appliance connected to the
venting system properly vents when tested as outlined above, return doors, windows, exhaust fans, fireplace dampers and any other
gas burning appliance to their previous conditions of use;
g. If improper venting is observed during any of the above tests, the
common venting system must be corrected.
Corrections must be in accordance with the latest edition of the
National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1 and/or CSA B149.1-05 Inst allation Codes.
8
Page 9
If resizing is required on any portion of the venting system, use the
V
appropriate table in Appendix G in the latest edition of the National
Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1 and/or CSA B149.1-05 Installation
Codes.
THERMOSTAT LOCATION
The thermostat should be placed approximately five feet from the
floor on a vibration-free, inside wall in an area having good air
circulation. Do not install the thermostat where it may be influenced by any of the following:
• Drafts, or dead spots behind doors, in corners, or under
cabinets.
• Hot or cold air from registers.
• Radiant heat from the sun.
• Light fixtures or other appliances.
• Radiant heat from a fireplace.
• Concealed hot or cold water pipes, or chimneys.
• Unconditioned areas behind the thermostat, such as an
outside wall.
DRAFTS OR DEAD SPOTS
-BEHIND DOORS
-IN CORNERS
-UNDER CABINETS
Thermostat Influences
Consult the instructions packaged with the thermostat for mounting instructions and further precautions.
V . COMBUSTION & VENTILA TION AIR REQUIREMENTS
WARN ING
TO
AVOID PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH
SUFFICIENT FRESH AIR FOR PROPER COMBUSTION AND
OF FLUE GASES MUST BE SUPPLIED
AIR BE SUPPLIED INTO THE FURNACE AREA
Improved construction and additional insulation in buildings have
reduced heat loss by reducing air infiltration and escape around
doors and windows. These changes have helped in reducing
heating/cooling costs but have created a problem supplying combustion and ventilation air for gas fired and other fuel burning appliances. Appliances that pull air out of the house (clothes dryers,
exhaust fans, fireplaces, etc.) increase the problem by starving
appliances for air.
House depressurization can cause back drafting or improper combustion of gas-fired appliances, thereby exposing building occupants to gas combustion products that could include carbon monoxide.
1. Headaches-Nausea-Dizziness, Flu-Like Symptoms.
2. Excessive humidity-heavily frosted windows or a moist
“clammy” feeling in the home.
3. Smoke from a fireplace will not draw up the chimney.
4. Flue gases that will not draw up the appliance vent pipe.
. M
OST HOMES REQUIRE OUTSIDE
.
HOT
COLD
,
ENTILATION
If this furnace is to be installed in the same space with other gas
appliances, such as a water heater, ensure there is an adequate
supply of combustion and ventilation air for the other appliances.
Refer to the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1
(Section 5.3), or CSA B149.1-05 Installation Codes (Sections 7.2,
7.3, or 7.4), or applicable provisions of the local building codes for
determining the combustion air requirements for the appliances.
Most homes will require outside air be supplied to the furnace area
by means of ventilation grilles or ducts connecting directly to the
outdoors or spaces open to the outdoors such as attics or crawl
spaces.
The following information on air for combustion and ventilation is reproduced from the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI Z223.1 Section 5.3.
5.3.1 General:
(a) The provisions of 5.3 apply to gas utilization equipment installed in
buildings and which require air for combustion, ventilation and dilution of flue gases from within the building. They do not apply to (1)
direct vent equipment which is constructed and installed so that all
air for combustion is obtained from the outside atmosphere and all
flue gases are discharged to the outside atmosphere, or (2) enclosed
furnaces which incorporate an integral total enclosure and use only
outside air for combustion and dilution of flue gases.
(b) Equipment shall be installed in a location in which the facilities for
ventilation permit satisfactory combustion of gas, proper venting
and the maintenance of ambient temperature at safe limits under
normal conditions of use. Equipment shall be located so as not to
interfere with proper circulation of air. When normal infiltration
does not provide the necessary air, outside air shall be introduced.
(c) In addition to air needed for combustion, process air shall be pro-
vided as required for: cooling of equipment or material, controlling
dew point, heating, drying, oxidation or dilution, safety exhaust,
odor control, and air for compressors.
(d) In addition to air needed for combustion, air shall be supplied for
ventilation, including all air required for comfort and proper working
conditions for personnel.
(e) While all forms of building construction cannot be covered in detail,
air for combustion, ventilation and dilution of flue gases for gas
utilization equipment vented by natural draft normally may be obtained by application of one of the methods covered in 5.3.3 and
5.3.4.
(f) Air requirements for the operation of exhaust fans, kitchen ventila-
tion systems, clothes dryers, and fireplaces shall be considered in
determining the adequacy of a space to provide combustion air
requirements.
5.3.2 Equipment Located in Unconfined Spaces:
In unconfined spaces (see definition below) in buildings, infiltration
may be adequate to provide air for combustion ventilation and dilution
of flue gases. However, in buildings of tight construction (for example,
weather stripping, heavily insulated, caulked, vapor barrier, etc.), additional air may need to be provided using the methods described in 5.3.3b or 5.3.4.
Space, Unconfined.
For purposes of this Code, a space whose volume is not less than 50
cubic feet per 1,000 BTU per hour of the aggregate input rating of all
appliances installed in that space. Rooms communicating directly with
the space in which the appliances are installed through openings not
furnished with doors, are considered a part of the unconfined space.
5.3.3 Equipment Located in Confined Spaces:
(a) All Air from Inside the Building: The confined space shall be pro-
vided with two permanent openings communicating directly with
an additional room(s) of sufficient volume so that the combined
volume of all spaces meets the criteria for an unconfined space. The
total input of all gas utilization equipment installed in the combined
9
Page 10
space shall be considered in making this determination. Each open-
A
ing shall have a minimum free area of 1 square inch per 1,000 BTU
per hour of the total input rating of all gas utilization equipment in
the confined space, but not less than 100 square inches. One opening shall be within 12 inches of the top and one within 12 inches of
the bottom of the enclosure.
NOTE: Each opening must have
a free area of not less than one
square inch per 1 000 BT U of
the total input rating of all equ i p ment in the enclosure, but not
less than 100 square inches.
Chimney or Gas Vent
Opening
Chimney o r Gas Vent
Ventilation louvers
(each end of attic)
NOTE: Th e inlet and ou tlet air
openings must each have a free
area of not less than one square
inch per 4000 BTU of the
total input rating of all equipment
in the enclosure.
Outlet A i r
Furnace
Water
Heater
Inlet air duct
[ends 1 ft (300 mm)
above floor]
Water
Heater
Furnace
Opening
Equipment Located in Confined Spaces; All Air from Inside
Building. See 5.3.3-a.
(b) All Air from Outdoors: The confined space shall be provided with
two permanent openings, one commencing within 12 inches of the
top and one commencing within 12 inches of the bottom of the
enclosure. The openings shall communicate directly, or by ducts,
with the outdoors or spaces (crawl or attic) that freely communicate
with the outdoors.
1. When directly communicating with the outdoors, each opening
shall have a minimum free area of 1 square inch per 4,000 BTU
per hour of total input rating of all equipment in the enclosure.
Chimney or Gas Vent
Ventil ation louver s
(each end of attic)
NOTE: Th e inlet and outlet ai r
openings must each have a free
area of not less than one square
inch per 4000 BTU of the
total inpu t rating of all equipmen t
in the enclosure.
Outlet Air
Water
Heater
lternate
air inlet
Furnace
Ventilation louvers for
unheated crawl space
Inlet Air
Equipment Located in Confined Spaces; All Air from Outdoors—
Inlet Air from Ventilated Crawl Space and Outlet Air to Ventilated
Attic. See 5.3.3-b
2. When communicating with the outdoors through vertical ducts,
each opening shall have a minimum free area of 1 square inch per
4,000 BTU per hour of total input rating of all equipment in the
enclosure.
Equipment Located in Confined Spaces; All Air from Outdoors
Through Ventilated Attic. See 5.3.3-b.
3. When communicating with the outdoors through horizontal ducts,
each opening shall have a minimum free area of 1 square inch per
2,000 BTU per hour of total input rating of all equipment in the
enclosure.
Chimney or Gas Vent
NOTE: The air duct openings
must have a free area of not
less than one square inch per
2000 BTU of the total input
rating of all equipment in the
Outlet air duct
Water
Heater
Furnace
Inlet air duct
*If the appliance room is located against an outside wall and the air openings communicate directly with the
outdoors, each opening shall have a free area of not less than one square inch per 4,000 BTU per hour of
the total input rating of all appliances in the enclosure.
enclosure*.
Equipment Located in Confined Spaces; All Air from Outdoors.
See 5.3.3-b.
4. When ducts are used, they shall be of the same cross-sectional
area as the free area of the openings to which they connect. The
minimum dimension of rectangular air ducts shall not be less
than 3 inches.
NOTE: The single opening must have
a free area of not less than one
square inch per 3000 BTU of
the total input rating of al l e quipment in the enclosure, but not less than
the sum of the areas of all vent
connectors in the confined space.
Chimney or Gas Vent
Water
Furnace
Heater
Alternate
Opening
Location
Opening
Equipment Located in Confined Spaces; All Air from Outdoors -
Single Air Opening. See 5.3.3-b.
10
Page 11
5. When directly communicating with the outdoors, the single opening shall have a minimum free area of 1 square inch per 3,000
BTU per hour of total input rating of all equipment in the enclosure.
5.3.4 Specially Engineered Installations:
The requirements of 5.3.3 shall not necessarily govern when special
engineering, approved by the authority having jurisdiction, provides an
adequate supply of air for combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue
gases.
5.3.5 Louvers and Grilles:
In calculating free area in 5.3.3, consideration shall be given to the blocking effect of louvers, grilles or screens protecting openings. Screens used
shall not be smaller than 1/4 inch mesh. If the area through a design of
louver or grille is known, it should be used in calculating the size of
opening required to provide the free area specified. If the design and free
area is not known, it may be assumed that wood louvers will have 20-25
percent free area and metal louvers and grilles will have 60-75 percent
free area. Louvers and grilles shall be fixed in the open position or
interlocked with the equipment so that they are opened automatically
during equipment operation.
5.3.6 Special Conditions Created by Mechanical Exhausting or Fireplaces:
Operation of exhaust fans, ventilation systems, clothes dryers, or fireplaces may create conditions requiring special attention to avoid unsatisfactory operation of installed gas utilization equipment. Air from
Inside Building. See 5.3.3-a.
VI. INSTALLA TION POSITIONS
NOTE: This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated
Upflow. A “Blocked Drain Kit” (0270K00012) is available and MUST
BE USED if the furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal
Right.
This furnace may be installed in an upright position or horizontal
on either the left or right side panel. Do not install this furnace on
its back. For upright upflow furnaces, return air ductwork may be
attached to the side panel(s) and/or basepan. For horizontal upflow
furnaces, return air ductwork must be attached to the basepan.
NOTE: Ductwork must never be attached to the back of the furnace.
Contact your distributor for proper airflow requirements and number of required ductwork connections. Refer to “Recommended
Installation Positions” figure for appropriate installation positions,
ductwork connections, and resulting airflow arrangements.
VII. HORIZONTAL APPLICA TIONS & CONSIDERA TIONS
FURNACE MUST BE LEVEL
ALTERNATE VENT/FLUE
LOCATION
GAS LINE WITH
DRIP LEG (3" MINIMUM)
DRAIN PAN
FURNACE MUST BE SUPPORTED
AT BOTH ENDS AND MIDDLE
FROM END TO END
4 3/4" MINIMUM
DRAIN TRAP
CLEARANCE
DRAIN LINE WITH 1/4" PER FOOT
DOWNWARD SLOPE
36" MINIMUM SERVICE
CLEARANCE REQUIRED
FURNACE MUST BE LEVEL
OR SLIGHTLY TILTED FORWARD
WITH THE DOORS 0" - 3/4"
BELOW THE BACK PANEL
Horizontal Furnace
DRAIN TRAP AND LINES
In horizontal applications the condensate drain trap is secured to
the furnace side panel, suspending it below the furnace. A minimum clearance of 4 3/4 inches below the furnace must be provided for the drain trap. Additionally, the appropriate downward
piping slope must be maintained from the drain trap to the drain
location. Refer to Section X, Condensate Drain Trap and Lines for
further details. If the drain trap and drain line will be exposed to
temperatures near or below freezing, adequate measures must
be taken to prevent condensate from freezing.
LEVELING
Leveling ensures proper condensate drainage from the heat exchanger and induced draft blower. For proper flue pipe drainage,
the furnace must be level lengthwise from end to end. The furnace
should also be level from back to front or have a slight tilt with the
access doors downhill (approximately 3/4 inches) from the back
panel. The slight tilt allows the heat exchanger condensate, generated in the recuperator coil, to flow forward to the recuperator coil
front cover.
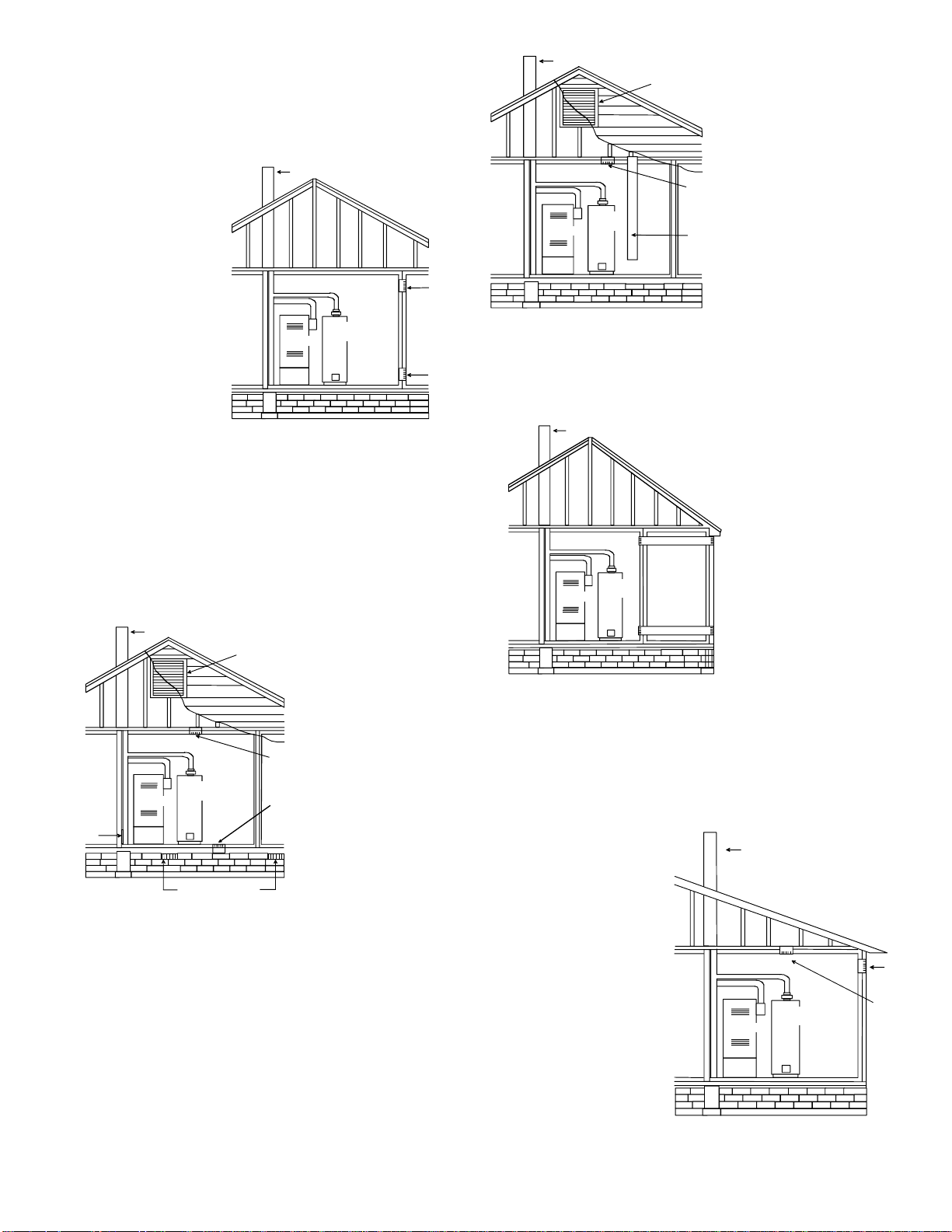
ALTERNATE VENT/FLUE CONNECTION
In horizontal installations provisions for alternate flue piping are
available for upflow furnaces with left discharge. This configuration allows the flue piping to be run vertically through the furnace.
Refer to the “Recommended Installation Positions” figure for further detail. The standard piping connections may also be used in
these positions. Refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion Air Pipe for details concerning the conversion to the alternate
vent/flue connections.
When using the horizontal alternate vent configuration, you must
use the RF000142 vent drain kit. See following illustration.
NOTE: This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated
Upflow. A “Blocked Drain Kit” is available and MUST BE USED if the
furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal Right. Check the
Serial/ Rating Plate on the furnace for the Kit P/N.
GENERAL
Horizontal applications, in particular, may dictate many of the
installation’s specifics such as airflow direction, ductwork connections, flue and combustion air pipe connections, etc. The basic
application of this furnace as a horizontal furnace differs only slightly
from an upright installation. When installing a furnace horizontally,
additional consideration must be given to the following:
11
Page 12

