Freescale Semiconductor Symphony DSP56724, Symphony DSP56725 Reference Manual

Symphony™ DSP56724/DSP56725
Multi-Core Audio Processors
Reference Manual
Document Number: DSP56724RM
Rev. 0
6/2008

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
Web Support:
http://www.freescale.com/support
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Technical Information Center, EL516
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
+1-800-521-6274 or
+1-480-768-2130
www.freescale.com/support
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
www.freescale.com/support
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku
Tokyo 153-0064
Japan
0120 191014 or
+81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor China Ltd.
Exchange Building 23F
No. 118 Jianguo Road
Chaoyang District
Beijing 100022
China
+86 010 5879 8000
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor
Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
+1-800 441-2447 or
+1-303-675-2140
Fax: +1-303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor
@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software implementers to use
Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted
hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the information
in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products
herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the
suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Freescale Semiconductor assume any
liability arising out of the application o r use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any
and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters
that may be provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary
in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters,
including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts.
Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or author ized for use as components
in systems intended for surgical implant into the b ody, or other applications intended to support or
sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use
Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall
indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor and its officers, emp loyees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and
distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney
fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injur y or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale Semiconductor was
negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other
product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2008. All rights reserved.
Document Number: DSP56724RM
Rev. 0, 06/16/2008

Contents
Chapter 1
Introduction
1.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
1.2 Block Dia g ram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
1.3 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
1.4 Overview of Peripherals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.4.1 Direct Memory Access Controller (DMA, DMA _1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.4.2 P ro g r a m In t e r ru p t Co n troller (PIC, PIC_ 1 ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
1.4.3 Enhanced Serial Audio Interfaces (ESAI, ESAI_1, ESAI_2, ESAI_3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.4.4 Serial Host Interfaces (SHI, SHI_1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.4.5 Tr i p l e Ti m e r s (TEC, TEC_1 ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.4.6 Watch Dog Timers (WDT, W D T_1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
1.4.7 Core Integration Modules (CIM, CIM_1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.4.8 Sony/Philips Digital Interface (S/PDIF). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.4.9 Asynchronous Sample Rate Converter (ASRC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.4.10 Externa l Me m o ry Control l e r (EMC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.4.11 Clock Generation Module (CGM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
1.4.12 Shared Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.4.13 Inter- C o r e Co m mu n i cation (ICC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.4.14 Shared Bus Arbiters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.4.15 Chip Configuration Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
1.4.16 JTAG Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 -9
Chapter 2
Signal Descriptions
2.1 Signal Groupings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
2.2 Signal s in Each Functi o n a l G ro u p . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2- 5
2.2.1 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.2 Ground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
2.2.3 SCAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 -6
2.2.4 Clock and P LL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2- 6
2.2.5 Reset P i n. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.2.6 Int e r rupt and Mod e Co n trol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
2.2.7 DS P Co r e -1 Non-Ma sk ab le Interr u p t (NMI1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.2.8 Serial Host Interface (SHI and SHI_1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
2.2.9 Enhanc ed Serial Audio Interface Signals (ESAI, ESAI_1, ESAI_2, ESAI_3) . . . . . . . . . 2-13
2.2.10 Watch Do g Ti m e r (WDT). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-24
2.2.11 Externa l Me m o ry Control l e r (EMC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
2.2.12 S/PDIF Audio Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-28
2.2.13 Dedicat e d P o rt G GPIOs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2- 28
2.2.14 JTAG/On CE Interface Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor iii

Chapter 3
Memory Map
3.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3.2 Data and Pr o g ram Memory Ma p s. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
3.3 Peripheral Regist er Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Chapter 4
DSP56300 Platform
4.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
4.2 DSP56300 Core Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4.3 DSP56300 Block Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.3.1 Data AL U . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4.3.2 Address Generation Unit (AGU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4.3.3 P ro g r a m Co n trol Unit ( PCU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4.3.4 Inter n a l Bu ses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 -5
4.3.5 OnCE Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Chapter 5
Core Configuration
5.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5- 1
5.2 Operat i n g Mo d e Reg ister (OMR ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
5.3 Status Register (SR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
5.4 DSP Cores Operatin g Mo d e s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 6
5.5 Interr u p t Pr iority Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
5.6 DMA Request Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5- 1 9
5.7 Chip ID Re g ister . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2 0
Chapter 6
Core Integration Module (CIM, CIM_1)
6.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
6.1.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.1.2 Reg i ster Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
6.2 Regist e r Descrip t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.1 Chip ID Regis ter (CHIDR ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
6.2.2 DMA S t a l l Re g is t e r (DMAS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
6.2.3 OnCE Global Data Bus Register (OGDB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
Chapter 7
Clock Generation Module (CGM)
7.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7- 1
7.1.1 Overview of Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7- 1
7.1.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 -2
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
iv Freescale Semiconductor

7.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7.1.4 Ext e rnal Signa l D escripti o n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2 Functional Descripti o n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.1 Clock s. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.2 Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.3 Interru p t s. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.4 Int e r n a l PL L Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
7.2.5 Low P o w e r Div ider. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7- 6
7.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.3.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.3.2 Reg i ster Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
7.3.3 Reg i ster Des c ri p t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 -7
Chapter 8
General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
8.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.2 Programming Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
8.2.1 P o rt C, Port E, Por t C1, Po rt E1 Signal s a n d Re g i st e r s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8.2.2 P o rt H Si g n als and Regi st ers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
8.2.3 P o rt H 1 Si g n als and Regi st ers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
8.2.4 P o rt A Si g n als and Regi st ers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-7
8.2.5 P o rt G Si g n als and Regi st ers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-9
8.2.6 Timer Event Counter Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-10
Chapter 9
Enhanced Serial Audio Interface (ESAI, ESAI_1, ESAI_2, ESAI_3)
9.1 ESAI Data and Contro l Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
9.1.1 S eri a l Transmit 0 Da ta Pin (SDO0 ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
9.1.2 S eri a l Transmit 1 Da ta Pin (SDO1 ) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
9.1.3 S eri a l Transmit 2 / Re c eive 3 Data Pi n (S D O 2 / SDI3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
9.1.4 S eri a l Transmit 3 / Re c eive 2 Data Pi n (S D O 3 / SDI2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
9.1.5 S eri a l Transmit 4 / Re c eive 1 Data Pi n (S D O 4 / SDI1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
9.1.6 S eri a l Transmit 5 / Re c eive 0 Data Pi n (S D O 5 / SDI0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
9.1.7 Rec eiver Seri al Clock (SCKR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
9.1.8 Transmitter Serial Clock (SCKT). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-6
9.1.9 F ram e S y n c fo r Re c ei v e r (FSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-7
9.1.10 Frame Sync for Transmitter (FST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-8
9.1.11 High Frequency Clock for Transmitter (HCKT) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-8
9.1.12 High Frequency Clock for Receiver (HCKR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-8
9.2 ESAI Pro g ramming Mod el . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 -9
9.2.1 ESAI Transmitter Clock Control Register (TCCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-9
9.2.2 ESAI Transmit Control Register (TCR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-13
9.2.3 ESAI Receive Clock Control Register (RCC R) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-23
9.2.4 ESAI Receive Control Register (RCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-27
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor v

