Page 1

GA-890FXA-UD7
AM3 socket motherboard for
AMD Phenom™ II processor/ AMD Athlon™ II processor
User's Manual
Rev. 2101
12ME-890FXA7-2101R
Page 2

Jun. 2, 2010
GA-890FXA-UD7
Motherboard
Jun. 2, 2010
Motherboard
GA-890FXA-UD7
Page 3
Copyright
© 2010 GIGA-BYTE TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. All rights reserved.
The trademarks mentioned in this manual are legally registered to their respective owners.
Disclaimer
Information in this manual is protected by copyright laws and is the property of GIGABYTE.
Changes to the specications and features in this manual may be made by GIGABYTE with-
out prior notice. No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, translated, transmitted, or
published in any form or by any means without GIGABYTE's prior written permission.
Documentation Classications
In order to assist in the use of this product, GIGABYTE provides the following types of documentations:
For quick set-up of the product, read the Quick Installation Guide included with the product.
For detailed product information, carefully read the User's Manual.
For instructions on how to use GIGABYTE's unique features, read or download the information
on/from the Support&Downloads\Motherboard\Technology Guide page on our website.
For product-related information, check on our website at:
http://www.gigabyte.com
Identifying Your Motherboard Revision
The revision number on your motherboard looks like this: "REV: X.X." For example, "REV: 1.0"
means the revision of the motherboard is 1.0. Check your motherboard revision before updating
motherboard BIOS, drivers, or when looking for technical information.
Example:
Page 4

Table of Contents
Box Contents ...................................................................................................................6
Optional Items .................................................................................................................6
GA-890FXA-UD7 Motherboard Layout ............................................................................7
GA-890FXA-UD7 Motherboard Block Diagram ...............................................................8
Chapter 1 Hardware Installation .....................................................................................9
1-1 Installation Precautions .................................................................................... 9
1-2 Product Specications .................................................................................... 10
1-3 Installing the CPU and CPU Cooler ............................................................... 13
1-3-1 Installing the CPU ...................................................................................................13
1-3-2 Installing the CPU Cooler .......................................................................................15
1-4 Installing the Hybrid Silent-Pipe Module ........................................................ 16
1-5 Installing the Memory ..................................................................................... 17
1-5-1 Dual Channel Memory Conguration .....................................................................17
1-5-2 Installing a Memory ...............................................................................................18
1-6 Installing an Expansion Card ......................................................................... 19
1-7 Setting up ATI CrossFireX™ Conguration .....................................................20
1-8 Installing the SATA Bracket ............................................................................ 21
1-9 Back Panel Connectors .................................................................................. 22
1-10 Internal Connectors ........................................................................................ 24
Chapter 2 BIOS Setup ..................................................................................................37
2-1 Startup Screen ............................................................................................... 38
2-2 The Main Menu .............................................................................................. 39
2-3 MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.) ........................................................................ 41
2-4 Standard CMOS Features .............................................................................. 47
2-5 Advanced BIOS Features .............................................................................. 49
2-6 Integrated Peripherals .................................................................................... 51
2-7 Power Management Setup ............................................................................. 56
2-8 PC Health Status ............................................................................................ 58
2-9 Load Fail-Safe Defaults .................................................................................. 60
2-10 Load Optimized Defaults ................................................................................ 60
2-11 Set Supervisor/User Password ...................................................................... 61
2-12 Save & Exit Setup .......................................................................................... 62
2-13 Exit Without Saving ........................................................................................ 62
- 4 -
Page 5

Chapter 3 Drivers Installation ........................................................................................63
3-1 Installing Chipset Drivers ............................................................................... 63
3-2 Application Software ...................................................................................... 64
3-3 Technical Manuals .......................................................................................... 64
3-4 Contact ........................................................................................................... 65
3-5 System ........................................................................................................... 65
3-6 Download Center ........................................................................................... 66
3-7 New Utilities ................................................................................................... 66
Chapter 4 Unique Features ...........................................................................................67
4-1 Xpress Recovery2 .......................................................................................... 67
4-2 BIOS Update Utilities ..................................................................................... 70
4-2-1 Updating the BIOS with the Q-Flash Utility .............................................................70
4-2-2 Updating the BIOS with the @BIOS Utility .............................................................73
4-3 EasyTune 6 .................................................................................................... 74
4-4 Easy Energy Saver ........................................................................................ 75
4-5 Q-Share .......................................................................................................... 77
4-6 SMART Recovery........................................................................................... 78
4-7 Auto Green ..................................................................................................... 79
4-8 Teaming ......................................................................................................... 80
Chapter 5 Appendix ......................................................................................................81
5-1 Conguring SATA Hard Drive(s) ..................................................................... 81
5-1-1 Conguring AMD SB850 SATA Controller .............................................................81
5-1-2 Conguring GIGABYTE SATA2/JMicron JMB362 SATA Controller ........................87
5-1-3 Making a SATA RAID/AHCI Driver Diskette ............................................................93
5-1-4 Installing the SATA RAID/AHCI Driver and Operating System ...............................95
5-2 Conguring Audio Input and Output ............................................................. 104
5-2-1 Conguring 2/4/5.1/7.1-Channel Audio .................................................................104
5-2-2 Conguring S/PDIF In/Out ....................................................................................106
5-2-3 Enabling the Dolby Home Theater Function ........................................................108
5-2-4 Conguring Microphone Recording ......................................................................109
5-2-5 Using the Sound Recorder ...................................................................................111
5-3 Troubleshooting............................................................................................ 112
5-3-1 Frequently Asked Questions ................................................................................11 2
5-3-2 Troubleshooting Procedure ..................................................................................113
5-4 POST Error Code ......................................................................................... 115
5-5 Regulatory Statements ................................................................................. 119
- 5 -
Page 6

Box Contents
GA-890FXA-UD7 motherboard
Motherboard driver disk
User's Manual
Quick Installation Guide
One IDE cable
Four SATA cables
I/O Shield
One SATA bracket
Two 2-Way CrossFireX bridge connectors
One Hybrid Silent-Pipe module kit
• The box contents above are for reference only and the actual items shall depend on the product package you obtain.
The box contents are subject to change without notice.
• The motherboard image is for reference only.
Optional Items
Floppy disk drive cable (Part No. 12CF1-1FD001-7*R)
2-port USB 2.0 bracket (Part No. 12CR1-1UB030-5*R)
2-port IEEE 1394a bracket (Part No. 12CF1-1IE008-0*R)
2-port SATA power cable (Part No. 12CF1-2SERPW-0*R)
S/PDIF In cable (Part No. 12CR1-1SPDIN-0*R)
COM port cable (Part No. 12CF1-1CM001-3*R)
LPT port cable (Part No. 12CF1-1LP001-0*R)
- 6 -
Page 7
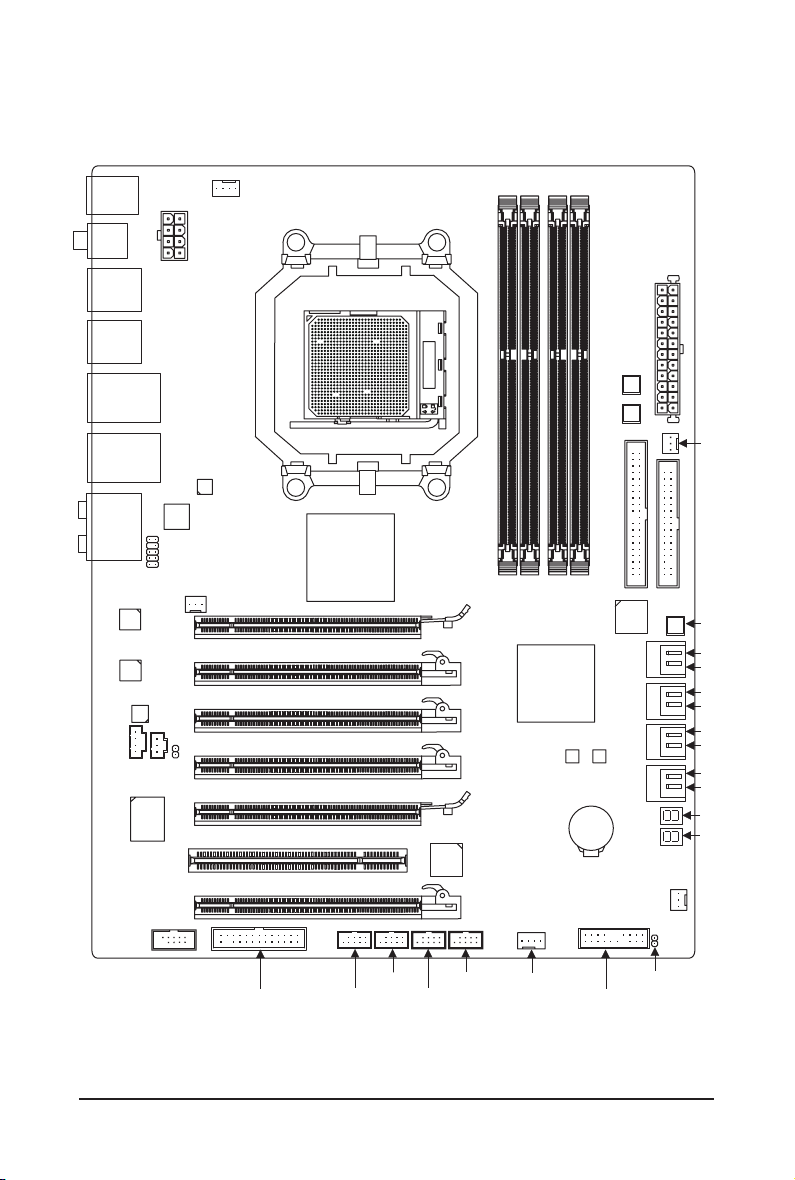
GA-890FXA-UD7 Motherboard Layout
KB_MS_USB
ATX_12V
RCA_SPDIF
USB_1394_ESATA_2
USB_1394_ESATA_1
USB_LAN2
USB30_LAN1
F_AUDIO
Realtek
RTL8111D
Realtek
RTL8111D
CODEC
CD_IN
NEC D720200F1
SPDIF_I
iTE
IT8720
AUDIO
JMicron JMB362
NB_FAN
SPDIF_O
PCI
PCIEX8_2
CPU_FAN
AMD 890FX
GA-890FXA-UD7
Socket AM3
PCIEX16_1
PCIEX4_1
PCIEX8_1
PCIEX4_2
PCIEX16_2
T.I.
TSB43AB23
DDR3_1
AMD SB850
DDR3_2
M_BIOS
DDR3_3
BAT
GIGABYTE
DDR3_4
SATA2
B_BIOS
PW_SW
RST_SW
IDE
ATX
FDD
SYS_FAN2
PWR_FAN
CMOS_SW
GSATA2_6
GSATA2_7
SATA3_4
SATA3_5
SATA3_2
SATA3_3
SATA3_0
SATA3_1
(Note)
TSR1
(Note)
TSL1
COM
F_USB3 F_USB1
LPT
F_1394
F_USB2
(Note ) For error code information, please refer to Chapter 5.
- 7 -
SYS_FAN1
CLR_CMOS
F_PANEL
Page 8
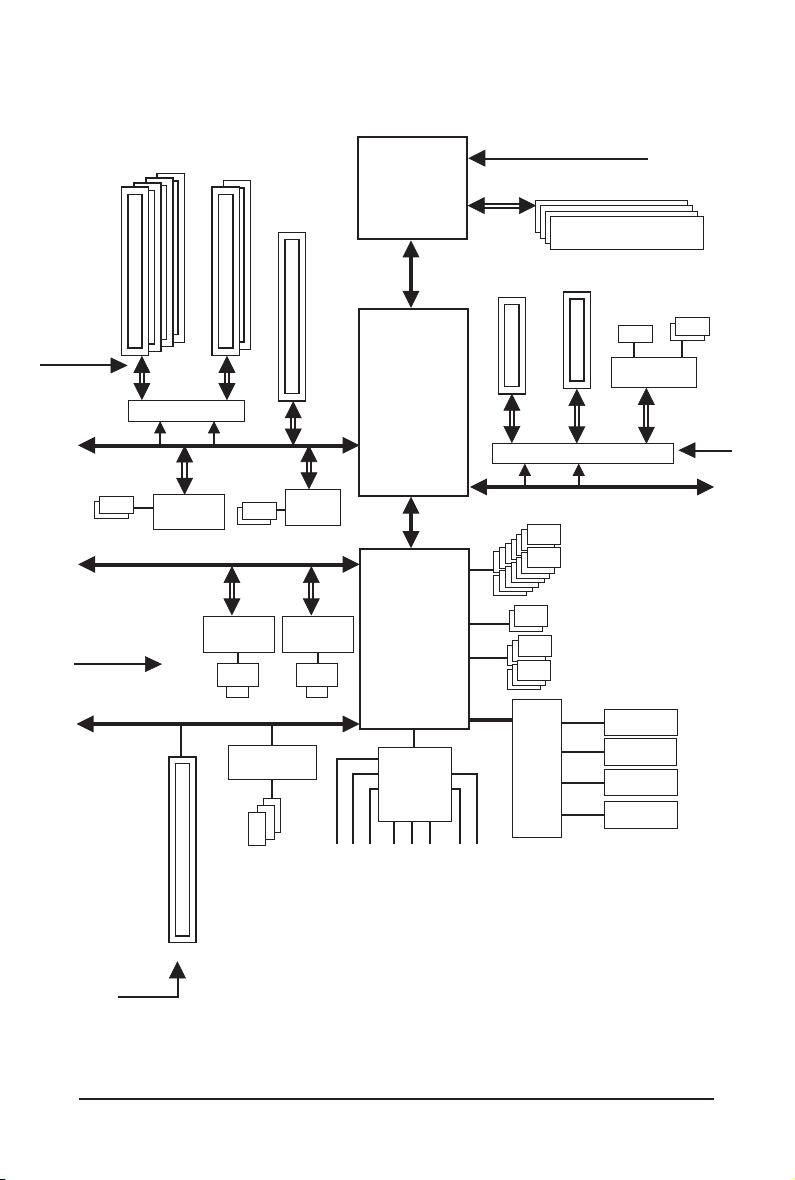
GA-890FXA-UD7 Motherboard Block Diagram
4 PCI Express x8
PCIe CLK
(100 MHz)
PCI Express
Bus
2 USB 3.0/2.0
PCI Express Bus
PCIe CLK
(100 MHz)
2 PCI Express x16
or
x8 x16
Switch
x1
NEC
D720200F1
2 SATA 3Gb/s
Realtek
RTL8111D
RJ45
PCI Bus
LAN1
1 PCI Express x4
JMicron
JMB362
x1
Realtek
RTL8111D
RJ45
LAN2
T.I.
TSB43AB23
CPU CLK+/- (200 MHz)
AM3 CPU
DDR3 1866 (O.C.)/1333/1066 MHz
Dual Channel Memory
x4
1 PCI Express x4
running at x1
ATA-133/100/66/
33 IDE Channel
or
+
x1
Switch
14 USB 2.0/1.1
GIGABYTE
SATA2
x1
(Note)
2 SATA 3Gb/s
PCIe CLK
(100 MHz)
Hyper Transport 3.0
1 PCI Express x4
AMD 890FX
x4
x1
x1
Dual BIOS
AMD SB850
6 SATA 6Gb/s
CODEC
LPC
Bus
iTE
IT8720
Floppy
LPT Port
COM Port
3 IEEE 1394a
1 PCI
PCI CLK
(33 MHz)
(Note) Two share the same ports with eSATA.
MIC
Line In
Line Out
S/PDIF In
S/PDIF Out
Side Speaker Out
Surround Speaker Out
Center/Subwoofer Speaker Out
- 8 -
PS/2 KB/Mouse
Page 9

Chapter 1 Hardware Installation
1-1 Installation Precautions
The motherboard contains numerous delicate electronic circuits and components which can
become damaged as a result of electrostatic discharge (ESD). Prior to installation, carefully read
the user's manual and follow these procedures:
• Prior to installation, do not remove or break motherboard S/N (Serial Number) sticker or
warranty sticker provided by your dealer. These stickers are required for warranty validation.
• Always remove the AC power by unplugging the power cord from the power outlet before
installing or removing the motherboard or other hardware components.
• When connecting hardware components to the internal connectors on the motherboard,
make sure they are connected tightly and securely.
• When handling the motherboard, avoid touching any metal leads or connectors.
• It is best to wear an electrostatic discharge (ESD) wrist strap when handling electronic com-
ponents such as a motherboard, CPU or memory. If you do not have an ESD wrist strap,
keep your hands dry and rst touch a metal object to eliminate static electricity.
• Prior to installing the motherboard, please have it on top of an antistatic pad or within an
electrostatic shielding container.
• Before unplugging the power supply cable from the motherboard, make sure the power sup-
ply has been turned off.
• Before turning on the power, make sure the power supply voltage has been set according to
the local voltage standard.
• Before using the product, please verify that all cables and power connectors of your hard-
ware components are connected.
• To prevent damage to the motherboard, do not allow screws to come in contact with the
motherboard circuit or its components.
• Make sure there are no leftover screws or metal components placed on the motherboard or
within the computer casing.
• Do not place the computer system on an uneven surface
• Do not place the computer system in a high-temperature environment.
• Turning on the computer power during the installation process can lead to damage to sys-
tem components as well as physical harm to the user.
• If you are uncertain about any installation steps or have a problem related to the use of the
product, please consult a certied computer technician.
.
- 9 - Hardware Installation
Page 10

1-2 Product Specications
CPU Support for AM3 processors:
AMD Phenom™ II processor/ AMD Athlon™ II processor
(Go to GIGABYTE's website for the latest CPU support list.)
Hyper Transport Bus 5200 MT/s
Chipset
Memory 4 x 1.5V DDR3 DIMM sockets supporting up to 16 GB of system memory
Dual channel memory architecture
Support for DDR3 1866 (O.C.)/1333/1066 MHz memory modules
(Go to GIGABYTE's website for the latest supported memory speeds and
memory modules.)
Audio
High Denition Audio
2/4/5.1/7.1-channel
Support for Dolby® Home Theater
LAN 2 x Realtek RTL8111D chips (10/100/1000 Mbit)
Support for Teaming
Expansion Slots 2 x PCI Express x16 slots, running at x16 (PCIEX16_1, PCIEX16_2)
1 x PCI slot
Multi-Graphics
Technology
Storage Interface South Bridge:
- 6 x SATA 6Gb/s connectors (SATA3_0~SATA3_5) supporting up to 6 SATA
6Gb/s devices
- Support for SATA RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10, and JBOD
GIGABYTE SATA2 chip:
- 2 x SATA 3Gb/s connectors (GSATA2_6, GSATA2_7) supporting up to
2 SATA 3Gb/s devices
- Support for SATA RAID 0, RAID 1, and JBOD
- 1 x IDE connector supporting ATA-133/100/66/33 and up to 2 IDE devices
JMicron JMB362 chip:
- 2 x eSATA 3Gb/s connectors (eSATA/USB Combo) on the back panel sup porting up to 2 SATA 3Gb/s devices
- Support for SATA RAID 0, RAID 1, and JBOD
iTE IT8720 chip:
- 1 x oppy disk drive connector supporting up to 1 oppy disk drive
North Bridge: AMD 890FX
South Bridge: AMD SB850
Realtek ALC889 codec
Support for S/PDIF In/Out
Support for CD In
Support for Smart Dual LAN
2 x PCI Express x16 slots, running at x8 (PCIEX8_1, PCIEX8_2)
2 x PCI Express x16 slots, running at x4 (PCIEX4_1, PCIEX4_2)
(All PCI Express slots conform to PCI Express 2.0 standard.)
Support for 2-Way/3-Way/4-Way ATI CrossFireX™ technology
(Note 2)
(Note 3)
(Note 2)
(Note 1)
Hardware Installation - 10 -
Page 11

USB
Combo, 6 via the USB brackets connected to the internal USB headers)
NEC D720200F1 chip
- Up to 2 USB 3.0/2.0 ports on the back panel
IEEE 1394 T.I. TSB43AB23 chip
- Up to 3 IEEE 1394a ports (2 on the back panel, 1 via the IEEE 1394a
bracket connected to the internal IEEE 1394a header)
Internal 1 x 24-pin ATX main power connector
Connectors 1 x 8-pin ATX 12V power connector
1 x oppy disk drive connector
1 x IDE connector
6 x SATA 6Gb/s connectors
2 x SATA 3Gb/s connectors
1 x CPU fan header
2 x system fan headers
1 x North Bridge fan header
1 x power fan header
1 x front panel header
1 x front panel audio header
1 x CD In connector
1 x S/PDIF In header
3 x USB 2.0/1.1 headers
1 x IEEE 1394a header
1 x serial port header
1 x parallel port header
1 x clearing CMOS jumper
1 x clearing CMOS button
1 x power button
1 x reset button
Back Panel 1 x PS/2 keyboard/mouse port
Connectors 1 x coaxial S/PDIF Out connector
1 x optical S/PDIF Out connector
6 x USB 2.0/1.1 ports
2 x USB 3.0/2.0 ports
2 x eSATA/USB Combo connectors
2 x IEEE 1394a ports
2 x RJ-45 ports
6 x audio jacks (Center/Subwoofer Speaker Out/Rear Speaker Out/
Side Speaker Out/Line In/Line Out/Microphone)
I/O Controller iTE IT8720 chip
South Bridge
- Up to 14 USB 2.0/1.1 ports
1 x S/PDIF Out header
(8 on the back panel, including 2 eSATA/USB
- 11 - Hardware Installation
Page 12

