GENESYS GL310MC3D Datasheet

Genesys Logic, Inc.
July 16, 1998July 16, 1998
Genesys Logic, Inc.
10F., No.11, Ln.3, Tsao Ti Wei, ShenKeng, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
TEL:886-2-2664-6655 FAX:886-2-2664-5757
http://www.genesyslogic.com.tw

Revision 1.0 July/16/19981
GL310MC PS/2 3D Mouse Controller
1. Features
l Low-cost solution for PS/2 3D mouse
l Compatible with Microsoft IntelliMouse
l I/O ports
- 6 special purpose I/O pins optimized for photo-sensor
- 2 I/O pins with LED drive capability
l Patent pending full-range detection for photo-sensor
- Removes the expensive process of matching LED and photo-sensor
- Improve end-product yield rate almost to 100%
- Huge cost saving
l Option to use wheel or button for scrolling
l Option to detect 2 or 4 pulses for one move
l R-C oscillator
- No expensive crystal oscillator required
- Reduce BOM
l Improved output drivers with slew-rate control to reduce EMI
l Minimal external components(2R or 3R + 2C) required for application circuit
l Tracking speed
- Up to 100µs/per sampling
l 6 MHz external clock
l Internal power-on reset(POR)
l Available in cost saving 16-pin PDIP
Revision 1.0 July/16/19982
GL310MC PS/2 3D Mouse Controller
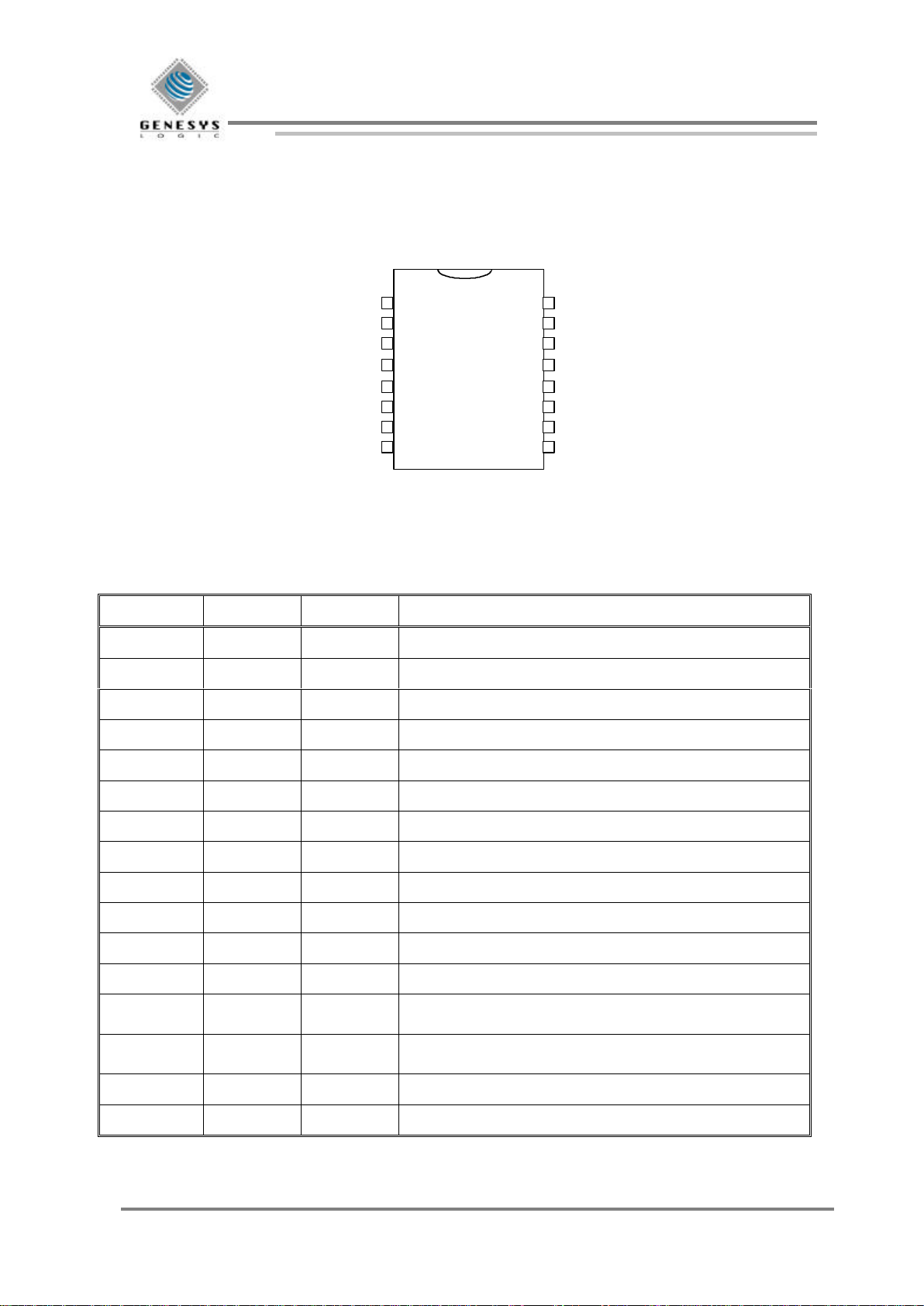
2. Pin Configuration
Figure 2-1. 16-Pin DIP
Pin Symbol I/O Description
1 X1 I Photo sensor input for X axis 1
2 X2 I Photo sensor input for X axis 2
3 Y1 I Photo sensor input for Y axis 1
