Page 1

FCC Compliance Statement:
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Per FCC Part 2 Section 2. 1077(a)
This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with limits for a Class B digital device,
Responsible Party Name: G.B.T. INC.
Phone/Fax No: (818) 854-9338/ (818) 854-9339
hereby declares that the product
Product Name:
Model Number:
Conforms to the following specifications:
FCC Part 15, Subpart B, Section 15.107(a) and Section 15.109(a),
Class B Digital Device
Supplementary Information:
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmfu l
and (2) this device must accept any inference received, including
that may cause undesired operation.
Representative Person's Name: ERIC LU
Signature:
Address: 18305 Valley Blvd., Suite#A
Mother Board
Date: Mar.23, 2001
LA Puent, CA 91744
GA-7DXR
Er ic Lu
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in
residential installations. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy, and if not installed and used
in accord ance with the instr uctions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guara nte e tha t i nterfer ence
will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause interference to radio or
television equipment reception, which can be
determined by turning th e equi pment off and on, the user i s encour aged to try t o
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
-Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
-Move the equipment away from the receiver
-Plug the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected
-Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for
additional suggestions
You are cautioned that any change or modifications to the equipment not
expressly approve by the party responsible for compliance could void Your
authority to operate such equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subjected to
the following two conditions 1) this device may not cause harmful interference
and 2) this device must a ccept any interference received , in cl uding interference
that may cause undesired operation.
Page 2
Declaration of Conformity
We, Manufacturer/Importer
(full address)
G.B.T. Technology Träding GMbH
Ausschlager Weg 41, 1F, 20537 Hamburg, Germany
( description of the apparatus, system, installation to which it refers)
(reference to the specification under which conformity is declared)
in accordance with 89/336 EEC-EMC Directive
Limits and methods of measurement
EN 55011
of radio disturbance char ac teristics of
industrial, scient ific and medical (ISM electrical equipment “ Harmonics”
high frequency equipment
Limits and methods of measurement
EN55013
of radio disturbance char ac teristics of
broadcast receivers and associated electrical equi pment “Voltage fluctuations”
equipment
Limits and methods of measurement
EN 55014
of radio disturbance char ac teristics of
portable tools and similar electric al
apparatus Residual, commer c ial and light indust r y
EN 55015
of radio disturbance char ac teristics of Industrial env ironment
fluorescent lam ps and luminaries
EN 55020
broadcast receivers and associated Industrial environment
equipment
EN 55022
of radio disturbance char ac teristics of appliances tools and similar apparatus
information technology equipment
DIN VDE 0855
part 10
part 12
household electrical appliances,
Limits and methods of measurement
Immunity fr om radio interference of
Limits and methods of measurement
Cabled distribution systems; Equipment
for receiving and/or
sound and television signals
distribution
declare that the product
from power systems (UPS)
Mother Board
GA-7DXR
is in conformity with
EN 61000-3-2*
EN60555-2
EN61000-3-3*
EN60555-3
EN 50081-1
EN 50082-1
EN 55081-2
EN 55082-2
ENV 55104
EN 50091- 2
Disturbances in supply systems caused
by household appliances and similar
Disturbances in supply systems caused
by household appliances and similar
Generic emission standar d P ar t 1:
Residual, commer c ial and light indust r y
Generic immunity standard Part 1:
Generic emission standard Par t 2:
Generic immunity standard Part 2:
Immunity requirem ents for household
EMC requirements for uninterruptible
CE marking
EN 60065
electronic and related apparatus for including electr ical business equipment
household and similar general use
EN 60335
electrical appl iances uninterruptible power system s (UPS )
Signature
The manufacturer also declares the conformity of above mentioned product
with the actual required safety standard s in accordance with LVD 73/23 EEC
Safety requirements for mains operated
Safety of household and similar
Date : Mar. 23, 2001 Nam e : Rex Li n
(Stamp)
Manufacturer/Importer
(EC conformity m ar k ing)
Safety f or information technology equipment
EN 60950
General and Safety r equirements for
EN 50091-1
:
Rex Lin
Page 3

7DXR
AMD AthlonTM/Duron
TM
Socket A Processor
Motherboard
USER'S MANUAL
AMD AthlonTM/DuronTM Socket A Processor Motherboard
REV 0.2 First Edition
R-02-01-010330
Page 4

Page 5
How This Manual Is Organized
This manual is divided into the following sections:
1) Revision List
2) Item Checklist
3) Features
4) Installation Guide
Manual revision information
Product item list
Product information & specification
Instructions on CPU & Memory Installation
5) Performance & Block Diagram
6) Suspend to RAM & Dual BIOS
7) Four Speaker & SPDIF
8) @BIOS™ & EasyTune
Four Speaker & SPDIF introduction
™
III
9) Raid
10) BIOS Setup
Instructions on setting up the BIOS
11) Technical Support/RMA Sheet
Product performance & block diagram
Instructions on STR & Dual BIOS
installation
@BIOS
& EasyTune
™
introduction
™
III
Instructions on Raid
software
Document equipment used for after sales
service
12) Appendix
General reference
Page 6
Table Of Content
Revision History P.1
Item Checklist P.2
Feature Summary P.3
7DXR Motherboard Layout P.5
Installation Guide P. 6
Page Index for Connectors / Panel and Jumper Definition P.15
Performance List P.38
Block Diagram P.39
Suspend to RAM Installation P.40
Dual BIOS Introduction P.46
Four Speaker & SPDIF Introduction P.53
@BIOSTM Introduction P.59
EasyTune
TM
Introduction P.60
III
Raid Introduction P.62
Page Index for BIOS Setup P.85
Technical Support / RMA Sheet P.119
Appendix P.120
Page 7
7DXR Motherboard
Revision History
Revision Revision Note Date
0.2 Initial release of the 7DXR motherboard user’s manual. Mar. 2001
The author assumes no responsibility for any errors or omissions that may appear in this
document nor does the author make a commitment to update the information contained herein.
Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Mar. 30, 2001 Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C
1
Page 8

