Page 1

ÿ
GE Power Management
Digital Breaker Failure Protection
Digital Breaker Failure Protection
Digital Breaker Failure ProtectionDigital Breaker Failure Protection
DBF
Instructions
Instructions
InstructionsInstructions
GEK 106168E
GEK 106168E
GEK 106168E GEK 106168E
Page 2

*(3RZHU0DQDJHPHQW
$Q\WKLQJ\RXFDQ·WILQG"
$Q\WKLQJQRWFOHDUHQRXJK"
,) <28 +$9( $1< &200(17 21 7+( &217(176 2) 7+(
35(6(17 0$18$/ .,1'/< )$; 86 $ &23< 2) 7+,6 3$*(
72*(7+(5 :,7+ $ &23< 2) 7+( 3$*( :+(5( <28 +$9(
)281' 7+( 352%/(0 72 7+( )$;180%(5
),//,1*,17+(48(67,21$,5(%(/2::(:,//%(+$33<72
62/9( <285 '28%76 $1' :( 7+$1. <28 )25 +(/3,1* 86
,03529(7+,60$18$/
&RPSDQ\
1DPH
$GGUHVV
3KRQH
(PDLO
'HVFULSWLRQRI\RXUTXHVWLRQRUVXJJHVWLRQ
0DQXDO*(.FRGH
)D[
Page 3

Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TABLE OF CONTENTSTABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATION........................................................................................... 1
1.1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION................................................................................................................................. 1
2. OPERATION LOGIC...................................................................................................................................... 3
2.1. PROTECTION FUNCTIONS.............................................................................................................................. 3
2.1.1. Overcurrent units.......................................................................................................................................... 3
2.2. MONITORING AND RECORDING FUNCTIONS.............................................................................................. 5
2.2.1 Measurement............................................................................................................................................... 5
2.2.2 Associated Breaker Status........................................................................................................................... 5
2.2.3 Target Lamps ............................................................................................................................................... 5
2.2.4 Circuit Breaker Breaking Capacity Monitoring ............................................................................................. 9
2.2.5 Built-in Self-Checking Unit.......................................................................................................................... 10
2.3. ANALYSIS FUNCTIONS......................................................................................................................................... 10
2.3.1 Event Recorder........................................................................................................................................... 10
2.3.1 Oscillography .............................................................................................................................................. 10
2.4. CONTROL.......................................................................................................................................................... 12
2.4.1 Tables of Settings ...................................................................................................................................... 12
2.4.2 Time Synchronization.................................................................................................................................. 13
2.4.3 Configurable Inputs and Outputs ............................................................................................................... 13
2.5. MAN-MACHINE INTERFACE (HMI)........................................................................................................................ 15
EMOTE COMMUNICATIONS................................................................................................................................16
2.6. R
3. SETTINGS.................................................................................................................................................... 17
4. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS.............................................................................................................. 21
4.1. M
4.2. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS ............................................................................................................................ 22
5. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION....................................................................................................................... 25
5.1. P
5.2. OPERATING THEORY.......................................................................................................................................... 27
6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS................................................................................................................................. 29
6.1. C
6.2. V
6.3. P
6.4. R
6.5. I
6.6. P
6.7. C
6.8. I
6.9. FUNCTIONS......................................................................................................................................................... 33
ODEL LIST....................................................................................................................................................... 21
4.1.1. Special Models........................................................................................................................................... 21
HYSICAL DESCRIPTION..................................................................................................................................... 25
5.1.1. Case.......................................................................................................................................................... 25
5.1.2. Electrical Connections............................................................................................................................... 25
5.1.3. Internal Construction................................................................................................................................. 25
5.2.1. Magnetic Module....................................................................................................................................... 27
5.2.2. CPU Board................................................................................................................................................ 27
5.2.3 Power Supply ............................................................................................................................................. 28
5.2.4 Keyboard and Display................................................................................................................................ 28
ONNECTIONS AND NECESSARY EQUIPMENT...................................................................................................... 29
ISUAL INSPECTION ........................................................................................................................................... 29
ANEL INSULATION TESTS.................................................................................................................................. 29
ELAY SETTING................................................................................................................................................. 30
NDICATORS........................................................................................................................................................ 30
OWER SUPPLY................................................................................................................................................. 30
OMMUNICATIONS .............................................................................................................................................. 31
NPUTS............................................................................................................................................................... 32
6.8.1 Digital inputs................................................................................................................................................ 32
6.8.2 IRIG-B Synchronizing Input........................................................................................................................ 32
6.9.1 50BF 1P Unit Test...................................................................................................................................... 33
6.9.2 50BF 3P Unit Test...................................................................................................................................... 34
6.9.3 Internal Arc Test......................................................................................................................................... 35
6.9.4 3P NO I FUNCTION.................................................................................................................................... 35
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection i
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
6.9.5 Neutral Overcurrent Unit Test.....................................................................................................................35
6.10. RELAY MEASUREMENT TESTS ...........................................................................................................................37
6.10.1. Current Measurement..............................................................................................................................37
6.10.2. Timing Measurement...............................................................................................................................37
7. INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE........................................................................................................39
7.1. I
NSTALLATION.....................................................................................................................................................39
ONNECTION-TO-GROUND AND DISTURBANCES SUPPRESSION............................................................................39
7.2. C
7.3. M
AINTENANCE....................................................................................................................................................39
8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY........................................................................................................................41
8.1. M
8.2. S
8.3. I
8.4. C
8.5. S
8.6. C
ENU TREE. ......................................................................................................................................................42
ETTINGS GROUP (SET KEY) ..............................................................................................................................43
NFORMATION GROUP (INF KEY)..........................................................................................................................46
ONTROL GROUP (ACT KEY) .............................................................................................................................47
INGLE KEY MENU .............................................................................................................................................48
ONFIGURATION MENU.......................................................................................................................................49
FIGURES .................................................................................................................................................................51
ii DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 6

LIST OF FIGURES
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1. Breaker Failure Logic (189C4114 Sheet 2)
Figure 2. External Connections (189C4114 Sheet 1)
Figure 3. Front View (226B7412 Sheet 9)
Figure 4. Rear View (226B7412 Sheet 10)
Figure 5. Dimensions Diagram (226B6086 sheet 10)
Figure 6. Panel drilling (226B6086H10)
Figure 7. RS232 Connection (DBF relay to PC)
Figure 8. RS232 Connection (DBF relay to MODEM)
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection iii
Page 7

LIST OF FIGURES
iv DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 8

1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATION
1.
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATION
1. 1.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONGENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATION
1.1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The DBF system is a microprocessor based breaker failure protection, control and measurement unit that has
different algorithms to allow its use on a wide range of applications in power systems.
The functions and information management of the unit can be performed remotely (computer connected to the
serial port RS232, fiber-optic or modem) or locally using the man-machine interface (HMI), which includes a 20
keys keypad, and a two line liquid crystal display (LCD) on the front of the relay.
The system provides the following functions:
a) Protection
• Low current level breaker failure protection, following a single or three phases initiation, with up to
two time delayed steps.
• High current level breaker failure protection, following a two/three (selectable by setting) phases
initiation.
• No current breaker failure protection, following a two/three (selectable by setting) phases initiation.
• Breaker internal arc detection.
b) Monitoring
• Current measurements for each phase and ground.
• Breaker status
• 16 fully configurable LED indicators
• One fixed relay status LED
• Breaker health monitoring (ΣI2t).
• Built-in self-check functions.
c) Analysis:
• Event recorder
• Oscillography
d) Control:
• 3 settings’ tables
• Time synchronization using the communications program, the IRIG-B input or the HMI (keypad and
display).
• Configurable inputs and outputs.
• User can build logic schemes using AND, OR and NOT gates and the internal digital signals of the
relay.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 1
Page 9

