Fuelab 51501 User Manual
Model Number 51501
Fuel Pressure Regulator
Operating and Installation Instructions
CCAAUUTTIIOONN!!
This product is to be installed only by persons knowledgeable in the repair and modification of vehicle fuel systems
and general vehicle systems modification. Only a qualified technician or mechanic who is aware of applicable
safety procedures should perform the installation of this product.
GASOLINE AND OTHER FUELS ARE FLAMMABLE AND CAN BE EXPLOSIVE!
Perform the installation in a well ventil ate d loc ation onl y to minim i ze the build up of fuel vapors . NO open flames,
smoking or other sources of ignition are to be present during installation, to prevent fire or explosion that can cause
serious injury or death. Grinding, cutting, and drilling must be performed with care to prevent ignition. Draining and
removal of all fuel and ventilation of vapors in vehicle and fuel system is recommended when performing such
procedures. Proper eye and personal protection is required at all times during installation.
WWAARRNNIINNGG!!
The Vehicle’s fuel system may be under pressure! Do not loosen any fuel connections until relieving all fuel system
pressure. Consult an applicable service manual for instructions to relieve fuel system pressure safely.
This product is intended for racing, off-road, or marine use only. This fuel system component is capable of altering
engine tuning and therefore not legal for sale or use on emission controlled motor vehicles.
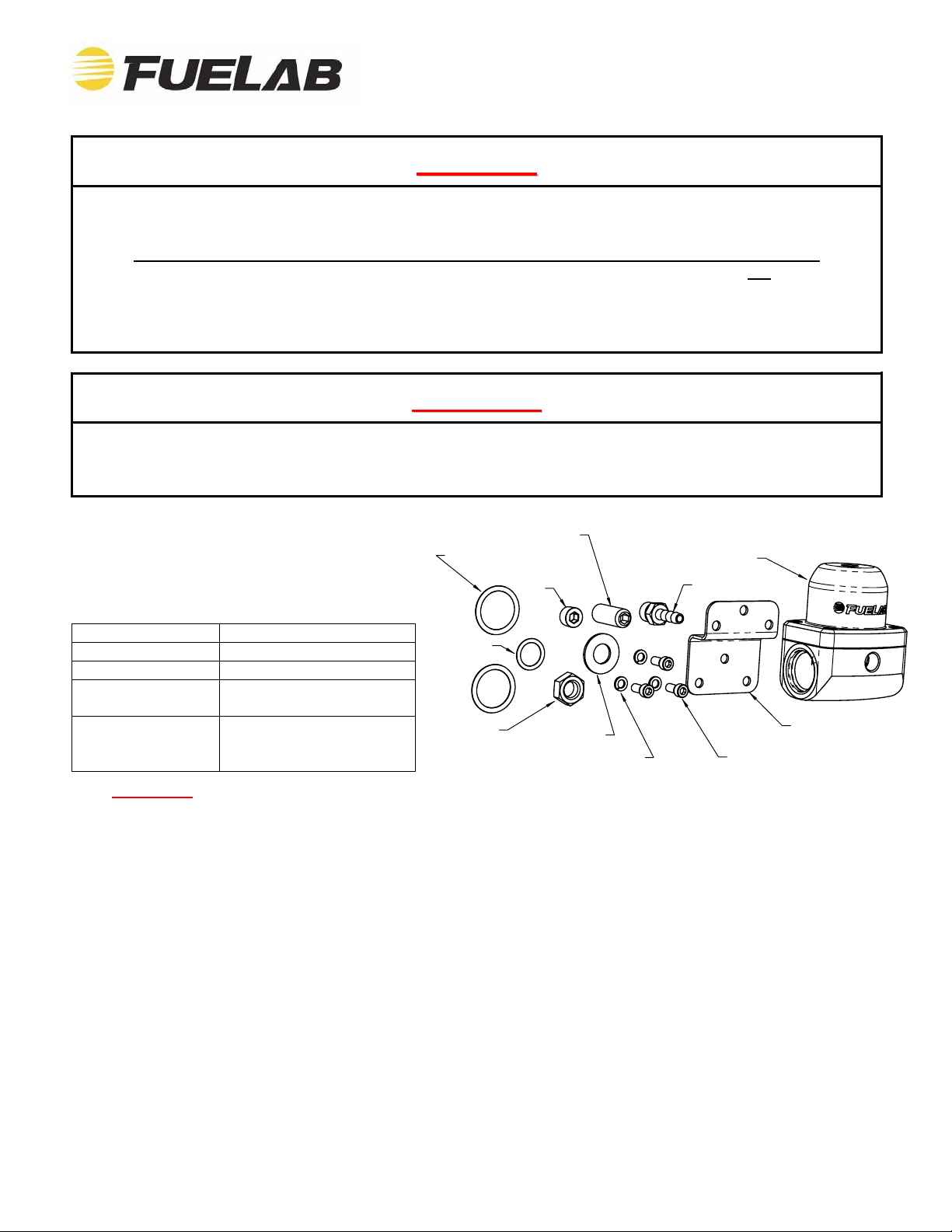
Product Contents:
Check the diagram and list of components
(right) to ensure that no components are
missing from box. Contact your Fuelab
distributor immediately for replacem ent.
