Gigabyte F71872F rev.027P Schematics

F71872F/FG
F71872
Super H/W Monitor + LPC IO
Release Date: Dec., 2006
Revision: V0.27P
F71872 Dec., 2006
V0.27P

F71872 Datasheet Revision History
Version Date Page Revision History
0.20P 07/07/2004 - Preliminary Release Version.
0.21P 07/28/2004 - Revise PWM Frequency Range
0.22P 10/12/2004 - Added BEEP/LED_VCC/LED_VSB/FANCTL Functions.
- Modified Application Circuit.
0.23P 02/25/2005 - Added 24MHz Clock Input.
0.24P 04/15/2005 109 Added “Green Package” Ordering Information.
0.25P 08/16/2005 - Added VID_OTF# Function for Vcore OTF use.
0.26P 09/05/2005 111 Updated Application Circuit.
F71872
0.27P 12/28/2006 5 Added Patent Note.
Please note that all data and specifications are subject to change without notice. All the trade marks of products and
companies mentioned in this data sheet belong to their respective owners.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Customers using or selling these products for use
in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Fintek for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sales.
F71872 Dec., 2006
V0.27P

F71872
Table of Contents
1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION.........................................................................................................................................................4
2 FEATURES....................................................................................................................................................................................4
3 KEY SPECIFICATIONS..............................................................................................................................................................5
4 PIN CONFIGURA T ION...............................................................................................................................................................6
5 PIN DESCRIPTIONS ...................................................................................................................................................................6
5.1 POWER PIN.........................................................................................................................................................................6
5.2 LPC INTERFACE.................................................................................................................................................................6
5.3 FDC...................................................................................................................................................................................8
5.4 UART PORT AND SIR.........................................................................................................................................................8
5.5 KBC I/F.............................................................................................................................................................................9
5.6 IEEE 1284 PARALLEL PORT .............................................................................................................................................10
5.7 H/W MONITOR.................................................................................................................................................................11
5.8 ACPI FUNCTION PINS.......................................................................................................................................................12
5.9 VID CONTROLLING PINS...................................................................................................................................................13
6 FUNCTION DESCRIPTION .....................................................................................................................................................14
6.1 POWER ON STRAPPING OPTIONS.......................................................................................................................................14
6.2 ACPI................................................................................................................................................................................14
6.3 PCI RESET AND PWROK SIGNALS ..................................................................................................................................16
6.4 HARDWARE MONITOR......................................................................................................................................................16
6.5 FDC.................................................................................................................................................................................23
6.6 UART..............................................................................................................................................................................24
6.7 PARALLEL PORT ...............................................................................................................................................................24
6.8 KEYBOARD CONTROLLER ................................................................................................................................................24
6.9 DYNAMIC VOLTAGE CHANGE APPLICATION .....................................................................................................................25
7 REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS....................................................................................................................................................27
7.1 GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTERS.........................................................................................................................................27
7.1.1 Software Reset Register Index 02h....................................................................................................................................27
7.1.2 Logic Device Number Register Index 07h.........................................................................................................................27
7.1.3 Chip ID Register Index 20h............................................................................................................................................... 28
7.1.4 Chip ID Register Index 21h............................................................................................................................................... 28
7.1.5 Vendor ID Register Index 23h ...........................................................................................................................................28
1
Dec., 2006
V0.27P

F71872
7.1.6 Vendor ID Register Index 24h ...........................................................................................................................................28
7.1.7 Software Power Down Register Index 25h........................................................................................................................28
7.1.8 UART IRQ Sharing Register Index 26h ............................................................................................................................ 29
7.1.9 Port Select Register Index 27h........................................................................................................................................... 29
7.1.10 Power LED Function Select Register Index 28h................................................................................................................29
7.1.11 Multi Function Select 1 Register Index 29h (Powered by VDD).......................................................................................30
7.1.12 Multi Function Select 2 Register Index 2Ah (Powered by VDD)...................................................................................... 31
7.1.13 Multi Function Select 3 Register Index 2Bh (Powered by VDD)......................................................................................32
7.1.14 Multi Function Select 4 Register Index 2Ch (Powered by VSB3V)..................................................................................32
7.1.15 Multi Function Select 5 Register Index 2Dh (Powered by VSB3V)..................................................................................33
7.2 FDC REGISTERS...............................................................................................................................................................34
7.2.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................34
7.2.2 FDC Configuration Registers...................................................................................................................................................34
7.2.3 Device Registers......................................................................................................................................................................37
7.3 UART1 REGISTERS..........................................................................................................................................................52
7.3.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................52
7.3.2 UART 1 Configuration Registers.............................................................................................................................................52
7.3.3 Device Registers......................................................................................................................................................................53
7.4 UART 2 REGISTERS .........................................................................................................................................................56
7.4.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................56
7.4.2 UART 2 Configuration Registers.............................................................................................................................................57
7.4.3 Device Registers......................................................................................................................................................................58
7.5 PARALLEL PORT REGISTERS .............................................................................................................................................62
7.5.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................62
7.5.2 Parallel Port Configuration Register........................................................................................................................................ 62
7.5.3 Device Registers......................................................................................................................................................................63
7.6 HARDWARE MONITOR REGISTERS....................................................................................................................................67
7.6.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................67
7.6.2 Hardware Monitor Configuration Registers............................................................................................................................. 68
7.6.3 Device Registers......................................................................................................................................................................69
7.7 KEYBOARD REGISTER......................................................................................................................................................88
7.7.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................88
7.7.2 KBC Configuration Registers..................................................................................................................................................89
7.7.3 Device Registers......................................................................................................................................................................90
7.8 GPIO REGISTERS .............................................................................................................................................................91
7.8.1 Logic Device Number Register................................................................................................................................................91
7.8.2 Configuration Registers ...........................................................................................................................................................92
2
Dec., 2006
V0.27P

F71872
7.9 VID REGISTER ...............................................................................................................................................................100
7.9.1 Logic Device Number Register..............................................................................................................................................100
7.9.2 VID Configuration Registers .................................................................................................................................................100
7.9.3 Device Registers....................................................................................................................................................................101
7.10 ACPI AND PME REGISTERS ...........................................................................................................................................103
7.10.1 Logic Device Number Register..............................................................................................................................................103
7.10.2 ACPI and PME Configuration Registers................................................................................................................................104
8 PCB LAYOUT GUIDE..............................................................................................................................................................106
9 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS...................................................................................................................................108
9.1 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATIN GS .....................................................................................................................................108
9.2 DC CHARACTERISTICS...................................................................................................................................................108
9.3 AC CHARACTERISTICS...................................................................................................................................................109
10 ORDERING INFORMATION..............................................................................................................................................109
11 PACK AGE D IMEN SIONS....................................................................................................................................................110
12 F71872 DEMO CIRCUIT......................................................................................................................................................111
3
Dec., 2006
V0.27P

1 General Description
The F71872 is the featured IO chip specifically for PC system. Equipped with one IEEE 1284 parallel
port , two UART port and FDC. The F71872 provides SIR and key board controller compatible with PS/2
keyboard and mouse as well, integrated with hardware monitor, supports 11 sets of voltage sensor and 4
voltage fault signal outputs, 3 sets of creative auto-controlling fans and 3 temperature sensor pins for the
accurate current type temp. Measurement for CPU thermal diode or external transistors 2N3906.
The F71872 provides flexible features for multi-directional application. For instance, supports CPU VID
(Intel CPU On The Fly) controlling and comply with VRM10.0, provides 24 GPIO pins which include
pulse/level mode selection, IRQ sharing function also designed in UART feature for particular usage and
F71872
accurate current mode H/W monitor will be worth in measurement of temperature.
Furthermore, the F71872 supports an automatic/dynamic over-voltage function (Vcore change) for
application of over-clocking or under clocking. This function provides a pin (VID_OTF#) by external trigger
signal to improve the CPU’s performance by voltage (Vcore) changing automatically when system is going to
run over-clocking or under-clocking. Due to achieve this action, suggest F75133S Loading Gauge can be the
part detects system/CPU loading to decide when issues the over-clocking/under-clocking and dynamic
signals for system executing. Briefly, user can gain more features on motherboard by these two parts which
improve performance and efficiency.
The F71872 is powered by 3.3V voltage, with the LPC interface in the package of 128-QFP.
2 Features
General Functions
¾ Comply with LPC Spec. 1.0
¾ Support DPM (Device Power Management), ACPI
¾ Support CPU VID (Intel CPU On The Fly) controlling and comply with VRM10.0
¾ Vcore monitoring supports dynamic VID
¾ Support automatic and dynamic vcore change function for over/under clocking use
¾ 24 GPIO Pins for flexible application
¾ 24/48 MHz clock input
FDC
¾ Compatible with IBM PC AT disk drive systems
¾ Variable write pre-compensation with track selectable capability
¾ Support vertical recording format
¾ DMA enable logic
¾ 16-byte data FIFOs
¾ Support floppy disk drives and tape drives
¾ Detects all overrun and under run conditions
¾ Built-in address mark detection circuit to simplify the read electronics
¾ Completely compatible with industry standard 82077
¾ 360K/720K/1.2M/1.44M/2.88M format; 250K, 300K, 500K, 1M, 2M bps data transfer rate
4
Dec., 2006
V0.27P

UART
Infrared
Parallel Port
F71872
¾ Two high-speed 16C550 compatible UART with 16-byte FIFOs
¾ Fully programmable serial-interface characteristics
¾ Baud rate up to 115.2K
¾ Support IrDA version 1.0 SIR protocol with maximum baud rate up to 115.2K bps
¾ One PS/2 compatible bi-directional parallel port
¾ Support Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) − Compatible with IEEE 1284 specification
¾ Support Extended Capabilities Port (ECP) − Compatible with IEEE 1284 specification
¾ Enhanced printer port back-drive current protection
Keyboard Controller
¾ 8042 based with optional F/W from AMIKKEYTM-2, with 2K bytes of programmable ROM,
and 256 bytes of RAM
¾ Asynchronous Access to Two Data Registers and One status Register
¾ Software compatibility with the 8042
¾ Support PS/2 mouse
¾ Support both interrupt and polling modes
¾ Fast Gate A20 and Hardware Keyboard Reset
¾ 6 MHz, 8 MHz, 12 MHz, or 16 MHz operating frequency
Hardware Monitor Functions
¾ 12 VID pins for VRM10.0 and CPU VID OTF (On The Fly)
¾ 3 current type accurate (±3) ℃ thermal inputs for CPU thermal diode and 2N3906 transistors
¾ 11 sets voltage monitoring (8 external and 3 internal powers)
¾ 4 voltage_fault# hardware signal outputs
¾ 3 fan speed monitoring inputs
¾ 3 fan speed auto-control (support 3 wire and 4 wire fans)
¾ Case intrusion detection circuit
¾ WATCHDOG comparison of all monitored values
¾ Issue PME# and independent Voltage_fault #
Package
¾ 128-pin PQFP
Noted: Patented TW207103 TW207104 US6788131 B1 TW235231 TW237183 TWI263778
3 Key Specifications
Supply Voltage 3.0V to 3.6V
Operating Supply Current 10 mA typ.
