Page 1

Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual
Group: Chiller
Part Number: 331975001
Effective: March 2012
Supersedes: January 2012
Air-Cooled Scroll Compressor Water Chillers
AGZ 010BS – AGZ 034BS, Packaged Chiller
AGZ 010BM – AGZ 034BM, Remote Evaporator
10 to 34 Tons, 35 to 120 kW
R-407C
60 Hertz
Software Version AGZSU0102D
IOMM 1155
Page 2

Table of Contents
Introduction........................................3
General Description...................................3
Inspection ..................................................3
Installation .................................................3
Handling ....................................................3
Location.....................................................4
Service Access...........................................4
Vibration Isolators .....................................5
Chilled Water System ................................9
Water Connections...................................11
Refrigerant Charge ..................................11
Unit Component Location .......................11
Glycol Solutions......................................12
Evaporator Water Flow and Pressure Drop12
R-407C Units ....................................14
Control Layout and Operation.......16
Control Center .........................................16
Start-up and Shutdown....................16
Pre Start-up..............................................16
Start-up ....................................................16
Sequence of Operation ............................17
Physical Data ....................................18
AGZ-BS, R-407C....................................18
AGZ-BM, R-407C...................................20
Electrical Data..................................22
Field Wiring.............................................22
R-407C ....................................................22
Notes for Electrical Data .........................25
Dimensions & Weights.....................27
Remote Evaporators ................................29
ACZ/AGZ Dimensions and Weights .......30
Lubrication.............................................. 31
Electrical Terminals ................................ 31
Condensers.............................................. 31
Refrigerant Sight glass............................ 31
Standard MicroTech II Controller. 32
Table of Contents .................................... 32
Overview................................................. 33
General Description ................................ 33
Setpoint Security..................................... 37
Equipment Protection Alarms ................. 37
Control Functions and Definitions.......... 38
Unit Enable ............................................. 39
Unit Mode............................................... 39
Power Up Start Delay ............................. 40
Ice Mode Start Delay .............................. 40
Unit State ................................................ 40
Evaporator Water Pump State Control .... 41
Condenser Fans....................................... 43
Low OAT Start........................................ 43
Circuit Capacity Overrides ..................... 43
Maximum LWT Rate .............................. 44
Low Ambient Lockout ............................ 44
Compressor Control................................ 44
Using the Controller................................ 47
Menu Screens.......................................... 48
BAS Interface................................... 60
Service............................................... 61
Thermostatic Expansion Valve ............... 61
Filter-Driers............................................. 61
Liquid Line Solenoid .............................. 61
Optional Controls.................................... 62
Troubleshooting Chart ............................ 65
System Maintenance ........................31
General ....................................................31
©2012 Daikin. Illustrations and data cover the Daikin product at the time of publication and we reserve the right to make
changes in design and construction at anytime without notice. ™® The following are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies: BACnet from ASHRAE; LONMARK, LonTalk, LONWORKS, and the LONMARK logo are managed,
granted and used by LONMARK International under a license granted by Echelon Corporation; Compliant Scroll from Copeland
Corporation; ElectroFin from AST ElectroFin Inc.; Modbus from Schneider Electric; FanTrol, MicroTech II, Open Choices, and
SpeedTrol from Daikin.
2 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 3

Introduction
General Description
Daikin air-cooled water chillers are complete, self-contained automatic refrigerating units. Every
unit is completely assembled, factory wired, charged, and tested. Each unit consists of air-cooled
condensers, Copeland Compliant Scroll hermetic compressor, brazed plate-to-plate evaporator,
and complete refrigerant piping. Liquid line components include sight-glass/moisture indicator,
solenoid valve, and thermal expansion valve. Other features include a compressor heater, and
evaporator heater for chilled water freeze protection.
The electrical control center includes all equipment protection and operating controls necessary for
automatic operation. Condenser fan motors are three-phase (except single-phase on No. 1 fan with
SpeedTrol option) and started by their own contactors and have inherent overload protection. Each
compressor has solid-state motor protection for inherent thermal overload protection except Model
AGZ 010 that has internal line breakage.
Software Version
This manual is based on software version AGZSU0102D. The software version can be displayed by
pressing the Enter and Menu keys simultaneously. Exit by pressing Menu.
Inspection
Check all items carefully against the bill of lading. Inspect all units for damage upon arrival. Report
shipping damage and file a claim with the carrier. Check the unit nameplate before unloading to be
sure it agrees with the power supply available. Units are shipped FOB factory and Daikin is not
responsible for physical damage after unit leaves the factory.
Note: Unit shipping and operating weights are listed on pages 18 and 19.
Installation
Note: Installation must be performed by trained, experienced personnel who are familiar
with local codes and regulations, especially concerning refrigerant release to the
atmosphere.
!
WARNING
Sharp edges and coil surfaces can cause personal injury. Avoid contact with them.
Handling
Be careful to avoid rough handling of the unit. Do not push or pull the unit from anything other than
the base. Block the pushing vehicle away from the unit to prevent damage to the sheet-metal cabinet
and end frame (see Figure 1). To lift the unit, lifting slots are provided in the base of the unit.
Arrange spreader bars and cables to prevent dam
HAZARD IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION
Warnings indicate potentially hazardous situations, which can result in property damage, severe personal
injury, or death if not avoided.
age to condenser coils or cabinet (see Figure 2).
!
WARNING
!
CAUTION
Cautions indicate potentially hazardous situations, which can result in personal injury or equipment
damage if not avoided.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 3
Page 4

Figure 1, Suggested Pushing Arrangement
BLOCKING REQUIRED
ACROSS FULL WIDTH
Figure 2, Suggested Lifting Arrangement
SPREADER BAR (2)
NOTE:: The fork lift slots can be used for
lifting by inserting sufficiently strong pipe
through them as shown in Figure 2.
Use the outboard slots on three-fan units
and the only two on two-fan units.
PIPE SLUNG THRU
OPENINGS IN LEGS (2)
Location
Unit Placement
AGZ units are for outdoor applications and can be mounted on a roof or at ground level. Set units on
a solid and level foundation. For roof-mounted applications, install the unit on a steel channel or Ibeam frame to support the unit above the roof. For ground level applications, install the unit on a
substantial base that will not settle. A one-piece concrete slab with footings extended below the frost
line is recommended. Be sure the foundation is level (within 1/2” [13 mm] over its length and width).
The foundation must support the operating weights listed in the Physical Data Tables on pages 18 and
19. It is recommended that the unit be raised a few inches with a suitable support, located at least
under the m
ounting locations, to allow
under it.
Since its operation is affected by wind, the unit should be located so that its length is parallel with the
prevailing wind. If this is not practical, use field fabricated wind deflectors.
water to drain from under the unit and to facilitate cleaning
Service Access
Each end of the unit must be accessible after installation for periodic service. Compressors, filterdriers, and liquid line solenoid valve are accessible from the end of the unit. High-pressure, lowpressure, and motor protector controls are on the compressor. Most operating, equipment protection,
and starting controls are located in the unit control box.
The fan deck with the condenser fans and motors can be removed from the top of the unit.
4 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 5

Clearances
The flow of air to and from the
condenser coil must not be limited.
Restricting airflow or allowing air
recirculation will result in a decrease in
unit performance and efficiency. There
must be no obstruction above the unit
that would deflect discharge air
downward where it could be
recirculated back to the inlet of the
condenser coil. The condenser fans are
propeller type and will not operate with
ductwork on the fan outlet.
Install the unit with enough side
clearance for air entrance to the coil and
for servicing. Provide service access to
the evaporator, compressors, electrical
control panel and piping components as
shown in Figure 3. Do not block access to
the unit with piping or conduit.
Do not allow debris to accumulate near the
unit. Air movement may draw debris into
the condenser coil causing air starvation.
Give special consideration to low ambient
operation where snow can accumulate.
Keep condenser coils and fan discharge free
of snow or other obstructions to permit
adequate airflow.
Sound Isolation
The low sound levels of the AGZ chiller are
suitable for most applications. When
additional sound reduction is necessary,
locate the unit away from sound sensitive
areas. Avoid locations beneath windows or
between structures where normal operating
sounds may be objectionable. Reduce
structurally transmitted sound by isolating
water lines, electrical conduit and the unit
itself. Use wall sleeves and rubber isolated
piping hangers to reduce transmission of
water or pump noise into occupied spaces.
Use flexible electrical conduit to isolate
sound through electrical conduit. Spring
isolators are effective in reducing the low
amplitude sound generated by the Discus
semi-hermetic compressors and for unit
isolation in sound-sensitive areas.
Figure 3, Clearance requirements
4 Ft. (1220mm)
Clearance for Air Inlet
4 Ft.
(1220mm)
Clearance for
Service Access
4 Ft. (1220mm)
Clearance for Air Inlet
The recommended minimum side clearance between two units
is 8 feet (2440mm).
The unit must not be installed in a pit or enclosure that is
deeper or taller than the height of the unit unless extra space
is provided. The minimum clearance on each side of the
unit is 6 feet (1828mm) when installed in a pit. The pit cannot
be deeper than the unit.
The minimum clearance to a side wall or building taller than
the unit height is 6 feet (1828mm) provided no solid wall
above 6 feet (1828mm) tall is closer than 12 feet (3658mm)
to the opposite side of the unit.
4 Ft.
(1220mm)
Clearance for
Service Access
Vibration Isolators
Vibration isolators are recommended for
all roof-mounted installations or wherever vibration transmission is a consideration.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 5
Page 6
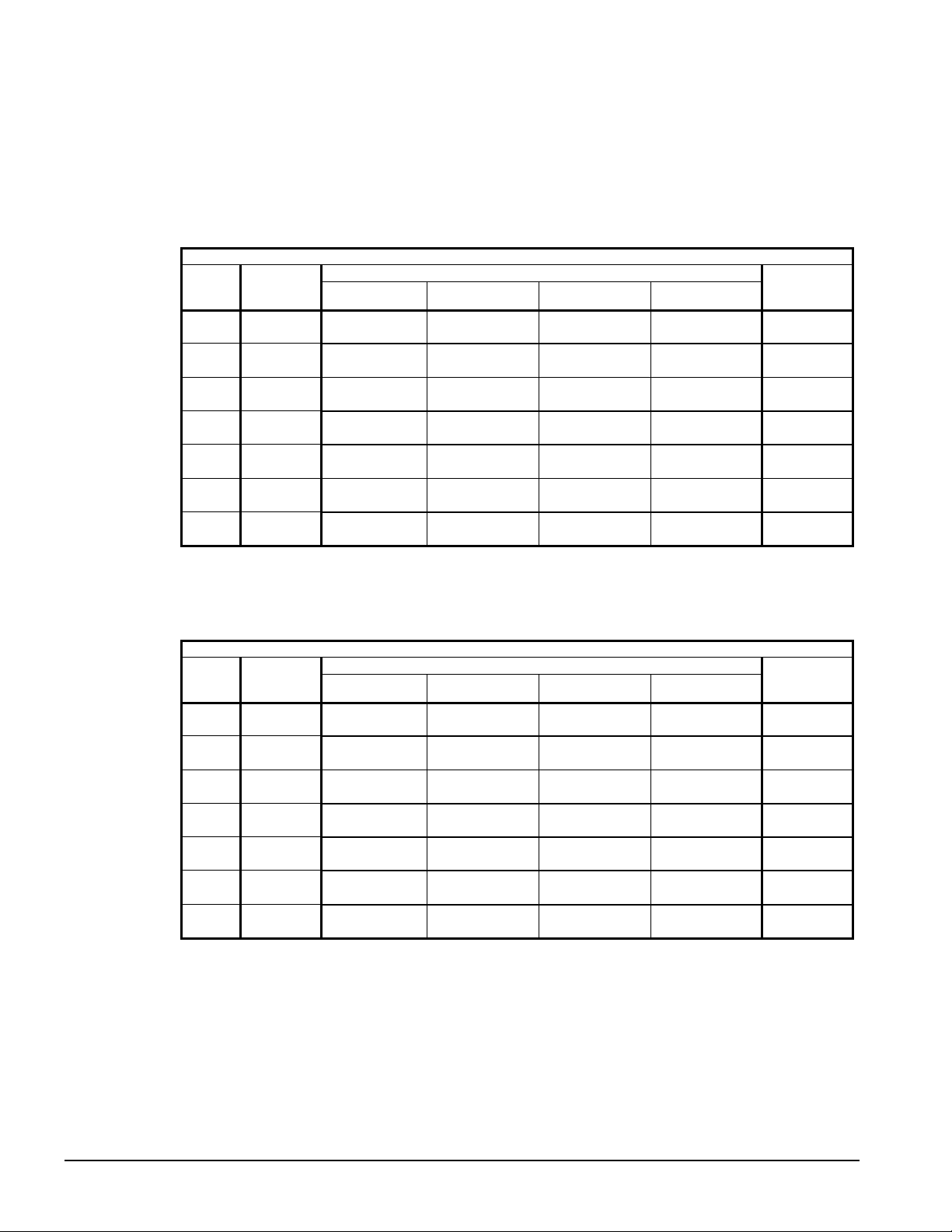
The unit should be initially placed on shims or blocks at the listed free height. When all piping,
wiring, flushing, charging, etc. is completed, the springs are adjusted upward to loosen the blocks
or shims that are then removed.
A rubber anti-skid pad is part of the isolator. Installation of spring isolators requires flexible
piping connections and at least three feet of flexible conduit to avoid straining the piping and
transmitting vibration and noise. These units cannot be bolted to isolators.
Table 1, Packaged & Remote Evaporator, R-I-S Isolator Locations, Aluminum Fins
UNIT
SIZE
010
013
017
020
025
029
034
OPER.
WGT
LBS.
1085
1170
1280
1505
1610
1800
2270
LF RF LB RB
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Lime Lime Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Lime Lime Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Lime Lime Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Charcoal Charcoal Brick Red Brick Red
Note: See dimension drawing for location of isolators.
R-I-S, ALUMINUM FINS
MOUNTING LOCATION
KIT PART
NUMBER
332325001
332325001
332325001
332325002
332325002
332325002
332325003
Table 2, Packaged & Remote Evaporator, R-I-S Isolator Locations, Copper Fins
UNIT
SIZE
010
013
017
020
025
029
034
OPER.
WGT
LBS.
1085
1170
1280
1505
1610
1800
2270
LF RF LB RB
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Lime Lime Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Lime Lime Brick Red Brick Red
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Charcoal Charcoal Lime Lime
RP-3 RP-3 RP-3 RP-3
Charcoal Charcoal Lime Lime
Note: See dimension drawing for location of isolators.
R-I-S, COPPER FINS
MOUNTING LOCATION
KIT PART
NUMBER
332325001
332325001
332325001
332325002
332325002
332325004
332325004
6 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 7
Table 3, Packaged & Remote Evaporator, Spring Isolator Locations, Al. Fins
,
UNIT
SIZE
010
013
017
020
025
029
034
OPER.
WGT
LBS.
1085
1170
1280
1505
1610
1800
2270
LF RF LB RB
C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340
Red Red Red Red
C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340
Red Red Red Red
C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Black Black Black Black
C1PE-1D-675 C1PE-1D-675 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340
Dark Purple Dark Purple Red Red
C1PE-1D-675 C1PE-1D-675 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340
Dark Purple Dark Purple Red Red
C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Dark Green Dark Green Black Black
C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Dark Green Dark Green Black Black
Note:
1. See dimension drawing for location of isolators.
2. C1PE designates one spring per housing.
SPRINGS, ALUMINUM FINS
MOUNTING LOCATION
KIT PART
NUMBER
332320001
332320001
332320003
332320004
332320004
332320006
332320006
Table 4, Packaged & Remote Evaporator, Spring Isolator Locations, Cu. Fins
SPRINGS
UNIT
SIZE
010
013
017
020
025
029
034
OPER.
WGT
LBS.
1085
1170
1280
1505
1610
1800
2270
LF RF LB RB
C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340 C1PE-1D-340
Red Red Red Red
C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Black Black Black Black
C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Black Black Black Black
C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Dark Green Dark Green Black Black
C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-510 C1PE-1D-510
Dark Green Dark Green Black Black
C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-675 C1PE-1D-675
Dark Green Dark Green Dark Purple Dark Purple
C1PE-1D-1200 C1PE-1D-1200 C1PE-1D-900 C1PE-1D-900
Gray Gray Dark Green Dark Green
Note:
1. See dimension drawing for location of isolators.
2. C1PE designates one spring per housing.
COPPER FINS
MOUNTING LOCATION
KIT PART
NUMBER
332320001
332320003
332320003
332320006
332320006
332320007
332320008
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 7
Page 8
.
S
S
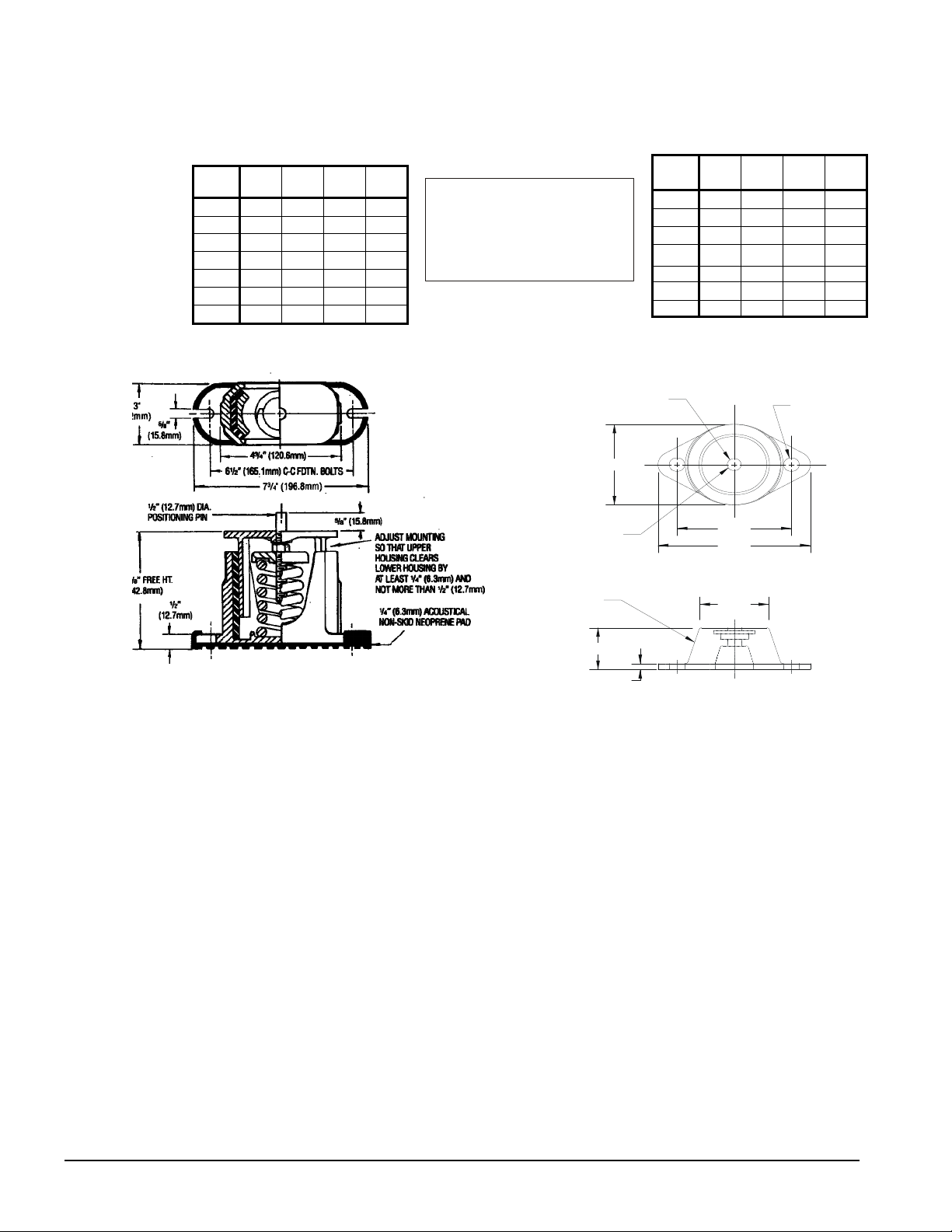
Corner Weights
Packaged Chiller
AGZ-
010A
013A
017A
020A
025A
029A
034A
RF LF RB LB
BS
279 275 267 263
315 297 288 271
344 323 316 297
502 475 271 257
531 496 301 282
583 238 353 326
779 761 369 361
RBI
LBI
Control
Panel
RFI
LFI
Remote Evaporator
AGZ-
BM
010A
013A
017A
020A
025A
029A
034A
LF RF LB RB
257 264 236 243
290 286 246 243
312 309 266 263
446 443 241 240
453 449 245 243
488 487 296 295
656 703 297 318
CP-1, Spring Isolator RP-3, Rubber-in-Shear Isolator
1/2-13 TAP
ø3.38
LOCATING PIN TO
BE INSTALLED HERE
MOUNTING MOLDED IN
DURULENE. WEATHER
RESISTANT (WR)
1.75 (R)
4.13
5.50
2.50
ø.56DIA
2 HOLES
.25
DRAWING NUMBER 3319880
ALL DIMENSION
ARE IN DECIMAL INCHE
8 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 9

