Page 1

L
L
A
A
U
U
Monitor Models:
1493
1793
1993
2093
2793
3693
Safety Isolating
Transformer Models:
ISO XFR-75W
ISO XFR-100W
N
N
A
A
M
M
E
E
C
C
I
I
V
V
R
R
E
E
S
S
Page 2
2 YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY
This product is warranted by CERONIX to be free of defects in material
and workmanship for a period of two years from the date of purchase.
All parts and labor are free of charge during the warranty period.
This warranty does not cover mechanical breakage due to physical abuse.
It is the customer's responsibility for shipping the defective unit to and from
CERONIX or one of the authorized service centers for repair.
Please attach a note describing the problem.
CERONIX Inc.
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, CA. 95602-7419
Phone: (530) 886-6400
FAX: (530) 888-1065
WEB: www.ceronix.com
CERONIX shall not be liable for any consequential damages, including
without limitation damages resulting from loss of use.
Ceronix will repair XX93 monitors after the 2 year warranty,
for a minimal charge, plus shipping to and from Ceronix.
®
Recognized under the Component Program of Underwriters Laboratories Inc., the
Canadian Standards Association, and TÜV Product Service.
Compliance to the following Standards:
IEC 60950, CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-00, ANSI/UL 60950, CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.
1-98, IEC 65:85 + A1:87 + A2:89 + A3:92.
ISO 9001:1994 Certified through TÜV Management Service.
COPYRIGHT 2002
CERONIX
All rights reserved.
The information contained in this manual
is subject to change without prior notice.
©
Page 3

ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual is specifically written to aid the service technician, repairing
CERONIX Models 1493, 1793, 1993, 2093, 2793, and 3693 color monitors.
There are three main sections:
1. General Description.
2. Circuit Description.
3. Repair Setup and Appendix.
Introduction Block
Diagram
Installation
Instructions
Description
BLOCK
Diagram
Schematics
&
Assembly
Drawings
Circuit
Description
Trouble
shooting
Handbook
Appendix
Convergence
Degaussing
P/O Form
PRAs
To understand how the Monitor works, it is best to know what each circuit
does and how each circuit relates to the other circuits. The Block Diagram is
presented in a simplified view and a comprehensive view to accomplish the goal of
understanding the whole unit. Once the general picture is clear, the complexity of
each circuit will be easier to understand.
The Circuit Description is also written in two views, a simplified view and a
detailed view to help give the reader a clear understanding of what each
component does. This understanding is most helpful for the more complex
problems or multiple problems that sometimes occur.
The power supply trouble shooting section describes methods used to power up
various monitor circuits, when there is a fault in the monitor, which disables the
power supply.
The appendix includes; filament voltage test, convergence procedure,
replacement parts purchase order form, degaussing coil attachment specification,
high pot test, wire routing drawing, production assembly drawings (PADs), C, I, J,
& K film resistor arrays and a parts list addendum. The parts list addendum is
used to add new information describing part changes. Tables, suitable for pasting
on these pages, will be published as new variations of the XX93 monitors are
produced.
i
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
About This Manual.............................................................................................................
Table of Contents................................................................................................................
CERONIX Monitor Simplified Block Diagram.................................................................
Installation Instructions; English, French, and German................................................
CERONIX Monitor Electrical Specification......................................................................
1493, 1793, 1993, 2093, 2793, and 3693 General Operation Description.
Video Interface, Amps & Beam Current Sense........
Auto Bias, Bias Sync Delay, & Auto Bright.............
CRT, Blanking, Sync, & Vertical deflection.............
Horizontal Deflection & Remote...............................
Horizontal Size & Power Supply...............................
P/S, Safety Shutdown Circuits, Degaussing.............
Monitor BLOCK DIAGRAM..............................................................................................
Monitor Schematics and Assembly Drawings
1493-CGA Main Board Schematic..(4233/4235)...............................................................
1493-CGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
1493-VGA/SVGA Main Board Schematic..(4200/4252)....................................................
1493-VGA/SVGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing........................................
1793-VGA Main Board Schematic..(4243/4244)..............................................................
1793-VGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
1793-SVGA Main Board Schematic ..(4247/4250)............................................................
1793-SVGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing.................................................
1993-VGA Main Board Schematic..(4221/4255)...............................................................
1993-VGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
1993-SVGA Main Board Schematic..(4249/4256).............................................................
1993-SVGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing.................................................
2093-CGA Main Board Schematic..(4112/4166)...............................................................
2093-CGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
2093-VGA Main Board Schematic..(4224/4227/4108)......................................................
2093-VGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
2793-CGA Main Board Schematic..(4104)........................................................................
2793-CGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
2793-VGA Main Board Schematic..(4231)........................................................................
2793-VGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
2793-VGA Main Board Schematic..(4254)........................................................................
2793-VGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
3693-CGA Main Board Schematic..(4172)........................................................................
3693-CGA Main Board Technician Assembly Drawing...................................................
Video Board Schematic......................................................................................................
Video Board Technician Assembly Drawing..(Component Side).....................................
Video Board Technician Assembly Drawing..(Conductor Side).......................................
Safety Critical Components for XX93 Monitors..(English)..............................................
Safety Critical Components for XX93 Monitors..(German)..............................................
Replacement Part List.......................................................................................................
Blocks A-D...............................
Blocks E-G...............................
Blocks H-L...............................
Blocks M-P..............................
Blocks Q-T...............................
Blocks U-Z...............................
i
ii-iii
1
2-4
5-8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45-63
Detailed Circuit Description
Video Interface Circuit, Function, Description (+ & - Analog)........................................
5.6V to 1.1V, -Analog, DC, Video Interface Circuit Description......................................
0V to .7V, +Analog, DC Video Interface Circuit Description...........................................
1Vp-p, +Analog, AC Video Interface Circuit Description.................................................
64
65
66
67
ii
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Video Amplifier Circuit, Function, Description.................................................................
Video Amplifier Circuit Description and Schematic.........................................................
Video Board Power Supply and Arc Protect Schematic....................................................
CRT Auto Bias and Auto Bright Circuit, Function, Description......................................
CRT Auto Bias, Auto Bright, and Vertical Sync Delay Circuit Description....................
CRT Auto Bias and Auto Bright Schematic......................................................................
Monitor, Block Diagram Review........................................................................................
Blanking, Master Gain, and Fault Circuit, Function, Description..................................
Blanking, Master Gain, and Fault Circuit Description....................................................
Blanking, Master Gain, Beam Limiter, and Fault Schematic.........................................
Vertical and Horizontal Sync Circuit Description.............................................................
Vertical Deflection Circuit Description and Schematic....................................................
Horizontal Deflection Circuit Description and Schematic................................................
Horizontal Raster Width Control Circuit Description......................................................
Horizontal Raster Width and Position Control Schematic...............................................
Dynamic Focus Circuit Function and Description............................................................
Vertical Booster Amplifier Circuit and Description..........................................................
Simplified Power Supply Circuit, Function, Description..................................................
Switch Mode Power Supply Circuit Description and Schematic......................................
Trouble Shooting and Repair
Equipment Setup for repairing the Model XX93 Monitor..(English)...............................
Equipment Setup for repairing the Model XX93 Monitor..(German)..............................
Power Supply Trouble Shooting Tips.................................................................................
Trouble Shooting Handbook...............................................................................................
Filament Voltage Test..(English).......................................................................................
Filament Voltage Test..(German)......................................................................................
Setup and Convergence Procedure..(English)...................................................................
Setup and Convergence Procedure..(German)...................................................................
Replacement Parts, Purchase Order Form........................................................................
1493 Degaussing Coil Attachment Specification...............................................................
1793, 1993, 2093 Degaussing Coil Attachment Specification...........................................
2793, 3693 Degaussing Coil Attachment Specification.....................................................
HighPot, for Shock Hazards, Circuit Description..(English)............................................
HighPot, for Shock Hazards, Circuit Description..(German)...........................................
Wire Routing Instructions..................................................................................................
Precision Resistor Arrays..(C, I, J).....................................................................................
Precision Resistor Array..(K)..............................................................................................
Precision Resistor Array..(Blue).........................................................................................
Vertical Deflection Amplifier-Booster Technician Assembly Drawing............................
Monitor Input Drive Signal Worksheet.............................................................................
Declaration of Conformity..................................................................................................
68
68-69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79-81
82-83
84
85
86
87
88-89
90-91
92
93
94
95-97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
ISO XFR-75W and ISO XFR-100W Safety Isolating Transformer..................................
Circuit Description..(English).............................................................................................
Auto Voltage Select Schematic and Assembly Drawing...................................................
Circuit Description..(German)............................................................................................
Installation Instructions.....................................................................................................
Specifications.......................................................................................................................
Isolation Transformer Trouble shooting..(English)...........................................................
Isolation Transformer Troubleshooting..(German)...........................................................
Manual Voltage Select Schematic and Assembly Drawing..............................................
Part List Addendum...........................................................................................................
115
116
117
118
119-121
122-123
124
125
126
127-130
iii
Page 6
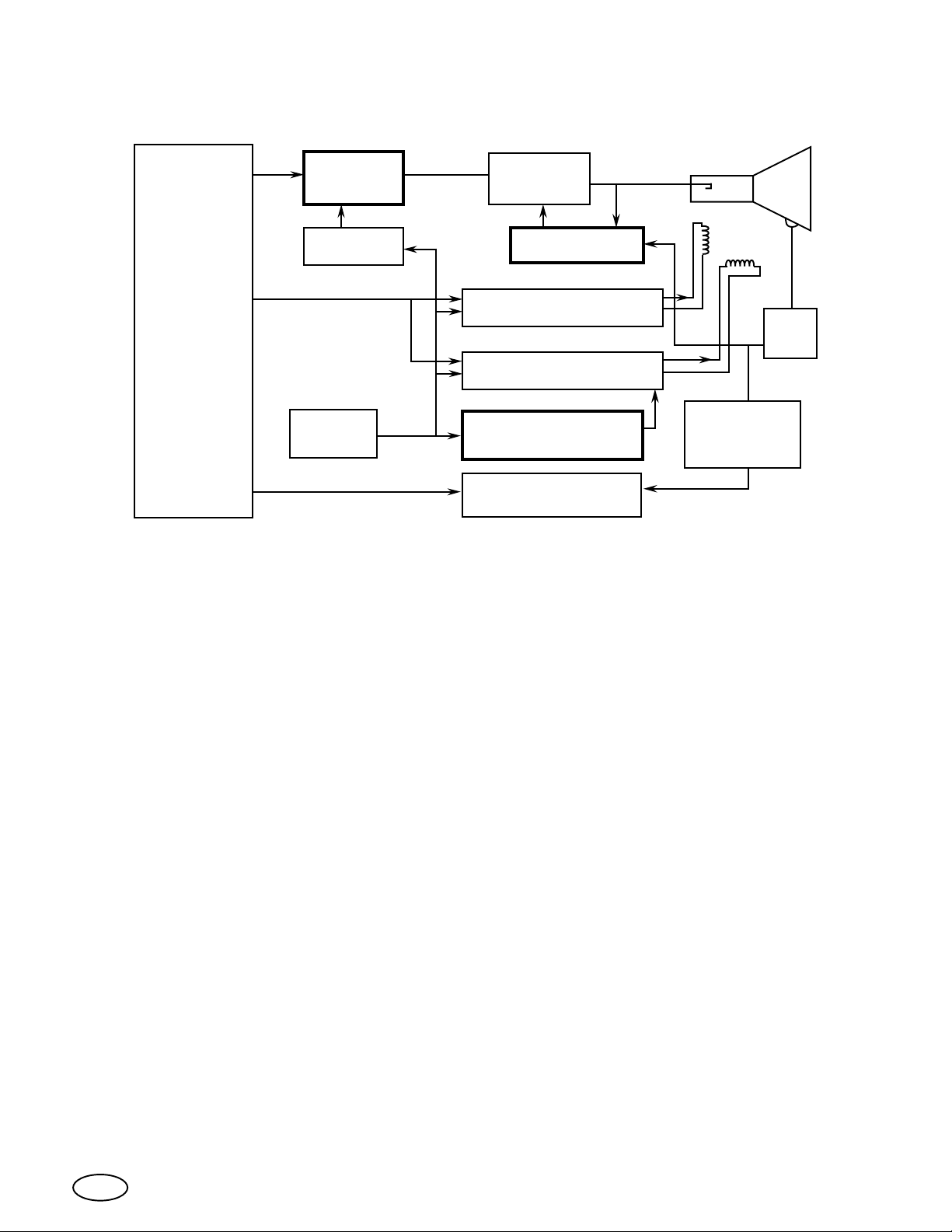
Monitor Simplified Block Diagram.
VIDEO
Output
Drive
Electronics
SYNC
Output
Isolated
Power
This block diagram gives a broad view of the circuit organization of the 1493,
1793, 1993, 2093, 2793, and 3693 monitors. The blocks with the bold outline
represent circuits which provide these monitors with a wide range of
operating conditions without the need for adjustment.
VIDEO
Interface
Blanking
Remote
Controls
VIDEO
Amps.
AUTO BIAS
Vertical Deflection
Horizontal Deflection
Horizontal Size
Control
POWER SUPPLY
CRT
FBT
IB
Fault &
High Temp.
Detection
The video interface circuit can be programmed to accept; +Analog AC or
DC coupled, -Analog, and 4 line TTL. The M. GAIN or contrast control is
located on the remote control board.
The auto bias circuit eliminates the need for the color setup procedure.
This circuit is designed to actively compensate for picture tube drift which
normally causes unbalanced color. The auto bias circuit also adjusts the
CRT gain to compensate for gain loss with age.
The horizontal size control circuit permits the horizontal size to be adjusted
from a remote control board. This circuit is also used to compensate for
pincushion distortion and blooming. Anti-blooming is accomplished by
correcting horizontal size variations which are caused by the additional load
on the flyback transformer under high beam current conditions.
Careful reading of all the information presented in this manual is a good
way to learn how to repair the CERONIX monitor.
1
Page 7
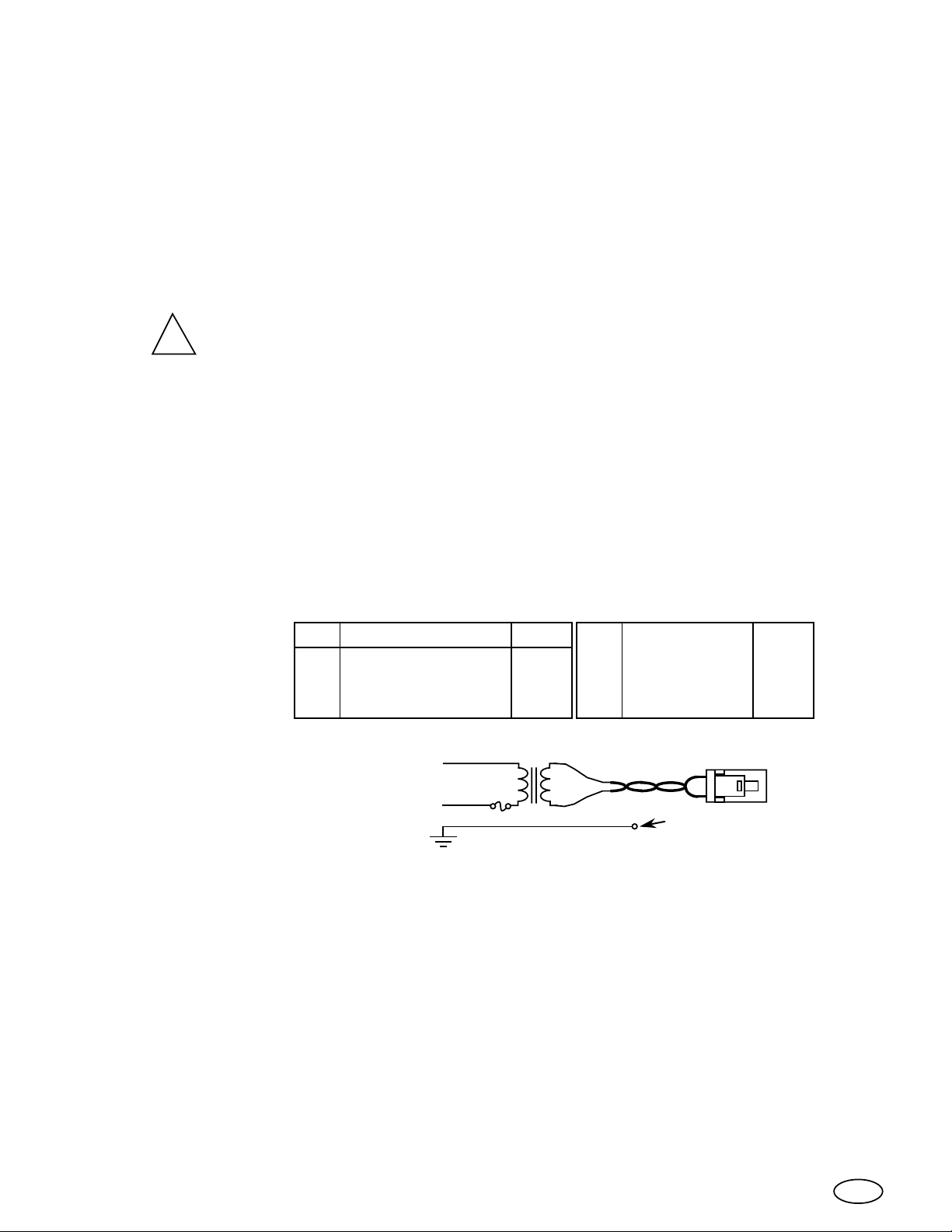
Installation Instructions For The XX93 Monitors.
1.
A 3 amp slow blow fuse (for the degaussing current) and a 75 VA isolation
transformer are the minimum requirements for using our monitor in a product.
2.
Unpack the monitor.
3.
Install the monitor in the enclosure.
4.
Connect the green/yellow ground wire to the earth ground connection on the enclosure.
This wire is connected to the ground screw, located on the monitor chassis behind the
serial number label.
Refer to the installation instructions supplied
by the system manufacturer for details of
mounting the monitor in the enclosure.
WARNING!
!
Failure to connect this ground wire before applying power is not
allowed, since this condition can produce a shock hazard. The
chassis to mains connector resistance shall not exceed 100mΩ.
Check that the following wires are properly connected;
5.
Green wire from the CRT aquadag braid to the video board.
A.
12 conductor flat cable from the video board to the main board.
B.
Red high voltage wire from the flyback transformer
C.
to the picture tube anode cap.
Yoke cable from the yoke to the main board.
D.
Remote cable from the remote control board to the main board.E.
Note;
6.
Plug in the
seven conductor
video connector.
7.
Plug in the power connector
from the isolation transformer.
Be sure these wires are secured such that they do not touch any metal parts.
Pin Signal
0
+12V from monitor.
1
Horizontal sync.
2
Vertical sync.
ISOLATION TRANSFORMER
Mains
Power
3A-T
FUSE
GREEN / YELLOW WIRE
Color
White
Yellow
Purple
75VA
Signal ground.
3
Red video.
4
Green video.
5
Blue video.
6
Gray
Red
Green
Blue
Attached to the
monitor chassis.
Apply power to the monitor and the drive electronics.
8.
Check the focus and, if necessary, adjust the top control on the flyback transformer.
9.
Adjust the controls on the remote control board for proper;
10.
Horizontal Raster Size.
Vertical Raster Size.
Vertical Raster Position.
Horizontal Picture Position.
Video Gain.
11.
For convergence instructions, see page 100 & 101.
2
Page 8
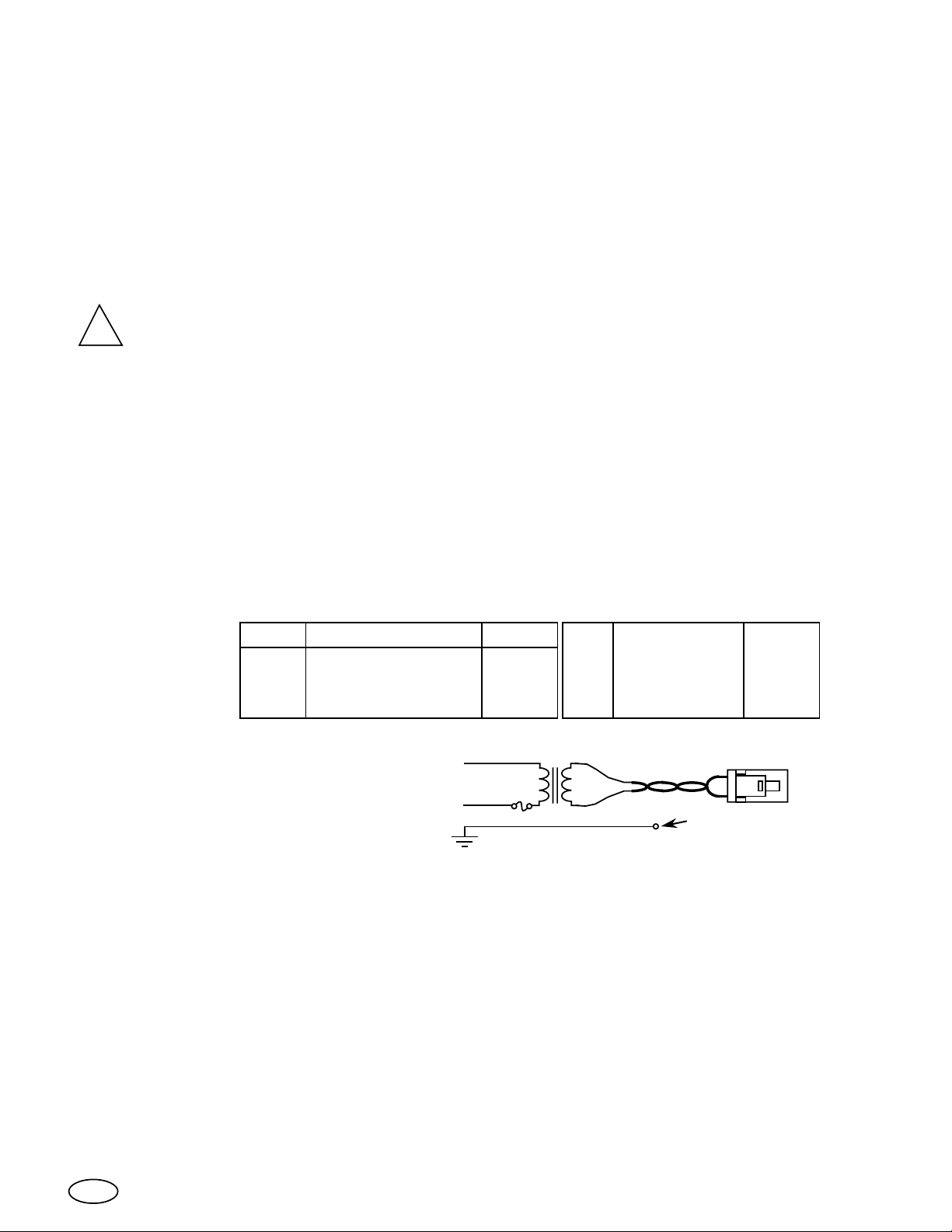
Instructions d´installation des écrans XX93.
1. Un fusible á fusion lente de 3 amp (pour le courant du champ magnétique d´adjustement) et un
transformateur d´isolation de 75 VA sont le minimum requis pour utiliser nos écrans dans un produit.
2. Déballer l´écran.
3. Installer l´écran dans son carter.
Se référer aux instructions d´installation foumies par le fabriquant
du systéme pour les détails de montage de l´écran dans le carter.
4. Relier le fil de terre vert/jaune á la prise de terre sur le carter. Ce cable est relié á la vis
de terre située sur le chassis de l´écran derriére l´étiquette portant le numéro de série.
ATTENTION! Il n´est pas permis de ne pas relier ce fil de terre avant de mettre le courant, car
!
cette situation pourrait provoquer un choc électrique dangereux.
La résistance du chassis aux pricipales connections ne doit pas depasser 100mΩ.
5. Vérifier que les fils suivants sont correctement reliés:
A. Le fil vert de la tresse du tube cathodique aquadag á la carte video.
B. Le cable plat á 12 conducteurs de la carte vidéo á la carte principale.
C. Le cable rouge haut voltage du retout du transformateur au capuchon de
l´anode du tube cathodique.
D. Le fit de bobinage du bobinage á la carte principale.
E. Le fil de télécommande de la carte de la télécommande á la carte principale.
Note: Soyez sur que ces fils sont connectés en toute sécurité de sorte qu´ils ne
touchent aucune partie métallique.
6. Brancher les
sept fils de la
connection vidéo:
Broche Signal Couleur
0
+ 12V de l´écran
1
Synchro Horizontale
2
Synchro Verticale
Blanc
Jaune
Violet
3
Signal de terre
4
Rouge vidéo
5
Vert vidéo
6
Bleu vidéo
Gris
Rouge
Vert
Bleu
TRANSFORMATEUR D'ISOLATION
7. Brancher les fils de courant
depuis le transformateur d'isolation:
Courant
Principaux
3A-T
75VA
FUSE
FIL VERT / JAUNE
Attasché au chassis
du moniteur.
8. Amener le courant á l´écran et au disque électronique.
9. Vérifier le foyer, et si nécessaire, régler le contróle sur le retour du transformateur.
10. Effectuer les réglages sur la carte de la commande á distance pour:
La taille du balayage horizontal.
La taille du balayage vertical.
La position du balayage fertical.
La position horizontale de l´image.
L´acquisition vidéo.
11. Pour les instructions de convergence, voir page 100 & 101.
3
Page 9
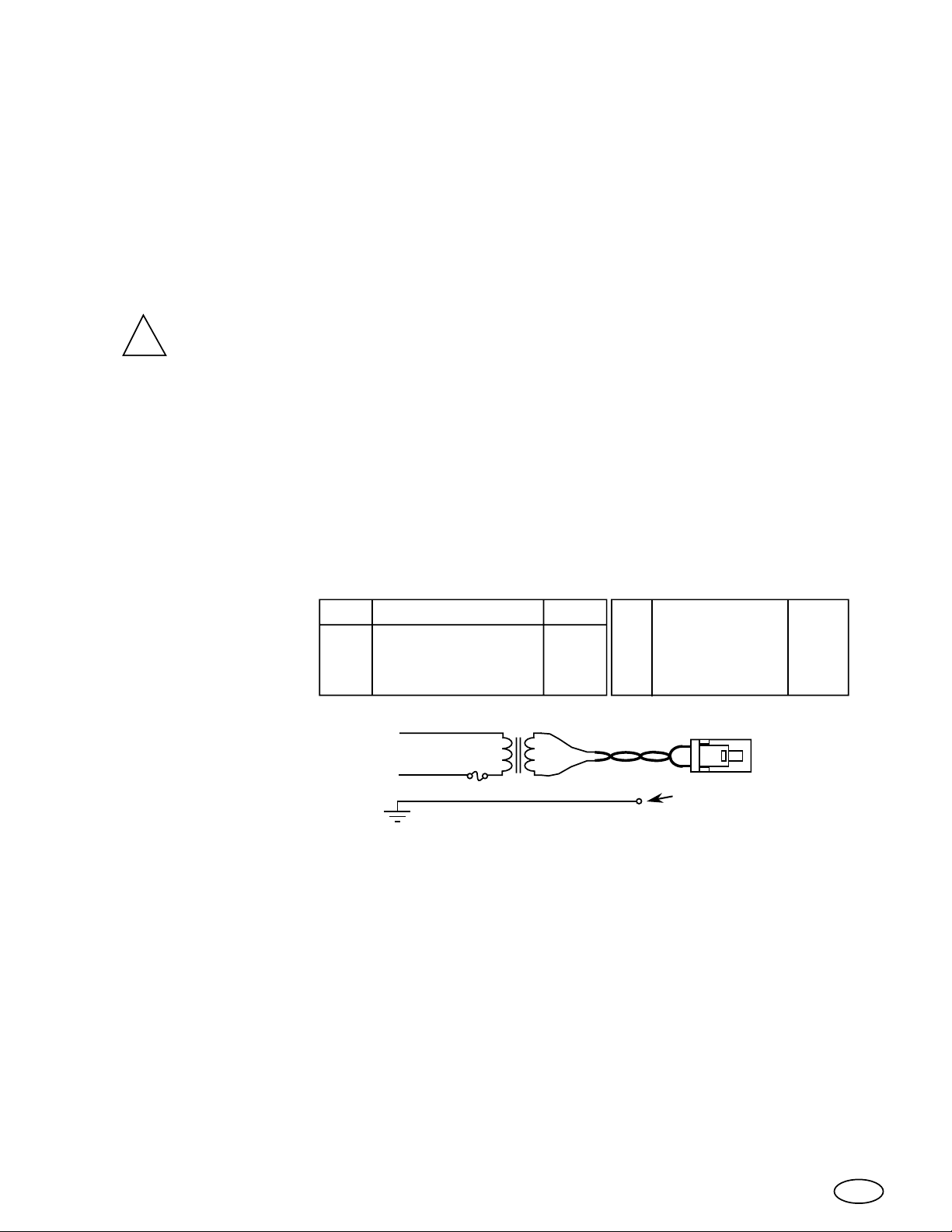
Installationsanweisungen für die XX93 Monitore.
1. Ein 3 Ampère-T sicherung (für die degaussing-Strömung) und ein 75 VA Isoliertransformator
ist die Minimum-Forderung für benutzen unseren Monitoren in einem Produkt.
2.
Packen Sie den Monitor aus.
Schließen Sie den Monitor
3.
im Gehause an.
4.
Verbinden Sie den Grüne/Gelben Schutzleiter zum Erdung anschluß auf dem Gehause.
Für Details, Folgen Sie den Installation-Anweisungen,
Vom Lieferanten der Antriebelektronik.
Dieser Draht ist verbunden zur der Erdung-Schraube auf dem Monitor-Chassis, und wird
hinter der Serien-Nummer-Aufschrift gefunden.
Unterlassen dieser Verbindung dieses Erdung-Drahts ist
WARNUNG!
!
gesetze widrig. Der Widerßtand von diesem anschluß biz
zum netzstecker darf 100mΩ nicht überschreiten.
Prüfe daß die folgenden Drähte ordentlich verbunden sind;
5.
Grüne Draht vom CRT aquadag zum Video Schaltpult.A.
B.
C.
D.
12 Leiter-Flachkabel vom Videoschaltpult zum Hauptschaltpult.
Rote hochspannungs Draht vom Flybacktransformator zur der Bildröhrenanode.
Jochkabel vom Joch zum Hauptschaltpult.
E. Fernsteuerung Kabel vom Fernsteuerungschaltpult zum Hauptschaltpult.
Notiz;
Stecken Sie den
6.
7 Leiter-VideoVerbindungsstecker ein.
Seien Sie sicher diese Drähte sind so befestigt daß sie kein Metallteil berühren.
0
+12V Von Monitor.
1
Horizontal sync.
Vertical sync.
2
FarbeSignalLeiter
Weiß
Gelb
Purpur
3
Signal-Erdung.
4
Rotes Video.
Grünes Video.
5
6
Blaues Video.
Grau
Rot
Grün
Blau
ISOLIERTRANSFORMATOR
7.
Stecken Sie den Stecker vom
Isoliertransformator ein.
Schalten Sie den Monitor und die Steuerung an.
8.
Prüfe Sie den Fokus und, wenn notwend, stell en Sie die obere Kontrolle ein auf dem
9.
Netzstrom
Grüne/Gelben Schutzleiter
3A-T
SICHERUNG
75VA
Verbindung ist auf dam
Monitore chassis.
Flybacktransformator.
10.
Stellen Sie die Kontrollen des Fernsteuerungsschaltung ein für richtige
- Horizontal Raster Größe.
- Vertical Raster Größe.
- Vertical Raster Position.
- Horizontal Bild Position.
- Video Kontrast.
Für Konvergenz-Anweisungen, auf seite 100 & 101.
11.
4
Page 10
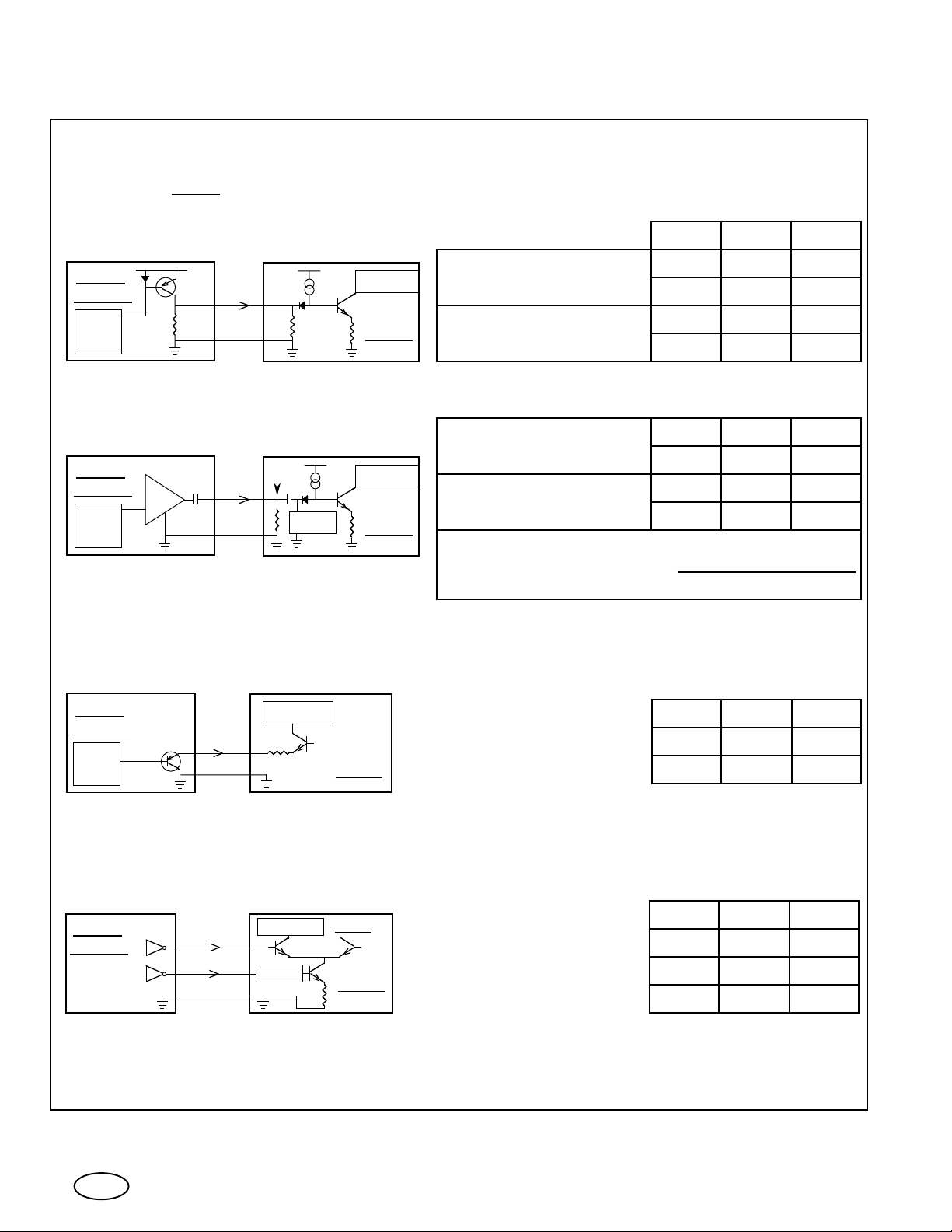
CERONIX
XX93 Monitor Electrical Specification.
INPUTS
Standard Video Configurations, available, are:
1.
A. Positive Analog, DC Coupled.
Video
Source
D-A
75Ω
Video
Gnd
.6mA
75Ω
B. Positive Analog, AC Coupled.
Video
Source
D-A
Zo=75Ω
Amp.
Video
Gnd
75Ω
10uA
Clamp
C. Negative Analog.
To Amp.
Monitor
To Amp.
Monitor
Min. Typ. Max
.75V
Video
1.0V
Video
.75V
Video
1.0V
Video
Black level
Saturated color
Black level
Saturated color 1.00V 1.02V 1.04V
Black level
Saturated color
Black level
Saturated color
0.00V 0.02V 0.04V
0.75V 0.77V 0.79V
0.00V 0.02V 0.04V
Blk-.02V
Blk+.73V Blk+.75V Blk+.77V
Blk-.02V Blk+0.00V Blk+.02V
Blk+.98V
Blank
Blk+1.00VBlk+1.02V
Blk+.02V
AC voltages are referenced to the R, G, & B
video input voltage during horizontal sync (Hs).
Blank is the black level voltage during Hs.
Video
Source
D-A
Video
Gnd
To Amp.
IN
R
V
Blk.+.7 V
Monitor
Black levelRed & Green
Blue Black level
Saturated color
D. 4 Line TTL also available.
Black level
Color on
Low intensity
Full intensity
*
R,G,B
Video
Intensity
Gnd
Video
Source
*
No pullup resistor on intensity line.
To Amp.
BIAS
+12V
V
Monitor
B
Note: RS170 and other voltage combinations optional for analog video.
5.4V 5.6V 5.8V
4.85V 5.05V 5.25V
.7V .9V 1.1V
0V
2.7V 3.5V
.2V .5V
6.0V
0V .2V .4V
4.5V 4.6V 4.8V
5
Page 11
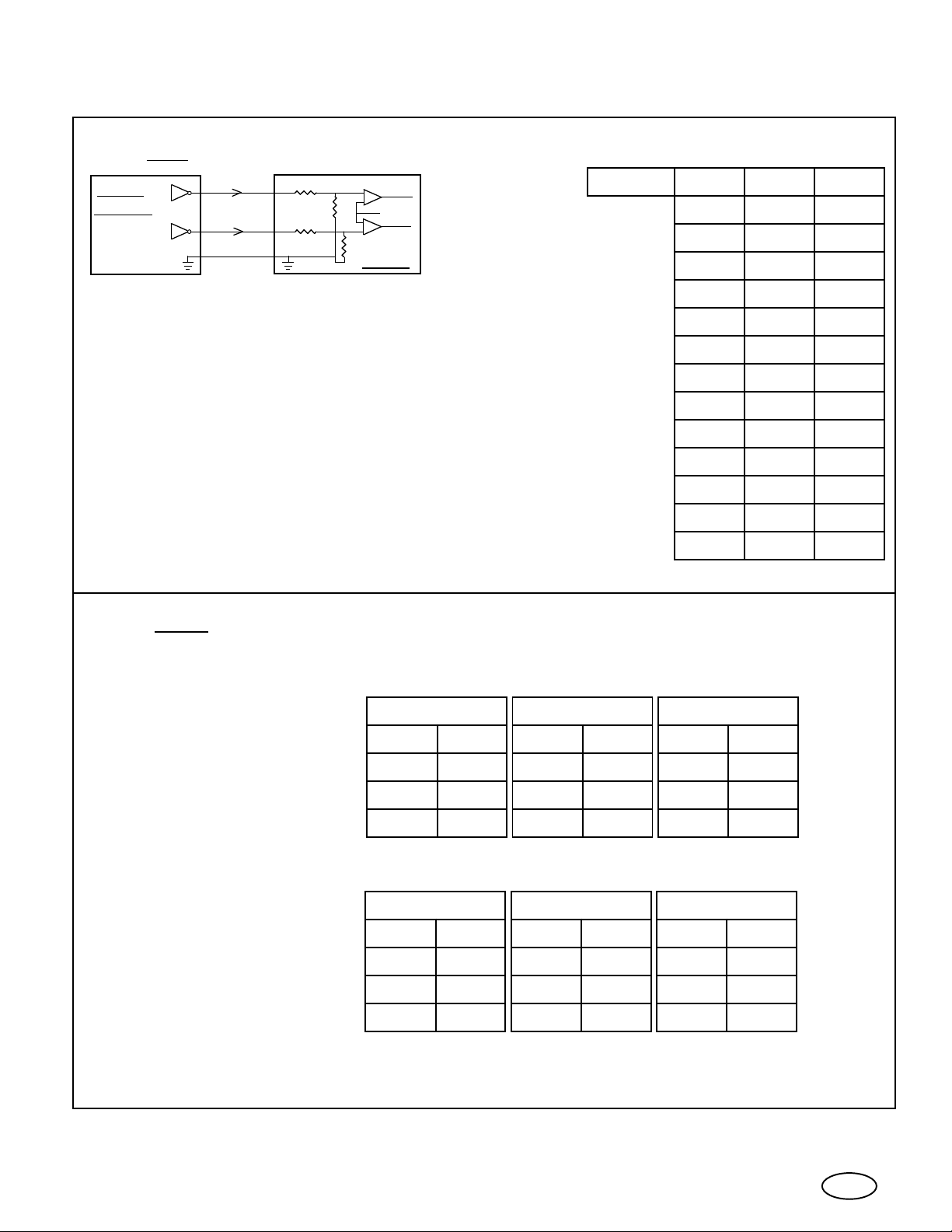
CERONIX
The Sync signals may be of either polarity and separate or composite.2.
XX93 Monitor Electrical Specification.
Sync
Source
For composite sync, vertical and horizontal
sync lines are connected together.
Hs
Vs
Gnd
1.8K
1.8K
220
Monitor
.15V
Ω,
2 PL
High input voltage
Low input voltage
Horizontal sync pulse
Vertical sync pulse
Horizontal frequencies:
Custom horizontal frequencies from 15KHz
to 39KHz are available upon request.
Vertical frequencies:
3.
The Power to the monitor is to be supplied by a secondary winding of an
isolation transformer.
Min. Typ. MaxModel
2.2V 3.5V 20V
-2.7V .30V .80V
1.5uS
65uS
15.5KHz 15.7KHz
29.3KHz 29.6KHz 29.9KHz
31.2KHz 31.5KHz 31.8KHz
34.9KHz 35.2KHz 35.6KHz
37.5KHz 37.9KHz 38.3KHz
4.0uS 12uS
.5mS 1.5mS
15.9KHz
55Hz45Hz 50Hz
61Hz51Hz 56Hz
65Hz55Hz 60Hz
75Hz65Hz 70Hz
120VAC 50Hz or 60Hz
230VAC 50HZ or 60Hz
Power
120VAC 50Hz or 60Hz
230VAC 50HZ or 60Hz
Power
Model 1493
Model 1793
Model 1993
Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
90VAC
180VAC
35W
90VAC145VAC
290VAC 290VAC180VAC
60W
40W 70W
145VAC 145VAC
Model 2093 Model 2793
90VAC
290VAC180VAC
45W 75W
Model 3693
Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
90VAC
180VAC
45W 75W 50W
290VAC 290VAC180VAC
90VAC145VAC
145VAC 145VAC
100W
90VAC
290VAC180VAC
50W 100W
6
Page 12

CERONIX
Five Controls are located on
4.
XX93 Monitor Electrical Specification.
a separate PCB for easy access.
Model 1493
Model 1793 Model 1993
Min. Max.Min. Max.Min. Max.
H SIZE--------------Horizontal raster size
V SIZE---------------Vertical raster size
V RAS. POS.-----Vertical raster position
H POS-------Horizontal picture position
M GAIN---------------------Master gain
10.1" 11.1" 11.9" 12.9"
7.3" 8.3" 8.6" 9.6"
0"
1" Right 1" Left 1" Right 1" Left
0mA .75mA 0mA .75mA 0mA
Model 2093
.50"
0"
Model 2793 Model 3693
.50"
13.4" 14.4"
9.8" 10.8"
0"
1" Right 1" Left
.50"
.75mA
Min. Max.Min. Max.Min. Max.
14.9" 15.9" 20.4" 21.4"
10.9" 11.9" 15.1" 16.1"
0"
1" Right 1" Left 1" Right 1" Left
0mA .75mA 0mA
.60"
0"
1.0"
1.5mA
27.4" 28.4"
20.3" 21.3"
0" 1.0"
1" Right 1" Left
0mA 1.5mA
The board Controls are located on the main PCB:
Focus and G2 on the FBT.
Optional board Controls are: pincushion, video black level, and horizontal hold control.
5.
Image
Environmental
6.
Color Temperature
Horizontal linearity
Vertical linearity
Pincushion
1493
17/19/2093
9300°K 9300°K 9300°K 9300°K
-2% +2%
-2% +2%
-2% +2%
-5% +5% -8% +8%
-5%
-3%
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
Operating humidity
Storage humidity
+5%
+3%
0° C
-8%
-5%
70° C
85° C-20° C
20% 80%
10% 95%
2793 3693
Min. Max.Min. Max.Min. Max.Min. Max.
-10% +10%
+8%
+5%
-10%
-8%
+10%
+8%
7
Page 13
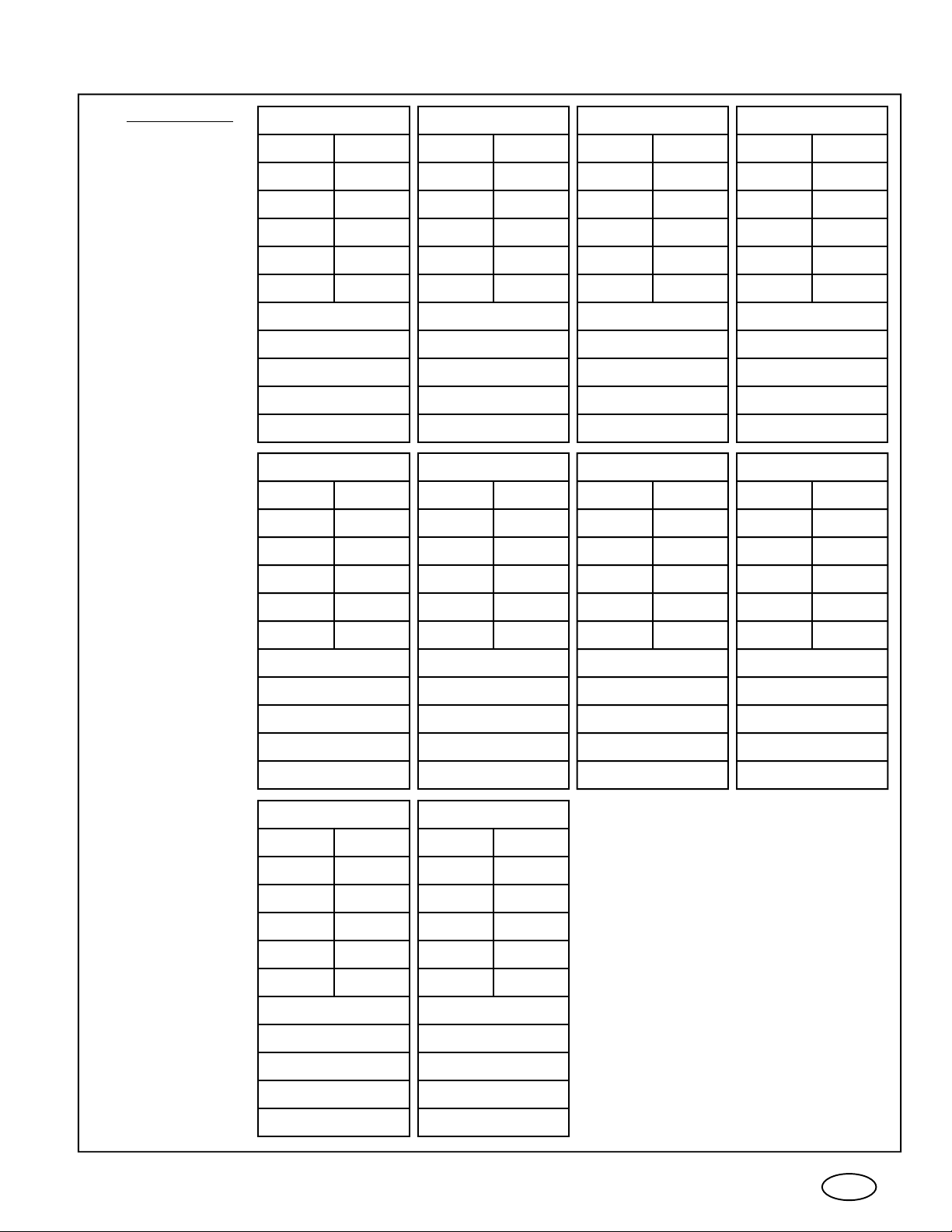
CERONIX
Picture tube
7.
XX93 Monitor Electrical Specification.
1493-CGA/VGA/SVGA
1793-VGA/SVGA
1793-SVGA
1993-VGA/SVGA
Useful diagonal
Useful horizontal
Useful vertical
Useful area
Spacing of dot/line trios
Phosphor Trio Type
Deflection angle
Light transmission
CRT surface
Phosphor
Useful diagonal
Useful horizontal
Useful vertical
Useful area
Inch mm
13.2 335 16.1 409
11.1 281 12.9 328
8.3 211 9.6 245
92.1 in 593 cm 124 in 804 cm
.0110" .28mm .0098" .25mm
Dot
16 407
12.9 328
9.7 246
125 in 807 cm
22
.0106" .27mm
Dot
90°
Approximately Approximately
57% 50%
Polished/Curved
P22
2093-CGA 2793-CGA
Approximately
53%
Polished/Curved
P22
2093-VGA
Inch mm
18.9 480 26.8 679
15.9 404 21.4 544
11.9 303 16.1 408
189 in 1,224 cm 345 in 2,220 cm
22 2 2
18.9 480
15.9 404
11.9 303
189 in 1,224 cm
22
InchInch mmmm
Dot
90°90°
AR / Flat
P22
InchInch mmmm
Inch mm
18 457
14.4 366
10.8 274
165 in 1,003 cm
2222 2 2
.0102" .26mm
Dot
100°
Approximately
45%
AR / Curved
P22
2793-VGA
Inch mm
26.8 679
21.4 544
16.1 408
345 in
2
2,220 cm
Spacing of dot/line trios
Phosphor Trio Type
Deflection angle
Light transmission
CRT surface
Phosphor
Useful diagonal
Useful horizontal
Useful vertical
Useful area
Spacing of dot/line trios
Phosphor Trio Type
Deflection angle
Light transmission
CRT surface
Phosphor
.0331" .84mm .0326" .83mm
Line
Approximately Approximately
40% 38%
Polished/Curved
P22
2793-VGA
Inch mm
26.6 676
21.3 541
16.0 406
341 in 2,196 cm
22
.0299" .76mm
Line / Variable
110°
Approximately
81%
Polished/Flat
P22
.0307" .78mm
Line
90°
Approximately
40%
Polished/Curved
P22
3693-CGA
Inch mm
35.5 902
28.4 721
21.3 541
605 in 3,901 cm
22
.0394" 1mm
Line
111°
Approximately
32%
Polished/Curved
P22
Line
110°90°
Polished/Curved
P22
.0326" .83mm
Line
110°
Approximately
38%
Polished/Curved
P22
8
Page 14