4 Y2 I Photo sensor input for Y axis 2
5 LB I Mouse left button, internal pulled high
6 MB I Mouse middle button, internal pulled high
7 RB I Mouse right button, internal pulled high
8 GND Ground Ground
9 PS2CLK I/O PS/2 mouse clock
10 PS2DAT I/O PS/2 mouse data
11 NC
12 NC
13 Z2 I Photo sensor input for horizontal scroll 1
horizontal scroll right button internal pulled up
14 Z1 I Photo sensor input for horizontal scroll 2
Horizontal scroll left button internal pulled up
15 CLK Clock 6MHz RC clock input
16 VDD Power Power
X1
X2
Y1
Y2
LB
MB
RB
GND
VDD
CLK
Z1
Z2
NC
NC
PS2DAT
PS2CLK
1 16
2 15
3 14
4 13
5 12
6 11
7 10
8 9
Revision 1.0 July/16/19983
GL310MC PS/2 3D Mouse Controller
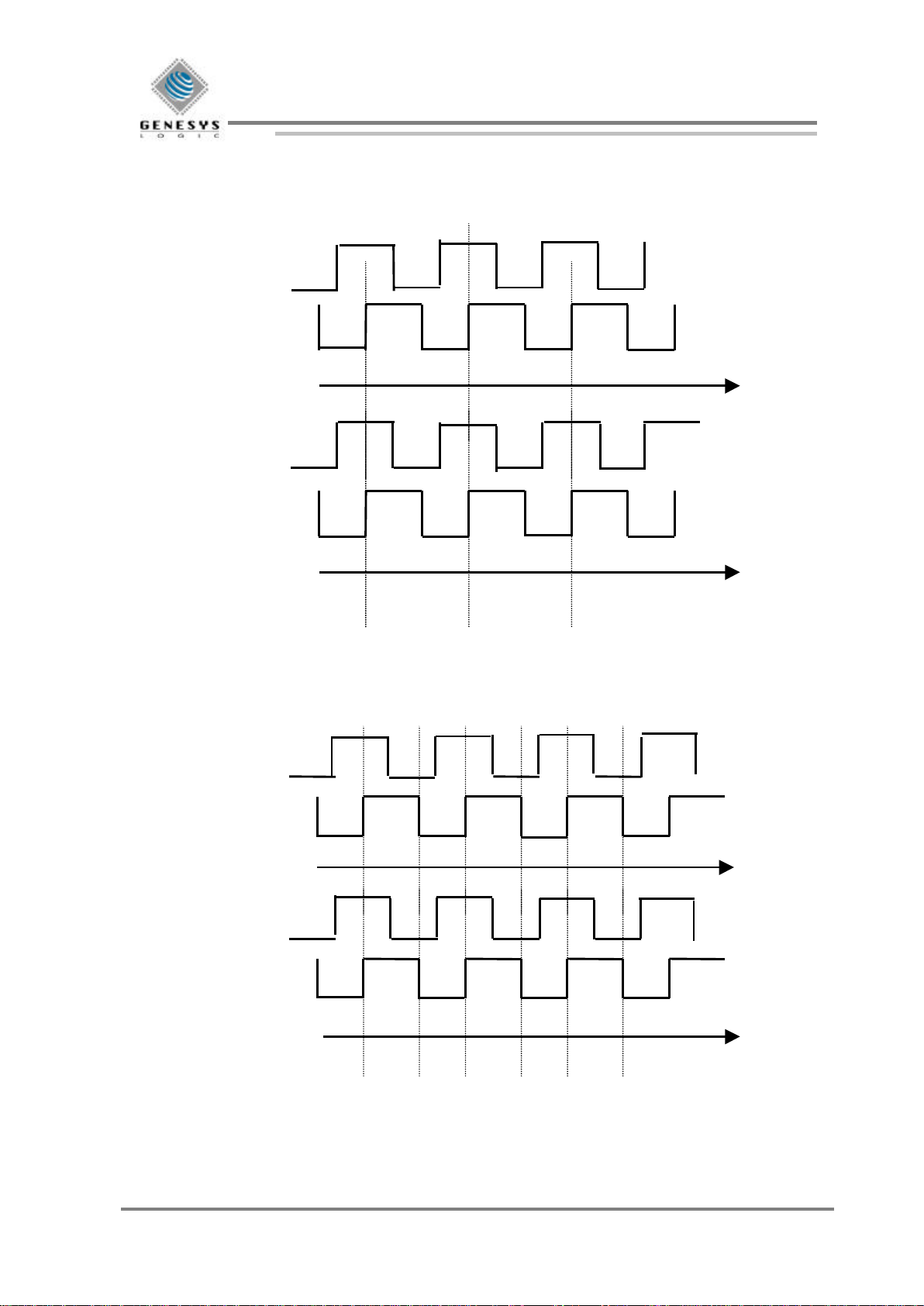
3. Scrolling control
3.1 Wheel Scrolling Control (4 pulses for one move)
3.2 Wheel Scrolling Control (2 pulses for one move)
Vertical scroll 1
Vertical scroll 2
Every colon scroll up 1 unit
Horizontal scroll 1
Horizontal scroll 2
Every colon scroll left 1 unit
Vertical scroll 1
Vertical scroll 2
Every colon scroll up 1 unit
Horizontal scroll 1
Horizontal scroll 2
Every colon scroll left 1 unit

Revision 1.0 July/16/19984
GL310MC PS/2 3D Mouse Controller
3.3 Button scrolling control
l Use button to control vertical/horizontal scrolling
l 320ms before 4
th
repeat
l 40ms after 4
th
repeat
3.4 GL310MC3D Series Selection Guide
l GL310MC3D2P
- PS/2 3D Mouse, wheel scrolling, 2 pulses for one move
