Page 1

GFI MailSecurity 10.1 for
Exchange/SMTP
User Guide
Page 2

Page 3

http://www.gfi.com
Email: info@gfi.com
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies,
names, and data used in examples herein are fictitious unless otherwise
noted. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form
or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the
express written permission of GFI Software Ltd.
GFI MailSecurity is copyright of GFI SOFTWARE Ltd. © 1999-2009 GFI
Software Ltd. All rights reserved.
Document Version: MSEC-UM-EN-1.00.002
Last updated: July 20, 2010
Page 4

Contents
1 About GFI MailSecurity 1
1.1 Introduction to GFI MailSecurity .................................................................. 1
1.2 Key features of GFI MailSecurity ................................................................ 1
1.3 GFI MailSecurity components ..................................................................... 2
1.4 GFI MailSecurity from a user's perspective ................................................. 3
1.5 Add-ons - GFI MailEssentials...................................................................... 3
2 Installing GFI MailSecurity 5
2.1 Introduction ................................................................................................. 5
2.2 Typical deployment scenarios ..................................................................... 5
2.3 Which installation mode should I use? ........................................................ 9
2.4 Hardware requirements ............................................................................ 10
2.5 Software requirements .............................................................................. 10
2.6 Important installation notes ....................................................................... 11
2.7 Preparing to install GFI MailSecurity on an IIS mail relay server ............... 12
2.8 Preparing to install GFI MailSecurity on your mail server .......................... 19
2.9 Installing GFI MailSecurity ........................................................................ 19
2.10 GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation Wizard ................................................. 23
2.11 Adding GFI MailSecurity to the Windows DEP Exception List ................... 27
2.12 Securing access to the GFI MailSecurity configuration/quarantine ............ 28
2.13 Securing access to the GFI MailSecurity Quarantine RSS feeds .............. 32
2.14 Accessing the GFI MailSecurity Configuration and Quarantine Store........ 34
2.15 Upgrading from GFI MailSecurity 8 to GFI MailSecurity 10.1 .................... 36
2.16 Upgrading from GFI MailSecurity 9 to GFI MailSecurity 10.1 .................... 39
2.17 Quarantine Upgrade tool ........................................................................... 39
3 General settings 41
3.1 Introduction to settings .............................................................................. 41
3.2 Define the administrator‟s email address .................................................. 41
3.3 Configuring proxy server settings for automatic updates ........................... 41
3.4 Adding Local Domains .............................................................................. 43
3.5 SMTP server bindings .............................................................................. 43
3.6 Managing local users in SMTP mode ........................................................ 44
4 Configuring virus checking 47
4.1 Configuring Virus Scanning Engines ......................................................... 47
Page 5

4.2 AVG configuration ..................................................................................... 48
4.3 Kaspersky configuration ............................................................................ 50
4.4 BitDefender configuration ......................................................................... 51
4.5 McAfee configuration ................................................................................ 52
4.6 Norman configuration ............................................................................... 54
4.7 Virus scanner actions ............................................................................... 55
4.8 Virus scanner updates .............................................................................. 57
4.9 Setting the Virus Scanning Engines scan priority ...................................... 58
4.10 Configuring Virus Scanning optimizations ................................................. 58
4.11 Configuring Information Store Scanning ................................................... 59
5 Configuring Content Filtering 63
5.1 Introduction ............................................................................................... 63
5.2 Creating a Content Filtering rule ............................................................... 63
5.3 Enabling/disabling rules ............................................................................ 70
5.4 Removing content filtering rules ................................................................ 70
5.5 Modifying an existing rule ......................................................................... 70
5.6 Changing the rule priority .......................................................................... 71
6 Configuring Attachment Filtering 73
6.1 Introduction to Attachment Filtering .......................................................... 73
6.2 Creating an Attachment Filtering rule ........................................................ 73
6.3 Removing attachment rules ...................................................................... 78
6.4 Make changes to an existing rule .............................................................. 79
6.5 Enabling/disabling rules ............................................................................ 79
6.6 Changing the rule priority .......................................................................... 79
7 Decompression engine 81
7.1 Introduction to the Decompression engine ................................................ 81
7.2 Configuring the decompression engine filters ........................................... 82
7.3 Configuring decompression filter actions .................................................. 86
7.4 Enable/disable decompression filters ........................................................ 87
8 The Trojan & Executable Scanner 89
8.1 Introduction to the Trojan & Executable Scanner ...................................... 89
8.2 Configuring the Trojan & Executable Scanner .......................................... 89
8.3 Trojan & Executable Scanner updates ...................................................... 91
9 The Email Exploit Engine 95
9.1 Introduction to e-mail exploits ................................................................... 95
9.2 Configuring the Email Exploit Engine ........................................................ 95
9.3 Email Exploit Engine updates ................................................................... 98
Page 6

10 The HTML Sanitizer 101
10.1 Introduction to the HTML Sanitizer .......................................................... 101
10.2 Configuring the HTML Sanitizer .............................................................. 101
11 Patch Checking 103
11.1 Introduction to Patch Checking ............................................................... 103
11.2 Downloading and installing software patches .......................................... 103
12 Quarantine 105
12.1 Introduction to the Quarantine Store ....................................................... 105
12.2 The Quarantine Store ............................................................................. 105
12.3 Search Folders ....................................................................................... 107
12.4 Approving emails from the Quarantine Store .......................................... 112
12.5 Deleting emails from the Quarantine Store ............................................. 113
12.6 Rescanning emails from the Quarantine Store ........................................ 114
12.7 View the full security threat report of an email ......................................... 115
12.8 Enable email approval via HTML approval forms .................................... 117
12.9 Quarantined mail from the user point of view .......................................... 118
12.10 Enable quarantine RSS feeds ................................................................. 119
12.11 Enable the Directory Harvesting filter on quarantined emails .................. 122
13 Reporting 127
13.1 Introduction to GFI MailSecurity Reporting.............................................. 127
14 Realtime Monitor 137
14.1 About the Realtime Monitor .................................................................... 137
14.2 Monitoring email activity .......................................................................... 137
15 Miscellaneous 139
15.1 Version Information ................................................................................. 139
16 Advanced topics 141
16.1 Customizing the notification templates .................................................... 141
16.2 Setting Virus Scanning API Performance Monitor Counters .................... 144
17 Troubleshooting 148
17.1 Introduction ............................................................................................. 148
17.2 Knowledge Base ..................................................................................... 148
17.3 Web Forum ............................................................................................. 148
17.4 Request technical support ...................................................................... 148
17.5 Build notifications .................................................................................... 148
18 Index 149
Page 7

1 About GFI MailSecurity
1.1 Introduction to GFI MailSecurity
The need to monitor email messages for dangerous, offensive or confidential
content has never been more evident. The most deadly viruses, able to
cripple your email system and corporate network in minutes, are being
distributed worldwide via email in a matter of hours (for example, the
MyDoom worm). Products that perform single vendor anti-virus scanning do
not provide sufficient protection. Worse still, email is likely to become the
means for installing backdoors (Trojans) and other harmful programs to help
potential intruders break into your network. Products restricted to a single
anti-virus engine will not protect against email exploits and attacks of this
kind.
Your only defense is to install a comprehensive email content checking and
anti-virus solution to safeguard your mail server and network. GFI
MailSecurity acts as an email firewall and protects you from email viruses,
exploits and threats, as well as email attacks targeted at your organization.
GFI MailSecurity is totally transparent to your users and does not require
additional user training.
1.2 Key features of GFI MailSecurity
Virus checking using multiple virus engines
GFI MailSecurity scans email for viruses using multiple anti-virus engines.
Scanning email at the gateway and at mail server level prevents viruses from
entering and/or spreading within your network. Furthermore, you can avoid
the embarrassment of sending infected emails to customers as GFI
MailSecurity also checks outgoing mail for viruses. GFI MailSecurity includes
the industrial strength Norman and BitDefender anti-virus engines that have
received various awards. You also have the option to add the AVG, McAfee
and Kaspersky anti-virus engines. Multiple anti-virus engines give you a
higher level of security since anti-virus engines complement each other and
lower the average response time to a virus outbreak. GFI MailSecurity also
includes an auto-update facility that allows you to configure the anti-virus
engines so that they automatically check and download any available updates
without administrator intervention.
Email attachment checking/filtering
GFI MailSecurity's key feature is the ability to check all inbound and outbound
email. It can quarantine all email with dangerous attachments, such as *.exe,
*.vbs and other files. Such attachments are more likely to carry a virus, worm
or email attack. Since email viruses can spread so quickly and cause
immense damage, it is best to quarantine such emails before they are
distributed to your email users. When GFI MailSecurity quarantines an email,
the administrator can review it and then delete or approve the message.
Furthermore, you might choose to quarantine mails carrying *.mp3 or *.mpg
files, as these hog bandwidth and can needlessly burden a mail server's disk
space.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 1
Page 8
The Attachment Checking module has effectively saved thousands of
companies from the LoveLetter virus.
Trojan and Executable Scanner
GFI MailSecurity is able to analyze incoming executables and rate the risklevel of an executable through a GFI patented process. Through the Trojan
and Executable Scanner, GFI MailSecurity can detect and block potentially
dangerous and unknown Trojans before they enter your network.
HTML Sanitizer
The advent of HTML email has made it possible for hackers/virus writers to
trigger commands by embedding them in HTML mail. GFI MailSecurity scans
the email body parts and any .htm/.html attachments for scripting code, and
cleans up the HTML by removing all the scripting code. The HTML Sanitizer
thus protects you from potentially malicious HTML email, containing HTML
viruses and attacks launched via HTML email.
Decompression filter
The decompression filter is used to decompress and analyze compressed
files (archives) attached to emails. This filter is able to check for and block
password-protected archives, corrupted archives and recursive archives.
Furthermore, this engine can also monitor the size and amount of the files
included in an archive. You can configure this filter to quarantine or delete
archives that exceed the specified file count or file size.
1.3 GFI MailSecurity components
GFI MailSecurity scan engine
The GFI MailSecurity scan engine analyzes the con tent of all inbound and
outbound email. If you install GFI MailSecurity on the Microsoft Exchange
machine, it will also scan the information store. If installed on a Microsoft
Exchange 2007/2010 machine, GFI MailSecurity will scan the information
store only if the Mailbox Server Role is installed. If you install GFI
MailSecurity on a Microsoft Exchange 2007/2010 machine with the Hub
Transport Server Role, it will also analyze internal email. When GFI
MailSecurity quarantines an email, it informs the appropriate
supervisor/administrator via Email/RSS feed, depending on the options you
configure.
GFI MailSecurity configuration
Through the GFI MailSecurity configuration, you can configure GFI
MailSecurity to fit your needs.
2 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 9
Screenshot 1 - GFI MailSecurity Configuration
1.4 GFI MailSecurity from a user's perspective
GFI MailSecurity is totally transparent to the user. This means that the user
will not notice that GFI MailSecurity is active until it blocks an email that
triggers a rule, for example, an email that contains a forbidden attachment or
a virus.
In the case of a suspicious attachment, GFI MailSecurity will quarantine the
email for review by the administrator. Optionally, the recipient will receive a
message indicating that the mail is awaiting administrator review. As soon as
the administrator approves the email, GFI MailSecurity will forward the email
to the recipient.
1.5 Add-ons - GFI MailEssentials
A companion product to GFI MailSecurity is GFI MailEssentials. GFI
MailEssentials adds a number of corporate email features to your mail server,
notably:
Anti-spam, using a variety of methods including Bayesian analysis
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 3
Page 10

Email management, including disclaimers, POP3 downloader and server-
based auto replies and more.
For more information, please visit the GFI website at http://www.gfi.com.
NOTE: GFI MailEssentials is available at a bundle price if purchased in
combination with GFI MailSecurity.
4 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 11

2 Installing GFI MailSecurity
2.1 Introduction
This chapter explains how to install and configure GFI MailSecurity. You can
install GFI MailSecurity directly on your mail server or you can choose to
install it on a separate machine configured as a mail relay/gateway server.
When installing on a separate machine, you must first configure the machine
to relay the inbound and outbound emails to your mail server prior to installing
this mail security software.
In order to function correctly, GFI MailSecurity requires access to the
complete list of all your email users and their email addresses. This is
required in order to configure content policy rules such attachment checking
and content checking. GFI MailSecurity can access the list of email users in
two ways: either by querying your Active Directory (requires installing this
software in Active Directory mode) or by importing the list from your SMTP
Server (requires installing this software in SMTP mode). The mode to be
used depends entirely on your network setup and the machine on which you
will be installing this mail security software. You can choose the required
access mode during the installation of GFI MailSecurity.
2.2 Typical deployment scenarios
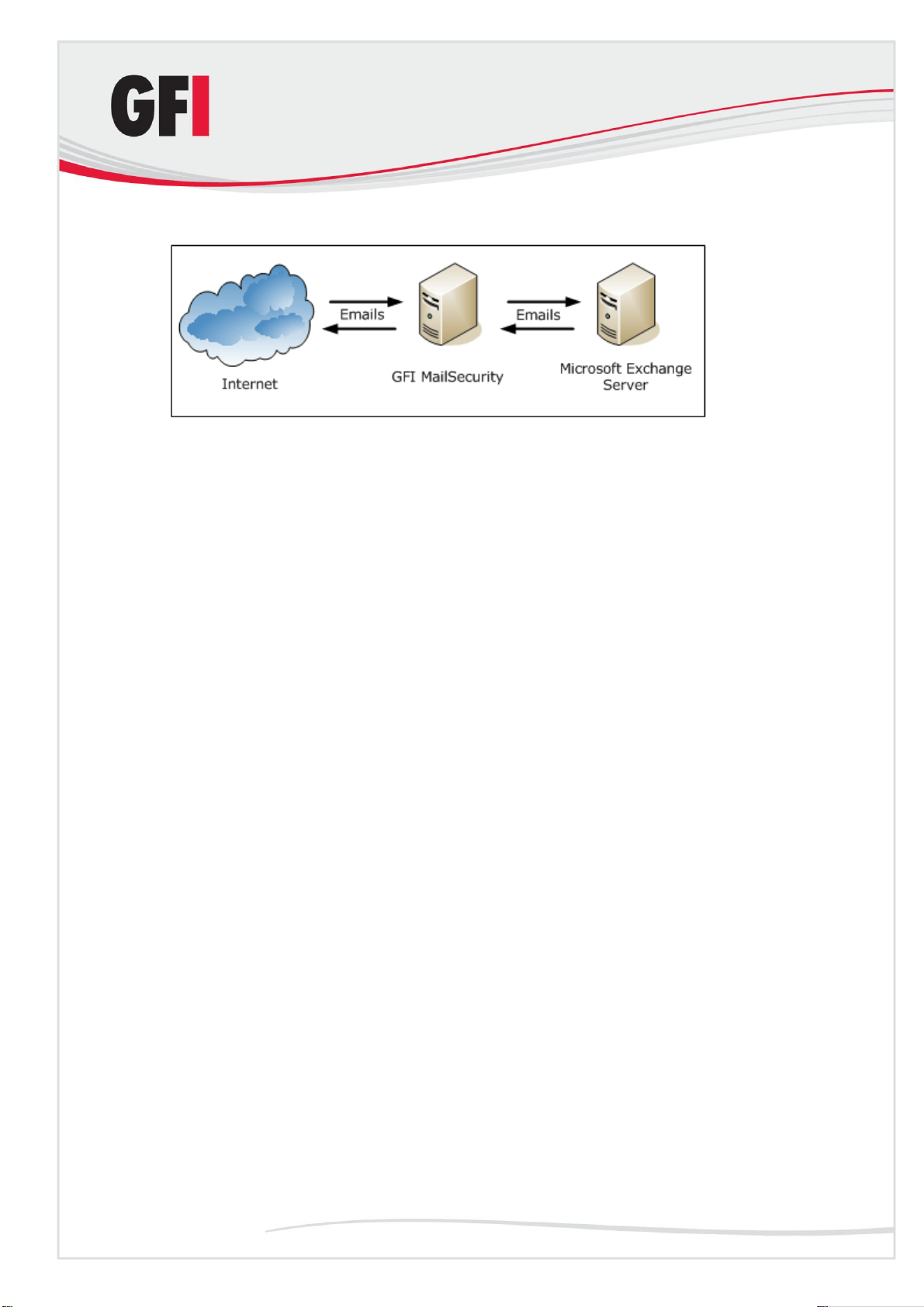
Installing GFI MailSecurity on your mail server
Figure 1 - Installing GFI MailSecurity on your mail server
You can install GFI MailSecurity directly on your mail server, without any
additional configuration required. Moreover you can also choose any of the
two installation modes (i.e., Active Directory mode or SMTP mode) to define
how GFI MailSecurity will retrieve the list of email users since your mail server
will have access to both the Active Directory as well as to the list of SMTP
users which is contained on the mail server itself.
NOTE: GFI MailSecurity can be only installed in the following Microsoft
Exchange 2007/2010 installations:
Edge Server Role
Hub Transport Role (and any other Microsoft Exchange 2007/2010 server
roles which are irrelevant to GFI MailSecurity)
Mailbox and Hub Transport Server Role (and any other Microsoft
Exchange 2007/2010 server roles which are irrelevant to GFI
MailSecurity)
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 5
Page 12
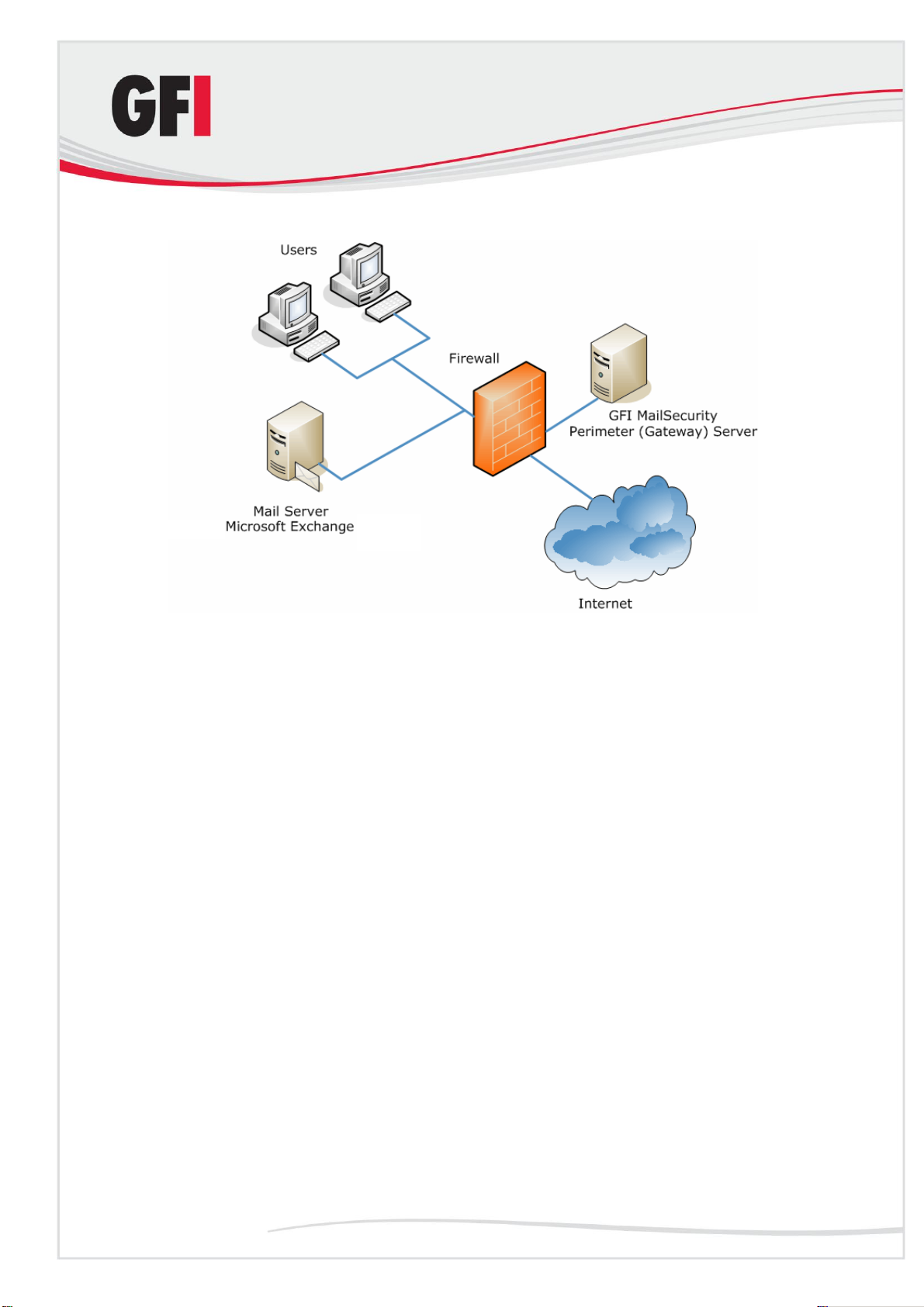
Installing GFI MailSecurity on a mail relay server
Figure 2 - Installing GFI MailSecurity on a mail gateway/relay server
When installing on a separate server (i.e., on a server which is not your mail
server), you must first configure that machine to act as a gateway (also
known as “Smart host” or “Mail relay” server) for all your email. This means
that all inbound email must pass through this machine for scanning before
being relayed to the mail server for distribution (i.e., it must be the first to
receive all emails destined for your mail server). The same applies for
outbound emails: The mail server must relay all outgoing emails to the
gateway machine for scanning before they are conveyed to the external
recipients via Internet (i.e. it must be the last 'stop‟ for emails destined for the
Internet). In this way, GFI MailSecurity checks all your inbound and outbound
mail before this is delivered to the recipients.
NOTE: You must install GFI MailSecurity in SMTP Gateway mode if you are
running Lotus Notes or another SMTP/POP3 server.
NOTE: If you are running a Windows NT network, the machine running GFI
MailSecurity can be separate from your Windows NT network - GFI
MailSecurity does not require Active Directory when installed in SMTP mode.
6 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 13
Installing GFI MailSecurity in front of your firewall
Figure 3 - Installing GFI MailSecurity on a separate machine on a DMZ
If running a Windows 2000/2003 firewall such as Microsoft ISA Server, a
good way to deploy GFI MailSecurity is to install it on a separate machine in
front of your firewall or on the firewall itself. This allows you to keep your
corporate mail server behind the firewall. GFI MailSecurity will act as a smart
host/mail relay server when installed on the perimeter network (also known as
DMZ - demilitarized zone).
NOTE: In a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 environment, the mail
relay server in the DMZ can be a machine running Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 with the Edge Transport Server Role installed.
When GFI MailSecurity is not installed on your mail server:
You can perform maintenance on your mail server whilst still receiving
email from the Internet.
Fewer resources are used on your mail server.
Additional fault tolerance - if anything happens to your mail server, you
can still receive email. This email is then queued on the GFI MailSecurity
machine.
NOTE: GFI MailSecurity does not require a dedicated machine when not
installed on the mail server. For example, you can install GFI MailSecurity on
your firewall (i.e. on your ISA Server) or on machines running other
applications such as GFI MailEssentials.
Installing GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Passive Cluster
NOTE: Installing GFI MailSecurity on a Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 cluster environment is currently not supported.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 7
Page 14

