Page 1
GPS 95 STD
PERSONAL NAVIGATOR
OWNER'S MANUAL
KOJC
TM
KPTS
KSGF
SM
Page 2

GPS 95 STD
Personal Navigator
OWNER'S MANUAL
TM
Page 3

© 1993 GARMIN, 9875 Widmer Road, Lenexa, KS 66215, USA
Printed in Taiwan.
All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted
in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying
and recording, for any purpose without the express written permission of
GARMIN.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. GARMIN
reserves the right to change or improve their products and to make changes
in the content without obligation to notify any person or organization of such
changes or improvements.
July, 1993 190-00054-00 Rev. A
Page 4

PREFACE
GARMIN thanks you for selecting our high performance, full featured
Personal NavigatorTM. The GPS 95 represents our continued commitment
to provide you with a portable navigation unit that is versatile, extremely
accurate, and easy to use. We are confident you will enjoy using your unit
for many years to come.
The GPS 95's rugged construction and quality components offer the reliability
demanded by the harshest operating environments. It may be used in
aircraft, marine vessels and land vehicles, as well as by hunters, hikers, and
military forces. The unit may be operated portably using its own battery pack,
or it may use a 5-40 volt DC external power source for fixed mounted
applications. You can even use a 115- or 230-volt AC adaptor for planning
trips at home.
This manual and accompanying quick reference card provide complete
information on safely operating the GPS 95 to its full potential. A sample trip
has been planned for you to practice your navigation skills using the built-in
simulator. Afterwards, try a trip of your own to realize the value of the GPS
95 as your Personal NavigatorTM. If you have any questions or comments,
our Product Support Department is eager to serve you. GARMIN is fully
committed to your satisfaction as a customer.
GARMIN International, Inc.
9875 Widmer Road
Lenexa, KS 66215
1-800-800-1020
(913) 599-1515
i
Page 5

CAUTION
The GPS system is operated by the government of the United States which
is solely responsible for its accuracy and maintenance. The system is under
development and is subject to changes which could affect the accuracy and
performance of all GPS equipment. Although the GPS 95 is a precision
electronic NAVigation AID (NAVAID), any NAVAID can be misused or
misinterpreted, and therefore become unsafe. Use the GPS 95 at your own
risk. To reduce the risk, carefully review and understand all aspects of this
Owner's Manual and thoroughly practice operation using the simulator mode
prior to actual use. When in actual use, carefully compare indications from
the GPS 95 to all available navigation sources including the information from
other NAVAIDs, visual sightings, charts, etc. For safety, always resolve any
discrepancies before continuing navigation.
NOTE: This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
ii
Page 6

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER PAGE
1 INTRODUCING THE GARMIN GPS 95 1-1
1.1 Capabilities 1-1
1.2 Basic Package 1-2
1.3 Optional Accessories 1-3
1.4 Operational Modes 1-4
2 GETTING STARTED 2-1
2.1 Front Panel 2-1
2.2 Softkey Operation 2-1
2.3 Cursor and Fields 2-2
2.4 Keypad Operation 2-2
2.5 Entering Data 2-4
2.6 Viewing Messages 2-5
2.7 Turning the GPS 95 On 2-5
2.8 Turning the GPS 95 Off 2-7
2.9 Learning to Use the GPS 95 2-7
3 WAYPOINTS 3-1
3.1 Waypoint Definition Page 3-2
3.2 Creating Waypoints 3-3
3.3 Waypoint List 3-5
3.4 Using Waypoints 3-6
3.5 Reviewing Waypoints 3-7
3.6 Proximity Alarm Waypoints 3-8
3.7 Nearest Waypoints 3-9
4 GETTING THERE FAST - GOTO 4-1
5 NAVIGATION INFORMATION 5-1
5.1 Navigation Summary Page 5-1
5.2 Map Display 5-3
iii
Page 7

5.3 Map Configuration 5-5
5.4 Present Position 5-6
5.5 Sample Trip 5-7
6 ROUTES 6-1
6.1 Route Definition 6-2
6.2 Creating and Copying Routes 6-3
6.3 Activating and Inverting Routes 6-4
6.4 Editing Routes 6-4
6.5 Deleting Routes 6-5
6.6 Active Route 6-5
6.7 Route List 6-6
7 AUTOSTORE
7.1 Creating Waypoints with Autostore
7.2 Building Routes with Autostore
TM
TM
TM
7-1
7-1
7-2
8 GPS STATUS AND AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS 8-1
8.1 Bar Graph Display 8-2
8.2 Satellite Status Page 8-3
8.3 Satellite Skyview Page 8-4
8.4 Auxiliary Menu 8-4
8.5 Operating Mode/Filters 8-4
8.6 Track Log Setup 8-5
8.7 Units/Heading Setup 8-7
8.8 Alarms/CDI Setup 8-8
8.9 Date/Time 8-10
8.10 Audio and Display Setup 8-11
8.11 Interface Setup 8-12
8.12 Map Datum Selection 8-14
8.13 Messages 8-15
8.14 Density Altitude/True Airspeed/Winds Loft 8-15
8.15 Sunrise/Sunset Planning 8-16
8.16 Trip and Fuel Planning 8-17
8.17 Vertical Navigation Planning 8-18
9 SAMPLE TRIP USING ROUTES 9-1
iv
Page 8

APPENDICES
A MESSAGES A-1
B GLOSSARY AND NAVIGATION TERMS B-1
B.1 Definitions B-1
B.2 Course To Steer (CTS) B-3
C INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE C-1
C.1 Specifications C-1
C.2 Electrical Wiring C-3
C.3 Yoke Mount Installation C-4
C.4 Yoke Mount Operation C-6
C.5 Portable Antenna Installation C-8
C.6 Battery Pack Operation C-8
C.7 Maintenance C-10
C.8 Product Support C-10
D MAP DATUMS D-1
E UTC TIME TO LOCAL TIME OFFSET E-1
F INDEX F-1
v
Page 9

CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCING THE GARMIN GPS 95
1.1 CAPABILITIES
The GPS 95 provides a host of powerful capabilities which were previously
found only in much larger systems:
· Performance: MultiTracTM receiver tracks and uses up to eight
satellites with high sensitivity, fast first fix, and continuous navigation
updates.
· Portability: Goes anywhere - air, sea or land. Built-in simulator for
trip planning or practicing navigation skills anywhere.
· Ease of Use: Graphic screens and intuitive guidance from the display
offer ease of operation.
· Navigation: Stores 500 alphanumeric user waypoints; 20 reversible
routes of 30 waypoints each. GOTO function sets instantaneous
course to waypoint of your choice. AutoStoreTM function builds routes
as you go. A flashing message annunciator keeps you fully informed
of your navigation status.
· Personalized: Customize your unit by selecting distance and speed
units, Course Deviation Indicator (CDI) sensitivity, keypad and display
features, map datums, and interface options.
· Low Power Consumption: Battery Saver operation draws less than
1.5 watts; provides up to four hours of continuous operation with the
AA battery pack.
· Trip Planning: Analyze distance, time, and fuel requirements for your
trip. Compute time of sunrise/sunset at your destination. Calculate
density altitude before you take off and true airspeed as you fly.
Vertical navigation guides you to your cruising altitude and puts you in
the traffic pattern before landing.
· Alarms: An alarm clock and timer allow the GPS 95 to watch the clock
for you. Arrival and CDI alerts help you safely navigate your aircraft.
· Interfaces: Interface with PC-based moving map programs using
NMEA 0183 output, with Differential GPS (DGPS) receivers using
RTCM (SC-104 version 2.0) input, or with marine autopilots and
1-1
Page 10

graphic plotters using NMEA 0180/0182/0183 outputs. An optional
PC kit is also available to download user waypoints and routes to your
PC for permanent record.
We encourage you to read this manual and experiment using the built-in
simulator. This will help you quickly master the many features of the GPS 95.
1.2 BASIC PACKAGE
Your GARMIN GPS 95 basic package includes:
· GPS 95 Unit
· AA Battery Pack
· Detachable Antenna
· Remote Antenna Cable w/Suction Cup Mount
· Yoke Mount
· Surface Mount
· Carrying Case
· Self-coiling Power/Data Cable
· Cigarette Lighter Adaptor
· Permanent Installation Wire Harness
· Lanyard
· Battery Terminal Cover
· Owner's Manual
· Quick Reference Card
· Warranty Card
The basic package allows you to use your GPS 95 for both portable and fixed
operations. The unit may be operated from the AA battery pack, or from an
external power source (5-40VDC) using the cigarette lighter adapter or
permanent installation wire harness.
Handheld Operation:
For handheld operation, the GPS 95 is powered by a AA battery pack which
should be filled with four high quality alkaline batteries commonly found in
retail stores. The detachable antenna is placed directly on the right side of
the unit. The carrying case will protect your GPS 95 when the unit is not is
use.
In order to track GPS satellites, the unit must be situated with the antenna
pointed straight up and should not be blocked by objects or people. (Signal
reception through thin fabric, such as canvas, may be adequate but degraded.)
1-2
Page 11

When using the GPS 95 inside the cockpit it may be desirable to use the
remote antenna cable for better satellite visibility. The detachable antenna
is removed from the GPS 95 and replaced by one end of the remote antenna
cable. The antenna is then placed on the other end of the cable and, using
the suction cup mount, is situated where the best satellite visibility is possible.
You may need to experiment to determine the best location for the antenna.
(See Appendix C for removal of the detachable antenna.)
A lanyard is provided to prevent accidental dropping of your GPS 95.
Connect the lanyard to the eyelet on the back (at the top) of the unit
Fixed Mount Operation:
A surface mount is supplied for panel mount installation. The lower half of
the surface mount is also used with the yoke mount. (See Appendix C for
instructions on yoke mount installation.) The unit may be operated using
aircraft power through the cigarette lighter adaptor or the permanent
installation wire harness. Note that there are three cable assemblies (not
counting the remote antenna cable). The self-coiling power/data cable plugs
directly into the back of the GPS 95. The other end of the self-coiling power/
data cable plugs into either the cigarette lighter adapter or the permanent
installation wire harness, according to your needs or preferences.
While using aircraft power, you may wish to leave the battery pack on the unit.
In the event of aircraft power failure, the GPS 95 will automatically switch to
battery power. If you do not desire to leave the battery pack on the unit, a
battery terminal cover is supplied to protect the battery contacts. Remove
the battery pack from the GPS 95 and slide the battery terminal cover on in
its place. (See Appendix C for removal of the battery pack.)
In addition to supplying power to the unit, the permanent installation wire
harness allows you to interface your GPS 95 with a PC-compatible computer
or an ARGUSTM unit. When connected to a PC-compatible computer, the
GPS 95 will provide navigation information for many of the of the popular
moving map programs. (See Appendix C for connection of the GPS 95 to
other devices.)
1.3 OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
The following optional accessories are available for your specific needs:
· Rechargeable NiCad Battery Kit
· PC Software Kit
1-3
Page 12

Rechargeable NiCad Battery Kit:
A rechargeable NiCad battery kit is available for use with the GPS 95. This
kit includes a rechargeable NiCad battery, an AC adaptor and a drop-in
charger base. Using the drop-in charger base, the NiCad battery is charged
in 12-14 hours (not to exceed 24 hours). The rechargeable NiCad battery kit
allows you to use the GPS 95 portably for extended periods.
PC Software Kit:
The PC Software Kit allows you to download route, waypoint and track data
from the GPS 95 to your PC-compatible computer. You may also edit this
data and upload it back into the GPS 95. With the software kit you can plot
data files and/or display current position in real-time on a grid map. Data files
can be printed for future reference. For planning purposes, the software kit
provides animated satellite orbit displays and allows you to print a satellite
visibility chart. The software kit includes both 3.5" and 5.25" diskettes, an
instruction manual and a PC interface cable.
1.4 OPERATIONAL MODES
While using your GPS 95, you may select from one of three operational
modes: Normal or Battery Saver modes for actual navigation, or Simulator
mode for practicing/trip planning. In Normal and Battery Saver modes,
typical time to first fix is less than 2.5 minutes. (If you have used your unit
within the hour, it may take as little as 15 seconds.) In Simulator mode the
GPS 95 will not acquire satellites, but will display a position based on the last
known location or any other position that you designate.
Normal mode offers continuous navigation updates and should be selected
when the GPS 95 will be used in a high dynamics environment (i.e., frequent
speed and heading changes). The GPS 95 will typically operate up to two
hours using the AA battery pack, or up to five hours using the optional NiCad
battery pack.
Battery Saver mode, suitable for most applications, offers position updates
that adapt to your needs while extending battery life. The GPS 95 will
typically operate up to four hours using the AA battery pack, or up to eight
hours using the optional NiCad battery pack.
Simulator mode allows you to simulate the operation of the GPS 95 while
at home or in your office. The simulator mode can be selected while learning
to use your GPS 95 and is ideal for planning routes and entering waypoints.
Keep in mind that the GPS 95 is not tracking satellites in the simulator mode.
YOU SHOULD NEVER ATTEMPT TO USE THE SIMULATOR MODE FOR
ACTUAL NAVIGATION.
1-4
Page 13
2.1 FRONT PANEL
Page Options
CHAPTER 2
GETTING STARTED
Page Annunciator
Softkeys
Message Annunciator
PWR
STAT
GO
AUTO
STO
CLR
ABC
1
JKL
4
TO
STU
7
DEF
MNO
VWX
GHI
NAV
3
2
PQR
5
8
0
WPT
6
YZ
RTE
9
ENT
TINA STINKS
The front panel consists of a 20-key keypad with a 85 x 64-pixel LCD display.
Both the display and keypad may be illuminated for nighttime operation.
2.2 SOFTKEY OPERATION
Information displayed on the LCD is commonly referred to as a “page.” The
GPS 95 works with softkey operation. At the bottom of the screen is a list of
page options. To select a different page, press the appropriate softkey below
the desired option. Please note that the page options must be highlighted in
order to use the softkeys. On the bottom line, extreme right, is the page
annunciator which indicates the current page you are viewing.
2-1
Page 14

2.3 CURSOR AND FIELDS
Cyclic Field
Confirmation Field
Bar Field
The area of the page which is highlighted in reverse video is called the
cursor. The cursor may be moved to locations on the page called fields
which allow you to enter data or change options. You will encounter five types
of fields.
· Numeric fields accept numbers only.
· Alphanumeric fields accept numbers as well as letters.
· Cyclic fields allow selection from several available options. A cyclic
field is preceded by a prompt ( ). You may cycle through the choices
by pushing CLR.
· Confirmation fields allow you to indicate your approval. For example,
you will be asked to confirm that you want to delete a waypoint.
Confirmation fields always end with a “?” character. Press ENT to
approve the confirmation field.
· Bar fields allow an adjustable scale entry with the length of the bar
representing the minimum to maximum setting. Use the arrow keys to
make adjustments in bar fields.
2.4 KEYPAD OPERATION
The PWR/STAT key is a dual function key that controls unit power
PWR
STAT
and system status. Pressing this when the unit is off will turn the
unit on. To turn the unit off, press and hold PWR/STAT until the
display is blank.
Pressing PWR/STAT momentarily while the unit is on will take you
to the status pages. (See Chapter 8.) If the message annunciator
is flashing and the tone sounds, you may push PWR/STAT to view
the message.
2-2
Page 15
GO
Pressing GOTO allows you to instantly define a destination
TO
waypoint and plot a course from present position to that
destination. (See Chapter 4.)
AUTO
STO
NAV
WPT
RTE
0
Pressing AUTOSTOre allows you to capture your present
position instantaneously. (See Chapter 7.)
Pressing NAV allows you to view position and navigation
information as well as the Map Display. (See Chapter 5.)
The WPT key allows you to create, edit, delete, and rename
user waypoints. The WPT key also allows you to view nearest
waypoints or define proximity waypoints. (See Chapter 3.)
The RTE key allows you to create, edit, review, activate, and
delete routes. (See Chapter 6.)
Pressing either of the arrow keys allows you to move the
cursor, scroll through information lists, and enter letters
of the alphabet.
The alphanumeric keys allow you to enter letters and
numbers. Use the arrow keys to select the desired
letter or number from a given alphanumeric key.
Pressing this key while the cursor is not on a numeric or
alphanumeric field allows you to change the backlight level.
There are two backlighting levels. On an alphanumeric field,
pressing this key allows you to enter a blank space or a zero.
CLR
ENT
Pressing CLR erases information in the cursor field. If the
cursor is over a cyclic field, pressing CLR will toggle through
several available options.
Pressing ENT confirms an entry or selection.
2-3
Page 16

