Page 1

DEH–40028A Installation Instructions
g
INTRODUCTION
GE Conversion Kits are designed for upgrading
existing GE low-voltage power circuit breakers,
rather than replacing the entire breaker. The Conversion Kits include ProTrip™ Trip Units, the latest
technological advance in GE trip systems.
ProTrip Conversion Kits are designed and tested to
conform to ANSI Standard C37.59, allowing the
retrofitter to properly install the kit and acceptance
test the breaker.
This publication covers installation of ProTrip Conversion Kits on GE types AK-50, AKU-50, AKS-50,
AKT-50, AK-75, and AK-100 low-voltage power circuit
breakers. Each Conversion Kit contains all the
components needed to convert from an existing GE
type EC trip system.
ProTrip™ Conversion Kits
For GE Types AK-50, AKU-50, AKS-50,
AKT-50, AK-75, and AK-100 Low-Voltage
Power Circuit Breakers
Page 2

2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1. GENERAL INFORMATION.......................................................................................................4
SECTION 2. BEFORE INSTALLATION..........................................................................................................4
SECTION 3. FRONT FRAME BREAKER CONVERSION
Relocating and Remounting the W and X Relays..........................................................................5
Installing the Flux Shifter Assembly ..............................................................................................6
Breakers with EC or Power Sensor Trip Systems ............................................................. 6
Breakers with a Side Bracket .............................................................................................. 7
AKU-50 Breakers Only........................................................................................................7
Breakers with ECS or SST Trip Systems ...........................................................................8
Installing the Trip Paddle................................................................................................................8
Adjusting the Flux Shifter...............................................................................................................8
Installing the Trip Unit Mounting Bracket......................................................................................9
EC or Power Sensor Trip System.......................................................................................9
ECS or SST Trip System.....................................................................................................9
SECTION 4. BACK FRAME CONVERSION
Crossbar Modification................................................................................................................... 11
Removing the Existing Trip Devices ............................................................................................12
AK-50 & AKS-50 Breakers with EC or Power Sensor Trip Systems................................ 12
AK-50 & AKS-50 Breakers with SST Trip Systems..........................................................12
AK-75 & AK-100 Breakers with EC or Power Sensor Trip Systems................................ 12
AK-75 & AK-100 Breakers with SST Trip Systems .......................................................... 12
Installing the Phase Sensors......................................................................................................... 13
AK-50 & AKS-50 Breakers ................................................................................................. 13
AK-75 & AK-100 Breakers.................................................................................................14
SECTION 5. INSTALLING THE TRIP UNIT
Configuring the Trip Unit.............................................................................................................. 15
SECTION 6 FOUR-WIRE GROUND FAULT OPTION
Installing the Fourth-Wire Disconnect .......................................................................................... 16
AK-50 & AKS-50 Stationary Breakers ............................................................................... 16
AK-50 & AKS-50 Draw-Out Breakers................................................................................17
AK-75 & AK-100 Draw-Out Breakers ................................................................................ 17
Installing the Neutral Sensor........................................................................................................ 19
SECTION 7. EQUIPMENT CONVERSION
Installing Mounting Brackets........................................................................................................ 21
SECTION 8. TESTING AND TROUBLE-SHOOTING
Testing........................................................................................................................................... 23
Trouble-Shooting..........................................................................................................................23
Nuisance Tripping on Ground Fault-Equipped Breakers................................................23
APPENDIX – DRILL TEMPLATES
Appendix 1. Drill Template for Flux Shifter Mounting................................................................ 27
Appendix 2. Drill Template for Trip Unit Mounting.....................................................................29
Appendix 3. Drill Template for Flux Shifter Mounting................................................................ 29
Page 3

3
LIST OF FIGURES
1. Relocation and remounting of the W and X relays................................................................................. 5
2. New X and W relay mounting brackets................................................................................................... 5
3. Flux shifter assembly............................................................................................................................... 6
4. Pattern for flux shifter mounting holes in the side frame...................................................................... 6
5. Flux shifter assembly mounted to the side frame.................................................................................. 6
6. Location of new hole in the flux shifter base..........................................................................................7
7. Locations of new holes for mounting the OFLO terminal block............................................................ 7
8. Existing trip paddles to be removed....................................................................................................... 8
9. Installing the new trip paddle.................................................................................................................. 8
10. Adjusting the flux shifter. ........................................................................................................................ 8
11. Mounting hole drill pattern for the trip unit mounting plate. ................................................................ 9
12. Trip unit mounting plate attached to the breaker front channel............................................................ 9
13. Trip unit mounting bracket attached to the mounting plate................................................................ 10
14. Actuator bracket attached to the left pole link...................................................................................... 11
15. Drill pattern for actuator bracket mounting holes. ............................................................................... 11
16. Existing EC trip devices before removal. .............................................................................................. 12
17. Removal of EC trip devices.................................................................................................................... 12
18. Parts provided for CT installation per pole........................................................................................... 13
19. CT post mounted in the breaker back frame......................................................................................... 13
20. CT installation completed...................................................................................................................... 13
21. Phase sensor installation on AK-75 & AK-100 breakers........................................................................ 14
22. Attaching the trip unit to the mounting plate....................................................................................... 15
23. Trip unit mounted on the breaker. ........................................................................................................ 15
24. Fourth-wire terminal board installation on AK-50 & AKS-50 stationary breakers............................... 16
25. Fourth-wire disconnect installed on AK-50 & AKS-50 draw-out breakers........................................... 17
26. Fourth-wire disconnect assembly for AKD-5 or AKD-6 equipment...................................................... 17
27. Fourth-wire disconnect assembly for AKD equipment......................................................................... 17
28. K-75 & AK-100 back frame conversion.................................................................................................. 18
29. Outline of the neutral sensor for AK-50 breakers.................................................................................. 19
30. Outline of the neutral sensor for AK-75 and AK-100 breakers.............................................................. 20
31. AK-50 & AKS-50 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD. ................................................................................ 21
32. AK-75 & AK-100 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD-5 & AKD-6. .............................................................. 21
33. AK-100 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD. ............................................................................................... 21
34. AK-50 & AKS-50 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD. ................................................................................ 22
35. Fourth-wire disconnect for AKD-5 & AKD-6.......................................................................................... 22
36. Cabling diagram for ProTrip™ trip units with ground fault on four-wire loads. ................................ 25
Page 4

