Page 1

R282-Z96
AMD EPYC™ 7002 DP Server System - 2U 12-Bay GPU & NVMe sku
User Manual
Rev. 1.0
Page 2

Copyright
© 2021 GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
The trademarks mentioned in this manual are legally registered to their respective owners.
Disclaimer
Information in this manual is protected by copyright laws and is the property of GIGABYTE.
Changes to the specications and features in this manual may be made by GIGABYTE without
prior notice. No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, translated, transmitted, or
published in any form or by any means without GIGABYTE's prior written permission.
Documentation Classications
In order to assist in the use of this product, GIGABYTE provides the following types of documentation:
User Manual: detailed information & steps about the installation, conguration and use of this
product (e.g. motherboard, server barebones), covering hardware and BIOS.
User Guide: detailed information about the installation & use of an add-on hardware or
software component (e.g. BMC rmware, rail-kit) compatible with this product.
Quick Installation Guide: a short guide with visual diagrams that you can reference easily for
installation purposes of this product (e.g. motherboard, server barebones).
Please see the support section of the online product page to check the current availability of these
documents.
For More Information
For related product specications, the latest rmware and software, and other information please visit our website at
http://www.gigabyte.com
For GIGABYTE distributors and resellers, additional sales & marketing materials are available from our reseller
portal: http://reseller.b2b.gigabyte.com
For further technical assistance, please contact your GIGABYTE representative or visit
https://esupport.gigabyte.com/ to create a new support ticket
For any general sales or marketing enquiries, you may also message GIGABYTE server directly by email:
server.grp@gigabyte.com
Page 3

Conventions
The following conventions are used in this user's guide:
NOTE!
Pieces of additional
information related to the current topic.
CAUTION!
Precautionary measures to
avoid possible hardware or software problems.
WARNING!
Alerts to any damage that might
result from doing or not doing specic actions.
Page 4

Server Warnings and Cautions
Before installing a server, be sure that you understand the following warnings and cautions.
WARNING!
To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to the equipment:
• Do not disable the power cord grounding plug. The grounding plug is an important safety
feature.
• Plug the power cord into a grounded (earthed) electrical outlet that is easily accessible at all
times.
• Unplug the power cord from the power supply to disconnect power to the equipment.
• Do not route the power cord where it can be walked on or pinched by items placed against it.
Pay particular attention to the plug, electrical outlet, and the point where the cord extends from
the server.
WARNING!
To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow the drives and the internal
system components to cool before touching them.
WARNING!
This server is equipped with high speed fans. Keep away from hazardous moving fan
blades during servicing.
CAUTION!
• Do not operate the server for long periods with the access panel open or removed. Operat-
ing the server in this manner results in improper airow and improper cooling that can lead to
thermal damage.
• Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
• Replace battery with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
• Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
CAUTION!
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced incorrectly or with an incorrect type. Replace the battery
only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Page 5

Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
CAUTION!
ESD CAN DAMAGE DRIVES, BOARDS, AND OTHER PARTS. WE RECOMMEND THAT YOU
PERFORM ALL PROCEDURES AT AN ESD WORKSTATION. IF ONE IS NOT AVAILABLE,
PROVIDE SOME ESD PROTECTION BY WEARING AN ANTI-STATIC WRIST STRAP ATTACHED TO CHASSIS GROUND -- ANY UNPAINTED METAL SURFACE -- ON YOUR SERVER
WHEN HANDLING PARTS.
Always handle boards carefully, they can be extremely sensitive to ESD. Hold boards only by
their edges without touching any components or connectors. After removing a board from its
protective ESD bag or from the system, place the board component side up on a grounded, static
free surface. Use a conductive foam pad if available but not the ESD bag. Do not slide the board
over any surface.
System power on/off: To service components within the server, please ensure the power has
been disconnected.
e.g. Remove the node from the server chassis (to disconnect power) or disconnect the power
from the server chassis.
Make sure the system is removed from the rack before opening the chassis, adding, or removing
any non hot-plug components.
Hazardous conditions, devices and cables: Hazardous electrical conditions may be present
on power, telephone, and communication cables. Turn off the system chassis and disconnect the
cables attached to the system before servicing the chassis. Otherwise, personal injury or equipment damage can result.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) and ESD protection: ESD can damage drives, boards, and
other parts. We recommend that you perform all procedures in this chapter only at an ESD workstation. If one is not available, provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap
attached to chassis ground (any unpainted metal surface on the server) when handling parts.
ESD and handling boards: Always handle boards carefully. They can be extremely sensi-tive to
electrostatic discharge (ESD). Hold boards only by their edges. After removing a board from its
protective wrapper or from the system, place the board component side up on a grounded, static
free surface. Use a conductive foam pad if available but not the board wrapper. Do not slide
board over any surface.
Page 6

Installing or removing jumpers: A jumper is a small plastic encased conductor that slips over
two jumper pins. Some jumpers have a small tab on top that can be gripped with n-gertips or
with a pair of ne needle nosed pliers. If the jumpers do not have such a tab, take care when us-
ing needle nosed pliers to remove or install a jumper; grip the narrow sides of the jumper with the
pliers, never the wide sides. Gripping the wide sides can dam-age the contacts inside the jumper,
causing intermittent problems with the function con-trolled by that jumper. Take care to grip with,
but not squeeze, the pliers or other tool used to remove a jumper, or the pins on the board may
bend or break.
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Hardware Installation ...................................................................................11
1-1 Installation Precautions .................................................................................. 11
1-2 Product Specications .................................................................................... 12
1-3 System Block Diagram ................................................................................... 16
Chapter 2 System Appearance ..................................................................................... 17
2-1 Front View ...................................................................................................... 17
2-2 Rear View ....................................................................................................... 18
2-3 Front Panel LEDs and Buttons ....................................................................... 19
2-4 Rear System LAN LEDs ................................................................................. 21
2-5 Power Supply Unit LED .................................................................................. 22
2-6 Hard Disk Drive LEDs .................................................................................... 23
Chapter 3 System Hardware Installation ......................................................................25
3-1 Removing and Installing the Chassis Cover .................................................. 26
3-2 Removing and Installing the Fan Duct ........................................................... 27
3-3 Removing and Installing the Heat Sink .......................................................... 28
3-4 Removing and Installing the CPU .................................................................. 29
3-5 Removing and Installing Memory ................................................................... 31
3-5-1 Eight-Channel Memory Conguration ....................................................................31
3-5-2 Removing and Installing a Memory Module ...........................................................32
3-5-3 Processor and Memory Module Matrix Table .........................................................32
3-5-4 DIMM Population Table ..........................................................................................33
3-6 Removing and Installing the GPU Card ......................................................... 34
3-7 Installing the Mezzanine Card ........................................................................ 36
3-7-1 Installing the OCP 3.0 Mezzanine Card .................................................................36
3-7-2 Installing the OCP 2.0 Mezzanine Card .................................................................37
3-8 Removing and Installing the Hard Disk Drive ................................................. 38
3-9 Installing and Removing an M.2 Device ......................................................... 40
3-10 Replacing the Fan Assembly .......................................................................... 41
3-11 Removing and Installing the Power Supply ....................................................42
3-12 Cable Routing ................................................................................................43
Chapter 4 Motherboard Components ...........................................................................49
4-1 Motherboard Components ............................................................................. 49
4-2 Jumper Settings ............................................................................................. 51
Chapter 5 BIOS Setup ..................................................................................................53
- 7 -
Page 8

5-1 The Main Menu .............................................................................................. 55
5-2 Advanced Menu ............................................................................................. 58
5-2-1 Trusted Computing .................................................................................................59
5-2-2 PSP Firmware Versions ..........................................................................................60
5-2-3 Legacy Video Select ...............................................................................................61
5-2-4 AST2500 Super IO Conguration ...........................................................................62
5-2-5 S5 RTC Wake Settings ...........................................................................................64
5-2-6 Serial Port Console Redirection .............................................................................65
5-2-7 CPU Conguration ..................................................................................................68
5-2-8 PCI Subsystem Settings .........................................................................................69
5-2-9 USB Conguration ..................................................................................................71
5-2-10 NVMe Conguration ...............................................................................................73
5-2-11 SATA Conguration.................................................................................................74
5-2-12 Network Stack Conguration ..................................................................................75
5-2-13 AMD Mem Conguration Status .............................................................................76
5-2-14 iSCSI Conguration ................................................................................................77
5-2-15 Tls Auth Conguration ............................................................................................78
5-2-16 Intel(R) I350 Gigabit Network Connection ..............................................................79
5-2-17 VLAN Conguration ................................................................................................81
5-2-18 MAC IPv4 Network Conguration ...........................................................................83
5-2-19 MAC IPv6 Network Conguration ...........................................................................84
5-3 AMD CBS Menu ............................................................................................. 85
5-3-1 Valhalla Common Options ......................................................................................86
5-3-2 DF Common Options ..............................................................................................89
5-3-3 UMC Common Options ..........................................................................................92
5-3-4 NBIO Common Options ..........................................................................................94
5-3-5 FCH Common Options ...........................................................................................99
5-3-6 NTB Common Options .........................................................................................102
5-3-7 SOC Miscellaneous Control .................................................................................103
5-4 AMD PBS Option Menu ............................................................................... 104
5-4-1 RAS ......................................................................................................................105
5-5 Chipset Setup Menu ..................................................................................... 107
5-6 Server Management Menu ........................................................................... 108
5-6-1 System Event Log ................................................................................................11 0
5-6-2 View FRU Information ..........................................................................................111
5-6-3 BMC Network Conguration .................................................................................11 2
5-6-4 IPv6 BMC Network Conguration .........................................................................11 3
5-7 Security Menu .............................................................................................. 11 4
5-7-1 Secure Boot ..........................................................................................................11 5
5-8 Boot Menu .................................................................................................... 11 7
5-8-1 UEFI NETWORK Drive BBS Priorities .................................................................11 9
- 8 -
Page 9

5-8-2 UEFI Application Boot Priorities ............................................................................120
5-9 Save & Exit Menu ......................................................................................... 121
5-10 ABL POST Codes ........................................................................................ 122
5-10-1 Start Processor Test Points ..................................................................................122
5-10-2 Memory test points ...............................................................................................122
5-10-3 PMU Test Points ...................................................................................................122
5-10-4 Original Post Code ...............................................................................................123
5-10-5 CPU test points .....................................................................................................124
5-10-6 Topology test points ..............................................................................................124
5-10-7 Extended memory test point .................................................................................124
5-10-8 Gnb Earlier init ......................................................................................................125
5-10-9 PMU test points ....................................................................................................128
5-10-10 ABL0 test points ...................................................................................................128
5-10-11 ABL5 test points ................................................................................................128
5-11 Agesa POST Codes ..................................................................................... 132
5-11-1 Universal Post Code .............................................................................................132
5-11-2 [0xA1XX] For CZ only memory Postcodes ...........................................................132
5-11-3 S3 Interface Post Code ........................................................................................135
5-11-4 PMU Post Code ....................................................................................................135
5-11-5 [0xA5XX] assigned for AGESA PSP Module ........................................................135
5-11-6 [0xA9XX, 0xAAXX] assigned for AGESA NBIO Module .......................................138
5-11-7 [0xACXX] assigned for AGESA CCX Module .......................................................140
5-11-8 [0xADXX] assigned for AGESA DF Module ..........................................................141
5-11-9 [0xAFXX] assigned for AGESA FCH Module ........................................................141
5-12 BIOS POST Beep code (AMI standard) ....................................................... 143
5-12-1 PEI Beep Codes ...................................................................................................143
5-12-2 DXE Beep Codes .................................................................................................143
- 9 -
Page 10