Hardware Monitor System voltage detection
CPU/system temperature detection
CPU/system/North Bridge fan speed detection
CPU overheating warning
CPU/system/North Bridge fan fail warning
CPU/system fan speed control
(Note 4)
BIOS 2 x 8 Mbit ash
Use of licensed AWARD BIOS
Support for DualBIOS
™
PnP 1.0a, DMI 2.0, SM BIOS 2.4, ACPI 1.0b
Unique Features Support for @BIOS
Support for Q-Flash
Support for Xpress BIOS Rescue
Support for Download Center
Support for Xpress Install
Support for Xpress Recovery2
Support for EasyTune
(Note 5)
Support for Easy Energy Saver
Support for Smart Recovery
Support for Auto Green
Support for ON/OFF Charge
Support for Q-Share
Bundled Software Norton Internet Security (OEM version)
Operating System Support for Microsoft® Windows® 7/Vista/XP
Form Factor XL-ATX Form Factor; 32.5cm x 24.4cm
(Note 1) Due to Windows 32-bit operating system limitation, when more than 4 GB of physical memory is
installed, the actual memory size displayed will be less than 4 GB.
(Note 2) The PCIEX8_1 slot shares bandwidth with the PCIEX16_1 slot and the PCIEX8_2 slot with
PCIEX16_2. The PCIEX16_1/PCIEX16_2 slot will operate at up to x8 mode when the PCIEX8_1/
PCIEX8_2 is populated.
(Note 3) The default bandwidth for the PCIEX4_2 slot is x1. When it is congured to x4 mode, the onboard
GSATA2_6, GSATA2_7, and IDE connectors will become unavailable because they share band width with the PCIEX4_2 slot. (Refer to Chapter 2, "Integrated Peripherals" for how to change the
operating bandwidth for the PCIEX4_2 slot.)
(Note 4) Whether the CPU/system fan speed control function is supported will depend on the CPU/system
cooler you install.
(Note 5) Available functions in EasyTune may differ by motherboard model.
Hardware Installation - 12 -
Page 13
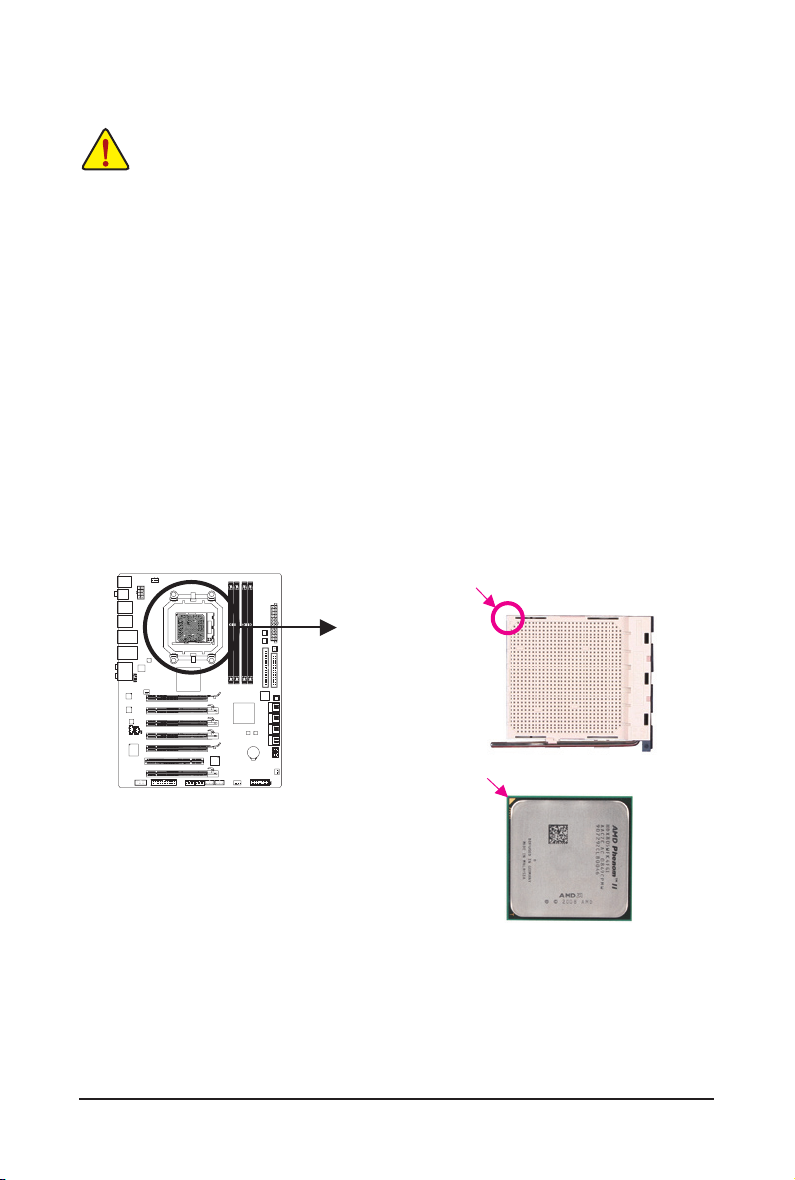
1-3 Installing the CPU and CPU Cooler
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the CPU:
• Make sure that the motherboard supports the CPU.
(Go to GIGABYTE's website for the latest CPU support list.)
• Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before installing
the CPU to prevent hardware damage.
• Locate the pin one of the CPU. The CPU cannot be inserted if oriented incorrectly. (Or you may
locate the notches on both sides of the CPU and alignment keys on the CPU socket.)
• Apply an even and thin layer of thermal grease on the surface of the CPU.
• Do not turn on the computer if the CPU cooler is not installed, otherwise overheating and dam-
age of the CPU may occur.
• Set the CPU host frequency in accordance with the CPU specications. It is not recommended
that the system bus frequency be set beyond hardware specications since it does not meet the
standard requirements for the peripherals. If you wish to set the frequency beyond the standard
specications, please do so according to your hardware specications including the CPU, graphics card, memory, hard drive, etc.
1-3-1 Installing the CPU
A. Locate the pin one (denoted by a small triangle) of the CPU socket and the CPU.
A Smal l Triangle Mark
Denotes Pin One of the
Socket
AM3 Socket
A Small Triangle Marking
Denotes CPU Pin One
AM3 CPU
- 13 - Hardware Installation
Page 14
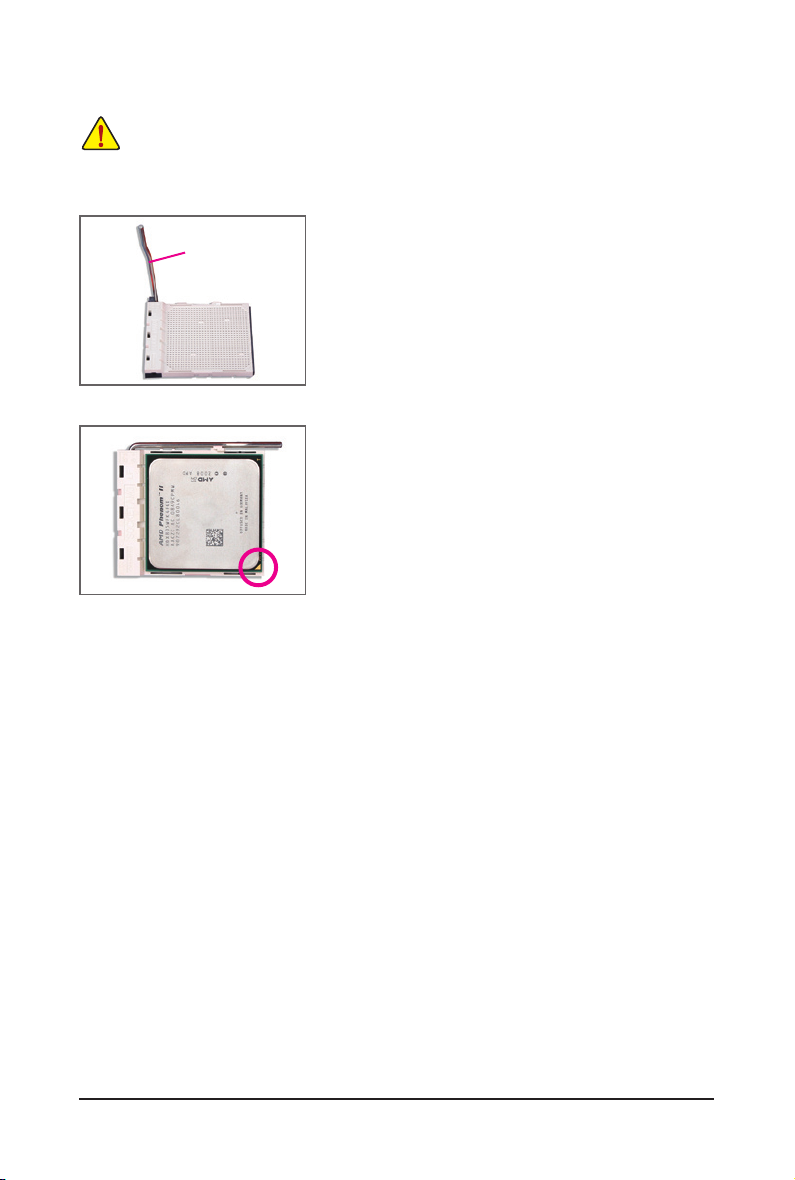
B. Follow the steps below to correctly install the CPU into the motherboard CPU socket.
• Before installing the CPU, make sure to turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the
power outlet to prevent damage to the CPU.
• Do not force the CPU into the CPU socket. The CPU cannot t in if oriented incorrectly. Adjust the
CPU orientation if this occurs.
Step 1:
CPU Socket
Locking Lever
Completely lift up the CPU socket locking lever.
Step 2:
Align the CPU pin one (small triangle marking) with the triangle mark
on the CPU socket and gently insert the CPU into the socket. Make
sure that the CPU pins t perfectly into their holes. Once the CPU is
positioned into its socket, place one nger down on the middle of the
CPU, lowering the locking lever and latching it into the fully locked
position.
Hardware Installation - 14 -
Page 15
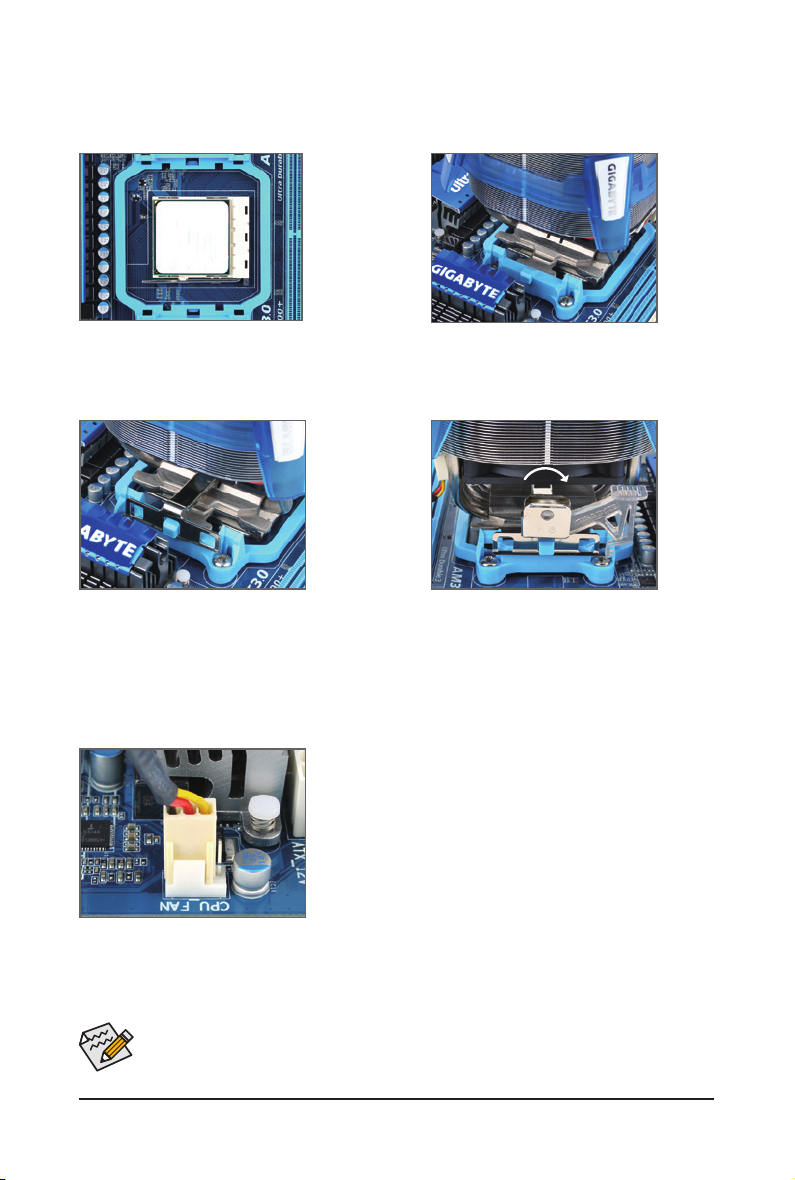
1-3-2 Installing the CPU Cooler
Follow the steps below to correctly install the CPU cooler on the CPU. (The following procedure uses the
GIGABYTE cooler as the example.)
Step 1:
Apply an even and thin layer of thermal grease
on the surface of the installed CPU.
Step 3:
Hook the CPU cooler clip to the mounting lug
on one side of the retention frame. On the other
side,push straight down on the the CPU cooler
clip to hook it to the mounting lug on the retention frame.
Step 5:
Finally, attach the power connector of the CPU cooler to the CPU
fan header (CPU_FAN) on the motherboard.
Step 2:
Place the CPU cooler on the CPU.
Step 4:
Turn the cam handle from the left side to the
right side (as the picture above shows) to lock
into place. (Refer to your CPU cooler installation
manual for instructions on installing the cooler.)
Use extreme care when removing the CPU cooler because the thermal grease/tape between the
CPU cooler and CPU may adhere to the CPU. Inadequately removing the CPU cooler may damage
the CPU.
- 15 - Hardware Installation
Page 16
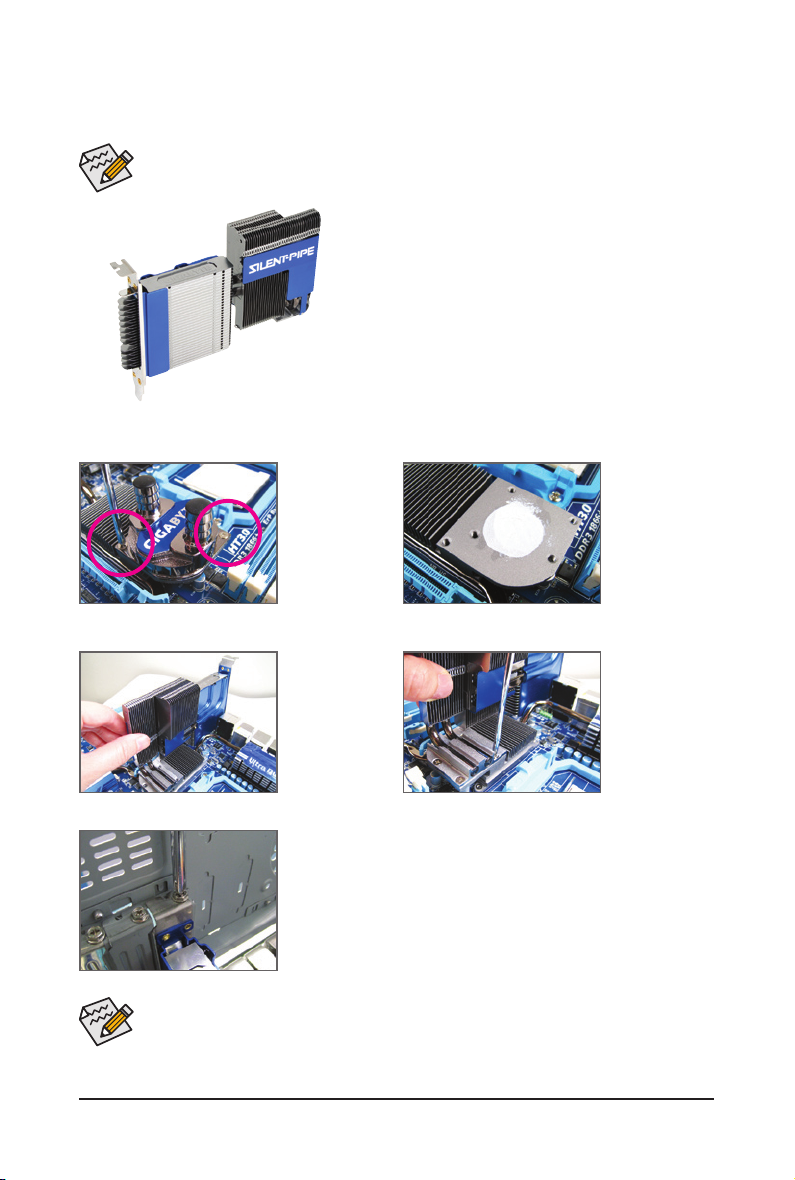
1-4 Installing the Hybrid Silent-Pipe Module
Read the following guideline before you begin to install the Hybrid Silent-Pipe module:
If you want to connect the front audio module from your chassis to the F_AUDIO connector on the motherboard, be sure to connect it before installing the Hybrid Silent-Pipe module to avoid interference.
Tools needed:
1. A Philip's screwdriver
2. Thermal grease
Hybrid Silent-Pipe
Follow the steps below to install the Hybrid Silent-Pipe module:
Step 1:
Unfasten the diagonally placed screws
from the waterblock
on North Bridge's
heatsink and then
remove the waterblock.
Step 2:
Apply an even thin
layer of thermal
grease on the surface of the heatsink.
Step 3:
Place the heatsink
of the Hybrid SilentPipe module atop
North Bridge's
heatsink as shown.
Step 5:
Secure the Hybrid Silent-Pipe bracket to the chassis back panel with a
screw to complete the installation.
For the waterblock, please use 3/8" ID x 1/2" OD or 3/8" ID x 5/8" OD tube. After connecting the
tubes, make sure they are attached to the waterblock securely and tightly and there is no leak.
(Note) The components received may vary in appearance from the products illustrated.
Hardware Installation - 16 -
Step 4:
Secure the heatsink
using the included
screws. (Use one
hand to hold the ns
to avoid shaking
during the installation.)
Page 17
1-5 Installing the Memory
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install the memory:
• Make sure that the motherboard supports the memory. It is recommended that memory of the
same capacity, brand, speed, and chips be used.
(Go to GIGABYTE's website for the latest supported memory speeds and memory modules)
• Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before installing
the memory to prevent hardware damage.
• Memory modules have a foolproof design. A memory module can be installed in only one direction. If you are unable to insert the memory, switch the direction.
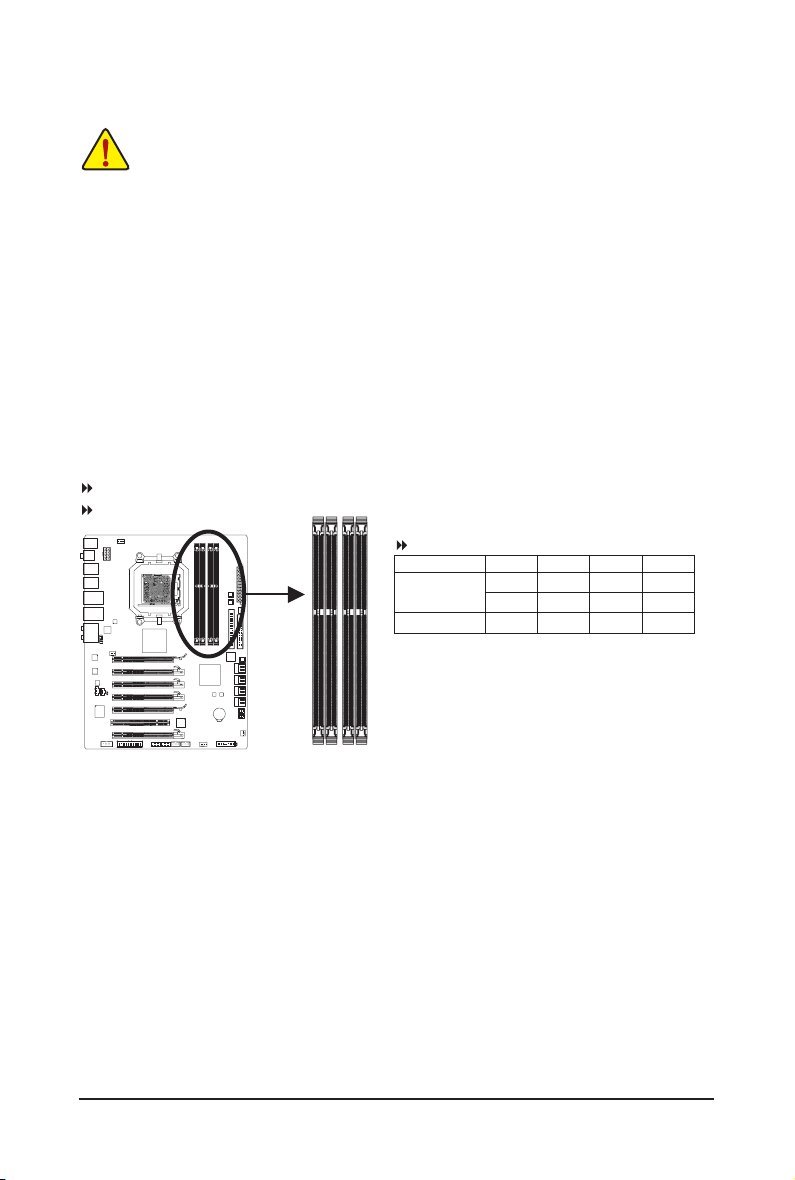
1-5-1 Dual Channel Memory Conguration
This motherboard provides four DDR3 memory sockets and supports Dual Channel Technology. After the
memory is installed, the BIOS will automatically detect the specications and capacity of the memory. Enabling Dual Channel memory mode will double the original memory bandwidth.
The four DDR3 memory sockets are divided into two channels and each channel has two memory sockets as
following:
Channel 0: DDR3_1, DDR3_2
Channel 1: DDR3_3, DDR3_4
DDR3_1
DDR3_2
Dual Channel Memory Congurations Table
Two Modules
Four Modules
(SS=Single-Sided, DS=Double-Sided, "- -"=No Memory)
DDR3_3
DDR3_4
DDR3_1 DDR3_2 DDR3_3 DDR3_4
DS/SS - - DS/SS - -
- - DS/SS - - DS/SS
DS/SS DS/SS DS/SS DS/SS
Due to CPU limitations, read the following guidelines before installing the memory in Dual Channel mode.
1. Dual Channel mode cannot be enabled if only one DDR3 memory module is installed.
2. When enabling Dual Channel mode with two or four memory modules, it is recommended that
memory of the same capacity, brand, speed, and chips be used and installed in the same colored
DDR3 sockets for optimum performance.
- 17 - Hardware Installation
Page 18
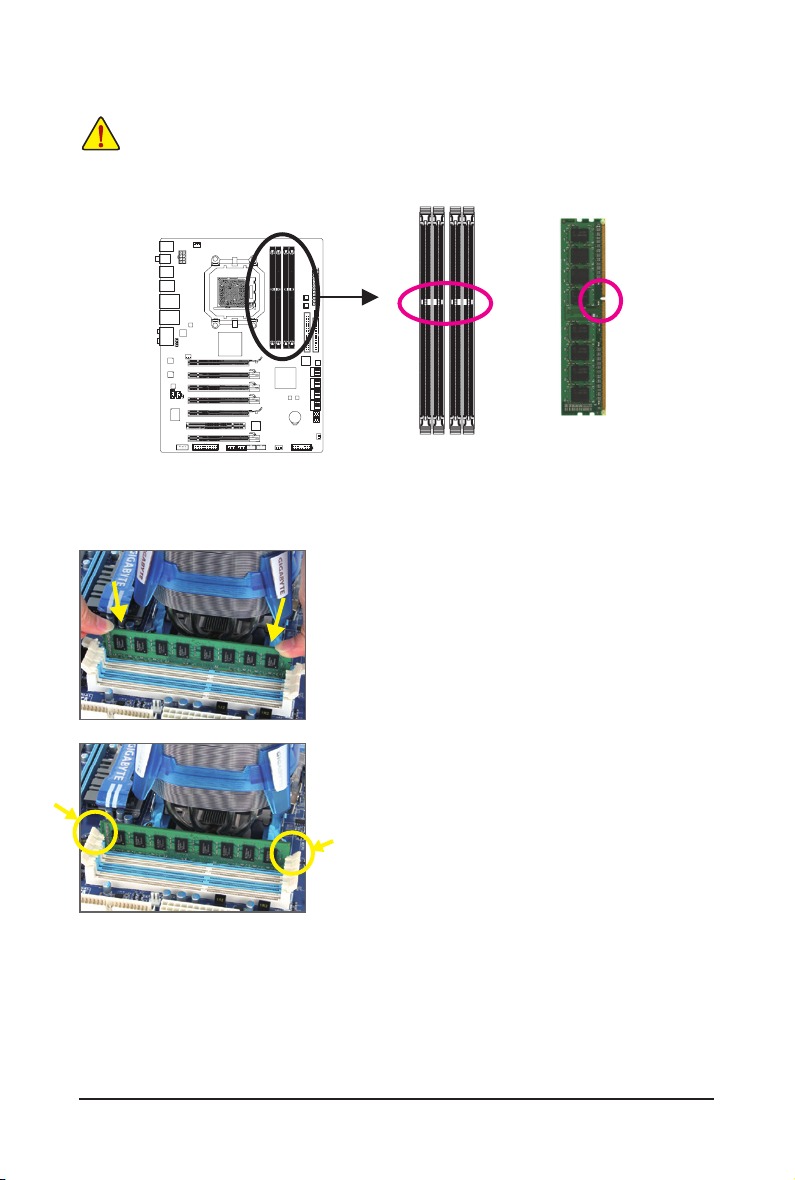
1-5-2 Installing a Memory
Before installing a memory module, make sure to turn off the computer and unplug the power
cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the memory module.
DDR3 and DDR2 DIMMs are not compatible to each other or DDR DIMMs. Be sure to install
DDR3 DIMMs on this motherboard.
Notch
DDR3 DIMM
A DDR3 memory module has a notch, so it can only t in one direction. Follow the steps below to correctly
install your memory modules in the memory sockets.
Step 1:
Note the orientation of the memory module. Spread the retaining
clips at both ends of the memory socket. Place the memory module
on the socket. As indicated in the picture on the left, place your ngers on the top edge of the memory, push down on the memory and
insert it vertically into the memory socket.
Step 2:
The clips at both ends of the socket will snap into place when the
memory module is securely inserted.
Hardware Installation - 18 -
Page 19
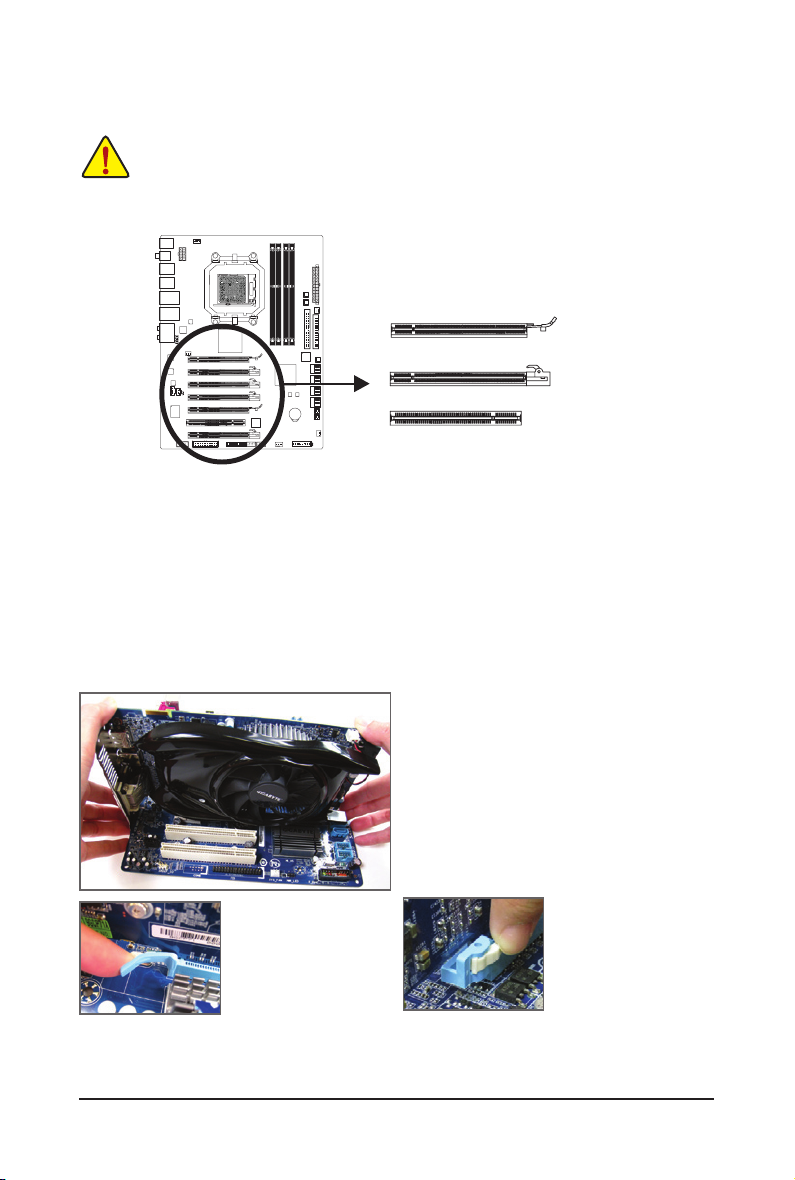
1-6 Installing an Expansion Card
Read the following guidelines before you begin to install an expansion card:
• Make sure the motherboard supports the expansion card. Carefully read the manual that came
with your expansion card.
• Always turn off the computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before installing
an expansion card to prevent hardware damage.
PCI Express x16 Slot (PCIEX16_1/PCIEX16_2)
PCI Express x16 Slot (PCIEX8_1/PCIEX8_2/PCIEX4_1/PCIEX4_2)
PCI Slot
Follow the steps below to correctly install your expansion card in the expansion slot.
1. Locate an expansion slot that supports your card. Remove the metal slot cover from the chassis back panel.
2. Align the card with the slot, and press down on the card until it is fully seated in the slot.
3. Make sure the metal contacts on the card are completely inserted into the slot.
4. Secure the card’s metal bracket to the chassis back panel with a screw.
5. After installing all expansion cards, replace the chassis cover(s).
6. Turn on your computer. If necessary, go to BIOS Setup to make any required BIOS changes for your
expansion card(s).
7. Install the driver provided with the expansion card in your operating system.
Example: Installing and Removing a PCI Express Graphics Card:
• Installing a Graphics Card:
Gently push down on the top edge of the card until
it is fully inserted into the PCI Express slot. Make
sure the card is securely seated in the slot and
does not rock.
• Re mo v in g t h e Ca r d
from the PCIEX16_1/
PCIEX16_2 Slot:
Gently push back on the
lever on the slot and then
lift the card straight out
from the slot.
• Re mo v in g t h e Ca r d
from the PCIEX8_1/
PCIEX8_2/PCIEX4_1/
PCIEX4_2 Slot:
Press the white latch at
the end of the PCI Express slot to release the
card and then pull the card
straight up from the slot.
- 19 - Hardware Installation
Page 20