Item Checklist
Item Checklist
The 7DXR Motherboard
;
Cable for IDE / Floppy device
;
CD (TUCD) for motherboard utilities
;
7DXR User’s Manual
;
Front USB Cable
;
2
Page 9
7DXR Motherboard
Features Summary
Form Factor
CPU
30.5 cm x 24.5 cm ATX size form factor, 4 layers PCB.
y
AMD AthlonTM/DuronTM (K7) Socket A Processor
y
256K/64K L2 cache on die
y
Supports 600MHz ~ 1GHz and above
y
Chipset 7DXR, consisting of:
AMD 761 Memory/PCI/AGP Controller
y
VT82C686B PCI Super-I/O Integrated Peripheral
y
Controller (PSIPC)
Clock Generator
ICS 94240
y
200/266 MHz DDR bus speeds
y
95/100/106/114/120/133/140/150 MHz system bus
y
speeds by CLK_SW DIP switch
Supports adjustable CPU frequency from 100MHz to
y
250MHz by 1MHz step in BIOS setup
Memory
I/O Control
Slots
3 184-pin DDR DIMM sockets
y
Supports PC1600 DDR or PC2100 DDR SDRAM
y
Supports up to 3GB DRAM (Max)
y
Supports only 2.5V DDR SDRAM
y
Supports 72bit ECC type DRAM integrity mode
y
VT82C686B
y
1 Universal AGP Pro slot 4X/2X (1.5V/3.3V) device
y
support
5 PCI slots supports 33MHz & PCI 2.2 compliant
y
1 AMR (Audio Modem Riser) slot
y
On-Board IDE
IDE 1and IDE 2 Supports PIO mode 3, 4 UDMA 33 /
y
ATA 66 / ATA100 IDE & ATAPI CD-ROM
IDE 3 and IDE 4 Compatible with Raid, Ultra ATA100,
y
Ultra ATA66, Ultra ATA33, EIDE
4 IDE bus master IDE ports for up to 8 ATAPI devices
y
On-Board
Peripherals
1 floppy port supports 2 FDD with 360K, 720K, 1.2M,
y
1.44M and 2.88M bytes
1 parallel ports supports Normal/EPP/ECP mode
y
2 serial ports (COM A & COM B)
y
4 USB ports
y
1 IrDA connector for IR
y
To be continued…
3
Page 10
Hardware Monitor
On-Board Sound
PS/2 Connector
BIOS
Additional Features
Features Summary
CPU/System fan revolution detect
y
CPU/System temperature detect
y
System voltage detect
y
CPU overheat warning detect
y
Creative CT5880 sound
y
Line In/Line Out/Mic In/AUX In (Optional)/CD In/
y
TEL (Optional)/Game Port/ Four Speaker & SPDIF
PS/2 Keyboard interface and PS/2 Mouse interface
y
Licensed AWARD BIOS, 2M bit flash ROM
y
Support Dual BIOS
y
Support Wake-On-LAN (WOL)
y
Support Internal / External Modem Ring On
y
Support USB KB/MS Wake up from S3
y
Includes 5 fan power connectors
y
Poly fuse for keyboard over-current protection
y
Support STR (Suspend-To-RAM) function
y
Support @BIOS™ and EasyTune
y
III
™
4
Page 11
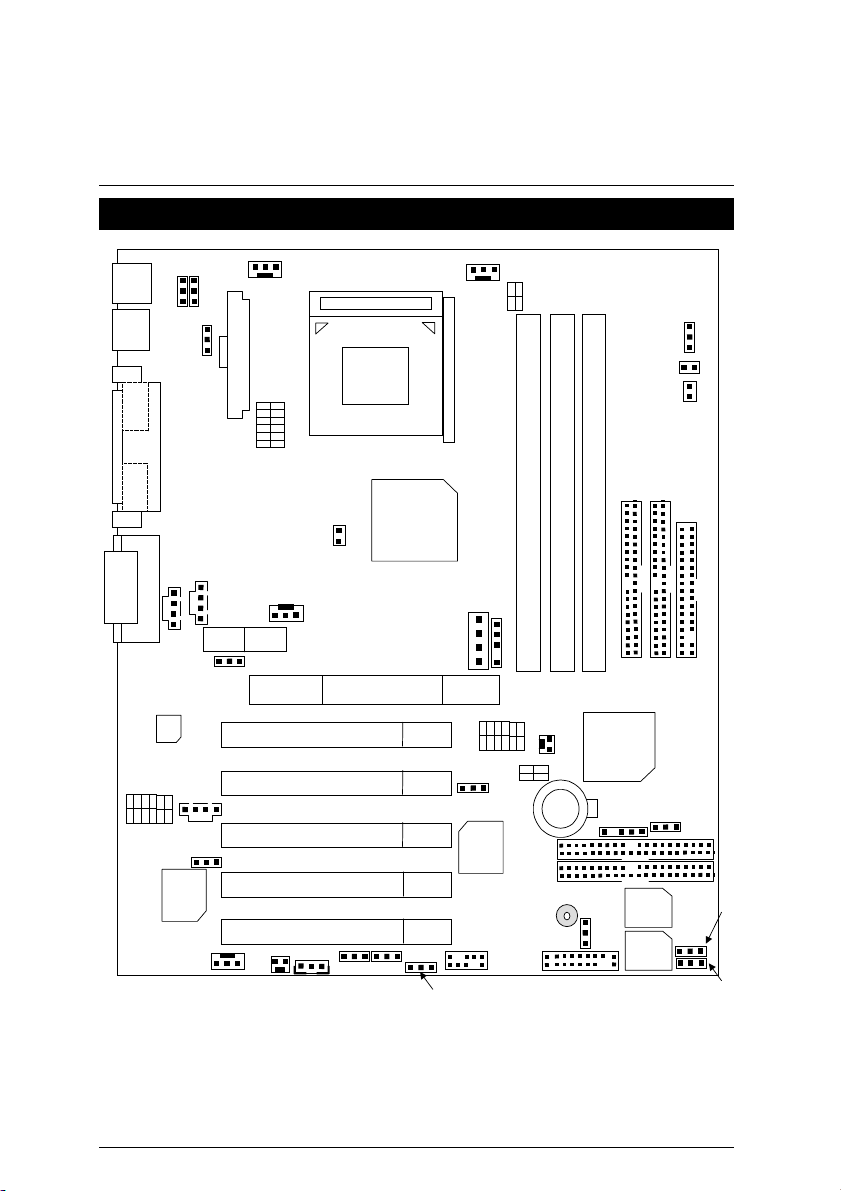
7DXR Motherboard
7DXR Motherboard Layout
PS/2
PS2_STR
USB1
COM A
LPT
COM B
Game & Audio
SW2
AMR_EN2
SYS_FAN2
(PS2_ STR_EN)
GUARDIAN
CDIN
CODEC
TELE
Creative
CT5880
RUSB_ON
(JP6)
AUXIN
AMR
(J6)
ATX POWER
PCI1
PCI2
PCI3
PCI4
PCI5
PWR_FAN
VCORE_OV
NB_FAN
(CHIP FAN)
SYS_FAN1
AMR_EN1
AGP_PRO
WOR
(J21)
WOL
Socket A
CPU
7DXR
J20 J19
CPU_FAN
AMD 761
(J40)
AGP_12V
PIDE_EN
(JP52)
USB2
FUSB_ON
(J8)
PDC
20265
SMB
CLK_SW
AGP_OV
F_PANEL
RAM_OV
DDR1
S_IRQ
BAT1
IDE4
IDE3
BUZ_EN
DDR2
BZ1
DIMM_LED
RAM_LED
DDR3
VT82C686B
IR
Backup
STR_EN
(J30)
IDE1
RAID_EN
(JP54)
BIOS
Main
BIOS
IDE2
FDD
CLR_CMOS
BIOS_WP
5
Page 12
Installation Guide
Installation Guide
Getting Started
WARNING!
Computer motherboards and expansion cards contain very delicate Integrated
Circuit (IC) chips. To protect them against damage from static electricity, you
should follow some precautions whenever you work on your computer.
1. Unplug your computer when working on the inside.
2. Use a grounded wrist strap before handling computer components. If you do not have one,
touch both of your hands to a safely grounded object or to a metal object, such as the
power supply case.
3. Hold components by the edges and try not touch the IC chips, leads or connectors, or
other components.
4. Place components on a grounded antistatic pad or on the bag that came with the
components whenever the components are separated from the system.
5. Ensure that the ATX power supply is switched off before you plug in or remove the ATX
power connector on the motherboard.
Installing the motherboard to the chassis…
If the motherboard has mounting holes, but they don’t line up with the holes on the base and
there are no slo ts to attach the spacers, do not become alarmed you can still attach the spacers
to the mounting holes. Just cut the bottom portion of the spacers (the spacer may be a little hard
to cut off, so be careful of your hands). In this way you can still attach the motherboard to the
base without worrying about short circuits. Sometimes you may need to use the plastic springs
to isolate the screw from the motherboard PCB surface, because the circuit wire may be near by
the hole. Be careful, don’t let the screw contact any printed circuit write or parts on the PCB that
are near the fixing hole, otherwise it may damage the board or cause board malfunctioning.
6
Page 13
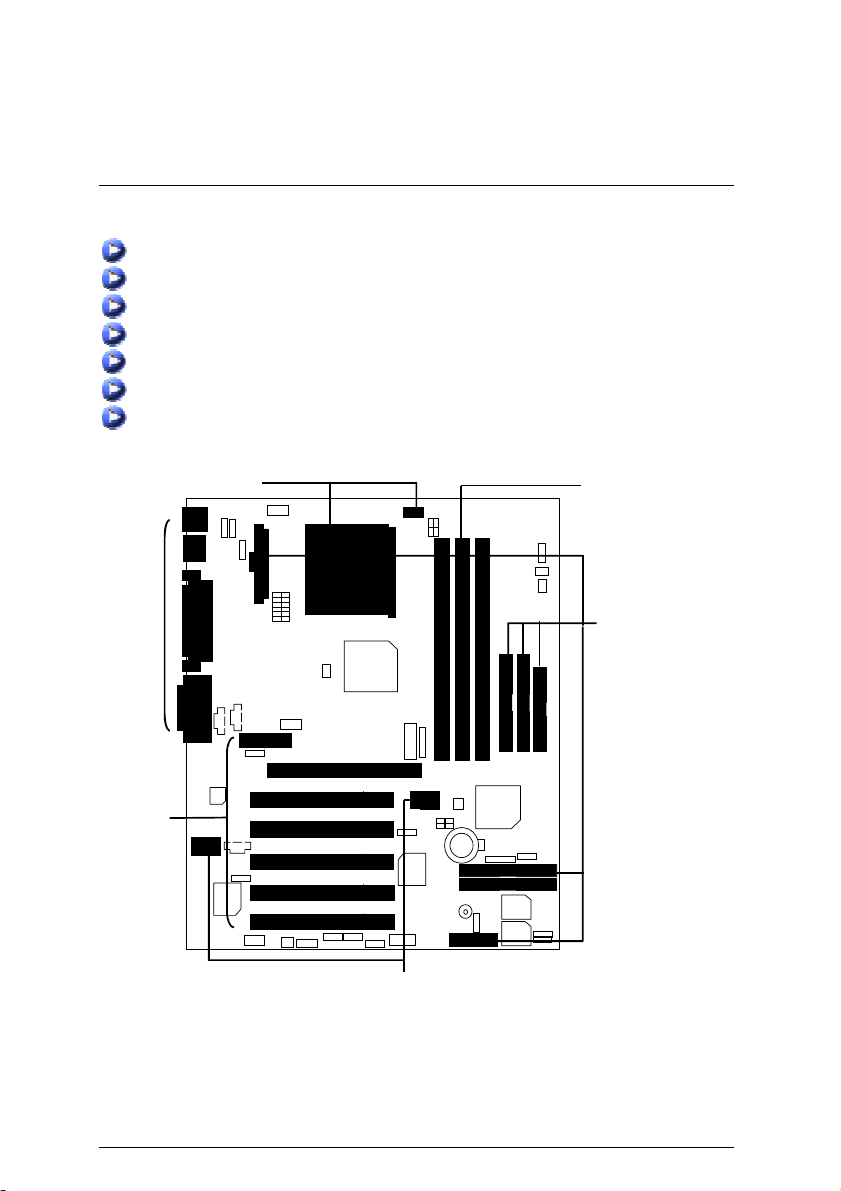
7DXR Motherboard
To set up your computer, you must complete the following steps:
Step 1 - Set system jumpers
Step 2- Install the Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Step 3-Install memory modules
Step 4-Install expansion cards
Step 5-Connect ribbon cables, cabinet wires, and power supply
Step 6-Set up BIOS software
Step 7-Install supporting software tools
Step 2
Step 3
Step 5
Step 4
Step 5
Step 1
7
Page 14
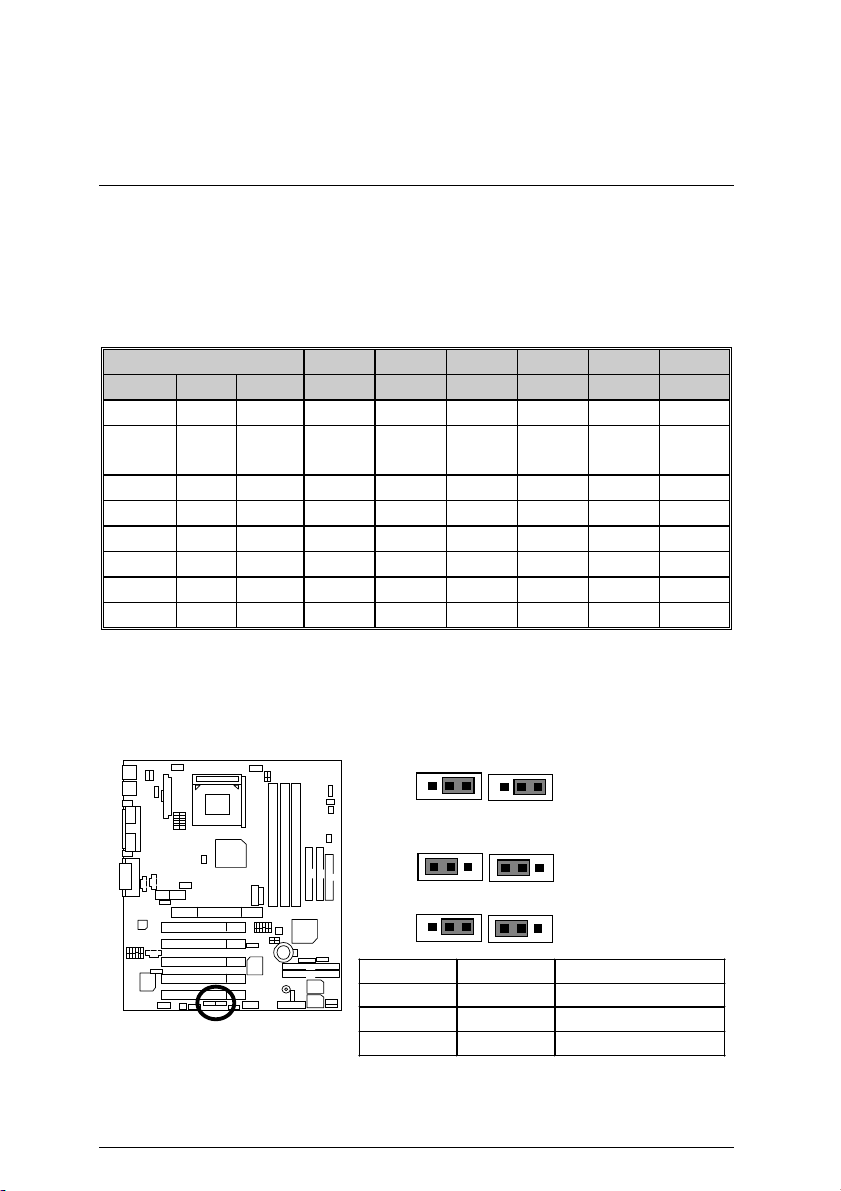
Installation Guide
CPU Speed Setup
The system bus speed is selectable at 95~150MHz. The user can select the system bus speed
by DIP switch
on CPU)
CLK_SW Select the System Speed: O: ON, X: OFF
CPU PCI AGP FS0 FS1 FS2 FS3 FS4 100-133
95 31.67 63.33 X O O O O X
100.99
(Default)
106 35.33 70.67 O X O X O X
114 38 76 O X O O X X
120 30 60 X X X O X X
133 33 66 O O O O O O
140 35 70 O X X X X O
150 37.5 75 X X X X X O
Please depend on your CPU frequency to setup.
¼¼¼¼
J19 & J20: CLK Speed (Optional)
CLK_SW
FREQ. SW1 SW2 SW3 SW4 SW5 SW6
33.66 67.33 O X O O O X
J19 & J20
or
(For 100MHz or 133MHz). (The frequency ratio depend
1
1
100 M Hz (D efault)
J20 J19
1
1
133 M Hz
1
1
66 M Hz
J19 J20 CLK Speed
2-3 close 2-3 close 100MHz(Default)
1-2 close 1-2 close 133MHz
1-2 close 2-3 close 66MHz
8
Page 15
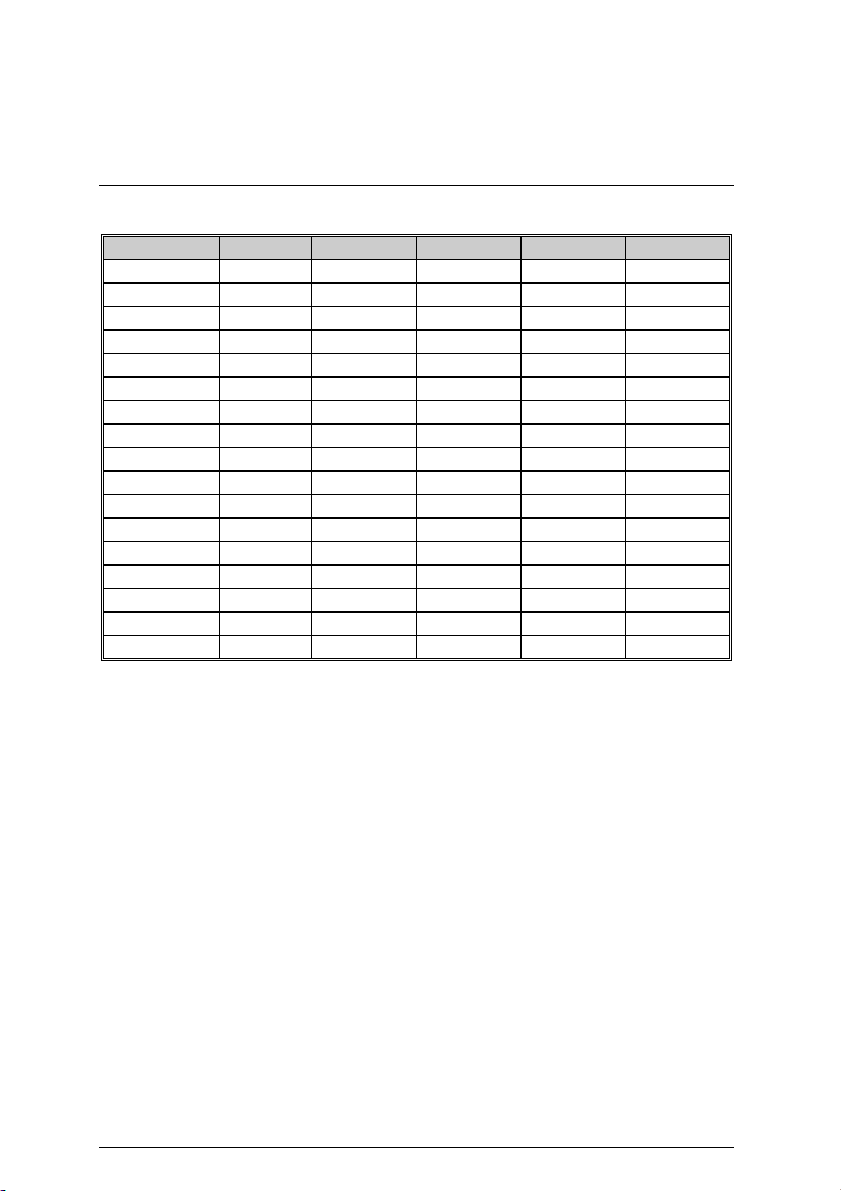
7DXR Motherboard
SW2 Select the CPU frequency Override: O: ON, X: OFF
Ratio 1 2 3 4 5
Auto (Default) X X X X O
5X O O X O X
5.5X X O X O X
6X O X X O X
6.5X X X X O X
7X O O O X X
7.5X X O O X X
8X O X O X X
8.5X X X O X X
9X O O X X X
9.5X X O X X X
10X O X X X X
10.5X X X X X X
11X O O O O X
11.5X X O O O X
12X O X O O X
12.5X X X O O X
This function will not be available if you are using a CPU with locked ratio.
¼
9
Page 16
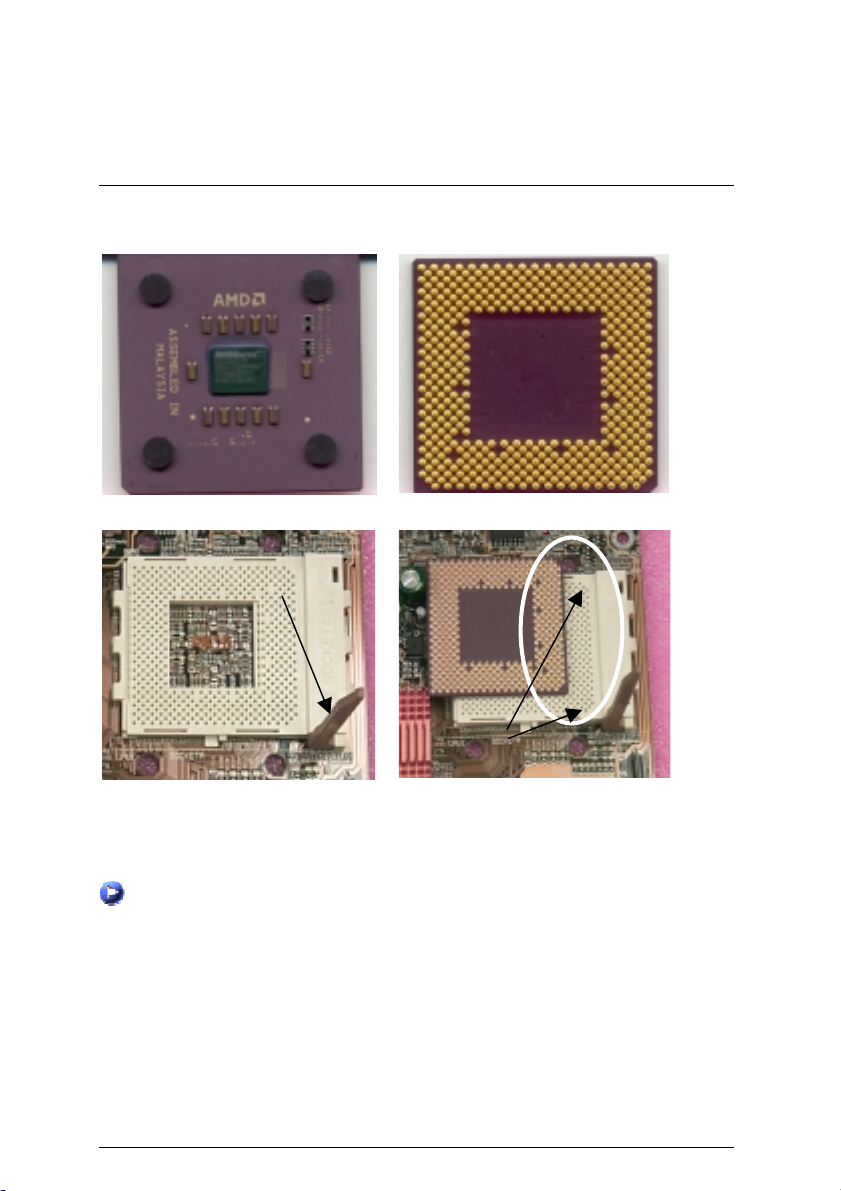
CPU Installation
Please make sure the CPU should be supported to the motherboard.
Installation Guide
CPU Top View
CPU Bottom View
Socket Actuation Lever
Blank
1.Pull the lever out and lift it up.
CPU Heat Sink Installation:
Beware: Please check that the heat sink is in good contact with the CPU before you turn on your
The poor contact will cause over heat, and might cause damage to your
system.
processor!
2.The notched corner should be orientated
toward the blank space on the socket nearest
the lever. The CPU will only fit in the orientation
as shown.
10
Page 17

7DXR Motherboard
3.Align CPU and insert it
(Please refer to your heatsink installation
manual for application of thermal grease to
provide better heat conduction between your
CPU and heatsink.)
5.Hook one end of the cooler bracket to the CPU socket.
6. Hook the other end of the cooler bracket to the CPU socket.
(Please refer to the cooler’s installation manual for detailed installation steps)
4.Use compliant fan approved by AMD.
11
Page 18
Installation Guide
Memory Installation
The motherboard has 3 dual inline memory module (DIMM) sockets. The BIOS will automatically
detects memory type and size. To install the memory module, just push it vertically into the
DIMM Slot .The DIMM module can only fit in one direction due to the notch. Memory size can
vary between sockets.
Total Memory Sizes With Registered DDR DIMM
Devices used on DIMM
64 Mbit
(4Mx4x4 banks)
64 Mbit
(2Mx8x4 banks)
64 Mbit
(1Mx16x4 banks)
128 Mbit
(8Mx4x4 banks)
128 Mbit
(4Mx8x4 banks)
128 Mbit
(2Mx16x4 banks)
256 Mbit
(16Mx4x4 banks)
256 Mbit
(8Mx8x4 banks)
256 Mbit
(4Mx16x4 banks)
512 Mbit
(16Mx8x4 banks)
512 Mbit
(8Mx16x4 banks)
1 DIMM
x64/x72
256 MBytes 512 MBytes 768 MBytes
128 MBytes 256 MBytes 384 MBytes
64 MBytes 128 MBytes 192 MBytes
512 MBytes 1 GBytes 1.5 GBytes
256 MBytes 512 MBytes 768 MBytes
128 MBytes 256 MBytes 384 MBytes
1 GBytes 2 GBytes 3 GBytes
512 MBytes 1 GBytes 1.5 GBytes
256 MBytes 512 MBytes 768 MBytes
1 GBytes 2 GBytes 3 GBytes
512 MBytes 1 GBytes 1.5 GBytes
2 DIMMs
x64/x72
3 DIMMs
x64/x72
12
Page 19
7DXR Motherboard
Total Memory Sizes With Unbuffered DDR DIMM
Devices used on
DIMM
64 Mbit
(2Mx8x4 banks)
64 Mbit
(1Mx16x4 banks)
128 Mbit
(4Mx8x4 banks)
128 Mbit
(2Mx16x4 banks)
256 Mbit
(8Mx8x4 banks)
256 Mbit
(4Mx16x4 banks)
512 Mbit
(16Mx8x4 banks)
512 Mbit
(8Mx16x4 banks)
1 DIMM
x64/x72
128 MBytes 256 MBytes 384 MBytes
64 MBytes 128 MBytes 192 MBytes
256 MBytes 512 MBytes 768 MBytes
128 MBytes 256 MBytes 384 MBytes
512 MBytes 1 GBytes 1.5 GBytes
256 MBytes 512 MBytes 768 MBytes
1 GBytes 2 GBytes 3 GBytes
512 MBytes 1 GBytes 1.5 GBytes
2 DIMMs
x64/x72
3 DIMMs
x64/x72
13
Page 20

