
2001
HAZARDGARD
®
ROOM AIR CONDITIONER
Models
SH14J30A-1
SH14J30A-A
SH20J30A-1
SH20J30A-A
Service & Parts
Manual
AMERICA’S BEST AIR CONDITIONER
HG2001 (8/01)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
Specifications.................................................................................................................... 4
Performance Data ............................................................................................................. 6
Component Operation & Testing....................................................................................... 4
Compressors .................................................................................................................... 4
Thermal Overload............................................................................................................. 4
Checking Compressor Efficiency...................................................................................... 5
Fan Motor ......................................................................................................................... 5
System Control Switch...................................................................................................... 5
Run Capacitor...................................................................................................................6
Thermostat........................................................................................................................ 6
Triac/Control Assembly..................................................................................................... 7
Low Ambient By-Pass Valve ............................................................................................. 8
Sealed Refrigeration System Repairs............................................................................... 8
Hermetic Component Replacement.................................................................................. 9
Special Procedure in the case of Compressor Motor Burn-Out........................................ 9
Rotary Compressor Special Troubleshooting & Service................................................... 10
Refrigerant Charge ........................................................................................................... 10
TROUBLESHOOTING
Troubleshooting SH14J30A.............................................................................................. 11
Troubleshooting SH20J30A.............................................................................................. 1 6
WIRING DIAGRAM
SH14J30A / SH20J30A .................................................................................................... 14
PARTS LIST
SH14J30A / SH20J30A Model Chassis Parts List ............................................................ 18
SH20J30A / SH20J30A Model Cabinet Parts List ............................................................ 19
2
SPECIFICATIONS
SH14J30A-1
SH14J30A
BTUH 14000/14000 19000/18800
E.E.R. - Btu/watt 8.0/8.0 8.5/8.5
Volts 230/208 230/208
Hertz/Phase 60/1 60/1
Amperes 7.8/8.5 9.9/10.8
Total Watts 1750/1750 2235/2210
Fuse/Breaker Size 15 20
Fan RPM 1095 1095
Evaporator Air CFM 375 425
Dehumidification-Pts./hr. 4.0 5.7
Width 25-15/16” 25-15/16”
Height 15-15/16” 17-15/16”
Depth 27-3/8” 27-3/8”
SH20J30A-1
SH20J30A
Min. Ext. into Room 5-7/8” 5-7/8”
Min. Ext to Outside 16-15/16” 16-15/16”
Net Weight 129 Lbs. 177 Lbs.
Shipping Weight 147 Lbs. 199 Lbs.
Maximum Temperature Rating 1200 C (2480 F) Ignition Temperature Rating
for Class 1, Division 2, Group D
PERFORMANCE EVAPORATOR AIR OPERATING ELECTRICAL R-22 COMP.
DATA * TEMP° F PRESSURES RATINGS REFRIG. OIL
DISCHARGE TEMP SUCTION DISCHARGE AMPS LOCKED CHARGE IN CHARGE IN
AIR DROP °F ROTOR AMPS OUNCES FLUID OZ.
SH14J30A-1
SH14J30A-A
SH20J30A-1
SH20J30A-A
* Rating Conditions: 80° F. Room Air Temperature and 59% Relative Humidity with 95° F. Outside Air Temperature at 40% Relative Humidity.
56.78 23.22 79 296 7.8 43 28 32
8.5
52.83 27.16 79.5 282 9.8 52 39 32
10.4
3
COMPONENT OPERATION AND TESTING
WARNING
DISCONNECT ELECTRICAL POWER TO
THE UNIT BEFORE SERVICING OR
TESTING
COMPRESSORS
Compressors are single phase, 208/230 volt.
All compressor motors are permanent split
capacitor type, using only a running capacitor
across the start and run terminal.
All compressors are internally spring mounted
and externally mounted on rubber isolators.