1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATION
e) Communication Interfaces
• Remote communications through three communication ports, one on the front of the relay and two
located on the rear.
• Human machine interface (HMI) consisting of 20 keys keypad and alphanumerical LCD (16
characters x 2 lines).
• Windows based GE-INTRO configuration software (for inputs, outputs, LEDs configuration) and
GE-LOCAL communications software (for relay monitoring, settings change, stored data retrieve, etc).
Both are part of the GE-NESIS software package (General Electric Network Substation Integrated
System).
2 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 10
2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.
2. OPERATION
2. 2.
(See f igur e 1 at the end of the Ins truc tion Manual)
OPERATION LOGIC
OPERATION OPERATION
LOGIC
LOGICLOGIC
2.1. PROTECTION FUNCTIONS
2.1.1. OVERCURRENT UNIT S
The DBF system incorporates the following overcurrent detectors:
• Three Single Phase Low-Level Overcur rent Detector s
(Used by the 50BF 1P function.)
• Three Single Phase High- Level Overcur rent Detector s.
(Used by the 50BF 3P function.)
• One G r ound Overcur rent Detector .
(Used by the 3P No I function.)
• Three Single-Phase current detectors for the internal arc function.
Low-Level Overcurrent Breaker Failure Unit – 50BF 1P
The breaker failure operation is star ted by detecting any single phase above a setpoint threshold (PH Lo-Set
Pickup setting), ANDed with a tripping signal (break er failure initiate signal) issued by the main feeder protection.
These breaker f ailure initiation signals can be s ingle-phas e or three-phase type at OR1, OR2 and OR3. There are
four digital signals available (50BF Initiate A, 50BF Initiate B
any digital input (contact converter). The factory digital input conf igur ation is the following (as shown in f igur e 1):
Digital Signal Input # Terminals
50BF Initiate A Input #1 C9 – D10
50BF Initiate B Input #2 D9 – D10
50BF Initiate C Input #3 C10 – D10
3P BF Initiate Input #7 E7 – E8
The AND1, AND2 and AND3 gates thus fully armed m ay perform (depending on settings) one or two time delayed
tripping steps. Use 50BF_1P setting ( permitted/Not permitted) and number of output stages (N. of Output
Stages) setting to enable this f unc tion and to set the number of steps. Timers T1 and T2nd control t he timing of
the f ir s t and second step respec tively (1_Phase T imer T 1 and 2nd Stage Timer settings).
If the tr ipping signal is three-pole type (digital input E7-E8 for the default factor y configuration), the s ignal will be
placed at the same time in OR1, OR2 and OR3 and then to AND1, AND2 and AND3.
High-Level Overcurrent Breaker Failure Unit – 50BF 3P
, 50BF Initiate C and 3P BF Initiate) assignable to
This func tion operates if high-Level overc urr ent is detected on 2 phases (or 3 phases if se tting BF Logic (3P/2P)
is set to 3P) and if 2 break er failure initiation inputs are energized (or j us t the 3P BF Initiate input, if Severe Fault
3P setting is set to permitted) .
The starting of this function is similar to the 50BF 1P, but in this case the current level setting range is higher (PH
Hi-Set Pickup s etting) and the output is controlled by the energization of two single pole initiation signals. This
function can also operate ener gizing the 3P BF Initiate signal, if Severe Fault 3P setting is set to ‘permitted’.
Other diff er enc e with res pect to the 50BF 1P f unc tion, is that the current in all the three phases must exceed the
setpoint, or at least one pair of phases. This is selected with BF Logic (3P/2P) setting. In the first case (BF Logic
(3P/2P) s et to 3P) the signal should progress through AND11 and AND12. If BF Logic (3P/2P) issetto2P,then
the signal will go through AND8, AND9 or AND10 and then AND13. The outputs of AND12 or AND13 ar e sent via
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 3
Page 11
2. OPERATION LOGIC
OR5 to the bottom input of AND4. Any pair of single BF initiation signals placed at AND5, AND6,orAND7 will
activate the top input of AND4. This input to AND4 can also be ON if there is a 3P BF Initiation and Severe Fault
3P setting is set to ‘permitted’.
Ground Overcurrent Breaker Failure Unit.
The breaker failure action based in this ground overcurrent function basically performs an additional breaker
failure function through AND19, when the 3P BF Initiate (or 2 Single Pole BF Initiate, if Low Load 2P
set to ‘permitted’) is present at OR10 and a ground current higher than Neutral Pickup setting is detected.
Breaker Failure without current (or very low current).
DBF includes internal logic to cover also no-current, or very low fault current BF applications. This function will
issue an output if the 3P BF Initiate input is energized (or 2 Single Pole BF Initiate, if Low Load 2P
to ‘permitted’), and at least one pole of the circuit breaker is still closed.
Breaker Arc Detection Device.
This function may close one output of the relay when it detects that: the circuit breaker is open and some amount
of current is present in any phase. There are two settings available for this function: ‘Internal Arc Pickup’toset
the current threshold and ‘Internal Arc Timer’ to coordinate the operation time of the unit with the time it takes for
the breaker and auxiliary elements to open.
setting is
setting is set
If the circuit breaker is open, then the 52/b contacts will energize the digital inputs corresponding to the circuit
breaker status (terminals C11-D12, D11-D12 and C12-D12 for the factory default configuration), and then the
upper input of AND16, AND17 and AND18. The other input will be energized if the DBF detects a current higher
than Internal Arc Pickup setting. The outputs of these AND gates are sent to OR8 and then to timer T4 (Internal
Arc Timer setting) to complete the arc detection function, this will close the auxiliary relay D2-C2 (according to the
factory default output configuration).
Reset of Latching Relays
The DBF breaker failure protection may be ordered with an expansion board, which includes two latching relays
that are operated in different ways depending on the number of steps selected (for additional reference see Figure
1), and will fix the tripping output once the breaker failure function has operated. A digital input through F11-F12
(factory default inputs configuration) (pulse signal, not sustained) resets these latching relays to its steady-state
position.
4 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 12
2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.2. MONITORING AND RECORDING FUNCTIONS
2.2.1 MEASUREMENT
The DBF system provides the continuous measurement of phase and ground current values.
These measurements can be accessed directly on the liquid crystal display (HMI) on the front of the relay, or via
the GE-LOCAL communication software.
2.2.2 ASSOCIATED BREAKER STATUS
The DBF system monitors the associated breaker status through the digital inputs 52/b (or 52/a), and it is
displayed on the local HMI or through the communications software.
2.2.3 TARGET LAMPS
The DBF incorporates 17 LED target lamps, one fixed LED (two colors) assigned to the system ready function,
and 16 user configurable red LEDs. These configurable LEDs are arranged in two columns of 8 LEDs each. The
configuration is done using the GE-INTRO software, and it consists on assigning an internal event (or an AND
gate of internal events) to an LED. The LED can be configured to have memory (if Vdc is removed or the event
causing the operation of the LED gets deactivated) or not and to blink or to be steady. The internal events must
be previously defined using the internal signals of the relay. It is possible to use AND, OR and NOT logic gates to
define these events. The available internal signals are listed in the following table.
The TARGET RESET button allows testing all target lamps if it is pushed for a short time (lighting up all of them),
or resets the sealed-in targets if it remains pressed for three seconds or more.
Please refer to GE_INTRO (configuration software) Instruction book (GEK-105594) for further information.
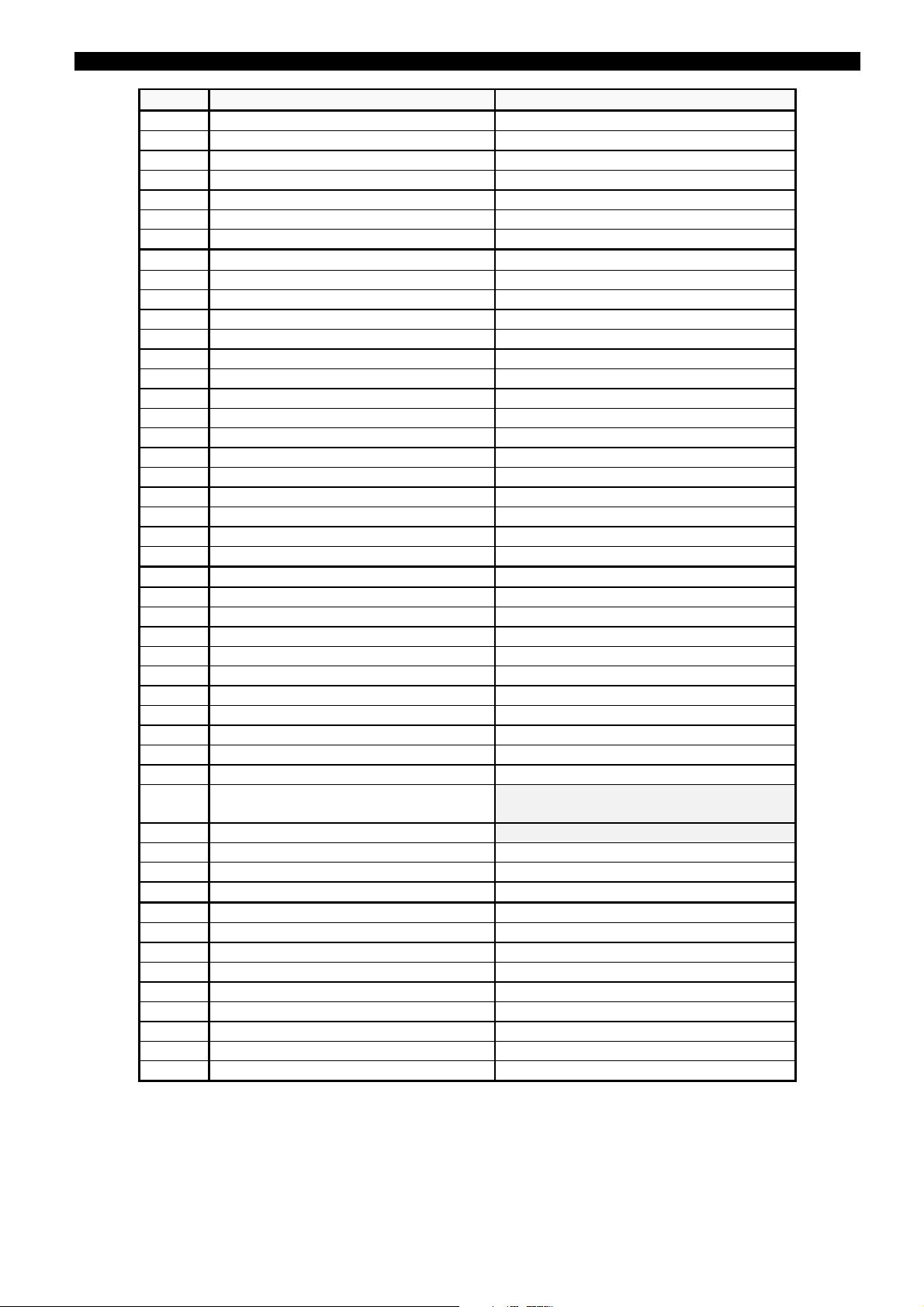
INTERNAL PROTECTION STATUS SIGNALS
Group Status Comment
1.0 Program Initiate Relay starts running (Vdc just applied).
1.1 Settings change User changes any setting
1.2 Write Counters User sets a value for any counter
1.3 Configuration Change User changes relay configuration
1.4 External Trigger Oscillography triggered by Dig. Input
1.5 Communications Trigger Osc. triggered by HMI or GE_LOCAL
1.6 Reset Operation Latched Relays Reset received
1.7
1.8
1.9
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
1.15
2.0 Input Nº 1 Digital Input #1 Status
2.1 Input Nº 2 Digital Input #2 Status
2.2 Input Nº 3 Digital Input #3 Status
2.3 Input Nº 4 Digital Input #4 Status
2.4 Input Nº 5 Digital Input #5 Status
2.5 Input Nº 6 Digital Input #6 Status
2.6
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 5
Page 13
2. OPERATION LOGIC
Group Status Comment
2.7 Optional Exp. Board
2.8 Input Nº 7 Digital Input #7 Status
2.9 Input Nº 8 Digital Input #8 Status
2.10 Input Nº 9 Digital Input #9 Status
2.11 Input Nº 10 Digital Input #10 Status
2.12 Input Nº 11 Digital Input #11 Status
2.13 Input Nº 12 Digital Input #12 Status
2.14 Input Nº 13 Digital Input #13 Status
2.15 Input Nº 14 Digital Input #14 Status
3.0 Breaker Failure Logic BF Logic = 3P
3.1 Hi-Set A Pickup Output of Hi-Set current detector ph A
3.2 Hi-Set B Pickup Output of Hi-Set current detector ph B
3.3 Hi-Set C Pickup Output of Hi-Set current detector ph C
3.4 50BF Pole A Initiate CC1 Dig. Input ON (default configuration)
3.5 50BF Pole B Initiate CC2 Dig. Input ON (default configuration)
3.6 50BF Pole C Initiate CC3 Dig. Input ON (default configuration)
3.7 Lo-Set A Pickup Output of Lo-Set current detector ph A
3.8 Lo-Set B Pickup Output of Lo-Set current detector ph B
3-9 Lo-Set C Pickup Output of Lo-Set current detector ph C
3.10 50BF 3 Phase Initiate CC7 Dig. Input ON (default configuration)
3.11 50BF Neutral Initiate Output of Neutral current detector
3.12 Internal Arc A Pickup Output of AND 16 in figure 1
3.13 Internal Arc B Pickup Output of AND 17 in figure 1
3.14 Internal Arc C Pickup Output of AND 18 in figure 1
3.15
4.0 Pickup
4.1 Trip 1
4.2 Trip 2
4.3 Internal Arc
4.4
4.5
4.6
4.7
4.8
4.9
4.10
4.11
4.12
4.13
4.14
4.15
5.0 Phase A Trip Output of Timer 1 phase A in figure 1
5.1 Phase B Trip Output of Timer 1 phase B in figure 1
5.2 Phase C Trip Output of Timer 1 phase C in figure 1
5.3 Three-Pole Trip with Current Output of Timer 2 in figure 1
5.4 Three-Pole Trip without Current Output of Timer 3 in figure 1
5.5 Second Stage Trip Output of AND 14 / 15 in figure 1
5.6
5.7
5.8
Any BF signal is activated. Output of OR
7infigure1
Any unit (except Internal Arc) has tripped.
Output of OR 6 in figure 1
Same as Trip 1 when 1 step is selected.
2ndstage when 2 steps are selected.
Output of AND 14 / 15 in figure 1
Trip from Internal Arc unit. Output of
Timer 4 in figure 1
6 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 14
2. OPERATION LOGIC
Group Status Comment
5.9
5.10
5.11
5.12
5.13
5.14
5.15
6.0
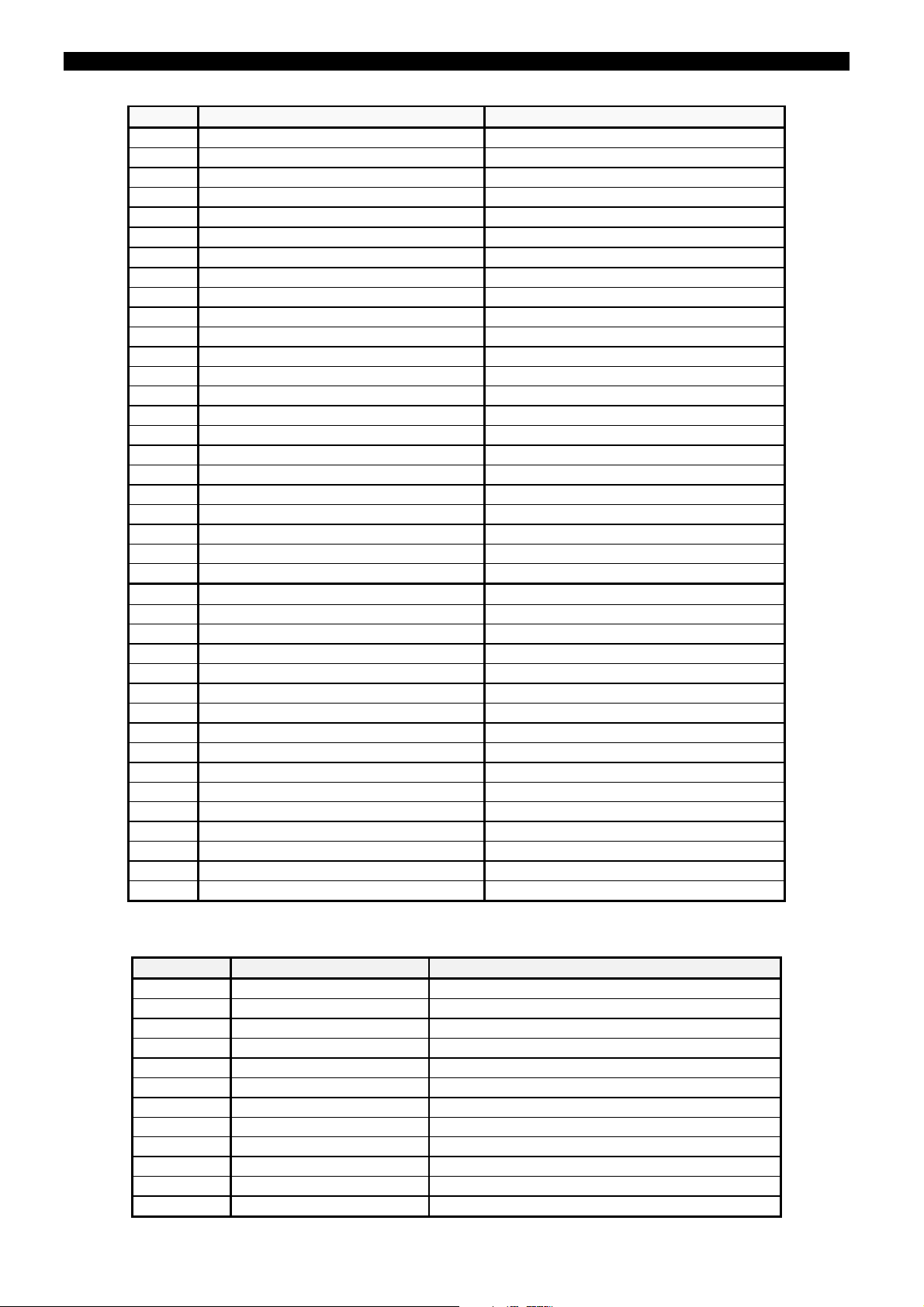
6.1 Parallel EEPROM Alarm Failure in parallel EEPROM
6.2 Serial EEPROM Alarm Failure in serial EEPROM
6.3 Out-of-Service Relay out of service
6.4 Default General Settings Relay with factory default settings
6.5 Default Table 1 Settings Table 1 with factory default settings
6.6 Default Table 2 Settings Table 2 with factory default settings
6.7 Default Table 3 Settings Table 3 with factory default settings
6.8
6.9
6.10
6.11 52 A Maintenance Alarm Accumulated I2t above limit for Phase A
6.12 52 B Maintenance Alarm Accumulated I2t above limit for Phase B
6.13 52 C Maintenance Alarm Accumulated I2t above limit for Phase C
6.14
6.15
7.0
7.1 Active Table 1 Setting Table #1 is the active Table
7.2 Active Table 2 Setting Table #2 is the active Table
7.3 Active Table 3 Setting Table #3 is the active Table
7.4
7.5
7.6 New Events There are new events stored in the DBF
7.7 Two Stages Set BF Logic set to 2 timed stages
7.8 Breaker Pole A Status CB Pole A Closed
7.9 Breaker Pole B Status CB Pole B Closed
7.10 Breaker Pole C Status CB Pole C Closed
7.11 Latching Relay 1 Status Optional Exp. Board: Latched#1
Closed
7.12 Latching Relay 2 Status Optional Exp.Boar: Latched#2 Closed
7.13
7.14
7.15
8.0
8.1
8.2
8.3
8.4
8.5
8.6
8.7
8.8
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 7
Page 15
2. OPERATION LOGIC
Group Status Comment
8.9
8.10
8.11
8.12
8.13
8,14
8.15
9.0
9.1
9.2
9.3
9.4
9.5
9.6
9.7
9.8
9.9
9.10
9.11
9.12
9.13
9.14
9.15
10.0 AND1 Output of internal AND gate #1
10.1 AND2 Output of internal AND gate #2
10.2 AND3 Output of internal AND gate #3
10.3 AND4 Output of internal AND gate #4
10.4 AND5 Output of internal AND gate #5
10.5 AND6 Output of internal AND gate #6
10.6 AND7 Output of internal AND gate #7
10.7 AND8 Output of internal AND gate #8
10.8 AND9 Output of internal AND gate #9
10.9 AND10 Output of internal AND gate #10
10.10 AND11 Output of internal AND gate #11
10.11 AND12 Output of internal AND gate #12
10.12 AND13 Output of internal AND gate #13
10.13 AND14 Output of internal AND gate #14
10.14 AND15 Output of internal AND gate #15
10.15 AND16 Output of internal AND gate #16
INTERNAL COMMUNICATION STATUS SIGNALS
Group Status Comment
1.0 Remote/Local Mode Relay in remote mode
1.1 Rear Connection Rear communication port in use
1.2 Front Connection Front communication port in use
2.0 Date/Time alarm Synch. Signal not received in setting t Timeout
2.1 Serial EEPROM Alarm Failure in serial EEPROM
2.2 Comm. Settings Relay with factory default settings
2.3 Protection Link Status of internal comm. with protection CPU
2.4 IRIG_B Link Relay synchronized by IRIG_B
3.0 - 3.15
8 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 16
Group Status Comment
4.0 - 4.15
5.0 -5.15
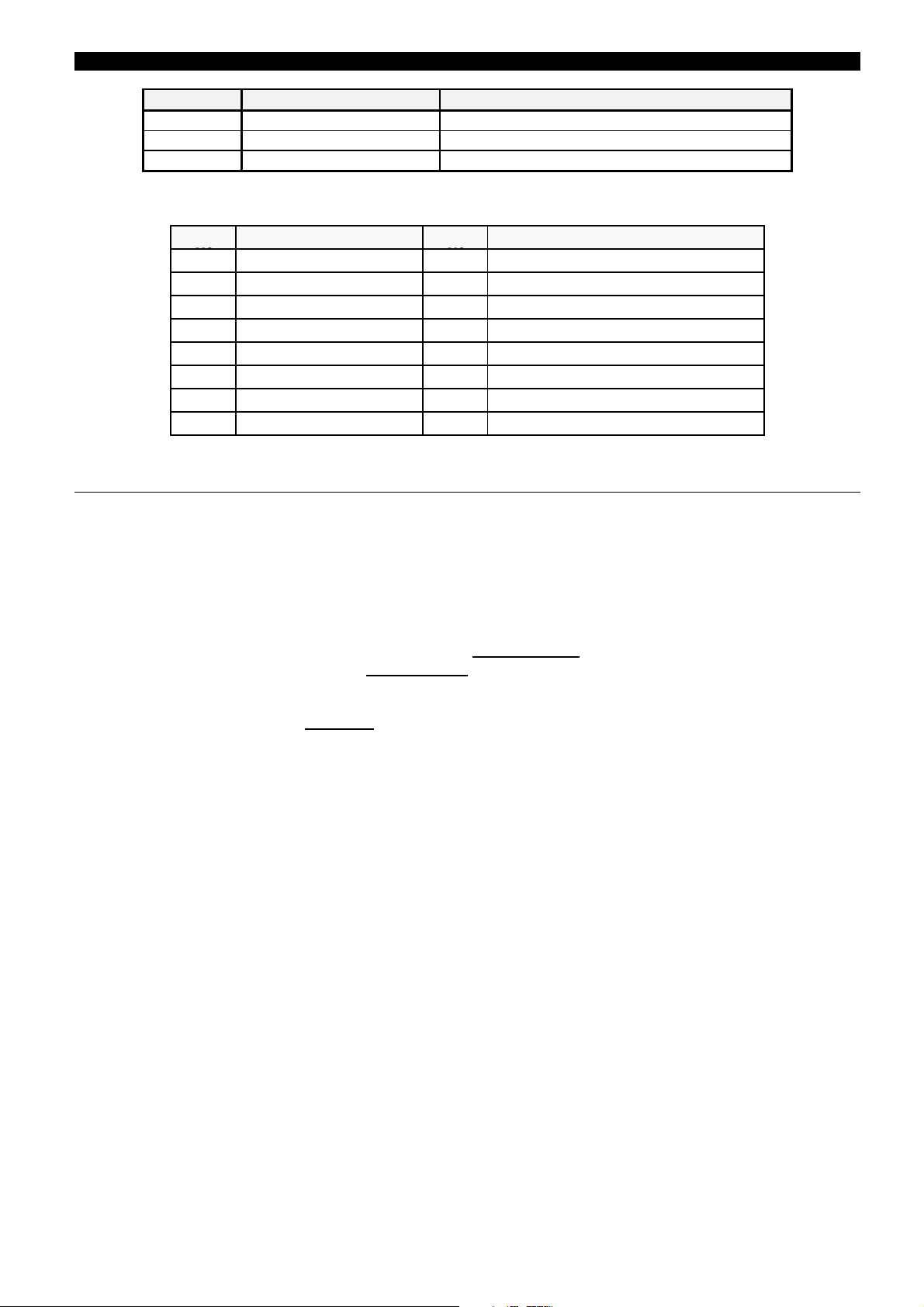
The DBF units are supplied with the following target LED’s default configuration:
2. OPERATION LOGIC
LED
LEFT COLUMN LED
RIGHT COLUMN
1 TRIP STAGE 1 9 LOW SET PICKUP
2 TRIPSTAGE2 10 50BFPOLEAINIT
3 PHASEATRIP 11 50BFPOLEBINIT
4 PHASEBTRIP 12 50BFPOLECINIT
5 PHASE C TRIP 13 INT. ARC A POLE
6 3PTRIPNOI 14 INT.ARCBPOLE
7 INT. ARC TRIP 15 INT. ARC C POLE
8 HIGH SET PICKUP 16 REMOTE COMMUNICATIONS
2.2.4 CIRCUIT BREAKER BREAKING CAPACITY MONITORING
To supervise the breaker health, the DBF system calculates and stores, for each operation, the accumulated
values of the square of the current multiplied by the opening time of the breaker (I
expressed in kA
The value I
2
sec.
2
t is accumulated and stored independently for each phase. These values can be accessed either by
2
t) on each phase. I2tis
the local HMI or by the GE-LOCAL communications software.
The function has an
Integration Time Selector
setting (kI2tOPMODE)whichcanbeusedtoassignafixed
opening time (given by another setting (kI2tINTTIME)). Otherwise the unit measures the time between the
tripping signal of the main feeder protection and the change of the status contacts of the circuit breaker (52/b).
The total
Breaking Current Limit
(kI2t LIMIT) setting fixes the maximum life breaking capability (it is recommended
to set this to the limit supplied by the manufacturer). When this threshold is reached in any phase, the system
may be configured to close an output, if the appropriate internal signal (52 A Maintenance Alarm, 52 B
Maintenance Alarm, 52 C Maintenance Alarm) is assigned to an output. In addition, the system also has a
counter for the tripping operations.
The purpose of these functions is to provide accurate data to perform the circuit breaker maintenance, based on
the actual breaking time and current values. Once this maintenance operation has been done, the values for both
2
t and number of opening operations, can be reset.
the I
In order to be able to take into account the history of the breaker, in the case where the breakers were already in
use before the installation of the relay, the system allows to set an initial value for the I
2
t and the number of the
previous breaking operations. Similarly, these values can be adjusted to a given value in order to take into account
operations carried out during protection testing.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 9
Page 17

