Page 1
Service & Parts Manual
2005
Room Air Conditioners
50 & 60 Hz Models
HG-SVC-PRTS-05 (4-05)
SH15L30-A
SH20L30-A
SH20L50-A
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
Specifi cations ................................................................................................................................... 3
Performance Data ............................................................................................................................ 3
Component Operation & Testing ...................................................................................................... 4
Compressors .................................................................................................................................... 4
Thermal Overload ............................................................................................................................ 4
Checking Compressor Effi ciency ...................................................................................................... 5
Fan Motor ......................................................................................................................................... 5
Solid State Relay .............................................................................................................................. 5
System Control Switch .................................................................................................................... 6
Run Capacitor ................................................................................................................................... 6
Thermostat ....................................................................................................................................... 6
Low Ambient Bypass Valve .............................................................................................................. 8
Sealed Refrigeration System Repairs .............................................................................................. 8
Hermetic Component Replacement ................................................................................................. 9
Special Procedure in the case of Compressor Motor Burn-Out ...................................................... 9
Rotary Compressor Special Troubleshooting & Service ................................................................ 10
Refrigerant Charge ......................................................................................................................... 10
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................. 11-13
Wiring Diagram ............................................................................................................................... 14
Cabinet Parts Diagram .................................................................................................................. 15
Chassis Parts Diagram .................................................................................................................. 16
Parts List .................................................................................................................................... 17-19
2
Page 3
FUSE
60 Hertz
BREAKER
RPM
Motor
CFM
Evap
REF.
R-22
Charge
Locked
Amps
ELECTRICAL RATINGS
Amps
OPERATING
PRESSURES
Sub-
Cooling
Amps
in OZ.
Rotor
Amps
Heat
Cool
(Lbs.)
Weight
Circulation
Room Sid e Air
T - D Fuse
Breaker or
Controls
Air Direction
Circuit Rating
16 250V - 15A 140 152
/
/16 250V - 15A 166 179
/16 250V - 15A 166 179
3
3
3
OPERATING TEMPERATURE CODE T3B
Heat
Super
Tem p
Liquid
Tem p
Suction
Tem p
Discharge
TEMP.
DEG. F
CONDENSER
TEMP. DEG. F
EVAPORATOR
Tem p.
TEMP. DEG. F
EVAPORATOR AIR
Discharge
E(in) E(out) Suction Discharge
Drop F.
Air
Moisture
Cooling Capacity Electrical Characteristics ( 60 Hertz) Energy
16 26
16 26
16 26
/
/
Removal
Effi ciency
(Pints/ Hr.) CFM
Ratio AHAM
Amps
AHAM Watts EER
(Inches)
Finished Hole
Thru-The-Wall
(Inches)
Outside Min. Max. Height Width Volts - Amps Net Shipping
Minimum
Extension
Into
Room
Minimum
Extension
Depth
Hood to
Louvers
Dimensions (Inches) Window Width
Depth
Overall
(BTU/Hr.- AHAM) Volts Rated
/
3
3
3
8 42 16
8 42 18
8 42 18
/
/
/
7
7
7
16 27
16 27
16 27
/
/
/
15
15
15
16 16
16 16
16 16
/
/
/
1
1
1
16 3
16 3
16 3
/
/
/
3
3
3
8 9
8 9
8 9
/
/
/
3
3
3
16 27
16 27
16 27
/
/
/
15
15
15
16 25
16 25
16 25
/
/
/
15
15
15
Height Width
60 Hz Models
SH15L30-A 54 26 52 56 206 129 61 108 16 98 76 258 8.2 - - 28.5 363 1100 15
SH20L30-A 46 34 46 46 125 196 52 97 8 28 75 271 10.1 - - 39.0 357 1100 20
50 Hz Model
Performance Data: Cooling
SH20L50-A 54 26 49 59 123 - - - - - - - 10.2 - - 34 434 1200 20
Product Specifications
SH15L30 15000/15000 230/208 7.9/8.7 1765/1765 8.5/8.5 4.0 8-way 375
SH20L30 19800/19500 230/208 10.0/10.9 2200/2167 9.0/9.0 5.7 8-way 375
Model
SH20L50 20000 220/240 10.2 2342 8.5 5.7 8-way 425
Installation Information
Model
SH15L30 15
SH20L30 17
SH20L50 17
Due to continuing engineering research and technology, specifications are subject to change without notice.
Manufactured under U.S. Design Patent DES 368, 306 decorative front; Utility Patent 5, 622, 058
3
MAXIMUM outdoor ambient operating temperature is 130°F (54°C).
MAXIMUM TEMPERATURE RATING FOR CLASS I, DIVISION 2, GROUPS A,B,C,D
Page 4
COMPONENT OPERATION AND TESTING
WARNING
DISCONNECT ELECTRICAL POWER TO THE
UNIT BEFORE SERVICING OR TESTING
COMPRESSORS
Compressors are single phase, 208/230 volt. All
compressor motors are permanent split capacitor
type, using only a running capacitor across the start
and run terminal.
