Page 1

Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe
User Guide
SK-91F467D-208PFV
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
MB91460 SERIES
EVALUATION BOARD
USER GUIDE
Page 2
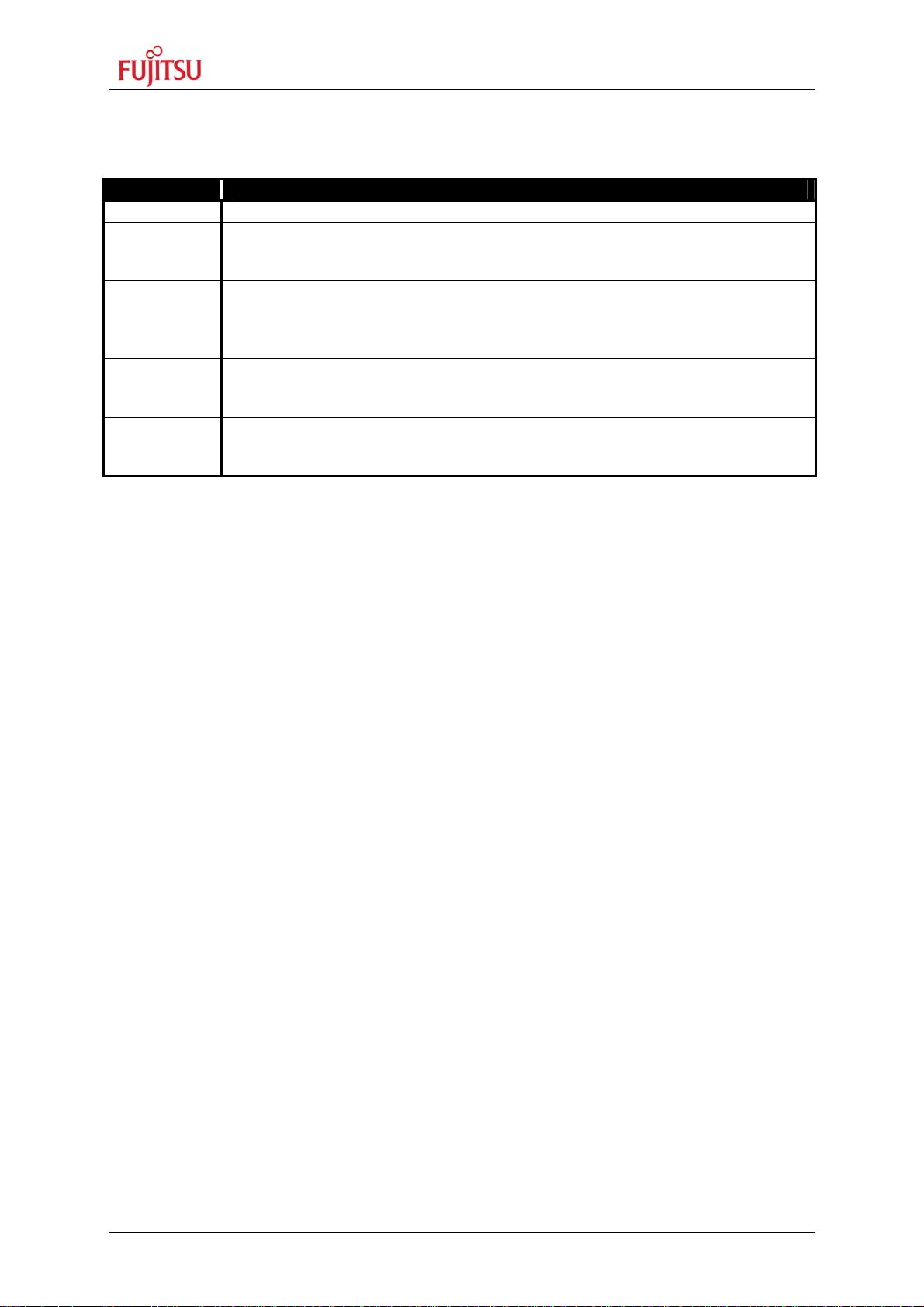
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Revision History
Revision History
Date Issue
22.11.2005 V1.0, UMa,
first official version
28.03.2006 V1.1, UMa
Updated the description of the SWB Monitor Debugger, which is now
located in the external flash.
13.04.2006 V1.2, UMa
Added chapter “Internal Flash Programming”
04.06.2006 V1.3, UMa
Changed chapter “Programming the Monitor Debugger”.
This document contains 60 pages.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 2 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 3

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Warranty and Disclaimer
Warranty and Disclaimer
To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH restricts
its warranties and its liability for the SK-91F467D-208PFV and all its deliverables (eg. software
include or header files, application examples, target boards, evaluation boards, engineering samples
of IC’s etc.), its performance and any consequential damages, on the use of the Product in
accordance with (i) the terms of the License Agreement and the Sale and Purchase Agreement under
which agreements the Product has been delivered, (ii) the technical descriptions and (iii) all
accompanying written materials. In addition, to the maximum extent permitted by applicable law,
Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH disclaims all warranties and liabilities for the performance of
the Product and any consequential damages in cases of unauthorised decompiling and/or reverse
engineering and/or disassembling. Note, the SK-91F467D-208PFV board and all its deliverables
are intended and must only be used in an evaluation laboratory environment.
1. Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH warrants that the Product will perform substantially in
accordance with the accompanying written materials for a period of 90 days form the date of
receipt by the customer. Concerning the hardware components of the Product, Fujitsu
Microelectronics Europe GmbH warrants that the Product will be free from defects in material
and workmanship under use and service as specified in the accompanying written materials
for a duration of 1 year from the date of receipt by the customer.
2. Should a Product turn out to be defect, Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH’s entire liability
and the customer’s exclusive remedy shall be, at Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH’s
sole discretion, either return of the purchase price and the license fee, or replacement of the
Product or parts thereof, if the Product is returned to Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH in
original packing and without further defects resulting from the customer’s use or the transport.
However, this warranty is excluded if the defect has resulted from an accident not attributable
to Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH, or abuse or misapplication attributable to the
customer or any other third party not relating to Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH.
3. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
disclaims all other warranties, whether expressed or implied, in particular, but not limited to,
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose for which the Product is not
designated.
4. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH’s
and its suppliers´ liability is restricted to intention and gross negligence.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, in no event shall Fujitsu
Microelectronics Europe GmbH and its suppliers be liable for any damages whatsoever
(including but without limitation, consequential and/or indirect damages for personal
injury, assets of substantial value, loss of profits, interruption of business operation,
loss of information, or any other monetary or pecuniary loss) arising from the use of
the Product.
Should one of the above stipulations be or become invalid and/or unenforceable, the remaining
stipulations shall stay in full effect.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 3 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 4

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Contents
Contents
REVISION HISTORY.............................................................................................................. 2
WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER........................................................................................... 3
CONTENTS ............................................................................................................................4
1 INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................ 7
1.1 Abstract..................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Features.................................................................................................................... 8
1.3 General Description .................................................................................................. 9
1.3.1 On Board Memory..................................................................................... 10
1.3.2 MCU Clocks .............................................................................................. 10
1.3.3 MCU Operating Mode ............................................................................... 10
1.3.4 External Bus interface Connectors............................................................ 10
1.3.5 CAN Bus ................................................................................................... 10
1.3.6 RS-232 and LIN ........................................................................................ 10
1.3.7 MCU Pins .................................................................................................. 10
1.3.8 User Buttons ............................................................................................. 10
1.3.9 User LEDs and Optional LCD ................................................................... 11
1.3.10 Power Supply ............................................................................................ 11
2 INSTALLATION............................................................................................................... 12
2.1 Jumper Settings ...................................................................................................... 14
2.2 Jumper Location ..................................................................................................... 15
2.3 Software Installation................................................................................................ 16
2.3.1 Installation of Softune Workbench ............................................................ 16
3 JUMPERS AND SWITCHES ........................................................................................... 17
3.1 MCU Operating-Mode (S5) ..................................................................................... 17
3.2 Power Supply.......................................................................................................... 18
3.2.1 MCU Power Supply Voltage...................................................................... 20
3.2.2 MCU Analogue Power Supply Voltage ..................................................... 20
3.3 CAN0 – CAN2......................................................................................................... 22
3.4 LIN / RS-232 UART................................................................................................. 22
3.4.1 UART 2 ..................................................................................................... 23
3.4.2 UART 4 (Flash Programming)................................................................... 24
3.4.3 UART 5 ..................................................................................................... 25
3.5 User Push Buttons INT0, INT1, INT2 and ICU0/TIN0............................................. 26
3.6 User DIP Switch 8 Bit (S4)...................................................................................... 26
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 4 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 5

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Contents
3.7 Reset Generation.................................................................................................... 27
4 CONNECTORS................................................................................................................ 29
4.1 Power Connector (X5)............................................................................................. 29
4.2 UART / LIN Connector (X1, X4, X8)........................................................................ 29
4.3 CAN Connector (X9, X10, X11) .............................................................................. 30
4.4 USER-LEDs and Optional LC-Display (D1-D16, J6)............................................... 31
4.5 In-Circuit-Programming Connector (X12)................................................................ 32
4.6 MCU Pin Connectors (J1-J4) .................................................................................. 32
4.7 External Bus Connectors (X13, X14) ...................................................................... 33
4.7.1 VG96ABC DIN 41612 (X13)...................................................................... 33
4.7.2 VG48ABC DIN 41612 (X14)...................................................................... 34
4.7.3 Distance between VG-Connectors............................................................ 34
5 GETTING STARTED ....................................................................................................... 35
5.1 Introduction to Softune Workbench......................................................................... 35
5.2 Project Start-up ....................................................................................................... 37
5.2.1 Create a New Project: ............................................................................... 37
5.3 Softune Workbench Monitor Debugger................................................................... 39
5.3.1 General Description .................................................................................. 39
5.3.2 Starting the SWB Monitor Debugger......................................................... 40
5.3.3 Basic Debugger Features ......................................................................... 42
5.4 Advanced Softune Workbench SWB Monitor Debugger Features ......................... 44
5.5 Memory Configuration............................................................................................. 46
6 PROGRAMMING THE INTERNAL FLASH..................................................................... 47
7 PROGRAMMING THE SWB MONITOR DEBUGGER.................................................... 51
8 TROUBLE SHOOTING.................................................................................................... 52
9 SILK-PLOT OF THE BOARD.......................................................................................... 53
9.1 Top Side.................................................................................................................. 53
9.2 Bottom Side ............................................................................................................ 54
10 PCB HISTORY................................................................................................................. 55
10.1 SK-91F467-208PFV V1.0 ....................................................................................... 55
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 5 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 6

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Contents
11 APPENDIX....................................................................................................................... 56
11.1 Related Products..................................................................................................... 56
11.2 Information on the WWW........................................................................................ 57
11.3 Tables 58
11.4 Figures 59
11.5 Abbreviations .......................................................................................................... 60
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 6 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 7

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Abstract
The SK-91F467D-208PFV is a multifunctional development board for the FUJITSU 32-bit
flash microcontroller MB91460 series.
It can be used stand-alone for software development and testing or together with the Softune
Workbench Monitor Debugger.
The board allows the designer immediately to start with the software and system
development, before his own final target system is available.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 7 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 8

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Introduction
1.2 Features
• Supports 32-bit flash microcontroller MB91F467D
• 9-12 V (2000 mA) unregulated external DC power supply
• 5 V, 3.3 V, 2.5 V and 1.8 V on-board switching regulators with power status LEDs
• Triple supply monitor to watch 5 V, 3.3 V and selectable 2.5 V or 1.8 V
• On-board Memory:
o 32 Mbit (4 MByte) SRAM
o 128 Mbit (16 MByte) flash
• All microcontroller resources available for evaluation
• All microcontroller pins routed to pin header
• In-circuit serial flash programming
• Three selectable RS-232 or LIN UART-interfaces
• Three high-speed CAN interfaces
• 16 User LEDs
• optional: alphanumeric standard LC-Display connectable
• Reset button, reset LED
• 4 User buttons, one 8 bit MCU port can be connected to DIP switches
• External bus interface routed to 96pin and 48pin DIN 41612 (VG) connectors
This board must only be used for test applications
in an evaluation laboratory environment.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 8 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 9