9.2.5 ESA I Common Con t r o l Register (S A ICR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-32
9.2.6 ESA I Status Re gister (SA IS R) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-34
9.2.7 ESAI Receive Shift Registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
9.2.8 ESAI Receive Data Registers (RX3, RX2, RX1, RX0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
9.2.9 ESAI Transmit Shift Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
9.2.10 ESAI Transmit Data Registers (TX5, TX4, TX3, TX2,TX1,TX0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
9.2.11 ESAI Tim e Slo t Register (TSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
9.2.12 Transmi t S lo t Mask Regist ers (TSMA, TSMB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
9.2.13 Receiv e Sl o t Ma sk Re g i sters (RSMA, RSMB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-43
9.3 Operat in g Mo d es. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4 4
9.3.1 ESAI Aft e r Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9- 4 4
9.3.2 ESAI Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 -44
9.3.3 ESA I Interrup t Re q u ests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-45
9.3.4 Op e r a t i n g Mo d e s— N o rmal, Netw o rk and On-D e m a n d. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9- 4 6
9.3.5 Seria l I /O Flags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4 7
9.4 GPIO—Pi n s a n d Reg isters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4 8
9.4.1 Po rt C C on trol Regist er (PCRC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-48
9.4.2 Po rt C Direction Re g i st er (PRRC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-48
9.4.3 Po rt C Data Regist er (PDRC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-49
9.5 ESAI Initialization Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9- 5 0
9.5.1 Initializing the ESAI Using Individual Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-50
9.5.2 Initializing Only the ESAI Transmitter Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-50
9.5.3 Initializing Only the ESAI Receiver Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-51
9.6 ESAI/ES A I_2 and ESAI_1/ESAI_3 Pin Swit c h . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-51
9.7 Internal Clock Connections Between ESAI and ESAI_1, ESAI_2 and ESAI_3 . . . . . . . . . . . 9-52
Chapter 10
Serial Host Interface (SHI, SHI_1)
10.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 0 -1
10.2 Serial Host Interface Inte rnal Arch ite ctu re. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
10.3 SH I Clock Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3
10.3.1 Serial Host Interface Programming Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-3
10.3.2 SHI Input / O u t p u t Shift Reg i ster (IOSR )— H o st Side. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-5
10.3.3 SHI Host Transmit Data Register (HTX)—DSP Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-6
10.3.4 SHI Host Rec eive Data F IF O (H RX)—DSP Si d e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-6
10.3.5 SHI Slav e Address Regi st er (HSAR)— D S P Side . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-7
10.3.6 HSAR I
10.3.7 SHI Clock Co n t ro l Regist er (HCKR)—DS P Si d e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-7
10.3.8 SHI Contr o l/ S t a t u s Register (H CS R)—DSP Sid e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-10
10.4 Cha racteri st i c s Of The SPI Bu s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-17
10.5 Characteristics Of The I
10.5.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 0 -18
10.5.2 I2C Data Tra n sfer Form at s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 0 - 2 0
10.6 SH I P ro g ramming Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-20
2
C Slave Address (HA[6:3], HA1)—Bits 23–20,18 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10- 7
2
C Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 0 -18
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
vi Freescale Semiconductor

10.6.1 SPI Sla v e Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 0 -21
10.6.2 SPI Master Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-22
10.6.3 I2C Slave Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-23
10.6.4 I2C Master Mo d e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-25
10.6.5 SHI Oper a t i o n Dur ing DSP Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-27
10.7 SH I P in - O u t s for Devic e Packages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-27
10.7.1 SHI Pin-Outs for Small Pin Count Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-27
Chapter 11
Triple Timer Module (TEC, TEC_1)
11.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1 -1
11.1.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1 -1
11.1.2 Triple Timer Module Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-1
11.2 Ind i v i d u a l Ti m e r Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-2
11.3 Op e ration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-3
11.3.1 Timer After Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-3
11.3.2 Timer Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-3
11.3.3 Timer Exceptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-4
11.4 Op e rating Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-4
11.4.1 Timer GPI O (Mode 0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-5
11.4.2 Reserv e d Mo d e s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11- 6
11.4.3 Special Cases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 -6
11.4.4 DMA Trig g er . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-6
11.5 Triple Timer Module Programming Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-7
11.5.1 Prescaler Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 1 -7
11.5.2 Timer Pr escaler Lo ad R eg ister (TPL R) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-8
11.5.3 Timer Prescaler Count Register (TPCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-9
11.5.4 Timer Co n t ro l / Status Register (TCSR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-9
11.5.5 Timer Loa d Re g i st er (TLR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-12
11.5.6 Timer Co m p are Register (TCPR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-12
11.5.7 Timer Count Register (TCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-12
Chapter 12
Watchdog Timer (WDT, WDT_1)
12.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 -1
12.2 WDT Pin-Outs for Differ e n t D ev i c e Packages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 - 1
12.3 WDT Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 -3
12.3.1 Watchdog Control Register (WCR). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-3
12.3.2 Watchdog Counter and WCNTR Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-4
12.3.3 Watchdog Modulus Register (WMR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-4
12.3.4 Watchdog Service Register (WSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-5
12.4 Watchdog Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-6
12.4.1 Wait Mod e. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12- 6
12.4.2 Debug Mod e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12-6
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor vii

12.4.3 Stop Mo d e. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 -6
Chapter 13
Inter-Core Communication (ICC)
13.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 -1
13.1.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 -1
13.1.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-3
13.2 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-3
13.2.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 - 3
13.2.2 Register Descri p t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 -5
13.3 Programming Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 -13
13.3.1 Inter- Co re Maskab l e Interrupts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-13
13.3.2 Inter- Co re Non-Ma sk a b l e Interru p t s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-14
13.3.3 Polli n g. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-15
13.3.4 Error In t e rru p t s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 - 1 5
13.3.5 Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13-16
Chapter 14
Shared Bus Arbiter
14.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 4 -1
14.1.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 4 -1
14.1.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-1
14.2 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-2
14.3 Fun ctional D e scriptio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14 -2
14.3.1 Share d Bus Arb i tration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14-2
Chapter 15
Shared Memory (Shared Memory)
15.1 Ov e rv i ew. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 5 -1
15.2 B lo ck Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-1
Chapter 16
Shared Peripheral Bus
16.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 6 -1
16.1.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-1
16.2 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16-2
16.3 Fun ctional D e scriptio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16 -2
Chapter 17
EMC Burst Buffer
17.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 7 -1
17.1.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 7 -2
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
viii Freescale Semiconductor

17.1.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17-3
17.2 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17-3
17.3 Fun ctional D e scriptio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17 -3
17.3.1 Burst Con t rol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17-3
17.3.2 Read Ac c ess . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 7 -5
17.3.3 Write Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 7 - 6
Chapter 18
S/PDIF—Sony/Philips Digital Interface
18.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 8 -1
18.1.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-3
18.1.2 Externa l Si g n a l D escripti o n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-3
18.1.3 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 - 4
18.2 R e g i st e r Descrip t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-5
18.2.1 S/PDIF Co n fi g u r a t i o n Re g i st e r (S CR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-5
18.2.2 CDText Co n tr o l Re g i st e r (SRCD) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-6
18.2.3 PhaseC o n fi g Reg ister (SRPC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-7
18.2.4 Interr u p t Reg isters (SI E, SIS, SIC). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-7
18.2.5 S/PDIF Reception Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-9
18.2.6 S/PDIF Transmiss i o n Reg isters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 -11
18.2.7 S/PDIF Fr eq Me as Register (SRFM). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18- 1 4
18.2.8 SPDIFTx Clk Regist e r (STC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18- 14
18.3 S/PDIF Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18- 1 5
18.3.1 Audio Data Recepti o n. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-15
18.3.2 Channel Status Reception . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-18
18.3.3 User Bit Reception . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-1 8
18.3.4 Validity Flag Reception . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-20
18.3.5 S/PDIF Receiver Interrupt Exception Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-21
18.3.6 Standa rd s Compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-22
18.3.7 S/PDIF PL O CK D et e c t i o n a n d Rxc lk O u t p u t . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 - 2 2
18.3.8 Measur i n g the Fr e q u en cy of SPDIF _ RcvClk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18- 2 2
18.4 S/PDIF Transmitter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-22
18.4.1 Audio Dat a Transmi ssi o n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-23
18.4.2 Channel S t a t u s Transmis si o n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-24
18.4.3 Validi t y Fl ag Transmiss i o n. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18-24
Chapter 19
Asynchronous Sample Rate Converter
19.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 9 -1
19.1.1 Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 9 -2
19.1.2 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19-3
19.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 -4
19.2 Mem o r y M ap a n d Reg i ster Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 -5
19.2.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 - 5
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor ix