Chilled Water System
Water Piping
Local authorities can supply the installer with the proper building and safety codes required
for proper installation.
Install piping with minimum bends and changes in elevation to minimize pressure drop.
Consider the following when installing water piping:
1. Vibration eliminators to reduce vibration and noise transmission to the building.
2. Shutoff valves to isolate the unit from the piping system during unit servicing.
3. Manual or automatic air vent valves at the high points of the system. Install drains at
the lowest points in the system.
4. Maintaining adequate system water pressure (expansion tank or regulating valve).
5. Temperature and pressure indicators located at the unit to aid in unit servicing. Pressure
gauge taps must be installed in the chilled water inlet and outlet piping or as shown in
Figure 4.
6. A strainer or other means of removing foreign matter from the water before it enters the
pump. Place the strainer far enough upstream to prevent cavitation at the pump inlet
(consult pump manufacturer for recommendations). The use of a strainer can prolong
pump life and keep system performance up.
7. A 40-mesh strainer is required in the water line just before the inlet of the evaporator.
This will help prevent foreign material from entering and decreasing the performance of
the evaporator.
!
CAUTION
If a separate disconnect is used for the 110V supply to the evaporator heating cable,
mark the disconnect clearly so the disconnect is not accidentally shut off during cold
seasons. Failure to do so can cause a failure of the evaporator.
8. The brazed plate evaporator has a thermostat and heating cable to prevent freeze-up
down to -20F (-29C). The heating cable should be wired to a separate 110V supply
circuit. As shipped from the factory, the heating cable is wired to the control circuit.
Protect all water piping to the unit from freezing.
9. If the unit is used as a replacement chiller on a previously existing piping system, flush
the system thoroughly before unit installation. Perform regular water analysis and
chemical water treatment on the evaporator immediately at equipment start-up.
10. When glycol is added to the water system for freeze protection, the refrigerant suction
pressure will be lower, cooling performance less, and water side pressure drop greater.
If the percentage of glycol is high, or if propylene is used instead of ethylene glycol, the
added pressure drop and loss of performance could be substantial. Reset the freezestat
and low leaving water alarm temperatures. The freezestat is factory set to default at
38F (3.3C). Reset the freezestat setting to approximately 4 to 5 degrees F (2.3 to 2.8
degrees C) below the leaving chilled water setpoint temperature. See the section titled
“Glycol Solutions” on page 12 for additional information concerning glycol.
11. Perform
a prelim
inary leak check before insulating the piping and filling the system.
12. Include a vapor barrier on the piping insulation to prevent condensation and possible
damage to the building structure.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 9
Page 10

Figure 4, Typical Field Evaporator Water Piping
Ai
r
Vent
Strainer
Inlet
P
Outlet
Drain
NOTES:
1. Chilled water piping within the unit enclosure must be insulated in the field.
2. Support piping independently of the unit and install per local codes.
Vibration
Eliminators
Flow
Switch
Isolation
Val ves
System Volume
It is important to have adequate water volume in the system to provide an opportunity for
the chiller to sense a load change, adjust to the change and stabilize. As the expected load
change becomes more rapid, a greater water volume is needed. The system water volume is
the total amount of water in the evaporator, air handling products and associated piping. If
the water volume is too low, operational problems can occur, including rapid compressor
cycling, rapid loading and unloading of compressors, erratic refrigerant flow in the chiller,
improper motor cooling, shortened equipment life and other undesirable occurrences.
For normal comfort cooling applications, where the cooling load changes relatively slowly,
we recommend a minimum system volume of three to four times the flow rate (GPM). For
example, if the design chiller flow rate is 120 GPM, we recommend a minimum system
volume of 360 to 480 gallons.
Since there are many other factors that can influence performance, systems may
successfully operate below these suggestions. However, as the water volume decreases
below these suggestions, the possibility of problems increases.
Variable Chilled Water flow
Variable chilled water flow systems are not recommended for this class of equipment due to
limited unloading capability.
Flow Switch
Mount a water flow switch in the leaving water line to shut down the unit when water flow
is interrupted.
A flow switch is available from Daikin
(part number 017503300). It is a
“paddle” type
switch and adaptable to
pipe sizes down to 1 1/4” (32mm)
nominal. Certain minimum flow rates
are required to close the switch and are
listed in Table 5. Install the switch as
shown in Figure 5. Connect the
normally open contacts of the flow
switch in the unit control center
at terminals 4 and 5. There is also a
set of normally closed contacts on the
switch that can be used for an indicator
light or an alarm to indicate when
a “no-flow” condition exists. Freeze
protect any flow switch that is installed
outdoors. Follow
10 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Figure 5, Flow Switch Installation
Page 11
installation instructions provided with the flow switch. Calibrate the flow switch to open at
one-half of nominal flow rate.
NOTE: Differential pressure switches are not recommended for outdoor
installation. They are subject to damage from freezing.
Table 5, Flow Switch Settings
(NOTE !)
Min.
Adjst.
Max.
Adjst.
Flow
Flow Lpm 0.8 1.1 2.2 2.8 4.3 11.4 22.9 35.9 38.6
Flow
Flow Lpm 2.8 4.1 6.1 7.3 11.4 27.7 53.4 81.8 90.8
NOTES:
1. A segmented 3-inch paddle (1, 2, and 3 inches) is furnished mounted, plus a 6-inch paddle loose.
2. Flow rates for a 2-inch paddle trimmed to fit the pipe.
3. Flow rates for a 3-inch paddle trimmed to fit the pipe.
4. Flow rates for a 3-inch paddle.
5. Flow rates for a 6-inch paddle.
inch 1 1/4 1 1/2 2 2 1/2 3 4 5 6 8 Pipe Size
mm 32 (2) 38 (2) 51 63 (3) 76 102 (4) 127 (4) 153 (4) 204 (5)
gpm 5.8 7.5 13.7 18.0 27.5 65.0 125.0 190.0 205.0
Lpm 1.3 1.7 3.1 4.1 6.2 14.8 28.4 43.2 46.6
gpm 3.7 5.0 9.5 12.5 19.0 50.0 101.0 158.0 170.0
No
gpm 13.3 19.2 29.0 34.5 53.0 128.0 245.0 375.0 415.0
Lpm 3.0 4.4 6.6 7.8 12.0 29.1 55.6 85.2 94.3
gpm 12.5 18.0 27.0 32.0 50.0 122.0 235.0 360.0 400.0
No
Water Connections
The unit has 3-inch holes for the chilled water piping to enter the unit. The connections are
made to the evaporator water connections located within the unit. Chilled water piping
within the unit must be insulated.
Refrigerant Charge
All units are designed for R-407C and are shipped with an operating charge. The operating
charge for each unit is shown in the Physical Data Tables on pages 18 and 19.
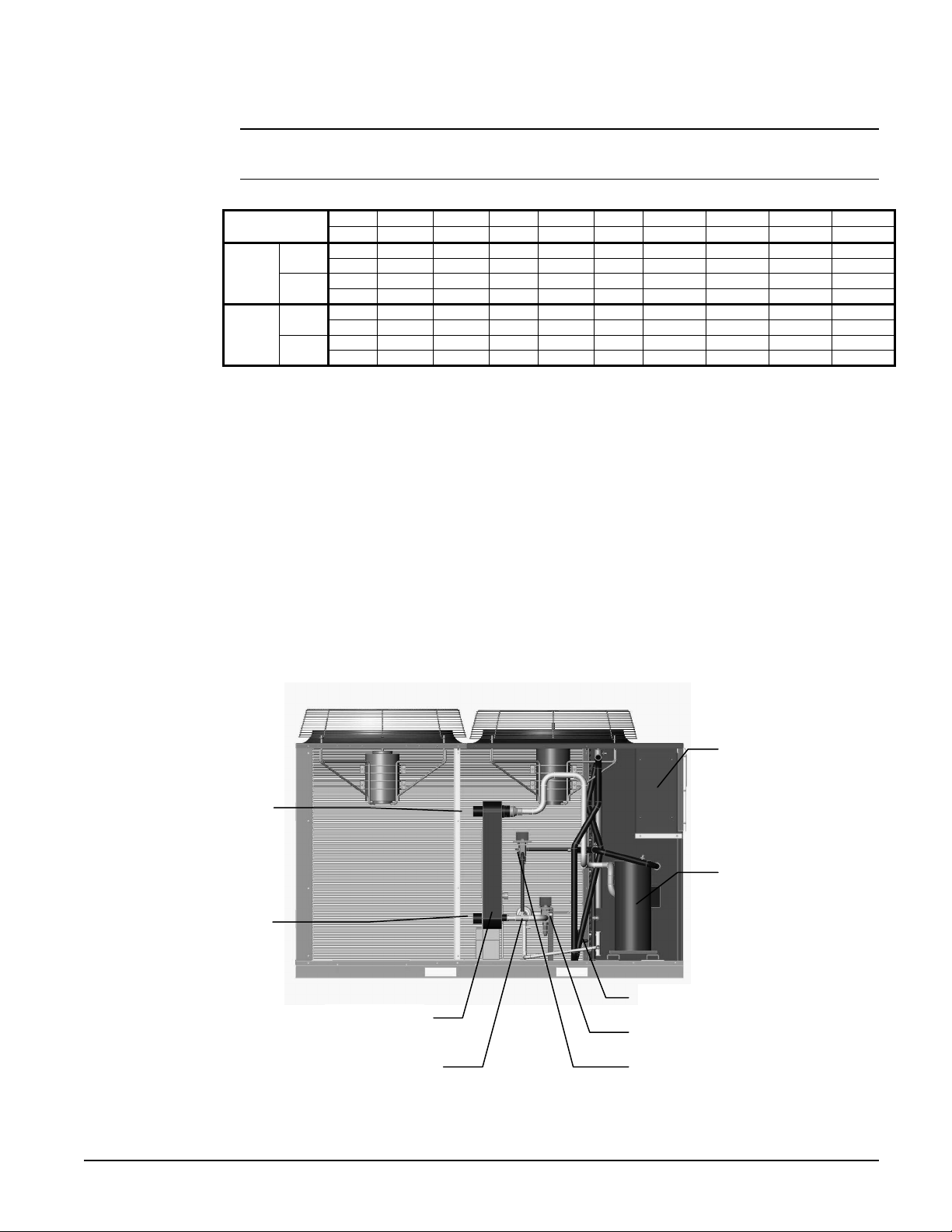
Unit Component Location
Chilled Water
Inlet Connection
Chilled Water
Outlet Connection
Evaporator
Control Panel
Tandem Scroll
Compressors
Charging Valve
Solenoid Valve, Expansion Valve
Optional Hot Gas Bypass Valve Filter Drier
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 11
Page 12

Glycol Solutions
The use of glycol antifreeze solutions will decrease unit capacity and increase the pressure
drop through the cooler. See Product Manual Catalog ACZAGZB1 for specific ratings and
correction factors.
!
CAUTION
Do not use automotive grade antifreeze. Industrial grade glycols must be used. Automotive
antifreeze contains inhibitors that will cause plating on the copper tubes within the chiller
evaporator. The type, storage, disposal, and handling of glycol used must be consistent
with local codes.
Evaporator Water Flow and Pressure Drop
Evaporator flow rate must fall between the minimum and maximum values shown in the
evaporator pressure drop curve, Figure 6. Flow rates outside of these limits result in a
chilled water Delta-T
Measure the chilled water pressure drop through the evaporator at field-installed pressure
taps. It is important not to include the effect of valves or strainers in these readings.
Do not vary the chilled water flow through the evaporator while the compressors are
operating.
outside the operating range of the controller
.
12 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 13
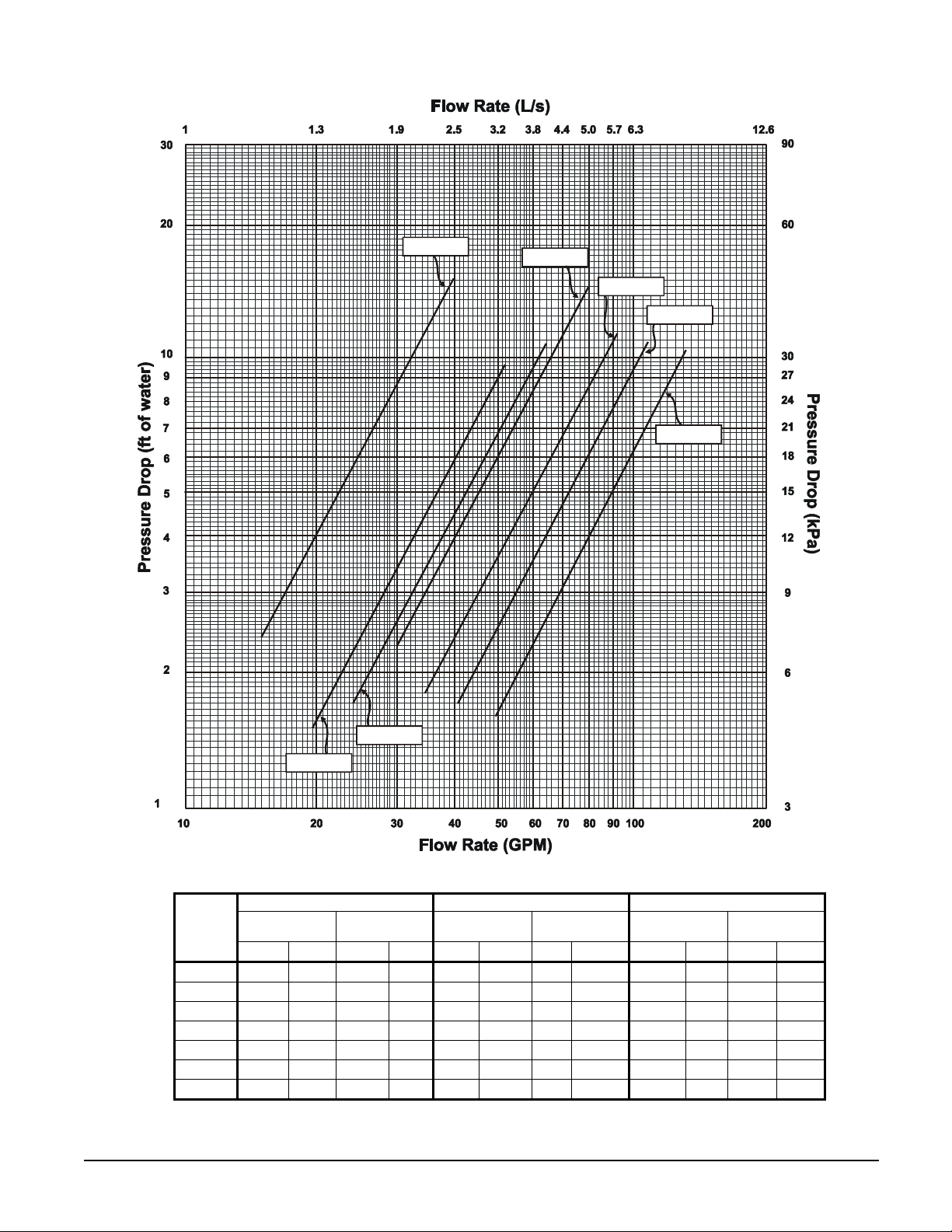
Figure 6, Evaporator Water Pressure Drop Curves
A
A
A
A
AGZ 010
GZ 020
GZ 025
GZ 029
GZ 034
AGZ 017
AGZ 013
Minimum Flow Nominal Flow Maximum Flow
AGZ
Model
010
013
017
020
025
029
034
Flow Rate
gpm L/s ft. kPa gpm L/s ft. kPa gpm L/s ft. kPa
15.0 0.9 2.4 7.1 24.0 1.5 5.8 17.3 40.0 2.5 15.2 45.5
19.5 1.2 1.5 4.5 31.2 2.0 3.7 11.0 52.0 3.3 9.6 28.9
24.0 1.5 1.7 5.0 38.4 2.4 4.1 12.2 64.0 4.0 10.7 32.1
30.0 1.9 2.3 6.8 48.0 3.0 5.6 16.7 80.0 5.0 14.5 43.4
34.5 2.2 1.8 5.3 55.2 3.5 4.3 13.0 92.0 5.8 11.4 34.3
40.7 2.6 1.7 5.0 65.0 4.1 4.0 12.1 108.4 6.8 10.9 32.6
49.8 3.1 1.6 4.7 79.7 5.0 3.9 11.7 132.8 8.4 10.4 31.2
Pressure
Drop
Flow Rate
Pressure
Drop
Flow Rate
Pressure
Drop
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 13
Page 14