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Introduction
1.3 General Description
The SK-91F467-208PFV supports the FUJITSU 32-bit flash microcontroller MB91F467D.
The starter-kit can be used as a stand-alone development platform, or instead of the flash
MCU MB91F467D, with the emulation system MB2198-01 and the adapter board (MB2198-
300) and the 208 pin probe cable board (PB-91467D-208PFV or PB-91467D-LS-208PFV).
This User Guide is describing PCB version V1.1. The PCB version is printed at the TOP side
of the starter-kit close to MB91F467D MCU [U1].
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 9 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 10

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Introduction
1.3.1 On Board Memory
SK-91F467D-208PFV: The starter-kit SK-91F467D-208PFV includes 32 Mbit (4 MByte)
SRAM memory and 128 Mbit (16 MByte) flash memory on board. The flash can be used with
3.3 V external bus supply voltage only (JP21: 2-3).
1.3.2 MCU Clocks
The board is supplied with a 4 MHz crystal as the main oscillation clock for the MCU. Using
the internal PLL of the MCU, internal clock rates up to 96 MHz can be achieved. The MCU
sub clock is connected to a 32.768 kHz crystal.
1.3.3 MCU Operating Mode
The operating mode of the microcontroller can be selected with the DIP-switch S5.
1.3.4 External Bus interface Connectors
Via DIN 41612 VG96ABC and VG48ABC connectors (external bus interface of the MCU), it
is possible to connect other devices e.g. user applications or Fujitsu graphic device sub
boards.
1.3.5 CAN Bus
Three high-speed CAN-transceivers (PCA82C250) are available to connect all available onchip CAN-controllers to 9-pin D-Sub connectors (X9, X10 and X11). The transceivers
provides differential transmit and receive capability between CAN-controller and CAN-bus.
1.3.6 RS-232 and LIN
Three separate RS-232 transceivers and three separate LIN transceivers are available to
connect the on-chip USARTs to the 9-pin D-Sub connectors.
The RS-232 transceivers generate the adequate RS-232 levels for receive (RXD) and
transmit (TXD) lines. The RTS signal can be shortcut to CTS using jumpers (some PC
software needs this connection).
Either the DTR line or the RTS line of X1, X4 or X8 connectors can be selected to generate
a system reset.
The LIN transceivers (TLE6259) generate the adequate levels to drive the bus line in LINsystems for automotive and industrial applications.
1.3.7 MCU Pins
All 208 pins of the microcontroller are connected to the edge connectors J1, J2, J3 and J4
and are directly available to the user.
1.3.8 User Buttons
There are four push buttons on board, which can be connected to input-ports of the
microcontroller. Some ports may support additional functions like external interrupts (INT0,
INT1 and INT2) and trigger for the Reload Timer or for the Input-Capture Unit (TIN0 / ICU0).
One additional button is reserved as system-reset-button to reset the MCU, but it is possible
to disconnect the RST-port with JP54.
It is possible to connect with DIP-switch S3 eight port input switches at S4 to the MCU port
P26. All eight ports can be switched separately to use e.g. only four ports as input.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 10 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 11

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Introduction
1.3.9 User LEDs and Optional LCD
Sixteen user-LEDs are connected via two pull-down resistor networks to port P25 and to port
P16. Parallel to the LEDs on port P25, the connector J6 can be used to connect a standard
alphanumeric display. The resistor networks RN2 and RN3 can be removed to free the ports.
1.3.10 Power Supply
The four on-board step-down switching regulators allow the user to connect an unregulated
DC input voltage between +9 V to +12 V (max. 2000 mA) to the starter-kit. The switching
regulators provide the voltages of 5 V(3 A), 3.3 V(3 A), 2.5 V(1.5 A) and 1.8 V(1.5 A) on the
starter-kit. These voltages give also the possibility to connect an optional graphic-controller
starter-kit to the board. The switching regulators are short circuit protected and provide a
thermal shutdown.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 11 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 12