Power Down Current (Suspension Mode) 6 mA typ.
5
Dec., 2006
V0.27P

4 Pin Configuration
F71872
5 Pin Descriptions
F71872
I/O
- TTL level bi-directional pin with 12 mA source-sink cap ability.
12t
I/OOD
I/OOD
- TTL level bi-directional pin, can select to OD or OUT by register, with 12 mA source-sink
12t
capability.
- TTL level bi-directional pin, can select to OD or OUT by register, with 16 mA source-sink
16t
6
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
capability.
F71872
I/OD
12t
I/OD
12ts5V
I/O
12ts5V
I/OD
16t,5V
I/O
8t-u47,5V
O
- Output pin with 12 mA source-sink capability.
12
- TTL level bi-directional pin, Open-drain outpu with 12 mA sink capability.
- TTL level bi-directional pin and schmitt trigger, Open-drain output with 12 mA sink capability,
5V tolerance.
- TTL level bi-directional pin and schmitt trigger with 12 mA sink capability, 5V tolerance.
- TTL level bi-directional pin, Open-drain outpu with 16 mA sink capability, 5V tolerance.
- TTL level bi-directional pin with 8 mA sink capability, pull-up 47k ohms, 5V tolerance.
AOUT - Output pin(Analog).
OD
12
OD
16-u10,5V
OD
24
IN
t5V
INts
IN
- TTL level input pin and schmitt trigger, 5V tolerance.
ts5V
- Open-drain output pin with 12 mA sink capability.
- Open-drain output pin with 16 mA sink capability, pull-up 10k ohms, 5V tolerance.
- Open-drain output pin with 24 mA sink capability.
- TTL level input pin,5V tolerance.
- TTL level input pin and schmitt trigger.
AIN - Input pin(Analog).
P - Power.
5.1 Power Pin
Pin No. Pin Name Type Description
4,35,99 VCC P Power supply voltage input with 3.3V
67 VSB P Stand-by power supply voltage input 3.3V
69 VBAT P Battery voltage input
86 AGND(D-) P Analog GND
15,50,74, 117 GND P Digital GND
5.2 LPC Interface
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
37 LRESET# INts VCC Reset signal. It can connect to PCIRST# signal on the host.
38 LDRQ# O12 VCC Encoded DMA Request signal.
39 SERIRQ I/O
40 LFRAM# INts VCC Indicates start of a new cycle or termination of a broken
41-44 LAD[3:0] I/O
47 PCICLK INts VCC 33MHz PCI clock input.
49 CLKIN INts VCC System clock input. According to the input frequency
VCC Serial IRQ input/Output.
12t
cycle.
VCC These signal lines communicate address, control, and data
12t
information over the LPC bus between a host and a
peripheral.
24/48MHz.
7
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
5.3 FDC
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
51
52
54 DRVA# OD24 VCC Drive Select A. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive A.
56 WDATA# OD24 VCC Write data. This logic low open drain writes
57 DIR# OD24 VCC Direction of the head step motor. An open drain output.
58 STEP# OD24 VCC Step output pulses. This active low open drain output
59 HDSEL# OD24 VCC Head select. This open drain output determines which disk
60 WGATE# OD24 VCC Write enable. An open drain output.
61 RDATA# IN
62 TRK0# IN
63 INDEX# IN
64 WPT# IN
65 DSKCHG# IN
DENSEL#
OD24 VCC Drive Density Select.
Set to 1 - High data rate.(500Kbps, 1Mbps)
Set to 0 – Low data rate. (250Kbps, 300Kbps)
OD24 VCC Motor A On. When set to 0, this pin enables disk drive 0.
MOA#
This is an open drain output.
This is an open drain output.
pre-compensation serial data to the selected FDD. An open
drain output.
Logic 1 = outward motion
Logic 0 = inward motion
produces a pulse to move the head to another track.
drive head is active.
Logic 1 = side 0
Logic 0 = side 1
VCC The read data input signal from the FDD.
ts5V
VCC Track 0. This Schmitt-triggered input from the disk drive is
ts5V
active low when the head is positioned over the outermost
track.
VCC This Schmitt-triggered input from the disk drive is active low
ts5V
when the head is positioned over the beginning of a track
marked by an index hole.
VCC Write protected. This active low Schmitt input from the disk
ts5V
drive indicates that the diskette is write-protected.
VCC Diskette change. This signal is active low at power on and
ts5V
whenever the diskette is removed.
F71872
5.4 UART Port and SIR
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
118 DCD1# IN
119 RI1# IN
120 CTS1# IN
O12 Infrared Transmitter Output. 66 IRTX/GPIO16
I/O
12t
INts Infrared Receiver input. 70 IRRX/GPIO30
I/OOD
t5V
VCC
General Purpose IO
VSB
12t
General Purpose IO. Open drain and drive select by register.
VCC Data Carrier Detect. An active low signal indicates the
modem or data set has detected a data carrier.
VCC Ring Indicator. An active low signal indicates that a ring
t5V
signal is being received from the modem or data set.
VCC Clear To Send is the modem control input.
t5V
8
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
F71872
121 DTR1#/ KBC_EN I/O
122 RTS1# I/O
123 DSR1# IN
124 SOUT1/
I/O
Config4E_2E
125 SIN1 IN
126 DCD2# IN
127 RI2# IN
128 CTS2# IN
1 DTR2# / RST_DRV I/O
8t-u47,5V
VCC
UART 1 Data Terminal Ready. An active low signal informs
the modem or data set that controller is ready to
communicate. Internal 47k ohms pulled high and disable
after power on strapping.
Power on strapping : 1 (Default) KBC Enable
0 KBC Disable
VCC UART 1 Request To Send. An active low signal informs the
8t-u47,5V
modem or data set that the controller is ready to send data.
Internal 47k ohms pulled high and disable after power on
strapping.
VCC Data Set Ready. An active low signal indicates the modem
t5V
or data set is ready to establish a communication link and
transfer data to the UART.
8t-u47,5V
VCC
UART 1 Serial Output. Used to transmit serial data out to
the communication link. Internal 47k ohms pulled high and
disable after power on strapping.
Power on strapping : 1 (Default) C
onfiguration register:4E
0 Configuration register:2E
VCC Serial Input. Used to receive serial data through the
t5V
communication link.
VCC Data Carrier Detect. An active low signal indicates the
t5V
modem or data set has detected a data carrier.
VCC Ring Indicator. An active low signal indicates that a ring
t5V
signal is being received from the modem or data set.
VCC Clear To Send is the modem control input.
t5V
8t-u47,5V
VCC
UART 2 Data Terminal Ready. An active low signal informs
the modem or data set that controller is ready to
communicate. Internal 47k ohms pulled high and disable
after power on strapping.
2 RTS2#/PWM_DC I/O
3 DSR2# IN
5 SOUT2
6 SIN2 IN
5.5 KBC I/F
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
45 KBRST# OD
Power on strapping : 1 (Default) : pin31/33/34/48/84 OD
0 Drive
8t-u47,5V
VCC
UART 2 Request To Send. An active low signal informs the
modem or data set that the controller is ready to send data.
Internal 47k ohms pulled high and disable after power on
strapping.
Power on strapping : 1 (Default) PWM Mode
0 Drive Linear Mode
VCC Data Set Ready. An active low signal indicates the modem
t5V
or data set is ready to establish a communication link and
transfer data to the UART.
I/O
VCC UART 2 Serial Output. Used to transmit serial data out to
8t-u47,5V
the communication link. Internal 47k ohms pulled high and
disable after power on strapping.
VCC Serial Input. Used to receive serial data through the
t5V
communication link.
VCC Keyboard reset. This pin is high after system reset. Internal
16-u10,5V
9
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
46 GA20 OD
80 KDAT I/OD
81 KCLK I/OD
82 MDAT I/OD
83 MCLK I/OD
16-u10,5V
5.6 IEEE 1284 Parallel Port
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
100 SLCT IN
101 PE IN
102 BUSY IN
103 ACK# IN
104 SLIN# I/OD
105 INIT#
106 ERR#
107 AFD# I/OD
108 STB# I/OD
109
110
111
112
113
114
I/O
PD0
I/O
PD1
I/O
PD2
I/O
PD3
I/O
PD4
I/O
PD5
ts5V
ts5V
ts5V
ts5V
I/OD
IN
ts5V
F71872
pull high 3.3V with 10k ohms. (KBC P20)
VCC Gate A20 output. This pin is high after system reset. Internal
pull high 3.3V with 10k ohms. (KBC P21)
VSB Keyboard Data.
16t,5V
VSB Keyboard Clock.
16t,5V
VSB PS2 Mouse Data.
16t,5V
VSB PS2 Mouse Clock.
16t,5V
VCC An active high input on this pin indicates that the printer is
selected. Refer to the description of the parallel port for
definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
VCC An active high input on this pin indicates that the printer has
detected the end of the paper. Refer to the description of the
parallel port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP
mode.
VCC An active high input indicates that the printer is not ready to
receive data. Refer to the description of the parallel port for
definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
VCC An active low input on this pin indicates that the printer has
received data and is ready to accept more data. Refer to the
description of the parallel port for the definition of this pin in
ECP and EPP mode.
VCC Output line for detection of printer selection. Refer to the
12ts5V
description of the parallel port for the definition of this pin in
ECP and EPP mode.
VCC Output line for the printer initialization. Refer to the
12ts5V
description of the parallel port for the definition of this pin in
ECP and EPP mode.
VCC An active low input on this pin indicates that the printer has
encountered an error condition. Refer to the description of
the parallel port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP
mode.
VCC An active low output from this pin causes the printer to auto
12ts5V
feed a line after a line is printed. Refer to the description of
the parallel port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP
mode.
VCC An active low output is used to latch the parallel data into the
12ts5V
printer. Refer to the description of the parallel port for the
definition of this pin in ECP and EPP mode.
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 0. Refer to the description of the
12ts5V
parallel port for the definition of this pin in ECP and EPP
mode.
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 1.
12ts5V
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 2.
12ts5V
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 3.
12ts5V
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 4.
12ts5V
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 5.
12ts5V
10
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
F71872
115
116
I/O
PD6
I/O
PD7
5.7 H/W Monitor
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
92-94, VIN7~VIN5 AIN VCC Voltage Input 7 ~ 5.
96-98 VIN3~VIN1 AIN VCC Voltage Input 3 ~ 1.