Refer to the block diagram on page 15 (foldout) when reading this description.
A
The Video Interface is designed around a custom IC and will accept DC or AC
coupled positive analog video signals. It can also be used with negative analog
and 4 line TTL. This IC has a built in multiplier circuit for the master gain
control and blanking functions. Resistors are used to protect the IC and to set
the gain. The programmed gain is dependent on the input signal amplitude
except with the TTL mode. Solder jumpers and component substations are used
to program the Video Interface for the type of input signal to be received. The
output of the IC drives the video amplifiers. This drive is a current where 0 mA
is black and 10 mA is a saturated color.
B
The Video Amplifiers are of the push pull type. They are built partly on thick
films and partly on the video PCB. Spreading out the amplifier reduces the
component heat and improves the life of the unit. The bandwidth is 25 MHz with
40Vp-p output. The rise and fall times are 20nS.
C
The Beam Current Feedback circuit directs most of the beam current of each
amplifier to the beam current buffer. The only time this current is measured, by
the auto bias circuit, is during the time of the three faint lines at the top of the
screen and three lines thereafter. The CRT auto bias circuit is designed to adjust
the video amplifier bias voltage such that the beam current of each of the three
guns is set to a specific programmed value.
D
The
current signal into a low impedance voltage. This voltage is applied to the auto
bias IC through a 200 ohm resistor. After the three lines of beam current are
measured, the program pulse from the auto bias IC, produces a voltage drop
across this 200 ohm resistor that equals the amplitude of the beam current
voltage.
9
Beam Current Buffer converts the, high impedance low current, beam
Page 15

E
The CRT Auto Bias IC is a combination of digital and analog circuitry. The
digital part is a counter and control logic which steps the analog circuits through a
sequence of sample and hold conditions. The analog part uses a transconductance
amplifier to control the voltage on a 10uF capacitor (one per gun). This voltage is
buffered and sent to the video amplifiers as the bias voltage. In monitors without
CRT auto bias, this voltage is adjusted manually using a setup procedure to set
the color balance. With CRT auto bias, the color balance is set during the end of
each vertical blanking time.
The control sequence is:
1.
The cycle starts with a sync pulse from the vertical oscillator (15KHz)
or from the vertical sync delay. 15H later the grid pulse starts.
2.
The grid pulse on G1 causes cathode current which can be seen as the
three faint white lines at the top of the screen. This cathode current is
transmitted by the beam current feedback to the beam current buffer
where it is converted to a voltage and applied to the CRT auto bias
input pin. At this time the CRT auto bias IC outputs a reference
voltage at its input pin which sets the voltage across the coupling
capacitor. This coupling capacitor voltage is directly dependent on
beam current.
After the grid pulse is over, the program pulse matches the voltage
3.
from the beam current buffer. If the voltage from the beam current
buffer, during the grid pulse, is the same as the voltage from the
program pulse, the bias is correct and no bias adjustment is made for
that vertical cycle.
F
The timing of the auto bias IC is synchronized to the vertical oscillator and the
flyback pulses. For horizontal frequencies higher than 15.7KHz a Vertical Sync
Delay may be needed to position the grid pulse, generated 3 gray lines, at the top
of the screen. The need for the delay circuit is dependent on the particular CRT
vertical retrace time.
G
The aging of the picture tube (CRT) not only affects the balance of the cathode
cutoff voltage, which is corrected by the auto bias circuit, but it also affects the
gain of the CRT. The
by sensing any common bias voltage change, from the auto bias circuit, and
adjusts the screen voltage to hold the average bias voltage constant. The lower
adjustment on the flyback transformer which is the screen voltage, is used to set
the auto bright voltage to the center of its range. Therefore, the auto bright
circuits sets up a second control feedback loop to reduce picture variation due to
CRT aging. The auto bright circuit is also used to turn off the beam current when
the monitor power is turned off.
Auto Bright circuit actively corrects for CRT gain changes
10
Page 16

H
The CRT for the 1493, 1793 and 2093 monitors have a 90° deflection angle. The
1993 incorporates 100° while the 2793 CRT has 110° and the 3693 has 111°
deflection angles. These picture tubes have integral implosion protection and a
EHT of 25KV.
H1
The Vertical Dynamic Focus amplifies the parabolic waveform across the
vertical coupling capacitor from about 3Vp-p to about 200Vp-p, depending on CRT
requirements. This waveform sharpens the top and bottom portion of the raster
on dual focus CRT's.
H2
The
horizontal coupling capacitor, using a transformer to produce 300Vp-p output from
an input that is about 33Vp-p. This waveform is added to the vertical dynamic
waveform and sharpens the right and left sides of the raster.
Blanking is accomplished by setting the gain of the interface IC to zero during
blank time. The Horizontal Blanking pulse is generated by amplifying the flyback
pulse. The Vertical Blanking pulse is started by the vertical oscillator one shot
and ended by the counter in the auto bias IC via the "bias out" pulse. The Master
Gain control, located on the remote PCB, sets the gain of the video signal when
blanking is not active. The Beam Current Limiter circuit, which is designed to
keep the FBT from overloading, will reduce the video gain if the maximum
average beam current is exceeded. Also, the beam current is reduced if the FBT
approaches maximum operating temperature.
The
used to receive sync, one for vertical sync and the other for horizontal sync.
Resistor dividers are used to protect the comparator IC from over voltage damage.
For customers who do not require interlace, an additional vertical sync
stabilization circuit is included. This circuit synchronizes the vertical sync to the
horizontal cycle.
Horizontal Dynamic Focus amplifies the parabolic waveform across the
I
J
Sync Interface can accept separate or composite sync. Two comparators are
K
Vertical Oscillator generates the vertical free running frequency when no
The
vertical sync is present. When sync is applied, the vertical oscillator synchronizes
to the leading edge of the sync pulse.
L
The Vertical Control & Output circuit consists of:
1. One shot.
2. Ramp generator.
3. Vertical drive.
4. Vertical output.
11
Page 17

The sync pulse from the LA7851 triggers a one shot in the LA7838 which clamps
the vertical ramp generation capacitor to 5V during the first half of vertical
retrace. The ramp generation capacitor then charges via a constant current set by
an external resistor. This resistor is connected to the V SIZE pot, located on the
remote control board, for the vertical size adjustment. The vertical drive is a
differential amplifier which compares the ramp voltage to the yoke return
feedback current. The yoke feedback current and voltage circuits are used to set
the vertical linearity. The vertical Output is a power driver, with thermal
protection, which drives the vertical deflection yoke. It also has a special pump up
circuit which doubles the output voltage during vertical retrace. This voltage
doubler also increases the efficiency of the circuit since the high retrace voltage is
not present across the power driver during the trace time.
M
The
loop to generate the horizontal timing. The H POS. adjustment, on the remote
control board, sets the sync delay time which controls the picture position. The
phase locked loop uses the flyback pulse to generate a sawtooth wave which is
gated with the delayed sync pulse to control the horizontal oscillator.
Horizontal Control incorporates a variable sync delay and a phase locked
N
The Horizontal Driver supplies the high base current necessary to drive the
horizontal output transistor which has a beta as low as three. A transformer is
used to step up the current from the driver circuit and also protects the horizontal
output transistor from a continuous turned on state. A special clamp circuit is
connected to the transformer which reduces the turnoff time of the horizontal
output transistor for reduced power dissipation.
O
The Horizontal Output transistor is mounted to the rear frame which acts as a
heat sink. The collector conducts the 900 volt primary flyback pulses which should
not be measured unless the equipment is specifically designed to withstand this
type of stress. A linear ramp current is produced in the horizontal yoke by the
conduction of the horizontal output transistor (trace time). A fast current reversal
(retrace time) is achieved by the high voltage pulse that follows the turn off of the
horizontal output transistor. This pulse is due to the inductive action of the yoke
and flyback transformer.
P
The main function of the Flyback Transformer (FBT) is to generate a 25,000 volt
(EHT) potential for the anode of the picture tube. This voltage times the beam
current is the power that lights up the phosphor on the face of the picture tube.
At 1.5mA beam current, for the 2793 monitor, the FBT is producing almost 38
watts of high voltage power. The FBT also sources the focus voltage, screen grid
voltage, filament power, and has two more secondaries which are used for control
functions. The FBT has a built in high voltage load resistor which stabilizes the
EHT, for the low beam current condition. This resistor also discharges the EHT,
when the monitor is turned off, which improves the safety of handling the
monitor.
12
Page 18