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Installation
2 Installation
Remove the board carefully from the shipping carton.
First check whether there are any damages before power on the starter-kit.
To supply the starter-kit use the delivered plug-in AC-DC Adapter (UPA 2000). Select the AC
plug adapter suitable for your country power sockets
Figure 2-1 AC plug adapter
and insert this adapter in the connection terminal on the AC-DC adapter.
Figure 2-2: AC plug adapter selection
Check the selected output DC voltage of the AC-DC plug-in adapter at the voltage selection
key. It should be 9 V! Change the output voltage only in a powered-down condition!
Figure 2-3: DC voltage selection
Select the low voltage adapter suitable to the power connector X5 at the SK-91F467D208PFV and plug it to the connecting socket in the right orientation (‘+’ connected to shield
and ‘GND’ connected to centre pin).
Figure 2-4: Low voltage adapter selection
Now connect the DC low voltage adapter to the starter-kit and plug in the plug-in power
supply to a power socket. The SK-91F467D-208PFV can be turned on with the on board
power switch S8 (or S9).
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 12 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 13
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Installation
For the power supply of the SK-91F467D-208PFV a DC input voltage of 9V – 12V is
recommended. The positive voltage (+) must be connected to the shield, and ground
(GND) must be connected to the centre of the connector X5!
After power-on of the SK-91F467D-208PFV, the four red power-on LEDs D24 (5 V), D30
(3.3 V), D34 (2.5 V) and D40 (1.8 V) should be light. The reset LED D18 should be off.
The starter-kit is delivered with programmed Softune Workbench (SWB) Monitor Debugger
in the external flash. The SWB Monitor Debugger checks also the external SRAM access at
CS1. In case of successful access to external SRAM the LED D1, D4 and D8 are on.
To use the SWB Monitor Debugger, the CPU mode selection must be set to the External
Reset Vector mode by setting DIP switch S5 to (On, Off, Off, Off), which is the delivery state.
To use the MCU with the internal flash, which is normally required for the final application,
the CPU mode selection must be set to the Internal Reset Vector mode by setting DIP switch
S5 to (Off, Off, Off, Off)
Figure 2-5: Starter-kit status after power on
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 13 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 14
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Installation
2.1 Jumper Settings
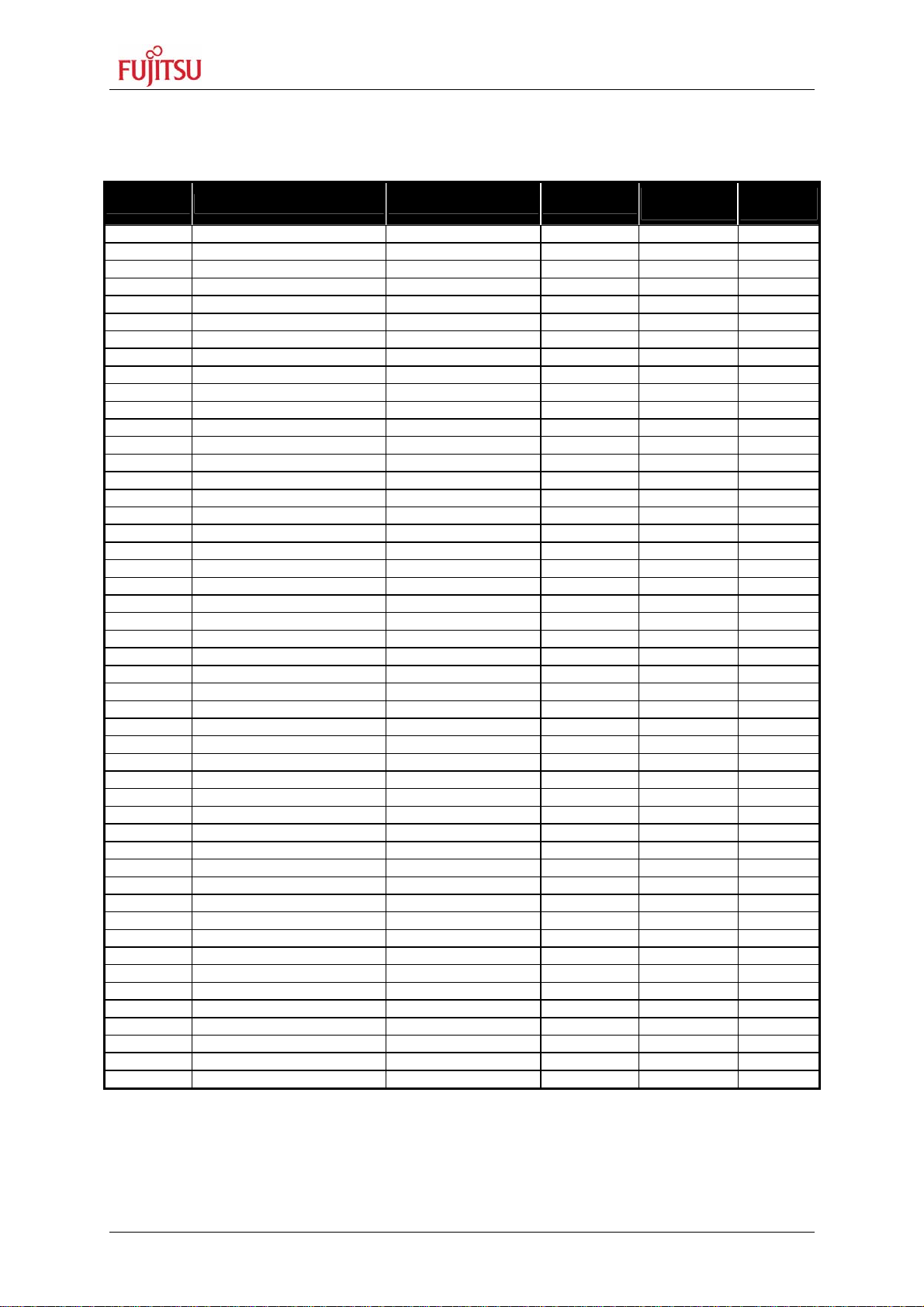
The following table lists all jumpers including its default setting and location on the starter-kit.
Jumper Description / Function Type Default
JP15 MCUVcc - AVcc Jumper 2 pin Closed E 9 1 / 3
JP16 AVcc - AVRH Jumper 2 pin Closed E 9 1 / 3
JP18 GND - AVss Jumper 2 pin Closed E 8 1 / 3
JP21 VDD35 MCUVcc / 3.3V Solder Jumper 3 pad 2-3 F 15 1 / 3
JP23 MCUVcc – HVDD5 Jumper 2 pin Closed E 10 1 / 3
JP25 MCUVcc – VDD5R Jumper 2 pin Closed E 11 1 / 3
JP26 Vcc - MCUVcc Jumper 2 pin Closed E 11 1 / 3
JP27 MCUVcc – VDD5 Jumper 2 pin Closed E 11 1 / 3
JP28 GND – HVSS5 Jumper 2 pin Closed E 6 1 / 3
JP29 DTR select DTR / /DTR Jumper 3 pin Open B 14 2 / 3
JP30 UART2 RTS - CTS Jumper 2 pin Open D 3 2 / 3
JP37 UART2 RxD RS232 / LIN Jumper 3 pin 2-3 F 5 2 / 3
JP39
JP42
JP43
JP44
JP46
JP47
JP51
JP54 RESET - MCU RST
JP57 UARTX RST Select
JP58
JP60 UART4 RxD RS232 / LIN
JP64 UART4 DTR / RTS
JP65 UART4 TxD RS232 / LIN
JP68 Vcc 5V / 3.3V
JP69 UART4 RS232 / LIN
JP71 UART4 LIN Enable
JP72 UART4 LIN Master Yes / No
JP78 UART5 RTS - CTS Jumper 2 pin Closed H 3 2 / 3
JP79 UART5 RxD RS232 / LIN Jumper 3 pin 1-2 J 5 2 / 3
JP80
JP81
JP82 CAN0 RxD Jumper 2 pin
JP83 CAN0 TxD Jumper 2 pin Closed D 19 2 / 3
JP84
JP85
JP86
JP87 CAN1 RxD Jumper 2 pin
JP88 CAN1 TxD Jumper 2 pin Closed F 19 2 / 3
JP89 CAN2 RxD Jumper 2 pin
JP90 CAN2 TxD Jumper 2 pin Closed M 4 2 / 3
JP91 Vin – Ext Voltage Solder Jumper 2 pad Closed G 18 3 / 3
JP92 INT0 Jumper 2 pin Closed G 15 3 / 3
JP93 INT1 Jumper 2 pin Closed G 15 3 / 3
JP94 INT2 Jumper 2 pin Closed G 15 3 / 3
JP95 ICU0/TIN0 Jumper 2 pin Closed G 15 3 / 3
JP96 Direct RESET Solder Jumper 3 pad 1-2 A 14 2 / 3
JP97 VCC1V8 to X14B2 Solder Jumper 2 pad Open H 16 3 / 3
UART2 DTR / RTS
Watch 1.8V
Watch 2.5V
UART2 TxD RS232 / LIN
UART2 RS232 / LIN
UART2 LIN Enable
UART2 LIN Master Yes / No
UART4 RTS - CTS Jumper 2 pin Closed
UART5 DTR / RTS
UART5 TxD RS232 / LIN
UART5 RS232 / LIN
UART5 LIN Enable
UART5 LIN Master Yes / No
Jumper 3 pin Open F 4 2 / 3
Solder Jumper 2 pad Open
Solder Jumper 2 pad Closed B 15 2 / 3
Jumper 3 pin 2-3 F 5 2 / 3
Jumper 3 pin 2-3 F 4 2 / 3
Jumper 2 pin Closed G 6 2 / 3
Jumper 2 pin Closed G 5 2 / 3
Jumper 2 pin Closed
Jumper 6 pin
Jumper 3 pin 1-2
Jumper 3 pin Open
Jumper 3 pin 1-2
Solder Jumper 3 pad 1-2
Jumper 3 pin 1-2
Jumper 2 pin Open
Jumper 2 pin Open
Jumper 3 pin Open J 4 2 / 3
Jumper 3 pin 1-2 K 5 2 / 3
Jumper 3 pin 1-2 K 4 2 / 3
Jumper 2 pin Open K 6 2 / 3
Jumper 2 pin Open K 6 2 / 3
Open H 6
Closed
Closed
Closed
Layout
Coordinates
B 15
B 15
F 3
H 5
H 4
H 5
B 16
H 4
H 6
H 6
D 19 2 / 3
G 19 2 / 3
M 4 2 / 3
Schematic
Page
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
2 / 3
Table 2-1: Jumper settings
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 14 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 15
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Installation
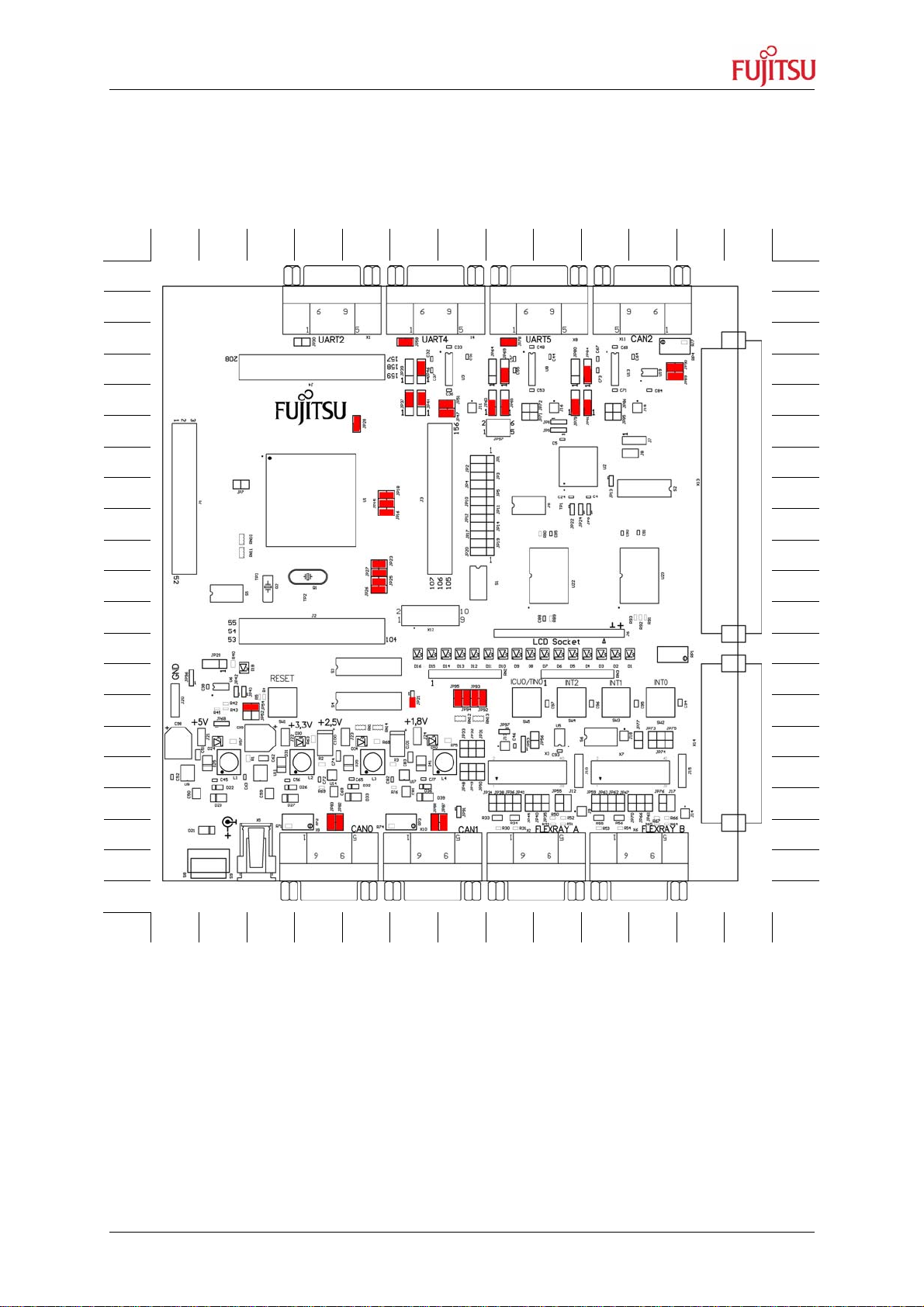
2.2 Jumper Location
The following picture shows the silk plot of the starter-kit with marked default jumper
settings.
A B C D E F G H J K L M N
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 13
14 14
15 15
16 16
17 17
18 18
19 19
20 20
21
21
A B C D E F G H J K L M N
Figure 2-6: Default jumper settings
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 15 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 16
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Installation
2.3 Software Installation
2.3.1 Installation of Softune Workbench
With the “SK-91F467D-208PFV” Fujitsu supplies a full working development environment
called Softune Workbench V6. The Softune Workbench also supports the SWB Monitor
Debugger which is pre-programmed into the external flash memory of the “SK-91F467D208PFV”. To develop own software and to work with the SWB Monitor Debugger of the “SK91F467D-208PFV” the Softune Workbench development environment must be installed first.
Follow the instructions for successful installation of the Softune Workbench.
1) Before starting the installation setup ensure that you are logged in with administrator
or poweruser permissions, otherwise the Softune Workbench installation will fail! Be
aware that Softune Workbench does not support multi-user support. Therefore
install- and user login must be the same.
2) Browse on the starter-kit CD-ROM into the directory Software\SWB_Install and start
the FRSTA*.exe.
3) Follow the installation instructions.
4) For the default installation path it is recommended to use c:\Softune32.
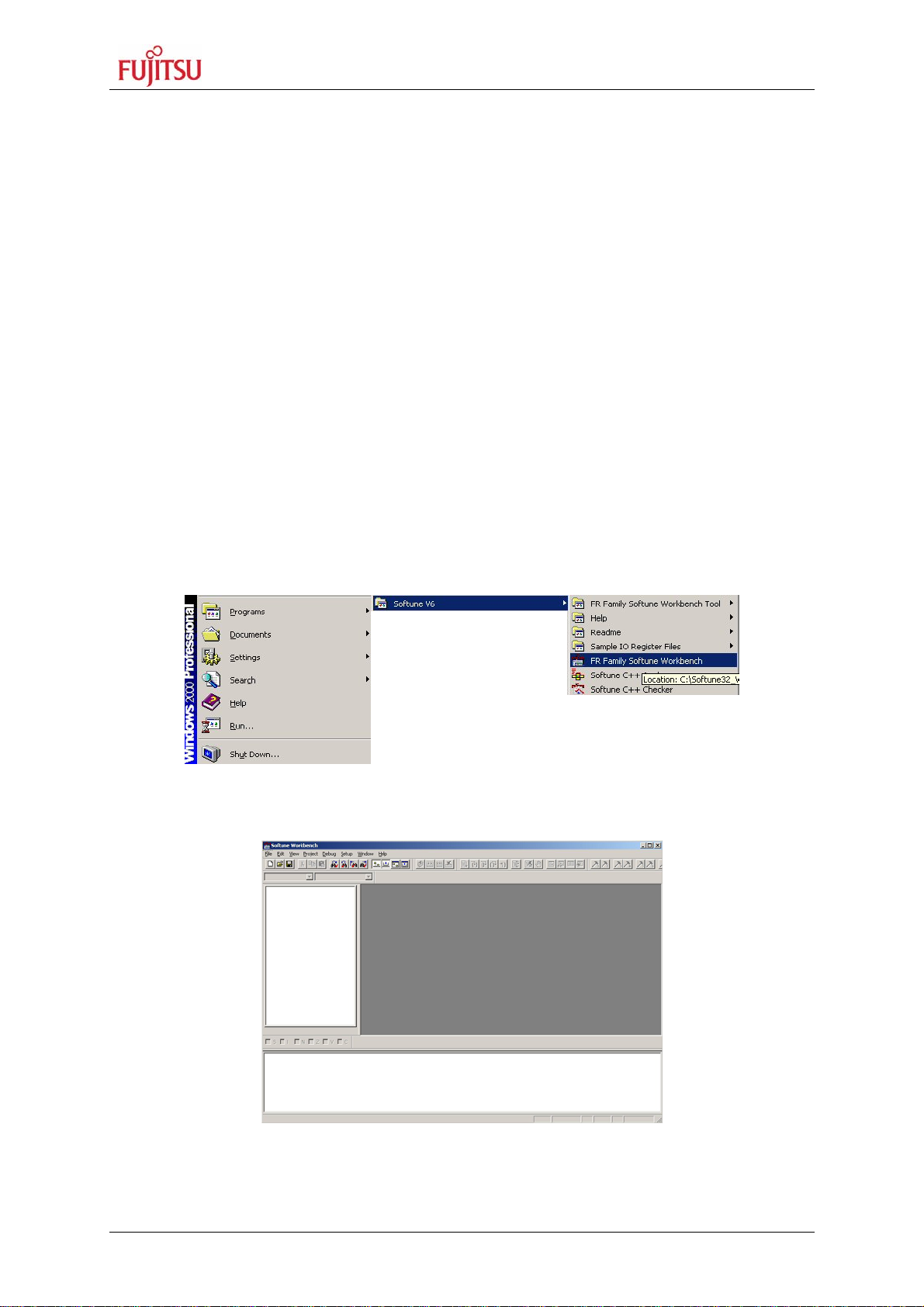
5) After the installation is finished. The FR Family Softune Workbench can be started
via the Windows “Start” menu.
Figure 2-7: Softune Workbench start menu location
6) When Softune Workbench was started the following window will be shown.
Figure 2-8: Softune Workbench V6 IDE
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 16 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 17
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3 Jumpers and Switches
This chapter describes all jumpers and switches that can be modified on the starter-kit. The
default setting is shown with a grey shaded area.
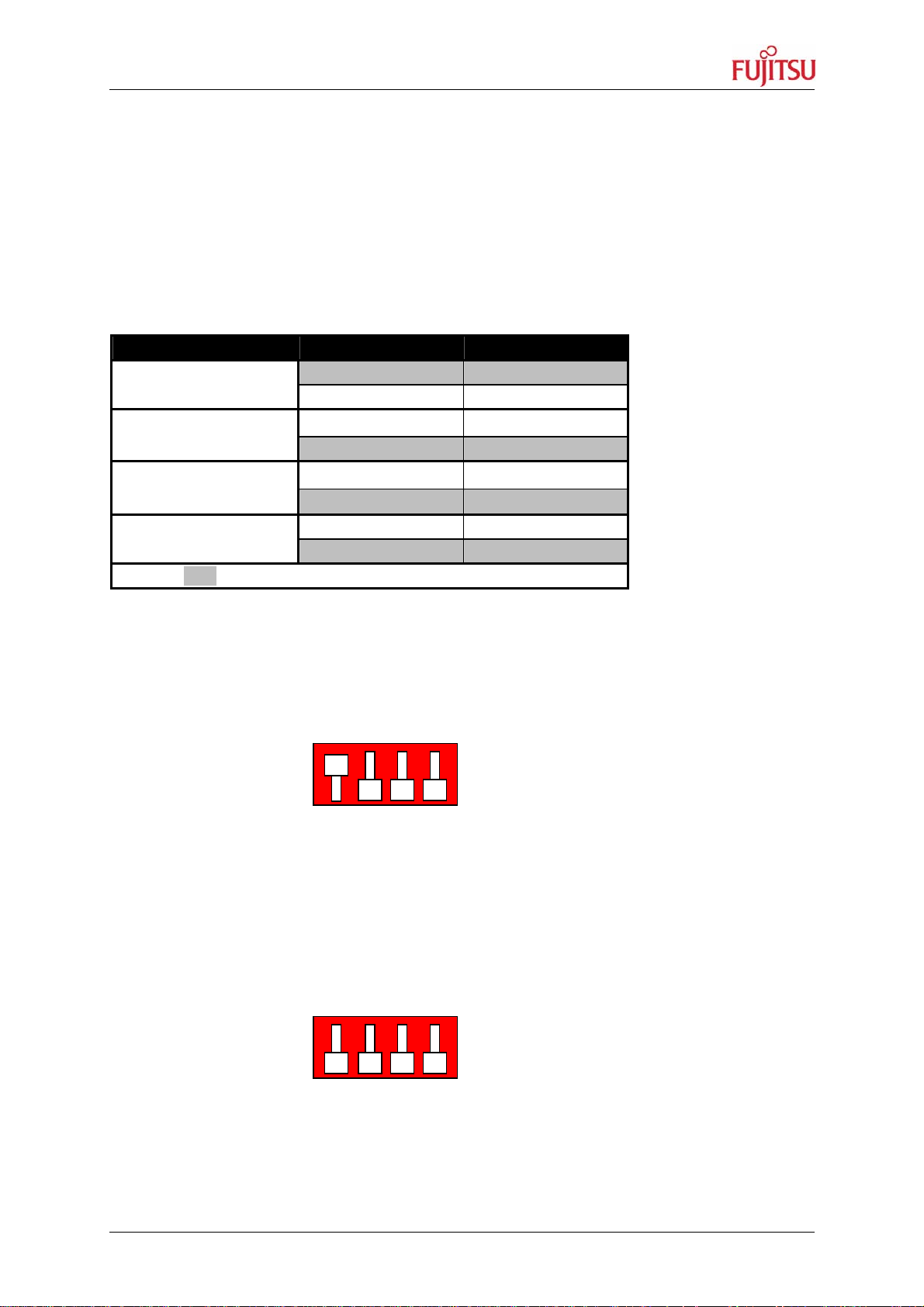
3.1 MCU Operating-Mode (S5)
The DIP-switch S5 is used to set the operating mode of the MCU. Ensure that the mode pin
settings correspond to the operation-mode of the application. For more detailed information
please check the hardware manual of the microcontroller.
DIP switch Setting Logical value
S5/1 (MD0)
ON (closed) 1 (high)
OFF (open) 0 (low)
S5/2 (MD1)
ON (closed) 1 (high)
OFF (open) 0 (low)
S5/3 (MD2)
ON (closed) 1 (high)
OFF (open) 0 (low)
S5/4 (Not used)
ON (closed) Not connected
OFF (open) Not connected
Default: grey
Table 3-1: MCU operating mode
By default, the “External ROM Mode Vector” is selected for the SWB Monitor Debugger,
which is pre-programmed into the external flash. In this mode the internal flash is
inaccessible.
DIP-Switch S5
(default setting)
MD0 MD1 MD2 nc
ON
OFF
1 2 3 4
Figure 3-1: MCU mode switch: External ROM Mode Vector
The “Internal ROM Mode Vector” of MB91F467D is normally required for the final
application, which should be stored in the internal flash. In this mode the internal flash is
accessible.
MD0 MD1 MD2 nc
DIP-Switch S5
(default setting)
1 2 3 4
ON
OFF
Figure 3-2: MCU mode switch: Internal ROM Mode Vector
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 17 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 18
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
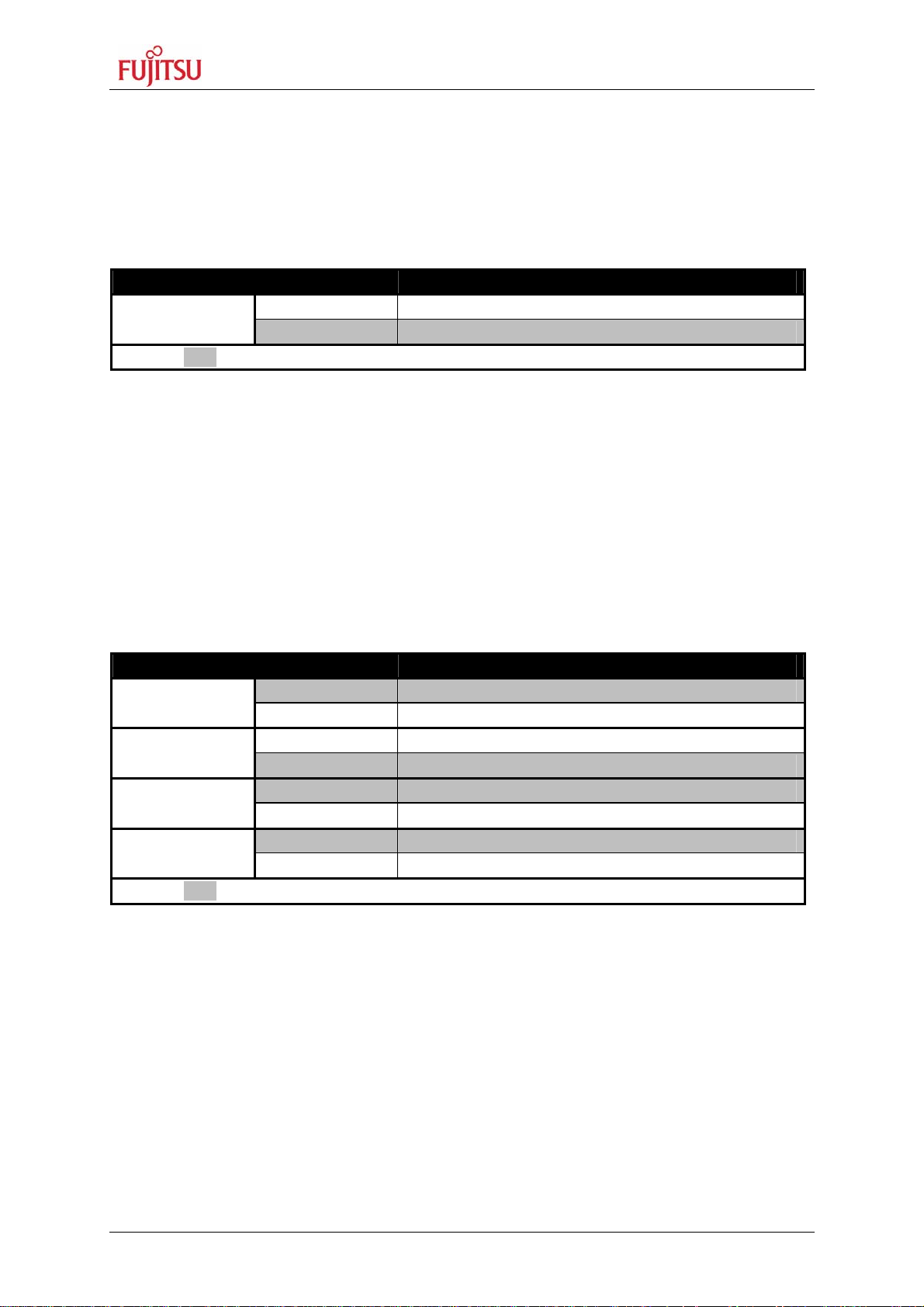
3.2 Power Supply
There are four on-board switching regulators to provide the voltages 5 V, 3.3 V, 2.5 V and
1.8 V on the starter-kit. With the power ON/OFF-switch S8 or S9 (S9 is a soldering option to
use a different switch), the main input voltage from DC-connector X5 will be connected to the
Vin voltage of the board. The Vin voltage supplies the switching regulators.
Switch Setting Description
S8 or S9
Default: grey
With JP91 the pins B14, B15 and B16 of the external bus interface connector X14 can be
connected to the Vin voltage, so that it is possible to supply the board from an external
connected board.
ON (1-2) Power ON
OFF (2-3) Power OFF
Table 3-2: Power switch
There is a triple supply monitor on-board, which monitors three of the four DC output
voltages and generates a system reset, in case with wrong levels of the on board voltages.
5 V and 3.3 V are always monitored and the third monitored voltage can be selected with the
solder jumpers JP42 and JP43.
With JP68 it is possible to select the whole board supply voltage Vcc to 5 V or 3.3 V
Jumper Setting Description
JP91
ON (closed) Vin is connected to X14 pins B14, B15 and B16
OFF (open) Vin is not connected to X14 pins B14, B15 and B16
JP42
ON (closed) Vcc1V8 is connected to supply monitor
OFF (open) Vcc1V8 is not connected to supply monitor
JP43
ON (closed) Vcc2V5 is connected to supply monitor
OFF (open) Vcc2V5 is not connected to supply monitor
JP68
1-2 Vcc is connected to 5 V
2-3 Vcc is connected to 3.3 V
Default: grey
Table 3-3: Power supply configurations
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 18 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 19