1-7 Setting up ATI CrossFireX™ Conguration
A. System Requirements
- The 2-Way CrossFireX technology currently supports Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 operating systems
- The 3-Way/4-Way CrossFireX technology currently supports Windows Vista and Windows 7 operating systems only
- A CrossFireX-supported motherboard with two/three/four PCI Express x16 slots and correct driver
- Two/three/four CrossFireX-ready graphics cards of identical brand and chip and correct driver
(Current ATI GPUs that support 3-Way/4-Way CrossFireX technology include the Radeon HD 3800 series, Radeon HD 4800
and Radeon HD 5800 series.)
- CrossFireX bridge connector(s)
- A power supply with sufcient power is recommended (refer to the manual of your graphics cards for the power requirement)
B. Connecting the Graphics Cards
Step 1:
Observe the steps in "1-6 Installing an Expansion Card" and install two/three/four CrossFireX-ready graphics cards on the
PCI Express x16 slots. The following table shows the recommended CrossFireX congurations with two/three/four cards.
Recommended 2/3/4-Way CrossFireX Congurations:
PCIEX16_1 PCIEX16_2 PCIEX8_1 PCIEX8_2 PCIEX4_1 PCIEX4_2
a
2-Way
a
3-Way
- -
a
4-Way
(Note)
a
-- -- - - - -
a
a
a
a
-- - - - -
a
a
a
- - - -
a
- - - -
Step 2:
Insert the CrossFireX bridge connector(s)
(Note)
in the CrossFireX gold edge connectors on top of the two/three/four cards.
Step 3:
Plug the display cable into the graphics card on the PCIEX16_1 slot.
C. Conguring the Graphics Card Driver
C-1. To Enable CrossFireX Function
For 2-Way CrossFireX:
A ft er i n st al l i n g th e
gra phi cs card drive r in
th e operating system,
go to the Catalyst Con-
trol Cente r. Browse to
the CrossFireX m enu
and s elect the Enable
CrossFireX™ check box.
Click OK to apply.
For 4-Way CrossFireX:
Browse to the CrossFireX
menu, select the Enable
CrossFireX™ check box,
and select the 4 GP Us
Procedure and driver screen for enabling
CrossFireX technology may differ by graphics cards. Refer to the manual that came
with your graphics cards for more information about enabling CrossFireX technology.
combination. Click OK to
apply.
(Note) The bridge connectors may be needed or not depending on your graphics cards.
Hardware Installation - 20 -
For 3-Way CrossFireX:
Browse to the CrossFireX
menu, select the Enable
CrossFireX™ check box,
and select the 3 GP Us
combination. Click OK to
apply.
Page 21

1-8 Installing the SATA Bracket
The SATA bracket allows you to connect external SATA device(s) to your system by expanding the internal
SATA port(s) to the chassis back panel.
• Turn off your system and the power switch on the power supply before installing or removing the
SATA bracket and SATA power cable to prevent damage to hardware.
• Insert the SATA signal cable and SATA power cable securely into the corresponding connectors
when installing.
SATA Bracket
External SATA
Connector
Power Connector
External SATA Connector
Follow the steps below to install the SATA bracket:
Step 1:
Locate one free PCI
slot and sec ur e the
SATA bracket to the
ch as sis back pa nel
with a screw.
Step 3:
Co nne ct th e pow er
c a b l e f r o m t h e
bracket to the power
supply.
Step 5:
Connect the other ends of the SATA signal cable and SATA power cable to
your SATA device. For SATA device in external enclosure, you only need to
connect the SATA signal cable. Before connecting the SATA signal cable,
make sure to turn off the power of the external enclosure.
SATA Signal Cable SATA Power Cable
The SATA bracket includes one SATA bracket, one
SATA signal cable, and one SATA power cable.
Step 2:
Connect the SATA cable from the bracket
to the SATA port on
your motherboard.
Step 4:
Plug one end of the
SATA signal cable
into the external SATA
connector on the
bracket. Then attach
the SATA power cable
to the power connector on the bracket.
- 21 - Hardware Installation
Page 22
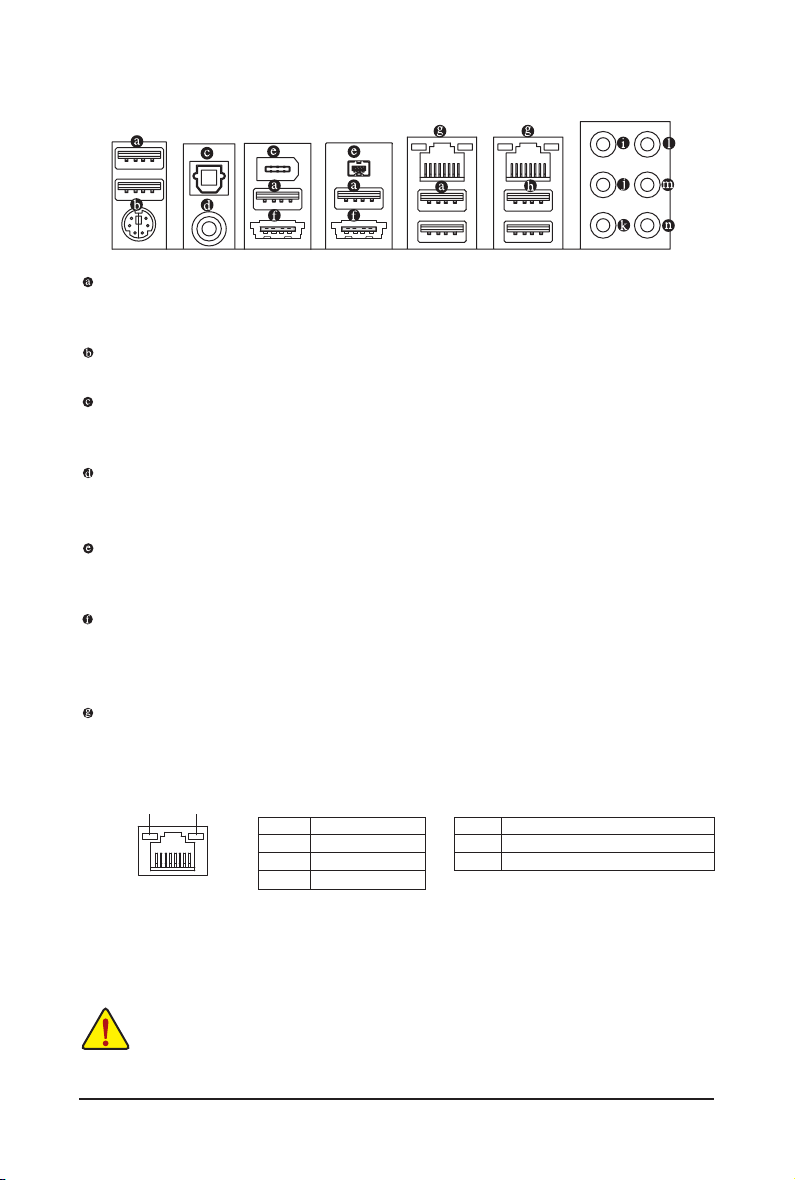
1-9 Back Panel Connectors
USB 2.0/1.1 Port
The USB port supports the USB 2.0/1.1 specication. Use this port for USB devices such as a USB key-
board/mouse, USB printer, USB ash drive and etc.
PS/2 Keyboard or PS/2 Mouse Port
Use this port to connect a PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse.
Optical S/PDIF Out Connector
This connector provides digital audio out to an external audio system that supports digital optical audio.
Before using this feature, ensure that your audio system provides an optical digital audio in connector.
Coaxial S/PDIF Out Connector
This connector provides digital audio out to an external audio system that supports digital coaxial audio.
Before using this feature, ensure that your audio system provides a coaxial digital audio in connector.
IEEE 1394a Port
The IEEE 1394 port supports the IEEE 1394a specication, featuring high speed, high bandwidth and
hotplug capabilities. Use this port for an IEEE 1394a device.
eSATA/USB Combo Connector
This connector supports SATA 3Gb/s and USB 2.0/1.1 specication. Use the port to connect an external
SATA device; or use this port for USB devices such as a USB keyboard/mouse, USB printer, USB ash
drive and etc.
RJ-45 LAN Port
The Gigabit Ethernet LAN port provides Internet connection at up to 1 Gbps data rate. The following de-
scribes the states of the LAN port LEDs.
Connection/
Speed LED
LAN Port
Activity LED
Connection/Speed LED:
State Description
Orange 1 Gbps data rate
Green 100 Mbps data rate
Off 10 Mbps data rate
Activity LED:
State Description
Blinking Data transmission or receiving is occurring
Off No data transmission or receiving is occurring
• When removing the cable connected to a back panel connector, rst remove the cable from your
device and then remove it from the motherboard.
• When removing the cable, pull it straight out from the connector. Do not rock it side to side to
prevent an electrical short inside the cable connector.
Hardware Installation - 22 -
Page 23