7 FANIN1 IN
8 FANCTL1 O12 VCC Fan 1 control output. This pin provides PWM duty-cycle
9 FANIN2 IN
10 FANCTL2 O12 VCC Fan 2 control output. This pin provides PWM duty-cycle
11 FANIN3 IN
12 FANCTL3 O12 VCC Fan 3 control output. This pin provides PWM duty-cycle
87 D3+ AIN VCC CPU thermal diode/transistor temperature sensor input.
88 D2+ AIN VCC CPU thermal diode/transistor temperature sensor input.
89 D1+ AIN VCC CPU thermal diode/transistor temperature sensor input.
90 VREF AOUT
73 PME#/GPIO21 OD12
26 GPIO0 I/OOD
27 GPIO1 I/OOD
28 GPIO2 I/OOD
29 GPIO3/
Voltage_Fault1#/
IRRX
12ts5V
12ts5V
ts
ts
ts
I/OD
I/OOD
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 6.
VCC Parallel port data bus bit 7.
ATX Power Good. 95 ATXPG/VIN4 AIN VCC
Voltage Input 4.
PCI Reset # signal input. 91 PCIRSTIN#/VIN8 AIN VCC
Voltage Input 8.
VCC Fan 1 tachometer input.
output or a voltage output.
VCC Fan 2 tachometer input.
output or a voltage output.
VCC Fan 3 speed input.
output or a voltage output.
VCC Voltage sensor output.
Generated PME event. It supports the PCI PME# interface.
This signal allows the peripheral to request the system to
12t
VSB
wake up from the S3 state.
General Purpose IO.
VCC General purpose IO.
12t
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
VCC General purpose IO.
12t
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
VCC General purpose IO.
12t
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
VCC
12t
General purpose IO.
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
Voltage fault indication for VIN1 abnormal event.
Infrared Receiver input. (Powered by Vcc)
11
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
F71872
36 GPIO4/
Voltage_Fault2#/
BEEP/
VID_OTF#
I/OOD
VCC
12t
General purpose IO.
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
Voltage fault indication for VIN2 abnormal event.
Beep Pin.
Voltage OTF Enable pin. This Pin can be selected to be a
input pin for VID_OTF enable.
53 GPIO5/
Voltage_Fault3#/
FANCTL
I/OOD
VCC
12t
General purpose IO.
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
Voltage fault indication for VIN3 abnormal event.
Fan 1 control output for Intel 4-pin Fan. All the registers are
as same as FANCTL1.
55 GPIO6/
Voltage_Fault4#/
WDTRST1#/
OVT#
I/OOD
VCC
12t
General purpose IO.
1. Support Level and Pulse mode output.
2. Open drain and drive select
3. Without input de-bounce.
Voltage fault indication for VIN4 abnormal event.
Watch dog timer signal output 1.
Over temperature signal output.
77 OVT#/
GPIO24/
WDTRST2#
I/OOD
VSB
12t
Over temperature signal output.(Default 85°C)
General purpose IO. Open drain and drive select by register.
Watch dog timer signal output 2.
5.8 ACPI function pins
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
30 RSTCON#/GPIO10 I/OD
32 PWROK1/GPIO12 I/OD
VCC
12t
VCC
16t
VCC
12t
VCC
16t
VCC
16t
RESET connect# with 50ms debouce function, it connects to
reset button, and also other reset source on the
motherboard. If the register RSTCON_EN (5h) is set to 1, the
pin 30 will infect PCIRST1# ~ PCIRST5# outcome. If the
register RSTCON_EN is set to 0, the pin 30 will infect
PWROK1 and PWROK2 outcome.
General purpose IO.
It is a output buffer of RSTCON# and LRESET#. 31 PCIRST1#/GPIO11 I/OOD
General purpose IO.
Pin1 RST_DRV = 1(high) : OD
= 0(low) : Drive
PWROK function, It is power good signal of VCC, which is
delayed 400ms (default) as VCC arrives at 2.8V.
General purpose IO.
It is a output buffer of RSTCON# and LRESET#. 33 PCIRST2#/GPIO13 I/OOD
General purpose IO.
Pin1 RST_DRV = 1(high) : OD
=0(low): Drive
It is a output buffer of RSTCON# and LRESET#. 34 PCIRST3#/GPIO14 I/OOD
General purpose IO.
12
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
Pin1 RST_DRV = 1(high) : OD
48 PCIRST5#/GPIO15
68 COPEN# INt VBAT Case Open Detection #. This pin is connected to a specially
72 PWSWOUT#
76 PSON#/GPIO23
78 PWROK2/GPIO25/
85 RSMRST#/GPIO27 I/OD
LED_VCC
/GPIO20
/GPIO22
LED_VSB
F71872
=0(low) : Drive
I/OOD
VCC
16t
It is a output buffer of RSTCON#,LRESET# and PCIRSTIN.
General purpose IO.
Pin1 RST_DRV = 1(high) : OD
=0(low) : Drive
Power LED for VCC.
designed low power CMOS flip-flop backed by the battery for
case open state preservation during power loss.
12t
VSB
S3# Input is Main power on-off switch input. 71 S3#/GPIO31
General purpose IO.
VSB Panel Switch Output. This pin is low active and pulse output.
It is power on request output#.
General purpose IO.
12t
VSB
12t
General purpose IO.
VSB Power supply on-off control output. Connect to ATX power
supply PS_ON# signal.
General purpose IO.
12t
VSB
12t
PWROK function, It is power good signal of VCC, which is
delayed 400ms (default) as VCC arrives at 2.8V.
IN
t
I/OD
OD12
I/OD
IN
Main power switch button input. 75 PWSWIN#
t
I/OD
OD12
I/OD
I/OD
General purpose IO.
Power LED for VSB
VSB
16t
It is a output buffer of RSTCON#,LRESET# and PCIRSTIN. 84 PCIRST4#/GPIO26 I/OOD
General purpose IO.
Pin1 RST_DRV = 1(high) : OD
=0(low) : Drive
VSB
12t
Resume Reset# function, It is power good signal of VSB,
which is delayed 66ms as VSB arrives at 2.3V.
General purpose IO.
5.9 VID controlling pins
Pin No. Pin Name Type PWR Description
13,14,
VIDIN[5:0] IN
16,17,
18,19
20-25 VIDOUT[5:0] OD12 VCC CPU VID output pins.
79 SLOTOCC# IN
ts
VCC CPU VID input pins.
1. Special level input VIHÆ 0.9, VIL Æ 0.6.
2. Power by VCC.
ts
VSB CPU SLOTOCC# input.
13
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
6 Function Description
6.1 Power on Strapping Options
The F71872 provides four pins for power on hardware strapping to select functions. There is a form to describe how
to set the functions you want.
Pin No. Symbol Value Description
1 Pin31/33/34/48/84 will be defined a Open Drain pin. (Default) 1 RST_DRV
F71872
6.2 ACPI
The Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is a system for controlling the use of power in a
computer. It lets computer manufacturer and user to determine the computer’s power usage dynamically.
S0, S3 and S5. S0 is a full-power state; the computer is being actively used in this state. The other two are
called sleep states and reflect different power consumption when power-down. S3 is a state that the
0 Pin31/33/34/48/84 will be defined a Drive pin.
1 Fan control mode: PWM mode. ( Default) 2 PWM_DC
0 Fan control mode: Linear mode.
1 KBC is enabled. (Default) 121 KBC_EN
0 KBC is disabled.
1 Chip selection in configuration 4E. (Default) 124 Config4E_2E
0 Chip selection in configuration 2E.
There are three ACPI states that are of primary concern to the system designer and they are designated
processor is powered down but the last procedural state is being stored in memory which is still active. S5 is a
state that memory is off and the last procedural state of the processor has been stored to the hard disk. Take
S3 and S5 as comparison, since memory is fast, the computer can quickly come back to full-power state, the
disk is slower than the memory and the computer takes longer time to come back to full-power state. However,
since the memory is off, S5 draws the minimal power comparing to S0 and S3.
It is anticipated that only the following state transitions may happen:
S0→S3, S0→S5, S5→S0, S3→S0 and S3→S5.
Among them, S3→S5 is illegal transition and won’t be allowed by state machine. It is necessary to enter S0
first in order to get to S5 from S3. As for transition S5→S3 will occur only as an immediate state during state
transition from S5→S0. It isn’t allowed in the normal state transition.
14
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
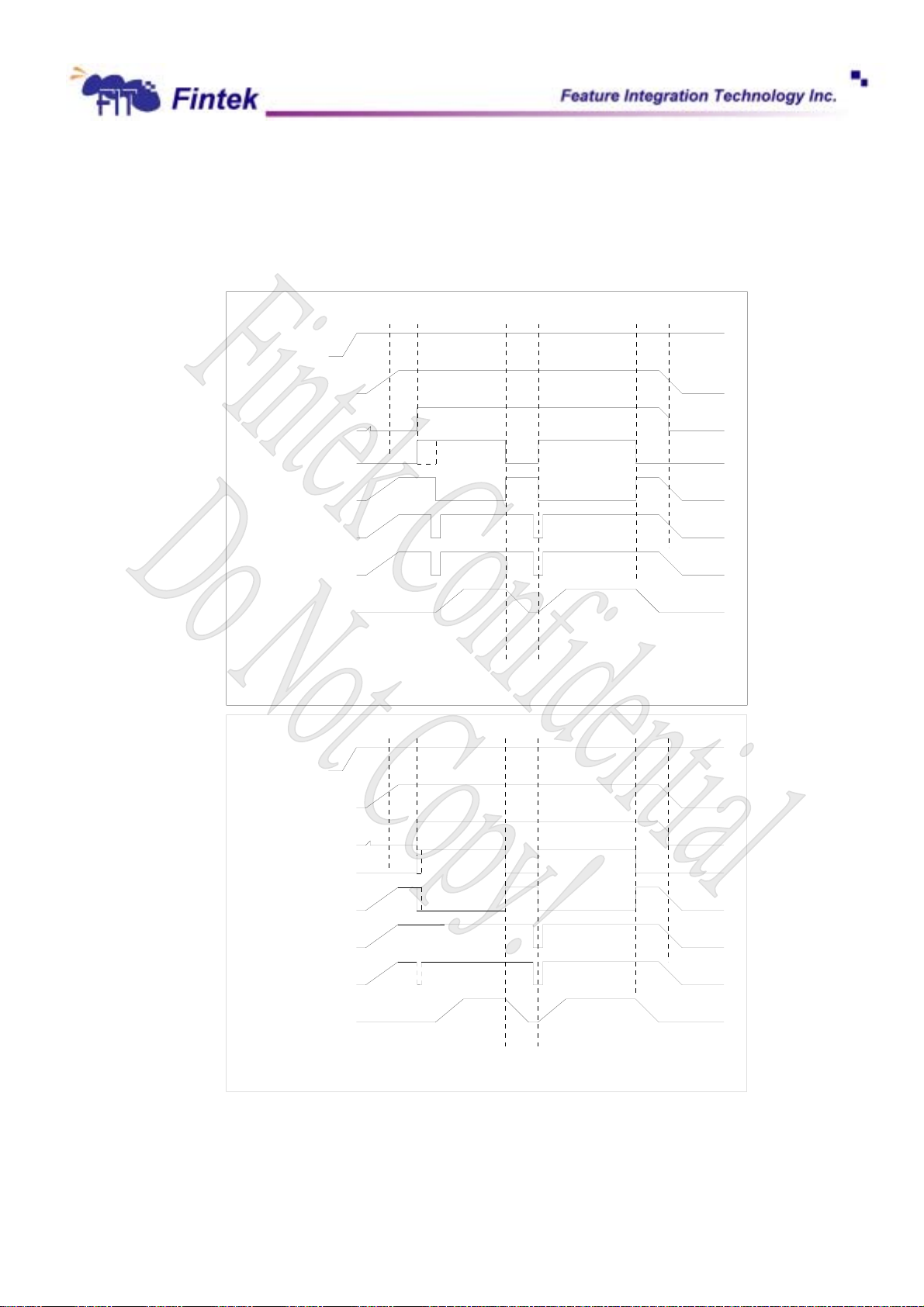
The below diagram described the timing, the always on and always off, keep last state could be set in
control register. In keep last state mode, one register will keep the status of before power loss. If it is power on
before power loss, it will remain power on when power is resumed, otherwise, if it is power off before power
loss, it will remain power off when power is resumed.