51501 Features and Performance Ratings:
Inlet Port Sizes -10AN Military Port
Seat Size Standard
Regulation Slope 3 PSI/GPM
Maximum Flow
Capacity
Pressure
Adjustment Range
2.5 GPM at 25 PSID
(570 LPH at 1.75 Bar)
Pressure Range “E”
25-90 PSID
(1.75-6.2 Bar)
-906 O-ring
Adjustment Screw
(2X) -910 O-ring
Jam Nut
Plug
Flat Washer
(3X) Bracket Lock Washers
Regulator
Barbed Fitting
Bracket
(3X) Bracket Screws
WARNING! Exceeding maximum flow capacity may result in an over-pressure operating condition.
Before Installation, Plan Entire Fuel System:
These instructions are limited to general topics of regulator component installation and may not include specific
information pertaining to your application. These instructions are written assuming the use of an electric fuel pump
capable of at least 100 PSIG outlet pressure and limited to the specified
regulator has an internal spring that can be changed for other pressure ranges, including “T” range, for 10-25 PSID
if required by the specific application. Lower, carbureted pressure ranges are recommended for a different model of
regulator only. Visit our company website for specific details pertaining to example fuel systems and other solution
ideas. Additional information including advanced troubleshooting, any special alerts and FAQ’s pertaining to this
and other products is also available.
General Regulator Performance Notes:
The notation “PSIG” means pressure in Pounds per Square Inch (PSI) relative to the prevailing atmospheric
condition or outside air. This is referred to as Gauge Pressure. The notation “PSID” means pressure in PSI relative
to another pressure source or called the Differential Pressure. The intake manifold pressure, when plumbed to the
regulator, changes the fuel pressure in a 1:1 ratio. When the engine idles (for example 12 Inches of Mercury or 6
PSIG of vacuum) fuel rail pressure will lower 6 PSI, when compared to the setting with the engine off. For boosted
applications, including turbo or superchargers, fuel rail pressure increases at a 1:1 ratio. An engine at 10 PSIG of
boost as measured in the intake manifold, will increase the fuel pressure by 10 PSIG. The actual readings of
pressure in a real world application would show a lower pressure, as the engine is using fuel that would normally be
returning back through the return line when the engine is off. The amount of pressure difference to expect is a
function of how much flow the engine is using (reference
Regulation Slope
Maximum Flow Capacity
, above).
105020121-1, Rev B Sheet 1 of 4
(above). This
Plumbing Planning Notes:
l
y
Minimize plumbing restrictions between fuel rail(s) and regulator for peak performance, use –6AN (3/8”) to –10AN
(5/8”) line as required per flow rate requirements of the vehicle’s engine and fuel pump. Typical performance EFI
applications use a “Y” block or “T” fitting to split the output of the fuel pump into one end of each fuel rail (for dual
fuel rail application). The opposite end of each fuel rail is plumbed to the
Inlet Ports
of the regulator. Plumb the
return line back to the fuel tank. Use of a –6AN (3/8”) return line is typically recommended for this model of
regulator. See diagram on next page as well as diagram below, to identify the ports used on the regulator. If only
one fuel rail is used for the application, use a
unused
Inlet Port
(“Y” block or “T” fitting not required in this case). The fuel line used must handle high pressure.
–10AN plug
(not supplied) and supplied
–910 O-ring
to plug the
The use of fuel line such as stainless steel braided line and “AN” style fitting connections is recommended. The fue
ports (two
–10AN Inlet Ports
and one
–6AN Return Port
) use “AN” or “military” style fittings. This plumbing standard
is commonly used with racing and high performance applications. See step 6 on next page for additional
information on this port standard. A fuel filter with a 60 micron or lower particle rating is required to be used
upstream of regulator and downstream from fuel pump to protect it and the fuel injectors from foreign object
damage. Reference the Schematic Diagram below for filter locations. Use of a liquid filled gauge exposed to
engine compartment heat is not recommended as the liquid inside the gauge may exert measurement errors.
NOT
plumb gauge port to any gauge mounted inside the vehicle or in passenger compartment. A line burst can
DO
spill fuel inside passenger compartment and on occupants, possibly causing serious injury or death. An electric
gauge or pressure transducer system is recommended for readings in a passenger compartment.