Installation Guide
DDR
1. The DIMM slot has a notch, so the DIMM
memory module can only fit in one direction.
2. Insert the DIMM memory module vertically
into the DIMM slot. Then push it down.
3. Close the plastic clip at both edges of the
DIMM slots to lock the DIMM module.
Reverse the installation steps when you
wish to remove the DIMM module.
DDR Introduction
Established on the existing SDRAM industry infrastructure, DDR (Double Data Rate)
memory is a high performance and cost-effective solution that allows easy adoption for
memory vendors, OEMs and system integrators.
DDR memory is a sensible evolutionary solution for the PC indust ry that builds on the
existing SDRAM infrastructure, yet makes awesome advances in solving the system
performance bottleneck by doubling the memory bandwidth. DDR SDRAM will offer a
superior solution and migration path from existing SDRAM designs due to its
availability, pricing and overall market support. PC2100 DDR memory (DDR266)
doubles the data rate through reading and writing at both the rising and falling edge of
the clock, achieving data bandwidth 2X greater than PC133 when running with the
same DRAM clock frequency. With peak bandwidth of 2.1GB per second, DDR
memory enables system OEMs to build high performance and low latency DRAM
subsystems that are suitable for servers, workstations, high-end PC’s and value
desktop SMA systems. With a core voltage of only 2.5 Volts compared to conventional
SDRAM's 3.3 volts, DDR memory is a compelling solution for small form factor
desktops and notebook applications.
14
Page 21
7DXR Motherboard
Page Index for Connectors/Panel and Jumper Definition Page
Connectors P.17
ATX Power P.17
AUXIN (AUX_IN) [Optional] P.22
AGP_OV (AGP 4X Overvoltage Switch) P.28
AGP_12V (J40) (Power for AGP Pro) P.27
COM A / COM B / LPT Port P.17
CDIN (CD Audio Line In) P.21
CPU_FAN (CPU Fan) P.25
Floppy Port P.19
Game & Audio Port P.20
IDE 1 (Primary) / IDE 2 (Secondary) Port P.20
IDE 3 / IDE 4 (Raid / ATA100) Port P.21
IR (IR Header) P.27
NB_FAN (J21) (CHIP FAN) P.28
PWR_FAN (Power Fan) P.24
PS/2 Keyboard & PS/2 Mouse Connector P.18
RAM_OV (RAM Overvoltage) P.30
RAM_LED (J30) / DIMM LED (DIMM LED Connector & DIMM LED)
P.26
[RAM_LED (J30) is optional]
SYS_FAN 1 (System Fan 1) P.24
SYS_FAN 2 (System Fan 2) P.25
SMB (External SMBUS Device Connector) [Optional] P.23
TELE (TEL) [Optional] P.22
USB1 (Rear USB Connector) P.18
USB2 (Front USB Connector) P.19
VCORE_OV (CPU Core Overvoltage Switch) [Optional] P.29
WOR (Ring Power On) P.23
WOL (Wake On Lan) P.26
Panel and Jumper Definition P.31
AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2 (AMR Selection) [Optional] P.35
BAT 1(Battery) P.36
BIOS_WP (BIOS Write Protect Function) [Optional] P.33
BUZ_EN (Internal Buzzer Connector) [Optional] P.32
CLR_CMOS (Clear CMOS Function) P.32
F_PANEL (2x11 pins jumper) P.31
15
Page 22

Installation Guide
FUSB_ON (J8) (Front USB Device Wake Up Selection) P.34
GUARDIAN (JP6) (Guardian) P.34
PIDE_EN (JP52) (Onboard Promise selection) P.35
PS2_STR (PS2_STR_EN) (PS/2 KB/MS STR Enable Selection) P.37
RAID_EN (JP54) (Raid / ATA100 Selection) P.36
RUSB_ON (J6) (Rear USB Device Wake up Selection) P.33
STR_EN (STR Selection) P.37
16
Page 23
7DXR Motherboard
Connectors
ATX Power
Please note:
AC power cord should only be inserted to your power supply unit after ATX power
cable and other related devices are firmly connected to the mainboard.
COM A / COM B / LPT Port
11
20
10
Pin No. Definition
1
3,5,7,13,15-17 GND
1,2,11 3.3V
4,6,19,20 VCC
10 +12V
12 -12V
18 -5V
8 Power Good
9 5V SB (stand by+5V)
14 PS-ON(Soft On/Off)
LPT Port
COM A
Please note:
This mainboard supports 2 standard COM ports and 1 LPT port. Device like printer
can be connected to LPT port ; mouse and modem etc can be connected to COM
ports.
COM B
17
Page 24
Connectors
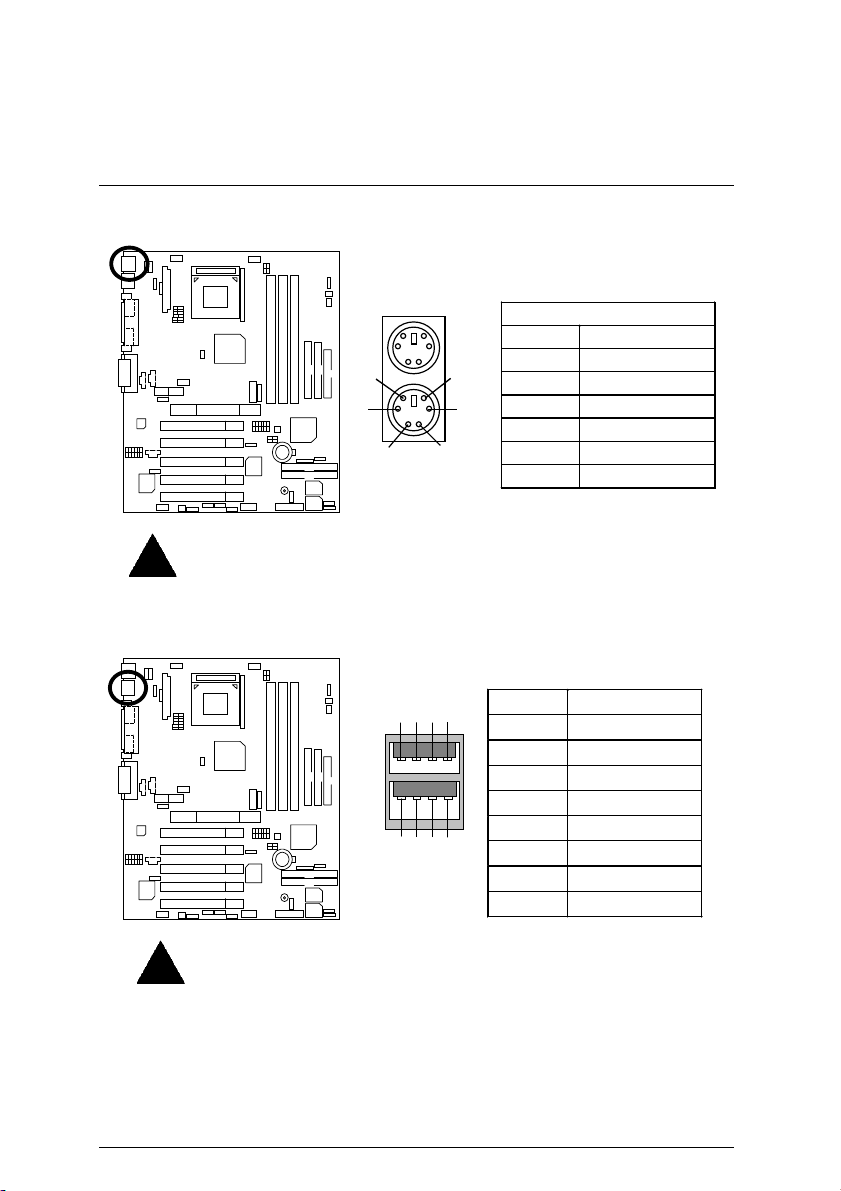
PS/2 Keyboard & PS/2 Mouse Connector
PS/2 Mouse
6
4
1 2
PS/2 Keyboard
Please note:
This mainboard supports standard PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 mouse interface
commector.
USB1: USB Connector
Please note:
Before you connect your device(s) into USB connector(s), please make sure your
device(s) has a standard USB interface like, USB keyboard, mouse, scanner, zip,
speaker… Also make sure your OS supports USB controller (Win 95 w/ USB
supperment, Win98, Windows 2000, Windows ME, Win NT w/ SP 6). If your OS
does not support USB controller, please contact OS vander for passible patch or
driver upgrade. For more information please contact your OS or device(s)
vanders.
8
6 5
7
1 2
3
4
PS/2 Mouse/ Keyboard
Pin No. Definition
5
3
1 Data
2 NC
3 GND
4 POWER
5 Clock
6 NC
Pin No. Definition
1 USB Power
2 USB D03 USB D0+
4 GND
5 USB Power
6 USB D17 USB D1+
8 GND
18
Page 25
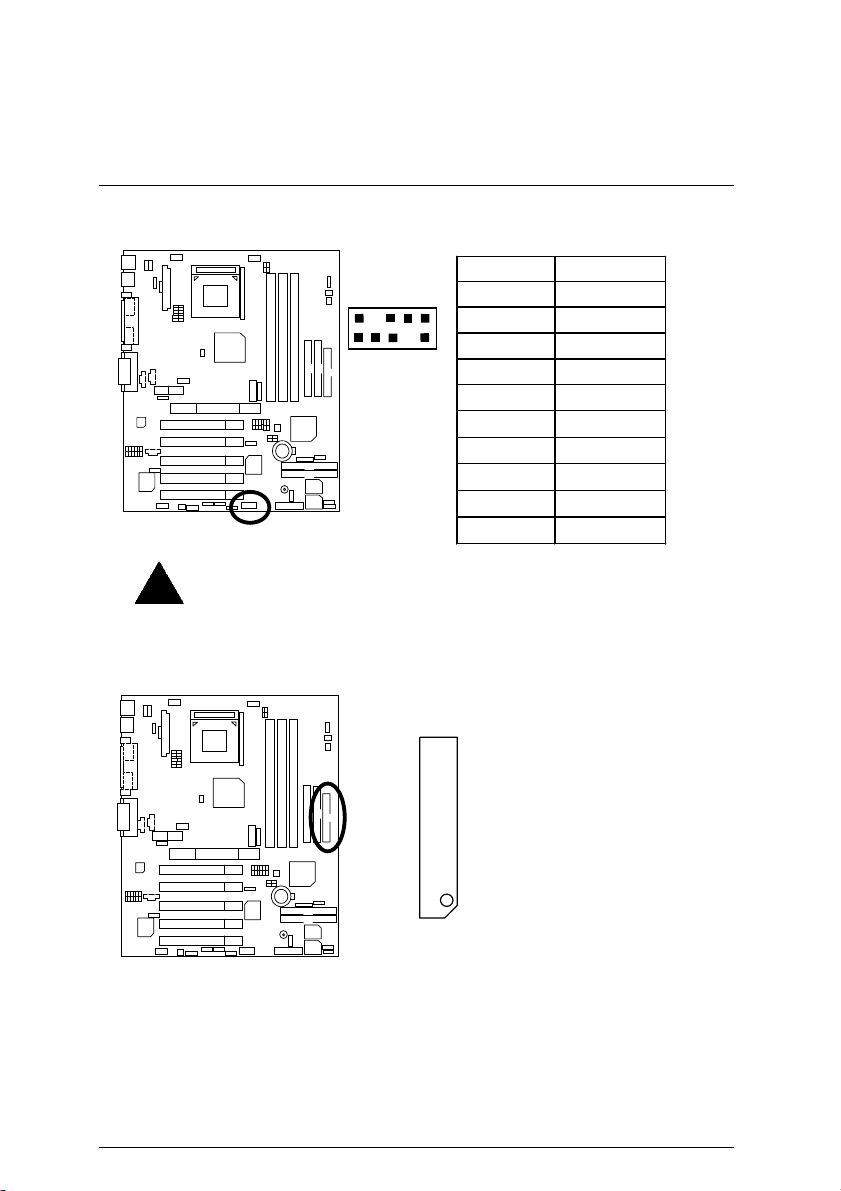
7DXR Motherboard
USB2: Front USB Connector
Please note:
Be careful with the polarity of the front panel USB connector. Check the pin
assignment while you connect the front panel USB cable. Please contact your
nearest dealer for optional front panel USB cable.
Floppy Port
2
1
Pin No. Definition
10
1 POWER
2 GND
9
3 USB D24 NC
5 USB D2+
6 USB D3+
7 NC
8 USB D39 GND
10 POWER
RED LINE
19
Page 26
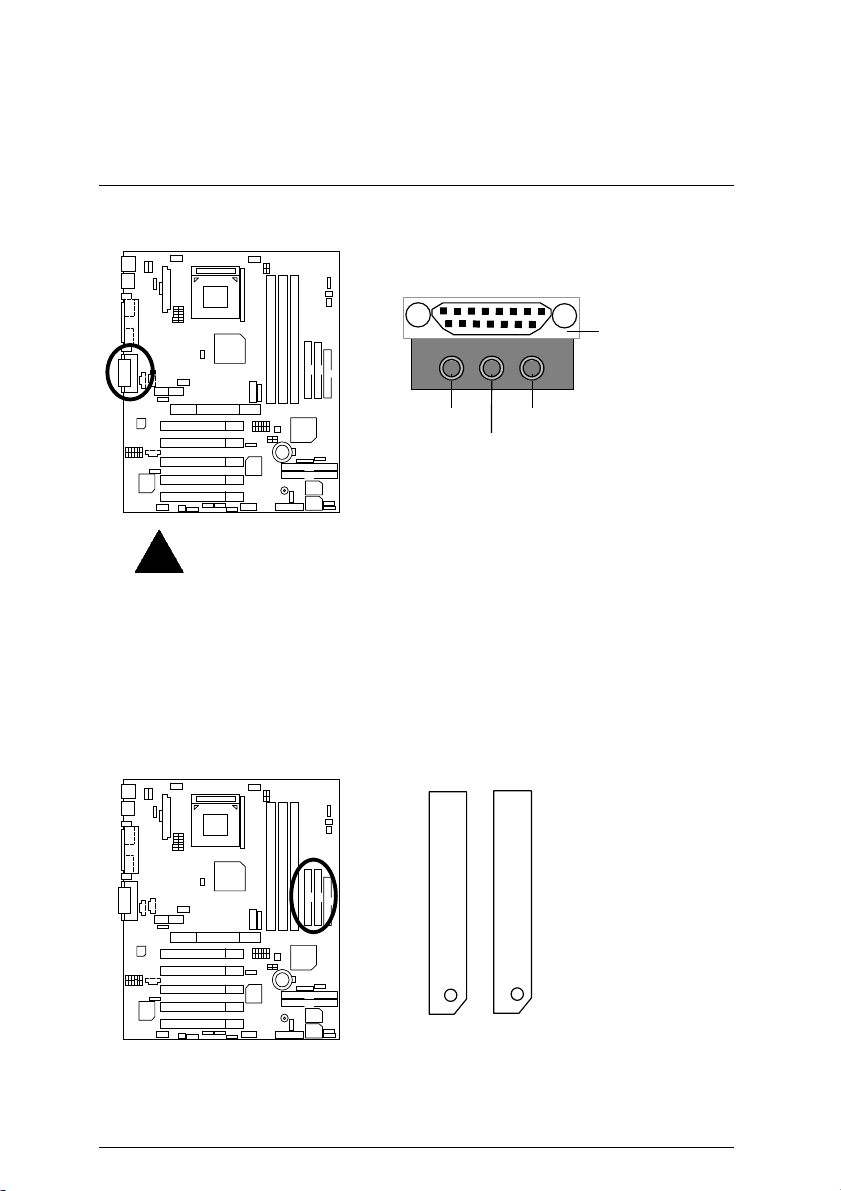
Connectors
Game & Audio Port
Line Out 1
Please note:
Line Out 1: Line Out or SPDIF (The SPDIF output is capable of providing digital
audio to external speakers or compressed AC3 data to an external Dolby digital
decoder). To enable SPDIF, simply insert SPDIF connector into Line Out1. Line
Out1 will become SPDIF Out automatically. (see page 56 for more information).
To enable Four Speaker (for Creative 5880 audio only), simply follow instructions
on page 53 and Line In will become Line Out2 to support second pair of stereo
speakers.
IDE1 (Primary), IDE2 (Secondary) Port
Game
Port
MIC In
Line In/Line Out 2
RED LINE
IDE 1
IDE 2
20
Page 27
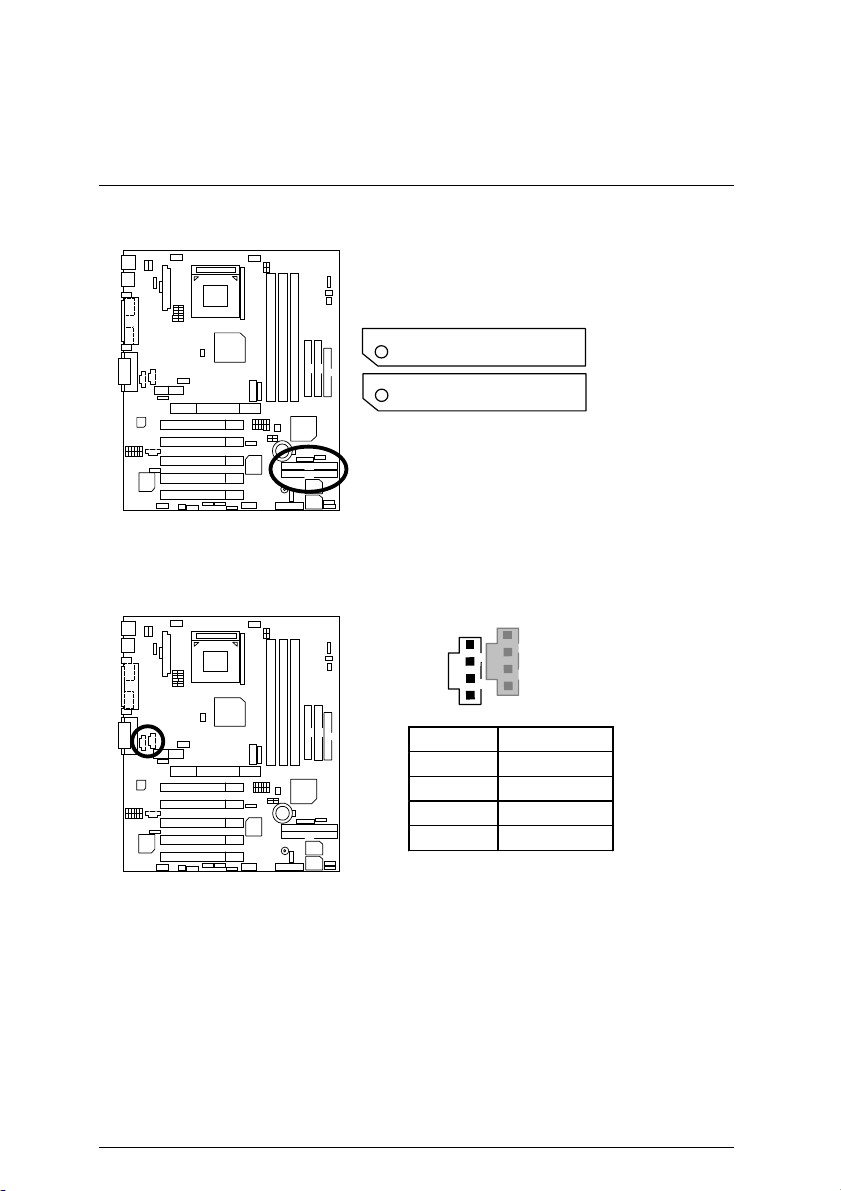
7DXR Motherboard
IDE3/IDE4 (Raid/ATA100) Port
CDIN: CD Audio Line In
IDE 4
IDE 3
RED LINE
1
Pin No. Definition
1 CD-L
2 GND
3 GND
4 CD-R
21
Page 28
Connectors
AUXIN: AUX_IN (Optional)
1
Pin No. Definition
1 AUX-L
2 GND
3 GND
4 AUX-R
TELE: TEL (The connector is for internal modem card with voice
connector) [Optional]
1
Pin No. Definition
1 Signal-In
2 GND
3 GND
4 Signal-Out
22
Page 29
7DXR Motherboard
WOR: Ring Power On
1
Pin No. D efin itio n
1 Signal
2 GND
SMB: External SMBUS Device Connector (Optional)
1
Pin No . Definition
1 SMB CLK
2 NC
3 GND
4 SMB DATA
5 +5V
23
Page 30
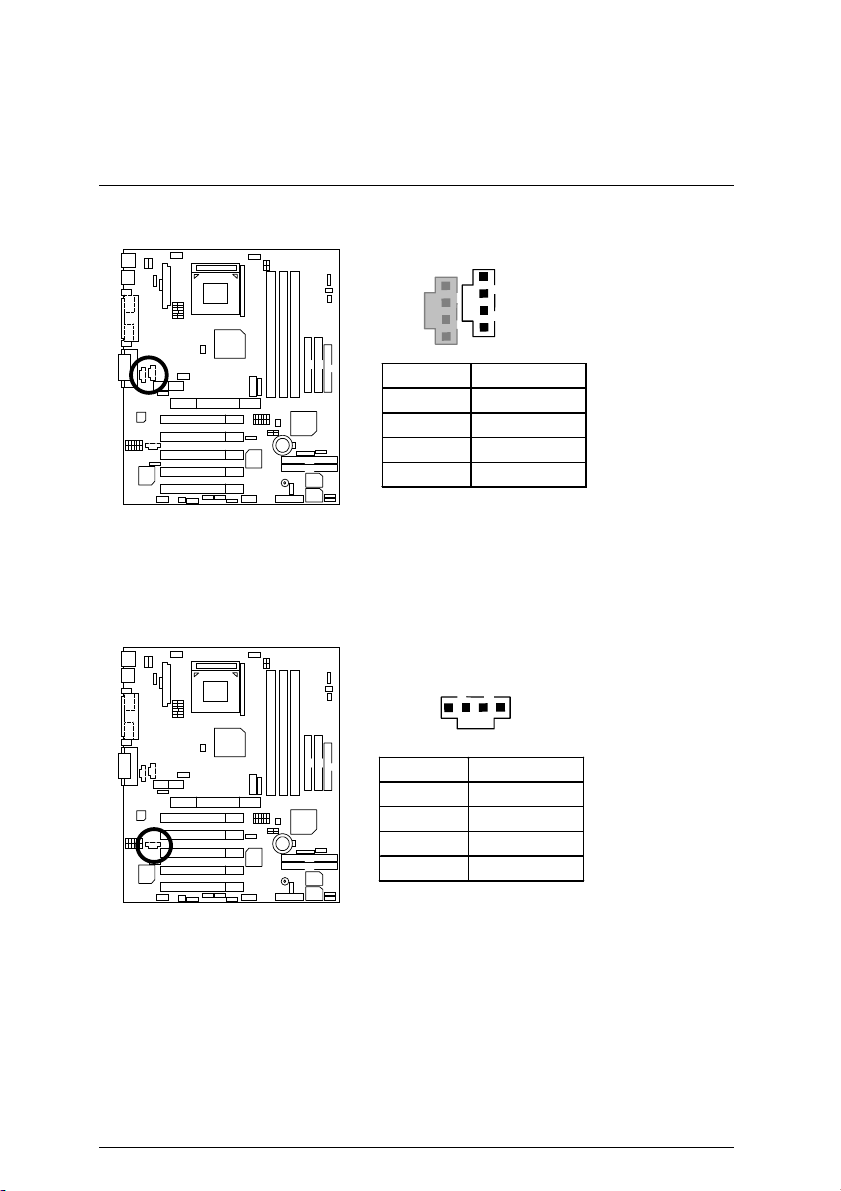
SYS_FAN1: System Fan 1
PWR_FAN: Power Fan
Connectors
1
Pin No. Definition
1 Control
2 +12V
3 SENSE
1
Pin No. Definition
1 Control
2 +12V
3 SENSE
24
Page 31