To install GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Passive cluster you must install GFI
MailSecurity on each node.
NOTE: Although you can install GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Passive
cluster, bear in mind that you still need to configure and manage a GFI
MailSecurity installation per node. The configuration settings and quarantine
emails are not shared between nodes.
On each node, you have to do the following:
Install GFI MailSecurity on the node local hard drive.
NOTE: Do not install GFI MailSecurity on the shared drive.
Install the GFI MailSecurity WWW virtual directory on the node‟s Default
Web Site.
If you are installing on an IIS cluster, make sure you bind GFI MailSecurity
to the Clustered SMTP Virtual Server instance.
The following steps show you how to install GFI MailSecurity in a typical
Active/Passive Cluster environment. For this scenario, assume the cluster,
named MAILCLUSTER, is made up of two nodes, named Node1 and Node2.
1. Using the Cluster Administrator console make Node1 active.
2. Install GFI MailSecurity on the local hard drive of Node2 as described in
the „Installing GFI MailSecurity‟ section of this chapter. When you reach the
IIS Setup step of the installation, select Default Web Site to host the GFI
MailSecurity WWW virtual directory.
NOTE: The Default Web Site IP address of Node2 should not be set to „All
unassigned‟. You should configure the Default Web Site to use the IP
address of the MAILCLUSTER machine.
3. When the GFI MailSecurity installation on Node2 completes, you should be
able to access the Node2 configuration using the following URL:
http://Node2/MailSecurity/
4. From the Cluster Administrator console, make Node2 active.
5. Install GFI MailSecurity on the local hard disk of Node1 as described in the
„Installing GFI MailSecurity‟ section of this chapter. When you reach the IIS
Setup step of the installation, select Default Web Site to host the GFI
MailSecurity WWW virtual directory.
NOTE: The Default Web Site IP address of Node1 should not be set to „All
unassigned‟. You should configure the Default Web Site to use the IP
address of the MAILCLUSTER machine.
6. When the GFI MailSecurity installation on Node1 completes, you should be
able to access the Node1 configuration using the following URL:
http://Node1/MailSecurity/
7. To access the product configuration of the currently active node use the
following URL: http://MAILCLUSTER/MailSecurity/.
NOTE: To access product configuration from a remote machine you must
configure the GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard application, making sure that
the MAILCLUSTER name/IP is specified for IIS Mode. For more information,
8 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 15
refer to Securing access to the GFI MailSecurity configuration/quarantine
section in this chapter.
NOTE: You will only be able to access the URL
http://MAILCLUSTER/MailSecurity/ if you assign the IP address of the
MAILCLUSTER machine to the Default Web Site for Node1 and Node2
during the IIS Setup installation step.
8. The installation of GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Passive cluster is now
complete.
NOTE: If Service Pack 2 for Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 is not installed
on a Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 cluster installation, Internet Information
Services Web sites that are hosted on the cluster will not start automatically
when an Exchange Server 2003 virtual server fails over to a cluster node.
More information about this issue can be found in Microsoft Knowledge Base
Article 885440.
Due to the above, the GFI MailSecurity configuration could become
unavailable following a failover or moving of an Exchange Virtual Server from
one node of the cluster to the other.
Installing Service Pack 2 for Exchange Server 2003 is thus recommended.
Guidelines on how to install Exchange Server 2003 service packs in a
clustered Exchange Server environment can be found in Microsoft Knowledge
Base Article 867624.
To uninstall GFI MailSecurity from the MAILCLUSTER cluster environment
outlined above, follow these steps:
1. Using the Cluster Administrator console make Node1 active.
2. Uninstall GFI MailSecurity from Node2.
3. Using the Cluster Administrator console make Node2 active.
4. Uninstall GFI MailSecurity from Node1.
5. The uninstallation of GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Passive cluster is now
complete.
Installing GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Active Cluster
Installing GFI MailSecurity on an Active/Active cluster is currently not
supported.
2.3 Which installation mode should I use?
Active Directory mode
When installed in Active Directory mode, GFI MailSecurity creates user-based
rules, such as Attachment Checking and Content Checking rules, based on
the list of users available in Active Directory. This means that the machine
running GFI MailSecurity must be behind your firewall and must have access
to the Active Directory containing all your email users (i.e., the machine must
be part of the Active Directory domain). You can install GFI MailSecurity in
Active Directory mode directly on your mail server as well as on any other
domain machine that is configured as a mail relay server in your domain.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 9
Page 16

SMTP mode
In SMTP mode, GFI MailSecurity will create user-based rules, such as
Attachment Checking and Content Checking rules, based on the list of email
users/addresses available on your mail server. This means that you must
install GFI MailSecurity in SMTP mode if your machine does not have access
to the Active Directory containing all your email users. This includes machines
that are not part of your Active Directory domain (i.e., non-domain machines)
as well as machines in a DMZ. However, you can still install GFI MailSecurity
in SMTP mode on your mail server as well as on any other machine that has
access to Active Directory containing all (email) users.
NOTE: Both installation modes have the same scanning features and
performance. The only difference between Active Directory and SMTP
installation mode is the way that GFI MailSecurity accesses/gathers the list of
email users for generating its scanning rules and notifications.
2.4 Hardware requirements
The hardware requirements for GFI MailSecurity are:
Pentium 4 (or equivalent) - 2Ghz
512MB RAM
1.5 GB of physical disk space
2.5 Software requirements
2.5.1 Supported Operating Systems
Windows Server 2008 Standard or Enterprise (x86 or x64) (R1 or R2)
Windows Server 2003 Standard or Enterprise (x86 or x64)
Windows 2000 Server/Advanced Server (Service Pack 1 or higher)
Windows XP professional
Windows Small Business Server 2000
Windows Small Business Server 2003
Windows Small Business Server 2008
2.5.2 Supported Mail Servers
Microsoft Exchange Server 2010, 2007, 2003, 2000 (SP1)
Lotus Notes 5.5, 5.0, 4.5, 4
Any SMTP/POP3 mail server
2.5.3 Other components
Microsoft .Net framework 2.0
MSMQ - Microsoft Messaging Queuing Service
Internet Information Services (IIS) - SMTP and World Wide Web services
Microsoft Data Access Components (MDAC) 2.8
10 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 17

2.6 Important installation notes
Windows XP
Since in Windows XP the version of Internet Information Services (IIS), is
included and is limited to serve only 10 simultaneous client connections,
installing GFI MailSecurity on a machine running Windows XP could affect its
performance.
Windows Server 2008
When installing on Windows Server 2008, the following pre-requisites are
required:
Web Server (IIS) role
ASP.NET
Windows Authentication Services
Microsoft SMTP Services
For more information, refer to:
http://kbase.gfi.com/showarticle.asp?id=KBID001596
Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
If you are installing on Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010, you need to
install one of the following roles;
Edge Server Role,
Hub Transport Role or,
Mail Server and Hub Transport roles.
GFI MailSecurity cannot be installed on a Microsoft Exchange 2007/2010
machine with only Mailbox Server Role installed. In addition, IIS SMTP
service is not required, since it has its own built in SMTP server.
Windows Small Business Server
When using Small Business Server, ensure you have installed Service Pack 2
for Exchange Server 2000 and Service Pack 1 for Exchange Server 2003.
Other installation configurations
Disable anti-virus software from scanning the GFI MailSecurity directories.
Anti-virus products are known to both interfere with normal operation as well
as slow down any software that requires file access. In fact, Microsoft does
not recommend running file-based anti-virus software on the mail server. For
more information, please refer to:
http://kbase.gfi.com/showarticle.asp?id=KBID001559.
GFI MailSecurity directories should never be backed up using backup
software.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 11
Page 18