2.5 ENTERING DATA
You may enter data such as waypoint identifiers and user waypoint
coordinates on certain pages. To enter data you must first move the
cursor to the desired field by pressing the right or left arrow key. A data
entry operation is completed by pressing the ENT key. If an error is made
during the data entry process, press the CLR key to remove the erroneous
character.
To enter a number...
· Press the key that is labeled with the desired number. The numbers
will fill in from the right side of the field and move to the left as each
new number is entered. For example, if you wish to enter “51” in a
three space field, you must press the 5 and 1 keys in that order. You
do not have to enter a leading zero. (Note: When entering numbers
in an alphanumeric field press the key that is labeled with the
desired number, then press the right or left arrow key twice.)
· Press CLR if you enter an incorrect number.
· Press ENT when you have filled all significant digits of the field with
numbers.
To enter a letter...
· Press the key that is labeled with the desired letter.
· Press the right or left arrow key until the desired letter is displayed.
· Press CLR if you enter an incorrect letter.
· Press ENT when all the characters are entered.
The GPS 95 features a keypad feedback tone which will sound each time
you press a key. If you enter data which is not appropriate for the field, the
feedback tone will quickly sound three times indicating an error. The
keypad feedback tone can be turned off if you wish. (See Section 8.10.)
2-4
Page 17

2.6 VIEWING MESSAGES
From time to time, the GPS 95 will use a message to tell you of conditions
needing attention. When the GPS 95 has a new message, the MSG
annunciator will flash. When this occurs, press PWR/STAT to view the new
message(s). Press PWR/STAT again to see the page you were viewing prior
to reading the message. (See Appendix A for a complete list of GPS 95
messages.)
While the MSG annunciator is flashing, the GPS 95 will also generate a tone
to alert you of the message. (If your unit is connected to an external alarm,
it will also be activated.) Messages that demand immediate attention such
as an arrival alarm generate a quick tone that will not stop until you view the
message. All other messages generate a slow tone that will cease after 15
seconds. The message tone may be turned off if you wish. (See Section
8.10.)
Important messages will remain on the Message Page after being viewed.
If this occurs, the MSG annunciator will be in view but will not flash. (If no
messages exist, the MSG annunciator will not be visible.) To review these
messages, press PWR/STAT to reveal the status menu options. Then press
the key underneath the “AUX” page option. With the arrow keys, highlight
“Messages” and press ENT.
2.7 TURNING THE GPS 95 ON
When the GPS 95 is turned on it will automatically perform internal checks
to ensure proper operation, begin acquiring satellites, and once a sufficient
number are received, display your present position. To see this power on
sequence, take the GPS 95 outside to a location that is well away from
buildings and other structures that might limit its view of the sky.
After you turn your GPS 95 on, it will conduct a series of self tests and display
the following notice:
2-5
Page 18
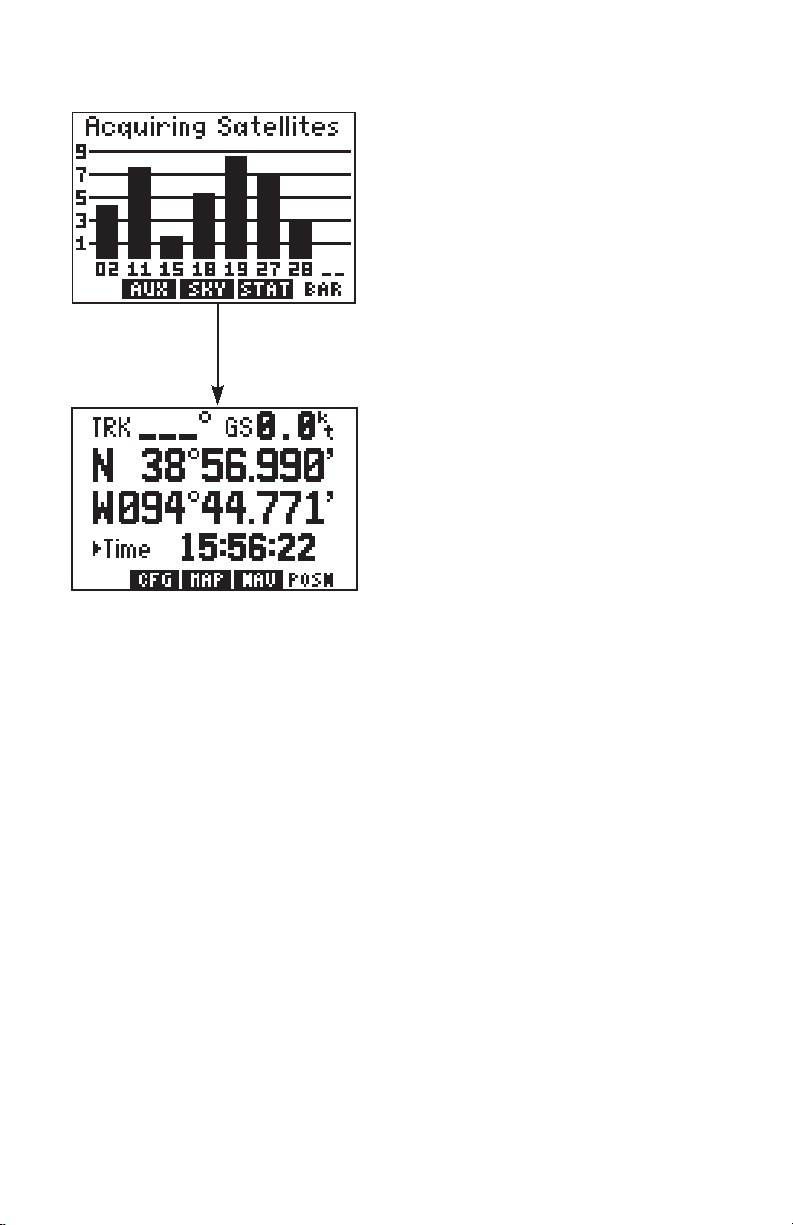
Following completion of the tests, the
Satellite Bar Graph Page will be
displayed and the GPS 95 will begin
acquiring satellites.
After a position is found (and if no keys
have been pressed), the Position Page
will be displayed and the unit is ready for
normal operation. The process of
satellite acquisition is fully automatic
and, under normal circumstances, will
take approximately 2-3 minutes to obtain
navigation information. (If the unit has
been used in the past hour, it may take as little as 15 seconds.) If the GPS
95 has been moved a considerable distance since it was last used, additional
time may be required as the unit performs an AutoLocateTM . AutoLocate
TM
will automatically locate satellites and compute your position regardless of
your location or where the unit was last used.
When four or more satellites with good geometry are available, the GPS 95
will automatically operate in the 3D mode in which latitude, longitude and
altitude are computed. If only three satellites are available, the unit will
operate in 2D mode in which only latitude and longitude are computed. When
operating in the 2D mode, the unit will use the last computed altitude or your
last entered altitude. (Section 5.4 describes how you may enter the altitude.)
Your GPS 95 will automatically update satellite orbital data as it operates. If
you have not operated your unit for a period of six months or longer, it will take
approximately 15 minutes to search the sky and collect new orbital data. You
will be informed when your unit is searching the sky with the message
“Searching the Sky.” Once satellite orbital data is collected, it will be stored
in memory. The memory is maintained by an internal battery, therefore the
data will not be lost when you turn your GPS 95 off or remove the battery
pack.
2-6
Page 19
If the GPS 95 cannot acquire enough satellites for 2D or 3D navigation, you
will be informed with the message “Poor GPS coverage”. If this situation
occurs, make sure the antenna is properly connected and not obstructed by
nearby buildings or other structures.
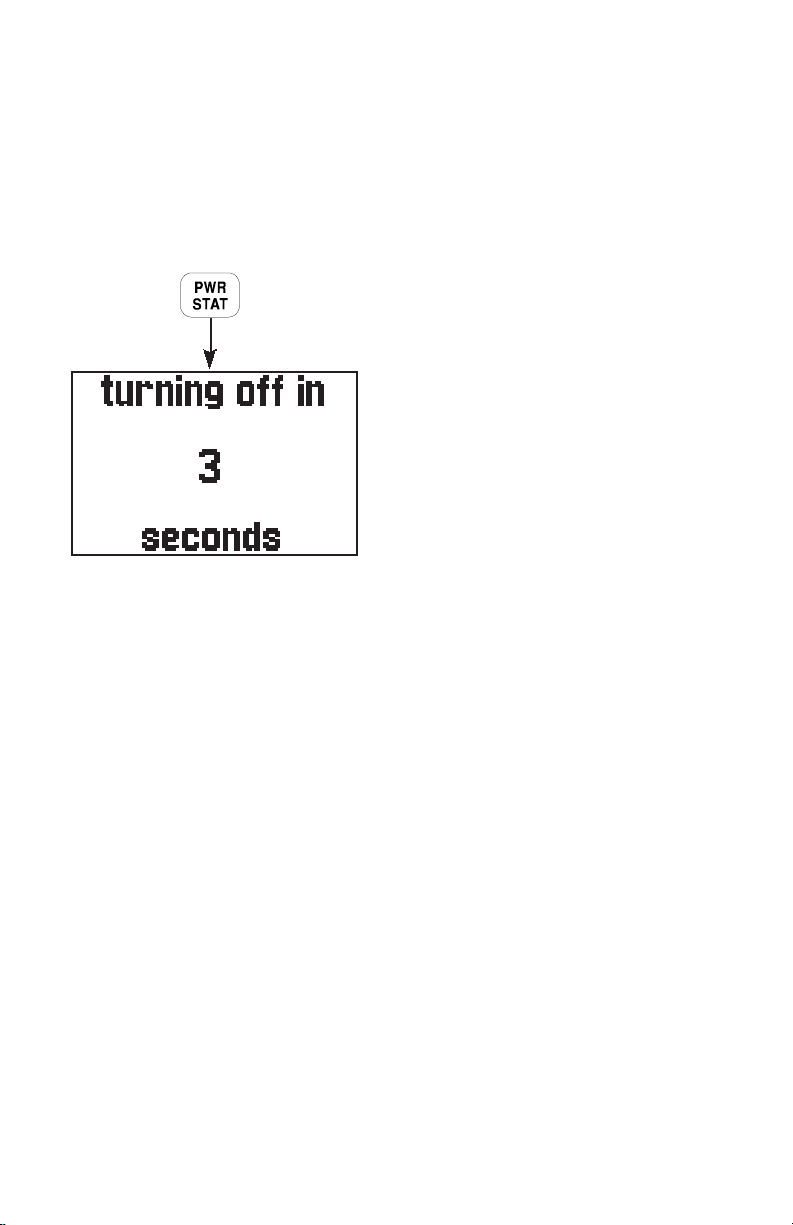
2.8 TURNING THE GPS 95 OFF
To turn the GPS 95 off, press and hold
the PWR/STAT key.
The Off Page will be displayed, the GPS
95 will perform a countdown and, after a
brief delay, will shut off. All user
waypoints, routes, and setup information
that you have entered will be maintained
while the unit is off - even if the battery
pack is removed.
2.9 LEARNING TO USE THE GPS 95
If you are using the GPS 95 for the first time, you are encouraged to read
Chapter 3 which introduces the GPS 95's waypoint features, Chapter 4 on
the use of the GOTO key, and Chapter 5 for navigating to a waypoint. A
sample trip is included in Chapter 5 to get you started on the use of the GOTO
key and the various navigation pages available on your GPS 95. You may
also want to read Chapter 8 on custom setups to configure the GPS 95 to your
preferences. Afterward, you may want to read through the rest of this manual
and make further use of the built-in simulator to practice with the advanced
features.
2-7
Page 20
CHAPTER 3
WAYPOINTS
The GPS 95 allows you to store up to 500 user waypoints. A basic waypoint
consists of an identifier (up to six letters and/or numbers) and its location.
You will have the opportunity to use waypoints extensively while operating
the GPS 95. For example, you can build a route using waypoints, you can
perform trip/fuel planning using waypoints, and you can even calculate the
time of sunrise and sunset for a waypoint of interest.
The GPS 95 features four primary waypoint pages. You may select the
desired page by pressing WPT and, if needed, the appropriate softkey.
WPT
Nearest Waypoint Page Waypoint Definition Page
Proximity Waypoint Page
Waypoint List Page
3-1
Page 21
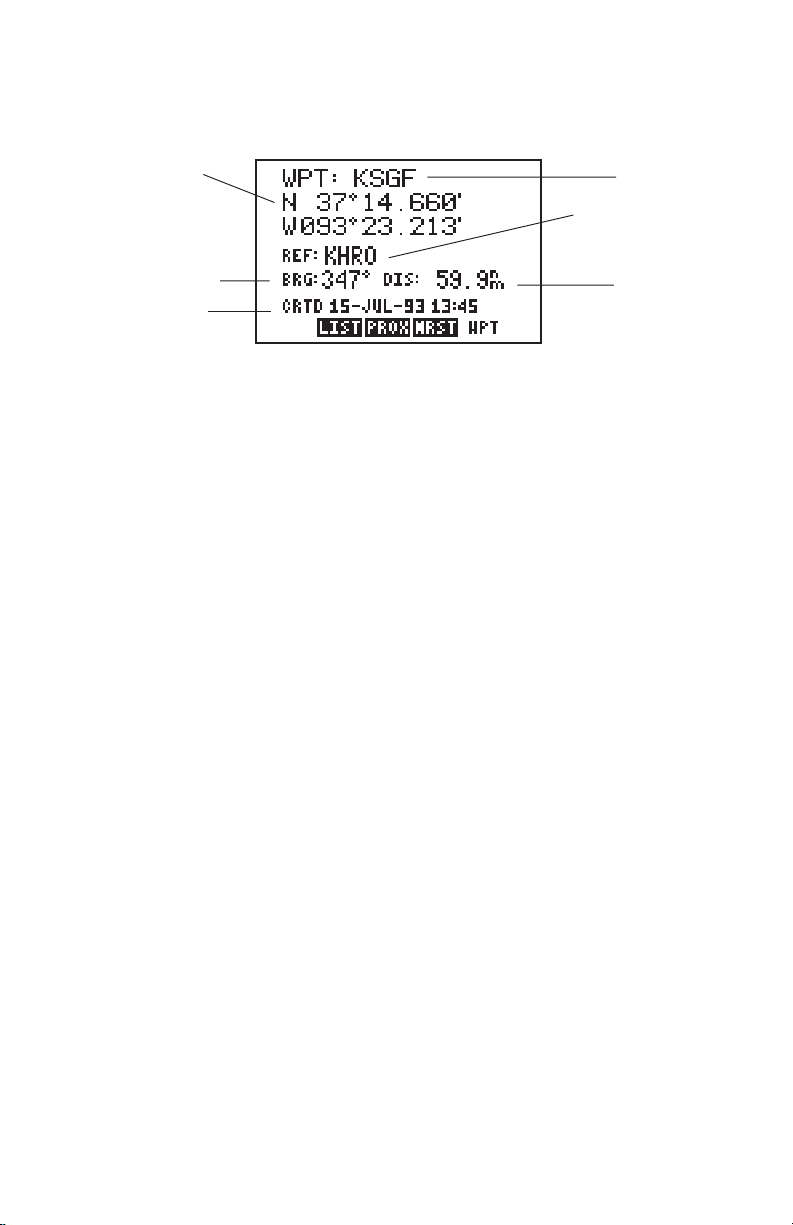
3.1 WAYPOINT DEFINITION PAGE
2
4
6
1
3
5
The Waypoint Definition Page allows you to create, edit and review waypoint
information.
This page displays the following waypoint information:
1) Waypoint identifier
2) Location (latitude/longitude or grid system)
3) Reference waypoint identifier
4) Bearing from reference waypoint to selected waypoint
5) Distance from reference waypoint to selected waypoint
6) User comments
Waypoints are selected by the identifier that you assign.
To select a waypoint...
· Press WPT and, if needed, the WPT softkey to display the Waypoint
Definition Page.
· Press the right arrow key to move the cursor to the right of “WPT”.
· Enter the identifier of the desired waypoint using the alphanumeric and
arrow keys. Press ENT. The information for the selected waypoint is
displayed.
You may select a reference waypoint by moving the cursor to the reference
waypoint identifier field and entering the desired waypoint identifier.
3-2
Page 22