2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.2.5 BUILT-IN SELF-CHECKING UNIT
The digital technology of the DBF system allows providing a built-in self-checking function which guarantees the
correct performance of the unit, and provides an external alarm in case of error detection.
Two built-in self-checking functions are performed, one when the unit is started up and the other during normal
operation. Internal tests are provided for power supply, program memory (ROM), working memory (RAM),
oscillography memory (RAM), and settings and calibration memory (EEPROM).
In addition, there is a hardware test for the Target LEDs, which lights them all up when the button TARGET
RESET is pressed. The sealed-in targets (latched) reset if the TARGET RESET button is kept pressed during
three seconds.
2.3. ANALYSIS FUNCTIONS.
The DBF system includes an event recorder and an oscillography waveform recorder with a resolution of 1 ms for
the first one, and 1 sample for the second one (1.04 ms at 60 Hz and 1.25 ms at 50 Hz). To avoid the loss of
date/time and oscillography records during any Vdc power failure, the unit is equipped with a capacitor, which
allows the information to be kept for at least 24 hours after power loss.
2.3.1 EVENT RECORDER.
The DBF system keeps a record of the last 144 events and stores for each one the following information: date and
time (accurate to one millisecond), the type of event, current RMS values during the event, and the state of the
unit (set of digital signals that describes the status of the relay at any given moment in time).
This event recorder is stored in a non-volatile memory and can be maintained indefinitely, even with no power
supply.
The list of events that the relay stores are factory fixed, and corresponds to standard relevant
situations/operations, like Settings Change, Program initiate, Active Table 1, Opening 52 phase C, Closing
52 phase C, Digital Input 1 Activated, etc.
2.3.1 OSCILLOGRAPHY
The DBF unit stores up to 4 oscillography records, with a resolution of 16 samples per cycle. Each record has a
maximum capacity of 66 cycles. The number of pre-fault cycles can be selected from 2 to 10 cycles. Each record
includes the following information:
• Date and time.
• Name of the signal that triggered the oscillography.
• Active settings table when recording
• Digital information (Status of internal digital signals)
• Instantaneous rms values of currents (I
A,IB,IC
and IN)
A configurable
mask
is available for selecting which functions or internal signals are able to trigger the
oscillography. It can either be triggered by a configurable digital input, by a command received from the
communication program (GE_LOCAL), or directly from the HMI.
10 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 18