F71872
VBAT
VSB
RSMRST#
S3#
PS_ON#
PSIN#
PSOUT#
VCC3V
VBAT
VSB
RSMRST#
S3#
PS_ON#
DEFAULT TIMING
Always off
PSIN#
PSOUT#
VCC3V
ALways ON TIMING
15
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
6.3 PCI Reset and PWROK Signals
The F71872 supports 5 output buffers for 5 reset signals. If the register RSTCON_EN (5h) is set to 1, the pin
RSTCON# will infect PCIRST1# ~ PCIRST5# outcome. Then, the result of PCIRST# outcome will be affected by
conditions as below:
PCIRST1# Æ Output buffer of RSTCON# and LRESET#.
PCIRST2# Æ Output buffer of RSTCON# and LRESET#.
PCIRST3# Æ Output buffer of RSTCON# and LRESET#.
PCIRST4# Æ Output buffer of RSTCON#, LRESET# and PCIRSTIN#
PCIRST5# Æ Output buffer of RSTCON#, LRESET# and PCIRSTIN#
F71872
+3.3V
+3.3V
S3#
S3#
ATXPG
ATXPG
RSTCON#
RSTCON#
So far as the PWROK issue is as above figure. PWROK is delayed 400ms (default) as VCC arrives 2.8V,
and the delay timing can be programmed by register. (100ms ~ 400ms)
In the figure, the RSTCON# will be implemented by register RSTCON_EN. If RSTCON_EN be set to 0, the
RSTCON# pin will affect PWROK outputs. If RSTCON_EN be set to 1, the RSTCON# pin will affect PCIRST
outputs (Default).
Delay
Delay
6.4 Hardware Monitor
PWROK1/2
PWROK1/2
RSTCON#
RSTCON#
LRESET#
LRESET#
PCIRSTIN#
PCIRSTIN#
PCIRST1~3#
PCIRST1~3#
PCIRST4~5#
PCIRST4~5#
6.4.1 Analog Input
The F71872 provides 8 pins (8-bit) ADC voltage inputs. These input voltages should be positive and is
limited at range of 0v to 2.048V. The minimum resolution (1-LSB) is 8mV. If the voltage is over this range, the
divider resistor must be added and the divided voltage is also in the range of 0V to 2.048V.
The maximum input voltage of the analog pin is 2.048V because the 8-bit ADC has a 8mv LSB. Really, the
application of the PC monitoring would most often be connected to power suppliers. The voltage range of 0V to
2.048V can be connected to these analog inputs. The 3.3V and VSB5V should be reduced a factor with
external resistors so as to obtain the input range..
There are 8 voltage inputs in the F71872 and the voltage divided formula is shown as follows:
16
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
R
2
×=
VVIN
V
+
12
RR
+
21
For instance, where V
If we choose R1=27K, R2=5.1K, the exact input voltage for V+12v will be 1.907V, which is within the
tolerance. As for application circuit, it can be refer to the figure shown as follows.
VIN(Lower than 2.048V)
R1
R2
F71872
F71872
is the analog input voltage.
+12V
VREF
R
10K, 1%
Typical Thermister
Connection
10K, 25 C
D1/D2/D3
6.4.2 Temperature Monitoring and Offset
The F71872 can be measured from 0°C to 140°C. The status depends on different situation. As
connected to a BJT thermal diode, detected temperature ranges from 0°C to 140°C without considering the
OFFSET effect. As connected to a thermistor, detected temperature ranges from 0°C to 127°C without
considering the OFFSET effect. The temperature format is as the following table:
Temperature ( High Byte ) Digital Output
D1/D2/D3
AGND(D-)
C
2200pF
2N3906
0°C 0000 0000
1°C 0000 0001
25°C 0001 1001
50°C 0011 0010
75°C 0100 1011
90°C 0101 1010
100°C 0110 0100
140°C 1000 1100
17
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
The F71872 provides offset register for each temperature. The offset value is an 7-bit, 2’s complement
value. The reading temperature value will be the result of the offset value added to the monitored value. The
offset format is as the following table:
The F71872 can provide two external thermal sensors to detect temperature. When monitored
F71872
Offset Value High Byte
63°C 0011 1111
2°C 0000 0010
1°C 0000 0001
0°C 0000 0000
-1°C 0100 0001
-2°C 0100 0010
-64°C 0100 0000
temperature exceeds the over-temperature threshold value, OVT# (pin77) will be asserted until the
temperature goes below the hysteresis temperature.
To
T
HYST
OVT#
6.4.3 Fan speed count
Inputs are provided by the signals from fans equipped with tachometer outputs. The level of these signals
should be set to TTL level, and maximum input voltage cannot be over VCC. If the input signals from the
tachometer outputs are over the VCC, the external trimming circuit should be added to reduce the voltage to
obtain the input specification. The normal circuit and trimming circuits are shown as follows:
18
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
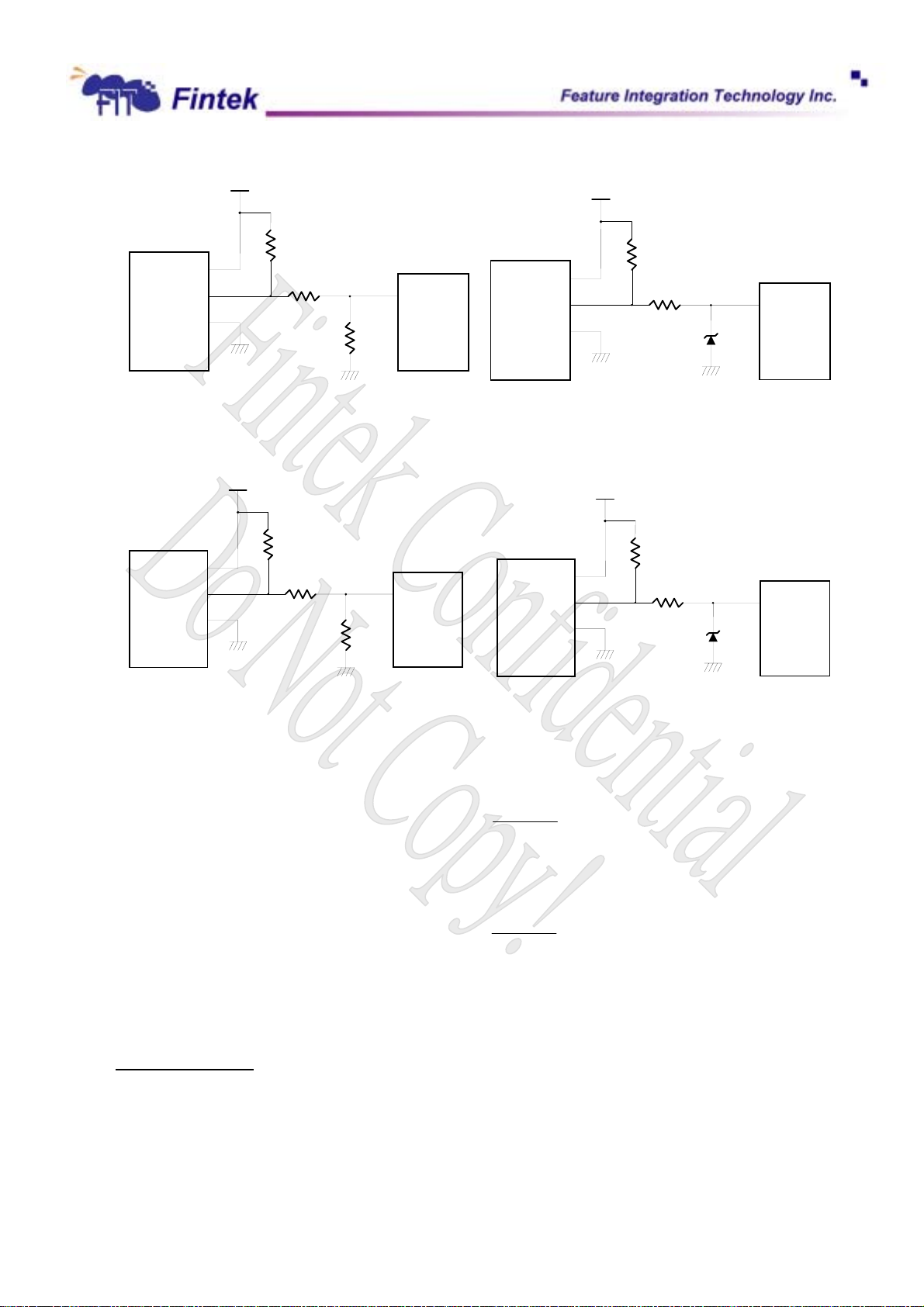
ote
F71872
+12V
Pull-up resister
4.7K Ohms
+12V
FAN Out
GND
Fan with Tach Pull-Up to +12V, or Totern-Pole
Output and Register Attenuator
22K~30K
Fan Input
10K
FANIN 1
F71872
FAN
Connector
Fan with Tach Pull-Up to +12V, or
Totem-Pole Putput and Zener Clamp
+12V
FAN Out
GND
+12V
Pull-up resister < 1K
or totem-pole output
> 1K
3.3V Zener
Fan Input
FANIN 1
F71872
+5V
FAN Out
GND
+5V
Pull-up resister
4.7K Ohms
1K~2.7K
Fan Input
10K
FANIN1
F71872
FAN
Connector
+5V
FAN Out
GND
+5V
Pull-up resister < 1K
or totem-pole output
> 1K
3.3V Zener
Fan Input
FANIN1
F71872
Fan with Tach Pull-Up to +5V, or Totern-Pole
Output and Register Attenuator
Fan with Tach Pull-Up to
+5V, or
T
m-Pole Putput and Zener
Determine the fan counter according to:
6
105.1 ×
RPM
Count
=
In other words, the fan speed counter has been read from register, the fan speed can be evaluated by the
following equation. As for fan, it would be best to use 2 pulses tachmeter output per round.
