Page 1
Instruction Manual
DIGITAL CONTROLLER
COMMUNICATION
FUNCTIONS (MODBUS)
TYPE: PXH
INP-TN514207-E
Page 2

Note: Windows® is the registered trade mark of Microsoft Corporation.
Note: Visual Basic® is the registered trade mark of Microsoft Corporation.
Note: MODBUS® is the registered trade mark of Gould Modicon.
z Exemption items from responsibility
The contents of this document may be changed in the future without prior notice.
We paid the utmost care for the accuracy of the contents. However, we are not liable for direct
and indirect damages resulting from incorrect descriptions, omission of information, and use of
information in this document.
Notice
Page 3

CONTENTS
CONTENTS....................................................................................................................... i
1. COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS ......................................................................................1
1.1 Outline..........................................................................................................................1
2. SPECIFICATIONS.................................................................................................................2
2.1 Communication Specifications ....................................................................................2
3. CONNECTION ......................................................................................................................3
3.1 Communication Terminal Allocation...........................................................................3
3.2 Wiring ..........................................................................................................................4
4. SETTING OF COMMUNICATION CONDITION...............................................................6
4.1 Setting items.................................................................................................................6
4.2 Setting Operation Method............................................................................................7
5. MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL......................................................................8
5.1 Outline..........................................................................................................................8
5.2 Composition of Message..............................................................................................9
5.3 Response of Slave Station..........................................................................................11
5.4 Function Code ............................................................................................................12
5.5 Calculation of Error Check Code (CRC-16)..............................................................13
5.6 Transmission Control Procedure................................................................................14
5.7 FIX Processing (Cautions in data write) ....................................................................16
6. DETAILS OF MESSAGE....................................................................................................17
6.1 Read-out of Word Data [Function code: 03H]......................................................17
6.2 Read-out of Read-out Only Word Data [Function code: 04H]....................................19
6.3 Write-in of Word Data (1 word) [Function code: 06H]...............................................21
6.4 Write-in of Continuous Word Data [Function code: 10H] ..........................................22
7. ADDRESS MAP AND DATA FORMAT.............................................................................24
7.1 Data Format................................................................................................................24
7.2 Communication Address Map ....................................................................................28
8. SAMPLE PROGRAM .........................................................................................................37
9. TROUBLESHOOTING .......................................................................................................43
INP-TN514207-E
i
Page 4
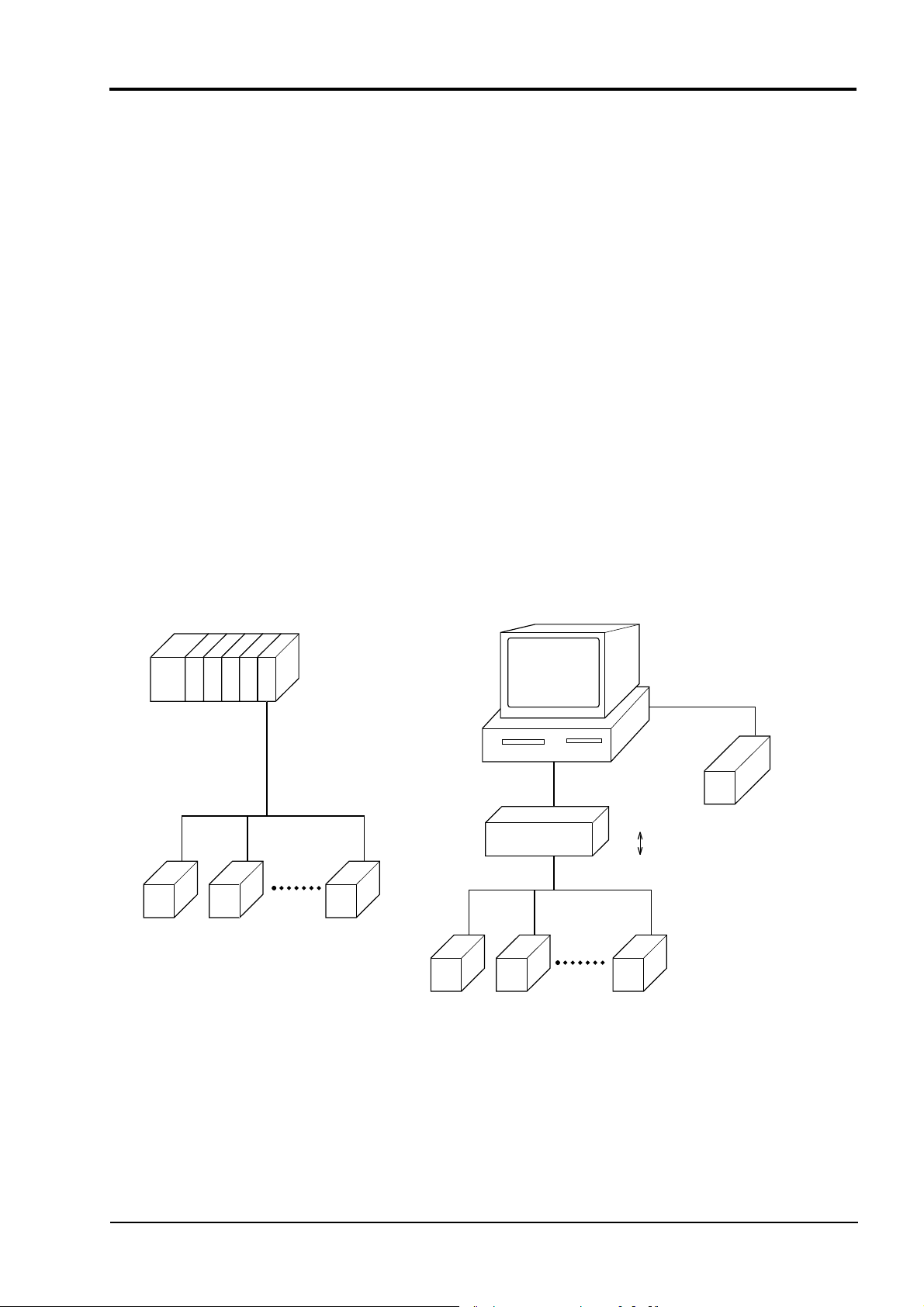
1. COMMUNICATION FUNCTIONS
1.1 Outline
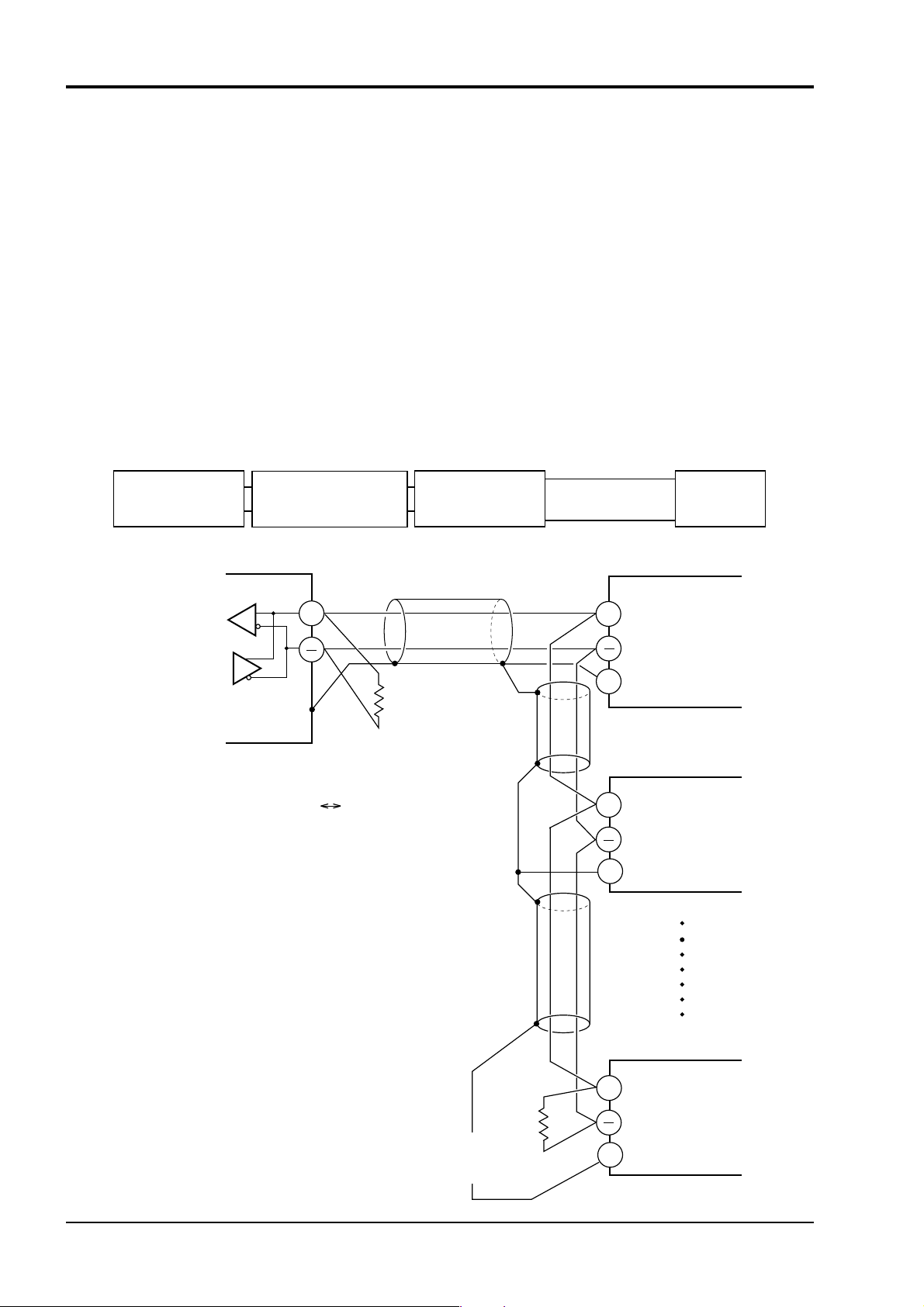
▪ Via RS-485 interface and PC loader interface, PXH provides communication functions of transmit-
ting and receiving data to and from host computer, programmable controller, graphic panel, etc.
▪ The communication system consists of master station and slave stations. For RS-485 communica-
tion, up to 31 slave stations (PXHs) can be connected per master station.
Note that, because the master station can communicate with only one slave station at a time, a party
to communicate with must be specified by the "Station No." set at each slave station.
For loader communication, one slave station (PXH) can be connected per master station.
▪ In order that the master station and slave station can communicate, the format of the trans-
mit/receive data must coincide. For the PXH, the format of the communication data is determined
by the MODBUS protocol.
▪ Please use an RS-232C ⇔ RS-485 converter in case of designating a personal computer or other
devices which have an RS-232C interface as a master station.
[RS-232C ⇔ RS-485 converter] (recommended article)
Type: RC-77 (isolated type)/ RA SYSTEMS make http://www.ras.co.jp
Type: K3SC-10 (isolated type)/ OMRON make http://www.omron.co.jp
RS-232C communication with PC is available upon connecting Type: ZZPPXH1*TK4H4563 to PC
loader interface where PXH is provided in standard.
Programmable
controller
RS-485
RS-232C
RS-485
Personal
computer
RS-232C
D-sub9 pin
RS-232C
RS-485 communication converter
Caution:
When using the RS-232C ⇔ RS-485 converter, pay attention to cable connection between the con-
verter and master station. If the cable is not connected correctly, the master station and slave station
cannot communicate. In addition, be careful about communication settings such as baud rate and
parity set for the converter.
PC loader
interface
INP-TN514207-E
1
Page 5
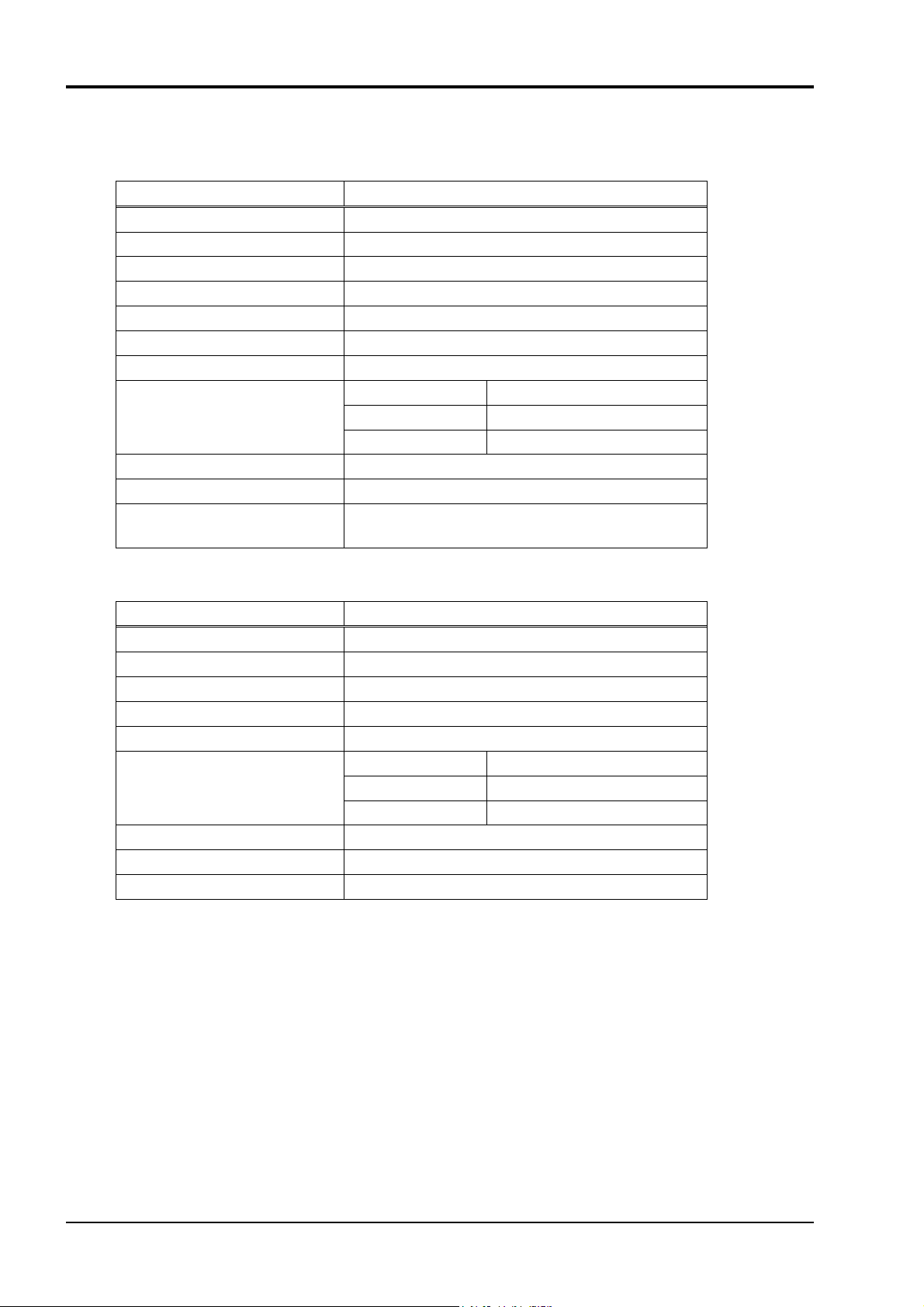
2. SPECIFICATIONS
2.1 Communication Specifications
■ RS-485
Item Specification
Electrical specification Based on EIA RS-485
Transmission method 2-wire, half duplex
Synchronous system Start-stop synchronous system
Connection format 1 : N
Number connectable units Up to 31 units
Transmission distance 500m max. (total extension distance)
Transmission speed 9600bps, 19200bps, 38400bps
Data format Data length 8 bits
Stop bit 1 bit
Parity none, even, odd (selectable)
Transmission code HEX value (MODBUS RTU mode)
Error detection CRC-16
Isolation
■ PC loader interface
Functional isolation between transmission circuit
and others (withstand voltage : 500V AC)
Item Specification
Electrical specification EIA RS232C
Transmission method 3-wire, half duplex, bit-sereal
Synchronous system Start-stop synchronous system
Connection format 1 : 1
Transmission speed 9600bps, 19200bps, 38400bps
Data format Data length 8 bits
Stop bit 1 bit
Parity none, even, odd (selectable)
Transmission code HEX value (MODBUS RTU mode)
Error detection CRC-16
Isolation Non-isolated from internal circuit
INP-TN514207-E
2
Page 6
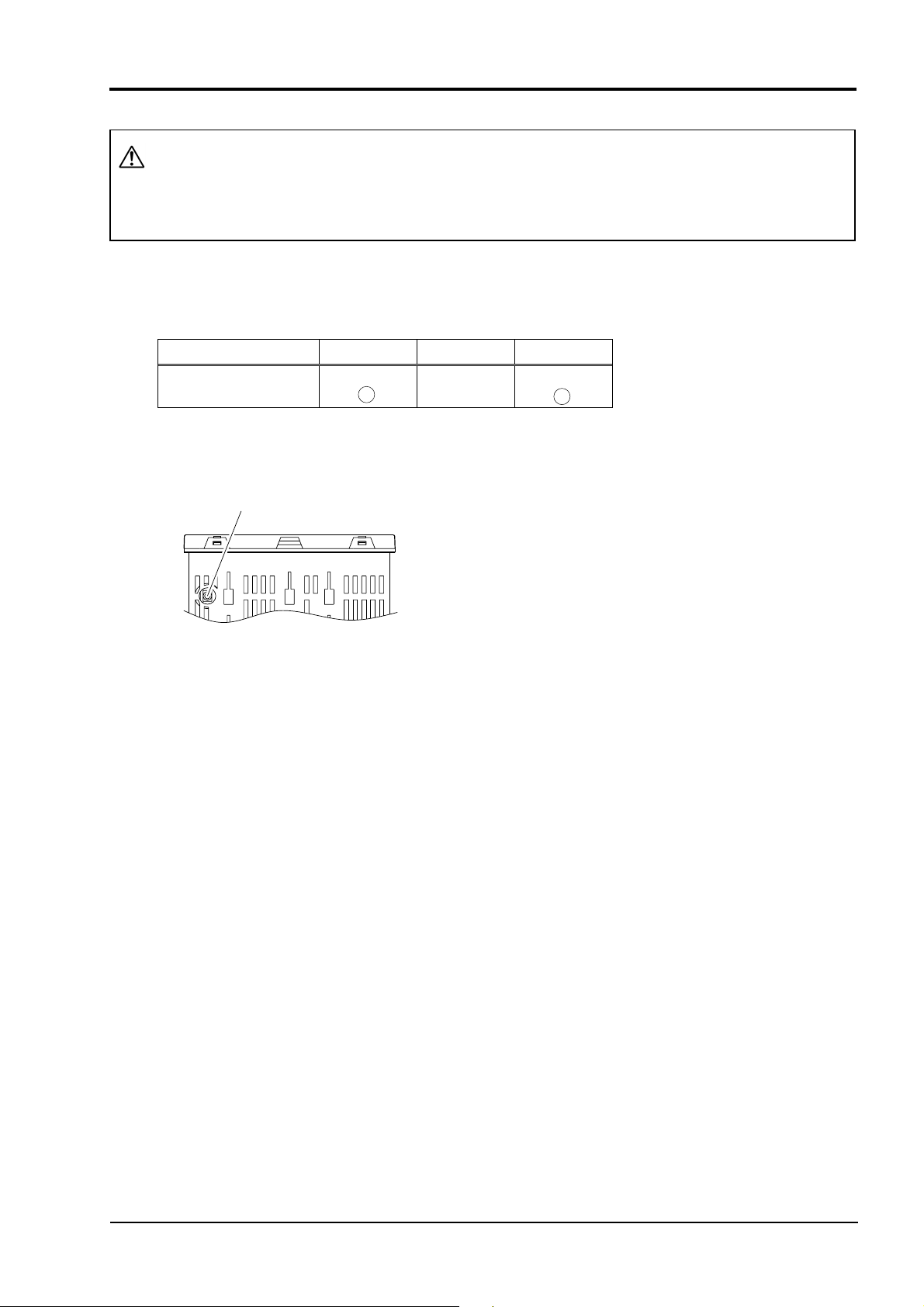
3. CONNECTION
WARNING
For avoiding electric shock and malfunctions, do not turn on the power supply until all wiring is
completed.
3.1 Communication Terminal Allocation
■ PXH9 (RS-485)
Terminal number (14) (15) (16)
Signal name
■ PXH9 (PC loader interface)
PC loader interface
RS485
+
SG
RS485
–
Φ2.5, 3-pole miniature jack
INP-TN514207-E
3
Page 7
3.2 Wiring
■ RS-485
▪ Use twisted pair cables with shield. Recommended: KPEV-SB (Furukawa Electric make)
▪ The total extension length of the cable is up to 500 m. A master station and up to 31 units of the
PXH can be connected per line.
▪ Both ends of the cable should be terminated with terminating resistors 100Ω (1/2W or more).
▪ If the PXH is to be installed where the level of noise applied to the PXH may exceed 1000 V, it is
recommended to install a noise filter in the master station side as below.
Recommended noise filter: ZRAC2203-11 (TDK make)
▪ If problematic in EMC at communication, loading the communication cable with ferrite can lower
the noise level.
Recommended ferrite core: ZCAT series (TDK make)
MSFC series (Morimiya Electric make)
Master station
(PC, etc.)
RS-232C⇔RS-485
Master station side
Twisted pair cable with shield
+
SG
RS-485 interface
or
RS-485 side of the RS-232C RS-485 converter
Terminating resistor
100Ω (1/2W)
Noise filter PXH
Transmission
cable
Slave (PXH)
+
SG
Slave (PXH)
+
SG
Slave (PXH)
▪ SG connection is not mandatory, but is
+
effective for remedying communication
errors attributable to noises.
Terminating
resistor
100Ω (1/2W)
SG
INP-TN514207-E
4
Page 8
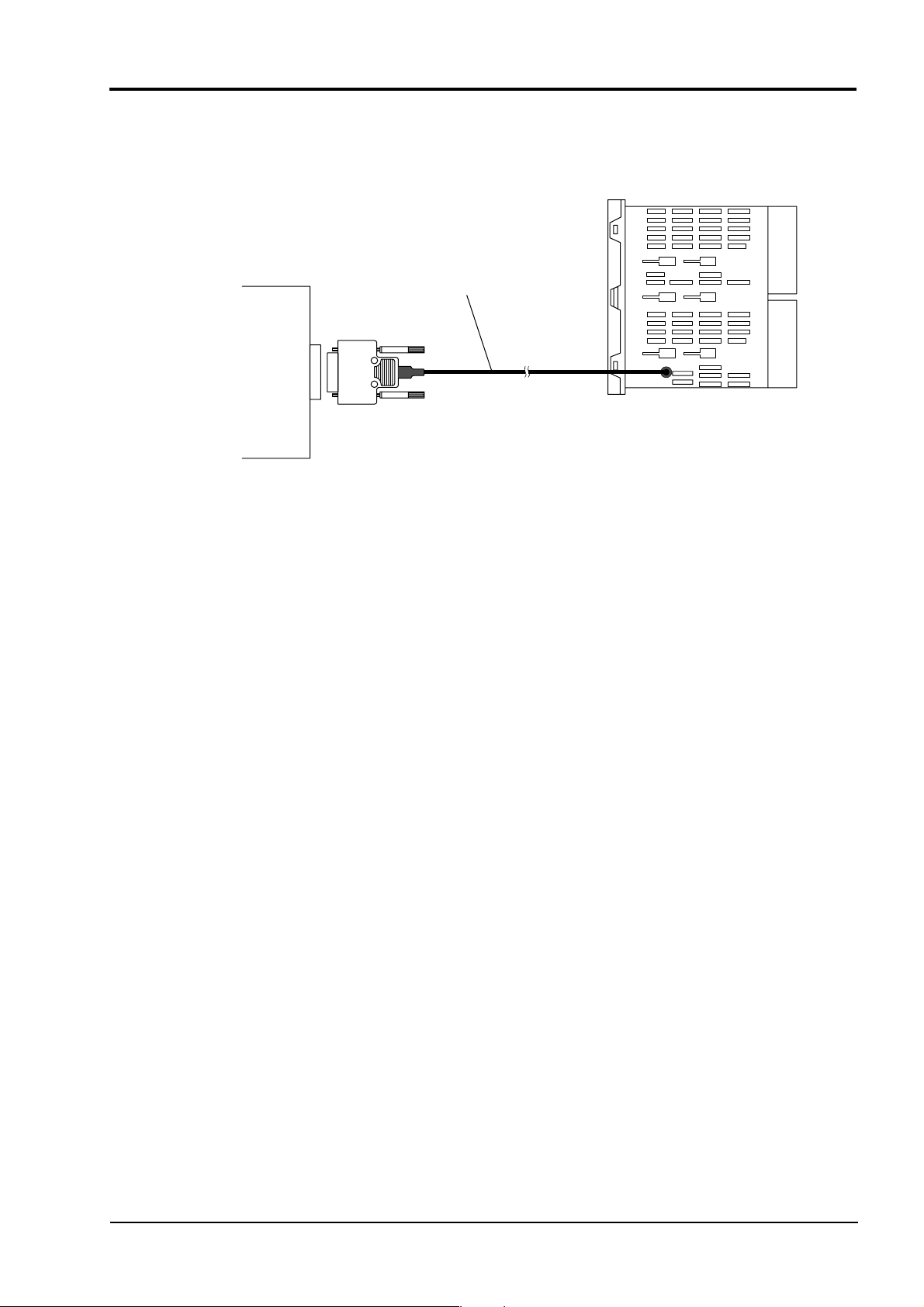
■ PC loader communication
▪ Use an optional PC loader communication cable (RS-232C).
PC loader communication cable
Master station side
(RS232C)
ZZPPXH1 TK4H4563
*
PC or the like
RS232C
D-Sub 9 pins
Bottom of PXH
INP-TN514207-E
5
Page 9
4. SETTING OF COMMUNICATION CONDITION
In order that the master station and instrument (PXH) can correctly communicate, following settings are required.
▪ All communication condition settings of the master station and those of instruments (PXH) are indentical.
▪ For RS-485 communication, different "station numbers (STN4)" are assigned to all PXHs which are con-
nected to a common line. (Any "Station No." is not shared by more than one instrument.)
▪ For PC loader communication, the station No. is fixed at "1".
Both for PC loader communication and RS-485 communication, same station No. "1" may be assigned.
4.1 Setting items
The parameters to be set are shown in the following table. Set them by operating the front panel
keys.
■ RS-485
CH B COM
Parameter
symbol
SPD4
――― Data length 8 bits Fixed (can not be changed)
――― Stop bit 1 bit Fixed (can not be changed)
BIT4 Parity setting odd
STN4 Station No. 1
■ PC loader communication
CH B COM
Parameter
symbol
SPD2
――― Data length 8 bits Fixed (can not be changed)
――― Stop bit 1 bit Fixed (can not be changed)
BIT2 Parity setting odd
――― Station No. 1 Fixed (can not be changed)
Item
Transmission
speed
Item
Transmission
speed
Value at
delivery
38400bps
Value at
delivery
38400bps
Setting range Remarks
96 : 9600bps
192 : 19200bps
384 : 38400bps
8n : none parity
8o : odd parity
8E : even parity
0 to 255
(0: communication function stop)
Setting range Remarks
96 : 9600bps
192 : 19200bps
384 : 38400bps
8n : none parity
8o : odd parity
8E : even parity
Set the same
communication
condition to
the master station
and all slave
stations.
Set a different
number to each
station.
Set the same
conditions as
the master station.
INP-TN514207-E
6
Page 10