AIR
DISCHA RGE
Side
Return
Duct
Connection
Connection
UPFLOW
UPRIGHT
ALTERNATE FL UE
PIPE LOCATIONS
AIR
DISCHA RGE
UPFLOW HORIZONTAL
LEFT AIR DISCHARGE
Bottom
Return
Duct
Connection
UPFLOW HORIZONTAL
RIGHT AIR DISCHARGE
Bottom
Return
Duct
ALTERNATE FL UE
PIPE LOCATIONS
Side
Return
Duct
Connection
Bottom
Return
Duct
Connection
DISCHA RGE
AIR
Recommended Installation Positions
NOTE: Alternate “vertical” piping connections can not be used when
an upflow furnace is installed with supply air discharging to the
right. In either case, use the standard flue and combustion air
piping connections.
ALTERNATE ELECTRICAL AND GAS LINE CONNECTIONS
This furnace has provisions allowing for electrical and gas line
connections through either side panel. In horizontal applications
the connections can be made either through the “top” or “bottom” of
the furnace.
DRAIN PAN
A drain pan must be provided if the furnace is installed above a
conditioned area. The drain pan must cover the entire area under
the furnace (and air conditioning coil if applicable).
FREEZE PROTECTION
Refer to Section VII, Horizontal Applications and Conditions - Drain
Trap and Lines.
FURNACE SUSPENSION
If the furnace is installed in a crawl space it must be suspended
from the floor joist or supported by a concrete pad. Never install the
furnace on the ground or allow it to be exposed to water. Refer to
Section IV, Location Requirements and Considerations - Furnace
Suspension for further details.
VIII. PROPANE GAS /HIGH AL TITUDE INST ALLATIONS
WARN ING
P
OSSIBLE PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY
OCCUR IF THE CORRECT CONVERSION KITS ARE NOT INSTALLED
APPROPRIATE KITS MUST BE APPLIED TO ENSURE SAFE AND PROPER
FURNACE OPERATION
A QUALIFIED INSTALLER OR SERVICE AGENCY
. ALL
CONVERSIONS MUST BE PERFORMED BY
.
This furnace is shipped from the factory configured for natural gas
at standard altitude. Propane gas installations require an orifice
. THE
change to compensate for the energy content difference between
natural and propane gas.
High altitude installations may require both a pressure switch and
an orifice change. These changes are necessary to compensate
for the natural reduction in the density of both the gas fuel and the
combustion air at higher altitude.
For installations above 7000 feet, please refer to your distributor
for required kit(s).
Altitude Gas Kit Orifice
Manifold
Pressure
Natural None #43 3.5" w .c.
0-7000
Propa ne
1
Supports Wh ite-Rodgers 1-s tag e valve only
2
Supports bo th Honey w ell and White-Rodgers 1- stage valv es
LPT-00*
LPT-03*
1
#55 10.0" w.c.
2
NOTE: In Canada, gas fur naces are certifie d to 4500 feet.
Pressure
Switch
Contact the distributor for a tabular listing of appropriate
manufacturer’s kits for propane gas and/or high altitude installations. The indicated kits must be used to insure safe and proper
furnace operation. All conversions must be performed by a qualified installer, or service agency.
IX. VENT/FLUE PIPE & COMBUSTION AIR PIPE
GENERAL
WARN ING
F
AILURE TO FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAN RESULT IN BODILY
INJURY OR DEATH
INSTRUCTIONS GIVEN IN THIS SECTION
U
PON COMPLETION OF THE FURNACE INSTALLATION, CAREFULLY
INSPECT THE ENTIRE FLUE SYSTEM BOTH INSIDE AND OUTSIDE OF
THE FURNACE TO ASSURE IT IS PROPERLY SEALED
FLUE SYSTEM CAN RESULT IN SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH
DUE TO EXPOSURE TO FLUE PRODUCTS, INCLUDING CARBON
MONOXIDE
A condensing gas furnace achieves its high level of efficiency by
extracting almost all of the heat from the products of combustion
and cooling them to the point where condensation takes place.
Because of the relatively low flue gas temperature and water condensation requirements, PVC pipe is used as venting material.
This furnace must not be connected to T ype B, BW , or L vent or vent
connector, and must not be vented into any portion of a factory built
or masonry chimney except when used as a pathway for PVC as
described later in this section. Never common vent this appliance
with another appliance or use a vent which is used by a solid fuel
appliance. Do not use commercially available “no hub connectors” other than those shipped with this product.
It is the responsibility of the installer to follow the manufacturers’
recommendations and to verify that all vent/flue piping and connectors are compatible with furnace flue products. Additionally, it is the
. C
AREFULLY READ AND FOLLOW ALL
.
WARN ING
. L
EAKS IN THE
.
None
12
Page 13

responsibility of the installer to ensure that all piping and connections possess adequate structural integrity and support to prevent
flue pipe separation, shifting, or sagging during furnace operation.
DUAL CERTIFICATION: NON-DIRECT/DIRECT VENT
This furnace is dual certified and may be installed as a non-direct
vent (single pipe) or direct vent (dual pipe) appliance. A non-direct
vent installation requires only a vent/flue pipe, while a direct vent
installation requires both a vent/flue pipe and a combustion air
intake pipe. Refer to the appropriate section for details concerning
piping size, length, number of elbows, furnace connections, and
terminations.
MATERIALS AND JOINING METHODS
WARNING
O AVOID BODILY INJURY, FIRE OR EXPLOSION, SOLVENT CEMENTS MUST BE
T
KEPT AWAY FROM ALL IGNITION SOURCES (I.E., SPARKS, OPEN FLAMES, AND
EXCESSIVE HEAT) AS THEY ARE COMBUSTIBLE LIQUIDS.
CEMENT VAPORS OR CONTACT WITH SKIN AND/OR EYES.
Two-three-inch nominal diameter PVC Schedule 40 pipe meeting
ASTM D1785, PVC primer meeting ASTM F656, and PVC solvent
cement meeting ASTM D2564 specifications must be used. Fittings must be DWV type fittings meeting ASTM D2665 and ASTM
D3311. Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cutting,
cleaning, and solvent cementing of PVC.
As an alternative to PVC pipe, primer, solvent cement, and fittings,
ABS materials which are in compliance with the following specifications may be used. Two-three-inch ABS Schedule 40 pipe must
meet ASTM D1527 and, if used in Canada, must be CSA listed.
Solvent cement for ABS to ABS joint s must meet ASTM D2235 and,
if used in Canada, must be CSA listed. The solvent cement for the
PVC to ABS transition joint must meet ASTM D3138. Fittings must
be DWV type fittings meeting ASTM D2661 and ASTM D331 1 and, if
used in Canada, must be CSA listed. Carefully follow the pipe
manufacturers’ instructions for cutting, cleaning, and solvent cementing PVC and/or ABS.
All 90° elbows must be medium radius (1/4 bend DWV) or long
radius (Long sweep 1/4 bend DWV) types conforming to ASTM
D3311. A medium radius (1/4 bend DWV) elbow measures 3 1/
16” minimum from the plane of one opening to the centerline of the
other opening for 2” diameter pipe, and 4 9/16” minimum for 3”
pipe.
VOID BREATHING
A
PROPER VENT/FLUE AND COMBUSTION AIR PIPING PRACTICES
Adhere to these instructions to ensure safe and proper furnace
performance. The length, diameter, and number of elbows of the
vent/flue pipe and combustion air pipe (when applicable) affects
the performance of the furnace and must be carefully sized. All
piping must be installed in accordance with local codes and these
instructions.
Piping must be adequately secured and supported to prohibit sagging, joint separation, and/or detachment from the furnace. Horizontal runs of vent/flue piping must be supported every three to five
feet and must maintain a 1/4 inch per foot downward slope, back
towards the furnace, to properly return condensate to the furnace’s
drain system. Allowances should be made for minor expansion
and contraction due to temperature variations. For this reason,
particular care must be taken to secure piping when a long run is
followed by a short offset of less than 40 inches.
Precautions should be taken to prevent condensate from freezing inside the vent/flue pipe and/or at the vent/flue pipe termination. It is our recommendation that all vent/flue piping exposed to
temperatures below 35°F for extended periods of time should be
insulated with 1/2” thick closed cell foam. Also all vent/flue piping
exposed outdoors in excess of the terminations shown in this
manual (or in unheated areas) should be insulated with 1/2” thick
closed cell foam. Inspect piping for leaks prior to installing insulation.
TERMINATION LOCATIONS
NOTES: Refer to Section IV, Location Requirements and
Considerations for combustion air contaminant restrictions.
The following bullets and diagram describe the restrictions con-
cerning the appropriate location of vent/flue pipe and combustion
air intake pipe (when applicable) terminations. Refer to Non-Di-
rect Vent (Single Pipe) Piping and Direct Vent (Dual Pipe) Piping
located in this section for specific details on termination construction.
• All terminations (flue and/or intake) must be located at
least 12 inches above ground level or the anticipated
snow level.
• Vent terminations (non-direct and direct vent) must
terminate at least 3 feet above any forced air inlet located
within 10 feet.
NOTE: This provision does not apply to the combustion
air intake termination of a direct vent application.
• The vent termination of a non-direct vent application must
terminate at least 4 feet below, 4 feet horizont ally from, or
1 foot above any door, window, or gravity air inlet into any
building.
• The vent termination of a direct vent application must
terminate at least 12 inches from any opening through
which flue gases may enter a building (door, window, or
gravity air inlet).
• The vent termination of vent pipe run vertically through a
roof must terminate at least 12 inches above the roof line
(or the anticipated snow level) and be at least 12 inches
from any vertical wall (including any anticipated snow
build up).
• A vent termination shall not terminate over public walkways
or over an area where condensate or vapor could create
a nuisance or hazard or could be detrimental to the
operation of regulators, relief valves, or other equipment.
• The combustion air intake termination of a direct vent
application should not terminate in an area which is
frequently dusty or dirty.
Non-Direct Vent
&
Direct Vent
Vent/Flue Terminations
Non-Direct Vent
Vent/Flue Termination
No Terminations
Above Walkway
Grade or Highest
Anticipated
Snow Level
3' min.
Forced Air
Inlet
<10'
12"
12" min.
12" min.
Direct Vent
Vent/Flue Termination
Vent Termination Clearances
4' min.
4'
min.
12"
min.
Non-Direct Vent
Vent/Flue Termination
13
Page 14

NOTE: In Canada, the Canadian Fuel Gas Code takes precedence
over the preceding termination restrictions.
CANADIAN VENTING REQUIREMENTS
In Canada, venting must conform to the requirements of the current CAN/CSA-B149.1-05 Installation Code. Use only CSA-listed,
ULC-S636 compliant two-three-inch diameter PVC or ABS pipe,
solvent cement, and fittings throughout. The certified piping should
be clearly marked with the ULC Std “S636” on the pipe and fittings.
Carefully follow the pipe manufacturers’ instructions for cutting,
cleaning, and solvent cementing PVC and/or ABS.
The vent can be run through an existing unused chimney provided
the space between the vent pipe and the chimney is insulated and
closed with a weather-tight, corrosion-resistant flashing.
STANDARD FURNACE C ONNECTIONS
It is the responsibility of the installer to ensure that the piping
connections to the furnace are secure, airtight, and adequately
supported.
As shipped, attachment “couplings” for vent/flue and combustion
air intake pipe connections are provided on the furnace’s top cover
(upflow). To use the standard connections, field supplied vent/flue
pipe and combustion air intake pipe (when applicable) should be
secured directly to the furnace at these locations.
VENT/FLUE PIPE
Vent/flue pipe can be secured to the vent/flue coupling using the
rubber coupling and worm gear hose clamps provided with this
furnace (see “Standard Connections” figure). The rubber coupling
allows separation of the vent/flue pipe from the furnace during
servicing. Combustion Air and Vent piping should be routed in a
manner to avoid contact with refrigerant lines, metering devices,
condensate drain lines, etc. If necessary, clearances may be
increased by utilizing two 45 deg. Long-Sweep Elbows and creating an “S” joint to provide additional space at connection locations. This joint can be rotated on the fitting to establish maximum clearance between refrigerant lines, metering devices, and
condensate drain lines, etc. This joint is the equivalent of one 90
deg. elbow when considering elbow count.
NOTE: For non-direct vent installations, a minimum of one 90°
elbow should be installed on the combustion air intake coupling
to guard against inadvertent blockage.
COMBUSTION AIR PIPE
DIRECT VENT INSTALLATIONS
On upflow units secure the combustion air intake pipe directly to
the air intake coupling. NOTE: Because of probable material conflicts, do not use other commercially available “no hub connectors”.
NON-DIRECT VENT INSTALLATIONS
A minimum of one 90° elbow should be installed on the combustion air intake “coupling” to guard against inadvertent blockage.
(DIRECT VE NT O N LY)
90 PVC
ELBOW
(NON-DIRECT VENT)
COMBUSTION
AIR PIPE
OR
RUBBER
COUPLING
WITH WORM
GEAR CLAM PS
UPFLOW
VENT/FLUE
PIPE
(NON-DIRECT VENT)
STANDARD CONNECTIONS
ALTERNATE FURNACE CONNECTIONS
If the standard locations are undesirable for a specific installation,
alternate side panel locations are available for vent/flue pipe connections. These locations may be of particular benefit to upright
upflow installations requiring additional access to an A coil or to
horizontal installations desiring vent/flue piping run vertically from
the side of the cabinet.
NOTE: Standard and alternate locations can be combined (i.e., an
installation may use the standard combustion air intake location
but use the alternate vent/flue location), if needed.
V
E
N
T
45 DEGREE
LONG-SWEEP
ELBOWS
Increased Clearance Configuration
NOTE: Do not use other commercially available “no hub connec-
tors” due to possible material conflicts. The vent/flue pipe can
also be secured using a PVC or ABS elbow or coupling using the
appropriate glue (see Section IX, Materials and Joining Methods.
WARN ING
E
DGES OF SHEET METAL HOLES MAY BE SHARP
PRECAUTION WHEN REMOVING HOLE PLUGS
.
. USE
GLOVES AS A
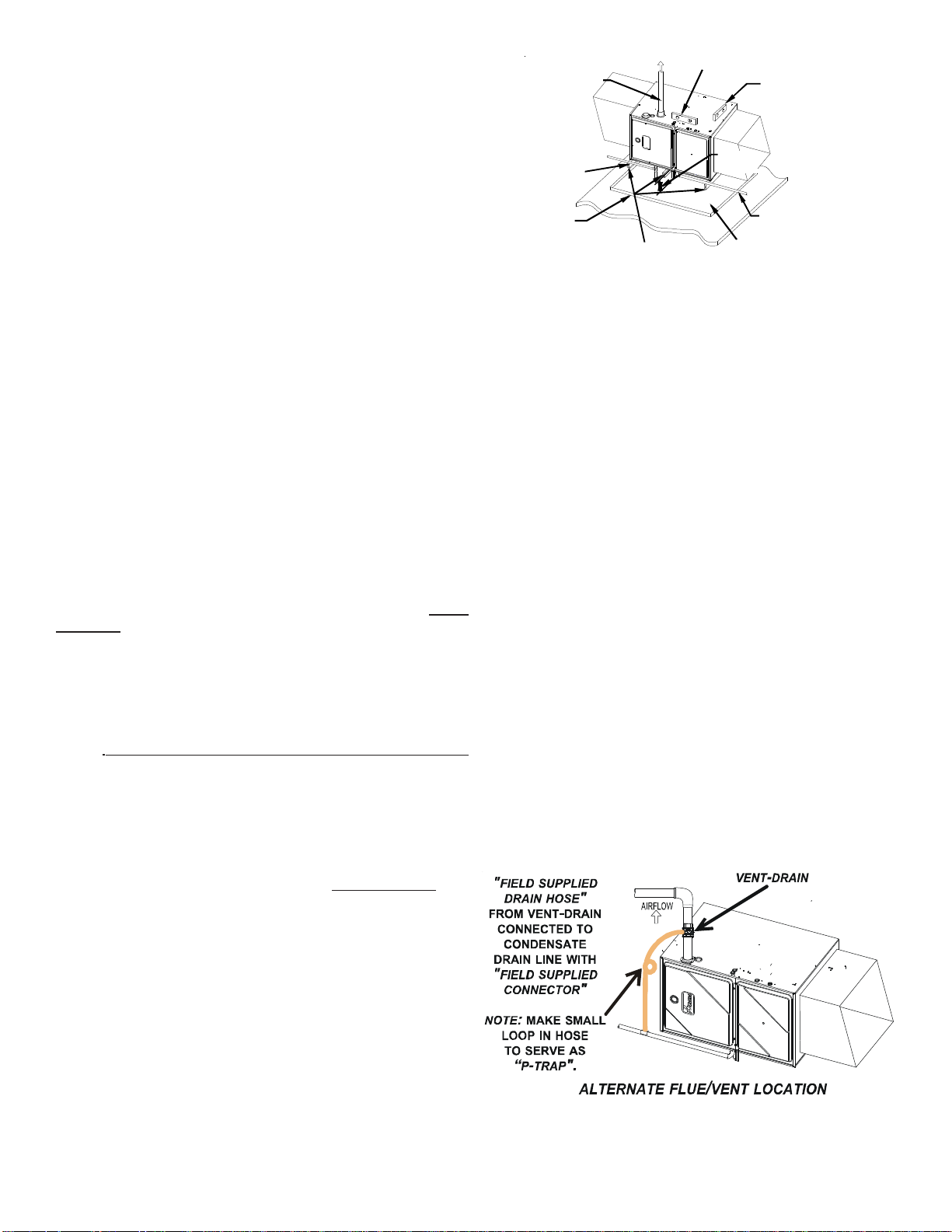
ALTERNATE VENT/FLUE LOCATION
The alternate vent/flue location is the large hole directly in line with
the induced draft blower outlet. To use the alternate vent/flue location refer to the following steps, the “Vent/Flue Pipe Cuts” figure,
and the “Alternate Vent/Flue Location” figure.
1. Remove and save the four screws securing the vent/flue
coupling to the furnace top panel.
2. Loosen the worm gear hose clamps on the rubber elbow
and detach it from both the induced draft blower and the
vent/flue pipe.
3. Remove the vent/flue pipe from the furnace.
4. Cut the vent/flue pipe 3.75 inches from the flanged end of
the pipe. See Vent/Flue Pipe Cuts figure. The section of
pipe attached to the coupling will reach through the side
panel to the induced draft blower. Discard remaining pipe
and elbows.
14
Page 15