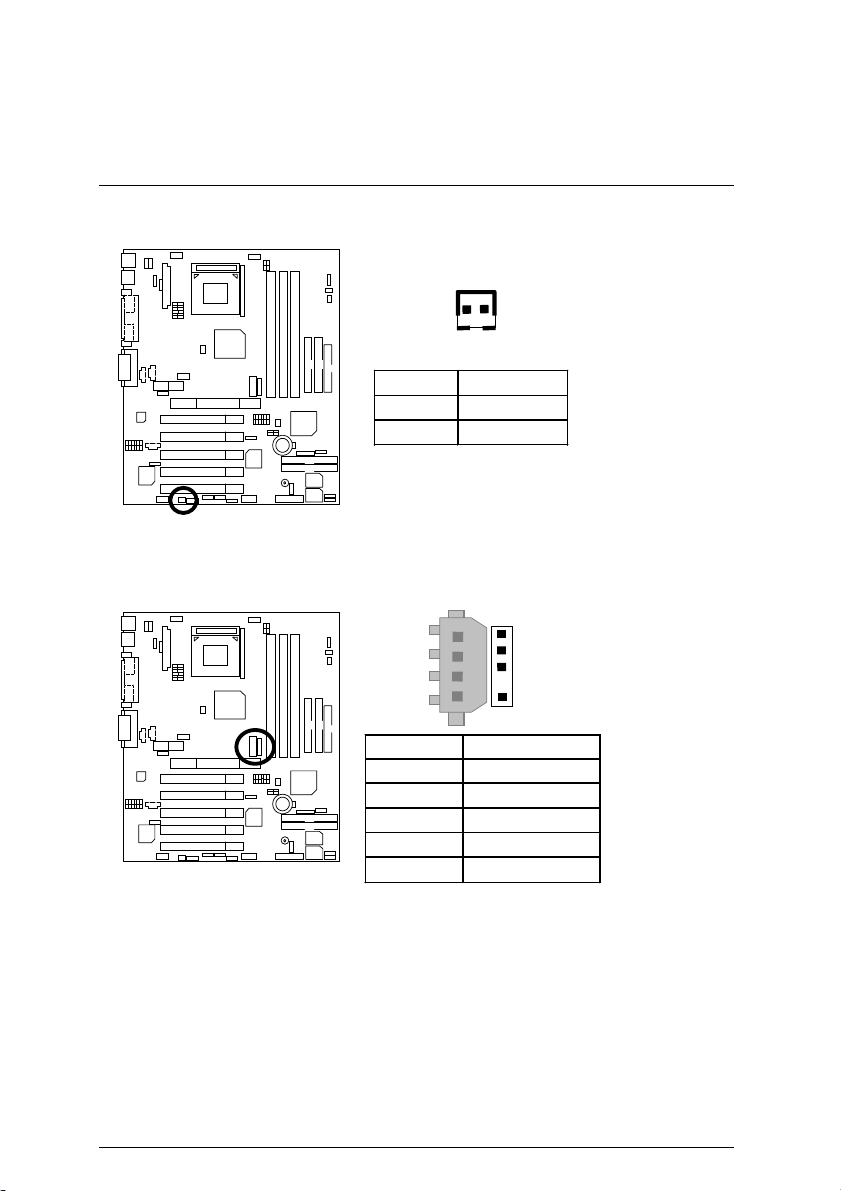
7DXR Motherboard
CPU_FAN: CPU Fan
Please note:
A proper installation of the CPU cooler is essential to prevent the CPU from
running under abnormal condition or damaged by overheating.
With support CPU guardian function CPU cooler must connect with this connector,
otherwise system could not boot.
SYS_FAN2: System Fan 2
1
Pin No. Definition
1 Control
2 +12V
3 SENSE
1
Pin No . D e fin itio n
1 Control
2 +12V
3 SENSE
25
Page 32

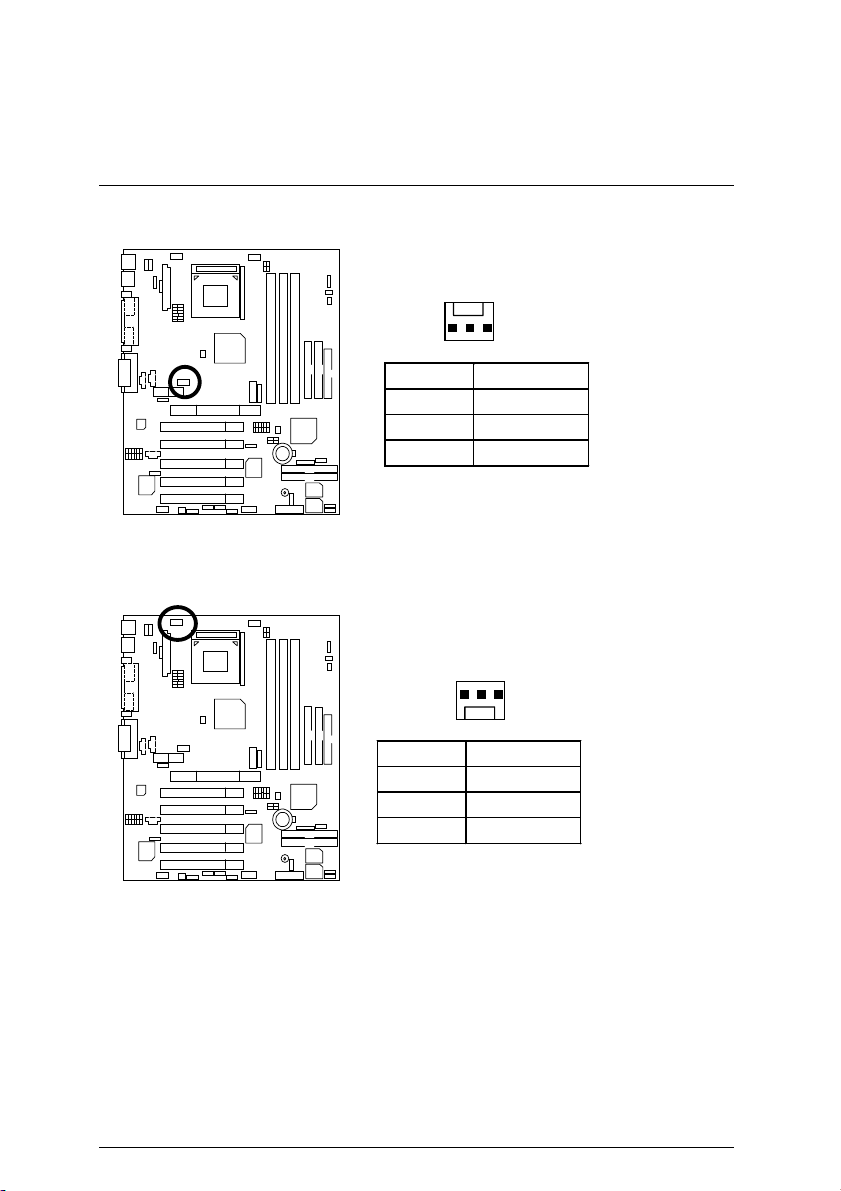
Connectors
WOL: Wake on LAN
1
Pin No. D efin itio n
1 +5V SB
2 GND
3 Signal
RAM_LED (J30) / DIMM_LED: DIMM LED Connector & DIMM LED
(RAM_LED (J30) is optional)
+
DIMM LED
1
DIMM LED Connector
Please note:
Do not remove memory modules while DIMM LED is on. It might cause short or
other unexpected damages due to the 2.5V stand by voltage. Remove memory
modules only when STR function is disabled by jumper and AC Power cord is
disconnected.
26
Page 33