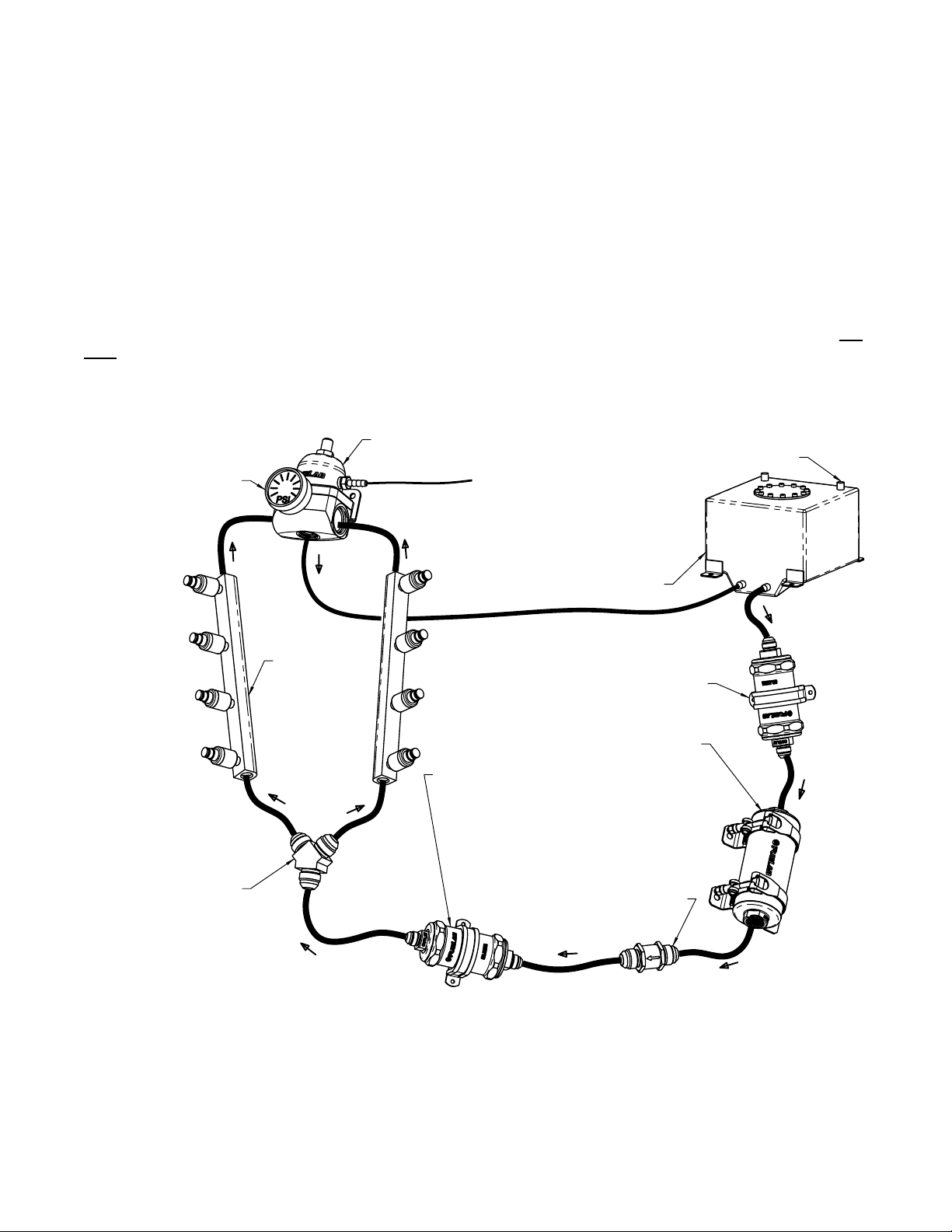
Typical EFI V-8 Fuel System Schematic Diagram:
Fuel Gauge Shown in
Gauge Port, Liquid Fille d
Gauge may have Error Due
to Temperature Variations.
51501 Regulator
To Engine Intake Manifold
Follow Fuel Cell Manufacturer's
Recommendations for Proper
Cell Vent Plumbing
Vented Fuel Cell or Fuel Tank.
Tank must be Plumbed According
to Maximum Pump Flow Rate.
Specifications and Recommendations.
Consult Pump Manufacturer's
(2X) Fuel Rails
with Injectors
Fuel Straining Filter Required, Typical
75 Micron Filter Recommended. Straining
Consult Pump Manufacturer's Specifications.
Micron Rating: 75-150, Fuelab
Filter may be Installed in Fuel Pump,
Y-Block or "T" Fitting,
to Split Flow into Two
Fuel Rail System
Fuelab Prodigy Series
Fuel Pump Recommended.
Fuel Filter with 60 Micron or
Lower Particle Rating is Required.
Fuelab Filter with 6, 10 or 40
Micron Rating is Recommended.
Check Valve Required for Reduced
Vehicle Emissions and Improved
Engine Starting. Valve may be Installed
in Fuel Pump,Typical OEM Pumps
do have this Valve Installed. Consult
Pump Manufacturer's Specifications
Fuel Pump
Installation Steps:
1. Disconnect the ground terminal from battery and allow the vehicle’s engine and exhaust system to cool.
Relieve fuel system per applicable service manual. Follow all Warnings and Cautions written on previous page
of these instructions.
2. Modify, remove or replace other fuel system components as required per established build plan (reference
notes on previous page and above).
3. Use the supplied bracket as a drilling template to mark holes for mounting bracket. Choose a location that
minimizes exposure to excessive heat, near fuel rails. Mounting bracket can be modified as required. Use
clear or colored enamel paint to protect bracket surface after an
modification.
105020121-1, Rev B Sheet 2 of 4
 Loading...
Loading...