FLANGE
(
)2345
6
3.75"
CUT HERE
Vent/Flue Pipe Cuts
5. Remove plastic plug from alternate vent/flue location.
Relocate and install plug in standard vent/flue location (top
cover).
6. Insert cut section of vent/flue pipe and coupling into alternate
vent/flue location. Using a rubber coupling and worm gear
hose clamps from the drain kit bag, attach the vent/flue pipe
and coupling to the induced draft blower. Secure the
coupling to the cabinet using the screws removed in step 1
or with field-supplied 3/8” #8 self drilling screws.
WARN ING
THE
RUBBER ELBOW IS NOT DESIGNED TO SUPPORT A LOAD
THE RUBBER ELBOW IS MOUNTED EXTERNALLY TO THE FURNACE
CABINET, EXTREME CARE MUST BE TAKEN TO ADEQUATELY SUPPORT
FIELD-SUPPLIED VENT/FLUE PIPING, AS DAMAGE CAN RESULT IN
LEAKS CAUSING BODILY INJURY OR DEATH DUE TO EXPOSURE TO
FLUE GASES, INCLUDING CARBON MONOXIDE
.
7. For upright installations, externally mount the rubber elbow
to the vent/flue coupling using a worm gear hose clamp.
Secure field supplied vent/flue piping to the rubber elbow
using a worm gear hose clamp. NOTE: Use of the alternate
vent/flue location for upright installations, requires the drain
trap be installed on the same side of the unit as the flue
pipe.
8. For horizontal installations, externally secure the fieldsupplied vent/flue pipe directly to the vent/flue coupling using
a PVC or ABS coupling or elbow.
UPFLOW
6
SECURE TO
ID BLOWER WITH
RUBBER COUPLING
AND HOSE
CLAMPS
3
REMOVE
PIPE
1
REMOVE
4 SCREWS
5
REMOVE
AND RELOCATE
2
DETACH RUBBER
ELBOW FROM
ID BLOWER AND
VENT/FLUE
PIPE
6
SECURE TO
CABINET WITH
SCREWS
. W
HEN
NON-DIRECT VENT (SINGLE PIPE) PIPING
Non-direct vent installations require only a vent/flue pipe. The vent
pipe can be run horizontally with an exit through the side of the
building or run vertically with an exit through the roof of the building.
The vent can also be run through an existing unused chimney;
however, it must extend a minimum of 12 inches above the top of
the chimney. The space between the vent pipe and the chimney
must be closed with a weather-tight, corrosion-resistant flashing.
For details concerning connection of the vent/flue pipe to the furnace, refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion Air -
Standard Furnace Connections or Alternate Furnace Connections
for specific details. Refer to the following Non-Direct Vent (Single
Pipe) Piping - Vent/Flue Pipe Terminations for specific details on
termination construction.
Although non-direct vent installations do not require a combustion
air intake pipe, a minimum of one 90° elbow should be attached to
the furnace’s combustion air intake if: an upright installation uses
the standard intake location. This elbow will guard against inadvertent blockage of the air intake.
VENT/FLUE PIPE LENGTHS AND DIAMETERS
Refer to the following table for applicable length, elbows, and pipe
diameter for construction of the vent/flue pipe system of a nondirect vent installation. In addition to the vent/flue pipe, a single 90°
elbow should be secured to the combustion air intake to prevent
inadvertent blockage. The tee used in the vent/flue termination
must be included when determining the number of elbows in the
piping system.
Non-Dir ect Ve nt (Singl e Pipe)
Maximum Allowable Length of Vent/Flue Pipe (ft)
Models
(kBTU_Tons)
Pipe
Size
in.
(4)
Number of Elbows
04 5_3 2 or 2 1/ 2 68 65 62 5 9 56 53 5 0
070_3
070_4
090_4
090_5
2 or 2 1/236333027242118
3 68656259565350
2 or 2 1/255524946434037
3 68656259565350
2 or 2 1/237343128252219
3 68656259565350
2 or 2 1/239363330272421
3 68656259565350
115_5 3 68656259565350
1) One 90° elbow should be secured to the combustion air intake connection.
2) Minimum requirement for each vent pipe is five (5) feet in length and one
elbow/tee.
3) Tee used in the vent/flue termination must be included when determining
the number of elbows in the piping system.
4) 2 1/2” or 3” diameter pipe can be used in place of 2” diameter pipe.
5) Increased Clearance Configurations using (2) 45 deg. Long Sweep
elbows should be considered equivalent to one 90 deg. elbow.
VENT/FLUE PIPE TERMINATIONS
The vent/flue pipe may terminate vertically, as through a roof, or
horizontally, as through an outside wall.
Vertical vent/flue pipe terminations should be as shown in the following figure. Refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion
Air Pipe - Termination Locations for details concerning location
(3) (5)
(1) (2)
78
UPFLOW/HORIZONTAL
Alternate Vent/Flue Location
15
Page 16

restrictions. The penetration of the vent through the roof must be
sealed tight with proper flashing such as is used with a plastic
plumbing vent.
Horizontal vent/flue pipe terminations should be as shown in the
following figure. Refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combus-
tion Air Pipe - Termination Locations for details concerning location restrictions. A 2 3/8” diameter wall penetration is required for
2” diameter pipe. A 3” diameter hole is required for a 2 1/2” pipe
and a 3 1/2” diameter hole is required for 3” diameter pipe. To
secure the pipe passing through the wall and prohibit damage to
piping connections, a coupling should be installed on either side
of the wall and solvent cemented to a length of pipe connecting
the two couplings. The length of pipe should be the wall thickness plus the depth of the socket fittings to be installed on the
inside and outside of the wall. The wall penetration should be
sealed with silicone caulking material.
In a basement installation, the vent/flue pipe can be run between
joist spaces. If the vent pipe must go below a joist and then up
into the last joist space to penetrate the header, two 45° elbows
should be used to reach the header rather than two 90° elbows.
TEE
WALL
INSIDE
ELBOW OR
COUPLING
OUTSIDE
COUPLING
MIN.
FROM
WALL
12"
90°ELBOW
12"
TO GROUND OR
HIGHEST ANTICIPATED
SNOW LEVEL
Horizontal Termination (Single Pipe)
12" MIN.
VENT/FLUE T E E
or
90° ELBOW TURNED
DOWN
TEE
or
TURNED
DOWN
12 " Min To
Roof Or
Highest Anticipated
Snow Level
Vertical Termination (Single Pipe)
12 " Min To
Roof Or
Highest Anticipate d
Snow Level
Vertical Termination (Single Pipe)
90º
MEDIUM RADIUS
ELBOWS
12" MIN.
TO ROOF OR
HIGHEST
ANTICIPATED
SNOW LEVEL
Horizontal Termination (Single Pipe)
Above Highest Anticipated Snow Level
DIRECT VENT (DUAL PIPE) PIPING
Direct vent installations require both a combustion air intake and
a vent/flue pipe. The pipes may be run horizontally and exit through
the side of the building or run vertically and exit through the roof of
the building. The pipes may be run through an existing unused
chimney; however, they must extend a minimum of 12 inches
above the top of the chimney. The space between the pipes and
the chimney must be closed with a weather tight, corrosion resistant flashing. Both the combustion air intake and a vent/flue pipe
terminations must be in the same atmospheric pressure zone.
Refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue and Combustion Air Pipe - Termi-
nation Locations or Concentric Vent Termination for specific details on termination construction. For details concerning connection of pipes to the furnace, refer to the Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe
and Combustion Pipe - Standard Furnace Connections or Alternate Furnace Connections.
VENT/FLUE AND COMBUSTION AIR PIPE LENGTHS AND DIAMETERS
Refer to the following table for applicable length, elbows, and
pipe diameter for construction of the vent/flue and combustion air
intake pipe systems of a direct vent (dual pipe) installation. The
number of elbows tabulated represents the number of elbows
and/or tees in each (Vent/Flue & Combustion Air Intake) pipe.
Elbows and/or tees used in the terminations must be included
when determining the number of elbows in the piping systems.
If the combustion air intake pipe is to be installed above a finished
ceiling or other area where dripping of condensate will be objectionable, insulation of the combustion air pipe may be required.
Use 1/2” thick closed cell foam insulation such as Armaflex or
Insultube where required.
Alternate Vertical Termination (Single Pipe)
16
Page 17

Direct Vent (Dual Pipe)
V
Maxi m um All owable Len gth of Vent/F l ue & Combustion
Air Intake Pipe (ft)
Unit Input
(Btu)
Vent/Flue /A ir In take
Termination
Pipe
Size
Number of El bows
(4)
(1)(2) (3)(5)
(in.) 2345678
045_3
Standard 2 or 2 1/2 68 65 62 59 56 53 50
Alternate 2 or 2 1/25552 4946434037
Standard 2 or 2 1/2 36 33 30 27 24 21 18
070_3
Alt ernate 2 or 2 1/2 23 20 17 14 11 8 5
Standard 3 68 65 62 59 56 53 50
Alternate 3 55 52 49 46 43 40 37
Standard 2 or 2 1/2 55 52 49 46 43 40 37
070_4
Alternate 2 or 2 1/24239 3633302724
Standard 3 68 65 62 59 56 53 50
Alternate 3 55 52 49 46 43 40 37
Standard 2 or 2 1/2 37 34 31 28 25 22 19
090_4
Alt ernate 2 or 2 1/2 24 21 18 15 12 9 6
Standard 3 68 65 62 59 56 53 50
Alternate 3 55 52 49 46 43 40 37
Standard 2 or 2 1/2 39 36 33 30 27 24 21
090_5
Alternate 2 or 2 1/22623 20171411 8
Standard 3 68 65 62 59 56 53 50
Alternate 3 55 52 49 46 43 40 37
115_5
Standard 3 68 65 62 59 56 53 50
Alternate 3 55 52 49 46 43 40 37
1) One 90° elbow should be secured to the combustion air intake connection.
2) Minimum requirement for each vent pipe is five (5) feet in length and one
elbow/tee.
3) Tee used in the vent/flue termination must be included when determining
the number of elbows in the piping system.
4) 2 1/2” or 3” diameter pipe can be used in place of 2” diameter pipe.
5) Increased Clearance Configurations using (2) 45 deg. Long Sweep
elbows should be considered equivalent to one 90 deg. elbow.
VENT/FLUE AND COMBUSTION AIR PIPE TERMINATIONS
The vent/flue and combustion air pipes may terminate vertically, as
through a roof, or horizontally, as through an outside wall.
Vertical pipe terminations should be as shown in the following
figure. Refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion Pipe -
Termination Locations for details concerning location restrictions.
The penetrations through the roof must be sealed tight with proper
flashing such as is used with a plastic plumbing vent.
VENT/FLUE
12" MIN.
COMBUSTION
AIR INTA KE
Horizontal terminations should be as shown in the following figure. Refer to Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion Pipe -
Termination Location for location restrictions. A 2 3/8” diameter
wall penetration is required for 2” diameter pipe. A 3” diameter hole
is required for a 2 1/2” pipe and a 3 1/2” diameter hole is required
for 3” diameter pipe. To secure the pipe passing through the wall
and prohibit damage to piping connections, a coupling should be
installed on either side of the wall and solvent cemented to a pipe
connecting the two couplings. The pipe length should be the wall
thickness plus the depth of the socket fittings to be installed on the
inside and outside of the wall. The wall penetration should be
sealed with silicone caulking material.
12" MIN
12" MIN. ABOVE
HIGHEST ANTICIP ATED
SNOW LE VEL
12" MIN. ABOVE
HIGHES T AN TICIPA TED
SNOW LE VEL
3" MIN
24" MAX
90º
MEDIUM RADIUS
ELBOW
3" MIN
24" MAX
Standard Horizontal Terminations (Dual Pipe)
90°
MEDIUM
RADIUS
ELBOW
24" MAX
3" MIN
24" MAX
AIR
INTAKE
12" M IN. ABOVE
HIGHEST ANTICIPATED
SNOW LEVEL
Alternate Horizontal Vent Termination (Dual Pipe)
12" MIN
ENT/FLUE
TEE
12" MIN. ABOVE
HIGHEST ANTICIPATED
SNOW LEVE L
SUPPORT
STRAPS
COMBUSTION
AIR INTAKE.
90°
MEDIUM
RADIUS
ELBOWS
3" MIN.
24" MAX.
12" MIN. ABOVE
HIGHEST ANTICIPATED
SNOW LEVEL
12" MIN.
TO ROOF OR
HIGHEST
ANTICIPATED
SNOW LEVEL
Standard Horizontal Terminations Above Anticipated Snow
Level (Dual Pipe)
Vertical Terminations (Dual Pipe)
17
Page 18