Line Voltage Overload
FIGURE 2 TYPICAL GROUND TEST
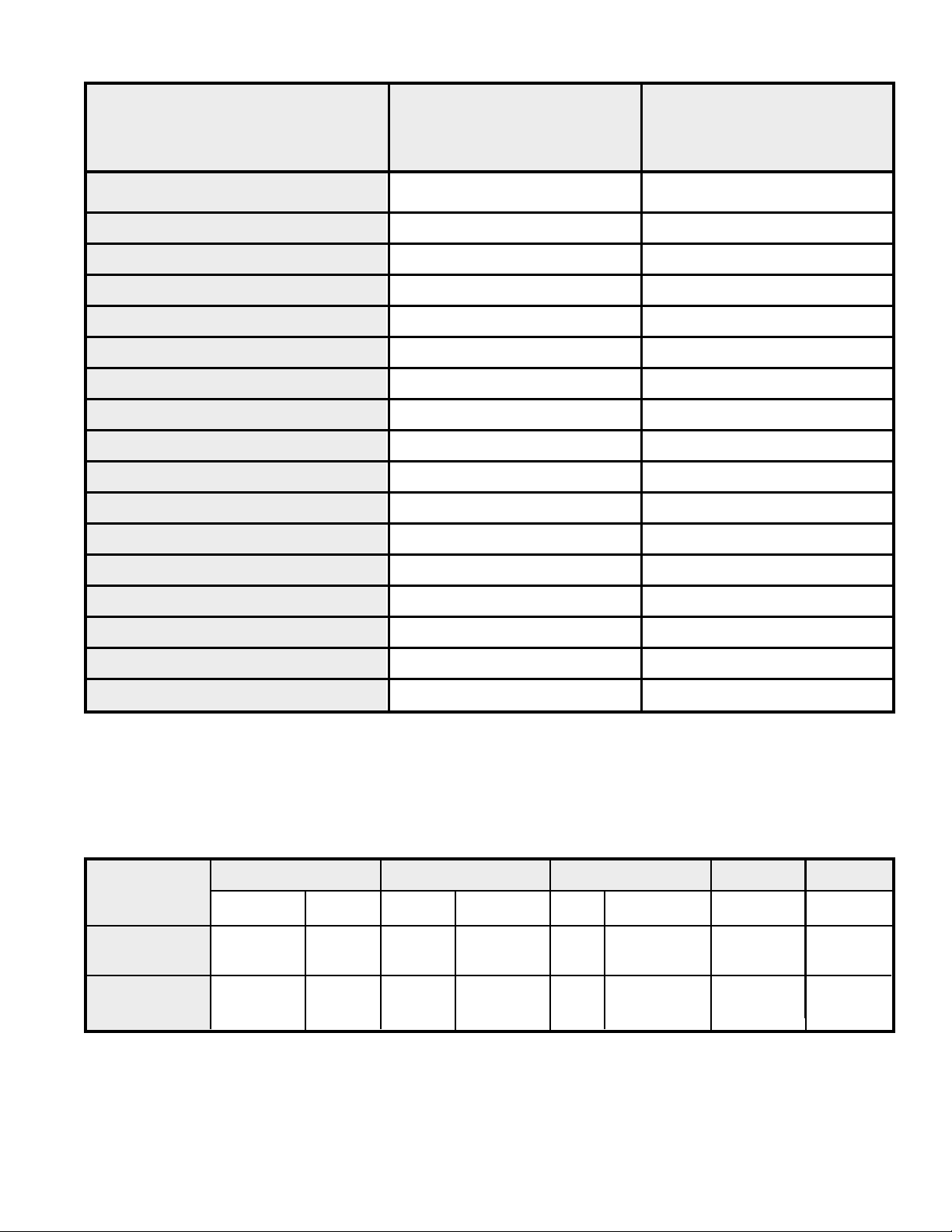
COMPRESSOR WINDING TEST
(See Figure 1.)
Remove the compressor terminal box cover
and disconnect the wires from the terminals.