USB 3.0/2.0 Port
The USB 3.0 port supports the USB 3.0 specication and is compatible to the USB 2.0/1.1 specication.
Use this port for USB devices such as a USB keyboard/mouse, USB printer, USB ash drive and etc.
Center/Subwoofer Speaker Out Jack (Orange)
Use this audio jack to connect center/subwoofer speakers in a 5.1/7.1-channel audio conguration.
Rear Speaker Out Jack (Black)
Use this audio jack to connect rear speakers in a 7.1-channel audio conguration.
Side Speaker Out Jack (Gray)
Use this audio jack to connect side speakers in a 4/5.1/7.1-channel audio conguration.
Line In Jack (Blue)
The default line in jack. Use this audio jack for line in devices such as an optical drive, walkman, etc.
Line Out Jack (Green)
The default line out jack. Use this audio jack for a headphone or 2-channel speaker. This jack can be
used to connect front speakers in a 4/5.1/7.1-channel audio conguration.
Mic In Jack (Pink)
The default Mic in jack. Microphones must be connected to this jack.
In addition to the default speakers settings, the ~ audio jacks can be recongured to per-
form different functions via the audio software. Only microphones still MUST be connected to
the default Mic in jack ( ). Refer to the instructions on setting up a 2/4/5.1/7.1-channel audio
conguration in Chapter 5, "Conguring 2/4/5.1/7.1-Channel Audio."
- 23 - Hardware Installation
Page 24
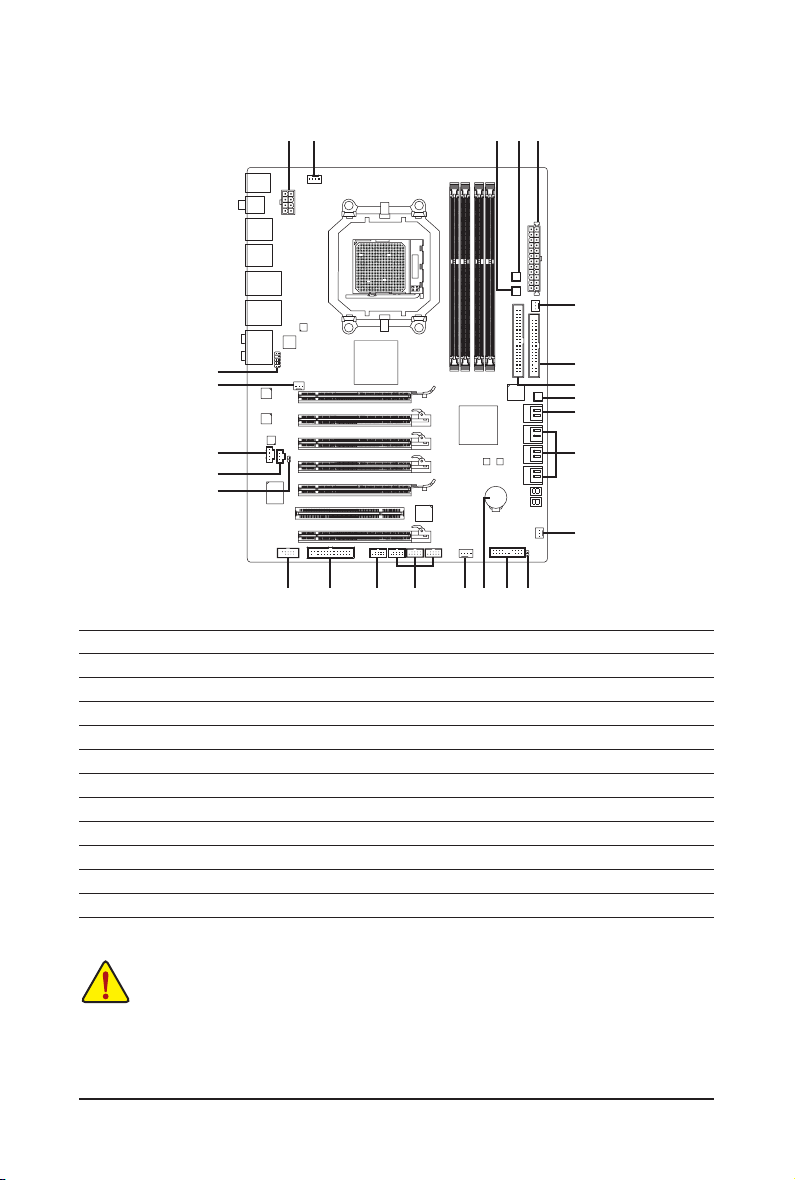
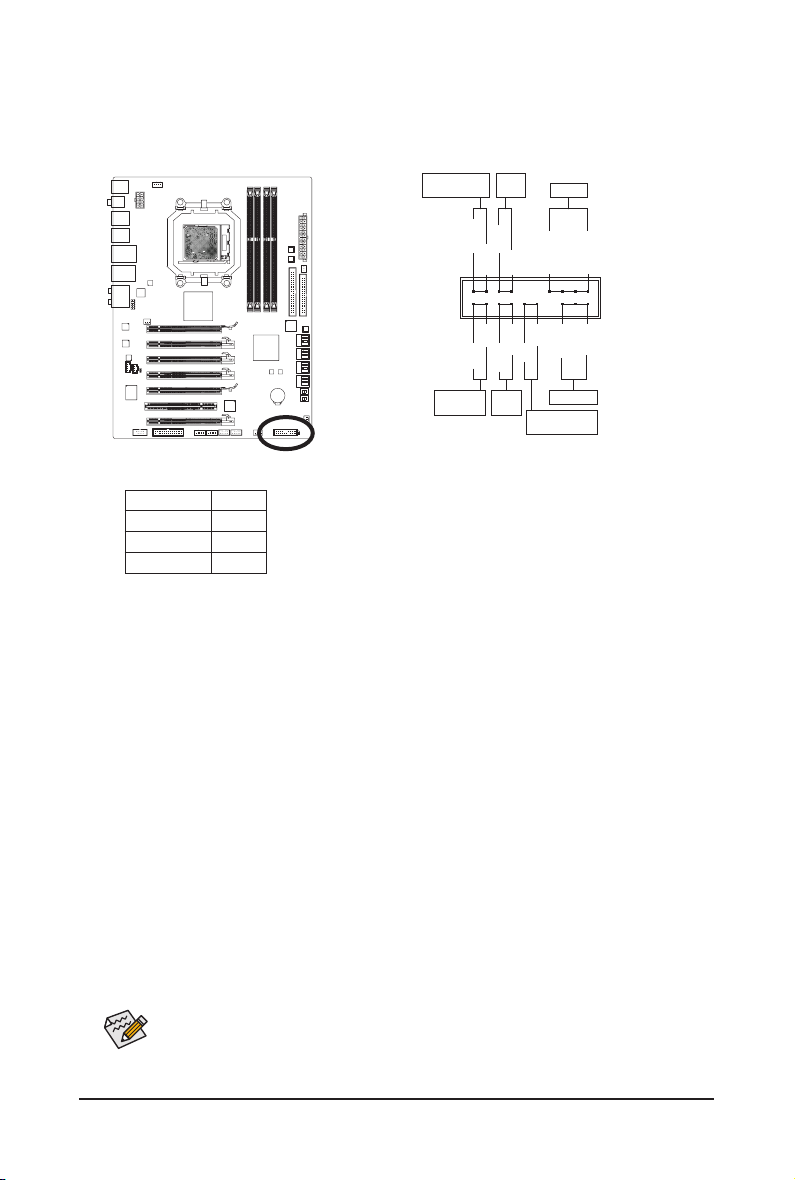
1-10 Internal Connectors
1
3
231722
2
5
12
6
13
14
15
1) ATX_12V
2) ATX
3) CPU_FAN
4) SYS_FAN1/SYS_FAN2
5) PWR_FAN
6) NB_FAN
7) FDD
8) IDE
9) SATA3_0/1/2/3/4/5
10) GSATA2_6/7
11) F_PANEL
12) F_AUDIO
20
18 16 4 11
13) CD_IN
14) SPDIF_I
15) SPDIF_O
16) F_USB1/F_USB2/F_USB3
17) F_1394
18) LPT
19) CLR_CMOS
20) COM
21) BAT
22) PW_SW
23) RST_SW
24) CMOS_SW
7
8
24
10
9
4
19
21
Read the following guidelines before connecting external devices:
• First make sure your devices are compliant with the connectors you wish to connect.
• Before installing the devices, be sure to turn off the devices and your computer. Unplug the
power cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the devices.
• After installing the device and before turning on the computer, make sure the device cable has
been securely attached to the connector on the motherboard.
Hardware Installation - 24 -
Page 25
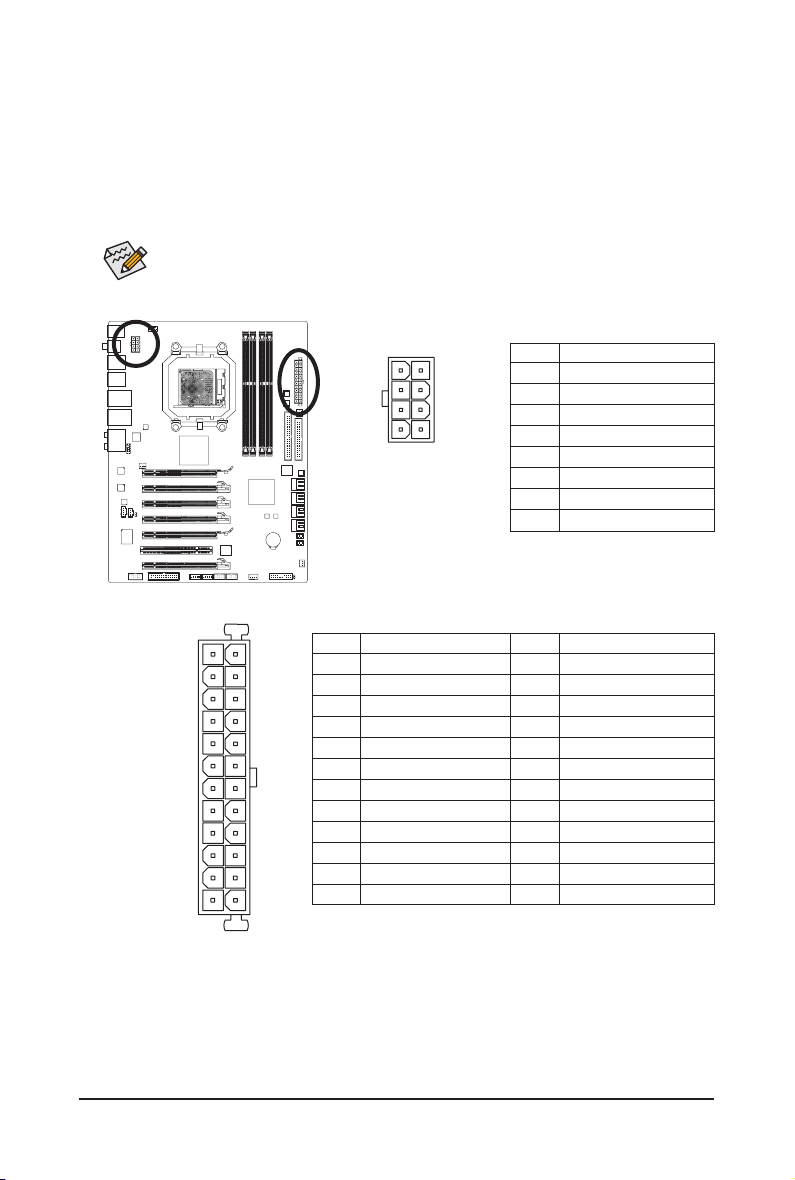
1/2) ATX_12V/ATX (2x4 12V Power Connector and 2x12 Main Power Connector)
With the use of the power connector, the power supply can supply enough stable power to all the com-
ponents on the motherboard. Before connecting the power connector, rst make sure the power supply
is turned off and all devices are properly installed. The power connector possesses a foolproof design.
Connect the power supply cable to the power connector in the correct orientation. The 12V power connector mainly supplies power to the CPU. If the 12V power connector is not connected, the computer will
not start.
To meet expansion requirements, it is recommended that a power supply that can withstand
high power consumption be used (500W or greater). If a power supply is used that does not
provide the required power, the result can lead to an unstable or unbootable system.
ATX_12V:
8
5
ATX_12V
4
1
Pin No. Denition
1 GND (Only for 2x4-pin 12V)
2 GND (Only for 2x4-pin 12V)
3 GND
4 GND
5 +12V (Only for 2x4-pin 12V)
6 +12V (Only for 2x4-pin 12V)
7 +12V
8 +12V
ATX
ATX:
2412
131
Pin No. Denition
1 3.3V
2 3.3V
3 GND
4 +5V
5 GND
6 +5V
7 GND
8 Power Good
9 5VSB (stand by +5V)
10 +12V
11 +12V (Only for 2x12-pin ATX)
12 3.3V (Only for 2x12-pin ATX)
Pin No. Denition
13 3.3V
14 -12V
15 GND
16 PS_ON (soft On/Off)
17 GND
18 GND
19 GND
20 -5V
21 +5V
22 +5V
23 +5V (Only for 2x12-pin ATX)
24 GND (Only for 2x12-pin ATX)
- 25 - Hardware Installation
Page 26
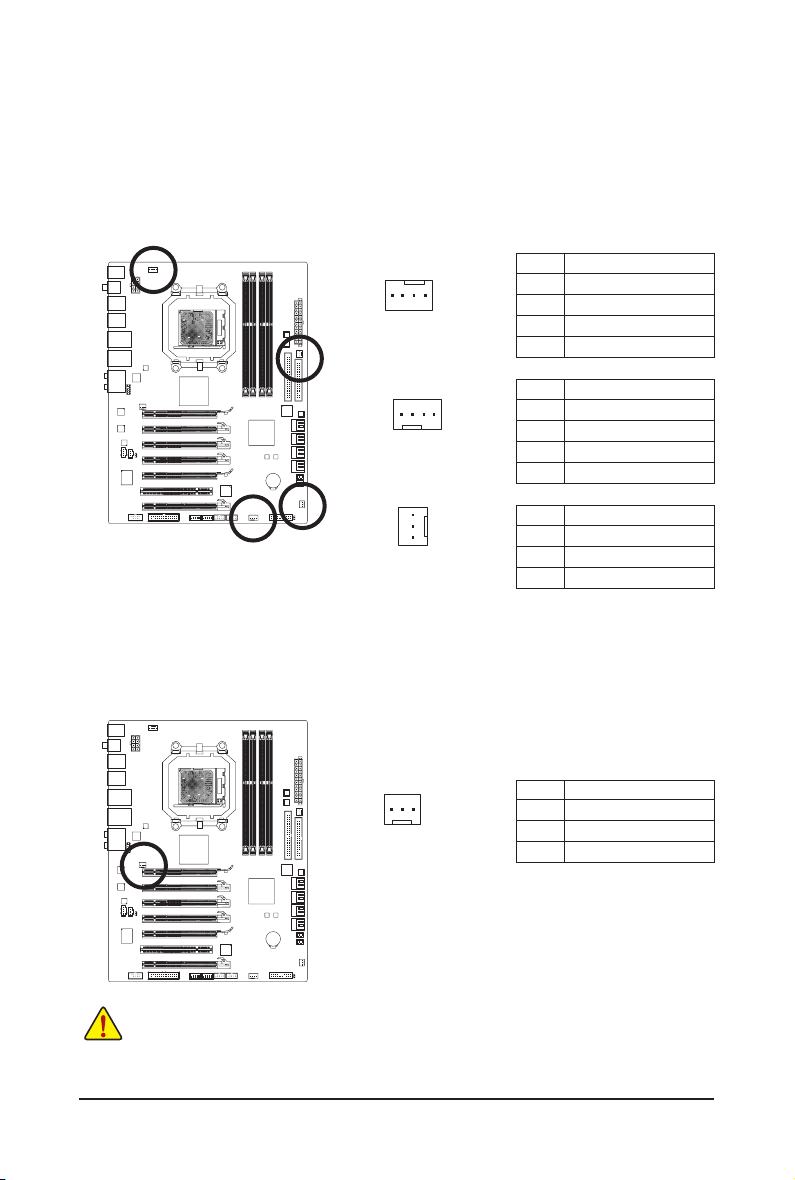
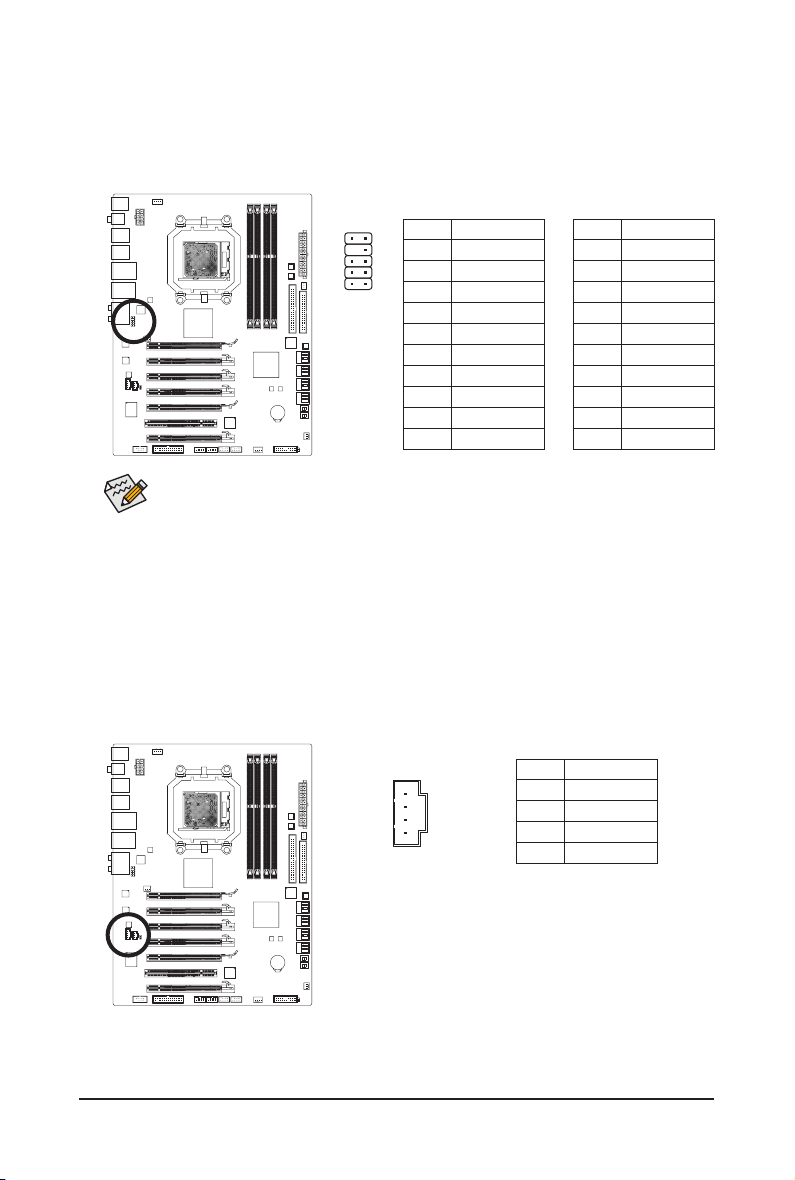
3/4/5) CPU_FAN/SYS_FAN1/SYS_FAN2/PWR_FAN (Fan Headers)
DEBUG
PORT
The motherboard has a 4-pin CPU fan header (CPU_FAN), a 4-pin (SYS_FAN1) and a 3-pin (SYS_
FAN2) system fan headers, and a 3-pin power fan header (PWR_FAN). Most fan headers possess a
foolproof insertion design. When connecting a fan cable, be sure to connect it in the correct orientation
(the black connector wire is the ground wire). The motherboard supports CPU fan speed control, which
requires the use of a CPU fan with fan speed control design. For optimum heat dissipation, it is recommended that a system fan be installed inside the chassis.
CPU_FAN:
Pin No. Denition
1
CPU_FAN
1
SYS_FAN1
1
SYS_FAN2/PWR_FAN
1 GND
2 +12V / Speed Control
3 Sense
4 Speed Control
SYS_FAN1:
Pin No. Denition
1 GND
2 +12V / Speed Control
3 Sense
4 Reserve
SYS_FAN2/PWR_FAN:
Pin No. Denition
1 GND
2 +12V
3 Sense
6) NB_FAN (North Bridge Fan Header)
Connect the North Bridge fan cable to this header. The fan header has a foolproof insertion design.
When connecting a fan cable, be sure to connect it in the correct orientation. Most fans are designed
with color-coded power connector wires. A red power connector wire indicates a positive connection and
requires a +12V voltage. The black connector wire is the ground wire.
1
Pin No. Denition
1 GND
2 +12V
3 NC
• Be sure to connect fan cables to the fan headers to prevent your CPU, North Bridge and
system from overheating. Overheating may result in damage to the CPU/North Bridge or the
system may hang.
• These fan headers are not conguration jumper blocks. Do not place a jumper cap on the
headers.
Hardware Installation - 26 -
Page 27
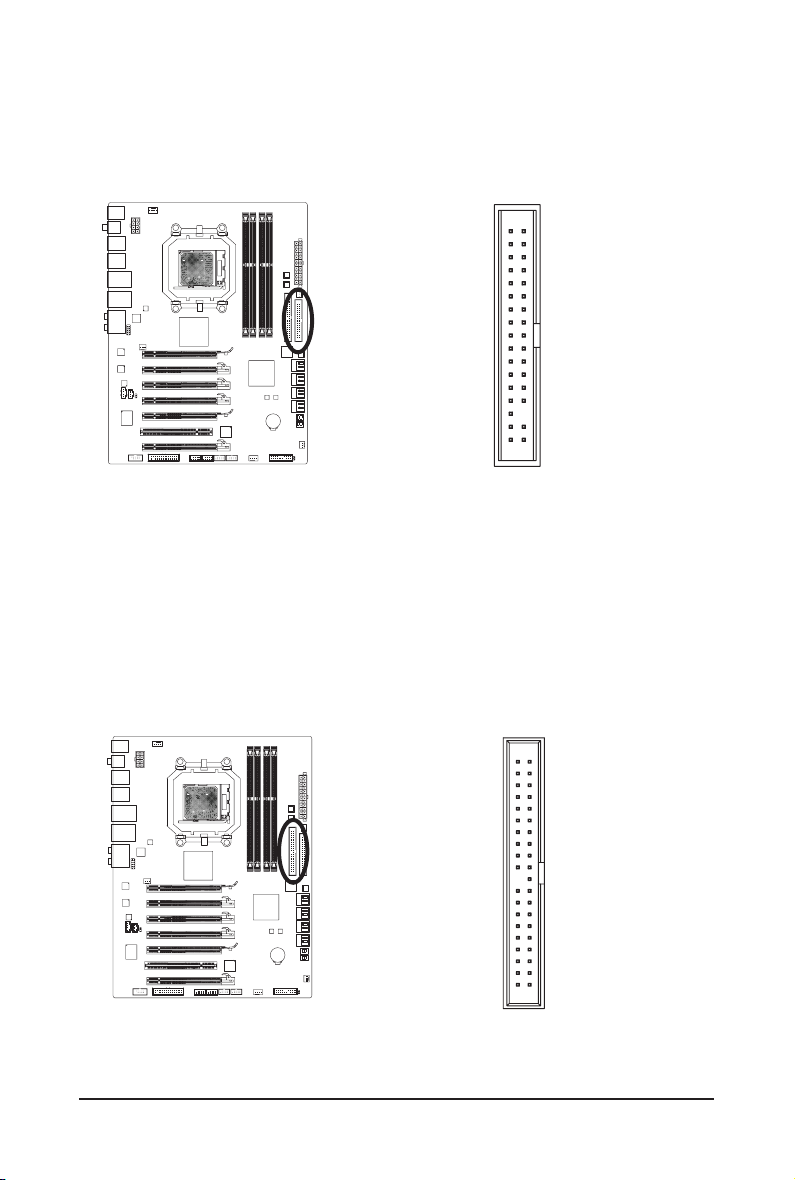
7) FDD (Floppy Disk Drive Connector)
This connector is used to connect a oppy disk drive. The types of oppy disk drives supported are:
360 KB, 720 KB, 1.2 MB, 1.44 MB, and 2.88 MB. Before connecting a oppy disk drive, be sure to locate
pin 1 of the connector and the oppy disk drive cable. The pin 1 of the cable is typically designated by a
stripe of different color. For purchasing the optional oppy disk drive cable, please contact the local dealer.
34
2
33
1
8) IDE (IDE Connector)
The IDE connector supports up to two IDE devices such as hard drives and optical drives. Before attach-
ing the IDE cable, locate the foolproof groove on the connector. If you wish to connect two IDE devices,
remember to set the jumpers and the cabling according to the role of the IDE devices (for example,
master or slave). (For information about conguring master/slave settings for the IDE devices, read the
instructions from the device manufacturers.)
40
39
2
1
- 27 - Hardware Installation
Page 28
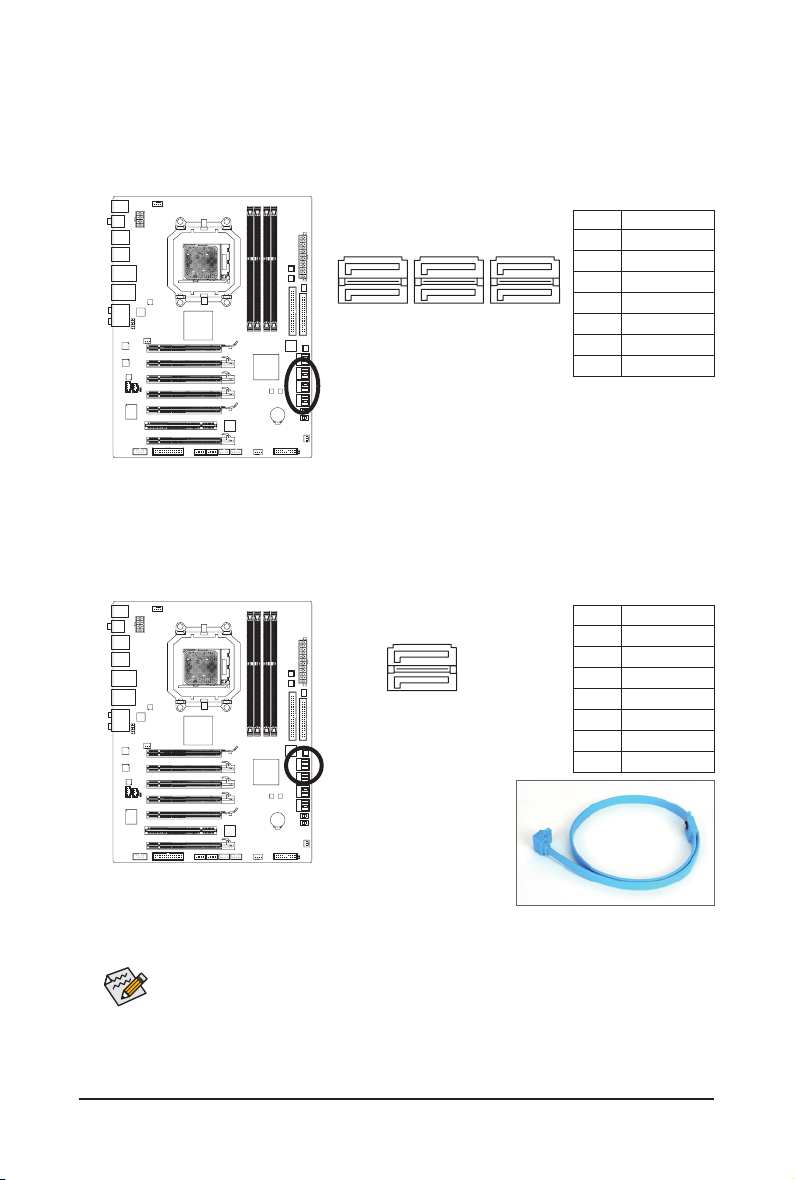
9) SATA3_0/1/2/3/4/5 (SATA 6Gb/s Connectors, Controlled by AMD SB850 South Bridge)
G.QBOFM
G.QBOFM
G.QBOFM
G.QBOFM
The SATA connectors conform to SATA 6Gb/s standard and are compaible with SATA 3Gb/s and SATA
1.5Gb/s standard. Each SATA connector supports a single SATA device. The AMD SB850 controller
supports RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10, and JBOD. Refer to Chapter 5, "Conguring SATA Hard
Drive(s)," for instructions on conguring a RAID array.
Pin No. Denition
SATA3_4SATA3_2SATA3_0
7
7
SATA3_5SATA3_3SATA3_1
1 GND
2 TXP
1
3 TXN
1
4 GND
5 RXN
6 RXP
7 GND
10) GSATA2_6/7 (SATA 3Gb/s Connectors, Controlled by GIGABYTE SATA2)
The SATA connectors conform to SATA 3Gb/s standard and are compatible with SATA 1.5Gb/s standards.
Each SATA connector supports a single SATA device.
and JBOD. Refer to Chapter 5, "Conguring SATA Hard Drive(s)," for instructions on conguring a RAID
array.
The GIGABYTE SATA2 supports RAID 0, RAID 1,
GSATA2_6
7 1
7 1
GSATA2_7
Pin No. Denition
1 GND
2 TXP
3 TXN
4 GND
5 RXN
6 RXP
7 GND
• A RAID 0 or RAID 1 conguration requires at least two hard drives. If more than two hard
drives are to be used, the total number of hard drives must be an even number.
• A RAID 5 conguration requires at least three hard drives. (The total number of hard drives
does not have to be an even number.)
• A RAID 10 conguration requires at least four hard drives and the total number of hard drives
must be an even number.
Hardware Installation - 28 -
Please connect the L-shaped end of
th e SATA cable t o your SATA hard
drive.
Page 29
11) F_PANEL (Front Panel Header)
Connect the power switch, reset switch, speaker, chassis intrusion switch/sensor and system status
indicator on the chassis to this header according to the pin assignments below. Note the positive and
negative pins before connecting the cables.
Message/Power/
Sleep LED
2
1
Hard Drive
Activity LED
MSG+
HD+
Power
Switch
MSG-
HD-
Reset
Switch
PW+
PW-
RES+
RES-
Speaker
SPEAK+
CI+
PWR+
CI-
Power LED
Chassis Intrusion
Header
SPEAK-
20
19
PWR-
• MSG/PWR (Message/Power/Sleep LED, Yellow/Purple):
System Status LED
S0 On
S1 Blinking
S3/S4/S5 Off
Connects to the power status indicator on the chassis front panel. The LED
is on when the system is operating. The LED keeps blinking when the system is in S1 sleep state. The LED is off when the system is in S3/S4 sleep
state or powered off (S5).
• PW (Power Switch, Red):
Connects to the power switch on the chassis front panel. You may congure the way to turn off your
system using the power switch (refer to Chapter 2, "BIOS Setup," "Power Management Setup," for
more information).
• SPEAK (Speaker, Orange):
Connects to the speaker on the chassis front panel. The system reports system startup status by is-
suing a beep code. One single short beep will be heard if no problem is detected at system startup. If
a problem is detected, the BIOS may issue beeps in different patterns to indicate the problem. Refer
to Chapter 5, "Troubleshooting," for information about beep codes.
• HD (Hard Drive Activity LED, Blue)
Connects to the hard drive activity LED on the chassis front panel. The LED is on when the hard drive
is reading or writing data.
• RES (Reset Switch, Green):
Connects to the reset switch on the chassis front panel. Press the reset switch to restart the computer
if the computer freezes and fails to perform a normal restart.
• CI (Chassis Intrusion Header, Gray):
Connects to the chassis intrusion switch/sensor on the chassis that can detect if the chassis cover
has been removed. This function requires a chassis with a chassis intrusion switch/sensor.
The front panel design may differ by chassis. A front panel module mainly consists of power
switch, reset switch, power LED, hard drive activity LED, speaker and etc. When connecting your
chassis front panel module to this header, make sure the wire assignments and the pin assignments are matched correctly.
- 29 - Hardware Installation
Page 30
12) F_AUDIO (Front Panel Audio Header)
The front panel audio header supports Intel High Denition audio (HD) and AC'97 audio. You may connect
your chassis front panel audio module to this header. Make sure the wire assignments of the module connector match the pin assignments of the motherboard header. Incorrect connection between the module
connector and the motherboard header will make the device unable to work or even damage it.
For HD Front Panel Audio: For AC'97 Front Panel Audio:
10
2
Pin No. Denition
9
1 MIC2_L
2 GND
1
3 MIC2_R
4 -ACZ_DET
5 LINE2_R
6 GND
7 FAUDIO_JD
8 No Pin
9 LINE2_L
10 GND
• The front panel audio header supports HD audio by default. If your chassis provides an AC'97
front panel audio module, refer to the instructions on how to activate AC'97 functionality via
the audio software in Chapter 5, "Conguring 2/4/5.1/7.1-Channel Audio."
• Audio signals will be present on both of the front and back panel audio connections simultaneously. If you want to mute the back panel audio (only supported when using an HD front panel
audio module), refer to Chapter 5, "Conguring 2/4/5.1/7.1-Channel Audio."
• Some chassis provide a front panel audio module that has separated connectors on each wire
instead of a single plug. For information about connecting the front panel audio module that
has different wire assignments, please contact the chassis manufacturer.
Pin No. Denition
1 MIC
2 GND
3 MIC Power
4 NC
5 Line Out (R)
6 NC
7 NC
8 No Pin
9 Line Out (L)
10 NC
13) CD_IN (CD In Connector)
You may connect the audio cable that came with your optical drive to the header.
Pin No. Denition
1 CD-L
2 GND
3 GND
1
Hardware Installation - 30 -
4 CD-R
Page 31

14) SPDIF_I (S/PDIF In Header)
This header supports digital S/PDIF In and can connect to an audio device that supports digital audio out
via an optional S/PDIF In cable. For purchasing the optional S/PDIF In cable, please contact the local
dealer.
Pin No. Denition
1 Power
2 SPDIFI
1
3 GND
15) SPDIF_O (S/PDIF Out Header)
This header supports digital S/PDIF Out and connects a S/PDIF digital audio cable (provided by expan-
sion cards) for digital audio output from your motherboard to certain expansion cards like graphics cards
and sound cards. For example, some graphics cards may require you to use a S/PDIF digital audio cable
for digital audio output from your motherboard to your graphics card if you wish to connect an HDMI
display to the graphics card and have digital audio output from the HDMI display at the same time. For
information about connecting the S/PDIF digital audio cable, carefully read the manual for your expansion card.
Pin No. Denition
1 SPDIFO
1
2 GND
- 31 - Hardware Installation
Page 32

G.QBOFM
16) F_USB1/F_USB2/F_USB3 (USB Headers)
G.QBOFM
The headers conform to USB 2.0/1.1 specication. Each USB header can provide two USB ports via an
optional USB bracket. For purchasing the optional USB bracket, please contact the local dealer.
Pin No. Denition
1 Power (5V)
9
10
1
2
2 Power (5V)
3 USB DX-
4 USB DY-
5 USB DX+
6 USB DY+
7 GND
8 GND
9 No Pin
10 NC
When the system is in S4/S5 mode, only the USB ports routed to the F_USB1 header can support the ON/OFF Charge function.
• Do not plug the IEEE 1394 bracket (2x5-pin) cable into the USB header.
• Prior to installing the USB bracket, be sure to turn off your computer and unplug the power
cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the USB bracket.
17) F_1394 (IEEE 1394a Header)
The header conforms to IEEE 1394a specication. The IEEE 1394a header can provide one IEEE 1394a
port via an optional IEEE 1394a bracket. For purchasing the optional IEEE 1394a bracket, please contact the local dealer.
9
10
• Do not plug the USB bracket cable into the IEEE 1394a header.
• Prior to installing the IEEE 1394a bracket, be sure to turn off your computer and unplug the
power cord from the power outlet to prevent damage to the IEEE 1394a bracket.
• To connect an IEEE 1394a device, attach one end of the device cable to your computer and
then attach the other end of the cable to the IEEE 1394a device. Ensure that the cable is securely connected.
Hardware Installation - 32 -
Pin No. Denition
1
2
1 TPA+
2 TPA-
3 GND
4 GND
5 TPB+
6 TPB-
7 Power (12V)
8 Power (12V)
9 No Pin
10 GND
Page 33

18) LPT (Parallel Port Header)
G.QBOFM
The LPT header can provide one parallel port via an optional LPT port cable. For purchasing the optional
LPT port cable, please contact the local dealer.
25
1
24
Pin No. Denition
1 STB-
2 AFD-
3 PD0
4 ERR-
5 PD1
6 INIT-
7 PD2
8 SLIN-
9 PD3
10 GND
11 PD4
12 GND
13 PD5
Pin No. Denition
14 GND
15 PD6
16 GND
17 PD7
18 GND
19 ACK-
20 GND
21 BUSY
22 GND
23 PE
24 No Pin
25 SLCT
26 GND
2
19) CLR_CMOS (Clearing CMOS Jumper)
Use this jumper to clear the CMOS values (e.g. date information and BIOS congurations) and reset the
CMOS values to factory defaults. To clear the CMOS values, place a jumper cap on the two pins to temporarily short the two pins or use a metal object like a screwdriver to touch the two pins for a few seconds.
Open: Normal
Short: Clear CMOS Values
• Always turn off your computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before clearing the CMOS values.
• After clearing the CMOS values and before turning on your computer, be sure to remove the
jumper cap from the jumper. Failure to do so may cause damage to the motherboard.
• After system restart, go to BIOS Setup to load factory defaults (select Load Optimized De-
faults) or manually congure the BIOS settings (refer to Chapter 2, "BIOS Setup," for BIOS
congurations).
- 33 - Hardware Installation
Page 34

20) COM (Serial Port Header)
The COM header can provide one serial port via an optional COM port cable. For purchasing the op-
tional COM port cable, please contact the local dealer.
Pin No. Denition
1 NDCD-
9
10
1
2
2 NSIN
3 NSOUT
4 NDTR-
5 GND
6 NDSR-
7 NRTS-
8 NCTS-
9 NRI-
10 No Pin
21) BAT (Battery)
The battery provides power to keep the values (such as BIOS congurations, date, and time information)
in the CMOS when the computer is turned off. Replace the battery when the battery voltage drops to a
low level, or the CMOS values may not be accurate or may be lost.
You may clear the CMOS values by removing the battery:
1. Turn off your computer and unplug the power cord.
2. Gently remove the battery from the battery holder and wait for one
minute. (Or use a metal object like a screwdriver to touch the positive
and negative terminals of the battery holder, making them short for 5
seconds.)
3. Replace the battery.
4. Plug in the power cord and restart your computer.
• Always turn off your computer and unplug the power cord before replacing the battery.
• Replace the battery with an equivalent one. Danger of explosion if the battery is replaced with
an incorrect model.
• Contact the place of purchase or local dealer if you are not able to replace the battery by yourself or uncertain about the battery model.
• When installing the battery, note the orientation of the positive side (+) and the negative side (-)
of the battery (the positive side should face up).
• Used batteries must be handled in accordance with local environmental regulations.
Hardware Installation - 34 -
Page 35

22/23/24) PW_SW/ RST_SW/ CMOS_SW (Quick Buttons)
This motherboard has 3 quick buttons: power button, clearing CMOS button and reset button. The power
button and reset button allow users to quickly turn on/off or reset the computer in an open-case environment when they want to change hardware components or conduct hardware testing. Use the clearing
CMOS button to clear the CMOS values (e.g. date information and BIOS congurations) and reset the
CMOS values to factory defaults when needed.
• Always turn off your computer and unplug the power cord from the power outlet before clearing the CMOS values.
• After system restart, go to BIOS Setup to load factory defaults (select Load Optimized De-
faults) or manually congure the BIOS settings (refer to Chapter 2, "BIOS Setup," for BIOS
congurations).
- 35 - Hardware Installation
Page 36