Vent
V
12" Min.
24" Max.
24" Max.
12" Min. Above
Highest Anticipated
Snow Level
3" Min.
Air Intake
Alternate Vent Termination Above Anticipated Snow Level
(Dual Pipe)
In a basement installation, the pipes may be run between the joist
spaces. If the pipes must go below the joist and then up into the
last joist space to penetrate the header, two 45° elbows should be
used to reach the header rather than two 90° elbows.
VENT/INTAKE TERMINATIONS FOR INSTALLATION OF MULTIPLE
DIRECT VENT FURNACES
If more than one direct vent furnace is to be installed vertically
through a common roof top, maintain the same minimum clearances between the exhaust vent and air intake terminations of
adjacent units as with the exhaust vent and air intake terminations
of a single unit.
If more than one direct vent furnace is to be installed horizontally
through a common side wall, maintain the clearances as in the
following figure. Always terminate all exhaust vent outlets at the
same elevation and always terminate all air intakes at the same
elevation.
ents
3" Min.
24" Max.
24" Max.
12" MIN. ABOVE
HIGHEST ANTICIPATED
3" Min.
SNOW LE VEL
3" Min.
Air
Intakes
90°
Medium
Radius
Elbows
24" Max.
Horizontal Venting Of Multiple Units
CONCENTRIC VENT TERMINATION
Refer to the directions provided with the Concentric Vent Kit (DCVK)
for installation specifications.
SIDE WALL VENT KIT
This kit is to be used with 2” or 3” direct vent systems. The vent kit
must terminate outside the structure and may be installed with the
intake and exhaust pipes located side-by-side or with one pipe
above the other. This kit is NOT intended for use with single pipe
(indirect vent) installations.
Refer to the directions furnished with the Side Wall Vent Kit (p/n
0170K00000S) for installation specifications.
X. CONDENSATE DRAIN LINES & DRAIN TRAP
GENERAL
A condensing gas furnace achieves its high level of efficiency by
extracting almost all of the heat from the products of combustion
and cooling them to the point where condensation takes place.
The condensate which is generated must be piped to an appropriate drain location.
In upright installations, the furnace’s drain hoses may exit either
the right or left side of the furnace. NOTE: If the alternate vent/flue
outlet is utilized in an upright installation, the drain trap and drain
connections must be located on the same side as the alternate
vent/flue outlet.
In horizontal installations, the drain hoses will exit through the
bottom (down side) of the unit with the drain trap suspended beneath the furnace. The field-supplied drain system must be in
accordance with all local codes and the instructions in the following sections.
Follow the bullets listed below when installing the drain system.
Refer to the following sections for specific details concerning furnace drain trap installation and drain hose hook ups.
• The drain trap supplied with the furnace must be used.
• The drain line between furnace and drain location must
be constructed of 3/4” PVC.
• The drain line between furnace and drain location must
maintain a 1/4 inch per foot downward slope toward the
drain.
• Do not trap the drain line in any other location than at
the drain trap supplied with the furnace.
• Do not route the drain line outside where it may freeze.
• If the drain line is routed through an area which may
see temperatures near or below freezing, precautions
must be taken to prevent condensate from freezing
within the drain line.
• If an air conditioning coil is installed with the furnace, a
common drain may be used. An open tee must be
installed in the drain line, near the cooling coil, to
relieve positive air pressure from the coil’s plenum.
This is necessary to prohibit any interference with the
function of the furnace’s drain trap.
UPRIGHT INSTALLATIONS
In an upright installation drain hoses are connected to drain ports
on the rubber elbow and the recuperator coil front cover. The drain
lines are then routed through the right or left side panel and into the
drain trap secured to the outside of the cabinet.
NOTE: Refer to Section X, Condensate Drain Lines and Drain Trap
- Alternate Vent/Flue Hose Connections for upright installations
using an alternate vent/flue outlet.
STANDARD RIGHT OR LEFT SIDE DRAIN HOSE CONNECTIONS
Upright installations using the standard vent/flue outlet require drain
hoses to be connected as follows. The following quantity of hoses,
tubes, and hose clamps are provided with the unit.
HOSE A
QTY: 1
HOSE B
DRAIN TRAP
QTY: 1
GREEN
HOSE CLAMPS
QTY : 3
RED
HOSE CLAMP
QTY: 1
TUBE 1
QTY: 1
SILVER
HOSE CLAMP
QTY : 1
Hose and Tube Identification
1. Remove the rubber plug/cap from the front cover drain port
(right or left side, depending on the intended drain trap
mounting).
QTY : 1
TUBE 2
QTY : 2
18
Page 19

2. Secure Hose A to front cover drain port with a red hose
clamp. Route hose to rear side panel grommet hole.
NOTE: For left side drainage, grommets will have to be relocated
to left side panel.
3. Cut and remove 1/4 inch from the end of the drain port on
the rubber elbow.
4. Insert Tube 1 into rubber elbow drain port and secure with
silver hose clamp. Angle tube outward toward front of
furnace.
5. Right side drains
Cut 17 3/4 inches from the long end (end opposite the
bend) of Hose B. Save the part with the bend and discard
the 17 3/4 inch piece that was cut. Secure the remaining
hose to Tube 1 with a green hose clamp. Route the other
end of Hose B to front right side panel grommet hole.
Left side drains
Cut “X” inches from the long end of Hose B and discard.
Refer to table for appropriate length to cut. Secure remaining
hose to Tube 1 with a green hose clamp. Route other end
of Hose B to front left side panel grommet hole.
Cabinet Width
(inches)
17 1/2
21
24 1/2 None
Models
(kBTU_Tons)
045_30
070_30
070_40
090_40
090_50
115_50
RIGHT SIDE
PANEL
RUBBER
ELBOW
RUBBER ELBOW
DRAIN P ORT
"X" Length to Cut From Long
End of Hose B
7 inches
3 1/2 inches
FRONT CO VE R
DRAIN P ORT
Upright “Standard” Connections - Right Side
LEFT
SIDE PANEL
FRONT COV ER
DRAIN PORT
RED HOSE
CLAMP
HOSE A
SIDE PANEL
DRAIN
HOLES
TUBE(S) 2
DRAIN
TRAP
RED HOSE
CLAMP
HOSE
A
GREEN
HOSE
CLAMPS
(3 PLACES)
SILVER HOSE CLAMP
TUBE 1
HOSE
B
SIDE PANE L
GROMMET
HOLES
TUBE(S) 2
DRAIN
TRAP
RUBBER
ELBOW
DRAIN PORT
SILVER HOSE
TUBE 1
GREEN HOSE
CLAMPS
(3 PLACES)
HOSE B
RUBBER
ELBOW
CLAMP
Upright “Standard” Connections - Left Side
19
Page 20

6. Insert short end of each Tube 2 through side panel grommet
holes. Secure tubes to Hose A and Hose B with green
hose clamps. Ensure hoses and tubes maintain a
downward slope for proper drainage and that they are not
kinked or binding.
For details concerning mounting of the drain trap, refer to Section
X, Condensate Drain Lines and Drain Trap - Upright Drain Trap
Mounting.
ALTERNATE VENT/FLUE DRAIN HOSE CONNECTIONS
Upright installations using the alternate vent/flue outlet will require
“right-side only” drain hoses to be connected as follows. Refer to
Section IX, Vent/Flue Pipe and Combustion Air Pipe for details on
alternate vent/flue pipe connection.
1. Remove the rubber plug/cap from the front cover right-side
drain port. Save for use in step 3.
2. Secure Hose A to front cover drain port with a red hose
clamp. Route hose to rear right side panel grommet hole.
3. Remove grommet from front right-side panel drain hole.
Seal hole in grommet with large end of plug. Reinstall
grommet and plug into side panel drain hole.
4. Cut 1/4 inch from the end of the drain port on the externally
mounted rubber elbow. Discard cut portion.
5. Insert Tube 1 into rubber elbow drain port and secure with
a silver hose clamp. Angle tube outward toward front of
furnace.
6. Cut 17 7/8 inches from the long end of Hose B and discard.
7. Secure remaining end of Hose B to exposed end of Tube 1
with a green hose clamp. Route hose toward right side
panel grommet holes.
8. Insert short end of one Tube 2 through rear right side panel
grommet drain hole. Secure tube to Hose A with a green
hose clamp.
9. Insert short end of remaining Tube 2 into Hose B from
rubber elbow and secure with green hose clamp. Ensure
hoses and tubes maintain a downward slope for proper
drainage and are not kinked or binding.
For details concerning mounting of the drain trap, refer to the following section.
UPRIGHT DRAIN TRAP MOUNTING (LEFT OR RIGHT SIDE PANEL)
1. Insert drain tubes into drain trap and position the drain trap
against the side panel. NOTE: Drain tubes must reach the
bottom of the drain trap.
2. Secure drain trap to side panel at the mounting holes
(dimples or crosshairs) located below the grommet drain
holes.
3. Attach PVC drain line to drain trap outlet with either a 90°
elbow or coupling.
Upright “Alternate” Connections - Right Side Only
20
Page 21

HORIZONTAL INSTALLATIONS
NOTE: This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated
Upflow. A “Blocked Drain Kit” is available and
MUST BE USED if the
furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal Right. Check the
Serial/ Rating Plate on the furnace for the Kit P/N.
RIGHT SIDE DOWN
WARN ING
A
BLOCKED DRAIN KIT IS REQUIRED FOR HORIZONTAL
INSTALLATIONS WITH THE RIGHT SIDE OR LEFT SIDE DOWN
PROTECTS AGAINST A BLOCKED CONDENSATE DRAIN
PROPERLY INSTALL THE KIT COULD LEAD TO BODILY INJURY OR
DEATH DUE TO CARBON MONOXIDE EXPOSURE
RED HOSE
HOSE A
HOSE B
SIDE PANEL
GROMMET
HOLES
. THE
. F
AILURE TO
.
FRONT COVER
DRAIN PO RT
CLAMP
KIT
NOTE: This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated
Upflow. A “Blocked Drain Kit” is available and
MUST BE USED if the
furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal Right. Check the
Serial/ Rating Plate on the furnace for the Kit P/N.
Horizontal installations with the right side down require that the
drain hoses be connected to the right side front cover drain port
and the rubber elbow drain port.
Make connections as follows:
1. Remove the rubber plug/cap from the coil front cover drain
port.
2. Secure Hose A to front cover drain t ap with a red hose clamp.
Route hose to rear right (down) side panel grommet holes.
3. Cut 1/4 inch from the end of the drain port on the rubber
elbow and discard.
FRONT
COVER
PRESSURE
TAP
RUBBER
ELBOW
TUBES 2
RUBBER ELBOW
SILVER HOSE
DRAIN TRAP
GREEN
HOSE
CLAMP
TUBE 1
(3 PLACES)
Horizontal Connections - Right Side Down
DRAFT BLOWER
FRONT
COVER
PRESSURE
TAP
LEFT SIDE
PANEL
FRONT COVER
DRAIN PORT
RED HOSE CLAMP
SIDE PANEL
GROMMET
HOLES
RIGHT
SIDE
PANEL
DRAIN PORT
CLAMP
INDUCED
DRAIN PORT
HOSE B
HOSE A
GREEN HOSE
CLAMPS
(3 PLACES)
TUBE(S) 2
DRAIN TRAP
Horizontal Connections - Left Side Down
21
Page 22

4. Insert Tube 1 into rubber elbow drain port and secure with a
silver hose clamp. Angle tube outward toward front of furnace.
5. Cut 17 3/4 inches from the long end (end opposite the bend)
of Hose B. Save the part with the bend and discard the
17 3/4 inch piece that was cut.
6. Secure remaining end of Hose B to exposed end of Tube 1
with a green hose clamp. Route hose to front right down
side panel grommet holes.
7. Cut 5 1/2 inches straight length from the long end (end with
taper) of each Tube 2. Save the 5 1/2” long pieces and
discard the pieces with the bends.
8. Insert approximately one inch of each Tube 2 through the
right down side panel grommet holes. Secure tubes to
Hose A and Hose B using green hose clamps. Ensure
hoses and tubes maintain a downward slope for proper
drainage and are not kinked or bound.
9. A “Blocked Drain Kit” MUST be installed for right side down
installations. The kit includes a front cover pressure switch
that must be used to protect against a blocked drain
condition. Install the front cover pressure switch per the
instructions included with the “Blocked Drain Kit”. Failure to
install the “Blocked Drain Kit” will void the warranty and could
lead to bodily injury or death.
For details concerning mounting of the drain trap, refer to Section
X, Condensate Drain Lines and Drain Trap - Horizontal Drain Trap
Mounting (Left or Right Side Panel).
LEFT SIDE DOWN
WARN ING
A
BLOCKED DRAIN KIT IS REQUIRED FOR HORIZONTAL
INSTALLATIONS WITH THE RIGHT SIDE OR LEFT SIDE DOWN
PROTECTS AGAINST A BLOCKED CONDENSATE DRAIN
PROPERLY INSTALL THE KIT COULD LEAD TO BODILY INJURY OR
DEATH DUE TO CARBON MONOXIDE EXPOSURE
. THE
KIT
. F
AILURE TO
.
6. Insert approximately one inch of each Tube 2 through left
side panel grommet hole. Secure tubes to Hose A and
Hose B with a green hose clamps. NOTE: Tube must
reach bottom of trap. Ensure hoses and tubes maintain a
downward slope for proper drainage and that they are not
kinked or binding.
7. A “Blocked Drain Kit” MUST be installed for left side down
installations. The kit includes a front cover pressure switch
that must be used to protect against a blocked drain
condition. Install the front cover pressure switch per the
instructions included with the “Blocked Drain Kit”. Failure to
install the “Blocked Drain Kit” will void the warranty and could
lead to bodily injury or death.
For details concerning mounting of the drain trap, refer to Section
X, Condensate Drain Lines and Drain Trap - Horizontal Drain Trap
Mounting (Left or Right Side Panel).
HORIZONTAL DRAIN TRAP MOUNTING (LEFT OR RIGHT SIDE PANEL)
NOTE: This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated
Upflow . A “Blocked Drain Kit” is available and MUST BE USED if the
furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal Right. Check the
Serial/ Rating Plate on the furnace for the Kit P/N.
1. Position the drain trap against side panel with drain tubes
inserted into trap. Note that the trap may be orientated with
the outlet facing either the furnace’s top cover or base pan.
2. Secure drain trap to side panel at the dimples or crosshairs
located on either side of the grommet drain holes.
3. Confirm that tubes reach bottom of drain trap and that all
hoses maintain a downward slope and are not kinked or
binding.
4. Attach PVC drain line to drain trap outlet with either a 90°
elbow or coupling.
XI. ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
WARN ING
NOTE: This furnace is shipped from the factory as a Dedicated
Upflow. A “Blocked Drain Kit” is available and MUST BE USED if the
furnace is installed Horizontal Left or Horizontal Right. Check the
Serial/ Rating Plate on the furnace for the Kit P/N.
Horizontal installations with the left side panel down will require
drain hoses to be connected to the left side front cover drain port
and the side drain port on the rubber elbow.
1. Remove the rubber plug/cap from the coil front cover left
(down) side drain port.
2. Secure Hose A to front cover drain port with a red hose
clamp. Route hose to rear left (down) side panel grommet
holes. NOTE: For left side drainage, grommets must be
relocated to left side panel.
3. Remove the rubber cap from the side drain port on the rubber
elbow.
4. Secure the short end of Hose B to rubber elbow side drain
port using a green hose clamp. NOTE: For left side drainage,
route hose to far left (down) side panel grommet holes.
NOTE: Horizontal left side connections (when using new
side port drain elbow) does not require connecting a hose
to the induced draft blower housing.
5. Cut 5 1/2 inches straight length from the long end (end with
taper) of each Tube 2. Save the 5 1/2” long pieces and
discard the pieces with the bends.
HIGH VOLTAGE!
T
O AVOID THE RISK OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK, WIRING TO
THE UNIT MUST BE POLARIZED AND GROUNDED
.
WARN ING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
O AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH DUE TO
T
ELECTRICAL SHOCK, DISCONNECT ELECTRICAL POWER
BEFORE SERVICING OR CHANGING ANY ELECTRICAL
WIRING
.
CAUTION
L
ABEL ALL WIRES PRIOR TO DISCONNECTION WHEN SERVICING
CONTROLS
DANGEROUS OPERATION
SERVICING
. W
IRING ERRORS CAN CAUSE IMPROPER AND
. V
ERIFY PROPER OPERATION AFTER
.
WIRING HARNESS
The wiring harness is an integral part of this furnace. Field alteration to comply with electrical codes should not be required. Wires
are color-coded for identification purposes. Refer to the wiring
diagram for wire routings. If any of the original wire as supplied
22
Page 23

with the furnace must be replaced, it must be replaced with wiring
material having a temperature rating of at least 105°C. Any replacement wiring must be copper conductor.
115 VOLT LINE CONNECTIONS
Before proceeding with electrical connections, ensure that the supply voltage, frequency, and phase correspond to that specified on
the unit rating plate. Power supply to the furnace must be N.E.C.
Class 1, and must comply with all applicable codes. The furnace
must be electrically grounded in accordance with local codes or, in
their absence, with the latest edition of The National Electric Code,
ANSI NFPA 70 and/or The Canadian Electric Code CSA C22.1.
Use a separate fused branch electrical circuit containing properly
sized wire, and fuse or circuit breaker. The fuse or circuit breaker
must be sized in accordance with the maximum overcurrent protection specified on the unit rating plate. An electrical disconnect
must be provided at the furnace location.
NOTE: Line polarity must be observed when making field
connections.
WARN ING
IN
UPRIGHT UPFLOW INSTALLATIONS, THE DRAIN TRAP MUST BE
MOUNTED ON THE OPPOSITE SIDE OF THE UNIT FROM THE JUNCTION
BOX
. T
HIS WILL REDUCE THE RISK OF WATER REACHING THE
JUNCTION BOX IN THE EVENT OF A BLOCKED DRAIN CONDITION
Connect hot, neutral, and ground wires as shown in the wiring
diagram located on the unit’s blower door. For direct vent applications, the cabinet opening to the junction box must be sealed air
tight using either a UL approved bushing such as Heyco Liquid
Tight or by applying a UL approved non-reactive sealant to bushing.
Line polarity must be observed when making field connections.
Line voltage connections can be made through either the right or
left side panel. The furnace is shipped configured for a left side
electrical connection with the junction box located inside the burner
compartment. To make electrical connections through the opposite side of the furnace, the junction box must be relocated to the
other side of the burner compartment prior to making electrical
connections. To relocate the junction box, follow the steps shown
below.
NOTE: Wire routing must not to interfere with circulator blower
operation, filter removal, or routine maintenance.
WARN ING
E
DGES OF SHEET METAL HOLES MAY BE SHARP
PRECAUTION WHEN REMOVING HOLE PLUGS
1. Remove the burner compartment door.
2. Remove and save the two screws securing the junction box
to the side panel.
3. Relocate junction box and associated plugs and grommets
to opposite side panel. Secure with screws removed in
step 2.
. USE
GLOVES AS A
.
.
STANDARD
JUNCTION BOX
LOCATION
*
***
*
ALTERNATE
JUNCTION BOX
LOCATION
*
**
*
Junction Box Relocation
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
T
O AVOID THE RISK OF INJURY, ELECTRICAL SHOCK OR
DEATH, THE FURNACE MUST BE ELECTRICALLY
GROUNDED IN ACCORDANCE WITH LOCAL CODES OR IN
THEIR ABSENCE, WITH THE LATEST EDITION OF THE
N
ATIONAL ELECTRIC CODE
.
To ensure proper unit grounding, the ground wire should run from
the furnace ground screw located inside the furnace junction box
all the way back to the electrical panel. NOTE: Do not use gas
piping as an electrical ground. To confirm proper unit grounding,
turn off the electrical power and perform the following check.
1. Measure resistance between the neutral (white) connection
and one of the burners.
2. Resistance should measure 10 ohms or less.
This furnace is equipped with a blower door interlock switch which
interrupts unit voltage when the blower door is opened for servicing. Do not defeat this switch.
24 VOLT THERMOSTAT WIRING
NOTE: Wire routing must not interfere with circulator blower
operation, filter removal, or routine maintenance.
Low voltage connections can be made through either the right or
left side panel. Thermostat wiring entrance holes are located adjacent to the junction box locations in the blower compartment. Wire
routing must not to interfere with circulator blower operation, filter
removal, or routine maintenance. Refer to the following figure for
thermostat connections to the integrated control module terminal
strip.
W
R
HEATING
ROOM
THERMOSTAT
Y
W
R
G
C
FURNACE
W
Y
R
G
HEATING AND
COOLING ROOM
THERMOSTAT
Y
W
R
G
C
FURNACE
Y
C
REMOTE
CONDENSIN G
UNIT
Thermostat Diagram
This furnace is equipped with a 40 VA transformer to facilitate use
with most cooling equipment. Consult the wiring diagram, located
on the blower compartment door, for further details of 115 Volt and
24 Volt wiring.
XII. GAS SUPPL Y AND PIPING
GENERAL
The furnace rating plate includes the approved furnace gas input
rating and gas types. The furnace must be equipped to operate on
the type of gas applied. This includes any conversion kits required
for alternate fuels and/or high altitude.
23
Page 24

