
Freescale Semiconductor
User Manual
Document Number:
MPC5604EEVB64UM
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation
board User Manual
For MPC5604E Evaluation/Validation
by: Pavel Bohacik
MSG Application Engineering
1 Introduction
The MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation Board (EVB) is
based on the e200z0 Power Architecture®. This board is
shipped with the PPC5604EEMLH 64-pin LQFP MCU
populated to allow the evaluation of the full functionality
of this part.
This board is designed as a validation platform with the
maximum flexibility. Where possible it is also designed
for power and speed but the primary goal of this system
is to allow main usecases of this processor.
2 References
• MPC5604ERM Reference Manual
• MPC5604E Data Sheet
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
3 EVB Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
4 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
5 Default Jumper Summary Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6 User Connector Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7 Known Bugs List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2011. All rights reserved.

EVB Features
3 EVB Features
The following is a list of evaluation board features:
MPC5604E External Interfaces
• Video Encoder Wrapper connected to Omnivision connector
• Serial Audio Interface connected to the Audio connector
• Onboard Ethernet physical interface plus MII lite connector
• Crystal / clock
• JTAG
• One LIN and one UART interface selectable through Jumper setting
• One FlexCAN interface
• External Interrupts
• ADC connector
NOTE
Before the EVB is used or power is applied, please read the complete
document on how to correctly configure the board. Failure to correctly
configure the board may cause irreparable component, MCU or VB
damage.
4 Configuration
This section details the configuration of each of the EVB functional blocks.
Throughout this document, all of the default jumper and switch settings are clearly marked with “(D)” and
are shown in blue text. This should allow a more rapid return to the default state of the EVB if required.
The EVB is designed with ease of use in mind and is segmented into functional blocks as shown below.
Detailed silkscreen legend is used throughout the board to identify all switches, jumpers and user
connectors.
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor2
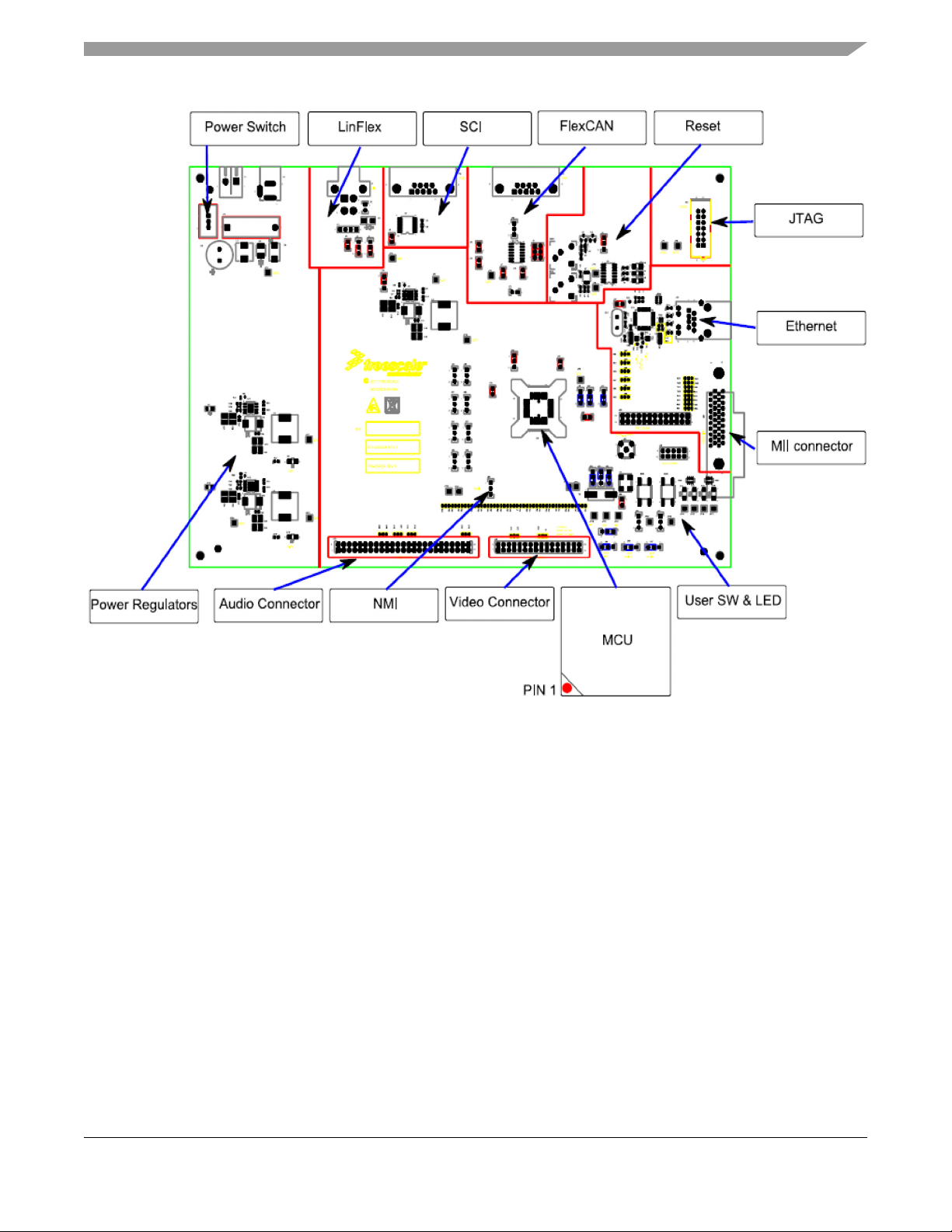
Configuration
Figure 1. Evaluation board silkscreen legend
4.1 Processor
The MPC5604E processor is the fundamental control chip on the MPC5604EEVB64. This is a version 1
Power Architecture running at a maximum core speed of 64 MHz. The MPC5604EEVB64 allows you to
fully evaluate the feature set of the MPC5604E MCU. Refer to Section 3, “EVB Features to review the list
of board features.