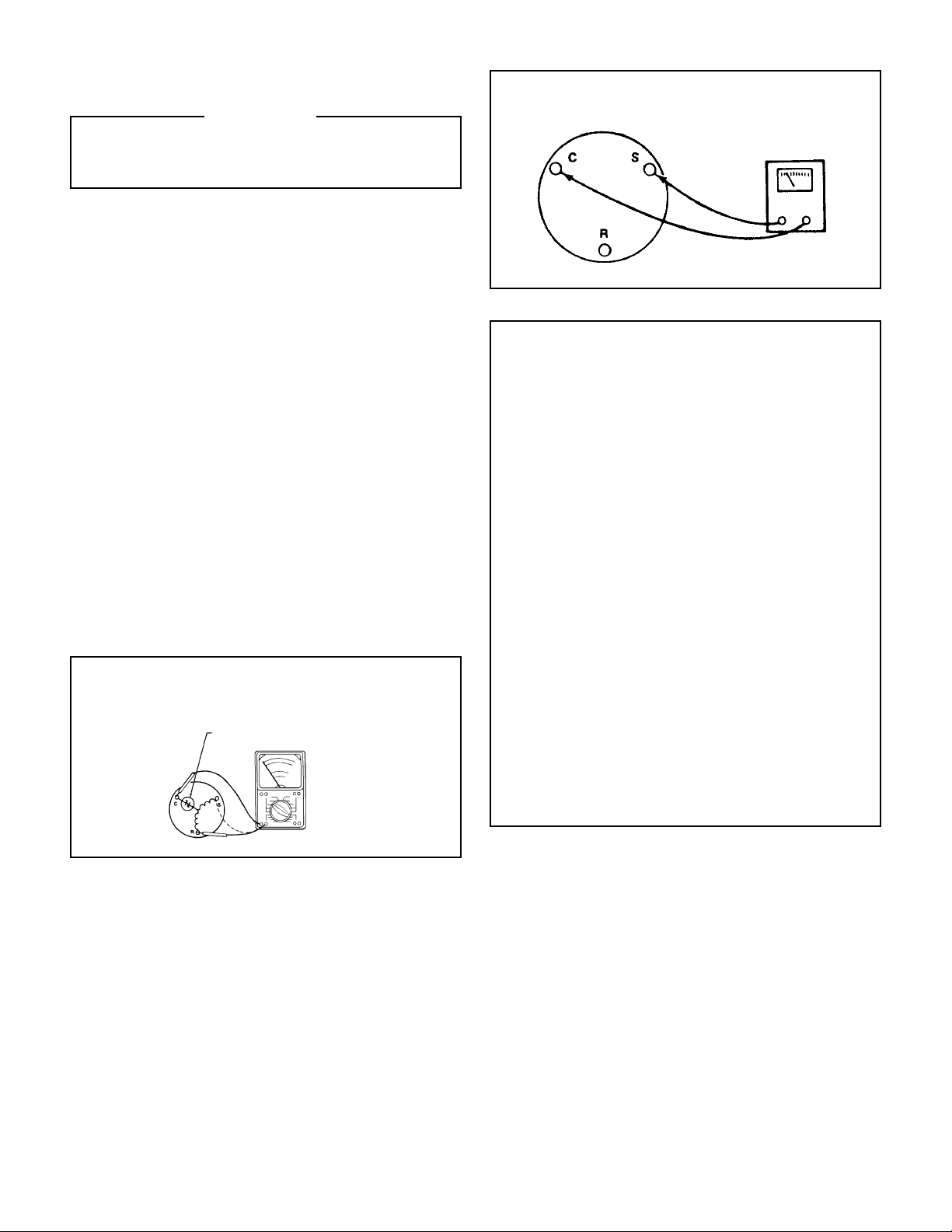
FIGURE 2 COMPRESSOR WINDING TEST
All compressors are internally spring mounted and
externally mounted on rubber isolators.
Line Voltage Overload
The compressor is equipped with an internal line
voltage overload. This overload is embedded in the
windings of the motor to sense the motor temperature.
The overload will open and disconnect the power to the
motor due to high temperatures caused by:
1. A locked rotor.
2. Excessive running amps.
3. High discharge temperature.
4. Low refrigerant charge.
FIGURE 1 INTERNAL OVERLOAD
LINE BREAK
INTERNAL OVERLOAD
OHMMETER
Testing Procedures
1. Terminal "C" and "S" - no continuity - open
winding - replace compressor.
2. Terminal "C" and "R" - no continuity - open
winding - replace compressor.
3. Terminal "R" and "S" - no continuity open
winding - replace compressor.
4. Terminal "C" and the shell of the compressor
– continuity – grounded motor – replace
compressor.
5. Should continuity exist between terminals
"R" and "S", but not between terminals
"C" and "S" and "C" and "R", the internal
overload may be open. If the compressor
is extremely hot, allow it suffi cient time to
cool. It may require as long as one hour for
the compressor to cool suffi ciently for the
internal overload to close.