Using an ohmmeter, check continuity across
the following:
The compressor is equipped with an internal
line voltage overload. This overload is
embedded in the windings of the motor to
sense the motor temperature. The overload will
open and disconnect the power to the motor
due to high temperatures caused by:
1. A locked rotor.
2. Excessive running amps.
3. High discharge temperature.
4. Low refrigerant charge.
FIGURE 1 COMPRESSOR WINDING TEST
Testing Procedures
1. Terminal "C" and "S" - no continuity open winding - replace compressor.
2. Terminal "C" and "R" - no continuity open winding - replace compressor.
3. Terminal "R" and "S" - no continuity
open winding - replace compressor.
4. Terminal "C" and the shell of the
compressor – continuity – grounded
motor – replace compressor.
5. Should continuity exist between
terminals "R" and "S", but not
between terminals "C" and "S" and
"C" and "R", the internal overload
may be open. If the compressor is
extremely hot, allow it sufficient time
to cool. It may require as long as one
hour for the compressor to cool
sufficiently for the internal overload to
close.
4
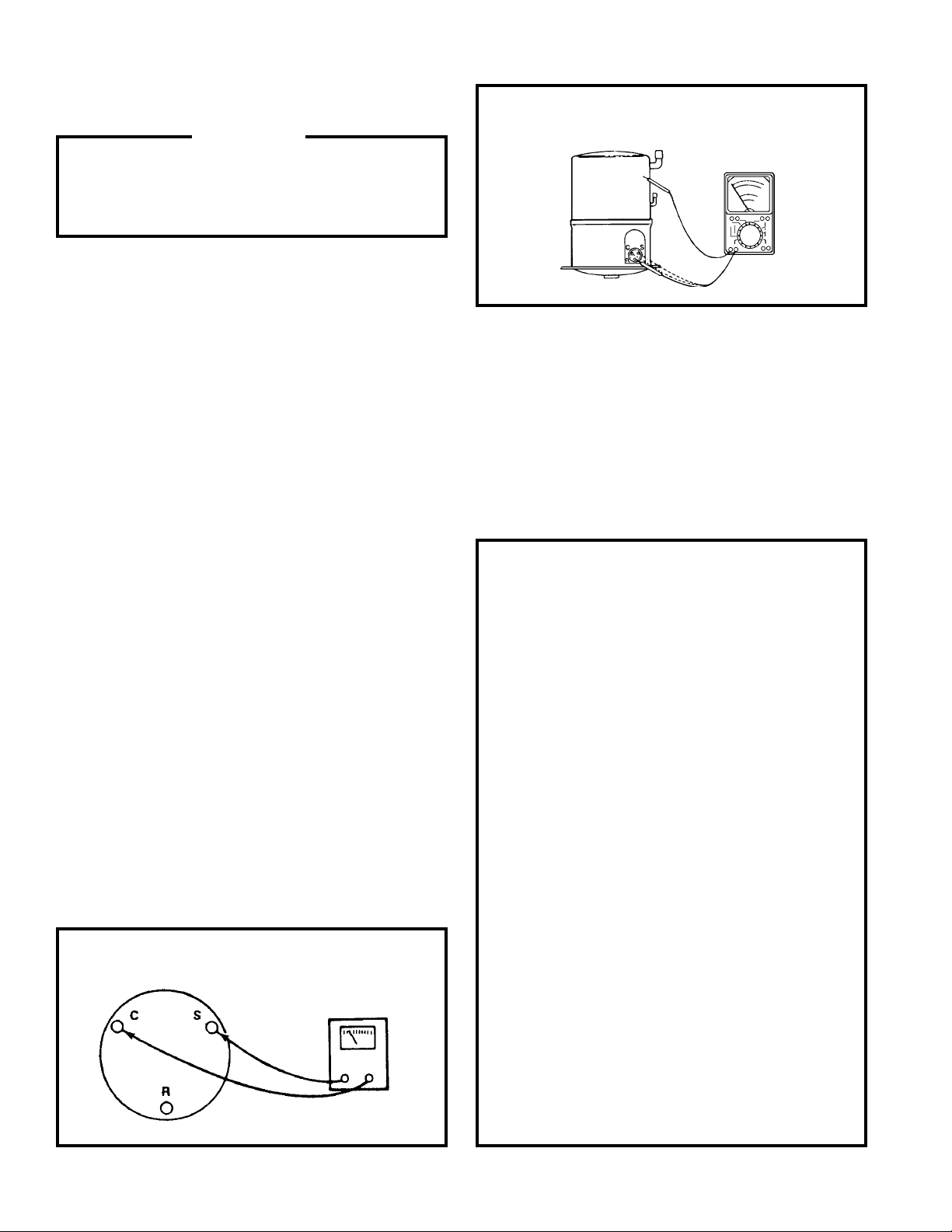
GROUND TEST
Use an ohmmeter set on its highest scale.