R-407C Units
AGZ chillers are available with R-407C refrigerant as non-ARI certified units. R-407C is a
zeotropic blend of three compounds, and as such exhibits the characteristic of glide. It does not
behave as one substance like R-22 does. Glide is the difference (in degrees F) between the
beginning and end phase-change process in either the evaporator or condenser. During these
processes, different ratios of the refrigerant’s components change phase from the beginning to the
end of the process. The following functions, conditions and settings will differ from units charged
with R-22.
1. Different physical data and electrical data
2. Polyolester lubricants are used instead of mineral oil.
3. The saturated pressure/temperature relationship
4. Control and alarm settings
5. Charging procedures
1. Lubrication. The units are factory-charged with polyoester (POE) lubricant and one of the
following lubricants must be used if lubricant is to be added to the system:
POEs are very hygroscopic and will quickly absorb moisture if exposed to air. Pump the
lubricant into the unit through a closed transfer system. Avoid overcharging the unit.
Copeland Ultra 22 CC
Mobil EAL Arctic 22 CC
ICI EMKARATE RL RL 32CF
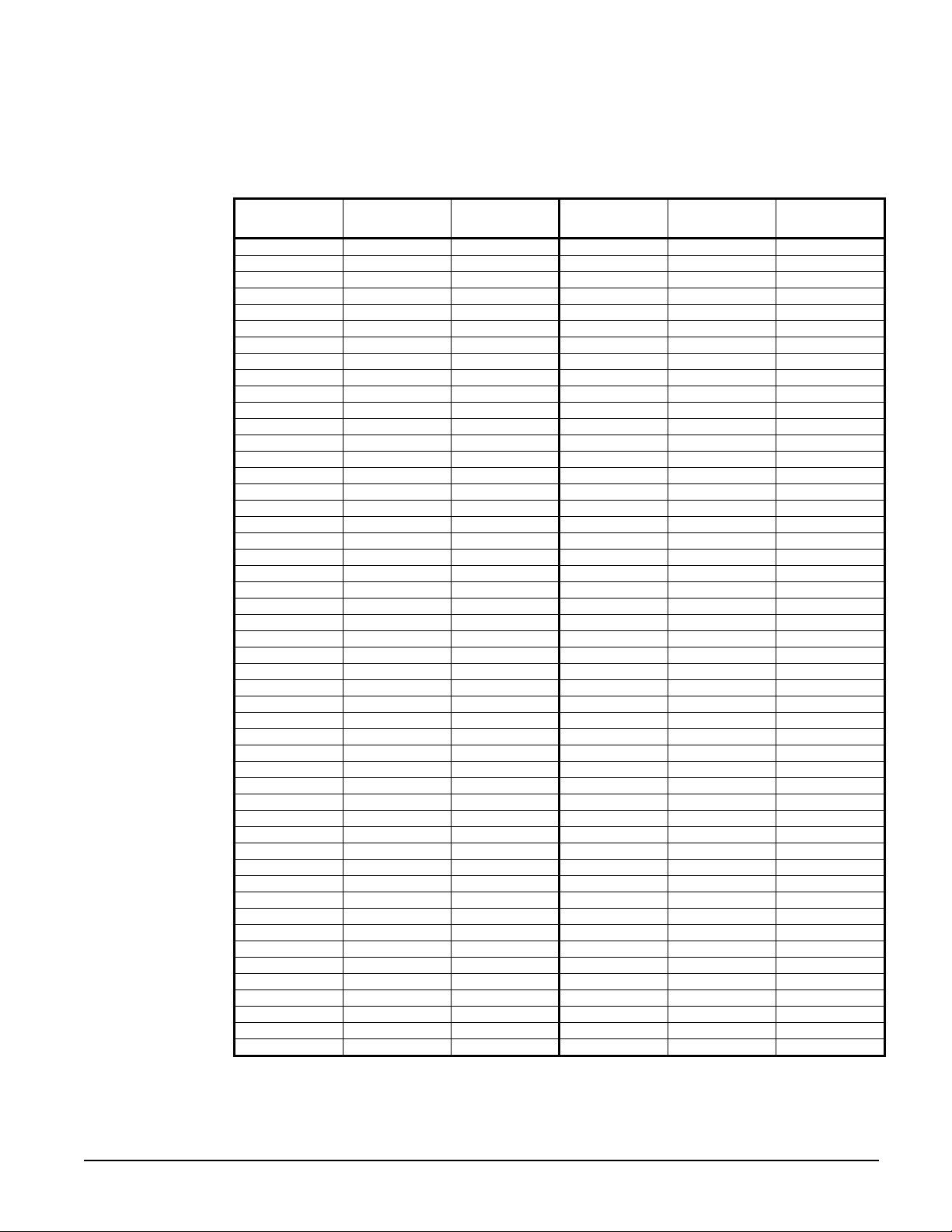
2. Pressure/temperature relationship. See Table 6 on page 15 for the saturated pressure-
erature chart. Due to refrigerant glide, use the following procedures for superheat and
p
tem
subcooling measurement.
To determine superheat, only vapor must be present at the point of measurement, no liquid.
Use the temperature reading, the pressure reading and the Saturated P/T Chart. If the
pressure is measured at 78 psig, the chart shows the saturated vapor
50.6F. If the temperature is measured at 60F, the superheat is 9.4 degrees F.
To determine subcooling, only liquid must be present, no vapor. Use the temperature
reading, the pressure reading and the Saturated P/T Chart. If the pressure is measured at 250
psig, the chart shows the saturated liquid
measured at 98F, the subcooling is 10.2 degrees F.
3. Control and alarm settings. The software that controls the operation of the unit is factory-
set for operation with R-407C.
4. Charging procedure. Packaged units are factory-charged with R-407C. Remote evaporator
units have a nitrogen/helium holding charge, which must be removed prior to system
charging procedure. Use the following procedure if recharging in the field is necessary:
Whether topping off a charge or replacing the circuit’s entire charge, always remove the
refrigerant from the charging vessel as a liquid. Many of the cylinders for the newer
refrigerants have a dip tube so that liquid is drawn off when the cylinder is in the upright
position. Do not vapor charge out of a cylinder unless the entire contents will be charged into
the system.
temperature to be 108.2F. If the temperature is
temperature to be
With the system in a 250-micron or lower vacuum, liquid can be charged into the high side.
Initially charge about 80 percent of the system total charge.
Start the system and observe operation. Use standard charging procedures (liquid only) to
top off the charge.
14 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 15
It may be necessary to add refrigerant through the compressor suction. Because the
refrigerant leaving the cylinder must be a liquid, exercise care to avoid damage to the
compressor. A sight glass can be connected between the charging hose and the compressor.
It can be adjusted to have liquid leave the cylinder and vapor enter the compressor.
Table 6, R-407C Pressure/Temperature Chart
Pressure
(PSIG)
20 -10.7 1.5 150 74.8 84.9
22 -8.2 4.0 155 76.8 86.8
24 -5.7 6.4 160 78.7 88.7
26 -3.4 8.7 165 80.6 90.5
28 -1.1 11.0 170 82.5 92.3
30 1.1 13.1 175 84.3 94.0
32 3.2 15.2 180 86.1 95.8
34 5.3 17.2 185 87.8 97.5
36 7.3 19.2 190 89.6 99.1
38 9.2 21.0 195 91.3 100.7
40 11.1 22.9 200 92.9 102.3
42 12.9 24.7 205 94.6 103.9
44 14.7 26.4 210 96.2 105.4
46 16.4 28.1 215 97.7 107.0
48 18.1 29.7 220 99.3 108.4
50 19.7 31.3 225 100.8 109.9
52 21.3 32.9 230 102.3 111.4
54 22.9 34.4 235 103.8 112.8
56 24.4 35.9 240 105.3 114.2
58 25.9 37.4 245 106.7 115.6
60 27.4 38.8 250 108.2 116.9
62 28.8 40.2 255 109.6 118.2
64 30.2 41.6 260 111.0 119.6
66 31.6 43.0 265 112.3 120.9
68 33.0 44.3 270 113.7 122.1
70 34.3 45.6 275 115.0 123.4
72 35.6 46.9 280 116.3 124.7
74 36.9 48.1 285 117.6 125.9
76 38.2 49.3 290 118.9 127.1
78 39.4 50.6 295 120.2 128.3
80 40.6 51.8 300 121.4 129.5
82 41.9 52.9 305 122.7 130.7
84 43.0 54.1 310 123.9 131.8
86 44.2 55.2 315 125.1 133.0
88 45.4 56.3 320 126.3 134.1
90 46.5 57.4 325 127.5 135.2
92 47.6 58.5 330 128.7 136.3
94 48.7 59.6 335 129.8 137.4
96 49.8 60.7 340 131.0 138.5
98 50.9 61.7 345 132.1 139.6
100 51.9 62.7 350 133.2 140.6
105 54.5 65.2 355 134.3 141.7
110 57.0 67.7 360 135.4 142.7
115 59.5 70.0 365 136.5 143.7
120 61.8 72.3 370 137.6 144.7
125 64.1 74.6 375 138.7 145.7
130 66.4 76.7 380 139.8 146.7
135 68.5 78.8 385 140.8 147.7
140 70.7 80.9 390 141.8 148.7
145 72.8 82.9 395 142.9 149.6
Liquid Temp
(°F)
Vapor Temp
(°F)
Pressure
(PSIG)
Liquid Temp
(°F)
Vapor Temp
(°F)
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 15
Page 16
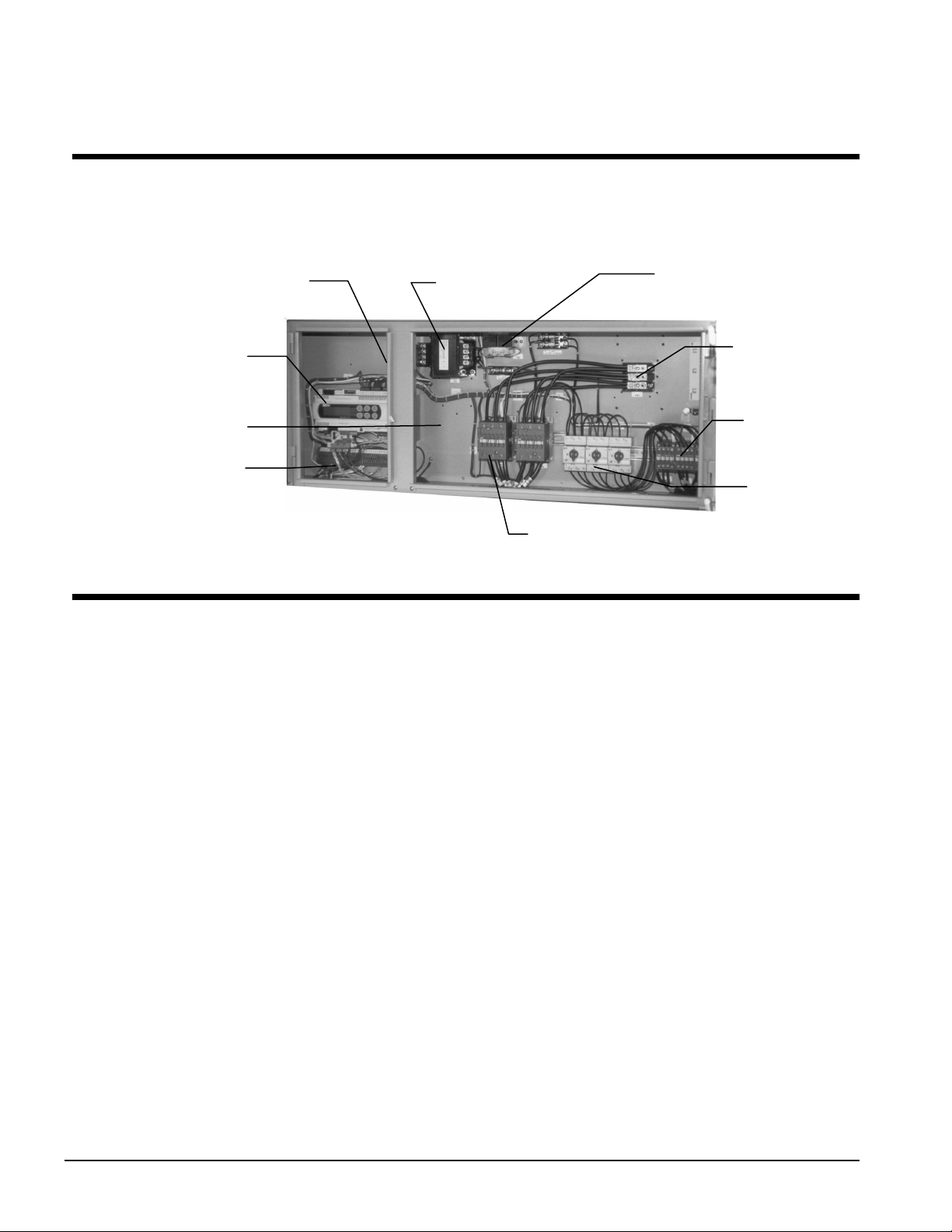
Control Layout and Operation
Control Center
All electrical controls are enclosed in a weatherproof control center with tool-locked, hinged
access doors. The left-hand section contains the microprocessor controller and control input and
output terminals. All high-voltage components are located on the right side of the panel.
ON/OFF Switch
MicroTech II
Controller
SpeedTrol Location
Field Connection
Termin als
Start-up and Shutdown
Pre Start-up
1. The chilled-water system should be flushed and cleaned. Proper water treatment is required to
prevent corrosion and organic growth.
2. Open all electric disconnects and check all electric connections for tightness.
3. Inspect all water piping for flow direction and correct connections at the evaporator.
4. Verify thermostat water temperature sensor is installed in the leaving water line (supply to
building). On all AGZ units the sensor well and sensor are factory mounted.
5. Check compressor oil level. The oil level should be visible in the oil sight glass.
6. Check voltage of the unit power supply and make certain voltage is within 10% of nameplate
rating. Check unit power supply wiring for proper ampacity and a minimum insulation
temperature of 75C. Check for proper phasing using a phase sequence meter.
7. Verify all mechanical and electrical inspections have been completed according to local codes.
8. Open control stop switch S1(off). Turn on the main power and control disconnect switches.
This will energize crankcase heaters. Wait at least 24 hours before starting up unit.
9. Open all water flow valves and start the chilled water pump. Check all piping for leaks and
vent the air from the evaporator as well as from the system piping. Flush the evaporator and
system piping to obtain clean, noncorrosive water in the evaporator.
Control
Transformer
24-Volt Trans.
Non-Fused Disc.
or
Power Block
Fan
Contactors
Fan
Protection
Compressor Contactors
Start-up
1. Set temperature controller to the desired chilled water temperature. Set the chilled water
Delta-T.
2. Start auxiliary equipment by turning on the following: time clock (if present), ambient
thermostat and/or remote on/off switch, chilled water pump.
3. If the controller calls for cooling, the unit will begin the start-up sequence.
16 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 17

4. After running the unit for a short time, check the oil level in the compressor (1/4 to 1/3
of the glass), rotation of fans, and flashing in refrigerant sight glass.
5. Verify superheat temperature is at the factory setting of 8 to 12 degrees F (4.4 to 6.7
degrees C).
After system performance has stabilized, complete the current AGZ Start-Up Form
6.
(obtainable from
benefits. Return the form to Daikin through your sales representative.
the local Daikin sales office) to establish inception of warranty
Sequence of Operation
Start-Up
With the control circuit power on, 115V power is applied through the control circuit fuse F1
to the compressor crankcase heaters, the compressor motor protections and the primary of
the 24V control circuit transformer. The 24V transformer provides power to the
microprocessor controller.
When a remote time clock, manual switch, or the unit controller turns on the chilled water
pump, the flow switch closes and satisfies the flow requirement. If the chilled water
temperature is above the stage-on temperature, and all equipment protection devices are
closed, the unit will start. The controller will operate the unit in response to the leaving
chiller water temperature or reset signals that may be present.
Equipment Protection Alarms
The following conditions will shut down the unit and activate the alarm circuit:
No evaporator water flow Low evaporator pressure
High condenser pressure Motor protection system
Phase voltage protection (Optional) Outside ambient temperature
Evaporator freeze protection Sensor failures
The following alarms will limit unit operation:
Condenser pressure stage down, unloads unit at high discharge pressures
Low ambient lockout, shuts off unit at low ambient temperatures
Low evaporator pressure hold, holds stage #1 until pressure rises
Low evaporator pressure unload, shuts off stage #2
Unit Enable Selection
Enables unit operation from local keypad, digital input, or Building Automation System.
Unit Mode Selection
Selects standard cooling, ice, glycol, or test operation mode.
Condenser fan control
Control of condenser fans is provided by the MicroTech II controller. The control steps
condenser fans based on discharge pressure.
Shutdown
As the leaving water control is satisfied, it will stage off the lag compressor unloading the
unit. The second stage will de-energize the liquid line solenoid valve SV1 and shut off the
lead compressor. The compressor crankcase heaters will energize when the compressors
shut off, keeping the small amount of refrigerant in the plate heat exchanger from migrating
to the compressor. See page 55 for detailed explanation of compressor staging.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 17
Page 18
Physical Data
AGZ-BS, R-407C
Table 7, Physical Data, AGZ 010BS through 017BS, Packaged, R-407C
PHYSICAL DATA
BASIC DATA
Unit Capacity @ ARI Conditions (1), Tons (kW) 10.0 (36.2) 13.7 (48.2) 15.8 (55.6)
Number Of Refrigerant Circuits 1 1 1
Unit Operating Charge, R-407C Lb. (kg) 22.0 (10.0) 24.0 (10.9) 31.0 (14.1)
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, In. 73.6 x 46.3 x 50.8 73.6 x 46.3 x 50.8 73.6 x 46.3 x 50.8
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, (mm) (1869) x (1176) x (1289) (1869) x (1176) x (1289) (1869) x (1176) x (1289)
Unit Operating Weight, Lb. (kg) 1095 (498) 1190 (541) 1300 (591)
Unit Shipping Weight, Lb. (kg) 1085 (493) 1170 (532) 1280 (582)
Add'l Weight If Copper Finned Coils, Lb. (kg) 176 (80.0) 176 (80.0) 264 (120.0)
COMPRESSORS
Type Scroll Scroll Scroll
Nominal Horsepower 6.0 / 6.0 7.5 / 7.5 9.0 / 9.0
Oil Charge Per Compressor of a Tandem Set, oz. (g) 60 (1701) 85 (2410) 110 (3119)
CAPACITY REDUCTION STEPS - PERCENT OF COMPRESSOR DSPLACEMENT
Standard Staging 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100
CONDENSERS - HIGH EFFICIENCY FIN AND TUBE TYPE WITH INTEGRAL SUBCOOLING
Coil Face Area, One of Two Sides, Sq. Ft. (M2) 30.3 (2.8) 30.3 (2.8) 30.3 (2.8)
Finned Height x Finned Length, In. 84 x 52 84 x 52 84 x 52
Finned Height x Finned Length, (mm) (2134) x (1321) (2134) x (1321) (2134) x (1321)
Fins Per Inch x Rows Deep: 16 x 2 16 x 2 16 x 3
Pumpdown Capacity Lb. (kg) 35.3 (16.0) 35.3 (16.0) 52.9 (24.0)
CONDENSER FANS - DIRECT DRIVE PROPELLER TYPE
Number Of Fans - Fan Diameter, In. (mm) 2 – 26 (660) 2 – 26 (660) 2 – 26 (660)
Number Of Motors - HP (kW) 2 – 1.0 (0.75) 2 – 1.0 (0.75) 2 – 1.0 (0.75)
Fan And Motor RPM, 60 Hz 1140 1140 1140
60 Hz Total Unit Airflow, CFM (l/s) 13950 (6584) 13950 (6584) 12000 (5664)
DIRECT EXPANSION EVAPORATOR - BRAZED PLATE-TO-PLATE
Connection Size Victaulic, In. (mm) 2 (51) 2 (51) 2 (51)
Water Volume, Gallons (L) 0.9 (3.6) 1.7 (6.3) 2.0 (7.6)
Maximum Refrigerant Working Pressure, psig (kPa) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103)
Maximum Water Pressure, psig (kPa) 350 (2413) 350 (2413) 350 (2413)
NOTE: Nominal capacity based on 95°F ambient air and 54°F/44°F water range.
010B 013B 017B
AGZ MODEL NUMBER
18 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 19
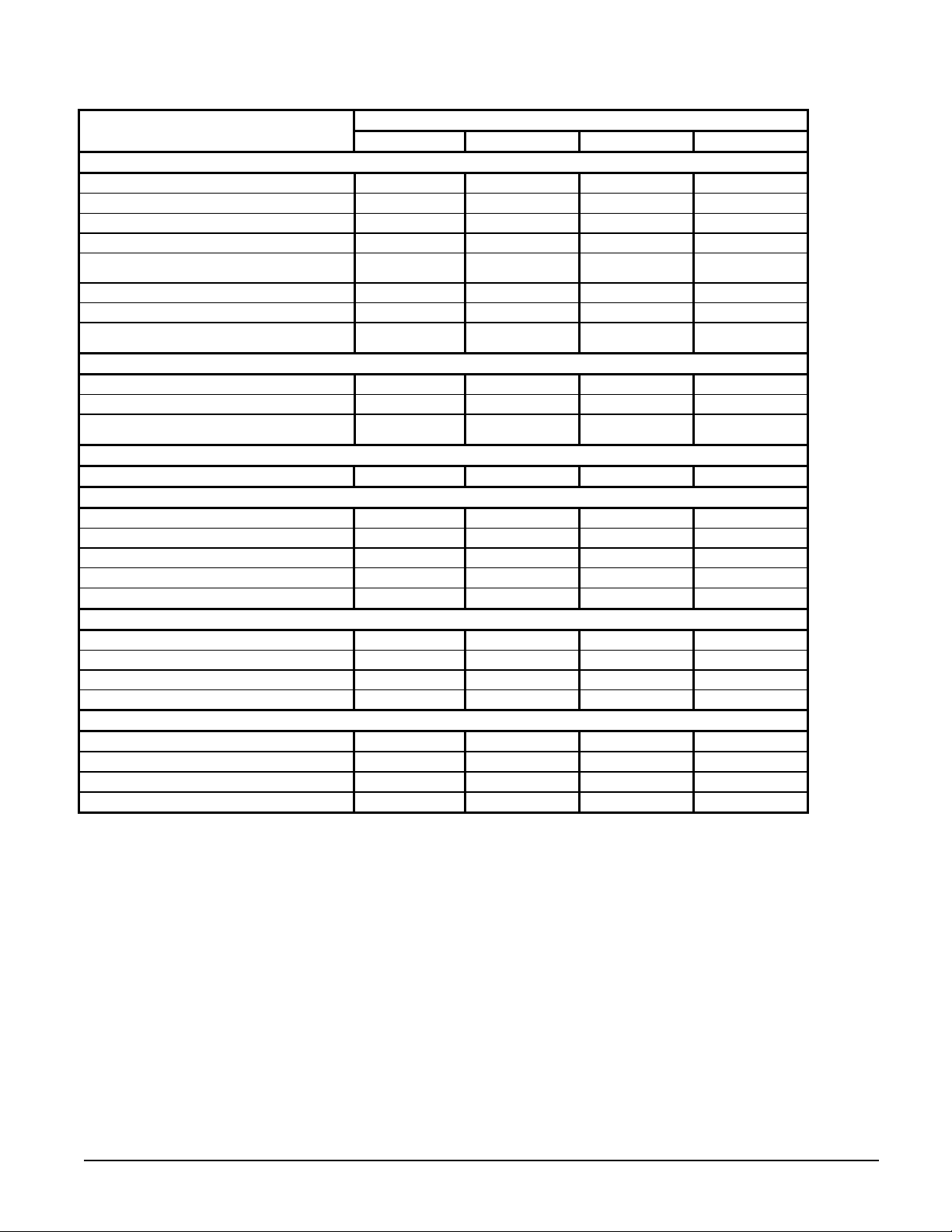
Table 8, Physical Data, AGZ 020BS through 034BS, Packaged, R-407c
PHYSICAL DATA
BASIC DATA
Unit Capacity @ ARI Conditions (1), Tons (kW) 20.6 (72.4) 22.7 (79.8) 27.7 (97.5) 34.0 (119.5)
Number Of Refrigerant Circuits 1 1 1 1
Unit Operating Charge, Lb. (kg) 38.0 (17.3] 42.0 (19.1) 47.0 (21.3) 50.0 (22.7)
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, In. 106.2x 46.3 x 50.8 106.2x 46.3 x 50.8 106.2x 46.3 x 58.8 106.2x 46.3 x 58.8
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, (mm)
Unit Operating Weight, Lbs. (kg) 1590 (723) 1635 (743) 1830 (832) 2315 (1052)
Unit Shipping Weight, Lbs. (kg) 1570 (714) 1610 (732) 1800 (818) 2270 (1032)
Add'l Weight If Copper Finned Coils, Lb. (kg)
COMPRESSORS
Type Scroll Scroll Scroll Scroll
Nominal Horsepower 12.0 / 12.0 13.0 / 13.0 15.0 / 15.0 20.0 / 20.0
Oil Charge Per Compressor of a Tandem Set,
oz. (g)
CAPACITY REDUCTION STEPS - PERCENT OF COMPRESSOR DISPLACEMENT
Standard Staging 0 –50 - 100 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100
CONDENSERS - HIGH EFFICIENCY FIN AND TUBE TYPE WITH INTEGRAL SUBCOOLING
Coil Face Area, One of Two Sides, Sq. Ft. (M2) 49.0 (4.6) 49.0 (4.6) 58.3 (5.4) 58.3 (5.4)
Finned Height x Finned Length, In. 84 x 84 84 x 84 100 x 84 100 x 84
Finned Height x Finned Length, (mm) (2134) x (2134) (2134) x (2134) (2545 ) x (2134) (2545 ) x (2134)
Fins Per Inch x Rows Deep 16 x 3 16 x 3 16 x 3 16 x 3
Pumpdown Capacity, Lb. (kg) 85.4 (38.8) 85.4 (38.8) 101.6 (46.2) 101.6 (46.2)
CONDENSER FANS - DIRECT DRIVE PROPELLER TYPE
Number Of Fans - Fan Diameter, In. (mm) 3 – 26 (660) 3 – 26 (660) 3 – 26 (660) 3 – 26 (660)
Number Of Motors - HP (kW) 3 – 1.0 (0.75) 3 – 1.0 (0.75) 3 – 1.0 (0.75) 3 – 1.0 (0.75)
Fan And Motor RPM, 60 Hz 1140 1140 1140 1140
60 Hz Total Unit Airflow, CFM (l/s) 20925 (9877) 20925 (9877) 19800 (9346) 19800 (9346)
DIRECT EXPANSION EVAPORATOR - BRAZED PLATE-TO-PLATE
Connection Size Victaulic, In. (mm) 2 (51) 2 (51) 2 (51) 2 (51)
Water Volume, Gallons (L) 2.2 (8.2) 3.0 (11.5) 4.0 (15.1) 5.6 (21.0)
Max. Refrigerant Working Pressure, psig (kPa) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103)
Maximum Water Pressure, psig (kPa) 350 (2413) 350 (2413) 350 (2413) 350 (2413)
NOTE: Nominal capacity based on 95°F ambient air and 54°F/44°F water range.
020B 025B 029B 034B
(2697) x (1176) x
(1289)
426 (194) 426 (194) 508 (231) 508 (231)
110 (3119) 110 (3119) 110 (3119) 158 (4479)
AGZ MODEL NUMBER
(2697) x (1176) x
(1289)
(2697) x (1176) x
(1493)
(2697) x (1176) x
(1493)
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 19
Page 20

