Page 1

100-PT-056 rev1
A Guide to Monitoring Contractions with Monica Devices
Monica detects the electrical activity of the myometrium to monitor uterine contractions
(UC). Uterine electrical activity, consisting of infrequent and low amplitude EHG
(electrohysterography) bursts which occur throughout most of pregnancy, but do not
generally result in contractions that are perceived by the patient. In late pregnancy, these
bursts often correspond to periods of perceived contractility by the patient (Braxton Hicks
contractions). During both term labour and preterm labour, bursts of EHG activity are
frequent, of large amplitude, and are correlated with large changes in intrauterine pressure
and pain sensationi.
Monica reliably identifies UC during active labour. Currently it is not able to determine
contraction strengthii. In established labour, Monica EHG technology is more reliable and
has higher sensitivity than tocodynamometry
on occasion from various sources;
1. Low-level or uncoordinated EHG activity not associated with an increase in
intrauterine pressure appear as small irregular deflections from the baseline. These
are easily identified during labour among the larger more regular ‘true’ contractions.
2. Maternal activity or vigorous fetal movement can change maternal abdominal surface
contours and produce what appears on the trace to be a UC. This is caused by small
changes in the electrode positions in relation to each other and to the underlying skin.
This may create confusion particularly during antepartum and early induction
monitoring, when regular true contractions are not present.
iii iv
. Nevertheless false positive UC can occur
Before any definitive clinical interpretation of UC information generated by Monica is made,
ensure, if possible that the patient is not moving and is in a comfortable and relaxed
position. If there is concern about false positive contractions during early labour or
induction, it can be helpful to have the patient use the event marker either on the AN24 or
Doppler CTG monitor to indicate when she feels a contraction and/or the fetus move.
Irregular high amplitude ‘ragged’ looking contractions that are coincidental with fetal or
maternal movements with no other clinical indication of UC should be discounted. They are
unlikely to be real contractions. As such, they should not influence medical intervention
unless corroborated by another device.
Using Monica UC provides a wireless and beltless solution that is more comfortable for the
patient than tocodynamometry (TOCO). Once the electrodes are on the abdomen they do
not need to be readjusted. This is different from TOCO which often requires adjustment of
transducer position and belt tension. The belts themselves can be uncomfortable for the
patient. In addition, in obese patients tocodynamometry can be very difficult and Monica
can offer a solution in monitoring this cohort of womenv. TOCO does not provide an
accurate measurement of the intensity and duration of the uterine contractionsvi
vii viii ix x
.
When using either TOCO or Monica, interpretation of the UC pattern should be done in the