This page intentionally left blank
- 10 -
Page 11

Chapter 1 Hardware Installation
1-1 Installation Precautions
The motherboard/system contain numerous delicate electronic circuits and components which
can become damaged as a result of electrostatic discharge (ESD). Prior to installation, carefully
read the service guide and follow these procedures:
• Prior to installation, do not remove or break motherboard S/N (Serial Number) sticker or
warranty sticker provided by your dealer. These stickers are required for warranty validation.
• Always remove the AC power by unplugging the power cord from the power outlet before
installing or removing the motherboard or other hardware components.
• When connecting hardware components to the internal connectors on the motherboard,
make sure they are connected tightly and securely.
• When handling the motherboard, avoid touching any metal leads or connectors.
• It is best to wear an electrostatic discharge (ESD) wrist strap when handling electronic
components such as a motherboard, CPU or memory. If you do not have an ESD wrist
strap, keep your hands dry and rst touch a metal object to eliminate static electricity.
•
Prior to installing the motherboard, please have it on top of an antistatic pad or within an
electrostatic shielding container.
• Before unplugging the power supply cable from the motherboard, make sure the power
supply has been turned off.
• Before turning on the power, make sure the power supply voltage has been set according to
the local voltage standard.
• Before using the product, please verify that all cables and power connectors of your
hardware components are connected.
• To prevent damage to the motherboard, do not allow screws to come in contact with the
motherboard circuit or its components.
• Make sure there are no leftover screws or metal components placed on the motherboard or
within the computer casing.
• Do not place the computer system on an uneven surface
• Do not place the computer system in a high-temperature environment.
• Turning on the computer power during the installation process can lead to damage to
system components as well as physical harm to the user.
• If you are uncertain about any installation steps or have a problem related to the use of the
product, please consult a certied computer technician.
.
- 11 - Hardware Installation
Page 12
1-2 Product Specications
NOTE:
We reser ve the right to make any changes to the product specications and p roduct-related
information without prior notice.
CPU
Chipset
Memory
LAN
Video
AMD EPYC™ 7002 series processor family
Dual processors, 7nm, Socket SP3
Up to 64 -core, 128 threads per processor
TDP up to 225W, cTDP up to 240W
Conditional support 280W
NOTE: If only 1 CPU is installed, some PCIe or memory functions might be
unavailable
Compatible with AMD EPYC™ 7001 series processor family
System on Chip
32 x DIMM slots
DDR4 memory supported only
8-Channel memory per processor architecture
RDIMM modules up to 128GB supported
LRDIMM modules up to 128GB supported
Memory speed: Up to 3200*/ 2933 MHz
NOTE: Follow BIOS setting and memory QVL list if running 3200 Mhz with 2DPC
2 x 1GbE LAN port (1 x Intel® I350 -AM2)
1 x 10/100/1000 management LAN
Integrated in Aspeed® AST2500
2D Video Graphic Adapter with PCIe bus interface
1920x1200@60Hz 32bpp
Hardware Installation - 12 -
Page 13
Expansion Slot
Storage
Riser Card CRS2014:
1 x PCIe x16 slot (Gen4 x16), FHFL
Riser Card CRS2026:
2 x PCIe x16 slot (Gen4 x16), FHFL
Riser Card CRS2026:
1 x PCIe x16 slot (Gen4 x16), FHFL
- 1 x PCIe x16 slot (Gen4 x16); Occupied by CNV3134, 4 x NVMe Gen4
HBA
1 x OCP 3.0 mezzanine slot with PCIe Gen4 x16 bandwidth from CPU_0
Supported NCSI function
1 x OCP 2.0 mezzanine slot with PCIe Gen3 x8 bandwidth (Type1, P1, P2)
Supported NCSI function
1 x M.2 slot:
M-key
PCIe Gen4 x4
Supports NGFF-2242/2260/2280/22110 cards
CPU TDP is limited to 225W if using M.2 device
NOTE: Suppor t is not provided for mixed GPU populations
Total 12 x 3.5"/2.5" SATA/SAS/Gen4 NVMe hot-swappable HDD/SSD bays
8 x SATA/SAS ports, 4 x SATA/Gen4 NVMe hybrid ports
Internal I/O
NOTE: SAS card is required for SAS devices support
1 x M.2 slot
1 x USB 3.0 header
1 x COM header
1 x TPM header
1 x Front panel header
1 x HDD back plane board header
1 x PMBus connector
1 x IPMB connector
1 x Clear CMOS jumper
1 x BIOS recovery jumper
- 13 - Hardware Installation
Page 14

Hardware Installation - 14 -
Page 15
System
Management
Power Supply
Aspeed® AST2500 management controller
AMI MegaRAC SP-X Solution web interface
Dashboard
JAVA Based Serial Over LAN
HTML5 KVM
Sensor Monitor (Voltage, RPM, Temperature, CPU Status etc.)
Sensor Reading History Data
FRU Information
SEL Log in Linear Storage / Circular Storage Policy
Hardware Inventory
Fan Prole
System Firewall
Power Consumption
Power Control
LDAP / AD / RADIUS Support
Backup & Restore Conguration
Remote BIOS/BMC/CPLD Update
Event Log Filter
User Management
Media Redirection Settings
PAM Order Settings
SSL Settings
SMTP Settings
2 x 2000W redundant PSU
80 PLUS Platinum
AC Input:
- 100-120V~/ 12A, 50-60Hz
- 180-240V~/ 10A, 50-60Hz
DC Input:
- 240Vdc/ 10A
DC Output:
- 1000W@100-120V, +12.2V/ 81.5A, +12Vsb/ 2.5A
- 1600W@180-199V, +12.2V/ 131A, +12Vsb/ 2.5A
- 1800W@200-220V, +12.2V/ 147.5A, +12Vsb/ 2.5A
- 2000W@221-240V, +12V/ 163.5A, +12Vsb/ 2.5A
- 15 - Hardware Installation
Page 16
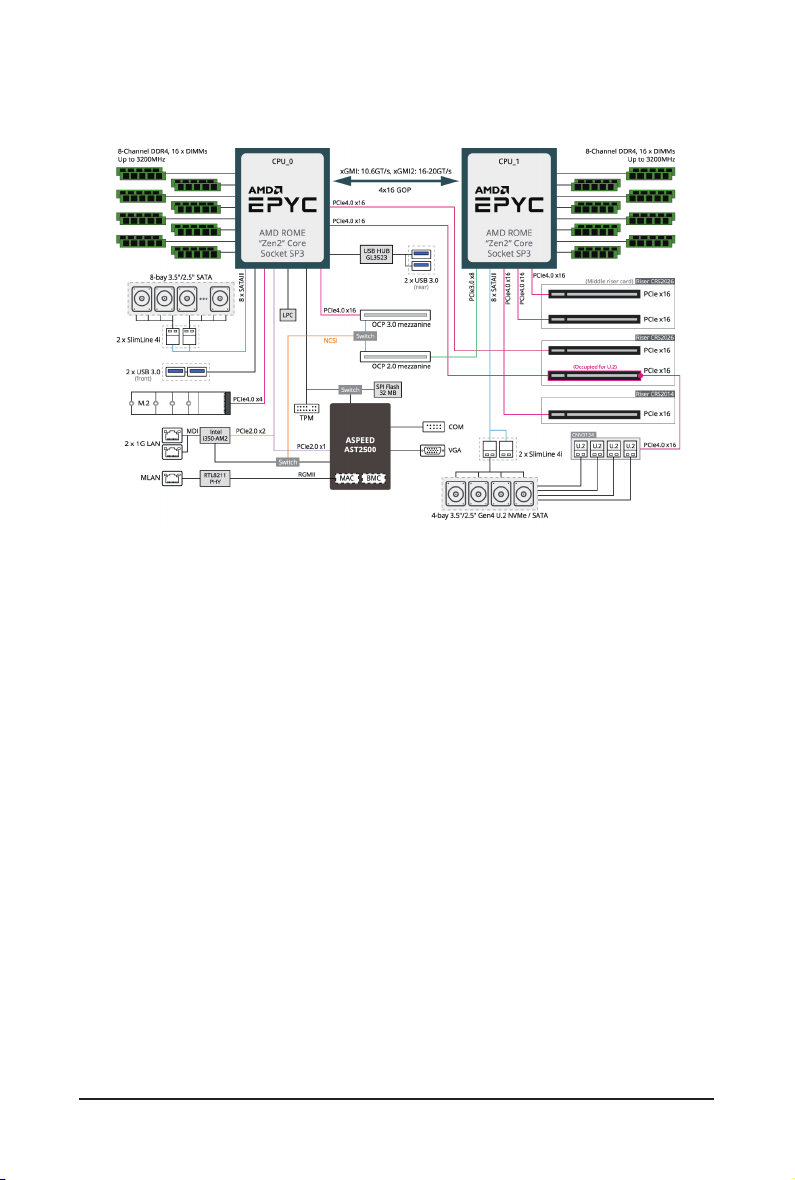
1-3 System Block Diagram
Hardware Installation - 16 -
Page 17
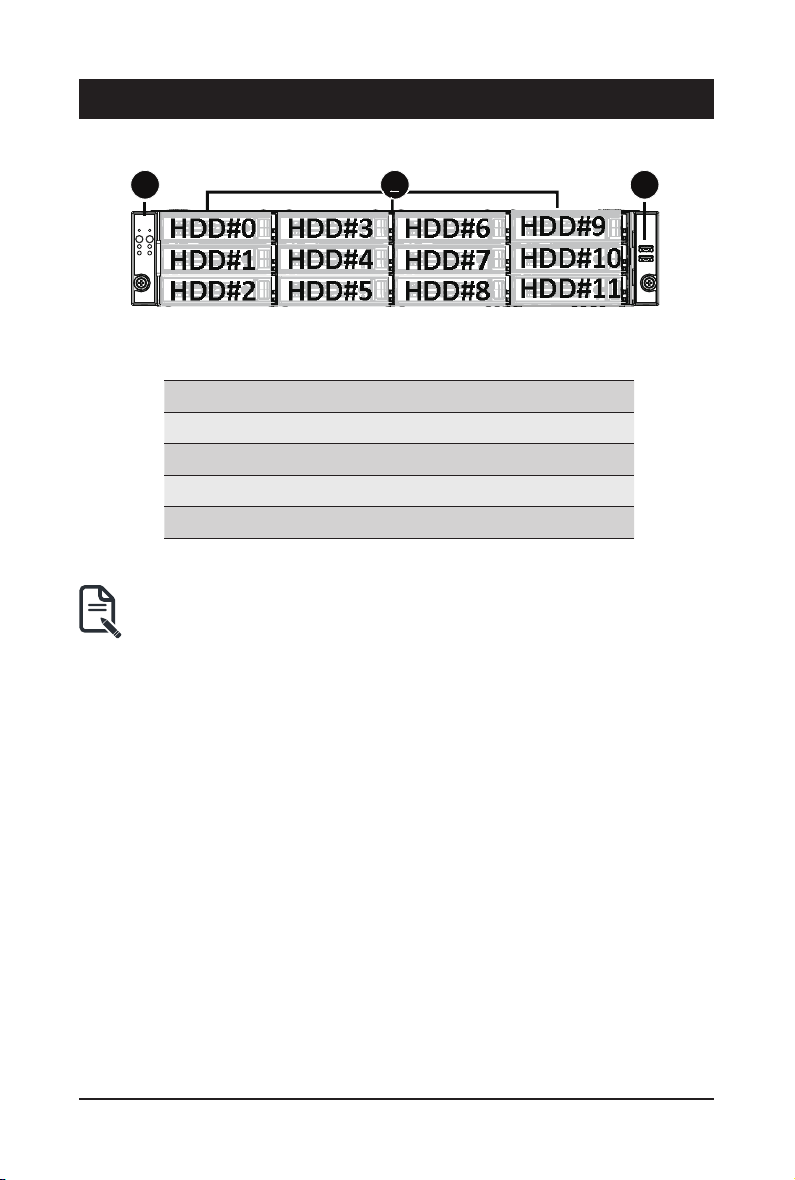
Chapter 2 System Appearance
1 32
HDD#2
HDD#5
HDD#8
2-1 Front View
HDD#0
HDD#1
HDD#3
HDD#4
HDD#6
HDD#7
HDD#9
HDD#10
HDD#11
No. Description
1.
2. 3.5" HDD Bays
3. Front USB 3.0 Ports
• Refer to section 2-3 Front Panel LEDs and Buttons for a detailed description of the
function of the LEDs.
Front Panel LEDs and Buttons
NOTE! The Green Latch Supports NVMe
- 17 - System Appearance
Page 18
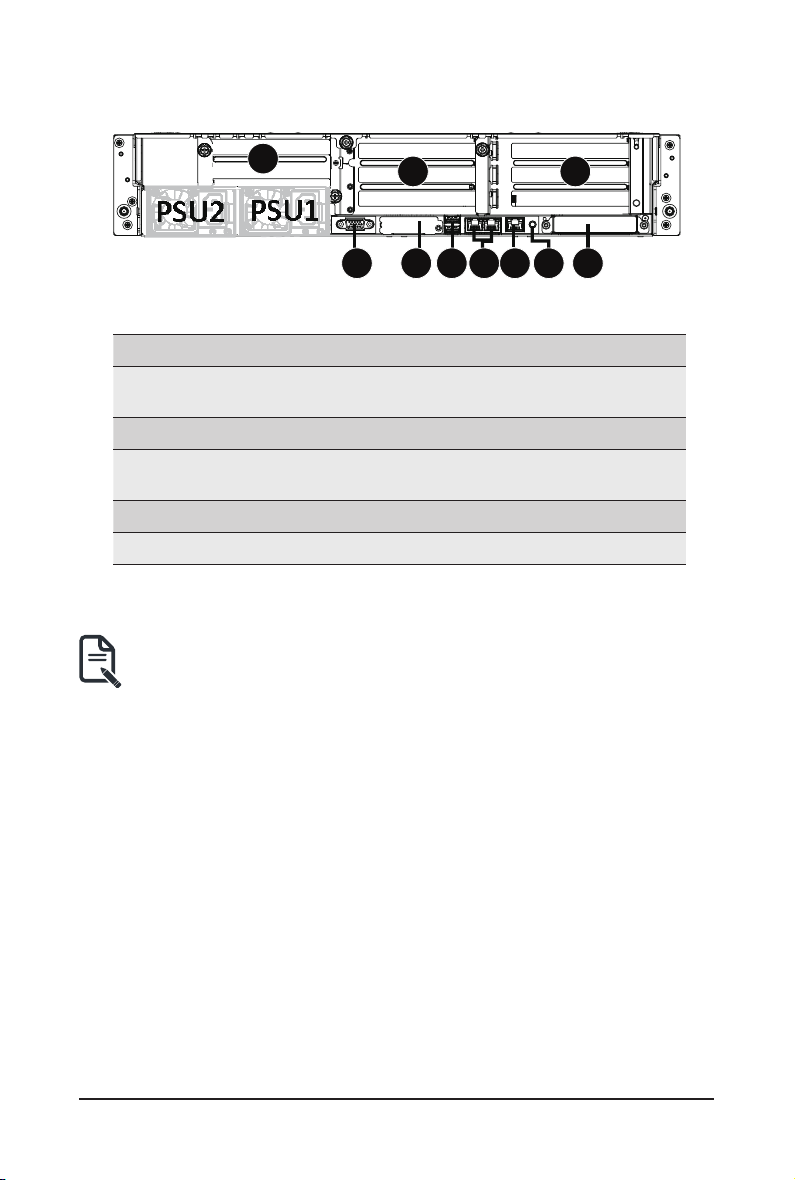
2-2 Rear View
PSU2
8
PSU1
9
7
No. Description No. Description
1. Mezzanine Slot (for OCP 3.0
Card, SFF Type, optional)
2. ID Button with LED 7. VGA Port
3. Server Management LAN
Port
4. 1 GbE LAN Ports 9. Full-Height GPU Card Slot
5. USB 3.0 Port x 2 10. Full-Height GPU Card Slot
• Refer to section 2-4 Rear System LAN LEDs for a detailed description of the function of
the LEDs.
6. Mezzanine Slot (for OCP 2.0 Card,
optional)
8. Full-Height GPU Card Slot
10
231456
System Appearance - 18 -
Page 19
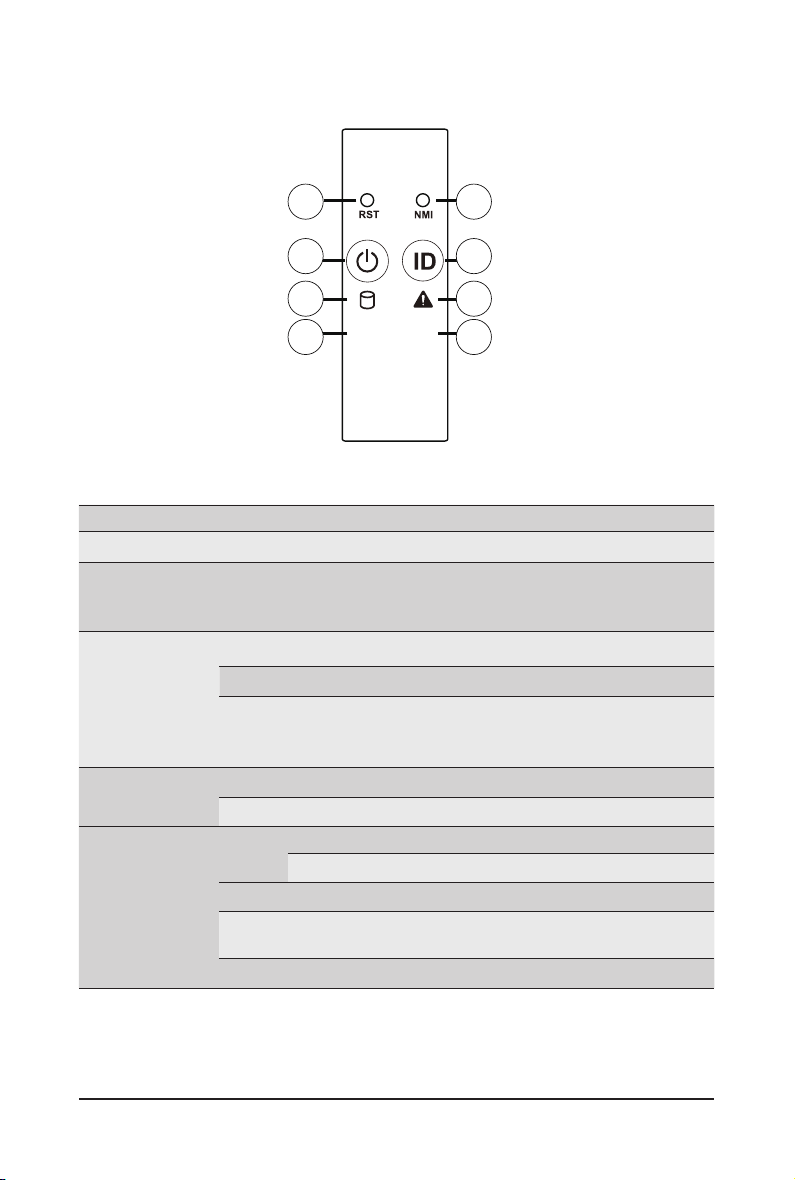
2-3 Front Panel LEDs and Buttons
1
3
5
On
Blink
Blink
L1
Press this button for the server to generate a NMI to the
processor. If multiple-bit ECC errors occur, the server will
effectively be halted.
- System is not powered on or in ACPI S5 state (power
off)
- System is in ACPI S4 state (hibernate mode)
Indicates locating the HDD.
Indicates accessing the HDD.
Indicates HDD error.
Indicates HDD rebuilding.
Indicates no HDD access or no HDD error.
7
No. Name Color Status Description
Reset Button -- -- Press this button to reset the system.
1.
NMI button -- --
2.
Green On Indicates the system is powered on.
3.
4.
5.
Power button
with LED
ID Button
with LED
HDD Status
LED
Green Blink System is in ACPI S1 state (sleep mode).
N/A Off
Blue On Indicates the system identication is active.
N/A Off Indicates the system identication is disabled.
Green
Amber On
Green/
Amber
N/A Off
L2
2
4
6
8
- 19 - System Appearance
Page 20