COMPRESSOR WINDING TEST (Figure 2.)
Remove the compressor terminal box cover and
disconnect the wires from the terminals. Using an
ohmmeter, check continuity across the following:
4
Page 5
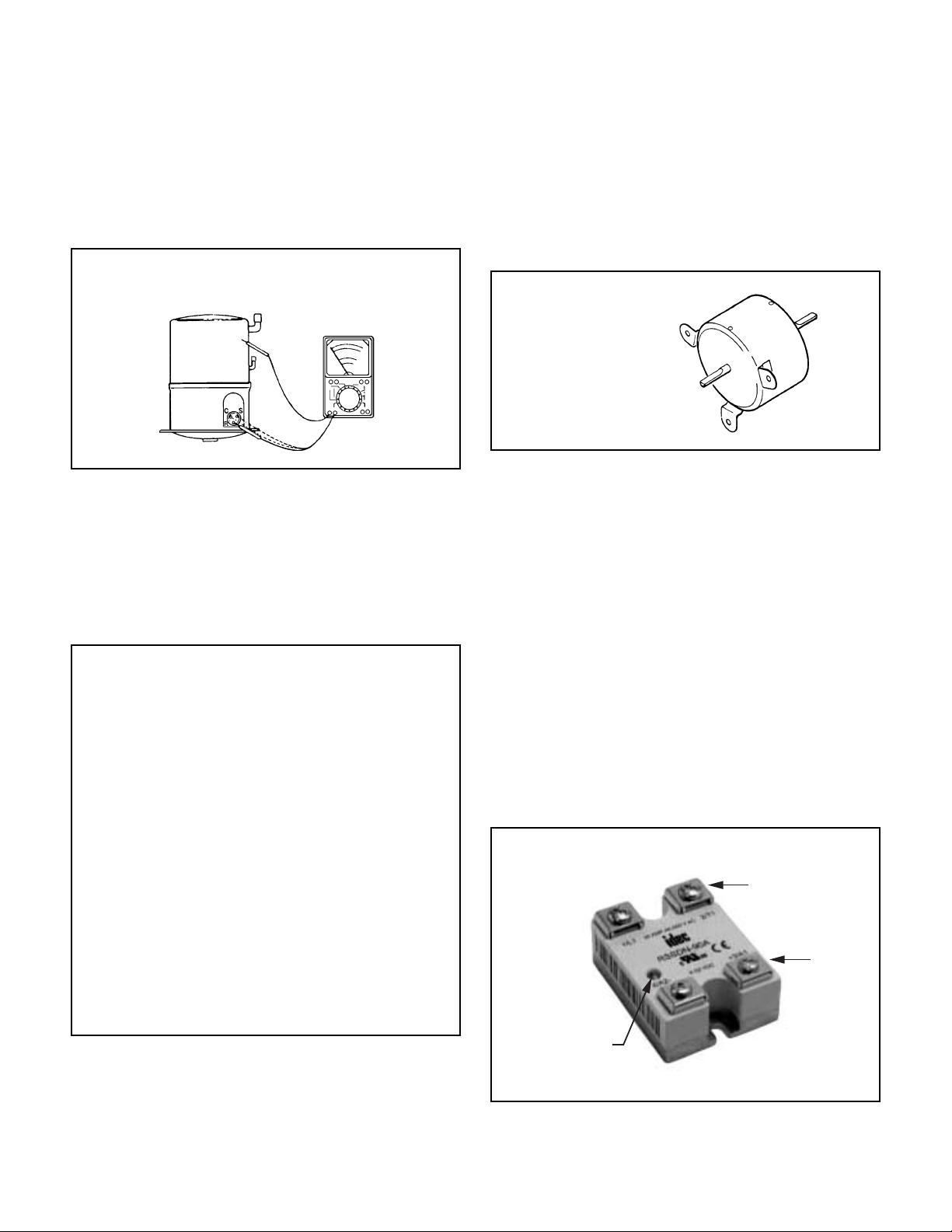
GROUND TEST
Use an ohmmeter set on its highest scale. Touch one
lead to the compressor body (clean point of contact,
as a good connection is a must) and the other probe
in turn to each compressor terminal. (See Figure 3.)
If a reading is obtained, the compressor is grounded
and must be replaced.
FIGURE 3 TYPICAL GROUND TEST
CHECKING COMPRESSOR EFFICIENCY
The reason for compressor ineffi ciency is normally
due to broken or damaged suction and/or discharge
valves, reducing the ability of the compressor to pump
refrigerant gas.
This condition can be checked as
follows:
1. Install a piercing valve on the suction and
discharge or liquid process tube.
2. Attach gages to the high and low sides of
the system.
FAN MOTOR (Figure 4)
A 230 volt single phase permanent split capacitor motor
is used to drive the evaporator blower and condenser
fan. A running capacitor is wired across the start and
run terminals of the motor.