4.2 Setting Operation Method
The following example shows how to set the communication conditions.
Example: For RS-485, set BIT4 parity at even and STN4 at 18.
Key
operation
SEL
∨
SEL
SEL
>∧∨
SEL
∨
SEL
Indication Description
200
LP01SV
200
PS1
0000
b COM
Ch
b. STN4
02 1
b. STN4
02 00001
b. STN4
02 00018
b. STN4
02 18
b. BIT4
04 8o
b. BIT4
04 8o
Operation status (PV/SV indication) or (PV/MV indication)
Press the SEL key to display PS1.
Press the ∨ key repeatedly until b.COM channel appears. (If
past over, press the ∧ key to return.)
Press the SEL key to display STN4 parameter.
Press the SEL key. The numeric value on the lower
indicator blinks and the setting mode is selected.
Press the >, ∧, or ∨ key to change the numeric value to 18.
Press the SEL key again. The numeric value stops blinking
and the setting is registered.
Press the ∨ key to display the BIT4 parameter.
Press the SEL key. The numeric value on the lower
indicator blinks and the setting mode is selected.
∧∨
SEL
DISP
DISP
b. BIT4
04 8E
b. BIT4
04 8E
b COM
Ch
LP01SV
200
200
Press the ∧ or ∨ key until the numeric value changes to 8E
(even parity).
Press the SEL key again. The numeric value stops blinking
and the setting is registered.
Press the DISP key to resume b.COM channel indication.
Press the DISP key to resume the operation status (PV/SV
indication).
* Be sure to turn off and on power so that the communication condition settings will affect the control.
INP-TN514207-E
7
Page 11
5. MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL
5.1 Outline
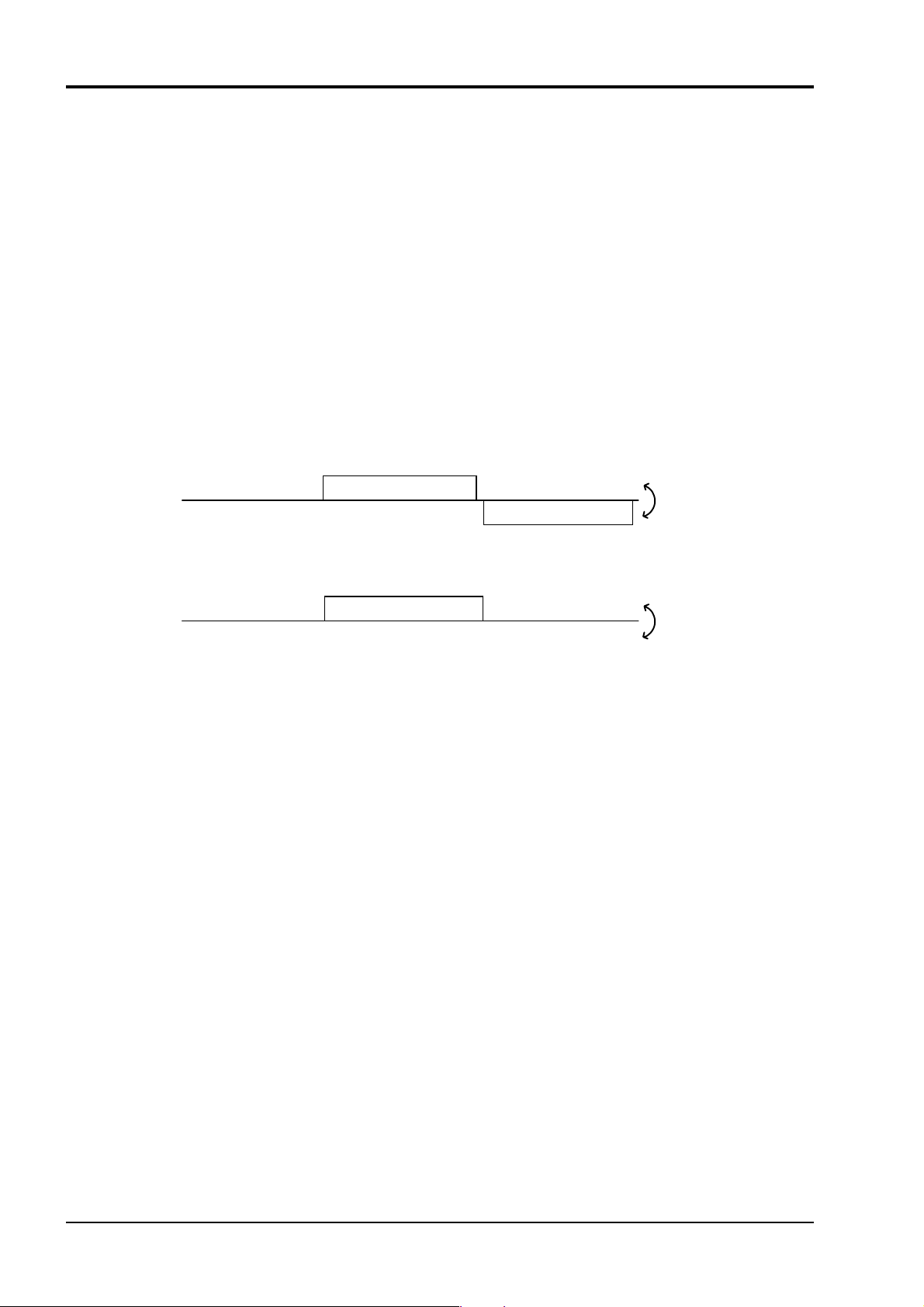
The communication system by the MODBUS protocol is that the communication always starts from
the master station and a slave station responds to the received message.
Transmission procedures is as shown below.
1) The master station sends a command message to a slave station.
2) The slave station checks that the station No. in the received message matches with the own station No.
or not.
3) If matched, the slave station executes the command and sends back the response message.
4) If mismatched, the slave station leaves the command message and wait for the next command
message.
a) In case when the station No. in the received command message matches with the own slave
station No.
Master to slave
Slave to master
b) In case when the station No. in the received command message mismatches with the own
slave station No.
Master to slave
Slave to master
The master station can individually communicate with any one of slave stations connected on the
same line upon setting the station No. in the command message.
Command message
Command message
Response message
(Not respond)
Data on
the line
Data on
the line
INP-TN514207-E
8
Page 12
5.2 Composition of Message
Command message and response message consist of 4 fields; Station No., Function code, Data and
Error check code. And these are sent in the following order.
Station No. (1 byte)
Function code (1 byte)
Data (2 to 69 bytes)
Error check code (CRC-16) (2 bytes)
Fig. 5-1 Composition of message
In the following, each field is explained.
(1) Station No
Station No. is the number specifying a slave station. For RS-485 communication, the command
is processed only by the slave station whose station No. matches with the No. set in the parameter "STN4".
For details of setting the parameter "STN4", refer to chapter 4.
For PC loader communication, the station No. is fixed at "1".
(2) Function code
This is a code to designate the function executed at a slave station.
For details, refer to section 5.4.
(3) Data
Data are the data required for executing function codes. The composition of data varies with
function codes. For details, refer to chapter 6.
A register number is assigned to each data in the indicating controller. For using the data by
communication, designate the register number.
Note that the register number transmitted on message is expressed as its relative address.
The relative address is calculated by the following expression.
Relateve address
The lower 4 digits of the
=
Register number
– 1
For example, when the resister number designated by a function code is 40003,
Relative address = (lower 4 digits of 40003) – 1
= 0002
is used on the message.
INP-TN514207-E
9
Page 13