19.2.2 Register Descri p t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 9 -7
19.3 I n t e rru p t s. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 9 - 2 7
19.4 DMA Reques ts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19- 2 7
19.5 Fun ctional D e scriptio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19 -28
19.5.1 Algorit h m D e scriptio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19-28
Chapter 20
Chip Configuration Module
20.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 0 -1
20.1.1 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 -1
20.2 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20-1
20.2.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 - 1
20.2.2 Register Descri p t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 0 -3
20.3 Programming Model. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 -15
20.3.1 ESAI/ESAI_1/ESAI_2/ESAI_3 Pin-Switching and Internal Connections . . . . . . . . . . . 20-15
20.3.2 ESAI_2 Da ta and SPDIF Data Pin Mux. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 0 - 1 5
20.3.3 Soft Re se t . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20-16
20.3.4 Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20-17
20.3.5 ESAI Pin Sw i t c h an d In t e r n a l Clock Conn ec t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 - 1 7
Chapter 21
External Memory Controller (EMC)
21.1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 1 -1
21.1.1 Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-2
21.2 Ext e r n a l Si g n a l D escripti o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 -3
21.2.1 Detail ed Si g n a l D escripti o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-4
21.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-7
21.3.1 Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 - 7
21.3.2 Register Descri p t i o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 1 -9
21.4 Fun ctional D e scriptio n . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 -39
21.4.1 Basic Architecture. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-4 0
21.4.2 General -Purpose Chip-Sel e ct Ma c h i n e (GPCM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 1 -42
21.4.3 SDRAM Ma c h i n e . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-56
21.4.4 User-P ro g rammabl e Ma c h i n es (UPMs) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-66
21.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-87
21.5.1 Interf a cing to Perip h erals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-87
21.5.2 Bus Turnaround . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-90
21.5.3 Interf ac i n g to SDRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21-91
Chapter 22
JTAG Controller
22.1 Ov e rv i ew. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 2 -1
22.2 Fe a t u res. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22-2
22.3 Ext e r n a l Si g n a l D escripti o n s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22 -4
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
x Freescale Semiconductor

About This Book
The Symphony™ DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual describes the
features and operation of the SymphonyTM DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors,
including, for example, their main features, architecture, function blocks, operation modes, pin signals,
clocks, interrupts, DMA operations, and memory maps.
The DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors are devices of the DSP5672x family of
programmable CMOS DSPs, designed using dual DSP56300 24-bit cores. The DSP56724/DSP56725 are
intended for automotive, consumer, and professional audio applications that require high performance for
audio processing. Potential applications include A/V receivers, car audio/amplifiers, and professional
audio equipment.
Revision History
The following table summarizes revisions to this document.
Table 1. Revision History
Revision Description
0 Initial release
Audience
The Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual provides to the
design engineer the necessary data to success fully integrate t he proces sor s into a wide variety of
applications.
The intended audience for this document includes system architects, system modeling teams, IC designers,
software architects/designers, and the platform integration and testing teams. The level of detail in this
document is intended to provide the reader with sufficient information to validate the capabilities of the
processes in the targeted applications.
Organization
This reference manual is organized into chapters that describe the operation and programming of the
processors. It includes brief summaries of the major components, as well as listings of the memory maps
for the processors and shared memories.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor xi

About This Book
This manual also contains chapters that describe the operations and configuration of the peripherals,
including the modules that provide bootmodes, memory, and connectivity.
Suggested Reading
The DSP56300 Family Manual (DSP56300FM) is suggested for a complete description of the Symphony
DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, and is necessary to design with the devices. This
document is helpful when used in conjunction with this reference manual.
Conventions
This reference manual uses the following conventions:
• OVERBAR is used to indicate a signal that is active when pulled low: for example, RESET.
• Logic level one is a voltage that corresponds to Boolean true (1) state.
• Logic level zero is a voltage that corresponds to Boolean false (0) state.
•To set a bit or bits means to establish logic level one.
•To clear a bit or bits means to establish logic level zero.
•A signal is an electronic construct whose state conveys or changes in state convey information.
•A pin is an external physical connection. The s ame pin can be used to connect a number of signals.
• Asserted means that a discrete signal is in active logic state.
— Active low signals change from logic level one to logic level zero.
— Active high signals change from logic level zero to logic level one.
• Negated means that an asserted discrete signal changes logic state.
— Active low signals change from logic level zero to logic level one.
— Active high signals change from logic level one to logic level zero.
• LSB means least significant bit or bits, and MSB means most significant bit or bits. R eferences to
low and high bytes or words are spelled out.
• Numbers preceded by a percent sign (%) are binary. Numbers preceded by a 0x are hexadecimal.
• Courier monospaced type indicate commands, command parameters, code examples, expressions,
data types, and directives.
• Italic type indicates replaceable command parameters.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
xii Freescale Semiconductor

Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
The SymphonyTM DSP56724 and DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors are devices of the DSP5672x
family of programmable CMOS DSPs, designed using multiple DSP56300 24-bit cores. The DSP56724
and DSP56725 are intended for automotive, consumer, and professional audio applications that require
high performance for audio processing. These processors also support professional audio applications,
including audio recording, signal processing and digital audio synthesis. Potential applications include
A/V receivers, car audio/amplifiers, and professional audio equipment. Additional device features include
support for digital audio compression/decompression, sound field processing, acoustic equalization and
other digital audio algorithms. With two DSP56300 cores, the DSP56724 (or DSP56725) device can
replace two DSP devices in designs, providing high MIPs and lower cost.
DSP56724/DSP56725 features include:
• Two DSP56300 enhanced cores: 400 MIPs (200 MIPs/core) with a 200 MHz clock; each core
includes:
— Highly parallel instruction set
— Hardware debugging support (JTAG TAP, OnCETM module)
— Eight-channel DMA controller
— Wait and Stop low-power standby modes
• Configurable and flexible arbitration method for the shared peripherals and shared memory blocks
• Powerful audio data communication ability:
— Four Enhanced Serial Audio Interface (ESAI) modules to transmit and receive audio data. Two
ESAI modules are provided for each core. For each ESAI, up to 4 receivers and up to 6
transmitters, master or slave. Protocols include I
AC97, network and other programmable protocols.
— One S/PDIF module is shared by the two cores to transmit and receive audio data in IEC958
format.
• Powerful host communication port: Two Serial Host Interface (SHI, SHI_1) modules, with one
module for each core. SHIs support SPI and I2C protocols, multi-master capability in I2C mode,
10-word receive FIFO, and support for 8, 16 and 24-bit words.
• Two triple-timer modules (TEC, TEC_1), with one timer module for each core.
• T wo watchdog timer modules (WDT, WDT_1), with one watchdog timer module for each core, to
prevent code runaway problems.
• An External Memory Controller (EMC) that can be accessed by both DSP cores, which supports
SDRAM, SRAM, EPROM, flash EPROM, burstable RAM, regular DRAM devices, and extended
2
S, Left-Justified, Right-Justified, Sony,
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-1