The motor is totally enclosed and is protected with a line
voltage overload located internally of the motor. The
motor shaft is stainless steel to resist corrosion.
FIGURE 4 FAN MOTOR
FAN MOTOR – TEST
Disconnect power to the unit.
1. Determine that the capacitor is serviceable.
2. Disconnect the black lead from the circuit
board.
3. Apply "live" test cord leads to the common
terminal of the capacitor and the black lead.
The motor should run at high speed.
SOLID STATE RELAY (Figure 5)
Two 50 amp rated 208/230 volt solid state relays
are used to energize the compressor and fan motor.
Terminals 3 and 4 are the 208/230 volt line side.
Terminals 1 and 2 are load side contacts.
3. Start the system and run a "cooling or
heating performance test."
If test shows:
A. Below normal high side pressure.
B. Above normal low side pressure.
C. Low temperature difference across the coil.
The compressor valves are faulty
- replace the compressor.
FIGURE 5 SOLID STATE RELAY
Line side
Load side
LED indicates
contacts closed
when lit
5
Page 6
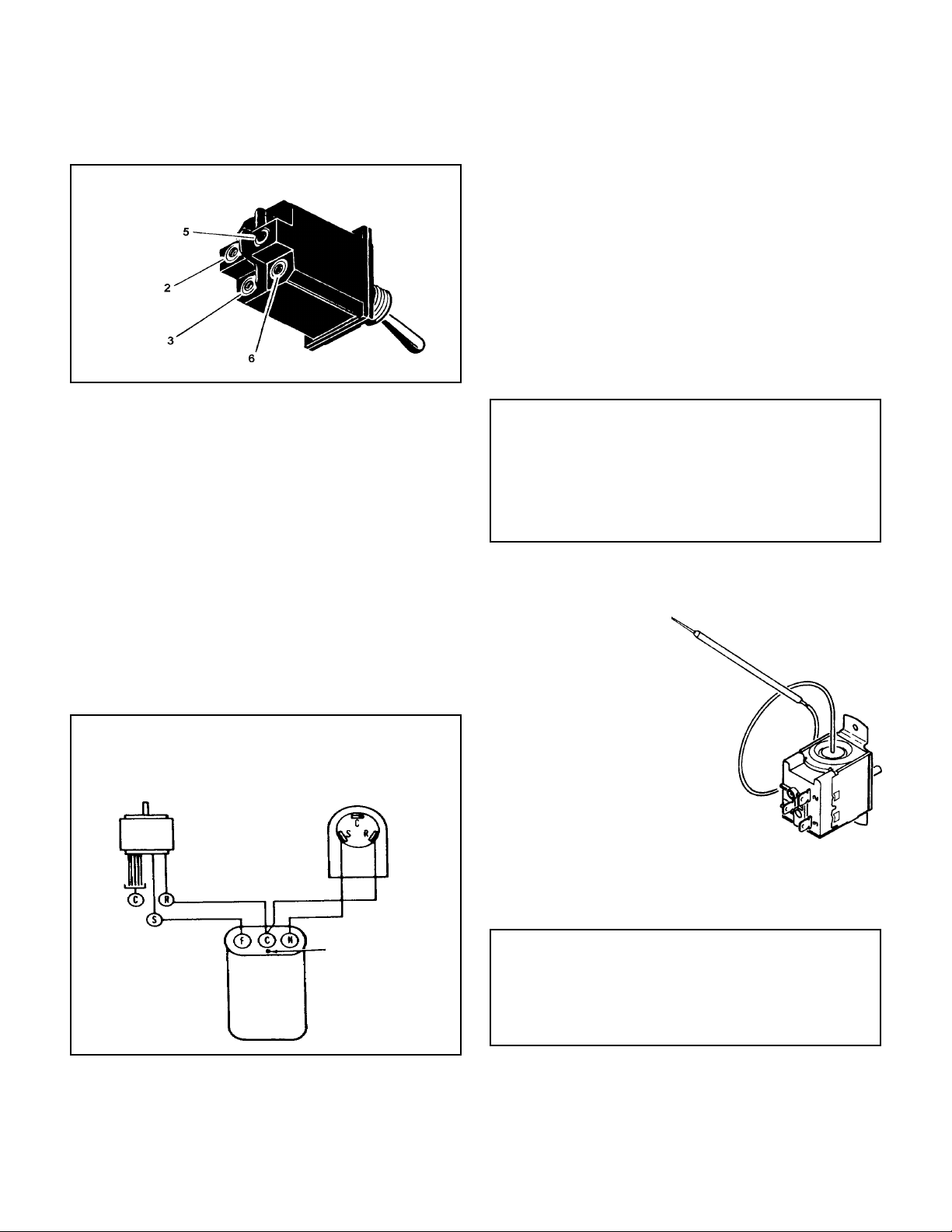
SYSTEM CONTROL SWITCH (Figure 6)
This switch is double pole, single throw. Check for
continuity between terminals 2 and 3, and 5 and 6.