6.
7/8.
System
Status LED
LAN1/2
Active/
Link LED
Green On
On
Amber
Blink
N/A Off
Green On
Green Blink
N/A Off
Indicates system is operating normally.
Indicates a critical condition, may include:
- System fan failure
- System temperature
Indicates non-critical condition, may include:
- Redundant power module failure
- Temperature and voltage issue
- Chassis intrusion
Indicates system is not ready, may include:
- POST error
- NMI error
- Processor or terminator is missing
Indicates a link between the system and the network or
no access.
Indicates data trasmission or receiving is occuring.
Indicates no data transmission or receiving is occuring.
System Appearance - 20 -
Page 21

2-4 Rear System LAN LEDs
1 2 1 221
No. Name Color Status Description
Yel l ow On 1 Gbps data rate
1GbE
1.
Speed LED
Green On 100 Mbps data rate
N/A Off 10 Mbps data rate
1GbE
Link/
2.
Activity
LED
Green
N/A Off
On
Blink Data transmission or receiving is occurring
Link between system and
network or no access
No data transmission or
receiving is occurring
- 21 - System Appearance
Page 22
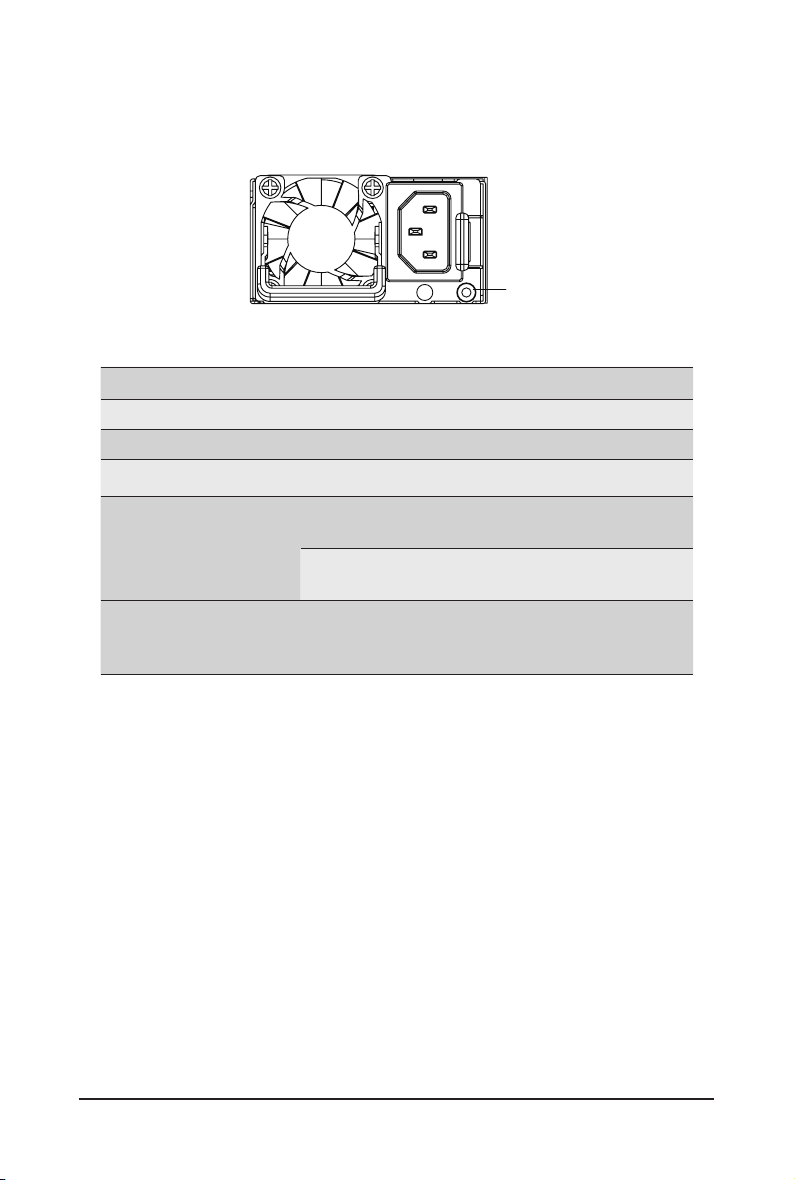
2-5 Power Supply Unit LED
PSU LED
State
OFF No AC power to all power supplies
0.5Hz Green Blinking AC present / only standby on / Cold redundant mode
2Hz Green Blinking Power supply rmware updateing mode
AC cord unplugged or AC power lost; with a second
Amber
0.5Hz Amber Blinking
power supply in parallel still with AC input power
Power supply critical event causing shut down:
failure, OCP, OVP, fan failure and UVP
Power supply warning events where the
power supply continues to operate:
high temp, high power, high current and slow fan
Description
System Appearance - 22 -
Page 23

2-6 Hard Disk Drive LEDs
LED #1
LED #2
RAID SKU
Disk LED (LED
No RAID
conguration
(via HBA)
RAID
conguration
(via HW RAID
Card or SW
RAID Card)
LED #2 HDD Present No HDD
Green ON OFF
on Back Panel)
Removed HDD
Slot (LED on
Back Panel)
Disk LED
Removed
HDD Slot
LED #1 Locate
Green ON (*1) OFF BLINK (*2) OFF
Amber OFF OFF OFF OFF
Green ON (*1) OFF -- --
Amber OFF OFF -- --
Green ON OFF BLINK (*2) OFF
Amber OFF ON
Green ON (*1) OFF (*3) -- --
Amber OFF ON (*3) -- --
HDD
Rebuilding HDD Access
Fault
(Low Speed:
2 Hz)
OFF OFF
NOTE:
*1: Depends on HBA/Utility Spec.
*2: Blink cycle depends on HDD's activity signal.
*3: If HDD is pulled out during rebuilding, the disk status of this HDD is regarded as faulty.
HDD Present
(No Access)
- 23 - System Appearance
Page 24

This page intentionally left blank
System Appearance - 24 -
Page 25

Chapter 3 System Hardware Installation
Pre-installation Instructions
Computer components and electronic circuit boards can be damaged electrostatic discharge.
Working on computers that are still connected to a power supply can be extremely dangerous.
Follow the simple guidelines below to avoid damage to your computer or injury to yourself.
• Always disconnect the computer from the power outlet whenever you are working inside the
computer case.
• If possible, wear a grounded wrist strap when you are working inside the computer case.
Alternatively, discharge any static electricity by touching the bare metal system of the computer
case, or the bare metal body of any other grounded appliance.
• Hold electronic circuit boards by the edges only. Do not touch the components on the board
unless it is necessary to do so. Do not ex or stress the circuit board.
• Leave all components inside the static-proof packaging until you are ready to use the component
for the installation.
- 25 - System Hardware Installation
Page 26