Introduction
data output DRAM devices. Note that the EMC is only available on DSP56724 devices, and is not
available on DSP56725 devices. The EMC includes:
— High performance SDRAM machine
— A general-purpose chip-select machine (GPCM)
— Up to three user-programmable machines (UPMs)
• A seamless hardware Asynchronous Sampling Rate Converter (ASRC) that is accessible to both
cores, to support different sample rate audio data transmission reception. Three data sampling rate
convert pairs can be supported at the same time. Different pairs can be used by different cores at
the same time.
• Inter-Core Communication (ICC) module:
— 32K shared memory between the two DSP56300 cores
— Supports a flexible arbitration system which allows multiple methods of arbitration
— Non-maskable and maskable interrupts between the two cores
— Poll data registers for simple data transfers
• Includes as many as 79 GP IO pins, s hared with other peripherals function pins; the actual number
is different for different device packages.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
1-2 Freescale Semiconductor
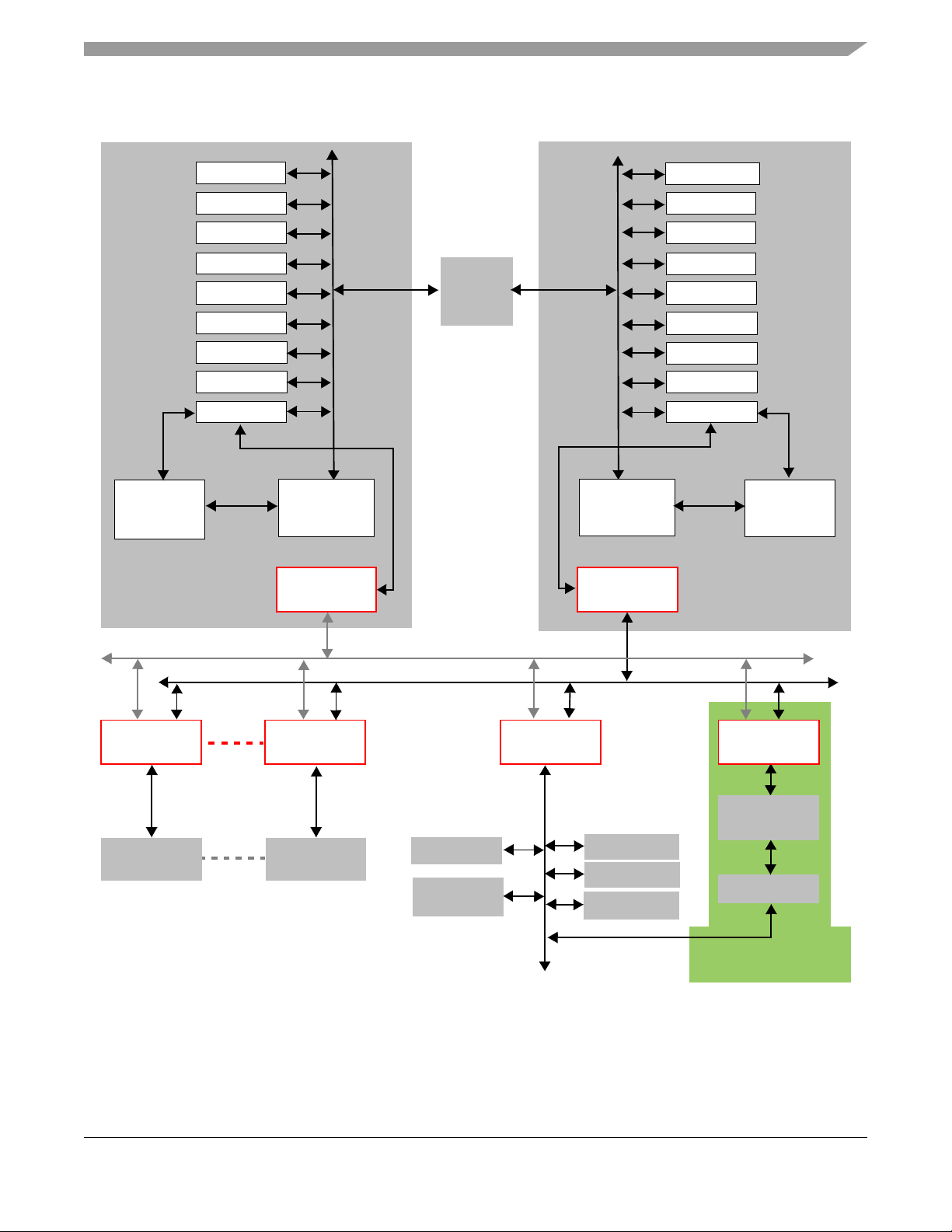
1.2 Block Diagram
DSP56300
Core-1
DSP56300
Core-0
Internal
Memory #0
S/PDIF
EMC
ESAI
Dedicated
Peripheral
Bus
Memory
Bus
Shared Bus#0
Shared Bus #1
Memory Bus
ESAI_1
SHI
TEC
PIC
DMA
WDT
CIM
ESAI_2
ESAI_3
SHI_1
TEC_1
PIC_1
DMA_1
WDT_1
CIM_1
Internal
Memory #1
GPIO A, G
Chip
Configuration
Shared Bus
Arbiter 7
Shared Mem0
(8K)
Core-0 Core-1
Memory Bus
Shared Mem7
(8K)
GPIO_1
GPIO
Inter-Core
Comm.
(ICC)
CGM
ASRC
Memory
Bus
Dedicated
Peripheral
Bus
Shared Bus
Arbiter 0
Shared Bus
Arbiter 9
Shared Bus
Arbiter 8
EMC Burst
Buffer
Shared
Peripheral Bus
Core/DMA
Arbiter
Core/DMA
Arbiter
The EMC is only available
on the DSP56724.
Introduction
Freescale Semiconductor 1-3
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
Figure 1-1. DSP56724/DSP56725 Block Diagram

Introduction
1.3 Features
In addition to high MIPS, the DSP56724/DSP56725 provides powerful and flexible audio data
communications and supports a wide variety of audio applications. This section provides a brief
description of the DSP56724/DSP56725 processor features.
The DSP56724/DSP56725 has two DSP56300 DSP cores. The high throughput of the DSP56300 family
of processors makes them well-suited for high-speed control, efficient signal processing, numeric
processing, and audio applications. Benefits of using DSP56300 cores include:
• Speed: The DSP56300 family supports most high-performance DSP applications.
• Precision: The data paths are 24 bits wide, providing 144 dB of dynamic range. Intermediate
results held in the 56-bit accumulators can range over 336 dB.
• Parallelism: Each on-chip execution unit, memory, and peripheral operates independently and in
parallel with the other units through a sophisticated bus system. The Data ALU, AGU, and program
controller operate in parallel so that the following operations can execute in a single instruction:
— An instruction pre-fetch
— A 24-bit × 24-bit multiplication
— A 54-bit addition
— Two data moves
— Two address-pointer updates using either linear or modulo arithmetic
• Flexibility: While many other DSPs require external communication devices to interface with
peripheral circuits (such as A/D converters, D/A converters, or processors), the DSP56300 family
provides on-chip serial and parallel interfaces that support various configurations of memory and
peripheral modules. The peripherals are interfaced to the DSP56300 family core through a
peripheral interface bus that provides a common interface to many different peripherals.
• Sophisticated Debugging: Freescale’s On-Chip Emulation (OnCE) technology allows simple,
inexpensive, and speed-independent access to the internal registers for debugging. With the OnCE
module, you can easily determine the exact status of the registers and memory locations, plus
identify which instructions were executed last.
• Phase Locked Loop (PLL)-Based Clocking: The PLL allows the chip to use almost any availa ble
external system clock for full-speed operation, while also supplying an output clock synchronized
to a synthesized internal core clock. It improves the synchronous timing of the external memory
port, eliminating the timing skew common on other processors.
• Invisible Pipeline: The seven-stage instruction pipeline is essentially invisible to the programmer ,
allowing straightforward program development in either assembly language or high-level
languages such as C or C++.
• Similar Instruction Set: The instruction mnemonics are similar to those used for microcontroller
units, making an easy transition from programming microprocessors to programming the device.
New microcontroller ins tructions, addressing modes, and bit field instructions allow for significant
decreases in program code size. The orthogonal syntax controls the parallel execution units. The
hardware DO loop and the repeat (REP) instructions make writing straight-line code obsolete.
• Low Power: Designed in CMOS, the DSP56300 family consumes very little power . T wo additional
low-power modes, Stop and Wait, further reduce power requirements. Wait is a low-power mode
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
1-4 Freescale Semiconductor

in which the DSP56300 core shuts down, but the peripherals and interrupt controller continue to
operate, so that an interrupt can bring the chip out of Wait mode. In Stop mode, even more of
circuitry is shut down for the lowest power consumption. Several different methods are available
to bring the chip out of Stop mode: hardware RESET, IRQA, and DE.
1.4 Overview of Peripherals
The peripherals include the following:
•DMA
•PIC
•ESAI
•SHI
•TEC
•WDT
•CIM
•S/PDIF
•ASRC
Introduction
•EMC
•CGM
• Shared memory
•ICC
• Shared bus arbiters
• Chip configuration module
• JTAG controller
1.4.1 Direct Memory Access Controller (DMA, DMA_1)
The DMA controller enables data transfers without any interactions with the DSP cores. During DMA
accesses, it supports any combination of source and destination between internal memory, internal
peripheral I/O, and external memory. DMA features include:
• Eight DMA channels supporting internal and external accesses
• One-, two-, and three-dimensional transfers (including circular buffering)
• End-of-block-transfer interrupts
• Triggering from interrupt lines and all peripherals
1.4.2 Program Interrupt Controller (PIC, PIC_1)
The Program Interrupt Controller arbitrates among all interrupt requests (internal interrupts and the five
external re q ue sts IRQA, IRQB, IRQC, IRQD, and NMI), and generates the appropriate interrupt vector
address.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-5