FIGURE 6 SWITCH, ON-OFF
CAPACITOR – TEST
1. Remove the capacitor from the unit.
2. Check for visual damage such as bulges, cracks,
or leaks.
3. For dual rated capacitors, apply an ohmmeter lead
to the common (C) terminal and the other probe to
the compressor (HERM) terminal. A satisfactory
capacitor will cause a defl ection on the pointer,
then gradually move back to infi nity.
4. Reverse the leads of the probe and momentarily
touch the capacitor terminals. The defl ection of the
pointer should be two times that of the fi rst check
if the capacitor is good.
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 to check the fan motor
capacitor.
CAPACITOR, RUN
A run capacitor is wired across the auxiliary and main
winding of a single phase permanent split capacitor
motor such as the compressor and fan motors. A single
capacitor can be used for each motor or a dual rated
capacitor can be used for both.
The capacitor’s primary function is to reduce the
line current while greatly improving the torque
characteristics of a motor. The capacitor also reduces
the line current to the motor by improving the power
factor of the load. The line side of the capacitor is
marked with a red dot and is wired to the line side of
the circuit (see Figure 7.)
FIGURE 7 RUN CAPACITOR HOOK–UP
COMPRESSOR
FAN
MOTOR
NOTE: A shorted capacitor will indicate a low
resistance and the pointer will move more to the
“0” end of the scale and remain there as long as
the probes are connected. An open capacitor
will show no movement of the pointer when
placed across the terminals of the capacitor.
THERMOSTAT
A cross ambient
thermostat is used to
maintain the desired
comfort level. The
thermostat reacts only to a
change in temperature at the
bulb location.
Important to the
successful operation
of the unit is the position
of the sensing bulb in
relation to the evaporator
(see Figure 8).
FIGURE 8 SENSING
BULB LOCATION
RED DOT
RANGE:
Thermostat
RUN CAPACITOR
(Part No. 618-225-02)
60° F ( ± 2° ) to 90° F( ± 4° )
6
Page 7

TEST
Remove the wires from the thermostat. Turn the
thermostat to its coldest position. Check to see if
there is continuity between the two terminals. Turn the
thermostat to its warmest position. Check continuity
to see if the thermostat contacts open.
Note: The temperature must be within the range listed
to check the thermostat. Refer to the troubleshooting
section in this manual for additional information on
thermostat testing.
7
Page 8

LOW AMBIENT BYPASS VALVE (Figure 9)
The HazardGard unit is designed to operate at low
outside ambient temperatures. This is accomplished by
the use of a bypass valve installed in the refrigeration
circuit. The valve is connected between the discharge
line at the compressor and the suction process tube.
The valve responds to suction pressure which, when
reduced in the system, causes the valve to open and
bypass hot gas from the high pressure side to the low
pressure side of the system. The hot gas entering the
compressor mixes with the cool gas returned through
the suction line, thus increasing the suction pressure.
The valve is preset to open when the suction pressure
reaches 50 psig. This pressure setting cannot be
altered. The system can be operated at outdoor
temperatures as low as 45°
coil will begin to accumulate frost.
To determine if the valve operates, block the return air
to the evaporator coil. Turn on the unit and touch the
tube at the bypass valve outlet which connects to the
suction process tube. When the low side pressure
reaches approximately 50 psig, the valve will begin
to open and the tube will get hot. This method will
determine if the valve is responding to the suction
pressure change.
F before the evaporator
SEALED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
REPAIRS
EQUIPMENT REQUIRED:
1. Voltmeter
2. Ammeter
3. Ohmmeter
4. E.P.A Approved Refrigerant Recovery System
5. Vacuum Pump (capable of 200 microns or less
vacuum).
6. Acetylene Welder
7. Electronic Halogen Leak Detector (G.E. Type
H-6 or equivalent).
8. Accurate refrigerant charge measuring device
such as:
a. Balance Scales - 1/2 oz. accuracy
b. Charging Board - 1/2 oz. accuracy
9. High Pressure Gauge - (0-400 lbs.)
10. Low Pressure Gauge - (30" - 150 lbs.)
FIGURE 9
LOW AMBIENT Bypass
VALVE
11. Vacuum Gauge - (0-1000 microns)
EQUIPMENT MUST BE CAPABLE OF:
1. Recovering CFC’s as low as 5%.
2. Evacuation from both the high side and low side
of the system simultaneously.
3. Introducing refrigerant charge into the high side of
the system.
4. Accurately weighing the refrigerant charge actually
introduced into the system.
5. Facilities for flowing nitrogen through the
refrigeration tubing during all brazing processes.
8
Page 9

HERMETIC COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
The following procedure applies when replacing
components in the sealed refrigeration circuit or
repairing refrigerant leaks. (Compressor, condenser,
evaporator, capillary tube, refrigerant leaks, etc.)