Q
The Remote Control PCB houses the:
CONTROL DESCRIPTION CIRCUIT
1. H SIZE ----------- Horizontal raster size --------- Diode modulator
2. V SIZE ----------- Vertical raster size ------------- Vertical control
3. V RAS. POS. --- Vertical raster position ------- DC current to V. yoke
4. H POS ------------ Horizontal picture position -- H. sync delay
5. M GAIN ---------- Master gain ---------------------- Video interface
R
The Horizontal Size Control circuit has four inputs:
# SIGNAL FUNCTION
1. Horizontal size ------------------------------ Horizontal size control
2. Beam current -------------------------------- Blooming control
3. Vertical linear ramp -----------------------
4. Vertical parabolic + V. linear ramp ---
(#4)-(#3)=Vertical parabolic
}
(Pincushion)
The horizontal size control circuit sums the four signals at one node plus the
feedback from the diode modulator to drive a switching mode power driver. The
output of the power driver is then connected to the diode modulator through an
inductor to complete the control loop.
S
The Diode Modulator is a series element of the horizontal tuned circuit. It forms
a node between GND and the normal yoke return circuit. If this node is shorted to
GND, the result is maximum horizontal size. Forward current in the diode
modulator, at the start of retrace, keeps the node voltage clamped to ground until
enough current flows from the horizontal tuned circuit to exceed this forward
current. The horizontal size, therefore, is controlled by controlling the current to
this diode via the horizontal size control circuit.
T
A Voltage Doubler is used in the power supply for two reasons:
13
1. To improve the efficiency of the power supply.
2. To permit 120 volt and 230 volt operation. For the 230 volt
operation the voltage doubler is replaced with a bridge rectifier.
Page 19
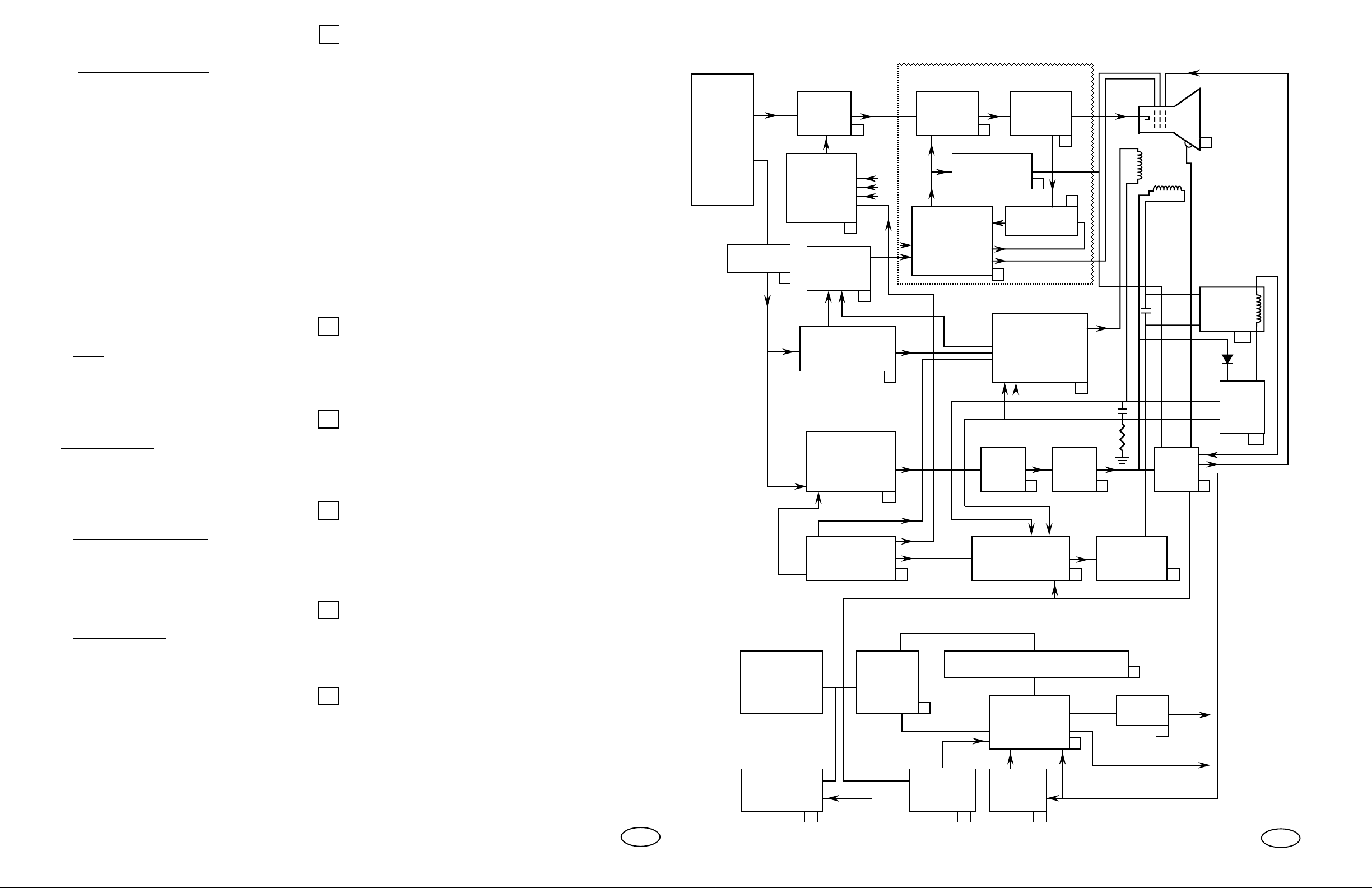
U
XX93 Monitor Block Diagram.
The Switching Regulator is synchronized to the horizontal pulse and drives a power
MOSFET. Unlike most regulators that have a common GND, this power supply has a common
V+ and current is supplied from V- to GND. The MOSFET is connected to V– and signal
ground (GND) through a transformer which is used as an inductor for series switch mode
regulation. An operational amplifier, voltage reference, comparator, and oscillator in the power
supply controller IC are used to accomplished regulation by means of pulse width modulation.
The transformer has two taps on the main winding which are used to generate the +16 volt
and +24 volt supplies. It also has a secondary which is referenced to V- and supplies the power
supply. Since the power supply is generating its own power, a special start up circuit is built
into the power supply controller IC that delays start up until the capacitor which supplies the
IC is charged up enough to furnish the current to start the power supply. This capacitor is
charged with current through a high value resistor from the raw dc supply. This self sustaining
action is why the power supply chirps when an overload or underload occurs. Additional
secondaries to drive the horizontal raster shift circuit and the video amplifiers are also included
in the power transformer.
V
The Load consists primarily of the horizontal flyback circuit. The power supply will not
operate without the load since the voltage that sustains the power supply comes from a
secondary in the power transformer and depends on some primary current to generate
secondary current.
W
A +12V regulator is used to supply current, to all the control circuits in the monitor, with the
exception of the power supply. Many of the control circuits are decoupled from the +12 volt line
with a resistor or diode to minimize noise from common current loops.
X
The Over Voltage Protect circuit is built into the power supply and monitors the flyback
transformer peak pulse voltage. This circuit will turn off the power supply and hold it off if the
EHT exceeds its maximum rated value. Since excessive X-ray output occurs with excessive
EHT, this circuit provides X-ray protection.
Y
The Fault Detector senses beam current and temperature. This circuit will activate the
power supply shutdown circuit if either the maximum temperature is sensed or if the beam
current becomes large enough to threaten the FBT.
Z
The Degaussing circuit is connected across the isolated AC line. A posistor is used to allow a
large current to flow, in the degaussing coil, on power up. This current is then gradually
reduced by the increased temperature of the positive temperature coefficient thermistor in the
posistor. A relay is used to short the degaussing coil after the degaussing operation. This
greatly reduces posistor residual current in the degaussing coil. When repairing a monitor, the
degaussing coil should be unplugged, to avoid possible damage to the degaussing coil shorting
relay.
GAME
VIDEO
RGB
SYNC
V. & H.
VIDEO
3
SYNC
Interface
2
Interface
BLANKING
V retrace
Beam limit
High temp. limit
VERTICAL
J
VERTICAL
s
V
F.B.P.
M. gain
SYNC
DELAY
3
AB
I
F
OSCILLATOR
LA7851
K
LA7851
HORIZONTAL
CONTROL
s
H
H. Pos.
Sync delay
M
V. Size &
V. Ras. Pos.
REMOTE
CONTROLS
(PCB)
ISOLATION
Transformer DOUBLER
(IN GAME)
DEGAUSSING
CIRCUIT
Z
VOLTAGE
Raw DC
320V
+24V
G2≈290V
2 For Dual Focus
On Video Board.
G1≈–20V
VIDEO
AMPS.
Bias
3
3
Bright
3
CRT AUTO
BIAS IC
H. sync (FBP)
V. sync
CA3224E
Auto
Beam
3
Current
Feedback
G
3
Beam current
buffer
Program pulse
Grid pulse
E
VERTICAL
CONTROL &
3
CRT
C
V
DY
DY
H
D
H
EHT≈25KV
Dynamic Focus
used only on Dual
Focus CRTs
Horizontal
Dynamic
Focus
H2
OUTPUT
LA7838
I. V. Feedback
EHTG2
V+
Vertical
Dynamic
Focus
P
L
+
H.H.
Driver
PINCUSHION
HORIZONTAL
Size Control
QR
+52V to +129V
(VIDEO & DEFLECTION)
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
Shutdown
OVER
VOLTAGE
PROTECT
T
V-
-200V
FAULT
DETECTOR
LOAD
Y
Output
NO
DIODE
Modulator
Beam Current
+12V
Regulator
Vertical Deflection
Sync
X
+16V
+24-27V
U
FBP
FBT
S
V
+12V
W
Supply
H1
2
14
15
Page 20
BB
12V
TC2 GND
+
GND
TC9 iB OFF
16V
CC3
ABA
464Ω
261
258
G
Beam current
Feedback
Beam current
Feedback
Beam current
Feedback
B+G+R=∑
SOCKET BOARD CONNECTOR (TC) 206
TC 6TC 10
0Ω
088
6.8K
099
PN2222
1
2
3
100B
5
0Ω
100A
10
6
1/2
7
LM393
5
+
210
OPEN
077
.039uF
081
1N4937
080
T
U
909Ω
064
227
10
396 11
A- BL
+12V
IN
R
G
B5
K
243
218
264
Red Video Amp.
0
Green Video Amp.
Blue Video Amp.
Auto Bias
V
Sync
1
2
3
4
5
6
TC7 Red
TC5 Green
TC 3 Blue
62K
+12
V
098
PN2222
379
200K
CS=.45"
383
Retrace Boost
VERTICAL BLANKING
22K
384
0Ω
CS=.74
389
GND
PN2907A
212
4-7VDC
Hs
4-9Vpp 61,B4
HORIZONTAL
BLANKING
PN2222A (CPQ1322)
2.15K
078
072
GND
FDH400
084
FDH400
086
FDH400
213
16 13
B
IN R
R
21 1415 7 8
A5
J
S
412Ω 105Ω 604Ω
260 244 245
+12V
P
239
oRo Go GAINM+ ENA
B
BL
Controls XRC5346A
R
225
223
226
7
236 235
1N4148
271
278
0Ω
1N4148
270
277
8
0Ω 0Ω 0Ω
281 280 283
VC
G
5
GND
GREEN
INPUT
286
288
9
RED
GND
VC
292
3
R
VC
4
INPUT
BB
16
Beam
Current
Buffer
510Ω
006
+12V
6.8K
250
1N4148
253
1
1K
1.8K
248
.047uF
GND
270Ω
093
VIDEO GAIN LINE
604Ω
076
4-7VDC
5-9Vpp
11.5-12.5V
0Ω
228
512
TTL
241
BG
242
VC
BLUE
INPUT
CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PPAA
0Ω
8
211
1/2
LM393
210
4
208
207
0VDC
56Vpp 63,D6
Vs
62,B4
GND
IN
B
A5
L
266
276
GND
B
VERTICAL
6
CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PPAA
VIDEO BOARD
ARC PROTECT
Auto
Bright
6.8K
251
2
2.3-
2.7V
1.8K
3
+
368
1.8K
252
Hs
+12V
GND
0Ω
293
12V
VC
0
4
R
233
231
232
1N4148
268
284
s
V
VC
SYNC
800
2-3VDC
4Vpp 64,C4
4.5-5.3V
5Vpp 16,E5
GND
1.8K
328
1.8K
H
s
HORIZONTAL
VC
SYNC
12
CRT
127V TC8
TC4
1N4007
090
68.1K
085
100uF
+
089
127K
087
100uF
+12V
209
Vs
Vs
+
100uF
267
221
PN2222
274
M & N reverse Hs.
325
270Ω
326
0Ω
270Ω
330
331
TC1
2.15K
272
273275
GND
M
N
M
N
.14-.16V
Product safety note: Components marked by the
Horizontal
RC5
Size
10K
481
When replacing any of these components, be sure to use the parts specified in the parts list.
+12V
GND
RC8
+127V
Vertical
Vertical
Position
RC3
RC
002
Horizontal
Master
RC2
2.15K
062
+16V
+12V
OUT IN
+
100uF
304
12.1K
Hs
329
500Ω
Size
Raster
1K
20K
Position
1K
Gain
Remote Control
490
PCB
0Ω
0Ω
295
067
7812
+
GND
296
56pF
1.8K
3
I1
352
482
RC6
750Ω
486
483
+12V
GND
RC4
220uF
298
7.3VDC
5.5Vpp
RC1
01,D6
RC7
Hs
484
485
Vs
+127V
FBP
GND
+16V
+
MPSA64
D
036
Beam Current
Limiter Circuit.
14
355
13
355
10uF
014
1N4148
018
LM339
1.5-2VDC 60,D6
LM339
+12V
PN2222A
071
75Ω
066
CPQ1322
7.15K
366
1K
012
1K
065
7.15K
+12V
364
PN2222
22K
323
4
5
6
7
270Ω
327
1/4
LM339
+
1/4
LM339
+
3
12
+12V
355
2
1
355
GND
6.8K
321
6.8K
322
+24V
470Ω, 1/2W
Relay
200V.5A
470
468
.093" pin
162A
.047uF
GND
CC
318
159
25Ω@25˚C, 2A
Posistor
158
.093" pins
Degaussing
CC2
Connector
162
100K
HEAT
SINK
378
510Ω
004
0Ω
203
1,000pF
369
100uF
+
376
18Ω
367
1N4007
333
0Ω
202
17
220uF
334
18Ω
063
GND
9
+
1/4
8
11
+
1/4
10
200K
.05VDC
246
7V pp 58,C5
255
PN2222
257
200K
256
33K
247
Inrush Current Limit
CPR0434
Black Wire.
CC1
161
symbol on this schematic have special characteristics important to safety.
LA7838
Vertical
Deflection
+12V
1
Ramp
Reset
One Shot
377
Tr.
234 567 8 9 1011 12 13
5.5-6.4V
3Vpp 21,D5
93.1K
375
28.0K
402
100K
403
+12V
GND
Vs
5.5-6.5V
1.2Vpp 19,D5
11-12.4V
20, D5
20 19 18 17 16 14 13
VERTICAL
V+
Horizontal
SYNC INPUT
2.7K
2
5
15.8K
020
CPR0432
100kΩ@25˚C
T
180
15.8K
353
1K
357
3.92K
3.92K
356
Vs,Hs
254
169
I4
12K
7
I2
8.8K22K
I3
GND
H. S. +12V
+6V
I BEAM
7-10VDC
61, C2
FBP
68.1K
15.8K
360
354
2.1-2.4VDC
Hs
4.6Vpp 59,D6
3.3nF
358
2.2nF
150
FR205
148
152
2.2nF
155
FR205
156
3A Fuse
146
145
PC
PC
120VAC
2
INPUT
1
out
Ramp
Gen.
V. size
Reset
out
R/C
Vs
or
VERTICAL VERTICAL
± SYNC INPUT
PICTURE
POSITION
8
Hs
IA
I12
Slope
Vs
.01uF
374
VERT.
O/S
4Vpp 02,D6
1nF
351
Ramp
.1uF
410
OSC.
1.2Ω, 1W
Control
50/60Hz
5-6VDC
1.4Vpp 22,E5
1uF
401
385
DELAYED
SYNC O/S
Hs
9
25K
I5 350
6,10
-1.4V -2.8V
2.33K
J13 J14
91.4K
J1
2SA1371E
1
529
112
0Ω
114A
10.6K
J5
JD
260Ω
+2.9V
J16
JC
130Ω
+1.4V
J15
11K
J2
2
23.2K
106
62K
220uF
143A
250V
0Ω
144
220uF
250V
163
36K
143B
0Ω
114
7
90K
J6
220uF
128
8,14
Vert.
Drive
5.5-6.5V
Vs
1.4Vpp
23,F4
Vs
+25V
Retrace
Booster
Drive
68.1KΩ
393
GND
127K
388
2.2M
365K
362
363
4-6VDC
V
2.8Vpp 18,D5
V. osc.
ADJ.
OSCILLATOR
7.3-8.7V
4Vpp 03,D6
VERTICAL
TR.
-.2VDC
Vs 5.5-6.3V
1.5Vpp 04,E6
330pF
11
330pF
45K
I6
1
GND
2.7K
392
1uF
391
127K
361
Vs
OSC. O/S
SAW TOOTH
GENERATOR
Hs7.3-8.7V
6.8K
I13
100K
173
100K
390
.01uF
414
3.8Vpp 17,E5
1.4Vpp 05,E6
6.8nF
348
62K
167A
FBP
GND
+6V
I BEAM
V+
101.6K
JBJA
J18
JE
20
4.67K
220uF
175
BZT03-D160
160Vz
181
100K
113
6
6.5-7.5VDC
1,000pF
110
3
5
88K
J4
4
3.3nF
108
56pF
J3
104
33.2K
J7
3-4VDC
6.8nF
102
41,D1
6.5-7.5VDC
.5-.8VDC
3.4-4.2VDC
.1-.5VDC
9
5.7-6.3VDC
3Vpp
47,D2
56pF
107
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
330pF
123
-265V
CAUTION! POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGES REFERENCED FROM V-.
SCOPE GND MUST NOT BE CONNECTED TO GND AND V- AT THE SAME TIME.
V- V-
Thermal Protection
Vert.
Out
GND
100pF
398
1N4007
470uF
382
382
380
1.5-2.7V
Vs
24,E4
24Vpp
4.5-5.3V
Vs
5Vpp 16,E5
V Ref.
MULTIPLIER
BIAS
Hs 3-7VDC
0Vpp
06,E6
+
1uF
347
18
1uF
+
H. +12V
I PRA
Video V+
+
100uF
120
+43V
250V
1N4937
121
GND
16.3-19VDC
55, E1
+15V
INPUT
+17V
ERROR
INPUT
AMP.
INPUT
Over
COMP.
Voltage
}
Protect
INPUT
Output
CONTROL &
FAULT SENSE
4uS
COMP.
DELAY
Rx
Osc.
Cx
+7.5V
OUTPUT
Current
SENSE
DRIVE
REF.
XRC5184
115
J PRA PINS:
+
V-
Boost
0Ω
395
Vs.1-.3VCD
15
GND
LA7851
784523
13
I7 I8
416
V+
100uF
+
118
+61V
1N4937
122
16
14.8-18VDC
0Ω
15
132
14
5.5-6.8VDC
3-5VDC
5Vpp 52,F1
12
13
3-6VDC
0.1VDC
1Vpp 51,F1
11
1-4VDC
12Vpp
10
9
J PRA
111
3,10,15,
4.7Ω
396
.1uF
397
22K
370
15.8K
408
PROTECT
HORIZONTAL
OSCILLATOR
.2Vpp 07,E6
33K10K
.01uF
220uF
100V
182
+127V
1N4937
167
30Ω
139
50,E2
&19
Vertical Linearity Circuit
DECREASES
200K
TOP AND
BOTTOM
412
VERT. SIZE.
I
D5
200K 200K
PN2222
411
1N4148
84.5K
407
406
GND
.4VDC
Hs
.7Vpp 12,E5
12
X-RAY
DISCHARGE
3.6Vpp 08,E6
14
1K
I9
6.8nF
+55V
1N4937
20
1.00M
17 18
14.7K
MPSA64
2,200pF
131
Hs3-4VDC
15
9.31K
I10
+ 1600Hz
0Ω
0Ω
198A
+16V
+
1,000uF
171
1
2
8
5
9
141
12
16
.1uF
124
V-
1.00M
15.8K
J11 J12
510Ω
12
D
134J10
J8
18Ω
133
1N4007
127
Hs2.4-3.4VDC
345346344
3.92K
418
5.4-6VDC
11, E5
+
comp.
-
5-6VDC
09,E6
7Vpp
H.Fo ADJ.
680Ω
I16
+800Hz
1,000uF
166
191K
126
38.3K
J9
13
116
PN2907A
372371
PN2222
1N4148
405
+12V
GND
11
415
H. V+
Hs
340Ω
I15
ICID
1N4937
170
1N4937
169
GND
6
3
4
10 / 11
0Ω
10
533
533/532
3,300pF
125
CPQ1304
136
0.33Ω
2W
137
100pF
129
200K
413
409
D5
H
INCREASES
TOP AND
BOTTOM
VERT. SIZE.
373
169K
404
10.8-12V
10, E6
3.92K
417
10
17
2.15K
336
170Ω
I14
+400Hz
16
IB
+61V
+43V
I BEAM
V+
1,000uF
450
1N4937
168
FR205
142
1N4148
130
No DVM
300Vpp 40,G1
HEAT
SINK
200pF
1KV
138
47Ω
1/2W, CC
140
V-
TP49, G1
0VDC
27Vpp 57,F1
FBP
GND
+6V
+
135
+25V
+25V
Hs
22-28V
.8Vpp 25,F7
V. +12V
0Ω
422
+43V
V+
+61V
+25V
0Ω
136A
1770Ω176
Vs
0Ω
196
2.2K.5W
341
+25V
FBP
GND
PS FBP
H. S.+12V
FBP
GND
+12V
PS FBP
PS FBP
FBP
+12V
GND
0Ω
Measurements
are taken with
a white screen.
Hs - 5uS/div.
Vs - 2mS/div.
0VDC
Hs
56V
EHT
470Ω
1/2W
465
FOCUS
SCREEN
Beam
4
3
FIL.
2
Current
GND
VERTICAL
DEFLECTION
YOKE
S4
S2
S1
FR205
440
FR205
438
1.5uF
250V
400V
443
HER205 HER205
477
.10Ω
.10Ω
1W
475
Vs
20VDC
15Vpp
37,I6
Min.Max.
H Size
GND
478
1W
476
28,D3
0Ω
524
&
525
CPT1538
12mH
447
YC4
445
.033uF
800V
1.6KV
441
0.1uF
200V
437
GND
0Ω
0Ω,
092
092A
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TC11
Fil.
TC12
Fil. Rtn.
Video
Board
800
NO DVM
Hs
.9KVpp
1N4007
+
100uF
200Ω 2W
12-18VDC
Hs
Horizontal Drive
2SC
4159
33Vpp 26,E7
337
GND
342
338
340
19
20
100Ω
I11
2,200pF
343
Transformer
CPT1505
2
332
3
1
4
12-18VDC
50Vpp
2SD1651
1N4007
435
1.2Ω
434
29,F6
27,G6
NC
433
0Ω
452
GND
Vs
V-
0Ω
466
390Ω, 2W
12-18VDC
1,000uF
35V
VRP
10.0K
I BEAM
022
+6V
VFB
10.0K
023
12.1K
+6V
034
I BEAM
V-
V HYP
H SIZE
+
449
0Ω
193
H. S. +12V
13
12
GND
15.8K
62K
011
421
0Ω
192
V
0 TO 7 VDC
+6V
4
1/4
14
LM324
033
11
High Temperature Or
Excessive Beam
037
Current, Monitor Shut
Down Circuit.
3
1/4
LM324
2
033
200K
I BEAM
V-
+6V
VFB
V HYP
H SIZE
0Ω
194
.33uF
10K
038
082
200K
040
6V
3.92K
009
68.1K
I BEAM
097
.1uF
010
H SIZE
V-
+6V
GND
+25V
HS +12V
44.2K
+
H SIZE
100uF
061
043
12.1K
045
GND
5
6
.01uF
047
109
HORIZONTAL WIDTH CONTROL
H. S. +12V
10.0K
029
5
1/4
LM324
6
033
Parabolic
Pincushion
Blooming
correction.
.01uF
054
8
1/2
7
LM392
049
4
10.0K
3-5Vpp
RAS. POS.
510Ω
021
1
10.0K
7
5.6-6.2VDC
2-3.6Vpp 33,B2
Correction
200K
044
44.2K
058
10K
055
095
Vs
31,F5
2SC3467
+
100uF
026
22K
017
200K
005
031
6V
3.3K
050
Vs
2
3
2-2.5VDC
4.4Vpp 39,B3
+
GND
28K
041
3.3K
042
1/2
LM392
6.8K
056
420
100uF
25V
035
0Ω
019
2SA
1371
008
9
10
28.0K
049
Hs
0Ω
191
100Ω
1/2W
394
GND
1/4
LM324
3.3K
053
-Linear
Pincushion
Correction
5.6-6.2VDC
1-1.7V 34,B2
096
1
6.8nF
057
+61V
+43V
10.0K
051
033
15.8K
030
3.3K
052
1N4937
462
2.7K
060
0Ω
8
Vs
Open
419F
22K
189
4.7Ω
185
4.7Ω
195
4-19VDC
27Vpp 36,J7
510Ω
0.8-7VDC
12Vpp 38,J7
461094
Screen
FOCUS
FLYBACK
TRANSFORMER
10
6
9
8
7
5
1
CPT1558
0Ω
Open
419B
419E
0Ω
419A
0Ω
188
HORIZONTAL YOKE
446
YC3
107V or 127VDC
120Vpp 250Vpp
H. Linearity
4VDC
20VDC
30Vpp 35,H7
200Vpp
Min.Max.
CPT1528
Hs
50uH
IRF520
460
Hs
EHT
453
YC1
426
YC2
427
Horizontal Raster Adj.
150Ω 1/2W
425
270Ω
SR
424
510Ω
423
SL
Hs
32,F6
H Size
Min.Max.
470Ω
430
1/2W
428
coil
1,000pF
432
431
Hs
H Size
444
457
458
0Ω
454
1nF
500V
4VDC
463
11Vpp
Ω
470
1/2W
464
6.8uF 100V
456
HORIZONTAL WIDTH DRIVE
No
.
LTR.No
.
X
X
X-
X-Y VDC
Y V
X-Y VDC
Sync.
TP-REF.Vp-p
WAVEFORM
LEGEND
BOARD PART No.
PART No. ON PRA.
PRA PIN No.
DC VOLTAGE RANGE,
{
USING A DMM.
USE V. or H. SYNC.
AC VOLTS
Peak to Peak
Measured with scope
TEST POINT
ASS. REF.
CERONIX
SCALE
:
DRAWN BY:
CERONIX Model 1493-CGA Monitor Circuit.
CERONIX
PART NO.
DATE & REV.
NONE
F. H.
2/18/92
CPA4233, CPA4235
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, California 95602
4/10/96-E1
9/30/96-E4
3/24/99-E5
03/06/02-E8
9
16
Page 21
9
ABCDEFGHI J
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
62K, 011
1K, 012
A64
036
15.8K, 037
10K, 038
200K, 040
28.0K,
039
039
043
44.2K,
044
200K,
12.1K, 045
046
0Ω, 048
062
2.15K,
18Ω, 063
064
909Ω,
1K, 065
75Ω, 066
0Ω,067
0Ω, 068
0Ω, 222
223 242
224
225
226
227
0Ω, 228
0Ω,
293
292
0Ω,
+
220uF
298
294
7812, 296
0Ω, 295
231
235
235
236
236
6
5
291
4
3
2
1
0
0
0Ω, 297
232
233
234
230
230
0Ω, 001
.1uF
010
10uF
+
014
041
3.3K,
.01uF, 047
071
070
070
221
237
288
290
300
100uF
Remote Connector
002
+
016
016
0Ω, 015
042
3.3K, 050
LM392
100uF
+
061
2222-Mot.
072
2222-Mot.
219
220
C5346A
241
239
238
285
286
287
301
302
+
304
CPS1804
1371
008
009
3.92K
4148, 018
22K, 017
LM324
033
12.1K, 034
10.0K, 051
049
240
0Ω,
303
052
3.3K,
3.3K, 053
.01uF, 054
10K, 055
6.8K, 056
6.8nF,
44.2K, 058
2.7K, 060
.039uF,
081
2.15K,
074
0Ω, 217
H400, 213
218
266
NORMAL POLARITY SHOWN
283
284
282
282
281
0Ω,
311
310
305
078
075
075
280
243264
0Ω,
4937,
604Ω,
263
+
100uF
267
278
308
.33uF
215
0Ω,
262
268
277
312
0Ω
019
15.8K, 020
510Ω, 021
10.0K, 022
10.0K, 023
0Ω, 032
10.0K, 031
030
15.8K,
057
082
080
077
077
076
206
0Ω, 214
0Ω, 216
244
105Ω,
260
261
412Ω,
270
271
276
313
307
315
316
510Ω, 004
003
200K, 005
006
+
026
10.0K, 029
097
096
10.0K, 095
0Ω, 094
093
270Ω,
088
0Ω,
127K, 087
CPS1757
LM393
0Ω, 211
210
247
247
1.8K, 248
6.8K, 250
33K,
254
2222
256
255
255
200K,
2222
259
15.8K,
3.3nF,
3.92K, 356
LM339
355
47nF,318
320
321
6.8k, 322
6.8K,
006510Ω,
527
024
025
4007, 090
6.8K, 251
0Ω, 365
127K, 361
1K,
357
22K, 323
007
100uF
+
035
100uF
68.1K,
28.0K,
0Ω, 083
+
100uF
089
H400,084
68.1K, 085
400, 086
12 pin video board connector.
+
100uF
209
212
2907
245
246
604Ω,
200K,
258
257
464Ω,
272
272
100K,
3.92K,
274
273
275
2222
319
309
317
0Ω, 314
027
028
0Ω, 092
0Ω, 092A
1.0K, 208
252
252
4148,253
1.8K,
22K, 370
1.8K, 368
18Ω, 367
7.15K,
7.15K,
2.2M, 363
365K, 362
365K, 362
360
358
0Ω. 324
1.8K, 325
099
6.8K,
205
205
47nF,207
366
366
364
270Ω, 326
100K, 113
1371
112
JA
105
106
62K, 098
2222
0Ω, 202
0Ω, 203
0Ω, 204
100uF
+
376
93.1K,
2222
200K, 372
200K, 371
.01uF
414
IA
352
56pF
354
68.1K,
0Ω, 328
270Ω, 327
270Ω, 330
0Ω, 114A
JB
JC & JD
1nF
110
3.3nF
108
56pF
107
56pF
104
103
103
6.8nF
102
101
10
0Ω, 100A
5
100B
201
381
0Ω, 200
199
399
377
1nF, 369
375
373
H
409
2907
411
200K, 413
200K, 412
Horizontal Control
351
1000pF,
12.1K, 329
15.8K, 353
4007,333
339
1.8K, 331
529
115A
J PRA, 111 Power Supply
127
4007, 116
+
380
1uF
347
334
402
404
404
+
+
382
1uF
401
403
407
407
415
120
383
200K,
0Ω, 389
346
.01uF
332
118
119
IB IC ID
348
220uF
0Ω, 198A
198
381A
470uF
50V
LA7838
374.01uF,
2222
330pF
H. Drive,
115
C5184
+
4007,
+
28.0K,
100K,
169K,
4148, 405
4148, 406
84.5K,
15.8K, 408
.1uF, 410
CPC1058
LA7851
350
6.8nF
306
CPT1505
349
18Ω, 133
0Ω, 114
JE
2.2nF
131
A64
124
.1uF
200K, 109
+
0Ω, 117
0Ω, 195A
0Ω,196
384
2222379
22K,
100pF,398
.1uF
250V
397
4.7Ω, 396
6.8nF
345
335
2.15K,
C4159
337
+
100uF
338
+
220uF
128
191K,
195
0Ω, 194
384A
1.2Ω,1W, 385
0Ω
400
0Ω, 395
100Ω,.5W,394
3.92K, 417
+
1uF
344
336
336
336
1.00M, 134
126
126
3.3nF
125
330pF
123
123
122
121
191
0Ω, 192
0Ω, 193
188
CPM
2028
378
127K,
392
393
1uF
391
391
2.7K,
68.1K,
3467
420
0Ω, 419A
3.92K, 418
416
I PRA
2.2nF,343
200Ω, 2W
149
529A
.33Ω, 2W, 137
CPQ1304
4148, 130
189
0Ω, 136A
Retighten nut after
wave soldering.
CPM2123, 135
+
1,000uF
35V
171
0Ω, 190
+
387
+
0Ω, 187
1,000uF
35V
388
390
100K,
424
423
S2
0Ω, 422
426 427
Yoke Connector .062" Pins
0Ω, 419B
390Ω, 2W, 421
470Ω
.5W
428
4007, 342
431
2.2K, .5W
341
340
0Ω,
132
132
47Ω, CC,140
0Ω, 531
136
449
448
425
SR
430
171A
171A
500
446
1,000pF
200pF, 138
136A
0Ω, 172
0Ω, 186
1,000uF
+
35V
501
+
502
508
0Ω,
432
1.2Ω, 434
30Ω,139
532
129
100pF
Jumper
under
heat sink.
4937, 170
4937, 169
4937, 168
167
4937,
185
173
0Ω, 184
100K,
450
504
503
509
447
445
1.5uF, 400V
473
2SD1651, 433
0Ω, 480
4007, 435
4937, 141
533
+
CPC1112
220uF, 100V
182
183
BZT03, 181
CPR
0432
0Ω,
180
452
451
451
505
506
0Ω
507
512
511
510
514
CPC1069
0.033uF, 800V
Label; WHV 333 H
FR205, 440
.10Ω,1W
.10Ω,1W
166
FR205, 142
0Ω, 177
0Ω, 178
515
444
443
0.10uF, 200V
475
476
62K, 143A
36K, 143B
0Ω, 165
0Ω, 165A
167A
62K,
+
220uF, 250V
175
0Ω, 176
0Ω, 525
0Ω, 526
FBT: 453
FBT: Hitachi BW02651,
CPT1558
516
442
517
441
FR205, 438
437
HER205
HER205
477
478
436
439
220uF, 250V
0Ω, 164
+
Black Wire
Degaussing Conn.
161
.093" PINS
12
162A
.093"
PIN
3
Blue Wires
0Ω, 524
0Ω, 466
465
470Ω, .5W, CC
0Ω, 454
150uH,
CPT1528
457
+
144
220uF, 250V
163
162
518
6.8uF, 100V,
456
151
0Ω, 152
154
153
120-230V, 14Ω
CPA4233
Hf = 15.75kHz
Vf = 60Hz
POWER
Wire Tie, 145A
CPS1753
145
150
FR205, 148
2.2nF
155
2.2nF
FR205, 156
POSISTOR
CPR0434
158
472
0Ω, 523
510Ω, 461
IRF520
50uH
CPT1511
458
3A-T
FUSE
146
Wired for;
120VAC, 50-60Hz
157
157
CL200, 159
522
521
468
RELAY
470
1/2W,CC
470Ω,
Residual Current
463
1nF
470Ω
4937, 462
.5W
464
460
CPA4235
Hf = 15.75kHz
Vf = 60Hz
147
520
DEGAUSSING
106
106
1
118
120
121
122
166
166
185
188
189
191
195
218
2
218
221
223
225
226
227
231
232
233
236
236
239
242
3
243
261
261
264
266
266
268
268
270
270
271
271
4
273
273
275
275
276
276
277
277
278
278
284
286
5
288
292 7 PIN HEADER
292 6 PIN HEADER
423 510Ω 5%,1/4W
424
425
430 0Ω JUMPER
430 LIN. INDUCTOR
431 LIN. INDUCTOR
431
444
444 1.5uF 5%,400V
447 12mH INDUCT.
6
529 191K 1%,1/4W
529A
532
533 0Ω JUMPER
CRT M34AFA13X07
V+ 51.3-52.7V DC.
V+
Hf
Video Negative Analog
7
NOTES
VALUE PART No. BD SCH
7.15K 1%,1/4W
8.06K 1%,1/4W
100uF, 25V
100uF, 25V
1N4937
1N4937
S.M.INDUCTOR
S.M.INDUCTOR
4.7Ω 5%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
22K 5%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
4.7Ω 5%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
340Ω 1%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
20.0K 1%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
88.7Ω 1%,1/4W
62K 5%,1/4W
20.0K 1%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
4.7Ω 5%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
340Ω 1%,1/4W
6.8K 5%,1/4W
20.0K 1%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
0Ω JUMPER
15.8K 1%,1/4W
100Ω 1%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
301Ω 1%,1/4W
1N4148
1N4148 REV.
1N4148
1N4148 REV.
1N4148 REV.
1N4148
412Ω 1%,1/4W
2.15K 1%,1/4W
1K 5%,1/4W
30Ω 5%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
301Ω 1%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
340Ω 1%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
301Ω 1%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
270Ω 5%,1/4W
150Ω 5%,1/4W
LIN. INDUCTOR
.68uF 5%, 250V
0Ω JUMPER
0Ω JUMPER
53.3-54.7V DC.
15.75kHz
Video Board
Video Board
Positive AnalogVideo
Power: 120VAC
CPR0142
CPR1068
CPC1102
CPC1102
CPD1253E2F2
CPD1253
CPT1552
CPT1562
CPR0003
CPR0050
CPR0015
CPR0050
CPR0003
CPR0050
CPR0129
CPR0050
CPR0153
CPR0050
CPR0125
CPR0018
CPR0153
CPR0124
CPR0003
CPR0050
CPR0129
CPR0013
CPR0153
CPR0050
CPR0050
CPR0145
CPR0120
CPR0050
CPR0128
CPD1251
CPD1251
CPD1251
CPD1251
CPD1251
CPD1251
CPR0130
CPR0138
CPR0009
CPR0033
CPR0124
CPR0128
CPR0124
CPR0129
CPR0124
CPR0128
CPR0124
CPR0124
CPR0124
CPS1752
CPS1781
CPR0006
CPR0004
CPR0367
CPR0050
CPT1539
CPT1517
CPT1539
CPC1042
CPC1069
CPT1538
CPR0169
CPR0050
CPR0050
CPR0050
CPP1711
52.0V DC.
54.0V DC.
CPA4242
CPA4234
0.00-1.00V
1.10-5.60V
D2
D2
E2
F2
H2
H2
G3
F3
F3
F3
E3
B4
B4
A4
A4
A5
A5
A5
A5
A5
A5
A5
A6
B5
B4
B5
B5
B5
B5
B6
B5
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
C6
C6
C6
C6
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
B6
A6
A6
A6
F5
F5
F5
F6
F6
F6
F6
H6
H6
G5
E1
F1
G1
G1
GG8
GG8
II5
II5
II6
II6
KK6
KK6
NN3
OO3
NN3
NN3
NN3
BB7
BB7
DD7
BB7
AA7
AA7
BB5
DD7
CC7
CC7
AA7
AA7
AA5
CC7
BB7
BB5
BB5
BB7
CC7
CC7
CC7
CC7
BB7
BB7
AA7
AA7
DD8
DD8
DD8
DD8
CC7
CC7
BB7
BB7
AA7
AA7
CC9
BB9
AA9
BB9
BB9
OO3
OO3
OO3
OO6
OO6
OO6
OO6
OO7
OO7
PP3
GG6
J
KK7
KK7
Model 1493-CGA
CPA4235
CPA4233
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
B
A
A
B
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
B
B
A
A
B
B
A
A
B
A
B
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
A
A
B
A
B
A
A
B
A
A
A
A
B
A
B
B
A
A
B
A
B
A
B
AB
ABCDEFGHI J
1717
Page 22
BB
12V
TC2 GND
+
GND
TC9 iB OFF
16V
ABA
1.21KΩ
15.8K
261
Beam current
Feedback
Beam current
Feedback
Beam current
Feedback
B+G+R=∑
SOCKET BOARD CONNECTOR (TC) 206
TC 6TC 10
0Ω
088
6.8K
099
PN2222
1
2
3
100B
5
0Ω
100A
10
6
1/2
7
LM393
5
+
210
28.0K
077
.01uF
081
1N4937
080
T
U
2.7K
064
258
G
10
396 11
A- BL
+12V
IN
R
G
B5
0Ω
K
243
0 Ω
84.5Ω
218
264
Red Video Amp.
0
Green Video Amp.
Blue Video Amp.
Auto Bias
V
Sync
1
2
3
4
5
6
TC7 Red
TC5 Green
TC 3 Blue
62K
+12
V
098
PN2222
379
200K
CS=.45"
383
Retrace Boost
VERTICAL BLANKING
22K
0Ω
CS=.74
389
384
GND
PN2907A
212
4-7VDC
Hs
4-9Vpp 61,B4
HORIZONTAL
BLANKING
PN2222A (CPQ1322)
1.8K
078
072
GND
FDH400
084
FDH400
086
FDH400
213
16 13
BoRo Go GAINM+ ENA
IN R
R
21 1415 7 8
A5
J
S
1.62K 604Ω 1.21K
260 244 245
+12V
B
BL
Controls XRC5346A
R
0Ω
225
15.8K
223
75Ω
226
7
0Ω
236 235
1N4148
75.0Ω 75.0Ω 75.0Ω
271
278
0Ω
1N4148
270
277
8
0Ω 0Ω 0Ω
281 280 283
75.0Ω
288
9
CPS
RED
GND
1752
VC
292
3
R
VC
4
INPUT
75.0Ω 75.0Ω
286
GND
G
VC
GREEN
5
INPUT
BB
Beam
Current
Buffer
510Ω
006
+12V
6.8K
250
1N4148
253
1
1K
1.8K
248
.047uF
GND
270Ω
093
VIDEO GAIN LINE
1.62K
076
4-7VDC
5-9Vpp
11.5-12.5V
0Ω
228
512
TTL
241
BG
15.8K
242
VC
BLUE
INPUT
CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PPAA
0Ω
8
211
1/2
LM393
210
4
208
207
0VDC
56Vpp 63,D6
Vs
62,B4
GND
IN
A5
L
0Ω
266
276
GND
B
VERTICAL
6
CC DD EE FF GG HH II JJ KK LL MM NN OO PPAA
VIDEO BOARD
ARC PROTECT
Auto
Bright
6.8K
251
2
2.3-
2.7V
1.8K
3
+
368
1.8K
252
Hs
+12V
GND
12V
VC
0
4
R
B
233
15.8K
231
232
1N4148
268
284
V
VC
SYNC
800
2-3VDC
4Vpp 64,C4
4.5-5.3V
5Vpp 16,E5
GND
0Ω
293
s
H
VC
12
CHUNGHWA
M34AFA13X07
CRT
127V TC8
1N4007
090
68.1K
085
100uF
+
089
127K
087
100uF
209
Vs
Vs
+
100uF
267
0Ω
221
PN2222
274
M & N reverse Hs.
1.8K
325
0Ω
328
1.8K
331
s
HORIZONTAL
SYNC
0VDC
Hs
56V
EHT
470Ω
1/2W
465
FOCUS
SCREEN
Beam
4
3
FIL.
2
Current
GND
VERTICAL
DEFLECTION
YOKE
S4
S2
S1
FR205
440
FR205
438
250V
443
HER205 HER205
477
.10Ω
.10Ω
1W
475
Vs
20VDC
15Vpp
37,I6
Min.Max.
H Size
GND
478
1W
476
28,D3
0Ω
524
&
525
CPT1538
12mH
447
YC4
445
1.6KV
441
22nF
630V
437
GND
0Ω
092A
0Ω,
092
TC11
22-28V
V. +12V
+25V
+25V
Hs
.8Vpp 25,F7
0Ω
422
FBP
+43V
FBP
FBP
+25V
0Ω
136A
1770Ω176
Vs
0Ω
196
2.2K.5W
341
+25V
V-
GND
PS FBP
H. S.+12V
V-
GND
+12V
PS FBP
V-
PS FBP
+12V
GND
+
0Ω
Measurements
are taken with
a white screen.
Hs - 5uS/div.
Vs - 2mS/div.
H SIZE
H SIZE
H SIZE
H SIZE
100uF
061
+
VRP
V HYP
I BEAM
V HYP
LTR.No
.
XY V
X-Y VDC
WAVEFORM
1N4007
342
100uF
338
200Ω 2W
340
+6V
I BEAM
+6V
.33uF
6V
+6V
No
.
X
TP-REF.Vp-p
VFB
+6V
I BEAM
VFB
082
3.92K
009
I BEAM
.1uF
010
043
12.1K
045
GND
X
X-Y VDC
Sync.
10.0K
10.0K
12.1K
12-18VDC
Hs
Horizontal Drive
2SC
4159
33Vpp 26,E7
337
20
19
100Ω
I11
2,200pF
343
Transformer
CPT1505
2
1
GND
0Ω
466
390Ω, 2W
1,000uF
35V
+
449
0Ω
193
H. S. +12V
022
023
034
62K
011
13
12
GND
15.8K
037
1/4
LM324
12-18VDC
3-5Vpp
421
0Ω
192
RAS. POS.
V
0 TO 7 VDC
+6V
4
510Ω
14
033
11
High Temperature Or
Excessive Beam
Current, Monitor Shut
Down Circuit.
3
1/4
1
LM324
2
033
200K
109
2SC3467
021
200K
005
HORIZONTAL WIDTH CONTROL
10.0K
029
1/4
LM324
033
correction.
7
7
2-3.6Vpp 33,B2
044
44.2K
058
10K
055
10.0K
095
10.0K
031
3.3K
5.6-6.2VDC
Correction
0Ω
194
10K
038
200K
040
097
GND
25V
HS +12V
5
6
.01uF
047
1/2
LM392
H. S. +12V
5
6
Parabolic
Pincushion
Blooming
.01uF
054
8
049
4
LEGEND
BOARD PART No.
PART No. ON PRA.
PRA PIN No.
DC VOLTAGE RANGE,
{
USING A DMM.
USE V. or H. SYNC.
TEST POINT
AC VOLTS
Peak to Peak
ASS. REF.
Measured with scope
Video
Board
800
NO DVM
Hs
.9KVpp
27,G6
2SC5690
31,F5
332
Vs
3
1N4007
4
1.2Ω
12-18VDC
50Vpp
435
434
Vs
29,F6
420
0Ω
191
433
GND
Open
419F
0Ω
451
NC
V-
419B
0Ω
419A
22K
189
4.7Ω
185
4.7Ω
195
+
22K
017
100uF
026
+
100uF
25V
035
0Ω
019
2SA
1371
008
100Ω
1/2W
394
GND
10.0K
051
9
1/4
8
LM324
10
6V
050
Vs
041
3.3K
042
2
1/2
LM392
3
2-2.5VDC
4.4Vpp 39,B3
GND
6.8K
056
28.0K
049
Hs
3.3K
053
-Linear
Pincushion
Correction
5.6-6.2VDC
1-1.7V 34,B2
096
1
3.3nF
057
033
15.8K
030
3.3K
052
1N4937
462
2.7K
060
0Ω
Vs
4-19VDC
27Vpp 36,J7
510Ω
461094
0.8-7VDC
12Vpp 38,J7
HORIZONTAL WIDTH DRIVE
CERONIX
SCALE
:
DRAWN BY:
CERONIX Model 1493-VGA, 1493-SVGA
CERONIX
PART NO.
DATE & REV.
NONE
F. H.
2/18/92
CPA4200, CPA4252
Product safety note: Components marked by the
Horizontal
RC5
TC1
TC4
Vertical
Vertical
Position
RC3
002
Horizontal
+127V
+12V
RC2
1K
062
+16V
+12V
+
100uF
304
12.1K
Hs
329
Vs
Size
Size
Raster
RC
Position
Master
Gain
Remote Control
490
PCB
0Ω
067
OUT IN
7812
GND
296
56pF
1.8K
3
I1
352
10K
481
500Ω
482
1K
483
20K
484
1K
485
0Ω
295
+
When replacing any of these components, be sure to use the parts specified in the parts list.
LA7838
HEAT
Vertical
SINK
378
Deflection
+12V
750Ω
486
+12V
GND
RC4
220uF
298
5.5Vpp
GND
7.3VDC
RC1
01,D6
RC8
RC6
RC7
Hs
510Ω
004
0Ω
203
1,000pF
369
Vs
100uF
+
376
18Ω
367
1N4007
333
0Ω
202
17
220uF
334
+12V
1
2
5
18Ω
+
10uF
014
1N4148
018
14
LM339
355
1.5-2VDC 60,D6
13
LM339
355
318
159
25Ω@25˚C, 2A
Posistor
158
.093" pins
Degaussing
CC2
Connector
162
063
GND
9
+
1/4
8
11
+
1/4
10
200K
.05VDC
246
7V pp 58,C5
PN2222
255
PN2222
100K
257
200K
256
Inrush Current Limit
CPR0434
Black Wire.
CC1
15.8K
020
CPR0432
100kΩ@25˚C
T
180
15.8K
353
1K
357
3.92K
3.92K
356
Vs,Hs
254
33K
247
PC
161
2
270Ω
326
270Ω
330
2.15K
272
412Ω30Ω
273275
GND
M
N
M
N
.14-.16V
+12V
22K
323
4
5
6
7
270Ω
327
1/4
LM339
+
1/4
LM339
+
+127V
FBP
GND
+16V
PN2222A
75Ω
+12V
3
355
12
071
066
CPQ1322
7.15K
366
2
1
355
GND
1K
012
1K
065
+12V
7.15K
364
6.8K
321
6.8K
322
Relay
200V.5A
+24V
470Ω, 1/2W
CC3
MPSA64
D
036
Beam Current
Limiter Circuit.
.047uF
GND
CC
470
468
.093" pin
162A
symbol on this schematic have special characteristics important to safety.
Ramp
Reset
One Shot
377
Tr.
234 567 8 9 1011 12 13
5.5-6.4V
3Vpp 21,D5
93.1K
375
28.0K
402
93.1K
403
+12V
GND
5.5-6.5V
1.2Vpp 19,D5
11-12.4V
20, D5
20 19 18 17 16 14 13
VERTICAL
V+
Horizontal
SYNC INPUT
2.7K
169
I4
12K
7
I2
8.8K22K
I3
GND
H. S. +12V
+6V
I BEAM
out
Ramp
Gen.
V. size
Reset
out
R/C
Vs
or
VERTICAL VERTICAL
± SYNC INPUT
PICTURE
POSITION
8
Hs
IA
I12
Ramp
Slope
Vs
.01uF
374
.1uF
410
VERT.
OSC.
O/S
4Vpp 02,D6
330pF
351
Control
50/60Hz
5-6VDC
1.4Vpp 22,E5
1uF
401
1.2Ω, 1W
385
DELAYED
SYNC O/S
Hs
9
25K
I5 350
6,10
Vert.
Drive
5.5-6.5V
Vs
1.4Vpp
23,F4
Retrace
Booster
Drive
+25V
Vs
470uF
68.1KΩ
393
GND
127K
388
2.2M
365K
362
363
4-6VDC
V
2.8Vpp 18,D5
V. osc.
ADJ.
OSCILLATOR
TR.
7.3-8.7V
4Vpp 03,D6
-.2VDC
Vs 5.5-6.3V
1.5Vpp 04,E6
330pF
11
330pF
45K
1
GND
2.15K
392
1uF
391
127K
361
Vs
VERTICAL
OSC. O/S
SAW TOOTH
GENERATOR
Hs7.3-8.7V
6.8K
I13
I6
100K
173
100K
390
3.3nF
.01uF
414
3.8Vpp 17,E5
1.4Vpp 05,E6
3.3nF
348
62K
167A
FBP
GND
+6V
I BEAM
V+
7-10VDC
61, C2
68.1K
354
2.1-2.4VDC
4.6Vpp 59,D6
3.3nF
358
3A Fuse
146
145
120VAC
230VAC
INPUT
FBP
15.8K
360
Hs
2.2nF
150
FR205
148
2.2nF-230V
FR205
230V
OPEN
152
2.2nF
155
FR205
156
2.2nF-230V
FR205
230V
PC
1
152
151
0Ω
153
154
-1.4V -2.8V
2.33K
J13 J14
91.4K
J1
2SA1371E
1
114A
10.6K
J5
260Ω
J16
130Ω
J15
11K
J2
2
106
62K
220uF
143A
250V
36K
144
143B
220uF
0Ω
250V
114
163
7
8,14
90K
J6
220uF
128
112
0Ω
JD
+2.9V
JC
+1.4V
23.2K
J3
105
101.6K
JBJA
J18
JE
20
4.67K
100K
113
6
6.5-7.5VDC
41,D1
1,000pF
110
3
5
6.5-7.5VDC
88K
J4
4
3.3nF
108
3.4-4.2VDC
56pF
.1-.5VDC
104
9
33.2K
5.7-6.3VDC
J7
3-4VDC
3Vpp
3.3nF
102
-195V
CAUTION! POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGES REFERENCED FROM V-.
SCOPE GND MUST NOT BE CONNECTED TO GND AND V- AT THE SAME TIME.
220uF
250V
175
BZT03-D160
160Vz
181
GND
1
INPUT
AMP.
2
INPUT
3
.5-.8VDC
COMP.
56pF
107
4
Output
FAULT SENSE
5
DELAY
6
Rx
Osc.
47,D2
7
Cx
8
+7.5V
200pF
123
V- V-
Thermal Protection
Vert.
Out
GND
100pF
398
1N4007
382
382
380
1.5-2.7V
Vs
24,E4
24Vpp
4.5-5.3V
Vs
5Vpp 16,E5
15
V Ref.
MULTIPLIER
BIAS
Hs 3-7VDC
0Vpp
06,E6
+
1uF
347
18
1uF
+
H. +12V
I PRA
416
Video V+
+108V
+
100uF
+
120
+101V +115V
1N4937
121
16.3-19VDC
55, E1
16
+15V
15
+17V
ERROR
INPUT
Over
Voltage
14
}
Protect
INPUT
CONTROL &
4uS
COMP.
OUTPUT
Current
SENSE
DRIVE
REF.
XRC5184
115
J PRA PINS:
12
13
+
11
10
9
V-
3,10,15,
Boost
0Ω
395
4.7Ω
396
.1uF
397
22K
370
Vs.1-.3VCD
15.8K
408
GND
LA7851
784523
.2Vpp 07,E6
13
I7 I8
.01uF
100uF
118
1N4937
122
14.8-18VDC
0Ω
132
5.5-6.8VDC
3-5VDC
5Vpp 52,F1
3-6VDC
0.1VDC
1Vpp 51,F1
1-4VDC
12Vpp
50,E2
J PRA
111
&19
Vertical Linearity Circuit
DECREASES
TOP AND
BOTTOM
VERT. SIZE.
D5
200K 200K
PN2222
1N4148
406
GND
.4VDC
.7Vpp 12,E5
X-RAY
PROTECT
HORIZONTAL
OSCILLATOR
Hs2.4-3.4VDC
3.6Vpp 08,E6
14
1K
33K10K
I9
3.3nF
345346344
220uF
50V
182
+127V
1N4937
167
+52V
1N4937
30Ω
139
141
.1uF
124
20
1.00M
17 18
14.7K
J11 J12
MPSA64
2,200pF
131
200K
412
I
411
127K
407
Hs
12
DISCHARGE
Hs3-4VDC
5-6VDC
15
680Ω
9.31K
I10
+ 1600Hz
0Ω
0Ω
198A
+16V
+
1,000uF
171
CPT1536
1
2
8
5
9
12
16
V-
1.00M
134J10
15.8K
510Ω
12
J8
18Ω
133
1N4007
D
127
3.92K
418
5.4-6VDC
11, E5
+
comp.
-
09,E6
7Vpp
H.Fo ADJ.
I16
+800Hz
1,000uF
166
127K
126
38.3K
J9
CPQ1304
13
116
PN2907A
372371
PN2222
1N4148
405
+12V
GND
H. V+
Hs
340Ω
I15
ICID
1N4937
1N4937
GND
10
136
0.33Ω
2W
100pF
129
10.8-12V
11
415
10
170Ω
+400Hz
170
169
6
3
4
1N4937
0Ω
533
3,300pF
125
137
27Vpp 57,F1
200K
413
409
D5
H
INCREASES
TOP AND
BOTTOM
VERT. SIZE.
373
100K
404
10, E6
3.92K
417
17
336
I14
16
IB
I BEAM
+108V
1,000uF
450
168
FR205
142
1N4148
No DVM
300Vpp 40,G1
HEAT
SINK
200pF
1KV
138
47Ω
1/2W, CC
140
V-
TP49, G1
0VDC
FBP
GND
+6V
+
130
135
Fil. Rtn.
Screen
FOCUS
EHT
FLYBACK
TRANSFORMER
10
6
9
8
7
5
1
CPT1516
0Ω
Open
419E
SR
0Ω
188
SL
HORIZONTAL YOKE
446
YC3
107V or 127VDC
120Vpp 250Vpp
H. Linearity
4VDC
20VDC
30Vpp 35,H7
200Vpp
Min.Max.
H Size
CPT1528
Hs
50uH
458
0Ω
454
IRF520
470
460
1/2W
Hs
4/10/96-E1
9/30/96-E4
Fil.
TC12
453
YC1
426
YC2
427
Horizontal Raster Adj.
150Ω 1/2W
425
270Ω
424
510Ω
423
Hs
32,F6
H Size
Min.Max.
470Ω
430
1/2W
428
coil
200pF
432
431
Hs
457
1nF
500V
4VDC
463
11Vpp
Ω
464
2.7uF 100V
456
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, California 95602
3/24/99-E5
03/06/02-E8
18 18
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Page 23
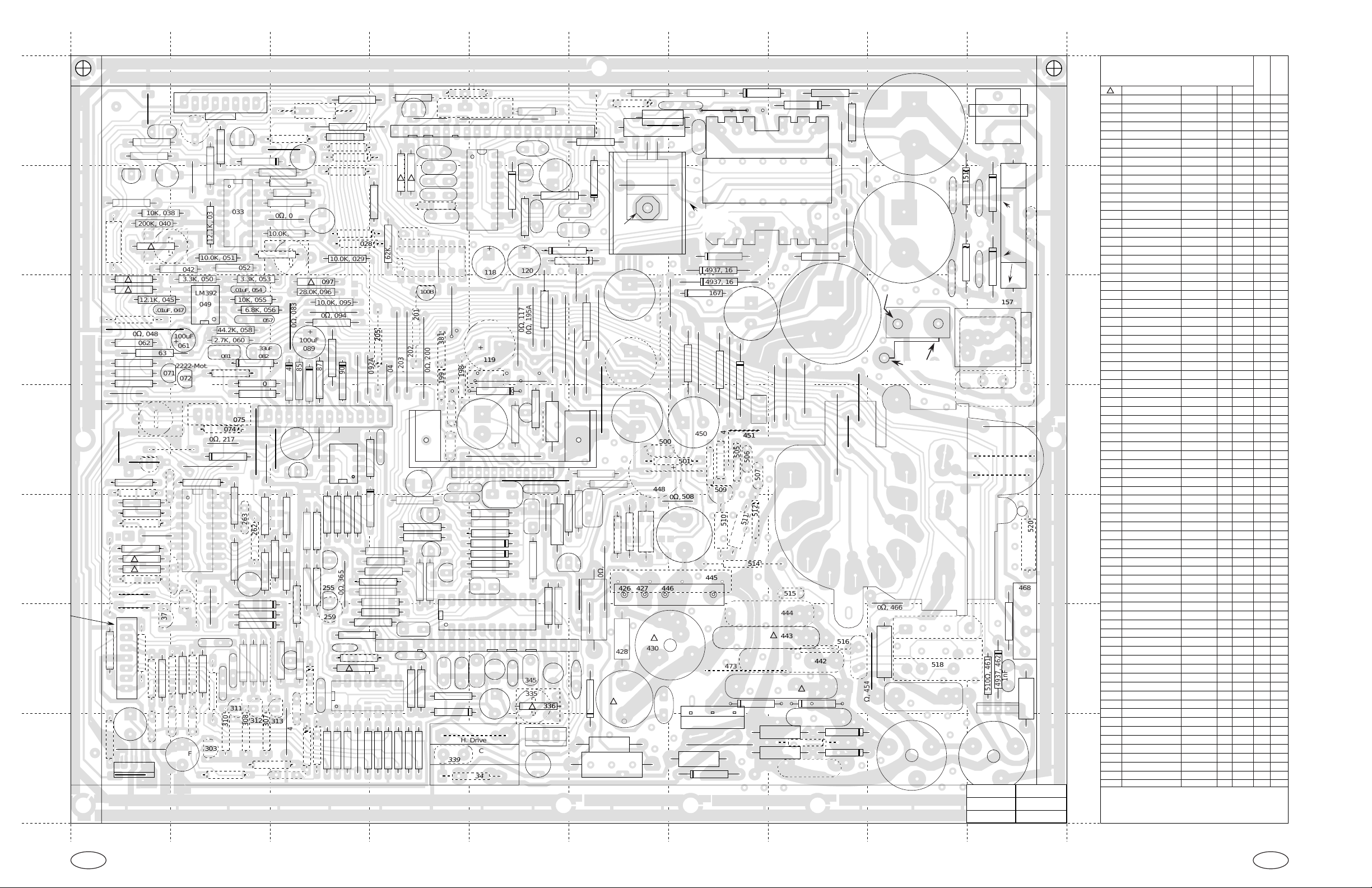
9
ABCDEFGHI J
1
2
3
4
5
7 Pin
Video
Input
Conn.
6
7
002
0Ω, 001
.1uF
010
62K, 011
1K, 012
10uF
A64
+
036
15.8K, 037
039
039
1K,
2.7K,
1K, 065
75Ω, 066
0Ω,067
0Ω, 068
0Ω, 222
15.8K, 15.8K,
75.0Ω,
15.8K,
230
230
0Ω,
0Ω,
293
292
0Ω,
220uF
298
294
7812, 296
0Ω, 295
014
10K, 038
200K, 040
041
3.3K,
043
044
12.1K, 045
.01uF, 047
046
0Ω, 048
062
18Ω, 063
064
0Ω
223 242
224
0Ω,
0Ω, 228
235
236
6
5
4
CPS1752
3
2
1
0
0
+
0Ω, 297
225
226
227
231
232
233
234
291
290
300
070
070
221
071
288
75.0Ω,
100uF
+
061
2222-Mot.
219
220
239
237
287
301
+
100uF
304
Remote Connector
CPS1804
+
016
016
0Ω, 015
10.0K, 051
042
3.3K, 050
LM392
049
072
2222-Mot.
0Ω, 217
0Ω, 218
C5346A
241
240
238
0Ω,
284
285
286
75.0Ω,
75.0Ω,
302
303
1371
008
009
3.92K,
22K, 017
LM324
033
12.1K, 034
3.3K,
.01uF, 054
10K, 055
44.2K, 058
2.7K, 060
.01uF,
081
078
1.8K,
075
075
074
H400, 213
243264
0Ω,
84.5Ω,
266
0Ω,
283
280
281
0Ω,
282
282
0Ω,
311
310
305
4148, 018
15.8K, 020
15.8K, 030
052
3.3K, 053
6.8K, 056
3.3nF,
.33uF
082
080
4937,
28.0K,
1.62K
215
0Ω,
263
262
+
100uF
267
4148, 268
4148, 270
4148, 271
277
278
75.0Ω,
75.0Ω,
312
308
007
0Ω
019
100uF
+
035
510Ω, 021
10.0K, 022
10.0K, 023
0Ω, 032
10.0K, 031
057
077
077
076
206
0Ω, 214
0Ω, 216
244
S
604Ω,
260
1.62K,
15.8K, 261
276
75.0Ω,
313
307
315
100uF
28.0K,096
0Ω, 083
+
100uF
089
H400,084
68.1K, 085
400, 086
12 pin video board connector.
+
100uF
209
212
2907
245
246
1.21K,
200K,
258
257
1.21K,
272
272
100K,
3.92K,
274
273
275
2222
412Ω
30Ω,
319
309
317
0Ω, 314
316
510Ω, 004
003
200K, 005
510Ω,
+
026
10.0K, 029
097
10.0K, 095
0Ω, 094
093
270Ω,
088
0Ω
127K, 087
CPS1757
LM393
0Ω, 211
210
247
247
1.8K, 248
6.8K, 250
33K,
254
2222
256
255
200K,
2222
259
15.8K,
3.3nF,
LM339
355
47nF,318
320
321
6.8k, 322
6.8K,
006
527
024
025
027
028
0Ω, 092
4007, 090
252
252
1.8K,
6.8K, 251
7.15K,
7.15K,
0Ω, 365
2.2M, 363
365K, 362
365K, 362
127K, 361
360
358
1K, 357
356
0Ω. 324
22K, 323
099
6.8K,
205
205
0Ω, 092A
47nF,207
1.0K, 208
4148,253
22K, 370
1.8K, 368
18Ω, 367
366
366
364
1.8K, 325
270Ω, 326
100K, 113
1371
112
JA
105
62K, 098
2N2222
0Ω, 203
0Ω, 204
+
93.1K,
2222
200K, 372
200K, 371
352
56pF
0Ω, 328
270Ω, 327
0Ω, 114A
JB
JC & JD
1nF
110
3.3nF
106
108
56pF
107
56pF
104
103
103
3.3nF,
102
101
10
0Ω, 100A
5
100B
201
0Ω, 200
0Ω, 202
100uF
376
375
373
409
411
200K, 413
200K, 412
.01uF
414
Horizontal Control
IA
354
12.1K, 329
68.1K,
15.8K, 353
4007,333
1.8K, 331
270Ω, 330
381
199
399
1nF, 369
H
2907
351
330pF
339
0Ω, 198A
198
381A
470uF
50V
377
2222
330pF
H. Drive,
529
J PRA, 111
115
C5184
100uF
+
4007, 382
+
LA7838
374.01uF,
28.0K,
93.1K,
100K,
4148, 405
4148, 406
127K,
15.8K, 408
.1uF, 410
CPC1058
LA7851
350
3.3nF
306
CPT1505
349
118
119
348
220uF
18Ω, 133
115A
Power Supply Control
2.2nF
131
A64
127
4007, 116
200K, 109
380
347
334
402
404
404
+
+
1uF
401
403
407
407
415
0Ω, 389
346
332
+
100uF
120
0Ω, 117
0Ω,196
383
200K,
.1uF
397
3.3nF
345
.01uF
250V
335
C4159
100uF
+
IB IC ID
1uF
0Ω, 114
200uF
127K,
124
.1uF
195
4.7Ω,
0Ω, 195A
384A
384
2222379
22K,
100pF,398
0Ω, 395
4.7Ω, 396
1uF
344
336
336
336
337
+
338
+
128
126
126
3.3nF
125
200pF
123
122
4937,
121
4937,
191
0Ω,
0Ω, 194
0Ω, 193
CPM
2028
1.2Ω,1W, 385
378
0Ω
400
393
68.1K
100Ω,.5W,394
3467
420
3.92K, 417
3.92K, 418
+
529A
1.00M, 134
4148, 130
189
22K,
0Ω, 192
188
0Ω,
388
127K,
100K,
392
1uF
391
391
2.15K,
0Ω, 422
0Ω, 419A
0Ω, 419B
390Ω, 2W, 421
416
I PRA
2.2nF,343
4007, 342
2.2K, .5W
200Ω, 2W
132
132
0Ω,
149
47Ω, CC,140
0Ω, 531
.33Ω, 2W, 137
CPQ1304
136
0Ω, 136A
Retighten nut after
wave soldering.
CPM2123, 135
+
1,000uF
0Ω, 190
35V
171
+
387
171A
171A
+
0Ω, 187
1,000uF
35V
449
500
+
390
426 427
Yoke Connector .062" Pins
470Ω
.5W
428
431
341
423
510Ω,
340
424
270Ω,
.5W
430
425
150Ω,
448
0Ω,
446
432
200pF
30Ω,139
200pF, 138
136A
under
heat sink.
4937,
0Ω, 172
185
0Ω, 186
4.7Ω,
1,000uF
+
35V
501
502
508
12mH
CPT1538
447
2SC5690, 433
1.2Ω, 434
129
100pF
Jumper
4937, 170
4937, 169
4937, 168
167
0Ω, 184
450
503
509
445
0Ω, 480
4007, 435
0Ω, 533
CPC1103
220uF, 35V
173
100K,
452
0Ω,
504
510
473
4937, 141
+
183
BZT03, 181
0Ω,
451
451
505
511
514
FR205, 440
CPR
0432
180
506
166
182
507
512
.10Ω,1W
.10Ω,1W
62K, 143A
FR205, 142
36K, 143B
CPT1536
0Ω, 164
0Ω, 165
0Ω, 165A
167A
62K,
+
220uF, 250V
175
.093"
PIN
0Ω, 176
0Ω, 177
0Ω, 178
FBT: Meritron T-8090B, CPT1516
515
444
443
442
441
FR205, 438
.022uF, 630V
437
475
476
HER205
436
HER205
439
0Ω, 525
0Ω, 526
FBT: 453
516
517
477
478
0Ω, 524
0Ω, 454
+
220uF, 250V
144
+
220uF, 250V
163
Black Wire
Degaussing Conn.
161
.093" PINS
12
162A
Blue Wires
3
0Ω, 466
465
.5W, CC
470Ω,
2.7uF, 100V
456
150uH,
CPT1528
457
162
518
Wire Tie, 145A
CPS1753
150
151
FR205,
2.2nF, 152
2.2nF
155
154
2.2nF
153
FR205,
2.2nF,
POSISTOR
CPR0434
120-230V, 14Ω
CPT1511
458
CPA4200
Hf = 31.5kHz
Vf = 50/60Hz
POWER
145
FUSE
FR205, 148
FR205, 156
157
157
158
472
0Ω, 523
522
521
1/2W,CC
4937, 462
510Ω, 461
IRF520
50uH
3A-T
146
147
Wired for;
230VAC, 50-60Hz
CL200, 159
520
468
RELAY
470
470Ω ,
DEGAUSSING
Residual Current
463
1nF
470Ω
.5W
464
460
CPA4252
Hfo = 35.2kHz
Vf = 56Hz
NOTES
VALUE PART No. BD SCH
041 12.1K 1%,1/4W CPR0144 A2 NN7 D
041 15.8K 1%,1/4W CPR0145 A2 NN7 C
1
043
36K 5%,1/4W
043
22.0K 1%,1/4W
22K 5%,1/4W
044
044
44.2K 1%,1/4W
097
62K 5%,1/4W D
097 CPR0146
169K 1%,1/4W C
105
140K 1%,1/4W
7.15K 1%,1/4W
106
8.06K 1%,1/4W
106
232
75.0Ω 1%,1/4W
88.7K 1%,1/4W
232
233
2
3
4.7Ω 5%,1/4W
0Ω JUMPER
233
2.7K 5%,1/4W
336
336
1.21K 1%,1/4W
2.7K 5%,1/4W
356
356 3.92K 1%,1/4W
430
0Ω JUMPER
430
27uH Inductor
431
Linearity Inductor
431
Linearity Inductor
441
7.5nF, 1.6KV
441
5.6nF, 1.6KV
443
.68uF, 250V
443
.47uF, 250V
CRT
M34AFA13X07
V+
106-108V DC.
Hf
31.5kHz
Hf 35.2kHz D
Vf
50/60Hz
Vf
56Hz
Video Board
Video Board
Video
Positive Analog
Power: 230VAC
CPR0017
CPR1063
CPR0015
CPR0154
CPR0018
CPR0172A3D1
CPR0142
CPR0168
CPR0124
CPR0125A5A5
CPR0003
CPR0050A5A5
CPR0012
CPR0134
CPR0012
CPR0140C6C6
CPR0050
CPT1546
CPT1517
CPT1539
CPC1061
CPC1063
CPC1042
CPC1050
CPP1711
107V DC.
CPA4134
CPA4253
0.00-0.70V
4
5
6
7
Model 1493-VGA, CPA4200
Model 1493-SVGA, CPA4252
A3
LL8
A3
LL8
A3
MM7
MM7
MM7
C3
C3 MM7
GG8
D2
GG8
D2
GG8
CC7
CC7DC
CC7
CC7DC
E6
KK4
KK4
E6
FF7
FF7
F6
OO6
F6
OO5
F6
OO6
F6
OO6
H6
PP6
H6
PP6
H6
PP7
H6
PP7
CPA4200
C
D
C
D
C
C
D
C
D
D
C
D
C
D
C
C
D
C
D
D
C
D
C
C
C
D
C
D
D
C
C
D
CPA4252
ABCDEFGHI J
1919
Page 24
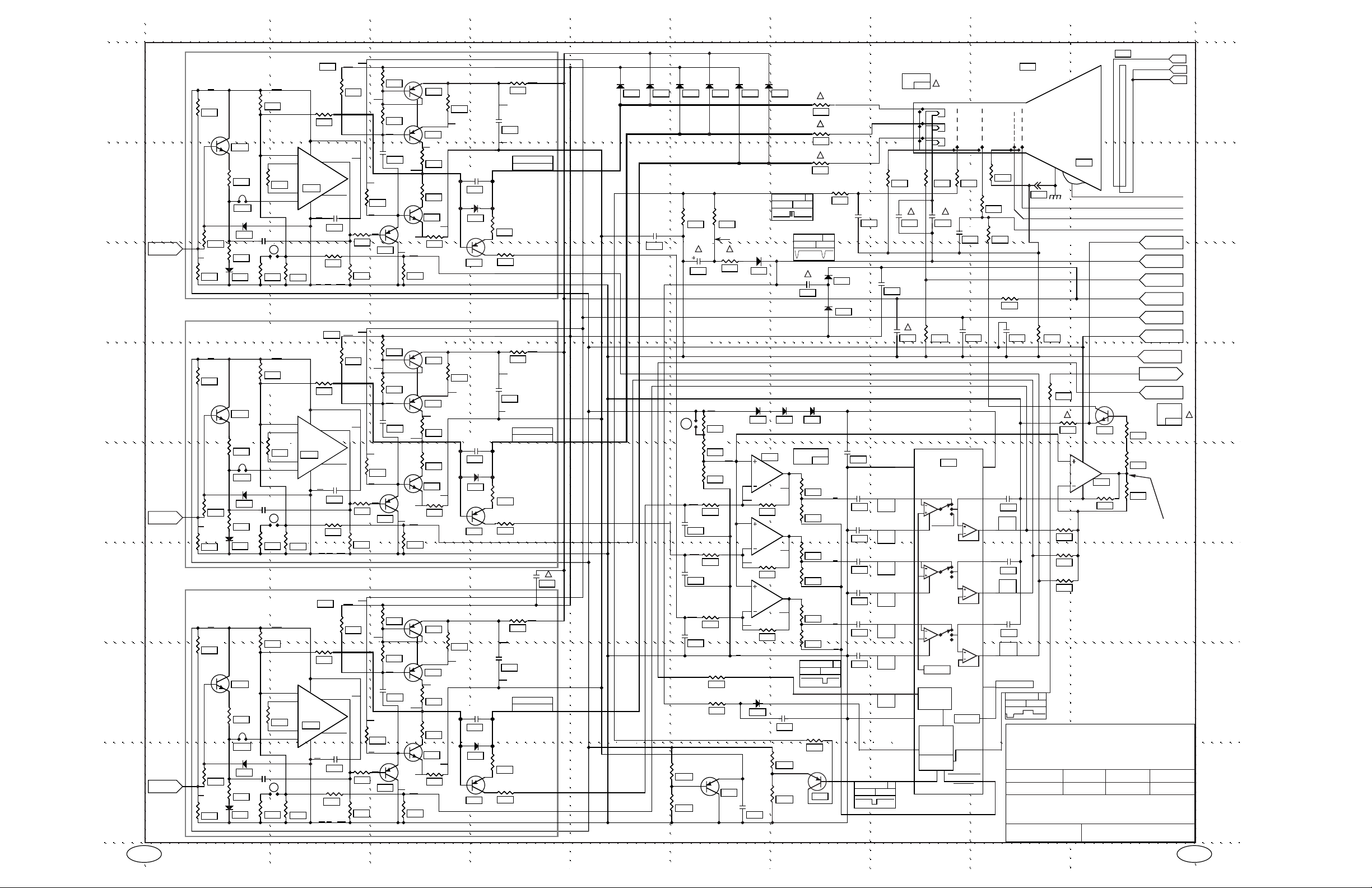
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
RED
TC7
GREEN
TC5
BLUE
TC3
QQ
RR SS
Red Video Amplifier
210
+12V
K34
606
K7
Jumper
K33
1.49K
K9
110
3
1.2K
K8
12
14
SOT
NE592
K32
Ω
301
K2
MMBT
3904
Ω
1N4148
3pF
K36
100Ω
1
1.50K
K1
K21
681Ω
K6
1N4148
K35
21K
K22
A
820Ω
K10
Green Video Amplifier
210
+12V
K34
606Ω
K7
Jumper
K33
1.49K
K9
1.2K
K8
1310
SOT
NE592
K32
12
14
301
K2
MMBT
Ω
3904
1N4148
3pF
K36
100Ω
1
1.50K
K1
K21
681Ω
K6
1N4148
K35
21K
K22
A
Ω
820Ω
K10
Blue Video Amplifier
+12V
210
K34
Ω
606
K7
Jumper
K33
1N4148
K36
681Ω
K6
K6
1N4148
K35
3pF
1.49K
K9
1.2K
A
21K
K22
1
3
SOT
NE592
K8
K32
12
14
820Ω
K10
301
K2
MMBT
1
1
1.50K
Ω
3904
100Ω
K21
K1
40.2K
K19
5
9
5
40.2K
K19
5
9
5912
937
40.2K
K19
10
5
5
811
7
8
.1uF
816
5.62K
K11
912
803
7
8
.1uF
816
5.62K
K11
7
8
.1uF
934
5.62K
K11
3
18
12.1K
K15
10
3
300
.5W
4
PN2907A
Ω
33
K20
2.2K
K5 K12
3
18
12.1K
K15
10
3
300
.5W
4
PN2907A
33Ω
K20
2.2K
K5
3
18
12.1K
K15
10
3
300
.5W
4
PN2907A
Ω
33
K20
2.2K
K5 K12
1295
17
K3
K3
8
GND
17
K3
8
GND
17
K3
K3
8
GND
+12V
560
140
Ω
812
560
140
Ω
822
560
140
Ω
945
Ω
K17
Ω
K16
16
.015uF
901
Ω
K17
Ω
K16
16
.015uF
824
K17
Ω
B14
K16
16
.015uF
885
PN2907A
20
2SC
3467
9
11
3.32K
PN2907A
20
2SC
3467
9
11
3.32K
K12
Ω
PN2907A
20
2SC
3467
9
11
3.32K
6
6
6
2SA
1370
19
180
205
2SA
1370
19
180
205
2SA
1370
19
180
205
832
833
K18
834
810
15Ω
827
828
K18
825
805
15
950
951
K18
953
943
15
Ω
Ω
K4
Ω
Ω
Ω
K4
Ω
Ω
Ω
K4
18
Ω
K14
15
1000pF
838
FDH400
840
7
2SA
1370
837
BIAS
GND
+12V
Ω
18
K14
15
1000pF
843
FDH400
841
7
2SA
1370
842
BIAS CONTROL LINE
GND
+12V
Ω
18
K14
15
1000pF
956
FDH400
958
7
2SA
1370
954
BIAS CONTROL LINE
TT UU VV WW
16V
120V
Ω
75
13
K13
14
.1uF
250V
913
7
Dark screen
80-110VDC
1.8K
836
1.8K
831
CONTROL LINE
Ω
75
13
K13
14
.1uF
250V
823
7
Dark screen
80-110VDC
1.8K
844
1.8K
830
75Ω
13
K13
14
.1uF
250V
887
7
Dark screen
80-110VDC
1.8K
955
1.8K
948
126V
9.3V
120V
126V
9.3V
120V
126V
9.3V
16V
957
16V
FDH
+12V
400
835
.1uF
817
FDH
400
899
FDH
C
For
XX92
1.8K
938
3.92K
940
400
845
100K
876
868
+126fV
+16V
+120V
+12V
GND
14
2,200pF
941
15
2,200pF
818
18
2,200pF
815
GND
FDH
400
849
1.8K
10
900Ω
C17
2.74K
C7
1.82K
C4
4K
C10
4K
C11
4K
C14
22K
891
2.7K
884
+9.3V
MPS A64
D
874
-30V
872
11
942
FDH
12
13
8
400
886
FDH400
870
903
5
1/4
LM324
6
13
3
1/4
LM324
2
16
1/4
LM324
19
GND
1N4148
888
.1uF
930
FDH
400
959
GRID PULSE
12Vp-p 95uS
FIL.
1N40071N4007 1N4007
905 906
920
7
12
5K
C9
1
17
5K
C12
14
20
5K
C15
2.2nF
889
1.8K
933
1.8K
931
900
851
883
Vs-23 to -27Vdc
0VDC
56V
31uS
857
C PRA-B
917
Ω
200
C8
68.1K
C3
200
C13
68.1K
C2
Ω
200
C16
68.1K
C1
8.4Vp-p 95uS
1K
890
PN2907A
928
10K 1/2W
873
Hs
1N4007
848
1N4937
847
+120V Source
7
Ω
5
4
1
Vs7.8 to 8.8Vdc
330pF
871
.1uF
907
.1uF
921
.047uF
922
.1uF
923
.047uF
924
.1uF
925
.047uF
926
9 to 10Vdc
9.6Vp-p 95uS
RED
GREEN
BLUE
1uF
50V
846
5.7-
6.3V
1.2-
2.5V
5.7-
6.3V
1.2-
2.5V
5.7-
6.3V
1.2-
2.5V
Vs
.1.5V
Hs
Vs
SOCKET
8
6
11
12
10
150Ω
1/2W
882
DAG GND
860
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Socket Board
877
G1 G2 Focus
5
97
0Ω
869
853854
1K
1/2W
855
2.2nF
2.2K
1/2W
881
150Ω
100K
FIL.
+127fV
+126V
+16V
18Ω
GND
+4.0V
AUTO BIAS IC
GND Vcc
879
927
.1uF
801
22
CA3224E
input
Blue
sw
normal
comp.
sw in grid pls. pos.
Green input Green
sw
comp.
Red input Red
sw
comp.
6V REF.
Start
COUNTER
FFCLQ
GND
EN
21 H. LINE
COUNTER
CL
DECODER
sw control
GRID
PROGRAM
PULSE
BIAS
5V REF
AUTO
BIAS
ACTIVE
PULSE
Blue
hold
cap.
hold
cap.
hold
cap.
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
ZZ
970
EHT
1/2W
880
1/2W
856878
PCB
YYXX
800
2
1
Green
Wire
961
BEAM OFF ON POWER DOWN.
DAG GND
Fil. GND
30Ω
859
.1uF
816
150
1/2W cc
875
Ω
+127V
+16V
+12V
GND
ABA
1K
Auto Bias Vs
10uF
+
895
2.1-
6.3V
10uF
+
894
2.1-
6.3V
10uF
+
892
2.1-
6.3V
4.6-5.2VDC
4.2Vp-p 360uS
866
33K
908
33K
910
33K
911
Vs2.2 to 2.7Vdc
858
10
9
2SC3675
850
Auto Bright
Circuit
4
1/4
8
LM324
920
11
3.3K
909
Adjust FBT bottom pot
for 4.0V to 4.4 at pin 8.
CERONIX
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, California 95602
Scale:
Drawn By:
VIDEO BOARD CIRCUIT
NONE
F. H.
DATE & REV.
4/16/96-E1
10/3/96-E4
2/2/98-E5
From Main PCB
971
Pin By Fuse
Pin By FBT
! UNPLUG !
DEGAUSSING
COIL BEFORE
WORKING ON
CHASSIS.
Degaussing
Coil
EHT
Red #1 FOCUS
White #2 FOCUS
SCREEN
TC 9
FIL.
TC 11
TC 12
TC 8
TC 1
TC 4
TC 2
TC 6
TC 10
CABLE
ASS.
62K
852
62K
912
15.8K
914
863
03/06/02-E7
CC1
CC2
CC3
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
40 40
QQ RR SS
VVUUTT
WW
YYXX ZZ
Page 25
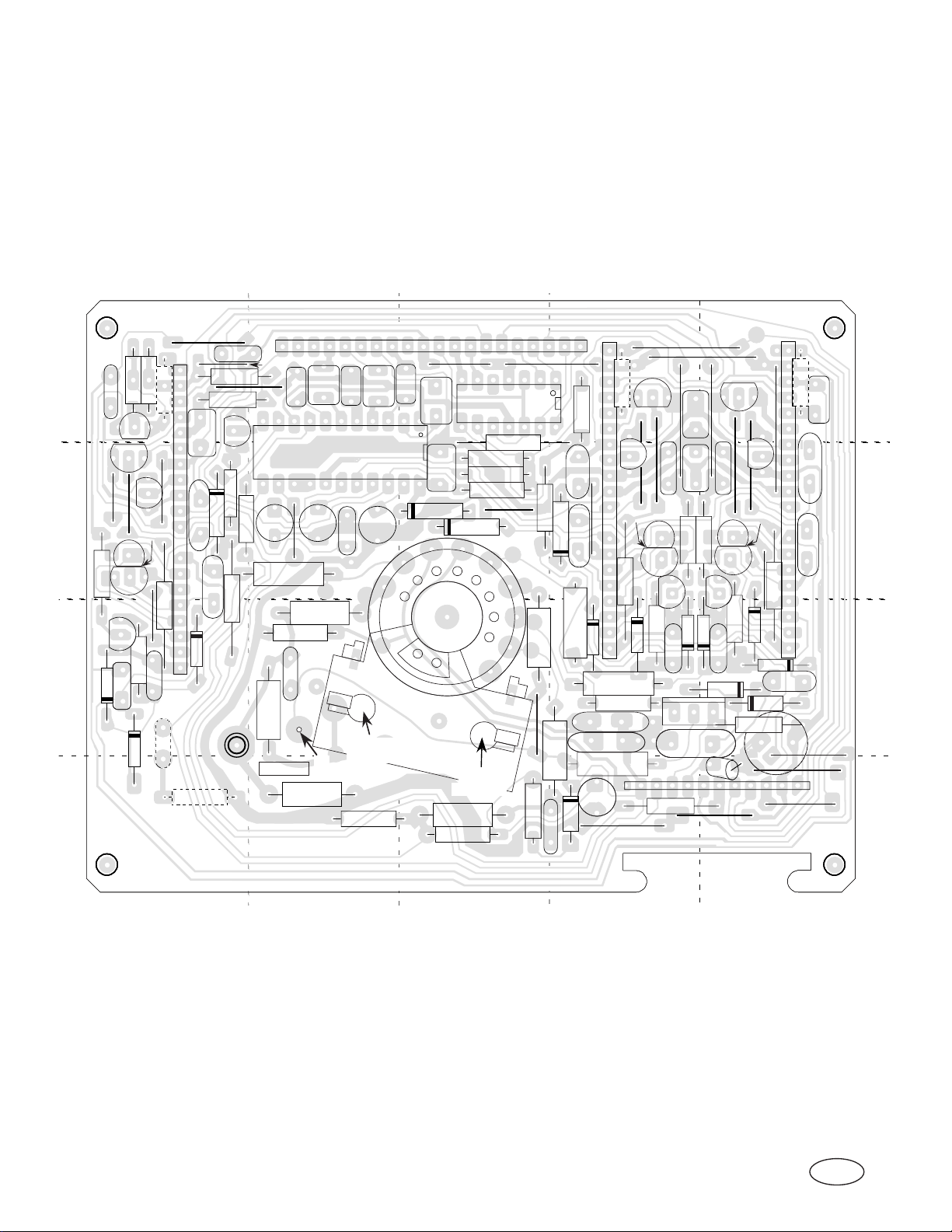
GREEN
FIL.
XX93 Video Board, Technician's Assembly Drawing.
View is from component side.
PNMLK
3467
805
2907
822
2.2nF,818
0Ω, 820
Glue
2907
827
828
844
1.8K,
848
4937
∆
+
+
GREEN
0Ω, 804
0Ω, 821
0Ω,826
H400
845
H400
1.0uF
858
858
∆
860
860
803
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
14
15
825
16
17
205Ω,
18
19
20
846
847
0Ω, 864
809
.1uF
801
.1uF
250V
823
250V
.015uF
824
GREEN
849
0Ω, 861
0Ω, 862
863
123456712
1
2
3
∆
4
924
47nF
2.2nF, 889
BLUE
882
CRT
SOCKET
FOCUS
WHITE WIRE
100K, 876
"C" PRA 917
922
.1uF
47nF
923
1234567891011
2221201918171615141312
1N4007
+
10uF
895
BLUE
11
12
877
1
877
∆
.1uF
921
.1uF
907
10K, CF
.5W
1.8K, 874
0Ω, 918
LM324
9
8
33K, 911
33K, 910
33K, 908
906
1N4007
FIL.
910
8
FOCUS
RED WIRE
873
920
121110
3.3K, 909
0Ω, 904
905
RED
G2
7
6
5
G1
0Ω, 915
13 14
2.2K
.5W
CF
881
.5W
855
872
872
∆
62K, 912
0Ω, 869
1K
CF
BLUE
0Ω, 936
1
2
3
4
940
941
2.2nF,
A64
942
3467
943
0Ω, 947
0Ω, 946
2907
950
1370
951
1.8K,948
1370
954
958
957
957
H400
∆
Model XX93-E7
Model XX93-E7
Video Board
Video Board
∆
937
937
1
938
939
2
3.92K
1.8K,
3
4
5
6
7
0Ω, 944
8
2907
9
945
10
11
Glue
13
14
15
953
16
17
205Ω,
0Ω, 952
18
955
19
20
1.8K,
1nF, 956
964
H400
959
CERONIX
CERONIX
964
0Ω,
.1uF
930
250V
887
H400
.1uF,
1.8K
1.8K,931
888
0.1uF
1N4148
250V
.015uF
885
886
.093"
Pin
963
2907
928
1K, 890
961
12 45678910111213 14 15 16 17 18 19
935
0Ω
932
+
892
∆
18Ω, 879
880
.5W
150Ω, CC
3
926
.1uF
925
47nF
CA3224E, 927
+
10uF
894
0Ω
893
883
883
150Ω, CC
.5W
2.2nF,878
G2
WIRE
150Ω, CC
.5W
875
934
933
10uF
22K,891
2.7K,884
PCB, 800
20
1234567
15.8K,914
.1uF
250V
913
903
250V
1N4007
.015uF
901
900
900
∆
100K, .5W, CF
∆
868
868
+
+
H400
870
330pF,871
RED
811
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2907
812
8
9
10
11
13
0Ω, 902
14
15
RED
16
899
17
18
19
H400
20
∆
62K, 852
∆
853
∆
854
0Ω, 867
819
Glue
834
205Ω,
835
851
851
856
3467
810
0Ω, 813
2907
832
1370
833
H400
0Ω,807
2.2nF,815
0Ω, 814
1370
837
1.8K,836
1nF, 838
2SC3675
1K, 866
0Ω, 808
.1uF
817
.1uF
816
1.8K,830
1.8K,831
1370
842
H400
H400
841
840
4007
850
∆
857
857
30Ω, 859
0Ω, 865
0Ω, 802
0Ω, 806
1370
1nF, 843
Note:
Common part values marked on drawing.
The values for components marked with
the ∆ (delta) can be found in the master
part list starting on page 45.
Fil. Rtn.
Filament
+127V
Red Input
Auto Bias Vs
0=Ib,Power Down
PNMLK
+12V
Blue Input
Green Input
Auto Bias Active
123456789101112
+16V
Signal Ground
41
Page 26
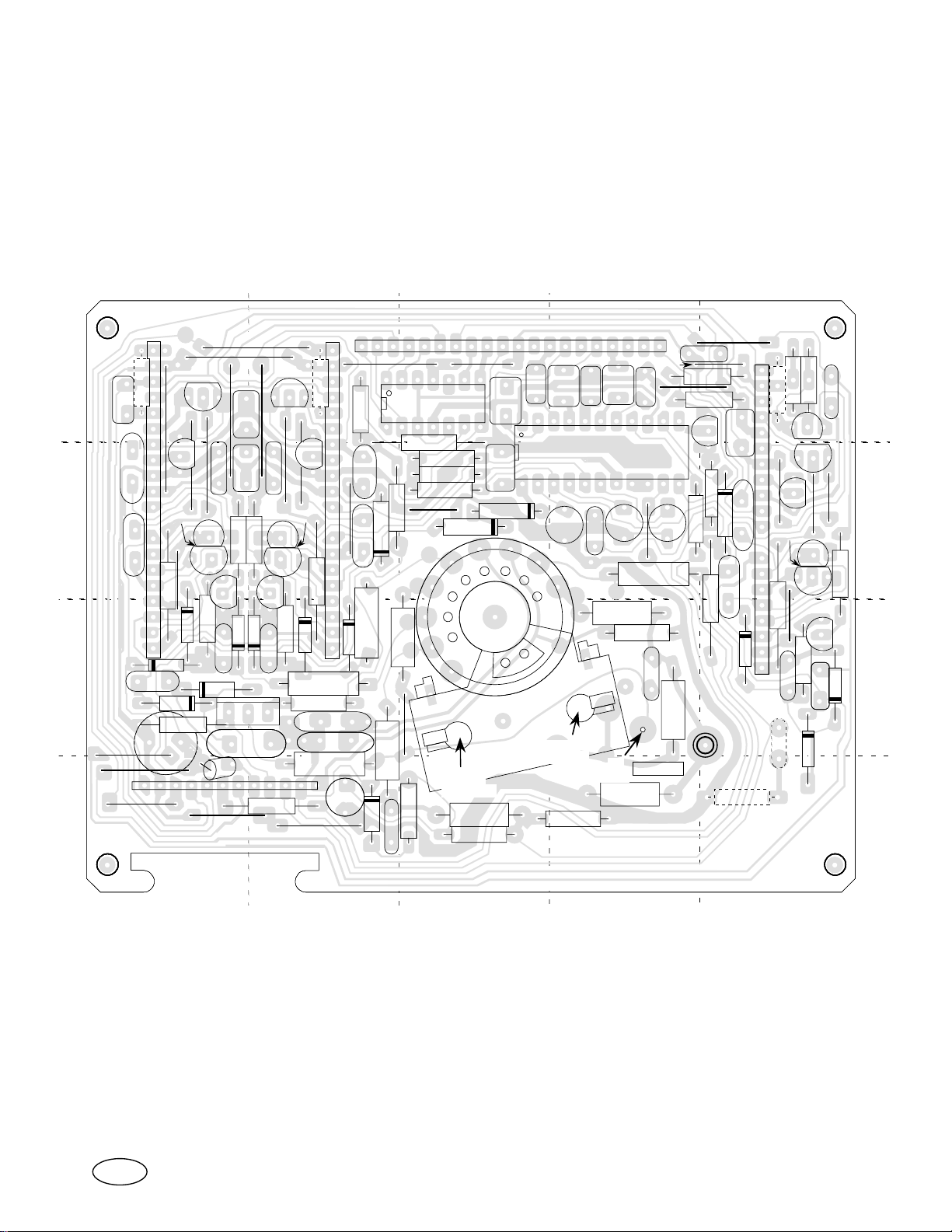
XX93 Video Board, Technician's Assembly Drawing.
View is from conductor side.
PNMLK
1
2
3
4
GREEN
803
1
809
2
3
.1uF
801
5
6
7
.1uF
8
250V
9
823
10
11
250V
.015uF
13
14
824
15
16
GREEN
17
18
19
20
849
H400
1.0uF
846
847
858
858
0Ω, 861
0Ω, 862
860
860
∆
863
1234567 12
0Ω, 864
0Ω, 804
2907
Glue
825
205Ω,
845
4937
∆
0Ω, 802
3467
822
0Ω, 821
0Ω,826
H400
∆
+
+
0Ω, 808
805
0Ω, 820
2907
827
1370
828
1370
844
1.8K,
848
4007
0Ω, 865
0Ω, 806
2.2nF,818
842
1nF, 843
850
30Ω, 859
0Ω,807
.1uF
817
.1uF
816
1.8K,830
1.8K,831
1370
837
H400
H400
841
840
2SC3675
∆
857
857
1K, 866
3467
810
2.2nF,815
2907
0Ω, 814
812
Glue
2907
832
1370
833
1.8K,836
H400
1nF, 838
851
62K, 852
854
100K, .5W, CF
856
0Ω, 867
0Ω, 813
835
853
RED
811
819
834
205Ω,
938
939
1.8K,
0Ω, 944
2907
945
Glue
953
0Ω, 952
205Ω,
1nF, 956
964
3.92K
A64
942
3467
943
2907
950
1370
951
955
1.8K,
H400
959
940
0Ω, 946
1370
954
957
957
∆
941
2.2nF,
0Ω, 947
1.8K,948
958
H400
1
2
3
4
9
8
906
910
8
10K, CF
"C" PRA 917
922
47nF
.1uF
921
1234567891011
.1uF
907
22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12
1N4007
FIL.
11
12
1
.5W
.1uF
923
CA3224E, 927
+
10uF
895
BLUE
877
CRT
SOCKET
877
∆
FOCUS
RED WIRE
100K, 876
924
47nF
2.2nF, 889
BLUE
150Ω, CC
882
WIRE
.1uF
925
G2
150Ω, CC
875
20
1
0Ω, 915
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
∆
∆
∆
0Ω, 902
RED
∆
868
868
+
+
1234567
15.8K,914
1314
.1uF
903
250V
62K, 912
913
1N4007
250V
.015uF
901
GREEN
899
900
900
870
∆
H400
2.2K
.5W
CF
881
0Ω, 869
1K
.5W
CF
855
330pF,871
H400
920
3.3K, 909
872
872
∆
LM324
12 11 10
33K, 911
33K, 910
33K, 908
0Ω, 904
905
RED
FIL.
G2
7
6
5
G1
RED WIRE
0Ω, 918
1N4007
FOCUS
873
1.8K, 874
3
926
+
10uF
894
893
883
883
.5W
18Ω, 879
PCB, 800
.5W
1245678910111213141516171819
935
47nF
0Ω
932
+
10uF
892
0Ω
∆
2.2nF,878
880
.5W
934
933
150Ω, CC
2907
928
22K,891
.093"
Pin
961
BLUE
0Ω, 936
.1uF,
1.8K
1.8K,931
1K, 890
2.7K,884
∆
937
937
0Ω,
1
2
3
4
.1uF
5
930
6
888
7
8
1N4148
250V
9
0.1uF
10
11
887
13
250V
.015uF
14
15
16
885
17
H400
18
19
886
20
963
CERONIX
CERONIX
Model XX93-E7
Model XX93-E7
Video Board
Video Board
964
PNMLK
123456789101112
+16V
Blue Input
+12V
Green Input
+127V
Signal Ground
Red Input
Auto Bias Active
42
Filament
Auto Bias Vs
Fil. Rtn.
0=Ib,Power Down
Note:
Common part values marked on drawing.
The values for components marked with
the ∆ (delta) can be found in the master
part list starting on page 45.
Page 27
Safety Critical Components for XX93 Monitors.
PRODUCT SAFETY NOTE:
Components marked by the symbol ! have special characteristics important to safety.
When replacing any of these components, be sure to use the parts specified in the parts
list.
An example of how the critical components are marked in the Master Part List is shown
below. See the Master Part List for specifying critical components.
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description
102 CPC1027 D2 HH8 6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film!
CAUTION:
CERONIX XX93 Monitors MUST USE AN APPROVED ISOLATION
TRANSFORMER.
The monitor chassis must be connected to earth ground via a common connection
in the system which contains the monitor.
X-RAY NOTE:
X-radiation is produced by electrons colliding with the phosphor and shadow mask at the
front of the picture tube. The X-radiation emanating from the front of the picture tube is
highly reduced due to the shielding affect of the leaded glass face.
It is also produced at the anode bulb contact. The X-radiation emanating from the anode bulb
contact is much higher than from the face due to less shielding.
X-radiation is directly proportional to beam current. It doubles for each 1.3KV increase of
the EHT voltage at the face and also doubles for each 3KV increase of the EHT at the anode
bulb contact.
From this information, it should be noted that when servicing monitor electronics, where the
back of the picture tube is facing the service person, that the beam current should be turned
down to avoid excessive exposure.
Due to the increase in X-Radiation emission with increase of EHT voltage, it is important that
the EHT voltage is checked.
To measure the EHT voltage: Connect the (-) lead of a volt meter to the monitor chassis so
that a reliable connection is made. Connect a high voltage probe to the (+) input of the meter
and at the anode contact of the picture tube.
The EHT should not exceed 26KV at 0 beam current.
43
Page 28
Sicherheit Kritische Bestandteile für Monitoren XX93.
PRODUKTSICHERHEIT ANMERKUNG:
Bestandteile gekennzeichnet durch das Symbol ! haben Sie die speziellen Eigenschaften,
die zur Sicherheit wichtig sind. Wenn Sie irgendwelche dieser Bestandteile ersetzen, seien
Sie sicher, die Teile zu benutzen, die in der Stückliste spezifiziert werden. Ein Beispiel von,
wie die kritischen Bestandteile in der Vorlagenstückliste gekennzeichnet werden, wird
unten gezeigt. Sehen Sie die Vorlagenstückliste für das Spezifizieren der kritischen
Bestandteile.
∆ Bd. # TeilNr. Bd. Sch. Ref. Beschreibung
102 CPC1027 D2 HH8 6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film!
VORSICHT:
MONITOREN CERONIX XX93 MÜSSEN EINEN ANERKANNTEN
LOKALISIERUNG TRANSFORMATOR BENUTZEN.
Das Monitorchassis muß an die Masse angeschlossen werden, die über einen
allgemeinen Anschluß im System gerieben wird, das den Monitor enthält.
RöNTGENSTRAHLANMERKUNG:
X-Strahlung wird durch die Elektronen produziert, die mit der Phosphor- und
Schattenschablone an der Frontseite des Abbildung Gefäßes zusammenstoßen. Die
X-Strahlung, die von der Frontseite des Abbildung Gefäßes ausströmt, liegt in hohem Grade
an der Abschirmung beeinflussen vom verbleiten Glasgesicht verringertes. Sie wird auch am
Anode Birne Kontakt produziert. Die X-Strahlung, die vom Anode Birne Kontakt ausströmt,
ist viel höher als vom Gesicht, das zu weniger abschirmen passend ist. X-Strahlung ist direkt
zum Lichtstrahlstrom proportional. Sie verdoppelt für jede Zunahme 1.3KV der
EHT-Spannung am Gesicht und verdoppelt auch für jede Zunahme 3KV des EHT am Anode
Birne Kontakt.
Von diesen Informationen sollte es beachtet werden daß, wenn man Monitorelektronik
instandhält, in der die Rückseite des Abbildung Gefäßes die Service-Person gegenüberstellt, daß
der Lichtstrahlstrom unten gedreht werden sollte, um übermäßige Berührung zu vermeiden.
Wegen der Zunahme der X-Radiationemission mit Zunahme der EHT-Spannung, ist es wichtig,
daß die EHT-Spannung überprüft wird.
Die EHT-Spannung messen: Schließen Sie die (-) Leitung eines Voltmeßinstruments an das
Monitorchassis an, damit eine zuverlässige Beziehung hergestellt wird. Schließen Sie eine
Hochspannungsprüfspitze an den (+) Input des Meßinstruments und am Anode Kontakt des
Abbildung Gefäßes an.
Das EHT sollte nicht 26KV bei 0 Lichtstrahlstrom übersteigen.
44
Page 29
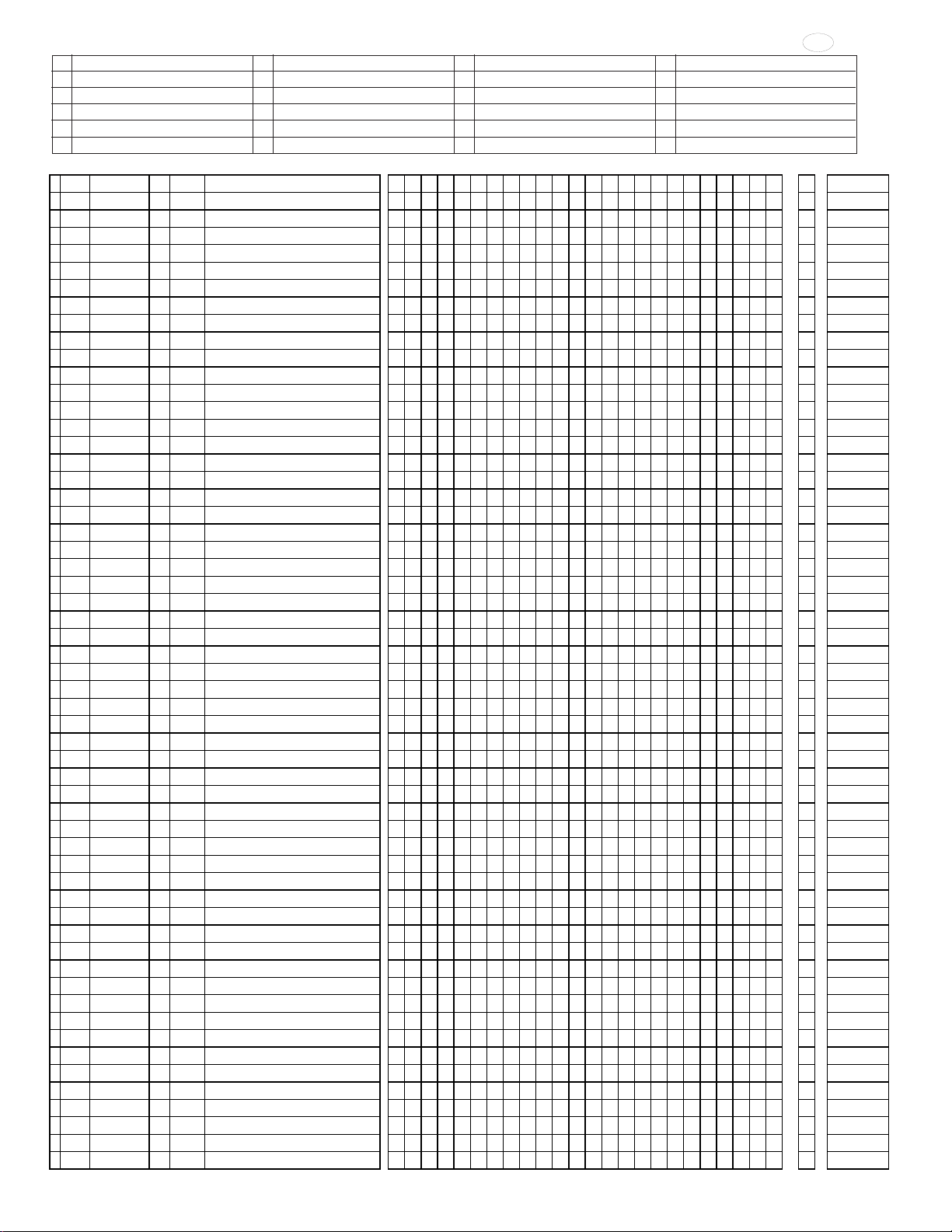
CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 45
r
CPB1614
Main PCB “93” REV. E8
001
CPR0050
A1
J
002
CPS1804
B1
EE2
004
CPR0006
C1
FF1
005
CPR0029
C1
NN5
006
CPD1251
C1
CC1
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
006
CPR0006
C1
CC2
510Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
008
CPQ1310
NN5
009
CPR0012
B1
LL7
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
009
CPR0134
B1
LL7
009
CPR0136
B1
LL7
1.62KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
009
CPR0138
B1
LL7
009
CPR0140
B1
LL7
010
CPC1058
A1
LL7
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
011
CPR0018
A1
MM4
012
CPR0009
A1
EE5
014
CPC1101
A2
FF5
015
CPR0050
B2
J
017
CPR0015
B1
NN4
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
018
CPD1251
B1
FF5
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
019
CPR0050
C1
NN4
0Ω, Jumper Wire
020
CPR0145
C2
FF5
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
021
CPR0006
C2
MM3
022
CPR0143
C2
MM3
023
CPR0143
C2
MM4
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
026
CPC1102
C2
NN4
027
CPR0006
C2
CC2
029
CPR0143
C2
MM5
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
030
CPR0142
C2
NN7
7.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
030
CPR0144
C2
NN7
030
CPR0145
C2
NN7
030
CPR0153
C2
NN7
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
030
CPR0163
C2
NN7
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
030
CPR0411
C2
NN7
10K ±20%, 1/5W, White Pot
031
CPR0143
C2
NN5
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
032
CPR0050
C2J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
033
CPI1405
B2
MM6
034
CPR0144
B2
MM4
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
035
CPC1102
C1
NN4
036
CPQ1302
A2
FF5
30V, .3A, PNP, D, MPSA64
037
CPR0145
A2
MM4
038
CPR0143
A2
MM6
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
040
CPR0029
A2
MM6
041
CPR0141
A2
NN7
4.42KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
041
CPR0144
A2
NN7
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
041
CPR0145
A2
NN7
041
CPR0153
A2
NN7
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
041
CPR0154
A2
NN7
041
CPR0163
A2
NN7
041
CPR0411
NN7
10K ±20%, 1/5W, White Pot
042
CPR0013
B2
NN7
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
042
CPR0024
B2
NN7
042
CPR0138
B2
NN7
042
CPR0140
B2
NN7
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
042
CPR0148
B2
NN7
24.3KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
042
CPR0163
B2
NN7
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
043
CPR0015
A3
LL8
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
0Ω, Jumper Wire
8 Cond. Straight Header
510Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
B1
A2
.1A, 300V, PNP, 2SA1371AE
1.21KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
0Ω, Jumper Wire
510Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
510Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
Quad OP Amp IC, LM324
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
44.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BACDGF H LN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BACDGFH
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC QD
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BA
BAC OQDF H PE
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
FH NE
G c
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
D
CFH NE
G
I
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
L R UI
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
L R
L
JK
N
N
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
OQP
OQPLI
R
OQP
O P
OGP
Q
R U
Q
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
UI
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
3.15TMS
0.01TMS
0.19TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01T
0.01MS
0.23TMS
0.01
0.01S
0.01T
0.01M
0.01
0.05TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.01T
0.01TMS
0.01S
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.33T
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.24TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.06TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01S
0.01
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.33T
0.01
0.01T
0.01M
0.01S
0.01
0.01
0.01
Page 30
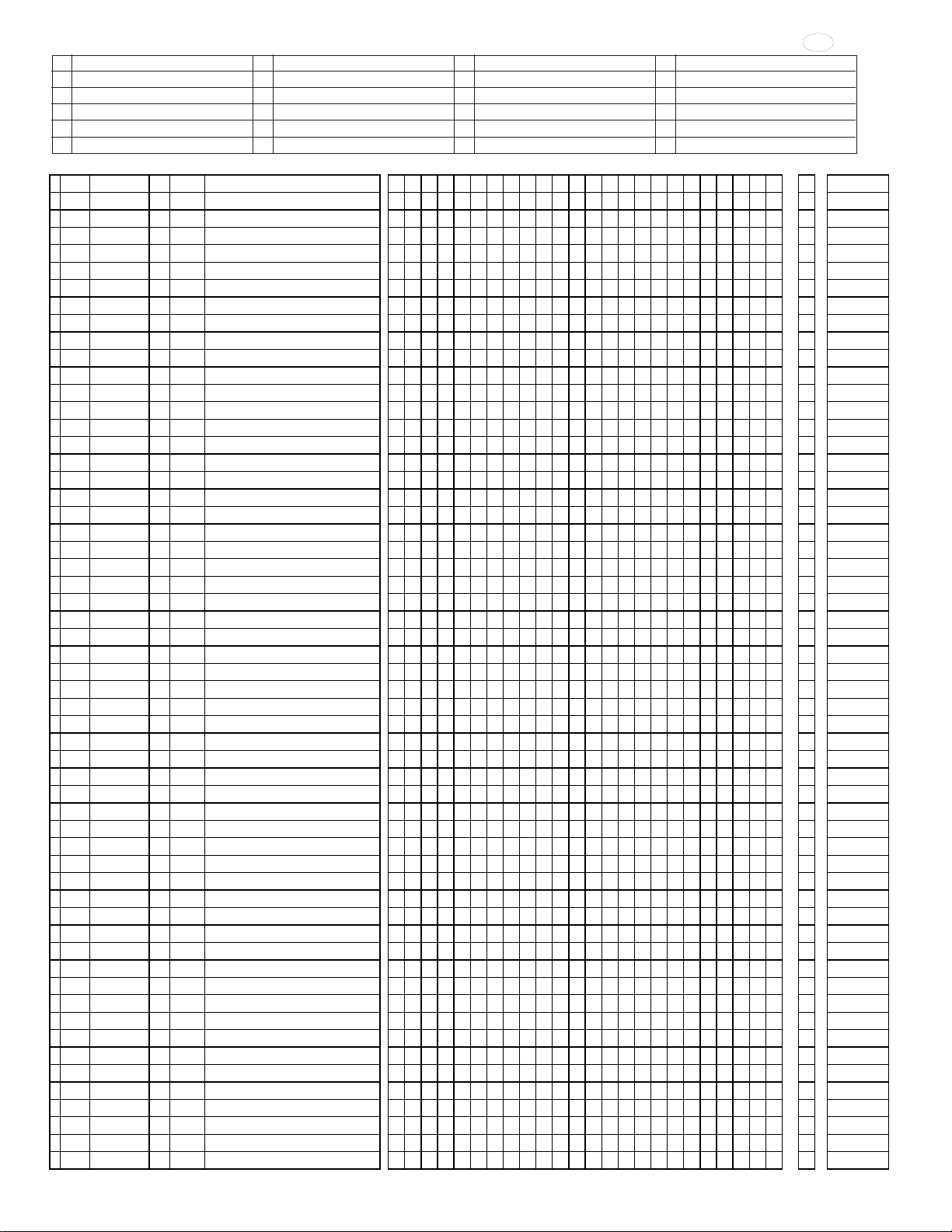
CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 46
r
043
CPR0016
A3
LL8
043
CPR0017
A3
LL8
043
CPR0018
A3
LL8
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
043
CPR0145
A3
LL8
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
043
CPR0153
LL8
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
043
CPR0154
A3
LL8
44.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
043
CPR0163
A3
LL8
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
044
CPR0015
A3
MM7
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
044
CPR0016
A3
MM7
044
CPR0017
A3
MM7
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
044
A3
MM7
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
044
CPR0029
A3
MM7
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
044
CPR0148
A3
MM7
24.3KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
044
CPR0154
MM7
044
CPR0163
A3
MM7
28.0K ±1%, 1/4W, MF
045
CPR0144
A3
LL8
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
047
CPC1032
B3
MM8
.01uF ±5%, 50V, Film
048
CPR0050
A3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
049
CPI1414
B3
MM8
OP Amp / Comp. IC, LM392
050
CPR0024
B3
NN6
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
051
CPR0143
B2
NN5
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
052
CPR0024
B2
NN7
052
CPR0138
B2
NN7
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
052
CPR0140
B2
NN7
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
052
CPR0148
B2
NN7
24.3KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
052
CPR0153
B2
NN7
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
053
CPR0024
B3
NN6
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
054
CPC1032
B3
MM7
.01uF ±5%, 50V, Film
055
CPR0143
B3
MM8
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
056
CPR0013
B3
NN8
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
057
CPC1027
B3
NN8
057
CPC1035
B3
NN8
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
058
CPR0154
B3
MM8
060
CPR0012
B3
NN8
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
061
CPC1102
B3
LL8
062
CPR0009
A3
EE3
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
062
CPR0138
A3
EE3
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
063
CPR0002
A3
FF5
18Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
064
CPR0012
A3
BB5
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
064
CPR0024
A3
BB5
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
064
CPR0126
A3
BB5
909Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
065
CPR0009
A3
EE6
066
CPR0124
A3
EE6
067
CPR0050
A4
EE3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
068
CPR0050
A4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
071
CPQ1322
B3
EE5
072
CPQ1322
B3
AA4
076
CPR0132
B4
604Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
076
CPR0136
B4
1.62KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
077
CPR0163
BB4
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
CPR0016
B3
BB4
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
078
CPR0011
B3
BB4
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CPR0012
B3
BB4
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
078
CPR0136
B3
BB4
1.62KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
078
CPR0138
B3
BB4
080
CPD1253
B3
BB4
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
081
CPC1027
B3
BB4
6800pf ±5%, 100V, Film
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF G
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
A3
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CPR0018
A3
B3
077
078
44.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film
44.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A, Motorola.
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A, Motorola.
CC5
CC5
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BA
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PNE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BANR U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAO
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAO
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAO
BAO
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
FH R
E
C
K
I
J
J
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
K
J
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
N
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
L
N
LI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LI
D L UI
C R
G
FHI
E
D L
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
COQDGFH PLI
E
E
E
E
CQDNR U
G
FH PLI
E
E
CQD R
G
FH P
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
FH P
E
CQDNR
C D
C D
G
FH PLNI
E
E
G c
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
P
ON
Q
O
P
R U
O P
R U
Q
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.01S
0.01
0.01T
0.01
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01S
0.01T
0.01
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.57TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TM
0.01S
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.07M
0.08TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01M
0.01
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.05TMS
0.05TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01
0.01S
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.07
Page 31