clinical context of the patient. It is always good practice to use manual palpation, maternal
perception of UC and observation in conjunction with any UC monitoring device.xi
xii
Monica Healthcare Ltd. Unit 8, Interchange 25 Business Park, Bostocks Lane, Nottingham, NG10 5QG, UK
www.monicahealthcare.com
Page 2
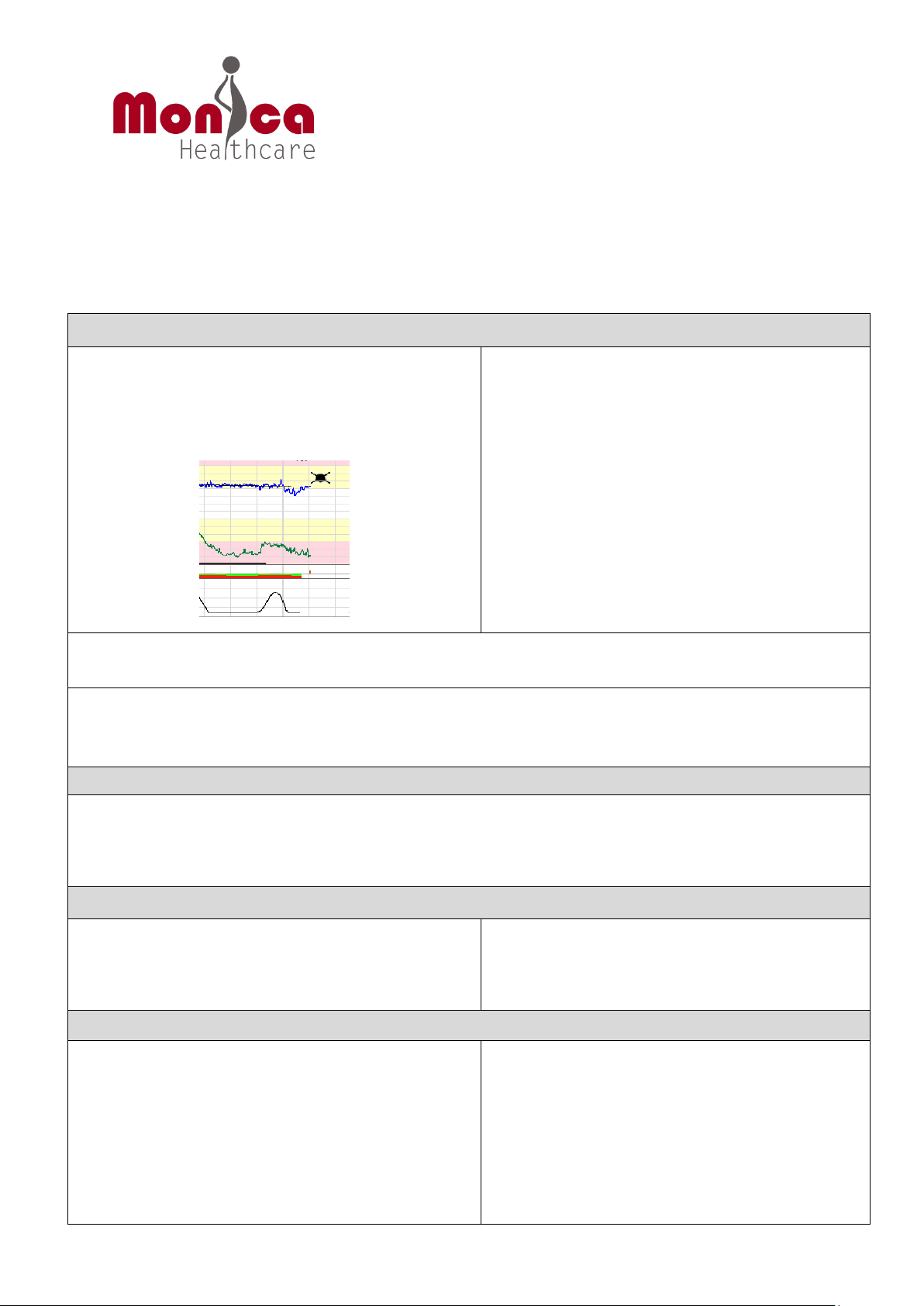
Monica provides information on the:
- Frequency of contractions
Peak
Monica cannot be used to assess:
- Resting tone
Monica VS
Monica UC, FHR and MHR are all
5 seconds before
Monica UC cannot be used to coach patients to commence contraction pain coping strategies or
2. Flat baseline and smooth UA waveform:
Monica UC has a baseline that is flat and has a relatively smooth contraction waveform even when the
l wall may
occasionally produce a trace similar to a UC. Clinical assessment will distinguish these movement
artefacts from real contractions.
Monica VS
Monica VS
If the AN24 is moved (maternal movement) and
the UC trace as a change in colour (black to grey).
This indicates that caution in making clinical
- Timing of the contraction
- Duration of Contractions
- Intensity of the contraction
Important Features of Monica UC
1. Time delay:
Monica Novii (IF24)
The displayed
synchronised. However, to extract the UC waveform
there is delay of approximately 2
the UC is seen.
Note: These delays are not significant – thermal printers of fetal monitors can add delays of up to 30 seconds and
central viewing stations can vary up to 1 minute.
To extract the FHR, MHR and UC waveform
all signals are delayed equally by 10 (15)
seconds.
actively push in the second stage of labour. Its value lies in providing an accurate picture of the pattern
of uterine contractions over time. It is not of value in making instant real time assessment.
patient is actively pushing. Active fetal or maternal movements that shift the abdomina
3. UC trace markings when used with:
Monica Novii/IF24
None
An ‘M’ at the beginning of the recording and a
small vertical spike appears every 5 minutes on
the UC trace indicates that Monica is being used.
4. Maternal movement indicator when used with:
Monica Novii/IF24
If the Novii POD or AN24 is in motion for
lasts for longer than 20 seconds it is highlighted on
more than 20 seconds due to maternal
movement a dark zig-zag line will appear on
interpretation of the UC and FHR is required.
the UC tracing. This indicates that caution
in making clinical interpretation of the UC
and FHR during the 20 seconds prior to &
Monica Healthcare Ltd. Unit 8, Interchange 25 Business Park, Bostocks Lane, Nottingham, NG10 5QG, UK
www.monicahealthcare.com
during the dark line is required
Page 3

5. Selecting Monica UC sensitivity and threshold: Antenatal / Induction or Established Labour
This gives the user the choice to best conform with the clinical situation; the Antenatal/Induction mode
is less sensitive to UC and removes some of the small deflections that may represent artefacts or
inconsequential contractions. It is, however, important to switch to labour mode once the patient is in
Monica Spike every
The ‘M’ symbol to
established labour.