2.7 Preparing to install GFI MailSecurity on an IIS mail relay server
In order to install GFI MailSecurity on a mail relay/gateway machine, it must
be running the IIS SMTP Service and World Wide Web service. You must
also configure the machine as an SMTP relay to your mail server. This means
that the MX record of your domain must be pointing to the gateway machine.
This section describes how you can configure your mail relay and install GFI
MailSecurity.
About Windows 2000/2003 IIS SMTP & World Wide Web services
The SMTP service is part of IIS, which is part of Windows 2000/2003/XP. It is
used as the message transfer agent of Microsoft Exchange Server
2000/2003, and has been designed to handle large amounts of mail traffic.
The World Wide Web service is also part of IIS. It uses the HTTP protocol to
handle web client requests on a TCP/IP network.
The IIS SMTP service and World Wide Web service are included in every
Windows 2000/2003/XP distribution.
Step 1: Verify installation of IIS SMTP and WWW services
GFI MailSecurity uses the Windows 2000/2003/XP IIS SMTP service as its
SMTP server.
1. On the taskbar, click Start ► Settings ► Control Panel. Double-click
Add/Remove Programs and then click Add/Remove Windows
Components.
2. From the dialog on display, locate and click the Internet Information
Services (IIS) component, then click Details.
3. Select the SMTP Service check box and World Wide Web Service check
box. Click OK to start the installation of the selected services. Follow the
onscreen instructions and wait until the installation completes.
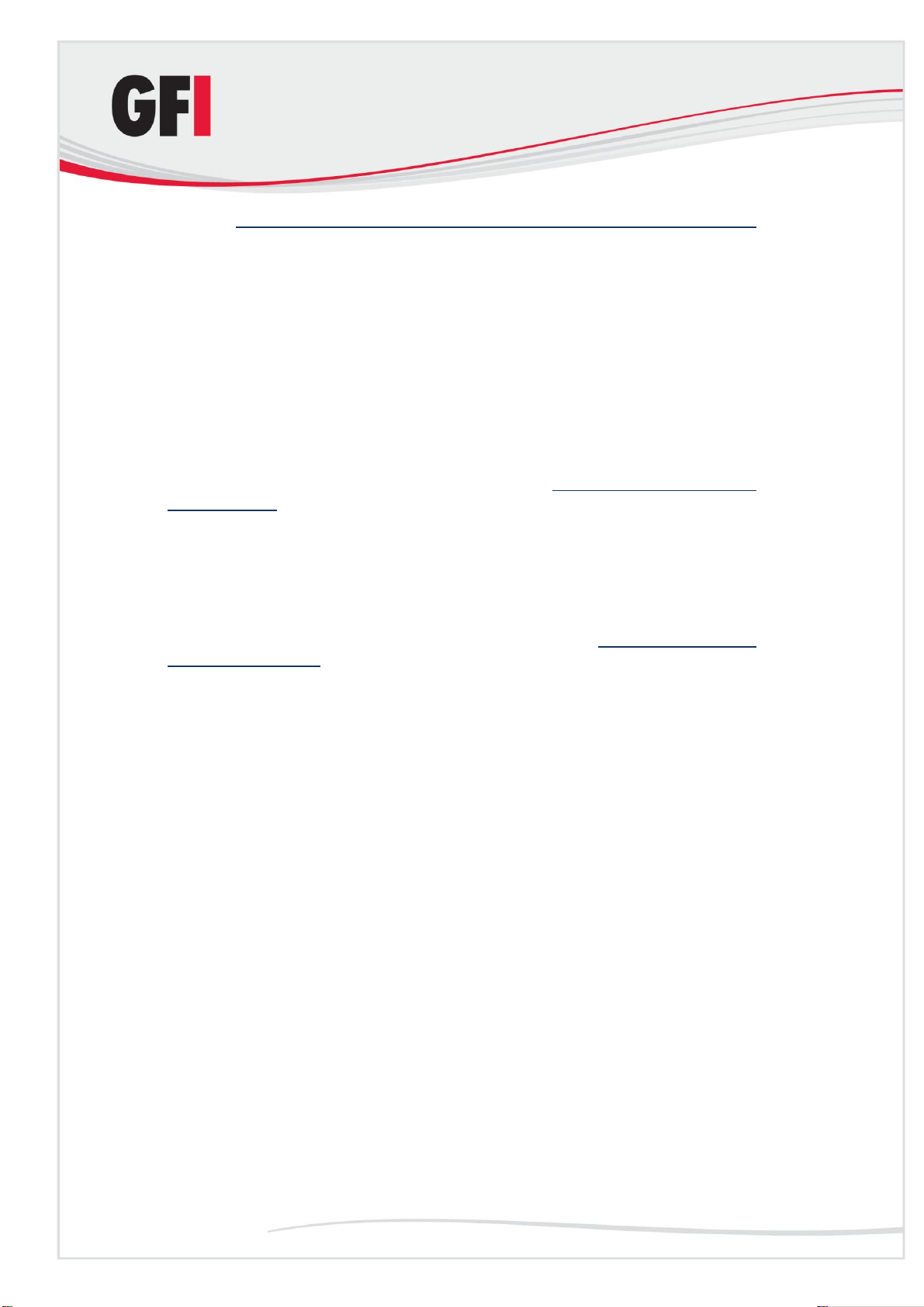
Step 2: Specify mail relay server name and assign an IP
1. On the taskbar, click Start ► Settings ► Control Panel. Double-click
Administrative Tools and then double-click Internet Information Services.
2. Expand the server name node, right-click the Default SMTP Virtual Server
node and then click Properties.
12 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 19
Screenshot 2 - Assign an IP address to the mail relay server
3. Assign an IP address to the SMTP relay server from the IP address list
and then click OK.
Step 3: Configure the SMTP service to relay mail to your mail server
Now you must configure the SMTP service to relay inbound messages to your
mail server.
Start by creating a local domain in IIS to route mail:
1. On the taskbar, click Start ► Settings ► Control Panel. Double-click
Administrative Tools and then double-click Internet Information Services.
2. Expand the server name node then expand the Default SMTP Virtual
Server and then click Domains. By default, you should have a Local
(Default) domain with the fully qualified domain name of the server.
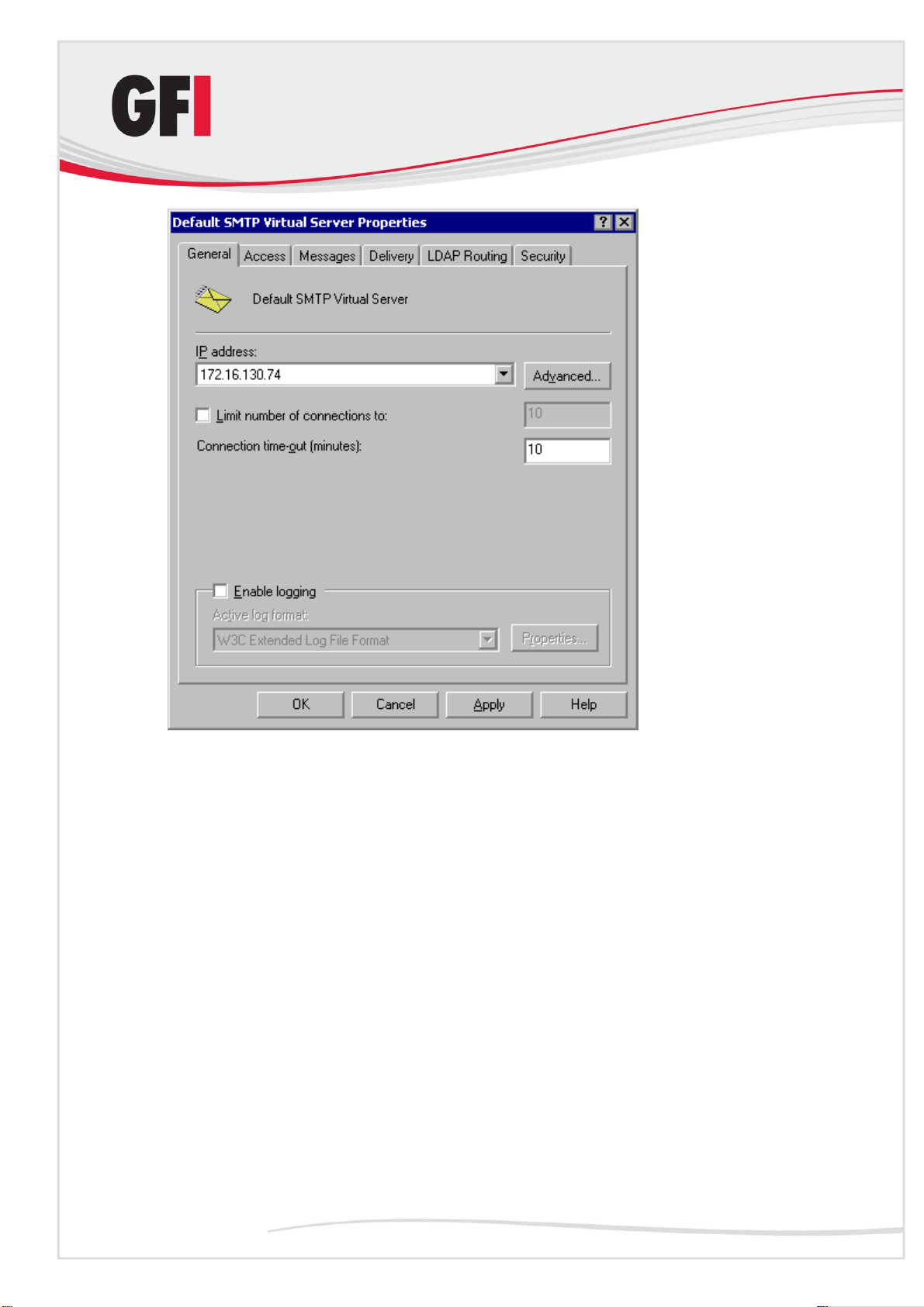
3. Configure the domain for inbound message relaying as follows:
a) Right-click the Domains node, and then click New ► Domain.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 13
Page 20
Screenshot 3 - SMTP Domain Wizard - Selecting domain type
b) Select Remote and then click Next.
c) Type the domain name in the Name box and then click Finish.
NOTE: Upon installation, GFI MailSecurity will import Local Domains from the
IIS SMTP service. If you add additional Local Domains in IIS SMTP service,
you must also add these domains to GFI MailSecurity because this does not
detect newly added Local Domains automatically. You can add more/new
Local Domains using the GFI MailSecurity configuration. For more
information, refer to the Adding Local Domains section in the General
Settings chapter of this manual.
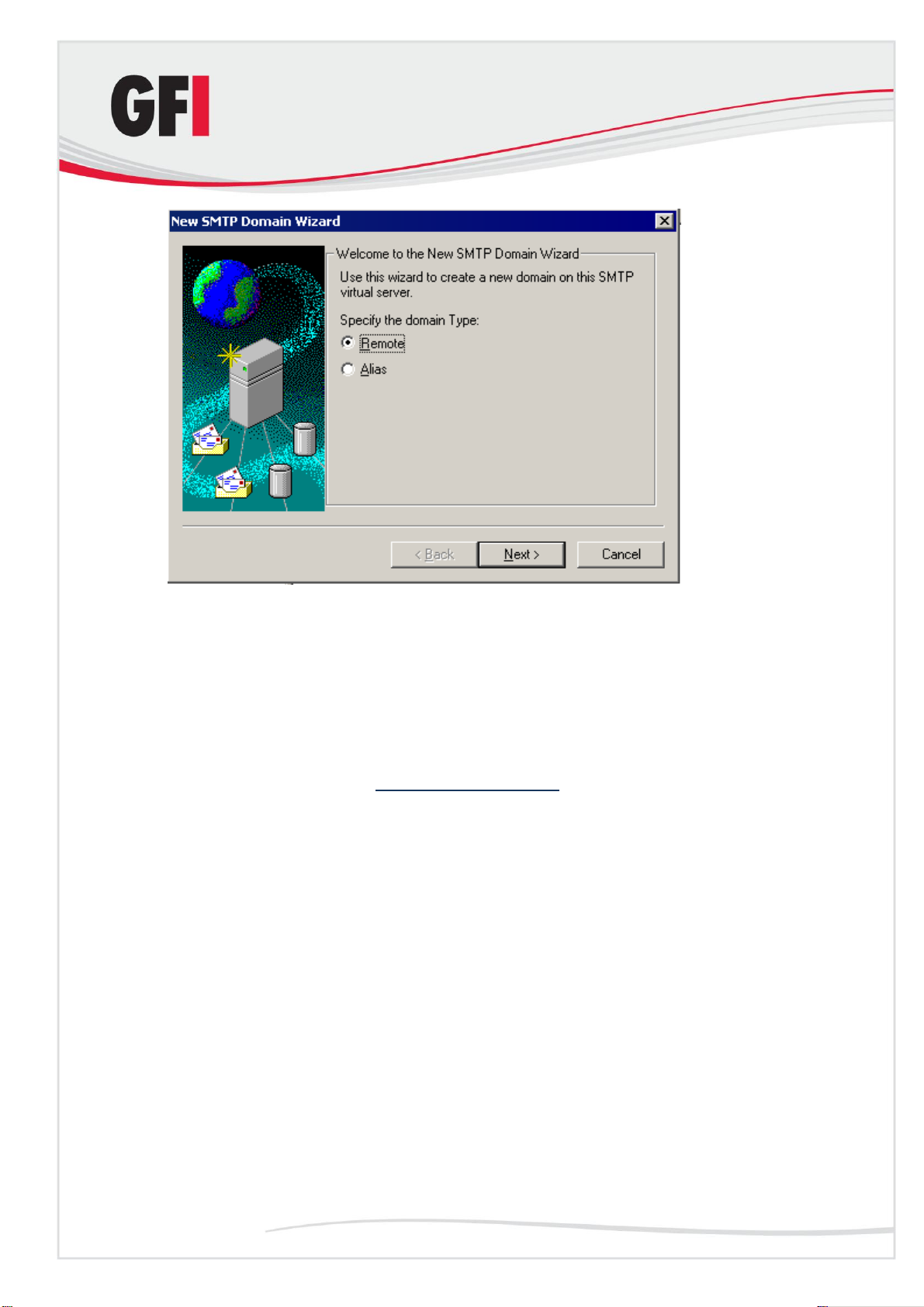
Configure the domain to relay email to your mail server:
1. Right-click the domain you just created and then click Properties. Select
the Allow the Incoming Mail to be relayed to this domain check box.
2. In the Route domain dialog box, click Forward all email to smart host and
type the IP address (in square brackets) of the server which will handle the
emails addressed to this new domain. For example, [123.123.123.123]
NOTE: The square brackets are used to differentiate an IP address from a
hostname (which does not require square brackets), i.e., the server detects
an IP address from the square brackets.
3. Click OK.
14 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 21
Screenshot 4 - Configure the new domain
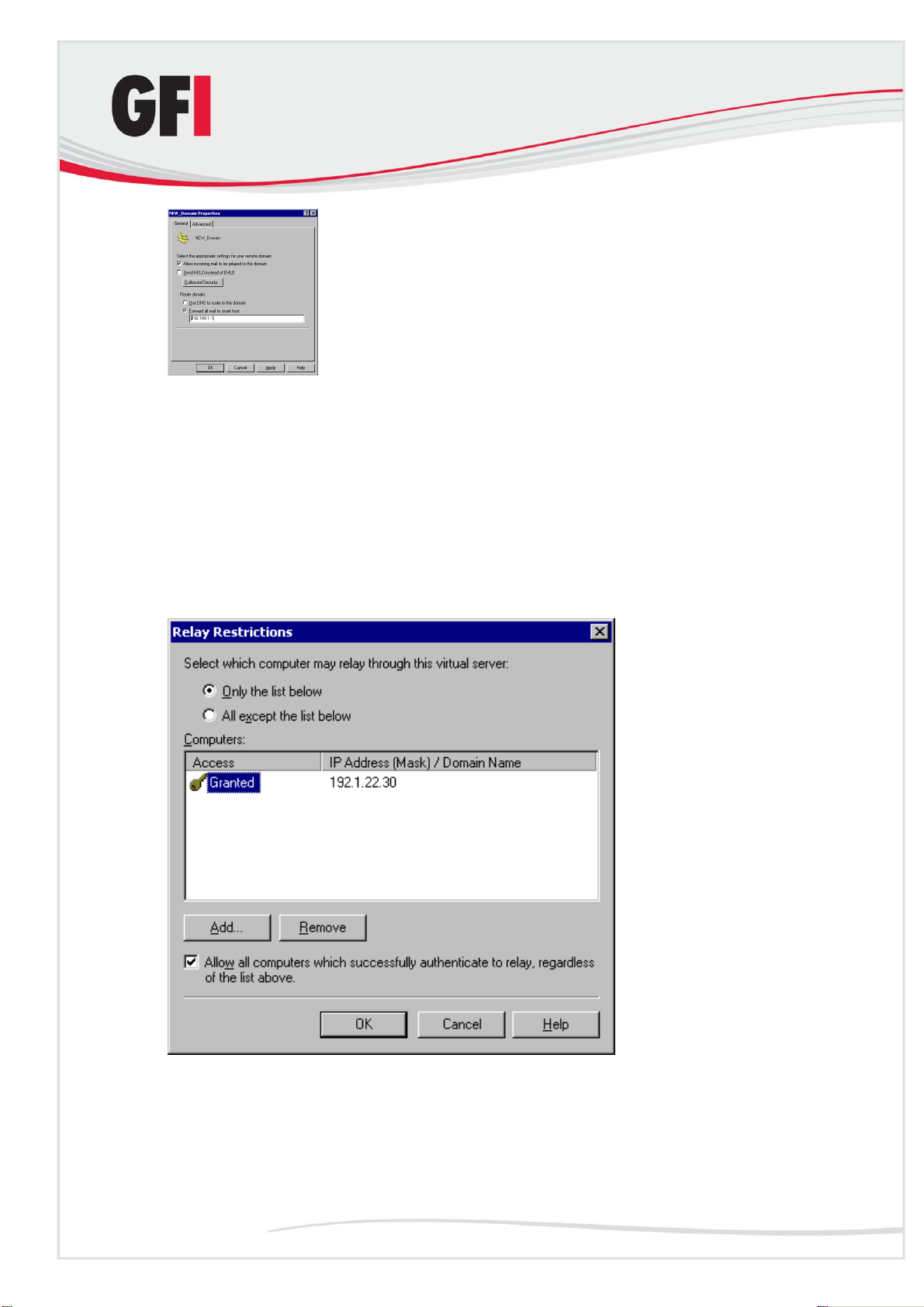
Step 4: Secure your mail relay server
In this step, you will set up your SMTP virtual server‟s mail Relay Restrictions.
This means that you must specify which machines may relay email through
this virtual server (i.e., effectively limit the servers that can send email via this
server).
1. Right-click the Default SMTP Virtual Server node and then click
Properties.
2. In the properties dialog box, click the Access tab and then click Relay to
open the Relay Restrictions dialog box.
Screenshot 5 - Relay Restrictions dialog
3. Click Only the list below and then click Add to specify the list of permitted
computers.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 15
Page 22
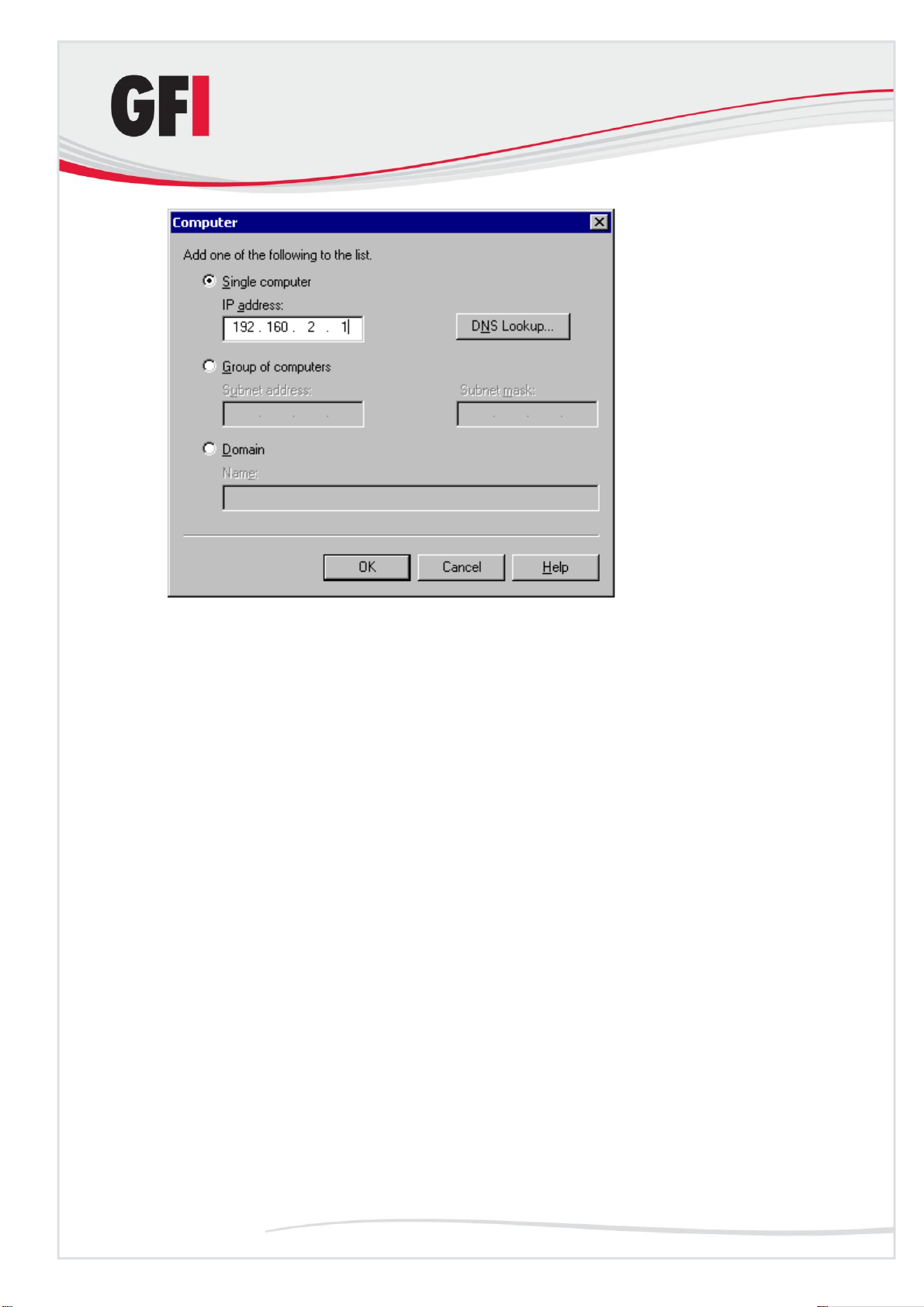
Screenshot 6 - Specify machines which may relay email via virtual server
4. In the Computer dialog box, specify the IP of the mail server that will be
forwarding the email to this virtual server and then click OK to add the entry to
the list.
NOTE: You can specify the IP of a single computer, group of computers or a
domain:
Single computer: Select this option to specify one particular host that will
relay email via this server. If you want to look up the IP address of a
specific host, click DNS Lookup.
Group of computers: Select this option to specify the base IP address
for the computers that you want to relay.
Domain: Select this option to include all the computers of a specified
domain. This means that the domain controller will openly relay emails via
this server. Please note that this option adds processing overhead, and
may reduce SMTP service performance because it includes reverse DNS
Lookups to verify the domain name of all IP addresses that try to relay.
Step 5: Configure your mail server to relay email via the Gateway server
After you have configured the IIS SMTP service to send and receive email,
you must configure your mail server to relay all email to the mail relay server:
If you have Microsoft Exchange Server 4/5/5.5:
1. Start the Microsoft Exchange Administrator and double-click on Internet
Mail Service to open the properties configuration dialog box.
16 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 23
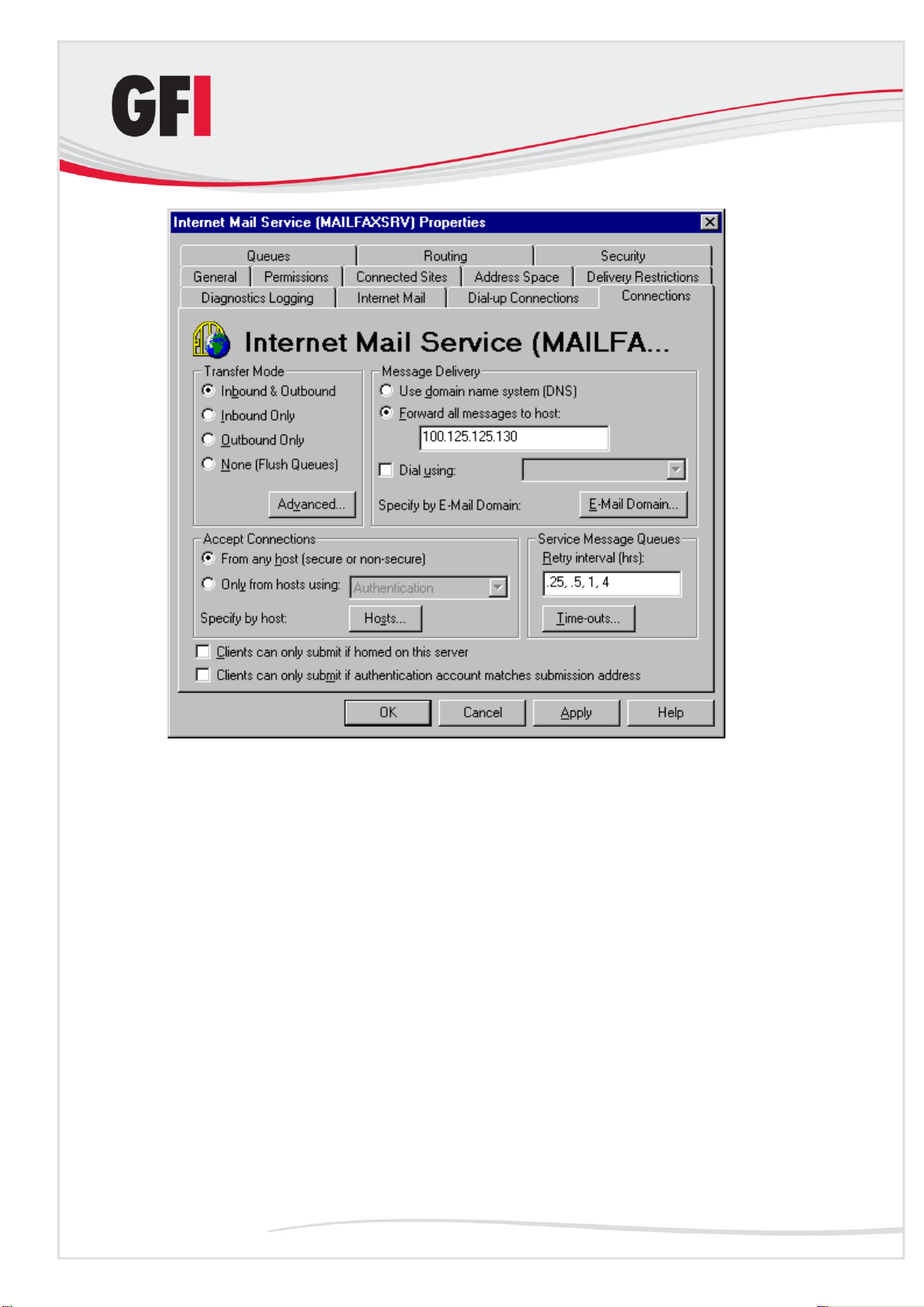
Screenshot 7 - The Microsoft Internet mail connector
2. Click the Connections tab and in the Message Delivery area click
Forward all messages to host. Type the computer name or IP of the
machine running GFI MailSecurity.
3. Click OK and restart the Microsoft Exchange Server from the services
applet.
If you have Microsoft Exchange Server 2000/2003:
You will need to set up an SMTP connection that forwards all email to GFI
MailSecurity:
1. Start the Exchange System Manager.
2. Right-click the Connectors Node, click New ► SMTP Connector and
then specify the connector name.
3. Click Forward all mail through this connector to the following smart
host, type in the IP of the GFI MailSecurity server (the mail relay/Gateway
server) and then click OK.
NOTE: Always enclose the IP address within square brackets [ ]. For
example, [100.130.130.10].
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 17
Page 24