Introduction
The Program Interrupt Controller supports the following:
• Both non-maskable and maskable interrupts
• Up to 18 DMA interrupts and 24 Peripheral interrupts
• Up to 9 non-maskable interrupts
1.4.3 Enhanced Serial Audio Interfaces (ESAI, ESAI_1, ESAI_2, ESAI_3)
The enhanced serial audio interfaces provide full-duplex serial GPIO pins or serial communications with
a variety of serial devices, including one or more industry-standard codecs, other DSPs, microprocessors
and other peripherals that implement the serial peripheral interface (SPI) serial protocol. Each ESAI
consists of independent transmitter and receiver sections, each with its own clock generator, and is a
superset of the DSP56300 family ESSI peripherals and the DSP56000 family SAI peripherals.
1.4.4 Serial Host Interfaces (SHI, SHI_1)
Each serial host interface provides a path for communications and program/coefficient data transfers
between the DSP core and an external host processor. The SHI can interface direc tly to either of two
well-known and widely used synchronous serial buses: the SPI bus and t he Phillips inter -integrated-circuit
control (I2C) bus. The SHI supports either the SPI or I2C bus protocol, as required, from a slave or a
single-master device. To minimize DSP overhead, the SHI supports single-, double- and triple-byte data
transfers. The SHI has a 10-word receive FIFO that permits receiving up to 30 bytes before generating a
receive interrupt, reducing the overhead for data reception.
1.4.5 Triple Timers (TEC, TEC_1)
Each Triple T imer is composed of a common 21-bit prescaler and three independent and identical general
purpose 24-bit timer event counters, with each timer having its own register set. Each timer can use internal
or external clocking, and can also interrupt the DSP after a specified number of events (clocks). Each of
the three timers can signal an external device after counting internal events. Each timer can also be used
to trigger DMA transfers after a specified number of events (clocks) have occurred.
Each of the three timers connects to the external world through bidirectional pins (TIO0, TIO1 and TIO2).
When a TIO pin is configured as input, the timer functions as an external event counter or can measure
external pulse width/signal period. When a TIO pin is used as output, the timer is functioning as either a
timer, a watchdog or a P ulse Width Modulator. When a TIO pin is not used by the timer, it can be used as
a General Purpose Input/Output Pin. Not all timer pins are available on all packages.
1.4.6 Watch Dog Timers (WDT, WDT_1)
Each watchdog timer is a 16-bit timer used to help software recover from runaway code. The timer is a
free-running down-counter used to generate a reset on underflow. Software must periodically service the
watchdog timer to restart the count down
.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
1-6 Freescale Semiconductor

Introduction
1.4.7 Core Integration Modules (CIM, CIM_1)
Each DSP core has a Core Integration Module. Each core integration module includes a chip ID register,
DMA stall monitor function, and OnCE global data bus (GDB) register.
1.4.8 Sony/Philips Digital Interface (S/PDIF)
The Sony/Philips Digital Interface (S/PDIF) audio module is a transceiver that allows the DSP to r eceive
and transmit digital audio via this module. There is one S/PDIF in each DSP56724/DSP56725 device,
shared by the two DSP cores. The DSP provides a single S/PDIF receiver with four multiplexed inputs,
and one S/PDIF transmitter with two outputs. The S/PDIF module can also transmit and receive the
S/PDIF channel status (CS) and user (U) data. Not all S/PDIF pins are available on all packages.
1.4.9 Asynchronous Sample Rate Converter (ASRC)
Incoming audio data to the DSP can be received from various sources at different sampling rates. Outgoing
audio data from the DSP can have different sampling rates, and additionally, it can be associated with
output clocks that are asynchronous to the input clocks. The Asynchronous Sample Rate Converter
(ASRC) converts the sampling rate of a signal associated to an input clock into a signal associated to a
different output clock.
The ASRC supports concurrent sample rate conversion of up to 10 channels of about 120 dB THD+N. The
sample rate conversion of each channel is associated to a pair of incoming and outgoing sampling rates.
The ASRC supports up to three sampling rate pairs. Although there is only one ASRC in the
DSP56724/DSP56725 device (shared by the two DSP cores), the three sample rate pairs can be used by
both DSP cores at the same time. The ASRC is hard-c ode d and imple mente d a s a c o-proce s sor, requiring
minimal CPU or DSP controller intervention.
1.4.10 External Memory Controller (EMC)
There is one EMC in each DSP56724 device, shared by the two DSP cores. Both cores can access external
memory using the EMC. (DSP56725 devices do not have an EMC.) The EMC provides a seamless
interface to many types of memory devices and peripherals over a shared address and data bus and
dedicated control signals. The memory controller in the EMC controls a parameteriz ed number of memory
banks shared by a high performance SDRAM machine, a general-purpose chip- select machi ne (GPCM),
and up to three user-programmable machines (UPMs).
With external latching, it supports connections to synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), SRAM, EPROM, flash
EPROM, burstable RAM, regular DRAM devices, extended data output DRAM devices, and other
peripherals. Support signals for external address latch (LALE) allows multiplexing of address with data
lines in devices with strict pin count limitations.
1.4.11 Clock Generation Module (CGM)
The Clock Generation Module generates all clocks in the DSP56724/DSP56725 device; the output is a
series of gated clocks. The CGM uses a low jitter phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has a wide range of
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-7

Introduction
frequency multiplications (1 to 256), predivider factors (1 to 32) and output divider (1 to 8). The CGM also
has a power saving clock divider (2i: i = 0 to 7).
In functional mode, the PLL control register (P CTL) sits on the Shared Peripheral bus; both DSP cores can
read and write these registers to change the chip’s working frequency. Additionally, each core can
independently enter stop or wait mode to save power. The shared peripherals enter power-saving mode
only when both DSP cores enter the stop mode.
1.4.12 Shared Memory
The shared memory is a shared memory space accessible by either DSP Core-0 or DSP Core-1. The
DSP56724/DSP56725 shared memory has four 8K x 24 words memory blocks for a total of 32K shared
words and is located starting from $030000. It can be accessed as X or Y memory (with zero wait states)
or as P memory (with 1 wait state).
The 8K x 24 words blocks are single port SRAMs; the Shared Bus Arbiter perform arbitration when the
two DSP cores try to access the same 8K x 24 SRAM block at the same time. No bus contentions occur
when the two DSP cores access different 8K x 24 SRAM blocks simultaneously.
1.4.13 Inter-Core Communication (ICC)
Using the inter-core communication module, each DSP core can issue a maskable interrupt or
non-maskable interrupt to the other core, and each core has its own write data register (which passes data
to the other core when the interrupt is generated). There are also poll data registers for inter-core data
exchange in the ICC. The ICC module interfaces with both cores’ dedicated peripheral buses.
1.4.14 Shared Bus Arbiters
The Shared Bus Arbiter provides arbitration between the two DSP cores for the shared peripherals, shared
memory and shared external memory interface (if available). It is a configurable arbiter, so users can
choose the arbitration method via the appropriate chip configuration registers. The Shared Bus Arbiter
supports using one of three arbitration schemes:
• Always round-robin method
• DSP Core-0 always has high priority
• DSP Core-1 always has high priority
1.4.15 Chip Configuration Module
The Chip Configuration module contains several registers which establish the mode of operation for
various internal blocks, modules, and some of the peripherals. These registers include:
• Control bits of Shared Bus Arbiters
• EMC Burst Mode control bits
• Pin mux/switch control of ESAI, S/PDIF, S/PDIF Rx Clock output mux on ESAI HCKR pins
• Shared peripherals Soft Reset triggering and auto-release
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
1-8 Freescale Semiconductor

Introduction
• EMC PLL control and status
1.4.16 JTAG Controller
In the DSP56724/DSP56725 devices, two separate DSP cores are supported, each with their own OnCE
and JTAG TAP controller. The two JTAG TAPs are daisy-chained, and appear to be two separate single
core devices to the outside world.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-9