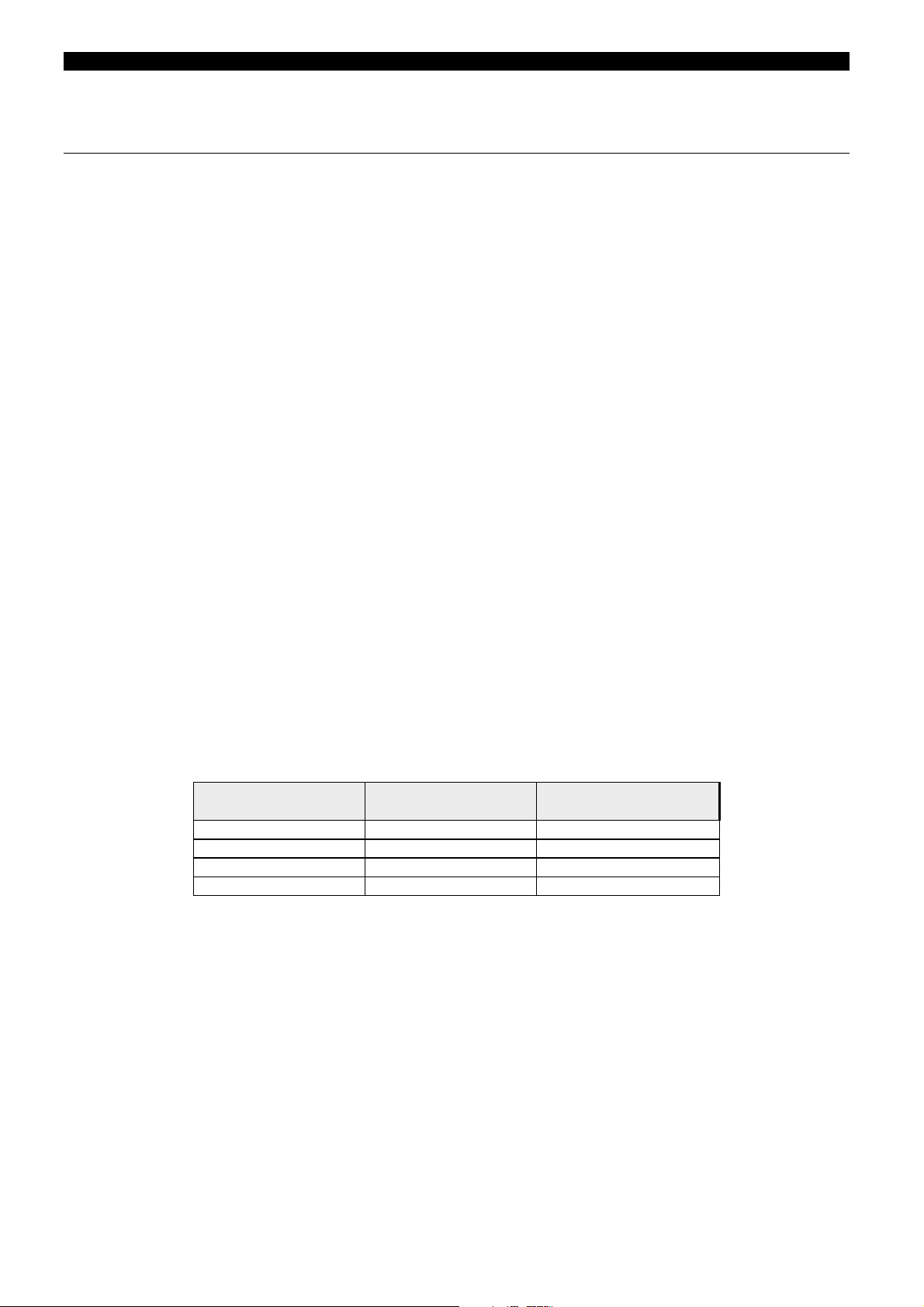
The user can select from the following list which signals may trigger the oscillography:
Events to Trigger the
Oscillography
PICKUP
1ST STAGE TRIP
2ND STAGE TRIP
INTERNAL ARC
50BF A TRIP
50BF B TRIP
50BF C TRIP
50BF 3P TRIP
EXTERNAL TRIGGER
COMM. TRIGGER
HI-SET A PICKUP
HI-SET B PICKUP
HI-SET C PICKUP
50BF A INIT
50BF B INIT
50BF C INIT
LO-SET A PICKUP
LO-SET B PICKUP
LO-SET C PICKUP
3 POLE 50BF INIT
NEUTRAL PICKUP
ARC A PICKUP
ARC B PICKUP
ARC C PICKUP
2. OPERATION LOGIC
The oscillography records are retrieved from the relay to the computer in COMTRADE international standard
format using the GE_LOCAL communications program. To draw the waveforms, digital flags, phasors and postfault analysis in general, it is suggested to use the GE_OSC oscillography program or any other that accepts
COMTRADE international format (IEEE-C37.111-1991). It is also possible to import the waveforms with
mathematical or spreadsheet programs (for example EXCEL
TM
).
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 11
Page 19
2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.4. CONTROL
2.4.1 TABLES OF SETTINGS
The DBF system has two types of settings stored in non-volatile memory (information is kept even when there is
no auxiliary voltage):
• Generic Settings.
• Specific Settings.
The
Generic
settings are grouped as follows:
GENERAL SETTINGS
BREAKER SETTINGS
ACTIVE TABLE SETTINGS
OSCILLOGRAPHY MASK
FUNCTION PERMISSION
For the
grouped as follows:
Only one setting table is active at a given time, and this is the table used by the system to run the different
functions included in it.
There is an "ACTIVE TABLE" setting that determines the settings table that is active at a given moment.
The active settings table can be changed by means of up to 2 digital inputs, referred to as "ACTIVE TABLE
SELECT 0" and "ACTIVE TABLE SELECT 1" which allow up to 4 combinations from 0 to 3. To do this it is
necessary to configure (using GE-INTRO software) two inputs to have these meanings. For applications which
require less tables (up to 2) it is possible to use only one input.
The selected combination is obtained from the binary coding of the 2 inputs mentioned (see following table). The
0-0 means selecting the table indicated in the "ACTIVE TABLE" setting, and numbers 0-1 to 1-1 select tables 1 to
3 respectively
specific
settings, the DBF allows to have up to 3 independent setting tables. These specific settings are
50BF SETTINGS
INTERNAL ARC SETTINGS
Table Selection
INPUT-1
0 0 Selected by setting
01 1
10 2
11 3
Table Selection
INPUT-0
Active Table
NOTE: if the inputs are programmed and used, energizing them, this selection has priority over the "ACTIVE
TABLE" setting and the table which is in fact used is determined by the status of the digital inputs.
12 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 20
2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.4.2 TIME SYNCHRONIZATION.
The DBF system includes an input for time synchronization. This input requires the connection of a device
to supply a demodulated IRIG-B output. In this way coordinated universal time is measured to a high degree of
accuracy and makes possible to tag events generated by the unit with a resolution of one millisecond.
The use of this input makes it possible to correlate data obtained from different units thanks to
synchronization with GPS satellites. In this way it is possible to obtain very useful information for analysis, crossreferencing the information provided by different units for a given incident.
Alternatively, it is possible to synchronize units by means of communications, using the GE-LOCAL
communications software, or manually by means of the HMI. If the IRIG-B input is used it has priority over time
setting by communications, since the time read by IRIG-B is much more accurate.
2.4.3 CONFIGURABLE INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
2.4.3.1 Digital Inputs
The DBF system has 6 digital inputs (two groups of 3 inputs with one common in each group). The inputs
can be configured by the user by means of the GE-INTRO configuration program. Using the optional expansion
board it is possible to increase the number of inputs up to a total of 14 (2 groups of 3 inputs with one common in
each group and 4 groups of 2 inputs with one common in each group). See the external connections diagram for
additional reference.
One of the following meanings can be assigned to any input: (For more detail about the configuration of the
inputs, see GE-INTRO Instruction Book).
Function P/L
Unused input
50BF Initiate A L
50BF Initiate B L
50BF Initiate C L
3P BF Initiate L
52a pole A L
52a pole B L
52a pole C L
52b pole A L
52b pole B L
52b pole C L
Latching Relays Reset P
External Trigger P
Active Table Select 0 L
Active Table Select 1 L
(L) indicates Level input
(P) indicates Pulse input
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 13
Page 21

2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.4.3.2 O utputs
The basic DBF system has 10 outputs as follows:
• 2 tripping contacts (A12-B12 and C1-D1)
• 1 Breaker failure pickup signaling (A11-B11)
• 1 Internal arc detection (C2-D2)
• 1 Equipment alarm (C3-D3)
• 5 configurable contacts (C4-D4 to C8-D8)
The optional expansion board for the DBF provides 6 additional latched contacts (E1-F1 to E6-F6). This outputs
are not configurable and are assigned as follows:
• 3 tripping contacts (TRIP 1st Stage) (E1-F1 to E3-F3)
• 3 tripping contacts (TRIP 2nd Stage) (E4-F4 to E6-F6)
The configurable outputs can be programmed using logic based on the internal protection states (pick-ups, trips,
alarms, etc.). The DBF has 66 different internal states, and these can be used to carry out logical operations NOT,
AND and OR, which gives the unit a great flexibility.
The output configuration is done using different levels. At the first level it is possible to use AND gates of up to 16
signals. The output is incorporated into the states matrix so that it can then be used in other AND gates of up to 16
inputs. This process can continue until the 16 ANDs are used.
Once the AND gates have been configured it is possible to create a second level with OR gates of 16 inputs
limited to the established groups of bytes, and whose logical outputs are assigned to physical outputs of the unit.
This means that we can configure the physical outputs with any internal signal from the status or any combination
of them made by means of the AND logic gates.
14 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 22

2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.5. MAN-MACHINE INTERFACE (HMI)
The DBF system includes as standard a 20 key keyboard and a 2-line liquid crystal display (LCD) with 16
characters per line. This display has highly reliable LED diode back lighting (the screen brightness can be adjusted
on the rear of the front board).
By means of this interface the user can change the settings, display measurements, carry out operations
and access information stored in the unit. The functions of this local interface and how to use it are described in
the section KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 15
Page 23