l GL310MC3D4P
- PS/2 3D Mouse, wheel scrolling, 4 pulses for one move
l GL310MC3D1B
- PS/2 3D Mouse, button scrolling
Revision 1.0 July/16/19985
GL310MC PS/2 3D Mouse Controller
4. PS/2 Protocol
The PS/2 protocol allows synchronous, bi-directional serial communication between the host and the
device. Either side may transmit a command or data byte at any time, although only one side can
transmit at one time. During initialization, the host sends command bytes to the device. Some
commands are followed by argument bytes. The device acknowledges each command and argument
byte with an ACK ($FA) byte, possibly followed by one or more data bytes. If the host has enabled
"Stream mode" transmission, then the device may send spontaneous data packets to the host describing
finger motions and button state changes.
4.1 Electrical interface
The PS/2 protocol includes two signal wires as well as +5V power and ground. The signal wires,
CLK and DATA, are bi-directional "open-collector" signals; they are normally held at a high (+5V)
level by a 5-10K pull-up resistor on the host, but either the host or the Mouse device can pull them
low at any time. When the port is idle, both signal wires are floating high. The host can inhibit the
device at any time by holding the CLK wire low.
Note that neither side ever actively pulls CLK or DATA high; to output a logic 1, the wire is left
undriven and allowed to float high.