Introduction
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
1-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Chapter 2 Signal Descriptions
2.1 Signal Groupings
Each product (DSP56724, DSP56725) is available in a variety of packages, which affects whether some
modules use dedicated or shared external pins. See Table 2-1.
Table 2-1. DSP56724/DSP56725 Shared/Dedicated Pins
DSP56724 DSP56725
Function Module
144-pin 80-pin
Timers TEC None None
TEC_1 None None
Enhanced Serial Audio Interface ESAI No SDO0, SDO1 No SDO0, SDO1
ESAI_1 No SDO0, SDO1, FST, FSR,
SCKT, SCKR, HCKT, HCKR
ESAI_2 No SDO0, SDO1, FST, FSR,
SCKT, SCKR, HCKT, HCKR
ESAI_3 No SDO0, SDO1 No SDO0, SDO1, HCKR
Serial Host Interface SHI All All
SHI_1 Only SS, others muxed with SHI Only SS; others muxed with SHI
Watchdog Timer WDT All All
WDT_1 Muxed with WDT Muxed with WDT
General Purpose I/O GPIO Only PG1, PG2 None
Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format S/PDIF Only SPDIFIN and SPDIFOUT1 None;muxed with ESAI_2’s
External Memory Controller EMC All Not applicable, because
1
Clock and Frame Sync signals can be shared with ESAI.
2
Clock and Frame Sync signals can be shared with ESAI_3.
1
2
No SDO0, SDO1, FST, FSR,
SCKT, SCKR, HCKT, HCKR
No SDO0, SDO1, FST, FSR,
SCKT, SCKR, HCKT, HCKR
SDO2, SDO3
DSP56725 does not have an
EMC module.
1
3
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-1
Signal Descriptions
The input and output signals of the DSP56724/DSP56725 are organized into functional groups, as listed
in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2. DSP56724/DSP56725 Signal Groups
Number of Signals
Signal Group Signal
DSP56724 DSP56725
144-Pin 80-Pin
Detailed
Description
Power, Ground, Scan, Clock, Interrupts Power (V
)2113Table 2 -3
DD
Ground (GND) 21 18 Tab le 2 -4
Scan Pins 1 1 Tab le 2 -5
Reset Pin 1 1 Tab le 2 -7
Clock and PLL Port G
Shared External Interrupt Pins /
Por t G
Mode Control
DSP Core-0 Peripheral Pins SHI Port H
ESAI Port C
ESAI_1 Port E
TEC – 0 0 —
WDT No GPIO
Function
DSP Core-1 Peripheral Pins SHI_1 Port H1
ESAI_2 Port C1
ESAI_3 Port E1
TEC_1 – 0 0 —
8
8
44Table 2 -6
55Table 2 -8
Table 2 -9
1
2
3
55Ta b le 2 - 1 1
10 10 Tab l e 2 - 1 3
44Ta b le 2 - 1 4
11Ta b le 2 - 1 7
4
5
6
11Ta b le 2 - 1 2
44Ta b le 2 - 1 5
10 9 Ta bl e 2 - 1 6
WDT_1 No GPIO
00—
Function
Por t A
8
7
8
20Ta b le 2 - 1 9
48 0 Ta bl e 2 - 1 8
20Ta b le 2 - 2 0
Pins of Shared Peripherals SPDIF Port G
9
EMC
GPIO PORT G and Mode Pins Port G
JTAG/OnCE Portfor the two DSP Cores 4 4 Tab le 2 - 2 1
Note: 1. Port H signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the SHI HREQ
signal.
2. Port C signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the ESAI signals.
3. Port E signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the ESAI_1 signals.
4. Port H1 signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the SHI_1 HREQ_1
signals.
5. Port C1 signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the ESAI_2 signals.
6. Port E1 signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the ESAI_3 signals.
7. Port A signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with the EMC.
8. Port G signals are the GPIO port signals that are multiplexed with S/PDIF, shared external maskable interrupts,
and PLL lock output signals.
9. DSP56724 products have an EMC; DSP56725 products do not have an EMC.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
2-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Signal Descriptions
60 WDT
59 PINIT/NMI
58 TDO
57 TDI
56 TCK
55 TMS
54 CORE_GND
53 CORE_VDD
52 SDO4/SDI1
51 SDO5/SDI0
50 IO_GND
49 IO_VDD
48 EXTAL
47 XTAL
46 PLLP_GND
45 PLLD_GND
44 PLLD_VDD
43 PLLA_GND
42 PLLA_VDD
41 PLLP_VDD
FST_3 21
HCKT_3 22
SDO2_1/SDI3_1 23
SDO3_1/SDI2_1 24
CORE_VDD 25
CORE_GND 26
SDO4_1/SDI1_1 27
SDO5_1/SDI0_1 28
FSR 29
SCKR 30
HCKR 31
SCKT 32
IO_VDD 33
IO_GND 34
CORE_VDD 35
CORE_GND 36
FST 37
HCKT 38
SDO2/SDI3 39
SDO3/SDI2 40
SDO2_3/SDI3_3 1
SDO3_3/SDI2_3 2
SDO4_3/SDI1_3 3
SDO5_3/SDI0_3 4
IO_VDD 5
IO_GND 6
CORE_VDD 7
CORE_GND 8
SPDIFIN1/SDO2_2/SDI3_2 9
SPDIFOUT1/SDO3_2/SDI2_210
SDO4_2/SDI1_2 11
SDO5_2/SDI0_2 12
FSR_3 13
SCKR_3 14
SCKT_3 15
GND 16
GND 17
GND 18
GND 19
GND 20
80 SCAN
79 MODA0/IRQA
78 MODB0/IRQB
77 MODC0/PLOCK
76 IO_GND
75 IO_VDD
74 CORE_GND
73 CORE_VDD
72 MODA1/IRQC
71 MODB1/IRQD
70 MODC1/NMI_1
69 SS/HA2
68 HREQ
/PH4
67 SCK/SCL
66 MOSI/HA0
65 MISO/SDA
64 SS_1
/HA2_1
63 RESET
62 CORE_GND
61 CORE_VDD
DSP56725
80-Pin
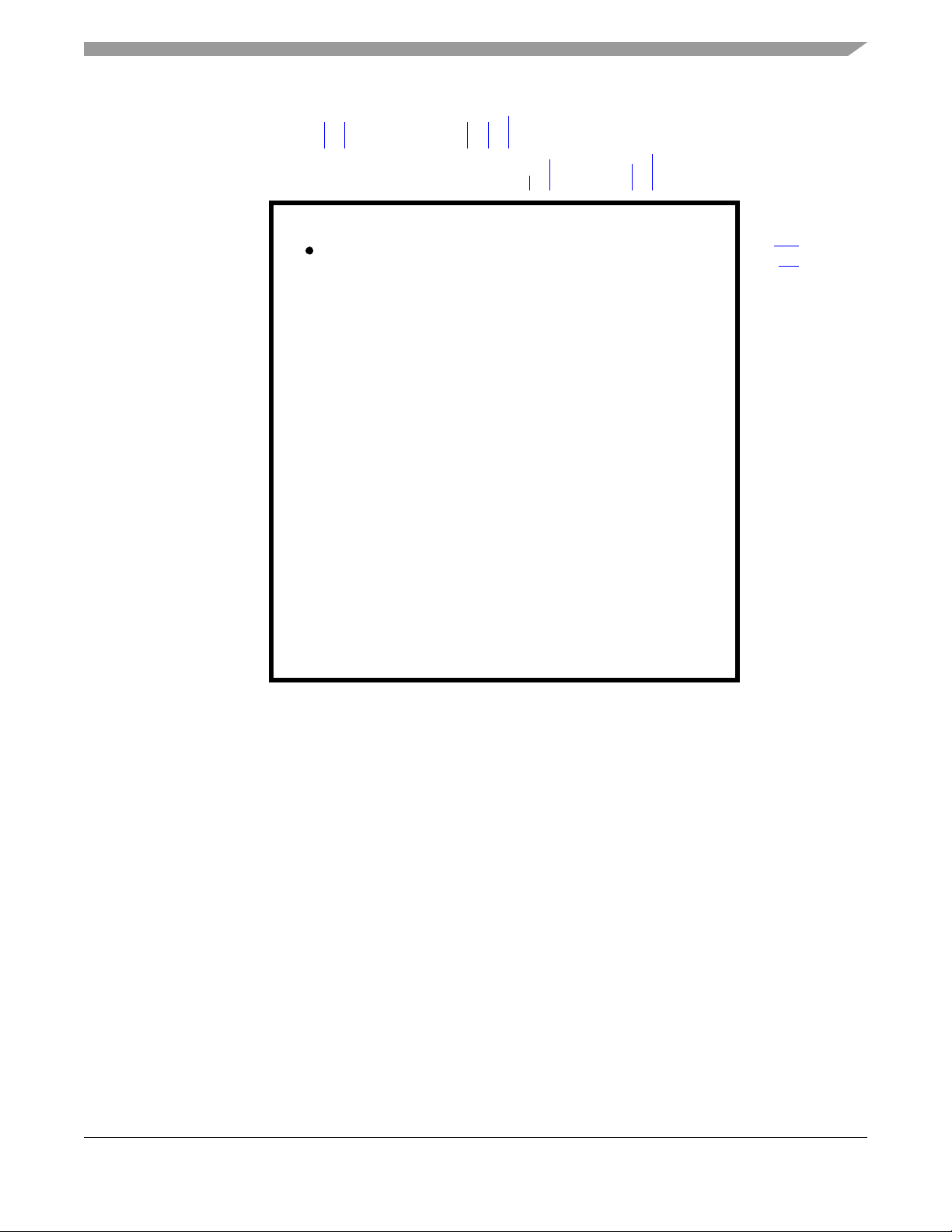
Figure 2-1. DSP56725 80-Pin Package Pin-Out
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-3
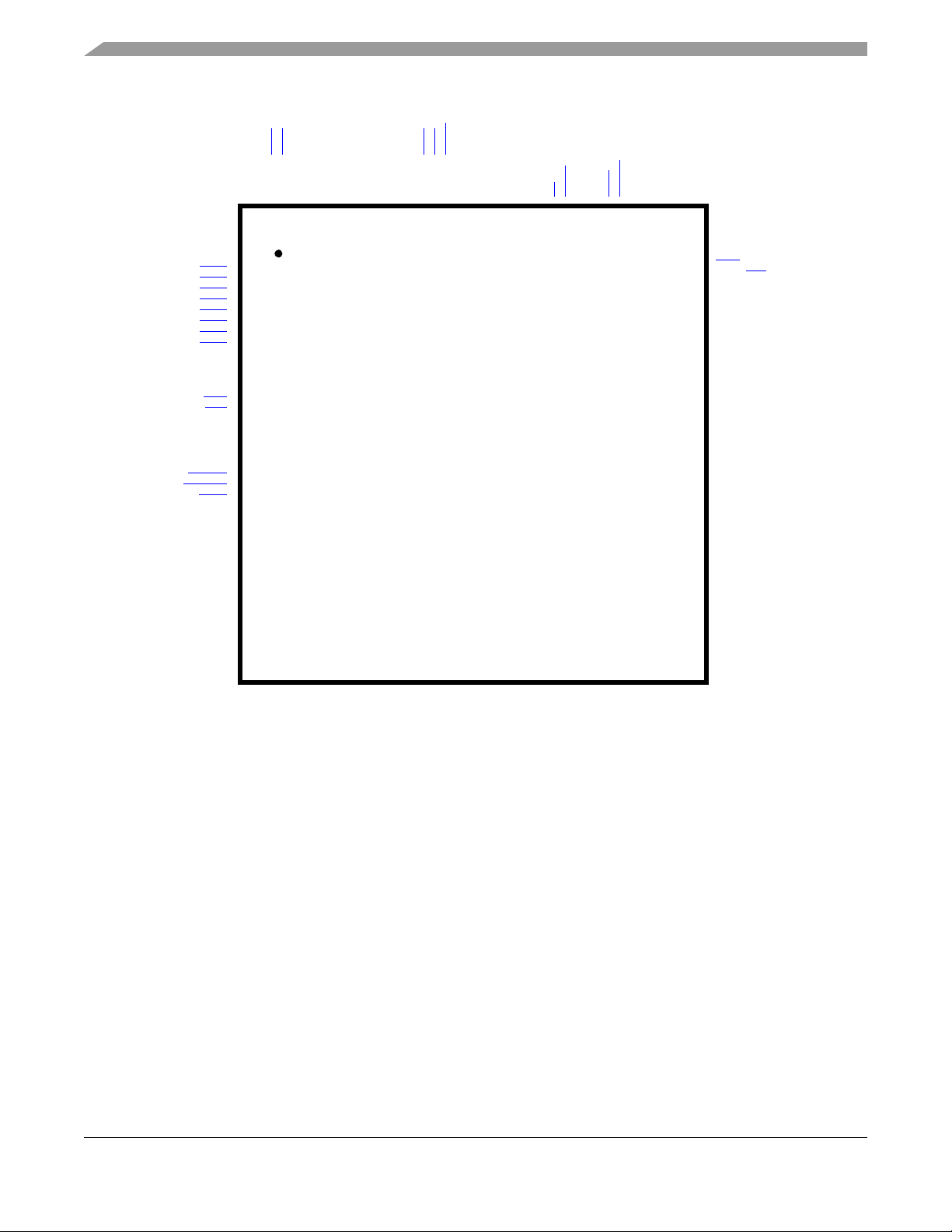
Signal Descriptions
108 IO_GND
107 IO_VDD
106 WDT
105 PINIT/NMI
104 TDO
103 TDI
102 TCK
101 TMS
100 SDO2_1/SDI3_1
99 SDO3_1/SDI2_1
98 SDO4_1/SDI1_1
97 SDO5_1/SDI0_1
96 CORE_GND
95 CORE_VDD
94 FSR
93 SCKR
92 HCKR
91 SCKT
90 FST
89 HCKT
88 SDO2/SDI3
87 SDO3/SDI2
86 SDO4/SDI1
85 SDO5/SDI0
84 SPDIFOUT1
83 SPDIFIN1
82 IO_GND
81 IO_VDD
80 EXTAL
79 XTAL
78 PLLP_GND
77 PLLD_GND
76 PLLD_VDD
75 PLLA_GND
74 PLLA_VDD
73 PLLP_VDD
LSYNC_IN 37
LSYNC_OUT 38
LAD23 39
LAD22 40
LAD21 41
LAD20 42
LAD19 43
LAD18 44
LAD17 45
CORE_VDD 46
CORE_GND 47
IO_VDD 48
IO_GND 49
LAD16 50
LAD15 51
LAD14 52
LAD13 53
LAD12 54
LAD11 55
LAD10 56
LAD9 57
IO_VDD 58
IO_GND 59