2. OPERATION LOGIC
2.6. REMOTE COMMUNICATIONS
The relay has 2 serial gates and three connectors. Gate 1 can be reached from the front of the relay in connector
1 (PORT 1 connector) or from the rear (PORT 2 connector). The second gate can be reached from connector 3
(PORT 3 connector) which is located on the rear.
There are different models, each with a different physical connection for the PORT 3 connector (RS-232/RS-485
or fiber-optic). In the "RS232" models the three connectors are RS232. In the "RS232 and fiber-optic" models the
PORT1 and PORT2 connectors are RS232 while the PORT3 connector is replaced by a fiber-optic connector.
The PORT 1 connector has priority over the PORT 2 connector and is selected when the DCD (Data Carrier
Detect) signal is activated. Figure 8 shows how to make the connections to a personal computer.
Gate 1 (PORT 1 and PORT 2 connectors) and 2 (PORT 3 connector) are independent and the unit can serve
them simultaneously.
The communications protocol is the same used for the rest of the GE digital protection systems and requires the
use of the GE-LOCAL software. PORT 3 protocol can be chosen between M-LINK and ModBus RTU. The
protocol is highly reliable and allows communication with different protection systems. It guarantees very efficient
data transfer (especially for the oscillography and other large files) along with error detection and automatic
communication recovery.
The status of the local/remote communication is indicated on the front of the unit by LED indicator 16 (the last LED
in the right-hand column, according to the default configuration.) Local communication refers to communication via
the keyboard/display (local display showing any information except for the initial DBF GENERAL ELECTRIC
screen), or via communications gate 1 (PORT 1, PORT2 connectors), and remote communication refers to
connection via gate 2 (PORT 3 rear connector).
Local and remote communications can exist at the same time, although there is only one possibility for changing
settings and carrying out operations, since this can only be done with the communication which has priority (local
communication) while the other is limited only to accessing information. When the local communication is
interrupted, either by the disconnection of PORT 1 connector or because the HMI is on the initial screen (a
situation which can be caused intentionally, or automatically if no key has been pressed for 15 minutes), the
remote communication recovers the ability to modify settings and carry out operations.
16 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 24

3. SETTINGS
3.
3. SETTINGS
3. 3.
This section describes the settings of the DBF relay and the procedure to modify them. Table 3 shows the list of
DBF settings, their range and resolution, and the factory default settings.
To view or to modify settings using the GE_LOCAL program connected to PORT 1, PORT 2 or PORT 3 the user
has to perform the following steps:
• Check that the available connection cable is in accordance with the diagram in Figure 7.
Check correspondence between DB-9 connector in the cable with available connector at PC
port (could be DB-9 or DB-25)
• Connect the cable between the relay (or modem) and the serial port of your computer.
• Run the GE-LOCAL software. For more details on the installation and use of the GE-LOCAL
software see instruction book GEK-105568.
• Make sure that the communication parameters in GE_LOCAL match with those set on the
DBF. Specifically, the parameters on the configuration of the local HMI are:
SETTINGS
SETTINGSSETTINGS
COMMUNICATION SPEED
∗
through PORT 1 or PORT 2 (means LOCAL), or PORT 3 (means NET)
∗
STOP BIT
NET
To modify or view the DBF communication parameters refer to Chapter 8, Section 8.1 “Menu Tree”.
IMPORTANT: It should be noted that in order to simplify the setting of the unit and for safety reasons, all settings
related with the configuration of the unit (configurable inputs and outputs, internal status events and target LED’s)
have been removed from the HMI facilities and also from the communications software GE_LOCAL. To perform
these configurations the GE_INTRO software (described in instruction book GEK-105569) must be used.
Common to all tables Range Default Step
Relay status In/out of service In-service
Identification 20 ASCII characters No ID
Frequency 50 / 60 Hz 50 Hz
Phase CT Ratio 1-4000 1 1
Neutral CT Ratio 1-4000 1 1
: Stop-bit corresponding to each one of the communication ways: LOCAL or
TABLE 3. Settings Table
: On the relay depending on whether communication is:
General Settings Group
Breaker Setting Group
Breaker Number 4 ASCII characters 0000
kI2t Operation Mode Fixed-Measured Fixed
Integration Time for kI2t 0.03-0.25s 0.06s 0.01s
kI2t Maximum Limit 1-999999 99999 1
Active table setting group
Active setting table # 1 - 3 1 1
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 17
Page 25

3. SETTINGS
Common to all tables Range Default Step
Oscillography Mask
Prefault Cycles 2-10 4 1
Arc Detection Enable-Disable Enable
Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
1stStage trip Enable-Disable Enable
2ndStage Trip Enable-Disable Enable
50BF A Trip Enable-Disable Enable
50BF B Trip Enable-Disable Enable
50BF C Trip Enable-Disable Enable
50BF 3P Trip Enable-Disable Enable
External Trigger Enable-Disable Enable
Communications Trigger Enable-Disable Enable
Hi-Set A Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Hi-Set B Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Hi-Set C Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
50BF A Init. Enable-Disable Enable
50BF B Init. Enable-Disable Enable
50BF C Init. Enable-Disable Enable
Lo-Set A Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Lo-Set B Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Lo-Set C Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
3P 50BF Init. Enable-Disable Enable
Neutral Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Arc A Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Arc B Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Arc C Pickup Enable-Disable Enable
Functions Permitted
50BF 1P function Permitted-Non-Permitted Non-Permitted
50 BF 3P Function Permitted-Non-Permitted Non-Permitted
3P No I Function Permitted-Non-Permitted Non-Permitted
Independent for each table Range Default Step
50BF Settings
PH Hi-Set Pickup 1-12A 2A 0.01A
PH Lo-Set Pickup 1-12A 1A 0.01A
Neutral Pickup 0.50-6A 1A 0.01A
1 Phase Timer T1 0.05-2s 0.5s 0.01s
3 Phase Timer T2 0.05-2s 1s 0.01s
3P No I Timer T3 0.05-2s 2s 0.01s
BF Logic (3P/2P) 2-Phases/3 Phases 2-Phases
Severe Fault 3P Permitted-Non-Permitted Non-Permitted
Low Load 2P Permitted-Non-Permitted Non-Permitted
Output Stages number 1-2 1 1
2nd Stage Timer 0.05-2s 2s 0.01s
Internal Arc Settings
Internal Arc Pickup 0.05-1A 1A 0.01A
Internal Arc Timer 0.10-2s 1s 0.01s
18 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 26

3. SETTINGS
COMMENTS ON SETTINGS:
1. The Identification setting allows the user to input a name for the unit (for example the name of the line or
feeder) with a maximum of 20 ASCII characters.
2. The Active Table setting allows selecting the table to be active during normal operation among the three
tables available on the DBF. This selection can also be done by means of digital inputs configured for this
purpose. The table input selection has priority over the table setting selection (if the input has been configured
to perform change of tables).
3. To set the breaker monitoring function it is necessary to set first the kI2t OP. Mode setting. If this is selected
as "measured" no other setting is required, since the time used for the calculation is the time taken by the unit
during the interval: trip order-52/b contact to close. If the “fixed” mode is selected it is necessary to set then the
kI2t Integration Time. In this case the time used will be always the set time (should be the rated operating
time of the circuit breaker provided by the manufacturer).
4. The Pre-Fault Cycles to be shown in every oscillography record may be adjusted from two to ten (2-10). In
any case the total number of cycles for any oscillography record is 66, regardless of pre-fault cycles setting.
5. The difference between the function permission and permitted trips settings is:
• The function permission setting enables or disables the function
• The trip permission setting allows to enable or disable any specific function to trip, but keeping always
active the function, providing thus capability to generate events, alarms and signals.
6. The overcurrent ranges shown in Table 3 correspond to models of 1-12A for phase and 0.5-6A for ground for
5A rated CT’s. Only PH Lo-Set Pickup, PH Hi-Set Pickup
range.
7. Sometimes the names used to describe the settings for both the local HMI and the communications program
are short or abbreviated. This is because of the space limitation imposed by text windows in the program.
and Neutral Pickup settings change with the
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 19
Page 27

3. SETTINGS
20 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 28

4. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
4.
4. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
4. 4.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICSTECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
4.1. MODEL LIST
Position DBF 1 - - - - 1 1 - - 0 0 A Description
Comm. Interface
0
51
2
3
6 Ranges
[[[[1]]]] See Table [1R]
71
2
8M
D
11 0
1
12 G
H
13,14 0 0 Special Models
15 A Revision
P2: RS232 + P3: RS232
P2: RS232 + P3: Plastic F.O.
P2: RS232 + P3: Glass F.O.
P2: RS232 + P3: RS485
Comm. Protocols
P1, P2, P3: Mlink
P1, P2: Mlink; P3: ModBus
Language
Spanish
English
Model
Basic Model
Enhanced Model (Expansion
board)
Power Supply
48-125 VDC
110-250 VDC
TABLE [[[[1R]]]] -RANGES
MODELS ABCDEFG
DBF PHASE
GROUND
The input voltage of the standard model corresponds to the Power Supply voltage. The following models have
been developed to allow the selection of an input voltage independently of the Power Supply.
The following codes should be placed as two last digits before A in the ordering code for selecting the desired
characteristics:
MOD 04: V inputs: 48 Vdc ±20%
MOD 05: V inputs: 110 Vdc ±20%
MOD 06: V inputs: 125 Vdc ±20%
MOD 07: V inputs: 250 Vdc ±20%
Example: If we want to order a relay model with a digital input voltage of 48 Vdc, the model should be:
DBF1*****11**04A.
1-12 A 0.2-2.4 A 1-12A 1-12 A 1-12 A 0.5-6 A 0.5-6 A
1-12 A 0.2-2.4 A 0.2-2.4 A 0.5-6 A 0.1-1.2 A 0.2-2.4 A 0.1-1.2 A
4.1.1. SPECIAL MODELS
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 21
Page 29

4. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
4.2. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
MECHANICAL
• Metal 19” rack case, 2 units high
• IP51 Protection (as per IEC 529)
• Local HMI: LCD (2 rows, 16 characters) and 20 key keyboard
• Rear connection for wiring: 4 blocks, 12 terminals each (6 blocks when optional expansion board)
• Dimensions: 437 x 164 x 88 mm
• Weight: Net 6 kg. Shipping 7 kg.
ELECTRICAL
• Frequency: 50 or 60 Hz (selectable by setting)
• Rated current: 1 or 5 A (different models)
• DC Power Supply 48/125 Vdc or 110/250 Vdc (different models)
• Operational range 80% to 120% of rated values
• Digital Input Voltage For standard models: 48-125, 110-250 VDC
• Thermal Capacity
Current circuits
- Permanent 4 x In
- 3s duration 50 x In
- 1 s duration 100 x In
• Temperature ranges
-Operation -20º C to + 55ºC
-Storage -40ºC to + 70ºC
• Humidity Up to 95% without condensation
• Trip contacts:
(according to selected model). For special models,
please refer to section 4.1.1.
AC
-Continuous Capacity 16A
-Rated Breaking Capacity 4000VA
-Make 25A for 4 sec
-Operating Time 8 ms or less
DC Breaking Capacity
- Resistive 9A at 30V
- Resistive 0.65A at 100V
- Inductive(L/R=40 ms) 0.5A at 30V
• Burden
-Current circuits 0.5 VA at I
• Consumption:
-At DC rated voltage 12 W idle state
-Digital inputs 8 mA (1 W at V
• Accuracy
-Current 5%
-Time 5% or 30ms (whichever is greater)
- Error index Class E-5 as per IEC 255-4
• Repeatability
-Operating value 1%
-Operating time 2% or 30 ms (whichever is greater)
=5A
r
0.1 VA at I
=1A
r
16 W all relays activated
= 125 VDC)
rated
22 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 30

4. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
COMMUNICATIONS
-RS232 using DB9 female connector (2/3 connectors depending on model)
- Mode: Half duplex
-1 mm plastic fiber-optic (depending on model)
Typical power output : -8dBm
Receiver sensitivity -39dBm
Numeric aperture N.A. 0.5
Wave length 660 nm (visible red)
HFBR-4516 type connector
-Glass fiber-optic 62.5/125 (depending on model):
Typical power output: -17.5 dBm
Receiver sensitivity -25.4 dBm
Numeric aperture N.A. 0.2
Wave length 820 nm (near infrared)
SMA type connector
STANDARDS
The DBF system complies with the following standards, which include the GE insulation and electromagnetic
compatibility standard and the standards required by Community Directive 89/336 for the EC market, in line with
European standards. It also complies with the European directive requirements for low voltage, and the
environmental and operating requirements established in ANSI standards C37.90, IEC 60255-5, IEC 60255-6 and
IEC 68.
Test Standard Class
Insulation test voltage IEC 60255-5 600V, 2kV
50/60 Hz 1 min.
Impulse voltage IEC 60255-5 5kV,0.5 J
1 MHz interference IEC 60255-22-1 III
Electrostatic discharge IEC 60255-22-2 IV
EN 61000-4-2 8kV
Immunity to radio interference IEC 60255-22-3 III
•Electromagnetic fields radiated with ENV 50140 10 V/m
amplitude modulation
•Electromagnetic fields radiated with ENV 50141 10 V/m
amplitude modulation. Common mode
•Electromagnetic fields radiated with ENV 50204 10 V/m
frequency modulation
•Fast transients IEC 60255-22-4 IV
EN 61000-4-4
•Magnetic fields at industrial EN 61000-4-8 30 Av/m
frequency
•RF emission EN 55011 B
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 23
Page 31

4. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
24 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 32

5. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
5.
5. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
5. 5.
CAUTION
The DBF contains electronic components that can be damaged by electrostatic discharge if currents flow
through some terminals of the internal components. The main source of electrostatic discharge currents
is the human body, especially in conditions of low humidity, carpeted floors and isolated footwear. Under
these conditions it is important to have special care when removing and handling the modules or some of
their internal components. Personnel handling the relay should check that their body is free from
electrostatic charge, either by touching a surface at ground potential or by using an electrostatic
wristband connected to earth.
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
HARDWARE DESCRIPTIONHARDWARE DESCRIPTION
5.1. PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION
5.1.1. CASE
The DBF case is made of stainless steel and consists of the main body and a covering lid. The main body of the
case contains the blocks of terminals necessary to carry out the external connections and guides to support the
trays that contain the internal parts of the relay. The trays can be pulled out in order to make easy the
maintenance and servicing of the relay.
5.1.2. ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
All the electrical connections for current channels, digital input and output relays are made using the terminal
blocks fixed to the rear part of the case. The connections required for communications are made using three DB-9
serial connectors, one on the front and two on the rear when using communication option RS-232. One of these
connectors is replaced by the corresponding fiber-optic connector in models including this option.
5.1.3. INTERNAL CONSTRUCTION
Internally the DBF unit is divided into 2 trays and a case. The case with the blocks of terminals is described above.
The lower tray carries the magnetic module and a printed circuit board which contains the power supply, the digital
inputs and also the trip outputs and auxiliary outputs on the basic version (model without expansion board).
The upper tray carries the board with the protection system CPU and the communications. This tray can also carry
as an option the input and output expansion board.
The front panel consists of a covered keyboard and a board which carries the alphanumeric display, the LEDs and
the Reset button. The model number (see list of models in Chapter 4) and the technical characteristics of the unit
are situated on the front panel of the relay.
The 16 indicator LEDs can be identified using labels which can be placed beside them, inside available plastic
holders.
A frontal bus is responsible for the connections between the lower and upper trays described above. Both trays
can be pulled out. To do so you first have to release the front panel which is fixed to the case with two screws and
pull it out, removing the flat cable which connects it to the CPU. It is then possible to remove the frontal bus.
The blocks of terminals situated on the rear of the case are identified with the letters A, B, C and D, and optionally
E and F, as shown in figure 9. In addition, each terminal is identified with a number.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 25
Page 33

5. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
The communications connectors are situated on left-hand side of the front and on the right-hand side of the rear of
the case. The front port is PORT 1 and the rear ports are PORT 2 and PORT3. The IRIG-B connection is made
using a block of two additional terminals.
26 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 34

5. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
5.2. OPERATING THEORY
The DBF unit measures current signals, performs complex calculations using internal data, stores relevant
incidents, pick-up tripping relays and generates information that can be used to determine the state of the
associated electrical system. The DBF functionality is related to the following modules:
- Magnetic module
- CPU board
- Power supply
- Keyboard and display
5.2.1. MAGNETIC MODULE
The magnetic module performs two essential functions: galvanic insulation and scaling analog input signals. In the
case of current transformers the input current for the primary winding is converted into a scaled voltage in the
secondary winding. Each current transformer must be linear in the whole measurement range of the relay.
5.2.2. CPU BOARD
The DBF uses two 16-bit microprocessors operating at a clock frequency of 20 MHz. One of these
microprocessors is used to perform the relay communications and the other performs the necessary calculations
for protection functions. In general the microprocessors are responsible to perform the input and output
calculations and operations at very high speed. The use of two microprocessors is especially recommendable to
make the protection and communication functions independent of each other inside the unit itself, and therefore
increase the reliability of the system.
The analogue-digital converter converts the voltage inputs into their digital equivalent with a resolution of 10 bits.
The unit code is stored in non-volatile EPROM memory while the settings and events are stored in EEPROM
memory. The data related to the oscillography is stored in RAM memory which is maintained using a capacitor,
thus avoiding the loss of information when the unit is disconnected.
A high-resolution real time clock is used to ensure that the date and time of all incidents can be time-tagged, with
a resolution of one millisecond. This clock can be synchronized externally using an IRIG-B demodulated signal..
The input and output functions are divided between the two microprocessors. The serial ports, the keyboard and
the display are controlled by the communications microprocessor. External communications are processed by a
serial communications controller circuit which contains a universal asynchronous transceiver (DUART). The digital
inputs and outputs are processed by the protection microprocessor.
The DBF contains 6 independent circuits to process digital inputs. These circuits check the presence or absence
of input voltage and are designed to isolate them electrically from the microprocessor, thus increasing the
reliability of the system.
On the front of the relay there is a set of 17 Target LED’s, one of which is fixed and indicates the operating state of
the unit. The rest are user-configurable using GE_INTRO software.
The button situated on the front is designed to check the state of the Target LED’s and to reset them by keeping it
pressed during 3 seconds.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 27
Page 35

5. HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
5.2.3 POWER SUPPLY
The DBF power supply can be 48-125 VDC or 110-250 VDC rated. The operating margin of the power supply is +
20%, and is galvanically isolated from the rest of the relay's circuits. The power supply provides ± 12 VDC to the
analog circuitry and the output relays, and ± 5 VDC for the digital circuits.
5.2.4 KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
The DBF display at the front of the relay is liquid crystal type and consists of two rows of 16 characters each. The
display has background light with variable lightness adjustable by a potentiometer located on the rear of the front
cover plate.
28 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 36

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.
6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6. 6.
ACCEPTANCE TESTS
ACCEPTANCE TESTSACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.1. CONNECTIONS AND NECESSARY EQUIPMENT
Necessary equipment:
• One current source
• One DC voltage source
• Precision timer for testing timed events
• One AC/DC voltmeter/ammeter
Connect the relay as indicated in the external connections diagram, Figure 2.
For safety reasons, the external protection earth should be securely grounded.
Apply dc rated voltage to terminals A10-B10
6.2. VISUAL INSPECTION
Check that the relay has not suffered any kind of damage due to transport and handling.
Check that all the screws are tight and the terminal blocks have not been damaged in any way.
6.3. PANEL INSULATION TESTS
!
If any insulation test would be performed on the panel where the relay is installed, the ground terminals
A9-B9 must remain ungrounded.
Do the following groups in the terminals of the relay:
Group 1: A10, B10
Group 2: A1 to A4, B1 to B4
Group 3: C9, C10, D9, D10, C11, C12, D11, and D12
Group 4: A11, B11, A12, and B12
Group 5: C1, D1, C2, D2, C3, and D3
Group 6: C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, D4, D5, D6, D7, and D8
If the relay has expansion board, then the following groups must be added:
Group 7: E7, F7, E8, F8, E9, F9, E10, F10, E11, F11, E12, and F12
Group 8: E1, F1, E2, F2, E3, F3, E4, F4, E5, F5, E6, and F6
Apply 2000V gradually between case and groups.
Apply 2000V gradually between groups.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 29
Page 37

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.4. RELAY SETTING
Introduce the following settings in the relay (by means of HMI or GE_Local software):
General Settings Group Value
Relay Status IN SERV
Identification N/A
Frequency 50 Hz / 60 Hz
Phase CT Ratio 1
Neutral CT Ratio 1
Breaker Settings Value
Breaker Number N/A
KI2t Op. Mode Fixed
KI2t INT. Time 0.06s
KI2t LIMIT 99999
Active Table Set Value
Active Table 1
Function Permit Value
50BF 1P Function No Per
50BF 3P Function No Per
3P NO INT Funct No Per
50BF Settings Table 1 Value
PH Hiset Pickup 2A
PH Loset Pickup 1A
Neutral Pickup 1A
1 Phase Timer T1 1s
3 Phase Timer T2 1s
3P No I Timer T3 2s
BF Logic (3p/2P) 2 PHASE
Severe Fault 3P Per
Low Load 2P No Per
Nº Output Stages 1
2ndStage Timer 2s
Internal Arc Settings Table 1 Value
Int Arc Pickup 1A
Int Arc Timer 1s
The specific settings required for each test are indicated; other settings do not affect the tests.
6.5. INDICATORS
Check that pressing the TARGET RESET button (with relay fed with rated dc power supply) all target LEDs light
up.
6.6. POWER SUPPLY
The relay operates with a dc power supply within ± 20% of the rated value. Check that the READY target LED in
the front of the relay lights up showing green color.
1. Apply dc rated voltage to terminals A10-B10
2. Change setpoint FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 1P FUNCTION to PERM.
3. Apply 2A to terminals A1-A2.
4. Energize digital input CC1 PHASE A BF INITIATE (C9-D10).
5. Wait 1second.
6. Check that the READY target LED in the front of the relay lights up showing green color.
7. Check the dc burden (see table below)
30 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 38

8. Remove the current from terminals A1-A2. Remove voltage from digital input CC1.
9. Repeat these steps with minimum and maximum voltages depending on the range of the relay.
Test voltages and typical burdens are listed below:
Model "G" (48/125 VDC)
Voltage (Vdc) Without Expansion Board With expansion Board
38 340 440
125 250 320
150 225 300
Model "H" (110/250 VDC)
Voltage (Vdc) Without Expansion Board With expansion Board
88 300 370
110 250 320
300 150 220
6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
DC Battery (mA)
DC Battery (mA)
6.7. COMMUNICATIONS
The object of this test is to check the communication ports of the relay (PORT1, PORT2 and PORT3). To do this
it is necessary to use a computer and the communications software GE_LOCAL. Figure 7 shows the series cable
and connection accessories necessary to establish the connection between the PC and the relay. Figure 8 shows
the cable and connectors necessary for remote connection (by MODEM) through PORT3.
The PC communication parameters necessary to match the relay default setting parameters are:
Relay number: 1
Remote port speed: 19200
Local port speed: 19200
Remote stop bit: 1
Local stop bit: 1
By using GE_Local communications software establish the connection and check that the relay communicates
through the three communication ports. Repeat this test with different baud rates and different power supply
voltages.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 31
Page 39

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.8. INPUTS
6.8.1 DIGITAL INPUTS
Log into the relay using the GE_LOCAL software and press INPUTS / OUTPUTS button on the first general
screen.
• Check that applying dc rated voltage between terminals:
C9 and D10 (CC1)
D9 and D10 (CC2)
C10 and D10 (CC3)
C11 and D12 (CC4)
D11 and D12 (CC5)
C12 and D12 (CC6)
their corresponding status windows turn red while the applied voltage remains present.
If the relay has the optional expansion board, check the same for the following contact converter inputs:
E7 and E8 (CC7)
F7 and E8 (CC8)
E9 and F8 (CC9)
F9 and F8 (CC10)
E10 and E11 (CC11)
F10 and E11 (CC12)
E12 and F11 (CC13)
F12 and F11 (CC14)
6.8.2 IRIG-B SYNCHRONIZING INPUT
Connect the output of an IRIG-B unit with decoded output to the IRIG-B input at the rear of the DBF. Special care
must be taken when making the connection because the input is polarized.
Check that the time measured by the two units is the same.
32 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 40