3.2 CREATING WAYPOINTS
When a waypoint identifier has been entered that does not exist in memory
the GPS 95 will assume you wish to create a new waypoint. You may create
a new waypoint using one of two methods: direct position entry (latitude/
longitude or grid system) or relative to an existing waypoint.
In order to create a waypoint by direct position entry the coordinates for the
new waypoint must be known and entered directly into the unit.
To enter the waypoint position directly...
· With the Waypoint Definition Page displayed, press the right arrow key
until the cursor is over the waypoint identifier field.
· Enter the identifier of the new waypoint using the alphanumeric and
arrow keys. Press ENT when complete. The cursor will move to the
position coordinates.
· Enter the position of the new waypoint. Press ENT after data is entered
into each field. The number of fields required for position entry will
depend on the position coordinate option selected. (See Section 8.7.)
If latitude and longitude coordinates are selected there will be four
fields if decimal degrees are used - two to define the hemispheres (“N”
or “S”, “E” or “W”) and two to enter the latitude and longitude degrees.
If latitude and longitude coordinates are selected with degrees, minutes
and decimal seconds, there will be eight data entry fields to define the
position since degrees, minutes and seconds are each divided into
their own field. If a grid system is selected it will have a different number
of fields depending on the format of the selected grid.
A new waypoint can be defined relative to another waypoint already
contained within the GPS 95's memory. When creating a new waypoint
relative to an existing waypoint, you will define a distance and bearing from
the existing waypoint to the new waypoint location.
3-3
Page 23

To create a waypoint offset from a reference waypoint...
· With the Waypoint Definition Page displayed, press the right arrow key
until the cursor is over the waypoint identifier field.
· Enter the identifier of the new waypoint using the alphanumeric and
arrow keys. Press ENT when complete.
· Press the right arrow key until the cursor is over the reference waypoint
identifier field.
· Enter the identifier of the desired reference waypoint and press ENT.
· Enter the bearing from the reference waypoint to the new waypoint
and press ENT. The bearing will be true or magnetic depending on the
unit setups. (See Section 8.7.)
· Enter the distance from the reference waypoint to the new waypoint
and press ENT. The distance will be in nautical miles, statute miles or
kilometers depending on the unit setups. (See Section 8.7.)
Once the waypoint location is created, the user comment field will automatically
be filled with the date and time the waypoint was created. You may enter a
different user comment by placing the cursor over this field and entering the
new comment with the alphanumeric and arrow keys, followed by ENT when
complete.
You may also modify the position of an existing waypoint from the Waypoint
Definition Page. A waypoint may be changed using the same procedures
described above for creating a waypoint, by direct position entry (latitude/
longitude or grid system) or relative to an existing waypoint. When modifying
an existing waypoint, the new position data is entered directly over the old
data. For a given data field, once the ENT key is pressed the position data
is updated. (NOTE: If a waypoint is being used for navigation, its position
cannot be modified. An attempt to modify the position of such a waypoint will
result in the message “Cannot change active waypoint”.)
3-4
Page 24

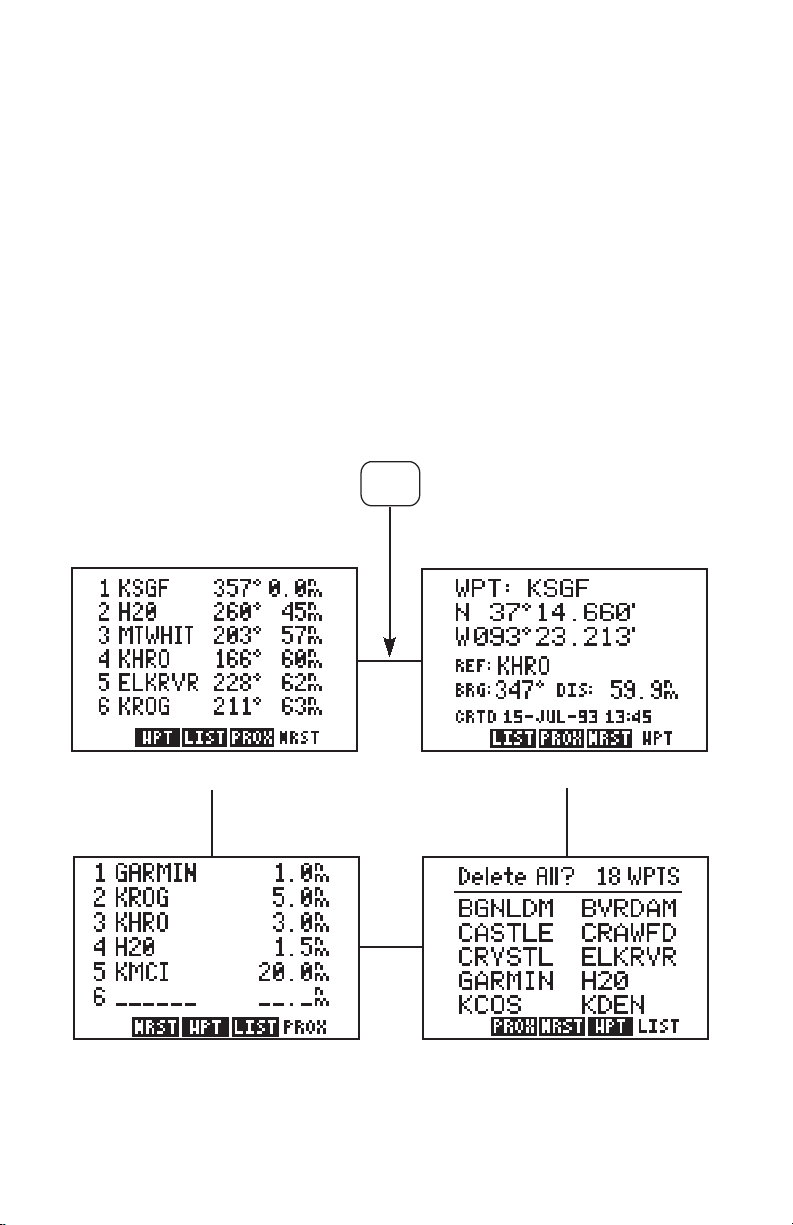
3.3 WAYPOINT LIST
The Waypoint List Page allows you to view all stored waypoints in your GPS
95. The list may be scrolled, with the arrow keys, to view all the waypoints.
From this page, waypoints may be selected for deletion, renaming or to
activate a GOTO. (See Chapter 4 for information on the GOTO function.)
To delete a waypoint...
· Select the Waypoint List Page by pressing WPT and the LIST softkey,
if needed.
· With the arrow keys, place the cursor on the desired waypoint.
· Press CLR and ENT.
· A confirmation page is displayed. Press ENT to confirm or CLR to
cancel.
NOTE: If you attempt to delete a proximity or route waypoint, a message will
be displayed. You must delete the proximity alarm or the route before you
can delete the waypoint. (See Sections 3.6 and 6.5.)
The Waypoint List Page also gives you the option of deleting all waypoints
at one time.
To delete all waypoints...
· Select the Waypoint List Page by pressing WPT and the LIST softkey,
if needed.
· With the arrow keys, place the cursor over “Delete All?” and press
ENT.
· A confirmation page is displayed. Press ENT to confirm the deletion
of all waypoints or CLR to cancel.
3-5
Page 25

NOTE: The “Delete All?” selection will delete all routes and proximity
waypoints as well.
From the Waypoint List Page you may also change the name of any
waypoint.
To rename a waypoint...
· Select the Waypoint List Page by pressing WPT and the LIST softkey,
if needed.
· With the arrow keys, place the cursor on the desired waypoint.
· Type in a new name for the waypoint and press ENT.
· A confirmation page is displayed. Press ENT to confirm the name
change or CLR to cancel.
3.4 USING WAYPOINTS
You may use waypoints on many GPS 95 pages. A waypoint is selected by
entering its identifier and pressing ENT.
The GPS 95 also offers a waypoint scanning feature which will simplify
waypoint entry. When scanning, the nine nearest waypoints will be displayed
first, followed by the entire list.
To select a waypoint by scanning identifiers...
· On a blank waypoint identifier field press the WPT key. (If the identifier
field is not blank, press CLR first.)
· Press the right arrow key to sequence through the available waypoints.
If you pass the desired waypoint, you may press the left arrow key to
scan backwards through the list.
· Once the desired waypoint is selected, press ENT to accept the
waypoint and complete the scan. The selected waypoint will be
displayed on the waypoint identifier field.
You may limit the scan by defining the starting letter, or letters, where you
wish the scan to begin. Limited scanning can save considerable time when
a large number of waypoints have been added to memory.
3-6
Page 26
To select a waypoint using a limited scan...
· Select a blank waypoint identifier field. (If the identifier field is not blank,
press CLR first.)
· Enter the starting letter, or letters, of the desired waypoint identifier.
You may limit the scan to the level that you desire. For example, if you
enter “C” the GPS 95 will scan through all waypoints that begin with the
letter “C”, but, if you enter “CRY” the GPS 95 will display only those
waypoints that begin with “CRY”.
· Press WPT to begin scanning.
· Press the right arrow key to sequence through the available waypoints.
If you pass the desired waypoint, you may press the left arrow key to
scan backwards through the list.
· Once the desired waypoint is selected, press ENT to accept the
waypoint and complete the scan. The selected waypoint will be
displayed on the waypoint identifier field.
3.5 REVIEWING WAYPOINTS
The GPS 95 allows you to quickly review waypoint information without
entering the waypoint identifier. For example, you may review information
regarding the waypoints in a route, or review the definition of the nearest
waypoints. In general, if the cursor is over a waypoint identifier, you may
quickly review the information about that waypoint.
To review a waypoint definition...
· Place the cursor over a waypoint identifier (using the arrow keys) and
press ENT. The Waypoint Definition Page is displayed showing
information for the selected waypoint.
· With the cursor over “USE?”, press ENT to exit the review process and
return to the previous page.
3-7
Page 27
3.6 PROXIMITY ALARM WAYPOINTS
The Proximity Waypoint Page allows you to define an alarm circle around
a waypoint. This feature is useful in defining an area around a TCA (Class
B), MOA, tower, etc. When you approach one of these waypoints the GPS
95 will notify you with an alarm tone and the message, “Prox Alarm [waypoint name],” if you enter the alarm circle.
The GPS 95 allows you to define a maximum of nine proximity waypoints.
Scroll through the proximity waypoint list using the arrow keys.
To set a proximity waypoint...
· Select the Proximity Waypoint Page by pressing WPT and the PROX
softkey, if needed.
· Place the cursor on a blank waypoint identifier field using the arrow
keys.
· Enter the identifier of the desired waypoint and press ENT. (NOTE: If
neither the waypoint name nor the location exists in memory, the
Waypoint Definition Page will be displayed. You must then enter the
waypoint location.)
· Enter the proximity alarm distance and press ENT. The proximity
alarm distance defines a radius from the waypoint.
If the newly created proximity alarm circle overlaps with an existing proximity
alarm circle, you will be informed of the overlap with the message “Proximity
Overlap”. As long as the overlap remains this message will be displayed
each time the GPS 95 is turned on. (WARNING: If you enter the overlap area
the unit will only inform you of the nearest waypoint.)
3-8
Page 28