Hardware Installation - 36 -
Page 37

Chapter 2 BIOS Setup
BIOS (Basic Input and Output System) records hardware parameters of the system in the CMOS on the
motherboard. Its major functions include conducting the Power-On Self-Test (POST) during system startup,
saving system parameters and loading operating system, etc. BIOS includes a BIOS Setup program that
allows the user to modify basic system conguration settings or to activate certain system features. When
the power is turned off, the battery on the motherboard supplies the necessary power to the CMOS to keep
the conguration values in the CMOS.
To access the BIOS Setup program, press the <Delete> key during the POST when the power is turned on.
To see more advanced BIOS Setup menu options, you can press <Ctrl> + <F1> in the main menu of the
BIOS Setup program.
To upgrade the BIOS, use either the GIGABYTE Q-Flash or @BIOS utility.
• Q-Flash allows the user to quickly and easily upgrade or back up BIOS without entering the operating
system.
• @BIOS is a Windows-based utility that searches and downloads the latest version of BIOS from the
Internet and updates the BIOS.
For instructions on using the Q-Flash and @BIOS utilities, refer to Chapter 4, "BIOS Update Utilities."
• Because BIOS ashing is potentially risky, if you do not encounter problems using the current
version of BIOS, it is recommended that you not ash the BIOS. To ash the BIOS, do it with
caution. Inadequate BIOS ashing may result in system malfunction.
• BIOS will emit a beep code during the POST. Refer to Chapter 5, "Troubleshooting," for the beep
codes description.
• It is recommended that you not alter the default settings (unless you need to) to prevent system
instability or other unexpected results. Inadequately altering the settings may result in system's
failure to boot. If this occurs, try to clear the CMOS values and reset the board to default values.
(Refer to the "Load Optimized Defaults" section in this chapter or introductions of the battery/
clearing CMOS button/jumper in Chapter 1 for how to clear the CMOS values.)
- 37 - BIOS Setup
Page 38

2-1 Startup Screen
The following screens may appear when the computer boots.
A. The LOGO Screen (Default)
Function Keys
B. The POST Screen
Motherboard Model
BIOS Version
Award Modular BIOS v6.00PG, An Energy Star Ally
Copyright (C) 1984-2010, Award Software, Inc.
GA-890FXA-UD7 F3d
.
.
.
.
<DEL>: BIOS Setup <F9>: XpressRecovery2 <F12>: Boot Menu <End>: Qflash
07/20/2010-RD890-SB850-7A66DG03C-00
Function Keys
Function Keys:
<TAB>: POST SCREEN
Press the <Tab> key to show the BIOS POST screen. To show the BIOS POST screen at system start-
up, refer to the instructions on the Full Screen LOGO Show item on page 50.
<DEL>: BIOS SETUP\Q-FLASH
Press the <Delete> key to enter BIOS Setup or to access the Q-Flash utility in BIOS Setup.
<F9>: XPRESS RECOVERY2
If you have ever entered Xpress Recovery2 to back up hard drive data using the driver disk, the <F9>
key can be used for subsequent access to Xpress Recovery2 during the POST. For more information,
refer to Chapter 4, "Xpress Recovery2."
<F12>: BOOT MENU
Boot Menu allows you to set the rst boot device without entering BIOS Setup. In Boot Menu, use the up
arrow key <h> or the down arrow key <i> to select the rst boot device, then press <Enter> to accept.
To exit Boot Menu, press <Esc>. The system will directly boot from the device congured in Boot Menu.
Note: The setting in Boot Menu is effective for one time only. After system restart, the device boot order
will still be based on BIOS Setup settings. You can access Boot Menu again to change the rst boot device setting as needed.
<END>: Q-FLASH
Press the <End> key to access the Q-Flash utility directly without having to enter BIOS Setup rst.
BIOS Setup - 38 -
Page 39

2-2 The Main Menu
Once you enter the BIOS Setup program, the Main Menu (as shown below) appears on the screen. Use arrow keys to move among the items and press <Enter> to accept or enter a sub-menu.
(Sample BIOS Version: F3d)
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
higf
Change CPU's Clock & Voltage
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
BIOS Setup Program Function Keys
<h><i><f><g> Move the selection bar to select an item
<Enter> Execute command or enter the submenu
<Esc> Main Menu: Exit the BIOS Setup program
Submenus: Exit current submenu
<Page Up> Increase the numeric value or make changes
<Page Down> Decrease the numeric value or make changes
<F1> Show descriptions of the function keys
<F2> Move cursor to the Item Help block on the right (submenus only)
<F5> Restore the previous BIOS settings for the current submenus
<F6> Load the Fail-Safe BIOS default settings for the current submenus
<F7> Load the Optimized BIOS default settings for the current submenus
<F8> Access the Q-Flash utility
<F9> Display system information
<F10> Save all the changes and exit the BIOS Setup program
<F11> Save CMOS to BIOS
<F12> Load CMOS from BIOS
Main Menu Help
The on-screen description of a highlighted setup option is displayed on the bottom line of the Main Menu.
Submenu Help
While in a submenu, press <F1> to display a help screen (General Help) of function keys available for the
menu. Press <Esc> to exit the help screen. Help for each item is in the Item Help block on the right side of
the submenu.
• If you do not nd the settings you want in the Main Menu or a submenu, press <Ctrl>+<F1> to
access more advanced options.
• When the system is not stable as usual, select the Load Optimized Defaults item to set your
system to its defaults.
• The BIOS Setup menus described in this chapter are for reference only and may differ by BIOS
version.
- 39 - BIOS Setup
Page 40

The Functions of the <F11> and <F12> keys (For the Main Menu Only)
F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
This function allows you to save the current BIOS settings to a prole. You can create up to 8 proles
(Prole 1-8) and name each prole. First enter the prole name (to erase the default prole name, use
the SPACE key) and then press <Enter> to complete.
F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
If your system becomes unstable and you have loaded the BIOS default settings, you can use this
function to load the BIOS settings from a prole created before, without the hassles of reconguring the
BIOS settings. First select the prole you wish to load, then press <Enter> to complete.
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Use this menu to congure the clock, frequency and voltages of your CPU, memory, etc.
Standard CMOS Features
Use this menu to congure the system time and date, hard drive types, oppy disk drive types, and the
type of errors that stop the system boot, etc.
Advanced BIOS Features
Use this menu to congure the device boot order, advanced features available on the CPU, and the pri-
mary display adapter.
Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to congure all peripheral devices, such as IDE, SATA, USB, integrated audio, and inte-
grated LAN, etc.
Power Management Setup
Use this menu to congure all the power-saving functions.
PC Health Status
Use this menu to see information about autodetected system/CPU temperature, system voltage and fan
speed, etc.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Fail-Safe defaults are factory settings for the most stable, minimal-performance system operations.
Load Optimized Defaults
Optimized defaults are factory settings for optimal-performance system operations.
Set Supervisor Password
Change, set, or disable password. It allows you to restrict access to the system and BIOS Setup.
A supervisor password allows you to make changes in BIOS Setup.
Set User Password
Change, set, or disable password. It allows you to restrict access to the system and BIOS Setup.
A user password only allows you to view the BIOS settings but not to make changes.
Save & Exit Setup
Save all the changes made in the BIOS Setup program to the CMOS and exit BIOS Setup. (Pressing
<F10> can also carry out this task.)
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all changes and the previous settings remain in effect. Pressing <Y> to the conrmation mes-
sage will exit BIOS Setup. (Pressing <Esc> can also carry out this task.)
BIOS Setup - 40 -
Page 41

2-3 MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
CPU Clock Ratio [Auto] 2800Mhz
CPU NorthBridge Freq. [Auto] 2000Mhz
CPU Host Clock Control [Auto]
x CPU Frequency(MHz) 200
PCIE Clock(MHz) [Auto]
PCIe Spread Spectrum [Disabled]
HT Link Width [Auto]
HT Link Frequency [Auto] 2000Mhz
Set Memory Clock [Auto]
x Memory Clock x6.66 1333Mhz
DRAMConguration [PressEnter]
System Voltage Optimized
********
System Voltage Control [Auto]
x CPU PLL Voltage Control Auto
x DRAM Voltage Control Auto
x DDR VTT Voltage Control Auto
x NB Voltage Control Auto
x HT Link Voltage Control Auto
x NB/PCIe/PLL Voltage Ctrl Auto
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
x CPU NB VID Control Auto
x CPU Voltage Control Auto
Normal CPU Vcore 1.3250V
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
********
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Menu Level
Menu Level
Item Help
Item Help
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
• Whether the system will work stably with the overclock/overvoltage settings you made is depen-
dent on your overall system congurations. Incorrectly doing overclock/overvoltage may result in
damage to CPU, chipset, or memory and reduce the useful life of these components. This page is
for advanced users only and we recommend you not to alter the default settings to prevent system
instability or other unexpected results. (Inadequately altering the settings may result in system's
failure to boot. If this occurs, clear the CMOS values and reset the board to default values.)
• When the System Voltage Optimized item blinks in red, it is recommended that you set the
System Voltage Control item to Auto to optimize the system voltage settings.
- 41 - BIOS Setup
Page 42

CPU Clock Ratio
Allows you to alter the clock ratio for the installed CPU. The adjustable range is dependent on the CPU
being used.
CPU NorthBridge Freq.
Allows you to alter the North Bridge controller frequency for the installed CPU. The adjustable range is
dependent on the CPU being used.
CPU Host Clock Control
Enables or disables the control of CPU host clock. Auto (default) allows the BIOS to automatically adjust
the CPU host frequency. Manual allows the CPU Frequency (MHz) item below to be congurable.
Note: If your system fails to boot after overclocking, please wait for 20 seconds to allow for automated
system reboot, or clear the CMOS values to reset the board to default values.
CPU Frequency(MHz)
Allows you to manually set the CPU host frequency. The adjustable range is from 200 MHz to 500 MHz.
This option is congurable only when CPU Host Clock Control is set to Manual. Important It is highly
recommended that the CPU frequency be set in accordance with the CPU specications.
PCIE Clock(MHz)
Allows you to manually set the PCIe clock frequency. The adjustable range is from 100 MHz to 150 MHz.
Auto sets the PCIe clock frequency to standard 100 MHz. (Default: Auto)
PCIe Spread Spectrum
Enables or disables PCIe Spread Spectrum. (Default: Disabled)
HT Link Width
Allows you to manually set the width for the HT Link between the CPU and chipset.
Auto BIOS will automatically adjust the HT Link Width. (Default)
8 bit Sets HT Link Width to 8 bit.
16 bit Sets HT Link Width to 16 bit.
HT Link Frequency
Allows you to manually set the frequency for the HT Link between the CPU and chipset.
Auto BIOS will automatically adjust the HT Link Frequency. (Default)
x1~x10 Sets HT Link Frequency to x1~x10 (200 MHz~2.0 GHz).
Set Memory Clock
Determines whether to manually set the memory clock. Auto lets BIOS automatically set the memory
clock as required. Manual allows the memory clock control item below to be congurable. (Default: Auto)
Memory Clock
This option is congurable only when Set Memory Clock is set to Manual.
X4.00 Sets Memory Clock to X4.00.
X5.33 Sets Memory Clock to X5.33.
X6.66 Sets Memory Clock to X6.66.
X8.00 Sets Memory Clock to X8.00.
BIOS Setup - 42 -
Page 43

DRAM Conguration
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
CPU Host Clock Control [Auto]
x CPU Frequency(MHz) 200
Set Memory Clock [Auto]
x Memory Clock x6.66 1333Mhz
DCTs Mode [Unganged]
DDR3 Timing Items [Auto] SPD Auto
x CAS# latency Auto 9T 9T
x RAS to CAS R/W Delay Auto 9T 9T
x Row Precharge Time Auto 9T 9T
x Minimum RAS Active Time Auto 24T 24T
x 1T/2T Command Timing Auto -- -x TwTr Command Delay Auto 5T 5T
x Trfc0 for DIMM1 Auto 110ns 110ns
x Trfc2 for DIMM2 Auto -- -x Trfc1 for DIMM3 Auto -- -x Trfc3 for DIMM4 Auto -- -x Write Recovery Time Auto 10T 10T
x Precharge Time Auto 5T 5T
x Row Cycle Time Auto 33T 33T
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
x RAS to RAS Delay Auto 4T 4T
**DCTs Drive Strength** DCT0 DCT1
ProcOdt(ohms) [Auto] 60 [Auto] 60
DQS Drive Strength [Auto] 1.0x [Auto] 1.0x
Data Drive Strength [Auto] 1.0x [Auto] 1.0x
MEMCLK Drive Strength [Auto] 1.25x [Auto] 1.25x
Addr/Cmd Drive Strength [Auto] 1.5x [Auto] 1.5x
CS/ODT Drive Strength [Auto] 1.5x [Auto] 1.5x
CKE Drive Strength [Auto] 1.5x [Auto] 1.5x
**DCTs Addr/Cmd Timing** DCT0 DCT1
Addr/Cmd setup time [Auto] 1T [Auto] 1/2T
Addr/Cmdnedelay [Auto] 22/64 [Auto] 0/64
CS/ODT setup time [Auto] 1/2T [Auto] 1/2T
CS/ODTnedelay [Auto] 0/64 [Auto] 0/64
CKE setup time [Auto] 1/2T [Auto] 1/2T
CKEnedelay [Auto] 0/64 [Auto] 0/64
Bank Interleaving [Enabled]
Channel Interleave [Enabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
DQS Training Control [Skip DQS]
CKE Power Down Mode [Disabled]
Memclock tri-stating [Disabled]
DRAMConguration
DRAMConguration
DRAMConguration
Menu Level
Menu Level
Menu Level
Item Help
Item Help
Item Help
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
- 43 - BIOS Setup
Page 44

CPU Host Clock Control, CPU Frequency (MHz), Set Memory Clock, Memory Clock
The settings under the four items above are synchronous to those under the same items on the MB In telligent Tweaker(M.I.T.) main menu.
DCTs Mode
Allows you to set memory control mode.
Ganged Sets memory control mode to single dual-channel.
Unganged Sets memory control mode to two single-channel. (Default)
DDR3 Timing Items
Manual allows all DDR3 Timing items below to be congurable.
Options are: Auto (default), Manual.
CAS# latency
Options are: Auto (default), 4T~12T.
RAS to CAS R/W Delay
Options are: Auto (default), 5T~12T.
Row Precharge Time
Options are: Auto (default), 5T~12T.
Minimum RAS Active Time
Options are: Auto (default), 15T~30T.
1T/2T Command Timing
Options are: Auto (default), 1T, 2T.
TwTr Command Delay
Options are: Auto (default), 4T~7T.
Trfc0 for DIMM1
Options are: Auto (default), 90ns, 110ns, 160ns, 300ns, 350ns.
Trfc2 for DIMM2
Options are: Auto (default), 90ns, 110ns, 160ns, 300ns, 350ns.
Trfc1 for DIMM3
Options are: Auto (default), 90ns, 110ns, 160ns, 300ns, 350ns.
Trfc3 for DIMM4
Options are: Auto (default), 90ns, 110ns, 160ns, 300ns, 350ns.
Write Recovery Time
Options are: Auto (default), 5T~8T, 10T, 12T.
Precharge Time
Options are: Auto (default), 4T~7T.
Row Cycle Time
Options are: Auto (default), 11T~42T.
RAS to RAS Delay
Options are: Auto (default), 4T~7T.
BIOS Setup - 44 -
Page 45

DCTs Drive Strength
**
**
ProcOdt(ohms)
Options are: Auto (default), 240 ohms, 120 ohms, 60 ohms.
DQS Drive Strength
Options are: Auto (default), 0.75x, 1.0x, 1.25x, 1.5x.
Data Drive Strength
Options are: Auto (default), 0.75x, 1.0x, 1.25x, 1.5x.
MEMCLK Drive Strength
Options are: Auto (default), 0.75x, 1.0x, 1.25x, 1.5x.
Addr/Cmd Drive Strength
Options are: Auto (default), 1.0x, 1.25x, 1.5x, 2.0x.
CS/ODT Drive Strength
Options are: Auto (default), 1.0x, 1.25x, 1.5x, 2.0x.
CKE Drive Strength
Options are: Auto (default), 1.0x, 1.25x, 1.5x, 2.0x.
DCTs Addr/Cmd Timing
**
**
Addr/Cmd setup time
Options are: Auto (default), 1/2T, 1T.
Addr/Cmd ne delay
Options are: Auto (default)
, 0/64~31/64.
CS/ODT setup time
Options are: Auto (default), 1/2T, 1T.
CS/ODT ne delay
Options are: Auto (default)
, 0/64~31/64.
CKE setup time
Options are: Auto (default), 1/2T, 1T.
CKE ne delay
Options are: Auto (default)
, 0/64~31/64.
Bank Interleaving
Enables or disables memory bank interleaving. Enabled allows the system to simultaneously access dif-
ferent banks of the memory to increase memory performance and stability. (Default: Enabled)
Channel Interleave
Enables or disables memory channel interleaving. Enabled allows the system to simultaneously access
different channels of the memory to increase memory performance and stability. (Default: Enabled)
DQS Training Control
Enables or disables memory DQS training each time the system restarts. (Default: Skip DQS)
CKE Power Down Mode
Determines whether to set the memory to power down mode when the CKE pin is closed. (Default: Dis-
abled)
Memclock tri-stating
Determines whether to enable memory clock tri-stating in CPU C3 or Alt VID mode. (Default: Disabled)
- 45 - BIOS Setup
Page 46

System Voltage Optimized
********
********
System Voltage Control
Determines whether to manually set the system voltages. Auto lets the BIOS automatically set the
system voltages as required. Manual allows all voltage control items below to be congurable. (Default:
Auto)
CPU PLL Voltage Control
Allows you to set the CPU PLL voltage.
Normal Supplies the CPU PLL voltage as required. (Default)
2.220V ~ 3.100V The adjustable range is from 2.220V to 3.100V.
Note: Increasing CPU voltage may result in damage to your CPU or reduce the useful life of the CPU.
DRAM Voltage Control
Allows you to set memory voltage.
Normal Supplies the memory voltage as required. (Default)
1.210V ~ 2.410V The adjustable range is from 1.210V to 2.410V.
Note: Increasing memory voltage may result in damage to the memory or reduce the useful life of the
memory.
DDR VTT Voltage Control
Allows you to set the memory VTT voltage.
Normal Supplies the memory VTT voltage as required. (Default)
0.720V ~ 1.050V The adjustable range is from 0.720V to 1.050V.
Note: Increasing memory voltage may result in damage to the memory or reduce the useful life of the
memory.
NB Voltage Control
Allows you to set the North Bridge voltage.
Normal Supplies the North Bridge voltage as required. (Default)
0.950V ~ 1.450V The adjustable range is from 0.950V to 1.450V.
HT Link Voltage Control
Allows you to set the HT Link voltage.
Normal Supplies the HT Link voltage as required. (Default)
1.100V ~ 1.460V The adjustable range is from 1.100V to 1.460V.
NB/PCIe/PLL Voltage Ctrl
Allows you to set the North Bridge PCIe PLL voltage.
Normal Supplies the North Bridge PCIe PLL voltage as required. (Default)
1.500V ~ 2.100V The adjustable range is from 1.500V to 2.100V.
CPU NB VID Control
Allows you to set the CPU North Bridge VID voltage. Auto sets the CPU North Bridge VID voltage as
required. The adjustable range is dependent on the CPU being installed. (Default: Normal)
Note: Increasing CPU voltage may result in damage to your CPU or reduce the useful life of the CPU.
CPU Voltage Control
Allows you to set the CPU voltage. Auto sets the CPU voltage as required. The adjustable range is de-
pendent on the CPU being installed. (Default: Normal)
Note: Increasing CPU voltage may result in damage to your CPU or reduce the useful life of the CPU.
Normal CPU Vcore
Displays the normal operating voltage of your CPU.
BIOS Setup - 46 -
Page 47

2-4 Standard CMOS Features
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
Date (mm:dd:yy) Fri, Mar 12 2010
Time (hh:mm:ss) 22:31:24
IDE Channel 0 Master [None]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [None]
IDE Channel 1 Master [None]
IDE Channel 1 Slave [None]
IDE Channel 2 Master [None]
IDE Channel 2 Slave [None]
IDE Channel 4 Master [None]
IDE Channel 4 Slave [None]
IDE Channel 5 Master [None]
IDE Channel 5 Slave [None]
IDE Channel 7 Master [None]
IDE Channel 7 Slave [None]
Drive A [1.44M, 3.5"]
Floppy 3 Mode Support [Disabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
Halt On [All, But Keyboard]
Base Memory 640K
Extended Memory 1022M
Standard CMOS Features
Menu Level
Standard CMOS Features
Menu Level
Item Help
Item Help
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Date (mm:dd:yy)
Sets the system date. The date format is week (read-only), month, date and year. Select the desired eld
and use the up arrow or down arrow key to set the date.
Time (hh:mm:ss)
Sets the system time. For example, 1 p.m. is 13:0:0. Select the desired eld and use the up arrow or
down arrow key to set the time.
IDE Channel 0, 1 Master/Slave
IDE HDD Auto-Detection
Press <Enter> to autodetect the parameters of the IDE/SATA device on this channel.
IDE Channel 0, 1 Master/Slave
Congure your IDE/SATA devices by using one of the two methods below:
- 47 - BIOS Setup
Page 48

•Auto Lets the BIOS automatically detect IDE/SATA devices during the POST. (Default)
•None If no IDE/SATA devices are used, set this item to None so the system will skip
the detection of the device during the POST for faster system startup.
Access Mode Sets the hard drive access mode. Options are: Auto (default), CHS, LBA, Large.
IDE Channel 2, 4, 5, 7 Master/Slave
IDE Auto-Detection
Press <Enter> to autodetect the parameters of the IDE/SATA device on this channel.
Extended IDE Drive
Congure your IDE/SATA devices by using one of the two methods below:
•Auto Lets the BIOS automatically detect IDE/SATA devices during the POST. (Default)
•None If no IDE/SATA devices are used, set this item to None so the system will skip
the detection of the device during the POST for faster system startup.
Access Mode Sets the hard drive access mode. Options are: Auto (default), Large.
The following elds display your hard drive specications. If you wish to enter the parameters manually,
refer to the information on the hard drive.
Capacity Approximate capacity of the currently installed hard drive.
Cylinder Number of cylinders.
Head Number of heads.
Precomp Write precompensation cylinder.
Landing Zone Landing zone.
Sector Number of sectors.
Drive A
Allows you to select the type of oppy disk drive installed in your system. If you do not install a oppy
disk drive, set this item to None. Options are: None, 360K/5.25", 1.2M/5.25", 720K/3.5", 1.44M/3.5",
2.88M/3.5".
Floppy 3 Mode Support
Allows you to specify whether the installed oppy disk drive is 3-mode oppy disk drive, a Japanese
standard oppy disk drive. Options are: Disabled (default), Drive A.
Halt On
Allows you to determine whether the system will stop for an error during the POST.
All Errors Whenever the BIOS detects a non-fatal error the system boot will stop.
No Errors The system boot will not stop for any error.
All, But Keyboard The system boot will not stop for a keyboard error but stop for all other errors.
(Default)
All, But Diskette The system boot will not stop for a oppy disk drive error but stop for all other
errors.
All, But Disk/Key The system boot will not stop for a keyboard or a oppy disk drive error but it
will stop for all other errors.
Memory
These elds are read-only and are determined by the BIOS POST.
Base Memory Also called conventional memory. Typically, 640 KB will be reserved for the
MS-DOS operating system.
Extended Memory The amount of extended memory.
BIOS Setup - 48 -
Page 49

2-5 Advanced BIOS Features
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
AMD C1E Support [Auto]
Virtualization [Disabled]
AMD K8 Cool&Quiet control [Auto]
CPU Unlock
CPU core Control [Auto]
x CPU core 0 Enabled
x CPU core 1 Enabled
x CPU core 2/3/4/5
Hard Disk Boot Priority [Press Enter]
First Boot Device [Hard Disk]
Second Boot Device [CDROM]
Third Boot Device [Floppy]
Password Check [Setup]
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability [Disabled]
Away Mode [Disabled]
Full Screen LOGO Show [Enabled]
Backup BIOS Image to HDD [Disabled]
IOMMU support [Disabled]
Init Display First [PCI Slot]
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
(Note)
[Disabled]
(Note)
Enabled
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
AMD C1E Support
Enables or disables the C1E CPU power-saving function in system halt state. When enabled, the power
consumption will be reduced during system halt state.
Auto
If a CPU that supports hardware C1E is installed, the BIOS will automatically enable the
hardware C1E function. If not, the C1E function will be disabled. (Default)
Enabled
If a CPU that supports hardware C1E is installed, the BIOS will automatically enable the
hardware C1E function. If not, the BIOS will enable the software C1E function.
Disabled Disables the C1E function.
Virtualization
Virtualization allows a platform to run multiple operating systems and applications in independent parti-
tions. With virtualization, one computer system can function as multiple virtual systems.
(Default: Disabled)
AMD K8 Cool&Quiet control
Auto Lets the AMD Cool'n'Quiet driver dynamically adjust the CPU clock and VID to
reduce heat output from your computer and its power consumption. (Default)
Disabled Disables this function.
CPU Unlock
(Note)
Allows you to determine whether unlock hidden CPU cores. (Default: Disabled)
CPU core Control
Allows you to determine whether to manually enable/disable CPU Core 1/2/3/4/5.
Auto Lets the BIOS to enable all CPU cores (number of cores available depends on the
CPU being used). (Default)
Manual Allows you to individually enable/disable CPU Core 1/2/3/4/5.
CPU core 0
This setting is xed. CPU Core 0 is always enabled.
CPU core 1, 2/3/4/5
Enables or disables CPU Core 1/2/3/4/5. (Default: Enabled)
(Note) This item is present only if you install a CPU that supports this feature.
(Note)
Advanced BIOS Features
Menu Level
- 49 - BIOS Setup
Item Help
Page 50