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.9. FUNCTIONS
6.9.1 50BF 1P UNIT TEST
1. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 1P FUNCTION to PER.
2. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 3P FUNCTION to NO PER.
3. Change setpoint TABLE 1/FUNCTION PERMIT/3P No INT FUNCT to NO PER.
4. Change setpoint 50BF SETTINGS/Nº OUTPUT STAGES to 2.
5. The precision timer will be started at the same time than the corresponding contact converter (digital input) is
energized. The timer stop input will be wired to any DBF contact under test, i.e. contact C4-D4.
6. Apply 2A to terminals A1-A2 (phase A).
7. Energize digital input CC1 PHASE A BF INITIATE (terminal C9-D10).
8. Check that after T1 time delay (1s), the following contacts are closed:
A12-B12
C4-D4
C5-D5
In case the relay under test includes an expansion board, check also the operation of the following contacts:
E1-F1
E2-F2
E3-F3
9. Check that after 2nd Stage Timer delay (2s), the following contacts are closed:
C1-D1
C6-D6
C7-D7
and if the relay is equipped with an expansion board also the following contacts must be closed:
E4-F4
E5-F5
E6-F6
10. Repeat steps 7, 8, 9 and 10 using phase B current (B1-B2 terminals) and CC2 PHASE B BF INITIATE (D9D10 terminals) to start the breaker failure operation.
11. Repeat steps 7, 8, 9 and 10 using phase C current (A3-A4 terminals) and CC3 PHASE C BF INITIATE (C10D10 terminals) to start the breaker failure operation.
12. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/Nº OUTPUT STAGES to 1.
13. Repeat steps 7 to 12 to check that in this case contacts C1-D1, C6-D6, C7-D7, E4-F4, E5-F5 and E6-F6 close
at the same time than contacts: A12-B12, C4-D4, C5-D5 and E1-F1, E2-F2, E3-F3 (if an expansion board is
available).
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 33
Page 41

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.9.2 50BF 3P UNIT TEST
The DBF relay outputs are factory set with the default settings shown in the external connections drawing (Figure
2).
1. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 1P FUNCTION to NO PER.
2. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 3P FUNCTION to PER.
3. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/3P No INT FUNCT to NO PER.
4. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/Nº OUTPUT STAGES to 2.
5. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/BF Logic (3P/2P) to 3 PHASE.
6. The precision timer will be started at the same time than the corresponding contact converter (digital input) is
energized. The timer stop input will be wired to any DBF contact under test, i.e. contact C4-D4.
7. Apply 3A to terminals A1-A2 (phase A), B1-B2 (phase B) and A3-A4 (phase C).
8. Energize digital input CC7 3 POLE BF INITIATE (if the relay has not an expansion board, energize digital
inputs CC1 PHASE A BF INITIATE and CC2 PHASE B BF INITIATE simultaneously).
9. Check that after T2 time delay (1s), the following contacts are closed:
A12-B12
C4-D4
C5-D5
10. Check that after 2nd Stage Timer delay (2s), the following contacts are closed:
C1-D1
C6-D6
C7-D7
11. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/Nº OUTPUT STAGES to 1.
12. Repeat steps 8 to 9. Check that after T2 time delay (1s), all the contacts are closed:
A12-B12 C1-D1
C4-D4 C6-D6
C5-D5 C7-D7
13. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/BF LOGIC (3P/2P) to 2 PHASE.
14. Apply 3A to terminals B1-B2 (phase B) and terminals A3-A4 (phase C).
15. Energize digital inputs CC2 PHASE B BF INITIATE and CC3 PHASE C BF INITIATE.
16. Check that after T2 time delay (1s), the following contacts are closed:
A12-B12 C1-D1
C4-D4 C6-D6
C5-D5 C7-D7
17. Repeat steps 15 to 17 choosing any other pair of phases to apply ac current and any other pair of BF initiation
inputs.
34 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 42

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.9.3 INTERNAL ARC TEST
1. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 3P FUNCTION to NO PER.
2. Change setpoint TABLE 1/INTERNAL ARC SETTINGS/INT ARC TIMER to 2s.
3. Energize digital input CC4 52/b A
4. Apply 2A to terminals A1-A2 (phase A).
5. Check that after INT ARC TIMER time delay, contact C2-D2 is closed.
6. Repeat steps 3, 4 and 5 for phases B (terminals B1-B2) with digital input CC5 52/b B and C (terminals A3-A4)
with digital input CC6 52/b C.
6.9.4 3P NO I FUNCTION
1. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 1P FUNCTION to NO PER.
2. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 3P FUNCTION to NO PER.
3. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/3P No INT FUNCT to PER.
4. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/Nº OUTPUT STAGES to 1
5. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/ 3P NO I TIMER T3 to 1s
6. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/LOW LOAD 2P to PER.
7. Energize digital input CC7 3P BF INITIATE. If the relay has not an expansion board, energize CC1 PHASE A
BF INITIATE and CC2 PHASE B BF INITIATE.
8. Check that after 3P NO I TIMER T3 (2s), the following contacts are closed:
C4-D4 A12-B12
C5-D5 C1-D1
C6-D6 C7-D7
9. If the relay is provided with an expansion board, check that also the following contacts are closed:
E1-F1 E2-F2
E3-F3 E4-F4
E5-F5 E6-F6
6.9.5 NEUTRAL OVERCURRENT UNIT TEST
1. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 1P FUNCTION to NO PER.
2. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 3P FUNCTION to NO PER.
3. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/3P No INT FUNCT to PER.
4. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/LOW LOAD 2P to PER.
5. Energize digital inputs CC4, CC5 and CC6 (52b inputs).
6. Energize digital inputs CC7 3P BF INITIATE. If the relay has not an expansion board, energize digital inputs
CC1 PHASE A BF INITIATE and CC2 PHASE B BF INITIATE.
7. Apply 2A to terminals B3-B4 (neutral).
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 35
Page 43

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
8. Check that after 3P NO I TIMER T3 (2s), the following contacts are closed:
A12-B12 C1-D1
C4-D4 C6-D6
C5-D5 C7-D7
9. If the relay is provided with an expansion board, check that also the following contacts are closed:
E1-F1 E2-F2
E3-F3 E4-F4
E5-F5 E6-F6
36 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 44

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
6.10. RELAY MEASUREMENT TESTS
6.10.1. CURRENT MEASUREMENT
1. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 1P FUNCTION to PER.
2. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/50BF 3P FUNCTION to NO PER.
3. Change setpoint GENERAL/FUNCTION PERMIT/3P No INT FUNCT to NO PER.
4. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/PH LOSET PICKUP to 5A (1A in relays with 1A nominal current).
5. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/1 PHASE TIMER T1 to 0.050s.
6. Change setpoint TABLE 1/50BF SETTINGS/Nº OUTPUT STAGES to 1.
7. Energize digital input 3POLE BF INITIATE (terminals E7-E8 for relays with expansion board). If the relay has
not expansion board, energize CC1 PHASE A BF INITIATE.
8. Increase current applied on A1-A2 (phase A) until contact A12-B12 closes. Check that the operating value of
the current is within ± 5% of setpoint (5A for relays with 5A nominal current and 1A for 1A nominal current
relays).
9. Repeat step 8 applying current on B1-B2 (phase B). If the relay has not an expansion board energize CC2
PHASE B BF INITIATE.
10. Repeat step 8 applying current on A3-A4 (phase C). If the relay has not an expansion board energize CC3
PHASE C BF INITIATE.
6.10.2. TIMING MEASUREMENT
1. Connect the stop input of the precision timer to the A12-B12 output (trip 1).
2. Apply the operating current level of the previous test to terminals A1-A2 (phase A).
3. Simultaneously energize the digital input 3POLE BF INITIATE and the starting input of the precision timer.
4. After 1 PHASE TIMER T1 (0.050s) the relay will trip.
5. Verify that the actual operating time is equal to 1 PHASE TIMER T1 (accuracy ± 5% or 30 ms, whichever is
greater).
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 37
Page 45

6. ACCEPTANCE TESTS
38 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 46

7. INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
7.
7. INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
7. 7.
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCEINSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
7.1. INSTALLATION
The relay should be installed in a clean, dry and dust-free place, with no vibrations.
The DBF system is supplied in a 19’’ rack case 2 units high. Figure 5 shows the dimension diagram.
The relay should be mounted on a vertical surface. Figure 6 shows a diagram for panel drilling.
Given that the design of the DBF unit is based on high performance digital technology it is not necessary to
calibrate the relay. However if the tests show that it is necessary to readjust the relay, it is recommended to return
the unit to the factory to check it.
7.2. CONNECTION-TO-GROUND AND DISTURBANCES SUPPRESSION
The terminal (see Figure 2) should be connected to ground so that the disturbance suppression circuits in the
system works correctly. This connection should be as short as possible (preferably 25 cm or less) to guarantee
maximum protection. In this way the capacitors that are internally connected between the inputs and ground divert
high frequency disturbances directly to ground without passing through the electronic circuits. Then the internal
circuitry is perfectly protected.
In addition this connection also guarantees the physical safety of the personnel when handling the relay, since the
whole casing is connected to ground.
7.3. MAINTENANCE
Given the important role that the protection relays play in the operation of any installation, a periodic program of
tests is highly recommended. The unit incorporates built-in diagnostic functions that permit the fast identification of
some of the most likely circuit failures. Testing the unit is recommended at intervals of 2 years or more. Although
the built-in diagnosis does not reduce the average time between failures, it does increase the availability of the
protection because it allows a drastic reduction in the average interruption time involved in detecting and repairing
the fault.
The set of tests which can be performed to test that all aspects of the DBF unit function properly is described in
detail in the chapter entitled ACCEPTANCE TESTS.
Since most of the protection and communications functions are integrated in two separate programs, it is unlikely
that faults will occur due to problems of wear and tear, short-circuits or aging which are typical in other
electromechanical protection systems, whether analogue or hybrid. Moreover, a failure in the communications
processor does not affect the protection functions, which are implemented by a dedicated processor.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 39
Page 47

7. INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
40 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 48

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.
8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8. 8.
The DBF has a 20 key keyboard and a liquid crystal DISPLAY with 32 characters, divided into two rows of 16
each. The following diagram shows the appearance of the DBF Keyboard:
KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
SET 1/Y 2 3/N CLR
INF 4 5 6
ACT 7 8 9
END + 0 . ENT
The keyboard program uses menus to access the different relay functions. These functions are divided into five
large groups, each of which is accessed using a different key. These groups are the following:
Information: Provides data about the state of the relay, alarms, breaker status, record of currents, events record,
etc. This menu is accessed using the INF key.
Control: Permits reset of latching relays, oscillography triggering and synchronizing. This menu is accessed by
pressing the ACT key.
Settings: Permits viewing and changing all the relay settings. This menu is accessed by pressing the SET key.
Configuration menu: Permits access to the system configuration and the modification of the passwords, access,
communication speeds, etc. This menu is accessed by keying in the code "7169" In order to access this mode the
relay should be on the main screen.
Single key menu: By pressing the ENT key the DBF can be operated in a simplified mode. It is not necessary to
remove the plastic cover on the front of the relay to access this mode. In steady state the DBF shows the following
message on the DISPLAY :
DBF
GENERAL ELECTRIC
At this point the five groups mentioned above can be selected. In order to select a different group the user must
return to this screen and press the key that corresponds to that group.
Once inside a group it is not possible to select a different one. Movement to any other group is carried out using
the following keys : ENT, CLR, and the up, down, left, right arrows. Their function is as follows:
ENT: Accepts the option that is shown on the screen. It is equivalent to go down one level in the menu tree.
CLR: Quits the option that is shown on the screen. It is equivalent to go up one level in the menu tree.
UP/DOWN ARROWS: Change options. The equivalent of a horizontal movement within a menu. When the
required option appears on the screen it can be selected with the ENT key.
LEFT/RIGHT ARROWS: Show the different possibilities of a given setting. It is not used for all settings. When the
required option appears on the screen it can be selected with the ENT key.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 41
Page 49