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
Figure 3-3: Voltage Test Points
Regulator Test point Voltage
U9 J21 +5V
U11 J22 +3.3V
U14 J23 +2.5V
U17 J24 +1.8V
- J20 GND
Table 3-4: Voltage Test Points
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 19 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 20

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.2.1 MCU Power Supply Voltage
JP21 With this jumper it is possible to connect the MCU external bus interface supply
VDD35 to 3.3 V. The MCU MB91460 series supports the function to supply the MCU
with 5 V so that the normal I/O ports work with 5 V and supply the external bus
interface with 3.3 V.
JP23 This jumper is used to connect the HVDD5 supply to MCUVcc. The HVDD5 is the
MCU supply voltage for the high current ports.
JP25 This jumper is used to connect the VDD5R MCU supply pins to MCUVcc.
JP26 This jumper is used to connect the Vcc voltage to MCUVcc.
JP27 This jumper is used to connect the VDD5 MCU supply pins to MCUVcc.
JP28 This jumper is used to connect the HVSS5 MCU pins to GND. HVSS5 are the GND
pins for the high current ports.
Note:
JP23, JP25, JP26, JP27 and JP28 can be used for
measurements of power consumption of the MCU.
Jumper Setting Description
JP21
1-2 VDD35 is connected to MCUVcc
2-3 VDD35 is connected to 3.3 V
JP23
ON (closed) HVDD5 is connected to MCUVcc
OFF (open) HVDD5 is not connected to MCUVcc
JP25
ON (closed) VDD5R is connected to MCUVcc
OFF (open) VDD5R is not connected to MCUVcc
JP26
ON (closed) MCUVcc is connected to Vcc
OFF (open) MCUVcc is not connected to Vcc
JP27
ON (closed) VDD5 is connected to MCUVcc
OFF (open) VDD5 is not connected to MCUVcc
JP28
ON (closed) HVSS5 is connected to GND
OFF (open) HVSS5 is not connected to GND
Default: grey
Table 3-5: MCU power supply SK-91F467D-208PFV
3.2.2 MCU Analogue Power Supply Voltage
The power supply as well as the reference voltage for the A/D-converter can be provided
internally or externally.
JP15 Connects power supply AVcc of the A/D converter to MCUVcc
JP16 Connects high reference voltage AVRH of the A/D converter to AVcc
JP18 Connects AVss of the A/D converter to GND
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 20 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 21