(4) Error check code
This is the code to detect message errors (change in bit) in the signal transmission.
On the MODBUS protocol (RTU mode), CRC-16 (Cycric Redundancy Check) is applied.
For CRC calculation method, refer to section 5.5.
INP-TN514207-E
10
Page 14
5.3 Response of Slave Station
(1) Response for normal command
To a relevant message, the slave station creates and sends back a response message which corre-
sponds to the command message. The composition of message in this case is the same as in
section 5.2.
Contents of the data field depend on the function code. For details, refer to Chapter 6.
(2) Response for abnormal command
If contents of a command message have an abnormality (for example, non-actual function code is
designated) other than transmission error, the slave station does not execute that command but
creates and sends back a response message at error detection.
The composition of response message at error detection is as shown in Fig. 5-2. The value used
for function code field is function code of command message plus 80
Table 5-1 gives error codes.
Function code + 80H
Error check(CRC-16)
Station No.
Error code
.
H
Error code Contents Description
01H Illegal function code Non-actual function code is designated.
02H Illegal data address A relative address of resister number to which the
03H Illegal data value Because the designation of number is too much,
(3) No response
Under any of the following items, the slave station takes no action of the command message and
sends back no response.
▪ A station number transmitted in the command message differs from the station number speci-
▪ A error check code is not matched, or a transmission error (parity error, etc.) is detected.
▪ The time interval between the composition data of the message becomes longer than the time
▪ Station No. of a slave station is set as 0.
▪ A write-in command is sent while executing FIX.
Fig. 5-2 Response message at error detection
Table 5-1 Error Code
Check for the function code.
designated function code can not be used.
the area where resister numbers do not exist is designated.
fied to the slave station.
corresponding to 24 bits. (Refer to section 5.6 Transmission Control Procedure.)
INP-TN514207-E
11
Page 15
5.4 Function Code
According to MODBUS protocol, register numbers are assigned by function codes.
Each function code acts on specific register number.
This correspondence is shown in Table 5-2, and the message length by function is shown in Table 5-3.
Table 5-2 Correspondence between function codes and objective address
Function code Resister No.
No. Function Object No. Contents
03H
04H
06H Write-in Holding register 4xxxx Read-out/write-in word data
10H
Read-out
(continuously)
Read-out
(continuously)
Write-in
(continuously)
Holding register 4xxxx Read-out/write-in word data
Input register 3xxxx Read-out word data
Holding register 4xxxx Read-out/write-in word data
Table 5-3 Function code and message length
Function
code
03H Read-out of word data 32 words 8 8 7 69
04H
*1
06H Write-in of word data 1 word 8 8 8 8
10H
*1) For PXH, all data is designated by 2 words.
Read-out of word data
(read-out only)
Write-in of continuous
word data
(write-in of word data) is used, only 1 lower word can be written in, and only 1 upper word
If 06
H
cannot.
Contents
Number of
designatable
data
15 words 8 8 7 35
32 words 11 73 8 8
[Unit:byte]
Command message Response message
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
INP-TN514207-E
12
Page 16

5.5 Calculation of Error Check Code (CRC-16)
CRC-16 is the 2-byte (16-bits) error check code. From the top of the message (station No.) to the
end of the data field are calculated.
The slave station calculates the CRC of the received message, and does not respond if the calculated
CRC is different from the contents of the received CRC code.
Fig. 5-3 shows the flow of the CRC-16 calculation system.
Set FFFFH (hexadecimal number) in CR.
Exclusive logical sum (XOR) is executed
with CR and one character (1 byte) of the I
characters, and its results is set in CR.
Start
Set 1 in I.
Explanation of variables
CR : CRC error check data (2 bytes)
I : Digits of calculation characters
in command message
J : Check on the number of times
of CR calculation
Set 1 in J.
Bit at right end
of CR is 1?
YES
Shift CR to right by 1 bit, and A001H and
exclusive logical sum (XOR) are executed
and its result is set in CR.
Add 1 to J.
NO
Calculation (8 times)
is finished?
J>8
YES
Add 1 to I.
NO
Shift CR to right by 1 bit.
INP-TN514207-E
NO
Calculation of all characters is
completed?
I>All characters
YES
End
Fig. 5-3 Flow of CRC-16 calculation
13
(Calculation is executed in the order
of command message station No.,
function code and data.)
CR calculation result shall be added
to the last command message in the
order of LOW byte and HIGH byte.
Page 17

5.6 Transmission Control Procedure
(1) Transmission procedure of master station
The master station must proceed to a communication upon conforming to the following items.
(1-1) Before sending a command message, provide 48 bits time or more vacant status.
(1-2) For 1 command message, each field part should be sent below 24 bits time interval.
(1-3) Within 24 bits time after sending a command message, receiving stand-by status
starts.
(1-4) Provide 48 bits time or more vacant status between the end of response message re-
ception and beginning of next command message sending [same as in (1-1)].
(1-5) For ensuring the safety, make a confirmation of the response message and make an
arrangement so as to provide 3 or more retries in case of no response, error occurrence, etc.
Note) The above definition is minimum requirement. For ensuring the safety, it’s recom-
mended the program for the master should be developed with 2 to 3 times margins.
Concretely, it is advised to arrange the program for 9600 bps with 10 ms or more for
vacant status (1-1), and within 1 ms for byte interval (1-2) and changeover from
sending to receiving (1-3).
(2) Description
1) Detection of the message frame
2) Response of this instrument (PXH)
Since the communication system uses the 2-wire RS-485 interface, there may be 2 statuses
on a line below. (The same goes with PC loader communication.)
(a) Vacant status (no data on line)
(b) Communication status (data is existing)
Instruments connected on the line are initially at a receiving status and monitoring the line.
When 24 bits time or more vacant status has appeared on the line, the end of preceding frame
is assumed and, within following 24 bits time, a stand-by status is posted. When data ap-
pears on the line, the instruments enter on receiving, and when 24 bits time or more vacant
status is detected again, and the end of that frame is assumed. I.e., data which appeared on
the line from the first 24 bits time or more vacant status to the next 24 bits time or more vacant status is fetched as one frame.
Therefore, one frame (command message) must be sent upon confirming the following.
(1-1) 48 bits time or more vacant status precedes the command message sending.
(1-2) For 1 command message, each byte should be sent below 24 bits time interval.
After a frame detection (24 bits time or more vacant status is detected), this instrument car-
ries out processing with that frame as a command message. If the command message is ad-
dressed to the own station, a response message is returned. Its processing time is about 10
ms (depends on contents of command message).
After sending a command message, therefore, the master station must observe the following
(1-3) Stand-by status is posted within 24 bits time after sending a command message.
INP-TN514207-E
14
Page 18