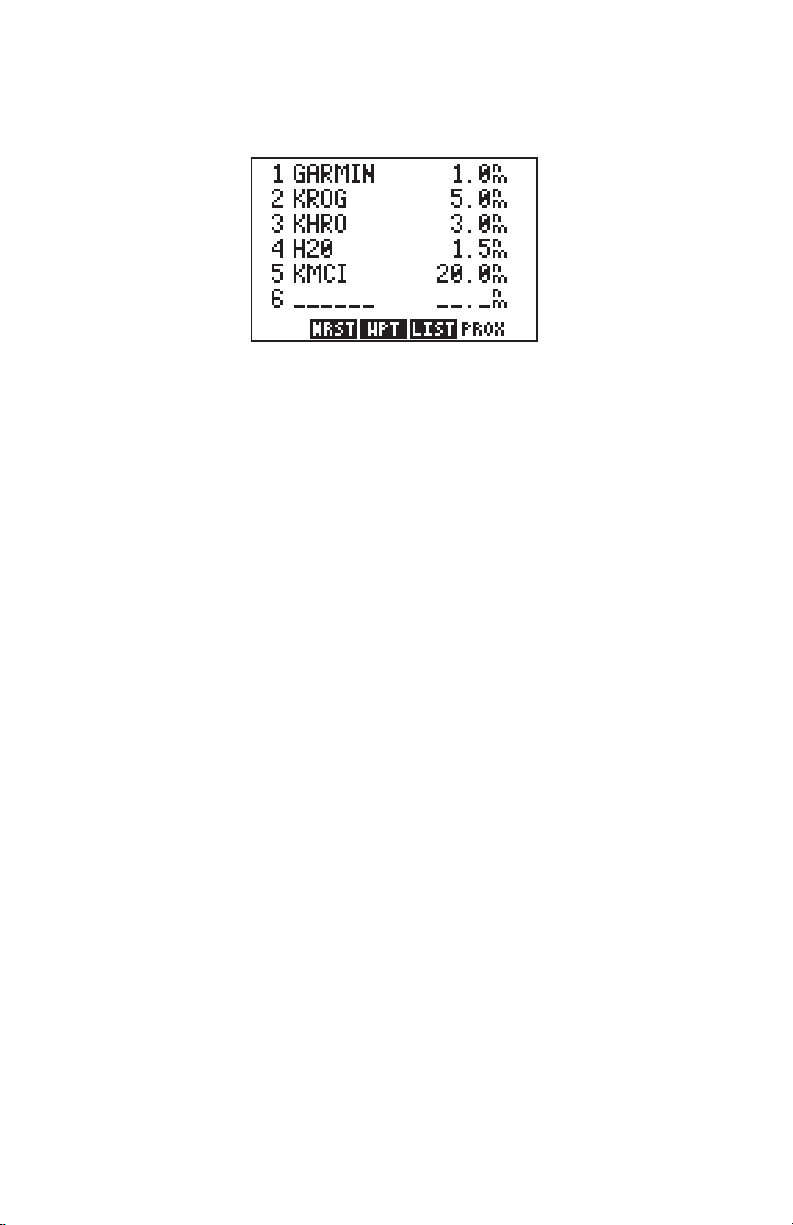
3.7 NEAREST WAYPOINTS
An important feature on the GPS 95 is the ability to display up to nine nearest
waypoints within 200 nautical miles of your present position. The bearing and
distance to each nearest waypoint is also displayed. The nearest waypoint
feature can be critical in finding a safe landing location in the event of an inflight emergency.
To view nearest waypoint information...
· Select the Nearest Waypoint Page by pressing WPT and the NRST
softkey, if needed. The six nearest waypoints will be displayed, along
with the bearing and distance to each.
· Use the arrow keys to scroll through the list and view additional nearest
waypoints (up to nine).
Keep in mind that you may view additional information for any nearest
waypoint by placing the cursor on the waypoint identifier and pressing ENT.
The nearest waypoint feature can be used in conjunction with the GOTO key
to provide instantaneous navigation information to a nearby waypoint.
Simply place the cursor over the desired nearest waypoint identifier and
press GOTO, followed by ENT. The GPS 95 will immediately plot a course
from your present position to the nearby waypoint. (See Chapter 4 for more
information on the GOTO key.)
3-9
Page 29

CHAPTER 4
GETTING THERE FAST - GOTO
The GOTO function allows you to quickly set a course from your position to
any waypoint.
To activate the GOTO function...
· Press GOTO. The GOTO Page will be displayed with the cursor on
the GOTO waypoint field. If the GPS 95 is currently navigating to a
waypoint, that waypoint will be offered as the default GOTO waypoint.
If the waypoint field is blank or the waypoint shown is not the desired
destination, type the new name right over the old name. NOTE: If a
non-existent waypoint name is entered, the GPS 95 will assume that
this is a new waypoint and will display a blank Waypoint Definition
Page where you may enter the new waypoint's coordinates.
· Confirm the GOTO waypoint by pressing ENT. The Navigation
Summary Page will be displayed with the D-bar on the CDI centered.
(See Section 5.1 for more information on the Navigation Summary
Page and the CDI.)
You may also select the desired GOTO waypoint identifier by scanning. (See
Section 3.4 for more information on waypoint scanning.) Alternatively, the
GOTO function may be quickly activated from any page (e.g., the Nearest
Waypoint Page or the Waypoint List Page) by placing the cursor over the
desired waypoint name and pressing GOTO. The GOTO Page will be
displayed with the cursor on the GOTO waypoint name. The GOTO function
will be activated when the ENT key is pressed.
You may cancel the GOTO function at any time.
4-1
Page 30

To cancel the GOTO function...
· Press GOTO. The GOTO Page will be displayed.
· Press CLR. The GOTO waypoint name will become blank.
· Press ENT. The GPS 95 will start to navigate using the active route,
if it has been programmed. (See Chapter 6.) Otherwise, the GPS 95
will stop computing waypoint navigation data.
4-2
Page 31

CHAPTER 5
NAVIGATION INFORMATION
The GPS 95 features four navigation pages. You may select the desired
page by pressing NAV and, if needed, the appropriate softkey.
NAV
Navigation Summary Page
Map Display
5.1 NAVIGATION SUMMARY PAGE
GOTO or
Active Leg
Field #1
Field #3
CDI
Present Position Page
Map Configuration Page
Field #2
Field #4
Relative Bearing
Pointer
5-1
Page 32

The Navigation Summary Page displays direction, distance and speed
information to guide you along a route or to a GOTO destination. Included
is a graphic course deviation indicator (CDI), at the bottom of the page, which
illustrates your position relative to the course. The current CDI scale setting
is shown at each end of the CDI scale. (See Section 8.8 for information on
setting the CDI scale.) A relative bearing pointer at the center of the CDI
indicates the bearing to the waypoint relative to the current ground track
(TRK). In the example shown, the current ground track is 347 degrees and
the bearing to our destination is 339 degrees. The relative bearing pointer
points slightly to the left indicating that our destination is ahead, but slightly
to the left of our current direction of travel.
At the top of the Navigation Summary Page the current GOTO destination is
displayed, or the “active leg” of a route when using the GPS 95’s route
navigation features. (See Chapter 6 for information on route navigation.)
During the process of acquiring satellites, the GPS 95 will not provide
navigation data. The top line of the Navigation Summary Page will indicate
this condition, as illustrated below.
If the GPS 95 has acquired satellites, but is not navigating to a waypoint (i.e.,
no GOTO destination or route has been activated), the top line of the
Navigation Summary Page will indicate that no destination has been defined,
as illustrated below.
5-2
Page 33

Notice that the Navigation Summary Page has four cyclic fields. With these
cyclic fields you may configure your GPS 95 to display navigation information
according to your preferences. (See Appendix B for a description of
navigation terms.) The field options are as follows:
Field #1 (top left)
· Bearing to destination waypoint (BRG)
· Course to steer (CTS)
· Desired track (DTK)
· Ground track (TRK)
· Off course error, or turn angle (TRN)
Field #2 (top right)
· Distance to destination waypoint (DIS)
· Cross track error (XTK)
· VNAV altitude (V)
Field #3 (bottom left)
· Ground track (TRK)
· Ground speed (GS)
Field #3 (bottom right)
· Ground speed (GS)
· Estimated time of arrival (ETA)
· Estimated time enroute (ETE)
5.2 MAP DISPLAY
Map Orientation
Scale Setting
Ground Speed
Present Position
5-3
Page 34

The GPS 95 also features a Map Display which shows a graphic top view of
your location. The current ground speed is indicated at the top right corner
of the display. The top left corner defines the orientation of the Map Display:
“North up”, “Ground track up”, or “Desired track up.” If “000” is shown, the
Map Display is oriented “North up.” (See Section 5.3 for selection of Map
Display orientation.) Your present position is shown in the middle of the
display. If the Map Display is oriented “Ground track up” your present
position is indicated by an aircraft symbol. If either “North up” or “Desired
track up” orientations are selected, the present position is indicated by a
crosshair (“+”).
Waypoints
Waypoint highlighted
(w/identifier)
You may select which items you wish to display. The Map Display can
provide up to nine nearest waypoints. GOTO or route waypoints which are
not part of the nine nearest waypoints will also be displayed. The track history
and/or the active route may also be shown as solid lines on the display.
Selection of which items to display is performed on the Map Configuration
Page. (See Section 5.3.)
You may view the identifier for any waypoint on the Map Display by moving
the cursor over that waypoint (with the arrow keys). By moving the cursor
around the page you can identify each waypoint shown. Keep in mind that
when the cursor is over a waypoint identifier you may review information
about that waypoint by pressing ENT, or plot a course to that waypoint by
pressing GOTO.
The scale distance for the screen (distance represented by the height of the
screen) is at the lower left corner of the screen. The scale number (directly
above the scale distance) may be changed to the level that you desire. You
may zoom in to a .5 nautical mile scale, or out to a maximum scale of 240
nautical miles.
5-4
Page 35

To set the Map Display scale...
· Press the left arrow key to place the cursor on the scale number.
· Press CLR to sequence through the available scale settings. (HINT:
The scale setting may also be selected by pressing the alphanumeric
key that corresponds to the desired scale.)
5.3 MAP CONFIGURATION
The Map Configuration Page allows you to tailor the GPS 95’s Map Display
to your preferences. As previously stated, the Map Display can show
waypoints, the active route, your track history and/or waypoint identifiers.
Any of these items may be turned on or off according to your preferences.
For example, when the Map Display is zoomed out to its maximum levels the
screen may appear too cluttered to be easily read. In this case, you could
turn off the information not needed to create a more legible display.
To turn display information on/off...
· Press NAV and the CFG softkey, if needed, to select the Map
Configuration Page.
· Place the cursor on the desired item using the arrow keys.
· Press CLR to toggle between “on” and “off”.
· If you wish to return to the Map Display: place the cursor on the menu
bar using the arrow keys, then press the MAP softkey.
5-5
Page 36

The Map Display orientation is also selected from the Map Configuration
Page. The Map Display may be oriented as follows:
· North up - The Map Display will always be displayed with north as the
top of the page.
· TRK up - Track up. The Map Display will be oriented such that your
current ground track direction is at the top of the page.
· DTK up - Desired track up. The Map Display will be oriented along
the course between the “active from” and “active to” waypoints.
5.4 PRESENT POSITION
As mentioned earlier, the Present Position Page is automatically displayed
when the GPS 95 is turned on and a position is obtained. The top line of this
page displays your ground track (TRK) and ground speed (GS). The next two
lines indicate your current position according to the coordinate format and
map datum selected. In the example shown above, the position is displayed
in degrees and decimal minutes of latitude/longitude. (See Section 8.3 for
more information on coordinate format selections and Section 8.8 for more
information on map datum selections.)
The bottom line of the Present Position Page is a cyclic field which can
display either altitude above mean sea level (MSL) or current time (UTC or
local). Select the desired option by placing the cursor on this field and
pressing CLR.
When the GPS 95 is performing 2D navigation, the last known altitude will be
used to calculate a present position. If the altitude is not accurate within a few
hundred feet you should manually enter your altitude.
To enter the altitude (2D only)...
· Use the arrow keys to place the cursor to the right of “Altitude”.
· Enter the correct altitude and press ENT.
5-6
Page 37

During the initial satellite acquisition, the displayed position is the last known
position stored in the GPS 95. If your position has moved a considerable
distance since the unit was last used, the GPS will perform an AutoLocate
TM
(See Section 2.7.) This process can take up to ten minutes as the GPS 95
determines its new location. Alternatively, you may enter a more accurate
initial position directly on the Present Position Page to speed up the
acquisition process. (You may also change the position at any time while you
are in simulator mode.)
5.5 SAMPLE TRIP
Your new GPS 95 is really very simple to operate. For the purpose of this
demonstration is assumed that the factory default settings, including the
selection of nautical units (knots, nautical miles, feet), have not been
changed. If these settings have been changed, the unit may display different
data than that presented here. (See Chapter 8 on unit setups.)
Turn the GPS 95 on. The unit will
display the welcome screen and
perform several diagnostic checks to
ensure that proper operation will occur.
The Satellite Bar Graph Page will be
displayed and the GPS 95 will begin to
acquire satellites.
Since this is a simulated trip, you will select the simulator mode and indicate
a starting location for the trip. Your simulated trip will begin at a waypoint
called GARMIN in Lenexa, Kansas.
5-7
Page 38

To select simulator mode and define a starting location...
ABC
ENT
1
Press the AUX softkey (the “1” key, in
this case) to display the Auxiliary Menu.
Place the cursor on “OP Mode” using
the right arrow key and press ENT.
The Operating Mode Page is displayed
showing the current operational mode.
5-8
CLR
*Repeat until desired
mode is selected
ENT
Place the cursor on the operational
mode field using the right arrow key.
Press CLR until “Simulator?” is
selected.
Press ENT to accept simulator mode.
The cursor is now on the reference
waypoint identifier. The waypoint,
GARMIN, will be entered here using
the alphanumeric keys.
Page 39

GHI
3
Press the “3” key, followed by the left
arrow key to select the letter “G”.
*Press alphanumeric and
ABC
1
arrow keys, as needed, to
select desired identifier
ENT
ENT
0
ENT
Press the “1” key followed by the left
arrow key, to select the letter “A”.
Continue pressing the desired
alphanumeric keys and, if needed, the
arrow keys to enter the “GARMIN”
waypoint. Press ENT when complete.
(NOTE: If the GARMIN waypoint is
not in memory its coordinates must be
entered to initialize the GPS 95 to that
location. Select the Present Position
Page and enter the coordinates for
GARMIN [N 38° 57.003' W 94°
44.767'].)
The cursor is over the reference
bearing. Since the simulation will begin
at GARMIN you do not need to define
a reference bearing from this point.
Press ENT.
The cursor is over the reference
distance. Enter a distance of zero and
press ENT. The initial position is now
set at the GARMIN waypoint.
NAV
*Plus POSN softkey
if needed
You can view your position coordinates
by pressing NAV and the POSN
softkey, if needed. The Present
Position Page is displayed.
5-9
Page 40

From your starting location at the “GARMIN” waypoint you may plot a course
and navigate to a nearby airport. For this sample trip you will fly to KCOU,
Columbia Regional Airport (N38° 49.078' W92° 13.175'). Before you can
navigate to this waypoint it must be added to the GPS 95's memory.
To create the “KCOU” waypoint...
WPT
*Plus WPT softkey, if
needed
Press WPT and the WPT softkey, if
needed, to select the Waypoint
Definition Page.
Press the right arrow key to place the
cursor on the waypoint identifier field.
5-10
JKL
4
ABC
1
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric and arrow
keys, if needed, to select
ENT
waypoint identifier
Enter the waypoint identifier, KCOU,
using the alphanumeric and arrow
keys. Begin by pressing the “4” key to
select the letter “K”.
Press the “1” key, followed by the right
arrow key, to select the letter “C”.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
and, if needed, arrow keys until the
waypoint identifier has been entered.
Press ENT when complete.
Page 41

CLR
*If need to select proper
hemisphere
ENT
Enter the latitude of KCOU (N38°
49.078'). Begin by selecting the proper
hemisphere. If “N” for north is not
displayed, press CLR.
Press ENT when the proper
hemisphere is selected.
GHI
3
VWX
8
ENT
JKL
4
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric keys to
enter the latitude minutes
ENT
*Enter the longitude using
the same steps shown
ENT
above
Enter the latitude degrees. Press the
“3” key and the “8” key. Press ENT
when complete.
Enter the latitude minutes. Begin by
pressing the “4” key.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
keys until the latitude minutes have
been entered. Press ENT when
complete.
Enter the longitude of KCOU (W92°
13.175') in the same manner as was
used for the latitude. Press ENT after
entering data into each field. (NOTE:
You do not need to enter the leading
zero for degrees. You may begin by
pressing the “9” key.)
5-11
Page 42

Once the waypoint is in memory, you may plot a course to it using the GOTO
function.
To select a destination waypoint...
GO
TO
Navigating to a waypoint is easy. Press
GOTO and the GPS 95 will display the
GOTO Page, as illustrated. Notice
that the cursor is to the right of “GOTO”.
On this field you will enter the identifier
of your destination waypoint, KCOU.
JKL
4
ABC
1
*Press the alphanumeric
and arrow keys as
needed to select desired
ENT
identifier
Press the “4” key to select the letter
“K”.
Press the “1” key, followed by the right
arrow key, to select the letter “C”.
Continue pressing the desired
alphanumeric keys and, if needed, the
arrow keys to enter the KCOU identifier.
Press ENT when complete.
The Navigation Summary Page is
displayed showing navigation
information for your trip to KCOU.
5-12
Page 43