Touch one lead to the compressor body (clean
point of contact, as a good connection is a
must) and the other probe in turn to each
compressor terminal. (See Figure 2.) If a
reading is obtained, the compressor is
grounded and must be replaced.
FIGURE 2 TYPICAL GROUND TEST
FIGURE 2 INTERNAL OVERLOAD
LINE BREAK
INTERNAL OVERLOAD
OHMMETER
CHECKING COMPRESSOR EFFICIENCY
The reason for compressor inefficiency is
normally due to broken or damaged suction
and/or discharge valves, reducing the ability of
the compressor to pump refrigerant gas.
This condition can be checked as
follows:
1. Install a piercing valve on the suction and
discharge or liquid process tube.
F AN MOTOR
A 230 volt single phase permanent split
capacitor motor is used to drive the evaporator
blower and condenser fan. A running capacitor
is wired across the start and run terminals of
the motor.
The motor is totally enclosed and is protected
with a line voltage overload located internally of
the motor. The motor shaft is stainless steel to
resist corrosion.
F AN MOTOR – TEST
Disconnect power to the unit.
1. Determine that the capacitor is
serviceable.
2. Disconnect the black lead from the circuit
board.
3. Apply "live" test cord leads to the
common terminal of the capacitor and the
black lead. The motor should run at high
speed.
FIGURE 5 SWITCH, ON-OFF
2. Attach gages to the high and low sides of
the system.
3. Start the system and run a "cooling or
heating performance test."
If test shows:
A. Below normal high side pressure.
B. Above normal low side pressure.
C. Low temperature difference across the
coil.
The compressor valves are
faulty - replace the compressor.
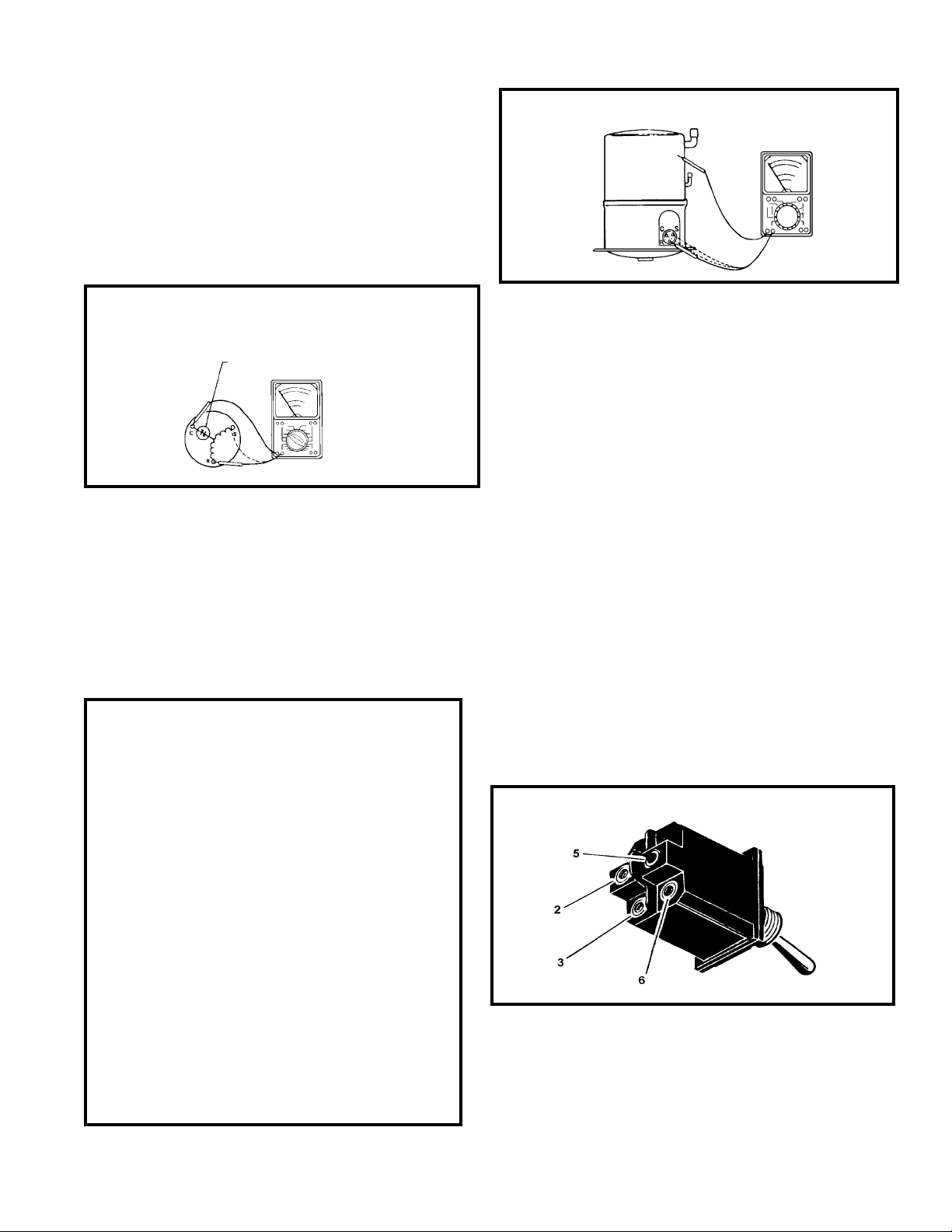
SYSTEM CONTROL SWITCH