Controll
station
Controll
station
→
←
PXH
PXH
POL1
Space of longer than 50msis needed.
(longer than 100ms is recommended.)
POL2
About 10 msec
POL1 response data
Data on line
POL1 POL2 POL1 response data
INP-TN514207-E
15
Page 19
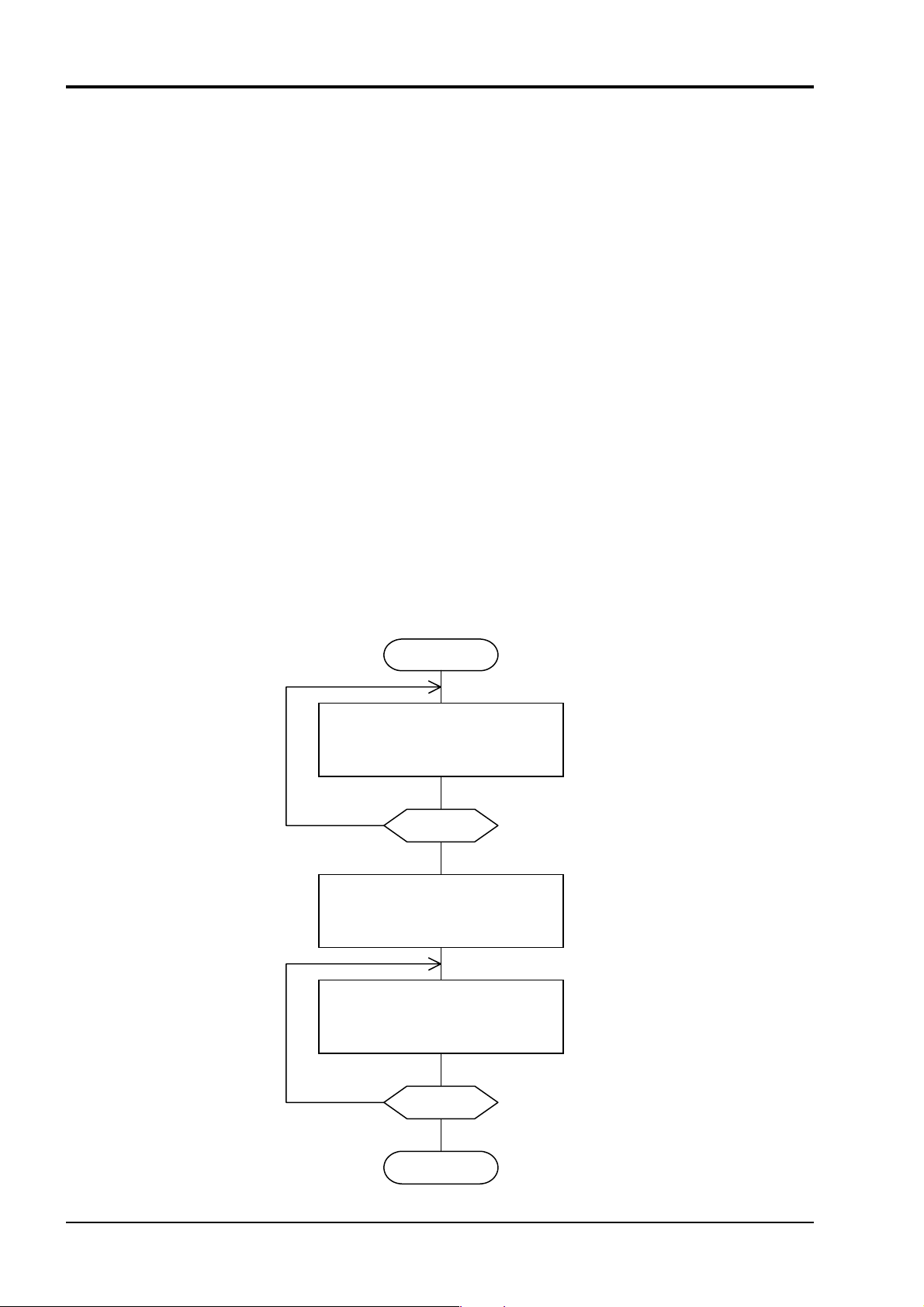
5.7 FIX Processing (Cautions in data write)
The instrument is provided inside with a non-volatile memory (EEPROM) for holding the setting pa-
rameters. Data written in the non-volatile memory is not lost even if turning off the power.
To hold parameters that were written in the internal memory via communication after turning off the
power, the FIX process is effective. It allows parameters to be written in nonvolatile memory.
Fig. 5-4 shows the FIX procedure.
Cautions:
▪ FIX processing takes approximately 5 seconds to 3 minutes (depending on how many parameters
were changed).
▪ While writing, do not turn off the power of the PXH. Otherwise, the data in the non-volatile
memory will be destroyed, whereby the PXH could not be used any longer.
▪ Don’t change parameters on the front panel when performing the FIX procedure, or memory error
may result.
▪ The non-volatile memory (EEPROM) is a device where the number of write-in times is limited.
The guaranteed number of write-in times of the non-volatile memory used on the instrument is
100,000 minimum. Therefore, limit the times of FIX processing to bare minimum, like when set-
ting parameters are changed. Refrain from carrying out the FIX processing periodically for example or while such is not absolutely required.
Start FIX
Read the FIX address
with function code : 03
relative address : 0C50
No
FIX=0?
H
H
Yes
Write ‘1’ into FIX address
with function code : 06
relative address : 0C50
Read the FIX
with function code : 03
relative address : 0C50
address
H
H
H
H
No
FIX=0?
Yes
End FIX
Fig. 5-4 FIX procedure
INP-TN514207-E
16
Page 20

6. DETAILS OF MESSAGE
6.1 Read-out of Word Data [Function code: 03H]
Function code Max. word number read-out in one message Relative data address Register No.
03H 32 words 0000H – 0E7F 40001-43712
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Read-out
word number
CRC data
Upper
Upper
* Arrangement of read-out word data
Upper Read-out byte number
Lower Upper
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
1 to 32
State of the first
word data
State of the next
word data
~
State of the last
word data
CRC data
Lower
Upper
Lower
Lower
Lower
Read-out word
number × 2
~
MSB LSB
Upper byte of contents of the first word data
Lower byte of contents of the first word data
Upper byte of contents of the next word data
Lower byte of contents of the next word data
~
~
Upper byte of contents of the last word data
Lower byte of contents of the last word data
(2) Function explanation
Words data are read-out, starting from read-out start No. until read-out word number. The slave
station transmits the read-out word data in the order of upper and lower bytes.
For PXH for which all data consists of 2 word units, data should be read out by units of 2 words.
Example: Suppose data is 99999 (00 01 86 9F
) Suppose data is 1
H
(1) (2) (3) (4)
(3) 86
(4) 9F
(1) 00
LH(Low word High byte)
LL(Low word Low byte)
HH(High word High byte)
00 LH
01 LL
00 HH
INP-TN514207-E
(2) 01
HL(High word Low byte)
17
00 HL
Page 21

(3) Message transmission
The following shows an example of reading out PV1F (PV1 full scale) from No. 1 station.
Relative address of PV1F (PV1 full scale): 0830
Number of data words: 02
(2 words per data)
H
H
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Station No. 01H
H
Function code 03H Function code 03H
Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Read-out
word number
CRC data
Upper 08H Read-out byte number 04H
Lower 30
Upper 00H
Lower 02
Upper C6
Lower 64
Upper 0FH
H
H
H
Upper F9H
H
* Meaning of read-out word data Upper data Lower data
PV1F lower data
PV1F upper data
CRC data
Lower A0H
Upper 00H
Lower 00H
Lower 05H
PV1F (PV1 full scale) 00 00 0F A0
= 4000
H
INP-TN514207-E
18
Page 22
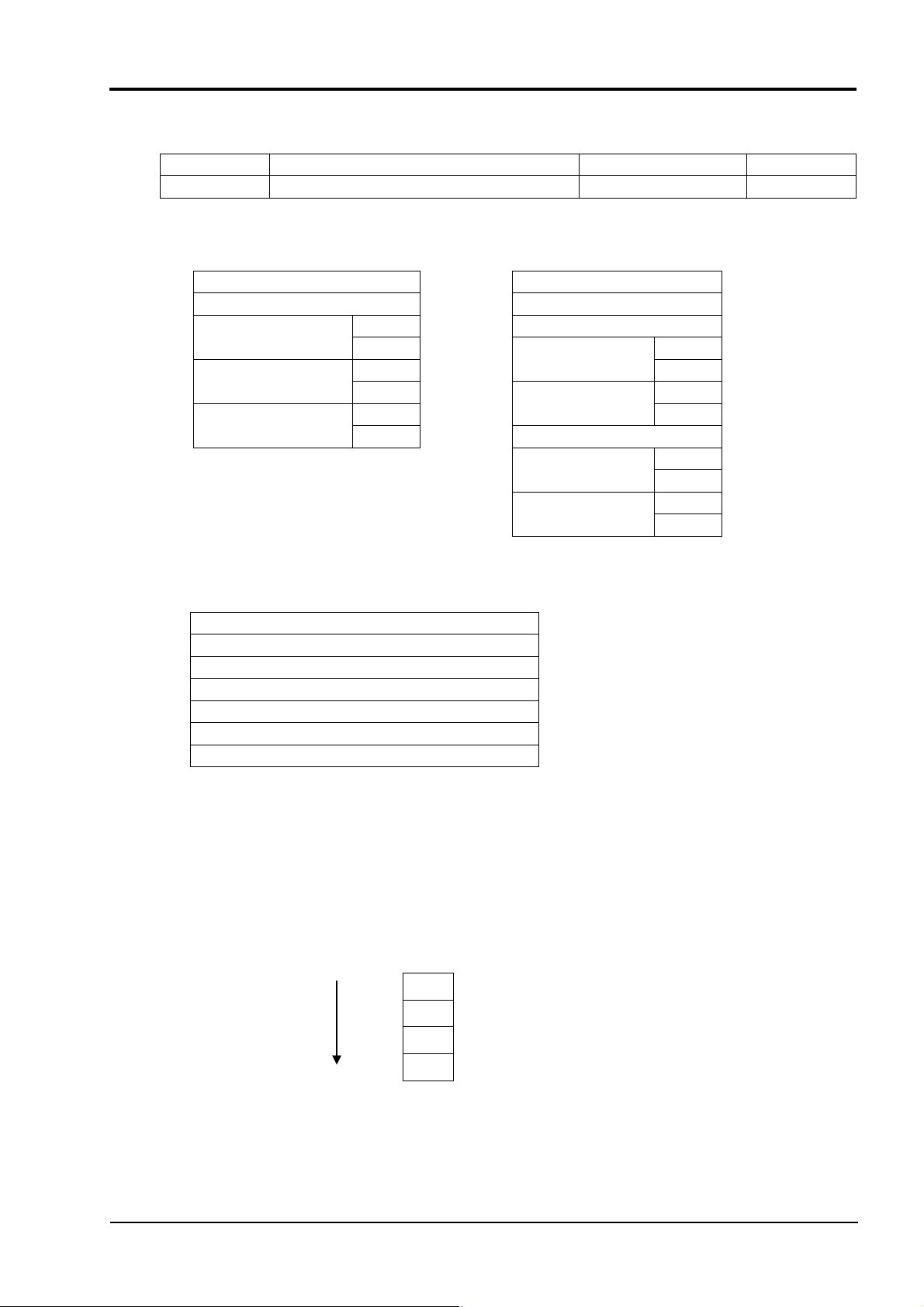
6.2 Read-out of Read-out Only Word Data [Function code: 04H]
Function code Max. word number read-out in one message Relative data address Register No.
04H 15 words 0000H – 0563 H 30001-31380
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Read-out
word number
CRC data
Upper
Upper
* Arrangement of read-out word data
Upper Read-out byte number
Lower Upper
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
1 to 15
State of the first
word data
State of the next
word data
~
State of the last
word data
CRC data
Read-out word
number × 2
Lower
Upper
Lower
~
Lower
Lower
MSB LSB
Upper byte of contents of the first word data
Lower byte of contents of the first word data
Upper byte of contents of the next word data
Lower byte of contents of the next word data
~
~
Upper byte of contents of the last word data
Lower byte of contents of the last word data
(2) Function explanation
Words data are read-out, starting from read-out start No. until read-out word number. The slave
station transmits the read-out word data in the order of upper and lower bytes.
For PXH for which all data consists of 2 word units, data is read out by units of 2 words.
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Example: Suppose data is –2 (FF FF FF FE
)
H
(3) FF LH
(4) FE LL
(1) FF HH
INP-TN514207-E
(2) FF HL
19
Page 23
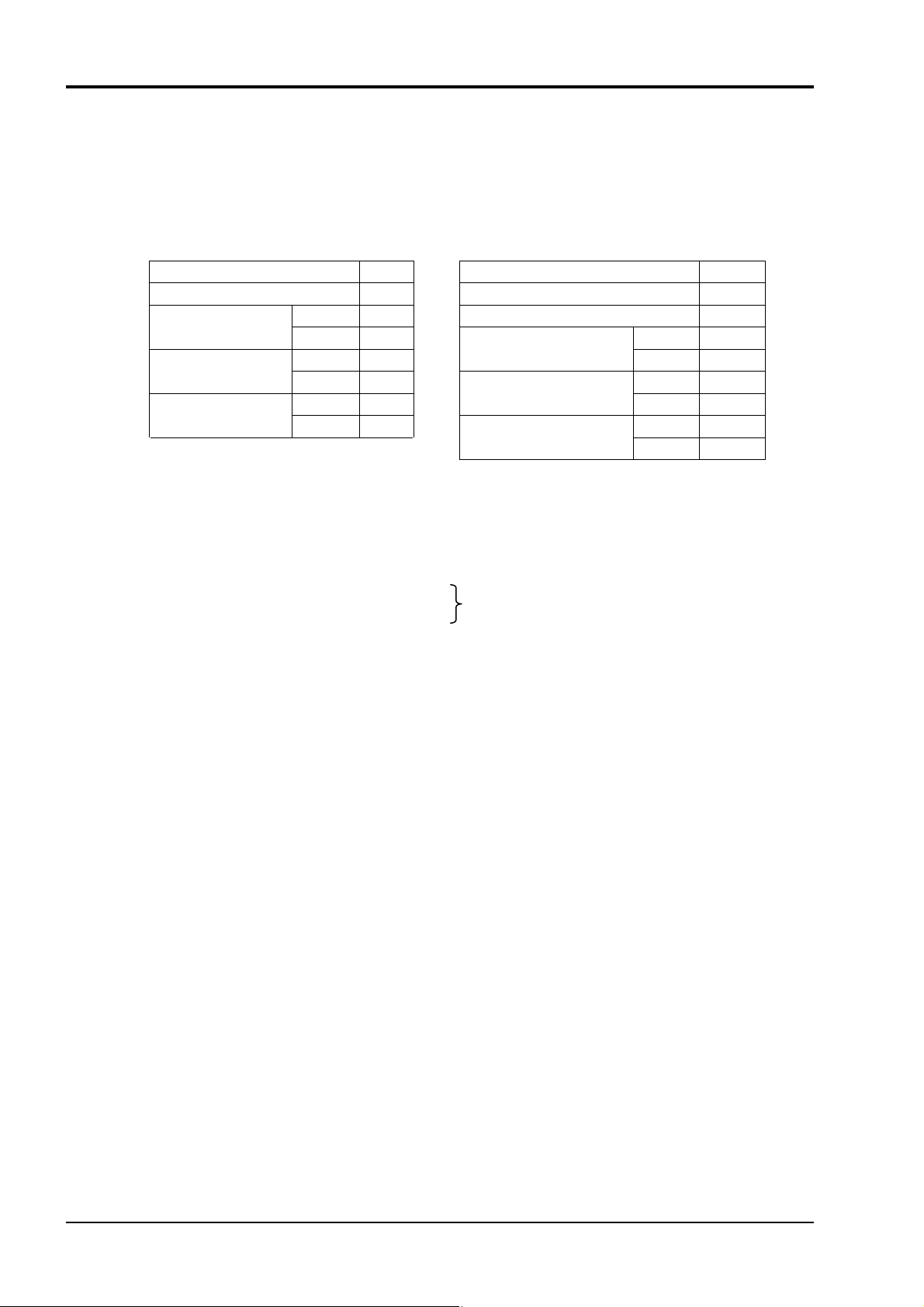
(3) Message transmission
The following shows an example of reading out PV value from No. 1 station.
Relative address of PV value: 0102
Data number: 02
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Function code 04H Function code 04H
Read-out start No.
(relative address)
Read-out
word number
CRC data
* Meaning of read-out word data
PV1 measurement data 00 01 38 80
If
decimal point position PV1D = 2
unit
H
(2 words per data)
H
Station No. 01H
H
Upper 01H Read-out byte number 04H
Lower 02
Upper 00H
Lower 02
Upper D1
Lower F7
PV1U = °C
Upper 38H
H
H
H
Upper 36H
H
H
PV1 lower data
PV1 upper data
CRC data
= 80000
800.00°C
Lower 80H
Upper 00H
Lower 01H
Lower CCH
INP-TN514207-E
20
Page 24
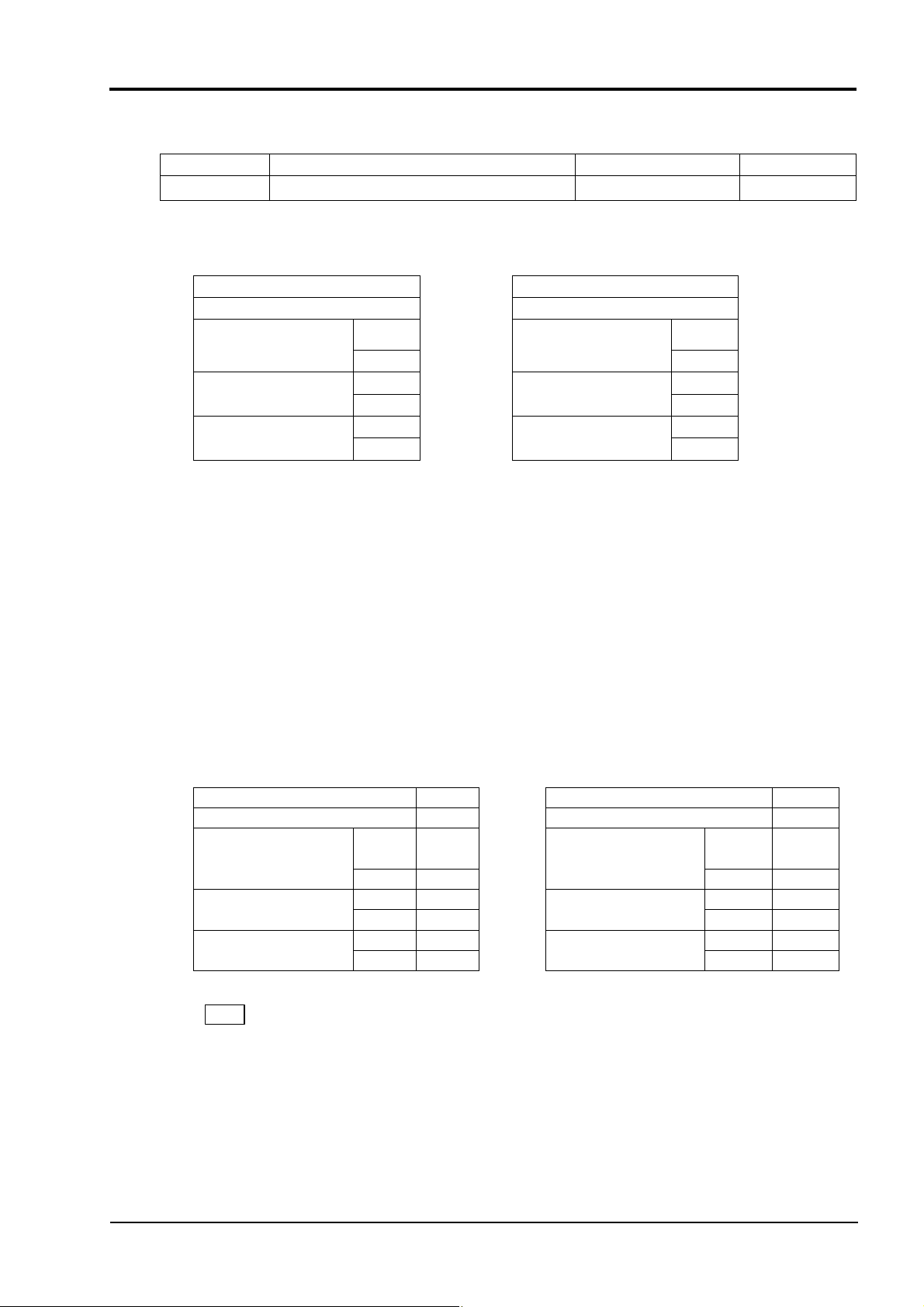
6.3 Write-in of Word Data (1 word) [Function code: 06H]
Function code
Max. word number write-in
06H 1 word
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Write-in designate No.
(relative address)
Write-in word
data
CRC data
(2) Function explanation
Designated data is written in word data of write-in designate No. Write-in data are transmitted
from master station in the order of upper and lower bytes.
For PXH, all data consist of 2 word units. If 06H (write-in of word data) is used, only 1 lower
word of 2 word data can be written in, and only 1 upper word of 2 word data cannot.
in one message Relative data address Register No.
40001-43711
0000
Upper Upper
Lower
Upper Upper
Lower
Upper Upper
Lower
Write-in designate No.
(relative address)
Write-in word
data
CRC data
0E7E
-
H
H
Lower
Lower
Lower
(3) Message transmission (example)
The following shows an example of setting 100.0 (1000
slave station.
Parameter "P1" Relative address: 0282
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Function code 06H Function code 06H
Write-in designate No.
(relative address)
State of write-in
designation
CRC data
Note
When setting is being locked, response is returned normally, but the command is not
executed. Make sure that setting is not locked to send the write-in command.
The setting lock parameter can be written in even if communication setting is invalidated.
If the write-in command message is sent to any slave station during the FIX process,
response is not returned from it.
=03E8H) to the parameter "P1" of No.1
D
H
Station No. 01H
H
Upper 02 H Upper 02H
Lower 82
H
Upper 03H Upper 03H
Lower E8
H
Upper 28H Upper 28H
Lower E4
H
Write-in designate No.
(relative address)
State of write-in
designation
CRC data
Lower 82
Lower E8
Lower E4H
H
H
INP-TN514207-E
21
Page 25
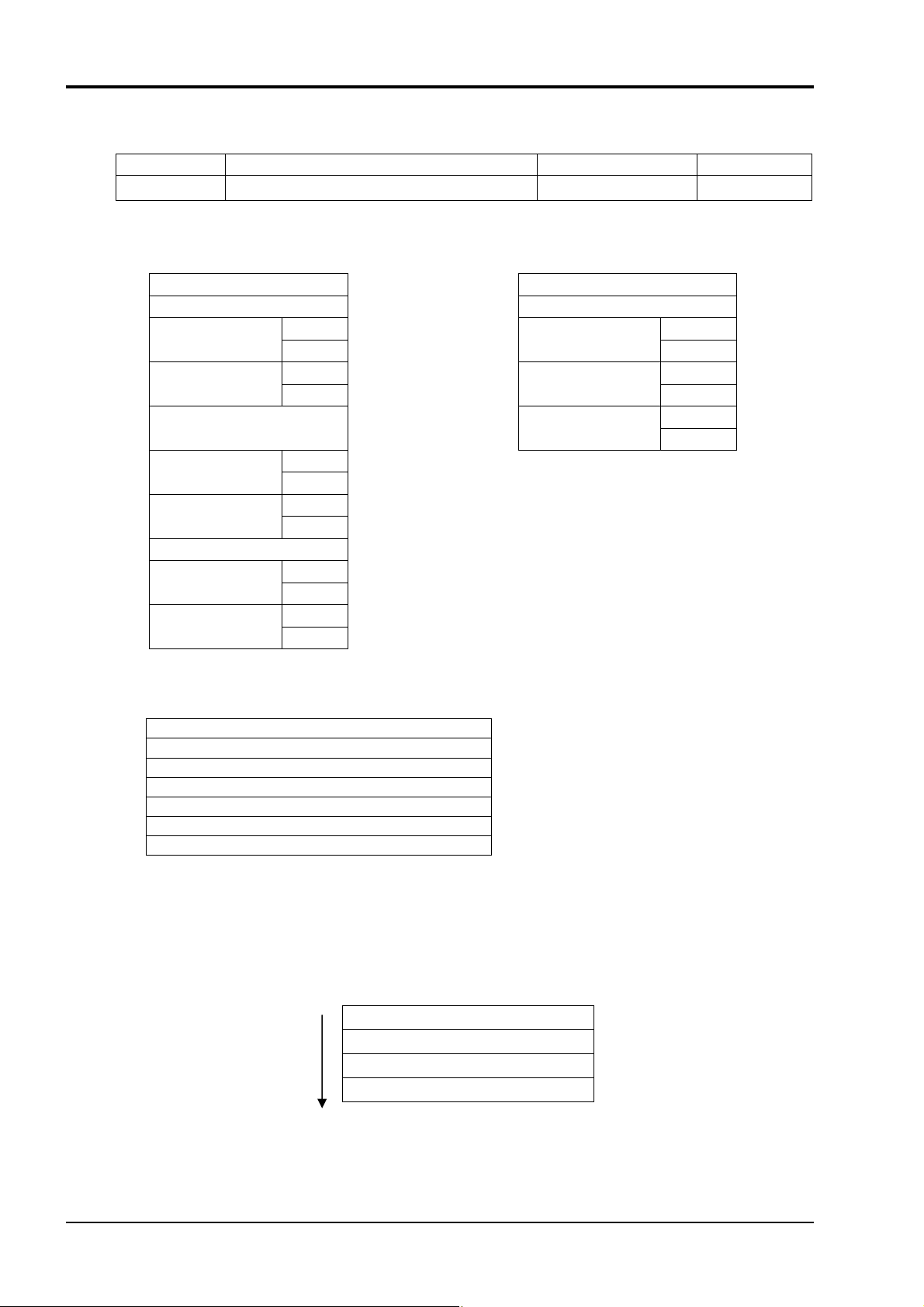
6.4 Write-in of Continuous Word Data [Function code: 10H]
Function code
10H 32 words
Max. word number write-in
in one message Relative data address Register No.
40001-43712
0000
0E7F
-
H
H
(1) Message composition
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. Station No.
Function code Function code
Write-in start No.
(relative address)
Write-in word
number
Write-in byte number
First write-in
word data
Next write-in
word data
~ ~
Last write-in
word data
CRC data
Upper Upper
Lower
Upper Upper
Lower
1 to 32
Write-in word
number × 2
Write-in start No.
(relative address)
Write-in word
number
CRC data
Lower
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
Upper
Lower
* Arrangement of write-in word data
MSB LSB
Upper byte of contents of the first word data
Lower byte of contents of the first word data
Upper byte of contents of the next word data
Lower byte of contents of the next word data
Upper byte of contents of the last word data
Lower byte of contents of the last word data
~~
(2) Function explanation
Words data are written in, starting from write-in start No. until write-in word number. Write-in
word data are transmitted from master station in the order of upper and lower bytes.
For PXH for which all data consists of 2 word units, write in data by units of 2 words in the order
illustrated below.
Lower word, upper byte (LH)
Lower word, lower byte (LL)
Upper word, upper byte (HH)
Upper word, lower byte (HL)
INP-TN514207-E
22
Page 26