4. Select the SMTP Server that must be associated to this SMTP Connector.
Click the Address Space tab, and then click Add. Click SMTP and then click
OK to accept the changes.
5. Click OK. All emails will now be forwarded to the GFI MailSecurity
machine.
If you have Lotus Notes:
1. Double-click the Address Book in Lotus Notes.
2. Click on Server item to expand its sub-items.
3. Click Domains and then click Add Domains.
4. In the Basics section, click Foreign SMTP Domain from the Domain
Type field and in the Messages Addressed to area, type “*” in the Internet
Domain box.
5. Under the Should be routed to area, specify the IP of the machine
running GFI MailSecurity in the Internet Host box.
6. Save the settings and restart the Lotus Notes server.
If you have an SMTP/POP3 mail server:
1. Start the configuration program of your mail server.
2. Search for the option to relay all outbound email via another mail server.
This option will be called something like Forward all messages to host.
Enter the computer name or IP of the machine running GFI MailSecurity.
3. Save the new settings and restart your mail server.
Step 6: The MX record of your domain must point to the mail relay server
NOTE: If your ISP manages the DNS server, ask this provider to update it for
you.
Since the new mail relay server must receive all inbound email first, you must
update the MX record of your domain to point to the IP of the new mail
relay/Gateway server. Otherwise, email will continue to go to your mail server
and by-pass GFI MailSecurity.
Verify the MX record of your DNS server as follows:
1. Open the command prompt, type nslookup and press Enter.
2. Type set type=mx and press Enter.
3. Type your mail domain and press Enter.
4. The MX record should return a single IP that must correspond to the IP of
the machine running GFI MailSecurity.
18 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 25
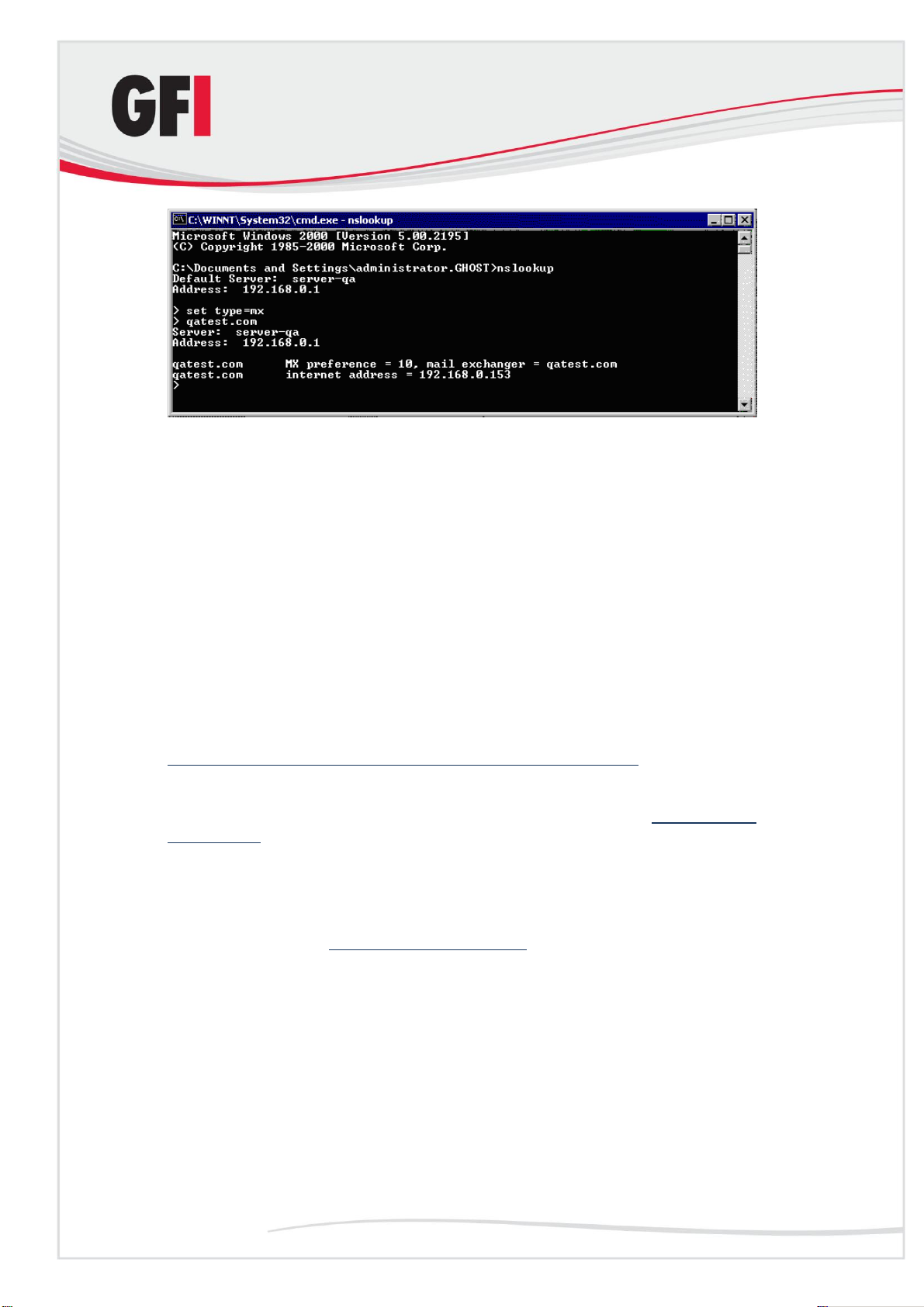
Screenshot 8 - Checking the MX record of your domain
Step 7: Test your new mail relay server
Before you proceed to install GFI MailSecurity, verify that your new mail relay
server is working correctly.
1. Test the IIS SMTP inbound connection of your mail relay server by sending
an email from an external account to an internal user (you can use web-mail,
for example MSN Hotmail, if you do not have an external account available).
Verify that the email client received the email.
2. Test the IIS SMTP outbound connection of your mail relay server by
sending an email to an external account from an email client. Verify that the
external user received the email.
NOTE: Instead of using an email client, you can send email manually through
Telnet. This will give you more troubleshooting information. For more
information, refer to this Microsoft Knowledge Base article:
http://support.microsoft.com/support/kb/articles/Q153/1/19.asp
Step 8: Install GFI MailSecurity on the mail relay server
For information on how to install GFI MailSecurity, refer to Installing GFI
MailSecurity section in this chapter.
2.8 Preparing to install GFI MailSecurity on your mail server
No additional configuration is required if you are installing GFI MailSecurity directly on your mail server. For information on how to install GFI MailSecurity, refer to Installing GFI MailSecurity section in this chapter.
2.9 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Before you install GFI MailSecurity, check the points below:
1. Make sure that you are logged on as Administrator or you are using an
account with administrative privileges.
2. Save any pending work and close all open applications on the machine.
3. Check that the machine you are installing GFI MailSecurity on meets the
system and hardware requirements specified earlier in this chapter.
To install GFI MailSecurity follow these steps:
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 19
Page 26

1. Run the GFI MailSecurity setup program by double-clicking on the
MailSecurity10.exe file. The installation wizard will perform some unpacking
operations and then display the Welcome page. Click Next to continue.
2. Read the license agreement displayed in the License agreement page
and click I accept the terms in the license agreement if you accept the
terms of the license agreement. Click Next to continue the installation.
NOTE: If upgrading from a previous version than GFI MailSecurity 10.1 SR8,
you will be asked to upgrade to the Firebird database. Selecting import will
prompt GFI MailSecurity to automatically launch the quarantine upgrade tool
after the installation. If you select not to import the quarantine database, any
previous quarantine data will not be used by the upgraded version. For
information on the quarantine upgrade tool, refer to Quarantine Upgrade tool
section in this manual.
3. Type the administrator email address in the Administrator Email box. If
you bought a license for GFI MailSecurity, type it in the License Key box. If
you do not have a license yet and want to evaluate GFI MailSecurity, leave
the default evaluation license key in the License Key box. Click Next to
continue the installation.
Screenshot 9 - Define if the server has access to all email users in the Active Directory
4. Setup will now ask you to select the mode that GFI MailSecurity will use to
retrieve the list of your email users. You must select one of the following
options:
Yes, all email users are available on Active Directory - Select this
option to continue installing GFI MailSecurity in Active Directory mode. In
20 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 27
this mode, GFI MailSecurity creates user-based rules, for example
Attachment Checking rules, based on the list of users available in the
Active Directory. This means that the machine on which GFI MailSecurity
is being installed must be behind your firewall (for example, Mail Server)
and must have access to the Active Directory containing all your email
users (i.e., the machine on which GFI MailSecurity is being installed must
be part of the Active Directory domain).
No, I do not have Active Directory or my network does not have
access to Active Directory (DMZ) - Select this option to continue
installing GFI MailSecurity in SMTP mode. In this mode, GFI MailSecurity
will create user-based rules, for example Attachment Checking rules,
based on the list of email users/addresses imported from your mail server.
You must select this mode if you are installing GFI MailSecurity on a
machine that does not have access to the Active Directory containing the
complete list of all your email users. This includes machines on a DMZ or
machines that are not part of the Active Directory Domain. However, you
can still choose this mode to install GFI MailSecurity on machines that do
have access to the Active Directory containing all your email users.
Click Next to proceed with the installation.
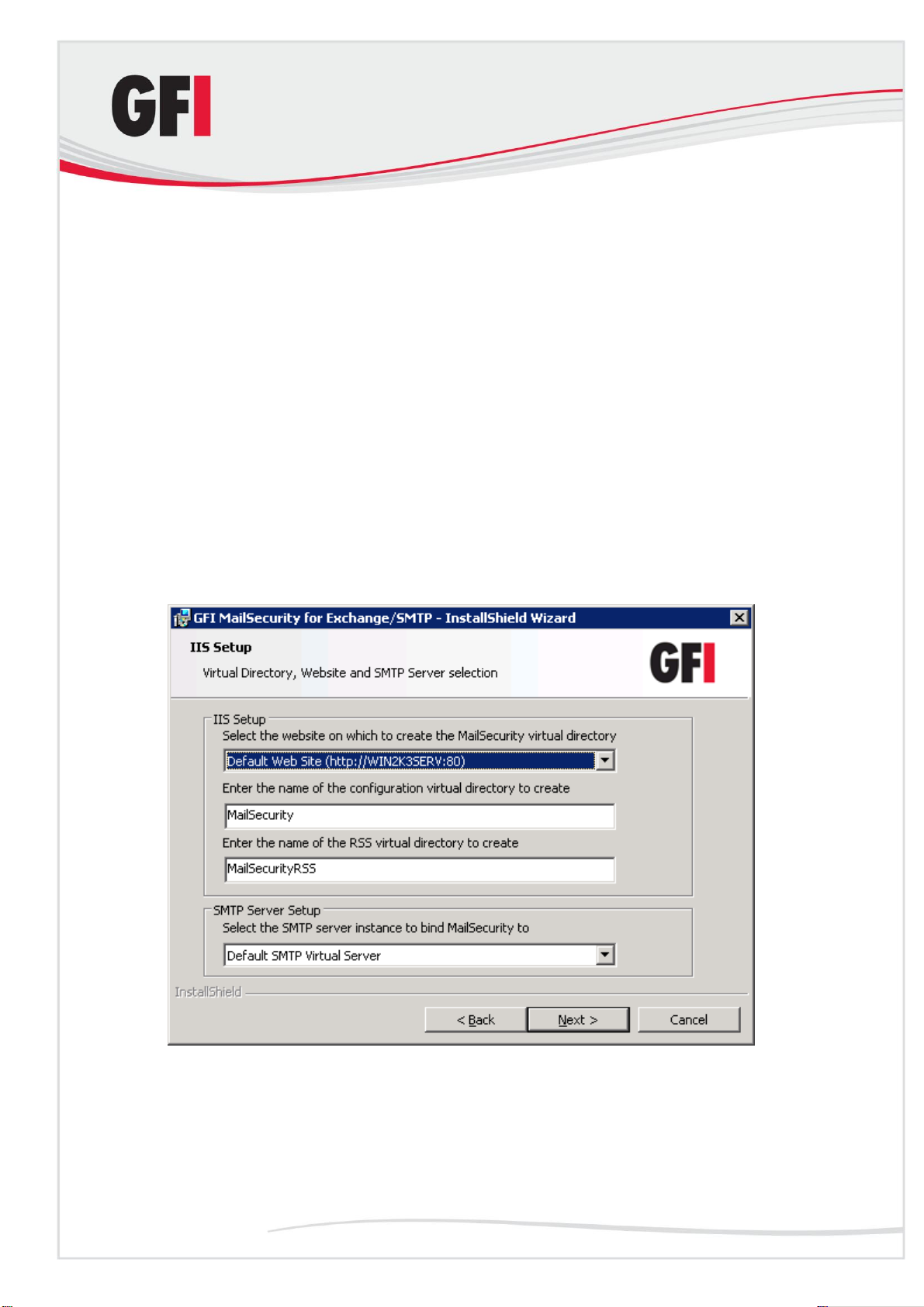
Screenshot 10 - Define your SMTP server and GFI MailSecurity virtual folder details.
5. You now need to select the server where you want to host the GFI
MailSecurity configuration pages. On this server, two virtual directories are
created to host the configuration pages and the quarantine RSS feeds. You
can specify custom virtual directory names if you want, or else leave the
defaults.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 21
Page 28

NOTE: If you are installing on a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
machine, the IIS SMTP service is not required, since it has its own built in
SMTP server. In such a case, the SMTP Server Setup area is not displayed
and you can click Next to continue and go to step 7 directly.
GFI MailSecurity relies on the IIS SMTP service to send and receive SMTP
mail. It binds to your default SMTP virtual server (i.e., the server specified in
the MX record of your DNS Server). However, if you have multiple SMTP
virtual servers on your domain, you can bind GFI MailSecurity to any
available SMTP virtual server. To change the default SMTP connection,
select the required server from the list of available SMTP Virtual Servers
provided in this dialog box.
NOTE: After installing the product, you can still bind GFI MailSecurity to
another SMTP virtual server from the GFI MailSecurity Configuration (GFI
MailSecurity ► Settings ► Bindings). For more information, refer to SMTP
server bindings section in this manual.
Click Next to continue the installation.
6. Setup will now search your network and will import a list of your Local
Domains from the IIS SMTP service. GFI MailSecurity determines if an email
is inbound or outbound by comparing the domain in a sender‟s address to the
list of local domains. If the address exists in the list, then the email is
outbound. Check that all your Local Domains have been included in the list on
display. If not, make sure to add any unlisted domain after the installation
completes. For more information, refer to the Adding Local Domains section
in this manual. Click Next to continue.
7. Setup will now ask you to define the folder where you want to install GFI
MailSecurity. GFI MailSecurity requires approximately 50 MB of free hard disk
space. Additionally, you must also reserve approximately 200 MB for
temporary files. Click Change to specify a new installation path or click Next
to install in the default location and proceed with the installation.
NOTE: If you are installing GFI MailSecurity on a x64 machine, it will be
installed under the c:\program files (x86)\ folder.
8. The installation wizard has now collected all the required installation
settings and is ready to install GFI MailSecurity. If you want to make changes
to these settings, click Back. Otherwise, click Install to start the installation
process.
9. During the installation, you are prompted that the setup needs to restart the
SMTP services. Click Yes to restart these services and finalize the
installation.
NOTE: If you are installing on a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
machine, you will not be prompted to restart the SMTP service.
10. When the installation completes, click Finish to close the installation
wizard.
NOTE: If you are installing on a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
machine, the installation will launch the GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation
22 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 29
Wizard. Refer to the following section for information on how to use this
wizard.
NOTE: If you are upgrading from a previous version (version 9 onwards) of
GFI MailSecurity, you might be prompted to upgrade your quarantine
database to a new Firebird database format. For more information, refer to
the Quarantine Upgrade tool section in this manual.
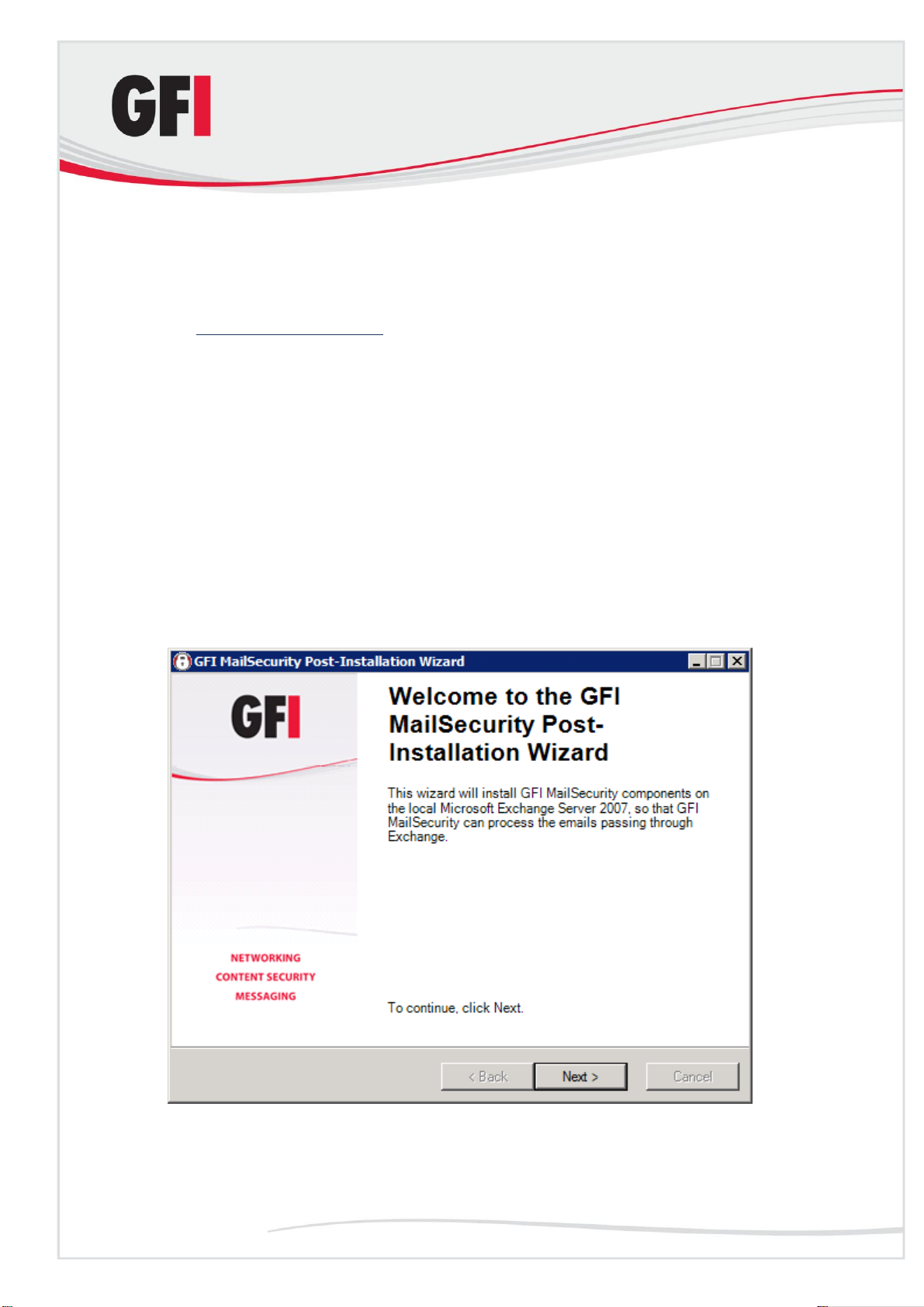
2.10 GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation Wizard
NOTE: This section applies only when installing GFI MailSecurity on a
Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 machine.
IMPORTANT: You need to complete this wizard for GFI MailSecurity to work
with Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010.
The GFI MailSecurity installation wizard launches the GFI MailSecurity Post-
Installation Wizard when you click Finish. The GFI MailSecurity PostInstallation Wizard registers GFI MailSecurity with the local installation of
Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 so that it can process and scan the
emails passing through the server.
To complete the GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation Wizard, follow these steps:
1. Click Next in the welcome page.
Screenshot 11 - GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation Wizard welcome page
2. The wizard will collect information from the Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 installation, such as the list of local domains and the server roles
installed, for example Hub Transport Server Role.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 23
Page 30
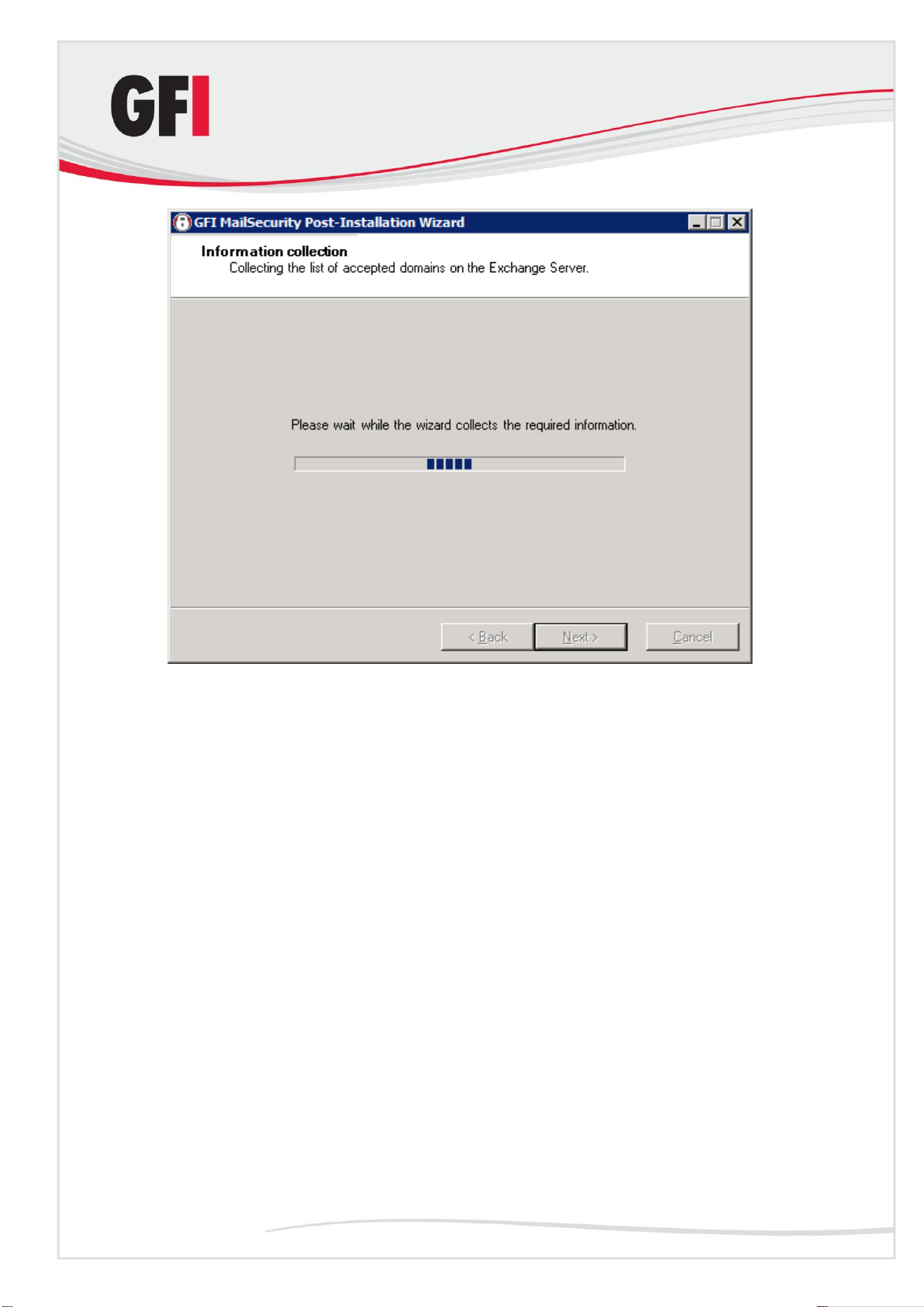
Screenshot 12 - Collecting information from Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
3. The wizard will display the accepted domain list collected from Microsoft
Exchange Server 2007/2010. If you need to specify another local domain,
type it in the Local domains box and click Add. If you want to remove a
domain that you added from this page, click on it from the list, and then click
Remove.
NOTE: The local domains you add from this page affect the GFI MailSecurity
installation only. The Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 accepted
domains list is not modified.
24 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 31