CORE_VDD 60
CORE_GND 61
LAD8 62
LAD7 63
LAD6 64
LAD5 65
LAD4 66
LAD3 67
LAD2 68
LAD1 69
LAD0 70
IO_GND 71
IO_VDD 72
CORE_VDD 1
CORE_GND 2
LALE 3
LCS0
4
LCS1
5
LCS2 6
LCS3
7
LCS4
8
LCS5 9
LCS6 10
LCS7 11
IO_VDD 12
IO_GND 13
CORE_VDD 14
CORE_GND 15
LWE
16
LOE
17
LGPL5 18
LSDA10 19
LCKE 20
LCLK 21
LBCTL 22
LSDWE
23
LSDCAS 24
LGTA 25
LA0 26
LA1 27
LA2 28
IO_VDD 29
IO_GND 30
PLLP1_GND 31
PLLP1_VDD 32
PLLD1_GND 33
PLLD1_VDD 34
PLLA1_GND 35
PLLA1_VDD 36
144 SCAN
143 MODA0/IRQA
142 MODB0/IRQB
141 MODC0/PLOCK
140 MODD0/PG1
139 FSR_3
138 SCKR_3
137 HCKR_3
136 SCKT_3
135 FST_3
134 HCKT_3
133 IO_GND
132 IO_VDD
131 CORE_GND
130 CORE_VDD
129 MODA1/IRQC
128 MODB1/IRQD
127 MODC1/NMI_1
126 MODD1/PG2
125 SDO2_2/SDI3_2
124 SDO3_2/SDI2_2
123 SDO4_2/SDI1_2
122 SDO5_2/SDI0_2
121 SDO2_3/SDI3_3
120 SDO3_3/SDI2_3
119 SDO4_3/SDI1_3
118 SDO5_3/SDI0_3
117 SS
/HA2
116 HREQ/PH4
115 SCK/SCL
114 MOSI/HA0
113 MISO/SDA
112 SS_1/HA2_1
111 RESET
110 CORE_GND
109 CORE_VDD
DSP56724
144-Pin
Figure 2-2. DSP56724 144-Pin Package Pin-Out
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
2-4 Freescale Semiconductor
2.2 Signals in Each Functional Group
2.2.1 Power
Table 2 - 3 . Powe r P i n s
Power Name Description
Signal Descriptions
PLLA_VDD
PLLP_VDD
PLLA1_VDD
PLLP1_VDD
PLLD_VDD
PLLD1_VDD
CORE_VDD Core Power
IO_VDD I/O Power
PLL Power
The voltage (3.3 V) should be well-regulated and the input should be provided with an extremely low impedance
path to the 3.3 V
PLL Power
The voltage (1.0 V) should be well-regulated and the input should be provided with an extremely low impedance
path to the 1.0 V
The voltage (1.0 V) should be well-regulated and the input should be provided with an extremely low impedance
path to the 1.0 V
The voltage (3.3 V) should be well-regulated and the input should be provided with an extremely low impedance
path to the 3.3 V
Timer I/O, and other IO signals. The user must provide adequate external decoupling capacitors.
power rail. The user must provide adequate external decoupling capacitors.
DD
power rail. The user must provide adequate external decoupling capacitors.
DD
power rail. The user must provide adequate decoupling capacitors.
DD
power rail. This is an isolated power for the SHI, SHI_1, ESAI, ESAI_1, ESAI_2, ESAI_3,
DD
2.2.2 Ground
Table 2-4. Ground Pins
Ground Name Description
PLLA_GND
PLLP_GND
PLLA1_GND
PLLP1_GND
PLL Ground
The PLL ground should be provided with an extremely low-impedance path to ground. The user must provide
adequate external decoupling capacitors.
PLLD_GND
PLLD1_GND
CORE_GND Core Ground
IO_GND I/O Ground
GND Ground
Freescale Semiconductor 2-5
PLL Ground
The PLL ground should be provided with an extremely low-impedance path to ground. The user must provide
adequate external decoupling capacitors.
The Core ground should be provided with an extremely low-impedance path to ground. This connection must
be tied externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate external decoupling
capacitors.
IO_GND is an isolated ground for the SHIs, ESAIs, Timer I/O and LIBU IO. This connection must be tied
externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate external decoupling
capacitors.
This connection must be tied externally to all other chip ground connections. The user must provide adequate
external decoupling capacitors.
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
Signal Descriptions
2.2.3 SCAN
Table 2-5. SCAN Signals
Signal
Name
SCAN Input Input SCAN
Type
State During
Reset
Manufacturing test pin. This pin should be pulled low.
Uses internal pull-down resistor.
2.2.4 Clock and PLL
Table 2-6. Clock and PLL Signals
Signal
Name
EXTAL Input Input External Clock / Crystal Input
XTAL Output Chip Driven Crystal Output
PLOCK Output MODC0
Type
State During
Reset
Input
An external clock source must be connected to EXTAL to supply the clock to the
internal clock generator and PLL.
Connects the internal Crystal Oscillator output to an external crystal. If an external
clock is used, leave XTAL unconnected.
PLL Lock/GPIO Port G Pin 0
During assertion of RESET
RESET
is de-asserted, the state of the PLOCK pin is latched into the Core-0 (MDC
of Core-0’s OMR). After RESET
when the internal PLL is locked.
Description
Description
, the PLOCK pin acts as a mode pin input, and when
is de-asserted, PLOCK is output “0”; and goes high
MODC0 Input MODC0
MODA0, MODB0, MODC0, and MODD0 levels select one of 16 initial chip operating
modes of DSP Core-0, and are latched into the DSP Core-0’s OMR when the
RESET
PG0 Input, Output,
Disconnected
PINIT/NMI
Input Input PLL Initial/Nonmaskable Interrupt for DSP Core-0
or
GPIO Port G0
When the PLOCK is configured as GPIO, this pin is individually programmable as
input, output, or internally disconnected.
Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
During assertion of RESET
(PEN) bit of the PLL control register, determining whether the PLL is enabled or
disabled.
After RESET
Schmitt-trigger input is a negative-edge-triggered nonmaskable interrupt (NMI)
request for DSP Core-0, internally synchronized to the internal system clock.
Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
signal is de-asserted.
, the value of PINIT/NMI is written into the PLL Enable
de-assertion and during normal instruction processing, the PINIT/NMI