4
SECTION 1. GENERAL INFORMATION
SECTION 2. BEFORE INSTALLATION
GE Conversion Kit installation is straightforward, but
does require careful workmanship and attention to
these instructions. Familiarity with the breaker is
highly desirable. The general approach is to first
remove the existing trip devices from the breaker,
then install the ProTrip components. Following this
procedure, the converted breaker is performance
tested before it is returned to service.
The majority of trip unit kit installations do not
require any customized assembly work. However,
some conversions may involve unusual mounting
conditions or accessory combinations that require
minor modifications and/or relocation of components. In most instances, this supplementary work
can be done on site.
In preparation for the conversion, the installer should
verify that the appropriate current sensors and trip
unit have been furnished. Whenever a ProTrip kit is
installed on a breaker with a four-wire system, an
associated neutral sensor (CT) is required for
separate mounting in the equipment. Ensure that
retrofitted breakers are applied within their shortcircuit ratings. For example, if the previous trip unit
provided long-time instantaneous protection, the
short-time rating of the ProTrip Trip Unit will govern
the application.
As a service-related consideration, the installation of
a ProTrip kit provides an excellent opportunity to
perform normal maintenance on the breaker, particularly when the front and back frames are separated. Such procedures are described in the installation and maintenance manuals supplied with the
breaker and equipment.
Before starting any work, turn off and lock out all
power sources leading to the breaker, both primary
and secondary. Remove the breaker to a clean, welllighted work area.
WARNING: Low-voltage power circuit breakers use
high-speed, stored-energy spring operating
mechanisms. The breakers and their enclosures
contain interlocks and safety features intended to
provide safe, proper operating sequences. For
maximum personnel protection during installation,
operation, and maintenance of these breakers, the
following procedures must be followed. Failure to
follow these procedures may result in personal
injury or property damage.
• Only qualified persons, as defined in the
National Electrical Code, who are familiar with
the installation and maintenance of low-voltage
power circuit breakers and switchgear assemblies, should perform any work on these breakers.
• Completely read and understand all instructions
before attempting any breaker installation,
operation, maintenance, or modification.
• Turn off and lock out the power source feeding
the breaker before attempting any installation,
maintenance, or modification. Follow all lockout and tag-out rules of the National Electrical
Code and all other applicable codes.
• Do not work on a closed breaker or a breaker
with the closing springs charged. Trip an OPEN
breaker and be sure the stored-energy springs
are discharged, thus removing the possibility
that the breaker may trip OPEN or the closing
springs discharge and cause injury.
• Trip the breaker OPEN, then remove the breaker
to a well-lighted work area before beginning
work.
• Do not perform any maintenance that includes
breaker charging, closing, tripping, or any other
function that could cause significant movement
of a draw-out breaker while it is on the draw-out
extension rails.
• Do not leave the breaker in an intermediate
position in the switchgear compartment. Always
leave it in the CONNECTED, TEST, or
DISCONNECTED position. Failure to do so could
lead to improper positioning of the breaker and
flashback.
Page 5
5
SECTION 3. FRONT FRAME BREAKER
CONVERSION
Front frame conversion consists of the following
steps:
1. Separation of the front and back breaker frames
for AK-50, AKU-50, AKS-50, and AKT-50 breakers.
(Frame separation is not necessary for AK-75 and