The GPS 95's simulator mode allows you to enter a ground speed which is
used to animate the navigation displays.
To enter a simulated speed...
Press the left arrow key to place the
cursor on the ground speed field
ABC
1
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric keys as
needed to enter ground
ENT
speed
(bottom right).
Enter a ground speed of 150 knots.
Begin by pressing the “1” key. Continue
pressing the alphanumeric keys until
“150” is displayed. Press ENT when
finished.
The GPS 95 now displays additional
navigation information as it simulates
a flight to KCOU. Notice the information
changing as the flight progresses.
Additional information is available from
the Navigation Summary Page. You may recall from Section 5.1 that this
information is viewed by highlighting one of the four cyclic fields and pressing
CLR. Take a look at one of those fields now.
To view additional navigation information...
CLR
Press the left arrow key twice to place
the cursor on the fourth cyclic field
(bottom right).
Press CLR to select “ETA”. This field
will now show at what time (UTC) you
will arrive at Columbia Regional Airport.
The GPS 95's Map Display is also
5-13
Page 44

useful to help “orient” yourself. The Map Display can show nearby waypoints
as points of reference.
To view the Map Display...
NAV
Press NAV.
The Map Display is shown indicating
your position at the center of the screen
and nearby waypoints.
Press the left arrow key to place the
cursor on the scale number.
*Continue pressing
CLR until desired
CLR
scale is selected
Press CLR (repeatedly) to select the
desired scale.
The simulated trip has demonstrated only a small portion of the GPS 95's
many features. Take a moment to experiment with your new unit. Review
Chapter 5 covering types of information on the Navigation Summary Page
and the Map Display. Look at waypoint information by taking another glance
at Chapter 3. Read Chapter 6 to learn more about routes. Customize your
unit according to your preferences as described in Chapter 8.
5-14
Page 45

CHAPTER 6
ROUTES
KSTL
KTUL
(Active from waypoint)
SGF
EOS
MAP
Active Leg
(Active to waypoint)
The GPS 95 offers a route navigation feature for you to navigate along a predefined sequence of waypoints.
The GPS 95 route capability allows you to create and store twenty routes,
numbered 0 through 19, containing up to 30 waypoints each. Routes 1 to 19,
the storage routes, can be activated to travel either in the order you entered
the waypoints or in reverse order. Route 0, the active route, is the route you
are navigating. The waypoint toward which you are navigating is called the
“active to” waypoint. The waypoint immediately behind you is called the
“active from” waypoint. The line that connects the “active from” and “active
to” waypoints is called the “active leg.”
The GPS 95 features automatic leg selection which will select the route
segment closest to your position as the active leg. The GPS 95 also features
automatic leg sequencing. As you pass a waypoint in the route, the unit will
automatically select the next waypoint as the “active to” waypoint.
6-1
Page 46

There are 3 route pages. You may select the desired page by pressing RTE
and, if needed, the appropriate softkey.
RTE
Route Definition Page
Active Route Page
Route List Page
6.1 ROUTE DEFINITION
The Route Definition page allows you to create, change, review, copy, and
activate routes. Remember that route 0 is always the active route. If you
create a route in route 0, you should copy it into an empty storage route (1-
19). When you activate a storage route, it will be copied to route 0 for
activation.
Route # Field Route Action Field
Desired
Track
Waypoint List
6-2
Leg Distance
Page 47

On the route number field, you may choose between routes 0 through 19 with
CLR. Next to this is a route action field which allows you to activate the route,
clear the route, copy the route to another location, or invert the order of the
waypoints in a route and activate it. The arrow keys allow you to scroll
through the list of waypoints in a route.
6.2 CREATING AND COPYING ROUTES
The Route Definition Page allows you to create new routes and to copy a
route to another location for later reference.
To Create a Route...
· Press RTE and, if needed, the
RTE softkey to display the Route
Definition Page.
· Move the cursor to the route
number field and press CLR until
you find an empty route. (HINT:
Although the route number field is
a cyclic field, to speed selection
you may also enter the desired
route number using the
alphanumeric keys.)
· Place the cursor on the first blank waypoint identifier field using the
arrow keys and type in a waypoint you wish to put in the route.
· Press ENT
· Repeat this process for each waypoint you want to add, up to a total
of 30.
To copy a route...
· Press RTE and, if needed, the
RTE softkey to display the Route
Definition Page.
· Highlight the route number field
with the cursor and select the route
number to copy from with CLR.
· Highlight the route action field with the arrow keys and press CLR until
“>Copy To>” is displayed.
· A third field now appears in the top right corner. Highlight this field and
select the destination route number with CLR.
· Press ENT. The route is now copied.
6-3
Page 48

6.3 ACTIVATING AND INVERTING ROUTES
Routes are also activated on the Route Definition Page. You may activate
any route in the displayed order, or in reverse order. (NOTE: Remember,
when a new route is activated, the previous contents of route 0 will be
overwritten. If you wish to save route 0, be sure to copy it to an empty route
first.)
To activate a route...
· Press RTE and, if needed, the
RTE softkey to display the Route
Definition Page.
· Highlight the route number field
with the cursor and select the route
number to activate with CLR.
· Highlight the route action field, and with CLR select “>Activate?”.
· Press ENT to activate the route.
To invert a route...
· Follow the same steps as above
for activating a route, but select
“>Invert?” at the route action field.
· Press ENT to activate the route in
an inverted order.
6.4 EDITING ROUTES
Existing routes may be edited from the Route Definition Page.
To Edit an Existing Route...
· Press RTE and, if needed, the
RTE softkey to select the Route
Definition Page.
· Highlight the route number field
with the cursor and select the route
you wish to edit.
6-4
Page 49

· To insert a waypoint into the route:
highlight the waypoint you want to
place the new waypoint in front of,
type in the new waypoint identifier
and press ENT. The new waypoint
is added to the route.
· To delete a waypoint from the
route: highlight the waypoint you
wish to delete, press CLR and
ENT.
· If you attempt to add a waypoint to a route that already contains 30
waypoints, you will be informed with the message, “Route is Full”.
NOTE: You may also edit a route from the Active Route Page. (See Section
6.6.)
6.5 DELETING ROUTES
You may delete an unwanted route from the Route Definition Page.
To delete a route...
· Highlight the route number field
and select the route you wish to
delete with CLR.
· Highlight the route action field and
select “>Clear?” with the CLR key.
· Press ENT to delete the route.
6.6 ACTIVE ROUTE
Active Leg
Distance
Waypoint List Cyclic Column:
- ETE
- ETA
- DTK
The Active Route Page displays the waypoints of the active route starting
with the “active from” and “active to” waypoints on the top line. Press the
ACTV softkey to select this page.
6-5
Page 50

The waypoint list displays route waypoints starting with the “active to”
waypoint. For each waypoint, additional information is available. The first
column displays Distance (DIS). The second column is a cyclic field that
displays Estimated Time Enroute (ETE, in hours/minutes or minutes/seconds,
as appropriate), Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA), or Desired Track (DTK).
You may scroll through the waypoint list with the arrow keys.
To edit the active route...
· To insert a waypoint: highlight the waypoint you want to place the new
waypoint in front of, type in the new waypoint identifier and press ENT.
The new waypoint is added to the route.
· To delete a waypoint: highlight the waypoint you wish to delete, press
CLR and ENT.
6.7 ROUTE LIST
The Route List Page displays a list of all routes currently stored in memory.
Press the LIST softkey to select this page. The Route List Page displays the
route numbers (far left), beginning waypoint, and final destination waypoint.
You may also activate or delete a route from the Route List Page.
To Activate a Route...
· Highlight the route you wish to activate with the arrow keys.
· Press ENT. The Route Definition Page is displayed with the “>Activate?”
action highlighted.
· Press ENT to Activate the route.
To Delete a Route...
· Highlight the route you wish to delete using the arrow keys. Press
CLR. The Route Definition Page is displayed with the “>Clear?” action
highlighted.
· Press ENT to delete the route.
6-6
Page 51

CHAPTER 7
TM
The Autostore
AUTOSTORE
TM
function allows you to capture your position at the touch of
a button for future reference. This function saves your current position as a
waypoint. Additionally, you may record your navigation path by inserting the
captured waypoints directly into a route.
AUTO
STO
The Autostore
optional storage route. An Autostore
TM
Page displays the waypoint identifier, captured position and
TM
waypoint identifier is pre-assigned as
a three digit number. You may change this to any name you desire.
Autostore
TM
waypoints may be used for any waypoint operation and will be
part of the 500 available waypoints.
7.1 CREATING WAYPOINTS WITH AUTOSTORE
Captured
Position
TM
Waypoint
Identifier
Route Storage
Number
7-1
Page 52

You may capture and save your position as a waypoint, without adding it to
a route, by leaving the route storage number field blank.
To capture present position ...
· Press AUTOSTO. The pre-assigned waypoint identifier and captured
position are displayed. (NOTE: The AutostoreTM location is captured
as soon as you press AUTOSTO. This allows you all the time you need
to change the waypoint identifier and/or confirm the Autostore
TM
operation.)
· If you wish to assign a different identifier to the waypoint: move the
cursor to the waypoint identifier field, enter the name of your choice and
press ENT. If you enter a waypoint identifier already used, you will be
informed with the message, “WPT Exists _____” (where the blank will
be filled in with the waypoint identifier). Enter a different identifier if this
occurs.
· Press ENT on a blank route storage number field to save the waypoint.
(If the route storage number field is not blank, the waypoint will be
added to the route shown.)
7.2 BUILDING ROUTES WITH AUTOSTORE
The GPS 95’s Autostore
TM
feature may also be used to build a route as you
TM
are flying. During your flight; as you reach each airport, NAVAID, landmark,
or turn to a new heading; you may capture your position and add it to a route.
Once you reach your destination you can then invert the route and follow the
same course back to where you started. Or, you may want the route for future
reference if you wish to make the same flight again.
7-2
Page 53

To build a route with AutostoreTM...
· From the starting location, press AUTOSTO to capture the position.
(NOTE: The unit must me in 2D or 3D navigation mode when capturing
your starting position. If the unit is still acquiring satellites, and you
press AUTOSTO, the last known position will be captured and saved.)
· If you wish to assign a different identifier to the waypoint: move the
cursor to the waypoint identifier field, enter the name of your choice
and press ENT. If you enter a waypoint identifier already used, you will
be informed with the message, “WPT Exists _____” (where the blank
will be filled in with the waypoint identifier). Enter a different identifier
if this occurs.
· Select a route to store the waypoint in by highlighting the route storage
number field and pressing CLR until the desired route number is
displayed. If the selected route is not empty, the AutostoreTM waypoint
will be added to the end of the existing route. (HINT: Although the route
storage number field is a cyclic field, to speed selection you may also
enter the desired route number using the alphanumeric keys.)
· Press ENT to add the waypoint to the selected route.
· Repeat these steps each time you arrive at a location you wish to add
to the route, up to a total of 30 waypoints per route.
7-3
Page 54

CHAPTER 8
GPS STATUS AND AUXILIARY FUNCTIONS
The GPS 95 contains a vast array of functions, many of which you may
custom tailor to your preferences. Additionally, the unit can provide current
status information regarding the satellites being received and display
messages relevant to your current operations. You may select the desired
page by pressing PWR/STAT and, if needed, the appropriate softkey.
PWR
STAT
Bar Graph Display
Satellite Status Page
Auxiliary Menu
Satellite Skyview Page
8-1
Page 55

8.1 BAR GRAPH DISPLAY
The GPS 95 continually monitors the
status of the satellites it tracks and
shows that information graphically on a
Bar Graph Display. Satellite numbers
(1-32) are represented along the bottom
of the graph; signal strength (1 to 9,
weakest to strongest) is represented
along the side. Once a satellite is
received, a bar is displayed showing
signal strength for that satellite. If a satellite is visible, but not being received,
the signal strength will be blank.
The receiver status is also shown at the top of the page. In this example, the
unit is acquiring satellites. The following is a list of possible receiver status
messages:
“Searching the Sky” The GPS 95 is in the process of searching the
sky for visible satellites. You will also be
informed of this condition with a “Searching
the Sky” message.
“Acquiring Satellites” The GPS 95 is in the process of acquiring
visible satellites.
“2D Navigation” The GPS 95 is in the 2D navigation mode.
The unit will calculate a horizontal position,
but not altitude.
“3D Navigation” The GPS 95 is in the 3D navigation mode and
will calculate altitude
“Simulating Navigation” The GPS 95 is in the simulator mode. This
mode should be used only for practice and trip
planning. Never use this mode for actual
navigation.
“Poor Coverage” The GPS 95 is unable to acquire sufficient
satellites for navigation.
“Need Altitude” The GPS 95 needs altitude in order to start
and/or continue 2D navigation. Go to the
Present Position Page and enter the altitude.
(See Section 5.4.)
8-2
Page 56

“Not Usable” The GPS 95 is unusable (possibly due to
incorrect initialization data or abnormal satellite
conditions). Turn the unit off and back on.
When operating with an RTCM input
selected, the Bar Graph Display will
denote each satellite for which
differential corrections are available
with a “D” at the bottom of the bar.
(See Section 8.11 for more information
on RTCM input selections.)
Furthermore, the differential navigation
status will also display at the top of the
page. There are two additional receiver status messages available when
using an RTCM input:
“2D Nav - Diff”” The GPS 95 has calculated a differentially-
corrected horizontal position. Altitude has not
been corrected.
“3D Nav - Diff”” The GPS 95 has calculated a differentially-
corrected position, including altitude.
8.2 SATELLITE STATUS PAGE
The Satellite Status Page shows the ID,
azimuth, elevation, and signal quality of
each visible satellite in a table format.
The receiver status, again, is displayed
at the top of the screen. The second line
displays two system quality values dilution of precision (DOP) and estimated
position error (EPE). EPE and DOP are
advisory information only and are not to
be used as absolute measures of accuracy. (See Appendix B for definitions
of these terms.)
8-3
Page 57

8.3 SATELLITE SKYVIEW PAGE
The Satellite Skyview Page shows the
azimuth and elevation of each visible
satellite in a graphic sky view format.
Additionally, DOP and EPE values are
shown on the right hand side of the
page. The display is always oriented
“north up” and is useful in determining
whether a satellite signal is being
blocked by part of the aircraft, buildings,
mountains, or other obstructions. If a satellite is not currently being received,
it will be highlighted on the display.
8.4 AUXILIARY MENU
The GPS 95's auxiliary pages allow you
to do setup functions to customize your
unit and E6-B calculations to plan your
flight. The 13 auxiliary pages are
accessible from the Auxiliary Menu by
highlighting the page you want and
pressing ENT. Once an auxiliary page
is selected PREV, AUX, and NEXT page
options will be displayed. The softkeys
allow changing to previous (PREV) and next (NEXT) auxiliary pages. The
AUX softkey takes you back to the Auxiliary Menu. (HINT: The PREV and
NEXT softkeys will only select the auxiliary pages of the same type - setups
or E6-B calculations. To change between types you must return to the
Auxiliary Menu first.)
The following sections describe the function of each auxiliary page.
8.5 OPERATING MODE/FILTERS
From this page, you may change
between various operating modes by
highlighting the operating mode field
and pressing CLR. You may select
simulator mode, normal mode, or battery
saver mode. (See Section 1.4 for a
description of each mode.)
8-4
Page 58