3-1 Removing and Installing the Chassis Cover
Before you remove or install the system cover
• Make sure the system is not turned on or connected to AC power.
Follow these instructions to remove the chassis cover:
1. Remove the screw securing the chassis cover.
2. Loosen the thumbnail screw securing the chassis cover.
3. Push down on the indentations located on the side of the chassis cover.
4. Slide the chassis cover to the rear of the system and then remove the cover in the direction of the
arrow.
5. To reinstall the chassis cover follow steps 1-4 in reverse order.
1
3
4
3
2
System Hardware Installation - 26 -
Page 27
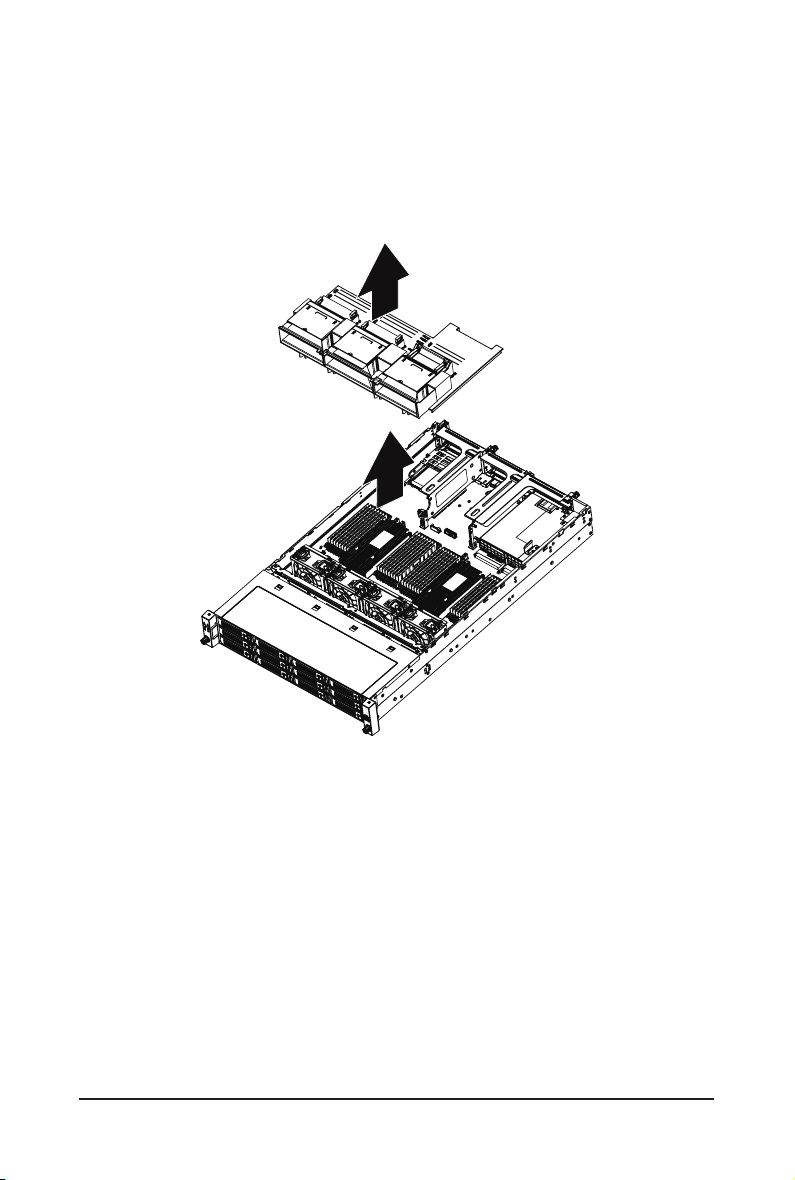
3-2 Removing and Installing the Fan Duct
Follow these instructions to remove the fan duct:
1. Lift up to remove the fan duct.
2. To reinstall the fan duct, align the fan duct with the guiding groove. Push down the fan duct until it is
rmly seated on the system.
- 27 - System Hardware Installation
Page 28
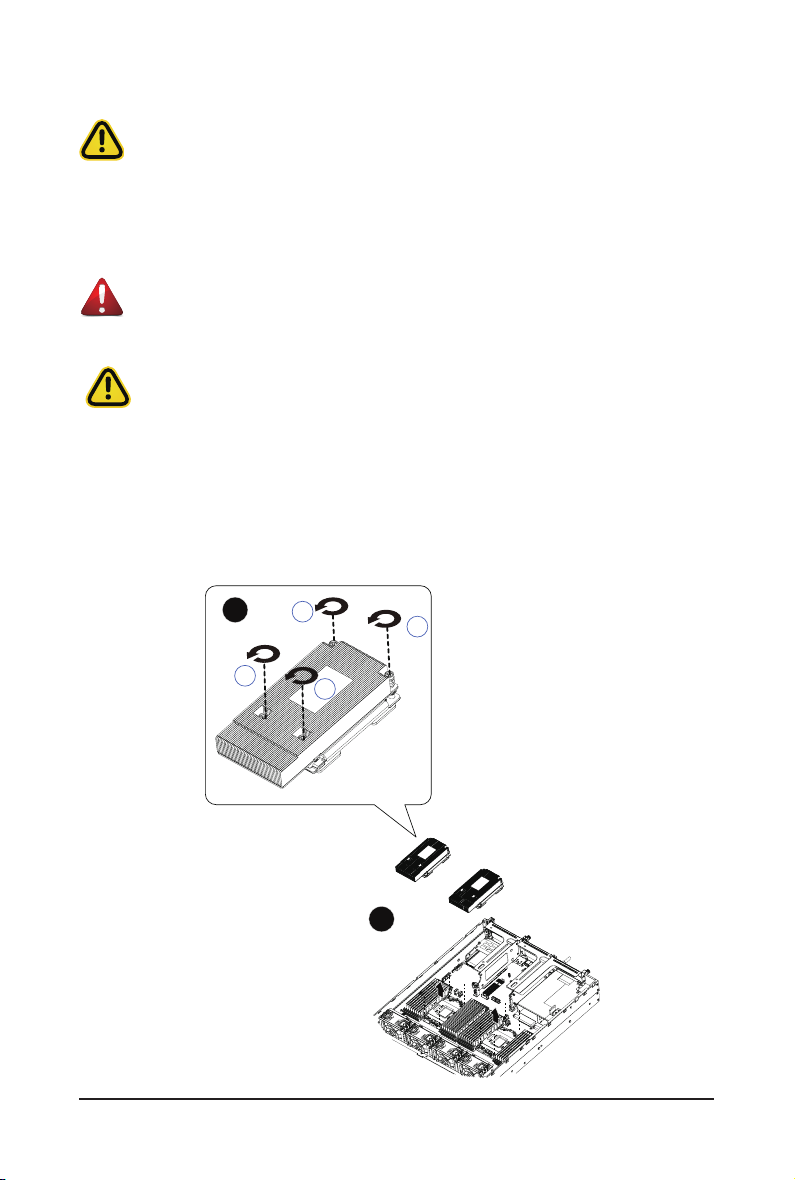
3-3 Removing and Installing the Heat Sink
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the heat sink:
• Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before installing
the heat sink to prevent hardware damage.
• Unplug all cables from the power outlets.
• Disconnect all telecommunication cables from their ports.
• Place the system unit on a at and stable surface.
• Open the system according to the instructions.
WARNING!
Failure to turn off the server before you start installing components may cause serious damage. Do
not attempt the procedures described in the following sections unless you are a qualied service
technician.
• When installing the heatsink to CPU, use T20-Lobe driver to tighten 4 captive nuts in sequence
as 1-4.
• The screw tightening torque: 0 ± 0.5 kgf-cm (22.0± 1.0 lbf-in).
Follow these instructions to install the heat sink:
1. Loosen the screws securing the heat sink in place in reverse order (4g3g2g1).
2. Lift and remove the heat sink from the system.
3. To install the heat sink, reverse steps 1-2 while ensuring that you tighten the captive screws in
sequential order (1g2g3g4) as seen in the image below.
1
4
2
3
2
System Hardware Installation - 28 -
1
Page 29
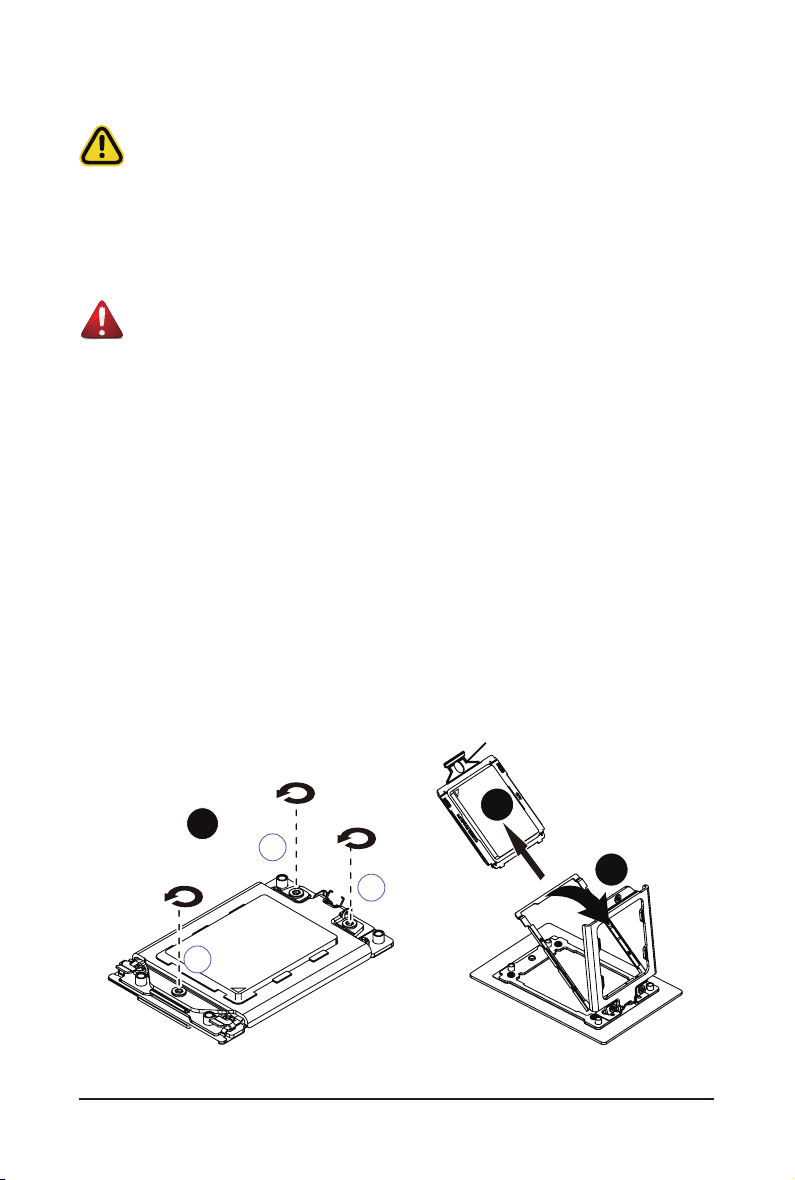
3-4 Removing and Installing the CPU
External cap
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the CPU:
• Make sure that the motherboard supports the CPU.
• Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before installing
the CPU to prevent hardware damage.
• Unplug all cables from the power outlets.
• Disconnect all telecommunication cables from their ports.
• Place the system unit on a at and stable surface.
• Open the system according to the instructions.
WARNING!
Failure to properly turn off the server before you start installing components may cause serious
damage. Do not attempt the procedures described in the following sections unless you are a
qualied service technician.
Follow these instructions to install the CPU:
1. Loosen the three captive screws securing the CPU cover in sequential order (1g2g3).
2. Flip open the CPU cover.
3. Remove the CPU carrier from the CPU frame using the handle on the CPU carrier.
4. Using the handle on the CPU carrier insert the new CPU carrier with CPU installed into the CPU
frame.
NOTE: Ensure the CPU is installed in the CPU carrier in the correct orientation, with the triangle
on the CPU aligned to the top left corner of the CPU carrier.
5. Flip the CPU frame with CPU installed into place in the CPU socket.
6. Flip the CPU cover into place over the CPU socket.
7. Tighten the CPU cover screws in sequential order (1g2g3) to secure the CPU cover in place.
8. Repeat steps 1-7 for the second CPU.
9. To remove the CPUs, follow steps 1-7 in reverse order.
1
3
2
2
1
3
- 29 - System Hardware Installation
Page 30
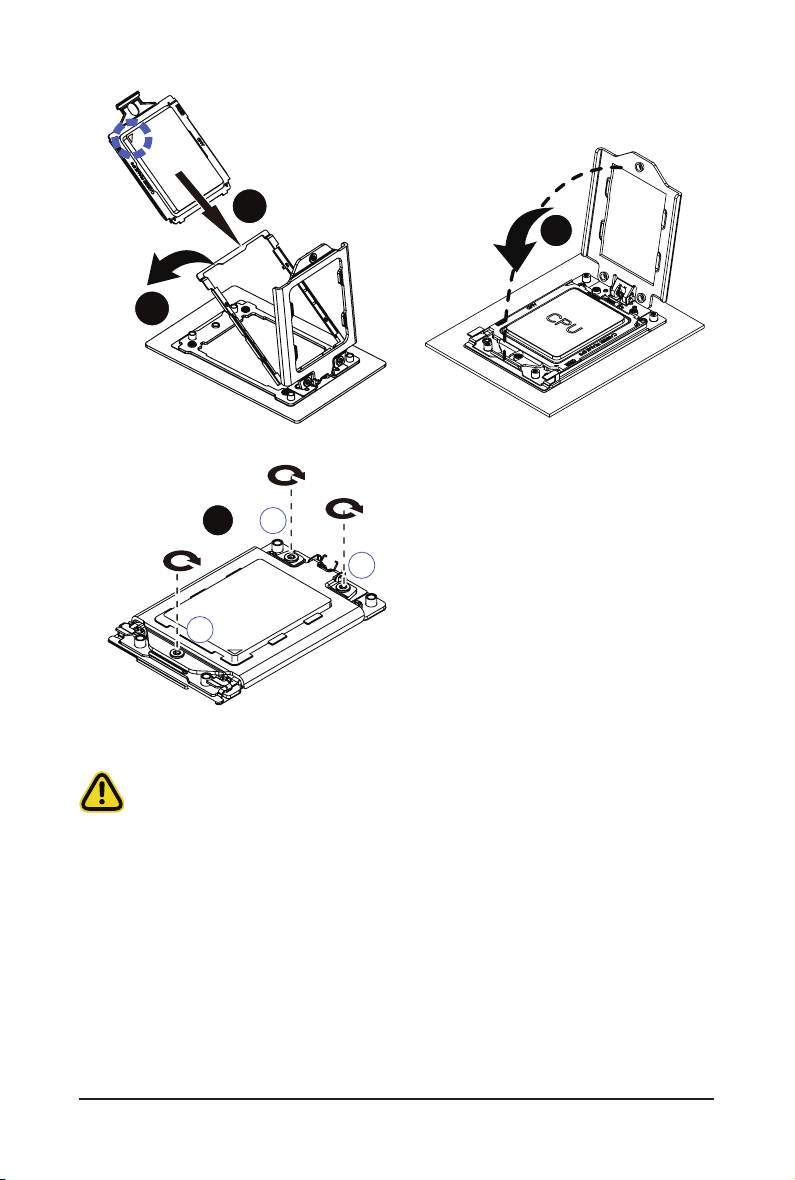
5
CPU
4
6
7
2
3
1
• Tighten the CPU cover screws in sequential order (1g2g3).
• The screw tightening torque: 16.1 ± 1.2 kgf-cm (14.0± 1.0 lbf-in)
System Hardware Installation - 30 -
Page 31