Screenshot 13 - Local domains list
4. Click Next to continue.
5. The wizard displays a list of the Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010
server roles detected on this machine, and a list of the GFI MailSecurity
components it needs to register for it to be able to process and scan emails
passing through the server.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 25
Page 32

Screenshot 14 - Server roles detected and list of components to install.
6. Click Next to install the required GFI MailSecurity components.
Screenshot 15 - Installing the required GFI MailSecurity components
26 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 33

7. In the finish page, the GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation wizard will list the
GFI MailSecurity components that it successfully installed. Click Finish to
close the wizard and complete the installation of GFI MailSecurity on a
Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 machine.
Screenshot 16 - GFI MailSecurity Post-Installation Wizard finish page
2.11 Adding GFI MailSecurity to the Windows DEP Exception
List
Data Execution Prevention (DEP) is a set of hardware and software
technologies that perform memory checks to help prevent malicious code
from running on a system.
The DEP technology is available only on Microsoft Windows XP with Service
Pack 2, Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (x32 Edition) with Service Pack 1
and Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (x64 Edition). On Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 (x32 Edition) with Service Pack 1 and Microsoft Windows Server
2003 (x64 Edition), DEP is by default turned on for all programs and services
except those that the administrator selects.
If you installed GFI MailSecurity on Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (x32
Edition) with Service Pack 1 or Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (x64 Edition),
you will need to add the GFI MailSecurity scanning engine executable
(GFiScanM.exe) and the Kaspersky Virus Scanning Engine executable
(kavss.exe) to the Windows Data Execution Prevention (DEP) exception list.
To add the GFI executables in the DEP exception list follow these steps:
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 27
Page 34

1. From the Start menu load the Control Panel and choose the System
applet.
2. From the Advanced tab, click Settings under the Performance area.
3. Click the Data Execution Prevention tab.
4. Click Turn on DEP for all programs and services except those I select.
5. Click Add and from the dialog box browse to the GFI MailSecurity
installation folder, <GFI\ContentSecurity\MailSecurity>, and choose
GFiScanM.exe.
6. Click Add and from the dialog box browse to the GFI MailSecurity
installation folder, <GFI\ContentSecurity\AntiVirus\Kaspersky\>, and choose
kavss.exe.
7. Click Apply and OK to apply the changes.
8. Restart the "GFI Content Security Auto-Updater Service" and the "GFI
MailSecurity Scan Engine" services.
2.12 Securing access to the GFI MailSecurity
configuration/quarantine
The GFI MailSecurity configuration and quarantine store can be accessed
through a web browser and thus it is imperative that you configure proper
access security so that only authorized users can set-up rules and manage
the quarantine store.
You can configure access security to the GFI MailSecurity configuration
pages and quarantine store via the GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard application.
To configure access security, follow these steps:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard shortcut found under Start ►
Programs ► GFI MailSecurity.
2. The GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard application is loaded. You now need
to select whether you want to allow only local access to the Configuration and
Quarantine Store or else both local and remote. To allow only local access,
click Local mode, so that the Configuration and Quarantine Store can only be
accessed when working directly on the server machine where GFI
MailSecurity is installed. On the other hand, to allow both local and remote
access, click IIS mode, so that authorized users, both from the local machine
and other remote machines, can access the GFI MailSecurity Configuration
and Quarantine Store.
28 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 35

Screenshot 17 - GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard
3. If you selected Local mode, you do not need to configure anything else. If
you selected IIS mode you now need to configure the Active Directory
accounts or groups that have access to the Configuration and Quarantine
Store, and you can change the virtual directory name where the GFI
MailSecurity pages are stored.
NOTE: If you select Local mode you need to add „http://127.0.0.1‟ to the list
of trusted sites in Internet Explorer. For further information, refer to Adding
local host to the trusted sites list section below.
Screenshot 18 - Local host address must be added to trusted sites list
4. To configure access security, click Security… next to the Virtual
Directory box.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 29
Page 36
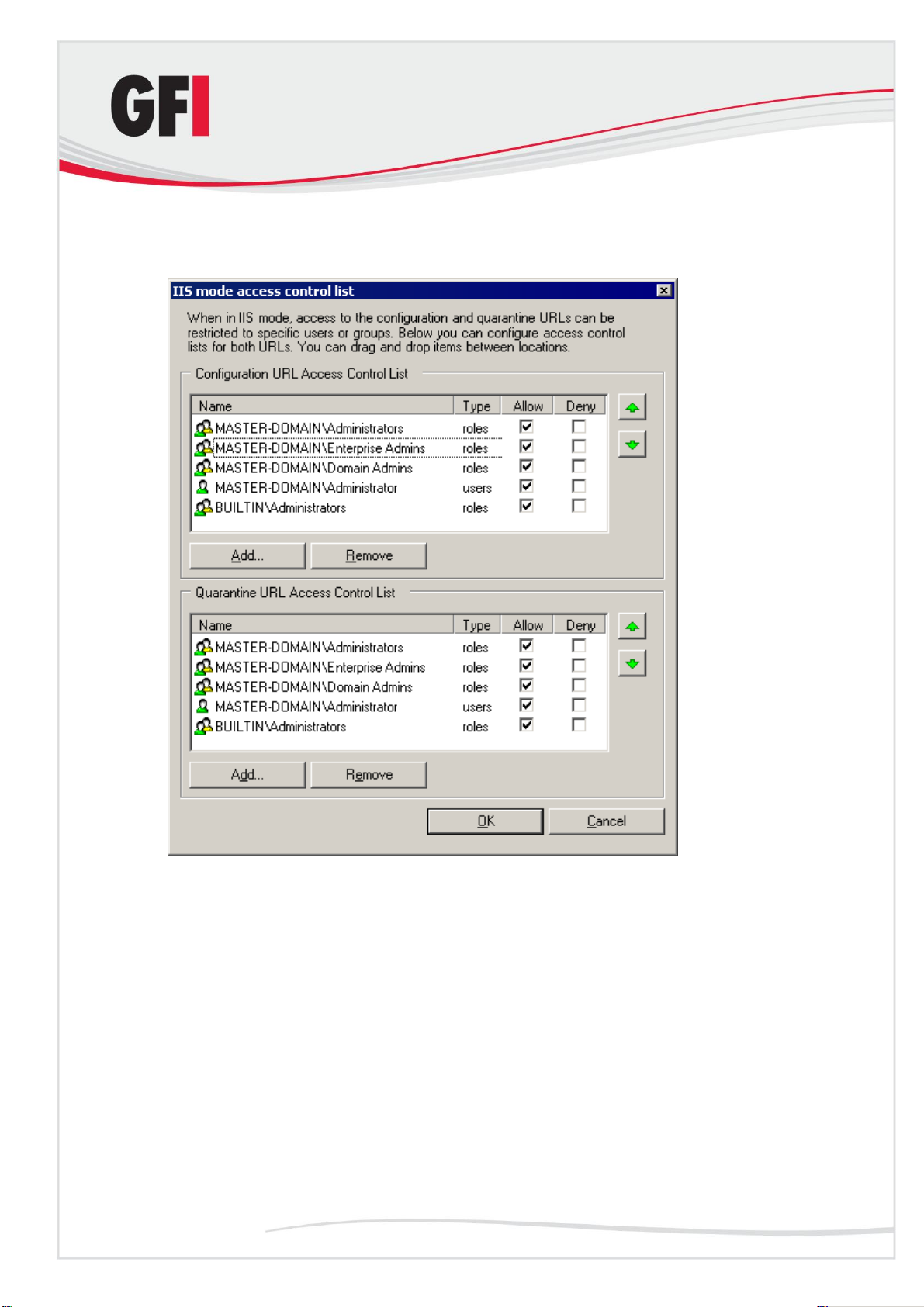
5. In the IIS mode access control list dialog box you can configure who gets
access to the configuration pages and the quarantine store in separate
access control lists.
Screenshot 19 - Configuration / Quarantine store Access Control Lists
6. To configure the accounts that get access to the configuration pages, use
the Add and Remove buttons underneath the Configuration URL Access
Control List. If you want to deny access to a listed account without removing
it from the list, select the check box under the Deny column.
7. To configure the accounts that get access to the quarantine store, use the
Add and Remove buttons underneath the Quarantine URL Access Control
List. If you want to deny access to a listed account without removing it from
the list, select the check box under the Deny column.
NOTE: To avoid reselecting the same accounts twice, once for each list, you
can easily drag and drop accounts and groups between the two lists.
8. When ready click OK.
9. If you want to specify a different virtual directory name, you can do so by
editing the entry in the Virtual directory box.
30 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 37

10. Click OK to save your changes. A progress bar shows you the progress
while applying the new settings.
Screenshot 20 - New SwitchBoard settings successfully applied
11. When the process completes, click OK.
Adding local host to the trusted sites list
When you configure GFI MailSecurity to be accessible only locally, you need
to add the local host address, „http://127.0.0.1‟, to the list of trusted sites in
Internet Explorer. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Click the Control Panel shortcut under the Start menu.
2. From the Control Panel open the Internet Options applet.
3. In the Internet Properties dialog box click the Security tab and then click
the Trusted sites icon from the Web content zone list.
Screenshot 21 - Internet properties dialog
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 31
Page 38

4. Click Sites.
5. In the Trusted sites dialog box specify „http://127.0.0.1‟ in the Add this
Web site to the zone box.
6. Click Add. The local host address is added to the Web sites list.
Screenshot 22 - Trusted sites dialog
7. Click Close.
8. Click OK in the Internet Properties dialog box to close it and save the new
settings.
2.13 Securing access to the GFI MailSecurity Quarantine RSS
feeds
You can configure GFI MailSecurity to create quarantine RSS feeds on
specific quarantine folders. To configure who can subscribe to the quarantine
RSS feeds, follow these steps:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard shortcut found under Start ►
Programs ► GFI MailSecurity.
2. In the GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard dialog box, click Security next to
the RSS Virtual Directory box.
32 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 39

Screenshot 23 - GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard
3. In the IIS mode access control list dialog box you can configure who can
subscribe to the quarantine RSS feeds.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 33
Page 40

Screenshot 24 - Quarantine RSS feeds Access Control Lists
4. Use the Add and Remove buttons underneath the RSS URL Access
Control List. If you want to deny access to a listed account without removing
it from the list, select the check box under the Deny column.
6. When ready click OK.
7. If you want to specify a different virtual directory name, you can do so by
editing the entry in the RSS Virtual directory box.
8. Click OK to save your changes. A progress bar shows you the progress
while applying the new settings.
Screenshot 25 - New SwitchBoard settings successfully applied
9. When the process completes, click OK.
2.14 Accessing the GFI MailSecurity Configuration and
Quarantine Store
This section will show you how to access the GFI MailSecurity Configuration
and Quarantine Store from the local machine or a remote machine.
Accessing the configuration from the GFI MailSecurity machine
To access the GFI MailSecurity configuration or quarantine store from the
same machine where GFI MailSecurity is installed, i.e. locally, follow these
steps:
34 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 41

1. Click the GFI MailSecurity shortcut found under Start ► Programs ►
GFI MailSecurity.
2. If you have configured GFI MailSecurity to be accessible only locally, via
the GFI MailSecurity SwitchBoard application, a viewer application will
automatically load up displaying the GFI MailSecurity configuration and
quarantine store.
Screenshot 26 - GFI MailSecurity accessed under local mode only
Accessing the configuration from a remote machine
To access the GFI MailSecurity configuration or quarantine store from a
remote machine, follow these steps:
1. Start Microsoft Internet Explorer.
2. In the address bar, specify the following address:
„http://<machine name>/<virtual directory name>‟ to access the configuration
or „http://<machine name>/<virtual directory name>/quarantine‟ to access the
quarantine store directly.
For example:
„http://win2k3entsvr.master-domain.com/mailsecurity‟ for the configuration or
„http://win2k3entsvr.master-domain.com/mailsecurity/quarantine‟ for the
quarantine store.
3. You will be prompted to specify a user name and password to authenticate
and determine whether you have access to the page requested. If the
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 35
Page 42

account specified has access, the GFI MailSecurity configuration or
quarantine store is displayed.
Screenshot 27 - GFI MailSecurity accessed under IIS mode
2.15 Upgrading from GFI MailSecurity 8 to GFI MailSecurity
10.1
Due to fundamental architectural changes between GFI MailSecurity 10.1 and
GFI MailSecurity 8, it is not possible to install GFI MailSecurity 10.1 on top of
an existing installation of GFI MailSecurity 8.
This section therefore shows you how to:
Replace your current GFI MailSecurity 8 installation with GFI MailSecurity
10.1.
Convert and import the GFI MailSecurity 8 configuration settings to GFI
MailSecurity 10.1‟s new configuration database format.
NOTE: If GFI MailSecurity 8 was installed in SMTP mode and GFI
MailSecurity 10.1 is installed in Active Directory mode, you will not be able to
convert and import the settings due to user-based rules. This also applies if
36 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 43