(Figure 5)
This switch is double pole, single throw. Check
for continuity between terminals 2 and 3, and 5
and 6.
5
CAP ACITOR – TEST
FIGURE 5 FAN MOTOR
CAP ACITOR, RUN
A run capacitor is wired across the auxiliary and
main winding of a single phase permanent split
capacitor motor such as the compressor and
fan motors. A single capacitor can be used for
each motor or a dual rated capacitor can be
used for both.
The capacitor’s primary function is to reduce
the line current while greatly improving the
torque characteristics of a motor. The capacitor
also reduces the line current to the motor by
improving the power factor of the load. The line
side of the capacitor is marked with a red dot
and is wired to the line side of the circuit. (See
Figure 6.)
FIGURE 6 RUN CAPACITOR HOOK–UP
COMPRESSOR
FAN
MOTOR
1. Remove the capacitor from the unit.
2. Check for visual damage such as bulges,
cracks, or leaks.
3. For dual rated capacitors, apply an
ohmmeter lead to the common (C) terminal and
the other probe to the compressor (HERM)
terminal. A satisfactory capacitor will cause a
deflection on the pointer, then gradually move
back to infinity.
4. Reverse the leads of the probe and
momentarily touch the capacitor terminals. The
deflection of the pointer should be two times
that of the first check if the capacitor is good.
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 to check the fan
motor capacitor.
NOTE: A shorted capacitor will indicate a
low resistance and the pointer will move
more to the “0” end of the scale and remain
there as long as the probes are connected.
An open capacitor will show no movement of
the pointer when placed across the
terminals of the capacitor.