AK-100 breakers.) Refer to the appropriate
installation and maintenance manuals supplied
with the breakers and equipment for instructions
on frame separation. Copies of these publications
may be obtained from your local GE sales office.
2. Relocation and remounting the W and X relays
on AK-50, AK-75, and AK-100 electrically operated
breakers with EC trip devices.
3. Installation of the flux shifter assembly and trip
paddle.
4. Installation of the trip unit mounting bracket.
5. Installation of the trip unit wiring harness.
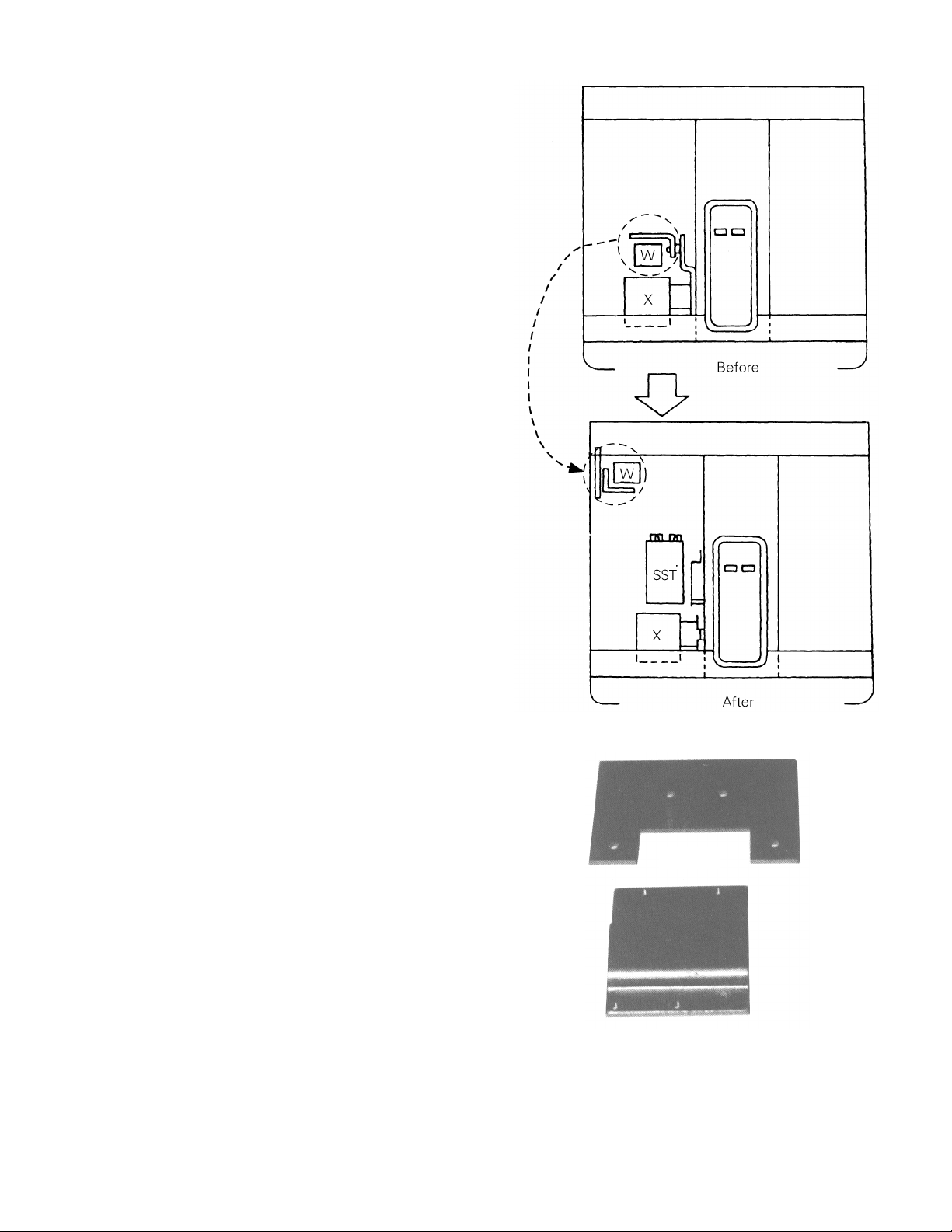
Relocating and Remounting the W and X
Relays
This step is necessary on electrically operated
breakers with EC trip devices. Figure 1 illustrates this
process. Figure 2 shows the new mounting brackets
supplied with the kit.
1. Remove the W relay and install the mounting
bracket supplied with the conversion kit to the
upper left side of the frame
2. Remove the X relay and its mounting bracket.
Use the new bracket supplied with the conversion kit to remount the X relay in its existing
position.
Figure 1. Relocation and remounting of the W and X relays.
W Relay
Figure 2. New X and W relay mounting brackets.
Page 6
6
Installing the Flux Shifter Assembly
The installation procedure for the flux shifter
assembly, illustrated in Figure 3, varies depending
on the type of breaker and existing trip device. In
some cases, mounting holes must be added, terminal blocks relocated, or breaker side rails removed.
Breakers with EC or Power Sensor Trip Systems
1. Drill the flux shifter mounting holes in the left
side of the breaker frame. The mounting hole
pattern is illustrated in Figure 4. A full-size template is provided in the Appendix.
2. Mount the new flux shifter to the inside of the
side frame with the three screws, lock washers,
flat washers, and nuts supplied, as shown in
Figure 5. Insert the screws from the outside of
the side frame.
Figure 4. Pattern for flux shifter mounting holes in the side frame.
Figure 3. Flux shifter assembly.
Mounting
Screws
Figure 5. Flux shifter assembly mounted to the side frame.
Flux Shifter
Assembly
Page 7
7
Breakers with a Side Bracket
1. Drill a 34” diameter hole into the flux shifter
assembly mounting base to provide the necessary clearance for the bracket. The location of the
new hole is shown in Figure 6.
2. Remove the side bracket from the frame and drill
the holes according to the pattern in Figure 4. A
full-size template is provided in the Appendix.
After the holes are drilled, return the side bracket
to its original location.
3. Mount the new flux shifter to the inside of the
side frame with the three screws, lock washers,
flat washers, and nuts supplied, as shown in
Figure 5. The upper two screws are inserted from
the outside of the frame, while the lower screw
must be inserted from the inside.
AKU-50 Breakers Only
For easier installation of the new flux shifter
assembly on AKU-50 breakers, the open-fuse lockout
(OFLO) may be removed from the breaker.
1. Remove the three bolts attaching the OFLO to the
base of the breaker.
2. The OFLO terminal block must be relocated on
the upper left side of the breaker. Some parts and
tool, not provided with the kit, are necessary for
this task:
• Six strips of 14 AWG wire
• Wire splice
• 12 butt splices
• Wire labels
• Drill and size F bit
•5/16-18 tap
• Flathead screw driver
• Two 5/16-18 bolts and lock washers
3. Drill and tap two holes for the 5/16-18 bolts. Fig-
ure 7 shows the hole locations.
4. Remove the three bolts securing the OFLO to the
breaker and lift off the OFLO device.
5. Remove the wires that connect the OFLO device
to the terminal block.
6. Cut the wires that connect to the coils where they
join and label the wires. Attach butt splices to all
twelve open ends.
7. Connect the strands of wire to the OFLO. Mount
the terminal block in its new location. DO NOT
complete the wire connections until the flux