AGZ-BM, R-407C
Table 9, Physical Data, AGZ 010BM through 017BM, Remote Evaporator, R-407C
PHYSICAL DATA
BASIC DATA
Unit Capacity @ ARI Conditions (1), Tons (kW) 10.0 (36.2) 13.7 (48.2) 15.8 (55.6)
Number Of Refrigerant Circuits 1 1 1
Unit Operating Charge, Lb. (kg) 13 (5.9) 14 (5.3) 17 (7.7)
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, In. 73.6 x 46.3 x 50.8 73.6 x 46.3 x 50.8 73.6 x 46.3 x 50.8
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, (mm) (1869) x (1176) x (1289) (1869) x (1176) x (1289) (1869) x (1176) x (1289)
Unit Operating Weight, Lb. (kg) 950 (431) 1276 (579) 1278 (580)
Unit Shipping Weight, Lb. (kg) 1025 (465) 1350 (613) 1363 (619)
Add'l Weight If Copper Finned Coils, Lb. (kg) [176 (80.0) [176 (80.0) [264 (120.0)
COMPRESSORS
Type Scroll Scroll Scroll
Nominal Horsepower 6.0 / 6.0 7.5 / 7.5 9.0 / 9.0
Oil Charge Per Compressor of a Tandem Set, oz. (g) 60 (1701) 85 (2410) 110 (3119)
CAPACITY REDUCTION STEPS - PERCENT OF COMPRESSOR DSPLACEMENT
Standard Staging 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100
CONDENSERS - HIGH EFFICIENCY FIN AND TUBE TYPE WITH INTEGRAL SUBCOOLING
Coil Face Area, One of Two Sides, Sq. Ft. (M2) 30.3 (2.8) 30.3 (2.8) 30.3 (2.8)
Finned Height x Finned Length, In. 84 x 52 84 x 52 84 x 52
Finned Height x Finned Length, (mm) (2134) x (1321) (2134) x (1321) (2134) x (1321)
Fins Per Inch x Rows Deep [16 x 2 16 x 2 16 x 3
Pumpdown Capacity Lb. (kg) 35.3 (16.0) 35.3 (16.0) 52.9 (24.0)
CONDENSER FANS - DIRECT DRIVE PROPELLER TYPE
Number Of Fans - Fan Diameter, In. (mm) 2 – 26 (660) 2 – 26 (660) 2 – 26 (660)
Number Of Motors - HP (kW) 2 – 1.0 (0.75) 2 – 1.0 (0.75) 2 – 1.0 (0.75)
Fan And Motor RPM, 60 Hz 1140 1140 1140
60 Hz Total Unit Airflow, CFM (l/s) 13950 (6584) 13950 (6584) 12000 (5664)
REMOTE DIRECT EXPANSION EVAPORATOR - BRAZED PLATE-TO-PLATE
Water Connection Size Victaulic, In. (mm) 2 (51) 2 (51) 2 (51)
Water Volume, Gallons (L) 0.9 (3.6) 1.7 (6.3) 2.0 (7.6)
Liquid Line Conn. Braze, inches 1.125 1.125 1.125
Suction Line Conn. Braze, Inches 2.125 2.125 2.125
Temperature Sensor Conn. NPT, Inches 0.75 0.75 0.75
Dry Weight, lbs (kg) 50 (22) 75 (34) 87 (39)
Operating Weight, lbs (kg) 58 (26) 88 (40) 109 (49)
Maximum Refrigerant Working Pressure, psig (kPa) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103)
Maximum Water Pressure, psig (kPa) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103)
Vent and Drain Conn. Field Field Field
NOTE: Nominal capacity based on 95°F ambient air and 54°F/44°F water range and does not take field-installed lines into account.
010B 013B 017B
AGZ MODEL NUMBER
20 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 21

Table 10, Physical Data, AGZ 020BM through 034BM, Remote Evaporator, R-407C
PHYSICAL DATA
BASIC DATA
Unit Capacity @ ARI Conditions (1), Tons (kW) 20.6 (72.4) 22.7 (79.8) 27.7 (97.5) 34.0 (119.5)
Number Of Refrigerant Circuits 1 1 1 1
Unit Operating Charge, Lb. (kg) 38.0 (17.3) 42.0 (19.1) 47.0 (21.3) 50.0 (22.7)
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, In. 106.2x 46.3 x 50.8 106.2x 46.3 x 50.8 106.2x 46.3 x 58.8 106.2x 46.3 x 58.8
Cabinet Dimensions, LxWxH, (mm)
Unit Operating Weight, Lbs. (kg) 1459 (662) 1478 (671) 1622 (737) 1817 (825)
Unit Shipping Weight, Lbs. (kg) 1558 (707) 1576 (716) 1719 (780) 1914 (869)
Add'l Weight If Copper Finned Coils, Lb. (kg) 426 (194) 426 (194) 508 (231) 508 (231)
COMPRESSORS
Type Scroll Scroll Scroll Scroll
Nominal Horsepower 12.0 / 12.0 13.0 / 13.0 15.0 / 15.0 20.0 / 20.0
Oil Charge Per Compressor of a Tandem Set,
oz. (g)
CAPACITY REDUCTION STEPS - PERCENT OF COMPRESSOR DISPLACEMENT
Standard Staging 0 –50 - 100 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100 0 – 50 – 100
CONDENSERS - HIGH EFFICIENCY FIN AND TUBE TYPE WITH INTEGRAL SUBCOOLING
Coil Face Area, One of Two Sides, Sq. Ft. (M2) 49.0 (4.6) 49.0 (4.6) 58.3 (5.4) 58.3 (5.4)
Finned Height x Finned Length, In. 84 x 84 84 x 84 100 x 84 100 x 84
Finned Height x Finned Length, (mm) (2134) x (2134) (2134) x (2134) (2545 ) x (2134) (2545 ) x (2134)
Fins Per Inch x Rows Deep 16 x 3 16 x 3 16 x 3 16 x 3
Pumpdown Capacity, Lb. (kg) 85.4 (38.8) 85.4 (38.8) 101.6 (46.2) 101.6 (46.2)
CONDENSER FANS - DIRECT DRIVE PROPELLER TYPE
Number Of Fans - Fan Diameter, In. (mm) 3 – 26 (660) 3 – 26 (660) 3 – 26 (660) 3 – 26 (660)
Number Of Motors - HP (kW) 3 – 1.0 (0.75) 3 – 1.0 (0.75) 3 – 1.0 (0.75) 3 – 1.0 (0.75)
Fan And Motor RPM, 60 Hz 1140 1140 1140 1140
60 Hz Total Unit Airflow, CFM (l/s) 20925 (9877) 20925 (9877) 19800 (9346) 19800 (9346)
REMOTE DIRECT EXPANSION EVAPORATOR - BRAZED PLATE-TO-PLATE
Connection Size Victaulic, In. (mm) 2 (51) 2 (51) 2 (51) 2 (51)
Water Volume, Gallons (L) 2.2 (8.2) 3.0 (11.5) 4. 0 (15.1) 5.6 (21.0)
Liquid Line Conn. Braze, inches 1.125 1.125 1.375 1.375
Suction Line Conn. Braze, Inches 2.125 2.125 2.125 2.125
Temperature Sensor Conn. NPT, Inches 0.75 0.75 0.75 0.75
Dry Weight, lbs (kg) 92 (42) 124 (56) 156 (71) 211 (96)
Operating Weight, lbs (kg) 110 (50) 148 (67) 188 (85) 255 (116)
Max. Refrigerant Working Pressure, psig (kPa) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103)
Maximum Water Pressure, psig (kPa) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103) 450 (3103)
Drain and Vent Connections Field Field Field Field
NOTE: Nominal capacity based on 95°F ambient air and 54°F/44°F water range and does not take field-installed lines into account.
020B 025B 029B 034B
(2697) x (1176) x
(1289)
110 (3119) 110 (3119) 110 (3119) 158 (4479)
AGZ MODEL NUMBER
(2697) x (1176) x
(1289)
(2697) x (1176) x
(1493)
(2697) x (1176) x
(1493)
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 21
Page 22

Electrical Data
Field Wiring
Wiring must comply with all applicable codes and ordinances. Warranty is void if wiring is
not in accordance with specifications. Copper wire is required for all power lead
terminations at the unit.
AGZ 010B through AGZ 034B units have single point power connection. A single field
supplied fused disconnect is required. The control transformer is factory mounted.
If the evaporator heater is on a separate disconnect switch from the main unit power supply,
the unit may be shut down without defeating the freeze protection provided by the
evaporator heater.
R-407C
Table 11, Electrical Data, R-407C
AGZ
Unit
Size
010B
013B
017B
020B
025B
029B
034B
NOTE: See page 25 for all Electrical Data notes.
Volts
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
Minimum
Circuit
Ampacity
(MCA)
58
54
27
22
77
77
39
30
82
80
41
33
113
113
51
41
129
129
61
51
148
139
72
58
187
182
85
73
Power Supply
Field Wire
Quantity
3 6 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 6 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 10 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 10 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 4 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 4 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 8 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 10 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 4 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 4 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 8 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 10 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 2 AWG 1 1.25 (32)
3 2 AWG 1 1.25 (32)
3 6 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 8 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 1 AWG 1 1.25 (32)
3 1 AWG 1 1.25 (32)
3 6 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 6 AWG
3 1/0 AWG 1 1.50 (38)
3 1/0 AWG 1 1.50 (38)
3 4 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 6 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 3/0 AWG 1 2.00 (51)
3 3/0 AWG 1 2.00 (51)
3 4 AWG 1 1.00 (25)
3 4 AWG
Wire
Gauge
75C
Hub (Conduit
Connection)
Quantity
1 1.00 (25)
1 1.00 (25)
Nominal
Size
In. (mm)
Field Fuse
or Breaker Size
Recommended Maximum
70 70
60 70
30 35
25 25
90 100
90 100
45 50
35 40
110 110
90 100
50 50
40 40
125 150
125 150
60 60
50 50
150 175
150 175
70 80
60 60
175 200
175 175
80 100
80 80
250 250
250 250
100 110
100 100
22 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 23

Table 12, Compressor & Fan Motor Amps, R-407C
AGZ
Unit
Size
010B
013B
017B
020B
025B
029B
034B
NOTE: See page 25 for all Electrical Data notes.
Volts
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
208
230
460
575
Rated Load Amps Locked Rotor Amps
Compressors Compressors
No. 1 No. 2
20.3 20.3
18.6 18.6
9.2 9.2
7.4 7.4
28.8 28.8
28.8 28.8
14.7 14.7
10.8 10.8
31.2 31.2
30.1 30.1
15.5 15.5
12.1 12.1
42.3 42.3
42.3 42.3
18.6 18.6
14.6 14.6
49.4 49.4
49.4 49.4
23.1 23.1
19.2 19.2
57.9 57.9
53.8 53.8
28.2 28.2
22.4 22.4
75.0 75.0
73.1 73.1
34.0 34.0
28.8 28.8
F.L. Amps
Fan
Motor
(Each)
5.8 2 21.4 156 156
5.8 2 23.7 156 156
2.8 2 10.7 75 75
2.5 2 11.0 54 54
5.8 2 21.4 195 195
5.8 2 23.7 195 195
2.8 2 10.7 95 95
2.5 2 11.0 80 80
5.8 2 21.4 225 225
5.8 2 23.7 225 225
2.8 2 10.7 114 114
2.5 2 11.0 80 80
5.8 3 21.4 245 245
5.8 3 23.7 245 245
2.8 3 10.7 125 125
2.5 3 11.0 100 100
5.8 3 21.4 300 300
5.8 3 23.7 300 300
2.8 3 10.7 150 150
2.5 3 11.0 109 109
5.8 3 21.4 340 340
5.8 3 23.7 340 340
2.8 3 10.7 173 173
2.5 3 11.0 132 132
5.8 3 21.4 505 505
5.8 3 23.7 505 505
2.8 3 10.7 225 225
2.5 3 11.0 180 180
No. of
Fans
Motor
(Each)
Fan
Across-The-Line
No. 1 No. 2
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 23
Page 24

Table 13, Field Wiring Data, R-407C
AGZ
Volts
Unit
Size
208 175
230 175
010B
460 175
575 175
208 175
230 175
013B
460 175
575 175
208 175
230 175
017B
460 175
575 175
208 175
230 175
020B
460 175
575 175
208 175
230 175
025B
460 175
575 175
208 175
230 175
029B
460 175
575 175
208 335 6 AWG – 400 kcmil
230 335 6 AWG – 400 kcmil
034B
460 175 14 AWG – 2/0
575 175 14 AWG – 2/0
NOTE:
1. High Interruptor or HSCCR Circuit Breakers are not available in these sizes
2. "Size" is the maximum amperage rating for the terminals or the main electrical device.
3. "Size" is the disconnect part number and not the amperage rating for the terminals or the main electrical device.
4. "Connection" is the range of wire sizes that the terminals on the electrical device will accept.
5. See page 25 for additional electrical notes.
Standard Power Block Terminal
Maximum
Terminal Amps
Wiring to
Connector Wire
Range
(Copper Wire Only)
14 AWG – 2/0 60
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 80 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 40 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 35 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 100
14 AWG – 2/0 100
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 60 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 50 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 100
14 AWG – 2/0 100
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 70 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 50 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 125
14 AWG – 2/0 125
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 80 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 60 14 AWG – 1 AWG 70 10 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 2/0 225
14 AWG – 2/0 225
14 AWG – 2/0 100
14 AWG – 2/0 60
14 AWG – 2/0 225
14 AWG – 2/0 225
14 AWG – 2/0 100
14 AWG – 2/0 100
Optional Disconnect Switch
Disconnect
Size
225
225
100
100
Wiring to
Connector Wire
Range
(Copper Wire Only)
14 AWG – 1 AWG
8 AWG - 1/0
8 AWG - 1/0
8 AWG - 1/0
8 AWG - 1/0
3 AWG – 3/0
3 AWG - 3/0
2 AWG - 4/0
2 AWG - 4/0
8 AWG - 1/0
14 AWG – 1 AWG
2 AWG - 4/0
2 AWG - 4/0
8 AWG - 1/0
8 AWG - 1/0
2 AWG - 4/0
2 AWG - 4/0
8 AWG - 1/0
8 AWG - 1/0
Wiring to High Interrupt
or HSCCR Circuit Breaker
Max.
Amps
125 3 AWG - 3/0
125 3 AWG - 3/0
125 3 AWG - 3/0
125 3 AWG - 3/0
175 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
175 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
200 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
200 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
100 10 AWG - 1/0
225 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
225 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
125 3 AWG - 3/0
N/A Note 1
N/A Note 1
150 6 AWG - 350 kcmil
125 3 AWG - 3/0
Connector Wire
(Copper Wire Only)
90 10 AWG - 1/0
80 10 AWG - 1/0
90 10 AWG - 1/0
Range
24 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 25