Below the operating mode field is a reference waypoint field to define an initial
position. In simulator mode you may designate a starting point from which
the simulation will begin. In normal and battery saver modes, the initial
position may be defined to reduce satellite acquisition time.
To define an initial position...
· Select the desired operating mode by placing the cursor on the
operating mode field and pressing CLR.
· Press ENT to select the desired mode.
· Enter the identifier of the desired reference waypoint and press ENT.
· Enter the bearing from the reference waypoint to the desired location
and press ENT. The bearing will be true or magnetic depending on the
unit setups. (See Section 8.7.)
· Enter the distance from the reference waypoint to the desired location
and press ENT. The distance will be in nautical miles, statute miles or
kilometers depending on unit setups. (See Section 8.7.) (Hint: If a
distance of zero is entered, the initial position will be at the selected
reference waypoint.)
The Operating Mode/Filters Page also allows you to set position and velocity
filters. Changing the filter settings will alter the GPS 95's response time to
changes in track or ground speed. To change the filter settings, highlight the
appropriate field and cycle through the filter settings (automatic, fast,
medium or slow) with CLR. The “fast” setting will provide instantaneous
response (three seconds maximum response time) to changing conditions.
The “medium” (approximately 20 seconds) or “slow” (approximately 120
seconds) settings may be more desirable for slow speed operation where
frequent ground track changes will occur (e.g., sailing or hiking). It is highly
recommended that you select the “Automatic” setting for most applications.
8.6 TRACK LOG SETUP
The Track Log Setup Page is used to
configure the track log function. A
track log is a record of your flight path
showing where you have been up to
your present position. The cyclic fields
on line one allow you to turn the track
storage on or off, and determine how
the track log will be stored in memory.
8-5
Page 59

The track storing function may be turned on and off by highlighting the first
status field and pressing CLR. From the next field, the track may be set to
“wrap” around through available memory (deleting the oldest track information
and using the memory to store the new track position), or to “fill” available
memory and then stop. The amount of memory, used at any given moment,
is also displayed. When available memory is filled or the track is no longer
needed, it may be cleared by highlighting “Clear Track Log?” and pressing
ENT. If the “fill” option is selected, a “memory full” message will be displayed
when all available memory has been used and you must clear the track log
to store additional track information.
The ground track is stored at a frequency that you can define either by: Time
“Interval”, “Resolution”, or “Distance”. Select the desired frequency unit by
highlighting this field and pressing CLR.
To store the Ground Track at selected time Intervals...
· Highlight the recording criteria field (third line) and select “Interval” with
CLR.
· Press ENT.
· Enter the time interval between stored positions starting with hours,
then minutes, then seconds. Press ENT after entering data in each
numeric field.
To store the Ground Track by Distance...
· Highlight the recording criteria field and select “Distance” with CLR.
· Press ENT.
· Enter the distance, and press ENT. When your position moves this
distance in any direction, a new position is added to the stored ground
track. NOTE: “Distance” storage may be preferable to “Resolution”
storage if the ground track will include a large number of turns.
If the planned course will be primarily straight line travel, you should select
“Resolution” storage. In this application, considerably less memory is used
for the same distance traveled.
To store the Ground Track by Resolution...
· Highlight the recording criteria field and select “Resolution” with CLR.
· Press ENT.
8-6
Page 60

· Enter the resolution range, and press ENT. When your position moves
this defined range off a projected course line, a new position is added
to the stored ground track.
8.7 UNITS/HEADING SETUP
The Units/Heading Page is used to
select the units to display for position,
distance, speed and heading
information. Select the desired position
units by highlighting the “POSN” field
and pressing CLR. You may choose
between decimal degrees
(hddd.ddddd°); degrees and decimal
minutes (hddd°mm.mmm’); degrees, minutes and decimal seconds
(hddd°mm’ss.s”); UTM/UPS coordinates; or various other regional grids.
Select the desired distance, speed and altitude units by highlighting the
“NAV” field and pressing CLR. You may choose between nautical (nautical
miles/knots/feet), statute ( miles/miles per hour/feet), or metric (kilometers/
kilometers per hour/meters) units. (NOTE: The NAV units setting also
defines the pressure, temperature and vertical speed units that will be used
for E6-B calculations.)
Heading information can be displayed referencing magnetic north
(automatically calculated or user-defined), referencing true north or referencing
calculated grid headings. Select the desired heading reference by highlighting
the “HDG” field and pressing CLR. When the “Auto Mag Vari[ation]” option
is selected, heading information will reference the automatically calculated
magnetic variation shown. For most applications, the “Auto Mag” feature will
provide accurate heading information. If the auto-magnetic variation is not
correct, you may define the magnetic variation by selecting “User Mag Var”.
If the “User Mag Var” option is selected, the magnetic variation is then
entered.
To enter a user-defined magnetic variation...
· Highlight the “HDG” field and select “User Mag Var” with CLR.
· Press the right arrow key.
· The variation direction is highlighted. To change the direction, press
CLR.
· Press ENT.
· Enter the variation degrees and press ENT.
8-7
Page 61

8.8 ALARMS/CDI SETUP
From the Alarms/CDI Page, you may
define three alarms (and turn them on
or off) and configure the graphic CDI to
your preference. Alarms are available
for course deviation, arrival at a
destination waypoint, and an alarm
clock.
The CDI alarm will notify you with an alarm tone and the message “CDI
Alarm” if you have deviated off course beyond the limit that you set. (This can
be useful while flying in an airway or navigating a narrow channel.)
To set the CDI alarm...
· Highlight the CDI alarm distance field.
· Enter the maximum allowable course deviation distance.
· Press ENT.
· The on/off cyclic field is highlighted. If the alarm is not turned on, press
CLR.
The arrival alarm will inform you with an alarm tone and the message “Arrival
at ____” (where the blank is filled in with a waypoint identifier) when you reach
your destination. The alarm distance will also be used to inform you when
you approach a route waypoint with the message “Approaching ____”
(again, with the blank filled in by a waypoint name).
To set the arrival alarm ...
· Highlight the arrival alarm distance and enter the distance from a
destination at which you want the alarm to sound.
· Press ENT.
· The on/off cyclic field is highlighted. If the alarm is not turned on, press
CLR.
The GPS 95 also features an alarm clock which can provide an alarm tone
and the message “Alarm Clock” at a time that you specify.
8-8
Page 62

To set the alarm clock...
· Highlight the alarm clock time and enter the desired alarm time. NOTE:
The alarm time may be either UTC or local time depending on the
setting on the Date/Time Page. (See Section 8.9.)
· Press ENT.
· The on/off cyclic field is highlighted. If the alarm is not turned on, press
CLR.
The graphic CDI may be configured to the desired scale and steering
orientation. Scale settings of ±.25, 1.25, or 5.00 units (nautical miles, statute
miles, or kilometers) are available. The scale setting represents the distance
from center of the CDI to either end.
To set the CDI scale...
· Highlight the CDI scale field.
· Press CLR to select the desired scale.
The CDI “Steer To” orientation determines how you interpret the “D-Bar”
when it moves. You may select a “Steer to >Center” or “Steer to >D-Bar”
orientation. A “Steer to Center” orientation, in effect, displays your position
as the “D-Bar” and the center of CDI is the desired track. Thus, when you
are off course, you would steer towards the center of the scale. A “Steer to
D-Bar” orientation is just the opposite. The “D-Bar” represents the desired
track and the center of the scale represents your position. When you are off
course, you then steer towards the “D-Bar”. A “Steer to D-Bar” orientation
is the typical setting for aviation use and will make the GPS 95's graphic CDI
respond much like the CDI on your instrument panel.
To set the CDI orientation...
· Highlight the “steer to” field.
· Press CLR to select the desired orientation.
8-9
Page 63

8.9 DATE/TIME
The Date/Time Page displays the UTC
(Coordinated Universal Time,
Greenwich Mean Time or Zulu Time)
date and time. The local offset or time
difference is shown on the next line.
For time zones west of the UTC zone,
enter a negative offset. (HINT: The
minus sign is on the “9” key.) Appendix
E contains a list of time offsets.
The cyclic field for “Display” options determines which time, UTC or Local,
will be displayed on all other GPS 95 pages.
To display UTC or local time...
· Highlight the time display field.
· Press CLR to select the desired time reference.
The timer field can be selected as “Count Up” or “Count Down” by highlighting
and pressing CLR. This timer is useful for measuring the elapsed time since
a certain event, or it can tell you when a specified amount of time has expired.
To set the count up timer...
· Place the cursor on the timer option field.
· Press CLR to select “count up”.
· Press the right arrow key.
· Press CLR and ENT to clear the hours field.
· Press CLR and ENT to clear the minutes field.
· Press CLR and ENT to clear the seconds field. The count up timer will
begin counting the elapsed time.
8-10
Page 64

To set the count down timer...
· Place the cursor on the timer option field.
· Press CLR to select “count down”.
· Press the right arrow key.
· Enter the number of hours to count down from and press ENT.
· Enter the number of minutes to count down from and press ENT.
· Enter the number of seconds to count down from and press ENT. The
count down timer will begin counting down from the selected time.
8.10 AUDIO AND DISPLAY SETUP
From the Audio/Display Page you can
turn the message and/or keypad tones
on and off, change the display contrast
and change the time-out for the display
backlighting.
The tone option allows you to turn the
GPS 95's audio tone on or off as
desired. You may turn the keypad
feedback tone off, but leave the message tone on; have both tones on; or
have both tones off.
To turn audio tones on/off...
· Highlight the tone option field.
· Press CLR to select the desired option.
You may also adjust the contrast of the GPS 95 display to your preferences.
To change the display contrast...
· Highlight “Change Contrast?” and press ENT.
· The contrast bar is highlighted. Press the left or right arrow key to
change the contrast level.
· When the desired contrast level is reached, press ENT.
The backlighting time-out determines the length of time the display and
keypad backlighting will remain on. If no keys are pressed for the specified
time, the backlighting will automatically shut off to conserve battery power.
8-11
Page 65

To set the backlighting time-out...
· Highlight the backlighting time-out field.
· Enter the desired time for backlighting to remain on. If you wish to have
the backlighting on at all times, enter zero.
· Press ENT.
8.11 INTERFACE SETUP
From the Interface Page, you may
select the input and/or output format
needed to connect your GPS 95 to
other equipment: PC, NMEA device,
etc. You may select no input/output
(NONE/NONE), GARMIN input/output
(GARMIN/GARMIN), NMEA output
(NONE/NMEA), RTCM input/NMEA
output (RTCM/NMEA) or RTCM input
(RTCM/NONE).
When the NMEA output is selected a second cyclic field appears. From this
second field you may select the desired NMEA format: NMEA 0180, NMEA
0182, or NMEA 0183.
To select a NMEA output...
· Place the cursor on the input/output format field.
· Press CLR until the desired NMEA output option (NONE/NMEA or
RTCM/NMEA) is displayed.
· Press the right arrow key.
· Select the desired NMEA format by pressing CLR.
A second cyclic field also appears
when the GARMIN input/output is
selected. The GARMIN option allows
you to exchange data such as
waypoints, routes, track logs and
satellite almanac data with another
GPS 95 or with a PC-compatible
computer. You may select between
acting as a host to data exchanges (Host), requesting data (Req) or sending
data (Send). During the data transfer process the number of data packets
being exchanged will be displayed.
8-12
Page 66

To select GARMIN input/output...
· Place the cursor on the input/output format field.
· Press CLR until the GARMIN input/output option is selected.
· Press the right arrow key.
· Select “Host”, “Req[uest]”, or “Send” by pressing CLR. (NOTE: You
should select the “Host” option when using the GPS 95 with a PC.
When exchanging data between two GPS 95s, one should be set to
“Host” and the second should be set to the desired data transfer option
- “Req[uest]” or “Send”.)
The GPS 95 can use Differential GPS
(DGPS) corrections in RTCM SC-104
version 2.0 format. DGPS corrections
in this format can be received from an
external device (capable of output in 6
to 8 byte format as specified by RTCM
SC-104 version 2.0) by connecting the
device to the input port on the back of
the GPS 95 and selecting an RTCM input interface mode. Two RTCM input
modes are available; one which allows no output and another which allows
NMEA output in 0180, 0182, or 0183 format.
To select an RTCM input...
· Place the cursor on the input format field.
· Press CLR until the desired RTCM input option (RTCM/NONE or
RTCM/NMEA) is displayed.
· Press the right arrow key.
· If RTCM/NONE is selected: Press CLR to select the appropriate baud
rate.
· If RTCM/NMEA is selected: Press CLR to select the desired NMEA
output format. (NOTE: With RTCM/NMEA selected the RTCM baud
rate is automatically set to 1200 or 4800.)
If the RTCM input is selected, but the GPS 95 is not connected to an RTCM
device, the unit will alert you with the message “No RTCM Input”. If the GPS
95 does not receive sufficient data to compute a DGPS-corrected position,
the message “No DGPS Position” will appear.
8-13
Page 67

8.12 MAP DATUM SELECTION
Select the desired map datum
reference from the Map Datum Page.
You may choose from 102 pre-defined
map datums, or you may define your
own. If the sectional/chart you are
using specifies a reference datum,
select that datum on your GPS 95. If
the sectional/chart does not specify a
reference datum, you may select each datum applicable to your region until
you find the datum that provides the best positioning at a known point. NOTE:
The GPS 95 is shipped from the factory with the WGS 84 datum selected.
To change the pre-defined datum...
· Highlight the “Change?” field and press ENT.
· With the arrow keys, find the desired datum and highlight it.
· Press ENT. The new datum is selected.
The user-defined datum option allows
you to custom-tailor a datum reference
from which all position coordinates are
calculated. All entries are defined as
differences from the WGS 84 standard
datum. (CAUTION: Selection and
use of the user datum function is for
individuals experienced in the use of
map datums. If the pre-defined map
datums do not correspond to the chart you are using and you are unsure of
the correct entries required to correspond to that chart, contact the chart
manufacturer. Incorrect entries for a user-defined datum may result in
substantial position errors.)
To define a user datum...
· Place the cursor over the cyclic field on line one.
· Press CLR to select “User-defined”.
· Enter the 5 parameters of the user map datum. The sign of the
parameters should follow the convention: WGS 84 - local geodetic
system.
8-14
Page 68

8.13 MESSAGES
You may recall from Section 2.6 that
some messages will remain on the
Message Page after being viewed.
When this occurs, the “MSG”
annunciator remains on (but does not
flash) in the lower left corner. To view
these messages, select “Messages”
from the Auxiliary Page. (See
Appendix A for a description of
available messages.)
8.14 DENSITY ALTITUDE/TRUE AIRSPEED/WINDS ALOFT
The GPS 95 provides density altitude,
true airspeed (TAS) and winds aloft
calculators for your convenience. The
density altitude and TAS calculations
will help you determine critical aircraft
performance data.
To calculate density altitude and true airspeed...
· Place the cursor on the indicated altitude (IAlt) field.
· Enter the indicated altitude from your altimeter and press ENT.
· Enter your calibrated airspeed (CAS) and press ENT. If you do not
know your calibrated airspeed, use indicated airspeed instead.
· Enter your current altimeter setting and press ENT.
· Enter the total air temperature (TAT). The GPS 95 will display the
resulting density altitude and true airspeed. (NOTE: TAT is the
temperature of the air including the heating effect caused by speed.
The temperature read on a standard outside air temperature gauge
found in most piston aircraft is TAT.)
The winds aloft calculation determines the direction (true) and speed of the
wind. This calculation requires TAS and heading information. If you have
already calculated density altitude and TAS, the TAS value will be used for
the winds aloft calculation; otherwise you may enter the correct TAS value.
8-15
Page 69