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
Jumper Setting Description
JP15
ON (closed) AVcc is connected to MCUVcc
OFF (open) AVcc is disconnected
JP16
JP18
ON (closed) AVRH is connected to AVcc
OFF (open) AVRH defined by resistor network
ON (closed) AVss is connected to GND
*1
OFF (open) AVss is disconnected
Default: grey
*1
By default the resistor network (R10 and R13) is not assembled on the board
Table 3-6: MCU ADC Supply
Note:
If JP15 or JP18 are open, the user has to supply an adequate analogue voltage supply (AVcc
and AVss) to the A/D-converter.
If JP16 is open, the potential divider comprising resistors R10 and R13 define AVRH.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 21 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 22

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.3 CAN0 – CAN2
Three high-speed CAN-transceivers (PCA82C250) are on-board to connect all available onchip CANs to 9-pin D-Sub connectors (X9, X10 and X11).
JP82 Connects MCU RX0 to CAN transceiver U15
JP83 Connects MCU TX0 to CAN transceiver U15
JP87 Connects MCU RX1 to CAN transceiver U18
JP88 Connects MCU TX1 to CAN transceiver U18
JP89 Connects MCU RX2 to CAN transceiver U19
JP90 Connects MCU TX2 to CAN transceiver U19
Jumper Setting Description
JP82
JP83
JP87
JP88
JP89
JP90
Default: grey
ON (closed) CAN0 RxD connected to MCU
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) CAN0 TxD connected to MCU
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) CAN1 RxD connected to MCU
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) CAN1 TxD connected to MCU
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) CAN2 RxD connected to MCU
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) CAN2 TxD connected to MCU
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
Table 3-7: CAN-MCU connection
3.4 LIN / RS-232 UART
There are three UART connectors X1, X4 and X8 (9-pin D-Sub) on-board, which can be
used for RS-232 or LIN communication (to get information in detail about pin usage, please
refer to chapter 4.2 UART / LIN Connector (X1, X4, X8)). The LIN transceiver needs to be
configured as LIN-master or LIN-slave.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 22 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 23

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.4.1 UART 2
UART2 (connector X1) is selected as LIN master at default setting.
JP37 Select, whether SIN2 is connected to RS-232- or LIN-transceiver
JP44 Select, whether SOT2 is connected to RS-232- or LIN-transceiver
JP46 Select, whether RS-232- or LIN-transceiver is connected to X1 pin2 (shared pin)
JP30 Some terminal programs needs a connection between CTS and RTS
JP39 Selects, whether DTR or RTS will be used for system reset generation
JP47 Enables the LIN transceiver
JP51 Selects, whether UART2 will be LIN master or LIN
slave
Jumper Setting Description
JP37
1-2 MCU SIN2 connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 MCU SIN2 connected to LIN transceiver
JP44
1-2 MCU SOT2 connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 MCU SOT2 connected to LIN transceiver
JP46
1-2 X1 pin2 is connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 X1 pin2 is connected to LIN transceiver
JP30
ON (closed) RTS and CTS is shortcut at connector X1
OFF (open) RTS and CTS is not shortcut at connector X1
JP39
1-2 DTR can be used for system reset
2-3 RTS can be used for system reset
JP47
ON (closed) LIN transceiver is enabled
OFF (open) LIN transceiver is not enabled
JP51
ON (closed) LIN master mode
OFF (open) LIN slave mode
Default: grey
Note:
UART2 has to be selected with
JP57 to generates a system reset
Table 3-8: UART2 settings
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 23 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 24

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.4.2 UART 4 (Flash Programming)
UART4 (connector X4) is selected as RS-232 at default setting. UART4 is also used to write
user software into the flash of the MCU.
JP60 Select, whether SIN4 is connected to RS-232- or LIN-transceiver
JP65 Select, whether SOT4 is connected to RS-232- or LIN-transceiver
JP69 Select, whether RS-232- or LIN-transceiver is connected to X4 pin2 (shared pin)
JP58 Some terminal programs needs a connection between CTS and RTS
JP64 Selects, whether DTR or RTS will be used for system reset generation
JP71 Enables the LIN transceiver
JP72 Selects, whether UART4 will be LIN master or LIN
slave
Jumper Setting Description
JP60
1-2 MCU SIN4 connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 MCU SIN4 connected to LIN transceiver
JP65
1-2 MCU SOT4 connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 MCU SOT4 connected to LIN transceiver
JP69
1-2 X4 pin2 is connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 X4 pin2 is connected to LIN transceiver
JP58
ON (closed) RTS and CTS is shortcut at connector X4
OFF (open) RTS and CTS is not shortcut at connector X4
JP64
1-2 DTR can be used for system reset
2-3 RTS can be used for system reset
JP71
ON (closed) LIN transceiver is enabled
OFF (open) LIN transceiver is not enabled
JP72
ON (closed) LIN master mode
OFF (open) LIN slave mode
Default: grey
Note:
UART4 has to be selected with
JP57 to generates a system reset
Table 3-9: UART4 settings
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 24 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Note:
UART4 is used as serial interface
for Softune Workbench Monitor
Debugger. Jumper J58 must be
closed.
Page 25

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.4.3 UART 5
UART5 (connector X8) is selected as RS-232 at default setting.
JP79 Select, whether SIN5 is connected to RS-232- or LIN-transceiver
JP81 Select, whether SOT5 is connected to RS-232- or LIN-transceiver
JP84 Select, whether RS-232- or LIN-transceiver is connected to X8 pin2 (shared pin)
JP78 Some terminal programs needs a connection between CTS and RTS
JP80 Selects, whether DTR or RTS will be used for system
reset generation
JP85 Enables the LIN transceiver
JP86 Selects, whether UART5 will be LIN master or LIN
slave
Jumper Setting Description
JP79
1-2 MCU SIN4 connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 MCU SIN4 connected to LIN transceiver
JP81
1-2 MCU SOT4 connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 MCU SOT4 connected to LIN transceiver
JP84
1-2 X4 pin2 is connected to RS-232 transceiver
2-3 X4 pin2 is connected to LIN transceiver
JP78
ON (closed) RTS and CTS is shortcut at connector X4
OFF (open) RTS and CTS is not shortcut at connector X4
JP80
1-2 DTR can be used for system reset
2-3 RTS can be used for system reset
JP85
ON (closed) LIN transceiver is enabled
OFF (open) LIN transceiver is not enabled
JP86
ON (closed) LIN master mode
OFF (open) LIN slave mode
Default: grey
Note:
UART5 has to be selected with
JP57 to generates a system reset
Table 3-10: UART5 settings
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 25 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 26

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.5 User Push Buttons INT0, INT1, INT2 and ICU0/TIN0
There are four user push buttons on the starter-kit, which can be connected to the
microcontroller.
JP92 – JP95 Connects the user push buttons (SW2 – SW5) to the microcontroller
Jumper Setting Description
JP92 (SW2)
JP93 (SW3)
JP94 (SW4)
JP95 (SW5)
Default: grey
ON (closed) Button INT0 is connected to the microcontroller
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) Button INT1 is connected to the microcontroller
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) Button INT2 is connected to the microcontroller
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
ON (closed) Button ICU0/TIN0 is connected to the microcontroller
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
Table 3-11: User push buttons
3.6 User DIP Switch 8 Bit (S4)
There is an 8 bit user-DIP-switch on-board, which can be connected to one MCU port (P26)
in order to set high- or lowlevel. S3, also an 8 bit DIP-switch, dis- / connects the eight
channels of S4 to the MCU pins. In case of other usage of these pins, open S3 switch
accordingly.
DIP switch Setting Logical value
S4/1 - 8
Default: grey
Table 3-12: S4 values
DIP switch Setting Description
S3/1 - 8
Default: grey
ON (closed) 0 (low)
OFF (open) 1 (high)
Note:
DIP-switch S3 is used to connect DIP-switch S4 to the MCU port
pins at port P26.
ON (closed) S4/1-8 connected to MCU port P26_0-7
OFF (open) No connection to the microcontroller
Table 3-13: S3 settings
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 26 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 27

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
3.7 Reset Generation
A system reset can be generated in different ways. The first possibility is to press the user
reset push button (SW1). Secondly, the supply monitor will generate a reset if an unusual
voltage is detected and third, a reset is raised if the selected UART generates one.
An active system reset is indicated by the reset LED D18.
The system reset will do a simultaneous reset of the microcontroller. The MCU can be
disconnected from the system reset signal.
JP96 The Reset push button can be used in two modes:
• Immediate reset
• Secured Reset (2s)
The selection is done by solder jumper JP96.
JP54 Connects the MCU to the system reset signal
Jumper Setting Description
JP54
JP96
Default: grey
ON (closed) Reset is connected to MCU INITX
OFF (open) No connection to the MCU
1-2 Reset is generated immediately when SW1 is
pressed
2-3 Reset is generated after SW1 is pressed 2s
Table 3-14: Reset connections
The triple supply monitor on-board has the possibility to watch 5V, 3.3V and the third voltage
is user configurable 2.5V or 1.8V. If any voltage fails, a system reset will be done.
JP42 Monitoring of 1.8V supply voltage
JP43 Monitoring of 2.5V supply voltage
Jumper Setting Description
JP42
ON (closed) Vcc1V8 connected to supply monitor
OFF (open) Vcc1V8 not connected to supply monitor
JP43
ON (closed) Vcc2V5 connected to supply monitor
OFF (open) Vcc2V5 not connected to supply monitor
Default: grey
Table 3-15: Supply monitor settings
By default 2.5V supply will be monitored. Do not close both jumpers simultaneously.
The system reset also can be done via any UART. Therefore the user has the possibility to
select one of the three on-board UARTs.
JP57 Select which UART should generate the system reset
JP29 The polarity of the DTR/RTS signal can be inverted by this jumper. Remove the
jumper to disable the UART reset function
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 27 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 28

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Jumpers and Switches
Jumper Setting Description
1-2 Reset will be done via UART2
JP57
3-4 Reset will be done via UART4
5-6 Reset will be done via UART5
JP29
1-2 No polarity inversion for the DTR/RTS signal
2-3 Polarity inversion for the DTR/RTS signal
Table 3-16: Reset UART selection
By default the UART reset is disabled.
Note:
During normal operation, the reset LED should be off!
If the reset LED is steadily on, check the power supply
voltages and the settings for the reset generation by UART.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 28 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 29

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Connectors
4 Connectors
4.1 Power Connector (X5)
The following figure shows the power connection jack of the starter-kit. This connector is
used to connect an external unregulated DC power supply voltage (9 V-12 V DC
recommended 2000 mA).
Shield is connected to positive voltage supply (+)
Centre is connected to ground (GND)
Figure 4-1 Power connector
4.2 UART / LIN Connector (X1, X4, X8)
Three 9-pin D-Sub female connectors are used for the serial interfaces LIN/UART2,
LIN/UART4 and LIN/UART5.
Take care, that the RS232 as well as the LIN signals are shared at the connectors and have
to be selected by jumpers (see chapter 3.4).
Figure 4-2 UART connector
Pin Number Pin Signal Description
1 +VBat Power from LIN bus
2
3 RXD RS-232 receive input
4 DTR Connected to DSR (pin 6)
5 GND Ground normally used for RS232 connection
6 DSR Connected to DTR (pin 4)
7 RTS Can be connected with CTS by jumper
8 CTS Can be connected with RTS by jumper
9 LGND Ground normally used for LIN connection
Shield GND Ground
TXD RS-232 transmit output
LIN Bi-directional LIN-interface
Table 4-1: UART connector signals
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 29 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Note:
Please use 1:1 cable for RS232 PC-connection.
Page 30

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Connectors
4.3 CAN Connector (X9, X10, X11)
Three 9-pin D-Sub male connectors are used for the CAN interfaces CAN0, CAN1 and
CAN2.
Figure 4-3: CAN connector
Pin Number Pin Signal Description
1 NC Not used
2 CANL LOW-level CAN voltage input/output
3 GND Ground
4 NC Not used
5 NC Not used
6 NC Not used
7 CANH HIGH-level CAN voltage input/output
8 NC Not used
9 NC Not used
Shield GND Ground
Table 4-2: CAN connector signals
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 30 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 31