Notes for Electrical Data
A
1. Unit wire size ampacity (MCA) is equal to 125% of the largest compressor-motor RLA
plus 100% of RLA of all other loads in the circuit.
2. The control transformer is furnished and no separate 115V power supply is required.
3. If a separate 115V power supply is used for the control circuit, then the wire sizing
amps is 10 amps for all unit sizes.
4. Recommended power lead wire sizes for three conductors per conduit are based on
100% conductor ampacity in accordance with NEC. Voltage drop has not been included.
Therefore, it is recommended that power leads be kept short. All terminal block
connections must be made with copper wire.
5. “Recommended Fuse Sizes” are selected at approximately 175% of the largest
compressor RLA, plus 100% of the RLA of all other loads in the circuit.
6. “Maximum Fuse or breaker size” is selected at approximately 225% of the largest
compressor RLA, plus 100% of all other loads in the circuit.
7. The recommended power lead wire sizes are based on an ambient temperature of 86°F
(30°C). Ampacity correction factors must be applied for other ambient temperatures.
Refer to the National Electrical Code Handbook.
8. Units must be electrically grounded according to national and local electrical codes.
Voltage Limitations:
Within 10 percent of nameplate rating
Important: Voltage unbalance not to exceed 2% with a resultant current unbalance of 6 to
10 times the voltage unbalance per NEMA MG-1, 1998 Standard. This is an important
restriction that must be adhered to.
Notes for “Compressor and Condenser Fan Amp Draw”:
1. Compressor RLA values are for wiring sizing purposes only but may not reflect normal
operating current draw at rated capacity.
2. Fan motor FLA values are approximate fan motor amp values at rated voltage.
Notes for “Field Wiring Data”
1. Requires a single disconnect to supply electrical power to the unit. This power supply
must either be fused or use a circuit breaker.
2. All field wiring to unit power block or optional non-fused disconnect switch must be
copper.
3. All field wire size values given in table apply to 75°C rated wire per NEC.
Standard Panel Ratings (kA)
Voltage
208-230
460
575
AGZ 010-017 AGZ 025-029 AGZ 034
5 10 10
5 5 10
5 5 5
GZ-B Model Size
Circuit Breakers
The circuit breaker used in the High Short Circuit panel option may have a higher trip rating
than the unit Maximum Overload Protection (MOP) value shown on the unit nameplate.
The circuit breaker is installed as a service disconnect switch and does not function as
branch circuit protection, mainly that the protection device must be installed at the point of
origin of the power wiring. The breaker (disconnect switch) is oversized to avoid nuisance
trips at high ambient temperature conditions.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 25
Page 26

Figure 7, AGZ 010A through AGZ 034A, Typical Field Wiring Diagram
B
A
G
G
UNIT MAIN
TERMINAL
BLOCK
GND LUG
TO COMPRESSOR(S)
AND FAN MOTORS
3 PHASE
POWER
SUPPLY
DISCONNECT
(BY OTHERS)
NOTE: ALL FIELD WIRING
TO BE INSTALLED AS NEC
CLASS 1 WIRING SYSTEM
WITH CONDUCTOR RATED
600 VOLTS
120VAC
CONTROL POWER
SEPARATE EVAP.
HEATER POWER
FIELD WIRED
FACTORY SUPPLIED ALARM
ALARM
BELL
OPTION
REMOTE STOP
SWITCH
(BY OTHERS)
ICE MODE
SWITCH
(BY OTHERS)
FIELD WIRED
ALARM BELL RELAY
CHW FLOW SWITCH
N
120VAC
(BY OTHERS)
HOT GAS BYPASS SOLENOID
TIME
CLOCK
---MANDATORY–(BY OTHERS)
4-20MA FOR
CHW RESET
(BY OTHERS)
FUSED CONTROL
TRANSFORMER
DISCONNECT
(BY OTHERS)
(BY OTHERS)
DISCONNECT
(BY OTHERS)
N
LIQUID LINE SOLENOID
120 VAC 1.0 AMP MAX
SV1
SV5
120 VAC 1.0 AMP MAX
CHW PUMP RELAY
(BY OTHERS)
120 VAC 1.0 AMP MAX
AUTO
ON
MANUAL
NOR. OPEN PUMP AUX.
CONTACTS (OPTIONAL)
AUTO
ON
MANUAL
CIRCUIT
10A
FUSE
(BY OTHERS)
OFF
+
-
OFF
FUSE
120
VAC
TB1-20
TB1
CONTROL
1
10A
2
6
15
13
16
14
12
17
11
17
CIRCUIT
GZ REMOTE EVAP ONLY
FUSE
N
MJ
IF SEPARATE EVAPORATOR
HEATER POWER OPTION
MJ
IS USED - REMOVE
MECHANICAL JUMPER
BETWEEN TB1-5 AND TB1-6
& TB1-15 AND TB1-16.
120 VAC
120 VAC
120 VAC
120 VAC
GND
TB2
IF REMOTE STOP
CONTROL IS USED,
843
REMOVE LEAD 843
FROM TERM. 25 TO 35.
GND
ALARM BELL
RELAY
COM NO
BELL
12
ALARM BELL OPTION
24VAC
25
35
22
31
26
36
22
33
34
28
38
FIELD WIRIN
FACTORY WIRIN
LABEL DWG. 330538401 REV.0
Note: See control and power wiring diagrams on unit control panel for specific unit information.
26 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 27

Dimensions & Weights
3.00
9
Figure 8, AGZ 010BS - 017BS, Packaged (See page 29 for additional dimensions and weights)
ACCESS
PANEL
QTY.2
EVAP.
INLET
31.70
11.27
EVAP.
OUTLET
14.66
5.17
POWER ENTRY
KNOCKOUT
(OTHER SIDE)
2.61
40.18
24.57
.875
.875
CONTROL
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUT
ACCESS DOORS
Y
CONTROL BOX
ACCESS
DOOR
POWER
ENTRY
51.00
46.18
49.06
L1, L2L3, L4
3.00
QTY.2
EVAP.
INLET
31.70
11.27
21.18
X
4.00
MOUNTING HOLES
DIA. 1.00 INCH
QTY. 4
DIM. A = AGZ020-025 = 24.6"
AGZ029-034 = 33.0"
DIM. B = AGZ020-025 = 40.2"
AGZ029-034 = 48.7"
Z
31.15
MOUNTING
HOLES
46.42
7.64
NOTE:
L2 & L4 ARE LOCATED ON1.
OPPOSITE SIDE OF UNIT.
ALL WEIGHTS ARE IN POUNDS.2.
R331987001
CERTIFIED, 2 FAN, AGZ-
00
Figure 9, AGZ 020BS - 034BS, Packaged (See page 29 for additional dimensions and weights)
ACCESS
PANEL
73.80
EVAP.
OUTLET
14.66
49.06 49.06
84.95
106.23
5.17
L1, L2L3, L4
X
21.18
.875
POWER ENTRY
KNOCKOUT
(OTHER SIDE)
2.67
.875
CONTROL
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUT
B
A
Y
CONTROL PANEL
ACCESS DOORS
ACCESS
DOOR
Z
31.10
MOUNTING
HOLES
46.38
R331987101
POWER
ENTRY
AGZ020-025 =51
AGZ029-034 = 5
7.64
CERTIFIED, 3 FAN, AGZ-B
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 27
Page 28

Figure 10, AGZ 010 - 017BM Remote Evap. (See page 29 for additional dimensions and weights
T
DIM. A
ACZ025-028
6"
9
ACCESS
PANEL
NOTE:
L2 & L4 ARE LOCATED ON1.
OPPOSITE SIDE OF UNIT.
ALL WEIGHTS ARE IN POUNDS.2.
5.17
HOT GAS
BYPASS
L1, L2L3, L4
Figure 11, AGZ 020BM - 034BM (See page 29 for additional dimensions and weights
ACCESS
PANEL
46.18
49.06
73.80
21.18
X
DIM. B = ACZ025-028 = 40.2"
DIM. C = ACZ025-033 = 18.8"
DIM. D = ACZ025-033 = 4.5"
18.84
9.19
4.56
5.06
8.86
4.00
MOUNTING HOLES
DIA. 1.00 INCH
=
ACZ033-039 = 33.0"
ACZ033-039 = 48.7"
ACZ039 = 12.6"
ACZ039 = 7.5"
POWER ENTRY
KNOCKOUT
(OTHER SIDE)
SUCTION
20.79
LIQUID
.875
.875
CONTROL
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUT
24.57
= 24.
CONTROL BOX
ACCESS DOORS
ACCESS
DOOR
31.15
MOUNTING
HOLES
46.42
R331987401
NOTE:
L2 & L4 ARE LOCATED ON1.
OPPOSITE SIDE OF UNIT.
ALL WEIGHTS ARE IN POUNDS.2.
00
POWER
ENTRY
51.00
Y
Z
7.64
CERTIFIED, 2 FAN, AGZ-B REMO
49.06 49.06
106.23
28 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
.875
POWER ENTRY
KNOCKOUT
(OTHER SIDE)
84.95
5.17
HOT GAS BYPASS
.875
CONTROL
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUT
D
2.67
SUCTION
C
9.19
L1,L2L3,L4
21.18
X
LIQUID
5.06
8.86
20.79
B
A
R331987501
CONTROL PANEL
ACCESS DOORS
POWER
ENTRY
ACCESS
DOOR
Z
31.10
MOUNTING
HOLES
46.38
CERTIFIED, 3 FAN, AGZ-B REMOTE
Y
7.64
ACZ025-028 =51
ACZ033-039 = 5
Page 29

Remote Evaporators
Figure 12, Remote Evaporators, for AGZ 010BM – 034BM
Suction
30.2
(767)
8.2 (208)
10.2 (260)
1.2
(30)
.35
(9)
3.5
(90)
A
3.5
(90)
Te mp Se n so r
1.2
(30)
Liquid
W1
Inlet
W2
Outlet
AGZ
Model
010
013
017
020
025
029
034
Liquid Line Conn.
Brazed, in (L).
1.125 2.125 0.75 2.0 3.6 (91)
1.125 2.125 0.75 2.0 6.0 (153)
1.125 2.125 0.75 2.0 7.1 (181)
1.125 2.125 0.75 2.0 7.7 (195)
1.125 2.125 0.75 2.0 10.6 (271)
1.375 2.125 0.75 2.0 13,8 (351)
1.375 2.125 0.75 2.0 19.0 (483)
Suction Line Conn.
Brazed, in (S).
Temp. Sensor
NPT, in. (TS)
Victaulic
Water Conn.
In. (W)
Dimension
“A”
in. (mm)
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 29
Page 30

ACZ/AGZ Dimensions and Weights
Table 14, Packaged Chiller, Dimensions and Weights
AGZ
UNIT
SIZE
010B
013B
017B
020B
025B
029B
034B
CENTER OF GRAVITY
28.00 21.50 23.40 1085 1095 398 392 149 147 2 279 275 267 263
27.40 21.40 23.90 1170 1190 452 426 150 141 2 315 297 288 271
27.50 21.60 24.00 1280 1300 493 463 167 157 2 344 323 316 297
38.50 21.80 23.90 1505 1525 564 534 209 198 2 502 475 271 257
39.50 19.40 24.00 1610 1635 593 554 239 224 2 531 496 301 282
41.00 22.75 24.20 1800 1830 645 595 291 269 2 583 538 353 326
35.60 23.70 23.50 2270 2315 890 869 259 253 2 779 761 369 361
(IN.)
X Y Z
SHIP WT.
(LBS)
OPN. WT.
(LBS)
Table 15, Remote Evaporator, Dimensions and Weights
AGZ
REMOTE
EVAP.
010B
013B
017B
020B
025B
029B
034B
CENTER OF GRAVITY
(IN.)
X Y Z
27.50 21.70 22.90 1000 1015 369 379 124 128 1.125 0.875 0.625
26.50 21.60 23.40 1065 1090 421 416 115 113 1.625 0.875 0.625
26.60 21.80 23.30 1150 1190 454 449 124 123 1.625 0.875 0.625
38.50 21.90 23.30 1370 1420 501 498 186 185 1.625 0.875 0.625
38.50 19.10 23.30 1390 1445 508 505 189 188 1.625 0.875 0.625
41.00 23.00 23.30 1565 1625 540 538 244 243 1.625 0.875 0.875
34.60 24.00 22.40 1975 2050 753 807 201 215 2.125 0.875 0.875
SHIP
WT.
(LBS)
OPN.
WT.
(LBS)
LIFTING CORNER WEIGHTS
(LBS)
L1 L2 L3 L4
LIFTING CORNER WEIGHTS
(LBS)
L1 L2 L3 L4 SUCTION LIQUID
EVAP.
CONN.
(IN.)
VICTAULIC
CONNECTION SIZES (IN. O.D.)
MOUNTING CORNER
WEIGHTS (LBS.)
M1 M2 M3 M4
HOT GAS
BYPASS
Table 16, Mounting Weights
REMOTE
EVAP
010B
013B
017B
020B
025B
029B
034B
MOUNTING CORNER WEIGHTS (LBS.)AGZ
M1 M2 M3 M4
257 264 236 243
290 286 246 243
312 309 266 263
446 443 241 240
453 449 245 243
488 487 296 295
656 703 297 318
30 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 31

System Maintenance
General
On initial start-up and periodically during operation, it will be necessary to perform certain
routine service checks. Among these are taking electric leg readings. Some readings are
readily available on the MicroTech II controller’s display.
Lubrication
No routine lubrication is required on the AGZ units. The fan motor bearings are of the
permanently lubricated type and require no lubrication.
Electrical Terminals
Electric shock hazard. Disconnect and tag out all sources of power to the unit before
continuing with following service or severe personal injury or death can result.
Normal heating and cooling of the wire will cause terminals to loosen. Retighten all power
electrical terminals every six months.
Condensers
Condensers are air-cooled and constructed with 3/8” (9.5mm) O.D. internally finned copper
tubes bonded in a staggered pattern into slit aluminum fins. No maintenance is ordinarily
required except the occasional removal of dirt and debris from the outside surface of the
fins. Use locally purchased foaming condenser coil cleaners for periodic cleaning of the
coil. Condenser cleaners may contain harmful chemicals, be careful when using cleaners.
Care should be taken not to damage the fins during cleaning. All chemical cleaners should
be thoroughly rinsed from the coils.
!
WARNING
Refrigerant Sight glass
Observe the refrigerant sight glass monthly. A clear glass of liquid indicates adequate subcooled refrigerant charge in the system to ensure proper feed through the expansion valve.
Bubbling refrigerant in the sight glass indicates the system is short of refrigerant charge.
Sub-cooling should be verified to prevent overcharging. Refrigerant gas flashing in the
sight glass could also indicate an excessive pressure drop in the line, possibly due to a
clogged filter-drier or a restriction elsewhere in the system. The sight glass indicates what
moisture condition corresponds to a given element color. If the sight glass does not indicate
a dry condition after about 12 hours of operation, the refrigerant or oil should be tested for
moisture.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 31
Page 32

Standard MicroTech II Controller
Table of Contents
Overview...............................................................................33
General Description...............................................................33
Compressor Motor Description ........................................33
FanTrol Head Pressure Control
Inputs/Outputs .................................................................
Setpoints ..........................................................................34
Equipment Protection Alarms...........................................36
Control Functions and Definitions....................................38
Limit Alarms....................................................................38
Control Functions ............................................................38
Unit Enable ......................................................................39
Unit Mode Selection ........................................................39
Unit State.........................................................................40
Evaporator Pump state .....................................................41
Condenser Fans................................................................43
Compressor Control .........................................................44
Using the Controller ..............................................................38
Display and Keyboard......................................................47
........................................33
34
Getting Started ......................................................................47
Menu Screens...................................................................48
Menu Matrix ....................................................................50
View Screens Defined ......................................................51
Alarm Screens Defined ....................................................53
Set Screens Defined .........................................................54
Softwar
32 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
e Version AGZSU0102D
Page 33

Overview
The MicroTech II controller’s state-of-the-art design will not only permit the chiller to run
more efficiently, but will also simplify troubleshooting if a system failure occurs. Every
MicroTech II controller is programmed and tested prior to shipment to contribute to a
trouble-free start-up.
Release Version
This manual covers Software Release AGZ SU0102D
Operator-friendly
The MicroTech II controller’s menu structure is separated into three distinct categories,
which provide the operator or service technician with a full description of current unit
status, control parameters, and alarms. Security protection prevents unauthorized changing
of the setpoints and control parameters.
The MicroTech II controller continuously performs self-diagnostic checks, monitoring
system temperatures, pressures and protection devices, and will automatically shut down a
compressor or the entire unit should a fault occur. The cause of the shutdown will be
retained in memory and can be easily displayed in plain English for operator review. The
MicroTech II chiller controller will also retain and display the time the fault occurred. In
addition to displaying alarm diagnostics, the MicroTech II chiller controller also provides
the operator with a warning of limit (pre-alarm) conditions.
Staging
The two scroll compressors are staged on and off as a function of leaving chilled water
temperature. Lead/lag is automatic and switched every ten starts.
General Description
Compressor Motor Protection
The solid-state compressor motor protector module incorporates a 2-minute “time-off” relay
utilizing the bleed-down capacitor principle. Any time the protection system opens or
power to the module is interrupted, the 2-minute “time-off” delay is triggered and the
module will not reset for two minutes. Once the 2-minute period has passed the motor
protector contacts M1 and M2 reset, provided the protection system is satisfied and power is
applied to the module.
Note: If the power circuit is broken once the 2-minute period is passed, the pilot
circuit will reset without delay when power is reapplied.
AGZ 010: The model AGZ 010 compressor has internal line breakage with automatic reset.
FanTrol Head Pressure Control
FanTrol is the standard method of head pressure control that automatically cycles the
condenser fan motors in response to condenser pressure. This function is controlled by the
microprocessor, maintains head pressure and allows the unit to run at low ambient air
temperatures down to 35F (1.7C). Fans are staged as follows:
Table 17, Fan Staging Pressures
Fan Two-Fan Unit Three-Fan Unit
Stage #1 On 150 psig, Off with unit On 150 psig, Off with unit
Stage #2 On 290 psig, Off 170 psig On 290 psig, Off 170 psig
Stage #3 -- On 310 psig, Off 180 psig
Note: Fan #1 is on with first compressor above 75F (24C).
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 33
Page 34