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
2-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Signal Descriptions
2.2.5 Reset Pin
Assert Reset to low and then high, to force a reset of the DSP cores. Table 2-7 provides the Reset pin
description information.
Table 2-7. Reset Pin
Signal
Name
RESET
State During
Type
Input Input RESET is an active-low, Schmitt-trigger input. When asserted, the chip is placed in the Reset
Reset
state and the internal phase generator is reset. The Schmitt-trigger input allows a slowly rising
input (such as a capacitor charging) to reset the chip reliably. When the RESET
de-asserted, the initial two cores operating modes are latched from the MODA0, MODB0,
MODC0, MODD0, MODA1, MODB1, MODC1, and MODD1 inputs. The RESET
asserted during power up. A stable EXTAL signal must be supplied while RESET
asserted. Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
Description
signal is
signal must be
is being
2.2.6 Interrupt and Mode Control
The interrupt and mode control signals select the operating mode of the DSP cores as the cores come out
of hardware reset. After RESET is de-asserted, these inputs are used as hardware interrupt request lines.
Table 2-8. Interrupt and Mode Control
Signal Name Type
MODA0/IRQA
Input MODA0
State During
Reset
Input
Description
Mode Select A0/External Interrupt Request A
MODA0/IRQA
the DSP clock. MODA0/IRQA
hardware reset, and becomes a two-core shared, level-sensitive or
negative-edge-triggered, maskable interrupt request input during normal
instruction processing, This pin can also be programmed as GPIO.
MODA0, MODB0, MODC0, and MODD0 levels select one of 16 initial chip
operating modes, and are latched into the DSP Core-0’s OMR when the RESET
signal is de-asserted. If the processor is in the stop standby state and the
MODA0/IRQA
is an active-low Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to
selects the initial Core-0 operating mode during
pin is pulled to GND, the processor will exit the stop state.
PG5 In put, Output,
or
Disconnected
MODB0/IRQB
Freescale Semiconductor 2-7
Input MODB0
Input
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
GPIO Port G5
When the MODA0/IRQA
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected; and can be controlled
by either of the two cores. Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
Mode Select B0/External Interrupt Request B
MODB0/IRQB
the DSP clock. MODB0/IRQB
during hardware reset and becomes a two-core shared, level-sensitive or
negative-edge-triggered, maskable interrupt request input during normal
instruction processing. This pin can also be programmed as GPIO.
MODA0, MODB0, MODC0, and MODD0 levels select one of 16 initial chip
operating modes, and are latched into the DSP Core-0’s OMR when the RESET
signal is de-asserted.
is an active-low Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to
is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
selects the initial DSP Core-0 operating mode
Signal Descriptions
Table 2-8. Interrupt and Mode Control (Continued)
Signal Name Type
PG6 In put, Output,
or
Disconnected
MODA1/IRQC
PG7 In put, Output,
MODB1/IRQD
Input MODA1
or
Disconnected
Input MODB1
State During
Reset
Input
Input
Description
GPIO Port G6
When the MODB0/IRQB
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected; and can be controlled
by either of the two cores. Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
Mode Select A1/External Interrupt Request C
MODA1/IRQC
the DSP clock. MODA1/IRQC
during hardware reset and becomes a level-sensitive or negative-edge-triggered,
maskable interrupt request input during normal instruction processing. This pin
can also be programmed as GPIO.
MODA1, MODB1, MODC1, and MODD1 levels select one of 16 initial chip
operating modes, and are latched into the DSP Core-1 OMR when the RESET
signal is de-asserted.
GPIO Port G7
When the MODA1/IRQC
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected; and this signal can be
controlled by either of the two cores. Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
Mode Select B1/External Interrupt Request D
MODB1/IRQD
the DSP clock. MODB1/IRQD
during hardware reset and becomes a level-sensitive or negative-edge-triggered,
maskable interrupt request input during normal instruction processing. This pin
can also be programmed as GPIO.
MODA1, MODB1, MODC1, and MODD1 levels select one of 16 initial chip
operating modes, and are latched into the DSP Core-1 OMR when the RESET
signal is de-asserted.
is an active-low Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to
is an active-low Schmitt-trigger input, internally synchronized to
is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
selects the initial DSP Core-0 operating mode
is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
selects the initial DSP Core-1 operating mode
PG8 In put, Output,
or
Disconnected
Symphony DSP56724/DSP56725 Multi-Core Audio Processors, Rev. 0
GPIO Port G8
When the MODB1/IRQD
programmable as input, output, or internally disconnected; and can be controlled
by either of the two cores. Uses an internal pull-up resistor.
is configured as GPIO, this signal is individually
2-8 Freescale Semiconductor
 Loading...
Loading...