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.1. MENU TREE.
The DBF has different menus divided into levels. The Level 0 is the steady state screen. The Level 1 of the
different menus is accessed by pressing the corresponding group key (SET, INF, etc.). The scrolling within a
given level is done by using the UP and DOWN arrows. It is possible to go down to levels 2 and 3 by pressing the
ENT key.Press CLR to go up a level within the menu tree. The Level 1 for each of the five groups is shown in the
following table :
Group Level 1 Description
VIEW SETTINGS View settings
SET
CHANGE SETTINGS Change settings
CHANGE COUNTER Change counters
Hidden menu, typing this
INF
ACT
ENT
7169
code:
STATUS Shows the status of the relay
SET DATE/TIME Change date and time
TRIGGERING Triggers the oscillography
I
a
I
n
Ia current in primary Amps
In current in primary Amps
I2t A COUNTER Accumulated kA2sec. for phase A
Nº OPENINGS Accumulated number opens
3/2-Phase Logic Shows logic for 50BF High Set.
50BF Pickup Shows status of 50BF
Relay ON/OFF Relay ON/OF condition
52A Status Breaker Pole A (open/closed)
52B Status Breaker Pole B (open/closed)
52C Status Breaker Pole C (open/closed)
LATCHING RELAY 1 Status Latching Relay 1 (open/closed)
LATCHING RELAY 2 Status Latching Relay 2 (open/closed)
DATE & TIME Shows date and time
NETWORK SPEED PORT3 (remote) comm. Speed
NETWORK STOP BITS PORT3 (remote) Stop bits
LOCAL SPEED PORT1&2 (local) comm. Speed
LOCAL STOP BITS PORT1&2 (local) Stop bits
LOCAL SETTINGS Local settings change allowed
REMOTE SETTINGS Remote settings change allowed
LOCAL OPERATION A Local operations allowed
REMOTE OPERATIONS Remote operations allowed
UNIT NUMBER Number of the unit
PASSWORD View/Change comm. Password
t TIME-OUT Max. t between 2 synch signals (only for
relays in DDS integrated systems)
42 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 50

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.2. SETTINGS GROUP (SET KEY)
This group allows to see and modify the DBF settings. It is accessed by pressing the SET key when the DBF is in
steady state. When the SET key is pressed the following message appears on the screen:
VIEW SETTINGS
PROTECTION
When the UP/DOWN arrows are pressed the message changes to:
MODIFY SETTINGS
PROTECTION
And the last UP/DOWN action gives:
MODIFY COUNTERS
PROTECTION
For the above windows, the menu tree is shown in the following tables. Note that to go down a level in the tree the
ENT key must be pressed, and the CLR keytogoup
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4
RELAY STATUS In/Out of service
IDENTIFICAT 20 characters
GENERAL SETTINGS
BREAKER SETTINGS
ACTIVE
TABLE SET
VIEW PROTECTION SETTINGS
OSCILLOS MASK
FREQUENCY 50 – 60 Hz
PHASE CT RATIO 1-4000
GROUND CT RATIO 1-4000
BREAKER NUMBER 4 digits
KI2t OP. MODE Fixed / Measuring
KI2t INT TIME 0.03 - 0.25 s
KI2t LIMIT 1 – 999999 kA2s
ACTIVE TABLE 1 –3
PREFAULT CYCLES 0-4
PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
1stSTAGE TRIP ENABLE/DISABLE
2ndSTAGE TRIP ENABLE/DISABLE
INTERNAL ARC ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF A TRIP ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF B TRIP ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF C TRIP ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF 3P TRIP ENABLE/DISABLE
EXTERNAL TRIGGER ENABLE/DISABLE
COMM. TRIGGER ENABLE/DISABLE
HI-SET A PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
HI-SET B PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
HI-SET C PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF A INIT ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF B INIT ENABLE/DISABLE
50BF C INIT ENABLE/DISABLE
LO-SET A PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
LO-SET B PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
LO-SET C PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
3 POLE 50BF INIT ENABLE/DISABLE
NEUTRAL PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
ARC A PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
ARC B PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
ARC C PICKUP ENABLE/DISABLE
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 43
Page 51

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4
FUNCTION
PERMIT
50BF SETTINGS T1
50 BF SETTINGS T2 Same than for TABLE 1
50 BF SETTINGS T3 Same than for TABLE 1
INTERNAL ARC SET T1
INTERNAL ARC SET T2 Same than for TABLE 1
INTERNAL ARC SET T 3 Same than for TABLE 2
50BF 1P FUNCTION PERM/NON-PERM.
50BF 3P FUNCTION PERM/NON-PERM.
3P NO INT FUNCT. PERM/NON-PERM.
PH HISET PICKUP 1.0-12A *
PH LOSET PICKUP 1.0-12A *
NEUTRAL PICKUP 0.5-6.0A *
1 PHASE TIMER T1 0.05-2s
3 PHASE TIMER T2 0.05-2s
3P NO I TIMER T3 0.05-2s
BF LOGIC (3P/2P) 3 PHASE/2 PHASE
SEVERE FAULT 3P PERM./NON-PERM.
LOW LOAD 2P PERM/NON-PERM
Nº OUTPUT STAGES 1 / 2
nd
STAGE TIMER 0.05-2s
2
INT ARC PICKUP 0.05-1A
INT ARC TIMER 0.1-2.0 s
To change any setting the procedure is as follows:
• Press the SET key.
• Select the option MODIFY SETTINGS (using ↑↓ arrow keys).
• Press ENT key.
• Select the required setting group in the menu tree (with ↑↓ arrow keys).
• Press ENT key.
• Select the required specific setting (with ↑↓ arrow keys).
• ENTER the value to be modified ( or select the required value from the list of available settings using
right/left arrow keys).
• Press the ENT key.
• Press the END key.
• The relay will request confirmation of the change by means of the following message:
CONFIRM
• To confirm the change, press the 1/Y key. (If not, press 3/N).
• The relay will then show the following message on the screen (LCD):
Y/N
SETTINGS CHANGE
EXECUTED
• Press the CLR key four times to return to the main first screen (rest).
44 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 52

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
If the setting entered is outside the limits of the valid range, the relay will not accept the change and will show the
following message:
SETTING OUT
OF RANGE
Some settings do not accepts numeric values; instead of that, different possibilities will be shown by pressing
left/right arrow keys.
To perform MODIFY OF PROTECTION COUNTERS, the available menus are:
Level 1 Lev el 2 Level 3 Valid Range
I2t A COUNTER 0-999999
I2t B COUNTER 0-999999
I2t C COUNTER 0-999999
MODIFY
COUNTERS
PROTECTION
Nº A OPENINGS 0-9999999
Nº B OPENINGS 0-9999999
Nº C OPENINGS 0-9999999
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 45
Page 53

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.3. INFORMATION GROUP (INF KEY)
On the steady-state(no communications request), the LCD display at the front of the relay shows the following:
DBF
GENERAL ELECTRIC
By pressing the INF key, the next screen will show:
STATUS
This group provides information about the DBF. Press the ENT key to access this group. The information
displayed is:
• Model of DBF relay
• Data Base Number
• Protection Software Version
• Comm. Software Version
• Phase A Current
• Phase B Current
• Phase C Current
• Neutral Current
• I2t phase A Counter
• I2t phase B Counter
• I2t phase C Counter
• Number of phase A Openings
• Number of phase B Openings
• Number of phase C Openings
• Type of Logic (2P/3P)
• High-set Pickup Status - ∅A
• High-set Pickup Status - ∅B
• High-set Pickup Status - ∅C
• Low-set Pickup Status - ∅A
• Low-set Pickup Status - ∅B
• Low-set Pickup Status - ∅C
• Neutral Pickup Status
• 50BF Initiation Status - ∅A
• 50BF Initiation Status - ∅B
• 50BF Initiation Status - ∅C
• 50BF 3Pole Initiation Status
• Arc Pickup - ∅A
• Arc Pickup - ∅B
• Arc Pickup - ∅C
• General 50BF Pickup Status
• Relay Ready
• Active Table Number
• Status of Circuit Breaker - ∅A
• Status of Circuit Breaker - ∅B
• Status of Circuit Breaker - ∅C
• Latching Relay 1 Status
• Latching Relay 2 Status
• Local Connection Status
• Date and Time Status
• Communications EEPROM Status
• Communication Settings (User or Default)
• Protection Link Status
• IRIG-B Link
• Actual Date and Time
46 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 54

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.4. CONTROL GROUP (ACT KEY)
Being on the steady-state screen of LCD at the front of the relay, by Pressing ACT key, the following will prompt:
SET
DATE/TIME
Pressing ENT key the system allows to set the date and time by entering the year, month, day hour, minutes and
seconds in this sequence. After each setting the ENT key must be pressed.
If instead of pressing the ENT key when the SET DATE/TIME screen appears, the arrow key (up or down) is
pressed, the next screen will be shown:
COMMUNICATION
TRIGGER
By pressing ENT key, the following sequence will be displayed:
• CONFIRM: Yes/No ?
• OPERATION EXECUTED/OPERATION CANCELED
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 47
Page 55

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.5. SINGLE KEY MENU
Being on the steady-state screen of LCD at the front of the relay, by Pressing ENT key, the “single key menu” will
be accessed. Then, the information displayed while step by step pressing ENT keyis:
• Phase A Current
• Neutral Current
2
t Phase A Counter
• I
• Number of phase A Openings
• Type of BF Logic
• 50BF Pickup Status
• Protection Status
• Circuit Breaker ∅A Pole Status
• Circuit Breaker ∅B Pole Status
• Circuit Breaker ∅C Pole Status
• Latching Relay 1 Status
• Latching Relay 2 Status
• Date and Time
48 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 56

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
8.6. CONFIGURATION MENU.
The DBF has a configuration unit which can only be accessed by means of the keyboard.
To enter the configuration, start from the main screen ‘DBF – GENERAL ELECTRIC’ and use the keyboard to
enter a four-digit code. If the code is correct the access to the configuration unit is permitted. If not it returns to the
main screen.
The code is unique for all the DBF relays and is not intended to be a password, but rather a simple safety
measure to avoid accidental changes to the configuration. This code is 7169, chosen to coincide with the ASCII
code for the initials GE.
After pressing 7169 at the front keyboard, and scrolling with the arrow keys, the following information will appear:
• NET. BAUDRATE : The speed in bauds which the DBF will use for serial communications through the remote
port. The possible speeds are between 1200 and 19200 bauds.
• NET.STOP BITS : The number of stop bits which are added to each byte which is transmitted on the serial
line. It is treated as a binary logic setting selected by means of the logic key 1/Y for 1 and 3/N for 2.
• LOC. BAUDRATE : as above but for local communications.
• LOC.STOPBITS:As above but for local communications.
• LOCAL SETTINGS: Settings changes by local communications (allowed/not allowed).
• REM SETTINGS : Settings changes by remote communications (allowed/not allowed).
• LOC OPERATIONS : Operations being performed by local communications (computer directly connected)
(allowed/not allowed).
• REM OPERATIONS : Operations being performed by remote communications (e.g. modem) (allowed/not
allowed).
• UNIT NUMBER : Each DBF is identified by a unit number which it uses to identify the messages which are
sent to it on the remote communications line. This number can be between 1 and 255.
• PASSWORD : To prevent unauthorized persons from communicating with the relay via a communications
program and changing the settings or performing operations, the relay has a password. This password can
only be seen on the relay display and takes the form of a number between 0 and 99999.
•tTIME-OUT:Set to 0 if the relay is not working in a DDS integrated system. Set to the maximum time
between two synch signals coming from the PC host, when the relay is working in a DDS integrated system. If
a new synch signal is not received in this time the relay will report an error.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 49
Page 57

8. KEYBOARD AND DISPLAY
50 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 58

FIGURES
FIGURES
FIGURES
FIGURESFIGURES
.
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 51
Page 59

FIGURES
FIGURE 1 BREAKER FAILURE LOGIC (189C4114 SHEET 2)
52 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 60

FIGURES
FIGURE 2. EXTERNAL CONNECTIONS (189C4114 SHEET 1)
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 53
Page 61

FIGURES
FIGURE 3. FRONT VIEW (226B7412 H9)
54 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 62

FIGURES
FIGURE 4 REAR VIEW (226B7412H10)
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 55
Page 63

FIGURES
FIGURE 5 DIMENSIONS DIAGRAM (226B6086H10)
56 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
Page 64

FIGURES
FIGURE 6 PANEL DRILLING (226B6086H10)
GEK-106168E DBF Breaker Failure Protection 57
Page 65

FIGURES
DBF
DB-9 Male
Connector
Label
NOTE
1
DB-9 Female
Connector
Leave shield unconnected at
1
both ends
FIGURE 7 RS232 CONNECTION (DBF RELAY TO PC)
DB-9 Male
Connector
DBF
Label
DB-9 Male
Connector
NOTE:
Leave shield unconnected
1
at both ends
1
FIGURE 8 RS232 CONNECTION (DBF RELAY TO MODEM)
58 DBF Breaker Failure Protection GEK-106168E
 Loading...
Loading...