GFI MailSecurity 8 was installed in Active Directory mode and GFI
MailSecurity 10.1 is installed in SMTP mode.
To upgrade from GFI MailSecurity 8 to GFI MailSecurity 10.1, follow these
steps:
1. Uninstall GFI MailSecurity 8.
2. When the GFI MailSecurity 8 uninstallation completes, certain files are left
behind under the root folder where GFI MailSecurity 8 was installed. One of
these files is the avapicfg.rdb file located in the Data sub-folder.
NOTE: Do not delete this file since it contains the GFI MailSecurity 8
configuration settings. You will need this file to migrate the settings from GFI
MailSecurity 8 to GFI MailSecurity 10.1.
3. Install GFI MailSecurity 10.1 as shown in the „Install GFI MailSecurity‟
section of this chapter.
NOTE: To install GFI MailSecurity 10.1, you need to have the following
installed on the machine:
Microsoft .Net framework 1.1 / 2.0
MSMQ - Microsoft Messaging Queuing Service.
Internet Information Services (IIS) - SMTP service and World Wide Web
service.
NOTE: Do not install GFI MailSecurity 10.1 to the same path where GFI
MailSecurity 8 was installed, to prevent files such as avapicfg.rdb from being
overwritten.
4. After the installation of GFI MailSecurity 10.1 is complete, you need to stop
all GFI-related services along with the IIS Admin service, from the Services
control applet. Then you can run the GFI MailSecurity 8 settings migration
tool.
NOTE: You must stop the following services before going on to the next step:
GFI Content Security Attendant Service
GFI Content Security Auto-Updater Service
GFI MailSecurity Attendant Service
GFI MailSecurity Scan Engine
IIS Admin
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
5. To convert and import the GFI MailSecurity 8 settings to the GFI
MailSecurity 10.1 configuration database, you need to run the msec8upg.exe
tool found in the GFI MailSecurity 10.1 folder, for example:
c:\program files\GFI\ContentSecurity\MailSecurity.
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 37
Page 44
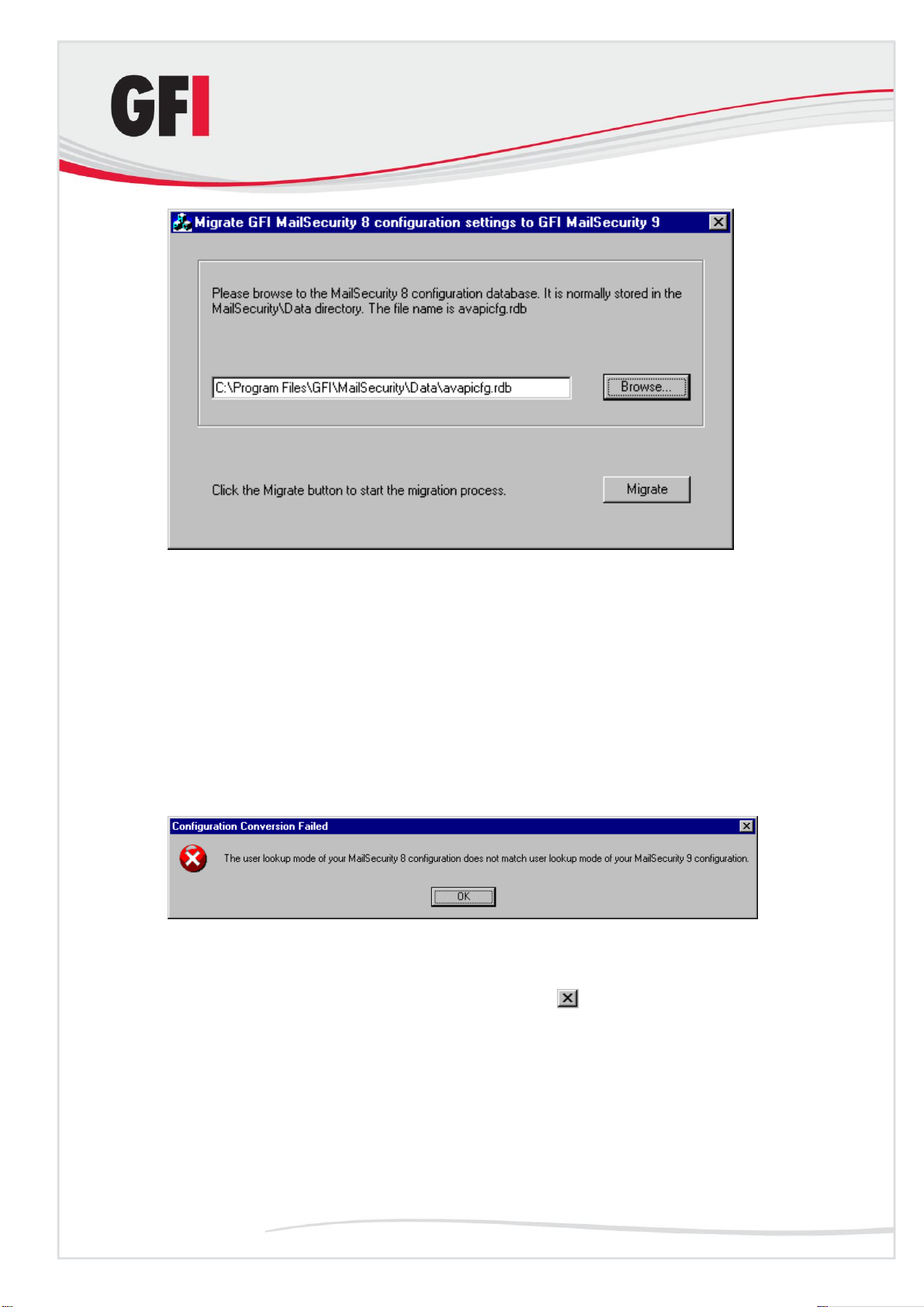
Screenshot 28 - GFI MailSecurity 8 configuration settings migration tool
6. Double-click the msec8upg.exe file.
7. When the tool loads, click Browse. Select the avapicfg.rdb file from the
data sub-folder under the GFI MailSecurity 8 root folder.
8. Click Migrate.
NOTE: If you click Migrate and the user lookup mode of GFI MailSecurity 8
and GFI MailSecurity 10.1 do not match (for example GFI MailSecurity 8 was
installed in SMTP mode and GFI MailSecurity 10.1 is installed in Active
Directory mode or vice versa), an error like the one shown below will be
displayed. In such a case, you will not be able to convert and import the
settings due to user-based rules.
Screenshot 29 - User lookup mode mismatch.
9. When the migration process completes, a Configuration was successfully
converted information dialog box will be displayed. Click OK to close the
information dialog box and click the close button to close the migration
tool.
10. You now need to start all the services that you stopped in step 4 above,
from the Services control applet.
11. Use the GFI MailSecurity 10.1 configuration to check that the GFI
MailSecurity 8 settings were migrated correctly.
38 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 45

2.16 Upgrading from GFI MailSecurity 9 to GFI MailSecurity
10.1
NOTE: The upgrade process cannot be reverted. If you upgrade GFI
MailSecurity to version 10.1, you cannot go back to version 9 of the product.
If you are currently using GFI MailSecurity 9, you can upgrade your current
installation. The GFI MailSecurity 9 configuration settings are kept. You need
to enter the fully purchased license key after the upgrade completes. For
information on how to obtain the new license key, visit
http://customers.gfi.com.
To upgrade:
1. Launch the GFI MailSecurity 10.1 setup file on the machine on which you
have installed GFI MailSecurity 9.
2. Setup will now proceed to install GFI MailSecurity 10.1 in exactly the same
manner as a new installation. However, it will not let you change the
destination folder.
3. To continue the installation, click Install. For a detailed description, of the
installation procedure, refer to the Installing GFI MailSecurity section earlier in
this chapter.
NOTE: During an upgrade you are also asked to upgrade your quarantine
database to the new Firebird database format. For more information, refer to
Quarantine Upgrade tool section in this manual.
2.17 Quarantine Upgrade tool
Starting from GFI MailSecurity 10 SR8, Quarantine information is stored in a
Firebird database format instead of Microsoft Access database. For upgrades
between version 9 and 10 and between previous builds of version 10 to GFI
MailSecurity 10 SR8, the Quarantine upgrade tool automates to the migration
of pre-existing quarantine data to the new Firebird database format.
NOTE: The old quarantine data will not be available until imported.
2.17.1 Using the quarantine upgrade tool
The Quarantine upgrade tool is automatically launched after installing the
upgrade to GFI MailSecurity SR8. In case you need to launch it manually,
navigate to the GFI MailSecurity installation folder (typically Program
Files\GFI\ContentSecurity\MailSecurity\) and run QssUpgrade.exe
Installing GFI MailSecurity GFI MailSecurity 10.1 39
Page 46

Screenshot 30 - Quarantine upgrade tool
1. Press Start button to start data migration.
2. Press Pause/Continue button to pause or continue data processing.
3. Press Stop button to cancel your data migration and restart at a later stage
by pressing Start again.
NOTE: Upgrading your quarantine to the firebird database format might take
long depending on the volume of your quarantine data.
40 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Installing GFI MailSecurity
Page 47

3 General settings
3.1 Introduction to settings
Screenshot 31 - GFI MailSecurity general settings page
The Settings node allows you to configure a number of general options,
including the administrator‟s email address, the Update URLs, the list of Local
Domains, the SMTP server bindings and the management of the user list
when GFI MailSecurity is installed in SMTP mode only. To configure the
general settings, click the GFI MailSecurity ► Settings node.
3.2 Define the administrator’s email address
GFI MailSecurity can be configured to send email notifications to the
administrator whenever a security threat is found in an email. To set up the
administrator‟s notification address:
1. Click the Settings node to open the General Settings page in the right
window.
2. In the General tab, specify the email address where you wish to send
email notifications addressed to the administrator in the Administrator Email
box.
3. Click Apply.
3.3 Configuring proxy server settings for automatic updates
GFI MailSecurity will automatically search and download updates (for
example, virus definitions updates and Trojan & Executable Scanner
definitions updates) from the GFI update servers.
General settings GFI MailSecurity 10.1 41
Page 48

If the server on which GFI MailSecurity is installed, connects to the internet
through a proxy server, you need to configure the proxy server settings as
follows:
1. Click the Settings node to open the general settings page.
2. Click the Updates tab.
3. Select the Enable proxy server check box. In the Proxy server and Port
boxes specify the Machine Name / IP of the proxy server and the port to
connect on respectively. If the proxy server requires authentication, select the
Enable proxy authentication check box and specify the user name and
password in the Username and Password boxes respectively.
Screenshot 32 - Updates server proxy settings
4. Click Apply.
42 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 General settings
Page 49

3.4 Adding Local Domains
Screenshot 33 - Local Domains list
GFI MailSecurity needs to know what your local domains are to be able to
classify an email as inbound or outbound. During installation, GFI
MailSecurity will import local domains from the IIS SMTP service. If, however,
you wish to add or remove local domains afterwards, you must follow these
steps:
1. Click the Settings node to open the general settings page.
2. Click the Local Domains tab and specify the name of the domain in the
Domain box.
3. Click Add to include the stated domain in the Local domains list. If you
want to remove a listed domain, select it from the list and click Remove.
4. Click Apply.
NOTE: You can use the local domains option if you want to configure local
mail routing in IIS differently, for example, to add domains that are local for
mail routing purposes but which are not local for your mail server.
3.5 SMTP server bindings
NOTE: The SMTP Server bindings tab is not visible when GFI MailSecurity is
installed on a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007/2010 machine.
General settings GFI MailSecurity 10.1 43
Page 50

Screenshot 34 - Binding GFI MailSecurity to a different SMTP Server
GFI MailSecurity relies on the IIS SMTP service to send and receive SMTP
mail. By default, it binds to your default SMTP virtual server. However, if you
have multiple SMTP virtual servers installed on your machine, you can select
to which one you want to bind GFI MailSecurity. You can select your virtual
SMTP server both during the installation stage as well as from the Bindings
tab after the installation. To change the current SMTP Virtual Server:
1. Click the Settings node to open the general settings page in the right
window.
2. Click the Bindings tab and select the required SMTP Virtual Server from
the available list of servers present in your domain.
3. Click Apply.
3.6 Managing local users in SMTP mode
When you install GFI MailSecurity in Active Directory mode, the list of local
users is stored in the Active Directory store. When you choose to install GFI
MailSecurity in SMTP mode, the list of local users is stored in a database
managed by GFI MailSecurity.
To populate and manage the user list when GFI MailSecurity is installed in
SMTP mode, a User Manager is available under the Settings node.
44 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 General settings
Page 51

Screenshot 35 - User Manager
The User Manager tab displays the current list of local users, and it allows
you to add or remove local users. The list of local users entered here is used
when configuring user-based rules, such as Attachment Checking rules and
Content Checking rules.
To add a new local user follow these steps:
1. Enter the email address in the Email address box.
2. Click Add.
NOTE: GFI MailSecurity uses the local domains list, configurable from the
Local Domains tab, to determine whether a new email address is local or
not. A notification dialog box is displayed if you enter a non-local user, as
shown in the screenshot below.
General settings GFI MailSecurity 10.1 45
Page 52

Screenshot 36 - Non-local user entered
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 to add more than one local user.
4. Click Apply.
To remove a local user follow these steps:
1. Select the local user you want to remove from the Local Users list.
2. Click Remove.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 to remove more than one local user.
4. Click Apply.
46 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 General settings
Page 53

4 Configuring virus checking
4.1 Configuring Virus Scanning Engines
The virus-checking feature of GFI MailSecurity scans all SMTP traffic,
inbound and outbound emails, for viruses using multiple Virus Scanning
Engines. When GFI MailSecurity is installed on the Microsoft Exchange
server machine, you can also configure GFI MailSecurity to scan the
information store for viruses.
NOTE: When GFI MailSecurity is installed on a Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 machine, Information Store Protection is available only when
the Mailbox Server Role and Hub Transport Server Role are installed.
GFI MailSecurity ships with both Norman and BitDefender Virus Scanning
Engine as standard. However, you can optionally license the AVG, Kaspersky
and McAfee Virus Scanning Engines, which are supported as well. All of the
aforementioned anti-virus packages are proven and reliable virus detection
engines, which have received many awards and certifications, including the
industry leading certifications of ICSA.
Screenshot 37 - Virus Scanning Engines status page
You can view the operational and license status of each Virus Scanning
Engine along with the execution sequence of the installed Virus Scanning
Engines by clicking on the GFI MailSecurity ► Virus Scanning Engines
node.
The Virus Scanning Engines are listed in the same order of priority used by
GFI MailSecurity to scan emails for viruses (Priority 0 being the highest or top
priority).
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 47
Page 54

Each Virus Scanning Engine must be configured separately. To configure
virus checking, click the required Virus Scanning Engine from the Status page
on display in the right window. Alternatively, you can expand the Virus
Scanning Engines node and click the required Virus Scanning Engine node
(for example, Kaspersky).
NOTE: If you are running GFI MailSecurity on a Microsoft Exchange machine
and the Information Store Scanning status is set to Disabled for all Virus
Scanning Engines, the Information Store Scanning feature is disabled. The
GFI MailSecurity configuration will inform you with a dialog that the
Information Store Scanning feature is going to be disabled since you are
trying to disable the only Virus Scanning Engine left which is set to scan the
Information Store. If you click OK, the particular virus-scanning engine will
have the Information Store Scanning feature disabled and so will the overall
Information Store Scanning feature. If you click Cancel, the virus-scanning
engine will not have the Information Store Scanning feature disabled and the
overall Information Store Scanning feature will remain active since there is at
least one virus-scanning engine that is still configured to scan the Information
Store.
Screenshot 38 - Information Store Scanning will be disabled.
If the overall Information Store Scanning feature is disabled, you need to
enable it from the Information Store Protection node before you can
configure any Virus Scanning Engine to scan the Information Store. If you try
to configure a Virus Scanning Engine to scan the Information Store and the
feature is disabled from the Information Store Protection node, the GFI
MailSecurity configuration will inform you about this with a dialog as shown in
the screenshot below.
Screenshot 39 - Enable Information Store protection before configuring a Virus Scanning Engine
4.2 AVG configuration
NOTE: The AVG virus engine must be purchased separately: This engine is
not included in the base product. As standard, GFI MailSecurity includes both
the Norman and the BitDefender anti-virus engines. For pricing information on
adding the AVG anti-virus engine, please visit the GFI website (www.gfi.com).
48 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 55

Screenshot 40 - Anti-virus Scanning Engines: AVG configuration page (General Tab)
To configure the AVG engine:
1. Expand the GFI MailSecurity ► Virus Scanning Engines node and then
click AVG.
2. To scan SMTP traffic using this Virus Scanning Engine, select the Enable
Gateway Scanning (SMTP) check box. You now need to select whether you
want to scan inbound and outbound emails using this Virus Scanning Engine.
To scan inbound emails select the Scan Inbound Emails through SMTP
Transport Event Sink check box. To scan outbound emails select the Scan
Outbound Emails through SMTP Transport Event Sink check box.
3. If you installed GFI MailSecurity on the Microsoft Exchange machine, you
will also have the option to scan the Information Store using this Virus
Scanning Engine. To scan the Information Store select the Enable
Information Store Virus Scanning (VSAPI) check box.
NOTE: When GFI MailSecurity is installed on a Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 machine, information store scanning is available only when the
Mailbox Server Role and Hub Transport Server Role are installed.
4. The configuration settings required in the Actions and Updates tabs are
identical for all the installed virus-scanning engines. For more information on
how to configure these parameters, refer to the Virus scanner actions and
„Virus scanner updates‟ sections in this chapter.
5. After you have configured all the required parameters, click Apply. All
changes and configuration settings will take effect immediately.
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 49
Page 56

NOTE: The section at the bottom of the General tab displays information on
the scanning engine. This includes the Virus database version and release
date. License details for the current anti-virus engine are also displayed.
AVG web site
For more information about the virus patterns included in the AVG engine,
visit the AVG website at http://www.grisoft.com.
4.3 Kaspersky configuration
NOTE: The Kaspersky virus engine must be purchased separately: This
engine is not included in the base product. As standard, GFI MailSecurity
includes both the Norman and the BitDefender anti-virus engines. For pricing
information on adding the Kaspersky anti-virus engine, please visit the GFI
website (www.gfi.com).
Screenshot 41 - Anti-virus Scanning Engines: Kaspersky configuration page (General Tab)
To configure the Kaspersky engine:
1. Expand the GFI MailSecurity ► Virus Scanning Engines node and then
click Kaspersky.
2. To scan SMTP traffic using this Virus Scanning Engine, select the Enable
Gateway Scanning (SMTP) check box. You now need to select whether you
want to scan inbound and outbound emails using this Virus Scanning Engine.
To scan inbound emails select the Scan Inbound Emails through SMTP
Transport Event Sink check box. To scan outbound emails select the Scan
Outbound Emails through SMTP Transport Event Sink check box.
50 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 57

3. If you installed GFI MailSecurity on the Microsoft Exchange machine, you
will also have the option to scan the Information Store using this Virus
Scanning Engine. To scan the Information Store select the Enable
Information Store Virus Scanning (VSAPI) check box.
NOTE: When GFI MailSecurity is installed on a Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 machine, information store scanning is available only when the
Mailbox Server Role and Hub Transport Server Role are installed.
4. The configuration settings required in the Actions and Updates tabs are
identical for all the installed Virus Scanning Engines. For more information on
how to configure these parameters, refer to Virus scanner actions and Virus
scanner updates sections in this chapter.
5. After you have configured all the required parameters, click Apply. All
changes and configuration settings will take effect immediately.
NOTE: The section at the bottom of the General tab displays information on
the scanning engine. This includes the Virus Scanning Engine version, virus
signature count and the date of the current virus signature files. License
details for the current anti-virus engine are also displayed.
Kaspersky web site
For more information about the virus patterns included in the Kaspersky
engine, visit the Kaspersky website at http://www.kaspersky.com.
4.4 BitDefender configuration
Screenshot 42 - Virus Scanning Engines: BitDefender configuration page (General Tab)
To configure the BitDefender engine:
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 51
Page 58

1. Expand the GFI MailSecurity ► Virus Scanning Engines node and then
click BitDefender.
2. To scan SMTP traffic using this Virus Scanning Engine, select the Enable
Gateway Scanning (SMTP) check box. You now need to select whether you
want to scan inbound and outbound emails using this Virus Scanning Engine.
To scan inbound emails select the Scan Inbound Emails through SMTP
Transport Event Sink check box. To scan outbound emails select the Scan
Outbound Emails through SMTP Transport Event Sink check box.
3. If you installed GFI MailSecurity on the Microsoft Exchange machine, you
will also have the option to scan the Information Store using this Virus
Scanning Engine. To scan the Information Store select the Enable
Information Store Virus Scanning (VSAPI) check box.
NOTE: When GFI MailSecurity is installed on a Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 machine, information store scanning is available only when the
Mailbox Server Role and Hub Transport Server Role are installed.
4. BitDefender Control also allows you to block or ignore emails with
attachments that contain macros. This feature can be configured by selecting
one of the following options:
Do not check macros - Select this option if you want GFI MailSecurity to
ignore macros and only scan emails for viruses.
Block all documents containing macros - Select this option if you want
to quarantine all emails that contain a macro (even if the macro is a
genuine one).
NOTE: Quarantining of emails depends on the Actions configured in the Virus
Scanning Engine. If you select Delete item in the Actions tab of the Antivirus
Engine, all emails containing macros will still be DELETED (i.e. they are NOT
Quarantined).
5. The configuration settings required in the Actions and Updates tabs are
identical for all the installed Virus Scanning Engines. For more information on
how to configure these parameters, refer to the Virus scanner actions section
and Virus scanner updates section in this chapter.
6. After you have configured all the required parameters, click Apply. All
changes and configuration settings will take effect immediately.
NOTE: The section at the bottom of the General tab displays information on
the scanning engine. This includes the Virus Scanning Engine version and
the virus signature count. License details for the current anti-virus engine are
also displayed.
BitDefender website
For more information about the virus patterns included in the BitDefender
engine, visit the BitDefender website at http://www.bitdefender.com
4.5 McAfee configuration
NOTE: The McAfee engine is purchased separately: the engine is not
included in the base product. As standard, GFI MailSecurity includes both the
52 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 59