6
RPM
=
105.1 ×
Count
6.4.4 Fan speed control
The F71872 provides 2 fan speed control methods: 1. Linear FAN Control 2. PWM Duty Cycle
Linear Fan Control
The range of DC output is 0~3.3V, controlled by 8-bit register (CR6Bh for FAN1, CR7Bh for FAN2 and
CR8Bh for FAN3). 1 LSB is about 0.013V. The output DC voltage is amplified by external OP circuit, thus to
reach maximum FAN OPERATION VOLTAGE, 12V.
The output voltage will be given as followed:
19
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
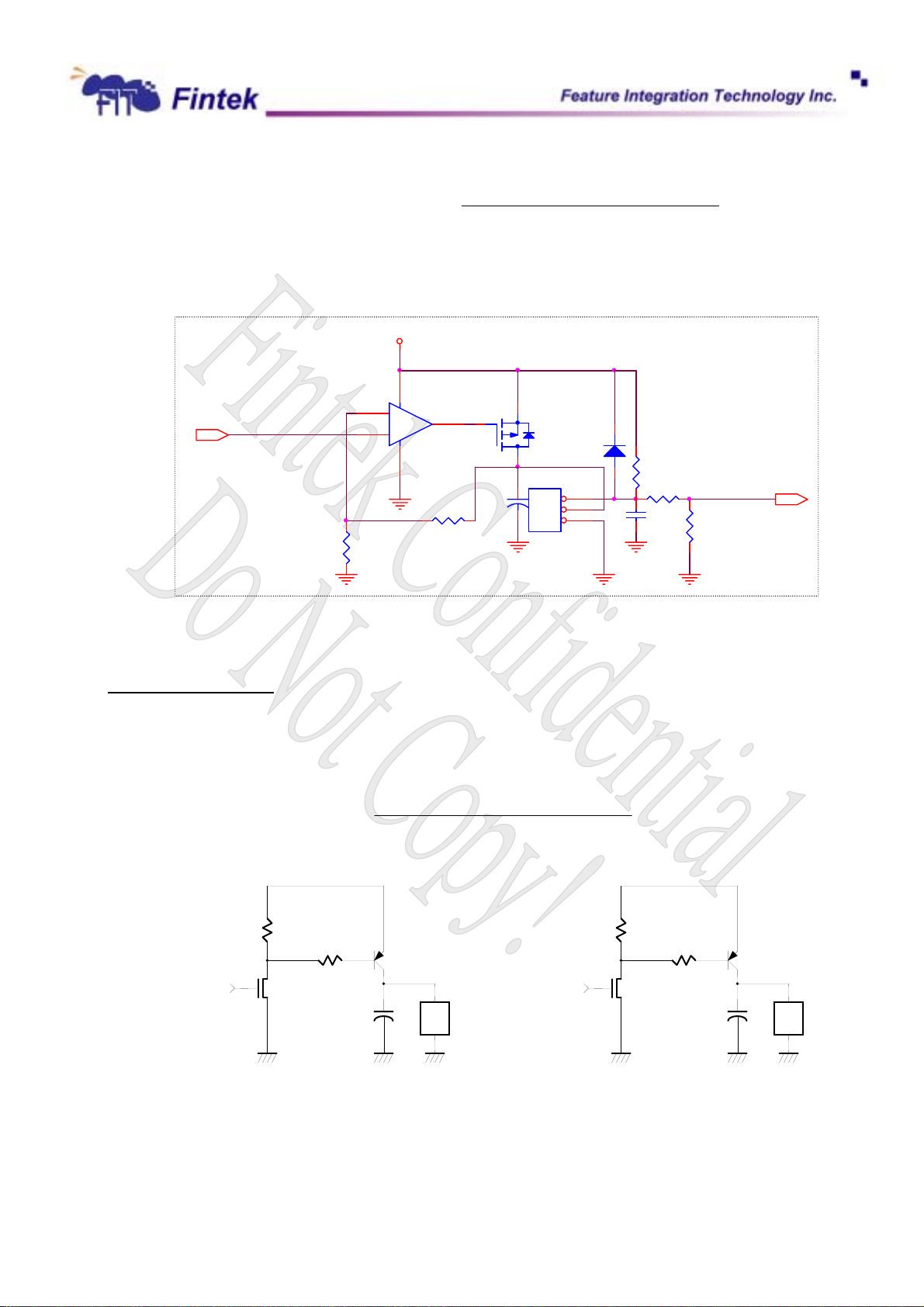
F71872
And the suggested application circuit for linear fac control would be:
DC OUTPUT VOLTAGE
3.9K
3.3(V) tageOutput_vol ×=
ValueRegister bit -8 Programmed
255
12V
84
3
+
2
-
LM358
R
PMOS
1
JP1
R10K
DC FAN Control with OP
C
47u
CON3
3
2
1
1N4148
D1
C
0.1u
R
4.7K
R27K
R
10K
FANIN MONITOR
PWM duty Fan Control
The duty cycle of PWM can be programmed by a 8-bit register which are defined in the CR6Bh, CR7Bh
and CR8Bh. The default duty cycle is set to 100%, that is, the default 8-bit registers is set to FFh. The
expression of duty can be represented as follows.
(%)Duty_cycle ×=
+12V
R1
R2
D
G
PWM Clock Input
NMOS
S
6.4.5 Fan speed control mechanism
There are 3 modes to control fan speed and they are manual, fan speed mode and temperature mode.
PNP Transistor
+
C
-
FAN
255
PWM Clock Input
ValueRegister bit -8 Programmed
R1
D
G
NMOS
S
+5V
%100
R2
PNP Transistor
+
C
-
FAN
For manual mode, it generally acts as PWM fan speed control. As for speed mode and temperature mode,
they are more intelligent fan speed control and described as below:
20
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
Fan Speed mode
Fan speed mode is an intelligent method according to expected fan speed pre-setting by BIOS. In the
beginning, fan speed will be operated at full speed and the F71872 will get the full speed count value. After
that, the fan speed will automatically rotate according to the expected fan speed setting by BIOS. For instance,
the register CR69h and CR6Ah are used for this mode of FAN1.
Temperature mode
At this mode, F71872 provides the clever system to automatically control fan speed related to
temperature system. The F71872 can provide three temperature boundaries and three intervals for user
setting, and each interval has its related fan speed count. All these values should be set by BIOS first. In the
F71872
F71872 design, the F71872 will auto-generate temperature boundaries (average value) between those
boundaries that user setting, and it will auto-produce interval fan speed count (average value) between users
setting value.
If the temperature value is set to 40, 50 and 90°C, it will auto-generate two temperature boundaries value
of 45°C (This value is calculated automatically by hardware design of the F71872. (450+40)/2 =45 ) and 70°C.
The same way, the related desired fan speed counts for each interval are 4200RPM, 3600RPM, 3000RPM,
2500RPM, 2000RPM and Stop Counts. When the temperature is within 50~70°C, the fan speed counts will be
3000RPM (Registers CRA4h~CRA9h, CRB4h~CRB9h and CRC4h~CRC9h). The F71872 will auto-adjust
PWMOUT (PWM_DUTY) to make fan speed match the expected value. It can be said that the fan will be
turned on with a specific speed set by BIOS and automatically controlled with the temperature varying. The
F71872 will take charge of all the fan speed control and need no software support.
Auto-Generated
(Average value)
90 Degree C
70 Degree C
50 Degree C
45 Degree C
40 Degree C
Desired Counts (RPM)
4200
3600
3000
2500
2000
Stop Counts
Auto-Generated
(Average value)
PWMOUT Duty-cycle operating process
In both “FAN SPEED” and “TEMPERATURE” modes, F71872 adjust PWMOUT (PWM_DUTY1 (CR6B)
of Fan1, PWM_DUTY2 (CR7B) of Fan2, PWM_DUTY3 (CR8B) of Fan3) duty-cycle according to current fan
count and expected fan count. It will operate as follows:
21
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
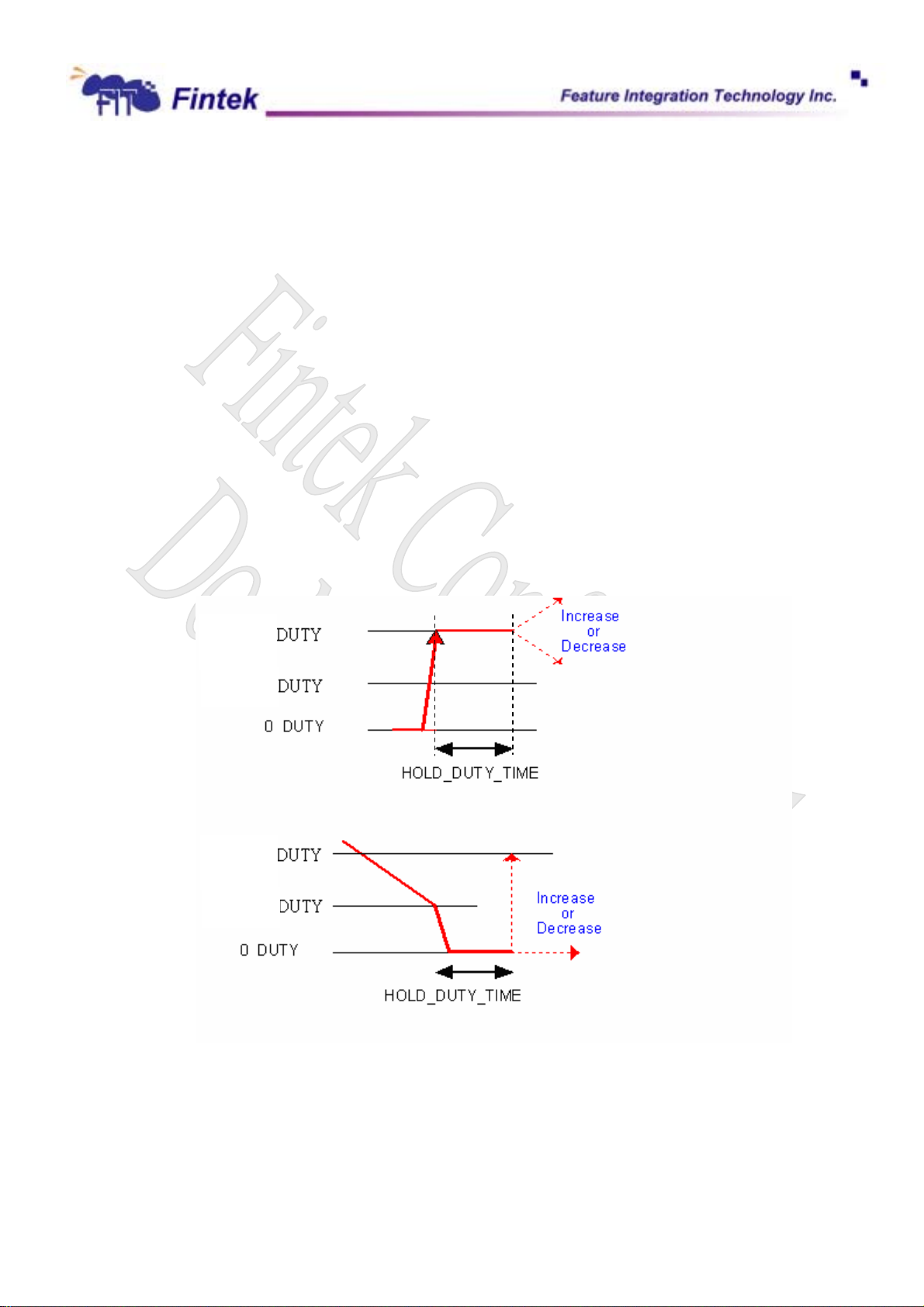
(1). When expected count is FFFFh, PWMOUT duty-cycle (PWM_DUTY)will be set to 00h to turn off fan.