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 47
r
081
CPC1032
B3
BB4
081
CPC1036
B3
BB4
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
081
CPC1040
B3
BB4
.015uF ±10%, 250V, Film
081
CPC1054
B3
BB4
.039uF ±5%, 100V, Film
082
CPC1041
B3
LL6
.33uF ±5%, 50V, Film
083
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
084
CPD1250
C3
AA5
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
085
CPR0155
C3
DD1
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
086
CPD1250
C3
AA5
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
087
CPR0157
C3
DD2
088
CPR0050
C3
BB1
0Ω, Jumper Wire
088
CPR0100
C3
BB1
2.2KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CC
089
CPC1102
C3
DD2
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
090
CPD1252
C3
DD1
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
092
CPR0050
C3
Jumper Wire
092
CPR0375
C3
PP0
.68Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
CPR0050
C3
Jumper Wire
093
CPR0004
C3
CC4
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
094
CPR0050
C3
NN8
0Ω, Jumper Wire
095
CPR0143
C3
MM8
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
096
CPR0163
C3
NN7
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
097
CPR0016
C3
MM7
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
097
CPR0018
C3
MM7
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
097
CPR0146
C3
MM7
097
CPR0155
C3
MM7
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
097
CPR0158
C3
MM7
84.5KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
097
CPR0163
C3
MM7
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
098
CPR0018
D2
BB1
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
099
CPR0013
D2
BB1
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
099
CPR0018
D2
BB1
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
100
CPI1416
D2
CC2
7 Bit Counter, CD4024B
CPR0050
D2
Jumper, pins 5 to 10.
CPQ1303
D3
BB2
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
101
CPC1058
D2
BB2
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
!
102
CPC1027
D2
HH8
!
102
CPC1035
D2
HH8
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
104
CPC1000
D2
HH7
56pF ±5%, 100V, Ceramic
105
CPR0017
D2
HH8
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
105
CPR0018
D2
GG8
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
105
CPR0029
D2
HH8
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
105
CPR0142
D1
GG8
7.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105
CPR0143
D2
HH8
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105
CPR0153
D2
HH8
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105
CPR0155
D1
GG8
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105
CPR0163
D2
HH8
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105
CPR0168
D1
GG8
8.06KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105
CPR0172
D1
GG8
140KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
106
CPR0138
D2
GG8
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
106
CPR0140
D2
GG8
106
CPR0142
D2
GG8
7.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
106
D2
GG8
8.06KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
107
CPC1000
D2
HH7
56pF ±5%, 100V, Ceramic
108
CPC1035
D2
HH7
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
109
CPR0029
E2
MM5
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
110
CPC1005
D1
HH6
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
!
111
CPR0501
E1
JJ9
112
CPQ1310
D1
HH6
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
.01uF ±5%, 50V, Film
C3
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
PP0 0Ω
092A
100A
100B
CPR0168
PP0 0Ω
169KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
BB2 0Ω
6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
“J” PRA Power Supply
.1A, 300V, PNP, 2SA1371AE
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BACDGF H LN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC QDGF H
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAQ
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BACDGF H LN R UI
BACDGF H LN R UI
BACDGF H LN R UI
BANR U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQH P
BDF I
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
COQD PL
N R U
FHI
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
D
C
G
FH
E
E
E
E
E
COQDGFH PLI
E
E
C Q
G
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
L UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
LN R UI
N
JK
LI
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
K
H
J
I
N
L
N R
K
J
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
OQP
OPN R
OP R U
OQP
OQP
OQP
P
R
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.03TS
0.04M
0.06
0.06
0.08TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01MS
0.04T
0.04TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01MS
0.01T
0.32T
0.01MS
0.04MS
0.05T
0.07M
0.08TS
0.01TMS
0.01S
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01M
0.01
0.01T
0.01M
0.01S
0.01
0.01TMS
0.08TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.79TMS
0.23TMS
Page 32

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 48
r
113
CPR0019
D1
HH6
114
CPR0050
HH8
0Ω, Jumper Wire
CPR0050
D1
HH6
0Ω, Jumper Wire
!
115
CPI1403
E2
II7
116
CPD1252
E2
JJ9
1A, 1N4007
117
CPR0050
E3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
118
CPC1102
E2
II5
119
CPC1104
E3
MM0
120
CPC1102
E2
II5
121
CPD1253
F2
II6
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
122
CPD1253
F2
II6
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
123
F2
HH9
330pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
123
CPC1006
HH9
200pF ±10%, 1KV, Ceramic
124
CPC1058
E2
JJ7
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
!
125
CPC1035
F2
KK7
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
126
CPR0156
E2
KK7
93.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
!
126
CPR0157
E2
KK7
!
126
CPR0171
E2
KK7
!
126
CPR0172
E2
KK7
140KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
!
126
CPR0174
E2
KK7
210KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
!
126
CPR0176
E2
KK7
226K ±1%, 1/4W, MF
!
CPR0146
E2
KK7
!
CPR0169
E2
KK7
191KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
127
CPQ1302
E2
JJ9
30V, .3A, PNP, D, MPSA64
128
CPC1103
E2
HH9
220uF, 50V, Electrolytic
129
CPC1009
G1
KK9
100pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
130
CPD1251
F2
KK7
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
130
CPD1253
F2
KK7
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
131
CPC1003
E1
JJ9
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
132
CPD1252
F1
JJ6
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
132
CPR0050
F1
JJ6
0Ω, Jumper Wire
133
CPR0002
E1
JJ8
18Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
134
CPR0147
F1
JJ7
135
CPM2037
F2
KK8
Heat Sink For P.S. FET.
135
CPM2123
F2
KK8
Heat Sink For P.S. FET.
!
136
CPQ1304
F2
KK8
CPR0050
F2
KK8
137
CPR0389
F1
KK8
.33Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
138
CPC1006
G1
KK8
200pF ±10%, 1KV, Ceramic
139
CPR0033
G1
JJ6
140
CPR0350
F1
KK8
141
CPD1253
G1
JJ6
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
!
142
CPD1264
H1
KK6
CPR0018
H1
HH8
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CPR0017
H1
HH8
!
144
CPC1107
I1
GG8
330uF, 250V, Electrolytic
!
144
CPC1111
I1
GG8
220uF, 2=0V, Electrolytic
145
CPS1753
J1
GG9
2 Cond. Right Angle Header
CPM2003
J1
Cable Tie, 4”
!
146
CPR0425
J2
GG9
3 Amp Slow Blo
!
148
CPD1264
J2
GG7
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
149
CPD1255
F1
JJ7
18V, 1W Zener D., 1N4746A
150
CPC1003
J2
GG7
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
!
151
CPD1264
J2
GG7
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
152
CPC1003
GG7
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
152
CPR0050
GG8
0Ω Jumper, CS=.40”
153
CPC1003
GG7
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
E1
114A
PS Control IC, XRC5184
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
1,000uF, 35V, Electrolytic
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
CPC1002
F2
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
365KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
126.5
126.5
136A
143A
143B
145A
I2
I2
I2
169KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
1.00MΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
4.5A, 450V, Mos Fet, 2SK1446LS
22 Gage Buss Wire under P/S
30Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
47Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BA LN
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN RI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGF H LI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC ODGFH PLNI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAO
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
I
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
J
K
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UIE
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UIE
LN R UI
LN R UI
LNI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
N R U
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
FH
E
COQD PLN R UI
E
E
G
FH
E
COQD P
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
CQD LI
CQD LI
G
FH PN R U
E
CQD LI
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R
R
PN R U
Q R U
R
U
U
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
3.33TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.22
0.04TMS
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.05TMS
0.08TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.01S
0.04
0.01
0.01
0.01M
0.06TMS
0.14TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.02
0.02TMS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.12
0.16TMS
1.19TMS
0.01TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.06TMS
0.02TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
1.35TS
0.97M
0.13TMS
0.01TMS
0.32TMS
0.03TMS
0.05M
0.02TMS
0.03TS
0.02TS
0.01M
0.02TS
Page 33

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 49
r
!
154
CPD1264
J2
GG7
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
155
CPC1003
J2
GG8
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
!
156
CPD1264
J2
GG9
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
157
CPR0434
J3
FF9
Posistor 230V, 14
158
CPR0434
J3
FF9
Posistor 230V, 14
!
159
CPR0426
J3
FF9
Inrush Current Limit
161
CPS1758
I3
FF9
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, CC1
162
CPS1758
I3
FF9
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, CC2
CPS1758
I3
EE9
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, CC3
!
163
CPC1107
I2
GG8
330uF, 250V, Electrolytic
!
163
CPC1111
I2
GG8
164
CPR0050
H2J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
165
CPR0050
H2J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
CPR0050
H2J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
!
166
CPT1536
H2
KK7
XX93 S. M. Power Inductor
!
166
CPT1552
H2
KK6
!
166
CPT1559
H2
KK6
1793 S. M. Power Inductor
!
166
CPT1562
H2
KK6
14/1993 S. M. Power Inductor
!
166
CPT1563
H2
KK6
XX93 S. M. Power Inductor
!
166
CPT1567
H2
KK6
XX93 S. M. Power Inductor
167
CPD1253
G3
JJ6
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
CPR0018
H2
II4
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CPR0050
H2
II4
0Ω, Jumper Wire
168
CPD1253
G3
KK6
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
169
CPD1253
G2
KK5
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
170
CPD1253
G2
KK5
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
171
CPC1104
F3
JJ6
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
172
CPR0050
G3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
173
CPR0019
G3
HH4
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
!
175
CPC1107
H3
II6
330uF, 250V, Electrolytic
!
175
CPC1111
H3
II6
176
CPR0050
H4
LL9
0Ω, Jumper Wire
177
CPR0050
H4
LL9
0Ω, Jumper Wire
178
CPR0050
H4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
180
CPR0432
G4
GG6
100KΩ @25°C Thermistor
181
CPD1256
G3
HH6
3W, 160V Zener, BZT03-D160
182
CPC1103
G3
JJ5
220uF, 50V, Electrolytic
182
CPC1112
G3
JJ5
220uF, 100V, Electrolytic
183
CPR0050
G3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
184
CPR0050
G3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
185
G3
NN3
186
CPR0050
G3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
187
CPR0050
F4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
188
CPR0050
F3
OO3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
189
CPR0015
F3
NN3
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
190
CPR0050
F3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
191
CPR0050
F3
NN3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
192
CPR0050
F3
MM3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
193
CPR0050
E3
MM3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
194
CPR0050
E3
MM5
0Ω, Jumper Wire
195
CPR0003
E3
NN3
CPR0050
E3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
196
E3
II1
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
196
CPR0004
E3
MM0
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CS=0.40”
196
CPR0050
E3
LL0
CPR0050
E3
LL0
0Ω, Jumper Wire
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
162A
220uF, 250V, Electrolytic
165A
XX93 S. M. Power Inductor
167A
167A
1,000uF, 35V, Electrolytic
171A
CPR0003
195A
CPD1252
196B
F3
220uF, 250V, Electrolytic
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
0Ω, Jumper Wire, CS=0.78”
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
Ω
Ω
A I
AC OQDGFH P
AC OQDGFH P
AC OQDGFH P
AC OQDGFH P
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN RIE
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
B
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PL UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BA
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC QD N
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
CQD LI
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
COQDPN R
G
F
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
COQD P U
G
F H
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
F H
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
L
H
JK
L UI
JK
N R
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
LI
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R
R U
R U
R U
R U
O P
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.03TS
0.02TMS
0.03TMS
0.51
0.51TMS
0.20TMS
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
1.35TS
0.97M
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
3.66TMS
3.99
3.15
2.89
2.89
0.02S
0.01S
0.01TM
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.22TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
1.35TS
0.97M
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.18TMS
0.22TMS
0.14S
0.33
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01S
0.01
0.01TM
0.01
Page 34

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 50
r
197
CPQ1307
E3
LL0
197
E3
LL0
0Ω Jumper, 0.600” Long.
198
CPR0033
D3
MM0
CPD1264
D3
JJ5
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
CPR0050
JJ5
0Ω, Jumper Wire
199
CPD1252
D3
LL0
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
200
CPR0050
D3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
201
CPR0029
D3
BB2
202
CPR0050
D3
FF3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
203
CPR0050
D3
FF1
0Ω, Jumper Wire
204
CPR0050
D3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
206
CPS1757
C4
CC1
207
CPC1036
D4
CC4
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
208
CPR0009
D4
CC3
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
209
CPC1102
C4
DD2
210
CPI1410
C4
CC3
Dual Comp. IC, LM393N
211
CPR0050
C4
CC3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
212
CPQ1301
C4
AA3
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
213
CPD1250
B4
AA5
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
214
CPR0050
C4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
215
CPR0050
B4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
216
CPR0050
B4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
217
CPR0050
B4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
218
CPR0050
BB7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
218
CPR0129
B4
340Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
221
CPR0050
A4
DD7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
222
CPR0050
A4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
223
CPR0140
A4
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
223
CPR0144
A4
BB7
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
223
CPR0145
A4
BB7
223
CPR0153
A4
BB7
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
225
CPD1252
A5
AA7
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
225
CPR0000
A5
AA7
2.2Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
225
CPR0003
A5
AA7
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
225
CPR0050
A5
AA7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
225
CPR0129
A5
AA7
340Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
226
A5
AA7
226
CPR0125
A5
AA7
226
CPR0127
A5
AA7
205Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
226
CPR0173
A5
AA7
64.9Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
227
CPR0018
A5
BB5
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
228
CPR0050
A5
CC5
231
CPR0141
A5
DD7
231
CPR0144
A5
DD7
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
231
CPR0145
A5
231
CPR0153
A5
DD7
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0121
A5
CC7
57.6Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0122
A5
CC7
232
CPR0124
A5
CC7
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0125
A5
CC7
88.7Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0127
A5
CC7
205Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0173
A5
CC7
64.9Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0175
A5
CC7
69.8Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
232
CPR0182
A5
CC7
54.9Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
233
CPD1252
A5
CC7
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
233
CPR0000
A5
CC7
2.2Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
233
CPR0003
A5
CC7
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
1.5A, 180V, NPN, 2SC4159E
CPR0050
30Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
198A
198A
CPR0124
D3
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
12 Cond. Straight Header
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
B4
BB7
BB7
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
88.7Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
0Ω, Jumper Wire, CS=.30”
4.42KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
DD7 15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
105Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
B
AC OQDGFH PN R U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
A
AC OQD P
A R
B
BAC OQDGFH P
A
A D
A D
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
G
F H
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
COQD P
G
FH
E
F H LI
E
G c
COQDGFH P U
E
E
COQD P
G
FH
E
C
G
FH P
E
G
F H
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
N
N
N
LI
LN R UI
N
LI
N
LI
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R U
R U
R
R U
OQP
R U
R U
R
R
OQ
R U
c
c
c
U
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.46
0.01TS
0.01
0.03
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01T
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.25TMS
0.04TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.17TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01T
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01S
0.01
0.01
0.01
Page 35

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 51
r
233
CPR0050
A5
CC7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
233
CPR0129
A5
CC7
340Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
235
CPR0050
A5
BB7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
236
CPR0050
A5
AA7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
236
CPR0129
340Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
237
CPQ1301
A6
BB7
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
238
CPQ1301
B5
CC7
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
239
CPR0010
B5
AA5
239
CPR0013
B5
AA5
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
240
CPR0050
B5J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
241
CPI1409
B5
BB6
242
CPR0141
B4
CC6
242
CPR0144
B4
CC7
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
242
CPR0145
B4
CC7
242
CPR0153
B4
CC7
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
243
CPD1252
B5
BB7
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
243
CPR0000
B5
BB7
2.2Ω ±5%, 1/4W, MF
243
CPR0003
B5
BB7
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
243
CPR0050
B5
BB7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
243
CPR0129
B5
BB7
340Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
244
CPR0122
B5
BB5
105Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
244
CPR0132
B5
BB5
604Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
245
CPR0132
C5
BB5
604Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
245
CPR0134
C5
BB5
1.21KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
246
CPR0009
C5
EE7
246
CPR0029
C5
FF7
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
247
CPR0016
C5
FF8
248
CPR0011
C5
CC3
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
250
CPR0013
C5
CC3
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
251
CPR0013
C5
CC3
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
252
CPR0011
C5
CC4
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
253
CPD1251
D5
CC3
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
254
CPC1036
C5
FF8
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
254
CPQ1303
C5
FF8
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
255
CPQ1303
C5
FF7
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
256
CPR0029
C5
FF8
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
257
CPR0019
C5
FF8
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CPR0011
C5
FF7
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
258
CPR0131
C5
BB5
464Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
258
CPR0134
C5
BB5
1.21KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
259
CPC1101
C6
FF7
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
260
CPR0130
C5
BB5
412Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
260
CPR0136
C5
BB5
1.62KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
261
CPR0050
B5
BB5
0Ω, Jumper Wire, 0.30” long.
261
CPR0145
B5
BB5
264
CPR0120
B5
BB7
264
CPR0124
B5
BB7
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
264
CPR0127
B5
BB7
205Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
264
CPR0152
B5
BB7
84.5Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
264
CPR0175
B5
BB7
69.8Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
266
CPQ1301
B5
CC7
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
266
CPR0050
B6
, Jumper Wire
266
CPR0128
B5
CC7
267
CPC1102
B5
DD6
268
CPD1251
B6
CC7
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
268
CPD1251
B6
CC7
270
CPD1251
B6
BB7
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
A6 AA7
4.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF c
Video Input IC, XRC5346A
4.42KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
257
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
100 Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
CC7 0Ω
301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
1N4148 Diode, Reverse Polarity.
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
AC OQDGFH P
B
B
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
A
AC OQD P
BAO
BAO
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAO
BAO
B
AC OQDGFH P
A R
AC OQDGFH PLNI
B
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
B
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
COQP
N
E
E
COQD P
G
FH
E
G
F H LI
E
G
FH P
CQDNR U
G
FH PLI
E
CQDNR U
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
FH P
E
CQDNR
G
FH P
E
CQDNR
E
CODGFH P
E
E
E
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LNI
N
N
LIE
N R U
N R U
N R U
LI
N R
LI
LN R UI
N
LI
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R U
R U
R U
R U
R U
U
U
U
Q
UE
R
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.01TS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.04
0.04
0.01M
0.01
0.01
2.47TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.01
0.01S
0.01
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04M
0.04TS
0.04TS
0.01TS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01M
0.03M
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01
0.01S
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.04
0.01TS
0.01M
0.04TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TS
Page 36