1. Recover the refrigerant from the system at the
process tube located on the high side of the system
by installing a line tap on the process tube. Apply
the gauge from the process tube to EPA approved
gauges from the process tube to the EPA approved
recovery system. Recover the CFC’s in the system
to at least 5%.
2. Cut the process tube below the pinch off in the
suction side of the compressor.
3. Connect the line from the nitrogen tank to the
suction process tube.
4. Drift dry nitrogen through the system and unsolder
the more distant connection fi rst. (Filter drier, high
side process tube, etc.)
5. Replace the inoperative component, and always
install a new fi lter drier. Drift dry nitrogen through
the system when making these connections.
6. Pressurize the system to 30 PSIG with proper
refrigerant and boost the refrigerant pressure to
150 PSIG with dry nitrogen.
NOTE: This procedure can be sped up by the
use of heat lamps, or by breaking the vacuum
with refrigerant or dry nitrogen at 5,000 microns.
Pressure system to 5 PSIG and leave in the system a minimum of 10 minutes. Recover refrigerant, and proceed with evacuation to a pressure
of 200 microns or a minimum of 10%.
11. Break the vacuum by charging the system from
the high side with the correct amount of refrigerant
specifi ed. This will prevent boiling the oil out of the
crankcase.
NOTE: If the entire charge will not enter the high
side, allow the remainder to enter the low side
in small increments while operating the unit.
12. Restart the unit several times after allowing
pressures to stabilize. Pinch off the process tubes,
cut and solder the ends. Remove the pinch off tool,
and leak check the process tube ends.
SPECIAL PROCEDURES IN THE CASE OF
COMPRESSOR MOTOR BURNOUT
1. Recover all refrigerant and oil from the system.
7. Leak test the complete system with the electric
halogen leak detector, correcting any leaks
found.
8. Reduce the system to zero gauge pressure.
9. Connect the vacuum pump to the high side and
low side of the system with deep vacuum hoses,
or copper tubing. (Do not use regular hoses.)
10. Evacuate the system to an absolute holding
pressure of 200 microns or less.
2. Remove the compressor, capillary tube and fi lter
drier from the system.
3. Flush the evaporator, condenser and all connecting
tubing with dr y nitro gen, or e quivalent , to remove al l
contamination from the system. Inspect the suction
and discharge lines for carbon deposits. Remove
and clean if necessary.
4. Reassemble the system, including a new drierstrainer and capillary tube.
5. Proceed with processing as outlined under hermetic
component replacement.
9
Page 10

ROTARY COMPRESSOR SPECIAL
TROUBLESHOOTING AND SERVICE
Basically, troubleshooting and servicing rotary compressors is the same as on the recip rocat ing co mpres sor with only a few exceptions.
1. Because of the spinning motion of the rotary, the
mounts are critical. If vibration is present, check
the mounts carefully.
2. The electrical terminals on the rotary are in a
different order than the reciprocating compressors.
The terminal markings are on the cover gasket.
Use your wiring diagram to insure the correct
connections.
All inoperative compressors returned to Friedrich
must have all lines properly plugged with the
plugs from the replacement compressor.
REFRIGERANT CHARGE
1. The refrigerant charge is extremely critical. Measure
the charge carefully and as exactly as possible to
the nameplate charge.
2. The correct method for charging the rotary is to
introduce liquid refrigerant into the high side of the
system with the unit off. Then start the compressor
and enter the balance of the charge, gas only, into
the low side.
The introduction of liquid into the low side, without
the use of a capillary tube, will cause damage to
the discharge valve of the rotary compressor.
NOTE:
10
Page 11

TROUBLESHOOTING
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSE TO CORRECT
Power disconnected. Check power source.
UNIT DOES NOT RUN.
EVAPORATOR COIL
FREEZES UP.
System switch in “Off”
position.
Branch circuit fuse blown or
circuit breaker tripped.
Inoperative system switch. Test for continuity.
Loose or disconnected wiring
at switch.
Inoperative switch (On-Off). Test for continuity, 3 and 2, 5 and 6.
Dirty Filter. Clean as recommended in Owner’s Manual.
Restricted air fl ow. Check for dirty or obstructed coil - clean as required.
Inoperative thermostat. Test for shorted thermostat or stuck contacts.
Short of refrigerant. De-ice coil and check for leak.
Partially restricted capillary.
Inoperative fan motor. Test and replace if inoperative.
Set switch correctly.
Replace fuse, reset breaker. If repeats, check fuse
or breaker size. Check for shorts in unit wiring and
components.
Check wiring and connections.
Connect per wiring diagram.
De-ice coil. Check temperature differential across coil.
Touch test coil return bends for same temperature. Test for
low running current.
COMPRESSOR RUNS
CONTINUALLY.
DOES NOT CYCLE
OFF.
THERMOSTAT DOES
NOT TURN UNIT ON.
THERMOSTAT DOES
NOT TURN UNIT OFF.
Excessive heat load. Test cooling performance of unit. Unit undersized.