shifter is installed.
8. Install the new flux shifter assembly as described
above and shown in Figure 5.
9. Connect the cables attached to the terminal block
and tie them together.
Figure 6. Location of new hole in the flux shifter base.
Figure 7. Locations of new holes for mounting the OFLO terminal
block.
Page 8
8
Breakers with ECS or SST Trip Systems
Paddle
1. Remove the ECS or SST trip unit.
2. Remove the existing flux shifter device and the
trip unit control harness.
3. Install the new flux shifter assembly as described
above and shown in Figure 5.
Installing the Trip Paddle
For breakers equipped with an ECS or SST trip system, the existing trip paddle is used with the new
flux shifter.
For all other breakers, the existing trip paddles must
be removed and the new trip paddle installed as
follows:
1. Remove and discard the three trip paddles on the
trip actuator bar, as shown in Figure 8.
2. Assemble the trip paddle and the threaded back
plate by inserting two of the 10-32 x 34" screws
and lock washers provided along the top edge.
3. Slip the trip paddle over the trip actuator bar
approximately one inch from the side frame, as
shown in Figure 9. Insert the remaining 10-32 x
3
4" screw and tighten the other screws to
secure the trip paddle in place.
Trip Paddles
Figure 8. Existing trip paddles to be removed.
1”
Adjusting the Flux Shifter
After the flux shifter and trip paddle are installed and
the breaker frames are reassembled, the following
adjustments must be made.
1. With the breaker OPEN and the mechanism
charged, set the gap between the trip paddle and
the end of the flux shifter rod at 0.10 inch, as
shown in Figure 10. Use a 0.10-inch diameter rod.
Set the adjuster end of the trip rod and lock it in
place with the jam nut. Note that removal of the
buffer stud will make the trip paddle easier to
install and adjust.
2. As the crossbar travels between the breaker
CLOSED and OPEN positions, the tang of the
actuator bracket must clear the buffer stud. If
there is insufficient clearance, loosen the two
mounting screws and rotate the bracket clockwise to take up mounting hole slack. Retighten
the screws.
3. Optional Test – The flux shifter may be tested by
closing the breaker and applying a 9 Vdc power
source to the flux shifter leads (the red wire is
positive). The breaker should trip.
Trip
Figure 9. Installing the new trip paddle.
Figure 10. Adjusting the flux shifter.
Page 9
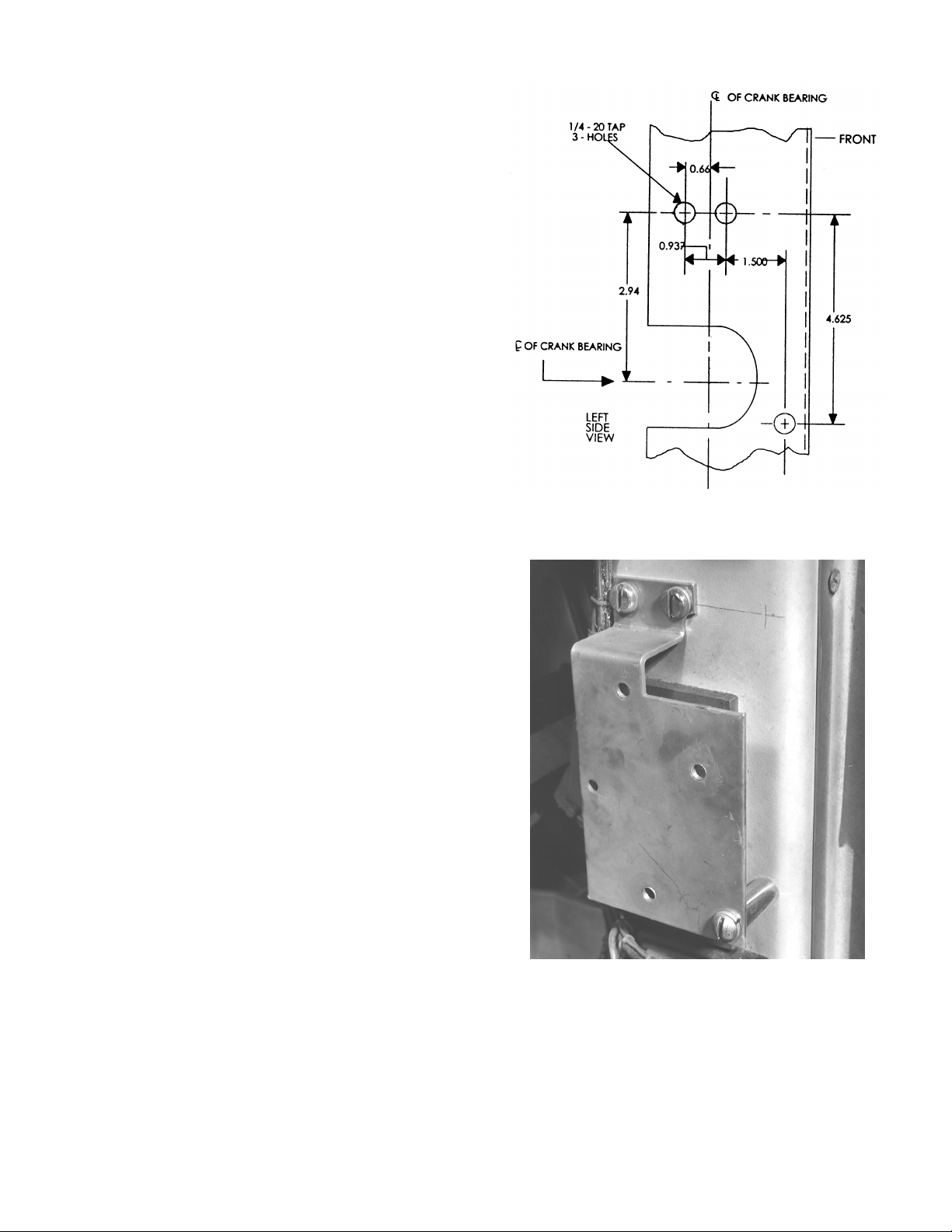
9
Installing the Trip Unit Mounting Bracket
The new ProTrip trip unit mounts to the left side of
the front channel. A mounting bracket is shock-mounted to a plate that is assembled to the front
channel.
EC or Power Sensor Trip System
1. The holes for the new mounting plate may have
to be added to the front channel. The drill pattern
is shown in Figure 11, with a full-size template in
the Appendix. Tap the holes for 1/4-20 screws.
2. Attach the new mounting plate, as shown in
Figure 12, with two short 1/4-20 screws and lock
washers on the top and the single long 1/4-20
screw and lock washer on the bottom. Be sure to
insert the spacer between the mounting plate and
the breaker channel, as shown.
3. Attach the trip unit mounting bracket to the plate
with two screws, lock washers, and flat washers,
as shown in Figure 13.
ECS or SST Trip System
Remove the existing mounting plate and bracket.
Install the new mounting plate and bracket, using the
holes closest to the front of the breaker, as described
in steps 2 and 3 above.
If the manual indicator assembly busing on AK-50
manual breakers interferes with the mounting
bracket installation, then the bracket must be modified. Cut off a 3/4 x 11/2 inch section from the right
front of the plate to provide clearance.
Figure 11. Mounting hole drill pattern for the trip unit mounting
plate.
Figure 12. Trip unit mounting plate attached to the breaker front
channel.
Page 10