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 52
r
270
CPD1251
B6
BB7
271
CPD1251
B6
AA7
Reverse Polarity.
271
CPD1251
B6
AA7
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
272
CPC1026
C6
DD7
1,000pF ±5%, 100V, Film
272
CPR0138
C5
DD7
272
CPR0140
C5
DD7
273
CPR0130
C6
DD8
273
CPR0136
C6
DD8
1.62KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
273
CPR0147
C6
DD8
CPR0138
C6
DD8
274
CPQ1303
C6
DD7
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
275
CPR0009
C6
DD8
275
CPR0033
C6
DD8
275
C6
DD8
275
CPR0143
C6
DD8
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
276
CPR0004
B6
CC7
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
276
CPR0124
B6
CC7
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
276
CPR0128
B6
277
CPR0004
B6
BB7
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
277
CPR0124
B6
BB7
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
277
CPR0128
B6
BB7
301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
277
CPR0129
B6
BB7
340Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
278
CPR0004
B6
AA7
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
278
CPR0124
B6
AA7
278
CPR0128
B6
AA7
280
CPC1041
B6
BB8
.33uF ±5%, 50V, Film
280
CPR0050
B6
BB8
0Ω, Jumper Wire
281
CPC1041
B6
AA8
.33uF ±5%, 50V, Film
281
CPR0050
B6
AA8
0Ω, Jumper Wire
283
CPC1041
B6
CC8
.33uF ±5%, 50V, Film
283
CPR0050
B6
, Jumper Wire
284
CPR0124
B6
CC9
284
CPR0128
286
CPR0124
B6
BB9
286
CPR0128
288
CPR0124
A6
AA9
288
CPR0128
A6
AA9
292
CPS1752
A6
BB9
292
CPS1781
A6
BB9
293
CPR0050
A6
DD5
0Ω, Jumper Wire
295
CPR0050
A7
EE3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
296
CPI1407
A7
EE3
297
CPR0050
A7J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
298
CPC1103
A7
FF3
220uF, 50V, Electrolytic
303
CPQ1301
B7
EE7
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
304
CPC1102
B7
EE3
305
CPR0012
B7
EE7
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
307
CPR0004
B7
CC8
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
308
CPR0004
B7
BB8
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
309
CPC1036
C6
EE8
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
310
CPR0004
B7
BB8
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
311
CPQ1303
B6
AA8
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
312
CPQ1303
B6
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
313
CPQ1303
C6
CC8
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
314
CPR0050
C7J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
315
CPR0004
C7
DD8
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
316
CPC1009
C7
EE7
100pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
1N4148 Diode, Reverse Polarity.
1N4148 Diode,
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
412Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
1.00MΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
273
CPR0122
B6 CC9 301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
B6 BB9 301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
30Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
105Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
CC7 301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
CC8 0Ω
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
75.0Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
301Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
7 Cond. Straight Header
6 Cond. Straight Header
12V, 1A, Regulator, 7812
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
BB8
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
B
B
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
AC OQDGFH PLI
B
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
B
AC OQDGFH PLI
AC OQDGFH P
B N
AC OQDGFH PLI
B
AC OQDGFH PLI
B N
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
BAC OQDGFH PLNI
AC OQDGFH PLRUI
AC OQDGFH PLRUI
AC OQDGFH PLRUI
AC OQDGFH PLRUI
B N
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
N
N
N
N
N
N
N
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R
R U
R
R U
R
R U
R U
R U
R U
R
R
R
R
R
R
R U
R U
R U
R U
R U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.01M
0.01M
0.01TS
0.07
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.01
0.01
0.01M
0.04TMS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01M
0.01
0.01TS
0.01M
0.08
0.01TMS
0.08
0.01TMS
0.08
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.18TS
0.16M
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.25TMS
0.01TMS
0.14TMS
0.04
0.04TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.04
0.01
0.04
0.04
0.04
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01
Page 37

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 53
r
317
CPD1251
C7
EE7
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
318
CPC1036
C6
FF8
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
318
CPR0050
C6
FF8
0Ω, Jumper Wire
319
CPD1251
C6
EE7
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
320
CPR0012
C7
FF7
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
321
CPR0013
C7
EE8
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
322
CPR0013
C7
EE8
6.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
323
CPR0015
C7
EE8
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
324
CPR0050
C7J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
325
CPR0011
C7
DD8
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
326
CPR0004
D7
DD8
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
327
CPR0004
D7
EE9
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
328
CPR0050
DD9
0Ω, Jumper Wire
329
CPR0144
D6
EE4
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
330
CPR0004
D7
DD9
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
331
CPR0011
D7
DD9
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
!
332
CPT1505
E7
NN1
333
CPD1252
D6
FF3
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
334
CPC1103
E6
FF4
220uF, 50V, Electrolytic
336
CPR0012
E6
KK4
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
336
CPR0024
E6
KK4
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
336
CPR0050
E6
KK4
0Ω Jumper Wire
336
CPR0134
E6
KK4
1.21KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
336
CPR0138
E6
KK4
337
CPQ1307
E7
MM1
1.5A, 180V, NPN, 2SC4159E
338
CPC1102
E7
LL1
338
CPC1103
E7
LL1
220uF, 50V, Electrolytic
340
CPR0390
F7
LL1
47Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
340
CPR0391
F7
LL1
340
CPR0398
F7
LL1
100Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
341
CPR0365
F7
LL0
470Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
341
CPR0368
F7
LL1
341
CPR0371
F7
LL0
1KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
342
CPD1252
F6
LL1
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
343
CPC1003
F6
MM1
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
344
CPC1100
E6
II4
!
345
CPC1027
E6
JJ4
!
345
CPC1035
E6
JJ4
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
346
CPC1032
E6
JJ4
.01uF ±5%, 50V, Film
347
CPC1100
E6
II4
348
CPC1035
E6
II4
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
348
CPC1027
E6
II4
350
CPC1025
D6
HH4
330pF ±5%, 50V, Film
351
CPC1025
D6
GG4
330pF ±5%, 50V, Film
351
CPC1026
D6
GG4
1,000pF ±5%, 100V, Film
352
CPC1000
D6
EE4
56pF ±5%, 100V, Ceramic
353
CPR0145
D6
354
CPR0155
D6
GG6
355
CPI1406
C6
FF7
Quad Comparator IC, LM339
356
CPR0012
C6
FF7
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
356
CPR0140
C6
FF7
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
357
CPR0009
C6
GG6
357
CPR0050
C6
358
CPC1035
GG7
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
358
CPR0050
C6
GG6
360
CPR0144
C6
GG6
12.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
360
CPR0145
C6
GG6
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
BAC OQDGFH PLI
E
JK
N R U
D7
Horizontal Drive Transformer
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
CQFPIE
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
J
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
G
D H L
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
200Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
2.2KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
1uF , 50V, Electrolytic
6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film
1uF , 50V, Electrolytic
6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film
BANR U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PN R U
BAC OQDGFH PN R U
E
E
E
BAC OQDPN R U
G
FH
E
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
E
E
E
BANR U
COQDGFH PLI
E
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
E
E
COQDGFH P
E
BANR
BAC OQDGFH P
E
COQDGFH P
E
K
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
LI
LI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LI
LN R UI
LI
BANR
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LI
JK
LN R UI
J
K
LN R U
JK
N R U
JK
N R U
J
FF6 15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
FF6 0Ω, Jumper Wire, CS=.30”
C6
0Ω, Jumper Wire, CS=.40”
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
E
E
E
E
DGFHIE
BAC OQP
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLI
E
E
BAC OQDGFH PIE
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R U
R
R U
O
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.01
0.04TS
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.72TMS
0.01TMS
0.14TMS
0.01TS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01M
0.46TMS
0.04M
0.14TS
0.04
0.03M
0.04TS
0.01
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.04TMS
0.07M
0.08TS
0.03TMS
0.04TMS
0.08TS
0.07M
0.06TMS
0.06TS
0.07M
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.18TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.08TS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01
Page 38
CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 54
r
360
CPR0153
C6
GG6
20.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
361
CPR0157
D6
HH2
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
362
CPR0171
D6
HH2
362
CPR0180
D6
HH2
309KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
363
CPR0034
D5
HH2
364
CPR0050
D5
EE6
364
CPR0142
D5
EE6
7.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
365
CPR0050
C5
J
366
CPR0142
D5
EE6
367
CPR0002
D5
FF3
18Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
368
CPR0011
D5
CC3
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
369
CPC1005
E4
FF1
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
370
CPR0015
D5
JJ2
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
371
CPR0029
D5
JJ1
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
372
CPR0029
D5
KK1
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
373
CPQ1303
D5
KK1
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
374
CPC1032
D5
GG1
.01uF ±5%, 50V, Film
375
CPR0018
D5
GG1
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
375
CPR0019
D5
GG1
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
375
CPR0157
D5
GG1
375
CPR0156
GG1
93.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
376
CPC1102
D4
FF3
!
377
CPA4265
E4
GG0
V. Deflection Boost
!
377
CPI1415
E4
GG0
378
CPM2028
F4
FF0
LA7838 Heat Sink.
378
CPM2028
F4
FF0
LA7838 Heat Sink.
378
CPM2037
F4
FF0
LA7838 Heat Sink.
378
CPM2121
F4
FF0
LA7838 Heat Sink.
378
CPM2122
F4
FF0
LA7838 Heat Sink.
378
CPM2141
F4
FF0
LA7838 Heat Sink.
379
CPQ1303
E4
BB2
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
380
CPC1109
II1
CPC1035
D4
HH1
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
382
CPD1252
E4
II1
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
382
CPR0019
E4
HH1
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
382
CPR0158
E4
HH1
84.5KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
383
CPR0029
E4
384
CPR0015
E4
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
385
CPR0375
E4
HH2
.68Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
385
CPR0376
E4
HH2
387
CPC1104
KK6
388
CPR0019
F4
HH2
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
388
CPR0029
F4
HH2
200KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, CF
388
CPR0157
F4
HH2
389
CPR0050
E4
, Jumper Wire, CS=.74”
390
CPR0019
F4
II1
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
390
CPR0157
F4
II1
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
391
CPC1043
F5
HH2
391
CPC1101
F5
HH2
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
392
CPR0011
F5
HH1
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
392
CPR0012
F5
HH1
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
392
CPR0138
F5
II1
2.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
392
CPR0141
F5
HH1
4.42KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
393
CPR0050
E5
HH1
0Ω, Jumper Wire
393
CPR0155
E5
HH1
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
393
CPR0158
E5
HH1
84.5KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
394
CPR0364
E5
NN3
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
365KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
2.2MΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
7.15KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
5
381A
D5
100uF, 25V, Electrolytic
V. Deflection IC, LA7838
E4
F3
470uF, 50V, Electrolytic
AA2 200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF (CS=.45)
AA2
1.2Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
1,000uF, 35V, Electrolytic
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
BB2 0Ω
1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
100Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGF H LN R U
BAC OQDGFH PN R U
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BACDGFH
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDPN
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDPN R U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC QDGF H
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAOQ
BAC QDGFH N R U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
FH
E
G
FH
E
E
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
FH P
E
C D
E
K
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
K
L
N R U
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LI
LI
LI
LN R UI
LNI
LN R UI
LNI
LNI
LI
N
LI
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
PI
O PLI
R
QN
TS
R U
R U
R
R
O P
R
R
R
O P
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
U
U
U
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.03TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01M
0.01TS
0.04TMS
1.31M
0.28M
0.28
0.12
0.28
0.30
0.68TS
0.04TMS
0.34TMS
0.08S
0.01TM
0.01
0.01S
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TS
0.02M
0.22
0.01
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.16TMS
0.03
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01
0.01TMS
Page 39

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 55
r
394
CPR0390
E5
NN3
47Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
394
CPR0397
E5
NN3
33Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
395
CPR0050
E5
II1
396
CPR0003
E5
JJ1
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
397
CPC1037
E5
JJ1
.1uF ±5%, 250V, Film
398
CPC1009
E4
II1
100pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
399
CPC1058
D4
LL0
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
400
CPR0050
E4
J
401
CPC1043
E5
HH1
402
CPR0017
E5
GG1
36K ±5%, 1/4W, MF
402
CPR0163
E5
GG1
28.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
CPR0154
E5
403
CPR0019
E5
GG2
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
403
CPR0155
E5
GG2
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
403
CPR0156
E5
93.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
403
CPR0157
E5
GG2
404
CPR0019
E5
KK1
404
CPR0146
E5
KK1
169KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
404
CPR0158
E5
KK1
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CPR0156
E5
KK1
93.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
404
CPR0157
E5
KK1
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
405
CPD1251
E5
KK1
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
406
CPD1251
E5
JJ1
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
407
CPR0019
E5
JJ1
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
407
CPR0146
E5
JJ1
169KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
407
CPR0157
E5
JJ1
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
407
CPR0158
E5
JJ1
84.5K ±1%, 1/4W, MF
407
CPR0017
E5
JJ1
407
CPR0155
E5
JJ1
407
CPR0018
E5
JJ1
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
407
CPR0154
E5
JJ1
408
CPR0145
E5
JJ3
409
CPQ1301
D5
KK0
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
410
CPC1058
E5
411
CPQ1303
D5
JJ1
30V, .6A, NPN, PN2222A
412
CPR0029
D5
JJ0
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
413
CPR0029
D5
KK0
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
414
CPC1032
D6
.01uF ±5%, 50V, Film
414
CPC1035
D6
II2
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
415
CPI1400
E6
KK3
H. Control IC, LA7851
!
416
CPR0502
E6
II4
“I” PRA Horizontal Control
417
CPR0140
E5
KK3
418
CPR0140
E5
KK2
CPR0050
F5
OO2
CPR0050
F6
OO2
CPR0050
F5
OO2
CPR0050
F5
NN2
420
CPQ1307
E5
NN3
1.5A, 180V, NPN, 2SC4159E
420
CPQ1308
E5
NN3
421
CPR0393
F6
MM2
422
CPR0050
F5
KK1
423
CPR0006
F5
510Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
424
CPR0004
F5
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
425
CPR0367
F5
150Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
425
CPR0379
F5
OO3
68Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
426
CPS1758
F5
OO2
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, YC1
426
CPS1759
F5
OO2
.062” Dia. Bead Pin, YC1
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
E
J
402.5
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
GG1 44.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
E
E
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BACDGF H LI
E
E
E
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UI
LN R UI
BA L
JK
GG2
CDGFH R
E
127KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
404.5
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
CD I
BA H
.5
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
E
E
J
K
L
JK
JK
K
C D
BA
.5
.5
419A
419B
419E
419F
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
68.1KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
44.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
GG2 .1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
II2
BAOQPN R U
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
0Ω, Jumper, Normal Vertical.
0Ω, Jumper, Normal Vertical.
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDF PNRU
BAC OQDF PNRU
0Ω, Jumper, Reverse Vertical. G
0Ω, Jumper, Reverse Vertical. G
.1A, 200V, NPN, 2SC3467AE
390Ω ±5%, 2W, MO
0Ω, Jumper Wire
OO3
OO3
OO3
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AC OQDGFH PN R UI
E
E
E
E
E
E
CDGF H
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
J
I
N
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UIE
JK
LN R UI
JK
LN R UI
J
J
K
H
H
LI
K
LI
J
K
LN R UI
JK
LN R UIE
JK
LN R UI
JK
JK
JK
L
G
F H
E
JK
LI
BAC OQDPN R U
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R U
OQPN R U
OPI
QN
R
OH PL
Q
R U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.04
0.03
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.07TMS
0.01TMS
0.05
0.01TMS
0.16TMS
0.01T
0.01S
0.01M
0.01
0.01T
0.01S
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.01S
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.01
0.01S
0.01M
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.05TMS
0.04TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.03TM
0.08S
1.59TMS
0.79TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01
0.46
0.18TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.03
0.02TS
0.01M
Page 40

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 56
r
427
CPS1758
F5
OO2
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, YC2
427
CPS1759
F5
OO2
.062” Dia. Bead Pin, YC2
428
CPR0365
F6
OO6
470Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
428
CPR0367
F6
OO6
CPR0371
F6
OO6
1KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
430
CPR0050
F6
OO6
430
CPT1506
F6
H. Linearity Inductor
430
CPT1539
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
430
CPT1546
F6
430
CPT1557
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
430
CPT1557
F6
OO5
H. Linearity Inductor (-3T)
430
CPT1566
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
430
CPT1569
F6
OO5
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1506
F6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1517
F6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1539
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1557
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1557
F6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1565
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1566
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
431
CPT1569
F6
OO6
H. Linearity Inductor
432
CPC1002
G6
OO6
330pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
432
CPC1006
F6
200pF ±10%, 1KV, Ceramic
432
CPC1026
G6
1,000pF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
433
CPQ1305
G7
NN1
5A,1.5KV, NPN, 2SD1651
!
433
CPQ1318
G7
NN1
12A,1.5KV, NPN, 2SC5690
434
CPR0376
G7
NN1
435
CPD1252
G7
NN1
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
436
CPD1272
H7
PP7
6A, 1KV, Fast D., HER605
!
437
CPC1034
H7
.022uF ±3%, 630V, Film
!
437
CPC1047
H7
.027uF ±3%, 800V, Film
!
437
CPC1076
H7
PP7
0.1uF ±5%, 200V, Film
438
CPD1264
H6
PP6
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
!
439
CPC1034
H7
.022uF ±5%, 630V, Film
!
439
CPC1047
H7
PP7
.027uF ±3%, 800V, Film
440
CPD1259
H6
PP6
3A, 1KV Fast Diode, TF307
440
CPD1264
G6
PP6
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
440
CPD1270
H6
PP6
6A, 800V Fast Diode, TF606
440
CPD1270
H6
PP6
6A, 800V Fast Diode, TF606
440
CPD1271
H6
PP6
6A, 1KV Fast Diode, TF607
440
CPD1271
H6
PP6
6A, 1KV Fast Diode, TF607
!
441
CPC1030
H6
.01uF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
441
CPC1051
H6
.012uF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
441
CPC1055
H6
8,200pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
441
CPC1057
H6
PP6
1,000pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
441
CPC1061
H6
7,500pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
441
CPC1063
H6
PP6
5,600pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
441
CPC1065
H6
PP6
6,800pF ±5%, 1.6KV, Film
!
441
CPC1075
H6
PP6
.033uF ±3%, 800V, Film
!
441
CPC1077
H6
PP6
1,500pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
442
CPC1030
H6
.01uF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
442
CPC1047
H6
PP6
.027uF ±3%, 800V, Film
!
442
CPC1051
H6
12,000pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
442
CPC1055
H6
8,200pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
442
CPC1057
H6
1,000pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
442
CPC1061
H6
PP6
7,500pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
!
443
CPC1042
H6
PP7
.68uF ±5%, 250V, Film
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
150Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
428
0Ω, Jumper Wire
OO5
OO5 27uH Inductor
OO6
OO6
OO6
OO6
OO6
1.2Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
PP7
PP7
PP7
PP6
PP6
PP6
PP6
PP6
PP6
PP6
PP6
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDPN R U
BAC OD
BQDGFH R U
A
BD R
AC Q
BA
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BA
BAC OQDPN R U
BAC OQDPN R U
BA
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
G
F H
E
G
E
E
C
E
G c
COQDGFH PLN R UI
E
COQDGFH PLN R UI
E
E
E
CQDF H PLN R UI
E
G
FH
E
G c
F
E
G
C Q
D
G c
C
JK
LI
JK
N
K
N
J
I
L
N
JK
I
L
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
JK
K
LN R U
J
I
JK
LI
K
N
J
I
J
LI
K
H
K
N
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
PL
QFH R
O P
OFH P
TS
O
R
OH
P
R
c
c
c
UI
U
U
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.02TS
0.01M
0.01
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01S
0.74M
0.61
0.76
0.77
0.77T
0.63
0.74M
0.77
0.61
0.77T
0.77S
0.60
0.63
0.01S
0.01TM
0.07
1.40
3.45TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.08M
0.46
0.28
0.03M
0.08TM
0.46S
0.12
0.03M
0.39T
0.39T
0.39S
0.39S
0.24
0.32
0.39
0.24M
0.31
0.35
0.33
0.46
0.30T
0.24
0.46
0.32MS
0.39
0.24
0.31T
0.55
Page 41

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 57
r
!
443
CPC1050
H6
.47uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
443
CPC1056
H6
PP7
.39uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
443
CPC1059
H6
PP7
.33uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
443
CPC1062
H6
PP7
.56uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
443
CPC1069
H6
PP7
1.5uF ±5%, 400V, Film
!
443
CPC1078
H6
PP7
1.6uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
444
CPC1042
H6
OO7
.68uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
444
CPC1050
H6
PP7
.47uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
444
CPC1050
H6
OO7
.47uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
444
CPC1059
H6
PP7
.33uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
444
CPC1062
H6
PP7
.56uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
444
CPC1069
H6
OO7
1.5uF ±5%, 400V, Film
445
CPS1758
G5
PP5
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, YC4
445
CPS1759
G5
PP5
.062” Dia. Bead Pin, YC4
446
CPS1758
G5
OO5
.093” Dia. Bead Pin, YC3
446
CPS1759
G5
.062” Dia. Bead Pin, YC3
447
CPT1538
G5
448
CPC1104
F4
MM2
449
CPC1104
F4
MM2
449
CPC1113
F4
MM2
2,200uF, 25V, Electrolytic
450
CPC1104
KK6
451
CPR0050
G4
NN1
452
CPR0050
G4
NN1
!
453
CPT1516
H5
!
453
CPT1544
H5
!
453
CPT1555
H5
OO2
!
453
CPT1558
H5
OO2
!
453
CPT1561
H5
OO2
!
453
CPT1568
H5
OO2
454
CPR0050
I6
456
CPC1044
I6
OO8
2.7uF ±10%, 100V, Film
456
CPC1064
I6
OO8
6.8uF ±5%, 100V, Film
457
CPT1504
I7
457
CPT1528
I7
457
CPT1560
I7
OO7
100uH Horz. Width Inductor
457
CPT1564
I7
OO7
70uH Horz. Width Inductor
458
CPT1511
J7
50uH Control Inductor
460
CPQ1315
J6
461
CPR0006
J6
NN8
462
CPD1253
J6
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
463
CPC1005
J6
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
464
CPR0365
J6
465
CPR0050
I6
PP1
0Ω Jumper Wire
465
CPR0352
470Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
466
CPR0050
I6
, Jumper Wire
468
CPR0433
J5
EE9
24V coil, 200V @ .5A Relay
470
CPR0352
J6
EE9
470Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
473
CPR0050
G6J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
475
CPR0374
H7
PP7
.10Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
476
CPR0374
H7
PP7
.10Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
477
CPD1266
H7
478
CPD1266
H7
480
CPR0050
G7J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
500
CPC1041
F4
NN4
.33uF ±5%, 50V, Film
501
CPR0009
G4
NN4
502
CPR0050
G4
NN5
503
CPR0017
G4
OO4
36K ±5%, 1/4W, MF
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
PP7
OO5
PP3 12 mH, H. Raster Shift Inductor
1,000uF, 35V, Electrolytic
1,000uF, 35V, Electrolytic
G4
I6 PP1
1,000uF, 35V, Electrolytic
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
31KHz, .75mA, FBT Meritron T-8090B
OO2
OO2 15KHz, 1.5mA, FBT Meritron CT-8227
31KHz, .45mA, FBT Meritron CT-8819 G
15KHz, FBT Hitachi BW02651
31KHz, FBT Meritron CT-8943
31KHz, FBT Meritron c
OO7 0Ω, Jumper Wire
OO7 750uH Horz. Width Inductor
OO7 150uH Horz. Width Inductor
OO7
OO8 8A, 100V, Mos Fet, IRF520
510Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
NN7
OO8
OO8 470Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
MM2 0Ω
PP7 2A, 400V, Fast D., HER205
PP7 2A, 400V, Fast D., HER205
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF G
0Ω, Jumper Wire G
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BA
A L
B
BAC OQDPN R U
BAC OQDPN R U
AC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BA
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BA R U
BAC OQD P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDPN R
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PN R
BAC OQDGFH PN R
BAC OQDGFH PN R
BAC OQDGFH PN R U
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
DF H PL
E
G c
N
J
I
K
G
FHE
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
E
E
E
COQD
G
FH PLN R UI
E
COQD P
FH
E
E
COQDGFH PLNI
E
FH
E
G
E
E
E
E
E
E
G
F H
E
E
E
G
F H
E
E
E
E
G
F H
E
F H
E
F H
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
LI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
N R U
LI
N R U
LI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LN R UI
LI
LN R UI
LN RI
LN RIE
LI
M
M
LI
LI
LI
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
O Q
R
O P
T
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
U
UE
UE
U
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
0.31
0.45
0.37M
0.50
0.79
0.68
0.55
0.31
0.31
0.37T
0.50S
0.79
0.02TS
0.01M
0.02TS
0.01M
0.74TMS
0.22S
0.22MS
0.22TMS
0.01S
0.01TM
12.78S
14.18M
13.13
12.78
13.13
13.13T
0.01TMS
0.37TMS
1.16
0.76M
0.74
0.75TS
0.58
0.70TMS
0.41TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.06TMS
0.01TMS
0.83TMS
0.06TMS
0.01T
0.07M
0.07M
0.01TMS
0.08T
0.01T
0.01T
0.01T
Page 42

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 58
r
CPR0151
G4
OO4
73.2KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
503
CPR0158
G4
OO4
84.5KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
504
CPR0147
G4
OO4
505
CPR0017
G4
OO4
36KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, MF
505
CPR0018
G4
OO4
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
505
CPR0145
G4
OO4
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
507
CPC1003
G4
PP3
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
507
CPC1057
G4
PP3
1,000pF ±3%, 1.6KV, Film
508
CPR0050
G5J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
509
CPQ1308
G4
OO4
510
CPR0034
G5
OO4
511
CPR0034
G5
OO4
512
CPD1252
G5
PP4
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
512
CPD12XX
G5
PP4
6A, 1,200V, BYD33U Diode
514
CPR0029
G5
OO4
200KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
515
CPC1002
H5
PP4
330pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
515
CPC1005
H5
PP4
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
516
CPR0004
H6
OO6
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
517
CPC1037
H6
OO5
.1uF ±5%, 250V, Film
517
CPC1068
H6
OO5
.01uF ±5%, 400V, Film
518
CPT1556
I6
PP4
Dynamic Focus Transformer
520
CPR0352
J5
PP1
470Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
521
CPR0050
J4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
522
CPR0050
J4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
523
CPR0050
J4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
524
CPR0050
H4
PP2
0Ω, Jumper Wire
525
CPR0050
H4
PP2
0Ω, Jumper Wire
526
CPR0050
H4J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
529
CPR0169
E1
GG6
191KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
529
CPR0170
E1
GG6
294KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
529
CPR0179
E1
GG6
392K ±1%, 1/4W, MF.
CPR0050
F1J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
531
CPR0050
F1J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
532
CPR0050
G1
KK7
0Ω, Jumper Wire
533
CPR0050
G1
KK7
0Ω, Jumper Wire, CS=.450”
600
CPB1615
Vertical Amplifier PCB
601
CPQ1314
W2
TIP32A Transistor
602
CPQ1313
W1
TIP31A Transistor
603
CPQ1313
W1
TIP31A Transistor
604
CPD1264
W1
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
605
CPR0376
W1
1.2Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
607
CPR0003
V1
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
608
CPR0003
V1
4.7Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
610
CPR0377
V1
3.3Ω ±5%, 1W, MO
611
CPD1264
V1
2A, 600V Fast D., FR205-F
612
CPI1415
V2
V. Deflection IC, LA7838
613
CPS1858
V2
Vertical Amp Wiring Cable
800
CPB1613
L4
YY0
Video Board PCB E7
801
CPC1058
YY2
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
802
CPR0050
J
803
CPR0510
P1
RR2
“K” PRA Video Amplifier
804
CPR0050
J
805
CPQ1308
SS4
806
CPR0050
J
807
CPR0050
N1J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
808
CPR0050
P1J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
810
CPQ1308
SS1
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
503.5
.5
1.00MΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF G
.1A, 200V, NPN, 2SC3467AE G
2.2MΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
2.2MΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF G
529A
P1
P1
P1
P1
P1
N1
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
.1A, 200V, NPN, 2SC3467AE
0Ω, Jumper Wire
.1A, 200V, NPN, 2SC3467AE
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
A LI
A
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UI
AHI
BC O QDGF PLN R U
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
H
G
F
E
F H
E
G
FH
E
G
F H
E
E
F H
E
G
F H
E
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
G
F H
E
E
E
E
E
G c
FH
E
G
F H LI
E
E
E
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LI
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
T
X
X
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
x
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.01
0.01
0.01T
0.02T
0.24T
0.01TMS
0.18T
0.01T
0.01T
0.01
0.01T
0.01T
0.01T
0.01T
0.07
0.07T
0.86T
0.06T
0.01T
0.01T
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.14X
0.14X
0.14X
0.03X
0.02X
0.01X
0.01X
0.02X
0.03X
1.31X
0.89TMS
0.05TMS
0.01TMS
1.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.18TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.18TMS
Page 43

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 59
r
811
CPR0510
RR0
“K” PRA Video Amplifier
812
CPQ1301
N2
SS2
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
813
CPR0050
J
814
CPR0050
J
815
CPC1003
VV5
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
816
CPC1058
N2
YY2
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
817
CPC1058
N1
UU2
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
818
CPC1003
VV5
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
820
CPR0050
J
821
CPR0050
J
822
CPQ1301
P2
SS4
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
823
CPC1037
TT3
.1uF ±5%, 250V, Film
824
CPC1040
SS3
.015uF ±10%, 250V, Film
825
CPR0127
SS4
205Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
826
CPR0050
J
827
CPQ1301
SS3
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
828
CPQ1309
SS3
830
CPR0011
TT4
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
831
CPR0011
TT2
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
832
CPQ1301
SS0
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
833
CPQ1309
SS0
834
CPR0127
SS1
205Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
835
CPD1250
UU0
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
836
CPR0011
TT1
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
837
CPQ1309
TT2
838
CPC1005
TT1
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
840
CPD1250
TT1
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
841
CPD1250
TT4
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
842
CPQ1309
P2
TT4
843
CPC1005
TT4
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
844
CPR0011
TT4
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
845
CPD1250
VV0
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
846
CPC1043
XX2
1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
847
CPD1253
WW2
1A, 600V, Fast D., 1N4937
848
CPD1252
WW2
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
849
CPD1250
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
850
CPQ1306
ZZ3
851
CPR0365
WW0
851
CPR0371
WW0
1KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
852
CPR0018
ZZ3
853
CPC1034
N3
XX1
.022uF ±3%, 630V, Film
853
CPC1035
N3
XX1
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
853
CPC1038
N3
XX1
.068uF ±5%, 100V, Film
853
CPC1040
N3
XX1
.015uF ±10%, 250V, Film
853
CPC1047
N3
XX1
.027uF ±3%, 800V, Film
853
CPC1058
N3
XX1
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
853
CPC1068
N3
XX1
.01uF ±5%, 400V, Film
!
854
CPC1026
N3
XX1
1,000pF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
854
CPC1027
N3
XX1
6,800pF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
854
CPC1035
N3
XX1
3,300pF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
854
CPC1038
N3
XX1
.068uF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
854
CPC1041
N3
XX1
0.33uF ±5%, 50V, Film
!
854
CPC1046
N3
XX1
.047uF ±5%, 200V, Film
!
854
CPC1052
XX1
!
854
CPC1054
N3
XX1
.039uF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
854
CPC1067
N3
XX1
.56uF ±5%, 100V, Film
!
854
CPC1073
N3
XX1
0.033uF ±5%, 200V, Film
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
N1
N2
N2
N2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
P2
N2
N2
N2
N2
N3
N3
N2
N3
N3
P3
P3
P3
P3
P3
P3
P3
P3 VV0
P3
N3
N3
N3
N3
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
.1A, 200V, PNP, 2SA1370AE
.1A, 200V, PNP, 2SA1370AE
.1A, 200V, PNP, 2SA1370AE
.1A, 200V, PNP, 2SA1370AE
.1A, 1.5KV, NPN, 2SC3675
470Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
.018uF ±5%, 200V, Film
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BA
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
G
H
D
FE
D
H LI
C
G
I
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
J
K
K
J
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
N R
LN R UIE
L
N R
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
OQP
O
Q
P
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v.
U
U
U
v.
v
v
v
v.
v
v
v
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
1.02TMS
0.04TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.05TMS
0.05TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.07TMS
0.06TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.23TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.23TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.23TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.23TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.16TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.88TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TMS
0.08
0.08
0.08
0.06T
0.46
0.05
0.07
0.07
0.07
0.08
0.08TS
0.08
0.32
0.07
0.06
0.18M
0.21
Page 44

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 60
r
!
854
CPC1076
N3
XX1
0.1uF ±5%, 200V, Film
855
CPR0371
N4
XX1
1KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
856
CPR0366
YY1
!
857
CPC1034
N3
WW2
.022uF ±3%, 630V, Film
!
857
CPC1037
WW2
.1uF ±5%, 250V, Film
!
857
CPC1040
N3
WW2
.015uF ±10%, 250V, Film
!
857
CPC1046
WW2
!
857
CPC1052
WW2
!
857
CPC1074
N3
WW2
.068uF ±5%, 200V, Film
858
CPR0019
P3
YY3
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
858
CPR0146
YY3
169KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
858
CPR0170
P3
YY3
294KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
859
CPR0032
YY2
860
XX2
10uF, 200V, Electrolytic
861
CPR0050
P3J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
862
CPR0050
J
863
CPS1772
ZZ3
863
CPS1849
P4
ZZ3
12 Cond. Video Cable, 17”
864
CPR0050
J
865
CPR0050
J
866
CPR0009
YY3
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
867
CPR0050
J
868
CPC1101
VV2
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
868
CPC1110
VV2
100uF, 50V, Electrolytic
869
CPR0050
M3
XX1
0Ω, Jumper Wire
870
CPD1250
VV2
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
871
CPC1002
WW1
330pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
872
CPR0004
VV2
270Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
872
CPR0011
M4
VV2
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
872
CPR0024
VV2
872
CPR0141
M4
VV2
4.42KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
872
CPR0143
M4
VV2
10.0KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
873
CPR0370
WW1
874
CPR0011
VV1
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
875
CPR0351
L4
YY2
150Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
876
CPR0019
L4
VV1
100KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
!
877
CPS1850
L3
XX0
Dual Focus CRT Socket
!
877
CPS1852
L3
XX0
Single Focus CRT Socket
878
CPC1003
XX1
879
CPR0002
L3
XX2
18Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF
880
CPR0351
YY1
881
CPR0368
M3
YY1
2.2KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
882
CPR0351
XX1
883
WW1
883
CPR0371
WW1
1KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
884
CPR0012
K2
VV6
2.7KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
885
CPC1040
SS6
.015uF ±10%, 250V, Film
886
CPD1250
VV0
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
887
CPC1037
TT6
.1uF ±5%, 250V, Film
888
CPD1251
VV6
10mA, 75V Diode, 1N4148
889
CPC1003
WW6
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
890
CPR0009
K2
WW7
1KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
891
CPR0015
K2
VV6
22KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
892
CPC1101
YY5
893
CPR0050
J
894
CPC1101
YY5
895
CPC1101
YY4
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
N4
N3
N3
N3
P3
P4
CPC1106 P3
P4
P4
P4
P4
N4
N4
N4
N4
N4
N4
M4
M4
M4
M4
L3
L3
L3
CPR0365 L2
L2
K3
K3
K2
K2
L2
L2
L2
L2
L2
100KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
.047uF ±5%, 200V, Film
.018uF ±5%, 200V, Film
30Ω ±5%, 1/4W, CF, Hairpin.
0Ω, Jumper Wire
12 Cond. Video Cable, 12”
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
10KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
150Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
150Ω ±10%, 1/2W, CC
470Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
0Ω, Jumper Wire
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
10uF, 50V, Electrolytic
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BA
BAC OQDPN R
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PNRE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC QDGF H LIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDPN R U
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
COQDGFH PE
G
F H
G
F H
CQD
G
F H
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LI
N U
LIE
N R U
LN R UIE
L UI
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
N R U
LIE
LIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LIE
N R
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
R
OPN R U
O P
v.
v
v
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
U
U
v.
v.
v.
v
v.
v
v
v.
v.
v
v
v
v
v.
v.
v
v
v
v.
v.
v.
v.
v.
v
v
v
v
v.
v.
v
v
v
v
v
v.
v.
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
0.28
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.08
0.07
0.06TS
0.32
0.07
0.14M
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.24M
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
1.24TMS
1.40
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.03
0.14TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01M
0.01
0.01
0.01TS
0.01
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.06TMS
0.01TMS
1.31
0.95TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.06TMS
0.01TMS
0.06TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.01TMS
0.06TMS
0.02TMS
0.07TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.03TMS
0.01TMS
0.03TMS
0.03TMS
Page 45

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 61
r
899
CPD1250
N3
UU0
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
900
CPR0365
N3
WW0
900
N3
WW0
901
CPC1040
SS1
.015uF ±10%, 250V, Film
902
CPR0050
J
903
CPD1252
VV3
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
904
CPR0050
J
905
CPD1252
WW3
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
906
CPD1252
WW3
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
907
CPC1058
WW4
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
908
CPR0016
YY4
909
CPR0024
M1
ZZ4
3.3KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
910
CPR0016
YY5
911
CPR0016
M2
YY5
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
912
CPR0018
ZZ4
62KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
913
CPC1037
TT0
.1uF ±5%, 250V, Film
914
CPR0145
ZZ4
15.8KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
915
CPR0050
J
917
CPR0506
WW4
“C” PRA, CRT Auto Bias
918
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
920
CPI1405
WW4
Quad OP Amp IC, LM324
921
CPC1058
WW4
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
922
CPC1036
WW4
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
923
CPC1058
WW5
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
924
CPC1036
WW5
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
925
CPC1058
WW5
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
926
CPC1036
WW6
.047uF ±5%, 50V, Film
927
CPI1402
L2
XX4
CRT Bias IC, CA3224E
928
CPQ1301
WW7
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
930
CPC1058
VV7
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
931
CPR0011
WW7
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
932
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
933
CPR0011
WW7
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
934
CPC1058
RR7
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
935
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
936
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
937
CPR0510
K1
RR5
“K” PRA Video Amplifier
937
CPR0511
K1
RR5
“Blue” PRA Video Amplifier
938
CPR0011
VV7
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
940
CPR0140
VV7
941
CPC1003
VV4
2,200pF ±20%, 1KV, Ceramic
942
CPQ1302
VV7
30V, .3A, PNP, D, MPSA64
943
CPQ1308
K2
SS7
.1A, 200V, NPN, 2SC3467AE
944
CPR0050
K2J 0Ω, Jumper Wire
945
CPQ1301
SS7
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
946
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
947
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
948
CPR0011
TT7
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
950
CPQ1301
SS5
60V, .6A, PNP, PN2907A
951
CPQ1309
SS6
952
CPR0050
J
0Ω, Jumper Wire
953
CPR0127
SS6
205Ω ±1%, 1/4W, MF
954
CPQ1309
TT7
955
CPR0011
TT7
1.8KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
956
CPC1005
TT6
1,000pF ±10%, 500V, Ceramic
957
CPC1043
TT5
1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
957
CPC1058
TT5
.1uF ±5%, 50V, Film
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
470Ω ±5%, 1/2W, CF
CPR0371
N2
N2
N2
M2
M2
M2
M2
M2
M2
M2
N2
N1
N1
M1
M1
M1
M1
M1
L1
L1
L1
L1
K1
K1
K1
L1
K1
K1
L1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K1
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K2
K3
K3
K3
K3
K3
1KΩ ±5%, 1/2W, CF
0Ω, Jumper Wire
0Ω, Jumper Wire
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
0Ω, Jumper Wire
3.92KΩ ±1%, 1/4W, MF
.1A, 200V, PNP, 2SA1370AE
.1A, 200V, PNP, 2SA1370AE
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BCD N R U
AOQ
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLIE
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
JK
JK
JK
LN R UIE
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UIE
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UIE
JK
JK
LN R UIE
JK
JK
LN R UIE
JK
JK
LN R UIE
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
G
FH PLIE
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
N R U
N R U
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
v
v.
v.
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v.
v.
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v.
v.
0.02TMS
0.01TS
0.01M
0.06TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.05TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.07TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.79TMS
0.01TMS
0.24TMS
0.05TMS
0.04TMS
0.05TMS
0.04TMS
0.05TMS
0.04TMS
3.47TMS
0.04TMS
0.05TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.05TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
1.02M
1.02TS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.02TMS
0.06TMS
0.18TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.04TMS
0.23TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.23TMS
0.01TMS
0.01TMS
0.16M
0.05TS
Page 46

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 62
r
958
CPD1250
TT7
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
959
CPD1250
K4
WW0
100mA, 200V Diode, FDH400
961
CPS1758
K4
YY1
.093” Bead Pin, Dag. GND
963
CPM2003
K4
Cable Tie, 4”
964
CPM2043
Video Board Cover
965
CPM2051
Video Board Insulating Sheet
!
971
CPS1766
ZZ0
!
971
CPS1771
ZZ0
!
971
CPS1786
ZZ0
2793, Degaussing Coil
!
971
CPS1828
ZZ0
1793, Degaussing Coil
!
971
CPS1856
ZZ0
3693, Degaussing Coil
!
971
CPS1860
ZZ0
1993, Degaussing Coil
CPS1775
14” Grounding Strap
CPS1791
CPS1792
27” Grounding Strap
A
A6
AA9
B
C
!
CRT
17”
!
CRT
17”
!
CRT
CPP1703
20”
0
!
CRT
CPP1707
27”
0
!
CRT
CPP1708
27”
5
!
CRT
CPP1711
14”
!
CRT
CPP1717
20”
0
!
CRT
CPP1721
36”
5
!
CRT
CPP1724
20”
0
!
CRT
CPP1725
19”
0
!
CRT
CPP1726
17”
0
!
CRT
CPP1727
17”
5
!
CRT
CPP1728
27”
CRT
CPS1831
17” Grounding Strap
CRT
CPS1846
36” Grounding Strap
CS
A6
DD9
CSync Pin 1&2 of Conn.292
G
Video, -Analog, Selection.
H
Vertical linearity Adjustment.
I
Vertical linearity Adjustment.
IA
D6
GG4
Reverse Horizontal Sync.
IC
E6
KK4
Horizontal Frequency Adj.
ID
E6
KK4
Horizontal Frequency Adj.
J
A5
Video, +Analog, Red Gain.
JC
D1
GG5
Power Supply V+ Adj.
JD
D1
HH7
Power Supply V+ Adj.
JE
E1
HH5
Power Supply V+ Adj.
K
Video, +Analog, Green Gain.
L
A5
CC7
Video, +Analog, Blue Gain.
M
CPM2024
Front Support Bracket
M
CPM2025
Rear Support Bracket
M
CPM2026
Right Support Bracket
M
CPM2029
Left Support Bracket
M
CPM2060
Rear Support Bracket
M
CPM2113
G6
H. Transistor Support
M
CPM2550
G6
H. Transistor Support Screw
M
CPM2551
G6
H. Transistor Support Screw
M
C6
DD9
Reverse Hs, AC Video Clamp.
N
C7
DD8
Reverse Hs, AC Video Clamp.
P
A5
AA5
Video, -Analog, Blue Offset.
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
K3
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQD P
BAC OQDGF PLN R UI
JK
JK
JK
J
JK
LN R UI
HE
1493, Degaussing Coil
BACD
2093, Degaussing Coil
G
HE
JK
LI
998
998
20” Grounding Strap
BA C
JK
998
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder conn
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
B6 BB9 Green Video, Input Line Filter.
B6 BB9 Blue Video, Input Line Filter.
B5 BB5
D5 KK1
D5 JJ1
B5 BB7
Red Video, Input Line Filter. s
Chunghwa M41AJR53X46
Orion M41KXU100XX01
RCA A48AAB37X01 CRT. c
RCA A68AEG25X07 CRT.
RCA A68AEG25X05 CRT. c
Chunghwa M34AFA13X07 CRT.cv
RCA A48AAB37X03 CRT.
RCA A90AEJ15X02 CRT. c
Chunghwa A48AGY13X87 CRT. v
Samsung M46QCY261X112 CRT.
Chunghwa M41AGE13X47R CRT.
Samsung M41QCJ761X172 CRT.
Samsung M68QCP891X002 CRT.
BACD
JK
FHE
G c
G
FHE
N
M
LI
BAC QDH NsMS
JK
BAC OQDH PIE
JK
G
BAC OQDF H P
JK
LN UIE
AA7
A
G
B
BAC OQDGFH P
JK
LN R UIE
BACD R
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
JK
LN R UIE
LN R UIE
LNIE
M
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
BAC OQDGFH P
BAC OQDGFH P
G
FH P
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
BAC OQDGFH PLN R UIE
B
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
OQPN
R
OQPLNI
R
S
R
Q
O P
T
R U
O PLRUI
T
TMS
R
TMS
P
P R
OQ
TMS
TMS
v
v
v
v.
v.
v.
c
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
c
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.02TMS
0.01MS
0.61TMS
0.18
1.70
3.15M
14.82TS
2.42
15.14
9.80
0.33
0.33M
0.77TS
s
s
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
U
c
c
c
c
122.5
300.3
288.7
87.50
105.0
918.7
101.5
245.0
140.0
218.7
c
c
U
c
0.33
0.79
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
U
UE
s
s
s
s
s
c
U
c
c
c
c
1.87TMS
0.18TM
0.42TMS
0.42TMS
0.26S
c
c
c
0.03TMS
s
s
s
Page 47

CERONIX XX93 Monitor Part List 63
r
Q
A2
NN7
R
C2
NN7
S1
Raster Shift, One Unit.
S2
Raster Shift, Two Units.
S4
Raster Shift, Four Units.
SL
G5
OO3
Raster Shift Left.
SR
G5
OO3
Raster Shift Right.
T
C5
BB4
M. Gain Limit Adjustment.
T
C5
BB4
M. Gain Limit Adjustment.
TR
G2
JJ6
U
C5
BB4
M. Gain Limit Adjustment.
V
D6
HH2
Vertical Frequency Adj.
W
C3
Touch Screen -V Set.
V+
107
106V to 108V
V+
111
110V to 112V
V+
114
113V to 115V
V+
124
123V to 125V
V+
127
126V to 128V
V+
52.0
51.3V to 52.7V
V+
54.0
53.3V to 54.7V
V+
54.5
54V to 55V
V+
55.5
55V to 56V
V+
64.5
64V to 65V
V+
70.0
69.5V to 70.5V
V+
72.5
72V to 73V
V+
77.5
77V to 78V
CPB1606
CPR0050
0Ω, Jumper Wire
CPD1252
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
CPD1267
TZL200B 200V ±5% .5W, Z.D.
CPR0016
CPR0171
!
CPR0425
CPR0431
250VAC, 6Ω, 0.145A R. Fuse.
CPC1037
.1uF ±10%, 250V, Film
CPR0157
127K ±1%, 1/4W, MF
CPD1252
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
CPD1252
1A, 1KV Diode, 1N4007
CPC1069
CPC1110
CPQ1315
CPD1257
CPD1269
P6KE27A 27V 600W, TVS
!
CPC1011
2,200pF ±20%, 250VAC
!
CPR0436
!
CPR0437
CPR0050
0Ω, Jumper Wire
CPR0360
!
CPC1011
2,200pF ±20%, 250VAC
CPM2047
ISO XFR 75W Housing
TX
CPM2146
ISO XFR 100W Housing
!TXCPT1507
75W Isolation Transformer.
!TXCPT1553
100W Isolation Transformer
!TXCPS1830
Input Power Cable
!TXCPS1762
Output Power Cable
TX
CPM2517
Vinyl Grommet
A CPA4233, 1493-CGA
B CPA4235, 1493-CGA
C CPA4200, 1493-VGA
D CPA4252, 1493-SVGA
E CPA4243, 1793-VGA
F CPA4244, 1793-VGA X Vertical Deflection Booste
G CPA4247, 1793-SVGA
H CPA4250, 1793-SVGA
I CPA4221, 1993-VGA
J CPA4255, 1993-VGA
K CPA4249, 1993-SVGA
L CPA4256, 1993-SVGA
M CPA4112, 2093-CGA
N CPA4166, 2093-CGA
O CPA4224, 2093-VGA
P CPA4227, 2093-VGA
Q CPA4108, 2093-VGA
R CPA4104, 2793-CGA
∆ Bd.# Part No. Bd. Sch. Ref. Description A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Com. PRICE
S
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
Solder Conn.
F5 PP3
F5 PP3
F5 PP3
Verrable Parabolic Pincushion Range.
Verrable -Linear Pincushion Range.
Cut pin1 of 166, solder pad 1&2.
K
ADFH P
G
G
J
J
JK
LRUIE
LI
LRUI
AQDF HE
C D
BQ
G
N
COQD
N RcTM
B
A
K
J
I
L
FE
G c
H
T500
T501
T502
T503
T504
T505
T506
T507
T508
T509
T510
T511
T512
T513
T514
T515
T516
T517
T518
T518
T519
T519
T520
TX
ISO XFR PCB. .062", CEM-1.
33KΩ ±5%, 1/4W, CF
365K ±1%, 1/4W, MF
3 Amp Slow Blow Fuse.
1.5uF ±5%, 400V, Film
100uF ±20%, 50V Electrolytic
IRF520 100V, 8A Mos Fet.
1N4742A 12V ±5%, 1W,
Relay; 8A, 250VAC, Coil; 24VDC
10A, DPDT Voltage Select
2.7Ω ±10%, 1W, CC Resistor.
S CPA4231, 2793-VGA
T CPA4254, 2793-VGA
U CPA4172, 3693-CGA
V ISO XFR-75W
W ISO XFR-100W
Q
TS
P
TS
O
P
S
U
U
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V W
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V W
V W
V W
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
s
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
c
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
W
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
W
t
t
W
t
t
t
t
0.40
0.01
0.01
0.12
0.01
0.01
0.32
0.55
0.07
0.01
0.01
0.01
0.79
0.14
0.41
0.04
0.23
0.09
1.30
2.68
0.01
0.61
0.09
3.47
14.88
28.44
0.60
0.51
0.08
Page 48