7DXR Motherboard
IR: IR Header
1
Pin No. Definition
1 VCC (+5V)
2 NC
3 IR Data Input
4 GND
5 IR Data Output
Please note:
Be careful with the polarity of the IR connector while you connect the IR. Please
contact you nearest dealer for optional IR device.
AGP_12V (J40): Power for AGP Pro
Pin No. Definition
Please note:
When using the AGP Pro Card, you must use the power connector (As the other
one for HDD). Otherwise, AGP Pro Card will not work.
1
1 +5V
2 GND
3 GND
4 +12V
27
Page 34

NB_FAN (J21): CHIP FAN
Pin No. Definition
1 GND
2 +12V
Please note:
If installed wrong direction, the Chip Fan will not work. Sometimes will damage the
Chip Fan. (Usually black cable is GND)
AGP_OV: AGP 4X Overvoltage Switch
Connectors
1
1 2
ON
SW1 SW2
1.5V (Default) OFF OFF
1.6V ON OFF
1.7V OFF ON
Please note:
The function provide AGP over voltage, Incorrect using it may cause your AGP
card damage. For power End-User use only!
28
Page 35

7DXR Motherboard
VCORE_OV: CPU Core Overvoltage Switch (Optional)
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 4 5 6
Auto X X X X X O
1.5V O X X X O X
1.525V X O X X O X
1.55V O O X X O X
1.575V X X O X O X
1.6V O X O X O X
1.625V X O O X O X
1.65V O O O X O X
1.675V X X X O O X
1.7V O X X O O X
1.725V X O X O O X
1.75V O O X O O X
1.755V X X O O O X
1.8V O X O O O X
1.825V X O O O O X
1.85V O O O O O X
Please note:
Provide CPU core voltage override function,Incorrect using it may cause your CPU
broken. For power End-User use only!
ON
O:ON, X:OFF
29
Page 36

RAM_OV: RAM Overvoltage
Please note:
Provide DDR voltage override function. Incorrect using may cause your DDR
broken. For power End-User only!
Connectors
1 2
ON
O:ON, X:OFF
SW1 SW2
2.5V (Default) OFF OFF
2.6V ON OFF
2.7V OFF ON
30
Page 37

7DXR Motherboard
Panel And Jumper Definition
GN
HD
1
F_PANEL: For 2X11 Pins Jumper
GN (Green Switch) Open: Normal Operation
Close: Entering Green Mode
GD (Green LED) Pin 1: LED anode(+)
Pin 2: LED cathode(−)
HD (IDE Hard Disk Active
LED)
Pin 1: LED anode(+)
Pin 2: LED cathode(−)
SPK (Speaker Connector) Pin 1: VCC(+)
Pin 2- Pin 3: NC
Pin 4: Data(−)
RE (Reset Switch) Open: Normal Operation
Close: Reset Hardware System
P+P−P−(Power LED)
Pin 1: LED anode(+)
Pin 2: LED cathode(−)
Pin 3: LED cathode(−)
PW (Soft Power Connector) Open: Normal Operation
Close: Power On/Off
Please note:
Please connect the power LED, PC speaker, reset switch and power switch etc of
your chassis front panel to the front panel jumper according to the pin assignment
above.
S P K
P−P−P+
RE
1
1
PW
GD
1
31
Page 38

Panel and Jumper Definiti on
BUZ_EN: Internal Buzzer Connector (Optional)
1
Enable
(Default)
Pin No. Definition
1-2 close Internal Buzzer Enable
(Default)
2-3 close Internal Buzzer Disable
CLR_CMOS: Clear CMOS Function
1
Disable
(Default)
Pin No . Defin itio n
1-2 Close Enable Clear CMOS
Function
2-3 Close Disable Clear CMOS
Function (Default)
Please note:
You may clear the CMOS data to its default values by this jumper.
1
Disable
1
Clear CMOS
32
Page 39

7DXR Motherboard
Pl
Pl
BIOS_WP: BIOS Write Protect Function (Optional)
1
Disable
(Default)
1
Protection
Write
Pin No. Definition
1-2 close Write Protect Enable
2-3 close Write Protect Dis able
(Default)
ease note:
To flash/upgrade BIOS on this MB BIOS_WP jumper must be opened. We
recommend BIOS_WP jumper to be set to“2-3 close”, whenever user is not try to
flash/upgrade the BIOS.
RUSB_ON (J6): Rear USB Device Wake up Selection
1
Rear USB
Pin No. Defin itio n
1-2 close Rear USB Device Wake up
2-3 close Rear USB Device Wake up
Disable
(Default)
Enable
Disable (Default)
1
Enable
ease note:
To use “USB KB/MS Wakeup from S3~S5” function, set BIOS setting “USB KB/MS
Wake up from S3~S5” to ENABLED and enable jumpers RUSB_ON (J6) &
STR_EN.
*(Power on the computer and as soon as memory counting starts, press
<Del>. Yo u will enter BIOS Setup. Select the item “POWER MANAGEMENT
SETUP”, then select “USB KB/MS Wake up from S3~S5”. Remember to save
the setting by pressing "ESC" and choose the “SAVE & EXIT SETUP”
option.)
33
Page 40

Panel and Jumper Definiti on
FUSB_ON (J8): Front USB Device Wake up Selection
Front USB
Please note:
To use “USB KB/MS Wakeup from S3~S5” function, set BIOS setting “USB
KB/MS Wake up from S3~S5” to ENABLED and enable jumpers FUSB_ON (J8) &
STR_EN.
*(Power on the computer and as soon as mem ory counting starts, press
<Del>. You will enter BIOS Setup. Select the item “POWER MANAGEMENT
SETUP”, then select “USB KB/MS Wake up from S3~S5”. Reme m ber to save
the setting by pressing "ESC " and choose the “SAVE & EXIT SETUP”
option.)
GUARDIAN (JP6): Guardian
Please note:
If CPU guardian function enable you must let CPU cooler connect with
CPU_FAN otherwise system could not boot.
1
Disable
(Default)
1
Enable
Pin No . Defin itio n
1-2 close
2-3 close
Front USB Device Wake
up Enable
Front USB Device Wake
up Disable (Default)
1
Disable
1
Enable
(Default)
Pin No . Definitio n
1-2 close Enable Guardian
Function (Default)
2-3 close Disable Guardian
Function
34
Page 41

7DXR Motherboard
AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2: AMR Selection (Optional)
1
AMR_EN1
1
AMR_EN1 AMR_EN2 Primary CODEC
1-2 close 1-2 close AMR Primary
2-3 close 2-3 close AMR Seco ndary
Please note:
7DXR:
If M/B has hardware audio (CT5880), your modem riser has been set to
“Primary” automatically. No Jumpers AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2 for 7DXR.
7DXR:
AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2: 1-2 close: If you don’t use onboard software
audio, your audio/modem riser must be “Primary”. Mainboard’s software audio will
be disabled. AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2: 2-3 close: If you use software
audio(onboard CODEC only), your modem riser must be “Secondary”.
There are two kind of AMR/MR card in the market, Primary and secondary. If your
AMR/MR card is primary, AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2 should be set to 1-2, if you
have secondary AMR/MR card AMR_EN1 & AMR_EN2 should be set to 2-3.
Warning! If Primary AMR/MR card is used, on-board audio will be disabled.
PIDE_EN (JP52): Onboard Promise Selection
1
Enable
(Default)
AMR_EN2
AC’97 Disabled
(Disabled Onboard
CODEC)
(Default)
1
Disable
Pin No . Defin itio n
1-2 close
Enable Promise function
(Default)
2-3 close Disable Prom ise function
35
Page 42

RAID_EN (JP54): Raid/ATA100 Selection
Panel and Jumper Definiti on
1 1
Please note:
If you want to use "Raid Mode”, your IDE3 and IDE4 must be connected with Hard
Driver. Please set PDIE_EN (JP52) as enable before adjusting RAID_EN (JP54).
BAT1: Battery
ATA 100 Mode
(Default)
Raid Mode
Pin No . Defin itio n
1-2 close Raid Mode
2-3 close ATA100 Mode (Default)
+
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if battery
is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or
equivalent type recommended
by the manufacturer.
Dispose of used batteries
according to the manufacturer’s
instructions.
36
Page 43

7DXR Motherboard
STR_EN: STR Selection
1
1
Disable
(Default)
Enable
Pin No. Definitio n
1-2 close STR Enable
2-3 close STR Disable (Default)
PS2_STR (PS2_STR_EN): PS/2 KB/MS STR Enable Selection
1
Disable
1
Enable
(Default)
Pin No. Definition
1-2 close Enable PS/2 KB/MS STR
function (Default)
2-3 close Disable PS/2 KB/MS STR
function
Please note:
Please set SRT_EN as enable before adjusting PS2_STR(PS2_STR_EN).
37
Page 44

Performance List
Performance List
The following performance table lists the results of some popular benchmark testing programs.
These data are provided as reference only and in no way guarantee the system shall perform,
and there is no responsibility for different testing data at exactly the same level. (The different
Hardware & Software configuration will result in different benchmark testing results.)
CPU
•
DRAM (128x1) MB PC266 DDR RAM (SAMSUNG K4H280838B-TCB0)
•
CACHE SIZE 384 KB included in AlthonTM
•
DISPLAY GA-GF2000 DDR (32MB)
•
STORAGE Onboard Promise RAID0 (IBM DTLA-307045 45GB x 2)
•
O.S. Windows 2000 + SP1 + DirectX8
•
DRIVER
•
AMD K7 Athlon
Display Driver at 1024 x 768 x 64k colors x 75Hz.
TUCD ver. 1.7
Processor AMD
Winbench99
TM
1333MHz processor
TM
Althon
1333MHz (266x5)
CPU mark 99 122
FPU Winmark 99 7310
Business Disk Winmark 99 11000
Hi-End Disk Winmark 99 25300
Business Graphics Winmark 99 640
Hi-End Graphics Winmark 99 1320
Winstone 2001
Business Winstone 2001 52.3
Content Creative Winstone 2001
If you wish to maximize the performance of your system, please
0
38
55.5
refer to the detail on P.96
Page 45

7DXR Motherboard
Block Diagram
AGPCLK (66MHz)
5 PCI
PCI (33MHz)
AGP
2X/4X
PCI Bus 33MHz
CT5880
Option
AC97
CODEC
AC-Link
AMR
AMD-K7
AMD
761
VT82C
686B
Floppy
PS/2
TM
System Bus 100/133MHz
33MHz
LPT Port
CPUCLK (100/133MHz)
100/133MHz
AGPCLK (66MHz)
14.318MHz
NPCLK (33MHz)
2.5V DDR SDRAM
HCLK (100/133MHz)
48MHz
4 USB Ports
Game Port
COM Ports
ATA66/100 IDE
Channels
PDC
20265R
AGPCLK (66MHz)
PCI (33MHz)
48MHz
14.318MHz
33MHz
ICS
94240
39
HCLK (100/133MHz)
NPCLK (33MHz)
AGPCLK (66MHz)
CPUCLK (100/133MHz)
Page 46

Suspend to RAM Installat i on
Suspend To RAM Installation
A.1 Introduce STR function:
Suspend-to-RAM (STR) is a Wi ndows 98 A CPI s leep mode function. When recovering from
STR (S3) sleep mode, the system is able, in just a few seconds, to r etrieve the last “state ” of
the system before it went to sleep and recover to that state. The “state” is stored in memory
(RAM) before the system goes to sleep. During STR sleep mode, your system uses only
enough energy to maintain critical information and system functions, primarily the system
state and the ability to recognize various “wake up” triggers or signals, respectively.
A.2 STR function Installation
Please use the following steps to complete the STR function installation.
Step-By-Step Setup
Step 1:
To utilize the STR function, the system must be in Windows 98 ACPI mode.
Putting Windows 98 into ACPI mode is fairly easy.
Setup with Windows 98 CD:
A. Insert the Windows 98 CD into your CD-ROM drive, select Start, and then Run.
B. Type (without quotes)
C. After setup completes, remove the CD, and reboot your system
(This manual assumes that your CD-ROM device drive letter is D:).
“D:\setup”
in the window provided. Hit the enter key or click OK.
40
Page 47

7DXR Motherboard
Step 2:
(If you want to use STR Function, please set jumper STR_EN Pin1-2 (Closed.)
1
Enable
Pin No. Definitio n
1-2 close STR Enable
2-3 close STR Disable (Default)
Step 3:
Power on the computer and as soon as memory counting starts, press <Del>. You will enter
BIOS Setup. Select the item
Type: S3 /STR”
EXIT SETUP”
Congratulation! You have completed the installation and now can use the STR function.
. Remember to save the s ettings by pr ess ing "ESC" an d choose the
option.
“POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP”,
then select
“ACPI Sleep
“SAVE &
41
Page 48

Suspend to RAM Installat i on
A.3 How to put your system into STR mode?
There are two ways to accomplish this:
1. Choose the “Stand by” item in the “Shut Down Windows” area.
A. Press the “Start” button and then select “Shut Down”
B. Choose the “Stand by” item and press “OK”
42
Page 49

7DXR Motherboard
2. Define the system ”power on” button to initiate STR sleep mode:
A. Double click “My Computer” and then “Control Panel”
B. Double click the “ Power Management” item.
43
Page 50

Suspend to RAM Installat i on
C. Select the “Advanced” tab and “Standby” mode in Power Buttons.
D. Restart your computer to complete setup.
Now when you want to enter STR sleep mode, just momentarily press the “Power on”
button.
A.4 How to recover from the STR sleep mode?
There are seven ways to “wake up” the system:
1. Press the “Power On” button.
2. Use the “PS/2 Keyboard Power On” function.
3. Use the “PS/2 Mouse Power On” function.
4. Use the “Resume by Alarm” function.
5. Use the “Modem Ring On” function.
6. Use the “Wake On LAN” function.
7. Use the “USB Device Wake Up” function.
44
Page 51

7DXR Motherboard
A.5 Notices:
1. In order for STR to function prop erly, several ha rdware and software requirements must
be satisfied:
A. Your ATX power s upply must comply with the ATX 2.01 specifi cation (provide more
than 720 mA 5V Stand-By current).
B. Your DDR SDRAM must be DDR-200 or DDR-266 compliant.
45
Page 52

Dual BIOS Introduction
Dual BIOS Introduction
A. What is Dual BIOS Technology?
Dual BIOS means that there are two system BIOS (ROM) on the motherboard, one is the
Main BIOS and the other is Backup BIOS. Under the normal circumstances, the system
works on the Main BIOS. If the Mai n BIOS is corrupt ed or damaged, the Backup BIOS c an
take over while the system is powered on. This means that your PC will still be able to run
stably as if nothing has happened in your BIOS.
B. How to use Dual BIOS?
a. Boot Screen
xxx xxx
Check System Health OK,
AMD-Athlon(tm)-650MHz (100x6.5)
Check NVRAM…
Wait…
Press F1 to enter Dual BIOS Utility. Press ESC to quit
( C ) American Megatrends Inc.,
62-0612-001199-00101111-071595-KT133-7ZX001-F
Award Modular BIOS v6.00PG, An Energy Star Ally
Copyright (C) 1984-2000, Award Software, Inc.
Press F1 to enter Dual BIOS Utility
46
Page 53

7DXR Motherboard
b. Dual BIOS Utility
c. Dual BIOS Item explanation:
Wide R ange Protection: Disabled (Default), Enabled
Status 1:
If any failure (ex. Update ESCD failure, checksum error or reset…) occurs in the Main
BIOS , just before the Operating System is loaded and after the power is on, and that
the Wide Range Protection is set to “Enable”, the PC will boot from Backup BIOS
automatically.
Status 2:
If the ROM BIOS on peripherals cards(ex. SCSI Cards, LAN Cards,..) emits
signals to request restart of the system after the user make any alteration on it,
the boot up BIOS will not be changed to the Backup BIOS.
Dual BIOS Utility V6.60.g.01K
(C) 1999, Gigabyte Technology Co., LTD.
Wide Range Protection :Disabled
Halt On BIOS Defects :Disabled
Auto Recovery :Enabled
Boot From :Main BIOS
BIOS Recovery :Main to Backup
F3: Load Default F5: Start BIOS Recovery
F7: Save And Restart F9: Exit Without Saving
Use <Space> key to toggle setup
47
Page 54