To calculate winds aloft...
· If you have not already calculated TAS: place the cursor over the TAS
field, enter the correct true airspeed and press ENT.
· Place the cursor over the heading (Hdg) field.
· Enter the current heading (magnetic) from your heading indicator and
press ENT. The GPS 95 will display the wind direction, speed, and the
head/tail wind you are encountering.
8.15 SUNRISE/SUNSET PLANNING
The Sunrise/Sunset Page allows you
to calculate the sunrise and sunset
times for a given waypoint location on
a selected date (from the year 1990
through 2089).
To calculate the sunrise/sunset times for a waypoint...
· Highlight the waypoint name field and enter the desired waypoint
name.
· Press ENT.
· The date field is highlighted. Enter the day, then month, then year to
calculate the sunrise/sunset times for. Press ENT on each
alphanumeric/numeric field.
· Once the year is selected and ENT is pressed, the calculated sunrise
and sunset times will be shown. Please note that the times shown will
be either UTC or local depending on the selection made on the Date/
Time Page. (See Section 8.9.)
8-16
Page 70

8.16 TRIP AND FUEL PLANNING
The Trip and Fuel Planning Page allows
you to calculate time and fuel
requirements between any two
waypoints or for any programmed
route. On the first cyclic field, you will
choose between waypoint (WPT) or
route (RTE) planning by highlighting
and pressing CLR. If route planning is
selected, you would then select the desired route number and the portion of
the route (a given leg or all of the route) to calculate for.
The final step is to enter speed and fuel flow rates. The GPS 95 will then
calculate the desired track (DTK), fuel requirements (REQ), distance (DIS),
and estimated time enroute (ETE).
To perform a trip and fuel plan, waypoint to waypoint...
· Highlight the first cyclic field (top
left), and press CLR to select
“WPTS:”.
· Highlight the waypoint name field
(second line), and enter the first
waypoint name followed by ENT.
· The second waypoint name field is
now highlighted. Enter the second
waypoint name followed by ENT.
· The speed (SPD) field is highlighted. Enter the planned speed, and
press ENT.
· The fuel flow (Flow) field is highlighted. Enter the estimated fuel flow
followed by ENT.
· The GPS 95 will now display the calculated figures.
8-17
Page 71

To perform a trip and fuel plan for a route...
· Highlight the first cyclic field (top
left) and select “RTE” with CLR.
· Highlight the next cyclic field and
select the desired route number by
pressing CLR.
· Highlight the “Leg>” field and select
the desired leg, or select “All” for the
entire route, using CLR.
· Highlight the “SPD:” field and enter the planned speed, followed by
ENT.
· Highlight the “Flow:” field and enter the estimated fuel flow followed by
ENT.
· The GPS 95 will now display the calculated figures.
NOTE: When “all” is selected, no desired track (DTK) will be shown since
this value only applies to an individual leg.
8.17 VERTICAL NAVIGATION PLANNING
8-18
Page 72

Pilots will find the GPS 95's vertical
navigation (VNAV) function useful for
calculating vertical speed
requirements. In order to use the
VNAV feature, aircraft ground speed
must be greater than 35 knots.
To calculate vertical speed requirements...
· Place the cursor on the initial (Frm) altitude field.
· Enter the initial altitude and press ENT.
· Enter the final (To) altitude and press ENT.
· Enter the offset distance, from the desired waypoint, at which you will
reach your final altitude. Press ENT.
· Select “Before” if the offset is before the waypoint, or “After” if the offset
is beyond the waypoint, by pressing CLR.
· If an active route is being used: press CLR to select the route waypoint
to which the offset applies.
· You now have defined how far before, or after, the indicated waypoint
you wish to be at the final altitude. The GPS 95 will display the required
vertical speed.
To activate the VNAV function...
· Review the calculated vertical speed. If you wish to change the vertical
speed: place the cursor on the vertical speed (At) field, enter the
desired vertical speed and press ENT.
· Place the cursor over the “VN” field.
· Press CLR to turn the VNAV function on. The VNAV status on the
bottom line will change from “Enter VNAV Profile” to “Begin at _____”
(with the blank indicating how long before the maneuver should begin),
or “Navigating” if the VNAV maneuver is already in progress. You will
be informed with the message “Start Altitude Change” when you are
less than 15 seconds from the point at which the VNAV maneuver is
to begin.
8-19
Page 73

When VNAV is active, this page will recommend the altitude and vertical
speed required to complete the maneuver. Remember that these are only
recommendations. You will be informed with the message “Final Altitude
Alert” when the recommended altitude is within 1000 feet of the final altitude.
The VNAV function will be cancelled automatically if the active route (or
GOTO) is changed in any way (e.g., setting a new GOTO destination or
adding a waypoint to a route). You will be informed with the message “VNAV
Cancelled” if this occurs. If the aircraft ground speed does not exceed 35
knots, or a route waypoint that has already been passed is selected, the GPS
95 will display an “Invalid profile” status on the bottom line. The GPS 95 will
display “No Active Waypoint” on the bottom line if no route, or GOTO
destination, has been activated.
WARNING: Altitude and climb rate should be controlled only by the pilot in
command with due regard for airspeed and other aircraft performance
limitations.
8-20
Page 74

CHAPTER 9
SAMPLE TRIP USING ROUTES
Now that you have gained a basic understanding for your GPS 95, you are
ready to explore the route capabilities of this unit. The sample illustrations
in this chapter assume that the factory default settings have not been
changed. If you have changed these parameters the unit may display slightly
different data than presented here.
You are planning a trip from St. Petersburg, Florida to the Dry Tortugas and
then on to Key West, Florida . Turn on the GPS 95 to begin this sample trip.
St. Petersburg
(KPIE)
Dry Tortugas
(DRYTG)
Key West
(KEYW)
9-1
Page 75

The welcome screen is displayed and
the GPS 95 performs several self tests.
After about five seconds the Satellite
Bar Graph Page is displayed and the
GPS 95 will begin acquiring satellites.
Since this is a simulated trip you do not
need to wait for the GPS 95 to acquire satellites. You will set the operating
mode to “simulator” and define the starting location (St. Petersburg).
Setting the simulator mode and initial position...
Select the Auxiliary Menu by pressing
ABC
1
the AUX softkey (the “1” key in this
case).
9-2
Press the right arrow key to place the
cursor over “op mode” and press ENT.
ENT
The Operating Mode Page is displayed
Page 76

CLR
*Press repeatedly until
“Simulator” is displayed
ENT
showing the current operational mode.
Press the right arrow to place the cursor
on the operational mode field.
Press CLR (repeatedly) until
“Simulator?” is displayed.
Press ENT to select simulator mode.
The cursor is on the reference identifier
field. Set the initial position by entering
the identifier for St. Petersburg, Florida
(KPIE).
JKL
4
PQR
6
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric and arrow
keys, if needed, to enter
the waypoint identifier
ENT
Press the “4” key to select the letter
“K”.
Press the “6” key followed by the left
arrow key to select the letter “P”.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
and, if needed, arrow keys until the
waypoint identifier has been entered.
Press ENT when complete.
The Waypoint Definition Page is
9-3
Page 77

CLR
*If needed to select
proper hemisphere
ENT
DEF
2
STU
7
ENT
displayed indicating that the position
coordinates for St. Petersburg, Florida
(KPIE) are not known.
Enter the latitude for KPIE (N27°
54.646'). Begin by selecting the proper
hemisphere. If “N” for north is not
displayed, press CLR.
Press ENT when the proper
hemisphere is selected.
Enter the latitude degrees. Press the
“2” key and the “7” key. Press ENT
when complete.
9-4
MNO
5
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric keys to
enter the latitude minutes
ENT
Enter the latitude minutes. Begin by
pressing the “5” key.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
keys until the latitude minutes have
been entered. Press ENT when
complete.
Enter the longitude of KPIE (W82°
Page 78

*Enter the longitude using
the same steps shown
ENT
above
ENT
41.244') in the same manner as was
used for the latitude. Press ENT once
data is entered into each field.
Press the right arrow key twice to
place the cursor on “USE?” and press
ENT.
Since the trip will begin at St.
Petersburg, there is no need to define
a reference bearing from this waypoint.
Press ENT.
ENT
ENT
Enter a distance of zero and press
ENT.
0
9-5
Page 79

Before you begin the trip, all waypoints used along the route must be in
memory. The location for St. Petersburg was just created when the initial
position was set. The position coordinates for the Dry Tortugas (DRYTG)
and Key West (KEYW) must still be entered. Below are the identifiers and
locations for waypoints used in this sample trip:
Indent Latitude Longitude
KPIE N27°54.646' W082°41.244'
DRYTG N24°38.430' W083°08.301'
KEYW N24°33.370' W081°45.574'
Creating the “DRYTG” and “KEYW” waypoints...
WPT
*Plus WPT softkey, if
needed
DEF
2
PQR
6
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric and
arrow keys, if needed,
ENT
to select waypoint
identifier
Press WPT and the WPT softkey, if
needed, to select the Waypoint
Definition Page.
Press the right arrow key to place the
cursor on the waypoint identifier field.
Enter the waypoint identifier, DRYTG,
using the alphanumeric and arrow
keys. Begin by pressing the “2” key,
followed by the left arrow, to select the
letter “D”.
Press the “6” key, followed by the right
arrow, to select the letter “R”.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
and, if needed, arrow keys until the
waypoint identifier has been entered.
Press ENT when complete.
9-6
Page 80

CLR
*If needed to select
proper hemisphere
Enter the latitude of DRYTG
(N24°38.430'). Begin by selecting the
proper hemisphere, If “N” for north is
not displayed, press CLR.
ENT
DEF
2
JKL
4
ENT
GHI
3
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric keys to
enter the latitude
minutes
ENT
Press ENT when the proper
hemisphere is selected.
Enter the latitude degrees. Press the
“2” key and the “4” key. Press ENT
when complete.
Enter the latitude minutes. Begin by
pressing the “3” key.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
keys until the latitude minutes have
been entered. Press ENT when
complete.
9-7
Page 81

*Enter the longitude
using the same steps
shown above
ENT
Enter the longitude of DRYTG
(W083°08.301') in the same manner
as was used for the latitude. Press
ENT once data is entered into each
field. (NOTE: You do not need to
enter the leading zero for degrees or
minutes. In both cases you may begin
by pressing the “8” key.)
Press the right arrow key three times
to place the cursor on the waypoint
identifier field.
ENT
*Enter KEYW waypoint
using same steps as
above for DRYTG
Enter the Key West (KEYW) waypoint
and its coordinates (N24° 33.370' W81°
45.574') using the same steps used to
create DRYTG. Press ENT after data
is entered into each field.
This trip will take you to an intermediate destination (Dry Tortugas) and then
a final destination (Key West). You could go to each destination using the
GOTO function as described in Chapter 4. (Select GOTO DRYTG, then,
upon reaching DRYTG, select GOTO KEYW.) However, for this sample trip,
the route capabilities of the GPS 95 will be utilized.
9-8
Page 82

To create the sample route...
RTE
*Plus RTE softkey, if
needed
CLR
Press RTE and the RTE softkey, if
needed, to select the Route Definition
Page.
Press the right arrow to place the
cursor on the route number field.
Press CLR to select route 1. Notice
that the route is empty; it does not
contain any waypoints. (If route 1 is
not empty, select a different route.)
JKL
4
PQR
Press the right arrow key twice to
place the cursor on the first waypoint
identifier field.
Enter the identifier for St. Petersburg
(KPIE). Begin by pressing the “4” key
to select the letter “K”.
6
Press the “6” key, followed by the left
arrow key, to select the letter “P”.
9-9
Page 83

*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric and
arrow keys, if needed,
ENT
to enter the waypoint
identifier
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
and, if needed, arrow keys until the
waypoint identifier is added to the route.
Press ENT when complete. The cursor
is on the second waypoint identifier
field.
*Enter the next
waypoint identifier
ENT
using the alphanumeric
keys
*Enter the next
waypoint identifier
ENT
using the alphanumeric
keys
Enter the identifier for the Dry Tortugas
(DRYTG) using the alphanumeric and
arrow keys. Press ENT when
complete. The cursor is now on the
third waypoint identifier field.
Enter the identifier for Key West
(KEYW) using the alphanumeric and
arrow keys. Press ENT when
complete. The Route Definition Page
should now appear as illustrated.
As you see, you have just created a route that will take you from St.
Petersburg, over the Dry Tortugas and on to Key West. Once activated, the
GPS 95 will calculate navigation data based on the route.
9-10
Page 84

To activate the sample route...
*Continue pressing until
“Activate” is highlighted
Press the right arrow key until
“Activate?” is highlighted. (If
“Activate?” is not displayed on this
field, you may select it by pressing
CLR.)
ENT
Press ENT to activate the route. The
Active Route Page is displayed. This
page displays the “active from” and
“active to” waypoints on line one, as
well as distance and time information
to each waypoint on the following lines.
The time information is blank since
you are not moving yet.
In order to animate the GPS 95's displays you will need to enter a simulated
speed.
To set the simulated speed...
*Plus NAV softkey, if
NAV
needed
Press NAV and the NAV softkey, if
needed, to select the Navigation
Summary Page.
Press the left arrow key to highlight the
ground speed field.
9-11
Page 85

ABC
1
*Continue pressing the
alphanumeric key to
enter the ground speed
ENT
Enter a ground speed of 150 knots.
Begin by pressing the “1” key.
Continue pressing the alphanumeric
keys until the ground speed has been
entered. Press ENT when complete.
The simulation velocity is now set.
The Navigation Summary Page will
indicate distance, speed, track, bearing
and CDI information. Notice the
distance is now decreasing as you fly
towards the Dry Tortugas!
As your flight progresses, you can monitor the nearest waypoints at any time.
This feature can be particularly valuable in the event of an in-flight emergency.
To view the nearest waypoints...
Press the WPT key and the NRST
WPT
*Plus NRST softkey, if
needed
softkey, if needed, to select the Nearest
Waypoint Page.
Up to six nearest waypoints are
instantly displayed along with bearing
and distance to each waypoint.
9-12
Page 86