10
Figure 13. Trip unit mounting bracket attached to the mounting
plate.
Page 11

11
SECTION 4. BACK FRAME
CONVERSION
The back frame conversion consists of the following
operations:
1. Modification of the crossbar assembly for the
flux shifter installation.
2. Removal of the existing trip devices.
3. Installation of the phase sensors.
4. Installation of the back frame harness.
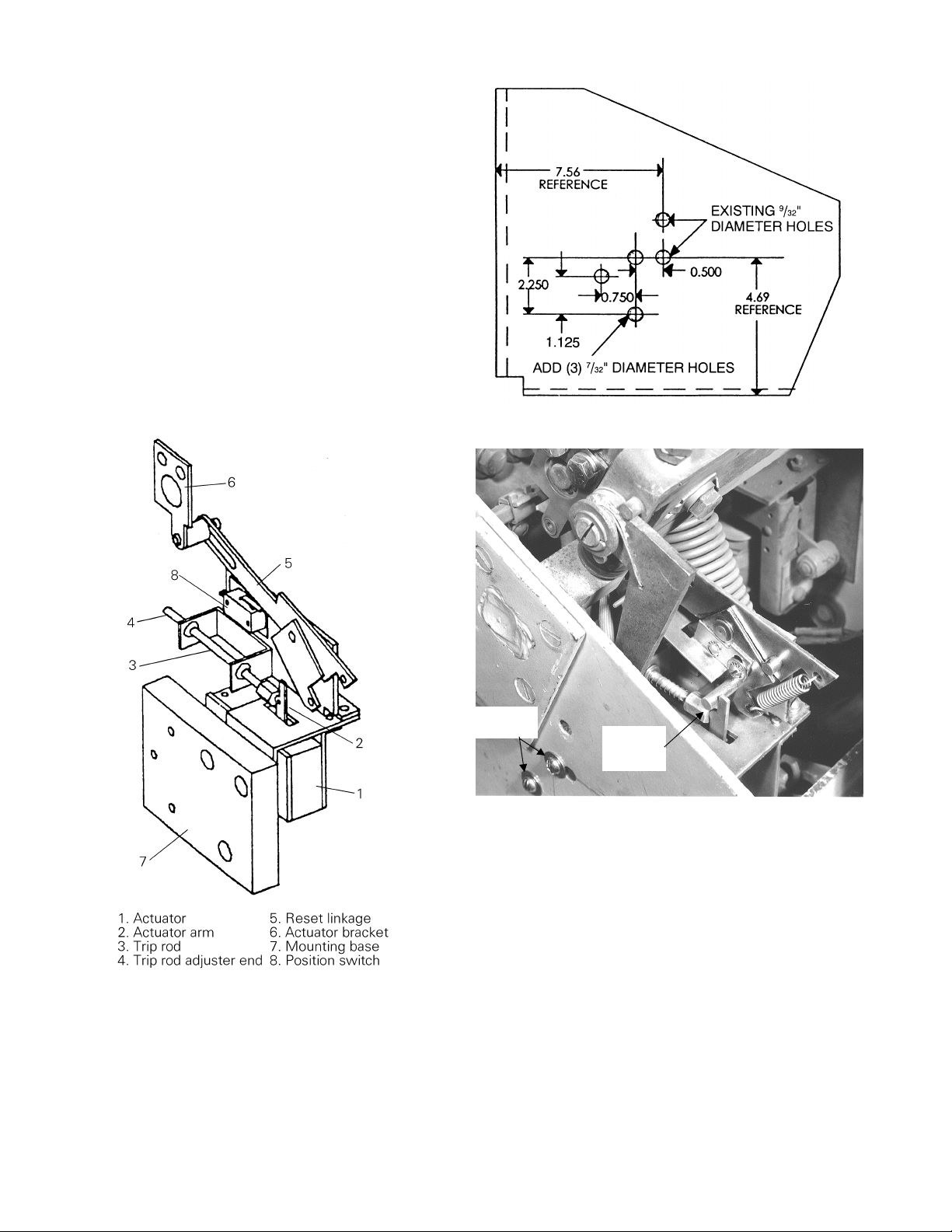
Crossbar Modification
The flux shifter reset linkage is driven by the actuator
bracket, as shown in Figure 3. The actuator bracket
must be assembled to the left side link of the left
pole, as shown in Figure 14.
If the actuator bracket mounting holes are not in the
left side link, the holes must be added. Drill and tap
two 5/16-18 holes using the pattern in Figure 15. A
full-size template is provided in the Appendix.
Left Pole
Link
Actuator
Bracket
Figure 14. Actuator bracket attached to the left pole link.
Figure 15. Drill pattern for actuator bracket mounting holes.
Page 12

12
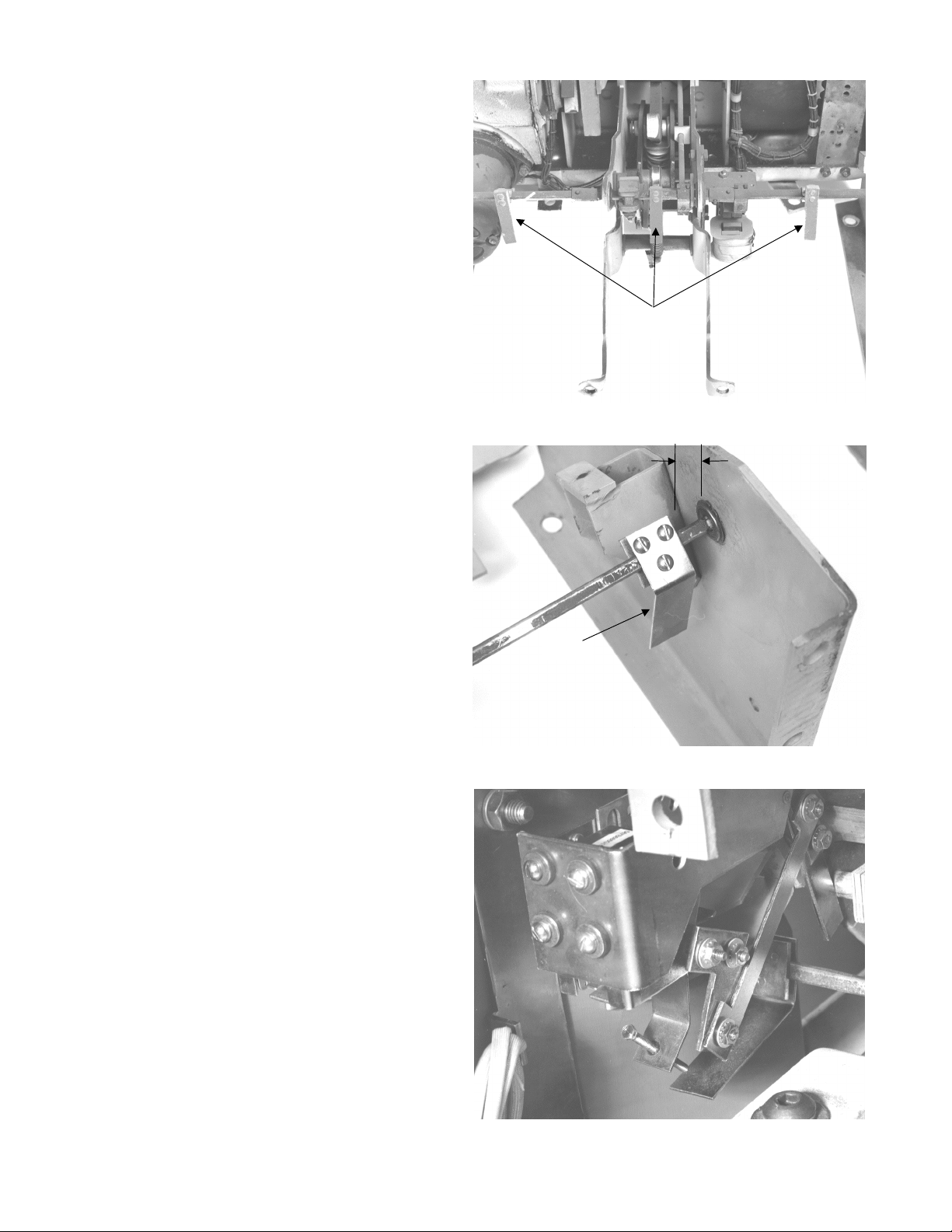
Removing the Existing Trip Devices
AK-50 & AKS-50 Breakers with EC or Power Sensor
Trip Systems
1. Remove and discard the two screws at the base
of each trip device, as shown in Figure 16. Discard the metal mounting brackets.
2. Remove and discard the small Philips-head
screw at the top of each trip device.
3. Remove and discard the four 516" Allen-head
bolts securing each trip coil. The coil can then be
lifted off and removed. Figure 17 shows one trip
completely removed, one with the cover
removed, and one still in place.
AK-50 & AKS-50 Breakers with SST Trip Systems
Remove the existing SST phase sensors in preparation for installing the new sensors.
AK-75 & AK-100 Breakers with EC or Power Sensor
Trip Systems
Remove the existing trip devices and harnesses and
discard.
Coil Mounting
Bolts
Cover Screws
and Clamps
Figure 16. Existing EC trip devices before removal.
AK-75 & AK-100 Breakers with SST Trip Systems
The new ProTrip phase sensors are visually identical
to the SST sensors. Remove the existing sensors and
discard.
Figure 17. Removal of EC trip devices.
Page 13