Hard Disk Boot Priority
Species the sequence of loading the operating system from the installed hard drives. Use the up or
down arrow key to select a hard drive, then press the plus key <+> (or <PageUp>) or the minus key <-> (or
<PageDown>) to move it up or down on the list. Press <Esc> to exit this menu when nished.
First/Second/Third Boot Device
Species the boot order from the available devices. Use the up or down arrow key to select a device
and press <Enter> to accept. Options are: Floppy, LS120, Hard Disk, CDROM, ZIP, USB-FDD, USB-ZIP,
USB-CDROM, USB-HDD, Legacy LAN, Disabled.
Password Check
Species whether a password is required every time the system boots, or only when you enter BIOS
Setup. After conguring this item, set the password(s) under the Set Supervisor/User Password item in
the BIOS Main Menu.
Setup A password is only required for entering the BIOS Setup program. (Default)
System A password is required for booting the system and for entering the BIOS Setup
program.
HDD S.M.A.R.T. Capability
Enables or disables the S.M.A.R.T. (Self Monitoring and Reporting Technology) capability of your hard
drive. This feature allows your system to report read/write errors of the hard drive and to issue warnings
when a third party hardware monitor utility is installed. (Default: Enabled)
Away Mode
Enables or disables Away Mode in Windows XP Media Center operating system. Away Mode allows the
system to silently perform unattended tasks while in a low-power mode that appears off.
(Default: Disabled)
Full Screen LOGO Show
Allows you to determine whether to display the GIGABYTE Logo at system startup. Disabled displays
normal POST message. (Default: Enabled)
Backup BIOS Image to HDD
Allows the system to copy the BIOS image le to the hard drive. If the system BIOS is corrupted, it will
be recovered from this image le. (Default: Disabled)
IOMMU support
Enables or disables AMD IOMMU support. (Default: Disabled)
Init Display First
Species the rst initiation of the monitor display from the installed PCI or PCI Express graphics card.
PCI Slot Sets the PCI graphics card as the rst display. (Default)
PEG Sets the PCI Express graphics card on the PCIEX16_1 slot as the rst display.
PEG1 Sets the PCI Express graphics card on the PCIEX8_1 slot as the rst display.
PEG2 Sets the PCI Express graphics card on the PCIEX16_2 slot as the rst display.
PEG3 Sets the PCI Express graphics card on the PCIEX8_2 slot as the rst display.
PEG4 Sets the PCI Express graphics card on the PCIEX4_2 slot as the rst display.
PEG5 Sets the PCI Express graphics card on the PCIEX4_1 slot as the rst display.
BIOS Setup - 50 -
Page 51

2-6 Integrated Peripherals
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
OnChip SATA Controller [Enabled]
OnChip SATA Type [Native IDE]
x OnChip SATA Port4/5 Type IDE
x OnChip SATA RAID5 Support Enabled
OnChip SATA3.0 Support [Enabled]
x OnChip SATA Port as ESP Press Enter
Onboard PCIE Devices [Press Enter]
Onboard Audio Function [Enabled]
Onboard 1394 Function [Enabled]
Onboard USB 3.0 Controller [Enabled]
USB Controllers [Enabled]
USB Legacy Function [Enabled]
USB Storage Function [Enabled]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3F8/IRQ4]
Onboard Parallel Port [378/IRQ7]
Parallel Port Mode [SPP]
x ECP Mode Use DMA 3
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
OnChip SATA Controller (AMD SB850, SATA3_0~SATA3_5 connectors)
Enables or disables the integrated SATA controller. (Default: Enabled)
OnChip SATA Type (AMD SB850, SATA3_0~SATA3_3 connectors)
Congures the operating mode of the SATA3_0~SATA3_3 connectors.
Native IDE Allows the SATA controller to operate in Native IDE mode. (Default)
Enable Native IDE mode if you wish to install operating systems that support Native
mode.
RAID Enables RAID for the SATA controller.
AHCI Congures the SATA controller to AHCI mode. Advanced Host Controller Interface
(AHCI) is an interface specication that allows the storage driver to enable advanced
Serial ATA features such as Native Command Queuing and hot plug.
OnChip SATA Port4/5 Type (AMD SB850, SATA3_4 and SATA3_5 connectors)
This option is congurable only when OnChip SATA Type is set to RAID or AHCI. Congures the oper-
ating mode of the integrated SATA3_4 and SATA3_5 connectors.
IDE Disables RAID for the SATA controller and congures the SATA controller to IDE
mode. (Default)
As SATA Type The mode depends on the OnChip SATA Type settings.
OnChip SATA RAID5 Support (AMD SB850, SATA3_0~SATA3_5 connectors)
Enables or disables RAID 5 support for the SATA controller integrated in the AMD SB850 South Bridge.
This option is congurable only when OnChip SATA Type is set to RAID.
OnChip SATA3.0 Support
Enables or disables the SATA 6Gb/s function integrated in the South Bridge. When set to Disabled, the
SATA controller will operate in SATA 3Gb/s mode. (Default: Enabled)
Integrated Peripherals
Menu Level
Item Help
- 51 - BIOS Setup
Page 52

OnChip SATA Port as ESP
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
Port0 as ESP [Disabled]
Port1 as ESP [Disabled]
Port2 as ESP [Disabled]
Port3 as ESP [Disabled]
Port4 as ESP [Disabled]
Port5 as ESP [Disabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
OnChip SATA Port as ESP
Menu Level
Item Help
Port0 as ESP/Port1 as ESP/Port2 as ESP/Port3 as ESP
This option is congurable only when OnChip SATA Type is set to AHCI. Enabled will speed up the hot
plug detection of the connected SATA device. (Default: Disabled)
Port4 as ESP/Port5 as ESP
This option is congurable only when OnChip SATA Type is set to AHCI and OnChip SATA Type
Port4/5 is set to as SATA Type. Enabled will speed up the hot plug detection of the connected SATA
device. (Default: Disabled)
BIOS Setup - 52 -
Page 53

Onboard PCIE Devices
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
PrimaryDualSlotCong [Auto]
SecondaryDualSlotCong [Auto]
PCIEX4_2SlotCong [AsX1Link]
Onboard GSATA/IDE Ctrl [Enabled]
Onboard GSATA/IDE Mode [IDE]
Onboard ESATA Controller [Enabled]
Onboard ESATA Mode [IDE]
Green LAN [Disabled]
Onboard LAN1 Function [Enabled]
Onboard LAN1 Boot ROM [Disabled]
SMART LAN1 [Press Enter]
Onboard LAN2 Function [Enabled]
Onboard LAN2 Boot ROM [Disabled]
SMART LAN2 [Press Enter]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Onboard PCIE Devices
Menu Level
Item Help
Primary Dual Slot Cong (PCIEX16_1 and PCIEX8_1 slots)
Species the operating bandwidth for the PCIEX16_1 and PCIEX8_1 slots.
Auto Lets the BIOS automatically congure this setting depending on the device being
installed. (Default)
X16 PCIEX16_1 operates at x16 and PCIEX8_1 becomes unavailable.
X8/X8 PCIEX16_1 and PCIEX8_1 operate at x8 respectively.
Secondary Dual Slot Cong (PCIEX16_2 and PCIEX8_2 slots)
Species the operating bandwidth for the PCIEX16_2 and PCIEX8_2 slots.
Auto Lets the BIOS automatically congure this setting depending on the device being
installed. (Default)
X16 PCIEX16_2 operates at x16 and PCIEX8_2 becomes unavailable.
X8/X8 PCIEX16_2 and PCIEX8_2 operate at x8 respectively.
PCIEX4_2 Slot Cong
Species the operating bandwidth for the PCIEX4_2 slot.
As X1 Link PCIEX4_2 operates at x1 mode. (Default)
As X4 Link PCIEX4_2 operates at x4 mode. Please note that due to bandwidth sharing, the
onboard IDE, GSATA2_6, and GSATA2_7 connectors will become unavailable.
Onboard GSATA/IDE Ctrl (GIGABYTE SATA2 Chip, IDE and GSATA2_6/7 Connectors)
Enables or disables the IDE and SATA controllers integrated in the GIGABYTE SATA2 chip. (Default:
Enabled)
Onboard GSATA/IDE Mode (GIGABYTE SATA2 Chip, GSATA2_6/7 Connectors)
Enables or disables RAID for the SATA controller integrated in the GIGABYTE SATA2 chip or congures
the SATA controller to AHCI mode.
IDE Congures the SATA controller to IDE mode. (Default)
AHCI Congures the SATA controller to AHCI mode. Advanced Host Controller Interface
(AHCI) is an interface specication that allows the storage driver to enable advanced
Serial ATA features such as Native Command Queuing and hot plug.
RAID/IDE Enables RAID for the SATA controller; the IDE controller still operates in IDE mode.
- 53 - BIOS Setup
Page 54

Onboard ESATA Controller (JMicron JMB362 Chip, eSATA Connectors on the Back Panel)
Enables or disables the SATA controller integrated in the JMicron JMB362 chip. (Default: Enabled)
Onboard ESATA Mode (JMicron JMB362 Chip, eSATA Connectors on the Back Panel)
Enables or disables RAID for the SATA controller integrated in the JMicron JMB362 chip or congures
the SATA controller to AHCI mode.
IDE Disables RAID for the SATA controller and congures the SATA controller to IDE
mode. (Default)
AHCI Congures the SATA controller to AHCI mode. Advanced Host Controller Interface
(AHCI) is an interface specication that allows the storage driver to enable advanced
Serial ATA features such as Native Command Queuing and hot plug.
RAID Enables RAID for the SATA controller.
Green LAN
When the onboard LAN function and Green LAN are enabled, the system will dynamically detect if a
LAN cable is connected or not. If not, the corresponding LAN controller will be disabled automatically.
(Default: Disabled)
Onboard LAN1/LAN2 Function
Enables or disables the onboard LAN function. (Default: Enabled)
If you wish to install a 3rd party add-in network card instead of using the onboard LAN, set this item to
Disabled.
Onboard LAN1/LAN2 Boot ROM
Allows you to decide whether to activate the boot ROM integrated with the onboard LAN chip.
(Default: Disabled)
SMART LAN1/LAN2 (LAN Cable Diagnostic Function)
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
Start detecting at Port.....
Part1-2 Status = Open / Length = 0m
Part3-6 Status = Open / Length = 0m
Part4-5 Status = Open / Length = 0m
Part7-8 Status = Open / Length = 0m
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
This motherboard incorporates cable diagnostic feature designed to detect the status of the attached LAN
cable. This feature will detect cabling issue and report the approximate distance to the fault or short. Refer to
the following information for diagnosing your LAN cable:
When No LAN Cable Is Attached...
If no LAN cable is attached to the motherboard, the Status elds of all four pairs of wires will show Open
and the Length elds show 0m, as shown in the gure above.
When LAN Cable Is Functioning Normally...
If no cable problem is detected on the LAN cable connected to a Gigabit hub or a 10/100 Mbps hub, the
following message will appear:
BIOS Setup - 54 -
SMART LAN
Menu Level
Item Help
Page 55

Start detecting at Port.....
Link Detected --> 100Mbps
Cable Length= 30m
Link Detected Displays transmission speed.
Cable Length Displays the approximate length of the attached LAN cable.
Note: The Gigabit hub will only operate at a speed of 10/100 Mbps in MS-DOS mode; it will operate at a
normal speed of 10/100/1000 Mbps in Windows mode or when the LAN Boot ROM is activated.
When a Cable Problem Occurs...
If a cable problem occurs on a specied pair of wires, the Status eld will show Short and then length
shown will be the approximate distance to the fault or short.
Example:
Explanation: A fault or short might occur at about 2m on Part 1-2.
Note: Part 4-5 and Part 7-8 are not used in a 10/100 Mbps environment, so their Status elds will show
Part1-2 Status = Short / Length = 2m
Open, and the length shown is the approximate length of the attached LAN cable.
Onboard Audio Function
Enables or disables the onboard audio function. (Default: Enabled)
If you wish to install a 3rd party add-in audio card instead of using the onboard audio, set this item to
Disabled.
Onboard 1394 Function
Enables or disables the onboard IEEE 1394 function. (Default: Enabled)
Onboard USB 3.0 Controller (NEC USB Controller)
Enables or disables the NEC USB controller. (Default: Enabled)
USB Controllers
Enables or disables the integrated USB controllers. (Default: Enabled)
Disabled will turn off all of the USB functionalities below.
USB Legacy Function
Allows USB keyboard to be used in MS-DOS. (Default: Enabled)
USB Storage Function
Determines whether to detect USB storage devices, including USB ash drives and USB hard drives
during the POST. (Default: Enabled)
Onboard Serial Port 1
Enables or disables the rst serial port and species its base I/O address and corresponding interrupt.
Options are: Auto, 2F8/IRQ3, 3F8/IRQ4(default), 3E8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, Disabled.
Onboard Parallel Port
Enables or disables the onboard parallel port (LPT) and species its base I/O address and correspond-
ing interrupt. Options are: 378/IRQ7 (default), 278/IRQ5, 3BC/IRQ7, Disabled.
Parallel Port Mode
Selects an operating mode for the onboard parallel (LPT) port. Options are: SPP (Standard Parallel Port)
(default), EPP (Enhanced Parallel Port), ECP (Extended Capabilities Port), ECP+EPP.
ECP Mode Use DMA
Selects DMA channel for the LPT port in ECP mode. This item is congurable only if Parallel Port Mode
is set to ECP or ECP+EPP mode. Options are: 3 (default), 1.
- 55 - BIOS Setup
Page 56

2-7 Power Management Setup
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
ACPI Suspend Type [S3(STR)]
Soft-Off by Power button [Instant-off]
USB Wake Up from S3 [Enabled]
Modem Ring Resume [Disabled]
PME Event Wake Up [Enabled]
HPET Support
Power On By Mouse [Disabled]
Power On By Keyboard [Disabled]
x KB Power ON Password Enter
AC Back Function [Soft-Off]
Power-On by Alarm [Disabled]
x Date (of Month) Everyday
x Resume Time (hh:mm:ss) 0 : 0 : 0
ErP Support [Disabled]
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
(Note)
[Enabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
ACPI Suspend Type
Species the ACPI sleep state when the system enters suspend.
S1(POS) Enables the system to enter the ACPI S1 (Power on Suspend) sleep state.
In S1 sleep state, the system appears suspended and stays in a low power mode.
The system can be resumed at any time.
S3(STR) Enables the system to enter the ACPI S3 (Suspend to RAM) sleep state (default).
In S3 sleep state, the system appears to be off and consumes less power than in
the S1 state. When signaled by a wake-up device or event, the system resumes to
its working state exactly where it was left off.
Soft-Off by Power button
Congures the way to turn off the computer in MS-DOS mode using the power button.
Instant-Off Press the power button and then the system will be turned off instantly. (Default)
Delay 4 Sec. Press and hold the power button for 4 seconds to turn off the system. If the power
button is pressed for less than 4 seconds, the system will enter suspend mode.
USB Wake Up from S3
Allows the system to be awakened from ACPI S3 sleep state by a wake-up signal from the installed USB
device. (Default: Enabled)
Modem Ring Resume
Allows the system to be awakened from an ACPI sleep state by a wake-up signal from a modem that
supports wake-up function. (Default: Disabled)
Power Management Setup
Menu Level
Item Help
(Note) Supported on Windows 7/Vista operating system only.
BIOS Setup - 56 -
Page 57

PME Event Wake Up
Allows the system to be awakened from an ACPI sleep state by a wake-up signal from a PCI or PCIe de-
vice. Note: To use this function, you need an ATX power supply providing at least 1A on the +5VSB lead.
(Default: Enabled)
HPET Support
Enables or disables High Precision Event Timer (HPET) for Windows 7/Vista operating system.
(Default: Enabled)
(Note)
Power On By Mouse
Allows the system to be turned on by a PS/2 mouse wake-up event.
Note: To use this function, you need an ATX power supply providing at least 1A on the +5VSB lead.
Disabled Disables this function. (Default)
Double Click Double click on left button on the PS/2 mouse to turn on the system.
Power On By Keyboard
Allows the system to be turned on by a PS/2 keyboard wake-up event.
Note: you need an ATX power supply providing at least 1A on the +5VSB lead.
Disabled Disables this function. (Default)
Password Set a password with 1~5 characters to turn on the system.
Any KEY Press any key on the keyboard to turn on the system.
Keyboard 98 Press POWER button on the Windows 98 keyboard to turn on the system.
KB Power ON Password
Set the password when Power On by Keyboard is set to Password. Press <Enter> on this item and set
a password with up to 5 characters and then press <Enter> to accept. To turn on the system, enter the
password and press <Enter>.
Note: To cancel the password, press <Enter> on this item. When prompted for the password, press <En-
ter> again without entering the password to clear the password settings.
AC Back Function
Determines the state of the system after the return of power from an AC power loss.
Soft-Off The system stays off upon the return of the AC power. (Default)
Full-On The system is turned on upon the return of the AC power.
Memory The system returns to its last known awake state upon the return of the AC power.
Power-On by Alarm
Determines whether to power on the system at a desired time. (Default: Disabled)
If enabled, set the date and time as following:
Date (of Month): Turn on the system at a specic time on each day or on a specic day in a month.
Resume Time (hh: mm: ss): Set the time at which the system will be powered on automatically.
Note: When using this function, avoid inadequate shutdown from the operating system or removal of the
AC power, or the settings may not be effective.
ErP Support
Determines whether to let the system consume less than 1W power in S5 (shutdown) state. (Default:
Disabled)
Note: When this item is set to Enabled, the following four functions will become unavailable:
PME event wake up, power on by mouse, power on by keyboard, and wake on LAN.
(Note) Supported on Windows 7/Vista operating system only.
- 57 - BIOS Setup
Page 58

2-8 PC Health Status
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
Hardware Thermal Control [Enabled]
Reset Case Open Status [Disabled]
Case Opened No
Vcore 1.364V
DDR3 1.5V 1.536V
+3.3V 3.280V
+12V 12.048V
Current System Temperature 38oC
Current CPU Temperature 36oC
Current CPU FAN Speed 1962 RPM
Current SYSTEM FAN1 Speed 0 RPM
Current SYSTEM FAN2 Speed 0 RPM
Current NB FAN Speed 0 RPM
CPU Warning Temperature [Disabled]
CPU FAN Fail Warning [Disabled]
SYSTEM FAN1 Fail Warning [Disabled]
SYSTEM FAN2 Fail Warning [Disabled]
NB FAN Fail Warning [Disabled]
CPU Smart FAN Control [Enabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
PC Health Status
Menu Level
Item Help
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
CPU Smart FAN Mode [Auto]
System Smart FAN Control [Enabled]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
PC Health Status
Menu Level
Item Help
Hardware Thermal Control
Enables or disables the CPU overheating protection function. When enabled, the CPU core voltage and
ratio will be reduced when the CPU is overheated. (Default: Enabled)
Reset Case Open Status
Keeps or clears the record of previous chassis intrusion status. Enabled clears the record of previous
chassis intrusion status and the Case Opened eld will show "No" at next boot. (Default: Disabled)
Case Opened
Displays the detection status of the chassis intrusion detection device attached to the motherboard CI
header. If the system chassis cover is removed, this eld will show "Yes", otherwise it will show "No". To
clear the chassis intrusion status record, set Reset Case Open Status to Enabled, save the settings to
the CMOS, and then restart your system.
BIOS Setup - 58 -
Page 59

Current Voltage(V) Vcore/DDR3 1.5V/+3.3V/+12V
Displays the current system voltages.
Current System/CPU Temperature
Displays current system/CPU temperature.
Current CPU/SYSTEM/NB FAN Speed (RPM)
Displays current CPU/system/North Bridge fan speed.
CPU Warning Temperature
Sets the warning threshold for CPU temperature. When CPU temperature exceeds the threshold,
BIOS will emit warning sound. Options are: Disabled (default), 60oC/140oF, 70oC/158oF, 80oC/176oF,
90oC/194oF.
CPU/SYSTEM/NB FAN Fail Warning
Allows the system to emit warning sound if the CPU/system/North Bridge fan is not connected or fails.
Check the fan condition or fan connection when this occurs. (Default: Disabled)
CPU Smart FAN Control
Enables or disables the CPU fan speed control function. Enabled allows the CPU fan to run at different
speed according to the CPU temperature. You can adjust the fan speed with EasyTune based on system
requirements. If disabled, the CPU fan runs at full speed. (Default: Enabled)
CPU Smart FAN Mode
Species how to control CPU fan speed. This item is congurable only if CPU Smart FAN Control is set
to Enabled.
Auto Lets the BIOS automatically detect the type of CPU fan installed and sets the optimal
CPU fan control mode. (Default)
Voltage Sets Voltage mode for a 3-pin CPU fan.
PWM Sets PWM mode for a 4-pin CPU fan.
System Smart FAN Control
Enables or disables the system fan speed control function. Enabled allows the system fan to run at dif-
ferent speed according to the system temperature. If disabled, system fan runs at full speed. (Default:
Enabled)
- 59 - BIOS Setup
Page 60

2-9 Load Fail-Safe Defaults
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
Load Fail-Safe Defaults (Y/N)? N
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
higf
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Press <Enter> on this item and then press the <Y> key to load the safest BIOS default settings.
In case system instability occurs, you may try to load Fail-Safe defaults, which are the safest and most stable
BIOS settings for the motherboard.
2-10 Load Optimized Defaults
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N)? N
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
higf
Load Optimized Defaults
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Press <Enter> on this item and then press the <Y> key to load the optimal BIOS default settings.
The BIOS defaults settings help the system to operate in optimum state. Always load the Optimized defaults
after updating the BIOS or after clearing the CMOS values.
BIOS Setup - 60 -
Page 61

2-11 Set Supervisor/User Password
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
Enter Password:
higf
Change/Set/Disable Password
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Press <Enter> on this item and type the password with up to 8 characters and then press <Enter>. You will
be requested to conrm the password. Type the password again and press <Enter>.
The BIOS Setup program allows you to specify two separate passwords:
Supervisor Password
When a system password is set and the Password Check item in Advanced BIOS Features is set to
Setup, you must enter the supervisor password for entering BIOS Setup and making BIOS changes.
When the Password Check item is set to System, you must enter the supervisor password (or user
password) at system startup and when entering BIOS Setup.
User Password
When the Password Check item is set to System, you must enter the supervisor password (or user
password) at system startup to continue system boot. In BIOS Setup, you must enter the supervisor
password if you wish to make changes to BIOS settings. The user password only allows you to view the
BIOS settings but not to make changes.
To clear the password, press <Enter> on the password item and when requested for the password, press
<Enter> again. The message "PASSWORD DISABLED" will appear, indicating the password has been cancelled.
- 61 - BIOS Setup
Page 62

2-12 Save & Exit Setup
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
Save to CMOS and EXIT (Y/N)? Y
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
higf
Save Data to CMOS
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Press <Enter> on this item and press the <Y> key. This saves the changes to the CMOS and exits the BIOS
Setup program. Press <N> or <Esc> to return to the BIOS Setup Main Menu.
2-13 Exit Without Saving
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
Quit Without Saving (Y/N)? N
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
higf
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all Data
Press <Enter> on this item and press the <Y> key. This exits the BIOS Setup without saving the changes
made in BIOS Setup to the CMOS. Press <N> or <Esc> to return to the BIOS Setup Main Menu.
BIOS Setup - 62 -
Page 63

Chapter 3 Drivers Installation
• Before installing the drivers, rst install the operating system.
• After installing the operating system, insert the motherboard driver disk into your optical drive.
The driver Autorun screen is automatically displayed which looks like that shown in the screen
shot below. (If the driver Autorun screen does not appear automatically, go to My Computer,
double-click the optical drive and execute the Run.exe program.)
3-1 Installing Chipset Drivers
After inserting the driver disk, "Xpress Install" will automatically scan your system and then list all the drivers
that are recommended to install. You can click the Install All button and "Xpress Install" will install all the recommended drivers. Or click Install Single Items to manually select the drivers you wish to install.
• Please ignore the popup dialog box(es) (e.g. the Found New Hardware Wizard) displayed
when "Xpress Install" is installing the drivers. Failure to do so may affect the driver installation.
• Some device drivers will restart your system automatically during the driver installation. After the
system restart, "Xpress Install" will continue to install other drivers.
• After "Xpress Install" installs all of the drivers, a dialog box will appear asking whether to install
new GIGABYTE utilities. Click Yes to automatically install the utilities. Or click No if you want to
manually select the utilities to install on the Application Software page later.
• For USB 2.0 driver support under the Windows XP operating system, please install the Windows
XP Service Pack 1 or later. After installing the SP1 (or later), if a question mark still exists in
Universal Serial Bus Controller in Device Manager, please remove the question mark (by
right-clicking your mouse and select Uninstall) and restart the system. (The system will then
autodetect and install the USB 2.0 driver.)
- 63 - Drivers Installation
Page 64