The symbols on the CTG trace - when Novii/IF24 used
highlight, at the start
of the recording, that
Monica is being used.
Only on CTG trace.
5 minutes to
highlight to the
user that Monica is
being used
Zig Zig thickening, on CTG trace, or light grey trace, on VS, indicates at least 20 second or longer
of maternal movement has occurred (inferred from movement of the POD/AN24 dev i ce that the
patient is wearing or that is on the bed beside her)
Trace examples:
1. Saturation of the UC
It is recommended that if the patient is in established labour to select the Labour mode on
t
he Novii/IF24, however if there is saturation of the UC then switch to the Induction Mode
2. Antenatal trace
The Antenatal Monica UC can be concerning to clinicians early in the process of inducing
labour or doing an NST. With TOCO there may be very little activity displayed, while
Monica, as discussed above, may trace frequent small waveforms on the UC channel. It is
important to take into account the clinical findings, use palpation and note if the fetus or
patient is moving a great deal. If appropriate, ask the patient to press the event marker on
Monica Healthcare Ltd. Unit 8, Interchange 25 Business Park, Bostocks Lane, Nottingham, NG10 5QG, UK
www.monicahealthcare.com
Page 4
the Monica device or use the fetal event marker on the EFM to indicate when there is a fetal
False UC related to, fetal/maternal
movement in this antenatal trace
movement
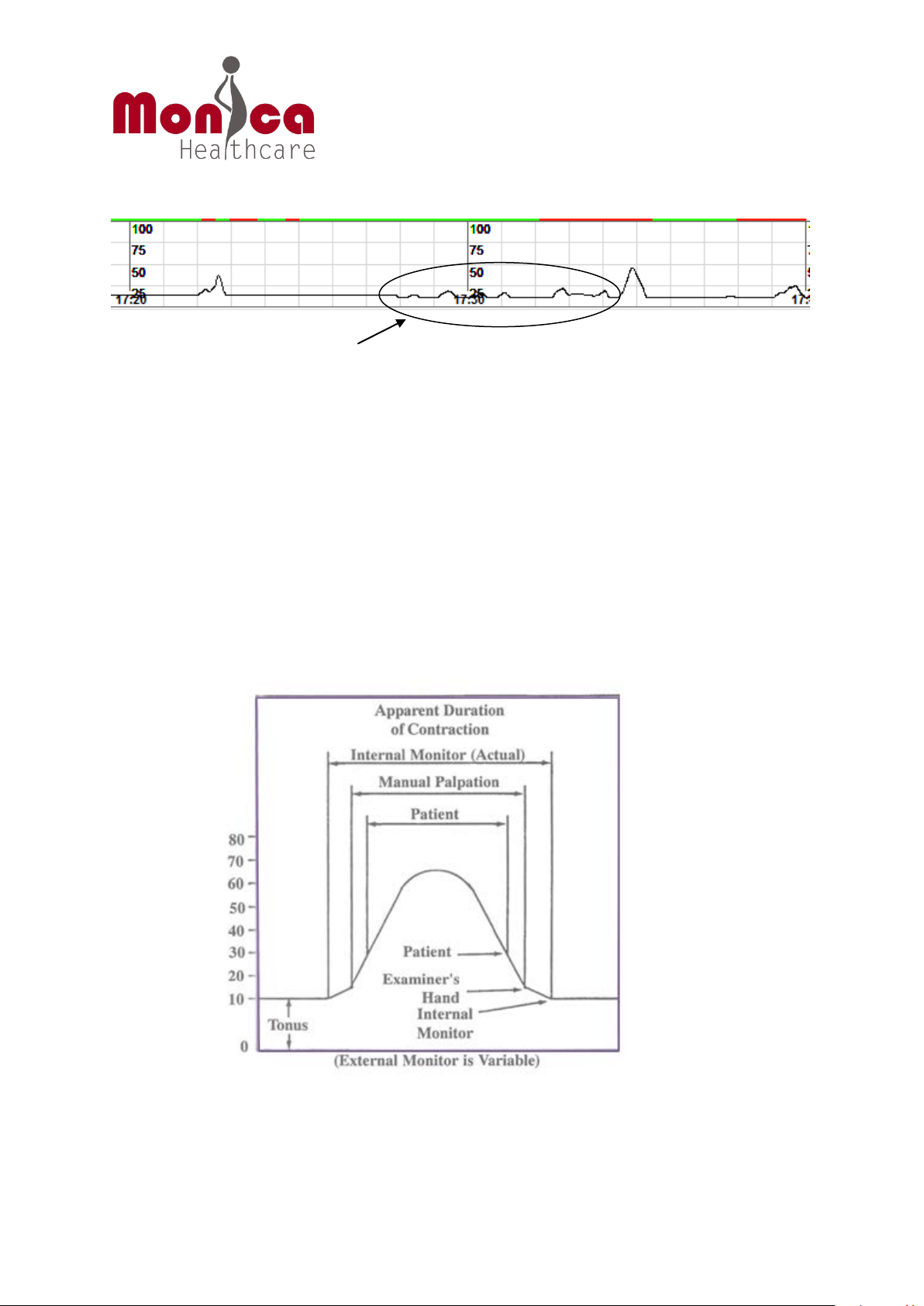
3. Assessment of Monica UC
Users of Monica should be aware that neither the EHG method nor traditional
tocodynamometry is useful to judge the absolute or relative strength of contractions and
duration of UC reliably. Consequently, Monica (like all other fetal/ maternal monitor
manufacturers) cautions against using external UC monitoring techniques to assess
contractile force. In this regard transabdominal palpation of the uterus and attention to the
patient’s pain pattern are necessary and sufficient to judge contraction strength when an
external UC monitor is in use. The diagram below shows a comparison of UC contractions by
patient, manual palpation and IUPC
10
. The diagram also highlights that contraction duration
is variable when using External UC monitors.
Monica Healthcare Ltd. Unit 8, Interchange 25 Business Park, Bostocks Lane, Nottingham, NG10 5QG, UK