CAUTION
TO
PREVENT UNRELIABLE OPERATION OR EQUIPMENT DAMAGE, THE
GAS MANIFOLD PRESSURE MUST BE AS SPECIFIED ON THE UNIT
RATING PLATE
ADJUSTING THE GAS VALVE PRESSURE REGULATOR
. O
NLY MINOR ADJUSTMENTS SHOULD BE MADE BY
.
Inlet gas supply pressures must be maintained within the ranges
specified below. The supply pressure must be constant and available with all other household gas fired appliances operating. The
minimum gas supply pressure must be maintained to prevent
unreliable ignition. The maximum must not be exceeded to prevent unit overfiring.
Inlet Gas Supply Pressure
Natural Gas
Propane Gas
Minimum:5.0" W.C. Maximum :10.0" W.C.
Minimum:11.0" W.C. Maximum :13.0" W.C.
HIGH ALTITUDE DERATE
When this furnace is installed at high altitude, the appropriate High
Altitude orifice kit must be applied. This is required due to the
natural reduction in the density of both the gas fuel and combustion air as altitude increases. The kit will provide the proper design
certified input rate within the specified altitude range.
High altitude kits are purchased according to the installation altitude and usage of either natural or propane gas. Contact your
distributor for a tabular listing of appropriate altitude ranges and
corresponding manufacturer’s high altitude (Natural, Propane Gas,
and/or Pressure Switch) kits.
Do not derate the furnace by adjusting the manifold pressure to a
lower pressure than specified on the furnace rating plate. The
combination of the lower air density and a lower manifold pressure
will prohibit the burner orifice from drawing the proper amount of
air into the burner. This may cause incomplete combustion, flashback, and possible yellow tipping.
In some areas the gas supplier may artificially derate the gas in an
effort to compensate for the effects of altitude. If the gas is artificially derated, the appropriate orifice size must be determined
based upon the BTU/ft3 content of the derated gas and the altitude.
Refer to the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1, and information
provided by the gas supplier to determine the proper orifice size.
A different pressure switch may be required at high altitude regardless of the BTU/ft
3
content of the fuel used. Contact your distributor
for a tabular listing of appropriate altitude ranges and corresponding manufacturer’s pressure switch kits.
PROPANE GAS CONVERSION
WARN ING
P
OSSIBLE PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY
OCCUR IF THE CORRECT CONVERSION KITS ARE NOT INSTALLED
APPROPRIATE KITS MUST BE APPLIED TO ENSURE SAFE AND PROPER
FURNACE OPERATION
A QUALIFIED INSTALLER OR SERVICE AGENCY
. ALL
CONVERSIONS MUST BE PERFORMED BY
.
. THE
This unit is configured for natural gas. The appropriate
manufacturer’s propane gas conversion kit, must be applied for
propane gas installations. Refer to the Section VIII, Propane Gas
/ High Altitude Installations section for details.
GAS VALVE
This unit is equipped with a 24 volt gas valve controlled during
furnace operation by the integrated control module. As shipped,
the valve is configured for natural gas. The valve is field convertible
for use with propane gas by replacing the regulator spring with a
propane gas spring from an appropriate manufacturer’s propane
gas conversion kit. Taps for measuring the gas supply pressure
and manifold pressure are provided on the valve.
The gas valve has a manual ON/OFF control located on the valve
itself. This control may be set only to the “ON” or “OFF” position.
Refer to the lighting instructions label or Section XIV, Startup Pro-
cedure & Adjustment for use of this control during start up and shut
down periods.
GAS PIPING CONNECTIONS
GENERAL
CAUTION
TO
AVOID POSSIBLE UNSATISFACTORY OPERATION OR EQUIPMENT
DAMAGE DUE TO UNDERFIRING OR EQUIPMENT, USE THE PROPER
SIZE OF NATURAL/PROPANE GAS PIPING NEEDED WHEN RUNNING
PIPE FROM THE METER/TANK TO THE FURNACE
.
When sizing a trunk line, be sure to include all appliances which
will operate simultaneously when sizing a trunk line.
The gas piping supplying the furnace must be properly sized based
on the gas flow required, specific gravity of the gas, and length of
the run. The gas line installation must comply with local codes, or
in their absence, with the latest edition of the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1.
Natural Gas Capacity of Pipe
Length of Nominal Black Pipe Size
Pipe in Feet 1/2" 3/4" 1" 1 1/4" 1 1/2"
10 132 278 520 1050 1600
20 92 190 350 730 1100
30 73 152 285 590 980
40 63 130 245 500 760
50 56 115 215 440 670
60 50 105 195 400 610
70 46 96 180 370 560
80 43 90 170 350 530
90 40 84 160 320 490
100 38 79 150 305 460
(Pressure 0.5 psig or less and pressure drop of 0.3" W.C.; Based on
0.60 Specific Gravity Gas)
BTUH Furnace Input
CFH =
Heat i ng Value of Gas (BT U/Cu bi c Foot)
In Cubic Feet of Gas Per Hour (CFH)
To connect the furnace to the building’s gas piping, the installer
must supply a ground joint union, drip leg, manual shutoff valve,
and line and fittings to connect to gas valve. In some cases, the
installer may also need to supply a transition piece from 1/2" pipe
to a larger pipe size.
The following stipulations apply when connecting gas piping. Refer to Gas Piping Connections figure for typical gas line connections to the furnace.
• Use black iron or steel pipe and fittings for building piping.
Where possible, use new pipe that is properly chamfered,
reamed, and free of burrs and chips. If old pipe is used, be
sure it is clean and free of rust, scale, burrs, chips, and old
pipe joint compound.
• Use pipe joint compound on male threads ONLY. Always
use pipe joint compound (pipe dope) that is APPROVED
FOR ALL GASSES. DO NOT apply compound to the first two
threads.
• Use ground joint unions.
• Install a drip leg to trap dirt and moisture before it can enter
the gas valve. The drip leg must be a minimum of three
inches long.
24
Page 25

• Install a 1/8" NPT pipe plug fitting, accessible for test gage
connection, immediately upstream of the gas supply
connection to the furnace.
• Always use a back-up wrench when making the connection
to the gas valve to keep it from turning. The orientation of the
gas valve on the manifold must be maintained as shipped
from the factory. Maximum torque for the gas valve connection
is 375 in-lbs; excessive over-tightening may damage the
gas valve.
• Install a manual shutoff valve between the gas meter and
unit within six feet of the unit. If a union is installed, the union
must be downstream of the manual shutoff valve, between
the shutoff valve and the furnace.
• Tighten all joints securely.
• Connect the furnace to the building piping by one of the
following methods:
– Rigid metallic pipe and fittings.
– Semi-rigid metallic tubing and metallic fittings.
Aluminum alloy tubing must not be used in exterior
locations. In order to seal the grommet cabinet
penetration, rigid pipe must be used to reach the
outside of the cabinet. A semi-rigid connector to the
gas piping may be used from there.
• Use listed gas appliance connectors in accordance with
their instructions. Connectors must be fully in the same
room as the furnace.
• Protect connectors and semirigid tubing against physical
and thermal damage when installed. Ensure aluminumalloy tubing and connectors are coated to protect against
external corrosion when in contact with masonry, plaster, or
insulation, or subjected to repeated wetting by liquids such
as water (except rain water), detergents, or sewage.
GAS VALVE
ALTERNATE
GAS LINE
LOCATI ON
PLUG IN
ALTERNATE
GAS LINE
HOLE
MANIFOLD
PIPE UNION
BURNERS
UPFLOW
MANUAL SHUT-OF F VALVE
(UPSTREAM F ROM GROUND
GROUND JOINT
PIPE U NION
GAS VALVE
BURNERS
ALTER NATE GA S
LINE LOCATION
MANIFOLD
JOINT PIPE UNION)
DRIP LEG
GROMMET IN STAND ARD
GAS LINE HOLE
PLUG IN A LTERNATE
GAS LINE HOLE
HORIZONTAL [UPFLOW MODEL]
NOTES: 1. WHEN GAS LINE IS IN THE ALTERNATE
LOCATION, SWAP THE POSITION OF
THE PLUG AND GROMMET
.
Gas Piping Connections
WARNING
E
DGES OF SHEET METAL HOLES MAY BE SHARP
PRECAUTION WHEN REMOVING HOLE PLUGS
GROMMET
. USE
MANUAL
SHUT OFF VALVE
(UPSTREAM FR OM
GROUND JOINT
PIPE UNION)
HEIGHT REQUIRED
BY LOCAL CODE
DRIP LE G
GLOVES AS A
GROUND JOINT
PIPE UNION
IN STA ND ARD
GAS LINE HO LE
DRAIN TRAP
2. DRIP LEG MAY TERMINATE WITH
A 1/2" X 1/8" PIPE PLUG TO
ACCOMMODATE LINE GAS
PRESSURE MEASUREMENT.
.
DIRECT/STANDARD INLET PIPING
When gas piping enters directly to the gas valve through the standard inlet hole, the installer must supply straight pipe with a ground
joint union to reach the exterior of the furnace. The rigid pipe must
be long enough to reach the outside of the cabinet to seal the
grommet cabinet penetration. A semi-rigid connector to the gas
piping can be used outside the cabinet per local codes.
INDIRECT/ALTERNATE INLET PIPING
When gas piping enters indirectly to the gas valve through the
alternate gas inlet hole the following 1/2 inch pipe fittings (starting
from the gas valve) to reach the outside of the cabinet must be
supplied:
• 1 - 90 degree street elbow.
• 1 - 2-1/2 inch pipe nipple.
• 1 - 90 degree elbow.
• 1 - Straight pipe
The straight pipe must be long enough to reach the outside
of the cabinet so as to seal the grommet cabinet penetration
and to install the ground joint union outside of the cabinet. A
semi-rigid connector to the gas piping can be used outside
the cabinet per local codes.
GAS PIPING CHECKS
Before placing unit in operation, leak test the unit and gas connections.
25
Page 26

WARN ING
TO
AVOID THE POSSIBILITY OF EXPLOSION OR FIRE, NEVER USE A
MATCH OR OPEN FLAME TO TEST FOR LEAKS
.
Check for leaks using an approved chloride-free soap and water
solution, an electronic combustible gas detector, or other approved
testing methods.
First Stage
Regulator
200 PSIG
Maximum
5 to 15 PSIG
(20 PSIG Max.)
Second Stage
Regulator
Continuous
11" W.C.
NOTE: Never exceed specified pressures for testing. Higher
pressure may damage the gas valve and cause subsequent
overfiring, resulting in heat exchanger failure.
Disconnect this unit and shutoff valve from the gas supply piping
system before pressure testing the supply piping system with pressures in excess of 1/2 psig (3.48 kPa).
Isolate this unit from the gas supply piping system by closing its
external manual gas shutoff valve before pressure testing supply
piping system with test pressures equal to or less than 1/2 psig
(3.48 kPa).
PROPANE GAS TANKS AND PIPING
WARN ING
IF
THE GAS FURNACE IS INSTALLED IN A BASEMENT, AN EXCAVATED
AREA OR A CONFINED SPACE, IT IS STRONGLY RECOMMENDED TO
CONTACT A PROPANE SUPPLIER TO INSTALL A GAS DETECTING
WARNING DEVICE IN CASE OF A GAS LEAK
• S
INCE PROPANE GAS IS HEAVIER THAN AIR, ANY LEAKING AS CAN
SETTLE IN ANY LOW AREAS OR CONFINED SPACES
• P
ROPANE GAS ODORANT MAY FADE, MAKING THE GAS
U
NDETECTABLE EXCEPT FOR WITH A WARNING DEVICE
.
.
.
A gas detecting warning system is the only reliable way to detect a
propane gas leak. Rust can reduce the level of odorant in propane
gas. Do not rely on your sense of smell. Contact a local propane
gas supplier about installing a gas detecting warning system. If
the presence of gas is suspected, follow the instructions on Page
4 of this manual.
All propane gas equipment must conform to the safety standards
of the National Board of Fire Underwriters, NBFU Manual 58.
For satisfactory operation, propane gas pressure must be 11 inch
w.c. at the furnace manifold with all gas appliances in operation.
Maintaining proper gas pressure depends on three main factors:
1. Vaporization rate, depending on temperature of the liquid,
and “wetted surface” area of the container or containers.
2. Proper pressure regulation. (Two-stage regulation is
recommended for both cost and efficiency).
3. Pressure drop in lines between regulators, and between
second stage regulator and the appliance. Pipe size will
depend on length of pipe run and total load of all appliances.
Complete information regarding tank sizing for vaporization, recommended regulator settings, and pipe sizing is available from
most regulator manufacturers and propane gas suppliers.
Since propane gas will quickly dissolve white lead and most standard commercial compounds, special pipe dope must be used.
Shellac-based compounds resistant to the actions of liquefied petroleum gases such as Gasolac
®
, Stalactic®, Clyde’s® or John
Crane® are satisfactory.
Refer to the following illustration for typical propane gas installations.
Propane Gas Installation (Typ.)
Sizing Between First and Second Stage Regulator*
Maximum Propane Capacities listed are based on 2 psig pressure drop at 10 psig setting.
Capacities in 1,000 BTU/hour.
Pipe or Nominal Pipe Size
Tubing Tubing Size, O.D. Type L Schedule 40
Length, 3/8" 1/2" 5/8" 3/4" 7/8" 1/2" 3/4"
Feet
10 730 1,700 3,200 5,300 8,300 3,200 7,500
20 500 1,100 2,200 3,700 5,800 2,200 4,200
30 400 920 2,000 2,900 4,700 1,800 4,000
40 370 850 1,700 2,700 4,100 1,600 3,700
50 330 770 1,500 2,400 3,700 1,500 3,400
60 300 700 1,300 2,200 3,300 1,300 3,100
80 260 610 1,200 1,900 2,900 1,200 2,600
100 220 540 1,000 1,700 2,600 1,000 2,300
125 200 490 900 1,400 2,300 900 2,100
150 190 430 830 1,300 2,100 830 1,900
175 170 400 780 1,200 1,900 770 1,700
200 160 380 730 1,100 1,800 720 1,500
To convert to capacities at 15 psig settings - multiply by 1.130
To convert to capacities at 5 psig settings - multiply by 0.879
Propane Gas Piping Chart I
Sizing Between Single or Second Stage Regulator and Appliance*
Maximum Propane Capacities Listed are Based on 1/2" W.C. pressure drop at 11" W.C. setting.
Capacities in 1,000 BTU/hour.
Pipe or Nominal Pipe Size
Tubing Tubing Size, O.D. Type L Schedule 40
Length, 3/8" 1/2" 5/8" 3/4" 7/8" 1-1/8" 1/2" 3/4" 1" 1-1/4" 1-1/2"
Feet
10 39 92 199 329 501 935 275 567 1,071 2,205 3,307
20 26 62 131 216 346 630 189 393 732 1,496 2,299
30 21 50 107 181 277 500 152 315 590 1,212 1,858
40 19 41 90 145 233 427 129 267 504 1,039 1,559
50 18 37 79 131 198 376 114 237 448 913 1,417
60 16 35 72 121 187 340 103 217 409 834 1,275
80 13 29 62 104 155 289 89 185 346 724 1,066
100 11 26 55 90 138 255 78 162 307 630 976
125 10 24 48 81 122 224 69 146 275 567 866
150 9 21 43 72 109 202 63 132 252 511 787
200 8 19 39 66 100 187 54 112 209 439 665
250 8 17 36 60 93 172 48 100 185 390 590
*Data in accordance with NFPA pamphlet NO. 54
Propane Gas Piping Chart II
XIII. CIRCULATING AIR & FIL TERS
DUCTWORK - AIR FLOW
Duct systems and register sizes must be properly designed for the
CFM and external static pressure rating of the furnace. Design the
ductwork in accordance with the recommended methods of “Air
Conditioning Contractors of America” Manual D.
Install the duct system in accordance with Standards of the National Board of Fire Underwriters for the Installation of Air Conditioning, Warm Air Heating and Ventilating Systems. Pamphlets No.
90A and 90B.
A closed return duct system must be used, with the return duct
connected to the furnace. NOTE: Ductwork must never be attached
to the back of the furnace. Flexible joints may be used for supply
and return connections to reduce noise transmission. To prevent
the blower from interfering with combustion air or draft when a
central return is used, a connecting duct must be installed between the unit and the utility room wall. Never use a room, closet,
or alcove as a return air chamber.
NOTE: Two side openings or a side opening and bottom opening
are required for airflow delivery of 1800 CFM and greater.
26
Page 27