(3) Message transmission (example)
The following shows an example of writing-in P1 = 100.0, I1 = 10, and D1 = 5.0 to No. 1 slave
station.
P1 = 03E8
I1 = 0064
D1 = 0032
(= 1000D)
H
(= 100D)
H
(= 50D)
H
Parameter "P1" Relative address:0282
Command message composition (byte) Response message composition (byte)
Station No. 01
Function code 10H Function code 10H
Write-in start No.
number
Write-in byte number 0CH Upper E1H
P1 lower data
P1 upper data
I1 lower data
I1 upper data
D1 lower data
D1 upper data
CRC data
Point
Since the transmission data can not include a decimal point, data of 100.0 is
transmitted as "1000".
For transmission format of each data, refer to the address map (Chapter 7).
When setting is being locked, response is returned normally. However, the
Caution
command is not executed. If the write-in command message is sent to any slave
station during the FIX process, response is not returned from it.
Data number:06H (2 words per data)
H
Station No. 01H
H
Upper 02H Upper 02H
Lower 82
H
Upper 00H Upper 00H Write-in word
Lower 06
H
Upper 03H
Lower E8
H
Write-in start No.
Write-in
word number
CRC data
Lower 82H
Lower 06
H
Lower 9BH
Upper 00H
Lower 00
H
Upper 00H
Lower 64
H
Upper 00H
Lower 00
H
Upper 00H
Lower 32
H
Upper 00H
Lower 00
H
Upper B6H
Lower D8
H
INP-TN514207-E
23
Page 27

7. ADDRESS MAP AND DATA FORMAT
7.1 Data Format
7.1.1 Transmission data format
The MODBUS protocol used in this instrument (PXH) is RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) mode.
Transmitted data is "numeric value" and not "ASCII code".
7.1.2 Engineering unit
This instrument can handle set value data or other data which are affected by input range as follows.
Engineering unit: Subjected to scaling to match the actual value according to input range
[Example] The value of "PV = 150" (input range: 0º to 400ºC)
Register No. Data (HEX) Data (decimal)
Engineering unit 0102 00000096H
● How to change the input range setting via communication
The input range setting is for full scale, base scale and decimal point position setting.
In order that the change of input range setting will affect the control, power must be turned off and
on, or the reset command must be executed.
Changing the decimal point position automatically changes the full scale and base scale settings.
Example: Changing the input range from 0 to 400, to 0.0 to 400.0
(1) PV1D = 0 → 1 (automatically changes as PV1F = 400 → 400.0, PV1B = 0 → 0.0)
↓
(2) FIX command (see 5.7)
↓
(3) Power OFF-ON or execute reset command (write 1 at relative address 0060H)
● Input range dependent data (see communication address map)
Input range dependent data must be reset after turning off and on power or after transmitting a reset
command subsequent to a change of input range.
(1) Input range setting change
↓
(2) FIX command (see 5.7)
↓
(3) Power off and on or execute reset (write 1 at relative address 0060H)
↓
(4) Reset all data depending upon by input range
→
150
INP-TN514207-E
24
Page 28

7.1.3 Handling of decimal point
No decimal point is added to transmission data.
For data given in the following table, carry out an alignment of decimal point. (Decimal point
should be removed in transmission, and should be added in receiving data.)
Word data [read-out/write-in]
Digits below
decimal point
Designate by UCD1
if TPLT = 10, 11
(0 to 3)
Designate by PV1D
if TPLT = 13, 14
(0 to 3)
AL3 40289
A3-L 40289
A3-H 40291 AI1F 42193
AL4 40305
A4-L 40305
A4-H 40307
AL5 40321 UCF1 42081
A5-L 40321
A5-H 40323 P1 40643
AL6 40337
A6-L 40337 D1 40647
A6-H 40339 MVH1 40659
AL7 40353 MVL1 40661
A7-L 40353 DMV1 40667
A7-H 40355 BAL1 40677
AL8 40369 PMV1 40685
A8-L 40369 ALP1 40833
A8-H 40371 BET1 40841
1HYS 40265 P-1 41027
2HYS 40281 I-1 41029
3HYS 40297 D-1 41031
4HYS 40313 BL-1 41045
5HYS 40329 P-2 41059
6HYS 40345 I-2 41061
7HYS 40361 D-2 41063
8HYS 40377 BL-2 41077
SV_L1 40641 P-3 41091
ARH1 40651 I-3 41093
ARL1 40653 D-3 41095
SH1 40655 BL-3 41109
SL1 40657 P-4 41123
HS1 40671 I-4 41125
SV1 41025 D-4 41127
ARH1 41035 BL-4 41141
ARL1 41037 P-5 41155
HYS1 41039 I-5 41157
REF1 41047 D-5 41159
SV2 41057 BL-5 41173
ARH2 41067 P-6 41187
ARL2 41069 I-6 41189
HYS2 41071 D-6 41191
REF2 41079 BL-6 41205
SV3 41089 P-7 41219
ARH3 41099 I-7 41221
ARL3 41101 D-7 41223
Kind Register No.
AL1 40257 PV1F 42097
A1-L 40257
A1-H 40259
AL2 40273
A2-L 40273 PV2F 42129
A2-H 40275
Digits below
decimal point
Designate by PV1D
(0 to 3)
Designate by PV2D
(0 to 3)
Designate by AI1D
(0 to 3)
Designate by UCD1
(0 to 3)
1 digit below
decimal point
Kind Register No.
PV1B 42099
PV1Z 42107
PV1S 42109
PV2B 42131
PV2Z 42139
PV2S 42141
AI1B 42195
AI1Z 42203
AI1S 42205
UCB1 42083
I1 40645
INP-TN514207-E
25
Page 29