Dual BIOS Introduction
Halt On BIOS Defects: Disabled (Default), Enabled
If the BIOS occurs a checksum error or the Main BIOS occurs a WIDE RANGE
PROTECTION error and Halt On BIOS Defects set to Enable, the PC will show messages
on the boot screen, and the system will pause and wait for the user’s instruction.
If Auto Recovery:
If Auto Recovery:
Auto Recovery: Enabled (Default), Disabled
When one of the Main BIOS or Backup BIOS occurs checksum failure, the working BIOS
will automatically recover the BIOS of checksum failure.
(In the Power Management Setup of the BIOS Setting, if ACPI Suspend Type is set to
Suspend to RAM, the Auto Recovery will be set to Enable automatically.)
(If you want to enter the BIOS setting, please press
appears.)
Boot From: Main BIOS (Default), Backup BIOS
Status 1:
The user can set to boot from main BIOS or Backup BIOS.
Status 2:
If one of the main BIOS or the Backup BIOS fails, this item
(Default)”
will become gray and will not be changed by user.
Disabled
Enabled
, it will show
, it will show
<or the other key to continue.>
<or the other key to Auto Recover.>
“Del”
key when the boot screen
“Boot From: Main BIOS
BIOS Recovery: Main to Backup
Auto recovery message:
BIOS Recovery: Main to Backup
The means that the Main BIOS works normally and could automatically recover the
Backup BIOS.
BIOS Recovery: Backup to Main
The means that the Backup BIOS works normally and could automatically recover the
Main BIOS.
(This auto recovery utility is set by system automatically and can’t be changed by user.)
48
Page 55

7DXR Motherboard
DualBIOS
GIGABYTE Technology is pleased to introduce DualBIOS technology, a hot spare for your
system BIOS. This newest “Value-added” feature, in a long series of innovations from
GIGABYTE, is available on GA-7DXR motherboard. Future GIGABYTE motherboards will also
incorporate this innovation.
What’s DualBIOSTM?
On GIGABYTE motherboards with DualBIOS there are physically two BIOS chips. For
simplicity we’ll call one your “Main BIOS” and the other we’ll call your “Backup” BIOS (your “hot
spare”). If your Main BIOS fails, the Backup BIOS almost automatically takes over on your
next system boot. Almost automatically and with virtually zero down time! Whether the
problem is a failure in flashing your BIOS or a virus or a catastrophic failure of the Main BIOS
chip, the result is the same - the Ba ckup BIOS backs you up, almost automatically.
TM
Technology FAQ
49
Page 56

Dual BIOS Introduction
I. Q: What is DualBIOSTM technology?
Answer:
DualBIOS technology is a patented technology from Giga-Byte Technology. The concept of this
technology is based on the redundancy and fault tolerance theory. DualBIOS
simply means there are two system BIOSes (ROM) integrated onto the motherboard. One is a
main BIOS, and the other is a backup BIOS. The mainboard will operate normally with the main
BIOS, however, if the main BIOS is corrupt or damaged for various reasons, the backup BIOS
will be automatically used when the system powered-On. Your PC will operate as before the
main BIOS was damaged, and is completely transparent to the user.
TM
technology
TM
II. Q: Why does anyone need a motherboard with DualBIOS
technology?
Answer:
In today’s systems there are more and more BIOS failures. The most common reasons are virus
attacks, BIOS upgrade failures, and/or deterioration of the BIOS (ROM) chip itself.
1. New computer viruses are being found that attack and destroy the system BIOS. They
may corrupt your BIOS code, causing your PC to be unstable or even not boot normally.
2. BIOS data will be corrupted if a power loss/surge occurs, or if a user resets the system, or
if the power button is pressed during the process of performing a system BIOS upgrade.
3. If a user mistakenly updates their mainboard with the incorrect BIOS file, then the system
may not be able to boot correctly . This may cause the PC system hang in operation or
during boot.
4. A flash ROM's life cycle is limited according to electronic characteristics. The modern PC
utilizes the Plug and Play BIOS, and is updated regularly. If a user changes peripherals
often, there is a slight chance of damage to the flash
With Giga-Byte Technology’s patented DualBIOS
hangs during system boot up, and/or loss BIOS data due to above reasons. This new
technology will eliminate valuable system down time and costly repair bills cause by BIOS
failures.
TM
ROM.
technology you can reduce the possibility of
50
Page 57

7DXR Motherboard
III. Q: How does DualBIOSTM technology work?
Answer:
1. DualBIOSTM technology provides a wide range of protection during the boot up procedure. It
protects your BIOS during system POST, ESCD update, and even all the way to PNP
detection/assignment.
2. DualBIOS
TM
provides automatic recovery for the BIOS. When the first BIOS used during
boot up does not complete or if a BIOS checksum error occurs, boot-up is still possible. In
the DualBIOS
or backup BIOS is corrupted, the DualBIOS
the wrong BIOS automatically.
3. DualBIOS
TM
utility, the "Auto Recovery" option will guarantee that if either the main BIOS
TM
technology will use the good BIOS and correct
TM
provides manual recovery for the BIOS. DualBIOSTM technology contains a
built-in flash utility, which can flash your system BIOS from backup to main and/or visa versa.
There is no need for an OS-dependent flash utility program.
4. DualBIOS
TM
contains a one-way flash utility. The built-in one-way flash utility will ensure that
the corrupt BIOS is not mistaken as the good BIOS during recovery and that the correct
BIOS (main vs. backup) will be flashed. This will prevent the good BIOS from being flashed.
IV. Q: Who Needs DualBIOSTM technology?
Answer:
1. Every user should have DualBIOSTM technology due to the advancement of computer
viruses.
Everyday, there are new BIOS-type viruses discovered t hat will destroy your system BIOS.
Most commercial products on the market do not have solutions to guard against this type of
virus intrusion. The DualBIOS
your PC:
Case I.) Vicious computer viruses may wipe out your entire system BIOS. With a
conventional single system BIOS PC, the PC will not be functional until it is sent for repairs.
Case II.) If the "Auto Recovery" option is enabled in the DualBIOS
corrupts your system BIOS,
correct the main BIOS.
Case III.) A user may override booting from the main system BIOS. The DualBIOS
may be entered to manually change the boot sequence to boot from the backup BIOS.
TM
technology will provide a state-of-the-art solution to protect
TM
utility, and if a viru s
the backup BIOS will automatically reboot the system and
TM
utility
51
Page 58

Dual BIOS Introduction
2. During or after a BIOS upgrade, if DualBIOSTM detects that the main BIOS is corrupt, the
backup BIOS will take over the boot-up process automatically. Moreover, it will verify the
TM
main and backup BIOS checksums when booting-up. DualBIOS
technology examines the
checksum of the main and backup BIOS while the system is powered on to guarantee your
BIOS operates properly.
3. Power Users will have the advantage of having two BIOS versions on their mainboard. The
benefit is being able to select either version BIOS to suit the performance system needs.
4. Flexibility for high-end desktop PCs and workstation/servers. In the DualBIOSTM utility,
the option can be set, "Halt On When BIOS Defects," to be enabled to halt your system with
a warning message that the main BIOS has been corrupted. Most workstation/servers require
constant operation to guarantee services have not been interrupted. In this situation, the "Halt
On When BIOS Defects" message may be disabled to avoid system pauses during normal
booting. Another advantage you gain from Giga-By te’s DualBIOS
TM
technology is the ability
to upgrade from dual 2 M bit BIOS to dual 4 Mbit BIOS in the future if ext ra BIOS storage is
need.
52
Page 59

7DXR Motherboard
Four Speaker & SPDIF Introduction
Four Speaker Introduction
A. What is Four Speaker?
The Creative CT5880 audio chip can support up to 4 speaker output. If you select “Four
speaker out”, Line In will be reconfigured as another line out to support a second pair of
speakers.
B. How to use Four Speaker?
Microsoft Windows 98 Second Edition setup procedure :
a. Click the audio icon along the task bar and select “Configure 3D Audio”
b. Select two speaker (Default)
53
Page 60

. Select “Four speaker” item.
c
Microsoft W indows Me setup procedure:
a. Go to “Control Panel”
Four Speaker & SPDIF Introduct i on
Double click “Sounds and Multimedia”.
54
Page 61

7DXR Motherboard
b. Select “Audio” Page, and click “Advanced” button.
c. Select “Quadraphonic Speakers” and click ok.
Click ”Advanced”.
Click “Quadraphonic Speakers”.
C. Four Speaker Application
The four speaker function will only be supported in application softwares that use Microsoft
DirectX and Creative EAX, for example, the game titles, software DVD player and MP3 player.
55
Page 62

SPDIF Introduction
Four Speaker & SPDIF Introduct i on
What is SPDIF?
A.
The SPDIF output is capable of providing digi tal audio to external speakers or compressed
AC3 data to an external Dolby digital decoder.
B. How to use SPDIF?
a. Click your mouse right button in “My Computer” and select the “Properties” item.
b. Click “Device Manager” item.
56
Page 63

7DXR Motherboard
c. Click “Sound, video and game controllers” item and select the “Creative Sound Blaster
PCI128” item.
d. Click “Settings” item and select the “Output Mode” item.
57
Page 64

Four Speaker & SPDIF Introduct i on
e. Click “Digital” item, Line Out will be reconfigure t o SPDIF Out.
f. Recommend you to select “Autosense”, It will automatically detect the ty pe (mono or st ereo)
of the audio connector that you plug into Line Out audio jack, the n configure Line Out to
either SPDIF or Speaker accordingly.
58
Page 65

7DXR Motherboard
@BIOS™ Introduction
Gigabyte announces
@BIOS™
Windows BIOS live update utility
Have you ever updated BIOS by yourself? Or
like many other people, you just know what
BIOS is, but always hesitate to update it?
Because you think updating newest BIOS is
unnecessary and actually you don’t know how to update it.
Maybe not like others, you are very experienced in BIOS updating and spend quite
a lot of time to do it. But of course you don’t like to do it too much. First, download
different BIOS from website and then switch the operating system to DOS mode.
Secondly, use different flash utility to update BIOS. The above process is not a
interesting job. Besides, always be carefully to store the BIOS source code correctly in
your disks as if you update the wrong BIOS, it will be a nightmare.
Certainly, you wonder why motherboard vendors could not just do something right
to save your time and effort and save you from the lousy BIOS updating work? Here it
comes! Now Gigabyte announces @BIOS
This is a smart BIOS update software. It could help you to download the BIOS from
internet and update it. Not like the other BIOS update software, it’s a Windows utility.
With the help of “@BIOS
Besides, no matter which mainboard you are using, if it’s a Gigabyte’s product*,
™
@BIOS
mainboard model and help you to choose the BIOS accordingly. It then downloads the
BIOS from the nearest Gigabyte ftp site automatically. There are several different
choices; you could use “Internet Update” to download and update your BIOS directly.
Or you may want to keep a backup for your current BIOS, just choose “Save Current
BIOS” to save it first. You make a wise choice to use Gigabyte, and @BIOS
your BIOS smartly. You are now worry free from updating wrong BIOS, and capable to
maintain and manage your BIOS easily. Again, Gigabyte’s innovative product erects a
milestone in mainboard industries.
buy a Gigabyte’s motherboard, you could find this amazing software in the attached
driver CD. But please remember, connected to internet at first, then you could have a
internet BIOS update from your Gigabyte @BIOS
help you to maintain the BIOS. This utility could detect your correct
For such a wonderful software, how much it costs? Impossible! It’s free! Now, if you
™
’, BIOS updating is no more than a click.
™
--the first Windows BIOS live update utility.
™
™
update
.
59
Page 66

EasyTune
TM
Introduction
III
EasyTune
Gigabyte announces
Introduction
III
™
EasyTune
III
™
Windows overdrive utilit y
“Overdrive” might be one of the most
common issues in computer field. But have
many users ever tried it? The answer is
probably “no”. Because “overdrive” is thought
to be very difficult and includes a lot of
technical know-how, sometimes “overdrive” is
even considered as special skills found only in some enthusiasts.
But as to the experts in “overdrive”, what’s the truth? They may spend quite a lot
of time and money to study, try and use many different hardware and software tools
to do “overdrive”. And even with these technologies, they still learn that it’s quite a
risk because the safety and stability of an “overdrive“ system is unknown.
Now everything is different because of a Windows overdrive utility
EasyTune
rule of “overdrive”. This is the first overdrive utility suitable for both normal and power
users. Users can choose either “Easy Mode” or “Advanced Mode” to run “overdrive”
at their convenience. For users who choose “Easy Mode”, they just need to click
“Auto Optimize” to have auto and immediate CPU overclocking. This software will
then overdrive CPU speed automatically with the result being shown in the control
panel. If someone prefers to “overdrive” by oneself, there is also another choice.
Click “Advanced Mode” to enjoy “sport drive” class overclocking. In “Advanced
Mode”, one can change the system bus speed in small increments to get ultimate
system performance. And no matter which mainboard is used, if it’s a Gigabyte’s
product*, EasyTune
Besides, different from other traditional over-clocking methods, EasyTune
doesn’t require users to change neither BIOS nor hardware switch/ jumper setting;
on the other hand, they can do “overdrive” at only one click. Therefore, this is a safer
way for “overdrive” as nothing is changed on software or hardware. If user runs
EasyTune
again and the side effect is then well controlled. Moreover, if one well-performed
system speed been tested in EasyTune
“Load” it in next time. Obviously, Gigabyte EasyTune
“overdrive” technology toward to a newer generation.
™
--announced by Gigabyte. This utility has totally changed the gaming
III
™
helps to perform the best of system.
III
™
over system’s limitation, the biggest lost is only to restart the computer
III
™
, user can “Save” this bus speed and
III
™
has already turned the
III
III
™
60
Page 67

7DXR Motherboard
This wonderful software is now free bundled in Gigabyte motherboard attached
driver CD. Users may make a test drive of “EasyTune
™
” to find out more amazing
III
features by themselves.
For further technical information, please link to: http://www.gigabyte.com.tw
Note: For the latest version of EasyTune
ÚÚÚÚ
TM
, please visit our website.
III
61
Page 68

Raid Introduction
What is RAID?
This motherboard implements two different types of RAID levels as follows:
Raid Introduction
RAID 0 (stripe)
For capacity --
however many HDDs are in the array. Any larger HDDs will simply be truncated. The
truncated space on the bigger HDDs will then be unusable.
For sustained data tran sfers --
twice the speed of the slowest HD D in the array. A RAID 0 array consisting of four HDDs will
transfer at about three times the speed of the slowest HDD in the array.
RAID 1 (mirror)
For capacity –
larger HDD will simply be truncated. The truncated space on the bigger HDD will then be
unusable.
For sustained data transfers --
HDD in the array. This motherboard array will read data at twice the rat e of the slowest HDD
in the array.
The motherboard array will be as big as the smallest HDD in the array times
A RAID 0 array consisting of two HDDs will transfer at about
This Motherboard array will be as big as the smallest HDD in the array. The
This motherboard arr ay will write data at the rate of the slowest
62
Page 69

7DXR Motherboard
About RAID Levels
Striping (RAID 0)
Reads and writes sectors of data interleaved between multiple drives. When any disk member
fails, it affects the entire array. Performance is better than a single drive since the workload is
balanced between the array members. This array type is for high performance systems.
Identical drives are recommended for performance as well as data storage efficiency. The disk
array data capacity is equal to the number of drive members times the smallest member
capacity. For example, one 1GB and 1 drives will form a 2GB (2 x 1GB) disk array.
Stripe Size -
performance. In the FastBuild BIOS, the “Desktop” default is 8KB while “Server” and “A/V
Editing” are 64KB.
a value can be set from 1KB to 1024KB sector size. The size can directly affect
63
Page 70

Raid Introduction
Mirroring (RAID 1)
Writes duplicate data on to a pair of drives while reads are performed in parallel. ATA RAID 1 is
fault tolerant because each drive of a mirrored pair is installed on separate IDE channels. If one
of the mirrored drives suffers a mechanical failure (e.g. spindle failure) or does not respond, the
remaining drive will continue to function. This is called
Fault Tolerance
. If one drive has a
physical sector error, the mirrored drive will continue to function.
RAID 1 (Mirroring)
On the next reboot, the FastBuildTM utility will display an error in the array and recommend to
replace the failed drive. Users may choose to continue using their PC, however Promise
recommends replacing the failed drive as soon as possible. See Chapter 4 for a functional
description.
Due to redundancy, the drive capacity of the array is half the total drive capacity. For example,
two 1GB drives that have a combined capacity of 2GB would have 1GB of usable storage. With
drives of different capacities, there may be unused capacity on the larger drive.
64
Page 71