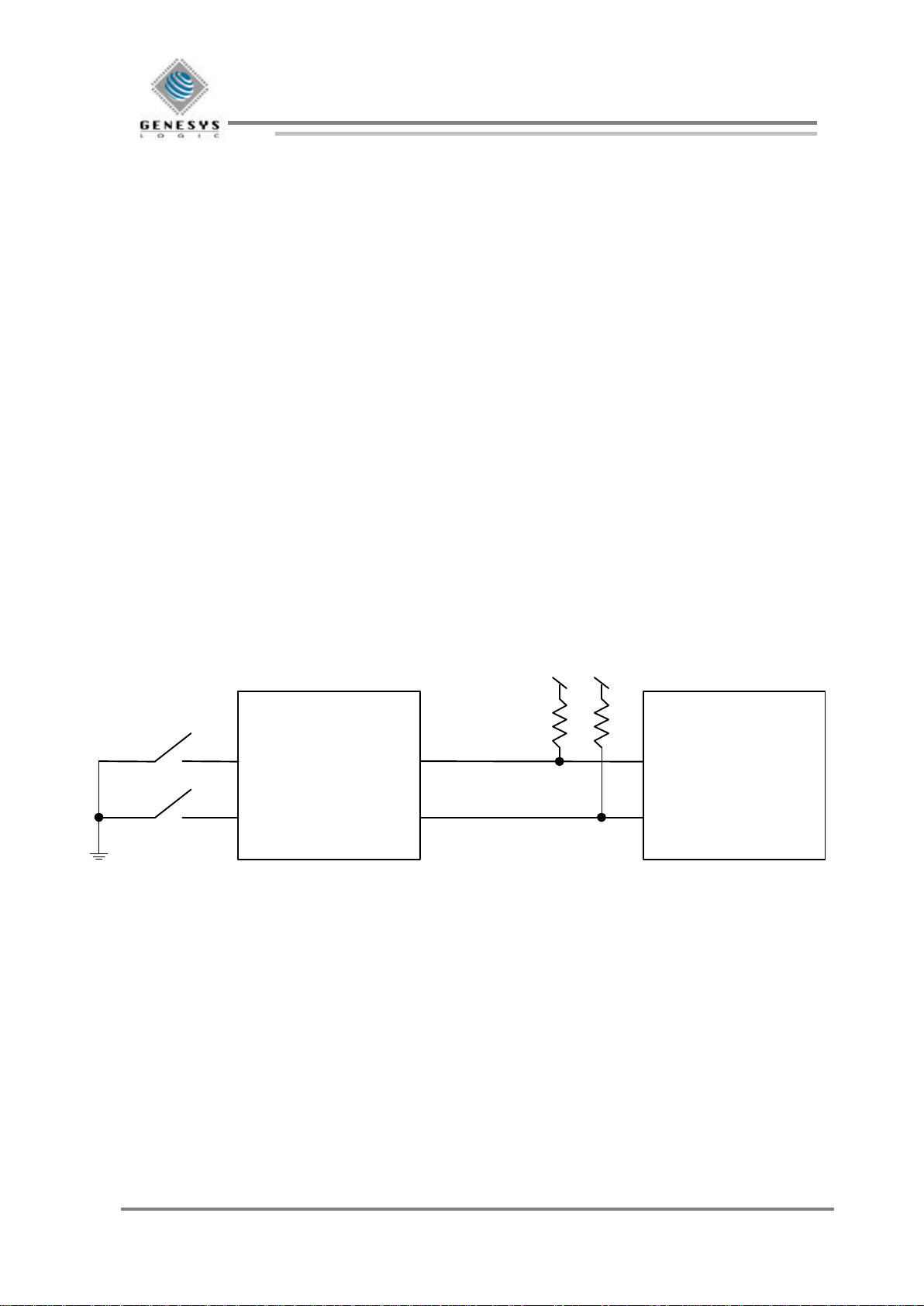
The following diagram shows the interconnections between the host and the PS/2 mouse device:
4.2 Byte transmission
Each byte transmitted between the device and the host includes a start bit ( a logic 0), eight data bits
(LSB first), a parity bit (odd parity), and a stop bit (a logic 1). Odd parity means the eight data bits
and the parity bit together contain an odd number of 1's . During transmission , the device pulses the
CLK signal low for each of the 11bits, while either the host or the device pulls the DATA wire low to
signal a logic 0 or allows DATA to float high to signal a logic 1.
Between transmissions, the bus can be in one of three states:
l Idle. If CLK and DATA are both high, there is no activity on the bus.
Host Computer
P/S 2 Mouse
Left
Right
CLK
DATA
CLK
DATA
Figure 4-1. PS/2 system diagram
 Loading...
Loading...