13
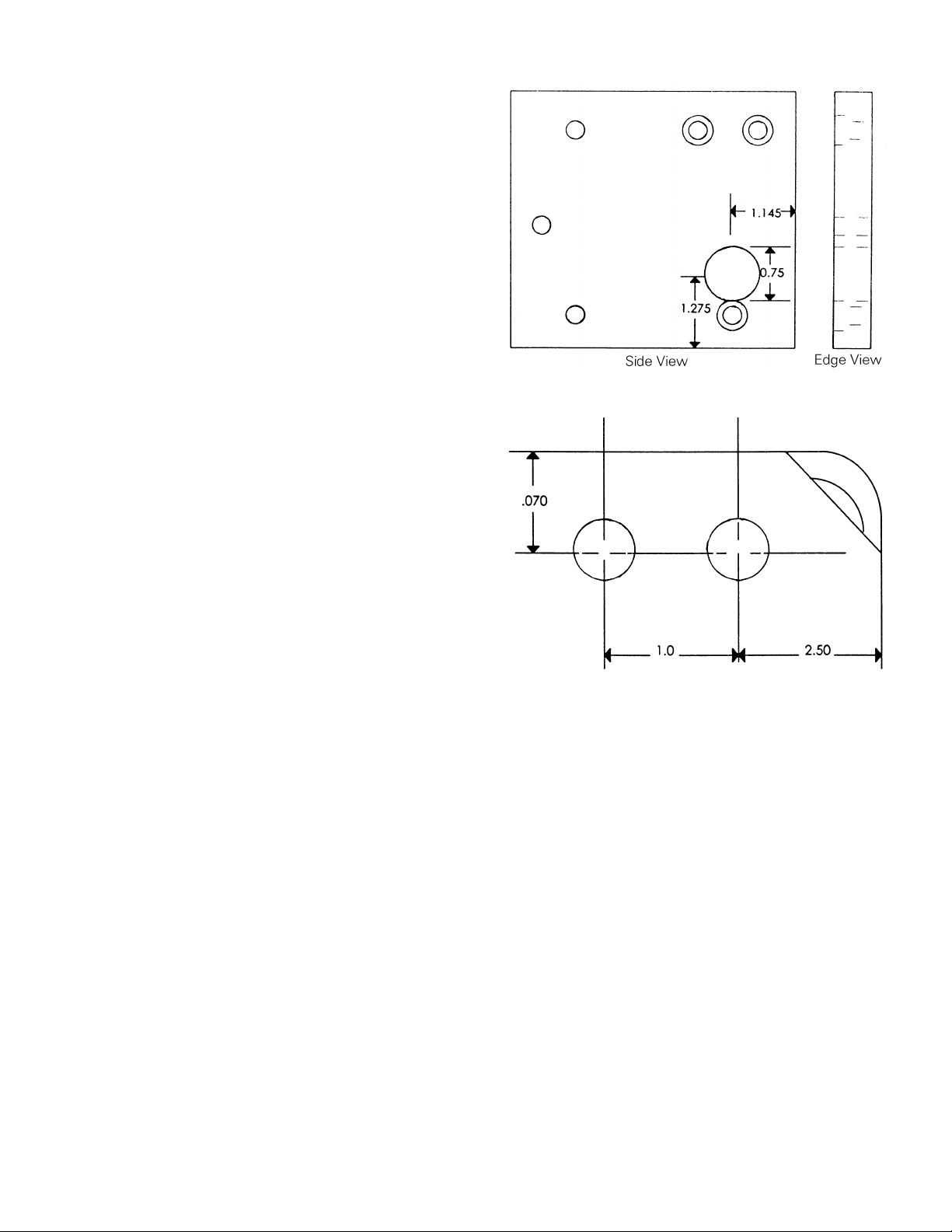
Installing the Phase Sensors
Harness
AK-50 & AKS-50 Breakers
Figure 18 shows the parts provided for assembly of
the CT on each pole.
1. Mount the new copper CT post to the back frame
with the two 38-16 x 112" bolts, flat washers,
and lock washers provided, as shown in Figure
19.
2. Fasten the three small insulated wire fasteners to
the back frame with the 14-20 x 134" screws
provided, as shown in Figure 20. One fastener is
mounted under each CT.
3. Place a CT over each copper post, first applying a
small amount of RTV or similar adhesive to
prevent the CTs from rotating.
4. Mount the top copper bus over each CT and
secure with the 12-13 x 112" Allen-head bolts,
lock washers, and flat washers provided.
5. Insert two 38-16 x 112" bolts, lock washers, and
flat washers through each top copper bus into
the contact arm assembly.
6. Tighten the 38-16 bolts to 200 in-lb and the 1213 bolts to 300 in-lb.
Figure 18. Parts provided for CT installation for one pole.
WARNING: Step 6 ensures critical electrical integrity
connections. The designated bolts must be correctly
tightened for proper operation. Failure to tighten
these bolts properly will cause a breaker failure,
resulting in property damage and/or personal
injury.
Figure 19. CT post mounted in the breaker back frame.
Top Copper
Bus
1
2-13
Bolt
3
8-16
Bolts
Wire
Figure 20. CT installation completed..
Wire
Fastener
Page 14