7DXR Motherboard
Creating Your Disk Array
You will now use the FastBuild BIOS utility to create your array using the attached drives. There
are two different scenarios in creating this array. You can create an array for performance, you
can create a Security array using new hard drives (recommended).
WARNING: If creating a Security array using an existing hard drive, backup
any necessary data. Failure to follow this accepted PC practice could result in
data loss.
1. Boot your system. If this is the first time you have booted with RAID, the FastBuild BIOS
will display the following screen.
FastTrak100 (tm) ”Lite” B I OS Version 1.xx (Build xxxx)
(c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
No array defined . . .
Press <Ctrl-F> to enter FastBuild (tm) Utility
Or press <ESC> key to conti nue booting the system.
2. Press <Ctrl-F> keys to display the FastBuild (tm) Utility Main Menu
3. Press “1” to display the Auto Setup Menu below. This is the fastest and easiest method to
creating your first array.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[Auto Setup Options Menu]
Opt i mize Array for: Perform ance
Typical Application usage: A/V Editing
[ Auto Setup Configuration ]
Mode.................................................Stripe
Spare Driver………………………………..0
Drives used in Ar r a y.................................2
Array Disk Capacity..........................16126
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [←, →, Space] Change Option [ESC] Exit [Ctrl-Y] Save
65
Page 72

Raid Introduction
Creating an Array for Performance
NOTE: This motherboard allows users to create striped arrays with 1, 2 drives.
To create an array for best performance, follow these steps:
1. Using the Spacebar, choose “Performance” under the
2. Select how you will use your PC most under the
Optimize Array for
section.
Typical Application usage
section The
choices are A/V Editing, Server, and Desktop (the default).
3. Press <Ctrl-Y> keys to Save and create the array.
4. Reboot your system.
5. Once the array has been created, you will need to FDISK and format the array as if it were
a new single hard drive.
6. Proceed to Installing Drivers section of the manual (see
RAID Manual of the TUCD
).
Creating a Security Array With New Drives
NOTE: This motherborad permit only two drives to be used for a single Mirrored array in Auto
Setup.
To create an array for data protection using new hard drives, follow these steps:
1. Using the Spacebar, choose “Security” under the
Optimize Array for
section.
2. Press <Ctrl-Y> keys to Save your selection.
3. The window below will appear.
Do you want the disk image to be duplicated to another? (Yes/No)
Y - Create and Duplicate
N - Create Only
4. Press “N” for the Create Only option.
5. A window will appear almost immediately confirming that your Security array has been
created. Press any key to reboot the system
Array has been created.
<Press Any Key to Reboot>
6. Proceed with normal FDISK and format procedures as if you had just installed a new hard
drive.
7. Once the arrayed drives have been formatted, proceed to the
RAID Manual of the TUCD
(see
) to install your operating system.
Installing Driver
chapter
66
Page 73

7DXR Motherboard
Creating a Security Array With An Existing Data Drive
NOTE: This motherboard permits only two drives to be used for a single Mirrored array in Auto
Setup.
You would use this method if you wish to use a drive that already contains data and/or is the
bootable system drive in your system. You will need another drive of identical or larger storage
capacity.
WARNING: Backup any necessary data before proceeding. Failure to follow
this accepted PC practice could result in data loss.
WARNING: If you wish to include your current bootable drive using the
Windows NT 4.x or Windows 2000 operating system as part of a bootable
Mirrored (RAID 1) array on your system, do NOT connect the hard drive to the
motherboard controller yet. You MUST install the Windows NT4 or 2000 driver
software first (see RAID Manual of the TUCD) to this drive while it is still attached to your
existing hard drive controller. For all other Operating Systems, proceed here.
Follow these steps:
1. Using the Spacebar, choose “Security” under the
Optimize Array for
section.
2. Press <Ctrl-Y> keys to Save your selection. The window below will appear.
Do you want the disk image to be duplicated to another? (Yes/No)
Y - Create and Duplicate
N - Create Only
3. Press “Y” for the Create and Duplicate option. The window below will appear asking you to
select the Source drive to use. FastBuild will copy all data from the Source drive to the
Target drive.
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
[Please Select A S ource Disk]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
1 :Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063
2 :Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063
[↑] Up [↓] [ESC] Exit [Ctrl-Y] Save
Source Disk
Target Disk
67
Page 74

Raid Introduction
4. Use the arrow keys to choose which drive contains the existing data to be copied.
5. Press [Ctrl-Y] keys to Save selection and start duplication. The following progress screen
will appear.
Start to duplicate the i mage . . .
Do you want to continue? (Yes/No)
Y – Continue N - Abort
6. Select “Y” to continue. If you choose “N” , you will be returned to step 1.
7. Once complete, the following screen will appear confirming that your Security array has
been created. Press any key to reboot the system
Array has been created.
<Press Any Key to Reboot>
8. Proceed to the
Installing Driver
chapter (see
RAID Manual of the TUCD
) to install the
RAID driver and/or operating system.
68
Page 75

7DXR Motherboard
Using FastBuild™ Configuration Utility
The FastBuildTM Configuration Utility offers several menu choices to create and manage the
drive array on the motherboard. For purposes of this manual, it is assumed you have already
created an array in the previous chapter and now wish to make a change to the array or view
other options.
Viewing BIOS Screen
When you boot your system with the RAID function and drives installed, the FastBuild BIOS will
detect the drives attached and show the following screen.
FastTrak100 (tm)”Lite” B I OS Version 1.xx (Build xx)
(c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Scanning IDE drives . . . . .
If an array exists already, the BIOS will display the following screen showing the board RAID
BIOS version and status of the array.
FastTrak100 (tm) “Lite”B I OS Version 1.xx (Build xxxx)
(c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
ID MODE SIZE TRACK-MAPPING STATUS
1 * 1*2 Mirror 16126M 611/128/32 Functional
Press <Ctrl-F> to enter FastBuild (tm) Utility....
The array status consists of three possible conditions:
Functional
Critical
- The array is operational.
- A mirrored array contains a drive that has failed or disconnected. The remaining
Functional, Critical, Offline
drive member in the array is functional. However, the array has temporar ily lost its ability to
provide fault tolerance. The user should identify the failed drive through the FastBuild
.
Setup
utility, and then replace the problem drive.
Offline
- A striped array has 1 drive that has failed or been disconnected. When the array
condition is “offline,” the user must replace the failed drive(s), then restore data from a backup
source.
69
Page 76

Raid Introduction
Navigating t he FastBuild™ Setup Menu
When using the menus, these are some of the basic navigation tips: Arrow keys highlights
through choices; [Space] bar key allows to cycle through options;
[Enter] key selects an option; [ESC] key is used to abort or exit the current menu.
Using the Main Menu
This is the first option screen when entering the FastBuildTM Setup.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
Auto Setup.......................................................[ 1 ]
View Drive Assignments...................................[ 2 ]
View Array .......................................................[ 3 ]
Delete Array.....................................................[ 4 ]
Rebuild Array...................................................[ 5 ]
Controller Configuration...................................[ 6 ]
[ Keys Available ]
Press 1...6 to Select Option [ESC] Exit
[ Main Menu ]
To create a new array automatically, follow the steps under “Creating Arrays Automatically” on
page 71. Promise recommends this option for most users.
To view drives assigned to arrays, see “Viewing Drive Assignments” on page 73.
To delete an array (but not delete the data contained on the array), select “Deleting An Array” on
page 80.
To rebuild a mirrored array, see “Rebuilding an Array” on page 82.
To view controller settings, see “Viewing Controller Configuration” on page 84.
NOTE: After configuring an array using FastBuild, you should FDISK and
format the arrayed drive(s) if you are using new, blank drives. Depending on
the type of array you are using.
70
Page 77

7DXR Motherboard
Creating Arrays Automatically
The Auto Setup <1> selection from the Main Menu can intuitively help create your disk array. It
will assign all available drives appropriate for the disk array you are creating. After making all
selections, use Ctrl-Y to Save selections. FastBuild will automatically build the array.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[Auto Setup Options Menu]
Opt i mize Array for: Perform ance
Typical Application usage: A/V Editing
[ Auto Setup Configuration ]
Mode.................................................Stripe
Spare Drive Count....................................0
Drives used in Ar r a y.................................2
Array Disk Capacity..........................16126
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [←, →, Space] Change Option [ESC] Exit [Ctrl-Y] Save
Optimize Array For
Select whether you want Performance (RAID 0), Security (RAID 1) under the “Optimize Array
for” setting.
Performance (RAID 0 Striping)
Supports the maximum performance. The storage capacity equals the number of drives
times the capacity of the smallest drive in the disk array.
NOTE: This motherboard permits striped arrays using 1, 2 drive attached in Auto Setup
mode.
Security (RAID 1 Mirroring)
Creates a mirrored (or fault tolerant) array for data security.
NOTE: Under the Security setting, This motherboard permits two drives to be used for a
single Mirrored array only.
71
Page 78

Raid Introduction
Defining Typical Application Usage
Allows the user to choose the type of PC usage that will be performed in order to optimize
how
This motherboard
handles data blocks to enhance performance. Your choice will determine
the block size used. You may choose from: A/V Editing (for audio/video applications, or any
similar application that requires large file transfers), Server (for numerous small file transfers), or
Desktop (a combination of large and small file sizes).
Creating Multiple Disk Arrays
1. If you plan to create multiple arrays, attach only the drives necessary to create the first disk
array and complete the <1> Auto Setup.
2. Install the additional drives needed for the second array and again use the <1> Auto
Setup.
NOTE: If you wish to customize the settings of individual disk arrays (such as block size), you
must manually create disk arrays with the Define Array <3> option from the Main Menu.
72
Page 79

7DXR Motherboard
Viewing Drive Assignments
The View Drive Assignments <2> option in the Main Menu displays whether drives are assigned
to a disk arrays or are unassigned.
Under the “Assignment” column, drives are labeled with their assigned disk array or shown as
“Free” if unassigned. Such “Free” drives can be used for a future array. Unassigned drives are
not accessible by the OS. The menu also displays the data transfer mode that relates to
speed used by each drive (U5 refers to 100MB/sec transfers, U4 refers to 66MB/sec transfers,
etc...)
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ View Drive Assignments ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity(MB) Assignment Mode
1 : Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Array 1 U5
1 : Slave QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Free U5
2 : Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Array 1 U5
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit Mode (U=UDMA, P=PIO, D=DMA)
73
Page 80

Raid Introduction
Manually Creating an Array
The Define Array <3> option from the Main Menu allows users to begin the process of manually
defining the drive elements and RAID levels for one or multiple disk arrays attached to this
motherboard. Users will commonly create one or two drive arrays with the motherboard, though
1
the motherboard will support a maximum of four arrays
.
NOTE: For most installations, We recommends the <1> Auto Setup for easy disk array creation.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity(MB) Status
Array 1 Stripe 2 16126 Functional
Array 2 —— —— —— ——
Array 3 —— —— —— ——
Array 4 —— —— —— ——
Note: * — Bootable Array
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit [Enter] Select [Space] Change Boot Drive
[Define Array Menu]
[ Keys Available ]
1. To manually create an array from the Define Array Menu, use the arrow keys to highlight
the array number you wish to define, and press [Enter] to select.
2. The Define Array Definition Menu will next appear that allows drive assignments to the disk
array (see next page).
1
A user may use a single drive in either striping mode with system. In this rare scenario,
the motherboard will create an individual array ID but will offer conventional controller
performance, depending on the drive type. At a later time, a second drive can be added to
the array and the array re-created to s upport RAID 1 mirroring.
74
Page 81

7DXR Motherboard
Selecting Array Type
Under the Definition section of this menu, highlight the Array # for which you want to
1.
assign a RAID level.
Use the [Space] key to cycle through two array types: Performance (RAID 0 Striping),
2.
Security (RAID 1 Mirroring).
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ Define Array Definition Menu ]
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity(MB) Status
Array 1 Stripe 2 16126 Functional
Stripe Block: 64 KB
[ Drive Assignments ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB) Assignment
1 : Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Y
1 : Slave QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 N
2 : Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Y
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit [Space] Select [Ctrl-Y] Save
Selecting Stripe Block
For RAID 0 Striped arrays only, you may manually select the “stripe block size.” Use the
Spacebar to scroll through choices progressing as follows (1, 2, 4, 8 , 16 . . . 1024).
The size selected affects how montherboard sends and retrieves data blocks from the drives.
You will need to perform your own testing to determine how the data block size is affecting your
particular use of the array. In general, a larger block size is better when handling large data
transfers (such as in A/V editing or graphics) while a smaller block size is better when handling
e-mail and other common server data. The default is 64K.
Assigning Drive(s) to Array
1. Under the [ Drive Assignments ] section, highlight a drive using the [↑] Up [↓] keys.
2. With the [Space] bar key, change the Assignable option to “Y” to add the drive to the disk
array.
75
Page 82

Raid Introduction
3. Press <Ctrl-Y> to save the disk array information. Depending on the array type selected,
the following scenarios will take place:
a) If choosing a Striping array, the initial Define Array Menu screen will appear with the
arrays defined. From there you may ESC to exit and return to the Main Menu of
FastBuild.
b) If you selected a Mirroring array for two drives, there is an additional window that
appears as described in order to create the array. To do this you will use either two
brand new drives, or one drive that contains existing data that you wish to mirror.
Creating A Mirrored Array Using New Drives
As described in the Drive Assignments Option section above, if you selected a mirroring array
and wish to use two new assigned drives, follow the directions here.
1. After assigning new drives to a Mi rroring array and saving the info rmation with <Ctrl-Y>,
the window below will appear.
Do you want the disk image to be duplicated to another? (Yes/No)
Y - Create and Duplicate
N - Create Only
2. Press “N” for the Create Only option.
3. A window will appear almost immediately confirming that your Security array has been
created. Press any key to reboot the system
Array has been created.
<Press Any Key to Reboot>
Adding Fault Tolerance to an Existing Drive
This motherboard will create a mirrored array using an existing system drive with data. You must
assign the existing drive and another drive of same or larger capacity to the Mirroring array. The
BIOS will send the existing data to the new blank drive.
WARNING: Backup any necessary data before proceeding. Failure to follow this
accepted PC practice could result in data loss.
WARNING: If you wish to include your current bootable drive using the Windows
NT 4.x or Windows 2000 operating system as part of a bootable Mirrored (RAID
1) array on your system, do NOT connect the hard drive to the system controller
yet. You MUST install the Windows NT4 or 2000 driver software first (see RAID
Manual of the TUCD) to this drive while it is still attached to your existing hard drive controller.
For all other Operating Systems, proceed here.
76
Page 83

7DXR Motherboard
After assigning the drives to a Mirroring array, press <Ctrl-Y> keys to Save your selection. The
window below will appear.
Do you want the disk image to be duplicated to another? (Yes/No)
Y - Create and Duplicate
N - Create Only
1. Press “Y” for the Create and Duplicate option. The window below will appear asking you to
select the Source drive to use. FastBuild will copy all data from the Source drive to the
Target drive.
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
[Please Select A S ource Disk]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
1 :Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063
2 :Master QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063
[↑] Up [↓] [ESC] Exit [Ctrl-Y] Save
Source Disk
Target Disk
2. Use the arrow keys to choose which drive contains the existing data to be
copied.
WARNING: All target drive data will be erased. Make sure you choose the correct
drive.
3. Press [Ctrl-Y] keys to Save selection and start duplication. The following confirmation
screen will appear.
Start to duplicate the image . . .
Do you want to continue? (Yes/No)
Y – Continue N - Abort
4. Select “Y” to continue. If you choose “N” , you will be returned to step 1.
5. Once “Y” is selected, the following progress screen will appear. The process will take a few
minutes.
Please Wait While Duplicating The Image
10% Complete
77
Page 84