VIDEO INTERFACE CIRCUIT, FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION (+ & - Analog).
The video interface circuit is a general
purpose RGB type input circuit. This circuit
connects the external video signal to the video
amplifiers. It can accept, DC or AC coupled
positive going analog, negative going analog,
and 4 line TTL.
SIMPLIFIED VIDEO INTERFACE CIRCUIT:
Black Level (5.6V)
1. NEGATIVE GOING ANALOG MODE.
Saturated Color (1V)
3.5V
RED
VIDEO
INPUT
301Ω
271
340Ω
236278
7.5V BIAS LINE
6.3V
2
3
-Analog Black Level (-A BL)
+12V
C5346
241
In the negative analog mode, the video signal
has a black level (5.6V) which is the -A BL
voltage. The saturated color is the lowest input
voltage (.9V-1.1V). The current amplitude to
the video amplifiers is defined by resistors 278
& 236 and the master gain voltage.
236
278
The particular mode of operation is selected by
inserting jumpers, different value components,
and solder bridges. The Production Assembly
Drawings (PADs) are given in the appendix
which describe the component differences.
200
RED channel shown
Blue channel only
Ω
3.6K
MG
16
6
12
VIDEO
AMPS
MASTER
GAIN&
BLANKING
4.7K
239
G
+12V
For the blue channel only, 15% of the output
current is subtracted by resistor
239
265 .
Signal sources with 8 bit drivers, that use 2
bits for the blue channel use this 15% offset.
To prevent input line ringing from exceeding
the saturated color voltage limit, a clamp diode
271
271 has been added.
Saturated Color (.70V)
2. POSITIVE GOING ANALOG MODE.
Black Level (0V)
RED
VIDEO
INPUT
15.8K
261
270Ω 15KHz
75Ω 31KHz
278
11
.44V
7.5V BIAS LINE
+ANALOG ENABLE
2
+12V
C5346
0-11V or 12V
15.8K
75Ω
288
75.0Ω
226
223
1
J
0Ω
241
In the positive analog mode, a bias current of
.6mA flows to the input pin 2. This current is
set by resistor
261
261 at the +Analog Enable
input pin 11. The .6mA produces a voltage,
across the parallel resistance of the game and
288 plus resistor 278 , at pin 2. If the
278288
external source resistance is 75 ohms, the black
level voltage at pin 2 is .18V for 15KHz and
.07V for the 31KHz.
200Ω
RED channel shown
3.6K
MG
16
12
VIDEO
AMPS
MASTER
GAIN &
BLANKING
The black level voltage is set by resistor
divider 223 & 226 to compensate for the
226223
bias current voltage drop. An optional,
variable black level, is accomplished with the
black level adjustment pot.
The input termination resistor 288
288
reduces video line ringing and produces a
dark screen when the video input connector
is disconnected.
The normal saturated color is set at .70
volts. Higher saturated color levels can be
accommodated with resistor or gain changes.
64
Page 49

5.6V to 1.1V, NEGATIVE ANALOG, DC COUPLED, VIDEO INTERFACE CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
Red Video Amp.
Green Video Amp.
Blue Video Amp.
FIL.
HSync
CRT Auto Bias
V
Sync
TC7 Red
TC5 Green
TC 3 Blue
Blanking & Beam Current Limit
FDH400
084
FDH400
086
FDH400
213
16 13 5 12396 11
BoRo Go GAINM+ ENA
B
IN R
R
R
Vertical O/S or Delayed Vertical O/S.
P
4.7K
239
BL
Controls XRC5346A
B+G+R=∑
ABA
TC 6TC 10
End Vertical Blanking
+12V
G
IN
Beam current
Feedback
Beam current
Feedback
Beam current
Feedback
Current
Buffer
SOCKET BOARD CONNECTOR (TC) 206
S
1.62K 604Ω 1.21K
260 244 245
1.21K
258
10
+12V
A- BL
R
G
Beam
T
TTL
U
2.7K
064
0Ω, CS=.30"
228
241
IN
BG
21 1415 7 8
340Ω 340Ω
236
301Ω
278
1N4148
271
218 266
340Ω 301Ω
277
1N4148
270
GND
301Ω
276
SOCKET BOARD
ARC PROTECT
Auto
Bright
VIDEO GAIN
LINE
1.62K
076
GND
R
B
4-7VDC
5-9Vpp 61,B4
4
1N4148
268
Vs
+12V
GND
0Ω
293
12V
VC
0
3.5V
800
+
PN2222
CRT
127V TC8
TC1 +16V
TC2 GND
TC4 +12V
+
100uF
209
Remote
1K
062
100uF
+12V
274
Control
RC2
11.5V-12.5V
The clamp
267
diodes are
installed
backwards with
respect to the
PCB legend.
TC11
TC12
PCB
+12V
M. GAIN
1K
485
GND
Note:
3.92K
272
2.15K1K
273275
0VDC
56V 28,D3
Filament
Fil. Ret.
Screen
Focus
EHT
+127V
+16V
+12V
GND
271
270
268
Hs
Video
R
VC
4
RED
INPUT
GND
VC
3
Connecter
292
G
VC
5
GREEN
INPUT
BLUE
INPUT
B
VC
6
In each of the video interface circuit configurations,
current from the interface circuit is converted to a
voltage at the CRT cathodes. The simplest current
path is accomplished by the negative analog video
interface configuration.
The voltage drop across the input resistors
236
236 , for the red channel, is the current which drives
278
278 and
the video amplifiers when the video gain line is at
8.2 volts. For a lower gain line voltage, part of the
current is directed to the +12 volt line. During blanking
all the input current flows to the +12 volt line.
and there is no video amplifier output. For the red and
green channels, a 1 volt change at the video input
produces a 15 volt change at the video amplifier output.
For the blue channel this change is 18 volts but resistor
265
265 subtracts the equivalence of .6 volts from the input
which results in the same saturated color as the red and
green channels.
270
The clamp diodes
271 268
271 , 270 , & 268 limit the
maximum current to the video amplifiers. This avoids
over driving the video amplifiers when undershoots at
the input cables are present. The clamp reference
voltage is set by resistors
transistor 274 . Load resistor 275 stabilizes this
274
272 , 273 , and buffer
272
273
275
buffered clamp voltage.
65
Page 50

0V to .7V, POSITIVE ANALOG, DC COUPLED, VIDEO INTERFACE CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
To Video Board
TC7 Red
TC5 Green
TC 3 Blue
Blanking & Beam Current Limit
FDH400
084
FDH400
086
FDH400
213
11.5-12.5V
+12V
GND
15.8K
261
16 13 9 6
o
o GAIN
RoG
R
B
IN R
R
+ EN
A
B
BL
Controls XRC5346A
+12V
IN
ST
- BL
R
1.21K
311
A
604Ω 1.21K
258
1.62K
260 244 245
10
G
0Ω
5
TTL
2.7K
228
064
U
241
BG
M
IN
21 1415 7 8
A5
0Ω
J
75.0Ω
15.8K* 15.8K* 15.8K*
225
1.87K
223
226
B5
0Ω
218
0Ω
A5
K
243
242
84.5Ω
264
L
1.62K
076
12
GND
R
B
VIDEO GAIN
LINE
4-7VDC
5-9Vpp
12V
VC
4
56pF
205Ω
265
0Ω
233
88.7Ω
232
0
2.15K2.15K
62,B4
+12V
GND
0Ω
293
234
231
Vs
1K
062
RC2
+
100uF
PN2222
221
267
*Replace
221 with a
0Ω jumper
for fixed
black level.
0Ω
10K
070
Remote
Control
M. GAIN
1K
GND
219
+12V
485
GND
PCB
+12V
GND
RED
1N4148
271
75Ω
288
GND
VC
3
GND
292
G
VC
5
75Ω 75Ω
278
R
VC
4
INPUT
277
GREEN
INPUT
1N4148
270
75Ω 75Ω
286
For DC coupled positive analog video signals, the
signal source black level is 0 volts. The standard
saturated color voltages are .7 volt and 1 volt.
The RGB video signals and sync are connected to
the monitor through the video input connector 292 .
Resistors 288 , 286 , & 284 terminate the video
284286288
292
lines and load the input such that, when no signal
source is connected, the screen is dark.
Resistors 278 , 277 , & 276 protect the video
interface IC 241 from transients. They also act as
278 277 276
241
load resistors for the clamp diodes. The clamp diodes
271 , 270 , & 268 limit the peak amplitude of the
270271
268
video, to prevent overdrive of the video amplifiers.
These diodes are connected to transistor
275
resistor
transistor 274 balances the clamp diode’s forward
275 . The base to emitter voltage of the
274
voltage for temperature compensation. Resistors
273
and 273 set the clamp voltage.
The gain of the input circuit is set by resistors
264 , & 232 .
232264
274
274 and load
272
272
226
226 ,
75Ω
276
GND
BLUE
B
INPUT
VC
6
Resistors 223 , 242 , & 231 produce a voltage drop
1N4148
268
284
GND
223
PN2222
274
30Ω
231242
3.92K
412Ω
across the gain resistors to offset the voltage drop
caused by the .6mA bias current across the input and
protection resistors. +12 volts to these resistors
produces a fixed black level. An optional black level
adjustment may replace the +12V with a range of
0 volts to 11.3 volts. Potentiometer 070 is buffered by
transistor
221
221 and resistor 219 which provide the
219
070
adjustment voltage.
The master gain line is connected to the video
241
interface IC
by the gain resistors
241 at pin 12. It multiplies the gain set
225
226
225 , 226 , etc. by 0 to 1.
Vertical and horizontal blanking set the gain to 0
during retrace. The gain is adjusted by the master
gain control
485 through load resistor 062 . The
485
062
maximum gain may also be limited by making solder
connections S , T , & U .
Diodes
S
084
084 , 086 , & 067 clamp the video lines
T
086
U
213
connected to the video board to prevent damage to the
video interface IC from arc related voltage spikes.
272
273275
66
Page 51

1Vp-p, POSITIVE ANALOG, AC COUPLED, VIDEO INTERFACE CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
16 13 5 12396 11
o
o GAIN
RoG
B
+ EN
A
B
BL
Controls XRC5346A
21 1415 7 8
A5
1N4937 1N4937 1N4937
J
225
1.87K
88.7Ω 100Ω
226
223
MPS2907
10
+12V
K
0Ω
218
- BL
A
243
264
MPS2907
TTL
2.15K
242
241
M
4
GND
INBGINRIN RR RG
RB
A5B5
L
233
2.15K
105Ω
232
231
MPS2907
+12V
GND
PN2222
221
+12V
PN2222
Black Level
Adjustment
is optional.
0Ω
219
10K
070
1nF
272
2.7K
305
MPS2907
270Ω 270Ω 270Ω
PN2222
R
VC
4
1N4148
237
311
RED
INPUT
271
75Ω
288
270Ω
310
GND
VC
PN2222
GND
G
VC
292
3
5
278
.33uF
281 280 283
277
312
.33uF
GREEN
INPUT
1N4148
238 266
270
270Ω
308
75Ω 75Ω
286
BLUE
INPUT
In the + analog AC coupled mode, the video black
level is set by a clamp circuit which is active during the
first part of horizontal sync. For this circuit to work
properly, the incoming video must be at the black level
voltage when horizontal sync starts and remain
blanked for at least 4.5uS.
The clamp circuit is dependent on the polarity of
incoming horizontal sync. For separate horizontal
sync, the sync polarity should be positive. For
composite sync, and positive going horizontal sync
pulses, resistor
320
320 (.30” long) is connected to the
inverting horizontal sync comparator which is the same
as separate, positive, horizontal sync. For composite
sync, with negative going horizontal sync pulses,
320
resistor
320 (.45” long) makes the connection to the
noninverting vertical sync comparator. This connection
is valid since the horizontal and vertical sync lines are
connected together for composite sync.
The clamping function is accomplished by turning on
transistor 303 at the start of horizontal sync through
the differentiating action of capacitor 316 and resistors
305 & 320 . The collector of this transistor is
connected to clamp transistors
through resistors 310 , 308 , & 307 with pull down
resistor 315 . The coupling capacitors 281 , 280 , &
283
283 at the video input are set to the black level voltage
303
316
320305
311 , 312 , & 313
310
308
315
307
313312311
280281
by the video source.
1N4148
276
PN2222
313
.33uF
For composite sync.
H. Sync.+
B
VC
6
H. Sync.
268
284
270Ω
307
GND
For separate -H sync
see schematic at DD8.
2
1
355
10K
275
270Ω
315
1.0M
273
320=.30”
320+.45”
274
2.7K
320
303
GND
1N4148
317
1N4148
319
47nF
309
100pF
316
If the coupling capacitor voltage, on the clamped side,
is high at clamp time, the clamp transistor shorts the
capacitor to GND by normal transistor action. If the
coupling capacitor voltage is low at clamp time the
clamp transistors act as dual diodes to raise the
capacitor voltage to GND, which is the black level
reference for the video input circuit.
The ground referenced video signal is then buffered
237 266238
by transistors
resistors 278 , 277 , & 276 . The buffer transistors
237 , 238 , & 266 through protection
277 276
278
are needed to reduce the .6mA bias current, from the
video interface IC, to under 10uA which limits the
coupling capacitor voltage buildup to 2mV during one
horizontal cycle.
Resistor
275 268270
275 and clamp diodes 271 , 270 , & 268
271
are connected to the coupling capacitors to limit the
voltage buildup when no sync is present. If this limit
did not exist, the monitor would show excessive
brightness without sync. When sync pulses are
present, capacitor 309 with rectifier diodes 317 &
319 and filter capacitor 272 apply a voltage to the
base of transistor 274 which raises the voltage on the
309
272319
274
317
clamp diodes to avoid interference with the video signal.
Diodes 226 , 243 , & 232 balance the base to
225 243 233
emitter voltage of the buffer transistors. The rest of
the video interface functions the same as the DC
coupled video interface circuit.
67
Page 52

+
VIDEO AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT, FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION.
The video amplifier, is a high speed push pull
amplifier, which can swing as much as 90 volts.
The maximum dynamic output swing is limited to
60 volts. The rest of the output voltage range is
reserved for bias adjustment.
+12V
1.49K
K9
1
NE592
14
836Ω
K10
VIDEO
INTERFACE
C5346
SIMPLIFIED VIDEO
AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT:
Ω
301
K2
1.50K
K1
2N
3904
K34
606
K7
681Ω
K6
K6
Ω
The video amplifier drive circuit is built on a
ceramic substrate which is a good heat sink.
The printed resistors and conductors are small
and have precise geometries which output a
faithful reproduction of the input signal with
good high frequency response and low overshoot.
127V
120V
40.2K
K19
5.62K
K11
560Ω
K17
12.1K
K15
16V
MPS2907
7
Bias Control Line
from Auto Bias IC
945
140Ω
B14
K16
.015uF
885
18
K14
2SA1370
OUTPUT
2SC3467
15Ω
K4
+9.25V line
The NE592 is a 120MHz emitter coupled
differential amplifier which is connected to a
push pull output stage. This output stage
has a low bias current of 3mA and a
bandwidth of 25MHz. Although at 25MHz,
the output stage current increases to 15mA.
VIDEO AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The video amplifier's output voltage, with
no input signal, is the black level which is the
picture tube cut off voltage. This voltage is set,
for each of the three video amplifiers, by the
auto bias circuit via the bias control line. This
black level voltage has a range of 80V to 110V.
The voltage swing at the output is 60 volts
for a 10 mA current signal from the C5346.
For this same 10 mA current signal, the
voltage swing at the video amplifier input is
1.5 volts and the input voltage swing at the
NE592 is .80 volts. The reason for using the
voltage divider K6 and K7 is that the C5346
minimum output voltage is 7.7 volts, and the
bias voltage at the NE592 input is 5.3 volts.
The input signal is buffered by a NPN
transistor K34 for low input capacitance.
Resistors K1 and K2 set the black level
input voltage at 10 volts. Resistor
schematic next page) and diode
the input against arc related transients.
Resistors
input bias voltage for the NE592. Diode
acts as a temperature compensator to match
the emitter to base diode in the
buffer transistor.
K6
K34
K1 K2
K6 and K7 are used to set the
K7K6
K7
K21
K21 (see
K36
K36 protect
K35
K35
The negative feedback circuit consists of
bias resistors
resistor K19 . The geometry of the feedback
K19
K9
K9 , K10 and output feedback
K10
circuit defines the AC negative feedback path.
The autobias output, which adjusts the black
level voltage, is also connected to this node
K11
through resistor
connects resistor K22 , which raises the video
K11 . Solder connection A
K22
A
amp. output voltage by 10V, for some CRTs.
The voltage gain of the differential
amplifier K32 is set by resistor K8 . The
output of the amplifier has a load resistor
K8K32
K5
K5
for faster low going transitions and is
buffered by a PNP transistor 945 with base
matching resistor
this buffer amplifier is
K20
K20 . The load resistor for
K3
K3 which is
945
connected to the 16 volt line.
The buffered output of the differential
amplifier is DC coupled to the NPN transistor
943
943 and AC coupled, by capacitor 885 , to
the PNP transistor 951 of the push-pull
output stage. Resistors K18 and 953
951
K18
885
953
protect the push-pull transistors from current
spikes caused by voltage transients when CRT
arcing occurs.
68
Page 53

VIDEO AMPLIFIER SCHEMATIC.
Blue Video Amplifier
210
301
K2
MMBT
3904
100Ω
K21
1
1.62K
K1
+12V
1.49K
Ω
K34
Ω
606
K7
Jumper
K33
K9
1.0K
K8
1
3
12
14
SOT
NE592
K32
1N4148
3pF
K36
681Ω
K6
K6
1N4148
K35
A
21K
K22
836Ω
K10
937
40.2K
K19
10
5
7
8
.1uF
934
5.62K
K11
1295
18
12.1K
K15
10
33
2.2K
3
3
150
.5W
4
MPS2907
Ω
K20
K5
17
K3
K3
8
GND
560
140
B14
16
.015uF
Ω
945
K17
Ω
K16
885
Ω
MPS2907
20
2SC
3467
9
11
3.32K
K12
2SA
1370
19
6
950
951
180
K18
205
953
943
15
K4
.1uF
957
75
14
Ω
18
K14
15
Ω
.1uF
250V
887
7
Dark screen
80-110VDC
1nF
Ω
956
FDH400
7
Ω
958
2SA
1370
954
BIAS CONTROL LINE
Ω
K13
1.8K
948
13
9.25V
PART
OF
AUTO
BIAS
1.8K
955
127V
16V
120V
BLUE
VIDEO
TO
CRT.
Beam
Current
Feedback
FROM
CA3224
GND
+12V
VIDEO INTERFACE
MG
VERTICAL and
HORIZONTAL
BLANKING,
Master Gain, &
Beam limiter
R G B
VIDEO SOURCE (external)
The bias current of the push-pull output
stage is set by resistors K14 , K15 , K16 ,
K17
K17 , and diode connected transistor 950 .
950
Transistor
transistor 951 to maintain the same base to
950 is thermally connected to
951
emitter voltage drop. Note that resistor K17
K14
K16K15
950
K17
adds 11mA to the diode connected transistor
950
950 . This current is available to drive the
951
base of transistor
951 during periods of high
frequency amplification. This high base
current is needed because, the beta of
transistor 951 is low for high current pulses
951
and when high frequency is amplified many
high current pulses occur. The mechanism
for transferring the current from
+12V
1.8K
938
MPS A64
D
942
3.92K
940
transistor
950
950 to the base of transistor 951
is the coupling capacitor 885 which charges
through resistor K16 on the positive part of
GND
885
K16
9.25V
.1uF
930
951
the signal and discharges through the base of
transistor 951 on the negative part of the
951
drive signal. Therefore the output stage,
bias current, is frequency dependent and has
a range of 3mA to 15mA.
Resistor K13 and capacitor 887 , which are
K13
887
connected to the 9.25 volt line, decouples the
video amplifier current pulses from the 127V
line. The 9.25 volt line is connected to the
emitter of the NPN push-pull transistor by
resistor K4 . This voltage establishes the
K4
output voltage of the NE592 in the middle of
it's ±2 volt drive range. The 9.25 volt line is
regulated by darlington transistor 942 with
voltage divider resistors
938 940
938 & 940 .
942
69
Page 54

VIDEO BOARD POWER SUPPLY AND ARC PROTECT SCHEMATIC.
+127fV
+120V
FDH
400
835
From Video Amp.
Grid Pulse
100K
876
GND
FIL.
+127fV
+16V
+120V
+12V
GND
100uF
50V
868
Power supply voltages shown, are
for the 2793-CGA monitor.
FDH
400
899
FDH
400
845
1.87K
874
-16V to-25V
872
FDH
400
849
10Vp-p 95uS
FDH400
870
+120V Source
FDH
400
886
RED
GREEN
BLUE
10K 1/2W
Vs-23 to -27Vdc
873
0VDC
56V 31uS
857
400
Hs
FDH
959
Caution! 2 pin degaussing coil plug (CC1 &
CC2) must be plugged in such that the pin
with the extra wire is closest to the fuse.
UNPLUG WHEN REPAIRING MONITOR.
1/2W
900
1/2W
851
1/2W
883
SOCKET
1N4005
848
1N4937
847
877
330pF
871
+
8
6
11
12
150Ω
1/2W
882
DAG GND
1uF
50V
846
+
200V
860
10
18Ω
G1 G2 Focus
5
97
0Ω
896
853854
FIL.
.1uF
801
879
1K
1/2W
855
2.2nF
30Ω
859
CC1
CC2
CC3
1
150Ω
1/2W
880
2.2K
1/2W
881
100K
1/2W
856878
DAG GND
.1uF
816
Auto Bright Control Output.
0Ω
962
Ω
150
1/2W cc
875
Green
Wire
961
From MAIN PCB
970
EHT
SCREEN
Socket Board
800
PCB
FIL.
Fil. GND
+127V
+16V
+12V
GND
971
Degaussing Coil
EHT
FOCUS
TC 11
TC 12
TC 8
TC 1
TC 4
TC 2
The high voltage in the CRT, through an arc, can
be conducted to any tube socket connection on the
video board. To reduce the danger of these arcs
causing component failure, a number of arc current
paths are provided. The tube socket has integral
spark gaps which conduct arc current to the tube
ground (aquadag). through dissipation resistor 882 .
882
The clamping voltage of the spark gaps to the
cathodes and G1 is about 1.5KV.
The peak arc current to the video amplifier
outputs is limited by resistors 900 , 851 , & 883 .
883851900
Each amplifier output is connected to two clamp
diodes
835 899 845 849 886 859
835 , 899 , 845 , 849 , 886 , & 859 to
provide a current return to ground via the power
175 860
supply filter capacitors
175 & 860 . The grid pulse
drive to G1 is protected by a low pass filter made up
of elements
856
856 and capacitor 878 also form a low pass filter for
855 , 871 , & 873 . Resistors 881 ,
855 871
878
873
881
the G2 to auto bright control output connection.
880
A dissipation resistor
880 is connected to the
focus spark gap to match the impedance of the
aquadag connection. This reduces reflections and
helps dissipate the arc energy. Resistor
879
879
supplies an additional ground path for arc energy.
G1 is connected to a negative voltage to increase the
cutoff voltage which reduces the dot size and produces a
sharper picture. This negative voltage is generated by
rectifying the negative peaks of the filament flyback
pulse with diode
872 . Resistor 872 is used to adjust the negative G1
870
870 , filter capacitor 868 , and resistor
872872
voltage for different FBTs. Resistor 876 provides a
868
876
fixed load to stabilize the -G1 voltage. The grid pulse is
developed across load resistor
874
874 by a PNP transistor.
The 120 volt line, which is also generated by the
filament voltage, is used to supply the video amplifier
output bias current. Capacitor 857 translates the GND
857
referenced filament flyback pulse to the 127 volt line.
Rectifier diodes
847 & 848 and filter capacitor 846
generate the V+ minus 7 volt supply. Capacitor 857 is
848847 846
857
also used to adjust this voltage for different FBTs.
The filament voltage is adjusted by capacitor 854
and diode (or resistor) 853 .
Resistor 859 and capacitor 860 decouples the video
859
853
860
854
amplifiers from the 127 volt line. This filter is needed,
in some models, to eliminate video amplifier distortion
caused by ripple current on the V+ line. This ripple
current is caused by the, V+ minus 7 volt line, power
supply.
70
Page 55

CRT AUTO BIAS AND AUTO BRIGHT CIRCUIT, FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION.
The auto bias circuit is a control system that
forms a closed loop for controlling the CRT bias
voltage. It generates a set of conditions where
the current near the cutoff voltage of each gun is
measured, and then adjusts the bias voltage of
the video amplifiers, to set the correct black level
voltage for each gun. This color balance
adjustment is necessary, since each gun in the
color picture tube can have a different cutoff
voltage, which also, will change as the CRT ages.
If the picture tube gain changes, the auto
bias circuit would adjust all three guns in the
same direction to maintain constant black
level. This effect reduces the auto bias
voltage range which is needed for the cathode
differential voltage adjustment. To prevent
this occurrence a second control loop is added
to the system. This second control loop is
called the auto bright circuit and corrects for
CRT gain changes. The auto bright circuit
senses any common bias voltage change and
controls the screen grid (G2) to hold the
common bias voltage constant.
SIMPLIFIED PICTURE TUBE VIDEO BIAS CONTROL CIRCUIT: (One channel shown)
VIDEO
INTERFACE
+
Video
Amp.
R
G
B
CA3224E
4.0V
Beam
Current
Buffer
LM324
+
5K
200
C8
68.1K
Ω
.1uF
921
comp.
.047uF
Vsync
sync
H
927
Blue
input
A
B
C
SW
normal
V ref.
GREEN CHANNEL
RED CHANNEL
Counter, Decoder
Control Logic
Blue
hold
cap.
10uF
+
895
B
G
R
Grid pulse
Program Pulse
Auto Bright
33K
33K
33K
Amplifier
+
LM324
920
15.8K
*
4.0V
Adjust FBT bottom pot for 4.0V to 4.4 at pin 8.
Note: Chassis before rev. E4, set to 4.6V.
+4.2V
8
*
G1 G2
169K
900Ω
1.8K
CRT
FBT
Screen
adj.
TC 9
+6V
-21V
The auto bias circuit performs all of its
sensing and bias corrections during the
sixteenth to the twenty first horizontal cycle,
after the vertical sync pulse. Before the
sixteenth cycle, the SW in the auto bias IC is
open ( SW in "C" position).
During the 16,17, and 18 horizontal cycle,
the CRT is brought out of cutoff by the grid
pulse. The resulting beam current produces
a voltage at the beam current buffer output.
This voltage is applied to the coupling
921
capacitor
921 . At the other side of the
coupling capacitor is the channel input, which
is clamped to V ref. (SW in "A" position). The
voltage amplitude of the amplifier output with
the cathode current information is then stored
in the coupling capacitor 921 during this
921
time.
During the next three horizontal cycles (19,
20, and 21), the SW is switched to pass current
to capacitor 895 which is the bias voltage
895
storage capacitor. At the same time a
program pulse is applied to resistor
C8
C8
which, if the bias was correct during the
previous cycle, exactly balances the voltage
stored in the coupling capacitor and no
difference is sensed at the channel input. The
channel amplifier, in this case, does not
output current and the voltage of capacitor
895 stays unchanged.
895
If the CRT cathode is too far into cutoff, less
beam current flows at the grid pulse time.
This causes the beam current buffer to output
a smaller negative pulse and less voltage is
stored in the coupling capacitor. The program
pulse amplitude (which is constant) is now
larger than the stored (beam current) voltage
and the channel amplifier will add current to
8 95 thus
the, bias voltage, storage capacitor
895
correcting the low bias voltage which caused
the cathode to be too far into cutoff. After the
program pulse is over, the SW is switched to
the open position again and the next time the
bias voltage can be adjusted is during the
next vertical blank time.
71
Page 56

CRT AUTO BIAS AND AUTO BRIGHT CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
The beam current feedback circuit uses a PNP video
transistor
954
954 to direct most of the beam current to the
auto bias circuit while passing the voltage waveform,
from the video amplifiers to the CRT cathodes. Diode
958 956
958 and capacitor 956 insure that no video waveform
distortion occurs. An additional benefit of this circuit is
that it protects the video amplifiers from the destructive
arc energy. Resistors 948 and 955 divide energy due
948
955
to CRT arcing, between the video amplifier transistors
954 . The
and the beam current feedback transistor
beam current is filtered by capacitor 941 and resistor
C10
C10 and is buffered by an operational amplifier, which
954
941
translates the beam current into a low impedance
voltage. This voltage is applied to a coupling capacitor
921 C8
921 through a 200 ohm resistor C8 .
The 200 ohm and the 68.1K resistor
C3
C3 forms the
program value which sets the black level voltage via the
action of the program pulse.
Capacitor 922 is used to stabilize the
922
transconductance amplifier which is used at the channel
input of the auto bias IC
the bias voltage of this channel in capacitor
927 . The auto bias IC stores
927
895 at pin
895
21. This voltage is buffered by an internal amplifier,
with output at pin 20, which is connected to the Blue
video amplifier bias control input.
Resistor 908 , 910 , and 911 are part of the auto
908
910
911
bright circuit. They are used to sum the bias voltage of
each of the three channels via a voltage node at the auto
bright amplifier, 920 pin 9. The resulting output
voltage then controls the screen grid via transistor 850 .
Resistor
881 protects the CRT grid from excessive
881
current during arcing. Capacitor
920
850
878 supplies a low
878
AC impedance to GND to insure that the CRT gain is
constant during each horizontal line. Resistor 858 and
914 defines the current gain of, and stabilizes, the auto
914
858
bright control loop.
Load resistor 909 eliminates crossover distortion from
the OP Amp.
909
920
920 . Resistor 852 and 856 protects the
856852
transistor and OP Amp. from damage due to CRT
arcing.
PNP transistor 928 is used as a voltage translator to
928
direct the grid pulse from the auto bias IC to G1. The
voltage on G1 is normally -15 to -27 volts depending on
which CRT is used. When the grid pulse at pin 11 is
933
low, the current from resistor
resistor 874 and produces a 10 volt pulse on the minus
G1 line. Capacitor 871 and resistors 855 & 873
protect transistor 928 from CRT arcing.
874
871
928
933 is conducted to
855 873
The auto bias IC (CA3224E) is designed for a supply
voltage of +10V and since the video amplifier requires
+12V, three diodes 903 , 905 , and 906 are used to
supply this IC. Resistors
C4 and C7 form a voltage
906905903
C7C4
divider which supplies the, auto bright, bias voltage to
the LM324
920
920 . The green and blue channel circuits
are identical to the red channel and are controlled by
the timing logic in the same way.
Refer to the waveforms at the bottom left of page 34
for the timing relationship. The vertical retrace boost
pulse, from the LA7838, (15KHz models) or the delayed
vertical sync pulse from the sync delay circuit (25 &
31KHz models) starts the 21 count auto bias state
counter. This pulse is applied to the auto bias IC
through resistor 891 . The negative going flyback
891
pulse which is used to heat the filament also supplies
the horizontal sync to the auto bias IC via diode
and resistor 888 . The grid pulse becomes active
888
884
884
between the 15 and 18 horizontal cycle and the program
pulse is active between the 18 and 21 horizontal cycle.
These two pulses in conjunction with the internal
control of the transconductance amplifier output switch
are what establish the timing for the measurement and
setting of the video bias.
CRT AUTO BIAS, VERTICAL SYNC CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
The auto bias vertical sync comes from from a buffer circuit
for 15KHz operation. For 31KHz operation this signal is
generated by a delay counter. For both cases, the vertical
boost pulse is "and" connected with the Vertical Osc. O/S to
provide flicker free operation and laser beam protection. In
the case of vertical deflection failure, the loss of the boost signal
causes the auto bias vertical sync to stop, which stops the auto
bias function, and blanks the screen via the vertical blanking
circuit, thus providing for laser beam protection.
PN2222
4
0Ω
100A
7
1
2
100
PN2222
200K
CS=.45"
383
Retrace Boost
+12
Hfo=15KHz
6.8K
099
510Ω
006
3
P
379
22K
384
+12
V
62K
62K
098
099
0Ω
CS=.74
389
200K
GND
Vertical Osc. O/S, LA7851 pin 16
201
Filament
1N4148
1
2
8,10,13
14
7
3
.1uF
101
006
CL 12
KL
NC
Vdd
Vss
CD4024
Autobias
CRT AUTO BIAS
VERTICAL SYNC
For Hfo=25-31KHz
1N4148
100
Delay
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6Q7
GND
11
9
6
5
4
1N4148
1N4148
1N4148
028
220pF
091
2H Dly.
024
4H Dly.
025
8H Dly.
027
16H Dly.
15.8K
381
+24V
72
The vertical oscillator one shot (LA7851 pin 16)
supplies the start timing for the auto bias vertical
sync. This signal is conducted to the emitter of
379
379 by jumper 389 . The base of 379 is connected
to the retrace boost pulse by resistor divider
and 384 . Combining these signals in this way
384
089 379
383
383
produces a collector waveform which has the vertical
oscillator one shot timing and is dependent on the
retrace boost pulse.
For the 15KHz case, transistor
100
100 inverts the
vertical oscillator one shot signal to produce the
099
CRT auto bias vertical sync signal. Resistor
is the pullup and resistor 006 reduces the
006
099
chance of arc damage to the transistor.
For the 31KHz case, the vertical oscillator one
shot signal is directed to the clear of the 7 bit
counter
100
100 . This O/S time out must occur after
the autobias delay time out and come before the
bias active pulse from the CA3224E. When the
clear is low, the counter counts horizontal pulses,
by the clock connected voltage divider 099 and
201 . When the counter outputs ones at each diode
201
099
connected output, further counts are inhibited by
006
diode 006 and pullup 381 . This diode "or" signal
381
is also used for the CRT auto bias vertical sync.
The delay is set to locate the grid pulse generated
3 faint lines at the top of the screen with full
vertical deflection. Capacitor
091 produces a
091
delay to avoid a race condition between the counter
clock and the auto bias horizontal sync.
Page 57

10K 1K
873 855
330pF
871
VIDEO
INTERFACE
+12V Line
Green &
Red BEAM
CURRENT
14
15
18
TC 10
V. Osc. O/S
V. Blanking
Filament Pls.
Bias active
Grid pulse
Program pulse
Vs7.8 to 8.8Vdc
8.4Vp-p 95uS
To CRT Grid #1
-15V to -27V
CRT AUTO BIAS AND AUTO BRIGHT SCHEMATIC.
1,000pF
956
FDH400
958
C7
2SA1370
954
C
11
5
+
Video
Amp.
Blue BEAM CURRENT
For XX92
2.74K
1.82K
C4
4K
C10
2,200pF
941
4K
C11
2,200pF
818
4K
C14
2,200pF
815
6
13
3
2
16
12
13
19
GND
1
+12V
1.8K
933
MPS2907
1.8K
874
1.8K
931
1.8K
955
1.8K
948
900Ω
C17
920
+
1/4
LM324
12
5K
C9
+
1/4
LM324
17
5K
C12
+
1/4
LM324
14
20
5K
C15
V. osc o/s or Delayed V. osc o/s
Grid pulse
9.6Vp-p 95uS
928
AUTO BRIGHT CIRCUIT
Adjust the bottom pot
on the FBT for +4.2V
8
920
15.8K
914
10
10
+
1/4
LM324
9
Blue video BIAS control line.
1N4005 X3
905 906903
3.8-
4.2V
7
Ω
200
C8
68.1K
C3
7
.1uF
921
.047uF
1
922
Ω
200
C13
68.1K
200
C16
68.1K
18
GND
C2
C1
Vs9 to 10Vdc
Ω
2.7K
884
5
4
1
.1uF
923
.047uF
924
.1uF
925
.047uF
926
22K
1N4148
+10V
.1uF
907
891
888
2,200pF
889
100K
852
3.3K
909
1.2-
2.5V
5.7-
6.3V
1.2-
2.5V
5.7-
6.3V
1.2-
2.5V
.2.6V
23V
10
1/2W
2SC3675
850
TC9
169K
858
100K,
856
R
G
B
1N4005
+12V
090
2.2nF, 1KV
878
Beam current off on
power down circuit.
68.1K
085
127K
087
board at DD1.
G2G1
100uF
+
089
On main
FBT
2.2K
1/2W
881
CRT
+16V
AUTO BIAS CIRCUIT
AUTO BIAS IC
1
GND Vcc
22
CA3224E
927
2
320
4
input
Blue
sw.
normal
comp.
sw. in grid pls. pos.
Green input
sw.
Blue
hold
cap.
Green
hold
cap.
5
comp.
6
Red input
sw.
Red
hold
cap.
7
comp.
6V REF.
8
9
11
START
COUNTER
FFCLQ
GND
21 H. LINE
COUNTER
CL
DECODER
sw. control
GRID
PULSE
EN
BIAS
5V REF
AUTO
BIAS
ACTIVE
PROGRAM
PULSE
21
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
10uF
+
895
2.5-
6.7V
10uF
+
894
2.5-
6.7V
10uF
+
892
2.5-
6.7V
4.6-5.2VDC
To
Vertical
Blanking
4.2Vp-p 360uS
33K
908
Green
Video Amp.
BIAS.
33K
910
Red
Video Amp.
BIAS.
33K
911
ABA
TC 6
Vs2.2 to 2.7Vdc
73
Page 58

Monitor, Block Diagram Review.
GAME
VIDEO
RGB
SYNC
V. & H.
3
SYNC
Interface
VIDEO
Interface
BLANKING
V retrace
Beam limit
M. gain
High temp. limit
VERTICAL
J
2
V
DELAY
VERTICAL
s
OSCILLATOR
HORIZONTAL
CONTROL
s
H
H. Pos.
Sync delay
On Video Board.
3
AB
F.B.P.
VIDEO
AMPS.
Bias
3
3
3
Auto
Bright
CRT AUTO
I
SYNC
F
BIAS IC
H. sync (FBP)
V. sync
CA3224E
Beam
3
Current
Feedback
G
Beam current
buffer
Program pulse
Grid pulse
E
VERTICAL
CONTROL &
OUTPUT
LA7851
I. V. Feedback
Driver
NO
LA7851
V. Size &
V. Ras. Pos.
K
M
PINCUSHION
C
3
LA7838
Output
G2≈290V
G1≈–20V
3
2 For Dual Focus
CRT
H
V
DY
EHT≈25KV
DY
H
D
Dynamic Focus
used only on Dual
Focus CRTs
Horizontal
Dynamic
Focus
H2
EHTG2
V+
Vertical
Dynamic
Focus
H1
2
P
L
+
H.H.
FBT
REMOTE
CONTROLS
ISOLATION
Transformer DOUBLER
(IN GAME)
DEGAUSSING
CIRCUIT
Z
+24V
74
(PCB)
QR
VOLTAGE
Raw DC
320V
V-
+52V to +129V
LOAD
T
-200V
FAULT
DETECTOR
Y
HORIZONTAL
Size Control
(VIDEO & DEFLECTION)
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
Shutdown
OVER
VOLTAGE
PROTECT
Sync
X
DIODE
Modulator
Beam Current
+16V
+24-27V
U
FBP
Regulator
Vertical Deflection
V
+12V
Supply
S
+12V
W
Page 59

BLANKING, MASTER GAIN, AND FAULT CIRCUIT, FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION.
SIMPLIFIED GAIN CONTROL CIRCUIT:
+12V
1K
MASTER GAIN
485
HORIZONTAL BLANKING
FLYBACK PULSE
0VDC
56Vpp 62,D6
Vertical Bias O/S
Hs
BIAS ACTIVE
HIGH Z
+2.5V
3
2
SIGNAL
CONDITIONING
CIRCUIT
+2.5V
+
1/2
LM393
1
210
GAIN SELECT
RESISTORS
1K
062
VERTICAL BLANKING
VIDEO GAIN LINE
PN2222
072
6
5
1/2
LM393
+
210
1N4148
253
.047uF
207
VIDEO INTERFACE
C5346
241
3.6K
One of three input circuits.
FAULT CIRCUIT
To P/S OVP
BEAM CURRENT LIMITER
+6V
MPSA64
7
PN2222
D
036
071
+12V
200Ω
LM324
033
+
+7.5V
1/4
10uF
014
3
+3.4V
2
beam current
From FBT
High Temp.
Beam Limit
1N4148
018
+
Video
Amp.
Total
+12V
28.0K
020
100K
T
@ 25°C
To
CRT
180
Blanking in this monitor is accomplished by
reducing the video gain to zero during the
vertical and horizontal blank time. During
video time, the gain is set by the master gain
control which is located on the remote control
PCB. If the overall beam current exceeds
.75mA or 1.5mA (depending on model) for
more then ten frames, the beam current
limiter circuit will reduce the video gain to
protect the FBT. A high temperature sensor,
close to the FBT, will also reduce the beam
current if the high temperature limit (70°C) is
exceeded.
The fault circuit senses the temperature
or beam current line and will turn off the
monitor if either of these signals exceeds the
beam current shut off value. If an abnormal
condition exists in the monitor or the cooling
system of the enclosure fails, the high
temperature sensor will activate the fault
circuit at 80°C. The fault circuit is also
turned on when the beam current becomes
large enough to damage the FBT. This
condition will happen if the video bias supply
(V+ –9V) on the video board fails. An OP
Amp. is used to sense the fault condition and
a transistor is used to transmit the fault
signal down to the power supply.
The video P-P voltage amplitude at the
cathodes, is the video input signal
amplitude times the master gain control
setting times the video amplifier gain.
The gain select resistors set the maximum
video gain via the master gain line. For a
greater range of brightness, (highlighting)
the video system is allowed to supply high
peak video currents which could damage
the FBT if sustained. The beam current
limiter circuit insures that the long term
maximum beam current is not exceeded.
Horizontal blanking is achieved by
amplifying the flyback pulse (FBP) with
transistor 072 . Vertical blanking starts
072
as soon as the LA7851 starts the vertical
retrace sequence and is terminated by the
auto bias, bias active signal. A comparator
is used to sense the vertical bias O/S, at pin
16 of the LA7851, which goes low when
vertical retrace starts. Capacitor 207
207
holds the vertical blanking active, between
the vertical bias O/S pulse, and the bias
active pulse. When the bias active line
goes high, the capacitor 207 is reset and
207
vertical blanking ends, after the bias active
line returns to it's high impedance state.
75
Page 60

BLANKING, MASTER GAIN, AND FAULT CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
The master gain control 485 is connected
485
to the video gain line through a 1K resistor
062
062 . The voltage range of the video gain
line is programmable via resistors 064 , 076
and solder bridges at S , T , & U .
S
064
UT
076
The solder bridges may connect resistors
244 245
244 , 245 , 258 , and 260 to the video gain
258
260
line. This arrangement permits a variety of
input signals and picture tubes to be used
with the same monitor PCB.
Horizontal blanking ( ) is added
to the gain line by transistors 072 . This
H
B
072
transistor pulls down on the gain line when
the flyback pulse is high. Capacitor 081 is
charged by diode 080 and resistor 093 such
080
081
093
that, as soon as the flyback pulse starts going
positive the NPN transistor 072 turns on
072
and horizontal blanking starts. The time
constant of capacitor 081 and resistors 078
and 093 is chosen such that the capacitor
093
081
078
will lead the FBP on the downward slope and
turn the horizontal blanking transistor off
just at the end of the FBP. This advanced
timing compensates for the turn off delay of
transistor 072 .
072
Vertical blank time is started when a low
going pulse from the LA7851 pin 16 causes
the output, pin 1, of the dual comparator
210
210 to go low. Capacitor 207 is discharged
through resistor 208 at this time. After the
208
207
end of the LA7851 pulse, the capacitor
207
207 holds the output, pin 7 of the
comparator, low until the bias active pulse
recharges the capacitor 207 through diode
253
253 . During the high time of the bias
207
active pulse, the comparator output pin 7 is
still low, because of the voltage drop across
the diode 253 . The end of vertical blank
253
time occurs when the bias active line
returns to it's high impedance state. The
capacitor 207 holds the charge from the
207
bias active pulse until the next vertical
blank time. The advantage of this type of
vertical blanking circuit is that, if the CRT
auto bias IC fails to produce a bias active
pulse, the screen stays blanked. This action
protects the CRT when the vertical
deflection system fails since the output of the
LA7838 boost pulse is needed for the CRT
auto bias vertical sync (CA3224E pin 8).
The video gain line will source up to 32mA
during blank time, which is the reason for
buffering the vertical blank comparator with
a PNP transistor 212 .
Resistors 251 and 252 supply a voltage
251 252
212
that is midrange relative to the LA7851 pulse
for maximum noise immunity.
Resistors 248 and 250 also supply another
248
250
midrange voltage for the bias active pulse
and the, vertical blanking, hold capacitor
207 to work against. Resistors 211 and
207
368
368 are used as jumpers.
211
The beam current limiter circuit uses the
base to emitter voltage of a darlington
transistor 036 to set the maximum beam
036
current. To sense the beam current,
capacitor 010 integrates the current pulses
010
produced by rectifying the high voltage
flyback pulses. The beam current is
converted to a voltage across resistor 009 .
009
This voltage is applied to a long time
constant RC circuit, resistor 011 and
capacitor 014 , before it is sensed by the
014
011
darlington transistor. The sharpness of the
limiting response is set by resistors 012 ,
065
and 066 . Transistor 071 then,
065
066
071
012
reduces the video gain by pulling down on
the master gain line upon excessive beam
current. The beam current is also reduced if
the FBT temperature sensor exceeds 74°C.
Resistor 020 sets the temperature at which
020
this circuit becomes active. The resistance
of thermistor 180 decreases with increasing
180
temperature until the voltage at the cathode
of diode 018 is low enough to turn on
transistor 036 which turns on transistor
071 and darkens the screen.
071
018
036
The fault circuit senses the temperature
or beam current line with a, comparator
connected, OP Amp. 033 at pin 2 (– input).
033
The + input of the OP Amp. is biased to
3 volts by a voltage divider, resistors 034
037
and 037 . The output of the, OP Amp. is
connected to a low pass filter, resistor 017
and capacitor 035 to insure that the fault
035
034
017
circuit does not become active on power up.
008
Transistor
008 conducts the fault signal to
the over voltage protect input of the power
supply IC. Resistor
translator transistor 008 and the power
005
005 protects the voltage
008
supply controller IC.
76
Page 61

BLANKING, MASTER GAIN, BEAM LIMITER, AND FAULT CIRCUITS SCHEMATIC.
Remote control PCB
+12V
1K
485
GND
6.8K
251
2
2.3-
2.7V
1.8K
3
368
1.8K
252
(BIAS ACTIVE)
From auto bias IC pin 13
2-3VDC
4Vpp 63,C4
Vs
(VERTICAL BIAS O/S)
From LA7851 pin 16
4.5-5.3V
5Vpp 16,E5
Vs
VIDEO GAIN LINE
4-7VDC
4-9Vpp 61,B4
Vs
VERTICAL
BLANKING
MPS2907
7
212
4-7VDC
4-9Vpp 61,B4
Hs
HORIZONTAL BLANKING
LM393
210
1/2
1K
062
RC2
MASTER
GAIN
+12V
6.8K
250
6
1N4148
253
5
+
1.8K
248
0Ω
8
211
1/2
1
LM393
1K
208
+
4
.047uF
GND
207
PN2222
072
0Ω
077
GND
+12V
BEAM CURRENT
LIMITER CIRCUIT.
PN2222
071
75Ω
066
Power supply
controller IC
C5184
115
078
1N4937
080
GAIN SELECT RESISTORS
1K
1K
1.62K
012
065
S
260
MPSA64
OVP
TU
604Ω 1.21K
244
1.21K
258
D
036
14
245
+
10uF
014
1N4148
018
7-10VDC
61, C2
GND
high temperature comparator.
Shutdown
270Ω
081
093
12
1.62K
+12V
Temperature
Excessive beam current or
076
GND
28.0K
020
T
Sensor
2.7K
064
62K
011
CPR0432
180
+6V
+3.4V
(FLYBACK PULSE)
From FBT pin 8
0VDC
56Vpp 62,D6
M
GAIN
VIDEO INTERFACE IC
FBT
453
Return
12.1K
034
009
BEAM CURRENT
.1uF
15.8K
037
010
GND
FAULT
CIRCUIT
3
22K
1
017
200K
005
2
1/4
LM324
033
0Ω
109
Hs
C5346
241
EHT
LIMIT
100uF
+
035
0Ω
2SA1371
8
4
019
GND
008
77
Page 62