3-5 Removing and Installing Memory
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the memory:
• Make sure that the motherboard supports the memory. It is recommended that memory of the
same capacity, brand, speed, and chips be used.
• Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before installing
the memory to prevent hardware damage.
• Memory modules have a foolproof design. A memory module can be installed in only one
direction. If you are unable to insert the memory, switch the direction.
3-5-1 Eight-Channel Memory Conguration
This motherboard provides 32 DDR4 memory sockets and supports Eight Channel Technology. After the
memory is installed, the BIOS will automatically detect the specications and capacity of the memory.
21
DIMM_P0_C0
DIMM_P0_C1
DIMM_P0_B1
DIMM_P0_D0
DIMM_P0_D1
DIMM_P0_A0
DIMM_P0_A1
DIMM_P0_B0
CPU0
DIMM_P0_G0
DIMM_P0_F1
DIMM_P0_F0
DIMM_P0_E1
DIMM_P0_E0
DIMM_P0_H1
DIMM_P0_H0
DIMM_P0_G1
DIMM_P1_L1
DIMM_P1_K1
DIMM_P1_K0
DIMM_P1_L0
DIMM_P1_J1
DIMM_P1_J0
CPU1
DIMM_P1_I1
DIMM_P1_I0
DIMM_P1_N0
DIMM_P1_M0
DIMM_P1_M1
- 31 - System Hardware Installation
DIMM_P1_N1
DIMM_P1_O0
DIMM_P1_O1
DIMM_P1_P0
DIMM_P1_P1
Page 32

3-5-2 Removing and Installing a Memory Module
Before installing a memory module, make sure to turn off the computer and unplug the power cord
from the power outlet to prevent damage to the memory module. Be sure to install DDR4 DIMMs on
to this motherboard.
Follow these instructions to install a DIMM module:
1. Insert the DIMM memory module vertically into the DIMM slot and push it down.
2. Close the plastic clip at both edges of the DIMM slots to lock the DIMM module.
3. Reverse the installation steps when you want to remove the DIMM module.
2
1
2
3-5-3 Processor and Memory Module Matrix Table
Processor and Memory Module Matrix Table
CPU#
Channel A/I Channel B/J Channel C/K Channel D/L Channel E/M Channel F/N Channel G/O Channel H/P
8 DIMMs
CPU0 A1 B1 C1 D1 E1 F1 G1 H1
16 DIMMs
CPU0 A1A0 B1B0 C1C0 D1D0 E1E0 F1F0 G1G0 H1H0
16 DIMMs
CPU0 A1 B1 C1 D1 E1 F1 G1 H1
CPU1 I1 J1 K1 L1 M1 N1 O1 P1
32 DIMMs
CPU0 A1 B1 C1 D1 E1 F1 G1 H1A0 B0 C0 D0 E0 F0 G0 H0
CPU1 I1 J1 K1 L1 M1 N1 O1 P1I0 J0 K0 L0 M0 N0 O0 P0
System Hardware Installation - 32 -
Page 33

3-5-4 DIMM Population Table
• When only one DIMM is used, it must be populated in memory slot DIMM1.
RDIMM Maximum Frequency Supported
DIMMs
Populated
1
1R
1
--
2
2
1
--
LRDIMM Maximum Frequency Supported
DIMMs
Populated
1
2
2S2R
2S4R
1
--
2
1
--
DIMM
2DR
DIMM
4DR
2R
--
1
--
1
2
--
1
--
1
2
Frequency (MT/s)
1.2V
3200
3200
2933
2933
2933
Frequency (MT/s)
1.2V
3200
3200
2933
Not Supported
2933
3DS RDIMM Maximum Frequency Supported
DIMM
DIMMs
Populated
1
2
2S2R
2S4R
Frequency (MT/s)
1.2V
1
2
- 33 - System Hardware Installation
2933
2666
Page 34

3-6 Removing and Installing the GPU Card
• Voltages can be present within the server whenever an AC power source is connected. This
voltage is present even when the main power switch is in the off position. Ensure that the system
is powered off and all power sources have been disconnected from the server prior to installing a
GPU card.
• Failure to observe these warnings could result in personal injury or damage to equipment.
• The GPU card assembly does not include a riser card or any cabling as standard. To install a
GPU card, a riser card must be installed.
Follow these instructions to install a GPU card:
1. Loosen the thumbnail screw securing the riser bracket from the rear side of the system.
2. Loosen the two thumbnail screws securing the riser bracket inside the system.
3. Lift up the riser bracket out of system.
4. Remove the screw securing the slot cover from riser bracket.
5. Orient the GPU card with the riser guide slot and push in the direction of the arrow until the GPU
card sits in the GPU card connector.
NOTE: Some riser brackets allow for single or multiple GPU cards.
Repeat steps 4-5 as necessary.
6. Secure the GPU card with the screw.
7. Repeat steps 1-3 to install the GPU card into the system.
1
System Hardware Installation - 34 -
Page 35

7
4
6
5
7
7
4
5
4
6
6
5
6
9
7
- 35 - System Hardware Installation
Page 36

3-7 Installing the Mezzanine Card
3-7-1 Installing the OCP 3.0 Mezzanine Card
Use of the following type of OCP 3.0 NIC is recommended:
• OCP 3.0 SFF with pull tab
• OCP 3.0 SFF with ejector latch
Follow these instructions to install an OCP 3.0 Mezzanine card:
1. Remove the two screws securing the OCP 3.0 card slot cover.
2. Remove the slot cover from the system.
3. Insert the OCP 3.0 card into the card slot ensuring that the card is rmly connected to the connector
on the motherboard.
4. Tighten the thumbnail screw to secure the OCP 3.0 card in place.
5. Reverse steps 3-4 to replace the OCP 3.0 card.
1
2
3
System Hardware Installation - 36 -
1
4
Page 37

3-7-2 Installing the OCP 2.0 Mezzanine Card
Follow these instructions to install an OCP 2.0 Mezzanine card:
1. Remove the screw securing the OCP 2.0 card slot cover.
2. Remove the slot cover from the system.
3. Align the screw holes on the OCP 2.0 card with the heads of the stand-off screws ensuring that the
ports on the card are properly tted into the rear panel of the system.
4. Press down on the OCP 2.0 card so that the connector on the card is firmly connected to the
connector on the motherboard and then secure three screws on the card.
5. Reverse steps 3-4 to replace the OCP 2.0 card.
4
3
2
1
- 37 - System Hardware Installation
Page 38

3-8 Removing and Installing the Hard Disk Drive
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the hard disk drive:
• Take note of the HDD tray orientation before sliding it out.
• The tray will not t back into the bay if it is inserted incorrectly.
• Make sure that the hard disk drive is connected to the connector on the backplane.
Follow these instructions to install a 3.5" hard disk drive:
1. Press the release button.
2. Extend the locking lever.
3. Pull the locking lever in the direction indicated to remove the 3.5" HDD tray.
4. Pull the sides of the HDD tray in the direction indicated.
5. Slide the hard disk drive into the HDD tray.
6. Push the sides of the HDD tray back in the direction indicated to secure the hard disk drive in place.
7. Reinsert the HDD tray into the slot and close the locking lever.
1
Press
2
Pull
3
Pull
System Hardware Installation - 38 -
Pull
4
Page 39

Push
5
Push
6
- 39 - System Hardware Installation
Page 40

3-9 Installing and Removing an M.2 Device
WARNING:
Installation of the thermal pad over the M.2 device is required when installing an M.2 device. Lack
of the thermal pad may result in system overheat and throttle the system performance.
CAUTION:
The position of the stand-off screw will depend on the size of the M.2 device. The stand-off screw
is pre-installed for 22110 cards as standard. Refer to the size of the M.2 device and change the
position of the stand-off screw accordingly.
Follow these instructions to install an optional M.2 device:
1. Insert the M.2 device into the M.2 connector.
2. Install the thermal pad of the M.2 device to the M.2 device.
3. Press down on the thermal pad.
4. Secure the M.2 device and its thermal pad to the motherboard with a single screw.
5. Reverse steps 1-4 to remove the M.2 device.
2
1
3
4
System Hardware Installation - 40 -
Page 41

3-10 Replacing the Fan Assembly
• The image below shows the system image of R282-Z90. The same process applies to R282-Z91
and R282-Z90.
Follow these instructions to replace a fan assembly:
1. Flip the latches on the top of the fan outwards.
2. Using the latches, lift up the fan assembly from the chassis.
3. Reverse the previous steps to install the replacement fan assembly.
1
2
- 41 - System Hardware Installation
Page 42

3-11 Removing and Installing the Power Supply
Before you remove or install the power supply unit:
• Make sure the system is not turned on or connected to AC power.
Follow these instructions to replace the power supply:
1. Flip up and then grasp the power supply handle.
2. Press the retaining clip on the right side of the power supply unit in the direction indicated.
3. Pull out the power supply unit using the handle.
4. Insert the replacement power supply unit rmly into the chassis. Connect the AC power cord to the
replacement power supply.
5. Repeat steps 1-4 for replacement of the second power supply.
3
1
2
4
System Hardware Installation - 42 -
Page 43

3-12 Cable Routing
Onboard SATA Cable
Onboard SATA Cable
- 43 - System Hardware Installation
Page 44

HDD Backplane Board Power Cable
HDD Backplane Board Signal Cable
System Hardware Installation - 44 -
Page 45

Front Panel USB 3.0 Ports Cable
Front Panel LEDs and Buttons Cable
- 45 - System Hardware Installation
Page 46

GPU Card Power Cable
System Hardware Installation - 46 -
Page 47

NVMe Card Cable
CNV3134
U2_A
U2_8
U2_9
CNV3134
U2_B
- 47 - System Hardware Installation
Page 48

NVMe Card Cable
CNV3134
U2_10
U2_C
U2_11
CNV3134
U2_D
System Hardware Installation - 48 -
Page 49

Chapter 4 Motherboard Components
DIMM_P0_D1
4-1 Motherboard Components
21
18
19
7
6
5
4
DIMM_P0_C1
DIMM_P0_D0
3
8
14
9
13
15
16 17
10
11
12
23
DIMM_P0_A0
DIMM_P0_A1
DIMM_P0_B0
DIMM_P0_B1
DIMM_P0_C0
1
2
CPU0
DIMM_P0_E1
DIMM_P0_E0
Item Description
1 HDD Back Plane Board Connector
2 Front Panel USB 3.0 Connector
3 Front Panel Connector
4 2 x 4 Pin P12V GPU Power Connector
5 2 x 4 Pin P12V GPU Power Connector
6 IPMB Connector
7 Serial Port Cable Connector
8 OCP Mezzanine Connector (OCP 3.0/SFF Type/Gen4 x16)
9 BMC Firmware Readiness LED
DIMM_P0_H0
DIMM_P0_G1
DIMM_P0_G0
DIMM_P0_F1
DIMM_P0_F0
DIMM_P0_H1
DIMM_P1_K1
DIMM_P1_L1
DIMM_P1_L0
DIMM_P1_K0
20
DIMM_P1_J1
DIMM_P1_J0
DIMM_P1_I1
DIMM_P1_I0
21 22
24
CPU1
DIMM_P1_N0
DIMM_P1_M0
DIMM_P1_M1
25
26
DIMM_P1_N1
DIMM_P1_O0
DIMM_P1_O1
DIMM_P1_P1
DIMM_P1_P0
- 49 - Motherboard Components
Page 50

10 TPM Module Connector (SPI Interface)
11 SlimLine SAS Connector (SLSAS_0/PCIe/SATA/Dened by SKUs)
12 SlimLine SAS Connector (SLSAS_1/PCIe/SATA/Dened by SKUs)
13 System Battery
14 Riser Connector #1 (PCIe Gen4/x32 Slot)
15 M.2 Connector (PCIe4 x4, Supports NGFF-22110)
16 2 x 4 Pin P12V GPU Power Connector
17 2 x 3 Pin Rear Back Plane Board Power Connector
18 OCP Mezzanine Connector (OCP 2.0/Gen3 x8)
19 Riser Connector #2 (PCIe Gen4/x32 Slot)
20 Riser Connector #3 (PCIe Gen4/x16 Slot)
21 Power Supply Connector#1 (Primary)
22 Power Supply Connector#2 (Secondary)
23 SlimLine SAS Connector (SLSAS_2/PCIe/SATA/Dened by SKUs)
24 SlimLine SAS Connector (SLSAS_3/PCIe/SATA/Dened by SKUs)
25 2 x 7 Pin HDD Back Plane Board Power Connector
26 2 x 3 Pin HDD Back Plane Board 12V Power Connector
Motherboard Components - 50 -
Page 51