BOTTOM RETURN AIR OPENING [UPFLOW MODELS]
The bottom return air opening on upflow models utilizes a “lance
and cut” method to remove sheet metal from the duct opening in
the base pan. To remove, simply press out the lanced sections by
hand to expose the metal strips retaining the sheet metal over the
duct opening. Using tin snips, cut the metal strips and remove the
sheet metal to free the duct flanges. Using the scribe line along the
duct flange as a guide, unfold the duct flanges around the perimeter of the opening using a pair of seamer pliers or seamer tongs.
NOTE: Airflow area will be reduced by approximately 18% if duct
flanges are not unfolded. This could cause performance issues
and noise issues.
WARN ING
Refer to Minimum Filter Area tables to determine filter area requirements.
COOLING AIRFLOW REQUIREMENT (CFM)
600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 2000
0453_XA 188* 192 240 288 --- --- ---
0703_XA --- 282 * 282* 282* 336 --- ---
0704_XA --- --- 26 0* 260* 336 384 --0904_XA --- --- 37 6* 376* 376* 384 ---
Input__Airflow
0905_XA --- --- --- 37 6* 376* 384 480
115_XA --- --- --- 47 0* 470* 470* 480
E
DGES OF SHEET METAL HOLES MAY BE SHARP
PRECAUTION WHEN REMOVING SHEET METAL FROM DUCT OPENING
CUT USING TIN SNIPS
CUT FOUR CORNERS
AFTER REMOVING SHEET
METAL
. USE
GLOVES AS A
PRESS OUT BY HAND
SCRIBE LINES OUTLINING
DUCT FLAN GE S
.
Duct Flange Cut Outs
When the furnace is used in connection with a cooling unit, the
furnace should be installed in parallel with or on the upstream side
of the cooling unit to avoid condensation in the heating element.
With a parallel flow arrangement, the dampers or other means
used to control the flow of air must be adequate to prevent chilled
air from entering the furnace and, if manually operated, must be
equipped with means to prevent operation of either unit unless the
damper is in the full heat or cool position.
When the furnace is installed without a cooling coil, it is recommended that a removable access panel be provided in the outlet
air duct. This opening shall be accessible when the furnace is
installed and shall be of such a size that the heat exchanger can be
viewed for visual light inspection or such that a sampling probe can
be inserted into the airstream. The access panel must be made to
prevent air leaks when the furnace is in operation.
When the furnace is heating, the temperature of the return air entering the furnace must be between 55°F and 100°F.
*Minimum filter area dictated by heating airflow requirement.
Permanent Minimum Filter Area (sq. in)
[Based on a 600 ft/min filter face velocity]
COOLI NG AIRFLOW REQUIREMENT (CFM)
600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 2000
0453_XA 376* 384 480 576 --- --- --0703_XA --- 564* 564* 564* 672 --- ---
0704_XA --- --- 564* 564* 672 768 ---
0904_XA --- --- 752* 752* 752* 768 ---
Input__Airflow
0905_XA --- --- --- 752* 752* 768 800
1155_XA --- --- --- 940* 940* 940* 800
*Minimum filter area dictated by heating airflow requirement.
Disposable Minimum Filter area (sq. in)
[Based on 300 ft/min filter face velocity]
UPRIGHT INSTALLATIONS
Depending on the installation and/or customer preference, differing filter arrangements can be applied. Filters can be installed in
the central return register or a side panel external filter rack kit
(upflows). As an alternative a media air filter or electronic air cleaner
can be used as the requested filter.
The following figure shows possible filter locations.
AIR FLO W
CENTRAL
RETURN
GRILLE
SIDE RETURN
EXTERNAL FILTER
FILTER
RACK KIT
(EITHER SIDE)
FILTERS - READ THIS SECTION BEFORE INSTALLING THE
RETURN AIR DUCTWORK
Filters must be used with this furnace. Discuss filter maintenance
with the building owner. Filters do not ship with this furnace, but
must be provided by the installer. Filters must comply with UL900
or CAN/ULCS111 standards. If the furnace is installed without filters, the warranty will be voided.
On upflow units, guide dimples locate the side return cutout
locations. Use a straight edge to scribe lines connecting the
dimples. Cut out the opening on these lines. NOTE: An
undersized opening will cause reduced airflow.
FILTER
Possible Upright Upflow
Filter Locations
27
Page 28

HORIZONTAL INSTALLATIONS
Filters must be installed in either the central return register or in the
return air duct work.
4. Replace the burner compartment door.
GAS SUPPLY PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
XIV . ST ARTUP PROCEDURE & ADJUSTMENT
Furnace must have a 115 VAC power supply properly connected
and grounded. Proper polarity must be maintained for correct operation. In addition to the following start-up and adjustment items,
refer to further information in Section XVI, Operational Checks.
HEAT ANTICIPATOR SETTING
The heat anticipator in the room thermostat must be correctly adjusted to obtain the proper number of cycles per hour and to prevent “overshooting” of the setting. Set the heat anticipator setting to
0.7 amps. Follow the thermostat manufacturer’s instructions on
how to adjust the heat anticipator setting.
DRAIN TRAP PRIMING
The drain trap must be primed prior to furnace startup. To prime, fill
the drain trap with water. This ensures proper furnace drainage
upon startup and prohibits the possibility of flue gases escaping
through the drain system.
FURNACE OPERATION
Purge gas lines of air prior to startup. Be sure not purge lines into
an enclosed burner compartment.
Check for leaks using an approved chloride-free soap and water
solution, an electronic combustible gas detector, or other approved
method. Verify that all required kits (propane gas, high altitude,
etc.) have been appropriately installed.
FURNACE STARTUP
1. Close the manual gas shutoff valve external to the furnace.
2. Turn off the electrical power to the furnace.
3. Set the room thermostat to the lowest possible setting.
4. Remove the burner compartment door.
CAUTION
TO
PREVENTUNRELIABLEOPERATIONOREQUIPMENTDAMAGE,THE
INLETGASSUPPLYPRESSUREMUSTBEASSPECIFIEDONTHEUNIT
RATINGPLATEWITHALLOTHERHOUSEHOLDGASFIREDAPPLIANCES
OPERATING
.
WARN ING
HIGHVOLTAGE!
D
ISCONNECTALLPOWERBEFORESERVICINGOR
INSTALLINGTHISUNIT
BEPRESENT
DAMAGE,PERSONALINJURYORDEATH
The line pressure supplied to the gas valve must be within the
range specified below. The supply pressure can be measured at
the gas valve inlet pressure tap or at a hose fitting installed in the
gas piping drip leg. The supply pressure must be measured with
the unit OFF. To measure inlet pressure, use the following procedure.
.F
.M
ULTIPLEPOWERSOURCESMAY
AILURETODOSOMAYCAUSEPROPERTY
.
Gas Valve
On/Off
Selector
Switch
OUTLET
Inlet Pres s ur e
Tap
INLET
NOTE: This furnace is equipped with an ignition device which
automatically lights the burner. Do not try to light the burner by
hand.
5. Move the furnace gas valve manual control to the OFF
position.
6. Wait five minutes then smell for gas. Be sure to check near
the floor as some types of gas are heavier than air.
7. If you smell gas after five minutes, immediately follow the
instructions on page 4 of this manual. If you do not smell
gas after five minutes, move the furnace gas valve manual
control to the ON position.
8. Replace the burner compartment door.
9. Open the manual gas shutoff valve external to the furnace.
10. Turn on the electrical power to the furnace.
11. Adjust the thermostat to a setting above room temperature.
12. After the burners are lit, set the thermostat to desired
temperature.
FURNACE SHUTDOWN
1. Set the thermostat to the lowest setting.
The integrated control will close the gas valve and extinguish
flame. Following a 15 second delay, the induced draf t blower
will be de-energized. After a 150-second delay period (fixed),
the circulator blower will be de-energized.
2. Remove the burner compartment door and move the furnace
gas valve manual control to the OFF position.
3. Close the manual gas shutoff valve external to the furnace.
Pressure Regulator
Adjustment
(Under Cap Screw)
Outlet Pressure
Tap
White-Rodgers Model 36G22
Pressu re Regulator
Inlet
Pressure
Tap
(under cap screw)
Outlet
Pressure
Tap
Gas Valve On/Off
Selector Switch
Honeywell Model VR8215 (Single-Stage)
1. Turn OFF gas to furnace at the manual gas shutoff valve
external to the furnace.
2. Turn OFF all electrical power to the system.
28
Page 29

3. Inlet pressure tap connections:
a. Honeywell VR8215 Valve:
Remove the inlet pressure boss plug. Install an 1/8” NPT
hose barb fitting into the outlet pressure tap.
b. White-Rodgers 36G22 valve:
Back inlet pressure test screw (inlet pressure boss) out
one turn (counterclockwise, not more than one turn).
4. Attach a hose and manometer to the outlet pressure barb
fitting (Honeywell valve) or inlet pressure boss (WhiteRodgers valve).
5. Turn ON the gas supply.
6. Turn On power and close thermostat “R” and “W” contacts
to provide a call for heat.
7. Using a leak detection solution or soap suds, check for
leaks at outlet pressure boss plug (Honeywell valve) or
screw (White-Rodgers valve). Bubbles forming indicate a
leak. SHUT OFF GAS AND REPAIR ALL LEAKS
IMMEDIATELY!
8. Measure the gas supply pressure with burners firing. Adjust
supply pressure using the Inlet Gas Supply Pressure table
shown below. If supply pressure reading differs from the
table, make necessary adjustments to pressure regulator,
gas piping size, etc., and/or consult with local gas utility.
Inlet Gas Supply Pressure
Natural Gas
Propane Gas
9. Turn OFF all electrical power and gas supply to the system.
10. Remove the manometer hose from the hose barb fitting or
inlet pressure boss.
11. Replace inlet pressure tap:
a. Honeywell VR8215 valve:
Remove the 1/8” NPT hose barb fitting from the inlet
pressure tap. Replace the inlet pressure boss plug and
seal with a high quality thread sealer.
b. White-Rodgers 36G22 valve:
Turn inlet pressure test screw in to seal pressure port
(clockwise, 7 in-lb minimum).
12. Retest for leaks. If bubbles form, shut down gas and repair
leaks immediately.
13. Turn ON electrical power and gas supply to the system.
14. Turn valve switch ON.
Minimum:5.0" W.C. Maximum :10.0" W.C.
Minimum:11.0" W.C. Maximum :13.0" W.C.
GAS MANIFOLD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
CAUTION
TO
PREVENTUNRELIABLEOPERATIONOREQUIPMENTDAMAGE,THE
GASMANIFOLDPRESSUREMUSTBEASSPECIFIEDONTHEUNITRATING
PLATE
.O
NLYMINORADJUSTMENTSSHOULDBEMADEBYADJUSTING
THEGASVALVEPRESSUREREGULATOR
.
WARNING
HIGHVOLTAGE!
D
ISCONNECTALLPOWERBEFORESERVICINGOR
INSTALLINGTHISUNIT
BEPRESENT
DAMAGE,PERSONALINJURYORDEATH
.F
.M
ULTIPLEPOWERSOURCESMAY
AILURETODOSOMAYCAUSEPROPERTY
.
Consult the appliance rating plate to ensure burner manifold pressure is as specified. If another outlet pressure is required, follow
these steps.
1. Turn OFF gas to furnace at the manual gas shutoff valve
external to the furnace.
2. Turn OFF all electrical power to the system.
3. Outlet pressure tap connections:
a. Honeywell VR8215 valve:
Remove the outlet pressure boss plug. Install an 1/8”
NPT hose barb fitting into the outlet pressure tap.
b. White-Rodgers 36G22 valve:
Back outlet pressure test screw (outlet pressure boss)
out one turn (counterclockwise, not more than one turn).
4. Attach a hose and manometer to the outlet pressure barb
fitting (Honeywell valve) or outlet pressure boss (WhiteRodgers valve).
5. Turn ON the gas supply.
6. Turn ON power and close thermostat “R” and “W” contacts
to provide a call for heat.
7. Using a leak detection solution or soap suds, check for
leaks at outlet pressure boss plug (Honeywell valve) or
screw (White-Rodgers valve). Bubbles forming indicate a
leak. SHUT OFF GAS AND REPAIR ALL LEAKS
IMMEDIATELY!
8. Measure the gas manifold pressure with burners firing.
Adjust manifold pressure using the Manifold Gas Pressure
table shown below.
Manifold Gas Pressure
Natural Gas 3.5" w.c.
Propane Gas 10.0" w.c.
9. Remove regulator cover screw from the outlet pressure
regulator and turn screw clockwise to increase pressure or
counterclockwise to decrease pressure. Replace regulator
cover screw.
10. Turn OFF all electrical power and gas supply to the system.
11. Remove the manometer hose from the hose barb fitting or
outlet pressure boss.
12. Replace outlet pressure tap:
a. Honeywell VR8215 valve:
Remove the 1/8” NPT hose barb fitting from the outlet
pressure tap. Replace the outlet pressure boss plug and
seal with a high quality thread sealer.
b. White-Rodgers 36G22 valve: Turn outlet pressure test
screw in to seal pressure port (clockwise, 7 in-lb
minimum).
13. Turn ON electrical power and gas supply to the system.
14. Close thermostat contacts to provide a call for heat.
15. Retest for leaks. If bubbles form, SHUT OFF GAS AND
REPAIR ALL LEAKS IMMEDIA TEL Y!
GAS INPUT RATE MEASUREMENT (NATURAL GAS ONLY)
The gas input rate to the furnace must never be greater than that
specified on the unit rating plate. To measure natural gas input
using the gas meter, use the following procedure.
1. Turn OFF the gas supply to all other gas-burning appliances
except the furnace.
2. While the furnace is operating, time and record one
complete revolution of the smallest gas meter dial.
This valve is shipped from the factory with the regulator preset (see
control label).
29
Page 30