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Connectors
4.4 USER-LEDs and Optional LC-Display (D1-D16, J6)
There are sixteen user LEDs on-board, D1-D8 connected to MCU port P25 and D9-D16
connected to MCU port P16. To disconnect the LEDs from the MCU, it is possible to remove
RN3 (D1-D8 at port P25) and RN2 (D9-D16 at port P16).
It is also possible to connect a standard LCD module with backlight to connector J6. With the
potentiometer RP1 the contrast of the LCD can be adjusted.
Pin 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 16 15
LCD DB7 DB6 DB5 DB4 - - - - E R/W RS VO Vcc GND LED- LED+
LED D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
Port P25_7 P25_6 P25_5 P25_4 P25_3 P25_2 P25_1 P25_0
MCU 187 186 185 184 181 180 179 178
Table 4-3: LED/LCD Signals
LCD contrast
(Port: P16_7)
D16
D9
(Port: P16_0)
D8
(Port: P25_7)
Figure 4-4: User LEDs / LCD
D1
(Port: P25_0)
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 31 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 32

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Connectors
4.5 In-Circuit-Programming Connector (X12)
There is a flash-programming socket on the starter-kit which makes it possible to program
the flash MCU with a special programming adapter. Mode pins and reset signal are also
available at this connector.
Figure 4-5: In-circuit programming connector
Pin Number Pin Signal Description
1 NC Not used
2 NC Not used
3 MD0 MCU mode-pin 0
4 MD2 MCU mode-pin 2
5 INITX MCU reset signal
6 SIN4 UART4 receive data
7 SOT4 UART4 transmit data
8 SCK4 UART4 clock
9 VCC Board supply voltage
10 GND Ground
Table 4-4: In-circuit programming connector
4.6 MCU Pin Connectors (J1-J4)
All MCU pins are directly connected to the four pin header around the MCU. The last two
pins of the pin header J1, J2, J3 and J4 are unused (see PCB silk plot).
Connector MCU Pins
J1 1-52
J2 53-104
J3 105-156
J4 157-208
Table 4-5: MCU pin connectors
The corresponding pin numbers of the MCU are written next to the connector pins on the
PCB.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 32 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 33

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Connectors
4.7 External Bus Connectors (X13, X14)
4.7.1 VG96ABC DIN 41612 (X13)
Pin Name MCU-P. Pin Name MCU-P. Pin Name MCU-P.
A1 2.5 V - B1 2.5 V - C1 2.5 V -
A2 3.3 V - B2 3.3 V - C2 3.3 V -
A3 5.0 V - B3 5.0 V - C3 5.0 V -
A4 GND - B4 GND - C4 GND -
A5 D0 192 B5 D1 193 C5 D2 194
A6 D3 195 B6 D4 196 C6 D5 197
A7 D6 198 B7 D7 199 C7 D8 200
A8 D9 201 B8 D10 202 C8 D11 203
A9 D12 204 B9 D13 205 C9 D14 206
A10 D15 207 B10 D16 2 C10 D17 3
A11 D18 4 B11 D19 5 C11 D20 6
A12 D21 7 B12 D22 8 C12 D23 9
A13 D24 10 B13 D25 11 C13 D26 12
A14 D27 13 B14 D28 14 C14 D29 15
A15 D30 16 B15 D31 17 C15 GND -
A16 GND - B16 GND - C16 GND -
A17 A0 18 B17 A1 19 C17 A2 20
A18 A3 21 B18 A4 22 C18 A5 23
A19 A6 24 B19 A7 25 C19 A8 28
A20 A9 29 B20 A10 30 C20 A11 31
A21 A12 32 B21 A13 33 C21 A14 34
A22 A15 35 B22 A16 36 C22 A17 37
A23 A18 38 B23 A19 39 C23 A20 40
A24 A21 41 B24 A22 42 C24 A23 43
A25 A24 44 B25 A25 45 C25 NC -
A26 NC - B26 NC - C26 NC -
A27 NC - B27 NC - C27 GND -
A28 P27_0 158 B28 P27_1 159 C28 P27_2 160
A29 P27_3 161 B29 P27_4 164 C29 P27_5 165
A30 P27_6 166 B30 P27_7 167 C30 GND -
A31 2.5V - B31 2.5V - C31 NC
A32 GND - B32 GND - C32 GND
Table 4-6: VG96 (X13) signals
Note:
The pin numbers of the VG connectors refer to the male connectors, that plugs
into the starter-kit. Please see chapter 5 to find the right orientation.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 33 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 34

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Connectors
4.7.2 VG48ABC DIN 41612 (X14)
Pin Name MCU-P. Pin Name MCU-P. Pin Name MCU-P.
A1 CSX0 56 B1 GND - C1 CSX1 57
A2 CSX2 58 B2 1.8V - C2 CSX3 59
A3 NC - B3 GND - C3 NC -
A4 CSX6 60 B4 1.8V - C4 RDY 55
A5 BGRNTX 51 B5 GND - C5 BRQ 54
A6 RDX 50 B6 NC - C6 WRX0 46
A7 WRX1 47 B7 NC - C7 WRX2 48
A8 WRX3 49 B8 NC - C8 ASX 62
A9 NC - B9 NC - C9 MCLKO 65
A10 DREQ0 189 B10 NC - C10 DACKX0 190
A11 DEOP0 191 B11 NC - C11 NC -
A12 INT12 97 B12 NC - C12 SDA0 99
A13 INT13 98 B13 NC - C13 SCL0 100
A14 SIN5 109 B14 Vin - C14 SOT5 110
A15 GND - B15 Vin - C15 SCK5 111
A16 INITX 73 B16 Vin - C16 GND -
Table 4-7: VG48 (X14) signals
Note:
The pin numbers of the VG connectors refer to the male connectors, that plugs
into the starter-kit. Please see chapter 5 to find the right orientation.
4.7.3 Distance between VG-Connectors
To connect own applications to the starter-kit the following figure shows the distance
between the VG DIN 41612 connectors.
Figure 4-6: Layout of DIN VG connectors
8,89 mm/
350 mil
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 34 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 35

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
5 Getting Started
Make sure that the FR Family Softune Workbench is installed on your PC and the “SK91F467D-208PFV” is ready to use (power-on (X5), serial connection (UART4) to COM port
of the PC).
5.1 Introduction to Softune Workbench
Start Softune Workbench. Select <File> <Open Workspace> to load the first example
“mb91460_io.wsp”. All examples can be found in the folder \Software\SWB_Samples on the
starter-kit CD-ROM. It is recommended to copy this folder to the local hard-drive. In the
project tree on the left side, you can open the “source”-folder which contains the source-files
registered to this project. A double-click on one of the files will invoke the built-in editor,
which supports syntax-highlighting, tags and various other functions.
Figure 5-1: Softune Workbench main window
Note:
You may customize the editor by a right-click on the editor
window.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 35 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 36

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
Whenever you modify the source-files, you have to re-compile and link the related files to
produce a valid loadmodule (ABS-file). This is done using the MAKE-function. MAKE
invokes the assembler, C-compiler and linker for FR whenever necessary (only modified files
will be re-compiled).
If you wish to re-compile the entire project regardless of any changes, you can use the
BUILD-function. To check for syntax-errors on a specific source-file, use the
COMPILE/ASSEMBLE function.
These three functions are available on the button-bar or from the main menu (Project –
Compile / Make / Build / Abort).
Click on MAKE or BUILD. Messages from the individual language tools will be fed into the
output window at the bottom of the main screen. If the tool chain (C-compiler → Assembler
→ Linker) was completed successfully, the message “No Error” will appear.
If you get any errors during build, an appropriate message will be generated. Try this with a
simple syntax-error (e.g. delete a semicolon “;” from the end of a C-line) and click on MAKE
again. You will now see a message like this:
Now Making...
--------------------Configuration: 91460_io.prj - Debug-------------------main.c
*** C:\SK-91F467-208PFV\91460_io\Src\main.c(81) E4065B: expected a ";"
*** C:\SK-91F467-208PFV\91460_io\Src\main.c(104) W1012B: warning: parsing restarts here after
previous syntax error
1 error detected in the compilation of
"C:\ SK-91F467-208PFV\91460_io\Src\main.c".
-----------------------------Error detected.
------------------------------
To locate the position in the source-file, where the error occurred, double-click on the
message. The editor will open the appropriate source-file, indicating the error highlighted in
red, depending on the customise settings of the editor. Correct the error and re-compile the
project as explained above.
If more errors occurred, you can go through the error list step by step using the menu “Edit –
Top/Previous/Next/Bottom Error” or using the appropriate buttons which have the same
functions:
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 36 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Note:
To get on-line help about a specific error, select the error
message and press F1. In many cases, you can get some useful
hints how to solve the problem. Of course, you can also use the
HELP-menu anytime during development or debugging.
Page 37

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
5.2 Project Start-up
In order to allow a quick and smooth project start-up Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe
supplies a template project as a reference. The easiest way to start a new project is to make
a copy of the template project and use this copy as a start-up. The template includes the
latest start91460.asm file, MCU header file, IRQ table, basic linker and C-Compiler settings.
Note:
In any case the settings done in the template must be checked and have to be
adjusted to the specific needs and settings of the final application. The template is
providing an example for building up a new project.
THIS SAMPLE CODE IS PROVIDED AS IS AND IS SUBJECT TO ALTERATIONS. FUJITSU
MICROELECTRONICS ACCEPTS NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS
OR/ELIGIBILITY FOR ANY PURPOSES. (C) Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
5.2.1 Create a New Project:
1. In order to start a new user-project use the “91460_template_91467d” project
2. Copy the folder 91460_template_91467d and rename the folder to e.g.
my_application
3. Enter the folder “my_application”
Rename “91460_template_91467d.prj” into “my_application.prj”
Rename “91460_template_91467d” into “my_application.wsp”
4. Edit “my_application.prj”
Rename “91460_template_91467d” -> “my_application”
5. Edit “my_application.wsp”
Rename “91460_template_91467d” -> “my_application”
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 37 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 38

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
Rename “91460_template_91467d”
into “my_application”
6. Start Softune Workbench and open your project
Figure 5-2: Open Softune Workbench workspace (*.wsp)
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 38 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 39

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
7. Select the active configuration STANDALONE. In this configuration the application is
linked for the available memory on flash-device, e.g. MB91F467D.
8. Use “Make”, or “Build” to compile and link the project for available memory on flash-
device. The generated output files can be found in the sub-folder STANDALONE of
the project folder. The *.mhx file (Motorola S-Record) is located in the ABS subfolder.
Note:
Always check the memory map of the linker settings and ensure
that this memory map is suitable for the application and target
system in use. Additionally the *.mp1 file should be checked to
ensure correct settings.
9. Now, the application can be debugged, therefore, please have a look at the next
chapter. Or the generated *.mhx file (Motorola S-Record) can be programmed with
the flash programming utility into the internal flash. Please keep in mind, that
therefore the mode pins have to be set to “Internal ROM Mode Vector”.
Note:
The starter-kit is delivered with the mode pin settings for the
“External ROM Mode Vector”, which allows to debug the
application with the pro-programmed SWB Monitor Debugger.
If the application should be programmed into the internal flash, the
mode pins have to be switched to the “Internal ROM Mode
Vector”.
5.3 Softune Workbench Monitor Debugger
5.3.1 General Description
Whenever you have created a valid load module successfully, you can switch from the
development mode to the debugging mode of Softune Workbench.
Basically, there are 3 types of debugging systems supported:
1. The software simulator: The simulator is part of the Softune Workbench and does
not require any target hardware. The simulator will cover the FR-core features,
but no peripheral functions. Therefore, you can use the simulator to verify
program flow, check for dynamic errors, look at the generated assembler code,
etc. .
2. The SWB Monitor Debugger: This debugger type requires an evaluation board
like the “SK-91F467-208PFV” connected to one of the COM-ports of your PC.
Explanations in this manual refer to the SWB Monitor Debugger only. For further
information please see also the application note “swb_monitor_debugger”
3. The emulator debugger: The in-circuit emulator (ICE) is a system, which allows a
connection to any target system using a probe-cable. The appropriate system for
the MB91460 series is the MB2198-01 system. More information about this
system can be found on the Fujitsu website.
Which debugger is used for the actual project can be configured in the project tree as shown
below or in the “Project – Setup Project – Debug” menu. The current selection is blue
marked (icon):
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 39 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 40