Restriction in line.
Refrigerant leak.
Thermostat contacts stuck.
Loss of charge in thermostat
bulb.
Loose or broken parts in
thermostat.
Incorrect wiring. Connect per wiring diagram.
System switch open. Test for continuity at switch terminals 2 and 3.
Thermostat set at coldest
point
Thermostat contacts stuck.
Switch (On - Off) shorted.
Check for partially iced coil. Check temperature split
across coil.
Check for presence of oil on silver soldered connections.
Check for partially iced coil. Check split across coil.
Check for low running amperage.
Check operation of thermostat. Replace if contacts
remain closed.
Place jumper across thermostat terminals. If unit
operates, replace thermostat.
Check as above.
Turn to highest temperature setting to see of unit will cycle
off.
Disconnect power to the unit. Remove cover of thermostat
and check if contact is stuck, if so replace thermostat.
Test switch for open contacts at terminals 2 and 3 with
switch in “Off” position.
11
Page 12

TROUBLESHOOTING (Continued)
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSE TO CORRECT
COMPRESSOR
ATTEMP TS TO
START, OR RUNS
FOR SHORT
PERIODS ONLY.
CYCLES ON
OVERLOAD.
Compressor attempts to start
before system pressures are
equalized.
Low or fl uctuating voltage.
Incorrect wiring. Connect per wiring diagram.
Shorted or incorrect capacitor.
Restricted or low air fl ow through
condenser coil.
Compressor running abnormally
hot.
Overload opens too soon.
Allow a minimum of two (2) minutes to allow pressures to
equalize before attempting to start.
Check voltage with unit operating. Check for other
appliances on the circuit. Unit should be on separate
circuit for proper voltage, and be fused separately.
Check by substituting a known good capacitor of correct
rating.
Check for proper fan speed or blocked condenser.
Check for kinked discharge line or restricted condenser.
Check amperage.
Change compressor if all other corrections above are
normal.
COMPRESSOR
DOES NOT START -
FAN MOTOR RUNS.
DOES NOT COOL,
OR COOLS ONLY
SLIGHTLY.
Thermostat contacts not closing.
Low voltage supply. Check for nameplate voltage.
Switch (On-Off) inoperative. Test for continuity.
Open capacitor.
Internal overload open.
Relay open Replace relay
Open or shorted compressor
windings
Thermostat open or inoperative.
Dirty air fi lter. Clean as recommended in Owner’s Manual.
Dirty or plugged condenser or
evaporator coil.
Poor air circulation in area being
cooled.
Low capacity - undercharge. Clean, check for leak and make repair.
Compressor not pumping
properly.
Check continuity of thermostat at coldest setting. Jump
contacts, if compressor runs, replace thermostat.
Check by substituting a known good capacitor of correct
rating.
Check voltage at compressor terminals. If voltage is
satisfactory, replace compressor.
Check windings for continuity and resistance. Direct test
compressor. If direct test fails, replace compressor.
Set to coldest position. Test thermostat and replace if
necessary.
Use steam or detergents to clean.
Adjust air louvers.
Check amperage draw against nameplate. If not
conclusive, make pressure test.
12
Page 13

TROUBLESHOOTING (Continued)
PROBLEM POSSIBLE CAUSE TO CORRECT
Defective switch (On-Off). Check continuity across terminals 2 and 3.
Check by substituting a known good capacitor of the
same rating.
Adjust motor mount to attain proper fan blade and
blower wheel clearance.
Check for deteriorated compressor grommets, or
missing mounting parts.
Adjust and tighten as required.
FAN MOTOR DOES
NOT RUN.
SWITCH (ON-OFF)
DOES NOT CUT
FAN MOTOR OFF.
NOISY AND/OR
VIBRATION.
Fan capacitor open.
Inoperative fan motor. Direct test fan motor.
Incorrect wiring of fan circuit. Connect per wiring diagram.
Relay open. Replace Relay.
Check for seized motor bearings. Rotate by hand, add oil, if noisy, replace.
Bound fan blade or blower wheel. Adjust for proper clearance.
Selector Switch Relay Replace selector switch. Replace relay.
Poor installation. Refer to Installation Instructions for proper installation.
Fan blade striking chassis.
Compressor vibrating.
Loose cabinet parts, improperly
mounted components, tubing
rubbing.
WATER LEAKS
INTO ROOM.
OUTSIDE WATER
LEAKS.
Evaporator drain pan
overfl owing.
Condensation forming on bottom
of base pan.
Water dripping from discharge
air grilles.
Evaporator drain pan cracked or
obstructed.
Water in center section of base
pan (compressor area).
Dirty Condenser coil. Clean with steam or detergent.
Fan blade and slinger ring
improperly positioned.
Clean obstructed drain trough.
Evaporator drain pan broken or cracked. Reseal or
replace.
Dirty evaporator coil, or extremely high humidity
conditions. Clean coil with steam or detergent.