Digits below
decimal point
Designate by UCD1
if TPLT = 10, 11
(0 to 3)
Designate by PV1D
if TPLT = 13, 14
(0 to 3)
ARH5 41163 AO1H 42437
ARL5 41165 A1LL 42439
HYS5 41167 A1LH 42441
REF5 41175 AO2L 42451
SV6 41185 AO2H 42453
ARH6 41195 A2LL 42455
ARL6 41197 A2LH 42457
HYS6 41199 KF1 40849
REF6 41207 B1F1 40851
SV7 41217 B2F1 40853
ARH7 41227
ARL7 41229
HYS7 41231
REF7 41239
Kind Register No.
HYS3 41103 BL-7 41237
REF3 41111 P1CU 42117
SV4 41121
ARH4 41131
ARL4 41133
HYS4 41135 A1CU 42211
REF4 41143 A1TF 42213
SV5 41153 AO1L 42435
Digits below
decimal point
1 digit below
decimal point
Kind Register No.
P1TF 42119
P2CU 42149
P2TF 42151
Word data [read-out only]
Digits below
decimal point
Designate by UCD1
if TPLT = 10, 11
(0 to 3)
Designate by PV1D
if TPLT = 13, 14
(0 to 3)
AIM 31345
MV1 30265
AO1 31105
AO2 31107
AMV1 31381
RCJ1 31057
Kind Register No.
PV1 30259 PV1 31025
SV1 30261
DV1 30263 PV2 31027
AI1 31031
7.1.4 Data when input is abnormal
When "UUUU" or "LLLL" is displayed on the face panel on account of over-range, under-range or
input burnout for example, PV read-out value (register No. 30259) is 105% or –5% of input range.
Presence of any input abnormality via communication can be detected by:
"Register No. 30269: Input abnormal status"
Digits below
decimal point
Designate by PV1D
(0 to 3)
Designate by PV2D
(0 to 3)
Designate by AI1D
(0 to 3)
Designate by UCD1
(0 to 3)
1 digit below
decimal point
2 digits below
decimal point
Kind Register No.
FFV1 31389
RCJ2 31059
7.1.5 Range of write-in data
When data is written in each parameter, the write-in data should be kept within the setting range.
PXH can accept the write-in data beyond the range, however, be careful since the PXH performance
will not be guaranteed.
INP-TN514207-E
26
Page 30

7.1.6 Floating decimal point type
The mathematical calculation constant uses the floating decimal point type at communication.
Type name Sign Bits
Floating decimal point type Yes 32 (2 words)
(1) Floating decimal point type data format
Floating decimal point (float) data of a binary number is expressed by the data format shown
in [Fig. 7-1].
31
se
s : Sign of mantissa part (1 bit)
e : Exponent part (8 bits)
m : Mantissa part (23 bits)
HH HL LH LL
Decimal point position of mantissa part
2324
16
80
m
Fig. 7-1 Floating decimal point type data format
INP-TN514207-E
27
Page 31

7.2 Communication Address Map
Caution: Never write data into addresses which are not disclosed to users.
Otherwise a failure may be caused.
For detailed contents about individual parameter function or setting range, refer to the user's manual.
Word data [read-out/write-in] : Function code [03
Relative
address
0000H 40001 REM1 Remote mode
0010H 40017 STBY Standby command
0014H 40021 AT Auto tuning command
0020H 40033 LACH Alarm unlatch command
0030H 40049 PLTN Palette signal selection 0 to 7
0040H 40065 LOC Key lock 0 to 5
0060H 40097 RES Reset command
0100H 40257 AL1 Alarm 1 setting
0100H 40257 A1-L Alarm 1 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0102H 40259 A1-H Alarm 1 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0104H 40261 1 TP Alarm 1 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0106H 40263 1 OP Alarm 1 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0108H 40265 1HYS Alarm 1 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
010AH 40267 1DLY Alarm 1 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0110H 40273 AL2 Alarm 2 setting
0110H 40273 A2-L Alarm 2 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0112H 40275 A2-H Alarm 2 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0114H 40277 2 TP Alarm 2 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0116H 40279 2 OP Alarm 2 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0118H 40281 2HYS Alarm 2 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
011AH 40283 2DLY Alarm 2 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0120H 40289 AL3 Alarm 3 setting
0120H 40289 A3-L Alarm 3 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0122H 40291 A3-H Alarm 3 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0124H 40293 3 TP Alarm 3 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0126H 40295 3 OP Alarm 3 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0128H 40297 3HYS Alarm 3 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
012AH 40299 3DLY Alarm 3 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0130H 40305 AL4 Alarm 4 setting
0130H 40305 A4-L Alarm 4 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0132H 40307 A4-H Alarm 4 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0134H 40309 4 TP Alarm 4 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0136H 40311 4 OP Alarm 4 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0138H 40313 4HYS Alarm 4 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
013AH 40315 4DLY Alarm 4 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0140H 40321 AL5 Alarm 5 setting
0140H 40321 A5-L Alarm 5 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0142H 40323 A5-H Alarm 5 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0144H 40325 5 TP Alarm 5 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0146H 40327 5 OP Alarm 5 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0148H 40329 5HYS Alarm 5 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
014AH 40331 5DLY Alarm 5 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
, 06H, 10H]
H
0: Auto
1: Remote
0: OFF
1: ON
0: AT Not activated
1: AT Activated
0: Latched
1: Unlatched
0: Operating
normally
1: Being reset
▪ Engineering unit setting
▪ Engineering unit setting
▪ Engineering unit setting
▪ Engineering unit setting
▪ Engineering unit setting
Write-in data
setting range
0: AT Stop
1: AT Execute
0: No effect
1: Unlatch
0: No effect
1: Execute resetting
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
INP-TN514207-E
28
Page 32

Relative
address
0150H 40337 AL6 Alarm 6 setting
0150H 40337 A6-L Alarm 6 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0152H 40339 A6-H Alarm 6 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0154H 40341 6 TP Alarm 6 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0156H 40343 6 OP Alarm 6 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0158H 40345 6HYS Alarm 6 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
015AH 40347 6DLY Alarm 6 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0160H 40353 AL7 Alarm 7 setting
0160H 40353 A7-L Alarm 7 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0162H 40355 A7-H Alarm 7 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0164H 40357 7 TP Alarm 7 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0166H 40359 7 OP Alarm 7 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0168H 40361 7HYS Alarm 7 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
016AH 40363 7DLY Alarm 7 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0170H 40369 AL8 Alarm 8 setting
0170H 40369 A8-L Alarm 8 low limit setting Absolute value alarm: 0 to 100%FS *
0172H 40371 A8-H Alarm 8 high limit setting Deviation alarm: –100 to 100%FS *
0174H 40373 8 TP Alarm 8 type 0 to 11, 16 to 32, 35 to 38
0176H 40375 8 OP Alarm 8 option 0 to 15 (0000B to 1111B)
0178H 40377 8HYS Alarm 8 hysteresis ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
017AH 40379 8DLY Alarm 8 delay time 0 to 9999 (sec or min)
0210H 40529 EXM1
0280H 40641 SV_L1 Local SV ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0282H 40643 P1 Proportional band 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
0284H 40645 I1 Integral time 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
0286H 40647 D1 Derivative time 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
028AH 40651 ARH1
028CH 40653 ARL1
028EH 40655 SH1 SV high limit *
0290H 40657 SL1 SV low limit
0292H 40659 MVH1 MV high limit setting
0294H 40661 MVL1 MV low limit setting
029AH 40667 DMV1
029CH 40669 DT1 Sampling rate 5 to 1000 (50 to 10000msec)
029EH 40671 HS1 Hysteresis setting ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
02A4H 40677 BAL1
02A6H 40679 TC1
02A8H 40681 REV1 Control action setting
02ACH 40685 PMV1
0340H 40833 ALP1
0348H 40841 BET1
0350H 40849 KF1
0352H 40851 B1F1
0354H 40853 B2F1
0400H 41025 SV1 Setpoint 1 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0402H 41027 P-1 Proportional band 1 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
0404H 41029 I-1 Integral time 1 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
0406H 41031 D-1 Derivative time 1 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
040AH 41035 ARH1
040CH 41037 ARL1
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
▪ Engineering unit setting
▪ Engineering unit setting
▪ Engineering unit setting
External manipulation
variable setting
Anti-reset windup high limit
setting
Anti-reset windup low limit
setting
MV change ratio limit
setting
Manipulating output
convergence value
Control output (MV1)
proportional period
Manipulating output preset
value
2 degrees of freedom
coefficient α
2 degrees of freedom
coefficient β
Sets Feed Forward Gain and
bias 1, bias 2.
[FF=KF1 × (Input − B1F) +
B2F]
Anti-reset windup high limit
1
Anti-reset windup low limit
1
–250 to 1250 (–25.0 to 125.0%)
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS)
–250 to 1250 (–25.0 to 125.0%)
0 to 1500 (0.0 to 150.0%)
–1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
1 to 150sec
0: NRML
1: REV
–250 to 1250 (–25.0 to 125.0%)
–3000 to 3000 (–300.0 to 300.0%)
0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
–10000 to 10000
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
Write-in data
setting range
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Turn off and
on power
INP-TN514207-E
29
Page 33
Relative
address
040EH 41039 HYS1 Hysteresis setting 1 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
0414H 41045 BL-1 Output convergence value 1 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
0416H 41047 REF1 PID change point 1 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0420H 41057 SV2 Setpoint 2 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0422H 41059 P-2 Proportional band 2 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
0424H 41061 I-2 Integral time 2 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
0426H 41063 D-2 Derivative time 2 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
042AH 41067 ARH2
042CH 41069 ARL2 Anti-reset windup low limit 2
042EH 41071 HYS2 Hysteresis setting 2 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
0434H 41077 BL-2 Output convergence value 2 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
0436H 41079 REF2 PID change point 2 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0440H 41089 SV3 Setpoint 3 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0442H 41091 P-3 Proportional band 3 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
0444H 41093 I-3 Integral time 3 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
0446H 41095 D-3 Derivative time 3 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
044AH 41099 ARH3
044CH 41101 ARL3 Anti-reset windup low limit 3
044EH 41103 HYS3 Hysteresis setting 3 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
0454H 41109 BL-3 Output convergence value 3 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
0456H 41111 REF3 PID change point 3 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0460H 41121 SV4 Setpoint 4 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0462H 41123 P-4 Proportional band 4 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
0464H 41125 I-4 Integral time 4 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
0466H 41127 D-4 Derivative time 4 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
046AH 41131 ARH4
046CH 41133 ARL4 Anti-reset windup low limit 4
046EH 41135 HYS4 Hysteresis setting 4 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
0474H 41141 BL-4 Output convergence value 4 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
0476H 41143 REF4 PID change point 4 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0480H 41153 SV5 Setpoint 5 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0482H 41155 P-5 Proportional band 5 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
0484H 41157 I-5 Integral time 5 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
0486H 41159 D-5 Derivative time 5 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
048AH 41163 ARH5
048CH 41165 ARL5 Anti-reset windup low limit 5
048EH 41167 HYS5 Hysteresis setting 5 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
0494H 41173 BL-5 Output convergence value 5 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
0496H 41175 REF5 PID change point 5 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
04A0H 41185 SV6 Setpoint 6 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
04A2H 41187 P-6 Proportional band 6 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
04A4H 41189 I-6 Integral time 6 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
04A6H 41191 D-6 Derivative time 6 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
04AAH 41195 ARH6
04ACH 41197 ARL6 Anti-reset windup low limit 6
04AEH 41199 HYS6 Hysteresis setting 6 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
04B4H 41205 BL-6 Output convergence value 6 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
04B6H 41207 REF6 PID change point 6 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
04C0H 41217 SV7 Setpoint 7 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
04C2H 41219 P-7 Proportional band 7 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9%)
04C4H 41221 I-7 Integral time 7 0 to 32000 (0.0 to 3200.0sec)
04C6H 41223 D-7 Derivative time 7 0 to 9999 (0.0 to 999.9sec)
04CAH 41227 ARH7
04CCH 41229 ARL7 Anti-reset windup low limit 7
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
Anti-reset windup high limit
2
Anti-reset windup high limit
3
Anti-reset windup high limit
4
Anti-reset windup high limit
5
Anti-reset windup high limit
6
Anti-reset windup high limit
7
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 100%FS)
Write-in data
setting range
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
INP-TN514207-E
30
Page 34