Composite
Sync
VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL SYNC CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
Vertical Sync
Horizontal Sync
{
Sync Interface
2 Comparators
For Interlaced Vertical Sync.
Vertical Sync To Horizontal Cycle Synchronization
and Composite Sync Decoder
+
To LA7851 pin 19
To LA7851 pin 1
Composite sync or separate vertical and horizontal sync
are buffered by two comparators in the sync interface
circuit. A vertical sync synchronization circuit is used to
insure a stable raster and functions as a sync separator.
Vertical Sync
7.15K
366
Horizontal
Sync
H
VC
1
GND
s
V
VC
2
364
1K
246
1.8K
325
0Ω
328
1.8K
331
s
Vertical
Sync
0Ω
Interlace (15KHz)
10uF
+
259
47nF
254
1.8K
257
+12V
22K
323
4
270Ω
326
5
6
270Ω
330
.14-.16V
GND
7
270Ω
327
1/4
LM339
+
1/4
LM339
+
12
0Ω
318
3
2
355
1
355
The synchronization circuit is bypassed, for interlaced
vertical sync, because this circuit rejects the half
horizontal line time variation used to generate the
interlaced vertical raster.
+12V
7.15K
364
6.8K
321
6.8K
322
Horizontal Sync
+
1/4
14
LM339
355
1.5-2VDC
+
1/4
13
LM339
355
200K
246
PN2222
255
100K
257
.047uF
318
GND
200K
256
9
8
59,D6
11
10
.05VDC
7V pp 60,C5
PN2222
33K
247
15.8K
353
1K
357
3.92K
356
Vs,Hs
254
FBP
354 360
2.1-2.4VDC
4.6Vpp 58,D6
358
15.8K68.1K
Hs
The sync interface comparators are biased to .15 volts,
by resistors 323 & 327 , to permit receiving low level
323
327
sync signals such as RS170. For low level composite
sync, the vertical and horizontal lines are tied together
and jumper 328 is left off. For normal amplitude sync,
(greater than 2.3 volts) resistors 325 & 326 form an
328
326325
attenuator to protect the sync interface comparators and
normalize the sync amplitude. This combination also
reduces noise sensitivity since the sync voltage amplitude
is low at the comparator input which slows the
comparator response and acts as a low pass filter.
For the interlaced sync case, the pullup resistor 321 is
left off and the voltage divider resistors 246 and 257 act
246
321
257
as the pullup. Also the vertical sync synchronization
comparators are disabled by changing the input resistors
to bias the comparators in the high output state and
resistor 366 is left off. Capacitor 254 acts as a sync
366
separator for composite interlaced sync. Capacitor 259
and jumper 364 are used to couple the composite sync to
364
254
259
the LA7851 vertical sync input pin 19.
The vertical sync synchronization window comparator
generates a pulse, a little after the midpoint of each
horizontal cycle. This pulse is shorted to GND by
transistors 255 except when vertical sync is active. The
255
two transistor circuit permits using either positive or
negative pulses for vertical sync.
Capacitor 318 couples the vertical sync pulses to
transistors 254 & 255 . When no sync pulse is present,
transistor 255 is turned on by resistor 246 . For a
negative vertical sync pulse, transistor 255 is turned off
by the negative pulse applied to resistor 257 and the
318
255
254
255
246
255
257
window comparator pulse is allowed to be the vertical sync
pulse. For positive vertical sync pulse, transistor 254 is
turned on by resistor 247 & 256 , which shorts the base
of transistor 255 to GND also allowing the window
255
247 256
254
comparator pulse to act as the sync pulse.
A sawtooth waveform is produced on integrating
354
358
353
360356
capacitor 358 by applying the flyback pulse to resistors
360 357
360 & 357 . This sawtooth waveform is connected to two
comparators which are biased by resistors 353 ,
356 , 354 , & 360 such that both comparator outputs are
high between 1.8 volts to 2.3 volts. This circuit would
produce a pulse on both the positive and negative slope
parts of the sawtooth waveform. Resistor 357 eliminates
357
the output pulse on the negative slope by introducing part
of the flyback pulse to pin 8 which keeps the comparator
from going high at this time. Resistors 364 & 366 act as
364 366
a pullup for the window comparator and apply a 6 volt bias
to the vertical sync input, LA7851 pin 19. At 6 volts, the
vertical sync input is inactive. It becomes active only
when the window comparator output and the ± sync
transistors are all high.
78
Page 63

VERTICAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT, FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION.
The LA7851 IC is used for the vertical oscillator. The LA7838 is a vertical deflection control
and high efficiency vertical yoke driver IC. Together they form a compact and efficient
vertical deflection system.
Vertical Sync
Vertical Oscillator
LA7851
Vertical
Linearity
Fine Tuning
6V
Vertical
Size
Clamp Enable Pulse
SIMPLIFIED VERTICAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT
One
2
Shot
5V
*
Clamp
+6V
Ramp Control Circuit
375
403
*
Voltage on 401
Current
Source
46 7
1uF
401
Drive
388
Retrace
Booster
Output
LA7838
392
391
9
13
12
Voltage Feedback
390393
Current Feedback
+23V to +27V
Vertical
Yolk
+
449
385
Yoke Current
Yoke Drive
The vertical oscillator in the LA7851
supplies timing to the vertical deflection IC
to maintain a raster with no sync present.
Vertical sync supplies the timing when sync
is present.
The one shot in the LA7838 clamps the
ramp forming capacitor
401
401 to 5V during the
first half of vertical retrace.
The ramp forming capacitor is supplied with
current by a current source at pin 6. The
current source has a fixed 6 volt input voltage
at pin 4. A linear ramp is generated if a fixed
resistor is connected from pin 4 to GND.
Feedback from the yoke current, via resistor
403 , is used to modify the linear ramp which
403
helps correct for nonlinearity introduced by
the voltage feedback circuit connected to
pin 7. The vertical size control is connected to
the current source input since adjusting the
slope of the ramp adjusts the vertical size.
This ramp with the clamp, as the discharge,
produces a sawtooth waveform which is
connected to the + input of the vertical control
differential amplifier at pin 6.
The combination, voltage and current,
feedback circuit senses the parabolic
waveform on the yoke coupling capacitor
449
449 and is connected to the yoke current
sense resistor 193 . This circuit is then
385
connected to the other input of the differential
amplifier at pin 7. A capacitor
391
391 smoothes the parabolic waveform and a
voltage divider is used to set the output bias
voltage. The time constant, of the capacitor
391 and resistor 392 , is set to produce good
392391
vertical linearity. An additional linearity
correction circuit is added to fine tune vertical
linearity. This circuit can be set to add or
subtract deflection from the upper and lower
portions of the raster.
The differential amplifier controls the
power output stage which drives the vertical
deflection yoke. The retrace booster is
turned on when the ramp voltage is set to
the clamp voltage and is reset when the yoke
feedback voltage balances the ramp voltage.
79
Page 64

VERTICAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
378
LA7838
Vertical
Deflection
+12V
HEAT
SINK
12 34 567 8 910
Remote Control Board
Vertical
Size
Vertical
Raster
Position
RC3
500Ω
482
1K
483
RC8
RC6
750Ω
486
RC4
510Ω
004
0Ω
203
1,000pF
369
18Ω
+12V SUPPLY
367
VERTICAL SYNC
Vs
The vertical sync comes from the
synchronized vertical sync interface
circuit for monitors without interlace.
For monitors with interlace the vertical
sync comes from the sync comparator
via a coupling capacitor and bypasses
the synchronizing circuit. Pin 19 of the
1N4005
382
H.+12V
LA7851 is the vertical sync input and will
start the next oscillator cycle on either the
positive or negative sync pulse. The vertical
410
oscillator capacitor
410 discharges to 4 volts
on the leading edge of the vertical sync by the
action of an internal transistor and resistor.
Capacitor 410 is then charged by resistor
362 until the next sync pulse or to
362
410
8 volts, which ever comes first. The V. osc.
frequency is set low such that the adjustment
resistor 363 can be used to act as a vertical
hold adjustment. Solder connection V is
363
V
used to make this adjustment.
The vertical oscillator triggers the vertical
oscillator one shot, which outputs a pulse to
trigger the vertical sync input, pin 2, of the
LA7838. This one shot is also used to
synchronize the CRT auto bias IC.
Resistor 361 & capacitor 414 set the
361
414
timeout which must be longer than the CRT
auto bias Vs delay and shorter than the
vertical blanking. Resistors 370 & 408
370 408
supply the pullup for this one shot.
377
375
100uF
+
376
VERTICAL
Ramp
Reset
One Shot
out
Tr.
R/C
5.5-6.4V
3Vpp 21,D5
44.2K
402
See
Table
403
V.+12V
GND
5.5-6.5V
1.2Vpp 19,D5
Vs
or
20 19
V+
VERTICAL VERTICAL
± SYNC INPUT
.01uF
Ramp
Reset
Slope
Vs
374
CPC1058
out
Gen.
Ramp
1.2Ω, 1W
385
.1uF
410
VERT.
OSC.
V. size
Control
50/60Hz
5-6VDC
1.4Vpp 22,E5
Vs
1uF
401
365K
362
V
V. osc.
ADJ.
OSCILLATOR
Vert.
Drive
+27V
5.5-6.5V
1.4Vpp
68.1K
GND
388
2.2M
363
4-6VDC
2.8Vpp 18,D5
Vs
23,F4
393
392
+
391
127K
361
Vs
18 17
VERTICAL
OSC. O/S
Retrace
Booster
Drive
470uF
390
.01uF
414
.1-.3VCD
3.8Vpp 17,E5
The one shot in the LA7838 clamps the ramp
forming capacitor 401 to 5 volts for about half of
the vertical retrace time. Capacitor 374 and
resistor
402
402 form the RC circuit for the ramp
401
384
reset one shot.
The ramp capacitor 401 is charged by current
401
from a current generator with a 6 volt input node
at pin 4. The vertical size is adjusted by the
482
vertical size control
4 via resistors 003 & 375 . The adjustment
range is set by resistor 375 and the maximum
deflection is set by resistor 403 . A third input
482 which is connected to pin
003
375
375
403
to pin 4 comes from the vertical linearity circuit.
This circuit uses the above and below GND parts of
the vertical current waveform separately.
Transistor
411 conducts when the vertical current
411
waveform is below GND. This transistor’s emitter
is referenced to GND by diode
371 . The emitter is connected to the vertical
371
current waveform through resistor
406 and resistor
406
407 which is
407
adjusted for each tube and yoke combination.
380
Vs
80
Page 65

VERTICAL DEFLECTION SCHEMATIC.
22-28V
.8Vpp 24,F7
Vs
Thermal Protection
Vert.
Out
Boost
GND
11 12 13
Vertical Linearity Circuit
V.+12V
DECREASES
TOP AND
BOTTOM
VERT. SIZE.
200K
412
I
D5
200K 200K
1N4005
382
1.5-2.7V
24Vpp 24,E4
Vs
0Ω
395
4.7Ω
396
.1uF
397
PN2222
1N4148
406
411
See
Table
GND
22K
370
4.5-5.3V
5Vpp 16,E5
Vs
15.8K
408
16 1415
GND
V. Ref.
LA7851
In similar manner, the positive half of the
vertical current waveform is conducted by
transistor 373 diode 405 , and resistors 372
404
and 404 . Both transistors 373 and 411 may
405373 372
373 411
be connected to pin 4 via solder connection H or
they may be connected to inverting transistor
409 and resistors 412 and 413 .
409
412
413
The inverting transistor is connected with
solder connection I and decreases the vertical
I
size at the top and bottom of the screen.
The ramp capacitor 401 is connected to a
401
differential amplifier at pin 6 and the negative
feedback from the yoke return line is connected
to pin 7. This negative feedback, which senses
the DC component of the vertical output voltage,
is also the current feedback for the LA7838. It is
388
made up of voltage divider resistors
390 + 393 and a wave shaping integrator.
390 393
The wave shaping integrator, capacitor
resistor 392 , is used as the primary vertical
392
388 and
391 and
391
linearity adjustment.
MPS2907
372371
PN2222
1N4148
405
1,000uF
35V
H
200K
D5
INCREASES
TOP AND
BOTTOM
VERT. SIZE.
373
See
Table
404407
+
449
196
Capacitor multiplier for the 2793.
+
270Ω
196
30Ω
198
1,000uF
119
413
409
H
.1uF
399
GND
2SC4159E
197
1N4005
199
2SC3467
RAS. POS.
V
0 TO 7 VDC
390Ω, 2W
421
12-16VDC
50Vpp 28,F6
420
100Ω
1/2W
394
Vs
YC1
426
YC2
427
VERTICAL
YOKE
The output of the vertical drive, differential
amplifier, is connected to the power amplifier
which drives the yoke. A booster circuit is
connected to the the power amplifier supply via
capacitor
380
380 and clamp diode 382 such that
382
when the booster is active, during vertical
retrace, the power supply to the vertical output
amplifier is doubled. Resistor
396
396 and capacitor 397 make up a high
397
frequency vertical output stabilization circuit.
The vertical output at pin 12 is connected to
421
the vertical yoke. Resistor
421 is a load resistor
across the yoke which stabilizes the vertical
deflection feedback loop. The yoke return is
decoupled by capacitor 449 and the vertical
current is sensed by resistor 385 . The vertical
449
385
raster position is adjusted by injecting current in
the vertical yoke return. This is accomplished
by transistor 420 , with emitter resistor 394 ,
and the V. RAS. POS. control 483 .
483
394420
A capacitive multiplier circuit is connected in
series with the 27 volt line, in the 27” monitor, to
reduce the ripple voltage due to beam current
variations. Transistor 197 conducts current
197
from the 27 volt line to the LA7838 deflection
supply input pin 8. Capacitor
196 and 198 form a low pass filter which is
198196
119 and resistors
119
connected to the base of this transistor. Diode
199 conducts the inductive current from the
199
vertical yoke during the first part of retrace.
A jumper at 196 replaces the capacitive
196
multiplier circuit in the chassis with smaller
CRTs.
81
Page 66

HORIZONTAL DEFLECTION CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
+12V Supply
Remote
Control
PCB
Horizontal
Position
20K
484
56pF
352
7.3VDC
5.5Vpp 01,D6
Horizontal
Sync
Hs
RC7
RC4
1N4007
333
0Ω
202
3
17
220uF
334
1.8K
I1
3.92K
418
2.7K
2
+24V to 27V Supply
5.4-6VDC
11, E5
Horizontal
SYNC INPUT
1 64 52 3
8
I4
7
NEG.
12K
I2
I3
GND
Hs
IA
8.8K22K
I12
1,000pF-15KHz
12
PICTURE
POSITION
330pF-31KHz
330pF-38KHz
11
+
comp.
-
O/S
7.3-8.7V
4Vpp 02,D6
351
100uF
338
200Ω 2W
GENERATORTR.
-.2VDC
6.8K
I13
45K
I6
I PRA
416
1N4007
340
Hs
2.2K.5W
+
341
3.92K
417
DELAYED
SYNC O/S SAW TOOTH
Hs
9
25K
I5
6,10
+24V
7.3-8.7V
4Vpp 03,D6
56Vpp 62,D6
Vs 3-4VDC
330pF
350
GND
0VDC
1.5Vpp 04,E6
11
1
Hs
2SC4159E
342
1.4Vpp 05,E6
348
6,800pF-15KHz
3,300pF-31KHz
3,300pF-38KHz
12-18VDC
33Vpp 27,E7
337
GND
MULTIPLIER
BIAS
Hs 2.4-3.4VDC
0Vpp
+
1uF
347
18
1uF
+
344
Hs
06,E6
10K
I7
The functions of the horizontal control circuits are:
1. To provide the horizontal output circuit
with a stable frequency with or without
incoming horizontal sync.
2. To be able to adjust the picture position,
horizontally, with respect to the raster.
3. To operate stability through periods of
missing horizontal sync pulses.
4. To keep the picture from drifting within
the operating temperature range.
All of these functions except for the picture
position adjustment are accomplished by the
phase locked loop. Delaying the horizontal
sync with an adjustable timer produces the
picture position adjustment.
The horizontal sync input circuit (pin 1) will
trigger the picture position one-shot (O/S) on
either the rising edge, or the falling edge, of the
horizontal sync pulse. To accomplish the edge
triggering, the sync pulse is differentiated by
capacitor
352 into two short pulses, one for the
352
rising edge and one for the falling edge of the
sync pulse. Which edge is the trigger depends
on the bias voltage at pin 1. For positive edge
triggering, the bias voltage is set to 7.8 volts by
resistors
I2 and I3 . For negative edge
I2 I3
triggering, the bias voltage is set to 4.1V by
connecting
I 12 via the solder connection IA .
I12
IA
The picture position O/S clamps timing capacitor
351
351 to 8.2 volts until horizontal sync triggers this O/S.
The voltage on the timing capacitor drops at a rate set
by the horizontal position control 484 and resistor
I 4 . When the voltage, at pin 2, drops below 4 volts
I4
the delayed sync O/S is triggered and capacitor 351 is
484
351
reset to its clamped voltage. The delayed sync O/S
functions the same as the picture position O/S with the
exception that it is not adjustable.
The flyback pulse, connected to pin 4 through
I6
resistor
I6 , starts the negative slope of the saw
tooth generator. When the sawtooth wave, which is
produced by a current to capacitor 348 , drops to 3
348
volts, the sawtooth generator switches back to the
positive slope part of the wave till the next FBP.
During the active part of the delayed sync pulse,
the multiplier gates current to capacitor 346 which
346
is dependent on the sawtooth voltage at the
delayed sync pulse time. Capacitor
347
347 sets the
"0" voltage for the multiplier which is the average
value of the sawtooth waveform.
If the delayed sync pulse occurs when the
sawtooth is at a low voltage part of its cycle,
346
capacitor
346 discharges and the oscillator
frequency lowers. If the delayed sync pulse occurs
at the top part of the sawtooth wave no current
flows to capacitor 346 . This action, phase locks
346
the horizontal oscillator to the incoming sync
pulses.
82
Page 67

19
20
100Ω
I11
2.2nF
343
Horizontal
Drive
Transformer
HORIZONTAL DEFLECTION SCHEMATIC.
1N4007
435
1.2Ω
434
2SC5690
433
GND
2
1
3
4
332
NO DVM
.9KVpp
Hs
27,G6
Video
Board
800
Fil.
Fil. Rtn.
Screen
FOCUS
EHT
To Yoke
TC11
TC12
170Ω
I14
+200Hz
16
E
I8
107V-127V
10.8-12V
10, E6
336
17
HORIZONTAL
OSCILLATOR
DISCHARGE
415
H. V+
9 107 8
LA7851
5.5-6.3V
Hs 5-6VDC
.2Vpp 07,E6
33K
13
.01uF
3.6Vpp 08,E6
14
1K
I8
345346
6,800pF-15KHz
3,300pF-31KHz
3,300pF-38KHz
The voltage on capacitor 346 controls the
Hs3-7VDC
7Vpp
H.Fo ADJ.
15
I10
680Ω
I16
+800Hz
G
I9
9.31K
Hs
09,E6
340Ω
I15
+400Hz
F
346
horizontal oscillator frequency via I8 . In the case
of missing horizontal sync pulses, the multiplier does
not sink current and flywheel capacitor 344 holds
the horizontal frequency constant. Resistor I7
344
I7
permits small rapid changes of the control voltage at
pin 7 for locking of the oscillator to horizontal sync.
The horizontal oscillator capacitor 345
345
charges to its upper voltage limit through resistors
I10 , I16 , I15 , I 14 , and 336 . This capacitor is
I14I15I10 I16
336
then discharged to the lower voltage limit through the
action of discharge pin 9 and resistor I 9 . The free
I9
running frequency (Hfo) may be adjusted by making
solder connections on the I PRA. (see page 65 for the I
PRA layout). In some cases where there are many
missing horizontal sync pulses, it is necessary to
adjust the Hfo closer than ±200 Hz. For fine tuning
the Hfo, resistor 336 is replaced with a pot.
336
The horizontal phase locked loop then consists
of an oscillator which sets the flyback timing.
The flyback pulse is then compared to the incoming
sync pulse and the difference voltage holds the
oscillator at the sync frequency.
The duty cycle of the horizontal drive transistor
is generated by comparing the oscillator waveform
against a fixed voltage. This fixed voltage is set by
resistors 417 and 418 .
417
418
451
452
452
To P/S
V-
FLYBACK
TRANSFORMER
10
6
EHT
1K
465
FOCUS
092
092A
9
8
7
5
SCREEN
Beam
4
Current
3
FIL.
2
1
453
GND
The horizontal output transistor 433 conducts
0Ω
467
433
about three amps of horizontal flyback
transformer primary current and deflection
yoke current. This transistor has a beta as low
as three. To supply the high base current, a
horizontal output transistor drive transformer is
used. The drive transformer 332 builds up
332
energy during the on time of the drive
transistor, 337 which is the off time of the
horizontal output transistor 433 . Capacitor
343 and resistor I 11 damps the drive
343
337
433
I11
transformer primary waveform. To reduce
power dissipated by the horizontal output
transistor during turnoff, a clamp circuit is
connected to the drive transformer primary.
This clamp consists of resistor 341 , capacitor
338 , and diode 342 .
338
342
341
The flyback transformer's main function is to
supply EHT to the CRT. It also supplies the
focus and screen grid voltages which are taps on
the EHT supply. There are three low voltage
secondaries. One supplies the filament
current, negative G1 voltage, and timing on the
video board. Another supplies sync and EHT
information to the power supply. The third
secondary drives the horizontal blanking circuit
and supplies sync for the horizontal PLL, the
horizontal width control, & the vertical sync
synchronizing circuits.
83
Page 68

HORIZONTAL RASTER WIDTH CONTROL CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
The purpose of the horizontal width control is to:
1. Provide a convenient means for adjusting
the horizontal raster size.
2. Correct pincushion distortion in the vertical axis.
3. Correct horizontal raster distortion caused by
periods of high beam current.
The horizontal width control circuit is comprised of
two main parts; The control circuit and the diode
modulator (DM). The control circuit combines four
signals in the monitor to produce the width control
circuit. These signals are:
Horizontal size - - - - - Vertical current (Iv) - Vertical parabolic + Iv
4. EHT return on the FBT
Beam current - - - - - - -
H. Size Pot.1.
V. current feedback resistor2.
Vertical yoke return.3.
The diode modulator controls the horizontal yoke
current which affects the horizontal size. This is
accomplished by the diode forward current. In effect,
the diode shorts out the horizontal width coil to the
extent of the diode forward current during the previous
horizontal trace time. The current used to control the
diode forward current comes from the diode modulator
and is controlled by the control circuit and the
switching mode driver.
The horizontal size voltage from the remote control
PCB 490 is applied directly to the current node
(LM392 Pin 5) of the control amplifier by resistor 043 .
490
043
For pincushion correction, two separate signals are
used. The inverted vertical current waveform
(TP 34) and the yoke return waveform (TP 33). The
yoke return waveform includes a parabolic and linear
component. The inverse of the linear component is
added to the yoke return waveform to correct the
pincushion. The vertical current waveform (Iv) is
inverted by an Op Amp and resistors 029 and 051 .
Resistor 031 level shifts the inverted Iv to + 6V.
031
029 051
The (vertical parabolic + Iv) is AC coupled by capacitor
082
082 and resistor 038 and 040 . It is then
040038
amplified by an Op Amp connected as a voltage
follower. Resistor 038 protects the Op Amp against
arc related voltage spikes. Load resistors 050 and
053 prevent cross over distortion of the Op Amps by
053
038
050
using only the current source transistors.
The inverted Iv and (parabolic voltage +Iv) are added
to the current node of the control amplifier by resistors
041 , 042 , 030 , & 052 which then makes up the
041
042 030 052
pincushion correction signal.
The beam current from the FBT is converted to a
voltage by resistors 009 and is filtered by capacitor
010
010 . Resistor 097 then connects the signal to the
009
097
current node of the control amplifier, which
accomplishes the blooming correction function.
These circuits are designed around a virtual ground,
the +6 volt line. This line is generated by buffering a
voltage divider
021
Resistor
021 and capacitor 026 form the output filter.
022 023
022 and 023 with an OP Amp.
026
The power output stage of the horizontal width
control circuit is a high efficiency switching mode
driver. The FBT pulse is integrated by capacitor
through resistor 095 and level shifted by resistor 058
095
057
057
058
to produce a saw tooth waveform. See waveform block
TP 39. By connecting one input of the comparator, in
the LM392 049 , to this sawtooth signal and the other
049
input to the control amplifier a switched signal with a
duty cycle dependent on the control voltage is
produced at the output. Resistors 055 and 056 form
055
056
a voltage divider which limits the control voltage
amplitude to be within the sawtooth waveform.
Resistor 060 acts as a pullup for the comparator
output. Resistor 461 couples the power MOSFET 460
to the comparator. Capacitor 463 and resistor 464
060
461
463
460
464
are connected as a snubber circuit to reduces noise due
to rapid drain transitions.
When the MOSFET is on (gate voltage high)
current increases in inductor 458 and when the
458
MOSFET is turned off the current is dumped in to the
24-27V line through diode 462 . The magnitude of
462
this current, from the diode modulator, is determined
by the duty cycle of the MOSFET which is a function
of the control voltage.
Diodes 477 and 478 with current equalizing
resistors
477 478
475 and 476 rectify the flyback waveform
475 476
present on the GND referenced node of the
horizontal tuned circuit. This current is conducted
457
through inductor
456
456 and then is controlled by the driver circuit.
Diodes 477 and 478 are the diode modulator
477
457 and integrated by capacitor
478
diodes and the forward current which the drive
circuit controls is the current which determines the
turn on delay of the GND referenced node of the
horizontal tuned circuit. An increase in the current
of diodes 477 and 478 produces a greater delay in
477 478
the GND referenced node, and reduces the amplitude
of the flyback pulse at this node, which results in an
increased horizontal size.
Capacitors 441 and 442 are the primary
441 442
horizontal tuning capacitors and must be the specified
value for a given chassis horizontal frequency and
yoke combination for proper operation of the monitor.
Capacitors
439 are the diode modulator horizontal tuning
439
capacitors. Diodes 440 and 438 clamp the GND
437
437 and
440
438
referenced node voltage to GND. Horizontal linearity
coil 431 stores energy from the flyback pulse and
431
injects it into the horizontal yoke in the reverse
direction of the yoke current to decrease deflection at
the start of trace to balance the decreased deflection at
the end of the horizontal trace due to I R losses in the
yoke during trace time. Capacitor 432 and resistor
428 keeps the linearity coil from ringing after retrace.
428
2
432
The raster may be shifted by making solder
connections: left SL or right SR . The amount of the
shift is set by solder connections S1 , S2 , & S4 .
Inductor
447 permits only the DC current to pass to
447
the yoke return. Resistors
SL
SR
S1 S4S2
423 424 425
423 , 424 , & 425 define
the size of the shift together with the V+ plus 5V and
V+ minus 5V supplies. Resistor 189 supplies a load
189
on the V+ ±5V lines to avoid over-voltage of the filter
capacitors. Resistors 185 , 195 act as fuses to protect
the PCB in the case where both SL and SR
185 195
SL SR
connections are made.
84
Page 69

+
V+(+5V)
V+(-5V)
Vert. Output
Vertical
Yoke
1,000uF
449
1.2Ω
385
.33uF
082
6V
FBT Pin 4
6V
009
I BEAM
.1uF
010
+6V
H. Width Adjustment
Range.
043
12.1K
045
H. Size
Control
GND
FBP, FBT Pin 8
HORIZONTAL RASTER WIDTH AND POSITION CONTROL SCHEMATIC.
Horizontal Raster Position Adjustment
0Ω
191
22K
189
4.7Ω
185
4.7Ω
195
H. S. +12V
10.0K
022
10.0K
023
0Ω
188
13
12
GND
SR
SL
+6V
4
1/4
LM324
11 100uF
14
033
+6 Volt
Source
68Ω 1W
425
150Ω 1/2W
424
270Ω
423
510Ω
021
+
026
S4
S2
S1
18Ω
063
+
12mH
447
+12V
Line
100uF
026
HORIZONTAL YOKE
HORIZONTAL WIDTH CONTROL
972
107V or 127VDC
250Vpp
120Vpp 32,F6
YC3
446
0Ω
430
Horizontal
Linearity
coil
431
20VDC
4VDC
200Vpp
30Vpp 35,H7
Min.Max.
Hs
457
50uH
458
0Ω
454
1nF
100V
463
460
Hs
470
1/2W
464
Min.Max.
Ω
Hs
H Size
428
432
Hs
H Size
4VDC
11Vpp
456
0Ω
194
10K
038
200K
040
5
6
Beam Current
Load Resistor.
097
GND
HS +12V
5
6
1/2
LM392
Amp.
8
4
.01uF
047
HS +12V
10.0K
1/4
LM324
033
Parabolic
Pincushion
Blooming
Correction.
.01uF
054
7
049
10.0K
029
7
5.6-6.2VDC
2-3.6Vpp 33,B2
Correction
044
44.2K
058
10K
055
095
10.0K
3.3K
050
031
6V
GND
Vs
9
10
1/4
LM324
3.3K
Pincushion
Correction
5.6-6.2VDC
1-1.7V 34,B2
041 030
See
6V
Q R
Table
042
1N4937
+24-27V Line
28.0K
1/2
LM392
Comp.
096
1
049
2
3
6.8K
056
2-2.5VDC
4.4Vpp 39,B3
Hs
057
10.0K
051
033
053
-Linear
462
2.7K
060
0Ω
8
Vs
See
Table
052
4-19VDC
27Vpp 36,J7
MTP
8N08
510Ω
461094
0.8-7VDC
12Vpp 38,J7
HORIZONTAL WIDTH DRIVE
YOKE
Matching
FR205
440
FR205
438
1.5KV 1.5KV
442
200V
444
200V
443
HER105 HER105
477
.68Ω
1W
475
20VDC
15Vpp
Min.Max.
478
.68Ω
1W
476
Vs
37,I6
H Size
100V
GND
Horizontal
Output
FBT Pin 10
YC4
445
441
.022uF
630V
437
439
85
Page 70

DYNAMIC FOCUS CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
Model 1793-31.5DF
12-18VDC
50Vpp 29,F6
1,000uF
35V
+
449
0VDC
1.6Vpp
1.2Ω, 1W
385
Vs
13-15VDC
3-5Vpp
Horizontal Drive
Transformer
CPT1505
2
1
YC1
426
YC2
427
Vs
31,F5
Vs
0Ω
502
332
3
4
VERTICAL
DEFLECTION
.33uF
500
1N4007
435
1.2Ω
434
YOKE
V+
1KΩ
501
NO DVM
.8KVp-p
433
1.00MΩ
504
2SC3467
191K
503
Hs
27,G6
0Ω
V+
452
H PLL
DM Drive
GND
OVP
P/S Sync
V-
Vs
509
36K
10
9
8
7
5
1
2.2MΩ
510
505
FLYBACK
TRANSFORMER
CPT1555
2,200pF
2.2MΩ
511
200KΩ
514
330pF
500V
515
GND
EHT
1/2W, CC
470Ω
13
520
FOCUS
#2 FOCUS
SCREEN
12
Dynamic Focus
11
4
0Ω
465
Beam Current
3
Filament
2
453
1KV
507
CPT1556
12
GND
1N4007
512
0.1uF
34
518
Hs
CRT
G1
Red Wire.
White Wire.
Screen Grid.
Vs
HORIZONTAL YOKE
Horizontal
Linearity &
250V
270Ω
517 1.6KV
Width coils.
516
.47uF
443
Horizontal Width Control.
(Diode Modulator)
.47uF
200V
444
.01uF
441
The dual focus CRTs require a waveform on the #2 focus grid. This voltage waveform is dependent on the
position of the beam on the CRT. The lowest voltage part of the waveform is in the center of the screen and the
highest voltage part of the waveform is at the corners of the screen.
The dynamic focus circuit produces a composite waveform which consists of the horizontal parabolic waveform
and the vertical parabolic waveform. This composite waveform is applied to the dynamic focus input, of the
flyback transformer, and produces a sharp picture on the dual focus picture tubes. Typically dual focus picture
tubes produces a sharper picture than the single focus picture tubes.
Dynamic Focus Circuit Operation: The vertical component of the dynamic focus circuit is derived by
amplifying the voltage waveform across the vertical yoke coupling capacitor. The horizontal component of the
dynamic to focus circuit is produced by applying the voltage waveform across the horizontal yoke coupling
capacitor to the dynamic focus transformer primary. This transformer steps up the horizontal parabolic
voltage from about 33V to about 300V to produce the horizontal component of the dynamic focus circuit.
Circuit Description: Transistor 509 amplifies the vertical parabolic waveform which exists across capacitor
449 . This waveform is coupled to the transistor base via capacitor 500 and resister 501 . The bias for this
transistor is generated by resistors
Note; Resister
505
505 is connected to the vertical feed back line and not to ground. The supply voltage for the
collector is produced by diode
The load resisters for this transistor are resistors
vertical parabolic waveform, is conducted through resister
focus input of the flyback transformer. Resisters
509
500
503
503 and 504 . The gain of this amplifier is defined by resister and 505 .
512
512 which rectifiers the primary flyback pulse and is integrated by capacitor 507 .
504
510 511
510 and 511 . The waveform on the collector, which is the
514 and through transformer 518 to the dynamic
514
514
514 and 501 provides arc protection for transistor 509 . The
501
501449
505
507
518
509
horizontal component of the dynamic focus waveform is produced by coupling the primary of the dynamic focus
transformer at 518 to the horizontal yoke coupling capacitors at 443 and 444 . Capacitor 515 provides a low
518
443
515444
impedance pass to ground for the horizontal parabolic waveform which is developed across the dynamic focus
transformer secondary at 518 . Capacitor 517 insures that there is no D. C. component across the
transformer primary. Resister 516 protects the dynamic focus transformer primary from overload.
The flyback transformer
518 517
516
453 couples the dynamic focus waveform to the #2 focus grid via an internal capacitor.
453
86
Page 71

+24V
8
Vertical Booster Amplifier Circuit, Circuit And Function Description.
Monitors with vertical deflection current which exceeds
LA7838
Vertical
Deflection
Retrace
Booster
Drive
Thermal Protection
Vert.
Out
377
GND
Boost
910111213
2.2 Ap-p cannot be driven directly by the LA7838 vertical
deflection IC. The vertical booster amplifier circuit
reduces the output current of the LA7838 by amplifying
the vertical deflection current. The LA7838 is mounted
on the vertical booster amplifier circuit board to allow the
boosters circuit to be inserted at the output of the LA7838.
1.2Ω
.68Ω
385
605
TIP31A
609
4.7Ω
608
4.7Ω
607
606
2,200uF
449
+
3.3Ω
610
+
+24V
602
FR205
470uF
380
TIP31A
603
TIP32A
601
Vertical
Deflection
Yoke
604
#3
#2
YC2
1N4007
382
FR205
611
#1
YC1
NPN
603
NPN
602
PNP
601
E
604
C
B
E
C
B
E
C
B
605
607
606
Vertical Amp. PCB
CPB1615
612, LA7838
135791113
608
609
610
611
Vertical Booster Circuit,
Operation. The following
waveforms are taken from
the 2793-VGA monitor.
See waveform #1 for the
vertical deflection current.
Waveform #2 shows the
LA7838 output current.
Waveform #3 shows the
current supplied by the
vertical booster amplifier
circuit. These current
waveforms describe how the
vertical booster circuit
reduces the LA7838 output
current to a current which is
well within the specification
of the IC.
PCB View;
Foil Side.
Vertical yoke drive, voltage waveform.
#1
Vertical yoke drive, current waveform.
#2
LA7838 output, current waveform.
#3
Vertical booster, current waveform.
44Vp-p
3.0Ap-p
0.6Ap-p
2.4Ap-p
The output of the LA7838 is connected to the yoke by a 3.3Ω resister at 610 . It also drives the
bases of transistors 601 and 603 through 4.7Ω stabilization resistors. When the voltage drop
across resistor 610 reaches ±.7V the respective transistor (601 for -.7V & 603 for +.7V) takes
601 603
610
610
over most of the additional vertical yoke drive current.
The retrace booster pulse, from the LA7838 pin 9, is connected to the retrace booster capacitor at
380
380 and is also buffered by an NPN transistor at 602 . The output of the retrace boost is
connected to the LA7838 at pin 13 and to the vertical booster NPN transistor at
Diodes 604 and 611 conduct current, right at the start of retrace. This current is produced by
604
611
the energy in the yoke, from the end of the last trace. Diode 382 supplies the deflection current
602
382
603
603 .
to both the LA7838 and the booster amplifier circuits during trace time.
Stabilization capacitors 606 and 609 are not used at present, but may be needed with other
606
609
output transistors.
87
Page 72

SIMPLIFIED POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT, FUNCTION, DESCRIPTION.
OSC.
V+
Res.
Comp.
ENABLE
C5184
DRIVER
115
FET
136
V-
FLYBACK
DIODE
142
GND
137
+
SECONDARIES
166
When the FET is turned off, the stored
energy in the inductor continues supplying
current to GND. But in this case, the
current path is from V+ to GND, instead of
V-to GND. During this part of the cycle,
the current in the inductor is decreasing.
+52V to +127V
AC
line
User supplied
Isolation
Transformer
+
+
V-
(-200V)
GND
Error Amp.
V
REF.
The switching regulator includes the
power FET 136 which passes current from
V- to GND through the inductor
136
166
166 .
During the time the FET is on, the current
in the inductor is increasing and the
inductor is storing energy.
Under normal conditions, the current will decrease to zero and the voltage will ring.
FET drain voltage
Current in inductor Current supplying GND
LOAD
H Dy & EHT
VIDEO
Voltage across
Current in diode
137
142
Current from VCurrent added to the +127V line
Flyback pulse
As can be seen from the waveforms, the
largest number of changes occur when the FET is
turned off. Also, the FET drain voltage switches
fast due to the high inductor current. To
minimize video interference from the power
supply, the power supply is synchronized to the
horizontal oscillator such that horizontal
blanking is coincident with the FET turn off time.
For the shorted +127V to GND condition, which also occur right on power up,
The C5184
IC. All of the control circuits that are
built into this IC work together to produce
one output signal, which is the FET drive
signal. This signal can take on many
shapes depending on the load conditions of
the power supply. The waveforms for
normal operation are shown above.
115
115 is the series regulator
the waveforms are:
FET Gate Drive
FET Drain Voltage
Inductor Current
The first FET pulse is a full on pulse
which causes current to flow in the inductor.
After the FET is turned off the current in
the inductor drops much more slowly than
normal since the inductor is discharging
into a much lower than normal voltage. If
the FET were turned on for full power in the
88
next cycle with current still flowing in the
flyback diode, a current spike of 6A would
occur, which is a power spike of 2,000W.
The reason for this is that the diode stores
charge when current flows which turns into
reverse current for a short time when the
voltage is reversed across the diode.
Page 73

SIMPLIFIED POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
The FET drive circuit avoids this problem
by sensing flyback diode conduction. If the
flyback diode conduction is sensed, the low
current start mode is selected. This mode
turns the FET on, to a current of .1A, for not
more than 4uS. If before or during the low
current FET on time, the flyback diode breaks
free, and the FET drain voltage goes down,
the flyback diode voltage comparator will
signal the regulator to permit the FET to be
turned on for a full power cycle. The cycle
after the last low power cycle in the waveform,
on the previous page, is an example of this
condition. The flyback diode voltage
comparator inputs are located at pins 12 & 13
of the C5184. The two resistor dividers ( see
next page ) J10 , J11 and J12 , 134 connect
the comparator across the flyback diode 142 .
J12 134J10 J11
142
The comparator enables the FET drive only
after a 10% voltage drop is measured across
this diode.
Another fault condition exists when the
FET exceeds 5A drain current. This
condition can occur if the oscillator frequency
is too low, the FET drain is shorted to GND or
V+, the transformer has a shorted secondary,
or the core is broken. In these cases the
voltage across the FET source resistor
137
137
exceeds 1.6V which is sensed by the over
current comparator at pin 11. If pin 11
exceeds 1.6V, the FET drive is set to 0V for
the rest of the cycle. In some cases, this
condition can produce an output waveform
which looks normal, but the voltage across the
load (+127V to GND) would be low or
unstable. A quick check for this condition is
to check the peak voltage across the FET
source resistor. CAUTION; Whenever
connecting a scope ground to V-, be sure that
the other scope probe or common grounded
devices are not connected to the monitor GND.
A 0-30 volt @ 1A, DC, isolated power supply
is a tool necessary for trouble shooting
CERONIX monitors. When trouble shooting
the power supply, it can be connected to Vand the +17V line to keep the power supply
running while checking the voltages and
waveforms to find the fault. Caution, do not
exceed 20 volts on the 17 volt line. It can also
be used to supply the GND to +16V line for
checking the horizontal circuit. If the
horizontal circuit does not work, the power
supply will chirp. Without the horizontal
circuit working, there is not enough load on
the power supply for transformer action to
keep the regulator IC +17V line up to the
minimum of +12V. A quick check for this
condition is to clip a 2-4K @ 10W power
resistor from GND to V+. If the chirping
stops, the horizontal is probably not working.
The heart of the power supply is the
oscillator which supplies the basic timing.
The FET drive is always low during the
negative slope of the oscillator or, when
synchronized, after the start of the sync pulse.
The low to high transition of the FET drive,
pin 10, is determined by the voltage at the
output of the error amplifier. If V+ goes up in
voltage, the error amplifier voltage goes up,
which then intersects the oscillator waveform
at a higher voltage and causes the FET on
time to start later and be shorter. This
negative feedback accomplishes the control
loop of the power supply.
The regulator IC has a built in reference
voltage which is used by the error amplifier
to set and hold the V+ constant. Solder
connections on the J PRA are used to adjust
V+ in steps of ±1.5V.
Most of the power supply fault conditions
cause the power supply to chirp because the
source of +17V for the C5184 is generated by
the power supply. A special circuit is built
into the C5184, which permits charging the
+17V line filter capacitor with only a very low
load from the C5184. This circuit turns the
rest of the C5184 on only after the voltage at
pin 15 reaches 17V. If the transformer does
not supply at least 12V to this line before the
filter capacitor discharges to 12V, the C5184
turns off. The reason for the audible chirp, is
that, the power supply is not full on for each
cycle which produces a frequency low enough
to hear. See the bottom waveform on the
previous page.
The over voltage protect ( OVP ) circuit,
when activated, turns off the regulator IC
until power is disconnected. This circuit is
connected to the rectified flyback pulse, which
outputs a voltage that is proportional to the
EHT. The circuit's main purpose is to protect
the user against excessive x-ray which is
caused by excessive EHT. The OVP circuit is
also activated if the monitor temperature goes
too high or if too much beam current is
demanded from the FBT. The purpose of the
last two functions is to protect the FBT and
the CRT from component failure on the main
or video boards.
89
Page 74

SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION.
Oscillator waveform without sync:
Oscillator waveform with sync:
FET drive, C5184 pin 10:
115
The series regulator IC
115 , controls
current to the monitor GND by pulse width
modulation. A PNP transistor
112
112 , has an
emitter current, that is directly proportional to
J1
the 127V line voltage due to resistor
adjustment resistors J13 & J14 . This
J13
J14
J1 and
current is transmitted to the power supply Vline, and is applied to a resistor J5 , J15 , &
J16
J16 . The voltage across these resistors is
J15J5
compared to a reference voltage by the error
amplifier. If the +127V line goes up the output
of the error amplifier voltage goes up.
The pulse width modulation, which controls the
+ 127V line voltage, is accomplished by turning
the FET drive on at some particular voltage
along the rising slope of the oscillator waveform.
This particular voltage is the error amplifier
output voltage. See waveforms above.
The FET drive is always off during the
negative slope of the oscillator, or just after the
sync pulse. Since the FET drive pulse is started
by the error amplifier voltage and terminated by
the end of the oscillator cycle, a control system
via pulse width modulation has been established.
The oscillator waveform is produced by charging
capacitor 102 with a constant current set by
resistor J7 to a voltage of 5V and then
102
J7
discharging the capacitor with double the
charging current to 2.5V. Adding the flyback
pulse, via capacitor 123 to this waveform
123
synchronizes the oscillator, since the oscillator
frequency is set below the horizontal frequency.
Resistors J2 , J4 and capacitor 108 limit the
J2
J4
108
error amplifier's AC gain, to hold the control loop
stable. Capacitor 107 holds the error amplifier
stable. Capacitor 110 reduces power supply
107
110
noise, but, if too large, will cause the power
supply to be unstable. The 127V line is adjusted
by making solder connections on the J PRA (refer
to page 65 for the layout)
and JD are used to raise the 127V line up to 4.5
JD
volts in steps of 1.5 volts. Connections JA and JB
. Solder connections JC
JC
JA JB
lower the 127V line as much as 4.5V.
The FET 136 works together with the
transformer 166 to provide a low resistance
136
166
current path from V- to GND. This low
resistance coupled with no large voltage times
current products is what makes the power
supply efficient. Resistor 137 provides a
137
means for sensing the FET current. In the low
current mode, it is used to set the 300mA current
and in the full on mode it is used to
Error Amp. V.
Fet Drive
With Sync
sense the max. current. Resistors 140 , 133
and capacitor 138 reduce power supply
electrical noise. Transistor
116
116 short the FET drive to V- when the
138
127 and diode
127
140
133
monitor is turned off to protect the FET from
conducting current with a still large drain
voltage. Resistors J10 , J11 , J12 and 134
J10
J11
J12 134
provide a means for checking flyback diode
142 conduction via a comparator. If the
142
comparator measures low flyback diode voltage
the FET is turned on to the .3A low current
mode. This mode is necessary for power up,
since initially the +127V line is 0V and no
reverse diode voltage exists. The over voltage
protect circuit, at pin 14, has a trip voltage of
8V and when it is activated, it shuts down the
power supply. The EHT is measured by
rectifying the flyback pulse, with diode 130 ,
130
from a secondary winding of the FBT.
Capacitors 125 , 124 and resistors 126 , J9
126 J9125 124
are connected as a low pass filter to smooth out
the simulated EHT voltage which is then
applied to the C5184 at pin 14. Resistor J8
J8
protects the IC current sense input from
voltage spikes and resistor 113 protects the
113
PNP transistor from momentary overvoltage
damage due to line spikes. Zener diode 181
181
protects the horizontal and video circuits from
overvoltage due to power supply failure. If the
+127V line exceeds 160V, the zener diode 181
181
shorts to GND the +127V line.
At the input to the power supply is a
voltage doubler which outputs between 240 to
425VDC depending on the AC line voltage. It
has a three amp fuse 146 to protect the PCB
traces, an inrush current limiter 159 to
protect the rectifier diodes 148 & 156 .
Capacitors 150 and 155 are used to reduce
150
146
159
148 156
155
diode noise from the monitor to the AC input.
For 220VAC operation the voltage doubler is
replaced by a full wave rectifier by adding
diodes 151 , 154 , capacitors 152 , 153 and
removing the jumper at 152 . 144 & 163
are the raw DC filter capacitors. Resistor J6
151 154
152
144
153152
163
J6
supplies the power supply start current and
resistors 143A and 143B balances the series
143B143A
connected filter capacitors for 220VAC
operation.
Caution! When working on a monitor with a
degaussing relay, 468 unplug the degaussing coil
468
to avoid causing the residual current relay to
close on a cold posistor. This can happen if the
24V line is energized by a external power supply.
90
Page 75

2.2nF
CC1
CC2
150
FR205
148
2.2nF-230V
152
FR205
230V
151
REMOVE
FOR
230V
0Ω
152
2.2nF
155
FR205
156
2.2nF-230V
153
FR205
230V
154
+24V
.5A,240V
Relay
GND
468
0Ω
471
CC3
-1.5V -3V
2.33K
J13 J14
193K
J1
2SA1371E
1
112
10.6K
J5
J16
J15
JD
+3V
JC
+1.5V
260Ω
130Ω
11K
J2
2
23.2K
See
Table
105
106
62K
143A
36K
144
143B
0Ω
250V
114
163
7
8,14
90K
J6
100uF
128
Inrush Current Limit
C-200-7
159
25-.5Ω
158
Posistor
CPR0430
CPR0434
TR250-145U
160
Degaussing
Connector
162
Degaussing Coil
SWITCH MODE POWER SUPPLY SCHEMATIC.
V+ plus 20V ---Video Supply +24, 28V to Vertical Deflection.
V+ plus 5V---H. Raster Shift
V+ minus 5V---H. Raster Shift
JBJA
113
5
88K
J4
3.3nF
108
20
1N5954B
160V Zener
181
6.5-7.5VDC
41,D1
6.5-7.5VDC
.5-.8VDC
56pF
107
3.4-4.2VDC
.1-.5VDC
9
5.7-6.3VDC
250V
175
GND
16.3-19VDC
1
INPUT
ERROR
AMP.
2
INPUT
3
COMP.
4
Output
CONTROL &
FAULT SENSE
4uS
5
DELAY
6
Rx
4.67K
100K
6
1,000pF
27
110
5
3
4
56pF
J3
104
103
33.2K
J7
Osc.
7
Cx
102
8
+7.5VREF.
3-4VDC
3Vpp
47,D2
220pF
123
V- V-
0VDC
27Vpp 57,F1
Hs
SCOPE GND MUST
POWER
SUPPLY
LOW VOLTAGE
SECONDARIES
V+ MODIFIER
SECONDARIES
The degaussing coil drive
circuit may use a dual posistor
158
158 or a single posistor with a
shorting relay 468 . The off
current of the single posistor is
large enough to cause raster
movement when there is a
PC
differance between the line
1
frequency and the vertical
161
PC
2
3A Fuse
146
145
230VAC
120VAC
INPUT
sync frequency.
+16V, 18V to 12V Regulator.
167A
V+
+
100uF
120
1N4937
121
+15V
+17V
INPUT
Over
Voltage
Protect
INPUT
COMP.
OUTPUT
Current
SENSE
DRIVE
XRC5184
115
J PRA PINS:
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGES REFERENCED FROM V-.NOTES:
VOLTAGE CURRENT CIRCUIT SUPPLIED DIODE
(V+)+20VDC
+
1N4937
55, E1
16
15
14
}
12
13
+
11
10
9
V-
J PRA
3,10,15,
17VDC
16VDC
24-27VDC
(V+) -5VDC
(V+)+5VDC
468
100uF
118
122
14.8-18VDC
132
18Vz
5.5-6.8VDC
3-5VDC
5Vpp
3-6VDC
0.1VDC
1Vpp 51,F1
1-4VDC
12Vpp
+
52,F1
50,E2
182
167
30Ω
139
149
0Ω
198A
+16V
+
1,000uF
171
V+
1N4937
141
12
.1uF
124
20
1.00M
17 18
14.7K
V-
J10
J11
12
1
2
8
5
9
From Fault Crcuit
16
1.00M
134
15.8K
J12
510Ω
J8
18Ω
133
D
1N4005
127
MPSA64
111
2,200pF
&19
131
NOT BE CONNECTED TO GND AND V- AT THE SAME TIME.
POWER SUPPLY CONTROL
7mA
500mA
350mA
150mA
150mA
60mA
VIDEO AND INPUT
V. & H. DEFLECTION
H. RASTER SHIFT - LEFT
H. RASTER SHIFT - RIGHT
1VIDEO BOOSTER
+
1mF
387
SMXFR
166
126
38.3K
J9
116
170
1N4937
169
GND
6
3
4
1N4937
168
10
3,300pF
125
2SK1446LS
136
13
0.33Ω
2W
137
100pF
129
141
170
168
121
122
167
1N4937
1,000uF
+
450
+28V
FR205
142
1N4148
130
No DVM
300Vpp 40,G1
HEAT
SINK
135
220pF
1KV
138
47Ω
1/2W
CC
140
V-
TP49, G1
FILTER CAP.
100uF
1,000uF
1,000uF
100uF
100uF
220uF
GND
128
171
173
118
120
174
91
Page 76