3. Calculate the number of seconds per cubic foot (sec/ft
g
p
3
) of
gas being delivered to the furnace. If the dial is a one cubic
foot dial, divide the number of seconds recorded in step 2
by one. If the dial is a two cubic foot dial, divide the number
of seconds recorded in step 2 by two.
4. Calculate the furnace input in BTUs per hour (BTU/hr). Input
equals the installation’s gas heating value multiplied by a
conversion factor (hours to seconds), divided by the number
of seconds per cubic foot. The measured input must not be
greater than the input indicated on the unit rating plate.
EXAMPLE:
Installation’s gas heating (HTG) value: 1,000 BTU/ft
3
(Obtained from gas supplier)
Installation’s seconds per cubic foot: 34 sec/ ft
3
Conversion Factor (hours to seconds): 3600 sec/hr
Input = (Htg. value x 3600) ÷ seconds per cubic foot
Input = (1,000 BTU/ft
3
x 3600 sec/hr) ÷ 34 sec/ ft
3
Input = 106,000 BTU/hr
Minor changes to the input rate may be accomplished through
manifold pressure adjustments at the gas valve. Refer to Section
XIV, Startup Procedure and Adjustment - Gas Manifold Pressure
Measurement and Adjustment for details. NOTE: The final mani-
fold pressure cannot vary by more than ± 0.3” w.c. from the specified setting. Consult your local gas supplier if additional input rate
adjustment is required.
5. Turn ON gas to and relight all other appliances turned off in
step 1. Be certain that all appliances are functioning properly
and that all pilot burners are operating.
TEMPERATURE RISE
Temperature rise must be within the range specified on the unit
rating plate. An incorrect temperature rise may result in condensing in or overheating of the heat exchanger. An airflow and temperature rise table is provided in the Specification Sheet applicable
to your model. Determine and adjust temperature rise as follows:
1. Operate furnace with burners firing for approximately ten
minutes. Ensure all registers are open and all duct
dampers are in their final (fully or partially open) position.
2. Place thermometers in the return and supply ducts as close
to the furnace as possible. Thermometers must not be
influenced by radiant heat by being able to “see” the heat
exchanger.
HEAT EXCHANGER
RADIATION "LINE OF SIGHT"
SUPPLY
AIR
T
SUPPLY
RISE =
T
T
-
SUPPLY
RETURN
T
RETURN
RETURN
AI R
Temperature Rise Measurement
3. Subtract the return air temperature from the supply air
temperature to determine the air temperature rise. Allow
adequate time for thermometer readings to stabilize.
4. Adjust temperature rise by adjusting the circulator blower
speed. Increase blower speed to reduce temperature rise.
Decrease blower speed to increase temperature rise. Refer
to Section XIV, Startup Procedure and Adjustment -Circulator
Blower Speeds for speed changing details.
CIRCULATOR BLOWER SPEEDS
WARN ING
TO
PREVENT PREMATURE FAILURE OF HEAT EXCHANGER, PROPERTY
DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH, DO NOT ADJUST THE LIMIT
CONTROL (FACTORY-SET
).
This furnace is equipped with a multi-speed circulator blower. This
blower provides ease in adjusting blower speeds. The Specification Sheet applicable to your model provides an airflow table, showing the relationship between airflow (CFM) and external static pressure (E.S.P .), for the proper selection of heating and cooling speeds.
The cooling blower speed is shipped set on HIGH, and the heating
blower speed is set as indicated in the Specification Sheet applicable to your model. These blower speeds should be adjusted by
the installer to match the installation requirements so as to provide
the correct heating temperature rise and correct cooling CFM.
To adjust the circulator blower speed, proceed as follows:
1. Turn OFF power to the furnace.
2. Select the heating and cooling blower speeds that match
the installation requirements from the airflow table in the
Specification Sheet.
3. Relocate desired motor leads to the circulator blower heat
and cool speed terminals on the integrated control module.
(T erminals are identified as HEA T and COOL (hot)). If heating
and cooling blower speeds are the same, a jumper wire
must be used between the heat and cool terminals.
4. Connect all unused blower motor leads to the “PARK”
terminals on the integrated control module. Any leads not
connected to the “PARK” terminals must be taped.
5. Turn ON power to furnace.
6. Verify proper temperature rise as outlined in Section XIV,
Startup Procedure and Adjustment - Temperature Rise.
Circulator Blower S
eeds
Low Red
Medium Low
Orange
Medium Blue
h
Hi
Common/Neutral
Black
White
XV . NORMAL SEQUENCE OF OPERA TION
POWER UP
The normal power up sequence is as follows:
• 115 VAC power applied to furnace.
• Integrated control module performs internal checks.
• Integrated control module LED will light.
• Integrated control module monitors safety circuits
continuously.
• Furnace awaits call from thermostat.
HEATING MODE
The normal operational sequence in heating mode is as follows:
• R and W thermostat contacts close, initiating a call for heat.
30
Page 31

• Integrated control module performs safety circuit checks.
• Induced draft blower is energized for 15 second prepurge
period causing pressure switch contacts to close.
• Igniter warm up begins after 15 second prepurge expires.
• Gas valve opens at end of igniter warm up period, delivering
gas to burners and establishing flame.
• Integrated control module monitors flame presence. Gas
valve will remain open only if flame is sensed.
• Circulator blower is energized on heat speed following a
fixed thirty second blower on delay.
• Furnace runs, integrated control module monitors safety
circuits continuously.
• R and W thermostat contacts open, completing the call for
heat.
• Gas valve closes, extinguishing flame.
• Induced draft blower is de-energized following a fifteen
second post purge.
• Circulator blower is de-energized following the heat off delay
period (fixed 150 seconds).
• Furnace awaits next call from thermostat.
COOLING MODE
The normal operational sequence in cooling mode is as follows:
• R and Y thermostat contacts close, initiating a call for cool.
• Integrated control module performs safety circuit checks.
• Outdoor fan and compressor are energized.
• Circulator blower is energized on cool speed following a
fixed five second on delay.
• Furnace circulator blower and outdoor cooling unit run,
integrated control module monitors safety circuits
continuously.
• R and Y thermostat contacts open, completing the call for
cool.
• Outdoor fan and compressor are de-energized.
• Circulator blower is de-energized following a fixed forty five
second cool off delay period.
• Furnace awaits next call from thermostat.
FAN ONLY MODE
The normal operational sequence in fan only mode is as follows:
• R and G thermostat contacts close, initiating a call for fan.
• Integrated control module performs safety circuit checks.
• Circulator blower is energized on heat speed.
• Circulator blower runs, integrated control module monitors
safety circuits continuously.
• R and G thermostat contacts open, completing the call for
fan.
• Circulator blower is de-energized.
• Furnace awaits next call from thermostat.
XVI. OPERA TIONAL CHECKS
BURNER FLAME
The burner flames should be inspected with the burner compartment door installed. A sight glass is provided for inspection purposes. Flames should stable, quiet, soft, and blue (dust may
cause orange tips but they must not be yellow). Flames should
extend directly outward from the burners without curling, floating, or
lifting off. Flames must not impinge on the sides of the heat exchanger firing tubes.
Check the burner flames for:
1. Good adjustment
2. Stable, soft and blue
3. Not curling, floating, or lifting off.
Burner Flame
XVII. SAFETY CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
GENERAL
A number of safety circuits are employed to ensure safe and proper
furnace operation. These circuits serve to control any potential
safety hazards and serve as inputs in the monitoring and diagnosis of abnormal function. These circuits are continuously monitored during furnace operation by the integrated control module.
INTEGRATED CONTROL MODULE
The integrated control module is an electronic device which, if a
potential safety concern is detected, the module will take the necessary precautions and provide diagnostic information through an
LED.
PRIMARY LIMIT
The primary limit control is located on the partition panel and monitors heat exchanger compartment temperatures. It is a normallyclosed (electrically), automatic reset, temperature-activated sensor. The limit guards against the overheating as a result of insufficient conditioned air passing over the heat exchanger.
AUXILIARY LIMIT
The auxiliary limit control(s) are located on or near the circulator
blower and monitors heat exchanger compartment temperatures.
They are a normally-closed (electrically), manual-reset, temperature activated sensors. These limits guard against overheating as
a result of insufficient conditioned air passing over the heat exchanger.
ROLLOUT LIMIT
The rollout limit controls are mounted on the burner/manifold assembly and monitor the burner flame. They are normally-closed
(electrically), manual-reset, temperature-activated sensors. These
limits guard against burner flames not being properly drawn into
the heat exchanger.
PRESSURE SWITCHES
The pressure switches are normally-open (closed during operation), single-pole single-throw, negative air pressure-activated
switches. They monitor the airflow (combustion air and flue products) through the heat exchanger via pressure taps located on the
induced draft blower and the coil front cover. These switches guard
31
Page 32

against insufficient airflow (combustion air and flue products)
through the heat exchanger and/or blocked condensate drain conditions.
FLAME SENSOR
The flame sensor is a probe mounted to the burner/manifold assembly which uses the principle of flame rectification to determine
the presence or absence of flame.
3. Manual thermostat cycle. Lower the thermostat so that
there is no longer a call for heat then reset to previous setting.
Interrupt thermostat signal to the furnace for 1 - 20 seconds.
NOTE: If the condition which originally caused the lockout still
exists, the control will return to lockout. Refer to Section XVIII,
T roubleshooting - Diagnostic Chart for aid in determining the cause.
XIX. MAINTENANCE
XVIII. TROUBLESHOOTING
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) PRECAUTIONS
NOTE: Discharge body’s static electricity before touching unit. An
electrostatic discharge can adversely affect electrical components.
Use the following precautions during furnace installation and ser-
vicing to protect the integrated control module from damage. By
putting the furnace, the control, and the person at the same electrostatic potential, these steps will help avoid exposing the integrated
control module to electrostatic discharge. This procedure is applicable to both installed and uninstalled (ungrounded) furnaces.
1. Disconnect all power to the furnace. Do not touch the
integrated control module or any wire connected to the control
prior to discharging your body’s electrostatic charge to
ground.
2. Firmly touch a clean, unpainted, metal surface of the
furnaces near the control. Any tools held in a person’s
hand during grounding will be discharged.
3. Service integrated control module or connecting wiring
following the discharge process in step 2. Use caution not
to recharge your body with static electricity; (i.e., do not move
or shuffle your feet, do not touch ungrounded objects, etc.).
If you come in contact with an ungrounded object, repeat
step 2 before touching control or wires.
4. Discharge your body to ground before removing a new
control from its container. Follow steps 1 through 3 if
installing the control on a furnace. Return any old or new
controls to their containers before touching any ungrounded
object.
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
WARN ING
WARN ING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
T
O AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH DUE TO
ELECTRICAL SHOCK, DISCONNECT ELECTRICAL POWER
BEFORE PERFORMING ANY MAINTENANCE
HANDLE THE IGNITER, HANDLE WITH CARE
THE IGNITER ELEMENT WITH BARE FINGERS, ROUGH
HANDLING OR VIBRATION COULD DAMAGE THE IGNITER
RESULTING IN PREMATURE FAILURE
SERVICER SHOULD EVER HANDLE THE IGNITER
. O
NLY A QUALIFIED
. IF
YOU MUST
. T
OUCHING
.
ANNUAL INSPECTION
The furnace should be inspected by a qualified installer, or service
agency at least once per year. This check should be performed at
the beginning of the heating season. This will ensure that all furnace components are in proper working order and that the heating
system functions appropriately. Pay particular attention to the following items. Repair or service as necessary.
• Flue pipe system. Check for blockage and/or leakage. Check
the outside termination and the connections at and internal
to the furnace.
• Heat exchanger. Check for corrosion and/or buildup within
the heat exchanger passageways.
• Burners. Check for proper ignition, burner flame, and flame
sense.
• Drainage system. Check for blockage and/or leakage.
Check hose connections at and internal to furnace.
• Wiring. Check electrical connections for tightness and/or
corrosion. Check wires for damage.
• Filters.
HIGH VOLTAGE!
O AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH DUE TO
T
ELECTRICAL SHOCK, DISCONNECT ELECTRICAL POWER
BEFORE PERFORMAING ANY SERVICE OR MAINTENANCE
.
Refer to the Troubleshooting Chart at the end of this manual for
assistance in determining the source of unit operational problems.
The red diagnostic LED blinks to assist in troubleshooting the unit.
The number of blinks refers to a specific fault code.
RESETTING FROM L OCKOUT
Furnace lockout results when a furnace is unable to achieve ignition after three attempts during a single call for heat. It is characterized by a non-functioning furnace and a one flash diagnostic LED
code. If the furnace is in “lockout”, it will (or can be) reset in any of
the following ways.
1. Automatic reset. The integrated control module will
automatically reset itself and attempt to resume normal
operations following a one hour lockout period.
2. Manual power interruption. Interrupt 115 volt power to the
furnace for 1 - 20 seconds.
FILTERS
CAUTION
TO
ENSURE PROPER UNIT PERFORMANCE, ADHERE TO THE FILTER
SIZES GIVEN IN THE RECOMMENDED MINIMUM FILTER SIZE TABLE OR
PECIFICATION SHEET APPLICABLE TO YOUR MODEL
S
*
MAINTENANCE
Improper filter maintenance is the most common cause of inadequate heating or cooling performance. Filters should be cleaned
(permanent) or replaced (disposable) every two months or as required. When replacing a filter, it must be replaced with a filter of
the same type and size.
FILTER REMOVAL
Depending on the installation, differing filter arrangements can be
applied. Filters can be installed in either the central return register
or a side panel external filter rack (upflow only). A media air filter or
electronic air cleaner can be used as an alternate filter. Follow the
filter sizes given in the Recommended Minimum Filter size table to
ensure proper unit performance.
32
Page 33

To remove filters from an external filter rack in an upright upflow
installation, follow the directions provided with external filter rack
kit. For further details, see your distributor.
HORIZONTAL UNIT FILTER REMOVAL
Filters in horizontal installations are located in the central return
register or the ductwork near the furnace.
To remove:
1. Turn OFF electrical power to furnace.
2. Remove filter(s) from the central return register or ductwork.
3. Replace filter(s) by reversing the procedure for removal.
4. Turn ON electrical power to furnace.
MEDIA AIR FILTER OR ELECTRONIC AIR CLEANER REMOVAL
Follow the manufacturer’s directions for service.
BURNERS
Visually inspect the burner flames periodically during the heating
season. Turn on the furnace at the thermostat and allow several
minutes for flames to stabilize, since any dislodged dust will alter
the flames normal appearance. Flames should be stable, quiet,
soft, and blue (dust may cause orange tips but they must not be
yellow). They should extend directly outward from the burners without curling, floating, or lifting off. Flames must not impinge on the
sides of the heat exchanger firing tubes.
INDUCED DRAFT AND CIRCULATOR BLOWERS
The bearings in the induced draft blower and circulator blower
motors are permanently lubricated by the manufacturer. No further
lubrication is required. Check motor windings for accumulation of
dust which may cause overheating. Clean as necessary.
CONDENSATE TRAP AND DRAIN SYSTEM (QUALIFIED SERVICER
ONLY)
Annually inspect the drain tubes, drain trap, and field-supplied drain
line for proper condensate drainage. Check drain system for hose
connection tightness, blockage, and leaks. Clean or repair as
necessary.
FLAME SENSOR (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY)
Under some conditions, the fuel or air supply can create a nearly
invisible coating on the flame sensor. This coating acts as an
insulator causing a drop in the flame sense signal. If the flame
sense signal drops too low the furnace will not sense flame and
will lock out. The flame sensor should be carefully cleaned by a
qualified servicer using emery cloth or steel wool. Following cleaning, the flame sense signal should be 1 to 6 microamps.
IGNITER (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY)
If the igniter and the surrounding air are at about 70°F and the
igniter wires are not connected to any other electrical components,
the resistance of the igniter should not exceed 200 ohms. If it does,
the igniter should be replaced.
FLUE PASSAGES (QUALIFIED SERVICER ONLY)
The heat exchanger flue passageways should be inspected at the
beginning of each heating season. If necessary, clean the passageways as outlined below.
4. Remove the induced draft blower and the drain and pressure
tap hoses from the recuperator coil front cover.
5. Remove the recuperator coil front cover to expose the coil
tubes and turbulators.
6. Remove the recuperator coil turbulators individually by slowly
pulling each turbulator forward firmly.
7. Clean the recuperator coil tubes using a long handle wire
brush, such as a gun cleaning brush.
8. Clean the primary heat exchanger tubes using a wire brush
attached to a length of high grade stainless steel cable,
such as drain cleanout cable. Attach a variable speed
reversible drill to the other end of the cable. Slowly rotate
the cable with the drill and insert it into one of the heat
exchanger tubes. While reversing the drill, work the cable
in and out several times to obtain sufficient cleaning. Repeat
for each tube.
9. Clean residue from furnace using a vacuum cleaner.
10. Replace the parts removed in the previous steps in reverse
order.
11. Turn on electrical power and gas to furnace. Check for
leaks and proper unit operation.
12. Severe heat exchanger fouling is an indication of an
operational problem. Perform the checks listed in Section
XIV, Startup Procedure and Adjustments to reduce the
chances of repeated fouling.
XX. BEFORE LEAVING AN INST ALLATION
• Cycle the furnace with the thermostat at least three times.
Verify cooling and fan only operation.
• Review the Owner’s Manual with the homeowner and
discuss proper furnace operation and maintenance.
• Leave literature packet near furnace.
XXI. REP AIR & REPLACEMENT PARTS
• When ordering any of the listed functional parts, be sure to
provide the furnace model, manufacturing, and serial
numbers with the order.
• Although only functional parts are shown in the parts list, all
sheet metal parts, doors, etc. may be ordered by description.
• Parts are available from your distributor.
Functional Parts List-
Gas Valve Blower Motor
Gas Manifold Blower Wheel
Natural Gas Orifice Blower Mounting Bracket
Propane Gas Orifice Blower Cutoff
Igniter Blower Housing
Flame Sensor Capacitor
Rollout Limit Switch Heat Exchanger
Primary Limit Switch Recuperator Coil
Auxiliary Limit Switch Coil Front Cover
Pressure Switch Integrated Control Module
Induced Draft Blower Transformer
Door Switch
1. Turn OFF the electrical power and gas supply to the furnace.
2. Disconnect the gas line and remove the burner/ manifold
assembly by removing the screws securing the assembly
to the partition panel.
3. Disconnect the flue pipe system from the induced draft
blower.
33
Page 34