14
AK-75 & AK-100 Breakers
1. The ProTrip phase sensors mount on the upper
breaker studs, as shown in Figure 21. The sensors held on the stud with locking rings. Leave
enough of the stud exposed for the primary fingers to engage. Engage the sensor’s antiturn lugs
with the notch in the locking ring. Before
tightening the locking rings, position each sensor
so that its leads exit between the pole bases, as
shown.
2. Mount the three sensor terminal boards to the
rear of the back frame using the hardware provided.
3. Form each sensor’s leads downward between the
pole bases.
Figure 21. Phase sensor installation on AK-75 & AK-100 breakers.
Page 15

15
SECTION 5. INSTALLING THE TRIP
Screw
Connector
UNIT
1. Remove the large screw from the rear of the trip
unit. Place the trip unit in position on the mounting plate, with the 50-pin connector aligned with
the opening in the plate. Secure with the large
screw, as shown in Figure 22.
2. Insert the 50-pin female connector on the wiring
harness into the trip unit connector through the
rear of the mounting plate. Secure to the mounting plate with the two small screws provided, as
shown in Figure 22.
3. Place the trip unit and mounting plate in position
on the support bracket mounted on the breaker.
Secure with the three screws, lock washers, and
flat washers through the holes in the mounting
plate into the tapped holes in the bracket, as
shown in Figure 23.
Configuring the Trip Unit
See DEH-40034 for detailed instructions for setting
up ProTrip trip units.
Trip Unit
Mounting
Plate
Trip
Unit
Trip Unit
Mounting
Wiring
Harness
Figure 22. Attaching the trip unit to the mounting plate.
Figure 23. Trip unit mounted on the breaker.
Page 16

16
SECTION 6 FOUR-WIRE GROUND
FAULT OPTION
The ground fault option for four-wire installations
requires the installation of an additional current
sensor on the neutral bus in the equipment. The
sensor is connected to the trip unit through the
connector provided in the wiring harness.
Installing the Fourth-Wire Disconnect
AK-50 & AKS-50 Stationary Breakers
The fourth-wire disconnect for stationary breakers
consists of a terminal board mounted to the lower
front channel, as shown in Figure 24.
• If the terminal board is already present on the
breaker, just replace the control harness. Maintain the following color code: white wire to
common, black wire to the tap.
• If the terminal board must be added, mount it as
shown in Figure 24. The mounting holes may
have to be added to the front channel.
Figure 24. Fourth-wire terminal board installation on AK-50 &
AKS-50 stationary breakers.
Page 17

17
AK-50 & AKS-50 Draw-Out Breakers
The fourth-wire disconnect for AK-50 and AKS-50
draw-out breakers mounts to the lower back frame,
as shown in Figure 25.
• If the terminal board is already present on the
breaker, just replace the control harness. Maintain the following color code: white wire to
common, black wire to the tap.
• If the disconnect must be added, mount it as
shown in Figure 25.
AK-75 & AK-100 Draw-Out Breakers
There are two fourth-wire disconnect designs used
with these breakers. One design is used on breakers
for GE type AKD switchgear, while the other applies
to breakers for GE types AKD-5 and AKD-6
equipment. The only difference is the bracket used
for mounting the disconnect to the breaker. Figures
26 and 27 show these two designs.
The conversion kit contains an assembled, ready-toinstall mounting block and bracket for AKD-5 and
AKD-6 installation, plus an addition bracket only for
type AKD equipment installations. For AKD equipment, remove the bracket from the assembled disconnect and replace it with the AKD bracket.
The fourth-wire disconnect for AK-75 and AK-100
draw-out breakers mounts to the lower back frame
as shown in Figure 28.
• If the terminal board is already present on the
breaker, just replace the control harness. Maintain the following color code: white wire to
common, black wire to the tap.
• If the disconnect must be added, mount it as
shown in Figure 28.
Figure 25. Fourth-wire disconnect installed on AK-50 & AKS-50
draw-out breakers.
Figure 26. Fourth-wire disconnect assembly for AKD-5 or AKD-6
equipment.
Figure 27. Fourth-wire disconnect assembly for AKD equipment.
Page 18

18
Figure 28. AK-75 & AK-100 back frame conversion.
Page 19

19
Installing the Neutral Sensor
The neutral sensor is an electrical duplicate of the
phase sensor, including the taps. Therefore, when
taps (if provided) are changed on the phase sensors,
the taps on the neutral sensor must be similarly
changed. For kits with fixed phase sensors, be sure
to use the corresponding tap on the neutral sensor.
Mount the neutral sensor on the outgoing neutral
lead, normally in the equipment bus or cable compartment. Figure 29 shows mounting details for the
neutral sensor for AK-50 breakers, while Figure 30
covers AK-75 and AK-100 breakers.
Figure 29. Outline of the neutral sensor for AK-50 breakers.
Page 20

20
Figure 30. Outline of the neutral sensor for AK-75 and AK-100 breakers
Page 21

21
SECTION 7. EQUIPMENT
CONVERSION
Installing Mounting Brackets
The equipment compartment contains the mating
portions of the fourth-wire disconnect and the neutral sensor. The same disconnect assembly is used
for types AKD, AKD-5, and AKD-6 switchgear.
Mounting brackets for AKD, AKD-5, AKD-6, and
AKD-8 switchgear applications are included in the
conversion kit. Figures 31, 32, 33, 34, and 35 are
mounting diagrams for the various applications.
Table 1 is a key to the numbers used in these figures
to indicate various hardware items.
Legend Description
225 Breaker portion of fourth-wire disconnect
226 Equipment portion of fourth-wire disconnect
Mounting bracket for AK-100 for AKD
229
230 10-32 x 1.375 inch mounting screw
231 Insulation
232 #10 lock washer
233 #10 flat washer
2351/8-20 flat washer
2361/8-20 lock washer
2371/4-20 nut
2381/4-20 x 1.25 inch mounting screw
239 Bracket
compartments
Figure 31. AK-50 & AKS-50 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD.
Figure 32. AK-75 & AK-100 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD-5 &
AKD-6.
Table 1. Legend for number symbols appearing in Figures 31–
35.
Figure 33. AK-100 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD.
Page 22