4-2 Jumper Settings
1
Clear CMOS
CLR_CMOS
Default
2
Enable
3
NCSI Switch
21
21
OFF
ON
SW2SW1
OFF
OFF
ONON
Onboard LAN
OCP2.0 Mezzanine
OCP 3.0 Mezzanine
DIMM_P0_C0
DIMM_P0_C1
DIMM_P0_B1
DIMM_P0_D0
DIMM_P0_D1
DIMM_P0_A0
DIMM_P0_A1
DIMM_P0_B0
CPU0
DIMM_P0_F0
DIMM_P0_E1
DIMM_P0_E0
-
21',3
J2
HOST_SMBUS_SEL
1
PMBUS_SEL
2
BIOS_PWD
3
4
BIOS_RCVR
DIMM_P0_H1
DIMM_P0_H0
DIMM_P0_G1
DIMM_P0_G0
DIMM_P0_F1
DIMM_P1_K1
DIMM_P1_K0
DIMM_P1_L1
DIMM_P1_L0
DIMM_P1_J1
ON
DIMM_P1_J0
DIMM_P1_I1
DIMM_P1_I0
CPU1
OFF
DIMM_P1_M0
DIMM_P1_M1
BIOS Defined
BIOS Defined
Clear supervisor
password
BIOS recovery mode
Normal
[Default]
Normal
[Default]
- 51 - Motherboard Components
DIMM_P1_N0
DIMM_P1_N1
DIMM_P1_O0
DIMM_P1_O1
DIMM_P1_P0
DIMM_P1_P1
Page 52

This page intentionally left blank
Motherboard Components - 52 -
Page 53

Chapter 5 BIOS Setup
BIOS (Basic Input and Output System) records hardware parameters of the system in the EFI on the
motherboard. Its major functions include conducting the Power-On Self-Test (POST) during system startup,
saving system parameters and loading operating system, etc. BIOS includes a BIOS Setup program that
allows the user to modify basic system conguration settings or to activate certain system features. When the
power is turned off, the battery on the motherboard supplies the necessary power to the CMOS to keep the
conguration values in the CMOS.
To access the BIOS Setup program, press the <DEL> key during the POST when the power is turned on.
• BIOS ashing is potentially risky, if you do not encounter problems of using the current BIOS
version, it is recommended that you don't ash the BIOS. To ash the BIOS, do it with caution.
Inadequate BIOS ashing may result in system malfunction.
• It is recommended that you not alter the default settings (unless you need to) to prevent system
instability or other unexpected results. Inadequately altering the settings may result in system's
failure to boot. If this occurs, try to clear the CMOS values and reset the board to default values.
(Refer to the Exit section in this chapter or introductions of the battery/clearing CMOS jumper in
Chapter 1 for how to clear the CMOS values.)
BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
<f><g> Move the selection bar to select the screen
<h><i> Move the selection bar to select an item
<+> Increase the numeric value or make changes
<-> Decrease the numeric value or make changes
<Enter> Execute command or enter the submenu
<Esc> Main Menu: Exit the BIOS Setup program
Submenus: Exit current submenu
<F1> Show descriptions of general help
<F3> Restore the previous BIOS settings for the current submenus
<F9> Load the Optimized BIOS default settings for the current submenus
<F10> Save all the changes and exit the BIOS Setup program
- 53 - BIOS Setup
Page 54

Main
This setup page includes all the items in standard compatible BIOS.
Advanced
This setup page includes all the items of AMI BIOS special enhanced features.
(ex: Auto detect fan and temperature status, automatically congure hard disk parameters.)
AMD CBS
This setup page includes the common items for conguration of AMD motherboard-related information.
AMD PBS Option
This setup page includes the common items for conguration of AMD CPM RAS related settings.
Chipset
This setup page includes all the submenu options for conguring the function of processor, network,
North Bridge, South Bridge, and System event logs.
Server Management
Server additional features enabled/disabled setup menus.
Security
Change, set, or disable supervisor and user password. Conguration supervisor password allows you to
restrict access to the system and BIOS Setup.
A supervisor password allows you to make changes in BIOS Setup.
A user password only allows you to view the BIOS settings but not to make changes.
Boot
This setup page provides items for conguration of boot sequence.
Save & Exit
Save all the changes made in the BIOS Setup program to the CMOS and exit BIOS Setup. (Pressing
<F10> can also carry out this task.)
Abandon all changes and the previous settings remain in effect. Pressing <Y> to the confirmation
message will exit BIOS Setup. (Pressing <Esc> can also carry out this task.)
BIOS Setup - 54 -
Page 55

5-1 The Main Menu
Once you enter the BIOS Setup program, the Main Menu (as shown below) appears on the screen. Use
arrow keys to move among the items and press <Enter> to accept or enter other sub-menu.
Main Menu Help
The on-screen description of a highlighted setup option is displayed on the bottom line of the Main Menu.
Submenu Help
While in a submenu, press <F1> to display a help screen (General Help) of function keys available for the
menu. Press <Esc> to exit the help screen. Help for each item is in the Item Help block on the right side of
the submenu.
• When the system is not stable as usual, select the Restore Defaults item to set your system
to its defaults.
• The BIOS Setup menus described in this chapter are for reference only and may differ by
BIOS version.
- 55 - BIOS Setup
Page 56

Parameter Description
BIOS Information
Project Name Displays the project name information.
Project Version Displays version number of the BIOS setup utility.
Build Date and Time Displays the date and time when the BIOS setup utility was created.
BMC Information
BMC Firmware Version Displays version number of the BIOS setup utility.
BIOS Information
Project Name Displays the project name information.
Project Version Displays version number of the BIOS setup utility.
Build Date and Time Displays the date and time when the BIOS setup utility was created.
BMC Information
BMC Firmware Version Displays version number of the BIOS setup utility.
Processor Information
CPU 0 Brand String / CPU 1 Brand
String / CPU Speed / Processor
Core / Microcode Patch
BIOS Setup - 56 -
Displays the technical information for the installed processor(s).
Page 57

Parameter Description
Total Memory
Memory Speed
(Note1)
(Note1)
Displays the total memory size of the installed memory.
Displays the frequency information of the installed memory.
VR Information
Version Displays VR version information.
AGESA PI Version
PI Version Displays AGESA PI version information.
Onboard LAN Information
LAN1 MAC Address
LAN2 MAC Address
(Note2)
(Note2)
Displays LAN MAC address information.
Displays LAN MAC address information.
System Date Sets the date following the weekday-month-day-year format.
System Time Sets the system time following the hour-minute-second format.
(Note1) The number of LAN ports listed will depend on the motherboard / system model.
(Note2) This section will display capacity and frequency information of the memory that the customer has
installed.
- 57 - BIOS Setup
Page 58

5-2 Advanced Menu
The Advanced menu display submenu options for conguring the function of various hardware components.
Select a submenu item, then press [Enter] to access the related submenu screen.
BIOS Setup - 58 -
Page 59

5-2-1 Trusted Computing
Parameter Description
Conguration
Security Device Support
SPI TPM Support Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled
Select Enable to activate TPM support feature.
Options available: Enable/Disable. Default setting is Enable.
- 59 - BIOS Setup
Page 60

5-2-2 PSP Firmware Versions
The PSP Firmware Versions page displays the basic PSP rmware version information. Items on this window
are non-congurable.
BIOS Setup - 60 -
Page 61

5-2-3 Legacy Video Select
Parameter Description
OnBrd/Ext VGA Select
Select between onboard or external VGA support.
Options available: Auto/Onboard/External. Default setting is Onboard.
- 61 - BIOS Setup
Page 62

5-2-4 AST2500 Super IO Conguration
Parameter Description
AST2500 Super IO Conguration
Super IO Chip Displays the super IO chip information.
BIOS Setup - 62 -
Page 63

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] to congure advanced items.
Serial Port
– Enable/Disable the Serial Port (COM). When set to Enabled allows
you to congure the Serial port 1/2 settings. When set to Disabled,
displays no conguration for the serial port.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Devices Settings
– Displays the serial port 1/2 device settings.
Change Settings
– Select an optimal setting for the Super I/O device:
– Options available for Serial Port 1:
Auto
IO=3F8h; IRQ=4;
Serial Port 1/2
Conguration
IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
IO=3E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
Default setting is Auto.
Options available for Serial Port 2:
Auto
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3;
IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
IO=2F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
IO=3E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12;
Default setting is Auto.
(Note1)
:
(Note2)
(Note2)
:
:
(Note1) Advanced items will appear when this item is set to Enabled.
(Note2) This item will appear when Serial Port is set to Enabled.
- 63 - BIOS Setup
Page 64

5-2-5 S5 RTC Wake Settings
Parameter Description
Enable or disable system wake on alarm event. Select Fixed Time, system
Wake system from S5
will wake on the time (HH:MM:SS) specied. Select Dynamic Time and the
system will wake at the current time plus an increase in minute(s).
Options available: Disabled/Fixed Time. Default setting is Disabled.
BIOS Setup - 64 -
Page 65

5-2-6 Serial Port Console Redirection
Parameter Description
COM1/SOL / COM2 Console
Redirection
(Note)
Legacy Console Redirection
Serial Port for Out-of-Band
Management / Windows
Emergency Management
Services (EMS) Console
Redirection
(Note)
COM1/SOL / COM2 Console
Redirection Settings
Select whether to enable console redirection for specied device. Console
redirection enables the users to manage the system from a remote location.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Selects a COM port for Legacy serial redirection. The options are
dependent on the available COM ports.
Selects a COM port for EMS console redirection. EMS console redirection
allows the user to congure Console Redirection Settings to support Out-of-
Band Serial Port management.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Press [Enter] to congure advanced items.
Please note that this item is congurable when COM1/SOL / COM2
Console Redirection is set to Enabled.
Terminal Type
– Selects a terminal type to be used for console redirection.
– Options available: VT100/VT100+/ANSI /VT-UTF8. Default setting
is ANSI.
(Note) Advanced items prompt when this item is set to Enabled.
- 65 - BIOS Setup
Page 66

Parameter Description
Bits per second
– Selects the transfer rate for console redirection.
– Options available: 9600/19200/38400/57600/115200. Default setting
is 115200.
Data Bits
– Selects the number of data bits used for console redirection.
– Options available: 7/8. Default setting is 8.
Parity
– A parity bit can be sent with the data bits to detect some
transmission errors.
– Even: parity bit is 0 if the num of 1's in the data bits is even.
– Odd: parity bit is 0 if num of 1's in the data bits is odd.
– Mark: parity bit is always 1. Space: Parity bit is always 0.
– Mark and Space Parity do not allow for error detection.
– Options available: None/Even/Odd/Mark/Space. Default setting is
None.
Stop Bits
– Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit
indicates the beginning). The standard setting is 1 stop bit.
Communication with slow devices may require more than 1 stop bit.
COM1/SOL / COM2 Console
Redirection Settings
(continued)
– Options available: 1/2. Default setting is 1.
Flow Control
– Flow control can prevent data loss from buffer overow. When
sending data, if the receiving buffers are full, a 'stop' signal can
be sent to stop the data ow. Once the buffers are empty, a 'start'
signal can be sent to re-start the ow. Hardware ow control uses
two wires to send start/stop signals.
– Options available: None/Hardware RTS/CTS. Default setting is
None.
VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support
– Enable/Disable the VT-UTF8 Combo Key Support.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Recorder Mode
– When this mode enabled, only texts will be send. This is to capture
Terminal data.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Resolution 100x31
– Enable/Disable extended terminal resolution.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Putty KeyPad
– Selects FunctionKey and KeyPad on Putty.
– Options available: T100/LINUX/XTERMR6/SCO/ESCN/VT400.
– Default setting is VT100.
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note) Advanced items prompt when this item is dened.
BIOS Setup - 66 -
Page 67

Parameter Description
Redirection COM Port
– Selects a COM port to display redirection of Legacy OS and Legacy
OPROM Messages.
– Options available: COM1/SOL / COM2. Default setting is COM1/
SOL.
Resolution
Legacy Console Redirection
Settings
Serial Port for Out-of-Band
Management / Windows
Emergency Management
Services (EMS) Console
Redirection Settings
– On Legacy OS, the number of rows and columns supported in
redirection.
Options available: 80x24/80x25. Default setting is 80x24.
Redirection After BIOS POST
– This item allows user to enable console redirection after OS has
loaded.
– Options available: Always Enable/Boot Loader. Default setting is
Always Enable.
Out-of-Band Mgmt Port
– Selects a serial port to remotely manage a Windows server OS.
– Options available: COM1/SOL / COM2. Default setting is COM1/
SOL.
Terminal Type
– Selects a terminal type to be used for console redirection.
– Options available: VT100/VT100+/ANSI /VT-UTF8. Default setting
is VT-UTF8.
Bits per second
– Selects the transfer rate for console redirection.
– Options available: 9600/19200/38400/57600/115200. Default setting
is 115200.
Flow Control
– Flow control can prevent data loss from buffer overow. When
sending data, if the receiving buffers are full, a 'stop' signal can
be sent to stop the data ow. Once the buffers are empty, a 'start'
signal can be sent to re-start the ow. Hardware ow control uses
two wires to send start/stop signals.
– Options available: None/Hardware RTS/CTS. Default setting is
None.
- 67 - BIOS Setup
Page 68

5-2-7 CPU Conguration
Parameter Description
CPU Conguration
SVM Mode
SMEE
CPU 0 Information Press [Enter] to view more information related to CPU 0.
CPU 1 Information Press [Enter] to view more information related to CPU 1.
Enable/disable the CPU Virtualization.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Controls the Secure Memory Encryption Enable (SMEE) function.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
BIOS Setup - 68 -
Page 69