Norman and the BitDefender anti-virus engine. For pricing information on
adding the MacAfee anti-virus engine, please visit the GFI website
(www.gfi.com).
The configuration options of the McAfee Virus Scanning Engine are identical
to those of the BitDefender engine. For more information on how to configure
these options, refer to BitDefender configuration section earlier in the manual.
NOTE: The section at the bottom of the General tab displays information on
the scanning engine. This includes the Virus Scanning Engine version, virus
signature count and the date of the current virus signature files. License
details for the current anti-virus engine are also displayed.
Screenshot 43 - Virus Scanning Engines: McAfee configuration page (General Tab)
McAfee website
For more information about the virus patterns included in the McAfee engine,
visit the McAfee website at http://www.mcafee.com
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 53
Page 60

4.6 Norman configuration
The configuration options of the Norman Virus Scanning Engine are identical
to those of the BitDefender engine. For more information on how to configure
these options, refer to BitDefender configuration section earlier in the manual.
NOTE: The section at the bottom of the General tab displays information on
the scanning engine. This includes the Virus Scanning Engine version, virus
signature count and the date of the current virus signature files. License
details for the current anti-virus engine are also displayed.
Screenshot 44 - Virus Scanning Engines: Norman configuration page
Norman website
For more information about the virus patterns included in the Norman Virus
Control (NVC) engine, visit the NVC website at http://www.norman.com
54 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 61

4.7 Virus scanner actions
Screenshot 45 - Virus Scanning Engine: Configuration page (Actions Tab)
In GFI MailSecurity, you can configure what each of the installed Virus
Scanning Engines should do whenever an infected email is detected. To
configure the actions of a virus scanner:
1. Select the virus scanner that you want to configure and click the Actions
tab.
2. Choose one of the following options:
Quarantine item - Select this option if you want to quarantine all virus-
infected emails detected by this Virus Scanning Engine. You can
subsequently review (approve/delete) all the quarantined emails.
Delete item - Select this option to delete all virus-infected emails detected
by this Virus Scanning Engine.
NOTE: This option overrides the settings configured in the General tab. i.e. If
in the General tab, you selected Block all emails containing a macro (i.e.
quarantine all emails even the ones having a genuine macro) but at the same
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 55
Page 62

time you have enabled the Delete item option, ALL emails containing a
macro will be deleted.
3. To send email notifications whenever an infected email is detected, enable
any of the following options:
Notify local user - Select this option if you want to notify the email local
users when this filter detects a virus.
NOTE: If a threat is detected in an outbound email, the recipients will receive
the original email with the malicious parts removed. A security notice is
attached to the email to inform the recipients what email parts were removed
and for what reason. This behavior is always enabled and is not affected by
this setting.
Notify administrator - Select this option if you want to notify the
administrator whenever this virus scanner detects an infected email.
4. Select the Log occurrence to this file check box and specify a log file
name in the box below, if you want to log the virus scanning activity to a log
file. You can specify either the file name only or else the full path to a custom
location on disk.
56 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 63

4.8 Virus scanner updates
Screenshot 46 - Virus Scanning Engines: Configuration page (Updates Tab)
You can configure GFI MailSecurity to download virus scanner updates
automatically or to notify the administrator whenever new updates are
available. To configure the automatic updates of a particular virus scanner:
1. Select the virus scanner that you want to configure and from the right
window, click the Updates tab.
2. Select the Automatically check for updates check box to enable the
auto-update feature.
3. From the Downloading options list, select one of the following:
Only check for updates - Select this option if you want GFI MailSecurity
to just check and notify the administrator whenever updates are available
for this virus scanner. This option will NOT download the available
updates.
Check for updates and download - Select this option if you want GFI
MailSecurity to check and automatically download any updates available
for this virus scanner.
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 57
Page 64

4. Specify how often you want GFI MailSecurity to check/download updates
for this Virus Scanning Engine, by specifying an interval value in hours.
Triggering the virus update manually
To check/download updates for the current Virus Scanning Engine
immediately, click Download updates.
4.9 Setting the Virus Scanning Engines scan priority
To configure the execution order of the Virus Scanning Engines, follow these
steps:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Virus Scanning Engines node.
Screenshot 47 - Virus Scanning Engines: scan priority list
2. In the right pane, the Virus Scanning Engines are listed in descending
order of priority.
NOTE: The priority assigned to each virus scanner determines the sequence
when each anti-virus engine gets to scan the content. The scanner with
priority 0 is the first to start scanning an email. Upon completion, the Virus
Scanning Engine with priority 1 scans the email and so on. This means that
the Virus Scanning Engine listed at the top of the list is the first to scan
emails, if it is enabled.
3. To change the virus scanning execution priority, click the (up) or (down)
arrows to respectively increase or decrease the priority of the virus
scanner. Repeat the same procedure until the virus scanner reaches the
desired position in the priority/execution sequence list.
4.10 Configuring Virus Scanning optimizations
From the GFI MailSecurity ► Virus Scanning Engines node you can
instruct GFI MailSecurity to stop virus scanning an item if a number of virus
scanning engines already detected a virus in that item.
To enable this option, select the Stop virus scanning the current item, if
viruses are detected by check box, and specify the number of virus
scanners that need to detect a virus to stop virus scanning, in the box. Click
Apply.
58 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 65

Screenshot 48 - Configure virus scanning optimizations
For example, if you select this option and enter 2 in the box, virus scanning
on an item that contains a virus is performed by at most two virus-scanning
engines, if they detect it. Emails that do not contain a virus are scanned by all
enabled virus-scanning engines anyway.
If you want to streamline further the path taken by items containing a virus,
select the Stop scanning even for non-virus related threats check box and
click Apply. This option will instruct GFI MailSecurity to stop further scanning
of the current item, such as with Attachment Checking and so on, since the
amount of virus-scanning engines you specified have detected a virus.
4.11 Configuring Information Store Scanning
NOTE: The Information Store Protection node is only available if you install
GFI MailSecurity on the Microsoft Exchange machine.
NOTE: When GFI MailSecurity is installed on a Microsoft Exchange Server
2007/2010 machine, Information Store Protection is available only when
the Mailbox Server Role and Hub Transport Server Role are installed.
This section will show you how to enable or disable Information Store
Scanning, and select the scan method used by VSAPI (Virus Scanning API).
To configure the Information Store Scanning feature, follow these steps:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Information Store Protection node.
2. In the Information Store Virus Scanning tab, you can enable or disable
Information Store Scanning by selecting/clearing the Enable Information
Store Virus Scanning check box accordingly. The status of the Virus
Scanning Engines used to scan the Information Store is also displayed.
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 59
Page 66

Screenshot 49 - Information Store Protection node
NOTE: When you disable Information Store Virus Scanning, the Information
Store Scanning option of all Virus Scanning Engines is disabled
automatically. When you enable Information Store Virus Scanning, the
Information Store Scanning option of all Virus Scanning Engines is enabled
automatically. This setting does not affect the Gateway scanning option of
each Virus Scanning Engine. The GFI MailSecurity configuration will prompt
you about this action as shown in the screenshot below. If you need to enable
or disable the Information Store Scanning option for a specific Virus Scanning
Engine, please refer to the Configuring Virus Scanning Engines section
earlier in this chapter.
Screenshot 50 - All Information Store Virus Scanning Engines have been enabled.
3. To configure what VSAPI scan method to use, click the VSAPI Settings
tab.
60 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring virus checking
Page 67

Screenshot 51 - VSAPI scan settings
4. From the VSAPI Settings tab, you can enable background Information
Store Scanning, by selecting the Enable background scanning check box.
This option will cause all the contents of the Information Store to be scanned,
which depending on the amount of items stored in the Information Store could
result in a huge processing load on the Exchange server. For this reason, it is
recommended that this option be only enabled during periods of low server
activity such as during the night.
5. Select a VSAPI scan method from the following:
On-access scanning - New items in the Information Store are scanned
as soon as they are accessed by the email client. This scan method will
thus introduce a short delay before the email client can display the
contents of a new message.
Pro-active scanning - New items added to the Information Store are
added to a queue for scanning. When a mail client tries to access an item
that is still in the queue, it will be allocated a higher scanning priority so
that it is scanned as soon as possible. This is the default and
recommended mode of operation, since in general the delay associated
with on-access scanning is avoided because new items are added to the
queue immediately and are usually scanned before a mail client requests
access to the item.
6. To save and instruct GFI MailSecurity to make use of the new settings,
click Apply.
Configuring virus checking GFI MailSecurity 10.1 61
Page 68

Page 69

5 Configuring Content Filtering
5.1 Introduction
The Content Filtering feature allows you to set up rules to filter emails
containing particular keywords or a combination of keywords in an email. A
rule is composed of:
Keywords to block in the email body, subject or attachment
Actions to take when a keyword is found
The users to which a rule applies.
NOTE: Although this feature can be used as a filter against spam email, it is
recommended to use dedicated software to block spam. For more
information, refer to:
http://kbase.gfi.com/showarticle.asp?id=KBID003342
Screenshot 52 - Content Filtering page
To configure keyword-blocking rules, navigate to the Content Filtering node
from the GFI MailSecurity Configuration. This page allows you to view, create,
enable, disable or delete rules.
5.2 Creating a Content Filtering rule
1. Navigate to GFI MailSecurity ► Content Filtering node and click Add
Rule….
Configuring Content Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 63
Page 70

Check inbound emails
Select this option to scan incoming emails
Check outbound emails
Select this option to scan outgoing emails
Screenshot 53 - Content Filtering: General Tab
2. Specify a name for the rule in the Rule name text box.
3. Select which emails to scan.
4. To block emails encrypted using PGP technology, select Block PGP
encrypted emails.
NOTE: PGP encryption is a public-key cryptosystem often used to encrypt
emails.
5. Select the Body tab to specify the keywords in the email body to block.
6. Select Block emails if content is found matching these conditions
checkbox to enable scanning of body for keywords.
64 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Content Filtering
Page 71

Screenshot 54 - Content Filtering: Body Tab- setting conditions
7. From the Condition entry area, key in keywords to block in the Edit
condition box. You can also use conditions AND, OR, AND NOT and OR
NOT to use a combinations of keywords.
8. To add the keyword or combination of keywords keyed in, click Add
Condition.
NOTE 1: To modify an entry in the Conditions list, select it and make the
required changes in the Condition entry box. Click Update to apply
changes.
NOTE 2: To remove an entry from the Conditions list, select it and click
Remove.
Configuring Content Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 65
Page 72

Match whole words only
Block emails when the keywords specified match whole
words.
Apply above conditions to
attachments
Select this option to apply this rule also to text in
attachments. In the Attachment filtering area specify the
attachments to apply or exclude from this rule.
Screenshot 55 - Content Filtering: Body Tab- configuring other options
9. From the Options area, configure other settings:
10. Select the Subject tab to specify keywords to block in the email subject.
66 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Content Filtering
Page 73

Screenshot 56 - Content Filtering: Subject Tab
11. Select Enable subject content checking to enable scanning for
keywords in the email subject.
12. In the Enter phrase text box, specify keywords to block, and click Add.
NOTE: To remove an added keyword, select it from the Phrases box and
click Remove Selected.
13. From the Options area, configure how keywords are matched. Select
Match whole words only to block emails where the keywords specified
match whole words in the subject.
14. Click the Actions tab to configure what should be done when this rule is
triggered.
15. To block an email that matches the rule conditions, select Block
attachment and perform this action and select one of the following options:
Configuring Content Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 67
Page 74

Quarantine email
Stores emails containing the keyword(s) in the Quarantine Store.
You can subsequently review (approve/delete) all the quarantined
emails. For more information about Quarantine refer to the
Quarantine chapter in this manual.
Delete email
Deletes emails containing the blocked keyword(s).
Move to folder
Moves the email to a folder on disk. Key in the full folder path where
to store blocked emails.
Notify
administrator
Notify the administrator whenever the rule is triggered.
Notify local user
Notify the email local recipients about the blocked email.
16. You can configure rule to send email notifications to the administrator
and/or user whenever an email containing an attachment is blocked. To do
this, from the Notification options area select:
17. To log the activity of this rule to a log file, select Log rule occurrence to
this file. In the text box specify:
Path and file name to a custom location on disk where to store the log file,
or
The file name only. The log file will be stored in the following default
location:
<GFI MailSecurity installation path>\ContentSecurity\MailSecurity\DebugL
ogs\<filename.txt>
18. By default, the rule is applied to all email users. GFI MailSecurity,
however, allows you to apply this rule to a custom list of email users. To
specify the users to apply this rule to, select Users/Folders tab
68 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Content Filtering
Page 75

Only this list
Apply this rule to a custom list of email users, groups or public
folders.
All except this list
Apply this rule to all email users except for the users, groups or
public folders specified in the list.
Screenshot 57 - Content Filtering: Users/Folders Tab
19. Specify the users to apply this rule to.
20. To add email users, user groups and/or public folders to the list, click
Add.
21. In the User Lookups window, specify the name of the email user/user
group or public folder that you wish to add to the list and click Check Names.
Matching users, groups or public folders are listed below.
NOTE: You do not need to input the full name of the users, groups or public
folder. It is enough to enter part of the name. GFI MailSecurity will list all the
names that contain the specified characters. For example, if you input „sco‟,
GFI MailSecurity will return names like „Scott Adams‟ and „Freeman Prescott„,
if they are available.
22. Select the check box next to the name(s) that you want to add to the list
and click OK.
NOTE 1: To remove entries from the list, select the user/user group/public
folder you want to remove and click Remove.
Configuring Content Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 69
Page 76

NOTE 2: If no names are included in the list, GFI MailSecurity automatically
applies this rule to all email users.
24. Repeat steps 21 to 23 to add all the required users to the list.
25. Click Apply.
5.3 Enabling/disabling rules
Enabled rules are rules that are active and GFI MailSecurity uses them during
scanning. Disabled rules are rules that are inactive and are not currently used
by GFI MailSecurity during email scanning.
1. Navigate to the GFI MailSecurity ► Content Filtering node.
2. From the Content Filtering page, select the checkbox of the rule(s) to
enable or disable.
3. Click Enable Selected or Disable Selected accordingly.
5.4 Removing content filtering rules
Screenshot 58 - Selecting a Content Filtering rule for removal
1. Navigate to the GFI MailSecurity ► Content Filtering node.
2. From the Content Filtering page, select the checkbox of the rule(s) that you
want to remove.
3. Click Remove Selected.
5.5 Modifying an existing rule
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Content Filtering node.
2. From the Content Filtering page, click the name of the rule to modify.
3. Perform the required changes in the rule properties and click Apply to
apply changes.
70 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Content Filtering
Page 77

5.6 Changing the rule priority
Content Filtering rules are applied in the same order, from top to bottom as
they are listed in the Content Filtering page (that is, rule with priority value 1 is
checked first). To change the sequence/priority of rules:
1. Navigate to GFI MailSecurity ► Content Filtering.
2. From the Content Filtering page, click the (up) or (down) arrows to
respectively increase or decrease the priority of the rule.
3. Repeat step 2 until rules are placed in the desired sequence.
Configuring Content Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 71
Page 78

Page 79

6 Configuring Attachment Filtering
6.1 Introduction to Attachment Filtering
This chapter explains how to set up Attachment Filtering in GFI MailSecurity.
The Attachment Filtering feature allows you to set up a policy regarding what
types of email attachments you will allow on your mail server. To set up such
a policy, GFI MailSecurity uses the concept of 'Rules'. A rule is a condition
that you set, such as, “block all executable attachments”. This means that an
Attachment Filtering rule allows you to block attachments of a certain type.
Screenshot 59 - Attachment Filtering page
In GFI MailSecurity, you can configure attachment rules from the Attachment
Filtering node. This page contains the options that enable you to create,
delete, enable or disable rules. In addition, it lists all the existing attachment
rules, including their status and the order in which these rules are applied to
emails (i.e. priority).
6.2 Creating an Attachment Filtering rule
To create an Attachment Filtering rule:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Attachment Filtering node.
2. From the Attachment Filtering page (in the right window), click Add Rule.
Configuring Attachment Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 73
Page 80

Screenshot 60 - Attachment Filtering: General Tab
3. Specify the name of the rule and select whether to apply this rule to
inbound and/or outbound emails by selecting the respective check boxes.
4. Decide on the type of attachment blocking required:
Block all - Select this option to block email attachments of any type.
Block this list - Select this option to block ONLY the listed attachment
types.
74 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Attachment Filtering
Page 81