Raid Introduction
6. Once mirroring is complete, the following screen will appear confirming that your Security
array has been created. Press any key to reboot the system
Array has been created.
<Press Any Key to Reboot>
Making a Disk Array Bootable
WARNING: In order for you to boot from an array on the system, your PC or
server must be configured in the CMOS Setup to use the system as a bootable
device (versus the onboard controller). This option is not available if the system is
being used as a secondary controller.
1. Once you have returned to the Define Array Menu window (bel o w), you will see the array(s)
you have created. You now may use the menu to select whic h previ ousl y-defi ned ar ray wi l l
be used as the bootable array.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx DELL (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity(MB) Status
* Array 1 Stripe 2 13044 Functional
Note: * — Bootable Array
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit [Enter] Select [Space] Change Boot Drive
[ Define Array Menu ]
2. Highlight the array which you want to boot from using the [↑] Up [↓] Down keys.
3. Press the [Space] bar key.
4. An * asterisk will appear next to the array number indicating it as bootable. The system will
now recognize this array as the first array seen
5. The system will then use this bootable array as the (fixed) boot C: drive.
NOTE: The bootable array must contain your configured operating system.
78
Page 85

7DXR Motherboard
How Orders Arrays
During startup, the disk arrays on the motherboard are recognized in this order: 1) The array set
to bootable in the FastBuildTM Setup, and 2) the Array number (i.e. Array 0, Array 1…).
This would be involved in determining which drive letters will be assigned to each disk array.
How Saves Array Information
All disk array data is saved into the reserved sector on each array member. We suggests that
users record their disk array information for future reference.
Another feature of the motherboard disk array system is to recognize drive members even if
drives are moved between different motherboard connectors(IDE3&IDE4). Since each drive’s
array data identifies itself to the array, it is possible to move or swap drives without modifying the
array setup. This is valuable when adding drives, or during a rebuild.
79
Page 86

Raid Introduction
Deleting An Array
The Delete Array <4> Menu option allows for deletion of disk array assignments. This is not the
same as deleting data from the drives themselves. If you delete an array by accident (and
before it has been used again), the array can normally be recovered by defining the array
identically as the deleted array.
WARNING: Deleting an existing disk array could result in its data loss. Make
sure to record all array information including the array type, the disk members,
and stripe block size in case you wish to undo a deletion.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ Delete Array Menu ]
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity(MB) Status
Array 1 Mirror 2 8063 Functional
Array 2 Stripe 1 8063 Functional
Array 3 Stripe 1 8063 Functional
Array 4 —— —— —— ——
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit [Del] Delete
1. To delete an array, highlight the Array you wish to delete and press the [Del] key.
2. The View Array Definition menu will appear (see below) showing which drives are
assigned to this array.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ Define Array Menu ]
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity(MB) Status
Array 1 Mirror 2 8063 Functional
Stripe Block: 64 KB
[ Drive Assignments ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB) Assignment
1 : MasterQUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Y
2 : MasterQUANTUMCR8.4A 8063 Y
80
Page 87

7DXR Motherboard
3. Confirm yes to the following warning message with the <Ctrl-Y> key to continue array
deletion:
Are you sure you want to delete this array?
Press Ctrl-Y to Delet e, others to Abort
4. After deleting the array, you should create a new array using Auto Setup or the Define
Array menu from the FastBuild Main Menu.
81
Page 88

Raid Introduction
Rebuilding A Mirrored Array
The Rebuild Array <5> Menu option is necessary to recover from an error in a mirrored disk
array. You will receive an error message when booting your system from the BIOS.
NOTE: Drives MUST be replaced if they contain any physical errors.
Follow these steps BEFORE using the Rebuild Array menu option:
1. On bootup, the system Startup BIOS will display an error message identifying which drive
has failed.
2. Press <Ctrl-F> keys to enter FastBuild Main Menu.
3. Select submenu Define Array <3>.
4. Select the failed array and identify the Channel and ID of the failed drive.
5. Power off and physically remove the failed drive.
6. Replace the drive with an identical model.
7. Reboot the system and enter the FastBuild Main Menu.
8. Select the <5> Rebuild Array option. The following screen will appear.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ Rebuild Array Menu ]
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Capacity(MB) Status
Array 1 Mirror 2 16126 Critical
Array 2 Stripe 1 8063 Functional
Array 3 Stripe 1 8063 Functional
Array 4 —— —— —— ——
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit [Enter] Select
9. Highlight the array whose Status is “Critical”.
10. Press [Enter]. The following screen will then appear (see next page).
82
Page 89

7DXR Motherboard
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ Rebuild Array Menu ]
Array No RAID Mode Total Drv Status
Array 2 Mirror 2 Critical
Stripe Block: Not Available
[ Select Drive for Rebuild ]
Channel:ID Drive Model Capacity (MB)
1 : Slave QUANTUMCR8.4A 8063
[ Keys Available ]
[↑] Up [↓] Down [ESC] Exit [Enter] Select
11. Under [Select Drive for Rebuild], highlight the replacement drive.
12. Press [Enter] and confirm that the data will be copied on to the selected drive. All data on
the replacement drive will be written over with mirror ed information from the array drive. A
progress bar will appear as below.
Please Wait While Duplicating The Image
10% Complete
13. Once the rebuild process is complete, the user will be asked to reboot the system.
83
Page 90

Raid Introduction
Viewing Controller Settings
The Controller Configuration <6> menu selection allows you to enable or disable the BIOS from
halting (the default) if it detects an error on boot up. You may also view the system resources
(Interrupt and I/O port address) of data channels.
FastBuild (tm) Utility 1.xx (c) 1995-2000 Promise Technology, Inc.
[ Adapter Configuration - Options ]
Halt On Error: Enable
[ System Resources Configuration ]
Channel 1 (IDE1) Interrupt : A I/O P ort : FFF0
Channel 2 (IDE2) Interrupt : A I/ O P ort : FFA8
[ Keys Available ]
[←, →, Space] Change Option [ESC] Exit
Halting BIOS On Bootup Errors
The [Adapter Configuration – Options] section allows you to enable or disable The system to
Halt operation at the BIOS startup screen should an error be detected. This is the only option
that can be changed on this screen.
Viewing System Resources
The [System Resources Configuration] section of this submenu displays the PCI slot interrupt
and port address used by the system. The resources used are determined by the Mainboard
PCI PnP BIOS for the PCI slot in which the system re sides.
In the rare case that there is a resource conflict, refer to the Mainboard BIOS documentation on
changes on resources allocated to the system PCI slot.
84
Page 91

7DXR Motherboard
Page Index for BIOS Setup Page
The Main Menu P.87
Standard CMOS Features P.90
Advanced BIOS Features P.94
Advanced Chipset Features P.96
Integrated Peripherals P.100
Power Management Setup P.105
PnP / PCI Configurations P.109
PC Health Status P.111
Frequency / Voltage Control P.113
Load Fail-Safe Defaults P.114
Load Optimized Defaults P.115
Set Supervisor / User Password P.116
Save & Exit Setup P.117
EXIT Without Saving P.118
85
Page 92

BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup
BIOS Setup is an overview of the BIOS Setup Interface. The interface allows users to modify the
basic system configuration, which is stored in battery-backed CMOS RAM so that the Setup
information can be retained when the power is turned off.
ENTERING SETUP
Power ON the computer and press <Del> immediately will allow you to enter Setup. If
unsuccessful, you can restart the system and try again by pressing the "RESET" bottom on the
system case. You may also restart by simultaneously pressing <Ctrl> − <Alt>− <Del> keys.
CONTROL KEYS
<↑> Move to previous item
<↓> Move to next item
<←> Move to the item in the left hand
<→> Move to the item in the right hand
<Esc> Main Menu - Quit and not save changes into CMOS
Status Page Setup Menu and Option Page Setup Menu - Exit current page
and return to Main Menu
<+/PgUp> Increase the numeric value or make changes
<-/PgDn> Decrease the numeric value or make changes
<F1> General help, only for Status Page Setup Menu and Option Pa ge Setup
Menu
<F2> Reserved
<F3> Reserved
<F4> Reserved
<F5> Restore the previous CMOS value from CMOS, only for Option Page
Setup Menu
<F6> Load the default CMOS value f rom BIOS default table, only for Option
Page Setup Menu
<F7>
<F8> Reserved
<F9> Reserved
<F10> Save all the CMOS changes, only for Main Menu
Load the Optimized Defaults
86
Page 93

7DXR Motherboard
GETTING HELP
Main Menu
The on-line description of the highlighted setup function is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Status Page Setup Menu / Option Page Setup Menu
Press F1 to pop up a small hel p window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the
possible selections for the highlighted item. To exit the Help Window press <Esc>.
The Main Menu
Once you enter Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu (Figure 1) will appear on the
screen. The Main Menu allows you to select from nine setup functions and two exit choices. Use
arrow keys to select among the items and press <Enter> to accept or enter the sub-menu.
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright( C ) 1984-2000 Award Software
Standard CMOS Features
Advanced BIOS Features Load Fail-Safe Defaults
Advanced Chipset Features Load Optimized Defaults
Integrated Peripherals Set Supervisor Password
Power Management Setup Set User Password
PnP/PCI Configurations Save & Exit Setup
PC Health Status Exit Without Saving
ESC:Quit
F10:Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type…
Figure 1: Main Menu
Frequency/Voltage Control
: Select Item
↑↓→ ←
87
Page 94

BIOS Setup
Standard CMOS Features
••••
This setup page includes all the adjustable items in standard compatible BIOS.
Advanced BIOS Features
••••
This setup page includes all the adjustable items of Award special enhanced features.
Advanced Chipset Features
••••
This setup page includes all the adjustable items of chipset special features.
Integrated Peripherals
••••
This setup page includes all onboard peripherals.
Power Management Setup
••••
This setup page includes all the adjustable items of Green function features.
PnP/PCI Configurations
••••
This setup page includes all the adjustable configurations of PCI & PnP ISA resources.
PC Health Status
••••
This setup page is for monitoring system status such as temperature, voltage, and fan
speed.
Frequency/Voltage Control
••••
This setup page is for controlling CPU clock and frequency ratio.
Load Fail-Safe Defaults
••••
Load Fail-Safe Defaults option l oads preset system parameter value s to set the system in
its most stable configurations.
Load Optimized Defaults
••••
Load Optimized Defaults option loads preset system parameter values to set the system in
its highest performance configurations.
Set Supervisor Password
••••
Set Change or disable password. It allows you to limit access to the system and/or BIOS
setup.
88
Page 95

7DXR Motherboard
Set User Password
••••
Set Change or disable password. It allows you to limit access to the system.
Save & Exit Setup
••••
Save CMOS value settings to CMOS and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
••••
Abandon all CMOS value changes and exit setup.
89
Page 96

BIOS Setup
Standard CMOS Features
The items in Standard CMOS Setup Menu (Figure 2) are divided into 9 categories. Each
category includes none, on e or m ore than one s etup it ems. Us e the a rrow s to highl ight the item
and then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to select the value in each item.
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright( C ) 1984-2000 Award Software
Date (mm:dd:yy) Wed , Feb 28 2001 Item Help
Time (hh:mm:ss) 2 : 31 : 24
IDE Primary Master None
IDE Primary Slave None
IDE Secondary Master None
IDE Secondary Slave None
century
Drive A 1.44M, 3.5 in.
Drive B None
Floppy 3 Mode Support Disabled
Video EGA / VGA
Halt On All, But Keyboard
Base Memory Size 640K
Extended Memory Size 63488K
Total Memory 64512K
Standard CMOS Features
Menu Level
Change the
Day, month,
Year and
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
↑↓→ ←
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Figure 2: Standard CMOS Features
Date
••••
The date format is <week>, <month> <day> <year>.
Week The week, from Sun to Sat, determined by the BIOS and is display-only
Month The month, Jan. Through Dec.
Day The day, from 1 to 31 (or the maximum allowed in the month)
Year The year, from 1994 through 2079
90
Page 97

7DXR Motherboard
Time
••••
The times format in <hour> <minute> <second>. The time is calculated based on the
24-hour military-time clock. For example, 1 p.m. is 13:00:00.
IDE Primary Master / Slave, Secondary Master / Slave
••••
The category identifies the type of hard disk from drive C to F that has been installed in the
computer. There are two settings: Auto, and Manual. Ma nual: HDD ty pe is user-d efinable;
Auto will automatically detect HDD type.
Note that the specifications of your drive must match with the drive table. The hard disk will
not work properly if you enter improper information for this category.
If you select User Type, related information will be asked to enter to the following items.
Enter the information directly from the keyboard and press <Enter>. Such information
should be provided in the documentation form your hard disk vendor or the system
manufacturer.
CYLS. Number of cylinders
HEADS number of heads
PRECOMP write precomp
LANDZONE Landing zone
SECTORS number of sectors
If a hard disk has not been installed select NONE and press <Enter>.
Drive A / Drive B
••••
The category identifies the ty pe of floppy disk drive A or dri ve B that has been install ed in
the computer.
None No floppy drive installed
360K, 5.25 in. 5.25 inch PC-type standard drive; 360K byte capacity.
1.2M, 5.25 in. 5.25 inch AT-type high-density drive; 1.2M byte c apacity (3.5 inch
when 3 Mode is Enabled).
720K, 3.5 in. 3.5 inch double-sided drive; 720K byte capacity
1.44M, 3.5 in. 3.5 inch double-sided drive; 1.44M byte capacity.
2.88M, 3.5 in. 3.5 inch double-sided drive; 2.88M byte capacity.
91
Page 98

Floppy 3 Mode Support (for Japan Area)
••••
BIOS Setup
Disabled Normal Floppy Drive.
Drive A Drive A is 3 mode Floppy Drive.
Drive B Drive B is 3 mode Floppy Drive.
Both Drive A & B are 3 mode Floppy Drives.
Video
••••
The category detects the type of adapter used for the primary system monitor, which must
match your video display card and moni tor. Although secondary monitors are s upported,
you do not have to select the type in setup.
EGA/VGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter/Video Graphics Array. For EGA, VGA,
SVGA, or PGA monitor adapters
CGA 40 Color Graphics Adapter, power up in 40 column mode
CGA 80 Color Graphics Adapter, power up in 80 column mode
MONO Monochrome adapter, includes high resolution monochrome adapters
Halt on
••••
The category determines whether the computer will stop if an error is detected during
power up.
NO Errors The system boot will not stop for any error that may be detected.
All Errors The system boot will stop on any error detected.
All, But Keyboard The system boot will not stop for a keyboard error; it will stop for
all other errors.
All, But Diskette The system boot will not stop for a disk error; it will stop for all
other errors.
All, But Disk/Key The system boot will not stop for a keyboard or disk error; it will
stop for all other errors.
(Default value)
(Default value)
92
Page 99

7DXR Motherboard
Memory
••••
The category is display-onl y which is determined by POST (Power On Self Test) of the
BIOS.
Base Memory Size
Extended Memory Size
The POST of the BIOS will determine the amount of base (or conventional)
memory installed in the system.
640 K for systems with 640 K or more memory installed on the motherboard.
The BIOS determines how much extended memory is present during the POST.
This is the amount of memory located above 1 MB in the CPU's memory
address map.
93
Page 100

Advanced BIOS Features
BIOS Setup
CMOS Setup Utility-Copyright( C ) 1984-2000 Award Software
Virus Warning Disabled Item Help
First Boot Device Floppy
Second Boot Device IDE-0
Third Boot Device CDROM
RAID/SCSI Boot Order RAID, SCSI
Ú
Floppy Drive Seek Disabled
BootUp Num-Lock On
Password Check Setup
HDD S.M.A.R.T Capability Disabled
:Move Enter:Select +/-/PU/PD:Value F10:Save ESC:Exit F1:General Help
↑↓→ ←
F5:Previous Values F6:Fail-Safe Defaults F7:Optimized Defaults
Advanced BIOS Features
Menu Level
Allows you to
choose the VIRUS
Warning feature
For IDE Hard disk
Boot sector
Protection. If this
Function is enable
And someone
Attempt to write
Data into this area
, BIOS will show
A warning
Message on
Screen and alarm
beep
Figure 3: Advanced BIOS Features
This item will be available when ”
Ú
Virus Warning
••••
First / Second / Third Boot device” is set to SCSI/RAID.
If it is set to enable, a warning will be displayed on the screen when there is any attempt to
write to the boot sector or partition table of the hard disk drive. The system will halt and the
following error message will appear in the mean time. You can run anti-virus program to
locate the problem.
Enabled Activates virus protection and displays a warning message whenever
anything attempts to write to the boot sector or the hard disk partition
table.
Disabled No warning message appears when anything attempts to write to the
boot sector or hard disk partition table.
(Default value)
First / Second / Third Boot Device
••••
Floppy Set your boot device priority to Floppy.
LS120 Set your boot device priority to LS120.
94
 Loading...
Loading...