3-2 Application Software
This page displays all the utilities and applications that GIGABYTE develops and some free software. You
can click the Install button on the right of an item to install it.
3-3 Technical Manuals
This page provides GIGABYTE's application guides, content descriptions for this driver disk, and the motherboard manuals.
Drivers Installation - 64 -
Page 65

3-4 Contact
For the detailed contact information of the GIGABYTE Taiwan headquarter or worldwide branch ofces, click
the URL on this page to link to the GIGABYTE website.
3-5 System
This page provides the basic system information.
- 65 - Drivers Installation
Page 66

3-6 Download Center
To update the BIOS, drivers, or applications, click the Download Center button to link to the GIGABYTE
website. The latest version of the BIOS, drivers, or applications will be displayed.
3-7 New Utilities
This page provides a quick link to GIGABYTE's lately developed utilities for users to install. You can click the
Install button on the right of an item to install it.
Drivers Installation - 66 -
Page 67

Chapter 4 Unique Features
4-1 Xpress Recovery2
Xpress Recovery2 is a utility that allows you to quickly compress and
back up your system data and perform restoration of it. Supporting NTFS,
FAT32, and FAT16 le systems, Xpress Recovery2 can back up data on
PATA and SATA hard drives and restore it.
Before You Begin:
• Xpress Recovery2 will check the rst physical hard drive
can only back up/restore the rst physical hard drive that has the operating system installed.
• As Xpress Recovery2 will save the backup le at the end of the hard drive, make sure to leave enough un-
allocated space in advanced (10 GB or more is recommended; actual size requirements vary, depending
on the amount of data).
• It is recommended to back up your system soon after the operating system and drivers are installed.
• The amount of data and hard drive access speed may affect the speed at which the data is backed up/
restored.
• It takes longer to back up a hard drive than to restore it.
System Requirements:
• At least 512 MB of system memory
• VESA compatible graphics card
• Windows XP with SP1 or later, Windows Vista
• Xpress Recovery and Xpress Recovery2 are different utilities. For example, a backup le created
with Xpress Recovery cannot be restored using Xpress Recovery2.
• USB hard drives are not supported.
• Hard drives in RAID/AHCI mode are not supported.
Installation and Conguration:
Turn on your system to boot from the Windows Vista setup disk.
A. Installing Windows Vista and Partitioning the Hard Drive
(Note)
for the operating system. Xpress Recovery2
Step 1:
Click Drive options.
(Note) Xpress Recovery2 checks the rst physical hard drive in the following sequence: The rst PATA IDE connector, the
second PATA IDE connector, the rst SATA connector, the second SATA connector and so forth. For example, when hard
drives are attached to the rst IDE and the rst SATA connectors, the hard drive on the rst IDE connector is the rst physical
drive. When hard drives are attached to the rst and second SATA connectors, the hard drive on the rst SATA connector is
the rst physical drive.
Step 2:
Click New.
- 67 - Unique Features
Page 68

Step 3:
When partitioning your hard drive, make sure to
leave unallocated space (10 GB or more is recommended; actual size requirements vary, depending
on the amount of data) and begin the installation of
Step 4:
After the operating system is installed, right-click
the Computer icon on your desktop and select
Manage. Go to Disk Management to check disk
allocation.
the operating system.
Step 5:
Xpress Recovery2 will save the backup le to the unallocated
space (black stripe along the top). Please note that if there is no
enough unallocated space, Xpress Recovery2 cannot save the
backup le.
B. Accessing Xpress Recovery2
1. Boot from the motherboard driver disk to access Xpress Recovery2 for the rst time. When you see the
following message:
Press any key to startup Xpress Recovery2
, press any key
to enter Xpress Recovery2.
2. After you use the backup function in Xpress Recovery2 for the rst time, Xpress Recovery2 will stay
permanent in your hard drive. If you wish to enter Xpress Recovery2 later, simply press <F9> during the
POST.
C. Using the Backup Function in Xpress Recovery2
Xpre ss Rec overy2 will automatical ly cre ate a
new partition to store the backup image le.
Step 1:
Select BACKUP to start backing up your hard drive
data.
Unique Features - 68 -
Step 2:
When nished, go to Disk Management to check
disk allocation.
Page 69

D. Using the Restore Function in Xpress Recovery2
Select RESTORE to restore the backup to your hard drive in
case the system breaks down. The RESTORE option will not be
present if no backup is created before.
E. Removing the Backup
Step 1:
If you wish to remove the backup le, select
REMOVE.
F. Exiting Xpress Recovery2
Step 2:
After the backup le is removed, no backup image
le will be present in Disk Management and hard
drive space will be freed up.
Select REBOOT to exit Xpress Recovery2.
- 69 - Unique Features
Page 70

4-2 BIOS Update Utilities
GIGABYTE motherboards provide two unique BIOS update tools, Q-Flash™ and @BIOS™. GIGABYTE
Q-Flash and @BIOS are easy-to-use and allow you to update the BIOS without the need to enter MS-DOS
mode. Additionally, this motherboard features the DualBIOS™ design, which enhances protection for the
safety and stability of your computer by adding one more physical BIOS chip.
What is DualBIOS™?
Motherboards that support DualBIOS have two BIOS onboard, a main BIOS and
a backup BIOS. Normally, the system works on the main BIOS. However, if the
main BIOS is corrupted or damaged, the backup BIOS will take over on the next system boot and copy the
BIOS le to the main BIOS to ensure normal system operation. For the sake of system safety, users cannot
update the backup BIOS manually.
What is Q-Flash™?
With Q-Flash you can update the system BIOS without having to enter operating
systems like MS-DOS or Window rst. Embedded in the BIOS, the Q-Flash tool
frees you from the hassles of going through complicated BIOS ashing process.
What is @BIOS™?
@BIOS allows you to update the system BIOS while in the Windows environ-
ment. @BIOS will download the latest BIOS le from the nearest @BIOS server
site and update the BIOS.
4-2-1 Updating the BIOS with the Q-Flash Utility
A. Before You Begin
1. From GIGABYTE's website, download the latest compressed BIOS update le that matches your motherboard model.
2. Extract the le and save the new BIOS le (e.g. 89FXAUD72.F1) to your oppy disk, USB ash drive, or
hard drive. Note: The USB ash drive or hard drive must use FAT32/16/12 le system.
3. Restart the system. During the POST, press the <End> key to enter Q-Flash. Note: You can access
Q-Flash by either pressing the <End> key during the POST or pressing the <F8> key in BIOS Setup.
However, if the BIOS update le is saved to a hard drive in RAID/AHCI mode or a hard drive attached to
an independent IDE/SATA controller, use the <End> key during the POST to access Q-Flash.
Award Modular BIOS v6.00PG, An Energy Star Ally
Copyright (C) 1984-2010, Award Software, Inc.
GA-890FXA-UD7 F3d
.
.
.
.
<DEL>: BIOS Setup <F9>: XpressRecovery2 <F12>: Boot Menu <End>: Qflash
07/20/2010-RD890-SB850-7A66DG03C-00
Because BIOS ashing is potentially risky, please do it with caution. Inadequate BIOS ashing may
result in system malfunction.
Unique Features - 70 -
Page 71

B. Updating the BIOS
When updating the BIOS, choose the location where the BIOS le is saved. The following procedure assumes that you save the BIOS le to a oppy disk.
Step 1:
1. Insert the oppy disk containing the BIOS le into the oppy disk drive. In the main menu of Q-Flash, use
the up or down arrow key to select Update BIOS from Drive and press <Enter>.
• The Save Main BIOS to Drive option allows you to save the current BIOS le.
• Q-Flash only supports USB ash drive or hard drives using FAT32/16/12 le system.
• If the BIOS update le is saved to a hard drive in RAID/AHCI mode or a hard drive attached to
an independent IDE/SATA controller, use the <End> key during the POST to access Q-Flash.
2. Select Floppy A and press <Enter>.
Q-Flash Utility v2.15
Flash Type/Size................................. SST 25VF080B 1M
Keep DMI Data Enable
Floppy A <Drive>
Load CMOS Default Enable
HDD 1-0 <Drive>
Update BIOS from Drive
Save BIOS to Drive
Enter : Run hi:Move ESC:Reset F10:Power Off
Total size : 0 Free size : 0
3. Select the BIOS update le and press <Enter>.
Make sure the BIOS update le matches your motherboard model.
Step 2:
The process of the system reading the BIOS le from the oppy disk is displayed on the screen. When the
message "Are you sure to update BIOS?" appears, press <Enter> to begin the BIOS update. The monitor will
display the update process.
• Do not turn off or restart the system when the system is reading/updating the BIOS.
• Do not remove the oppy disk, USB ash drive, or hard drive when the system is updat-
ing the BIOS.
0le(s)found
Step 3:
When the update process is complete, press any key to return to the main menu.
Q-Flash Utility v2.15
Flash Type/Size................................. SST 25VF080B 1M
Keep DMI Data Enable
Load CMOS Default Enable
Update BIOS from Drive
Save BIOS to Drive
Enter : Run hi:Move ESC:Reset F10:Power Off
!! Copy BIOS completed - Pass !!
Please press any key to continue
- 71 - Unique Features
Page 72

Step 4:
Press <Esc> and then <Enter> to exit Q-Flash and reboot the system. As the system boots, you should see
the new BIOS version is present on the POST screen.
Step 5:
During the POST, press <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup. Select Load Optimized Defaults and press <Enter>
to load BIOS defaults. System will re-detect all peripheral devices after a BIOS update, so we recommend
that you reload BIOS defaults.
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
MB Intelligent Tweaker(M.I.T.)
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features
Integrated Peripherals
Power Management Setup
PC Health Status
ESC: Quit
F8: Q-Flash F10: Save & Exit Setup F12: Load CMOS from BIOS
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N)? Y
: Select Item F11: Save CMOS to BIOS
higf
Load Optimized Defaults
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults
Set Supervisor Password
Set User Password
Save & Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
Press <Y> to load BIOS defaults
Step 6:
Select Save & Exit Setup and then press <Y> to save settings to CMOS and exit BIOS Setup. The procedure is complete after the system restarts.
Unique Features - 72 -
Page 73

4-2-2 Updating the BIOS with the @BIOS Utility
A. Before You Begin
1. In Windows, close all applications and TSR (Terminate and Stay Resident) programs. This helps prevent
unexpected failures when performing a BIOS update.
2. During the BIOS update process, ensure the Internet connection is stable and do NOT interrupt the
Internet connection (for example, avoid a power loss or switching off the Internet). Failure to do so may
result in a corrupted BIOS or a system that is unable to start.
3. Do not use the G.O.M. (GIGABYTE Online Management) function when using @BIOS.
4. GIGABYTE product warranty does not cover any BIOS damage or system failure resulting from an inad-
equate BIOS ashing.
B. Using @BIOS
1. Update the BIOS Using the Internet Update Function:
Click Update BIOS from GIGABYTE Server, select the @BIOS server site closest to your location and
then download the BIOS le that matches your motherboard model. Follow the on-screen instructions to
complete.
If the BIOS update le for your motherboard is not present on the @BIOS server site, please
manually download the BIOS update le from GIGABYTE's website and follow the instructions in
"Update the BIOS without Using the Internet Update Function" below.
2. Update the BIOS without Using the Internet Update Function:
Click Update BIOS from File, then select the location where you save the BIOS update le obtained
from the Internet or through other source. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete.
3. Save the Current BIOS File:
Click Save Current BIOS to File to save the current BIOS le.
4. Load BIOS Defaults after BIOS Update:
Select the Load CMOS default after BIOS update check box and then the system will automatically
load BIOS defaults after BIOS update and after the system restarts.
C. After Updating the BIOS
Restart your system after updating the BIOS.
Make sure that the BIOS le to be ashed matches your motherboard model. Updating the
BIOS with an incorrect BIOS le could cause your system not to boot.
- 73 - Unique Features
Page 74

4-3 EasyTune 6
GIGABYTE's EasyTune 6 is a simple and easy-to-use interface that allows users to ne-tune their system
settings or do overclock/overvoltage in Windows environment. The user-friendly EasyTune 6 interface also
includes tabbed pages for CPU and memory information, letting users read their system-related information
without the need to install additional software.
The EasyTune 6 Interface
Tabs Information
Tab Function
The CPU tab provides information on the installed CPU and motherboard.
The Memory tab provides information on the installed memory module(s). You can select memory
module on a specic slot to see its information.
The Tuner tab allows you to change system clock settings and voltages.
• Easy mode allows you to adjust the CPU FSB only.
• Advanced mode allows you to individually change system clock settings and voltages settings
using the sliders.
• Easy Boost is an easy-to-use auto-overclocking function
automatically experiments all sorts of overclocking congurations till it hangs. After restart, the
system will operate with the optimum congurations tested to let the CPU reach the best
overclocking performance.
• Core Boost is congurable only in Advanced mode. With Core Boost
hidden CPU cores or disable the cores that have been activated
• Save allows you to save the current settings to a new prole (.txt le).
• Load allows you to load previous settings from a prole.
After making changes in Easy mode/Advanced mode, be sure to click Set for these changes to take
effect or click Default to restore to default values.
The Graphics tab allows you to change the core clock and memory clock for your ATI or NVIDIA
graphics card.
The Smart tab allows you to specify a Smart Fan mode. Smart Fan allows the CPU fan speed to be
changed linearly based on the CPU temperature thresholds you set.
The HW Monitor tab allows you to monitor hardware temperature, voltage and fan speed and set
temperature/fan speed alarm. You can choose the alert sound from the buzzer or use your own sound
le (.wav le).
(Note 1) Before enabling Easy Boost, right-click the EasyTune 6 icon in the notication area. Select Auto overclock
last tune on the next reboot to allow the system to work with the optimum overclocking conguration after restart.
(Note 2) Restart the computer after enabling Core Boost for the settings to take effect.
(Note 3) The number of CPU cores that can be enabled/disabled depends on the CPU being used.
Available functions in EasyTune 6 may differ by motherboard model. Grayed-out area(s) indicates that the item is
not congurable or the function is not supported.
Incorrectly doing overclock/overvoltage may result in damage to the hardware components such as CPU, chipset,
and memory and reduce the useful life of these components. Before you do the overclock/overvoltage, make sure
that you fully know each function of EasyTune 6, or system instability or other unexpected results may occur.
Unique Features - 74 -
(Note 1)
. When activated, the system
(Note 2)
enabled, you can unlock
(Note 3)
.
Page 75

4-4 Easy Energy Saver
GIGABYTE Easy Energy Saver is a revolutionary technology that delivers unparalleled power savings with
a click of the button. Featuring an advanced proprietary software design, GIGABYTE Easy Energy Saver is
able to provide exceptional power savings and enhanced power efciency without sacricing computing performance.
The Easy Energy Saver Interface
A. Meter Mode
In Meter Mode, GIGABYTE Easy Energy Saver shows how much power they have saved in a set period of
time.
Meter Mode - Button Information Table
Button Description
1 Easy Energy Saver On/Off Switch (Default: Off)
2 Dynamic CPU Frequency Function On/Off Switch (Default: Off)
3 CPU Throttling Display
4 CPU Voltage Display
5 3-Level CPU Voltage Switch (Default:1)
6 Current CPU Power Consumption
7 Meter Time
8 Power Saving (Calculate power savings based on time)
9 Meter/Timer Reset Switch
10 Meter Mode Switch
11 Total Mode Switch
12 Close (Application will enter Stealth Mode)
13 Minimize (Application will continue to run in taskbar)
14 INFO/Help
15 Live Utility Update (Check for the latest utility version)
(Note 2)
(Note 1)
• The above data is for reference only. Actual performance may vary depending on motherboard model.
• CPU Power and Power Scores are for reference only. Actual results may vary based on testing method.
- 75 - Unique Features
Page 76

B. Total Mode
In Total Mode, users are able to see how much total power savings they have accumulated in a set period of
time since activating Easy Energy Saver for the rst time
(Note 3)
.
Total Mode - Button Information Table
Button Description
1 Easy Energy Saver On/Off Switch (Default: Off)
2 Dynamic CPU Frequency Function On/Off Switch (Default: Off)
3 CPU Throttling Display
4 CPU Voltage Display
5 3-Level CPU Voltage Switch (Default:1)
(Note 2)
6 Current CPU Power Consumption
7 Time/Date Easy Energy Saver Enabled
8 Total Power Savings (Total power saving with Easy Energy Saver enabled)
9 Meter Mode Switch
10 Total Mode Switch
11 Close (Application will enter Stealth Mode)
12 Minimize (Application will continue to run in taskbar)
13 INFO/Help
14 Live Utility Update (Check for the latest utility version)
(Note 1)
(Note 4)
C. Stealth Mode
In Stealth Mode, the system continues to work with the user-dened power saving settings, even after the
system is restarted. Re-enter the application only if you want to make any changes or completely close the
application.
(Note 1) Maximize system power saving with Dynamic CPU Frequency Function; system performance may
be affected.
(Note 2) 1: Normal Power Saving (default); 2: Advanced Power Saving; 3: Extreme Power Saving.
(Note 3) The total amount of power saved will be recorded until re-activated when only the Easy Energy
Saver is under the enable status, and power savings meter is unable to reset to zero.
(Note 4) Easy Energy Saver Meter will automatically reset when the total power saving reaches 99999999
Watts.
Unique Features - 76 -
Page 77

4-5 Q-Share
Q-Share is an easy and convenient data sharing tool. After conguring your LAN connection settings and
Q-Share, you are able to share your data with computers on the same network, making full use of Internet
resources.
Directions for using Q-Share
After installing Q-Share from the motherboard driver disk, go to Start>All Programs>GIGABYTE>Q-Share.
exe to launch the Q-Share tool. Find the Q-Share icon in the notication area and right-click on this icon
to congure the data sharing settings.
Figure 1. Data Sharing Disabled Figure 2. Data Sharing Enabled
Options Descriptions
Option Description
Connect ... Displays the computers with data sharing enabled
Enable Incoming Folder ... Enables data sharing
Disable Incoming Folder ... Disables data sharing
Open Incoming Folder : Accesses the shared data folder
C:\Q-ShareFolder
Change Incoming Folder : Changes the data folder to be shared
C:\Q-ShareFolder
Update Q-Share ... Updates Q-Share online
About Q-Share ... Displays the current Q-Share version
Exit... Exits Q-Share
(Note)
(Note) This option is available only when data sharing is NOT enabled.
- 77 - Unique Features
Page 78

4-6 SMART Recovery
With SMART Recovery, users can quickly create backups of changed data les
(Note 1)
or copy les from a spe-
cic backup on PATA and SATA hard drives (partitioned on NTFS le system) in Windows Vista.
Instructions:
In the main menu, click the Cong button to open the Smart Recovery Preference dialog box.
The Smart Recovery Preference dialog box:
Button Function
Enable Enables automatic daily backup
(Note 2)
Schedule Sets a daily backup schedule
Capacity Sets the percentage of hard drive space used for
saving backups
• The hard drive must have more than 1 GB of capacity.
• Each partition can accommodate up to 64 backups (the actual
limit depends on the size of each partition). When this limit is
reached, the oldest backup will be ovewritten.
(Note 3)
Instructions for copying les/folders from a backup:
To browse through your backups made at different time, select a
backup time using the time scroll bar on the right or at the bottom of
the screen. If you want to copy back a le/folder, select the le/folder
you wish to copy and click the Copy button.
The les/folders listed on the screen are read-only so you cannot edit
their contents.
(Note 1) The changed data refers to the data that has been modied, deleted, or newly added since the last backup.
(Note 2) The system will make an automatic backup on changed data only once everyday. If the computer is turned on for
a long time, the backup will be performed at the scheduled backup time. If the computer is turned off before the
scheduled backup time, the backup will be performed on the next boot.
(Note 3) We recommend that you preserve at least 25 percent of the hard drive space to optimize the storage space for
the backups. The backups of the changed data will be stored in the original partition of the data.
Unique Features - 78 -
Page 79

4-7 Auto Green
Auto Green is an easy-to-use tool that provides users with simple options to enable system power savings
via a Bluetooth cell phone. When the phone is out of the range of the computer's Bluetooth receiver, the sys-
tem will enter the specied power saving mode.
The Conguration dialog box:
First, you have to set your Bluetooth cell phone as a portable key. On the Auto Green
main menu, click Congure and then click Congure BT devices. Select the Bluetooth cell phone that you want to use as the portable key
display your Bluetooth cell phone, click Refresh to let Auto Green re-detect the device.)
Before creating a Bluetooth cell phone key, make sure your motherboard
has a Bluetooth receiver and you have turned on the search and Bluetooth
functions on your phone.
Configuring the Bluetooth cell phone key:
After you select a cell phone, the Add Bluetooth Device Wizard as shown on the left
will appear. Enter a passkey (8~16 digits recommended) which will be used for pairing
with the cell phone. Then enter the same passkey on your cell phone.
Configuring other Bluetooth settings:
On the Other Settings tab, you can set how much time it takes to scan your Bluetooth
cell phone key, how many times to rescan the key to make sure it is in range of your
computer, and when to turn off the hard drive if the system energy saving state lasts
over the predetermined period of time. After completing the settings, click Set for the
settings to take effect and then click Exit to quit.
• Device Scan Time (sec.):
Set the length of time Auto Green scans your Bluetooth cell phone key, ranging from 5 to 30 seconds in 5-second increment.
Auto Green searches for the key based on the length of time you set.
• Rescan Times:
Set how many times Auto Green will rescan your Bluetooth cell phone key if it does not detect it, ranging from 2 to 5 times. Auto
Green will keep rescanning according to the times you set. When the times limit is reached and your Bluetooth cell phone key
is still not detected, the system will enter the selected energy saving mode.
• Turn off HD:
Set when to turn off the hard drive. If the system inactivity time exceeds the specied time limit, the hard drive will be turned off.
Selecting a system energy saving mode:
Depending on your needs, select a system power saving mode on the Auto Green
main menu and click Save to save the settings.
Button Description
Standby Enters Power on Suspend mode
Suspend Enters Suspend to RAM mode
Disable Disables this function
The Bluetooth dongle included in the motherboard package
you to wake up the system from Suspend to RAM mode without the
need to press the power button rst.
(Note 1)
. (If the screen doesn't
(Note 2)
allows
(Note 1) If your cell phone has been congured as the Auto Green key, you'll not be able to use it to connect to other Blu-
etooth device(s) when Auto Green is enabled.
(Note 2) Whether the Bluetooth dongle is included depends on the motherboard models. Before installing the Bluetooth
dongle, be sure to turn off other Bluetooth receiver on your computer.
- 79 - Unique Features
Page 80

4-8 Teaming
Dual LAN with Teaming functionality enabled allows two single connections to act as one single connection
for twice the transmission bandwidth, making data transmission more effective and also improving the quality
of transmission of distant image(s). Fault tolerance on the dual LAN network prevents network downtime by
transferring the workload from a failed port to a working port.
• The speed of transmission is subject to the actual network environment or status even with Teaming enabled.
• To enable Teaming or Bonding (IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation) feature, it is required that the connected net-
work switch or router device supports the IEEE 802.3ad LACP standard. Please refer to your network switch
or router device manual for further details.
Select Realtek Ethernet Diagnostic Utility and
click Install.
Step 1:
Insert the motherboard driver disk and select Appli-
cation Software, Install Application Software. Click
Install under Realtek Ethernet Diagnostic Utility for
installation. Restart your system when completed.
Step 3:
Choose Teaming and click the Create Team button.
Step 5:
After you complete the setup, you will see the third
virtual network interface. Go to Local Area Connec-
tion Status and you will see the connection speed is
2.0 Gbps.
Step 2:
Click the Start icon . Point to All Programs,
Realtek, Diagnostic Uti lity, Realtek Ethernet
Diagnostic Utility to access the utility.
Step 4:
Give a name for the Team,
e.g. Teaming, and set up
the Teaming mode based
on your hub's specificati on s. Se le ct th e check
boxes for the two available
adapters and click OK.
Removing the Existing Teaming:
To remove the existing Teaming, click the item you
created, and then click the Remove button.
Unique Features - 80 -
Page 81

Chapter 5 Appendix
5-1 Conguring SATA Hard Drive(s)
To congure SATA hard drive(s), follow the steps below:
A. Install SATA hard drive(s) in your computer.
B. Congure SATA controller mode in BIOS Setup.
C. Congure a RAID array in RAID BIOS.
D. Make a oppy disk containing the SATA RAID/AHCI driver for Windows XP.
E. Install the SATA RAID/AHCI driver
Before you begin
Please prepare:
• At least two SATA hard drives (to ensure optimal performance, it is recommended that you use two hard
drives with identical model and capacity). If you do not want to create RAID, you may prepare only one
hard drive.
• An empty formatted oppy disk.
• Windows Vista/XP setup disk.
• Motherboard driver disk.
5-1-1 Conguring AMD SB850 SATA Controller
A. Installing SATA hard drive(s) in your computer
Attach one end of the SATA signal cable to the rear of the SATA hard drive and the other end to available
SATA port on the motherboard. If there is more than one SATA controller on your motherboard, refer to
"Chapter 1," "Hardware Installation," to identify the SATA controller for the SATA port. (For example, on this
motherboard, the SATA3_0~SATA3_5 ports are supported by the AMD SB850 South Bridge.) Then connect
the power connector from your power supply to the hard drive.
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
and operating system.
(Note 2)
(Note 1) Skip this step if you do not want to create RAID array on the SATA controller.
(Note 2) Required when the SATA controller is set to AHCI or RAID mode.
- 81 - Appendix
Page 82