Block all except this list - Select this option to block attachment types
that are not included in the list.
NOTE: To add an attachment type to the list, input the required full file name
or file extension in the box next to the Add button. When ready, click Add.
You can use asterisk (*) wildcards to replace characters or strings in the
attachment type/extension. For example, specifying *orders*.mdb blocks all
mdb files which contain the string 'orders' in the file name. Specifying *.jpg will
block all jpg files.
NOTE: To remove an entry from the list, select it and click Remove Selected.
5. Additionally, you can specify a file size in kilobytes as a threshold. This has
the effect of blocking all attachments with a file size bigger than the one you
specify irrespective of whether it matches an entry in the list. To enable this
option, select the Block all files greater than the following size in Kb
check box and specify the maximum file size (in KB) allowed without blocking.
Screenshot 61 - Attachment Filtering: Actions Tab
6. After you have specified what the attachment rule should check for, you
must specify what this rule should do whenever it finds the specified
Configuring Attachment Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 75
Page 82

attachment(s). Click the Actions tab to open the rule actions configuration
page.
7. Select the Block attachment and perform this action check box if you
want to quarantine, delete or move the blocked emails to a particular folder.
Additionally, select one of the following options:
Quarantine email: Select this option to quarantine the email containing
the attachment for review by an administrator. For more information, refer
to Quarantine chapter in this manual.
Delete email: Select this option to delete the email and attachment
completely.
Move to folder: This option will move the email to the specified folder.
Input the folder name in the box provided underneath this option.
NOTE: Please note that you cannot configure actions to affect a single
attachment within an email. Actions will always affect the whole email
containing the attachment.
8. You can configure an attachment rule to send email notifications to the
administrator and/or user whenever an email containing an attachment is
blocked. You can configure the required notifications by selecting any of the
following options:
Notify local user: Select this option if you want to notify the email local
users when this filter blocks an attachment.
NOTE: If a threat is detected in an outbound email, the recipients will receive
the original email with the malicious parts removed. A security notice is
attached to the email to inform the recipients what email parts were removed
and for what reason. This behavior is always enabled and is not affected by
this setting.
Notify administrator: Select this option if you want to send email
notifications to the administrator whenever an email containing an
attachment is blocked. The administrator‟s email address is specified
during the installation of GFI MailSecurity but can still be changed from
the GFI MailSecurity configuration (GFI MailSecurity ► Settings node ►
General tab). For more information refer to Define the administrator‟s
email address section in this manual.
9. Select the Log rule occurrence to this file check box and specify a log
file name in the box below, if you want to log all rule activity to a log file. You
can specify either the file name only or else the full path to a custom location
on disk.
NOTE: You can configure an attachment rule using any combination of
actions. For example, you can opt not to block emails containing the
attachment, but to simply notify the user or log the occurrence to file.
10. Now, you must specify the users to whom this rule applies. By default,
GFI MailSecurity will apply the rule to all email users. However, if you want
this rule to affect a selection of users only, click the Users/Folders tab.
76 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Attachment Filtering
Page 83
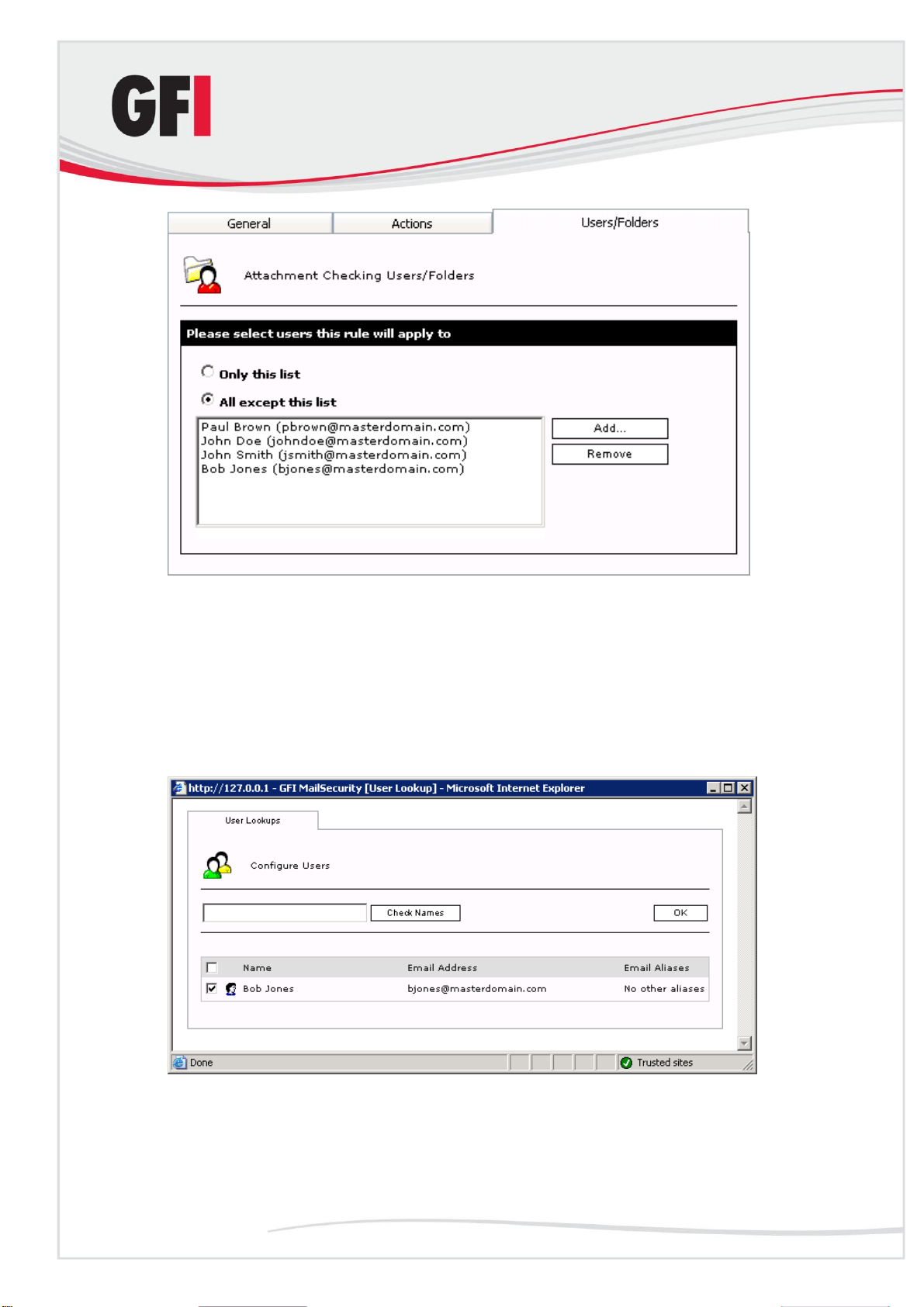
Screenshot 62 - Attachment Filtering: Users/Folders Tab
11. Choose one of the following options:
Only this list - Select this option if you want to apply this rule to all email
users/groups or public folders present in the list.
All except this list - Select this option if you want to apply this rule to all
email users, groups or public folders NOT present in the list.
12. To add email users, user groups and/or public folders to the list, click
Add.
Screenshot 63 - Add users to an attachment Filtering rule
13. In the add users window, specify the name of the email user/user group or
public folder that you wish to add to the list.
14. Click Check Names to query the Active Directory or the imported list of
SMTP addresses (depending on how you installed GFI MailSecurity), to
Configuring Attachment Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 77
Page 84

check if the specified entry exists. Any user, group or public folder that
matches will be listed below.
NOTE: You do not need to input the full name of the user/user group or public
folder. It is enough to enter at least three characters. GFI MailSecurity will list
all the names that contain the specified characters. For example, if you input
„ott‟, GFI MailSecurity will return names like „Scott Adams‟ and „Freeman
Prescott„, if they are available.
15. Select the check box at the start of the listed name(s) to indicate the ones
that you wish to add to the list and click OK.
NOTE: You can select all the listed names at once by selecting the check box
next to the Name column heading at the top-left of the list.
NOTE: Repeat steps 12 to 15 to add all the users you want to the list.
NOTE: To remove entries from the list, select the user/user group/public
folder you want to remove and click Remove.
NOTE: If no names are included in the list, GFI MailSecurity will automatically
apply this rule to all the email users in Active Directory/SMTP address list.
16. Click Apply.
6.3 Removing attachment rules
Screenshot 64 - Selecting an attachment Filtering rule for removal
To Remove an Attachment Filtering rule:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Attachment Filtering node.
2. From the Attachment Filtering page (in the right window), select the check
box of the rule(s) that you want to remove.
78 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Configuring Attachment Filtering
Page 85

NOTE: You can select all check boxes in one go by selecting the check box
next to the Rule column heading at the top-left of the list.
3. Click Remove Selected to delete the selected rules.
6.4 Make changes to an existing rule
To modify an existing rule:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Attachment Filtering node.
2. From the Attachment Filtering page (in the right window), click the name of
the rule that you want to modify.
3. Make the required changes (for example, Rename the rule, etc.) in the rule
properties and click Apply to accept the changes you made. Changes will
take effect immediately.
6.5 Enabling/disabling rules
You can check and change the status of a rule (i.e. enabled/disabled) from
the Attachment Filtering page. To enable or disable an existing rule:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Attachment Filtering node.
2. From the Attachment Filtering page (in the right window), select the check
box of the rule(s) that you want to enable or disable.
3. Click Enable Selected or Disable Selected accordingly. The status
change is displayed immediately under the Status column.
6.6 Changing the rule priority
Attachment Filtering rules are applied in the same order, from top to bottom,
as they are listed in the Attachment Filtering page. However, you can change
the sequence/priority of a rule as follows:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Attachment Filtering node.
2. From the Attachment Filtering page (in the right window), click the (up)
or (down) arrows to respectively increase or decrease the priority of the
required rule(s). Repeat until the rule reaches the desired position in the list
(i.e. until the rule is assigned the desired priority).
NOTE: You can check the priority of rules from the Attachment Filtering page.
The priority value of each rule is displayed in the Priority column.
Configuring Attachment Filtering GFI MailSecurity 10.1 79
Page 86

Page 87

7 Decompression engine
7.1 Introduction to the Decompression engine
The Decompression engine decompresses and analyzes archives attached to
an email.
Screenshot 65 - The decompression engine filters list
The following is a list of archive filters included in the decompression engine:
Check password protected archives
Check corrupted archives
Check for recursive archives
Check size of uncompressed files in archives
Check for amount of files in archives
Scan within archives
You can configure each of the above listed filters separately. This means that
you can specify what each decompression filter should do with emails
containing particular archives.
Decompression engine GFI MailSecurity 10.1 81
Page 88

7.2 Configuring the decompression engine filters
Check password protected archives
Screenshot 66 - Configuring password protected archives options
This filter allows you to quarantine or delete emails that contain passwordprotected archives. To configure this filter:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node.
2. From the list of available filters (in the right window), click on Check
password protected archives.
3. Select the Check password protected archives check box to enable this
filter.
4. Specify what to do with emails containing password-protected archives by
selecting one of the following options:
Quarantine - Select this option to quarantine the emails that contain a
password-protected archive. The administrator can later review these
quarantined emails and approve or delete them accordingly.
Automatically Delete - Select this option to delete emails containing
password-protected archives.
5. Click the Actions tab to configure any actions to be performed whenever
an email containing a password-protected archive is detected and blocked.
For more information on how to configure actions refer to Configuring
decompression filter actions section in this chapter.
6. Click Apply.
Check corrupted archives
This filter allows you to quarantine or delete emails that contain corrupted
archives. The configuration options of this filter are identical to those of the
Check password protected archives.
82 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Decompression engine
Page 89

Check for recursive archives
Screenshot 67 - Configuring recursive archives options
This filter allows you to quarantine or delete emails that contain recursive
archives. Recursive archives, also known as nested archives, are archives
that contain other/multiple levels of sub-archives (i.e. archives within
archives). A high number of archive levels can indicate a malicious archive:
Recursive archives can be used in a DoS (Denial of Service) attack, since
most content scanning and anti-virus packages crash while attempting to
scan nested archive levels.
To configure this filter:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node.
2. From the list of available filters (in the right window), click on Check for
recursive archives.
3. Select the Check for recursive archives check box to enable this filter
and specify the maximum number of nested archives permitted.
IMPORTANT: If you disable the Check for recursive archives rule, GFI
MailSecurity will not scan or quarantine recursive archives, thus bypassing
the anti-virus checking.
4. Decide on what to do with emails containing nested archives that exceed
the specified limit by selecting one of the following options:
Quarantine - Select this option to quarantine the emails that contain
recursive archives. The administrator can later review these quarantined
emails and approve or delete them accordingly.
Automatically Delete - Select this option to delete emails containing
recursive archives that exceed the specified nesting limit.
5. Click the Actions tab to configure any actions to be performed whenever
an email containing a recursive archive is detected and blocked. For more
Decompression engine GFI MailSecurity 10.1 83
Page 90

information on how to configure actions refer to the Configuring the
decompression engine filters section in this chapter.
6. Click Apply.
Check size of uncompressed files in archives
Screenshot 68 - Configuring checks for the size of uncompressed files in archives
This filter allows you to block or delete emails with archives that exceed the
specified physical size when uncompressed. Hackers sometimes use this
method in a DoS (Denial of Service) attack: By sending an archive that can
be uncompressed to a very large file, they can often crash content security or
anti-virus software.
To configure this filter:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node.
2. From the list of available filters (in the right window), click on Check size of
uncompressed files in archives.
3. Select the Check size of uncompressed files in archives check box to
enable this feature and specify the maximum size (in MB) allowed for
uncompressed files, received within an archive.
IMPORTANT: If you disable the Check size of uncompressed files in
archives rule, GFI MailSecurity will not scan or quarantine archive
attachments, thus bypassing the anti-virus checking.
4. Decide on what to do with emails containing archived files that exceed the
specified size when un-compressed.
Quarantine - Select this option to quarantine the emails that contain
these archives. The administrator can later review these quarantined
emails and approve or delete them accordingly.
Automatically Delete - Select this option to delete emails containing
archived files that when un-compressed, exceed the specified size limit.
84 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Decompression engine
Page 91

5. Click the Actions tab to configure any actions to be performed whenever
this filter detects and blocks emails containing an archive. For more
information on how to configure actions refer to Configuring the
decompression engine filters section in this chapter.
6. Click Apply.
Check for amount of files in archives
Screenshot 69 - Configuring the amount of files in archive check
This filter allows you to quarantine or delete emails that contain an excessive
amount of compressed files within an attached archive. You can specify the
number of files allowed in archive attachments from the configuration options
included in this filter.
To configure this filter:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node.
2. From the list of filters (in the right window), click on Check for amount of
files in archives.
3. Select the Check for amount of files in archives check box to enable this
filter and specify the maximum amount of files allowed in an archive.
IMPORTANT: If you disable the Check for amount of files in archives rule,
GFI MailSecurity will not scan or quarantine archive attachments, thus
bypassing the anti-virus checking.
4. Decide on what to do with emails containing archives that exceed the
specified limit of contained files by selecting one of the following options:
Quarantine - Select this option to quarantine the emails that contain
these archives. The administrator can later review these quarantined
emails and approve or delete them accordingly.
Decompression engine GFI MailSecurity 10.1 85
Page 92

Automatically Delete - Select this option to delete emails containing
archived files that when uncompressed contain more files than the limit
specified.
5. Click the Actions tab to configure any actions to be performed whenever
this filter detects and blocks emails containing an archive. For more
information on how to configure actions, refer to Configuring the
decompression engine filters section in this chapter.
6. Click Apply.
Scan within archives
Through the Scan within archives option, you can disable Attachment
Filtering and Content Filtering of files in archives.
Configure this option as follows:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node.
2. From the list of filters (in the right window), click on Scan within archives.
3. Select the Scan within archives check box to scan any archive
attachments present in an email using the decompression and attachment
scanning rules.
7.3 Configuring decompression filter actions
Screenshot 70 - Decompression filter actions
To configure the actions to be performed whenever a particular filter blocks
emails containing archives:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node and from the right
window select the required filter.
86 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 Decompression engine
Page 93

2. Click the Actions tab and select any of the following actions:
Notify local user - Select this option if you want to notify the email local
users when the email contains an archive file that infringes a
decompression engine rule.
NOTE: If a threat is detected in an outbound email, the recipients will receive
the original email with the malicious parts removed. A security notice is
attached to the email to inform the recipients what email parts were removed
and for what reason. This behavior is always enabled and is not affected by
this setting.
Notify administrator - Select this option to send email notifications to the
administrator whenever an email containing an archive is quarantined.
Log occurrence to this file - Select this option to log the event whenever the
selected decompression filter blocks an email. In the box below, specify either
a file name only or the full path to the log file.
3. Click Apply.
7.4 Enable/disable decompression filters
Screenshot 71 - Decompression tool filters list
To enable or disable any of the available decompression filters:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Decompression node.
2. In the right window, select the check box of the filter(s) that you want to
enable or disable.
3. Click Enable selected or Disable selected accordingly.
NOTE: You can select all check boxes in one go by selecting the check box
next to the Description column heading at the top-left of the list.
Decompression engine GFI MailSecurity 10.1 87
Page 94

Page 95

8 The Trojan & Executable Scanner
8.1 Introduction to the Trojan & Executable Scanner
GFI MailSecurity includes an advanced Trojan and Executable Scanner,
which is able to analyze and determine the function of an executable file. This
scanner can subsequently quarantine any executables that perform
suspicious activities (such as a Trojan).
What is a Trojan horse?
The Trojan horse got its name from the old mythical story about how the
Greeks gave their enemy a huge wooden horse as a gift during the war. The
enemy accepted this gift and brought it into their fortress. During the night,
Greek soldiers crept out of the horse and attacked the city.
In computers a Trojan horse is a way of penetrating a victim‟s computer
undetected, allowing the attacker unrestricted access to the data stored on
that computer. Subsequently the attacker can manipulate the data and can
cause great damage to the victim, just like the citizens of Troy.
A Trojan can be a hidden program that runs on your computer without your
knowledge. Furthermore, hackers sometimes hide Trojans into legitimate
programs that you normally use.
Difference between Trojans and viruses
The difference between Trojans and viruses is that Trojans are often „one-off‟
(„tailor made‟) executables, targeted to obtain information from a specific
target (user/system). In general, a hacker deploys a Trojan to create a
backdoor on a system, thus gaining unrestricted access to the system.
Signature based anti-virus software, are unable to detect one-off Trojans.
Indeed any application that only uses signatures to detect malicious software
will not be effective in detecting such threats. These include specialized antiTrojan software. The main reason is that signature based software can only
detect known viruses and Trojans. That is why such applications need
frequent updates.
How does the Trojan & Executable Scanner work?
GFI MailSecurity is able to rate the risk-level of an executable file by
decompiling the executable, and detecting in real time what the executable
might do. Subsequently, it compares capabilities of the executable to a
database of malicious actions and then rates the risk level of this executable
file. With the Trojan & Executable scanner, you can detect and block
potentially dangerous, unknown or one-off Trojans before they penetrate your
network.
8.2 Configuring the Trojan & Executable Scanner
From the Trojan & Executable Scanner node, you can define the level of
security that you require and the actions you want GFI MailSecurity to take on
emails containing malicious executable files.
Configuring the security level
The Trojan & Executable Scanner GFI MailSecurity 10.1 89
Page 96

Screenshot 72 - Trojan and Executable Scanner: General Tab
To configure the Trojan & Executable Scanner:
1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Trojan & Executable Scanner node.
2. From the configuration options (in the right window), select the Enable
Trojan & Executable Scanner check box to activate this filter.
3. Specify the emails you want to check for Trojans and other malicious
executables by selecting any of the following options:
Check inbound emails - Select this option to scan inbound emails for
Trojans and malicious executable files.
Check outbound emails - Select this option to scan outbound emails for
Trojans and malicious executable files.
4. Choose the required level of security by selecting one of the following
options:
High Security - Select this option to quarantine almost all executables. If
the executable file contains any known malicious signature it will get
immediately quarantined.
Medium Security - Select this option to quarantines only suspicious
executables. If the executable contains one high-risk signature or a
combination of high-risk and low-risk signatures it will be quarantined.
90 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 The Trojan & Executable Scanner
Page 97

Low Security - Select this option to quarantine all malicious executables.
If the executable contains at least one high-risk signature, it will be
immediately quarantined.
Configuring actions
Screenshot 73 - Trojan and Executables Scanner: Actions Tab
5. Click the Actions tab to configure the actions you want GFI MailSecurity to
take on emails containing a malicious executable. Select any of the following
options:
Notify local user - Select this option if you want to notify the email local
users when this filter detects a malicious executable.
NOTE: If a threat is detected in an outbound email, the recipients will receive
the original email with the malicious parts removed. A security notice is
attached to the email to inform the recipients what email parts were removed
and for what reason. This behavior is always enabled and is not affected by
this setting.
Notify administrator - Select this option to send email notifications to the
administrator whenever an email containing malicious executable is
quarantined.
Log occurrence to this file - Select this option to log the event whenever
the Trojan & Executable Scanner detects an infected email. In the edit box
below, specify either the file name only or the full path to the log file.
6. Click Apply.
8.3 Trojan & Executable Scanner updates
You can configure GFI MailSecurity to download Trojan & Executable
Scanner updates automatically or to notify the administrator whenever new
updates are available. To configure automatic updates:
The Trojan & Executable Scanner GFI MailSecurity 10.1 91
Page 98

1. Click the GFI MailSecurity ► Trojan & Executable Scanner node.
2. Click the Updates tab in the Trojan & Executable Scanner page (in the
right window).
3. Select the Automatically check for updates check box to enable the
auto-update feature.
4. From the Downloading options list, select one of the following download
options:
Only check for updates - Select this option if you want GFI MailSecurity
to just check and notify the administrator whenever updates are available
for the Trojan & Executable Scanner. This option will NOT download the
available updates.
Check for updates and download - Select this option if you want GFI
MailSecurity to check and automatically download any updates available
for the Trojan & Executable Scanner.
5. Specify how often you want GFI MailSecurity to check/download updates
for the Trojan & Executable Scanner, by typing an interval in hours.
6. Click Apply.
Screenshot 74 - Trojan and Executable Scanner: Updates tab
Triggering the Trojan & Executable Scanner update manually
92 GFI MailSecurity 10.1 The Trojan & Executable Scanner
Page 99

To check/download updates for the Trojan & Executable Scanner
immediately, click Download updates.
The Trojan & Executable Scanner GFI MailSecurity 10.1 93
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...