(2). When expected count is 0000h, PWMOUT duty-cycle (PWM_DUTY) will be set to FFh to turn on fan
with full speed.
(3). If both (1) and (2) are not true and KEEP_STOP (see INDEX 60h) is set to 0:
F71872
(a). When PWMOUT duty-cycle decrease to STOP_DUTY(≠ 00h), obviously the duty-cycle will
decrease to 00h next, F71872 will keep duty-cycle at 00h 3 seconds
compare current fan count and expected count in order to increase or decrease its duty-cycle.
This ensures that if there is any glitch during the 3 seconds
1
period, F71872 will ignore it.
(b). When PWMOUT duty-cycle increase from 00h to START_DUTY(≠ 00h), F71872 also will keep
duty-cycle at START_DUTY 3 seconds
1
. After that, F71872 starts to compare current fan count
and expected count in order to increase or decrease its duty-cycle. This ensures that if there is
any glitch during the 3 seconds
1
period, F71872 will ignore it.
1
. After that, F71872 starts to
Note 1: The period of HOLD_DUTY_TIME can be programmed at INDEX 67h of FAN1.
START
STOP
START
STOP
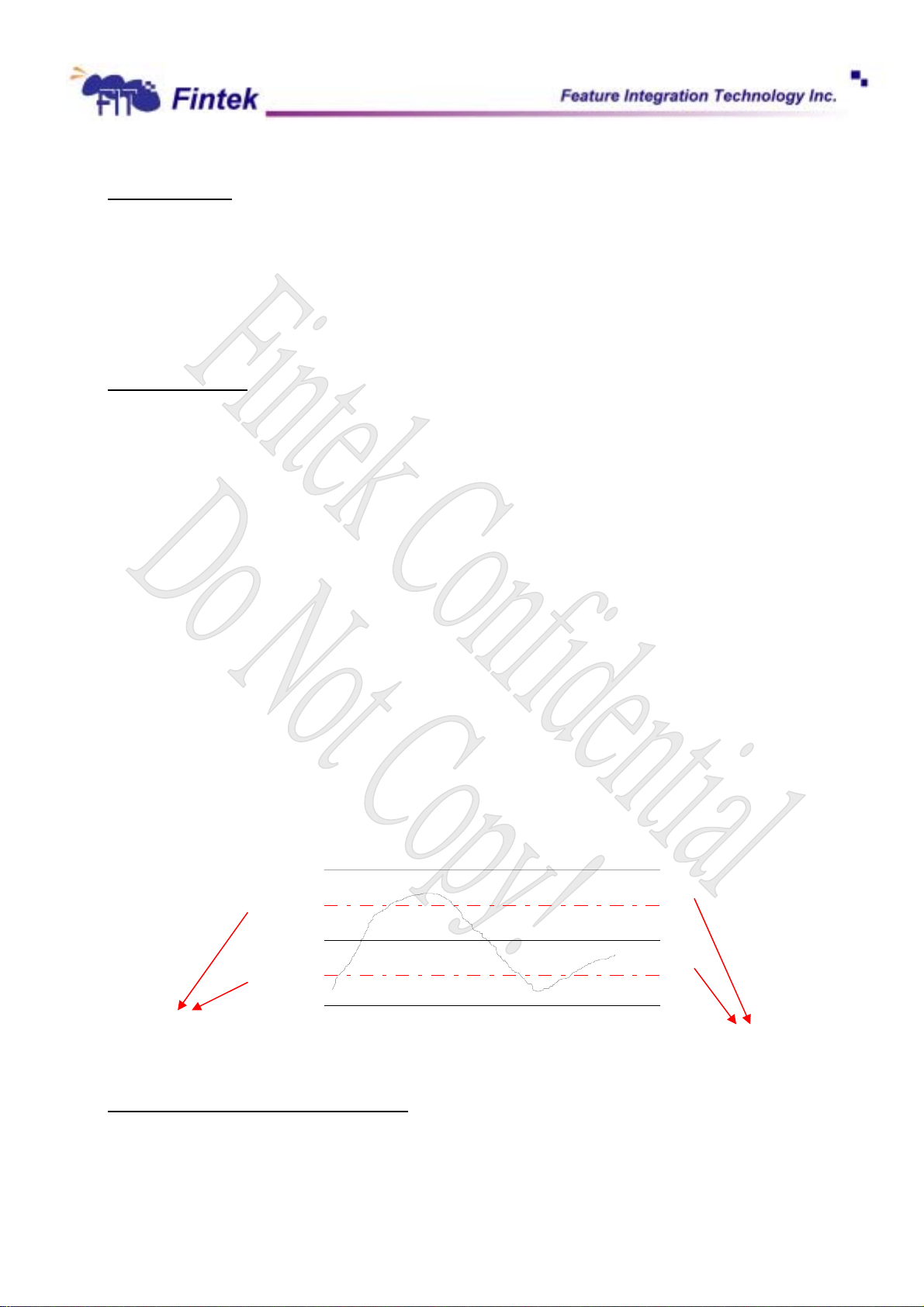
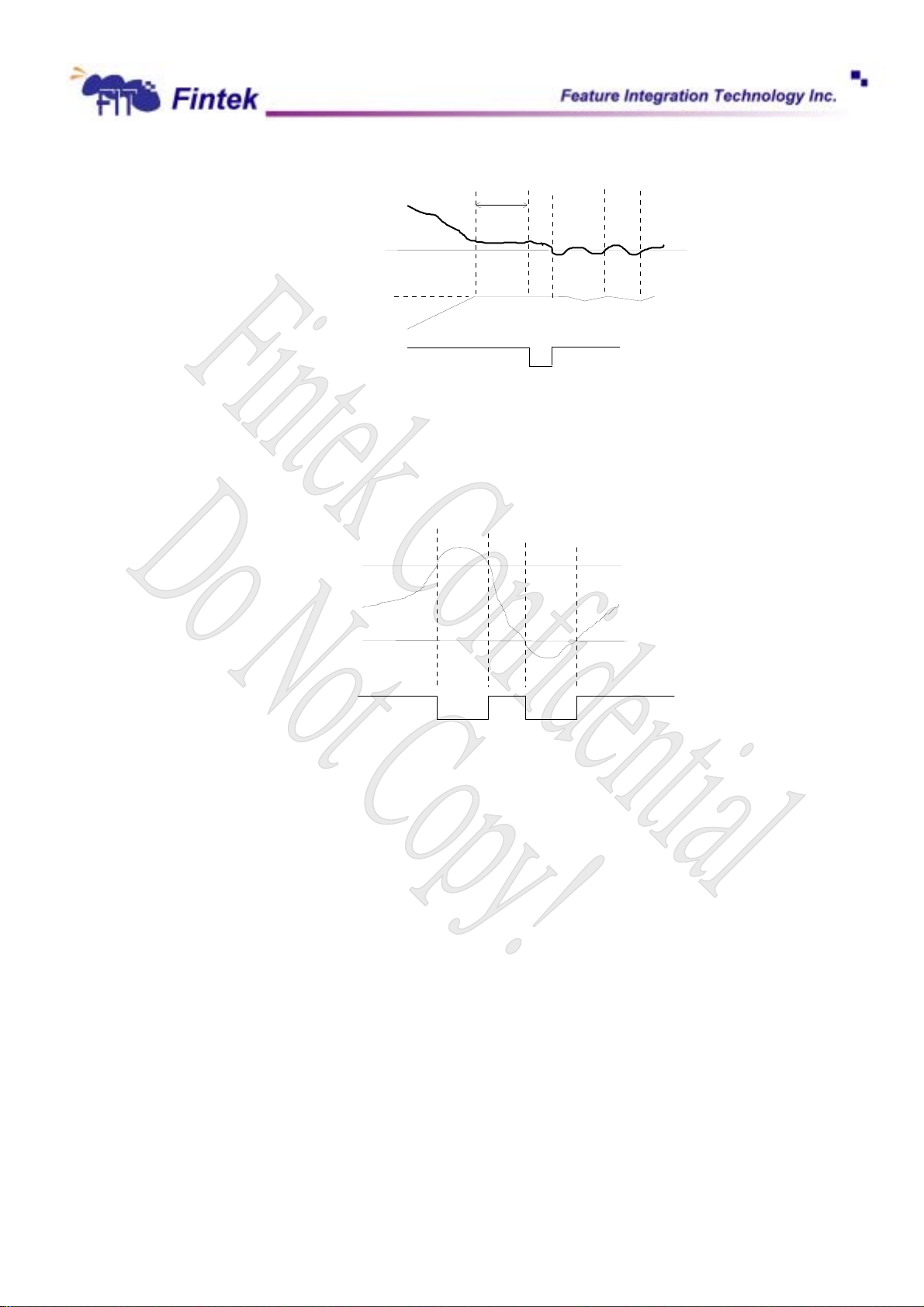
6.4.6 FAN_FAULT#
Fan_Fault will be asserted ( throuth PME# Pin 73) when the fan speed doesn’t meet the expected fan
speed within a programmable period (default is 3 seconds) when PWMOUT duty-cycle is 100%.
22
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
)
F71872
Current Fan Count
Expected Fan Count
100%
Duty-cycle
Fan_Fault#
6.4.7 VOLT_FAULT# (Voltage Fault Signal)
When voltage leaps from the security range setting by BIOS, the warning signal VOLT_FAULT# will be
activated. Shown in figure.
High limit
3 sec(default
Low limit
VOLT_FAULT#
6.5 FDC
The Floppy Disk Controller provides the interface between a host processor and one floppy disk drives. It
integrates a controller and a digital data separator with write pre-compensation, data rate selection logic,
microprocessor interface, and a set of registers. The FDC supports data transfer rates of 250 Kbps, 300 Kbps,
500 Kbps, and 1 Mbps. It operates in PC/AT mode and supports 3-mode type drives.
The FDC configuration is handled by software and a set of Configuration registers. Status, Data, and
Control registers facilitate the interface between the host microprocessor and the disk drive, providing
information about the condition and/or state of the FDC. These configuration registers can select the data rate,
enable interrupts, drives, and DMA modes, and indicate errors in the data or operation of the FDC/FDD. The
controller manages data transfers using a set of data transfer and control commands. These commands are
handled in three phases: Command, Execution, and Result. Not all commands utilize all these three phases.