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
There are some little restrictions, when using the SWB Monitor Debugger:
1) Due to the fact that the application code is located in the external RAM, the execution
speed of the code is slower, because of the slower external bus access.
2) Depending on the used linkage option of the SWB Monitor Debugger, CS 0 and CS 1
are required for the external memory. The affected CS has to be switched off in the
start-up of the application. (#set CS0 OFF, #set CS1 OFF).
3) Since some settings for the SWB Monitor Debugger during start-up are required, the
start-up file cannot be debugged. After starting the SWB Monitor Debugger, the
program execution stops at main(). Furthermore, the clock settings of the application
start-up are omitted. For the desired clock settings the SWB Monitor Debugger has to
be adapted.
4) To indicate the current state of the SWB Monitor Debugger a certain port is used.
This feature can also be disabled to give the port free for the application.
To stop the execution of the program the external interrupt INT0 is used. This feature can
also be disabled to give the port free for the application. The “abort” button of the Softune
Workbench is not fully supported. A detailed explanation of the necessary changes of the
SWB Monitor Debugger can be found in the application note “mb91460_swb_monitor
_debugger”.
5.3.2 Starting the SWB Monitor Debugger
After software development the SWB Monitor Debugger can be used for debugging.
1) Please make sure, that SWB Monitor Debugger is programmed into the external
Flash. To use the Monitor Debugger, the CPU Mode selection must be set to
“External ROM Mode Vector” mode by setting DIP switch S5 to (On, Off, Off, Off).
The correct start-up of the SWB Monitor Debugger is indicated by D2, D4 and D8
Figure 5-3: Correct start-up of the SWB Monitor Debugger
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 40 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 41

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
2) To start the SWB Monitor Debugger, double-click the entry
“Mondeb_57K6_com1.sup” for communication via COM1 (57K6 baud, 8N1) or
“Mondeb_57K6_com2.sup” for communication via COM2 (57K6 baud, 8N1).
Figure 5-4: Start SWB Monitor Debugger with external flash and SRAM
3) Since some settings for the SWB Monitor Debugger during start-up are required, the
start-up file can not be debugged. The settings are done with the help of procedure
files. After starting the SWB Monitor Debugger, the program execution stops at
main().
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 41 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 42

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
5.3.3 Basic Debugger Features
After starting the SWB Monitor Debugger, the source window will be opened which contains
locate-arrows for each (possible) source-line, the original source-code,
Figure 5-5: SWB debugging window
Breakpoint-indicators and the assembler code (in “mixed view”). The current program
position will be indicated by a yellow line. Use right-click in the source window to configure
the view (add/remove control characters, view mixed source code, breakpoint …)
Note:
You can choose “mixed view” from the context menu (right-click)
to display source and assembly code at the same time. The
command “go to current” will take you to the active code line!
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 42 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 43

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
In the following the basic features of the SWB Monitor Debugger are described.
GO: Executes the program continuously from the memory location pointed to by the
current program counter (PC) until a termination factor occurs.
STEP IN: Executes the program stepwise according to the listing in the source
window (steps in C- or ASM). Note that interrupts are disabled during step execution!
STEP OVER: Executes the program stepwise except call-instructions (which will be
executed until return). Interrupts are not disabled during a continuous CALL...RETURN
execution.
STEP OUT: Executes the program continuously to the parent function (until
RETURN). Interrupts are enabled. Note, that debug information is required for this function.
EXECUTE UNTIL CURSOR: Automatically sets a breakpoint at the actual cursor
position and executes continuously until this breakpoint, which will be deleted
afterwards.
Each valid code line in a debugger window automatically has a locator (blue arrow) and a
breakpoint-option (circle). Note that some C-lines may not be displayed with locators and
breakpoints, because the compiler has created “optimized” assembler-code. Select “mixed
view” in order to check the compiler output.
Instead of single-steps, you may also use the arrows to directly execute your program until a
certain line of your source-code:
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 43 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 44

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
ABORT: Forcibly terminates execution. This button is not fully supported by the
SWB Monitor Debugger and may cause malfunction if used to abort “continuous
operation” of the MCU.
This command button can only be used to abort single code line operations
Example: for(k=DELAY_CONSTANT; k>0; k--);
Use the button INT0 on the “SK-91F467-208PFV” for ABORT function.
To ABORT continuous execution, you have to use the INT0 button on the starter-
kit.
5.4 Advanced Softune Workbench SWB Monitor Debugger Features
In the following advanced features of the SWB Monitor Debugger are described.
TOGGLE BREAKPOINT: Sets or deletes breakpoint at the current source line:
To set or delete a breakpoint, click the circles at the beginning of a source-line.
A indicates an active breakpoint. Hit “Run continuously” to execute code until
reaching this line. A list of all breakpoints can be found under the “Debug – Breakpoint”
menu. 255 Software-Breakpoints (using TRAP replacement) are possible.
Note:
To set breakpoints at positions which are currently not visible (e.g.
because the source window of that module is not open), you can
also enter a symbolic label directly in the “Breakpoint” menu.
Example: Enter “main” in the address-field and confirm. The new
breakpoint will automatically be assigned to the address of the
“main()”-function.
REGISTER WINDOW: Displays the CPU-register window. Updated registers appear
in red. Setup in context menu defines which Registers should be displayed.
WATCH WINDOW: Displays the current variables to „watch“. Double-click on any
variable in your code then specify watch in context menu to add to watch window. All listed
variables in a watch window can be displayed in any number format. Use Edit to directly
change the contents.
MEMORY WINDOW: Displays memory areas in various formats defined by Setup
(context menu). Changing of address/data is possible when debugger is not executing.
The memory window can be very helpful to check the registers or the frame memory of the
connected graphic controller!
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 44 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 45

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
DISASSEMBLER: Disassembles the content of the code memory beginning from
actual PC position and displays the result in a separate window. Individual
assembler-lines can be changed using the „inline assemble“-function.
DEBUG - STACK: Displays the current stack contents in terms of function calls.
Parameters, if any, are displayed in brackets.
DEBUG - VECTOR: Reads out and displays the actual interrupt-vector table. Use the “jump”
function to display any code areas pointed to by an interrupt vector (e.g. interrupt service
routines used in your program).
DEBUG - CALL: This function can be used to “call” any routine defined in your code when
the debugger is on hold.
DEBUG – LOAD TARGET FILE: Starts a new download of the current load module (ABS
file). Usually this function will be executed automatically after starting the debugger (defined
in debug settings; see „Project-Setup-Debug“). However, this function can be useful to re-
initialize the debugger for the current debug session.
VIEW - SYMBOL: This function displays all (global) symbols of the current project.
Information about the type (char, integer etc.) and the location (address in RAM or register)
can be shown using „detail“.
VIEW - LOCAL: Similar to View-Symbol, but only local variables of the current function are
shown.
VIEW - COMMAND: From this window, the debugger can be controlled using a command
line input. All GUI functions are available as individual commands.
In order to document or save debugging details such as memory contents, all outputs fed to
the command console can be written to a file (“logging”).
A whole “program” of commands (incl. flow control) can be written to a PRC-file and
executed. Procedure-files are simple text-files with the extension “.PRC” and can be created
by the Softune Workbench editor or any other text editor. To execute a procedure-file, use
the command window menu or the “file-open” menu during debugging.
Note:
Procedure-files can be very helpful to configure the debugenvironment automatically, perform automated tests (e.g. when a
new C-module has to be tested) or to enhance basic emulator
functions such as breakpoints. Using a procedure file, breakpoints
can be defined dynamically depending on program conditions.
See the “Command Reference Manual” (on-line help) for detailed
information about the available command and parameter syntax.
Some procedure files exist already included in the example project
directory.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 45 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 46

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Getting Started
5.5 Memory Configuration
The following picture shows the linkage map and the memory organisation, if the SWB
Monitor Debugger is used with external flash and SRAM.
2:8000h
4:0000h
F:FC00h
F:FFFFh
14:FFFFh
(MB91467D)
Internal RAM/Flash External Flash
Appl. Data
Appl. Code
Appl. Vector Table
2:8000h
2:FFFFh2:FFFFh
4:0000h
Internal RAM External SRAM
Appl. Data
Not accessable
CS 1
Appl. Code
Appl. Vector Table
Free
MDE Data
4:0000h
F:FC00h
F:FFFFh
14:FFFFh (MB91467D)
3F:F000h
3F:FFFFh
100:0000h
10F:FC00h
10F:FFFFh
11F:FFFFh
17F:FFFFh
MDE Vector Table
CS 0
MDE Code
Free
Figure 5-6: Default linkage map for the SWB Monitor Debugger of the MB91467D
On the left hand site the memory organisation of the normal operation mode of the
microcontroller MB91F467D can be seen, the whole application is internal. For this operation
mode the mode pins have to be set to 0-0-0, hence DIP switch S5 has to be set to off, off,
off, off.
On the right hand site the microcontroller runs in the external reset-vector mode, which
requires the mode pins setting 1-0-0, hence DIP switch S5 has to be set to on, off, off, off. In
this mode the internal flash is not accessible any more. The external SRAM takes the place
of the internal flash. The kernel of the SWB Monitor Debugger is located in the external
flash.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 46 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 47

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Programming the internal Flash
6 Programming the internal Flash
This chapter describes the serial asynchronous programming of the internal flash with the
help of the ‘FME-FR Programmer’ in automatic mode. For other programming possibilities,
please see the application note mcu-an-300012-e-mb91460_flash_programming.pdf.
1) For serial asynchronous programming SUB-D9 connector X4 which is connected to
UART4 has to be used. The following jumper setting is needed.
Jumper Setting Description
JP60 1-2 closed MCU SIN4 connected to RS-232 transceiver
JP65 1-2 closed MCU SOT4 connected to RS-232 transceiver
JP69 1-2 closed X4 pin2 is connected to RS-232 transceiver
Table 6-1: Jumper setting on starterkit SK-91F467D-208PFV
2) If the programming software should generate a reset signal on RTS or DTR line, refer
to the following jumper list.
Jumper Setting Description
closed RTS and CTS is shortcut at connector X4
JP58
open RTS and CTS is not shortcut at connector X4
1-2 closed DTR can be used for system reset
JP64
2-3 closed RTS can be used for system reset
JP57 3-4 closed Reset will be done via UART4
1-2 closed No polarity inversion for the DTR/RTS signal
JP29
2-3 closed Polarity inversion for the DTR/RTS signal
Table 6-2: Jumper settings for reset signal on starterkit SK-91F467D-208PFV
3) The CPU Mode selection must be set to internal reset vector mode by setting DIP
switch S5 to (Off, Off, Off, Off)
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 47 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 48

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Programming the internal Flash
JP29
JP58
X4
JP60 JP64
JP57
JP65 JP69
Figure 6-1: Jumper setting on starterkit SK-91F467D-208PFV
4) Start the ‘FME-FR Programmer’ and connect the UART4 to your serial PC
communication port. A straight cable connection has to be used.
5) Choose the microcontroller device (“MB91F467D”) as device type and browse to the
mhx-file you want to program to the embedded flash memory of the microcontroller.
Press the button “Automatic Mode” to start programming.
6) After that, immediately reset the microcontroller.
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 48 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 49

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Programming the internal Flash
RESET MCU
Figure 6-2: Settings for Automatic Mode
7) If your hardware supports MCU reset via DTR or RTS signal lines of the PC’s COM
port, go to sheet “Signals” and select the appropriate reset signal line. The
programmer now resets the microcontroller automatically before starting the
programming sequence and you do not have to reset the MCU manually immediately
after pressing the button “Automatic Mode”.
Figure 6-3: Reset Signal Settings
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 49 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 50

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Programming the internal Flash
The software now automatically writes a flash loader to the microcontroller, does a blank
check and erases the flash memory if necessary. After that the user application is
programmed to the embedded flash memory.
During this sequence the actual progress status can be seen by checked off steps on the
“Automatic” sheet and the messages below in the message box.
If the programming sequence is ended successfully, you will receive the output shown in
figure 7.
The Addresses 0x14:8000 to 0x14:800F cannot be written in automatic mode. This is a built
in security feature to prevent unintended writing to the Flash Security Vectors and Boot
Security Vectors. Otherwise it would be possible to secure flash content and to lock the
microcontroller for serial programming/reading/erasing by not being able to enter the internal
loader anymore. If you want to use these features explicitly, you have to program these
dedicated addresses by using the “Prog Word” Function of the step-by-step mode.
Figure 6-4: Successful Programming in Automatic Mode
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 50 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 51