Relative
address
04CEH 41231 HYS7 Hysteresis setting 7 ▪ Engineering unit setting (0 to 50%FS) *
04D4H 41237 BL-7 Output convergence value 7 –1000 to 1000 (–100.0 to 100.0%)
04D6H 41239 REF7 PID change point 7 ▪ Engineering unit setting (–25 to 125%FS) *
0820H 42081 UCF1
0822H 42083 UCB1
0824H 42085 UCD1
0830H 42097 PV1F PV1 full scale
0832H 42099 PV1B PV1 base scale
0834H 42101 PV1D PV1 decimal point position 0 to 3
0836H 42103 PV1T PV1 input type 0 to 9, 12 to 14, 16 to 20, 26, 27
0838H 42105 PV1U PV1 input unit
083AH 42107 PV1Z PV1 zero adjustment *
083CH 42109 PV1S PV1 span adjustment
0844H 42117 P1CU PV1 input router cut point –1 to 1250 (–0.1 to 125.0%) (–1: OFF)
0846H 42119 P1TF
0850H 42129 PV2F PV2 full scale
0852H 42131 PV2B PV2 base scale
0854H 42133 PV2D PV2 decimal point position 0 to 3
0856H 42135 PV2T PV2 input type 0 to 9, 12 to 14, 16 to 20, 26, 27
0858H 42137 PV2U PV2 input unit
085AH 42139 PV2Z PV2 zero adjustment *
085CH 42141 PV2S PV2 span adjustment
0864H 42149 P2CU PV2 input router cut point –1 to 1250 (–0.1 to 125.0%) (–1: OFF)
0866H 42151 P2TF
0890H 42193 AI1F AI1 full scale
0892H 42195 AI1B AI1 base scale
0894H 42197 AI1D AI1 decimal point position 0 to 3
0896H 42199 AI1T AI1 input unit 16 to 18
089AH 42203 AI1Z AI1 zero adjustment *
089CH 42205 AI1S AI1 span adjustment
08A2H 42211 A1CU AI1 input router cut point –1 to 1250 (–0.1 to 125.0%) (–1: OFF)
08A4H 42213 A1TF
0970H 42417 AO1T AO1 output type
0972H 42419 AO2T AO2 output type
0982H 42435 AO1L AO1 output base scale
0984H 42437 AO1H AO1 output full scale
0986H 42439 A1LL AO1 output low limit
0988H 42441 A1LH AO1 output high limit
0992H 42451 AO2L AO2 output base scale
0994H 42453 AO2H AO2 output full scale
0996H 42455 A2LL AO2 output low limit
0998H 42457 A2LH AO2 output high limit
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
Mathematical calculation
full scale
Mathematical calculation
base scale
Mathematical calculation
decimal point position
PV1 input filter time
constant
PV2 input filter time
constant
AI1 input filter time
constant
–19999 to 99999
0 to 3
–19999 to 99999
0: °C
1: °F
2: non
▪ Engineering unit setting (–50 to 50%FS)
0 to 9000 (0.0 to 900.0sec)
–19999 to 99999
0: °C
1: °F
2: non
▪ Engineering unit setting (–50 to 50%FS)
0 to 9000 (0.0 to 900.0sec)
–19999 to 99999
▪ Engineering unit setting (–50 to 50%FS)
0 to 9000 (0.0 to 900.0sec)
1: PV 5: AiM
2: SV 6: S1
3: MV 7: S2
4: DV 8: S3
–1300 to 1300
(–130.0 to 130.0%)
–250 to 1050 (–25.0 to 105.0%)
–1300 to 1300
(–130.0 to 130.0%)
–250 to 1050 (–25.0 to 105.0%)
Write-in data
setting range
Affected by
input range
*
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Turn off and
on power
Turn off and
on power
Turn off and
on power
Turn off and
on power
INP-TN514207-E
31
Page 35

Relative
address
0A00H 42561 CALC Calculation 0 to 11
0A02H 42563 TPLT Template number 10, 11, 13, 14, 16
0A04H 42565 OTYP Output type number 10 to 13
0A30H 42609 RIH1 Remote setting inhibition
0A40H 42625 RAC1
0A50H 42641 A-M1 A/M mode
0A60H 42657 CND1
0A74H 42677 STBO Standby action setting 0, 1
0A80H 42689 TRK1
0A90H 42705 PLTS
0A92H 42707 F1 User assign key 1 (F1)
0A94H 42709 F2 User assign key 2 (F2)
0A96H 42711 F3 User assign key 3 (F3)
0AA0H 42721 BRD1
0AE0H 42785 DI01 DI1 function selection
0AE2H 42787 DI02 DI2 function selection
0AE4H 42789 DI03 DI3 function selection
0AE6H 42791 DI04 DI4 function selection
0AE8H 42793 DI11 DI11 function selection
0AEAH 42795 DI12 DI12 function selection
0AECH 42797 DI13 DI13 function selection
0AEEH 42799 DI14 DI14 function selection
0AF0H 42801 DI15 DI15 function selection
0B50H 42897 DS00 Parameter mask 00
0B52H 42899 DS01 Parameter mask 01
0B54H 42901 DS02 Parameter mask 02
0B56H 42903 DS03 Parameter mask 03
0B58H 42905 DS04 Parameter mask 04
0B5AH 42907 DS05 Parameter mask 05
0B5CH 42909 DS06 Parameter mask 06
0B5EH 42911 DS07 Parameter mask 07
0B60H 42913 DS08 Parameter mask 08
0B62H 42915 DS09 Parameter mask 09
0B64H 42917 DS10 Parameter mask 10
0B66H 42919 DS11 Parameter mask 11
0B68H 42921 DS12 Parameter mask 12
0B6AH 42923 DS13 Parameter mask 13
0B6CH 42925 DS14 Parameter mask 14
0B6EH 42927 DS15 Parameter mask 15
0B70H 42929 DS16 Parameter mask 16
0B72H 42931 DS17 Parameter mask 17
0B74H 42933 DS18 Parameter mask 18
0B76H 42935 DS19 Parameter mask 19
0B78H 42937 DS20 Parameter mask 20
0B7AH 42939 DS21 Parameter mask 21
0B7CH 42941 DS22 Parameter mask 22
0B7EH 42943 DS23 Parameter mask 23
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
0: OFF
1: ON
Whether to use R-ACK or
not
Power-ON starting mode
setting
Whether to select tracking
or not
Palette change method
selection
Burnout direction designation (MV1)
0: inhibit
1: enable
0: A–M
1: A
0: Auto
1: Remote
2: Manual
0: OFF
1: ON
0: PLTn
1: SV
2: PV
0 to 27
0: HOLD
1: LO
2: UP
3: EXMV
0 to 255
0 to 65535 (0000H to FFFFH)
Write-in data
setting range
Affected by
input range
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Turn off and
on power
INP-TN514207-E
32
Page 36
Relative
address
0B80H 42945 DS24 Parameter mask 24
0B82H 42947 DS25 Parameter mask 25
0B84H 42949 DS26 Parameter mask 26
0B86H 42951 DS27 Parameter mask 27
0B88H 42953 DS28 Parameter mask 28
0B8AH 42955 DS29 Parameter mask 29
0B8CH 42957 DS30 Parameter mask 30
0B8EH 42959 DS31 Parameter mask 31
0B90H 42961 DS32 Parameter mask 32
0B92H 42963 DS33 Parameter mask 33
0B94H 42965 DS34 Parameter mask 34
0B96H 42967 DS35 Parameter mask 35
0B98H 42969 DS36 Parameter mask 36
0B9AH 42971 DS37 Parameter mask 37
0B9CH 42973 DS38 Parameter mask 38
0B9EH 42975 DS39 Parameter mask 39
0BA0H 42977 DS40 Parameter mask 40
0BA2H 42979 DS41 Parameter mask 41
0BA4H 42981 DS42 Parameter mask 42
0BA6H 42983 DS43 Parameter mask 43
0C00H 43073 PAS1 Security setting 1
0C02H 43075 PAS2 Security setting 2
0C04H 43077 PAS3 Security setting 3
0C22H 43107 STN4 RS-485 station No. 0 to 255
0C24H 43109 SPD4
0C26H 43111 BIT4 RS-485 bit format
0C30H 43121 SPD2
0C32H 43123 BIT2 RS-232C bit format
0C50H 43153 - FIX command
0DC0H 43521 K01
0DC2H 43523 K02
0DC4H 43525 K03
0DC6H 43527 K04
0DC8H 43529 K05
0DCAH 43531 K06
0DCCH 43533 K07
0DCEH 43535 K08
0DD0H 43537 K09
0DD2H 43539 K10
0DD4H 43541 K11
0DD6H 43543 K12
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
0 to 65535 (0000H to FFFFH)
0 to 65535 (0000H to FFFFH)
RS-485 communication
speed
RS-232C communication
speed
Mathematical calculation
constant 1
Mathematical calculation
constant 2
Mathematical calculation
constant 3
Mathematical calculation
constant 4
Mathematical calculation
constant 5
Mathematical calculation
constant 6
Mathematical calculation
constant 7
Mathematical calculation
constant 8
Mathematical calculation
constant 9
Mathematical calculation
constant 10
Mathematical calculation
constant 11
Mathematical calculation
constant 12
0: 9.6k
1: 19.2k
2: 38.4k
0: 8N
1: 8O
2: 8E
0: 9.6k
1: 19.2k
2: 38.4k
0: 8N
1: 8O
2: 8E
0: Not writing in
1: Now writing in
memory
▪ Floating decimal point type
99999 to 0.0000
–0.001 to –9999
Write-in data
setting range
0: No effect
1: Write-in request
Affected by
input range
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Turn off and
on power
INP-TN514207-E
33
Page 37
Relative
address
0DD8H 43545 K13
0DDAH 43547 K14
0DDCH 43549 K15
0DDEH 43551 K16
0E00H 43585 ATP1 Auto tuning type
0E20H 43617 DO1 DO1 output designation
0E22H 43619 DO2 DO2 output designation
0E24H 43621 DO3 DO3 output designation
0E26H 43623 DO4 DO4 output designation
0E30H 43633 DO11 DO11 output designation
0E32H 43635 DO12 DO12 output designation
0E34H 43637 DO13 DO13 output designation
0E36H 43639 DO14 DO14 output designation
0E38H 43641 DO15 DO15 output designation
0E70H 43697 C1 LED C1 assign
0E72H 43699 C2 LED C2 assign
0E74H 43701 LDO1 LED DO1 assign
0E76H 43703 LDO2 LED DO2 assign
0E78H 43705 LDO3 LED DO3 assign
0E7AH 43707 LDO4 LED DO4 assign
0E7CH 43709 LDO5 LED DO5 assign
0E7EH 43711 LALM LED ALM assign
0EA0H 43745 CN01
0EA2H 43747 CN02
0EA4H 43749 CN03
0EA6H 43751 CN04
0EA8H 43753 CN05
0EAAH 43755 CN06
0EACH 43757 CN07
0EAEH 43759 CN08
0EB0H 43761 CN09
0EB2H 43763 CN10
0EB4H 43765 CN11
0EB6H 43767 CN12
0EB8H 43769 CN13
0EBAH 43771 CN14
0EBCH 43773 CN15
0EBEH 43775 CN16
Register
No.
Parameter
name
Parameter contents Read-out data
Mathematical calculation
constant 13
Mathematical calculation
constant 14
Mathematical calculation
constant 15
Mathematical calculation
constant 16
Constant 1 used for template
Constant 2 used for template
Constant 3 used for template
Constant 4 used for template
Constant 5 used for template
Constant 6 used for template
Constant 7 used for template
Constant 8 used for template
Constant 9 used for template
Constant 10 used for template
Constant 11 used for template
Constant 12 used for template
Constant 13 used for template
Constant 14 used for template
Constant 15 used for template
Constant 16 used for template
▪ Floating decimal point type
99999 to 0.0000
–0.001 to –9999
0: NRML
1: LPV
0 to 255
0 to 255
–19999 to 99999
Write-in data
setting range
Affected by
input range
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Turn off and
on power
Turn off and
on power
INP-TN514207-E
34
Page 38
Word data [read-out only] : Function code [04H]
Relative
address
0100H 30257
0102H 30259 PV1
0104H 30261 SV1
0106H 30263 DV1
0108H 30265 MV1
010CH 30269 FAULT1
0310H 30785
0312H 30787
0314H 30789
0316H 30791
0318H 30793
031AH 30795
031CH 30797
031EH 30799
0340H 30833 ALM1 Alarm 1 status
0342H 30835 ALM2 Alarm 2 status
0344H 30837 ALM3 Alarm 3 status
0346H 30839 ALM4 Alarm 4 status
0348H 30841 ALM5 Alarm 5 status
034AH 30843 ALM6 Alarm 6 status
034CH 30845 ALM7 Alarm 7 status
034EH 30847 ALM8 Alarm 8 status
0400H 31025 PV1 PV1 measurement value *
0402H 31027 PV2 PV2 measurement value *
0406H 31031 AI1 Ai1 measurement value *
0420H 31057 RCJ1
0422H 31059 RCJ2
0450H 31105 AO1 AO1 output value
0452H 31107 AO2 AO2 output value
Register
No.
Parameter
name
PID
MODE1
ALM1
(RELAY)
ALM2
(RELAY)
ALM3
(RELAY)
ALM4
(RELAY)
ALM5
(RELAY)
ALM6
(RELAY)
ALM7
(RELAY)
ALM8
(RELAY)
Parameter contents Read-out data
0001H: Fault status
0002H: Standby status
0004H: Remote Ack
0008H: Other than auto mode
0010H: Auto mode request
0020H: Remote mode request
Current control mode
Process variable (PV) used
for control currently
Currently used setpoint
(SV)
Currently used deviation
(DV)
Currently used manipulating
value (MV)
Currently used input error
status information
Alarm 1 status (relay status)
Alarm 2 status (relay status)
Alarm 3 status (relay status)
Alarm 4 status (relay status)
Alarm 5 status (relay status)
Alarm 6 status (relay status)
Alarm 7 status (relay status)
Alarm 8 status (relay status)
PV1 RCJ measurement
value
PV2 RCJ measurement
value
0040H: Auto tuning status
0080H: Normal operation status
0100H: PV tracking status
0200H: Local SV status
0400H: Remote SV status
0800H: Local + PV tracking status
1000H: Forced manual mode status
2000H: EX-MV mode status
4000H: Manual mode status
–25999 to 105999
(Input scale: –5 to 105% FS)
–19999 to 99999 (within settable range) *
–125998 to 125998
(Input scale: –105 to 105% FS)
–250 to 1250 (–25.0 to 125.0%)
Normal: 0
Over: 1
Under: 2
Excitation: 1, Non-excitation: 0
Excitation: 1, Non-excitation: 0
ON: 1, OFF: 0
–214783647 to 214783648
–250 to 1250 (–25.0 to 125.0%)
Affected by
input range
*
*
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Corresponding bit to
relevant status
is "1".
INP-TN514207-E
35
Page 39

Relative
address
0470H 31137 DI01 DI1 to 4 input status
0472H 31139 DI11 DI11 to 15 input status
04D0H 31233 DO01 DO1 to 4 output status
04D2H 31235 DO11 DO11 to 15 output status
0540H 31345 AIM
0550H 31361
0552H 31363
0554H 31365
0556H 31367
0558H 31369
055AH 31371
055CH 31373
055EH 31375
0564H 31381 AMV1
056CH 31389 FFV1 Feed Forward value –214783647 to 214783648
Register
No.
Parameter
name
ALM
DLY 1
ALM
DLY 2
ALM
DLY 3
ALM
DLY 4
ALM
DLY 5
ALM
DLY 6
ALM
DLY 7
ALM
DLY 8
Parameter contents Read-out data
DI1: 8000H
DI2: 4000H
DI3: 2000H
DI4: 1000H
DI11: 8000H
DI12: 4000H
DI13: 2000H
DI14: 1000H
DI15: 0800H
DO1: 1
DO2: 2
DO3: 4
DO4: 8
DO11: 1
DO12: 2
DO13: 4
DO14: 8
DO15: 16
Mathematical calculation
result
Alarm 1 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 2 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 3 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 4 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 5 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 6 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 7 delay timer remaining time monitor
Alarm 8 delay timer remaining time monitor
EXMV value
(External analog value)
–214783647 to 214783648 *
0 to 9999
–214783647 to 214783648
Affected by
input range
Remarks or
corresponding
parameter
Corresponding bit to ON
is "1".
Corresponding bit to ON
is "1".
Corresponding bit to ON
is "1".
Corresponding bit to ON
is "1".
Mathematical
calculation
scale
INP-TN514207-E
36
Page 40