B. Conguring SATA controller mode in BIOS Setup
Make sure to congure the SATA controller mode correctly in system BIOS Setup.
Step 1:
Turn on your computer and press <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup during the POST (Power-On Self-Test).
Make sure OnChip SATA Controller is enabled. To enable RAID for the SATA3_0/1/2/3 connectors, set On-
Chip SATA Type to RAID. To enable RAID for the SATA3_4/5 connectors, set OnChip SATA Type to RAID
and set OnChip SATA Port4/5 Type to As SATA Type (Figure 1). To enable support for RAID 5, set OnChip
SATA RAID5 Support to Enabled.
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
OnChip SATA Controller [Enabled]
OnChip SATA Type [RAID]
OnChip SATA Port4/5 Type [As SATA Type]
OnChip SATA RAID5 Support [Enabled]
OnChip SATA3.0 Support [Enabled]
x OnChip SATA Port as ESP Press Enter
Onboard PCIE Devices [Press Enter]
Onboard Audio Function [Enabled]
Onboard 1394 Function [Enabled]
Onboard USB 3.0 Controller [Enabled]
USB Controllers [Enabled]
USB Legacy Function [Enabled]
USB Storage Function [Enabled]
Onboard Serial Port 1 [3F8/IRQ4]
Onboard Parallel Port [378/IRQ7]
Parallel Port Mode [SPP]
x ECP Mode Use DMA 3
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals
Figure 1
Menu Level
Item Help
Step 2:
Save changes and exit BIOS Setup.
The BIOS Setup menus described in this section may differ from the exact settings for your moth-
erboard. The actual BIOS Setup menu options you will see shall depend on the motherboard you
have and the BIOS version.
Appendix - 82 -
Page 83

C. Conguring RAID set in RAID BIOS
Enter the RAID BIOS setup utility to congure a RAID array. Skip this step and proceed with the installation of
Windows operating system for a non-RAID conguration.
Step 1:
After the POST memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins, look for a message which
says "Press <Ctrl-F> to enter RAID Option ROM Utility" (Figure 2). Press <Ctrl> + <F> to enter the RAID
BIOS setup utility.
RAID Option ROM Version 3.2.1540.15
(c) 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
NoArrayisdened..
Press <Ctrl-F> to enter RAID Option ROM Utility...
Figure 2
Step 2:
Main Menu
This is the rst option screen when you enter the BIOS RAID Setup utility. (Figure 3).
To view the disk drives assigned to arrays, press <1> to enter the View Drive Assignments window.
To create an array, press <2> to enter the LD View/LD Dene Menu window.
To delete an array, press <3> to enter the Delete LD Menu window.
To view controller settings, press <4> to enter the Controller Conguration window.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[ Main Menu ]
View Drive Assignments........................... [ 1 ]
LDView/LDDeneMenu...................... [2]
Delete LD Menu....................................... [ 3 ]
ControllerConguration............................[4]
[ Keys Available ]
Press 1..4 to Select Option [ESC] Exit
Figure 3
- 83 - Appendix
Page 84

Create Arrays Manually
To create a new array, press <2> to enter the LD View Menu window (Figure 4). To create an array, press
<Ctrl+C> to access the LD Dene Menu.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[ LD View Menu ]
< There is no any LD >
[h] Up [i]Down[PaUp/PaDn]SwitchPage[Ctrl+C]DeneLD
[Enter] View LD [Ctrl+V] View Single Disk [ESC] Exit
[ Keys Available ]
Figure 4
In the LD Dene Menu, use the up or down arrow key to move to an item for further conguration (Figure 5).
Option ROM Utility (c) 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
LD No LD Name RAID Mode Drv
LD 1 Logical Drive 1 RAID 0 0
Stripe Block: 64 KB Fast Init: ON
Gigabyte Boundary: ON Cache Mode: WriteThru
Port:ID Drive Model Capabilities Capacity (GB) Assignment
01:00 WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 79.89 N
02:00 WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 80.02 N
[h] Up [i] Down [PaUp/PaDn] Switch Page [Space] Change Option
[Ctrl+Y] Save [ESC] Exit
[LDDeneMenu]
[ Drives Assignments ]
[ Keys Available ]
[ Keys Available ]
Figure 5
Appendix - 84 -
Page 85

In the following procedure, we'll create RAID 0 as an example.
1. Under the RAID Mode section, press the <SPACE> key to select RAID 0.
2. Set the Stripe Block size. 64 KB is the default.
3. Under the Drives Assignments section, press the up or down arrow key to highlight a drive.
4. Press the <SPACE> key or <Y>to change the Assignment option to Y. This action adds the drive to the
disk array. The Drv section will show the number of disks assigned.
5. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> keys to save the information. The message in Figure 6 will appear. Press <Ctrl+Y> to
input the array name. If you do not input the array name, the default array name will be used.
Please press Ctrl-Y key to input the LD name
or press any key to exit.
If you do not input any LD name, the default
LD name will be used.
Figure 6
6. When the next message appears, press <Ctrl>+<Y> to clear the MBR or press other keys to ignore this
option.
Fast Initialization option has been selected
It will erase the MBR data of the disks.
<Press Ctrl-Y key if you are sure to erase it>
<Press any other key to ignore this option>
Figure 7
7. Then, the message in Figure 8 will appear. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> to set the capacity of the RAID array or
press other keys to set the array to its maximum capacity.
Press Ctrl-Y to Modify Array Capacity or press any
other key to use maximum capacity...
Figure 8
8. After the creation is complete, the screen will return to LD View Menu where you will see the newly-
created array.
9. Press <Esc> to return to Main Menu and press <Esc> again if you want to exit the RAID BIOS utility.
- 85 - Appendix
Page 86

View Drive Assignments
The View Drive Assignments option in the Main Menu displays whether the attached hard drives are assigned to a disk array or are unassigned. Under the Assignment column, drives are labeled with their assigned disk array or shown as Free if unassigned.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
[ View Drives Assignments ]
Port:ID Drive Model Capabilities Capacity (GB) Assignment
01:00 WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 79.89
Extent 1 79.82 LD 1-1
02:00 WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 80.2
Extent 1 80.02 LD 1-2
[h] Up [i] Down [PaUp/PaDn] Switch Page [Ctrl+H] Secure Erase
[ESC] Exit
[ Keys Available ]
Figure 9
Delete an Array
The Delete Array menu option allows for deletion of disk array assignments.
Deleting an existing disk array could result in loss of data. Record all array information including the
array type, the disk members, and stripe block size in case you wish to undo a deletion.
1. To delete an array, press <3> in the Main Menu to enter the Delete LD Menu. Then highlight the array you
wish to delete and press the <Delete> key or the <Alt>+<D> keys.
2. The View LD Denation Menu will appear (as shown in Figure 10) showing which drives are assigned to
this array. Press <Ctrl>+<Y> if you are sure to delete the array or other keys to abort.
3. When the array is deleted, the screen will return to Delete LD Menu. Press <Esc>to return to Main Menu.
Option ROM Utility (c) 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
LD No LD Name RAID Mode Drv Capacity(GB)
LD 1 GBT RAID 0 2 80
Stripe Block: 64 KB Cache Mode: WriteThru
Port:ID Drive Model Capabilities Capacity (GB)
01:00 WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 79.89
02:00 WDC WD800JD-22LSA0 SATA 3G 80.02
[ViewLDDenationMenu]
[ Drives Assignments ]
Press Ctrl-Y to delete the data in the disk!
or press any other key to abort...
[ Keys Available ]
[ Keys Available ]
Figure 10
Appendix - 86 -
Page 87

5-1-2 Conguring GIGABYTE SATA2/JMicron JMB362 SATA Controller
A. Installing SATA hard drive(s) in your computer
Attach one end of the SATA signal cable to the rear of the SATA hard drive and the other end to available
SATA port on the motherboard. See the table below for the SATA controllers and their corresponding SATA
ports. Then connect the power connector from your power supply to the hard drive.
B. Conguring SATA controller mode in BIOS Setup
Make sure to congure the SATA controller mode correctly in system BIOS Setup.
Step 1:
Turn on your computer and press <Delete> to enter BIOS Setup during the POST (Power-On Self-Test). Go
to the Onboard PCIE Devices sub-menu under the Integrated Peripherals menu. See the table below for
conguring different SATA controllers for RAID (Figure 1).
Controller Connectors BIOS Settings
GIGABYTE GSATA2_6/7 Set Onboard GSATA/IDE Ctrl
SATA2 Set Onboard GSATA/IDE Mode
JMicron eSATA ports Set Onboard ESATA Controller to Enabled
JMB362 Set Onboard ESATA Mode
to
to
to
RAID
Enabled
RAID/IDE
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright (C) 1984-2010 Award Software
PrimaryDualSlotCong [Auto]
SecondaryDualSlotCong [Auto]
PCIEX4_2SlotCong [AsX1Link]
Onboard GSATA/IDE Ctrl [Enabled]
Onboard GSATA/IDE Mode [RAID/IDE]
Onboard ESATA Controller [Enabled]
Onboard ESATA Mode [RAID]
Green LAN [Disabled]
Onboard LAN1 Function [Enabled]
Onboard LAN1 Boot ROM [Disabled]
SMART LAN1 [Press Enter]
Onboard LAN2 Function [Enabled]
Onboard LAN2 Boot ROM [Disabled]
SMART LAN2 [Press Enter]
: Move Enter: Select +/-/PU/PD: Value F10: Save ESC: Exit F1: General Help
higf
F5: Previous Values F6: Fail-Safe Defaults F7: Optimized Defaults
Onboard PCIE Devices
Menu Level
Figure 1
Step 2:
Save changes and exit BIOS Setup.
The BIOS Setup menus described in this section may differ from the exact settings for your moth-
erboard. The actual BIOS Setup menu options you will see shall depend on the motherboard you
have and the BIOS version.
- 87 - Appendix
Item Help
Page 88

C. Conguring a RAID array in RAID BIOS
Enter the RAID BIOS setup utility to congure a RAID array. Skip this step and proceed to the installation of
Windows operating system for a non-RAID conguration.
After the POST memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins, look for a message which
says "Press <Ctrl-G> to enter RAID Setup Utility" (Figure 2). Press <Ctrl> + <G> to enter the RAID setup utility.
Gigabyte Technology Corp. PCI Express to SATAII Host Controller ROM v1.07.16G
Copyright (C) 2005-2009. Gigabyte Technology.
HDD0 : ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
HDD1 : ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
Press <Ctrl-G> to enter RAID Setup Utility ...
Figure 2
In the ma in screen of the RAID se tup utili ty (Figur e 3), use the up or down arrow key to highlight
through choices in the Main Menu blo ck . Hi ghlight the ite m that you wi sh to execute and pre ss
<Enter>.
[ Main Menu ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Create RAID Disk Drive
Delete RAID Disk Drive
Revert HDD to Non-RAID
SolveMirrorConict
Rebuild Mirror Drive
Save And Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Capacity Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
[fgTAB]-Switch Window [hi]-Select ITEM [ENTER]-Action [ESC]-Exit
Figure 3
Note: In the main screen, you can select a hard drive in the Hard Disk Drive List block and press <Enter> to
see detailed information about the selected hard drive.
Appendix - 88 -
Page 89

Create a RAID Array:
In the main screen, press <Enter> on the Create RAID Disk Drive item. Then the Create New RAID screen
appears (Figure 4).
[ Create New RAID ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Name: GRAID
Level: 0-Stripe
Disks: Select Disk
Block: 128 KB
Size: 240 GB
ConrmCreation
[fg]-Move Cursor [DEL,BS]-Delete Character [ENTER]-Next [ESC]-Abort
_
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Available Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
[ Help ]
Enter RAID Name
Enter a string between 1 to 16 characters
in length for the created RAID drive to be
identiedbysystemBIOSorOS.
Figure 4
The Create New RAID block displays all the items that need to be set for creating an array (Figure 5).
Steps:
1. Enter Array Name: Under the Name item, enter an array name with 1~16 letters (letters cannot be special
characters) and press <Enter>.
2. Select RAID Mode: Under the Level item, use up or down arrow key to select RAID 0 (Stripe), RAID 1
(Mirror) or JBOD (Figure 5). Then press <Enter> to move onto the next step.
[ Create New RAID ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Name: GRAID
Level: 0-Stripe
Disks: Select Disk
Block: 128 KB
Size: 240 GB
ConrmCreation
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Available Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
[ Help ]
Select RAID Level
RAID 0 - Data striped for performance
RAID 1 - Data mirrored for redundancy
JBOD - Data concatenated for huge
temporarily disk required
[hi]-Switch RAID Level [ENTER]-Next [ESC]-Abort
Figure 5
- 89 - Appendix
Page 90

3. Assign Array Disks: After a RAID mode is selected, RAID BIOS automatically assigns the two hard drives
installed as the RAID drives.
4. Set Block Size (RAID 0 only): Under the Block item, use the up or down arrow key to select the stripe
block size (Figure 6), ranging from 4 KB to 128 KB. Press <Enter>.
[ Create New RAID ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Name: GRAID
Level: 0-Stripe
Disks: Select Disk
Block: 128 KB
Size: 240 GB
ConrmCreation
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
[hi]-Switch RAID Block Size [ENTER]-Next [ESC]-Abort
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Available Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
[ Help ]
Setting Stripe Block
Select a stripe size which will be used to
divide data from/to seperate RAID members.
The following are typical values:
RAID 0-128KB
Figure 6
5. Set Array Size: Under the Size item, enter the size of the array and press <Enter>.
6. Conrm Creation: After all of the items above are congured, the selection bar automatically jumps to the
Conrm Creation item. Press <Enter>. When prompted to conrm your selection (Figure 7), press <Y> to
conrm or <N> to abort.
[ Create New RAID ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Name: GRAID
Level: 0-Stripe
Disks: Select Disk
Block: 128 KB
Size: 240 GB
ConrmCreation
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Available Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB Non-RAID
Create RAID on the select HDD (Y/N) ? Y
[ Help ]
CONFIRM RAID CREATION
ALL DATA ON THE SELECTED HARD DISK
WILL BE LOST WHEN EXIT WITH SAVING
[fg]-Switch Unit [DEL,BS]-Delete Number [ENTER]-Next [ESC]-Abort
Figure 7
Appendix - 90 -
Page 91

When nished, the new RAID array will be displayed in the RAID Disk Drive List block (Figure 8).
[ Main Menu ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Create RAID Disk Drive
Delete RAID Disk Drive
Revert HDD to Non-RAID
SolveMirrorConict
Rebuild Mirror Drive
Save And Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Model Name RAID Level Capacity Status Members(HDDx)
RDD0: GRAID 0-Stripe 240 GB Normal 01
[fgTAB]-Switch Window [hi]-Select ITEM [ENTER]-Action [ESC]-Exit
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Capacity Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
Figure 8
To check more detailed information about the array, use the <Tab> key while in the Main Menu block to move
the selection bar to the RAID Disk Drive List block. Select the array and press <Enter>. A small window displaying the array information will appear in the center of the screen (Figure 9).
[ Main Menu ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Create RAID Disk Drive
Delete RAID Disk Drive
Revert HDD to Non-RAID
SolveMirrorConict
Rebuild Mirror Drive
Save And Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Model Name RAID Level Capacity Status Members(HDDx)
RDD0: GRAID 0-Stripe 240 GB Normal 01
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Capacity Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
[ RAID Information ]
Name: GRAID
Level: 0-Stripe
Block: 128 KB
Capacity: 240 GB
Members: HDD 01
Status: Normal
[fgTAB]-Switch Window [hi]-Select RAID [ENTER]-Detail [ESC]-Exit
Figure 9
- 91 - Appendix
Page 92

7. Save and Exit Setup: After conguring the RAID array, select the Save And Exit Setup item in the main
screen to save your settings before exiting the RAID BIOS utility, then press <Y> (Figure 10).
[ Main Menu ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Create RAID Disk Drive
Delete RAID Disk Drive
Revert HDD to Non-RAID
SolveMirrorConict
Rebuild Mirror Drive
Save And Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Model Name RAID Level Capacity Status Members(HDDx)
RDD0: GRAID 0-Stripe 240 GB Normal 01
[fgTAB]-Switch Window [hi]-Select ITEM [ENTER]-Action [ESC]-Exit
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Capacity Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
Save to Disk & Exit (Y/N) ? Y
Figure 10
Now, you may proceed to create the SATA RAID/AHCI driver diskette and the installation of the SATA RAID/
AHCI driver and operating system.
Delete the RAID Array:
To delete the array, select Delete RAID Disk Drive in the main menu and press <Enter>. The selection bar
will move to the RAID Disk Drive List block. Press the <SPACE> key on the array to be deleted; a small tri-
angle will appear to mark the selected array. Press <Delete>. When prompted to conrm your selection (Figure
11), press <Y> to conrm or <N> to cancel.
[ Main Menu ] [ Hard Disk Drive List ]
Create RAID Disk Drive
Delete RAID Disk Drive
Revert HDD to Non-RAID
SolveMirrorConict
Rebuild Mirror Drive
Save And Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving
[ RAID Disk Drive List ]
Model Name RAID Level Capacity Status Members(HDDx)
RDD0: GRAID 0-Stripe 240 GB Normal 01
Gigabyte Technology Corp. RAID Setup Utility v1.07.16G
Model Name Capacity Type/Status
HDD0: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
HDD1: ST3120026AS 120 GB RAID Inside
ALL DATA ON THE RAID WILL LOST!!
ARE YOU SURE TO DELETE (Y/N) ? N
[hi]-SelectRAID [SPACE]-MarkDelete [DEL]-Conrm [ESC]-Abort
Figure 11
Appendix - 92 -
Page 93

5-1-3 Making a SATA RAID/AHCI Driver Diskette
(Required for AHCI and RAID Mode)
To successfully install operating system onto SATA hard drive(s) that is/are congured to RAID/AHCI mode,
you need to install the SATA controller driver during the OS installation. Without the driver, the hard drive may
not be recognized during the Windows setup process. First of all, copy the driver for the SATA controller from
the motherboard driver disk to a oppy disk. For installing Windows Vista, you also can copy the SATA controller driver from the motherboard driver disk to a USB ash drive. See the instructions below about how to
copy the driver in MS-DOS and Windows mode.
In MS-DOS mode:
Prepare a startup disk that has CD-ROM support and a blank formatted oppy disk.
Steps:
1: Boot from the startup disk.
2: Remove the startup disk and insert the prepared oppy disk and the motherboard driver disk (here we as-
sume that the drive letter for your optical drive is D:\).
3: At the A:\> prompt, type the following command. Press <Enter> after the command:
• For the AMD SB850, type (Figure 1):
A:\>copy d:\bootdrv\SB8xxx\x86\*.*
• For the GIGABYTE SATA2/JMicron JMB362, type (Figure 2):
A:\>copy d:\bootdrv\gsata\32bit\*.*
Figure 1 Figure 2
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
(Note 1) Type the driver directory based on the operating system to be installed. Refer to the following table
for the SATA driver directories for different Windows operating systems.
Operating System Directory
Windows XP 32-bit Bootdrv\SBxxx\x86
Windows XP 64-bit Bootdrv\SBxxx\x64
Windows Vista 32-bit (AHCI mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxV\AHCI\LHx86
Windows Vista 32-bit (RAID mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxV\RAID\LH
Windows Vista 64-bit (AHCI mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxV\AHCI\LHx64
Windows Vista 64-bit (RAID mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxV\RAID\LH64A
Windows 7 32-bit (AHCI mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxW7\AHCI\Win7x86
Windows 7 32-bit (RAID mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxW7\RAID\W7
Windows 7 64-bit (AHCI mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxW7\AHCI\Win7x64
Windows 7 64-bit (RAID mode) Bootdrv\SBxxxW7\RAID\W764A
(Note 2) Change the directory from \32bit to \64bit for copying the Windows 64-bit driver.
- 93 - Appendix
Page 94

In Windows mode:
Steps:
1: Use an alternative system and insert the motherboard driver disk.
2: From your optical drive folder, double click the Menu.exe le in the BootDrv folder (Figure 3). A Command
Prompt window will open similar to that in Figure 4.
3: Insert the blank formatted disk. Select the controller driver by pressing the corresponding letter from the
menu and press <Enter>. For example, from the menu in Figure 4,
• For the AMD SB850, select 3) ATi AHCI/RAID Driver for XP for Windows XP operating system.
• For the GIGABYTE SATA2/JMicron JMB362, select 1) GIGABYTE GSATA driver for 32bit system for
Windows XP 32-bit operating system.
Your system will then automatically copy the driver les to the oppy disk. Press any key to exit when nished.
Figure 4
Figure 3
Appendix - 94 -
Page 95

5-1-4 Installing the SATA RAID/AHCI Driver and Operating System
With the SATA RAID/AHCI driver diskette and correct BIOS settings, you are ready to install Windows Vista/
XP onto your hard drive(s). The followings are examples of Windows XP and Vista installation.
A. Installing Windows XP
Step 1:
Restart your system to boot from the Windows XP setup disk and press <F6> as soon as you see the message "Press F6 if you need to install a 3rd party SCSI or RAID driver" (Figure 1). A screen will then appear
asking you to specify additional device.
Windows Setup
Press F6 if you need to install a third party SCSI or RAID driver.
Figure 1
Step 2:
For the AMD SB850:
Insert the oppy disk containing the SATA RAID/AHCI driver and press <S>. Then a controller menu similar
to Figure 2 below will appear. Select AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller-x86 platform and press
<Enter>.
Windows Setup
YouhavechosentocongureaSCSIAdapterforusewithWindows,
using a device support disk provided by an adapter manufacturer.
Select the SCSI Adapter you want from the following list, or press ESC
to return to the previous screen.
AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller-x86 platform
AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller-x64 platform
ENTER=Select F3=Exit
Figure 2
- 95 - Appendix
Page 96

For the GIGABYTE SATA2/JMicron JMB362:
Insert the oppy disk containing the SATA RAID/AHCI driver and press <S>. Then a controller menu similar
to Figure 3 below will appear. Select RAID/AHCI Driver for GIGABYTE GBB36X Controller (x32) and press
<Enter>.
Windows Setup
YouhavechosentocongureaSCSIAdapterforusewithWindows,
using a device support disk provided by an adapter manufacturer.
Select the SCSI Adapter you want from the following list, or press ESC
to return to the previous screen.
RAID/AHCI Driver for GIGABYTE GBB36X Controller (x32)
ENTER=Select F3=Exit
Figure 3
Step 3:
On the next screen, press <Enter> to continue the driver installation. After the driver installation, you can proceed with the Windows XP installation.
Appendix - 96 -
Page 97

B. Installing Windows Vista
The procedure below assumes that only one RAID array exists in your system.
For the AMD SB850:
Step 1:
Restart your system to boot from the Windows Vista setup disk and perform standard OS installation steps.
When a screen similar to that below appears (RAID hard drive will not be detected at this stage), select Load
Driver (Figure 4).
Step 2:
Insert the motherboard driver disk (Method A) or the removable storage device such as USB ash drive that
contains the SATA RAID/AHCI driver (Method B), then specify the location of the driver (Figure 4). Note: For
users using a SATA optical drive, be sure to copy the driver les from the motherboard driver disk to a USB
ash drive before installing Windows Vista (go to the BootDrv folder and save the whole SBxxxV folder to
the USB ash drive). Then use Method B to load the driver.
Method A:
Insert the motherboard driver disk into your system and browse to the following directory:
\BootDrv\SBxxxV\RAID\LH
For Windows Vista 64-bit, browse to the LH64A folder.
Method B:
Insert the USB ash drive containing the driver les and browse to the LH (for Windows Vista 32-bit) or
LH64A (for Windows Vista 64-bit) folder.
Figure 4
Figure 5
- 97 - Appendix
Page 98

Step 3:
When a screen as shown in Figure 6 appears, select AMD AHCI Compatible RAID Controller and click
Next.
Figure 6
Step 4:
After the driver is loaded, the RAID drive will appear. Select the RAID drive and then click Next to continue
the OS installation (Figure 7).
Figure 7
Appendix - 98 -
Page 99

For the GIGABYTE SATA2/JMicron JMB362:
Step 1:
Restart your system to boot from the Windows Vista setup disk and perform standard OS installation steps.
When a screen similar to that below appears (RAID/AHCI hard drive(s) will not be detected at this stage),
select Load Driver (Figure 8).
Figure 8
Step 2:
Insert the motherboard driver disk (Method A) or the oppy disk/USB ash drive that contains the SATA RAID/
AHCI driver (Method B), then specify the location of the driver (Figure 9). Note: For users using a SATA optical drive, be sure to copy the driver les from the motherboard driver disk to a USB ash drive before installing Windows Vista (go to the BootDrv folder and save the whole GSATA folder to the USB ash drive). Then
use Method B to load the driver.
Method A:
Insert the motherboard driver disk into your system and browse to the following directory:
\BootDrv\GSATA\32Bit
For Windows Vista 64-bit, browse to the 64Bit folder.
Method B:
Insert the USB ash drive containing the driver les and browse to \GSATA\32Bit (for Windows Vista 32-bit)
or \GSATA\64Bit (for Windows Vista 64-bit).
Figure 9
- 99 - Appendix
Page 100

Step 3:
When a screen as shown in Figure 10 appears, select GIGABYTE GBB36X Controller and click Next.
Figure 10
Step 4:
After the driver is loaded, select the RAID/AHCI drive(s) where you want to install the operating system and
then click Next to continue the OS installation (Figure 11).
Figure 11
Appendix - 100 -
 Loading...
Loading...