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Programming the SWB Monitor Debugger
7 Programming the SWB Monitor Debugger
The following procedure describes the installation process for the SK-91F467D-208PFV and
the MB91F467D.
1) The CPU mode selection must be set to internal reset vector mode by setting DIP
switch S5 to (Off, Off, Off, Off)
2) Program the monitor-programmer “91460_mondeb_uart4_extbus_flash_sram” into
the external Flash, e.g. with the help of the FME Flash Programmer V3.11 or later.
Please see the chapter above and the application note mcu-an-300012-emb91460_flash_programming.pdf, too. Please use the automatic mode. The settings
for CS0 should be ASR0: 0100, ACR0: 8822, AWR0: 3378.
3) Please, power-off the SK-91F467D-208PFV.
4) The CPU Mode selection must be set to external reset vector mode by setting DIP
switch S5 to (On, Off, Off, Off)
5) The correct start-up of the SWB Monitor Debugger is indicated by D2, D4 and D8.
Figure 7-1: Correct Start-Up of the SWB Monitor Debugger
6) The SWB Monitor Debugger is now ready to use.
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 51 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 52

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Trouble shooting
8 Trouble shooting
Problem Solution
Starter-kit does not power-on correctly.
Some or all of the power LEDs (D24, D30,
D34, D40) do not light.
Starter-kit stays in reset.
LED D18 (Reset indicator) lights up
permanently.
The communication from Softune
Workbench to the evaluation board fails
(Communication errors).
The windows of the debugger are empty. * This is due to wrong (maybe old) file path
When trying to program the application to
the embedded flash, the programmer
stops at first address with “loading error” !
Hardware units such as LEDs, user
buttons, UART are not working.
Optional LC-Display at J6 does not work
Graphic sub-board does not work Check power supply 9-12V/1500mA. Reduce
Check voltage supply and jumpers :
∗ The voltage on DC-Power plug should be in the
range of 9-12V. The plug should have ‘+’ on shield
and ‘–‘ on the centre. The power supply should be
able to supply at least 500 mA. To support both,
the “SK-91F467D-208PFV” and a graphic subboard the supply should be able to supply 1500mA.
* The LEDs should light up after switching on the
board. Use a millimetre to see whether 5V,3.3V,
2.5V and 1.8V are present on the Vcc/GND test
measurement points J21, J22, J23 and J24.
∗ Check jumper positions according to chapter 2.1
∗ Remove all user extensions of the starter-kit
∗ LED D18 (Reset) should flash. If D18 lights up
permanently, the voltage is too low. Increase the
voltage supply and check available supply current
to solve the problem.
∗ Remove all user extensions on the board to avoid
any shortcuts or leakage current!
∗ Make sure your COM-port number and the baud
rate settings are correct (see debugger
introduction). The default COM-port is 1 and the
default baud rate is 57.6 kBaud.
∗ Make sure no other programs are using the same
COM-port on your PC. Close all other applications
(e.g. flash programmer utilities, terminals etc.)
* Check if RTS/CTS is closed on the CPU module
(check jumper JP58, 60, 65 are closed).
* Use only a RS232 extension 1:1 cable.
information. Closing all windows in the debugger
and re-open should fix the problem.
* You are probably trying to program a program to
the flash which is linked for the external RAM area.
Check for details the linker memory map and the
linker output mapping file *.mp1 file.
∗ Make sure you have enabled these units on the
evaluation board using the appropriate jumpers.
See the provided examples and the hardware
manual for information on how to control the
peripherals.
∗ Adjust the potentiometer RP1 to adjust contrast
of LCD. Remove resistor network RN3.
external bus clock frequency.
Table 8-1: Trouble shooting
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 52 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 53

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
X13
Silk-Plot of the Board
9 Silk-Plot of the Board
9.1 Top Side
A B C D E F G H J K L M N
1
UART2
X1
X4
UART4
X8
UART5
2 2
3 3
X11
1
CAN2
4
4
C32
B32
A32
5 5
6
6
7 7
8 8
9 9
(female)
VG96
10 10
11 11
12
C1B1A1
12
13 13
14
15
RST
ICU0
INT2
INT1
INT0
14
C16
B16
A16
15
16 16
17 17
18
19 19
C1
X14
VG48 (female)
18
B1
A1
20
21
A B C D E F G H J K L M N
Power
Switch
20
Power
CAN0
X9
CAN1
X10
21
Figure 9-1: Board layout (top side)
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 53 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 54

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Silk-Plot of the Board
9.2 Bottom Side
A B C D E F G H J K L M N
1
1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 6
7 7
8 8
9 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 13
14 14
15 15
16 16
17 17
18 18
19 19
20 20
21 21
A B C D E F G H J K L M N
Figure 9-2: Board layout (bottom side)
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 54 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 55

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
PCB History
10 PCB History
10.1 SK-91F467-208PFV V1.0
Part Problem Fixed
U20 Wrong UB/LB connection (WRX2 and WRX3 has to be connected) V1.1
X14 Connect 1.8V supply not directly to X14 (add jumper) V1.1
U6 Additionally pull-up resistors for MCU and ASSP reset line V1.1
Reset button connection (SW1), add further option to activate reset
U6
U9 Add C=220uF/16F between Vcc5V and GND V1.1
U11 Add C=220uF/16F between Vcc3V3 and GND V1.1
U14 Add C=100uF/16F between Vcc2V5 and GND V1.1
U17 Add C=100uF/16F between Vcc1V8 and GND V1.1
directly when pressing SW1. Actually, SW1 must be pressed 2s to
activate reset. (add solder jumper to select one option)
V1.1
Table 10-1: History PCB V1.0
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 55 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 56

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Appendix
11 Appendix
11.1 Related Products
• SK-91F467D-208PFV Evaluation board with MB91F467D
• SK-91F467-FLEXRAY Evaluation board with MB91F467D and MB88121A
• SK-91460-MAIN Evaluation main board for MB91460 Series
• SK-91460-91F467D-208PFV MCU-board incl. MB91F467D for SK-91460-MAIN
• ADA-91V460-91F467D Conversion adapter MB91V460 to MB91F467D
• MB2198-01 Emulator debugger main unit
• MB2198-10 DSU cable
• MB2198-300 Adapter board for MB91V460 emulation chip (BGA-660P)
• MB91V460 Emulation chip of MB91460 Series
• PB-91467D-208PFV Probe cable for MB91F467D target system
(Recommended for SK-91F467D-208PFV)
• PB-91467D-NLS-208PFV Probe cable for MB91F467D target system
(Recommended for SK-91F467-FLEXRAY)
• NQPACK208SD Socket for package FPT-208P-M01 and FPT-208P-M04
Tokyo Eletech Corp. www.tetc.co.jp/e_tet.htm
• HQPACK208SD306H Header for FPT-208P-M01 e.g.: MB91F467D
• YQPACK208SD Joint connector extension for NQPACK208SD
• YQSOCKET208SDN Joint connector socket for NQPACK208SD
• MB91F467D Flash chip of MB91460 Series
• MB88121A FlexRay Communication Controller
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 56 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 57

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Appendix
11.2 Information on the WWW
Information about FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS Products
can be found on the following Internet pages:
Microcontrollers (8-, 16- and 32-bit), Graphics Controllers
Datasheets and Hardware Manuals, Support Tools (Hard- and Software)
http://www.fme.gsdc.de/gsdc.htm
Automotive products: MCU, Graphic display controller, MPEG en/decoder, gyro sensors
http://www.fujitsu.com/emea/services/industries/automotive/
Linear Products: Power Management, A/D and D/A Converters
http://www.fujitsu.com/emea/services/microelectronics/linears/
Media Products: SAW filters, acoustic resonators and VCOs
http://www.fujitsu.com/emea/services/microelectronics/saw/
For more information about FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS
http://emea.fujitsu.com/microelectronics
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 57 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 58

11.3 Tables
SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Appendix
Table 2-1: Jumper settings .................................................................................................... 14
Table 3-1: MCU operating mode............................................................................................ 17
Table 3-2: Power switch.........................................................................................................18
Table 3-3: Power supply configurations................................................................................. 18
Table 3-4: Voltage Test Points............................................................................................... 19
Table 3-5: MCU power supply SK-91F467D-208PFV ........................................................... 20
Table 3-6: MCU ADC Supply ................................................................................................. 21
Table 3-7: CAN-MCU connection .......................................................................................... 22
Table 3-8: UART2 settings..................................................................................................... 23
Table 3-9: UART4 settings..................................................................................................... 24
Table 3-10: UART5 settings................................................................................................... 25
Table 3-11: User push buttons............................................................................................... 26
Table 3-12: S4 values ............................................................................................................ 26
Table 3-13: S3 settings .......................................................................................................... 26
Table 3-14: Reset connections .............................................................................................. 27
Table 3-15: Supply monitor settings ...................................................................................... 27
Table 3-16: Reset UART selection ........................................................................................ 28
Table 4-1: UART connector signals ....................................................................................... 29
Table 4-2: CAN connector signals ......................................................................................... 30
Table 4-3: LED/LCD Signals.................................................................................................. 31
Table 4-4: In-circuit programming connector ......................................................................... 32
Table 4-5: MCU pin connectors ............................................................................................. 32
Table 4-6: VG96 (X13) signals............................................................................................... 33
Table 4-7: VG48 (X14) signals............................................................................................... 34
Table 6-1: Jumper setting on starterkit SK-91F467D-208PFV .............................................. 47
Table 6-2: Jumper settings for reset signal on starterkit SK-91F467D-208PFV .................... 47
Table 8-1: Trouble shooting ................................................................................................... 52
Table 10-1: History PCB V1.0................................................................................................ 55
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 58 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
Page 59

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Appendix
11.4 Figures
Figure 2-1 AC plug adapter.................................................................................................... 12
Figure 2-2: AC plug adapter selection ................................................................................... 12
Figure 2-3: DC voltage selection............................................................................................ 12
Figure 2-4: Low voltage adapter selection ............................................................................. 12
Figure 2-5: Starter-kit status after power on .......................................................................... 13
Figure 2-6: Default jumper settings........................................................................................ 15
Figure 2-7: Softune Workbench start menu location.............................................................. 16
Figure 2-8: Softune Workbench V6 IDE................................................................................. 16
Figure 3-1: MCU mode switch: External ROM Mode Vector ................................................. 17
Figure 3-2: MCU mode switch: Internal ROM Mode Vector................................................... 17
Figure 3-3: Voltage Test Points ............................................................................................. 19
Figure 4-1 Power connector................................................................................................... 29
Figure 4-2 UART connector ................................................................................................... 29
Figure 4-3: CAN connector .................................................................................................... 30
Figure 4-4: User LEDs / LCD ................................................................................................. 31
Figure 4-5: In-circuit programming connector ........................................................................ 32
Figure 4-6: Layout of DIN VG connectors.............................................................................. 34
Figure 5-1: Softune Workbench main window ....................................................................... 35
Figure 5-2: Open Softune Workbench workspace (*.wsp)..................................................... 38
Figure 5-3: Correct start-up of the SWB Monitor Debugger................................................... 40
Figure 5-4: Start SWB Monitor Debugger with external flash and SRAM.............................. 41
Figure 5-5: SWB debugging window...................................................................................... 42
Figure 5-6: Default linkage map for the SWB Monitor Debugger of the MB91467D.............. 46
Figure 6-1: Jumper setting on starterkit SK-91F467D-208PFV ............................................. 48
Figure 6-2: Settings for Automatic Mode ............................................................................... 49
Figure 6-3: Reset Signal Settings .......................................................................................... 49
Figure 6-4: Successful Programming in Automatic Mode...................................................... 50
Figure 7-1: Ready for programming......................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Figure 7-2: Programming finished............................................ Error! Bookmark not defined.
Figure 7-3: Correct start-up of the SWB Monitor Debugger..... Error! Bookmark not defined.
Figure 9-1: Board layout (top side) ........................................................................................ 53
Figure 9-2: Board layout (bottom side) .................................................................................. 54
© Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH - 59 - FMEMCU-UG-910014-13
Page 60

SK-91F467D-208PFV V1.1
Appendix
11.5 Abbreviations
ADC Analogue Digital Converter
ASSP Application Specific Standard Product
CAN Controller Area Network
CS Chip Select
FME Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
LB Lower Byte
LIN Local Interconnect Network
MCU Microcontroller Unit
PCB Printed Circuit Board
SRAM Static Random Access Memory
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
UB Upper Byte
UG User Guide
USART Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
FMEMCU-UG-910014-13 - 60 - © Fujitsu Microelectronics Europe GmbH
 Loading...
Loading...