In an actual emergency you could instantly plot a course to a nearest
waypoint by highlighting the desired waypoint (using the arrow keys),
pressing GOTO and ENT. The GPS 95 would override the route and provide
navigation information to direct you to the selected waypoint.
Experiment with your GPS 95!
· Now that you have started on a trip to the Dry Tortugas, why don't you
take some time to experiment with the GPS 95? Press each function
key to get familiar with the available pages. Examine the Active Route
Page and the Navigation Summary Page as the simulation progresses.
If you want, change the simulation speed. You won't break the GPS
95 even if you enter a speed of 999 knots.
· As you progress through the simulation, the GPS 95 will alert you with
a message when you are within one minute of reaching the Dry
Tortugas. When passing DRYTG, the GPS 95 will automatically
sequence to the next waypoint, KEYW.
· At some point during the simulation you may wish to try the GOTO
function. Suppose severe weather was reported in the Dry Tortugas
area. You wish to shorten your trip by heading directly to Key West.
Simply press the GOTO key and enter KEYW. The GPS 95 will set an
instantaneous course and you are on your way to Key West.
· If you have not customized your unit, this may be a good time to review
Chapter 8 for information concerning custom settings. Doing so will
help you understand what each setting will do.
· If you wish to stop the simulation, simply turn the GPS 95 off. We
recommend that you delete the route and waypoint created in this
simulation prior to using your unit again. (See Section 3.3 for
information on deleting waypoints and Section 6.5 for information on
deleting routes.)
9-13
Page 87

APPENDIX A
MESSAGES
The GPS 95 uses the Message Page to communicate important information
to you. Some messages are advisory in nature, others are warnings that may
require your intervention. This appendix provides a complete list of messages
and their meanings. Please pay careful attention to all messages.
Alarm Clock - The alarm time for the alarm clock has been reached.
Approaching ____ - You are less than one minute from reaching the
indicated waypoint.
Arrival at ____ - Your craft has entered the arrival alarm circle for the
indicated destination waypoint.
Battery Low - The battery pack is low on power. AA batteries should be
replaced or the rechargeable battery pack should be recharged for continued
operation.
Can't Chng Activ WPT - An attempt has been made to modify the position
of the “active to” or “active from” waypoint. The GPS 95 will not allow the
modifications.
CDI Alarm - Your course deviation has exceeded the limit that you specified
on the Alarms/CDI Page.
Degraded Accuracy - The accuracy of the GPS 95 position is degraded
beyond 500 meters due to satellite geometry or data quality. Additional cross
checking should be performed by the user to verify the integrity of the GPS
position.
Final altitude alert - The suggested VNAV altitude is within 1000 feet of the
final altitude entered on the VNAV Page.
Leg Not Smoothed- The upcoming leg is too short for smooth waypoint
transitions. Expect a rapid change in the CDI.
Memory Battery Low - The battery that sustains user memory is low and
should be replaced by an authorized GARMIN service center as soon as
possible. Failure to do so may result in loss of stored data, including all
waypoints and routes.
A-1
Page 88

Need Altitude - The GPS 95 needs altitude to start and/or continue 2D
navigation. Press NAV and enter your current altitude. The altitude you enter
should be as accurate as possible. An inaccurate altitude will result in an
inaccurate position and navigation information.
No DGPS Position - An RTCM input has been selected, but not enough
DGPS data is available to calculate a corrected position.
No RTCM Input - An RTCM input has been selected, but no data is being
received or the input data is in the wrong format.
Osc Needs Adjustment - The GPS 95 has detected excessive drift in its
internal crystal oscillator which may result in longer acquisition time. The unit
should be taken to an authorized GARMIN service center as soon as
possible.
Poor GPS Coverage - The GPS 95 cannot acquire sufficient satellites
necessary to provide navigation.
Pwr Down and Re-init - The GPS 95 is unable to compute a position due
to abnormal satellite conditions. Power down the unit and verify that the
position on the Position Page is within a few degrees of your actual position.
Prox Alarm ____ - Your craft has penetrated the alarm circle of a proximity
waypoint.
Proximity List Full - An attempt has been made to add more than nine
waypoints to the proximity list. The GPS 95 will not allow more than nine
proximity waypoints.
Proximity Overlap - The circles defined by two proximity waypoints overlay.
When entering the area of the overlap, the GPS 95 will alert you of the closest
proximity waypoint, but not both. You should be certain this condition is
desirable.
Proximity Waypoint - An attempt has been made to delete a waypoint for
which a proximity alarm has been defined. You must remove the waypoint
from the proximity list before the waypoint can be deleted.
Received Invalid Wpt - A waypoint was received in an upload/transfer
operation that has an invalid identifier or position.
Receiver Failed - The GPS 95 has detected a failure in the receiver
hardware. If the message persists, the GPS 95 is unusable and should be
taken to an authorized GARMIN service center.
A-2
Page 89

ROM Failed - The GPS 95 has detected a failure in its permanent memory.
If this message occurs, the unit is unusable and should be taken to an
authorized GARMIN service center.
Route is Full - An attempt has been made to add more than 30 waypoints
to a route. The GPS 95 will not allow more than 30 waypoints per route.
Route Not Empty - An attempt has been made to copy a route to a nonempty route. The GPS 95 will not allow you to copy a route to a non-empty
route.
Route Waypoint - An attempt has been made to delete a waypoint which is
a member of one or more routes. You must remove the waypoint from all
routes before the waypoint can be deleted.
RTCM Input Failed - The GPS 95 was receiving RTCM inputs, but the data
signal has been interrupted.
Searching the Sky - The GPS 95 is in the search-the-sky mode. Allow the
unit to complete its data collection before turning it off. This process takes
approximately 15 minutes.
Start altitude chng - The altitude change entered on the VNAV Page is
about to begin.
Steep Turn Ahead - This message appears approximately one minute prior
to a turn that requires a bank angle in excess of 25 degrees in order to stay
on course.
Stored Data Lost - Stored user data, including waypoints, routes, and
satellite orbital data has been lost due to a low memory battery.
Timer Expired - The count down timer has expired.
Track Memory Full - The track memory is full. Go to the Track Log Setup
Page to clear the memory.
Transfer Completed - Data transfer operations are complete.
VNAV cancelled - The VNAV function has been cancelled due to a change
in the active route.
WPT Exists ____ - You have entered a waypoint name on the AutoStore
TM
Page that already exists in memory. Enter a waypoint name that does not
exist.
WPT Memory Full - The waypoint memory is full. You should delete unused
waypoints to make room for new waypoints.
A-3
Page 90

APPENDIX B
GLOSSARY AND NAVIGATION TERMS
B.1 DEFINITIONS
This section provides an illustration of and definitions for the terms used in
this manual.
B-1
Page 91

Velocity/time terms:
GS Ground speed. GS is the speed measured relative to a ground
position; also known as velocity over ground (VOG).
ETA Estimated time of arrival. ETA is the estimated time you will reach
the “active to” waypoint based on current GS. This time is selectable
as either UTC or local.
ETE Estimated time enroute. ETE is the time it will take to reach the
“active to” waypoint based on current GS.
Direction terms:
DTK Desired track. DTK is the course between the “from” and “to”
waypoints. In the case of the GOTO function, the “from” waypoint
is the location at which the GOTO function was activated.
BRG Bearing. BRG is the direction from your present position to the
“active to” waypoint.
CTS Course to steer. CTS is the recommended direction to steer in order
to reduce cross track error and stay on course. (See Section B.2 for
an example using CTS.)
TRK Track. TRK is the direction of movement relative to a ground
position.
TRN Turn angle. TRN is the difference between BRG and TRK. “L”
indicates you should turn to the left, “R” indicate you should turn to
the right. The degrees indicate the angle you are off course.
Distance terms:
DIS Distance. DIS is the great circle distance from your position to the
“active to” waypoint.
XTK Crosstrack. XTK is the cross track error, or distance that you are off
course. If the crosstrack error exceeds the CDI scale setting, the
XTK distance will also be displayed on the appropriate side of the
CDI.
V VNAV altitude. V is the recommended altitude at which you should
be in order to accomplish a VNAV maneuver. This information is
only available when the VNAV function has been activated.
B-2
Page 92

Satellite terms:
DOP Dilution of precision. DOP is a measure of the satellite geometry
quality and hence the relative accuracy of your position (one
meaning the best and ten meaning poor).
EPE Estimated position error. EPE, which is computed using the satellite
geometry (DOP), signal and data quality, receiver tracking status
and other factors, is an overall measure of your position accuracy.
B.2 COURSE TO STEER (CTS)
Course To Steer is a GARMIN exclusive that recommends an optimal
direction to steer that will guide you to the course and proceed efficiently
along your route.
B-3
Page 93

As an example, suppose you activate the route illustrated above. The GPS
95 chooses the closest leg with a desired track of 45 degrees but your
position happens to be two nautical miles off course. The unit will automatically
compute the optimal course to steer (which is due north in this example).
Press the NAV key until the Nav Summary Page is displayed, then select
“CTS” on the first cyclic field. Using the CTS direction (000°), turn so that the
track (TRK) and CTS direction match.
As you approach the course, CTS will slowly change and, once on course,
will be identical to the desired track.
B-4
Page 94

APPENDIX C
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
C.1 SPECIFICATIONS
GPS 95 SPECIFICATIONS
—————————————————————————————-
PHYSICAL
Case: Waterproof
Size: Portable: 3.23"w x 6.26"h x 1.46"d
(82mm x 159mm x 37mm)
Fixed: 3.23"w x 4.87"h x 1.46"d
(82mm x 124mm x 37mm)
Weight: 14 ounces (0.4 kg) without battery pack 19
ounces (0.54 kg) with battery pack
POWER
Input Alkaline battery pack (4 AA size)
Rechargeable battery pack (Optional)
12 or 24 volt DC with power cable (5-40 VDC)
115 or 230 volt AC with AC Adapter
*
Consumption 1.6 watts in Normal mode (without backlighting)
ENVIRONMENTAL
Temperature: -15°C to +70°C (+5°F to +158°F ) operating
-40°C to +70°C (-40°F to +158°F) storage
Humidity: 95% non-condensing
PERFORMANCE
Receiver: MultiTracTM, tracking up to 8 satellites
Frequency: L1, 1.57542 GHz
Acquisition Time: 2 minutes 2D
(typical) 2.5 minutes 3D
15 seconds Warm Start (with ephemeris)
C-1
Page 95

Update Rate: Once per second, continuously
Accuracy: Position: 15 meters (49 ft) RMS
Velocity: 0.1 knots RMS steady state
Dynamics: 999 knots velocity, 3g dynamics
INTERFACES
NMEA 0180
NMEA 0182
NMEA 0183 (Version 1.5; December 1987)
Approved sentences:
GPBWC, GPGLL, GPRMB, GPRMC, GPR00, GPWPL, GPXTE
Proprietary sentences:
PGRMZ
Transmission rate:
GPBWC, GPGLL, GPRMB, GPRMC, GPXTE, and PGRMZ
transmitted once every two seconds.
GPR00 transmitted once every (# of all waypoints + 1) * 2
seconds. For example, if there are two route waypoints, this
sentence will be transmitted once every six seconds.
**
GPWPL transmits all route waypoints in (# of route waypoints + 1)
* 2 seconds. For example, if there are two route waypoints, this
sentence will be transmitted twice every six seconds.
—————————————————————————————-
NOTES:
* All specifications are subject to change without notice.
** Subject to accuracy degradation to 100m 2DRMS under the United
States Department of Defense imposed Selective Availability program.
(Due to satellite geometry, altitude error is typically two to three times
the horizontal position error.)
C-2
Page 96

C.2 ELECTRICAL WIRING
The GPS 95 power/data cable allows you to connect the unit to vehicle power
systems, other electronics, and a remote alarm/beeper. The power/data
cable has a 7-pin intermediate connector to facilitate quick disconnection of
all electrical connections and easy removal of the entire yoke mount from the
aircraft. The GPS 95 is supplied with two wire harnesses: one with a cigarette
lighter plug for temporary use and the other for permanent wiring. The figures
below illustrate the two wiring options.
OR
To connect to vehicle power systems...
· Connect the RED harness lead (with fuse) to the positive (+) side of a
5-40 volt DC power source.
· Connect the BLACK harness lead to the negative (-) side of the 5-40
volt DC power source.
The GPS 95 will drive a remote alarm or relay that requires no more than 100
milliamps of current. (WARNING: Devices which draw current in excess of
100 milliamperes may damage your unit and will void your warranty. Consult
the instructions included with the remote alarm or relay for current drain
information.)
C-3
Page 97

To connect to a remote alarm system...
· Connect the BLUE harness lead to the negative side of a transistor
alarm or relay switch.
· Connect the positive side of the alarm or relay to the positive side of
the 5-40 volt DC power source.
The GPS 95 may be connected to a PC-compatible computer using a NMEA
0183 data interface or to marine electronics such as an autopilot or plotter
which use an N MEA 0180, NMEA 0 182 or NMEA 0183 data interface. The unit
can provide data for up to three NMEA “listeners” simultaneously. Refer to
installation instructions of these devices for further information.
To connect the GPS 95 to an NMEA electronic device...
· Connect the BROWN harness lead to the NMEA “A” line of a two-wire,
shielded cable.
· Connect the BLACK harness lead to the NMEA “B” line of the shielded
cable.
· Connect the BLACK harness lead to the shield of the shielded cable.
(The opposite end of the shield should not be grounded.)
C.3 YOKE MOUNT INSTALLATION
The GPS 95 is equipped with a yoke mount which can quickly be attached
to the control yoke for easy access and visibility without blocking the view of
the instrument panel. The yoke mount can quickly be detached and stowed
in the carrying bag along with the GPS 95 radio and any other accessories
you might wish to take with you. The clamp that comes with the standard
yoke mount will fit the control yoke of more than 90% of general aviation
aircraft. If the standard clamp will not fit your aircraft, call our toll-free product
support number to exchange for the proper type of clamp for your aircraft.
Generally, the standard clamp will not fit the following: Bonanza/Baron,
Commanche, large Piper twins, and some other large Beech models.
The GPS 95 can also be fix mounted to a surface using the surface mount.
Before permanent mounting, you may wish to apply power to the unit and
look at the display in the desired mounting location to ensure you have the
desired viewing angle.
C-4
Page 98

To attach the yoke mount to the control yoke...
· Loosen the lower knob.
· Slide the clamp over the control yoke shaft just behind the control
wheel.
· Tighten the lower knob securely.
· Make sure that the clamp is as close as possible to the control wheel
and check to make sure that the yoke travel is not limited or
hindered in any way by the yoke mount.
To adjust the yoke mount viewing angle...
· Loosen the upper knob.
· Rotate the bracket up or down on the ratchet.
· Tighten the upper knob securely.
C-5
Page 99

The yoke mount is designed to allow the GPS 95 to be installed either with
or without the battery pack attached.
To adjust the yoke mount to accept the GPS 95 with the battery pack
attached...
· Loosen the coinslot screw.
· Lower the cradle to its lowest position.
· Tighten the coinslot screw. When adjusted properly, the coinslot
screw should fit completely into the counterbore in the cradle so that
all surfaces are flush.
C.4 YOKE MOUNT OPERATION
The yoke mount has been designed for easy insertion and removal of your
GPS 95 if you wish to use the unit in another airplane or vehicle, to plan at
home, or to prevent theft.
C-6
Page 100

To insert the GPS 95 into the yoke mount...
· Tilt the top of the GPS 95 into the yoke mount as shown.
· Engage the slot in the top of the GPS 95 into the raised bump in the
yoke mount bracket.
· Rotate the bottom of the GPS 95 into the yoke mount until the unit
latches securely into place.
· Connect the antenna or antenna cable. No other electrical connections
are required; all power and data connections are made through the 6pin connector mounted in the yoke mount bracket.
To remove the GPS 95 from the yoke mount...
· Disconnect the antenna or antenna cable.
C-7
 Loading...
Loading...