23
Dec., 2006
V0.27P

6.6 UART
The F71872 provides two UART ports and supports IRQ sharing for system application. The UARTs are
used to convert data between parallel format and serial format. They convert parallel data into serial format on
transmission and serial format into parallel data on receiver side. The serial format is formed by one start bit,
followed by five to eight data bits, a parity bit if programmed and one ( 1.5 or 2 ) stop bits. The UARTs include
complete modem control capability and an interrupt system that may be software trailed to the computing time
required to handle the communication link. They have FIFO mode to reduce the number of interrupts
presented to the host. Both receiver and transmitter have a 16-byte FIFO.
F71872
6.7 Parallel Port
The parallel port in F71872 supports an IBM XT/AT compatible parallel port ( SPP ), bi-directional paralle
port ( BPP ), Enhanced Parallel Port ( EPP ), Extended Capabilities Parallel Port ( ECP ) mode. Refer to the
configuration registers for more information on selecting the mode of operation.
6.8 Keyboard Controller
The keyboard controller is implemented using 8 bits microcontroller that is capable of executing the 8042
instruction set. the 8 bit microcontroller has 256 bytes of RAM for DATA memory and 2kbytes of ROM for
program storage.
The keyboard controller receives serial data from keyboard or PS/2 mouse, check parity of data and
placed data in output buffer, the keyboard controller will interrupt system when data is placed in its output
buffer.
Keyboard and mouse interface
The kbclk is keyboard clock which is pin p26 of microcontroller and kbdat is Keyboard data which is pin
p27 of microcontroller. The moclk is Mouse clock which is pin p23 of microcontroller and modat is mouse data
which is pin p22 of microcontroller.
Kbirq and moirq
The kbirq is keyboard interrupt system signal which is pin p24 of microcontroller and moirq mouse is
interrupt system which is pin p25 of microcontroller.
24
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
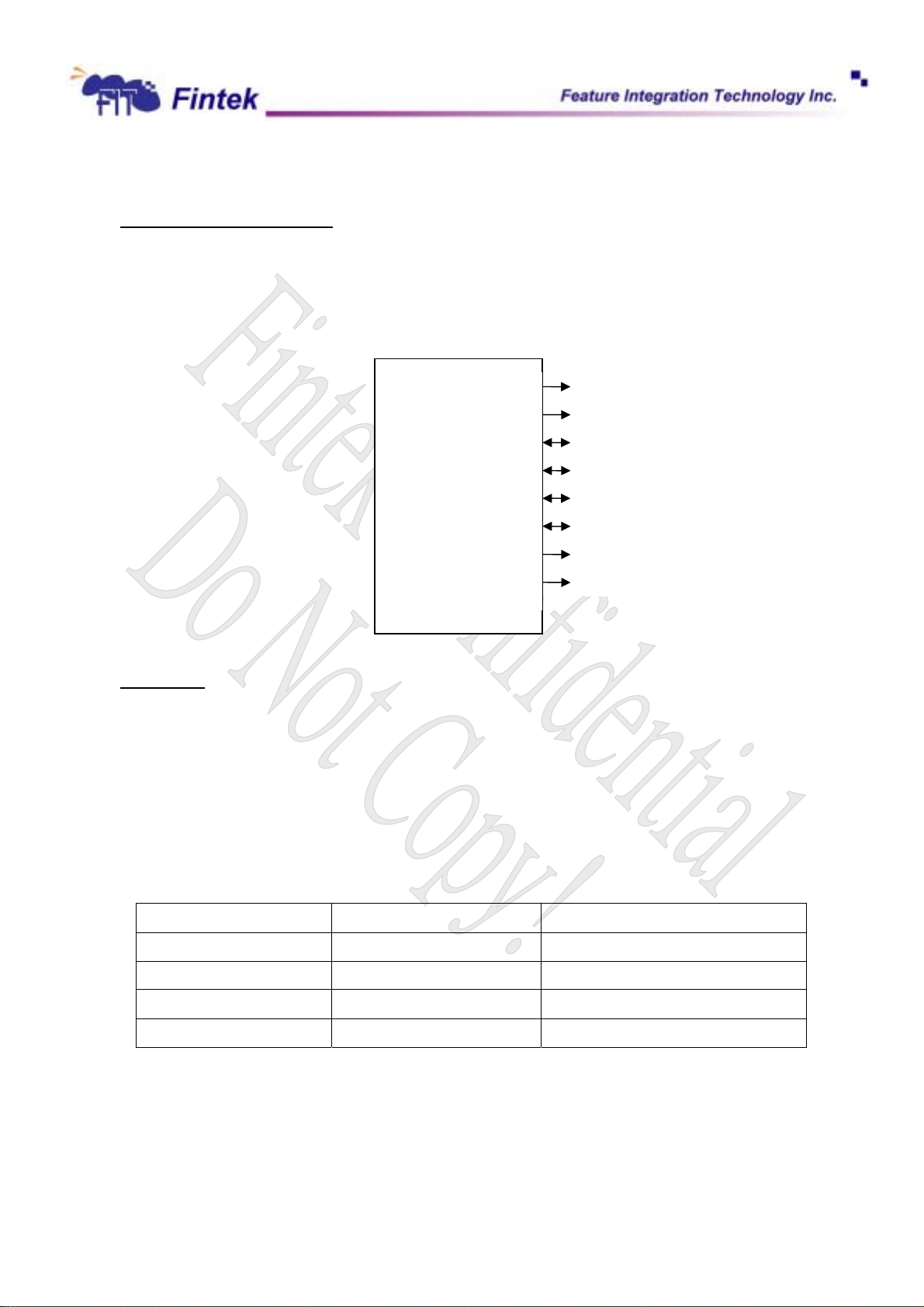
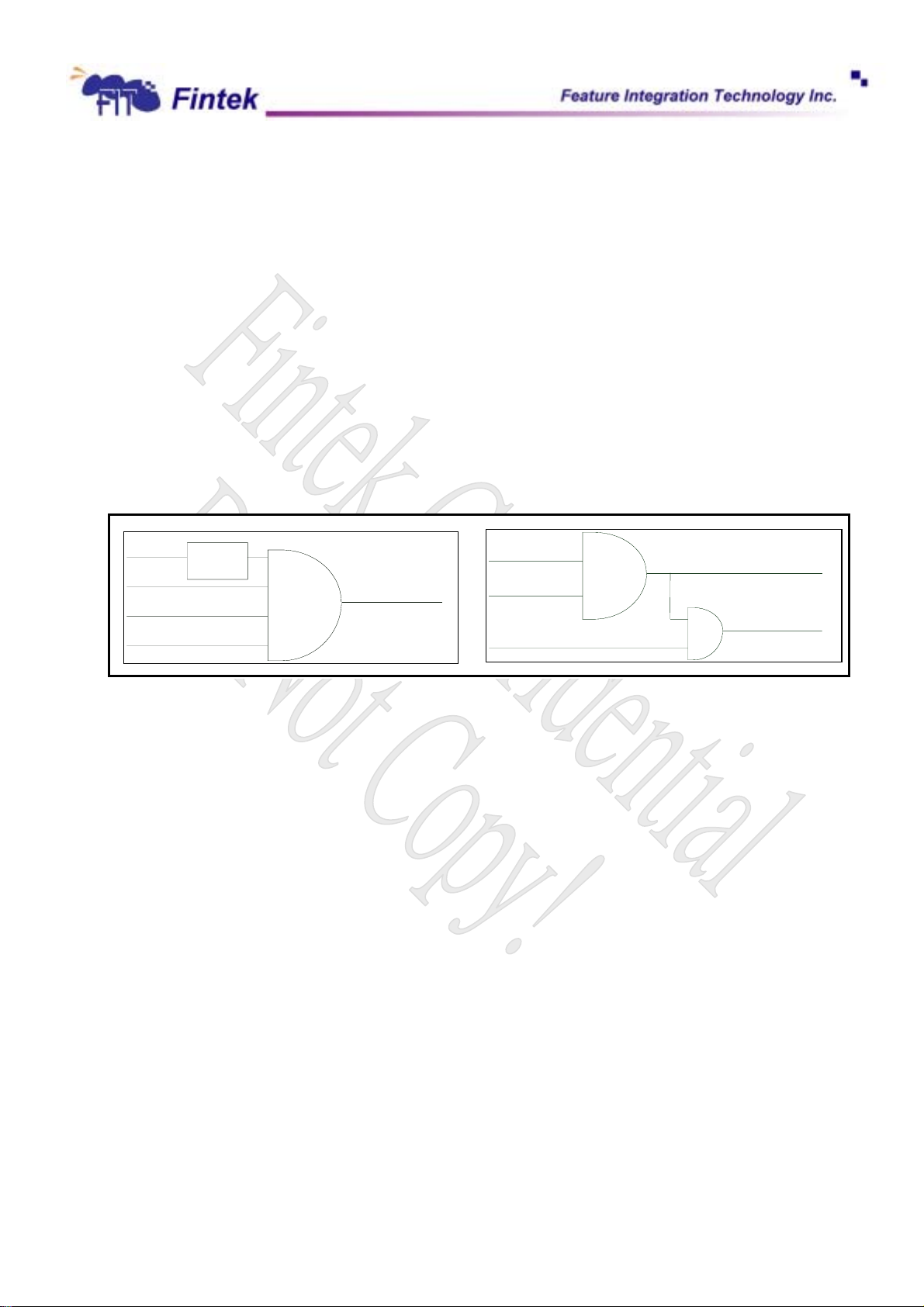
Keyboard reset and GateA20
Keyboard reset (kbrst_n) is pin p20 of microcontroller or hardware decode. It is selected by bit 0 of clock
select register(index F0h).GateA20 is pin p21 of microcontroller or hardware decode, It is selected by bit 1 of
clock select register(index F0h)
F71872
Kbrst_n
Gatea20
kbclk
kbdat
moclk
modat
kbirq
moirq
KBC
P20
P21
P26
P27
P23
P22
P24
P25
Host Phase
The table is keyboard controller interface with the system.
Read data: this is an 8 bit read only register, when system read this register; the interrupt and obf flag will be
cleared.
Write data: this is an 8 bit write only register, when system write this register, the ibf flag will be set.
Read status: this is an 8 bit read only register, it replay KBC status.
Write command: this is an 8 bit write only register, when system write this register, the ibf flag will be set.