OSCILLOSCOPE
Equipment Setup For Repairing The Model XX93 Monitor.
+17.1
DVM
No DVM
320Vpp
1-4VDC
12Vpp 50,E2
115
VAC
40,G1
0 to 30V 0 to 30V
ISOLATION
TRANSFORMER
ISOLATED
DUAL 1A DC
POWER
SUPPLY
VARIABLE
Test
Generator
or
Signal
Source
No.
LTR.No.
X
X
XY V
X-Y VDC
X-Y VDC
WAVEFORM
Sync.
TP-REF.Vp-p
CERONIX Model XX93
Legend Description
Represents the XX93 board part number. The parts list gives the
{
CERONIX PART NUMBER which is indexed to the board part number.
Part numbers of the resistors on the PRA indicated by LTR.
PRA pin number. To determine which PRA the pin number
{
belongs to, look for the nearest PRA part number on that line.
DC voltages are measured to GND except in the power supply
where V- is the reference. Use a DVM for DC measurements.
Test Point, board cross REFerence location.
The waveform is normally checked with a oscilloscope.
{
It has a P-P voltage amplitude of
CAUTION: When making measurements
on the power supply be sure that the other
scope probe is not connected to GND.
Vp-p
.
Measurements
are taken with
a white screen.
Hs - 5uS/div.
Vs - 2mS/div.
No
.
LTR.No
.
X
XY
X-Y VDC
WAVEFORM
TRANSFORMER
When all else fails,
connect 20 volts to the
power supply 17 volt
line and slowly
increase the AC
voltage up to just
before the the power
supply chirps. This is
called the smoke test.
LEGEND
BOARD PART No.
PART No. ON PRA.
X
X-Y VDC
Sync.
TP-REF.Vp-p
PRA PIN No.
DC VOLTAGE RANGE,
{
USING A DMM.
USE V. or H. SYNC.
AC VOLTS
Peak to Peak
Measured with scope
TEST POINT
ASS. REF.
92
Page 77

Ausrüstung Gegründet Für Die Reparatur Des Monitors Des Modells XX93.
OSZILLOGRAPH
+17.1
DVM
No DVM
320Vpp
1-4VDC
12Vpp 50,E2
40,G1
115
VAC
0 to 30V 0 to 30V
LOKALISIERUNG
TRANSFORMATOR
LOKALISIERTE
DOPPEL 1A
GLEICHSTROM
VERSORGUNGSTEIL
VARIABLER
Prüfen Sie
Generator
oder
Signalquelle
No.
LTR.No.
X
X
XY V
X-Y VDC
X-Y VDC
WAVEFORM
Sync.
TP-REF.Vp-p
TRANSFORMATOR
Wenn ganz sonst
ausfällt, schließen Sie
20 Volt an das
Versorgungsteil eine
17-Volt-Zeile an und
erhöhen Sie langsam die
CERONIX Modell XX93
AC Spannung bis, kurz
bevor das
Versorgungsteil
zwitschert. Dieses wird
Legende Beschreibung
Dieses stellt die Teilnummer des Brettes XX93 dar. Die Stückliste gibt die
{
CERONIX-Teilnummer, die zur Brettteilnummer registriert wird.
die Feuerprobe genannt.
Teilnummern der Widerstände auf dem PRA angezeigt von LTR.
PRA Anschlußstiftzahl. Gehört, um festzustellen welchem PRA die
{
Anschlußstiftzahl, suchen Sie nach der nächsten PRA Teilnummer auf dieser Zeile.
Gleichstromspannungen werden gemessen, um ausgenommen in das Versorgungsteil
zu reiben, in dem V- die Referenz ist. Verwenden Sie ein DVM für Gleichstrommessen.
Prüfpunkt, Brettquerverweisstandort.
Die Wellenform wird normalerweise mit einem
{
Oszillograph überprüft. Sie hat einen P-P
Spannung Umfang .
VORSICHT: Wenn Sie Messen auf
dem Versorgungsteil bilden, seien Sie
sicher, daß die andere
Vp-p
Messen werden
mit einem
weiflen
Bildschirm
genommen.
Bereichprüfspitze nicht an Erden
angeschlossen wird.
Hs - 5uS/div.
Vs - 2mS/div.
No
LTR.No
.
X
XY
V
X-Y VDC
Wellenform
LEGENDE
X
X-Y VDC
Sync.
TP-REF.Vp-p
BRETTTEIL-Nr.
TEIL-Nr. AUF PRA.
PRA Anschlußstift-Nr.
GLEICHSTROM
{
{
Spannung
STRECKE MIT A DMM
VERWENDEN Sie V.- oder
H.-Synchronisierung.
Volt
Wechselstrompaek
zur Spitze.
Gemessen mit oszillograph.
PRüFPUNKT
ASS. REF.
93
Page 78

POWER SUPPLY, TROUBLE SHOOTING TIPS.
SAFETY FIRST; Use only one hand when working on a powered up monitor to avoid electrical shock.
Always wear safety glasses.
Many of the failures that cause burnt
components and boards are eliminated by the
load sensitive switching mode power supply in
the CERONIX monitor. This feature can cause
problems with servicing the monitor if the proper
trouble shooting approach is not used. The
equipment setup, shown here, is necessary for
efficient trouble shooting of the CERONIX
monitors.
Problems that cause the power supply to chirp are:
1. Insufficient V+ line load.
2. Overloaded V+, +24V, or +16V lines.
3. Shorted V+, +24V, or +16V lines.
4. Power supply component failure.
5. Raw DC (V+ to V-) voltage too low.
A quick check for the insufficient V+ load is to
1.
connect a 2K to 4K ohm 10 watt power resistor
from GND to the V+ (cathode of diode 181 ). If the
181
chirping stops, proceed to check the horizontal
deflection circuit. First disconnect the board from
the AC supply. Then connect 16 volts to the 16V
line at the cathode of 169 . Also connect 24 volts
to the 24V line at the cathode of diode 168 and to
V+ at the cathode of diode 181 on the monitor.
169
168
181
Now the complete horizontal and vertical circuits
can be checked with the oscilloscope and DVM.
The flyback waveform will be about 170Vp-p
instead of 900Vp-p which permits checking even
the H. output transistor, collector, waveform.
For the overloaded supply line problems, the
2.
monitor power supply can be made to run
continuously by connecting the external power
supply to the 17V line. To accomplish this,
connect the external supply 0V clip lead to V(resistor
137
137 lead by the power transformer) and
+20V clip lead to the monitor power supply +17V
141
line (cathode of diode
141 ). Sometimes the
monitor will operate normally in this mode, in
which case, watch for smoke and after a few
minutes of operation disconnect the power
connections and carefully feel around the
conductor side of the board for hot spots. Overload
conditions will not harm the power supply unless
there is a problem in the power supply. If the
power supply is suspect, read the
TEST section on this page. Next check the DC
POWER SUPPLY
voltage of each of the power supply outputs. The
overloaded line will have a lower than normal
voltage reading. The defective component can be
located by measuring the voltage drop along the
trace of this line.
3.
If the V+ crowbar zener 181 is shorted, a fault
181
exists in the power supply which permitted the V+
line to exceed +160V. First replace the zener.
Never operate the monitor without the crowbar
zener installed. Then read the
TEST section on this page. Shorts on the V+, 24V,
POWER SUPPLY
and 16V lines other than the crowbar zener are not
likely to be connected to the power supply even
though the power supply chirps. By operating the
power supply with the +20V external power supply
many of these problems can be found using the
same procedure as are used in trouble shooting
monitors with linear power supplies.
The power supply may chirp if:
4.
The transformer core is broken or a
winding is shorted.
The .33 ohm current sensing
resistor value is too high.
The +17V line is open. (goes away
when external. PS is used)
There is a line voltage range of about 60% to
5.
70% AC line voltage where a correctly
operating monitor will chirp.
POWER SUPPLY TEST
To verify that the power supply is working
correctly, connect the 17V line, as indicated in
section 2 on this page. Also connect the
oscilloscope GND to V- and the oscilloscope probe to
the FET drive (anode of diode 116 ). There should
116
be a waveform at this point. If there is no FET
drive waveform, check the voltages and waveforms
on the C5184 pins and compare them to the
voltages and waveforms on the schematic.
Connect the AC power cord with the AC voltage,
from the variable transformer turned down to 0
volts. TAKE CARE NOT TO TOUCH THE
OSCILLOSCOPE AND MONITOR CHASSIS
DURING THIS TEST, SINCE THE VOLTAGE
DIFFERENCE CAN BE AS HIGH AS 400 VOLTS.
Connect the DVM to GND and V+. Slowly
increase the AC line voltage and observe the power
supply response. Do not exceed +145V on V+. If
the monitor runs normally, a fault may still exist
in the power supply +17V line circuit. Note; if
the crowbar zener is shorted and the FET is
internally shorted, the C5184 IC 115 should also
115
be replaced.
94
Page 79

Trouble Shooting Handbook
The information that is written in this handbook is to help repair XX93 Monitors.
Here is a guideline in which this handbook will follow:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Color problems.
No video with power.
No V-H sync.
Retrace lines.
No power.
Always wear safety glasses.
Caution; Use only one hand
when working on a powered up
monitor to avoid electrical
shock.
Color Problems.
A helpful hint when working with color problems is by identifying the
color of the three grid lines at the top of the screen.
When there is a missing color and the lines are white the problem lies in the video
interface section. This means it can be found between the customers game and pin 8 of
the Video Amplifier (K-Film). If the lines are not white it would be a output problem,
which is anything after pin 8 to the picture tube.
If the problem is excessive blue, green, or red background color,
tap on related K-film to see if it is defective.
If blue is the problem, check for damaged traces around the outside of
the video board, since most of these traces go to the blue K-film.
If monitor shuts down due to excessive color, disconnect the filament for
voltage tests. (Desolder CRT socket pin 9.)
Note: All voltage measurements are: DC with -lead to GND unless other wise noted.
Problem Tests Probable Solution
Missing
Check voltage on 75Ω input
1.
resistors
288 286 284
,, &.
If 0V to .05V, check video
connector and drive electronics.
Color.
241
Refer to the
schematic for
the specific pin
numbers of
each color.
Pins, listed in
table, are in
order of Red,
Green,
and Blue.
Tests should
preformed in order
to reduce chance of
replacing wrong
component.
If voltage, IC
2.
241 pins 16, 13, or 9
less than 7V & K-Films pin 1>8V.
If voltage, K-Film pin 1 is 10V and
3.
IC 241 Pins 1,15, & 8 are .3 to.7V.
If voltage, K-Film pin 1 over 10.6V
4.
Desolder pin 1. Make open to trace.
Color may be tested by connecting a clip
lead to GND and a 1.62KΩ resistor.
Contact the resistor to K-Film pin 1.
If voltage, K-Film pin 20, different
5.
than voltage at CRT socket pin.
If voltage, K-Film pin 20 is
6.
over 115V.
Arc
suppression
diodes:
Red
Green
Blue
835 899
845
886 959
Check for open between IC and
associated K-Film.
Ohm gain resistors at pins, if OK
replace video interface IC
If pin 1 over 10.6V, replace K-Film.
If pin 1 is 10V, replace the diode of
213 086 084
missing color
,, &.
If still missing color, replace IC
Resistance between these two
points should not exceed 1.1KΩ.
First replace, for shorted arc
suppression, diodes of affected color.
Then try replacing the K-Film.
849
If not solution, change the
transistors in the amplifier.
241
241 .
241
241 .
95
Page 80

Problem Probable Solution
Turn down M. Gain.
Excessive
color.
Turn down
G2 (bottom
pot of FBT)
1.
Measure voltage of K-Film pin 1
for each color. If affected color
has a .3V difference then others
Desolder pin 1. Make open to trace.
2.
Measure voltage across cap. 846 .
if excessive
color is too
Tests
846
If pin 1 still different
replace K-Film.
If pin 1 voltage same as others,
replace IC .
241
If this voltage is less than 5V,
check filament pulse. If OK
replace capacitor
bright.
3.
Refer to the
schematic for
the specific pin
numbers of
each color.
Tests should
preformed in
order to reduce
chance of
replacing
wrong
component.
Turn up M. Gain.
Measure voltage,
of affected color,
base to emitter:
4.
Ohm check,
CRT socket.
pin of effected
color to pin 12.
5.
Measure voltage, of affected color,
Red
Green
Blue
Red, pin 8
Green, pin 6
Blue, pin 11
K-Film pin 4.
837
842
954
If the voltage is greater than .7V
or 0V , Replace the transistor.
If resistance is below 2K, replace
the CRT socket.
If voltage is 3-8V replace the
2SC3467 & the PNP transistor pair.
If voltage is less than 2V replace
PNP transistor connected to pin.
857
857 .
Problem Probable Solution
1.
No Picture.
Check that the
master gain pot
is turned up.
Note; Blanking should be > 5V.
Measure blanking voltage on
215
jumper
215 . If .6V to 1V check
vertical output for waveform.
2.
Check light from filament.
If no light check FBP before and
after capacitor
Measure voltage on Blue K-Film
3.
pin 7. This voltage should be 9.3V.
Measure G2 voltage on
4.
CRT socket 877 pin 7.
877
Tests
854 .
The vertical booster pulse supplies
part of vertical sync to the auto bias
927
927 . With no sync to pin 8 of
IC
927
927 , vertical blanking is not reset.
If FBT waveform is the same on both
sides of the filament adjustment cap.
854854
854 , ohm out the filament circuit.
If this voltage is over 10V, replace
transistor 942 .
942
If this voltage is under 100V, check
that the FBT bottom pot is turned
up. Replace CRT Socket if GND to
G2 is less than 100KΩ.
Measure voltage on LM324 920
5.
pin 8.
Problem Probable Solution
1.
No
Sync.
Tests should
preformed in
order to reduce
chance of
replacing wrong
component.
Vertical osc. frequency adjustment;
2.
Check H. free running freq. (Hfo)
Check sync waveforms at input of
3.
LA7851. Hs=pin 1, Vs=pin 19.
4.
Check voltage, LM339,
Normal range is 5V to 7V.
Tests
920
355
355 pin 14.
If this voltage is 9-11V, replace the
C-Film 917 and or LM324 920 .
917 920
Add or remove V solder connection. p30
If out ±500Hz of sync, adj. Hfo.
If input sync to the LA7851 is OK
and picture roles replace IC
Also should check other voltages in this circuit.
If outside range replace IC 355 .
415
415 .
355
p75
96
Page 81

Problem Probable Solution
1.
Retrace
Lines .
Turn down M. Gain to minimum.
Measure voltage, auto bias IC 927
pins 2, 4, & 6 for 5.5V to 6.5V.
Also measure voltage, pins 3, 5,
Tests
927
If any of the voltages are
not in the listed voltage
range, replace IC 927 .
& 7 for 1.1V to 2.7V
927
2.
Measure voltage, LM324 920
pin 5. Should be less than 4.5V.
920
connection) & pin 5 voltage is 4.8V
add a 7.15K resistor pins 8 to 11.
Otherwise replace C-Film.
If old style C-Film (no solder
215
3.
Check video gain line (J
scope sync on Vs
215
331 , .2mS/cm,
and verify V. & H. blanking.
Problem Probable Solution
Monitor
Shuts
Down.
1.
2.
If shutdown right after power up.
3.
Disable shutdown; clip V- to 109 .
4.
Problem Probable Solution
1.
No
With power applied, check voltage
ground to (V-) anode of diode
Tests
019
Tests
215 )
109
156
156 .
If either V. or H. blanking is
missing, go to that circuit for
further tests.
Check voltage across cap. 846 5-10VIf screen turns bright & shutdown.
Check V+, Hfo, & EHT at power up.
If solution, check fault circuit.Disable fault; clip 019 to GND.
Measure EHT,
should be less than 27KV.
If 0V to 100V, ohm out fuse 146 &
inrush current limiter 159 25Ω to .5Ω.
Power.
Measure voltage, V+ line is 0V &
2.
PS chirps
Ohm out crowbar zener diode 181 .
Also ohm out H. output Xsr 433 .
846
146
159
181
433
If fuse is blown.
3.
Ohm out 160V crowbar zener
If the power supply chirps and
4.
high voltage can be heard.
If the power supply chirps, check
5.
for shorted secondary voltages by;
Disconnect power to chassis.
Apply external DC PS to 16V
line at cathode of diode
Apply second DC voltage to 24V
line at cathode of 168 .
168
FBT Check at low voltage;
169
169 .
181
181 .
If the zener is shorted and the fuse
115
146
146 ,
136181
is blown, replace fuse
zener 181 , power FET 136 ,
and the C5184 IC 115 .
Ohm out the 17V line; V- to anode
141 139
of
141 , 141 , 149 , 139 , 132 ,
149141
J-Film pins 8-14 & IC
First, ohm out diodes;
132
115
115 pin 15.
142 168
142 , 168 ,
169 , 181 .
169 181
If PS current less than .5A and 12V
line=11.5V to 12.5V, go to next test.
If PS current less than .3A, line OK.
433
Check base of H. output
433 for
drive waveform. If OK connect 24V
line to V+ line and check flyback
waveform at collector of
433
433 .
(Without H. deflection load, PS
chirps) If large and small pulses
observed, replace the FBT.
97
Page 82

Filament Voltage Test.
When replacing either the flyback transformer or the video
board, the filament voltage may not be correct.
Measuring the filament voltage is not accurate using a true
RMS voltage meter, because of the high frequency components,
which make up the filament voltage. An oscilloscope, with RMS
capability, may be used to measure the filament voltage.
Although a visual check of the filament color is a indicator of the
filament voltage, it is a good practice to check the filament voltage if
there is any doubt about this important monitor parameter.
The following filament voltage test is an accurate method of
finding the true RMS voltage to the filament. This is accomplished
by comparing the light output of the filament when it is driven by
the monitor to the light output of the filament with an applied DC
voltage using a loaded photocell.
62K,912
0Ω, 902
250V
RED
H400
899
.015uF
901
900
903
1N4005
470Ω, CF
G2
6
GREEN
5
G1
1K
CF
855
0Ω, 904
905
8
0Ω, 898
7
RED
1N4005
9
8
7
6
5
877
1N4005
FIL.FIL.
0Ω, 896
0Ω, 897
10
9
CELL
906
18Ω, 879
10
BLUE
11
12
1
CRT
10uF
895
2.2nF,889
11
GAPS
GND
SOCKET
XX93
Video Board
+
12
SETUP:
62K,852
10
11
13
14
205Ω
15
16
17
18
19
20
470Ω, CF
FR205
853
.033uF, 854
100K, CF
To find the filament voltage;
1. Solder two short buss wires to the filament pins to clip on.
+
10uF
0 to 30V 0 to 30V
+6.30V
DVM
+
ISOLATED
DUAL 1A DC
POWER
SUPPLY
++
.150V
DVM
24.3K
98
2. Use black tape to secure the photocell over the hole in
the plastic CRT socket connector. Caution: Be sure
not to move the photocell between the two tests.
Record the DC voltage output from the photocell with the monitor running normally.
3.
The monitor should be powered up for 10 minutes before making this measurement.
4.
Turn off the monitor.
Connect the variable voltage, 1 amp, DC power supply to the filament.
5.
The negative lead to the filament ground at the CRT socket pin 10.
Adjust the power supply voltage for the photocell reading, recorded in step 3.6.
The equivalent filament RMS voltage is now recorded by measuring the DC voltage
7.
at the CRT socket pins 9 and 10.
Page 83

HeizfadenSpannung Test.
Wenn der EHT-Transformator oder die Videokarte geändert wird, kann
die Heizfadenspannung falsch sein.
Die Heizfadenspannung besteht aus Hochfrequenzbestandteilen. Genaues Messen
der Heizfadenspannung kann nicht mit einem Effektivwertmeßinstrument erhalten
werden. Ein Oszillograph mit Effektivwertmessen-Fähigkeit kann benutzt werden,
um die Heizfadenspannung zu messen.
Obgleich ein Sichtprüfen der Heizfadenfarbe eine Anzeige der
Heizfadenspannung ist, ist es gutes üblich, die Heizfadenspannung zu
überprüfen, wenn es irgendeinen Zweifel ¸ber diesen wichtigen
Monitorparameter gibt.
Der folgende Heizfadenspannung Test ist eine genaue Methode des
Findens der zutreffenden Effektivwertspannung zum Heizfaden. Dieses
wird vollendet, indem man die helle Ausgabe des Heizfadens vergleicht,
wenn es durch den Monitor zur hellen Ausgabe des Heizfadens mit einer
angewandten Gleichstromspannung mit einer einprogrammiert Fotozelle
angetrieben wird.
62K,912
0Ω, 902
RED
H400
899
.015uF
250V
901
900
903
1N4005
470Ω, CF
G2
6
GREEN
5
G1
1K
CF
855
0Ω, 904
905
8
0Ω, 898
7
RED
1N4005
9
8
7
6
5
1N4005
0Ω, 896
0Ω, 897
9
877
CELL
10
FIL.FIL.
906
18Ω, 879
10
BLUE
11
12
1
CRT
10uF
895
2.2nF,889
11
GAPS
GND
SOCKET
Videokarte
+
12
XX93
+
10uF
0 to 30V 0 to 30V
+6.30V
DVM
+
KONFIGURATION:
10
11
13
14
205Ω
15
16
17
18
19
20
470Ω, CF
62K,852
FR205
853
.033uF, 854
100K, CF
LOKALISIERTE
DOPPEL 1A
GLEICHSTROM
VERSORGUNGSTEIL
++
.150V
DVM
24.3K
Die Heizfadenspannung finden;
Löten Sie zwei kurze bussleitungen zu den Heizfadenanschlußstiften weich.1.
2.
Benutzen Sie schwarzes Band, um die Fotozelle über der Bohrung im
Plastik-CRT-Einfaßung Stecker zu sichern.
Vorsicht: Seien Sie sicher, die Fotozelle nicht zwischen die zwei Tests zu
verschieben.
Speichern Sie die Gleichstromspannung, die von der Fotozelle mit dem
3.
Monitor ausgegeben wird, der normalerweise läuft. Der Monitor Muß
laufen damit 10 Minuten die Heizfadenspannung messen.
4.
Drehen Sie weg den Monitor Ab.
Schließen Sie die variable Spannung, 1 Ampere, Gleichstrom-Versorgung zum
5.
Heizfaden an. Das Negativ führen zu den Heizfaden, der am CRT-Einfaßung
Anschlußstift 10 gerieben wird.
Stellen Sie die Versorgungsteilspannung auf das Fotozelle Messen ein, gespeichert
6.
in Jobstep 3.
Die gleichwertige Heizfadeneffektivwertspannung wird jetzt gespeichert, indem man die
7.
Gleichstromspannung an den CRT-Einfaßung Anschlußstiften 9 und 10 mißt.
99
Page 84

SETUP AND CONVERGENCE PROCEDURE
Use a knife to brake free the magnetic rings
1.
on the yoke, which are usually locked with
red varnish. Bring the adjustment tabs on
each pair of magnetic rings in line for the
starting point.
Loosen the yoke clamp. Remove the yoke
2.
wedges and the tape from the CRT.
3.
Connect a test generator to the video input.
Adjust the yoke position, on the CRT neck,
7.
to the center of purity. One way to locate
this yoke position is to make a felt pen mark
on the CRT neck at the rear extreme of
purity and another mark at the front extreme
of purity. Make a third mark between the
two marks and set the yoke to this position.
Rotate the yoke to line up, the raster top line,
with the top of the picture tube. Tighten the
yoke clamp. Tilt the yoke side to side and up
and down while watching the red field to
verify that purity is good.
Turn the monitor on. Switch the test
4.
generator to red field. Adjust the horizontal
and vertical raster size, on the remote control
board, for under scan. Let the monitor run
for at least half an hour.
Check the auto bright control voltage with a
5.
DVM. Connect the DMM to GND and pin 8
of the LM324
920
920 on the video board. The
voltage range is 4.0V to 4.4V. If out of
range, adjust this voltage to 4.2V by using
pliers to rotate the bottom knob on the FBT.
Degauss the picture tube and front part of
6.
the frame.
CAUTION: To avoid electrical shock,
take care not to touch the yoke conductors or
push against the anode cap.
Always keep one hand free to avoid making a
complete electrical circuit.
8. If the yoke position adjustment does not
produce good purity, adjust the purity
magnets. Tabs closest to the yoke winding.
Switch the generator to the red/blue grid.
9.
Adjust the 4 pole magnets (center pair)
for convergence of the red and blue guns in
the center of the screen.
Tilt the yoke up and down for the best
10.
convergence around the edge of the grid.
Insert the top yoke wedge. Tilt the yoke side
to side for the best convergence around the
edge of the grid and insert the rest of the
yoke wedges. Secure the wedges with tape.
Switch the generator to the white grid.
11.
Adjust the 6 pole magnets (Pair closest to the
video board) for convergence of the green
gun. Step #10 and this step may have to be
repeated for optimum convergence.
100
If the corner convergence is still not
12.
acceptable, shunts may be used to correct
this problem.
Shunts are available from CERONIX.
Shunt order number is CPM2011.
Page 85

SETUP UND KONVERGENZ PROZEDUR
1.
Benutzen Sie eine scharfes Messer, um die
magnetischen Ringe auf dem Joch frei zu
bremsen, die normalerweise mit rotem Lack
gesperrt werden. Holen Sie die
Justagetabulatoren auf jedem Paar
magnetischen Ringen in der Zeile für den
Ausgangspunkt.
Lösen Sie den Klemmring des Jochs.
2.
Löschen Sie die Jochkeile von der CRT.
Löschen Sie das Band von der CRT.
3.
Schließen Sie einen Testgenerator an den
videoinput an.
4.
Schalten Sie den Monitor ein. Schalten Sie
den Testgenerator zum roten Feld. Justieren
Sie die horizontale und vertikale
Rastergröße, mit dem Fernbedienungbrett,
für Unterscan. Lassen Sie den Monitorlauf
für mindestens halbe Stunde.
Überprüfen Sie die helle
5.
Steuerselbstspannung mit einem DVM.
Schließen Sie das DMM an erden und
Anschlußstift 8 des LM324 920 auf der
Videokarte an. Die Spannung Strecke ist
4.0V zu 4.4V. Wenn aus Strecke heraus,
justieren Sie diese Spannung auf 4.2V, indem
Sie Zangen verwenden, um den unteren
Drehknopf auf dem FBT zu drehen.
Degauss die CRT und das Vorderteil des
6.
Monitorchassis.
920
Justieren Sie das Joch auf die CRT, um
7.
Mitte der Reinheit zu erreichen.
Ein Weg, diese Joch Position zu finden, soll
eine Kugelschreiber Markierung auf dem
DATENSICHTGERäT Hals an der
Hinterseite und den vorderen Extremen der
Reinheit machen.
Machen Sie eine dritte Markierung
zwischen den zwei Markierungen und Satz
das Joch zu dieser Position.
Drehen Sie das Joch auszurichten, die
raster oberste Linie, mit dem Oberteil Rohr
des Bilds.
Ziehen Sie die Joch Klammer fest. Kippen
Sie die Joch Seite zu Seite und auf und ab
während Zuschauen des roten Felds zu
beglaubigen, daß jene Reinheit gut ist.
8.
Wenn die Joch Position Regelung gute
Reinheit nicht herstellt, stellen Sie den
Reinheit Magneten ein. Diese sind die
magnetischen Ringe der nächst Joch
Winden.
9.
Schalten Sie den Generator zum rot/blauem
Raster. Stellen Sie den 4 Stange Magneten
(Mitte Paar) für Zusammenlaufen vom roten
und blauen in der Mitte des Schirms ein.
Kippen Sie das Joch auf und ab für das
10.
beste Zusammenlaufen um die Kante des
Rasters. Fügen Sie den obersten Joch Keil
ein. Kippen Sie die Joch Seite zu Seite für
das beste Zusammenlaufen um die Kante des
Rasters und fügen Sie den restlichen Joch
Keile ein. Befestigen Sie die Keile.
VORSICHT: Um elektrischen Schlag zu
vermeiden, berühren Sie nicht sich zu den
Jochleitern oder -presse gegen die Anode
Schutzkappe.
Halten Sie immer eine Hand frei beim
Arbeiten auf Elektronik.
Schalten Sie den Generator zum weißen
11.
Raster. Stellen den 6 Stange Magneten
(Paaren nahst zum Videoausschuß) für
Zusammenlaufen vom grünen. Schritt #10
und dieser Schritt können für das günstigste
Zusammenlaufen wiederholt werden müssen.
Wenn die Eckkonvergenz noch nicht
12.
annehmbar ist, können Shunts benutzt
werden, um dieses Problem zu beheben.
Shunts sind von CERONIX vorhanden.
Shuntauftragsnummer ist CPM2011.
101
Page 86

Date
CERONIX, INC.
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, California 95602-7419
Tel. (530) 886 - 6400
Fax. (530) 888 - 1065
WEB. www.ceronix.com
REPLACEMENT PARTS PURCHASE ORDER FORM
Purchase Order No.
Name
BILL TO
STREET & N0.
CITY
Phone No.
Shipping Information
Comments
CERONIX
Part No.
1
2
STATE ZIP
Requisition No.
SHIP TO
STREET & N0.
CITY
STATE ZIP
Fax No.
Description PriceQuantity
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Please copy form and fill in, parts order, on copy.
102
Page 87

DEGAUSSING COIL ATTACHMENT SPECIFICATION.
.
.
103
ATTACH THE
GROUNDING
STRAP FIRST.
With the degaussing coil leads centered on the bottom of the
CRT, FORM THE COIL to avoid the remote control board.
For The Model 1493 Video Monitor
Use degaussing coil part number CPS1766.
INSTALL A WIRE TIE through
the top hole in the left CRT ear.
INSTALL WIRE TIES through
the bottom hole in the left CRT ear.
INSTALL A WIRE TIE through
the top hole in the right CRT ear
INSTALL WIRE TIES through
the bottom hole, with the
grounding strap spring, in the
right CRT ear.
Page 88

Degaussing Coil & Grounding Strap Attachment Specification.
For The Model 1793, 1993, 2093 Video Monitor.
The first item to attach to the picture tube is the grounding strap. Lay the tube face
1.
down on a soft surface. Slide the folded over end of the braided wire over the top left
CRT mounting ear (The braided wire is oriented to the left). Attach the spring at the
other end to the left hole of the right bottom mounting ear.
2. Next attach the degaussing coil. Locate the connector wires at the bottom center of
the CRT. Form the degaussing coil to the contour of the tube at the top two corners.
Attach and tighten two 3" wire ties on the inside hole of the top two corners.
Loosely attach two 15" wire ties around the degaussing coil and around the bottom
ears. Tighten the wire ties.
CAUTION: The ground cable from the enclosure to the monitor chassis
must be connected before applying power to the monitor.
3" Wire Tie
2PL
CPM2003
Grounding Strap
CPS1791
Degaussing coil Connector
Plugs in main board left side of fuse.
Top of CRT
Anode Connection
Degaussing
coil
CPS1771
CPS1828
CPS1847
CPS1860
Ground
Connector.
Attach to
CRT socket
board.
15" Wire Tie
2PL
CPM2013
Spring
104
3 Blue
2
Blue
1
Black
Schematic:
1
2
Bottom
View
(pins)
3
Plugs in main board left side of
flyback transformer.
Yoke Connector.
Page 89

Degaussing Coil & Grounding Strap Attachment Specification.
For The Model 2793 and 3693 Video Monitor.
1. The first item to attach to the picture tube is the grounding strap. Lay the tube face
down on a soft surface. Slide the folded over end of the braid over the left top CRT
mounting ear. Attach the spring at the other end to the, right side top, slot in the
rimband. Pull the bare wire through the bottom slot in the rimband (tension the
spring) and back around the braid. The coils of the spring should measure about 1.25".
2. Next attach the degaussing coil. Locate the connector wires at the bottom center of
the CRT. Loosely attach the degaussing coil with 5" wire ties as shown below.
Adjust the coil for an equal size top and bottom coil half. Tighten the wire ties.
3. Plug the yoke connectors on the yoke as shown below.
CAUTION: The ground cable from the enclosure to the monitor chassis
must be connected before applying power to the monitor.
Grounding Strap
Yellow
Brown
Degaussing coil Connector
Plugs in main board left side of fuse.
Top of CRT
Anode Connection
Blue
Red
Degaussing
coil
CPS1786
CPS1856
Ground
Connector.
Attach to
CRT socket
board.
3 Blue
2
Blue
1
Black
Schematic:
1
2
Bottom
View
(pins)
Yoke Connector.
3
Plugs in main board left side of
flyback transformer.
105
Page 90

Highpot, For Shock Hazards, Circuit Description.
For the models 1493,1793, 1993, 2093, 2793, and 3693 video monitors.
It is the responsibility of the company which uses the Ceronix
monitor in there system to make sure that no shock hazards
exist. Below is a description of the highpot test to verify that
the monitor is properly connected to an isolation transformer.
Once the monitor is installed in the enclosure, the protective
earth ground connection must be connected. The connection
point is located on the inside of the main board metal frame
behind the serial number label.
Building wiring
AC line
Primary Line
GROUND
Machine in which the monitor is used.
The MONITOR is connected to
the enclosure ground via the
signal cable, monitor support
hardware, and the protective
earth ground wire.
The chassis ground must be
connected to earth ground.
All the large accessible metal
parts are connected to ground.
FUSE
Isolation
Transformer
106
HIGH
POT
TESTER
Page 91

Highpot, Für Schock Gefahren, StromkreisBeschreibung.
Für die Modelle 1493,1793,1993,2093,2793, und 3693 videomonitoren.
Es ist die Verantwortung der Firma, die den Ceronix Monitor in dort
system benutzt, sich zu vergewissern, daß kein Schock Gefahren
existieren. Unten ist eine Beschreibung Prüfung des highpot zu
beglaubigen, daß der Monitor ordentlich an einen Isolierung Umformer
angeschlossen wird.
Nachdem der Monitor in der Einschlieflung installiert wird, muß der
schützende Erde Erdanschluß verbunden werden. Der Anschluß Punkt
wird sich auf dem innerhalb des Hauptausschusses Metalls Rahmens
hinter dem Seriennummer Etikett befunden.
Gebäudeverdrahtung
Wechselstromezeile
PrimärZeile
ERDEN
Maschine, in der der Monitor benutzt wird.
Der MONITOR wird an den
Einschließung Erden über das
Signalkabel, Monitor Stütze
Hardware und den schützende
Erde Erdungsdraht
angeschlossen.
Der Chassiserden muß an die
Masse Erdletung angeschlossen
werden.
SICHERUNG
Lokalisierung
Transformator
Alle großen zugänglichen
Metallteile werden an erden
angeschlossen.
HIGHPOT
Prüfvorrichtung
107
Page 92

Wire Routing Instructions.
,
.
d
n
e
s
Attach the protective earth
green / yellow, ground wire
Rout yoke wires
over CRT neck.
Fold remote cable to clear
CRT and add wire tie.
Shorten EHT wire
and add wire tie.
Shorten focus wire
and add wire tie.
Plug in video board.
Rout G2 wire aroun
CRT socket, shorte
with loop, and add
wire tie.
108
Fold video flat cable to
avoid contacting the
metal frame. Secure
fold with a wire tie.
Finished assembly with th
different voltage type wire
not touching each other.
Page 93

1
Program
Precision Resistor Arrays (PRAs).
Make solder connection CA when using these C PRAs for replacement parts on the XX92 product line.
ΩΩ
200ΩΩ
68.1K
C13
RED
GREEN BLUE 12V 4.8V BLUE BLUE
ΩΩ
200ΩΩ
C16
23 5678910 131415161718192011412
H.
Program
BlankPULSE i BeamPULSE
200ΩΩ
Program
ΩΩ
C8
20K 1.82
K
GND
C6C5
NC
68.1K68.1K
C3C2C1
2.74K 1.82
CA
ΩΩ
900ΩΩ
C17
LINE LINE Amp out Amp FBPULSEi Beam i Beam i sense Amp FBi sense Amp out Amp FBi sense Amp out
K
C4C7
5.00K
4K
C9
BLUE GREEN GREEN
4K
C11C10
5.00K
C12
GREEN RED RED RED
14
4K
C14
13 14576LM324 Pin No. 2
5.00K
C15
AUTO BIAS RESISTOR ARRAY "C Film"
C
P/N CPR0506
IA - Inverts Horizontal Sync. IB, IC, & ID Adjust the Horizontal Oscillator Frequency. For 31.5KHz Operation; IB=Hfo +400 Hz, IC=Hfo +800Hz, & ID=Hfo +1,600Hz.
2.78K
20K
I13
I5
PLL
O/S
45K
I6
1
FBP
1.8K
I1
12K
I2
23 5678910 1314151617181920
H. Pos.
H. Sync
POT
Cap.
8.8K
I12
IA
22K
HORZ.
GND GND
+12V
2.7K
I4
I3
H. Sync
H. Pos.
Output
O/S
1 LA7851 Pin No.
IB IC ID
ΩΩ
340ΩΩ
ΩΩ
11
PLL
SYNC
170ΩΩ
10K
I7
I15
I14
33K
PLL
output
Cap.
1K
I8
OSC.
680ΩΩ
ΩΩ
I16
I9
Osc.Dis-
charge
987432
9.31K
Hfo
SET
I10
H. +12V
Line
Fly-
wheel
Cap.
200
1/2
I11
H. Drive
Damper
200
1/2
I11
Damper
Cap.
I
Horizontal Control Resistor Array "I Film"
P/N CPR0502
JA - Decreases V+ line by 1.5V
JB - Decreases V+ line by 3V
91.4K
2.33K
J13
J1
JA JB
11K
23.2K
J3
J2
1
V+
SENSEV+Adj.
2345678910 121314151617181920
V-
-FB CAP.
E. AMP.
JC - Increases V+ line by 1.5V
JD - Increases V+ line by 3V
4.67K
J14
130ΩΩ
ΩΩ
JC
J15
ΩΩ
260ΩΩ
J16
JD
127K
10.6K
J4
E. Amp
Output
J5
1/2 Raw
E. Amp
+Input
21 C5184 Pin No. 11 15 14 13 12
V-, 100V to 300V below GND.
POWER SUPPLY RESISTOR ARRAY. "J"
P/N CPR0501
45K
J6
33.2K
Osc.
17V V-
DC
Rx
45K
J17
ΩΩ
510ΩΩ
J7
FET
i Sense
J8
FET
Source
Normally GND -200V.
Power Supply Resistor Array "J Film"
Power Supply Resistor Array "J Film"
101.6K
JE
+17V V-
J18
38.8K
J9
O.V.P.
LOAD
1M
14.7K
D 142
+ Comp.
15.8K
J11 J12
D 142
- Comp. V-
J10
V+
J
J
P/N CPR0501
P/N CPR0501
109
Page 94

Precision Resistor Arrays (PRAs).
1234 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
678 10115912
K
A - Increases Output Voltage by 10V
100Ω
301Ω
VIDEO
INPUT
1.62K
K21
K2
K1
3904
B
C
1N4148
+12V
LINE
K34
606Ω
E
K36
K7
1N4148
K35
150Ω
150Ω
K3B
NPN 9.25V
+16V
LINE
GND
K3A
689Ω
NPN
K6
0Ω
K33
21K
K22
820Ω
A
K13
5.62K
K11
PNP E
CAP.
K10
18Ω
K14
PNP
E
12.1K
K15
140Ω
PNP
40.2K
K19
560Ω
180Ω
K16
K17
PNP B
120V
DIODE
B
LINE
K18
PNPCAMP
Output
K
P/N CPR0510
12
2.2K
34567
1.2K
NE592
K8
K32
11 12
10
9
8
13
K5
1.49
K
K9
14
15Ω
3.32K 75Ω
33Ω
K20
K4
LINE
NE592
OutputB
E
+12V
GND GND
LINE
AUTO
BIAS
K12
127V
LINE
Video Amplifier Resistor Array "K Film"
110
Page 95

Precision Resistor Arrays (PRAs).
1234 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
678 10115912
BLUE
A - Increases Output Voltage by 10V
100Ω
240Ω
VIDEO
INPUT
1.29K
K1
K21
K2
3904
B
+12V
LINE
606Ω
C
K34
1N4148
E
K36
K7
1N4148
K35
150Ω
150Ω
K3B
NPN 9.25V
+16V
LINE
GND
K3A
689Ω
NPN
K6
0Ω
K33
21K
K22
820Ω
A
K13
5.62K
K11
PNP E
CAP.
K10
18Ω
K14
PNP
E
12.1K
K15
140Ω
PNP
40.2K
K19
560Ω
180Ω
K16
K17
PNP B
120V
DIODE
B
LINE
K18
PNPCAMP
Output
12
2.2K
34567
1.2K
NE592
K8
K32
11 12
10
9
8
13
K5
1.49
K
K9
14
15Ω
3.32K 75Ω
33Ω
K20
K4
LINE
NE592
OutputB
E
+12V
GND GND
LINE
AUTO
BIAS
K12
127V
LINE
BLUE
P/N CPR0511Video Amplifier Resistor Array "BLUE Film"
111
Page 96

CPM2501
1
CPM2501
x 3
2
CPM2005
x 3
CPM2002
x 3
3
VERTICAL DEFLECTION
BOOSTER ASSEMBLY
CERONIX CPA4267
603
603
NPN
NPN
TIP31ATIP31A
E
C
B
E
C
B
FR205
604
604
1W
605
605
1.2Ω,
606
606
607
4.7Ω, 607
608
4.7Ω, 608
609
609
VWXYZ
610
610
1W
3.3Ω,
FR205
611
611
602
602
NPN
NPN
E
C
B
E
C
B
CPB1615
CPB1615
Vertical Amp. PCB
Vertical Amp. PCB
PNP
PNP
ECB
ECB
HEATSINK
CPM2141
601
601
TIP32A
612, LA3838
612, LA7838
Complete Assembly View (Top view)
CABLE: CPS1858
CABLE: CPS1858
12345678910111213
12345678910111213
VWXYZ
9
112
Board Assembly View (Component side)
1
2
3
Page 97

The "Drive Signals To The Monitor Input" form is included here for those people who have
problems interfacing their drive electronics with the Ceronix Monitor.
DRIVE SIGNALS to the MONITOR INPUT
voltage and waveforms, work sheet.
CERONIX
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, CA, USA 95602-7419
Fax (530) 888-1065
VIDEO:
With no load, the black level voltage of the video drive signal is:
To simulate the monitor input resistance.
With 75Ω load on the video drive signal
or other load.Ω
If available, sketch the video drive circuit on the back of a copy of this form.
For the following measurements use an oscilloscope.
With no load, the saturated color voltage is:
Company name:
Date:
For CERONIX Monitor
Model number:
RED GREEN BLUE
RED GREEN BLUE
the black level voltage is:
the saturated color voltage is:
Horizontal or composite sync:
Horizontal frequency:
Horizontal sync pulse time:
Compare your sync to
this table and check
the best fit.
For composite sync.
Sketch if different.
KHz
uS
"High" voltage:
"Low" voltage:
Vertical sync:
Vertical frequency: Hz "High" voltage: V
Vertical sync pulse time: uS "Low" voltage: V
Check correct polarity.
V
V
call (530) 886-6400.
Complete form and send to:
or FAX us (530) 888-1065
CERONIX, INC.If there are any questions,
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, CA. 95602-7419
113
Page 98

DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer:
Equipment:
Standards:
C. CERONIX
13350 New Airport Road
Auburn, California 95602
USA
Component Color Monitor.
Models: 1493-CGA, 1493-VGA, 1493-SVGA.
1793-VGA, 1793-SVGA.
1993-VGA, 1993-SVGA.
2093-CGA, 2093-VGA.
2793-CGA, 2793-VGA.
3693-CGA.
Component Isolation Transformer Assembly.
Models: ISOXFR-75W, ISOXFR-100W.
IEC 60950, 3rd Edition
'National Differences: AT, AU, CA, DE, ES, FR, GB, HU, RU, US, ZA.'
CAS/CAN 60950-00
UL 60950, 3rd Edition
IEC 65:85 + A1:87 + A2:89 + A3:92, 5th Edition
'National Differences: KR.'
Authorized
Signatory:
Title:
Date:
I hereby declare that the equipment named above has been tested and
found to comply with the relevant sections of the above referenced
specifications. The unit complies with all essential requirements of
the standards. The declaration is issued under the sole responsibility
of the manufacturer.
Don Whitaker
President
February 26, 2002
02
114
Page 99

Models:
ISO XFR-75W
ISO XFR-100W
SAFETY ISOLATING TRANSFORMER
115
Page 100

Circuit Function Description.
The basic function of the ISO XFR-75W and ISO XFR-100W is to
isolate the line power for monitors requiring an isolation transformer.
The transformer is designed to have a low leakage flux value which
allows it to be mounted close to the CRT. To accomplish the low
leakage flux, the transformer has two sets of primary and secondary
coils mounted on a modified toroid type core. The ideal transformer
would be a toroid but this type transformer is expensive because it is
difficult to wind.
A relay is used to connect the two primary coils in series or parallel to
accommodate 240VAC or 120VAC line voltages. Before power is
applied, the relay connects the transformer primary windings in series to
avoid excessive primary current for the 240VAC case. The control
circuit energizes the relay when the line voltage is 120VAC.
240VAC
or
120VAC
50 or 60 Hz
Input
240VAC
or
120VAC
Relay Control
Output
Circuit Description.
T518
T506
T504
T514
T507
T503
T511
T508 T502
T515
T520T517
T508
T510T513
T512
T518
T512
T516
T505T509
T504
T513
The fuse 506 protects the mains wires and the control PCB.
The power transformer has two internal 2 amp temperature sensitive fuses.
Each primary half has one, built in, series connected fuse.
A resettable fuse 507 is connected to the relay driver power supply.
This fuse protects the relay control circuit from square wave input which would
occur if an inverter is used as the power source. Capacitor 512 supplies
current from the line to capacitor 513 through diode 510 which forms the, relay
control, power supply. Diode 511 charges capacitor 512 during the negative
going part of the line wave. Transient Voltage Suppressor 516 regulates the
24V power supply and protects the relay coil from over heating.
The Mos Fet 514 shorts out the 24 volt power supply when the input line
voltage is 240VAC.
The input line voltage, at which the Mos Fet turns on, is set by the Mos Fet turn
on voltage (about 4V), the voltage drops across resistors 509 , 505 , 504 , and
the zener diode 503 . 154VAC is the approximate line voltage at which the
relay 518 switches. Capacitor 508 and diode 502 keep the Mos Fet turned
on for the complete AC cycle to eliminate ripple current in the capacitor 513 .
Resistor 504 limits the peak current to capacitor 508 to avoid relay switching
due to line transients. The zener diode 515 which is connected from the Mos
Fet source to gate protects the Mos Fet gate against over voltage. Resistor
T519
519 is needed to limit the mains current when the relay arcs across both sets of
contacts. Capacitors 517 and 520 reduce the relay T518 contact noise which
may be generated when switching.
116
 Loading...
Loading...