Symptoms of Abnormal
Operation
• Furnace fails to operate.
• Integrated control module
diagnostic LED provides
no signal.
• LED is Steady On.
Associated
Associated
LED Code
LED Code
NONE
ON
CONTINUOUS
ON
Troubleshooting Chart
Fault Description(s) Possible Causes
Fault Description(s) Possible Causes Corrective Action
2
2
• No 115 volt power to
furnace, or no 24 volt
power to integrated
control module.
• Blown fuse or circuit
breaker.
• Integrated control
module has an
internal fault.
• Normal Operation • Normal Operation • None
• Manual disconnect switch
OFF, door switch open, or
24 volt wires improperly
connected or loose.
• Blown fuse or circuit
breaker.
• Integrated control module
has an internal fault.
• Assure 115 and 24 volt
power to furnace
integrated control
module.
• Check integrated control
module fuse (3A).
Replace if necessary.
• Check for possible shorts
in 115 and 24 volt circuits.
Repair as necessary.
• Replace bad integrated
control module.
Cautions and Notes
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
• Replace
integrated
control module
fuse with 3A
automotive fuse.
• Read precautions
in “Electrostatic
Discharge” section
of manual.
• Normal Operation
• Furnace fails to operate.
• Integrated control module
diagnostic LED is
flashing ONE (1) flash.
• Furnace fails to operate.
• Integrated control module
diagnostic LED is
flashing TWO (2)
flashes.
• Induced draft blower
runs continuously with
no further furnace
operation.
• Integrated control module
diagnostic LED is
flashing THREE (3)
flashes.
1
1 FLASH
2
2 FLASHES
3
3 FLASHES
• Furnace lockout due
to an excessive
number of ignition
“retries” (3 total)1.
• Pressure switch
circuit is closed.
• Induced draft
blower is not
operating.
• Pressure switch
circuit not closed.
• Induced draft blower
is operating.
• Failure to establish flame.
Cause may be no gas to
burners, front cover
pressure switch stuck open,
bad igniter or igniter
alignment, improper orifices,
or coated/oxidized or
improperly connected flame
sensor.
• Loss of flame after
establishment. Cause may
be interrupted gas supply,
lazy burner flames (improper gas pressure or
restriction in flue and/or
combustion air piping), front
cover pressure switch
opening, or improper
induced draft blower
performance.
• Induced draft blower
pressure switch contacts
sticking.
• Shorts in pressure switch
circuit.
• Pressure switch hose
blocked, pinched or
connected improperly.
• Blocked flue and/or inlet air
pipe, blocked drain system,
or weak induced draft
blower.
• Incorrect pressure switch
setpoint or malfunctioning
switch contacts.
• Loose or improperly
connected wiring.
• Locate and correct
gas interruption.
• Check front cover
pressure switch
operation (hose, wiring,
contact operation).
Correct if necessary.
• Replace or realign
igniter.
• Check flame sense
signal. Sand sensor if
coated and/or oxidized.
• Check flue piping for
blockage, proper
length, elbows, and
termination.
• Verify proper induced
draft blower performance.
• Replace induced draft
blower pressure
switch.
• Repair short.
• Inspect pressure
switch hose. Repair, if
necessary,
• Inspect flue and/or inlet
air piping for blockage,
proper length, elbows,
and termination. Check
drain system. Correct
as necessary.
• Correct pressure
switch setpoint or
contact motion.
• Tighten or correct
wiring connection.
• Turn power
OFF prior to
repair.
• Igniter is
fragile, handle
with care.
• Sand flame
sensor with
emery cloth.
• See “Vent/Flue
Pipe” section
for piping
details.
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
• Replace pressure
switch with proper
replacement part.
• Turn power
OFF prior to
repair.
• Replace
pressure
switch with
proper
replacement
part.
1
Integrated control module will automatically attempt to reset from lockout after one hour.
2
LED Flash code will cease if power to the control module is interrupted through the disconnect or door switch.
34
Page 35

Troubleshooting Chart
Symptoms of Abnormal
Operation
• Circulator blower runs
continuously. No furnace
operation.
• Integrated control
module diagnostic LED
is flashing FOUR (4)
flashes.
• Induced draft blower and
circulation blower runs
continuously. No furnace
operation.
• Integrated control
module diagnostic LED
is flashing FIVE (5)
flashes.
• Circulator blower runs
continuously. No furnace
operation.
• Integrated control
module diagnostic LED
is flashing SIX (6)
flashes.
Associated
LED Code
4
4 FLASHES
5
5 FLASHES
6
6 FLASHES
Fault Description(s) Possible Causes Corrective Action Cautions and Notes
2
• Primary or auxiliary
limit circuit is open.
•Faulty primary or auxiliary
limit switch.
•Insufficient conditioned air
over the heat exchanger.
Blocked filters, restrictive
ductwork, improper
circulator blower speed, or
failed circulator blower.
•Loose or improperly
connected wiring.
• Check primary/auxiliary
limit. Replace if
necessary.
• Check filters and
ductwork for blockage.
Clean filters or remove
obstruction.
• Check circulator blower
speed and performance. Correct speed
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
• Replace primary/
auxiliary limit with
proper replacement
part.
• Replace blower
with correct
replacement part.
or replace blower if
necessary.
• Tighten or correct
wiring connection.
• Flame sensed with
no call for heat.
• Short to ground in flame
sense circuit.
•Correct short at flame
sensor or in flame
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
sensor wiring.
• Rollout limit circuit is
open.
•Flame rollout.
•Misaligned burners, blocked
flue and/or air inlet pipe, or
failed induced draft blower.
•Loose or improperly
connected wiring.
•Faulty rollout limit.
• Check burners for
proper alignment.
• Check flue and air inlet
piping for blockage,
proper length, elbows,
and termination.
Correct as necessary.
• Check rollout limit.
Replace if necessary.
• Check induced draft
blower for proper
performance. Replace, if necessary.
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
• See “Vent/Flue
Pipe” section for
piping details.
• Replace rollout
limit with correct
replacement part.
• Replace induced
draft blower with
correct replacement part.
• Tighten or correct
wiring connection.
• Normal furnace
operation.
• Integrated control
module diagnostic LED
is flashing SEVEN (7)
flashes.
7 FLASHES
7
• Flame sense
microamp signal is
low.
•Flame sensor is coated/
oxidized.
•Flame sensor incorrectly
positioned in burner flame.
•Lazy burner flame due to
improper gas pressure or
combustion air.
• Sand flame sensor if
coated/oxidized.
• Inspect for proper
sensor alignment.
• Check inlet air piping
for blockage, proper
length, elbows, and
termination.
• Compare current gas
pressure to rating plate
info. Adjust as
needed.
• Furnace fails to operate.
• Integrated control
module diagnostic LED
is flashing continuously.
C
CONTINUOUS/
RAPID FLASH
•Polarity of 115 or 24
volt power is
reversed.
• Polarity of 115 volt AC
power to furnace or
integrated control module is
reversed.
• Orange and gray wires to
transformer are reversed.
• Review wiring diagram
to correct polarity.
• Reverse orange and
gray wires going to
transformer.
• Poor unit ground.
• Verify proper ground.
Correct if necessary.
1
Integrated control module will automatically attempt to reset from lockout after one hour.
2
LED Flash code will cease if power to the control module is interrupted through the disconnect or door switch.
35
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
• Sand flame sensor
with emery clot.
• See “Vent/Flue
Pipe” section for
piping details.
• See rating plate for
proper gas
pressure.
• Turn power OFF
prior to repair.
Page 36

GKS9 WIRING DIAGRAM
A
A
A
A
A
A
E
W
B
L
R
L
B
YL
OR
OR
R
T
O
N
I
W
T
C
E
R
H
MOSTAT AT 0.
E
E
M
C
P
E
L
P
I
E
L
P
EED
N
"PAR
NDED
AN
RD
O
C
H
T
N
WITH
D
S
A
A
S
K
"
COMPA
D
O
(
OPEN WHEN
DOO
GR
BR
R
E
V
R
P
A
5
T 1
0
N
E
R
MINALS
TER
O
C
D
O
E
T
M
R
R
O
S
W
T
C
I
OPEN)
R
BK
BK
GY
L
B
F
L
A
SE
N
L
O
L
W
O
H
I
HI
I
NTEGR
P
L
P
A
M
7
S
TS MUST BE U
E
T
H
N
R
F
U
°
USE
C
.
C
T
T
S
O
H
E
F
O
F
N
O
R
T
O
M
N
H
M
S
W
UG
.
O
ME,
I
NTE
N
T
24V THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS
E
O
R
V
V
O
O
V
O
V
IN
T
A
S
E
M
CE
PER
P
D
.
.
E
C.
C
G
Y
W
R
INTEGRATED CONTROL MODULE
J
TION
U
N
C
OX
B
W
B
A
T
L
G
O
AGE
T
L
T
L
AGE (115V
LT
A
E
G
J
U
E
T
R
T
E
E
D
C
O
C
ON
N
W
HEN
D
U
B
S
T
E
N
C
O
D
I
S
D
A
R
C
ATE
D
R
G
L
N
A
D
T
O
MICRO
TH (3
)
R
X
F
M
-
H
I
I
N
H
L
I
-
E
N
R
DOO
I
TCH
S
W
TO 115VAC/ 1
O
V
E
H
K
(24V
)
E
D
I
L
E
F
)
D
I
F
E
L
O
N
N
I
C
T
M
R
N
A
I
L
L
T
O
N
A
NTRO
L
N
O
E
I
C
T
V
I
I
E
S
C
R
E
P
R
C
L
A
E
T
C
U
S
R
O
O
E
R
JUM
P
C
O
ONT
R
L
A
C
O
DES.
L
C
O
F
G
R
N
D
B
O
V
2
4
A
C
I
M
H
U
I
F
IER
D
C
A
2
V
4
C
A
1
1
V
TAT
N
C
115
COOL-
A
O
O
B
ES
RCU
N
F
T
I
P
L
T
S
G
V
A
W
A
MPAR
P
M
N
G
N
O
O
S
C
C
E
C
A
R
E
5
R
W
Y
FUS
E
D
I
N
E
G
E
R
T
T
A
CON
R
T
O
L
M
U
O
L
D
E
C
S
T
I
O
HO
T
P
A
T
E
K
A
C
R
D
N
H
T
-
HEA
H
E
E
S
N
O
E
T
H
H
(
)
I
K
B
D
M
E
(
L
B
OR (ME
D
L
(
D
W
R
O
I
C
TOR
M
N
T
E
T
R
A
E
T
M
N
T
D
B
K
W
H
D
U
N
I
C
W
BL
O
C
R
W
E
4 VAC
2
U
E
R
M
H
U
I
D
FIE
I
H
C
T
I
R
O
T
MI
E
A
V
A
S
G
O
24V THERM
S
N
O
C
O
N
E
CTI
.
MAY
UNIT
SO
THIS
DO
.
TO
DEATH
INSTALLING
AILURE
OR
. F
OR
INJURY
PRESENT
SERVICING
BE
MAY
PERSONAL
,
BEFORE
DAMAGE
SOURCES
POWER
ALL
POWER
PROPERTY
ULTIPLE
ISCONNECT
HIGH VOLTAGE!
D
CAUSE
M
DIAGN
LED
D
G
N
R
B
B
R
C
O
L
W
B
R
E
C
URNER
B
C
R
D
O
R
H
W
D
I
R
P
SWI
C
2
I
N
C
O
HOT
R
SU
N
G
I
0
STEADY ON = NORMAL OPERATION
R
G
Y
W
H
B
K
O
R
1
3
2
5
6
G
Y
8
9
211
1
R
XFMR-H
L
A
N
M
I
R
4
)
L
O
W
)
DR
D
E
E
R
Y
L
R
2
E
L
V
2
S
1
I
-
H
N
E
L
P
D
R
)
B
K
F
A
T
O
K
P
BR
G
Y
K
P
4
R
O
7
BL
G
1
0
Y
G
D
TERMINALS
115 VAC NEU TRA L
R
Y
L
O
R
R
B
W
H
PK
W
H
K
B
K
M
A
AUXI
I
U
N
B
LOWER
H
W
B
L
NUAL
L
P
W
P
I
F
H
U
A
L
R
R
Y LIMIT
O
W
D
U
P
WH
WH
BL
E
E
S
T
E
C
K
R
D
R
G
N
D
C
NO
G
A
O
N
I
T
O
P
L
R
F
R
P
E
ES
S
S
R
U
OFF = CONTROL FAILURE
1
1 FLASH =
2 FLASHES = PRESSURE SWITCH STUCK CLOSED
2
3
3 FLASHES = PRESSURE SWITCH STUCK OPEN
4
4 FLASHES = OPEN HIGH LIMIT
5
5 FLASHES = FLAME SENSE WITHOUT GAS VALVE
6
6 FLASHES =
C
CONTINUOUS/RAPID FLASHES = REVERSED 115 VAC POLARITY
PK
P
N
K
COLOR
YL
Y
OR
PU
N
G
G
B
K
014
E
L
R
O
P
URPLE
R
LACK
B
C
LOW
A
E
0
ODES
N
G
E
N
F
E
0
0
:
236
I
B
B
R
O
W
R
W
IT
H
H
W
L B
L
B
U
E
GY
R
A
G
R
D
RED
.
E
V
R
C
T
O
N
ES:
N
1
.
SET H
2. MANUFACT
E
3
.
A
I
F
H
A
Y
V
I
F
4
HE
.
B
LOW
U
5.
N
I
NY
I
NG
T
EAT
F
O
A
ATING A
L
E
R
U
ST
M
ANTIC
U
T
TEM
E
B
PAT
I
R
ER'S
S
H
GIN
E
I
R
O
P
E
RAT
ND
O
O
C
D
A
S
M
U
S
M
P
E
E
R
O
P
E
A
U
L
T
NENTL
R O
C
L WIR
E RAT
R
I
N
B
E
N
F
I
I
ED REPL
G B
P
T
M
O
O
R
A
E
S S
U
G
N
I
OF AT
W
O
L
ER
S
D
O
L
E
A
C
U
O
R
G
Y
I
M
H
U
I
F
E
R
I
D
T
R (
6
)
D
N
G
8
(
V
C
M
(
9
MV(1
2
O
P
T
N
I
O
S
E
S
R
P
S (
1
)
0
P
PSO
4
(
L
H
I
(7
)
(1
O
L
H
2
O
R
1
(
5
1
O
R
(
S
N
D
C
O
A
E
H
CURRENT PRO
N
G
N
O
L F
R
R
S
E
)
F
L
H
OT
I
G
I
D
B
L
CIRCULATO
H
-
U
J
L
N
O
WITCH
1
M
U
S
T
I
N
L
W
B
N
T
24 VA
1
E
R
FAC
E
R
L
WR
T
C
G
C
5
S
R
I
ON
N
T
D
C
V
E
O
C
C
V
A
ENSOR
E
B
D
E
C
E
Q
R
R
O
TION
U
)
)
)
A
U
)
)
1
)
O
T
Ø /60 HZ POWER SUPPLY WITH
F
I
S
W
C
SWI
T
V
E
O
P
ROT. DEVIC
.
G
M
T
E
I
UST BE
R
P
LAC
NNECTIN
.
E
D
W
B
W
G
L
O
NLY
O
EFO
,
.
O
C
E
R
TAPED
R
A
TED
R
G
I
T
E
N
O
C
C
V
4
0
S
T
RAN
X
U
D
O
M
OL
N
T
R
L
E
C
2
GAS
A
L
V
V
E
1
M
E
B
LOW
ID
R
RESSURE
P
W
S
I
TCH
O
N
E
R
FOR
M
INTEGRATED CONTROL MODULE
LINE NEUTRALS
N
N
O
C
S
D
I
ECT
N
EVI
C
E
D
N
N
D
G
L
N
I
P
M
NT
G
D
E
F
IELD
N
D
G
E
L
SPLI
C
D
E
I
C
T
E
M
)
H
P
.
(
T
E
I
G
R
T
N
I
R
P
E
(
H
S
S
.
)
R
ENT
C
U
R
R
E
I
W
G
N
T
H
R
I
MATERIAL
I
E
N
U
R
L
S.
USE
D
D
E
A
Wiring is subject to change, always refer to the wiring diagram on the unit for the most up-to-date wiring.
36
 Loading...
Loading...