Inputs/Outputs
Table 18, Inputs and Outputs
Analog Inputs
# Description Signal Source Range
1 Reset of Leaving Water Temperature 4-20 mA Current
2 Evaporator Refrigerant Pressure 0.5 to 4.5 VDC (NOTE 1)
3 Condenser Refrigerant Pressure 0.5 to 4.5 VDC (NOTE 1)
4 Leaving Evaporator Water Temperature
5 Outside Ambient Temperature
Thermister (10k at 77F, 25C)
Thermister (10k at 77F, 25C)
NOTE 1: Value at the converter board input. Value at the converter board output is 0.1 VDC – 0.9 VDC.
Analog Outputs
# Description Output Signal Range
1-4 None -- --
Digital Inputs
# Description Signal Signal
1 Unit OFF Switch 0 VAC (Stop) 24 VAC (Auto)
2 Remote Start/Stop 0 VAC (Stop) 24 VAC (Start)
3 Evaporator Water Flow Switch 0 VAC (No Flow) 24 VAC (Flow)
4 Motor Protection 0 VAC (Fault) 24 VAC (No Fault)
5 Ice Mode Switch 0 VAC (Normal) 24 VAC (Ice)
6 Phase Voltage Fault 0 VAC (Fault) 24 VAC (No Fault)
7 Open -- --
8 Open -- --
0 to10 degrees
60F max inlet
0 to 132 psi
3.6 to 410 psi
-58 to 212°F
-58 to 212°F
Digital Outputs
# Description Load Output OFF Output ON
1 Alarm Alarm Indicator Alarm OFF Alarm ON
2 Evaporator Water Pump Pump Contactor Pump OFF Pump ON
3 Liquid Line Solenoid Cooling OFF Cooling ON
4 Motor Control Relay #1 Starter Compressor OFF Compressor ON
5 Motor Control Relay #2 Starter Compressor OFF Compressor ON
6 Condenser Fan #1 Fan Contactor Fan OFF Fan ON
7 Condenser Fan #2 Fan Contactor Fan OFF Fan ON
8 Condenser Fan #3 Fan Contactor Fan OFF Fan ON
Setpoints
The setpoints shown in Table 19 are battery-backed and remembered during power off, are
factory set to the Default value, and can be adjusted within the value shown in the Range
column.
The PW (password) column indicates the password level that must be entered in order to
change the setpoint. Passwords are as follows:
O = Operator [0100]
M = Manager, [2001] M level settings are not normally changed for chilled water airconditioning applications.
34 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 35

Table 19, Setpoints
Description Default Range PW
Unit
Unit Enable OFF OFF, ON O
Unit Mode COOL
Control Source SWITCHES
Available Modes COOL
Display Units
Language ENGLISH ENGLISH, O
Cool LWT
Ice LWT
Evap Delta T
Startup Delta T
Stop Delta T 0.5F 0 to 3.0F O
Max Pulldown Rate 1.0F
* Refrigerant Type (Note 1) None R22, R407c -BAS Protocol Modbus BACnet, LONWORKS, Modbus M
Ident Number 001 001 to 999 M
Baud rate 9600 1200,2400,4800,9600,19200 M
* SpeedTrol Option N N,Y M
Password 0000 0000 to 9999 --
Staging
Stage Up Delay 120 20 to 240 sec M
Stage Down Delay 30 10 to 60 sec M
Timers
Evap Flow Proof 3 sec 1 to 10 sec M
Evap Recirculate Timer 30 sec 15 to 300 sec. M
Low Evap Pressure Delay 30 sec 15 sec to 30sec M
Ice Time Delay 12 hrs. 1 to 23 hrs M
Clear Ice Delay NO No, Yes M
Start-Start 15 min 10 to 60 min M
Stop-Start 5 min 3 to 20 min M
Stage Up Delay 240 sec. 20 to 480 sec. M
Stage Down Delay 30 sec. 10 to 60 sec. M
Comp 1 Enable On Off, On
Comp 2 Enable On Off, On
Alarms
Evaporator Freeze
Low Evap Pressure 58 psi 30 to 60 psi M
Low Evap Pressure-Hold 59 psi 31 to 65 psi M
Low Evap Pressure-Unload 59 psi 31 to 65 psi M
High Condenser Stage Down 370 psi 365 to 375 psi M
High Condenser Pressure 380 psi 380 to 390 psi M
* Phase Voltage Protection N N,Y M
* Low Ambient Lockout
Condenser Fans
Fan Stages 2 2-3
Speedtrol Option No No,Yes
Stage #1 On (OAT<75F)
Stage #2 On 290 psi 230 to 330 psi M
Stage #3 On 300 psi 230 to 330 psi M
Stage #1 Off 140 psi 130 to 170 M
Continued next page.
COOL
COOL w/Glycol
ICE w/Glycol
TEST
SWITCHES, KEYPAD,
NETWORK
COOL
COOL w/GLYCOL
COOL/ICE w/GLYCOL
TEST
F/psi F/psi
44. 0F 20.0 to 60.0 F
40. 0F 20.0 to 40.0 F
10. 0F 6.0 to 16.0 F
10.0F 1.0 to 15.0 F
0.5 to 5.0F
36.0 F 18 to 42 F
35.0 F –2 to 60 F
200psi 140 to 200 psi M
O
O
M
O
O
O
O
O
M
M
M
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 35
Page 36

Description Default Range PW
Stage #2 Off 180 psi 150 to 200 psi M
Stage #3 Off 190 psi 150 to 200 psi M
Sensor Offsets
Evaporator Refrig Press Sensor Offset 00.0 psi -20.0 to 20.0 psi
Condenser Refrig Press Sensor Offset 00.0 psi -20.0 to 20.0 psi
Leaving Evaporator Water Temp Sensor
Outside Ambient Temperature Sensor
NOTES:
1. This setting is a one-time only setting and is made in the factory.
2. (*) These items are factory set prior to shipment.
0.0 F -5.0 to 5.0 F
0.0 F -5.0 to 5.0 F
Automatic Adjusted Ranges
The following are setpoints that will be limited based on the option(s) selected.
Evaporator Leaving Water Temperature
Mode Range
Unit Mode = Cool
Unit Mode = Cool w/Glycol
Evaporator Freeze Temperature
Mode Range
Unit Mode = Cool
Unit Mode = Cool w/Glycol, Ice
w/Glycol
40 to 60F
20 to 60F
36 to 42F
18 to 42F
Low Ambient Lockout Temperature
SpeedTrol Range
SpeedTrol = N
SpeedTrol = Y
35 – 60F
-2 – 60F
Low Evaporator Pressure Hold and Unload
Mode Refrigerant Range
Unit Mode = Cool R407c 58 to 65 Psig
Unit Mode = Cool w/Glycol, Ice w/Glycol R407c 20 to 65 Psig
Dynamic Default Values
Some setpoints will have different default values loaded depending on the value of other
setpoints.
Low Evaporator Pressure Hold
Refrigerant Default Value
R407C 60 psi
Low Evaporator Pressure Unload
Refrigerant Default Value
R407C 59 psi
36 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 37

Setpoint Security
All setpoints are protected by using passwords. Two four-digit passwords provide
OPERATOR and/or MANAGER levels of access to changeable parameters. Once a
password has been entered, it remains valid for 15 minutes after the last key-press on the
unit controller.
After a valid password has been entered, setpoints may be changed. If the operator attempts
to edit a setpoint on a controller while the correct password is not active, no action will be
taken.
Passwords can be entered using the ENTER PASSWORD screen which is the last screen in
the SET UNIT SPs column.
The password is entered by pressing the ENTER key, scrolling to the correct value with the
UP and DOWN arrow keys, and pressing ENTER again. The entered password is not
shown after the enter key is pressed. Once the correct password has been entered, the
PASSWORD screen indicates which password is active (operator or manager). If the wrong
password is entered, there is no level of access so the active password displays “none”.
Entering an incorrect password while a password is active will render that password
inactive.
Equipment Protection Alarms
Equipment protection alarms execute rapid compressor shutdown (no pumpdown cycle),
triggers the alarm output, lights the red alarm light on the controller left arrow button and
registers it in the alarm log.
The following table identifies each equipment protection alarm, gives the condition that
causes the alarm to occur, and states the action taken because of the alarm. Otherwise, the
alarm is manually reset, requiring the operator to clear the alarm.
Table 20, Shutdown Alarms
Description Occurs When:
No Evaporator Water Flow
(See NOTE)
Low Evaporator Pressure
High Condenser Pressure
Mechanical High Pressure MHP input is low Rapid Stop Manual
Motor Protection
Phase Voltage Protection
(opt)
Low Ambient Restart Fault
Evaporator Freeze Protect Evap LWT < Evaporator Freeze SP Rapid Stop Manual
Leaving Evaporator Water
Temperature Sensor Fault
Evaporator Pressure Sensor
Fault
Condenser Pressure Sensor
Fault
Outside Ambient
Temperature Sensor Fault
Evap Pump State = RUN and Flow Switch Digital
Input = No Flow and time greater than Evap Flow
Proof SP
Evaporator Press < Low Evap Pressure SP start
Low Evap Pressure Time Delay – if after Time
Delay if Evap Press > SP continue else stop
Condenser Press > High Condenser Pressure
SP
Digital Input = High Motor Temperature
On Power Up – Delay 150 Sec. before checking
If Phase Voltage Protection = Y, Then Digital
Input = Phase/Voltage Problem
Failed three consecutive low ambient start
attempts
Sensor shorted or open Rapid Stop Manual
Sensor shorted or open Rapid Stop Manual
Sensor shorted or open Rapid Stop Manual
Sensor is open or shorted Rapid Stop Manual
NOTE: Beginning with this software version, two automatic resets per day (beginning at 12:00 am)
are allowed on the flow loss alarm. The Unit State remains on Auto and the evaporator will go back
to Start, waiting for flow.
Action
Taken
Rapid Stop Auto/Manual
Rapid Stop Manual
Rapid Stop Manual
Rapid Stop Manual
Rapid Stop
Rapid Stop Manual
Reset
Phase/Voltage
Input Returns
to Normal
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 37
Page 38

Events (Limit Alarms)
The following events limit the operation of the chiller in some way as described in the
Action Taken column. These alarms are auto-clearing based on reaching the conditions in
the reset column.
Table 21, Events (Limit Alarms)
Description Occurs When: Action Taken Reset
Condenser Pressure
High Unload
Failed Pumpdown
Low Evaporator
Pressure – Hold
Low Evaporator
Pressure – Unload
NOTE: SP = Setpoint
Pressure > High Condenser Stage
Down setpoint
Unit is pumping down for over 60
seconds
Pressure < Low Evap Pressure–Hold
setpoint
Pressure < Low Evap Pressure–
Unload setpoint
Control Functions and Definitions
Control Band
Control Band = Evap delta setpoint * 0.6
Upper and Lower Control Band
The control band is normally centered around the active LWT setpoint. If the chiller is not
set up to use glycol, then the control band will be shifted up relative to the LWT setpoint to
keep the lower end of the control band at least at 39F. If the band doesn’t need to be
shifted to achieve this, it will remain centered on the active LWT setpoint.
Shutoff Stage #2
Shut down unit N/A
Hold @
Stage 1
Shutoff
Stage 2
Condenser Press drops
below (SP – 100psi)
Evap Press rises above
(SP + 8psi)
Evap Press rises above
(SP + 10 psi)
In the staging logic, an upper and lower control band are used. The lower control band is
calculated as follows:
IF Active LWT Setpoint – 39 < 0.5 * Control Band THEN
Lower Control Band = Active LWT Setpoint – 39
ELSE Lower Control Band = 0.5 * Control Band
The upper control band is then Control Band – Lower Control Band
Leaving Water Reset
The leaving water reset input uses a 4-20mA signal to reset the leaving water setpoint to a
higher value. The adjustment varies linearly from 0 to 10F, with a reset of 0 for a 4mA
signal and a reset of 10 for a 20mA signal.
Active LWT Setpoint
The active LWT setpoint represents the current control setpoint based on unit mode and
reset. If unit mode is ice, then the active setpoint is equal to the ice setpoint. If the unit
mode is cool, the active setpoint is the cool setpoint plus the leaving water reset value.
LWT Error
LWT error compares the actual LWT to the active LWT setpoint. The equation is:
LWT error = LWT – active LWT setpoint
LWT Slope
LWT slope is calculated such that the slope represents a time frame of one minute.
Every 12 seconds, the current LWT is subtracted from the value 12 seconds back. This
value is added to a buffer containing values calculated at the last five intervals. The final
result is a slope value that is an average over the past 60 seconds.
38 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 39

Pulldown Rate
The slope value calculated above will be a negative value as the water temperature is
dropping. For use in some control functions, the negative slope is converted to a positive
value by multiplying by –1.
Refrigerant Saturated Temperature
R407C Saturated Temperature
Evaporator dew point and condenser midpoint are calculated using 32-bit math. The
equation is as follows:
If Pressure < 120 psi Then
2
Saturation = [Pressure x 145/105] – [(Pressure
)/2000] – 250
If Pressure >= 120 psi Then
2
Saturation = [Pressure x 46/94] – [Pressure
/25000] + 145
Evaporator Approach
The evaporator approach is calculated for each circuit. The equation is as follows:
Evaporator Approach = LWT – Evaporator Saturated Temperature
Suction Superheat
Suction superheat is calculated for each circuit using the following equation:
Suction superheat = Suction Temperature – Evaporator Saturated Temperature
Pumpdown Pressure
The pressure to which a circuit will pumpdown is based on the Low Evaporator Pressure
Unload setpoint. The equation is as follows:
Pumpdown pressure = Low evap pressure unload – 15 psi , with the calculated value
limited to a minimum of 10 psi.
Unit Enable
Enabling and disabling the chiller is controlled by the Unit Enable Setpoint with options of
OFF and ON. This setpoint can be altered by the Unit OFF input, Remote input, keypad
entry, and BAS request. The Control Source Setpoint determines which sources can change
the Unit Enable Setpoint with options of SWITCHES, KEYPAD or NETWORK.
Changing the Unit Enable Setpoint can be accomplished according to the following table.
NOTE: An “x” indicates that the value is ignored.
Unit Off
Input
OFF x x x x OFF
x SWITCHES OFF x x OFF
ON SWITCHES ON x x ON
ON KEYPAD x OFF x OFF
ON KEYPAD x ON x ON
ON NETWORK x x OFF OFF
ON NETWORK OFF x x OFF
ON NETWORK ON x ON ON
Control Source
Setpoint
Remote
Input
Key-
Pad Entry
BAS
Request
Unit
Enable
Unit Mode
The overall operating mode of the chiller is set by the Unit Mode Setpoint with options of
COOL, COOL w/Glycol, ICE w/Glycol, and TEST. This setpoint can be altered by the
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 39
Page 40

keypad, BAS, and Mode input. Changes to the Unit Mode Setpoint are controlled by two
additional setpoints.
Available Modes Setpoint: Determines the operational modes available at any time with
options of COOL, COOL w/Glycol, COOL/ICE w/Glycol, ICE w/Glycol and TEST.
Control Source Setpoint: Determines the source that can change the Unit Mode Setpoint
with options of KEYPAD, NETWORK, or SWITCHES.
When the Control source is set to KEYPAD, the Unit Mode stays at its previous setting until
changed by the operator. When the Control source is set to BAS, the most recent BAS
mode request goes into effect even if it changed while the Control source was set to
KEYPAD or DIGITAL INPUTS.
Changing the Unit Mode Setpoint can be accomplished according to the following table.
NOTE: An “x” indicates that the value is ignored.
Control Source
Setpoint
x x x x
x x x x COOL w/Glycol COOL w/Glycol
SWITCHES OFF x x COOL/ICE w/Glycol COOL w/Glycol
SWITCHES ON x x COOL/ICE w/Glycol ICE w/Glycol
KEYPAD x COOL w/Glycol x COOL/ICE w/Glycol COOL w/Glycol
KEYPAD x ICE w/Glycol x COOL/ICE w/Glycol ICE w/Glycol
NETWORK x x COOL COOL/ICE w/Glycol COOL w/Glycol
NETWORK x x ICE COOL/ICE w/Glycol ICE w/Glycol
x x x x ICE w/Glycol ICE w/Glycol
x x x x TEST TEST
Mode
Input
Unit Test Mode
The unit test mode allows manual testing of controller outputs. Entering this mode requires
the following conditions.
Unit Switch = OFF
Manager password active.
Available Unit Mode setpoint = TEST
A test menu can then be selected to allow activation of the outputs. It is possible to switch
each digital output ON or OFF and set the analog outputs to any value.
Power Up Start Delay
After powering up the unit, the motor protectors may seem to not work properly for up to
150 seconds. After the control is powered up, no compressor can start for 150 seconds. In
addition, the motor protect inputs are ignored during this time so as to avoid tripping a false
alarm.
Keypad Entry
BAS
Request
Available Modes
Setpoint
COOL
Unit Mode
COOL
Ice Mode Start Delay
An adjustable start to start ice delay timer will limit the frequency with which the chiller
may start in Ice mode. The timer starts when the first compressor starts while the unit is in
ice mode. While this timer is active, the chiller cannot restart in Ice mode. The time delay
is user adjustable.
The ice delay timer may be manually cleared to force a restart in ice mode. A setpoint
specifically for clearing the ice mode delay is available. In addition, cycling the power to
the controller will clear the ice delay timer.
Unit State
The Unit shall always be in one of three states. These states are Off, Auto, and Pumpdown.
Transitions between these states are shown in the following diagram (Figure 13, Unit State
Diagram
40 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
).
Page 41

T1: Off to Auto
All of the following must be true:
Unit Enabled
No Alarm
IF Unit Mode = Ice THEN [Ice Timer Expired]
T2: Auto to Pumpdown
Any of the following must be true:
Keypad Enable = Off
BAS Enable = Off
Remote Switch = Off
Pumpdown Alarm Active
T3: Pumpdown to Off
Any of the following must be true:
Unit Alarm
Unit Switch Off
No Compressors Running
T4: Auto to Off
Any of the following must be true:
Unit Alarm
Unit Switch Off
No Compressors Running AND [Unit Mode = Ice AND Ice Delay Active]
Figure 13, Unit State Diagram
Power On
T3
Pumpdown Auto
Unit State Diagram
Off
T2
T4
T1
Evaporator Water Pump State Control
Operation of the evaporator pump is controlled by the state-transition diagram shown below.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 41
Page 42

Figure 14, Evaporator Pump State
Evaporator Pump
States
Power ON
OFF
T1
T3
T4
RUN
T5
See transition code on following page.
T2
START
42 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 43

Transitions:
T1 – Transition from Off to Start
Requires any of the following
Unit state = Auto
LWT < Freeze setpoint - 1
T2 – Transition from Start to Run
Flow ok for time > evaporator recirculate time
T3 – Transition from Run to Off
Unit state = Off AND LWT > Freeze setpoint
T4 – Transition from Start to Off
Unit state = Off AND LWT > Freeze setpoint
T5 – Transition from Run to Start
Requires all of the following
Evaporator water flow loss for time > evaporator flow proof setpoint
Condenser Fans
Condenser fans are staged up and down based on the fan stage setpoint. These setpoints
define pressures at which fans will start or stop.
Fan 1 will start with the first compressor when the ambient temperature is greater than 75F.
Below 75F, this fan starts when the condenser pressure gets up to the Stage #1 On setpoint.
Fan 2 will start when the condenser pressure gets up to the Stage #2 On setpoint, and fan 3
will start when the condenser pressure gets up to the Stage #3 On setpoint.
Fan 3 will stop when the condenser pressure drops to the Stage #3 Off setpoint, and Fan 2
will stop when the condenser pressure drops to the Stage #2 Off setpoint. Fan 1 will stop
when the pressure drops down to the Stage #1 Off setpoint.
Low OAT Start
In order to avoid low pressure alarms at startup, low OAT start logic allows for running at
low pressures for a longer time than normal as well as multiple start attempts.
A low OAT start is initiated if the condenser saturated temperature is less than 85F when
the compressor starts. Once this happens, the circuit is in this low OAT start state for a time
equal to the low OAT start timer setpoint. During this time, the freezestat logic and the low
pressure events are disabled. The absolute limit of 5 psi is still enforced.
At the end of the low OAT start, the evaporator pressure is checked. If the pressure is
greater than, or equal to, the low evaporator pressure unload setpoint, the start is considered
successful. If the pressure is less than the unload setpoint, the start is not successful and the
compressor will stop. Three start attempts are allowed before tripping on the restart alarm.
So if on the third attempt, the start is not successful, the restart alarm is triggered.
The restart counter is be reset when either a start is successful or the circuit is off on an
alarm.
Circuit Capacity Overrides
The following conditions override the automatic capacity control when the chiller is in Cool
Mode only. These overrides keep the unit from entering a condition in which it is not
designed to run.
Low Evaporator Pressure
If the evaporator pressure drops below the Low Evaporator Pressure Hold setpoint, the Low
Evaporator Pressure Inhibit event is triggered. This can occur with either one or two
compressors running. When triggered, the second compressor will not be allowed to start if
only one is currently running. If both compressors are already running, no action is taken.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 43
Page 44