5-2-8 PCI Subsystem Settings
Parameter Description
PCI Bus Driver Version Displays the PCI Bus Driver version information.
Change the PCIe lanes.
SLOT1_F / SLOT1_R / SLOT2_F /
SLOT2_R / SLOT3 / OCP1 / OCP2
(Note1)
Lanes
SLOT1_F / SLOT1_R / SLOT2_F /
SLOT2_R / SLOT3 / OCP1 / OCP2 I/O
(Note1)
ROM
Onboard LAN Controller
Onboard LAN I/O ROM
(Note2)
(Note2)
PCI Devices Common Settings
Above 4G Decoding
(Note1) This section is dependent on the available PCIe Slot.
(Note2) This section is dependent on the available LAN controller.
Options available:
Auto / x16 / x8 x8 / x8 x4 x4 / x4 x4 x8 / x4 x4 x4 x4
(OCP2 Lanes only features Auto / x8 / x4 x4.)
Disabled. Default setting is Auto.
When enabled, this setting will initialize the device expansion
ROM for the related PCI-E slot.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable the onboard LAN devices.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable the onboard LAN devices and initializes device
expansion ROM.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable memory mapped I/O to 4GB or greater address
space (Above 4G Decoding).
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
- 69 - BIOS Setup
Page 70

Parameter Description
If the system has SR-IOV capable PCIe devices, this item Enable/
SR-IOV Support
Disable Single Root IO Virtualization Support.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
BIOS Setup - 70 -
Page 71

5-2-9 USB Conguration
Parameter Description
USB Conguration
USB Module Version Displays the USB version.
USB Controllers Displays the supported USB controllers.
USB Devices Displays the USB devices connected to the system.
Enable/disable the Legacy USB support fuction. AUTO option disables
Legacy USB Support
XHCI Hand-off
USB Mass Storage Driver
(Note)
Support
Port 60/64 Emulation
USB hardware delays and
time-outs
USB transfer time out
legacy support if no USB devices are connected. DISABLE option will
keep USB devices available only for EFI applications.
Options available: Auto/Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable the XHCI (USB 3.0) Hand-off support.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable the USB Mass Storage Driver Support.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enables the I/O port 60h/64h emulation support. This should be enabled
for the complete USB Keyboard Legacy support for non-USB aware OS.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
The time-out value for Control, Bulk, and Interrupt transfers.
Options available: 1 sec/5 sec/10 sec/20 sec. Default setting is 20 sec.
(Note) This item is present only if you attach USB devices.
- 71 - BIOS Setup
Page 72

Parameter Description
Device reset time-out
Device power-up delay
Mass Storage Devices
AMI Virtual CDROM0 1.00 /
HDisk0 1.00
USB mass storage device Start Unit command time-out.
Options available: 10 sec/20 sec/30 sec/40 sec. Default setting is 20 sec.
Maximum time the device will take before it properly reports itself to the
Host Controller. "Auto" uses default value: for a Root port it is 100 ms, for
a Hub port the delay is taken from Hub descriptor.
Options available: Auto/Manual. Default setting is Auto.
Mass storage device emulation type. AUTO enumerates devices
according to their media format. Optical drives are emulated as CDROM,
drives with no media will be emulated according to a drive type.
Options available: Auto/Floppy/Forced FDD/Hard Disk/CD-ROM. Default
setting is Auto.
BIOS Setup - 72 -
Page 73

5-2-10 NVMe Conguration
Parameter Description
NVMe controller and Drive
Information
Displays the NVMe devices connected to the system.
- 73 - BIOS Setup
Page 74

5-2-11 SATA Conguration
BIOS Setup - 74 -
Page 75

5-2-12 Network Stack Conguration
Parameter Description
Network Stack
Ipv4 PXE Support
Ipv4 HTTP Support
Ipv6 PXE Support
Ipv6 HTTP Support
IPSEC Certicate
PXE boot wait time
Media detect count
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
Enable/Disable the UEFI network stack.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable the Ipv4 PXE feature.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Enable/Disable the Ipv4 HTTP feature.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Enable/Disable the Ipv6 PXE feature.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Enable/Disable the Ipv6 HTTP feature.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Enable/Disable the IPSEC Certicate feature.
Wait time in seconds to press ESC key to abort the PXE boot.
Press the <+> / <-> keys to increase or decrease the desired values.
Number of times the presence of media will be checked.
Press the <+> / <-> keys to increase or decrease the desired values.
(Note) This item appears when Network Stack is set to Enabled.
- 75 - BIOS Setup
Page 76

5-2-13 AMD Mem Conguration Status
Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Channel A/BC/D/E/F/G/H
– DIMM0 Presence
CPU 0
CPU 1
– DIMM1 Presence
– Chipset/Bank Interleave
Dram EC
Dram Parity
Dimm Sensor Fine Grain Mode
Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Channel I/J/K/L/M/N/O/P
– DIMM0 Presence
– DIMM1 Presence
– Chipset/Bank Interleave
Dram EC
Dram Parity
Dimm Sensor Fine Grain Mode
BIOS Setup - 76 -
Page 77

5-2-14 iSCSI Conguration
Parameter Description
iSCSI Initiator Name
Add Attempt Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Delete Attempt Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Change Attempt Order Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Press [Enter] and name iSCSI Initiator. Only IQN format is accecpted.
Range: from 4 to 223
- 77 - BIOS Setup
Page 78

5-2-15 Tls Auth Conguration
Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Enroll Cert
– Press [Enter] to enroll a certicate
Server CA Conguration
– Commit Changes and Exit
– Discard Changes and Exit
Delete Cert
Client Cert Conguration N/A
• Enroll Cert Using File
• Cert GUID
Input digit character in 1111111-2222-3333-44441234567890ab format.
BIOS Setup - 78 -
Page 79

5-2-16 Intel(R) I350 Gigabit Network Connection
- 79 - BIOS Setup
Page 80

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] to congure advanced items.
Link Speed
– Allows for automatic link speed adjustment.
– Options available: Auto Negotiated/10 Mbps Half/10 Mbps Full/100
Mbps Half/100 Mbps Full. Default setting is Auto Negotiated.
NIC Conguration
Blink LEDs
UEFI Driver Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
Adapter PBA Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
Device Name Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
Chip Type Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
PCI Device ID Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
PCI Address Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
Link Status Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
MAC Address Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
Virtual MAC Address Displays the technical specications for the Network Interface Controller.
Wake On LAN
– Enables power on of the system via LAN. Note that conguring
Wake on LAN in the operating system does not change the value of
this setting, but does override the behavior of Wake on LAN in OS
controlled power states.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Identies the physical network port by blinking the associated LED.
Press the numeric keys to adjust desired values.
BIOS Setup - 80 -
Page 81

5-2-17 VLAN Conguration
- 81 - BIOS Setup
Page 82

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] to congure advanced items.
Create new VLAN
VLAN ID
– Sets VLAN ID for a new VLAN or an existing VLAN.
– Press the <+> / <-> keys to increase or decrease the desired values.
The valid range is from 0 to 4094.
Priority
– Sets 802.1Q Priority for a new VLAN or an existing VLAN.
Enter Conguration Menu
– Press the <+> / <-> keys to increase or decrease the desired values.
The valid range is from 0 to 7.
Add VLAN
– Press [Enter] to create a new VLAN or update an existing VLAN.
Congured VLAN List
– Enable/Disable the VLAN.
– Options available: Enable/Disable. Default setting is Disabled.
Remove VLAN
– Press [Enter] to remove an existing VLAN.
(Note) Only Supported when Congured VLAN List is set to Enabled.
BIOS Setup - 82 -
Page 83

5-2-18 MAC IPv4 Network Conguration
Parameter Description
Congured
Enable DHCP
Local IP Address
Local NetMask
Local Gateway
Local DNS Servers
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
(Note)
Save Changes and Exit Press [Enter] and then choose to save or discard the changes made.
Indicates whether network address is congured successfully or not.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled. Default setting is Disabled.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Enabled.
Press [Enter] to congure local IP address.
Press [Enter] to congure local NetMask.
Press [Enter] to congure local Gateway
Press [Enter] to congure local DNS servers
(Note) This item will appear on the screen when Congured is set to Enabled.
- 83 - BIOS Setup
Page 84

5-2-19 MAC IPv6 Network Conguration
Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
Interface Name
Interface Type
MAC address
Host address
Route Table
Gateway addresses
DNS addresses
Enter Conguration Menu
Interface ID
– The 64-bit alternative interface ID for the device. The string is
colon separated e.g. ff:dd:88:66:cc:1:2:3.
DAD Transmit Count
– The number of consecutive Neighbor Solicitaion messages sent
while performing Duplicate Address Detection on a tentative
address. A value of zero indicates that Duplicate Addres Detection
is not performed.
Policy
Save Changes and Exit
BIOS Setup - 84 -
Page 85

5-3 AMD CBS Menu
AMD CBS menu displays submenu options for configuring the CPU-related information that the BIOS
automatically sets. Select a submenu item, then press [Enter] to access the related submenu screen.
- 85 - BIOS Setup
Page 86

5-3-1 Valhalla Common Options
Parameter Description
Valhalla Common Options
Press [Enter] for more options.
Custom Core Pstates
– Allows you to accept or decline custom core pstates. When
Performance
Prefetcher settings
Core Watchdog
CCD/Core/Thread Enablement
– Allows you to accept or decline enabling CCDs, processor cores
Press [Enter] for more options.
L1 Stream HW Prefetcher
– Option to enable or disable L1 Stream HW Prefetcher
– Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
L2 Stream HW Prefetcher
– Option to enable or disable L2 Stream HW Prefetcher
– Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Press [Enter] for more options.
Core Watchdog Timer Enable
– Enable or disable CPU watchdog timer.
– Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
accepted you can disable or customize ceratin pstates.
and threads. When accepted you can control the number of CCDs
to be used, the number of cores to be used, and whether to enable
or disable symmetric multithreading.
BIOS Setup - 86 -
Page 87

Parameter Description
From a workaroud for GCC/C000005 issue for XV Core on CZ A0,
RedirectForReturnDis
Platform First Error Warning
Core Performance Boost
Global C-State Control
Power Supply Idle Control
Opcache Control
SEV ASID Count
SEV-ES ASID Space Limit
Control
Streaming Stores Control
Local APIC Mode
ACPI_CST C1 Decaration
MCA error thresh enable
SMU and PSP Debug Mode
setting MSRC001_1029 Decode Conguration (DE_CFG) bit 14
[DecfgNoRdrctForReturns] to 1.
Options available: Auto/1/0. Default option is Auto.
Enable/Disable PFEH, cloak individual banks, and mask deferred error
interrupts from each bank.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Enabled.
Allows you to disable CPB.
Options available: Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Controls the IO based C-state generation and DF C-states.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Congures the power supply idle control.
Options available: Low Current Idle/Typical current Idle/Auto. Default
option is Auto.
Enables or disables the Opcache.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
This eld species the max. valid ASID, which affects the maximum
system physical address space. 16TB of physical address space is
available for systems that support 253 ASIDs, while 8TB of physical
address space is available for systems that support 509 ASIDs.
Options available: 253 ASIDs/509 ASIDs/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Space limit control for SEV-ES ASIDs.
Options available: Auto/Manual. Default option is Auto.
Enables or disables the streaming stores functionality.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Sets the Local APIC mode.
Options available: xAPIC/x2APIC/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Determines whether or not to declare the C1 state to the OS.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Enable MCA error thresholding.
Options available: False/True/Auto. Default option is Auto.
When this option is enabled, specic uncorrected errors detected by the
PSP FW or SMU FW will hand and not reset the system.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
- 87 - BIOS Setup
Page 88

Parameter Description
By default (Auto) the bronze workaround is applied.
Bronze workaround: DbReq and PDM function as expected, breakpoint
redirect capability compromised.
Xtrig7 Workaround
PPIN Opt-in
Silver workaround: DbReq, PDM, and breakpoint redirect function as
expected, SCAN capability compromised.
Options available: Auto/No Workaround/Bronze Workaround/Silver
Workaround. Default option is Auto.
Turns on PPIN feature.
Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
BIOS Setup - 88 -
Page 89

5-3-2 DF Common Options
Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for conguration of advanced items.
DRAM scrub time
– Provides a value that is the number of hours to scrub memory.
– Options available: Disabled/1 hour/4 hours/8 hours/16 hours/24
Poison scrubber control
Scrubber
– Allows you to enable or disable poison scrubber control.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Redirect scrubber control
– Allows you to enable or disable redirect of scrubber control.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Redirect scrubber limit
– Allows you to set the redirect scrubber limit.
– Options available: 2/4/8/Innite/Auto. Default option is Auto.
hours/48 hours/Auto. Default option is Auto.
- 89 - BIOS Setup
Page 90