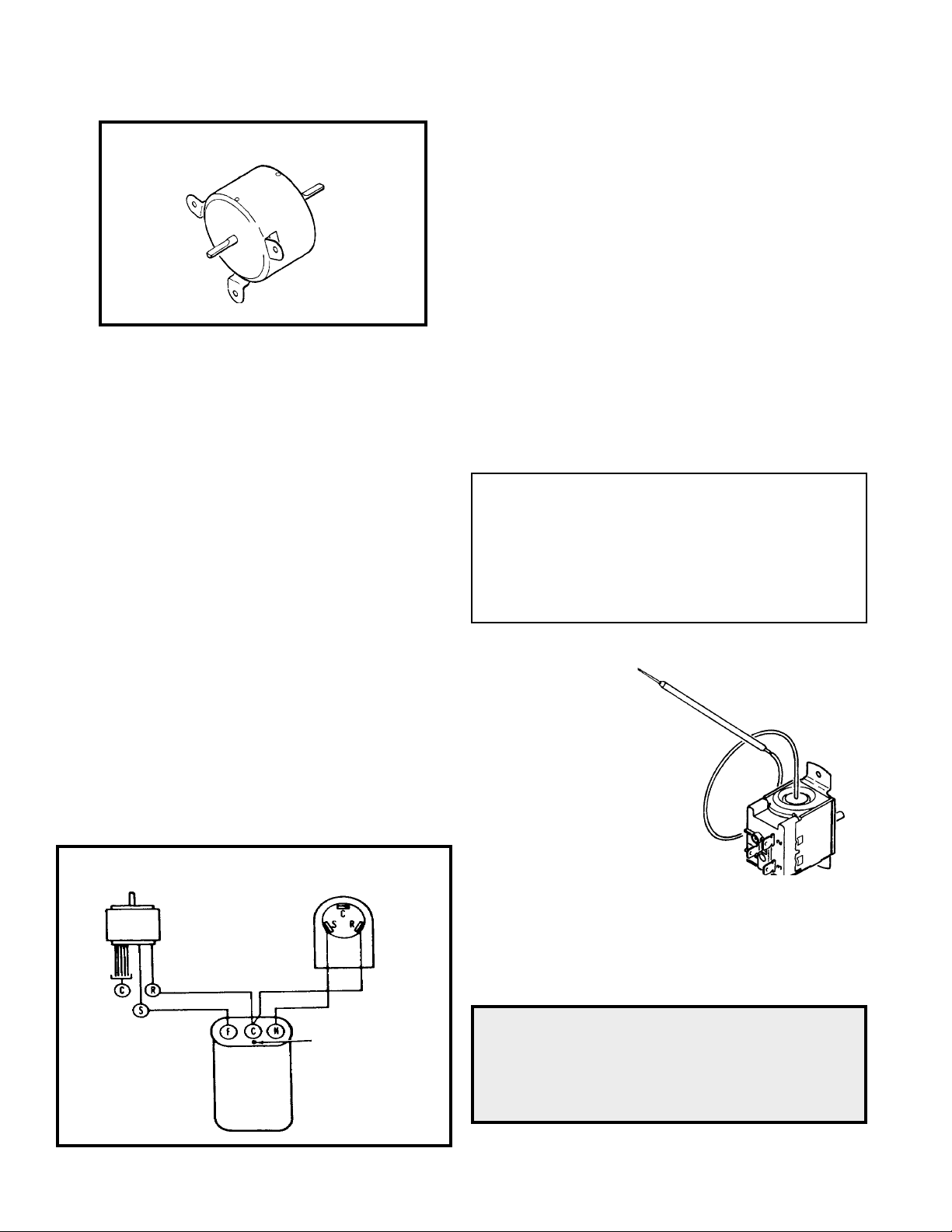
THERMOSTAT
A cross ambient
thermostat is
used to maintain
the desired
comfort level.
The thermostat
reacts only to a
change in
temperature at
the bulb location.
Important to the
successful operation
FIGURE 7 SENSING
BULB LOCATION
of the unit is the position of the sensing bulb in
relation to the evaporator. See Figure 7.
RED DOT
RANGE:
Thermostat
(Part No. 618-225-02)
RUN CAPACITOR
6
60° F ( ± 2° ) to 90° F( ± 4° )
 Loading...
Loading...