Host address R/W Function
60h R Read data
60h W Write data
64h R Read status
64h W Write command
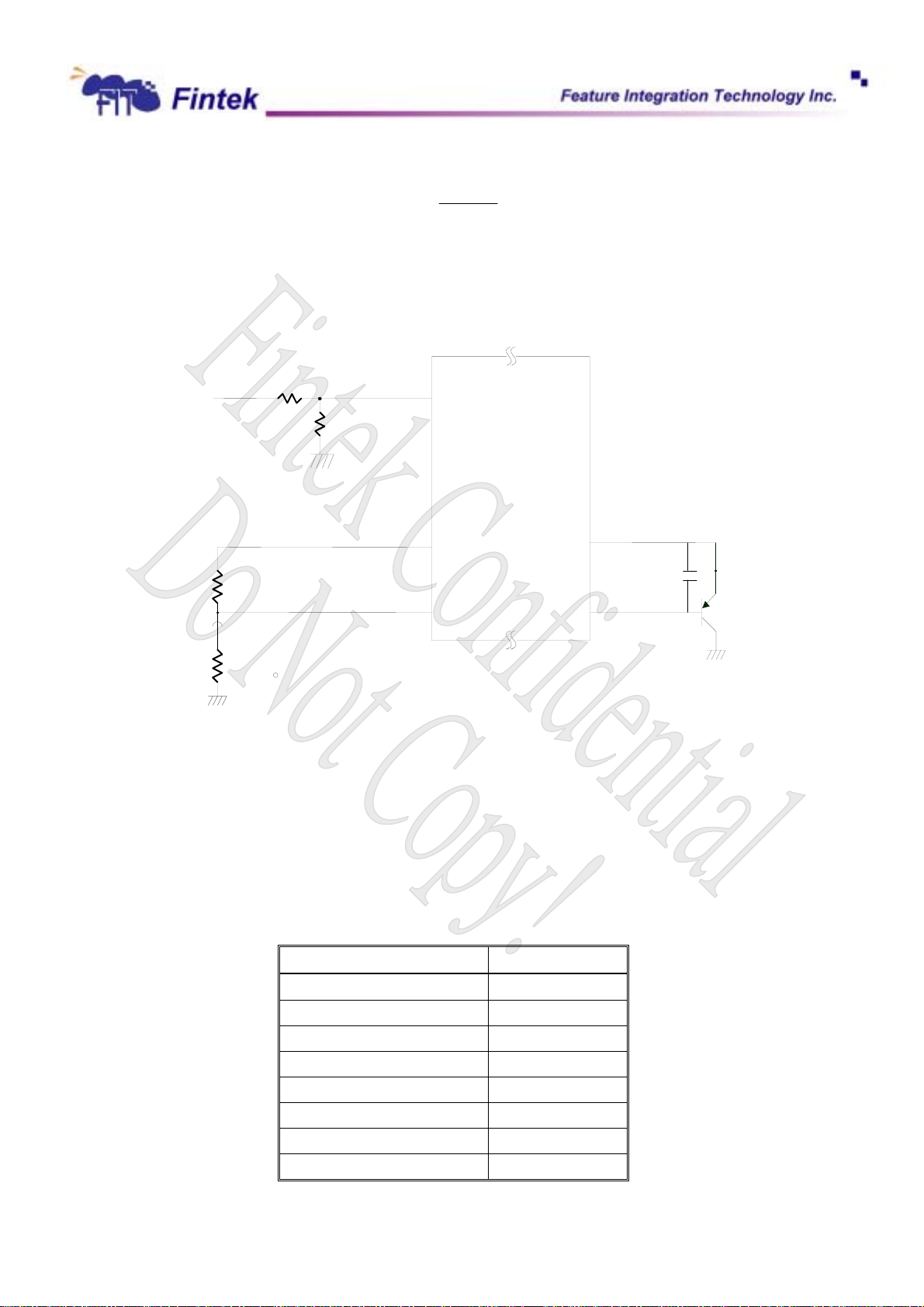
6.9 Dynamic Voltage Change Application
The F71872 supports an automatic/dynamic over-voltage function for application of over-clocking or
under clocking. This function provides a pin by external trigger signal to improve the CPU’s performance by
25
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
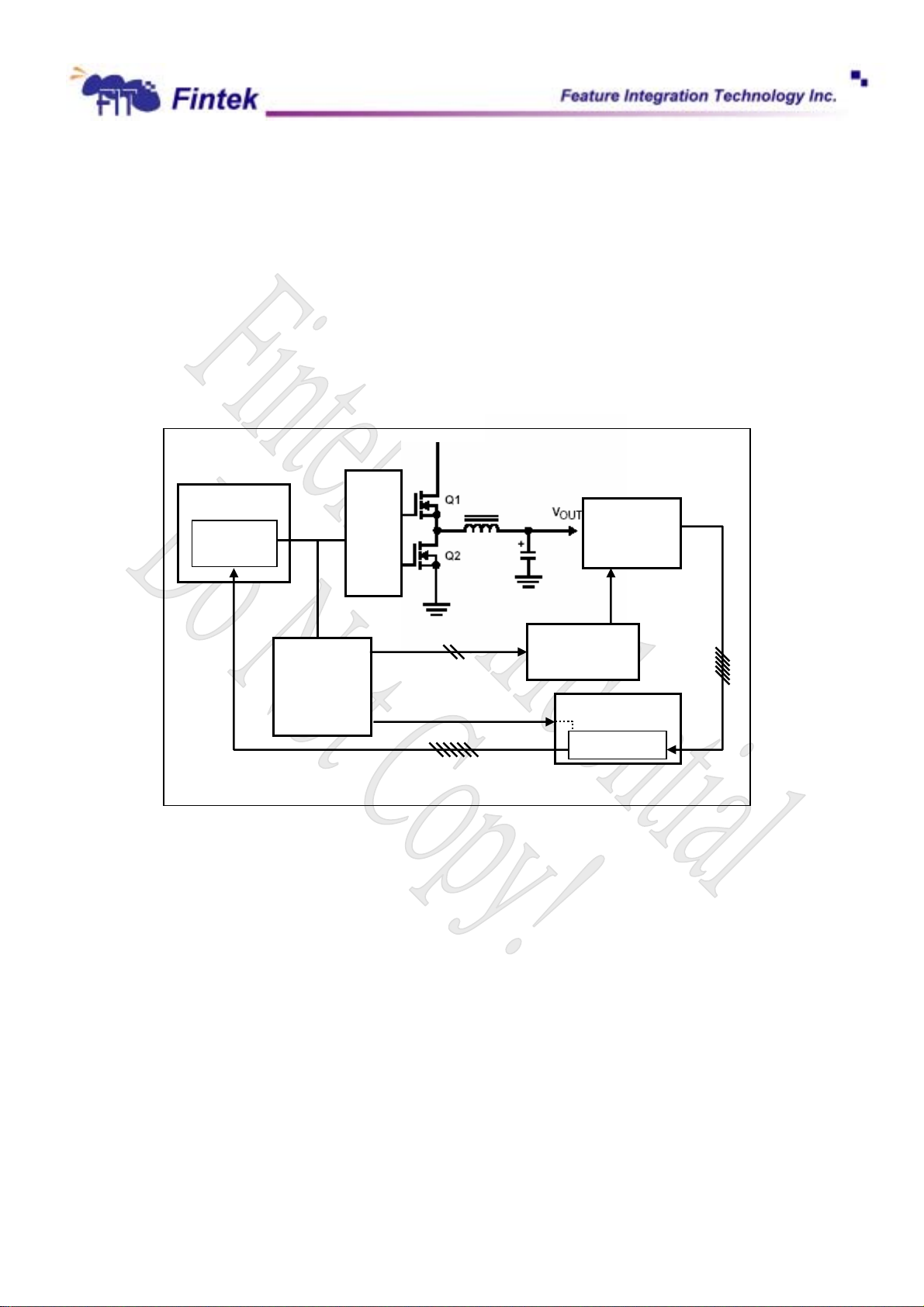
r
voltage changing automatically when system is going to run over-clocking or under-clocking. As the sketch
shows as below, due to achieve this action, suggests using F75133S Loading Gauge to be a part that detects
system/CPU loading to decide when issues the over-clocking/under-clocking and trigger VID signals for
system executing. For instance, user would like to ensure system stably and run over-clocking/under-clocking
on MB, the F75133S will sense the PWM duty to know the loading status. If the system loading reach the limit
of over-clocking, F75133S will issue signal to F71872 to trigger Vcore increasing automatically for proper
Vcore for running over-clocking, secondly F75133S issues signal to CLK Gen for over-clocking. That’s what
F71872
the F71872 facilitates system steady by auto-changing Vcore with F75133S when runs over-clocking.
Power Supply
PWM
Controlle
F75133S
Loading
Gauge IC
PWM
Buffer
CPU
CLK Gen.
F71872F
VID Machine
26
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
F71872
7 Register Descriptions
7.1 Global Control Registers
The configuration register is used to control the behavior of the corresponding devices. To configure the
register, using the index port to select the index and then writing data port to alter the parameters. The default
index port and data port are 0x4E and 0x4F respectively. Pull down the SOUT1 pin to change the default value
to 0x2E/0x2F (Can be programmed by register!). To enable configuration, the entry key 0x87 must be written to
the index port. To disable configuration, write exit key 0xAA to the index port. Following is a example to enable
configuration and disable configuration by using debug.
-o 4e 87
-o 4e 87 ( enable configuration )
-o 4e aa ( disable configuration )
7.1.1 Software Reset Register Index 02h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-1 Reserved - - Reserved
0 SOFT_RST R/W 0 Write 1 to reset the register and device powered by VDD ( VCC ).
7.1.2 Logic Device Number Register Index 07h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-0 LDN R/W 00h 00h: Select FDC device configuration registers.
01h: Select UART 1 device configuration registers.
02h: Select UART 2 device configuration registers.
03h: Select Parallel Port device configuration registers.
04h: Select Hardware Monitor device configuration registers.
05h: Select KBC device configuration registers.
06h: Select GPIO device configuration registers.
07h: Select VID device configuration registers.
0ah: Select PME & ACPI device configuration registers.
27
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
7.1.3 Chip ID Register Index 20h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-0 CHIP_ID1 R 03h Chip ID 1 of F71872.
7.1.4 Chip ID Register Index 21h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-0 CHIP_ID2 R 41h Chip ID2 of F71872.
F71872
7.1.5 Vendor ID Register Index 23h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-0 VENDOR_ID1 R 19h Vendor ID 1 of Fintek devices.
7.1.6 Vendor ID Register Index 24h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-0 VENDOR_ID2 R 34h Vendor ID 2 of Fintek devices.
7.1.7 Software Power Down Register Index 25h
Bit Name R/W Default Description
7-6 Reserved - - Reserved
5 SOFTPD_KBC R/W 0
4 SOFTPD_HM R/W 0
3 SOFTPD_PRT R/W 0
2 SOFTPD_UR2 R/W 0
1 SOFTPD_UR1 R/W 0
0 SOFTPD_FDC R/W 0
Power down the KBC device. This will stop the KBC clock.
Power down the Hardware Monitor device. This will stop the Hardware Monitor
clock.
Power down the Parallel Port device. This will stop the Parallel Port clock.
Power down the UART 2 device. This will stop the UART 2 clock.
Power down the UART 1 device. This will stop the UART 1 clock.
Power down the FDC device. This will stop the FDC clock.
28
Dec., 2006
V0.27P
 Loading...
Loading...