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options.
NUMA notes per socket
– Species the number of desired NUMA (Non-uniform Memory
Access) notes per socket. Zero will attempt to interleave the two
sockets together.
– Options available: NPS0/NPS1/NPS2/NPS4/Auto. Default option
is Auto.
Memory interleaving
– Allows for disabling memory interleaving. Note that NUMA nodes
per socket will be honored regardless of this setting.
– Options available: Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Memory interleaving size
– Controls the memory interleaving size. The valid value are AUTO,
Memory Addressing
ACPI
256 bytes, 512 bytes, 1Kbytes or 2Kbytes. This determines the
starting address of the interleave (bit 8, 9, 10 or 11).
– Options available: 256 Bytes/512 Bytes/1 KB/2KB/Auto. Default
setting is Auto.
1TB remap
– Attempt to remap DRAM out of the space just below the 1TB
boundary. The ability to remap depends on DRAM conguration,
NPS, and interleaving selection, and may not always be possible.
– Options available: Do not remap/Attempt to remap.Auto. Default
option is Auto.
DRAM map inversion
– Inverting the map will cause the highest memory channels to get
assigned the lowest addresses in the system.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Press [Enter] for more options.
ACPI SRAT L3 Cache as NUMA Domain
– Enabled: Each CCX in the system will be declared as a separate
NUMA domain.
– Disabled: Memory Addressing \ NUMA nodes per socket will be
declared.
– Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
ACPI SLIT Distance Control
– Determines how the SLIT distances are declared.
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Auto.
ACPI SLIT remote relative distance
– Set the remote socket distance for 2P systems as near (2.8) or far
(3.2).
– Options available: Near/Far/Auto. Default option is Auto.
BIOS Setup - 90 -
Page 91

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options.
GMI encryption control
– Control GMI link encryption.
– Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
xGMI encryption control
– Control xGMI link encryption.Options available: Disable/Enable/
Auto. Default option is Auto.
CAKE CRC perf bounds control
– Control CAKE CRC perf bounds
– Options available: Auto/Manual. Default option is Auto.
Link
Disable DF to external IP
Sync Flood Propagation
Disable DF sync ood
propagation
Freeze DF module queues on
error
CC6 memory region encryption
System probe lter
Memory Clear
PSP error injection support
4-link xGMI max speed
– Set 4-link xGMI max speed.
– Options available: 10.667Gbps/13Gbps/16Gbps/18Gbps/Auto.
Default option is Auto.
3-link xGMI max speed
– Set 3-link xGMI max speed.
– Options available: 10.667Gbps/13Gbps/16Gbps/18Gbps/Auto.
Default option is Auto.
xGMI TXEQ Mode
– Select XGMI TXEQ/RX vetting Mode.
– Options available: TXEQ_Disabled/TXEQ_LAne/TXEQ_Link/
TXEQ_RX_Vet/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Disable SyncFlood to UMC & downstream slaves.
Options avaialble: Sync ood disabled/Sync ood enabled/Auto.
Default option is Auto.
Enable/Disable DF SyncFlood.
Options avaialble: Sync ood disabled/Sync ood enabled/Auto.
Default option is Auto.
Controls DF PIE Cong. Disabling this options sets DF:PIECong.
Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Control whether or not the CC6 save/restore memory is encrypted.
Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Controls whether or not the probe lter is enabled. Has no effect on parts
where the probe lter is fuse disabled.
Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
When this feature is disabled, BIOS does not implement MemClear after
memory training (only if non-ECC DIMMs are used).
Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Select True to enable error injection.
Options available: False/True. Default option is False.
- 91 - BIOS Setup
Page 92

5-3-3 UMC Common Options
Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options.
Enforce POR
– Press [Enter] to congure the enforcement of Plan Of Record
DRAM Controller Conguration
DDR4 Common Options
– Press [Enter] to congure DRAM controller options.
CAD Bus Conguration
– Press [Enter] to congure CAD Bus options.
Data Bus conguration
– Press [Enter] to congure Data Bus options.
Common RAS
– Press [Enter] to congure Common RAS options.
Security
– Press [Enter] to congure UMC security options.
(POR) which enables enforcement of POR restrictions for DDR4
frequency and voltage programming. Memory speeds will be
capped at Intel guidelines.
BIOS Setup - 92 -
Page 93

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options
Chipselect Interleaving
– Interleave memory blocks across the DRAM chip slects for node 0
– Options available: Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
BankGroupSwap
– Congures the BankGroupSwap. BankGroupSwap (BGS) is a
memory mapping option in AGESA that alters how applications get
assigned to physical locations within the memory modules. When
this option sets to Auto, it is null.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
BankGroupSwapAlt
– Congures the BankGroupSwapAlt.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
DRAM Memory Mapping
NVDIMM Press [Enter] for more options.
Memory MBIST
Address Hash Bank
– Enable or disable bank address hashing.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Address Hash CS
– Enable or disable CS address hashing.
– Options available: Auto/Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Auto.
Address Hash Rm
– Enable or disable RM address hashing.
– Options available: Auto/Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Auto.
SPD Read Optimization
– Enable or disable SPD Read Optimization. Enabled = SPD reads
are skipped for Reserved elds and most of upper 256 Bytes,
Disabled = read all 512 SPD Bytes.
– Options available: Auto/Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Auto.
Press [Enter] for more options
MBIST Enable
– Enable or disable Memory MBIST.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled. Default option is Disabled.
Data Eye
– Press [Enter] for more options.
- 93 - BIOS Setup
Page 94

5-3-4 NBIO Common Options
Parameter Description
NBIO Common Options
IOMMU
ACS Enable
PCIe ARI Support
PCIe Ten Bit Tag Support
HD Audio Enable
Enable/Disable IOMMU.
Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default setting is Disabled.
AER must be enabled for ACS enable to work.
Options available: Enable/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Enables Alternative Routing ID Interpretation.
Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Enables PCIe ten bit tags for supported devices. Auto = Disabled
Options available: Disable/Enable/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Enables or disables HD Audio.
Options available: Enable/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
BIOS Setup - 94 -
Page 95

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options.
Determinism Control
– Auto = Use the fused determinism, Manual = User can set
customized determinism.
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Manual.
cTDP Control
– Auto = Use the fused TDP, Manual = User can set customized
TDP. TDP is used to dene the RC thermal model only.
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Manual.
Fan Control
– Press [Enter] to congure the fan control table.
CLD0_VDDP Control
– Manual = User can set customized CLD0_VDDP voltage.
– Options available: Auto/Manual. Default option is Auto.
EfciencyModeEn
– 0 = use performance optimized CCLK DPM settings, 1 = use
power efciency optimized CCLK DPM settings.
– Options available: Auto/Enabled. Default option is Auto.
SMU Common Options
Package Power Limit Control
– Auto = Use the fused PPT, Manual = User can set PPT. PPT will
be used as the ASIC power limit.
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Manual.
xGMI Link Width Control
– Auto = Use degault xGMI link width controller, Manual = User can
set custom xGMI link width controller settings.
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Auto.
APBDIS
– 0 = not APBDIS (mission mode), 1 = APBDIS.
– Options available: 0/1/Auto. Default option is Auto.
DF Cstates
– Enable or disable DF C-states.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
CPPC
– Enable or disable CPPC.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
BoostFmaxEn
– Auto = Use degault Fmax, Manual = User can set boost Fmax.
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Auto.
- 95 - BIOS Setup
Page 96

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options.
NBIO RAS Global Control
– Options available: Manual/Auto. Default option is Auto.
NBIO RAS Control
– 0 = Disabled, 1 = MCA, 2 = Legacy.
– Options available: Disabled/MCA/Legacy. Default option is MCA.
Egress Poison Severity High
– Enter a value. Each bit set to 1 enables high severity on the
associated IOHC egress port. A bit of 0 indicates low severity.
Egress Poison Severity Low
– Enter a value. Each bit set to 1 enables high severity on the
associated IOHC egress port. A bit of 0 indicates low severity.
NBIO SyncFlood Generation
– This value may be used to mask SyncFlood caused by NBIO RAS
options. When set to TRUE SyncFlood from NBIO is masked.
When set to FALSE NBIO is capable of generating SyncFlood.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
NBIO SyncFlood Reporting
– This value may be used to enable SyncFlood reporting to APML.
When set to TRUE SyncFlood will be reported to APML. When set
to FALSE that reporting will be disabled.
NBIO RAS Common Options
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Disabled.
Egress Poison Mask High
– Enter a value. These set the enable mask for masking of errors
logged in EGRESS_POISON_STATUS. For each bit set to 1,
errors are masked. For each bit set to 0, errors trigger response
actions.
Egress Poison Mask Low
– Enter a value. These set the enable mask for masking of errors
logged in EGRESS_POISON_STATUS. For each bit set to 1,
errors are masked. For each bit set to 0, errors trigger response
actions.
Uncorrected Converted to Poison Enable Mask High
– Enter a value. These set the enable mask for masking of
uncorrectable parity errors on internal arrays. For each bit set to
1, a system fatal error event is triggered for UCP errors on arrays
associated with that egress port. For each bit set to 0, errors are
masked.
Uncorrected Converted to Poison Enable Mask Low
– Enter a value. These set the enable mask for masking of
uncorrectable parity errors on internal arrays. For each bit set to
1, a system fatal error event is triggered for UCP errors on arrays
associated with that egress port. For each bit set to 0, errors are
masked.
BIOS Setup - 96 -
Page 97

Parameter Description
System Hub Watchdog Timer
– Enter a value. This value species the timer interval of the
SYSHUB watchdog timer in miliseconds.
SLINK Read Response OK
– This value species whether SLINK read response errors are
converted to an Okay response. When this value is set to TRUE,
read response errors are converted to Okay responses with data
of all FFs. When set to FALSE read response errors are not
converted.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Disabled.
SLINK Read Response Error Handling
– This value species whether SLINK write response errors are
converted to an Okay response. When this value is set to 0, write
response errors will be logged in the MCA. When set to 1, write
response errors will trigger an MCOMMIT error. When this value is
set to 2, write response errors are converted to Okay responses.
– Options available: Enabled/Trigger MCOMMIT Error/Log Errors in
MCA. Default option is Log Errors in MCA.
NBIO RAS Common Options
(continued)
Log Poison Data from SLINK
– This value species whether poison data propogated from SLINK
will generate a deferred error. When this value is set to TRUE,
deferred errors are enabled. When set to FALSE, errors are not
generated.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Disabled.
PCIe Aer Reporting Mechanism
– This value selects the method of reporting AER errors from PCI
Express. A value of 0 indicates that the hardware will report the
error through MCA. A value of 1 allows OS First handling of the
errors through generation of a system control interrupt (SCI). A
value of 2 provides for Firmware First handling of errors through
generation of a system management interrupt (SMI).
– Options available: OS First/MCA/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Edpc Control
– (0) Disabled; (1) Enabled; (3) Auto.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default option is
Disabled.
NBIO Poison Consumption
– Options available: Auto/Enabled/Disabled. Default option is Auto.
- 97 - BIOS Setup
Page 98

Parameter Description
Sync Flood on PCIe Fatal Error
– When 'Sync Flood on PCIe Fatal Error' is True,
PcdAmdPcieSyncFloodOnFatal should be set to True. When 'Sync
NBIO RAS Common Options
(continued)
Enable AER Cap
Early Link Speed
Hot Plug Handling mode
Presence Detect Select mode
Preferred IO Device
Flood on PCIe Fatal Error' is False, PcdAmdPcieSyncFloodOnFatal
should be set to False. When 'Sync Flood on PCIe Fatal Error' is
Auto, PcdAmdPcieSyncFloodOnFatal should retain its AGESA
default.
– Options available: Auto/True/False. Default option is Auto.
Enables Advanced Error Reporting Capabilty.
Options available: Enable/Disabled/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Sets Early Link Speed.
Options available: Auto/Gen1/Gen2. Default option is Auto.
Controls the Hot Plug Handling mode.
Options available: A0 Mode/OS First (No Error Handling)/OS First (Error
Handling - Not Implementd/Firmware First (Not Implemented)/Auto.
Default option is Auto.
Controls the Presence Detect Select mode.
Options available: OR/And/Auto. Default option is Auto.
Enter a value for the preferred IO device.
[23:16] Bus Number
[15:8] Dev Number
[7:0] Fun Number
BIOS Setup - 98 -
Page 99

5-3-5 FCH Common Options
Parameter Description
FCH Common Options
SATA Enable
– Enable or disable OnChip SATA controller.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
SATA RAS Support
– Enable or disable SATA RAS support.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
SATA Conguration Options
Sata Disabled AHCI Prefetch Function
– Enable or disable Sata Disabled AHCI Prefetch Function.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Aggressive SATA Device Sleep Port 0
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Aggressive SATA Device Sleep Port 1
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
- 99 - BIOS Setup
Page 100

Parameter Description
Press [Enter] for more options.
XHCI Controller0 Enable
– Enable or disable USB3 controller.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
XHCI Controller1 Enable
USB Conguration Options
SD Dump Options
AC Power Loss Options
I2C Conguration Options
Uart Conguration Options
ESPI Conguration Options
– Enable or disable USB3 controller.
– Options available: Enabled/Disabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
USB ecc SMI Enable
– Options available: Enabled/Off/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
MCM USB enable
– Press [Enter] for advanced congurations.
Press [Enter] for more options.
SD Conguration Mode
– Select SD Mode.
– Options available: SD Dump disabled/SD Dump Enabled. Default
setting is SD Dump disabled.
Press [Enter] for more options.
AC Loss Control
– Select AC Loss Control Method.
– Options available: Power Off/Power On/Last State. Default setting
is Last State.
Press [Enter] for more options.
I2C 0/1/2/3/4/5 Enable
– Enable or disable I2C 0/1/2/3/4/5.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Press [Enter] for more options.
Uart 0 Enable
– Uart 0 has no HW FC if Uart 2 is enabled.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Uart 1 Enable
– Uart 1 has no HW FC if Uart 3 is enabled.
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Uart 2 Enable (no HW FC)
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Uart 3 Enable (no HW FC)
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
Press [Enter] for more options.
ESPI Enable
– Options available: Disabled/Enabled/Auto. Default setting is Auto.
BIOS Setup - 100 -
 Loading...
Loading...