www.monicahealthcare.com
Page 5

i
R, Garfield., Maner, W. Physiology and Electrical Activity of Uterine Contractions
Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2007), 18(3): 289–295.
ii
Miller, J,. Ty-Torredes, K,. Schindel, M,. Harman, C,. Baschat, A. Non-invasive detection of
significant uterine activity: American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, (2008) Volume 199,
Issue 6, Pages S225-S225
iii
Hayes-Gill, B., Hassan, S., Mirza, F G., Ommani,S., Himsworth, J., Solomon, M.,
Brown, R., Schifrin , B., Cohen, W R. Accuracy and Reliability of Uterine Contraction Identification
Using Abdominal Surface Electrodes: Clinical Medicine Insights, Women’s Health 2012:5 65–75
iv
FDA summary K101801 510 (K) http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf10/K101801.pdf
v
Tammy, Y., Nguyen, T., Marossero, D., Edwards, R. Monitoring Contractions in Obese Parturients.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: (2007) Vol. 109, No 5 1136-1140
vi
Bakker, P., Rijsiwijk, S., Geijn, H. Uterine activity monitoring during labor: J Perintal. Med. 35
(2007) 468-477
vii
Bakker, J., Verhoeven, C., Janssen, P., Van Lith, J., Van Oudgaarden, E., Bloemenkamp, K.,
Papatsonis, D., Mol, B., Van der Post, J. Outcomes after Internal verses External Tocodynamometry
for Monitoring Labor: N Engl J Med.(2010)362;4
viii
Chia, YT., Arulkumaran, S., Soon, SB., Norshida, S., Ratnam, SS: Induction of Labour: does internal
tocography result in better obstetric outcome than external tocography: Aust N Z J Obstet
Gynaecol.(1993) May;33(2):159-61
ix
Iams, J., Newman, R.,Thom,E., Goldenberg, R., Mueller-Heubach, E., Moawad,A., Sibai,B., Caritis, S.,
Miodovnik, M., Paul, R., Dombrowski, M., McNellis, D: Frequency of Uterine Contractions and the
Risk of Spontaneous Preterm Delivery: N Engl J Med (2002) Vol 346,No4
x
Freeman, R K., Garite, T J., Nageotte, M P. Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring. Williams and Wilkins,
Baltimore (1991), Page 81
xi
Spencer, K. The Primal Touch of Birth: Midwives: Mothers and Massage Midwifery today 2004
issue 70
xii
Burvill, S. Midwifery diagnosis of labour onset: British Journal of Midwifery (2002) 10: 600-605
Monica Healthcare Ltd. Unit 8, Interchange 25 Business Park, Bostocks Lane, Nottingham, NG10 5QG, UK
www.monicahealthcare.com
 Loading...
Loading...