Repair and clean, or replace as required.
Remove condenser shroud, Clean and remove old
sealer from base pan and shroud. Apply new sealer,
reinstall and check.
Adjust fan blade to 1/2" clearance from condenser coil.
13
Page 14

WIRING DIAGRAM
MODELS SH15L30-A, SH20L30-A, SH20L50-A
14
Page 15

HAZARDGARD CABINET PARTS
15
Page 16

HAZARDGARD CHASSIS PARTS
16
Page 17

HAZARDGARD PARTS LIST
REF DESCRIPTION PART NO# MODELS CODE
ELECTRICAL PARTS
SH15L30-A
1 COMPRESSOR 61193549 1 600
1 COMPRESSOR 61193550 1 600
1 COMPRESSOR 61193565 1 600
2 MOTOR, FAN 61871426 1110
2 MOTOR, FAN 61871427 1110
2 MOTOR, FAN 61871450 1110
5 SWITCH, ON-OFF DPST 60935300 1 1 1 130
* INSULATOR, ELECTRICAL 61829700 1 1 1 399
* RELAY, SOLID STATE 61108800 2 2 2 399
6 THERMOSTAT 61825502 1 1 1 120
7 CAPACITOR 20/7.5 440 V. 61080546 1 1 1 150
7 CAPACITOR 25/7.5 440 V 61080547 1 1 1 150
* HARNESS, WIRE, COMP. 61821308 1 1 1 399
REF DESCRIPTION PART NO# MODELS CODE
REFRIGERATION PARTS
SH15L30-A
9 EVAPORATOR COIL 61850100 1 400
9 EVAPORATOR COIL 61850001 1 1 400
10 CONDENSER COIL 62050400 1 410
10 CONDENSER COIL 62050401 1 1 410
* DRIER, LIQUID 60308101 1 1 1 480
CAPILLARY TUBE 01390005 1471
CAPILLARY TUBE 03760518 22471
VALVE, BY-PASS 60809500 1 1 1 520
SH20L30-A
SH20L30-A
SH20L50-A
SH20L50-A
17
Page 18

HAZARDGARD PARTS LIST
REF DESCRIPTION PART NO# MODELS CODE
CHASSIS PARTS
SH15L30-A
26 SHROUD, CONDENSER 61803601 1720
26 SHROUD, CONDENSER 61804901 11720
27 BRACE, COND.SHROUD 61802600 333722
22 FAN BLADE, COND. 60542003 1710
22 FAN BLADE, COND. 60542004 11710
23 BLOWER WHEEL, EVAP. 60610616 1700
23 BLOWER WHEEL, EVAP. 60610617 11700
30 SCROLL 61814905 1743
30 SCROLL 61817505 11743
29 BLOWER FRONT 61817300 1742
29 BLOWER FRONT 61817400 11742
35 PLENUM ASSEMBLY 61831005 111753
17 DECORATIVE PANEL 61822602 111760
11 KNOB, CONTROL 61493905 111761
37 GRILLE, INTAKE 61808905 1772
37 GRILLE, INTAKE 6 1811110 1 1 772
* LATCH, INTAKE GRILLE 61989000 222752
* FILTER, AIR 60865808 1754
* FILTER, AIR 60865809 11754
* HOLDER, FILTER 61823000 222756
8 HOLDER, THERMOSTAT 61829800 1 1 1 999
25 FAN MOTOR MOUNT 61802500 1 900
25 FAN MOTOR MOUNT 61804100 1 1 900
32 BASE PAN 61803414 11 1730
* DRAIN PAN, EVAP. 61803800 1 1 1 840
34 BOLT, COMP. MOUNT 91400400 333791
, GROMMET, COMP. MOUNT 01193549 333790
36 OUTER SHELL 61825703 1770
36 OUTER SHELL 61825704 1 1 770
* REAR GRILLE 61803800 1771
* REAR GRILLE 61818801 1 1 771
40 ANGLE, WINGBOARD TOP 61819701 1 1 1 999
41 ANGLE,WINGBORD SIDE 61819801 2 2 2 999
38 WINGBOARD 60294408
38 WINGBOARD 60294409 1 1 999
* BAG, ASSY. HARDWARE 60846016 1 1 1 999
* GASKET, CHASSIS 61717301 11 1780
OPTIONAL ACCESSORY ITEMS
* DRAIN KIT, DC-2 01900235 111
* START KIT, CAP.\RELAY 01900312 11 1
1 999
SH20L30-A
SH20L50-A
18
Page 19

19
Page 20

Use Factory Certifi ed Parts.
FRIEDRICH AIR CONDITIONING CO.
Post Office Box 1540 · San Antonio, Texas 78295-1540
4200 N. Pan Am Expressway · San Antonio, Texas 78218-5212
(210) 357-4400 · FAX (210) 357-4480
www.friedrich.com
Printed in the U.S.A.
HG-SVC-PRTS-05 (4-05)
 Loading...
Loading...