If the evaporator pressure drops below the Low Evaporator Pressure Unload setpoint, the
Low Evaporator Pressure Unload event is triggered. This can only occur when both
compressors are running. When triggered, one compressor is shut off.
These events are logged to an event log when they occur. Both remain active until the
evaporator pressure rises 5 psi above the hold setpoint or both compressors are off.
High Condenser Pressure
If the discharge pressure rises above the High Condenser Pressure Unload setpoint and both
compressors are running, the High Condenser Pressure Unload event is triggered. One
compressor will be shut off when this occurs.
This event will also be logged to an event log when it occurs. It will remain active until the
condenser pressure drops 100 psi below the unload setpoint. While active, the second
compressor cannot turn back on.
Maximum LWT Rate
The maximum rate at which the leaving water temperature can drop is limited by the
Maximum Pulldown Rate setpoint when the unit mode is Cool. If the rate exceeds this
setpoint, no more compressors can be started until the Pulldown Rate is less than the
setpoint. Running compressors will not be stopped as a result of exceeding the maximum
pulldown rate.
Low Ambient Lockout
If the OAT drops below the low ambient lockout setpoint, then the unit will do a normal
stop. Once the lockout has been triggered, no compressors will start until the OAT rises to
the lockout setpoint plus 5F.
Compressor Control
Compressor Available
A compressor is available to start when the following are true:
Unit state = auto
Evap state = run
Low OAT lockout is not active
Power up start delay is expired
No limit events active
No cycle timers active for the compressor
Compressor enable setpoint = On
Compressor Start/Stop Timing
This section determines when to start or stop a compressor. There are two separate
functions used, one for staging up and one for staging down.
Stage Up Now
The Stage Up Now flag is set based on the following tests:
If Unit mode = Cool, AND
no compressors are running, AND
LWT error > Start delta + Upper Control Band, AND
Motor Protect Timer is expired, AND
Stage up timer is expired, THEN
Stage Up Now = True
ALSO
44 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 45

If Unit Mode = Cool, AND
At least one compressor is running, AND
LWT error > Upper Control Band, AND
Pulldown rate <= Max pulldown rate, AND
Compressors running < unit capacity limit, AND
Stage up timer is expired, THEN
Stage Up Now = True
ALSO
If Unit Mode = Ice, AND
no compressors are running, AND
LWT error > Start delta + Upper Control Band, AND
Motor Protect Timer is expired, AND
Ice Delay Timer is expired, AND
Stage up timer is expired, THEN
Stage Up Now = True
ALSO
If Unit Mode = Ice, AND
LWT error > 0, AND
At least one compressor running, THEN
Stage Up Now = True
Stage Down Now
The Stage Down Now flag is set based on the following tests:
If Unit Mode = Cool, AND
LWT error < -(Lower Control band), AND
More than one compressor is running, AND
Stage down timer is expired, THEN
Stage Down Now = True
ALSO
If Unit Mode = Cool, AND
LWT error < -(Lower Control band) - stop delta, AND
One compressor is running, AND
Stage down timer is expired THEN
Stage Down Now = True
ALSO
If Unit Mode = Cool, AND
Number of compressors running > Demand limit, AND
Stage down timer expired, THEN
Stage Down Now = True
ALSO
If Unit Mode = Ice, AND
LWT error < 0, THEN
Stage Down Now = True
Compressor Sequencing
Compressor staging is based primarily on compressor run-hours and starts. Compressors
that have less starts will normally start before those with more starts. Compressors that
have more run-hours will normally shut off before those with less run-hours.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 45
Page 46

In the event of a tie on number of starts, the lower numbered compressor will start first. In
the event of a tie on run-hours, the lower numbered compressor will shut off first. Run
hours are compared in terms of tens of hours.
Next On = 1 if compressor 1 starts <= compressor 2 starts or compressor 2 not available,
and compressor 1 available
Next On = 2 if compressor 1 starts > compressor 2 starts or compressor 1 not available, and
compressor 2 available
Next Off = 1 if compressor 1 run hours > compressor 2 run hours
Next Off = 2 if compressor 1 run hours <= compressor 2 run hours
Compressor State
A compressor will start when all of the following conditions exist:
The compressor is “next on”
Stage Up Now is set
The compressor is available to start
A compressor will stop when any of the following conditions exist:
Unit state = Off
Low Ambient start attempt failed
Stage Down Now is set, both compressors are running, and the compressor is “next off”
Pumpdown is complete
Normal Shutdown
If a condition arises that requires the unit to shut down, but it is not an emergency situation,
then a pumpdown will be performed. A normal shutdown will be initiated when any of the
following occur:
Unit State = Pumpdown
Circuit Switch = Off
Low Ambient Lockout
A normal stage down occurs, and only one compressor is running
Unit mode = Ice AND the ice setpoint is reached
Pumpdown Procedure
If both compressors are running, shut off the appropriate compressor based on
sequencing logic
With one compressor left running, turn off hot gas output and liquid line output
Keep running until evaporator pressure reaches the pumpdown pressure, then stop
compressor
If evaporator pressure does not reach pumpdown pressure within two minutes, stop
compressor and log pumpdown failure alarm
Rapid Shutdown
A situation may arise that requires the unit to shut down immediately, without doing a
pumpdown. This rapid shutdown will be triggered by any of the following:
Unit State = Off
Stop Alarm
All compressor and liquid line outputs are turned off immediately for a rapid shutdown.
46 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 47

Liquid Line Solenoid
A
t
The liquid line output shall be on any time a compressor is running and the unit is not
performing a pumpdown. This output should be off at all other times.
Using the Controller
4x20 Display & Keypad
The 4-line by 20-character/line liquid crystal display and 6-key keypad are shown below.
Figure 15, Display (in MENU Mode) and Keypad Layout
Key to Screen
Air Conditioni ng
Red Alarm Ligh
<
LARM
<
VIEW
<
MENU Key
SET
ARROW Keys (4)
ENTER Key
Note that each ARROW key has a pathway to a line in the display. Pressing an ARROW
key will activate the associated line when in the MENU mode.
Getting Started
There are two basic procedures to learn in order to utilize the MicroTech II controller:
1. Navigating through the menu matrix to reach a desired menu screen and knowing where
a particular screen is located.
2. Knowing what is contained in a menu screen and how to read that information or how
to change a setpoint contained in the menu screen.
Navigating Through the Menus
The menus are arranged in a matrix of screens across a top horizontal row. Some of these
top-level screens have sub-screens located under them. The general content of each screen
and its location in the matrix are shown in Figure 17. A detailed description of each menu
begins on page 50.
s
There are two way
One is to scroll through the matrix from one screen to another using the four ARROW keys.
to navigate through the menu matrix to reach a desired menu screen.
The other way is to use shortcuts to work through the matrix hierarchy. From any menu
screen, pressing the MENU key will take you to the top level of the hierarchy. The display
will show ALARM, VIEW, and SET as shown in Figure 15. This corresponds to the second
row of screens on Figure 17. One of these groups of screens can then be selected by
pressing the key
For exam
ple, selecting
connected to it via the pathway
ALARM will go the next row of menus under ALARM (ALARM
shown in Figure 15.
LOG or ACTIVE ALARM). Selecting VIEW will go the next level of screens under VIEW
(VIEW UNIT STATUS or VIEW UNIT TEMP). Selecting SET will go to a series of
screens for looking at and changing setpoints.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 47
Page 48

MENU Key
The MENU key is used to switch between the shortcut method (known as the MENU mode
and as shown in Figure 15) and scrolling method (known as the SCROLL mode). The
MENU m
ode is the shortcut to specific groups
of menus used for checking ALARMS, for
VIEWING information, or to SET setpoint values. The SCROLL mode allows the user to
move about the matrix (from one menu to another, one at a time) by using the four ARROW
keys. A typical menu screen is shown in Figure 16.
MENU key from any menu screen will automatically return you to the MENU
Pressing
the
mode as shown in Figure 15.
Figure 16, Display in the Shortcut (SCROLL) M
Menu Screens
Various menus are shown in the controller display. Each menu screen shows specific
information; in some cases menus are used only to view the status of the unit, in some cases
they are used for checking and clearing alarms, and in some case they are used to set
setpoint values.
The menus are arranged in a matrix of screens across a top horizontal row. Some of these
top-level screens have sub-screens located under them. The general content of each screen
and its location in the matrix are shown in Figure 17. A detailed description of each menu
begins on page 50.
Air Conditioni ng
VIEW UNIT STATUS
Unit = COOL
Compr. #1/#2=OFF/OFF
Evap Pump = RUN
ARROW Keys
ode and Keypad Layout
MENU Key
ENTER Key
The
ARROW
keys on the controller are used to navigate through the menus. The keys are
also used to change numerical setpoint values contained in certain menus.
Changing Setpoints
Pressing the ENTER key changes the function of the ARROW keys to the editing function
as shown below:
LEFT key Default
RIGHT key Cancel
UP key Increment
DOWN key Decrement,
, changes a value to the factory-set default value.
, cancels any change made to a value and returns to the original setting.
, increases the value of the setting
decreases the value of a setting.
These four edit functions are indicated by one-character abbreviation on the right side of the
display (this mode is entered by pressing the ENTER key).
Most menus containing setpoint values have several different setpoints shown on one menu.
When in a setpoint menu, the ENTER key is used to proceed from the top line to the second
line and on downward. The cursor will blink at the entry point for making a change. The
ARROW keys (now in the edit mode) are used to change the setpoint as described above.
When the change has been made, press the ENTER key to enter it. No setting is changed
until the ENTER key is pressed.
48 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 49

For example, to change the chilled water setpoint:
1. Press MENU key to go to the MENU mode (see Figure 15).
2. Press SET (the UP
Key) to go to the setpoint menus.
3. Press UNIT SPs (the Right key) to go to setpoints associated with unit operation.
4. Press the DOWN key to scroll down through the setpoint menus to the third menu which
contains Evap LWT=XX.XF.
5. Press the ENTER key to move the cursor down from the top line to the second line in
order to make the change.
6. Use the ARROW keys (now in the edit mode as shown above) to change the setting.
7. When the desired value is achieved, press ENTER to enter it. The cursor will
automatically move down.
At this point, the following actions can be taken:
1. Change another setpoint in this menu by scrolling to it with the ENTER key
2. Using the ENTER key, scroll to the first line in the menu. From there the ARROW keys
can be used to scroll to different menus.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 49
Page 50

Figure 17, Menu Matrix
UNIT COMP REFRIGERANT FANS
VIEW UNIT
STATUS 1-3
TEMP 1-3
(Right side of matrix continued from above)
"ALARM" MENUS "SET" MENUS
ALARM LOG (LAST)
TYPE, TIME
ALARM LOG
(NEXT TO LAST)
ALARM LOG
(SECOND TO LAST)
ALARM LOG
LAST 25 SHOWN
SET UNIT SPs, (5)
SET UNIT SPs, (6)
SET UNIT SPs, (7)
SET UNIT SPs, (8)
SET UNIT SPs, (9)
SET UNIT SPs,
SET UNIT SPs,
SET UNIT SPs,
VIEW COMP #1
STATUS
Continued
ACTIVE ALARM
(1)
TYPE, TIME
ACTIVE ALARM
(2)
TYPE, TIME
ADDITIONAL
ACTIVE ALARM
(3)
CLEAR/VIEW
SET UNIT SPs, (4)
"VIEW" MENUS
VIEW COMP #2
STATUS
SET UNIT SPs, (1)
MODE
SET UNIT SPs, (2)
MODE
COOL/GLYCOL/
ICE
SET UNIT SPs, (3)
TEMP EVAP LWT
MISC
CLOCK
ENGLISH
PROTOCOL
EVAP OFFSET
COND OFFSET
(10) LWT OFFSET
(11) AMBIENT
OFFSET
(12) ENTER
PASSWORD
"MENU"
VIEW EVAP/COND PRESS (1) VIEW UNIT
VIEW EVAP APPROACH (2)
SET COMP
SPs (1)
STOP/START
SET COMP
SPs (2) INTER-
STAGE
SET LIMIT
SET LIMIT
SET LIMIT
SET LIMIT
ALARMS (1)
EVAP PRESS
SET LIMIT
ALARMS (2)
FREEZE/ FLOW
ALARMS (3)
COND PRESS
ALARMS (4)
PHASE/VOLT
LOW AMB
LOCKOUT
ALARMS (5)
LOW EVAP PR
VIEW FAN
STAGING
SET FANS (1)
STAGES
FANTROL
SET FANS (2)
STAGE ON
SET FANS (3)
STAGE OFF
Menu Structure (Hierarchical)
As discussed previously, a hierarchical menu structure can be used to access the various
screens. One to twelve levels are used with two or three being typical. Optionally, the last
menu selection can access one of a set of screens that can be navigated with the UP/DOWN
ARROW keys (see the scrolled menu structure below).
50 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 51

Menu selection is initiated by pressing the MENU key that changes the display from a
regular data screen to a menu screen. Menu selections are then made using the arrow keys
according to labels on the right side of the display (the arrows are ignored). When the last
menu item is selected, the display changes to the selected data screen. An example follows
showing the selection of the “VIEW COMPRESSOR (n) screen.
Suppose the initial screen is as below or any other menu screen:
ALARM LOG
(data)
(data)
(data)
After pressing the MENU key,
the top level menu screen will show:
< ALARM
< VIEW
< SET
After pressing the “VIEW” menu key,
a menu screen will show:
VIEW < UNIT
< COMPRESSOR
< REFRIGRANT
< FANS
Selection of any of these will advance to the appropriate data menu. For example, after pressing the
“REFRIGERANT” menu button, the selected data screen will show:
VIEW REFRIG
PSI F
SAT EVAP XXX.X XX.X
SAT COND XXX.X XX.X
The ARROW keys will automatically return to the “scroll” mode at this time.
Screen Definitions VIEW
This section contains information on each screen. The menu screens are in order of the
matrix in Figure 17, going from left to right and then down when there are sub-menus.
m
Many
enus are self-explanatory.
VIEW UNIT
VIEW UNIT STATUS (1)
Unit = AUTO
Cool Stages=0
Evap Pump = RUN
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 51
Page 52

Unit states can be:
Auto Off:Ice Mode Timer Off:All Comps Disabled
Off:Unit Alarm Off:Keypad Disable Off:Remote Switch
Off:BAS Disable Off:Unit Switch Auto:High LWT Pulldn
Auto:Cycle Timers Auto:Wait for load Auto:OAT Lockout
Auto:Evap Recirc Auto:Wait for flow Auto:Pumpdown
Auto:Evap Press Low Auto:Cond Press High Off:Test Mode
as determined from the Unit State variable, the Unit Mode setpoint, the Unit Enable and the
presence of an alarm.
Pump states can be:
Off Start Run
VIEW UNIT STATUS (2)
Stg Up Delay=XXX sec
Stg Dn Delay=XXX sec
Ice Delay=xxhr XX mn
Ice delay line is only visible when in the ICE mode.
VIEW UNIT STATUS (3)
D.O. D.I.
12345678 123456
00000000 000000
VIEW UNIT TEMP (1)
Evap LWT = XX.XF
Outside Amb = XX.XF
LWT Target = XX.XF
VIEW UNIT TEMP (2)
LWT Pulldn=XX.X F/m
Control Band=XX.X F
VIEW UNIT TEMP (3)
StgUp@ XX.X Dn@ XX.X
Start Unit @ XX.X
Shutdown Unit @ XX.X
See page 38 for an explanation of these settings.
VIEW COMPRESSORS
VIEW COMP#1 (1)
State = OFF LEAD
Cycle Timer: XXmin
Manual Disable
Cycle timer only visible when active. Manual Disable visible only when compressor is
disabled via manual enable setpoint.
52 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 53

VIEW COMP#1 (2)
Hours = XXXXX
Starts = XXXXX
Above two screens duplicated for compressor #2.
VIEW REFRIGERANT
VIEW REFRIG (1)
EVAP Press = XX.Xpsi
COND Press - XX.Xpsi
VIEW REFRIG (2)
Evap Dew = XXX.XF
Cond Mid = XXX.XF
EvapApproach = XX.XF
Approach is the difference between the leaving fluid temperature and the saturated
evaporator temperature. It is an indication of the evaporator efficiency; an increasing
approach temperature indicates decreasing heat transfer efficiency.
VIEW FANS
VIEW FANS
Stages ON = X of X
Screen Definitions – ALARM
ALARM ACTIVE (X) ALARM ACTIVE (X)
Alarm Description No more alarms
hh:mm:ss dd/mmm/yyyy Press ENTER to clear
all active alarms
If the unit is off on a shutdown alarm or running but in a limit alarm condition, the cause
and date will appear in the upper screen. If there is a simultaneous occurrence of more than
one alarm, the others will appear in additional screens below this one, accessed by the
DOWN ARROW. Either type alarm will light a red light in back of the LEFT-KEY. The
light will go out when the fault is cleared.
To clear the fault, scroll down to the last screen and press ENTER. If other faults have
appeared, they will all be cleared at the same time.
ALARM LOG (1)
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 53
Page 54

High Condenser Press
hh:mm:ss d/mmm/yyyy
The last 25 alarms, either shutdown or limit, are shown in this menu with subsequent menus
stored under it. ARROW DOWN from this menu will go to the next-to-last alarm, ARROW
DOWN again will go to the second from last, and so on through the last 25 occurrences.
The screens are numbered (1), (2), (3), etc.
Screen Definitions – SET
Changing setpoints; in general, setpoints are changed as follows:
1. Select the desired menu by scrolling through SET menus with the UP and DOWN
ARROWS.
2. When the desired menu is selected, select the desired entry by moving between lines
using the ENTER key.
3. If a numerical value is being changed, use the INCREMENT key (UP ARROW) to
increase or the DECREMENT key (DOWN ARROW) to decrease the value of the
setpoint.
If a word type setpoint (for example, YES or NO) is to be selected, the choices are
loaded into the menu and selected by scrolling through the available setpoint options
using the UP ARROW key.
4. Enter the desired value or word into the controller by pressing the SET key.
SET UNIT SETPOINTS (SP)
SET UNIT SPs (1)
Unit Enable=OFF
Mode=COOL
Source=KEYPAD
Unit Enable is an external signal or a keypad setting that keeps the unit off when the setting
is OFF and allows it to run if there is a call for cooling. The source for the signal is selected
in the 4
1. KEYPAD, in which case the selection is made in line 2 and would be normally selected
2. SWITCHES, in which an external switch is wired across terminals #25 and #35. (See
3. NETWORK, used with BAS signal, which is wired to the three com
Unit Mode settings can be
1. COOL, normal setting used with chilled water air-condition applications.
2. COOL w/GLYCOL, used with low temperature, glycol applications. It allows a lower
3. ICE w/GLYCOL, used with ice storage systems, allows changing from chilled glycol
th
line and can be:
as ON. This is the normal setting when no external signals are controlling the unit.
wiring diagram page 26).
unication ports.
m
LWT setpoint to be used.
operation to lower temperature ICE operation. In ICE, the unit runs at full load until the
ICE setpoint is reached, at which time the unit shuts off. A three-position switch wired
to terminals #28 and #38 initiates the change from glycol cooling to making ice. (See
wiring diagram on page 26.)
54 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 55