8. SAMPLE PROGRAM
This section concerns data read-out/write-in sample program by Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 (SP6) (enclosed
to CD-ROM).
Note that the program shown here is for reference for you to create a program and not for guaranteeing all
actions.
Before executing the program, make sure of the communication conditions in the following procedure.
▪ Parity, communication speed: Must be set in this program to match the instrument.
Precautions for some RS-232C ⇔ RS-485 converter
The transmission data itself may precede the answer data from the slave station. In such a case, discard
as many data as transmission bytes found there, and then process it as answer data.
Applicable OS
Windows 2000 Professional
Windows XP Professional Edition
Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. and Fuji Electric Instruments Co., Ltd. will not be responsible for damages
attributable to use of the sample program nor infringement of rights owned by third parties.
Use the program upon admitting the above.
INP-TN514207-E
37
Page 41

(a) Example of data read-out
Operation: 2 word data of a designated address is read-out and displayed at a time.
Used function code: 03
, 04H
H
Read-out word number: 2
' Variable declaration ***************************************************************************************************************
Dim idx As Integer
Dim Ansdat() As Byte ' For storing answer data
Dim Rxbuff As Variant ' Receive data buffer
Dim PauseTime ' Sets the communication wait time
' Required wait time depends on transmission speed and transmission frame length
Dim Stno As Byte ' Communication station number
Private Sub Form_Load()
' Initializing the variable ************************************************************************************************************
Stno = 1
Main.Visible = True
End Sub
'-----------------------------------------'Read continuous words sample program
'Function code : 03H, 04H
'Number of words : 2
'------------------------------------------
Private Sub TX1_Click()
TX1.Enabled = False
' Communication port setting ********************************************************************************************************
If Com5.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 5 ' COM5
ElseIf Com4.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 4 ' COM4
ElseIf Com3.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 3 ' COM3
ElseIf Com2.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 2 ' COM2
Else
Comm_port = 1 ' COM1
End If
If SPD192.Value = True Then
Comm_speed = "19200," ' 19200bps
ElseIf SPD96.Value = True Then
Comm_speed = "9600," ' 9600bps
Else
Comm_speed = "38400," ' 38400bps
End If
If Even1.Value = True Then
Comm_parity = "E," ' Even parity
ElseIf Odd1.Value = True Then
Comm_parity = "O," ' Odd parity
Else
Comm_parity = "N," ' No parity
End If
PauseTime = 0.2 ' Sets the wait time (0.2 sec)
idx = 0
' Opening the communication port ****************************************************************************************************
MSComm1.CommPort = Comm_port ' COM port setting
MSComm1.Settings = Comm_speed & Comm_parity & "8,1" ' Speed / Party / 8bit_Data / Stop_1bit
MSComm1.PortOpen = True ' Opens a port
' Setting the opposite station number for communication **********************************************************************************
St = Val(Stno1(idx).Text)
Stno = St Mod 256
Stno1(idx).Text = Str(Stno)
' Address processing ******************************************************* ********************************************************
AD$ = Str(Val(Address(idx).Text) - 1)
AD$ = Right$(("00000" & AD$), 5)
Area = Val(Left$(AD$, 1))
Adrsh = Int(Val(Right$(AD$, 4)) / 256)
Adrsl = Val(Right$(AD$, 4)) Mod 256
INP-TN514207-E
38
Page 42

' Transmission command generation **************************************************************************************************
Select Case Area
Case 3
ReDim Txdat(7) As Byte ' Secures 8 byte array
Txdat(0) = Stno ' Station No.
Txdat(1) = &H4 ' Command
Txdat(2) = Adrsh ' High address
Txdat(3) = Adrsl ' Low address
Txdat(4) = &H0 ' Number of read-in words (High)
Txdat(5) = &H2 ' Number of read-in words (Low)
Txsu = 5 ' Number of transmission data
Case 4
ReDim Txdat(7) As Byte ' Secures 8 byte array
Txdat(0) = Stno ' Station No.
Txdat(1) = &H3 ' Command
Txdat(2) = Adrsh ' High address
Txdat(3) = Adrsl ' Low address
Txdat(4) = &H0 ' Number of read-in words (High)
Txdat(5) = &H2 ' Number of read-in words (Lo)
Txsu = 5 ' Number of transmission data
Case Else ' For other value
MSComm1.PortOpen = False ' Closes COM port
TX1.Enabled = True
Exit Sub
End Select
' Transmitting a command **********************************************************************************************************
' Generation of CRC for transmission data
GoSub 10000 ' CRC calculation
Txdat(Txsu + 1) = CRC1 '
Txdat(Txsu + 2) = CRC2 '
' Transmitting a generated command
MSComm1.Output = Txdat ' Transmits 1 byte
' Waiting until all answer data is received
Start = Timer ' Saves the waiting start time
Do While Timer < Start + PauseTime ' Whether time setting elapsed
DoEvents ' Transfers the control to another process
If ((Start + PauseTime) - Timer) > PauseTime Then
Start = Timer
End If
Loop
' Fetching the answer data into byte array
MSComm1.InputMode = comInputModeBinary ' Designates binary mode
length = MSComm1.InBufferCount ' Acquires required number of receive data bytes
MSComm1.InputLen = 0 ' Designates acquisition of all data
Rxbuff = MSComm1.Input ' Fetches receive data into receive buffer
Ansdat = Rxbuff ' Assigns byte array to receive data
' CRC calculation for receive data
Ansu = length – 3 ' Receive data length
GoSub 20000 ' CRC calculation
' Error check
If (length = 0) Then ' No anser
Noans = Noans + 1: Rx_data.Caption = "Noans": GoTo 150
ElseIf ((Ansdat(length - 2) <> CRC1) + (Ansdat(length - 1) <> CRC2)) Then ' CRC error
CRCErr = CRCErr + 1: Rx_data.Caption = "CRCErr": GoTo 150
ElseIf Ansdat(1) >= &H80 Then ' Command error
CMDErr = CMDErr + 1: Rx_data.Caption = "CMDErr": GoTo 150
End If
' Processing of normal receive data
wrk1 = Ansdat(3)
wrk2 = Ansdat(4)
wrk3 = Ansdat(5)
wrk4 = Ansdat(6)
If Ansdat(5) > 128 Then ' If receive data is negative
Rx_data.Caption = Str(((wrk3 * (2 ^ 24)) + (wrk4 * (2 ^ 16)) + (wrk1 * (2 ^ 8)) + wrk2) - (2 ^ 32))
Else
Rx_data.Caption = Str(((wrk3 * (2 ^ 24)) + (wrk4 * (2 ^ 16)) + (wrk1 * (2 ^ 8)) + wrk2))
End If
150
MSComm1.PortOpen = False ' Closes COM port
TX1.Enabled = True
Exit Sub
INP-TN514207-E
39
Page 43

' ******************************************************************************************************************************
10000 ' CRC calculation subroutine IN:Txdat(Txsu) / OUT CRC1,CRC2 ***************************************************************
CRC = &HFFFF
For i = 0 To Txsu Step 1
CRC = CRC Xor Txdat(i)
For J = 1 To 8 Step 1
CT = CRC And &H1
If CRC < 0 Then CH = 1 Else: CH = 0: GoTo 11000
11000 CRC = Int(CRC / 2)
20000 ' CRC calculation subroutine IN:Ansdat(Ansu) / OUT CRC1,CRC2 **************************************************************
21000 CRC = Int(CRC / 2)
End Sub
CRC = CRC And &H7FFF
If CH = 1 Then CRC = CRC Or &H4000
If CT = 1 Then CRC = CRC Xor &HA001
Next J
Next i
CRC1 = CRC And &HFF
CRC2 = ((CRC And &HFF00) / 256 And &HFF)
Return
CRC = &HFFFF
For i = 0 To Ansu Step 1
CRC = CRC Xor Ansdat(i)
For J = 1 To 8 Step 1
CT = CRC And &H1
If CRC < 0 Then CH = 1 Else: CH = 0: GoTo 21000
CRC = CRC And &H7FFF
If CH = 1 Then CRC = CRC Or &H4000
If CT = 1 Then CRC = CRC Xor &HA001
Next J
Next i
CRC1 = CRC And &HFF
CRC2 = ((CRC And &HFF00) / 256 And &HFF)
Return
INP-TN514207-E
40
Page 44

(b) Example of data write-in
Operation: Writes 2 word data into a designated address
Used function code: 10
H
Number of write-in words: 2
'-----------------------------------
'Write 2 words sample program
'Function code : 10H
'Number of words : 2
'-----------------------------------
Private Sub Write_command_Click()
Write_command.Enabled = False
' Communication port setting ***************************************************************************************************
If Com5.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 5 ' COM5
ElseIf Com4.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 4 ' COM4
ElseIf Com3.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 3 ' COM3
ElseIf Com2.Value = True Then
Comm_port = 2 ' COM2
Else
Comm_port = 1 ' COM1
End If
If SPD192.Value = True Then
Comm_speed = "19200," ' 19200bps
ElseIf SPD96.Value = True Then
Comm_speed = "9600," ' 9600bps
Else
Comm_speed = "38400," ' 38400bps
End If
If Even1.Value = True Then
Comm_parity = "E," ' Even parity
ElseIf Odd1.Value = True Then
Comm_parity = "O," ' Odd parity
Else
Comm_parity = "N," ' No parity
End If
PauseTime = 0.2 ' Sets the wait time (0.2 sec)
idx = 1
' Opening the communication port ************************************************************************************************
MSComm1.CommPort = Comm_port ' Com port
MSComm1.Settings = Comm_speed & Comm_parity & "8,1" ' Speed / Party / 8bit_Data / Stop_1bit
MSComm1.PortOpen = True ' Open com port
' Setting the opposite station number for communication *******************************************************************************
St = Val(Stno1(idx).Text)
Stno = St Mod 256
Stno1(idx).Text = Str(Stno)
' Address processing ***********************************************************************************************************
AD$ = Str(Val(Address(idx).Text) - 1)
AD$ = Right$(("00000" & AD$), 5)
Area = Val(Left$(AD$, 1))
Adrsh = Int(Val(Right$(AD$, 4)) / 256)
Adrsl = Val(Right$(AD$, 4)) Mod 256
' Transmission command generation ***********************************************************************************************
Select Case Area
Case 4
'Normal sending data is processed.
Dim byteData(3) As Byte
Dim sHex As String
sHex = Right("00000000" & Hex(Val(Write_data.Text)), 8) ' Decimal → hexadecimal
byteData(0) = CByte("&H" & Mid(sHex, 1, 2)) 'hh byte
byteData(1) = CByte("&H" & Mid(sHex, 3, 2)) 'hl byte
byteData(2) = CByte("&H" & Mid(sHex, 5, 2)) 'lh byte
byteData(3) = CByte("&H" & Mid(sHex, 7, 2)) 'll byte
INP-TN514207-E
41
Page 45

ReDim Txdat(12) As Byte ' 13 bytes
Txdat(0) = Stno ' Station No.
Txdat(1) = &H10 ' Command
Txdat(2) = Adrsh ' High address
Txdat(3) = Adrsl ' Low address
Txdat(4) = &H0 ' Number of write-in words (High)
Txdat(5) = &H2 ' Number of write -in words (Lo)
Txdat(6) = &H4 ' Number of write -in bytes
Txdat(7) = byteData(2) ' Write-in data (Lo high)
Txdat(8) = byteData(3) ' Write-in data (Lo lo)
Txdat(9) = byteData(0) ' Write-in data (High high)
Txdat(10) = byteData(1) ' Write-in data (HIgh lo)
Txsu = 10 ' Number of transmission data
Case Else ' For other
MSComm1.PortOpen = False ' Closes COM port
Write_command.Enabled = True
Exit Sub
End Select
' Transmitting a command ********************************************************************************************************
' Generation of CRC for transmission data
GoSub 10000 ' CRC calculation
Txdat(Txsu + 1) = CRC1 '
Txdat(Txsu + 2) = CRC2 '
' Transmitting a generated command
MSComm1.Output = Txdat ' Transmits 1 byte
' Waiting until all answer data is received
Start = Timer ' Saves the waiting start time
Do While Timer < Start + PauseTime ' Whether time setting elapsed
DoEvents ' Transfers the control to another process
If ((Start + PauseTime) - Timer) > PauseTime Then
Start = Timer
End If
Loop
MSComm1.PortOpen = False ' Closes COM port
Write_command.Enabled = True
Exit Sub
' ********************************************************************************************************************************
10000 ' CRC calculation subroutine IN:Txdat(Txsu) / OUT CRC1,CRC2 *****************************************************************
CRC = &HFFFF
For i = 0 To Txsu Step 1
CRC = CRC Xor Txdat(i)
For J = 1 To 8 Step 1
CT = CRC And &H1
If CRC < 0 Then CH = 1 Else: CH = 0: GoTo 11000
CRC = CRC And &H7FFF
11000 CRC = Int(CRC / 2)
If CH = 1 Then CRC = CRC Or &H4000
If CT = 1 Then CRC = CRC Xor &HA001
Next J
Next i
CRC1 = CRC And &HFF
CRC2 = ((CRC And &HFF00) / 256 And &HFF)
Return
End Sub
INP-TN514207-E
42
Page 46

9. TROUBLESHOOTING
If the communication is unavailable, check the following items.
□ Whether all devices related to communication are turned on.
□ Whether wirings are correct. (Whether polarities are correct.)
□ Whether the number of connected instruments and connection distance are as specified.
□ Whether communication conditions coincide between the master station (host computer) and slave sta-
tions (PXH).
□ Transmission speed : 9600bps, 19200bps, 38400bps
□ Data length : 8 bits
□ Stop bit : 1 bit
□ Parity : □ odd
□ even
□ none
□ Whether send/receive signal timing conforms to Section 5.4 in this manual.
□ Whether the station No. designated as send destination by the master station coincides with the station No.
of the connected PXH. (For PC loader communication, the station No. is fixed at "1".)
□ Whether, at RS-485 communication, more than one instrument connected on the same transmission line
does not share the same station No.
□ Whether, at RS-485 communication, the station No. of instruments is not set at 0.
If it is 0, the communication function does not work.
□ Whether, at RS-485 communication, the 11th digit of type code of this controller is R.
(PXH9□□□□ – □□R□□-□)
□ Whether, at RS-485 communication, settings of communication conditions for RS-232C ⇔ RS-485 con-
verter are correct.
INP-TN514207-E
43
Page 47

Head office
6-17, Sanbancho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 102-0075,
http://www.fesys.co.jp
Sales Div.
International Sales Dept.
No.1, Fuji-machi, Hino-city, Tokyo 191-8502,
Phone: 81-42-585-6201, 6202 Fax: 81-42-585-6187
http://www.fic-net.co.jp
Japan
Japan
 Loading...
Loading...