22
Figure 34. AK-50 & AKS-50 fourth-wire disconnect for AKD.
Figure 35. Fourth-wire disconnect for AKD-5 & AKD-6.
Page 23

23
SECTION 8. TESTING AND TROUBLESHOOTING
WARNING: Do not change taps on the current sen-
sors or adjust the trip unit settings while the
breaker is carrying current. Failure to adhere to
these instructions will void all warranties.
Testing
Before installing a converted breaker back into
service, perform the following steps:
1. Verify that the trip unit is securely installed by
performing a continuity test on the CT wiring and
the trip unit.
a. Disconnect the black CT wires at each phase
sensor.
b. Check for continuity with a continuity tester or
VOM from the white lead of the phase A CT to
the white lead of the phase B CT.
c. Repeat this continuity test for the white leads
of the phase A and phase C CTs.
d. Measure the resistance across each phase
sensor and compare the values measured to
the values listed in Table 1.
e. Reconnect the black CT leads to all of the
phase sensors. Ensure that this is done before
continuing with performance testing of the
breaker.
CAUTION: In addition to the continuity test described
in Step 1 and before performance testing of the
converted breaker, each phase of the breaker
should be primary injected with a current level of
about 10%, but no more than 20%, of the CT rating.
During the application of test current, activate the
trip unit screen by depressing the battery button on
the trip unit face and check that the test current is
displayed on the screen for each phase tested. If the
trip unit fails to display the test current, stop the
test immediately and verify the installation of the
trip unit and wire harness before proceeding with
any additional testing.
WARNING: If the converted breaker is energized or
tested by primary injection with a sufficiently high
test current with a loose or open circuit between the
CTs and the trip unit, damage will occur to the trip
unit, wire harness, 36-pin trip unit connector, and
CTs. Failure to adhere to these instructions will void
all warranties.
2. Check the insulation on the primary circuit with a
1,000-volt Meggar.
3. Measure the resistance across the line and load
terminals for each phase using a micro-ohmme-
ter or millivolt tester. If the resistance differs
considerably from phase to phase, the electrical
connections may not be properly tightened or it
could also indicate improper contact wipe.
4. To verify that the breaker has been properly
retrofitted, perform a primary injection test on
each phase. This test will check the CTs, bus,
wiring harness, flux shifter, and trip unit as a
complete system.
a. A high-current, low-voltage power supply
should be connected across each line and load
terminal to simulate an overcurrent fault.
b. Set the long-time trip at 0.5 to minimize the
breaker stress.
c. When ground fault is installed, the test can be
performed by wiring two adjacent poles in
series or by using the GE Digital Test Kit, cat.
no. TVRMS2. This will prevent the breaker
from tripping because of an unbalanced current flow.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to use GE Test Kit cat. no.
TVTS1 or TVRMS on this trip unit.
Trouble-Shooting
When malfunctioning is suspected, first examine the
breaker and its power system for abnormal conditions such as the following:
• The breaker is not tripping in response to overcurrent conditions or incipient ground faults.
• The breaker is remaining in a trip-free state
because of mechanical interference along its trip
shaft.
• The shunt trip (if present) is activating improperly.
Nuisance Tripping on Ground Fault-Equipped
Breakers
When nuisance tripping occurs on breakers equipped
with ground fault trip, a probable cause is the
existence of a false ground signal. Each phase sensor
is connected to summing circuitry in the trip unit.
Under no-fault conditions on three-wire load circuits,
the currents add to zero and no ground signal is
developed. This current sum is zero only if all three
sensors have the same electrical characteristics. If
one sensor differs from the others (such as by a
different rating or wrong tap setting), the circuitry
can produce an output sufficient to trip the breaker.
Similarly, a discontinuity between any sensor and
the trip unit can cause a false trip signal.
The sensors and their connections should be closely
examined if nuisance tripping is encountered on any
breaker whose ProTrip trip unit has previously
demonstrated satisfactory performance. After dis-
Page 24

24
connecting the breaker from all power sources, perform the following procedure:
1. Check that all phase sensors are the same type
(current range).
2. Verify that the tap settings on all three phase sensors are identical.
3. Verify that the wiring harness connections to the
sensors have the proper polarity (white lead to
common, black lead to tap), as shown in the
cabling diagram in Figure 36.
4. On ground fault breakers serving four-wire loads,
check that the neutral sensor is properly connected, as indicated in Figure 36. In particular,
check the following:
a. Verify that the neutral sensor has the same rat-
ing and tap setting as the phase sensors.
b. Verify continuity between the neutral sensor
and its equipment-mounted secondary disconnect block. Also check for continuity from the
breaker-mounted neutral secondary disconnect block through to the trip unit wiring harness connector.
c. If the breaker’s lower studs connect to the
power source, then the neutral sensor must
have its load end connected to the source.
d. Verify that the neutral conductor is carrying
only the neutral current associated with the
breaker’s load current (the neutral is not
shared with other loads).
5. If the preceding steps fail to identify the problem,
then measure the sensor resistances. The appropriate values are listed in Table 2. Since the
phase and neutral sensors are electrically
identical, their resistances should agree closely.
Breaker CT Rating, A Resistance, ohms
300
400
AK-50
AKS-50
AK-75
AK-100
Table 2. CT resistance values.
600
800
1200
1600
1200
1600
2000
3000
1600
2000
3000
4000
20–24
27–32
42–50
58–68
93–109
130–154
20–24
28–34
37–44
61–72
36–43
47–55
75–88
108–127
Page 25

25
Figure 36. Cabling diagram for ProTrip™ trip units with ground fault on four-wire loads.
Page 26

Page 27

APPENDIX – DRILL TEMPLATES
Appendix 1. Drill Template for Flux Shifter Mounting
Page 28

Page 29

Appendix 2. Drill Template for Trip Unit Mounting
Appendix 3. Drill Template for Flux Shifter Mounting
Page 30

Page 31

Page 32

These instructions do not cover all details or variations in equipment nor do they provide for every possible
contingency that may be met in connection with installation, operation, or maintenance. Should further
information be desired or should particular problems arise that are not covered sufficiently for the purchaser’s
purposes, the matter should be referred to the GE Company.
g
GE Industrial Systems
General Electric Company
41 Woodford Ave., Plainville, CT 06062
 Loading...
Loading...