SET UNIT SPs (2)
Available Modes
=COOL w/Glycol
Set w/ FP Switch Off
Available Modes settings can be COOL, COOL w/Glycol, ICE w/Glycol, or TEST as
selected from the available modes imbedded in the menu. The 4
ON/OFF switch on the front panel (FP) must be in the OFF position before the MODE can
be changed. This prevents a mode change while the unit is operating.
th
line is a reminder that the
SET UNIT SPs (3)
Evap LWT = XX.XF
Ice LWT = XX.XF
EvapDeltaT= XX.XF
SET UNIT SPs (4)
StartDelta= XX.XF
StopDelta= XX.XF
Staging
StartDelta is the number of degrees above the temperature setting that determines when the
lead compressor starts. Compressor start and stop is determined by the control band and
StartDelta settings. The control band is automatically set of 60% of the EvapDeltaT (chilled
water temperature in minus chilled water temperature out) selected in menu 3 above. The
staging routine has been changes in this software version compared to previous versions.
See page 38 for more details and an example.
a warm
For
temperature. The lag will start after the start interval has timed out. The chilled water
temperature will begin to be pulled down. At shut down temperature, the lag compressor
will shut off. If the temperature climbs above that temperature within the StageDownTimer
setting (default at 30 sec.), the lead compressor will remain on. This would be normal
operation. If for some reason the temperature does not rise, the lead compressor will also
shut off.
start-up the lead compressor will start at any temperature above the start
SET UNIT SPs (5)
Max Pulldn=X.XF/min
Evap Recirc= XXX sec
LowAmbLock= XX.X F
SET UNIT SPs (6)
Ice Time Delay=XXhrs
Clear Ice Delay=No
SET UNIT SPs (7)
CLOCK
dd/mmm/yyyy
hh:mm:ss
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 55
Page 56

SET UNIT SPs (8)
Units = F/psi
Lang = ENGLISH
Refrig = Select Type
Units settings are only °F/psi at the present time. °C/kPa will be available later.
Lang (Language) settings can be only ENGLISH at present.
Refrig (Refrigerant) selection is done at the factory prior to shippment.
SET UNIT SPs (9)
Protocol = NONE
Ident Number=001
Baud Rate=9600
SET UNIT SPs (10)
Evaporator Refrig
Press Sensor
Offset= 00.0 psi
The pressure/temperature offsets on menus 10 through 13 correct the controller's display of
the parameters. The sensors used in these units have a high degree of repeatability but may
need correction (offset). An accurate pressure gauge or thermometer is used to determine
the correct temperature or pressure. A positive or negative offset value is then entered to
make the controller reading agree with the measured value.
SET UNIT SPs (11)
Condenser Refrig
Press Sensor
Offset= 00.0 psi
SET UNIT SPs (12)
Leaving Evaporator
Water Temp Sensor
Offset= 00.0oF
SET UNIT SPs (13)
Outside Ambient
Temperature Sensor
Offset= 00.0oF
SET UNIT SPs (14)
ENTER PASSWORD XXXX
Active Password
Level:None
Two four-digit passwords provide OPERATOR and MANAGER levels of access to
changeable parameters. The passwords are preprogrammed into the controller. The
Operator Password is 0100. Either password must be entered using the ENTER
PASSWORD (12) screen before a protected setting can be changed.
56 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 57

This screen can be accessed either through the SET OTHER menu or by simply pressing the
ENTER key while on one of the SET screens. The controller will automatically go from the
screen with the setting change to this screen. After the correct password has been entered,
the controller will automatically return to the original set screen.
Once a password has been entered, it remains valid for 15 minutes after the last key-press.
SET COMP SPs
SET COMP SPs (1)
Clear Cycle Tmr=No
Stop-Start =XXmin
Start-Start =XXmin
This menu sets the anti-recycle timers. Stop-Start is the time required before starting a
compressor after it has stopped. Start-Start is the time required before starting a compressor
after the last time it has started. It recommended that these default values not be changed.
SET COMP SPs (2)
InterStageUp=XXXsec
InterStageDn=XXXsec
InterStageUp is the time delay since the last stage change before a compressor can stage on.
InterStageDn is the time delay since the last stage change before a compressor can stage off
normally (not by an alarm).
SET COMP SPs (3)
Compressor 1=Enable
Compressor 2=Enable
ALARM SETPOINTS
SET ALARM LMTS (1)
LowEvPr
Hold=XXXpsi
Unload=XXXpsi
The LowEvPrHold and LowEvPrUnld have the same default value of 59 psi. If two
compressors are running, the LowEvPrUnld is in effect and the lag compressor will be shut
off to unload the unit. If one compressor is running, the LowEvPrHold is in effect and the
lag compressor is prevented from starting, thereby holding the unit capacity.
The last action to take place is the shutoff of all compressors running when the
LowEvPrStop setting is reached (default is 58 psi).
SET ALARM LMTS (2)
Evap Freeze= XX.XF
EvapFlowProof=XXXsec
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 57
Page 58

Evap Freeze (the unit freeze protection shutdown) is actually a stop alarm and shuts off the
unit when the LWT reaches 36F. It is cleared by going to the CLEAR ALARM menu in
the ACTIVE ALARM hierarchy.
EvapFlowProof is the flow switch interlock. Closing the flow switch and therefor proving
the existence of chilled water flow resets this trip.
SET ALARM LMTS (3)
High Cond Pressure
Unload = XXXpsi
Stop = XXXpsi
HighCondPr (the unit high-discharge-pressure shutdown) is a stop alarm that shuts off the
unit when the discharge pressure reaches the setting. The default setting is 380 psi. The
Stop is a shutdown alarm that stops the unit when the discharge pressure reaches the
setpoint.
SET ALARM LMTS (4)
PhaseVoltage=YES/NO
LowOATLockTmr=XXXsec
LowAmbientLock prevents unit operation below the setting. If the unit is equipped with the
standard FanTrol pressure-activated control, the available range is 35F to 60F with a
default of 35F. With the optional SpeedTrol variable speed control, the range becomes
–2F to 60F with default of 0F. Input to line 3 of the next screen, SET FANS SP (1),
informs the controller which type of control is installed and which range of setting to allow.
SET FANS STAGES
SET FANS SPs (1)
Fan Stages= X
Speedtrol = NO
The Fans line tells the controller the number of fans on the unit. The UP ARROW toggles
between 1, 2, and 3. 1 is not used; 2 should be used for Models AGZ 010, 013, and 017;
and 3 should be used for AGZ 020, 025, 029, and 034.
Speedtrol tells the controller whether the optional SpeedTrol is installed in the unit. The UP
ARROW toggles between YES and NO. The setting changes the range available: YES =
35F to 60F, with 35F being the recommended setting; NO = -2F to 60F, with 0F
being the recommended setting.
SET FANS SPs (2)
Stage ON psi
#1 #2 #3
XXX XXX XXX
SET FANS SPs (3)
Stage Off psi
#1 #2 #3
UNIT XXX XXX
58 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 59

These two menus set the on and off staging pressures for the fans. The third fan stage
setting is only for three fan units. These settings are used with both FanTrol and SpeedTrol.
SpeedTrol takes effect when the last fan is running after FanTrol cycles off the others.
Screen Definitions – TEST
The test screens are only available when the unit is in TEST mode. Using these screens, any
digital output can be controlled manually.
TEST UNIT (1)
Alarm Signal= OFF
Evap Water Pump=OFF
TEST UNIT (2)
Liquid Line Sol=OFF
Compressor #1 = OFF
Compressor #2 = OFF
TEST UNIT (3)
Fan Motor #1 = OFF
Fan Motor #2 = OFF
Fan Motor #3 = OFF
Editing, Review
Editing is accomplished by pressing the ENTER key until the desired field is selected. This
field is indicated by a blinking cursor under it. The arrow keys shall then operate as defined
below.
CANCEL ................... Reset the current field to the value it had when editing began.
DEFAULT ................. Set value to original factory setting.
INCREMENT ............ Increase the value or select the next item in a list.
DECREMENT ........... Decrease the value or select the previous item in a list.
During edit mode, the display shall show a two-character-wide menu pane on the right as
shown below.
SET UNIT SPs (X) <D
(data) <C
(data) <+
(data) <-
Additional fields can be edited by pressing the ENTER key until the desired field is
selected. When the last field is selected, pressing the ENTER key switches the display out
of “edit” mode and returns the ARROW keys to “scroll” mode.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 59
Page 60

BAS Interface
Daikin's Protocol Selectability feature is available as a factory-installed option or as a retrofit
item available for installation after the unit is shipped.
If an interface module was ordered, one of the following
was shipped with the equipment. Additional copies of referenced Daikin’s documents may be
obtained from the local Daikin sales office, from the local Daikin Factory Service office,
from the Daikin Technical Response Center, located in Staunton, Virginia (540-248-0711) or
downloaded from www,DaikinApplied.com.
IM 735, L
IM 736, BACnet Communication Module Installation
IM 743, Modbus Communication Module Installation
ED 15062-0, Microtech II Chiller Protocol Information – BACnet and L
ED 15063-0, Microtech II Chiller Unit Controller Protocol Information – Modbus
The above are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies: BACnet from the
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc., LonTalk,
LONMARK and LONWORKS from Echelon Corporation, and Modbus and ModbusRTU from
Schneider Electric.
ONWORKS Communication Module Installation
BAS interface installation manuals
ONWORKS
60 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 61

Service
Disconnect and tag out all power sources to the unit before doing any service inside the unit.
Failure to do so can cause severe personal injury or death.
Service on this equipment is to be performed by qualified service personnel with special
regard to regulations concerning release of refrigerant to the atmosphere.
Note: Repeated tripping of equipment protection controls must be investigated and
corrected.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is responsible for allowing the proper amount of refrigerant to enter
the evaporator regardless of cooling load. It does this by maintaining a constant superheat.
(Superheat is the difference between refrigerant temperature as it leaves the evaporator and
the saturation temperature corresponding to the evaporator pressure.) Typically, superheat
should run in the range of 8F to 12F (4.4C to 6.6C).
!
WARNING
!
CAUTION
The superheat setting can be adjusted by removing the cap at the bottom of the valve to
expose the adjustment screw. Turn the screw clockwise (when viewed from the adjustment
screw end) to increase the superheat setting and counterclockwise to reduce superheat.
Allow time for system rebalance after each superheat adjustment.
The expansion valve, like the solenoid valve, should not normally require replacement, but
if it does the unit must be pumped down by following the steps involved when changing a
filter-drier.
If the problem can be traced to the power element only, unscrew the element from the valve
body without removing the valve, but only after pumping the unit down.
Filter-Driers
If the pressure drop across the filter-drier is in the 6 to 10 psi range, it should be monitored
and changed when the pressure drop reaches 10 psi. To change the liquid line sealed filter,
de-energize the unit and pump out the refrigerant. After changing the filter-drier, check for
leaks before recharging and returning unit to operation.
Liquid Line Solenoid
The liquid line solenoid valve does not normally require any maintenance. It may, however,
require replacement of the solenoid coil. The solenoid coil may be removed from the valve
body without opening the system by disconnecting power to the unit. The coil can then be
removed from the valve body by simply removing the nut or snap ring located at the top of
the coil.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 61
Page 62

Optional Controls
SpeedTrol Head Pressure Control
The SpeedTrol method of head pressure control operates in conjunction with FanTrol by
modulating the motor speed on system #1 fan in response to condenser pressure. By
reducing the speed of the last fan as the condensing pressure falls, the unit can operate to
0F (-18C) ambient air temperature.
The SpeedTrol fan motor is a single-phase, 230/460 volt, thermally protected motor
specially designed for variable speed operation. The solid-state speed control is mounted in
the unit control panel and is connected to a Schrader fitting on the liquid line. The control is
factory-set to start modulating fan speed at 230 psig, and it will maintain a minimum
condensing pressure of 170 to 180 psig. Minimum starting voltage for SpeedTrol motors is
120 volts.
A low ambient timer function is included in the microprocessor. When the solenoid valve
and lead compressor are energized by the controller, the low pressure cutout control is
bypassed and the compressor is allowed to start with the low pressure control open.
After about 2-3/4 minutes, the time delay will open and the low pressure cutout function is
again operable. If the system has not built up enough evaporator pressure to close the low
pressure setting, the compressor will stop.
Due to the vertical condenser design, it is recommended that the unit be oriented so that
prevailing winds blow parallel to the unit length, thus minimizing effects on minimum
ambient operation. If it is not practical to orient the unit in this manner, a wind deflector
should be constructed.
Hot Gas Bypass
Hot gas bypass is a system for maintaining evaporator pressure at or above a minimum
value. The purpose for doing this is to keep the velocity of the refrigerant as it passes
through the evaporator high enough for proper oil return to the compressor when cooling
load conditions are light. It also maintains continuous operation of the chiller at light load
conditions.
The solenoid valve should be wired to open whenever the liquid line solenoid valve is
energized. This can be accomplished by wiring the hot gas solenoid (SV5) in parallel with
the liquid line solenoid at terminals 14 and 16. The pressure-regulating valve is factory-set
to begin opening at 58 PSIG when the air-charged bulb is in an 80F ambient temperature.
The bulb can be mounted anywhere as long as it senses a fairly constant temperature at
various load conditions. The compressor suction line is one such mounting location. It is
generally in the 50F to 60F range.
eratures, the valve will
Figure 19 indicates that when the bulb is sensing 50F to 60F tem
begin opening at 54 PSIG. This setting can be changed as indicated above, by changing the
pressure setting, remove the cap on the bulb and turn the adjustment screw clockwise. To
lower the setting, turn the screw counterclockwise. Do not force the adjustment beyond the
range it is designed for, as this will damage the adjustment assembly.
The regulating valve opening point can be determined by slowly reducing the system load
(or increasing the required chiller water temperature setting indicated on the unit
thermostat), while observing the suction pressure. When the bypass valve starts to open, the
refrigerant line on the evaporator side of the valve will begin to feel warm to the touch.
p
62 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 63

!
y
b
WARNING
The hot gas line may become hot enough to cause injury in a very short time. Avoid contact
during valve checkout.
On installations where the condensing unit is remote from the evaporator, it is recommended
that the hot gas bypass valve be mounted near the condensing unit to minimize the amount
of refrigerant that will condense in the hot gas line during periods when hot gas bypass is
not required.
Figure 18, Hot Gas Bypass Piping
Suction Line
Hot Gas Bypass
Solenoid Valve
Adjustable
Remote Bul
External Equalizer
Connection to Suction
Side of Evaporator
Discharge
Line
Hot Gas
pass Valve
B
To Evaporator Inlet
After Expansion Valve
Figure 19, Hot Gas Bypass Adjustment
80
70
60
50
40
VALVE OPENING PRESSURE (PSIG)
30
30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110
REMOTE BULB ADJUSTMENT RANGE
M
U
IM
X
A
M
G
N
I
T
T
E
S
Y
OR
T
C
A
F
M
U
M
I
N
I
M
TEMP (°F) AT BULB LOCATION
RANGE
ADJUSTMENT
MODEL AGZ 029 – 034, Post 2004 Production
Model AGZ 029 and 034 built after January 2004 may have a hot gas bypass valve as
shown as shown in Figure 20.
The valve is adjusted using the adjusting screw show in the drawing.
The range is 0
to 100
psi with about 16 psi change for one turn of the screw. Turning clockwise will increase the
valve setting.
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 63
Page 64

The load must be varied to properly set these valves. The load should be decreased so that
the suction pressure decreases. The valve is then adjusted to maintain the correct suction
pressure, which is the normal pressure at full load. The load should then be increases above
the valve setting so that it closes. Operation can be checked by again reducing the load and
noting when the valve opens (a hissing sound and/or pressure rise at the valve outlet
indicates that the valve has opened).
Figure 20, ACZ 033 - 039 Hot Gas Bypass Valve
Adjusting
Screw
64 AGZ 010B through 034B IOMM 1155
Page 65

Troubleshooting Chart
Troubleshooting can present risks of severe personal injury or death from burns, cuts,
electrocution, strangulation and asphyxiation. Troubleshooting must be done by trained,
experienced technicians only.
Table 22, Troubleshooting Chart
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSES POSSIBLE CORRECTIVE STEPS
1. Main switch open
Fuse blown, breakers open
2.
COMPRESSOR
WILL NOT RUN
COMPRESSOR
NOISY OR
VIBRATING
HIGH
DISCHARGE
PRESSURE
LOW
DISCHARGE
PRESSURE
HIGH SUCTION
PRESSURE
LOW SUCTION
PRESSURE
UNIT WILL NOT
LOAD OR
UNLOAD
LOAD/UNLOAD
INTERVAL TOO
SHORT
COMPRESSOR
LOSES OIL
MOTOR
OVERLOAD
RELAYS OPEN
OR BLOWN
FUSES
COMPRESSOR
THERMAL
SWITCH OPEN
3. Thermal overloads tripped
4. Defective contactor or coil
5. System off by protection device
6. No cooling required
7. Liquid line solenoid will not open
8. Motor electrical problem
9. Loose wiring
1. Refrigerant flooding compressor
Improper line support
2.
3. Wo
rn compressor
1. Noncondensables in system
2.
Refrigerant overcharge
3. Fan not running
4. Dirty condenser coils
5. FanTrol out of adjustment
1. Faulty condenser control
2.
Low refrigerant charge
3. Low suction pressure
1. Excessive load
2. Expansion valve overfeeding
1. Lack of refrigerant
Evaporator dirty
2.
3. Clogged filter-drier
4. Expansion valve malfunctioning
5. Low condensing temperature
1 Faulty controller sensor/broken wire
2. Stages not set for application
1. Erratic water thermostat
2.
Insufficient wa
1. Lack of refrigerant
Suction superheat too high
2.
3. Crankcase heater burned out
1. Low voltage during high loads
2.
Defective or grounded motor wiring
3. Loose power w
4.
High condensing temperature
5. Unbalanced voltage
1. Operating beyond design conditions 1. Add facilities so conditions are within allowable
ter flow
iring
!
WARNING
1. Close switch
2. Check electrical circuits and motor windings for
shorts. Check for overloads and loose
connections. Replace fuse or reset breaker.
3.
Check unit when back on line, auto reset
4. Repair or replace
5. Determine cause and correct
6. None, should start on call for cooling
7. Repair or replace coil
8. Check motor for open or short circuit, or burnout
9. Check all wire junctions. Tighten all terminals.
Check expansion valve setting
1.
2. Relocate or add supports
3. Replace
1. Remove with authorized procedures
Remove excess
2.
3. Check electrical circuit
4. Clean coil
5. Adjust FanTrol setting
1. Check condenser control operation
2. Check for leaks. Add refrigerant
3. See low suction pressure steps below
1. Reduce load or add capacity
2. Check remote bulb. Regulate superheat
1. Check for leaks. Repair and replace refrigerant.
2. Clean chemically
3. Replace
4. Check and adjust for proper superheat
5. Check discharge pressure control settings
1.
Replace
2. Adjust thermostat setting
1. Replace
2.
Adjust flow
1. Check for leaks and repair
2. Adjust superheat
3. Replace crankcase heater
1. Check supply voltage
2. Replace compressor
3. Check all connections and tighten
4. See steps for high discharge pressure
5. Check voltage. Contact power company.
limits
IOMM 1155 AGZ 010B through 034B 65
Page 66

Daikin Training and Development
Now that you have made an investment in modern, efficient Daikin equipment, its care
should be a high priority. For training information on all Daikin HVAC products, please visit
us at www.DaikinApplied.com and click on training, or call 540-248-9646 to speak to the
Training Department.
Warranty
All Daikin equipment is sold pursuant to Daikin's Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale
and Limited Product Warranty. Consult your local Daikin Representative for
warranty details. Refer to form 933-430285Y. To find your local representative, go
to www.DaikinApplied.com
This document contains the most current product information as of this printing. For the
most up-to-date product information, please go to www.DaikinApplied.com.
Daikin Applied
800.432.1342
www.DaikinApplied.com
IOMM 1155 (3/12)
 Loading...
Loading...