4.2 Power
The EVB requires an external power supply voltage of 12V DC, minimum 1A. This allows the EVB to be
easily used in a vehicle if required. The single input voltage is regulated on-board using switching
regulators to provide the necessary EVB and MCU operating voltages of 5.0 V, 3.3 V and 1.2 V. For
flexibility there are two different power supply input connectors on the EVB as detailed below.
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3
Configuration
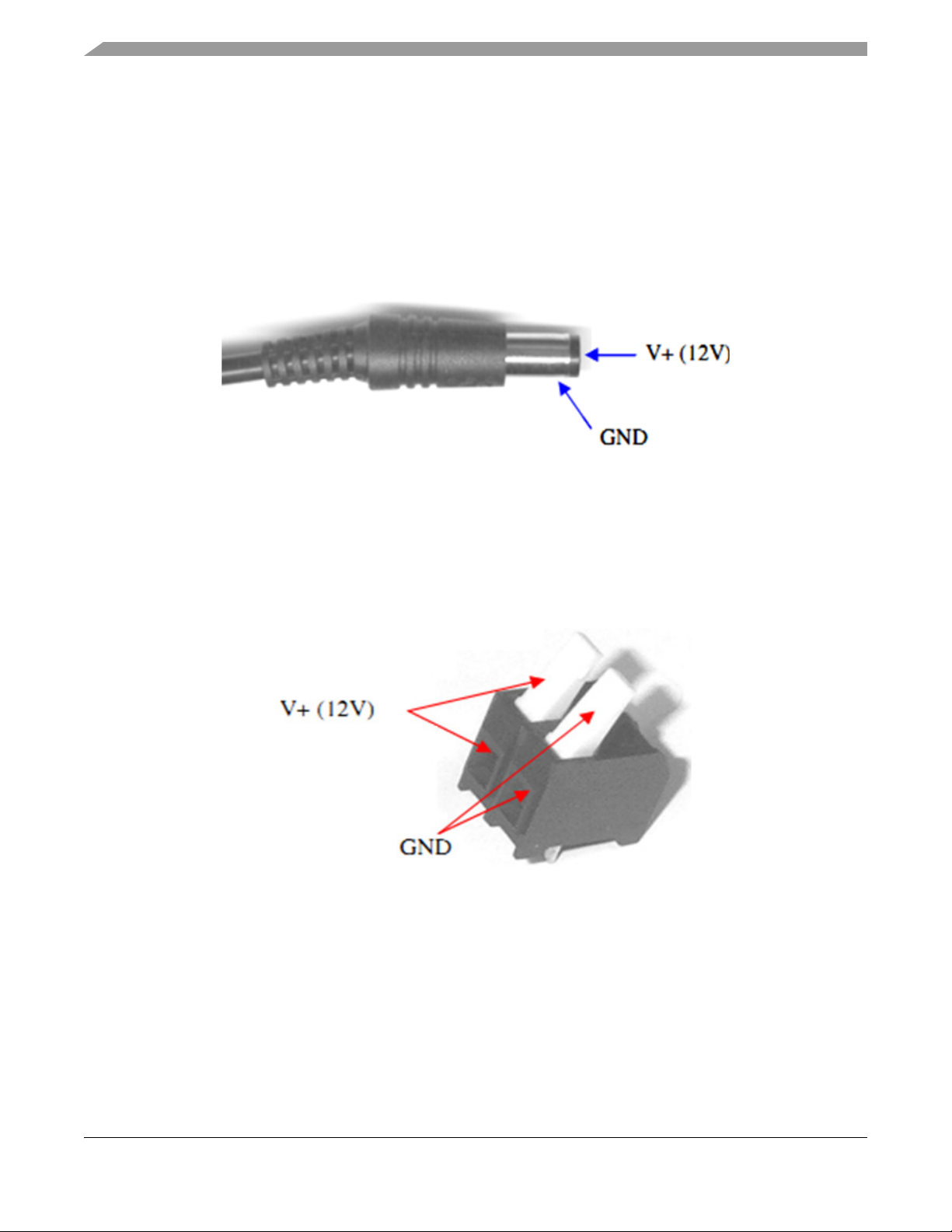
4.3 Power supply Connectors
2.1 mm Barrel Connector – P4:
This connector should be used to connect the supplied wall-plug mains adapter.
NOTE
If a replacement or alternative adapter is used, care must be taken to ensure
that the 2.1 mm plug uses the correct polarization as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. 2.1 mm Power Connector
2-Way Lever Connector – P1:
This can be used to connect a bare wire lead to the EVB, typically from a laboratory power supply. The
polarization of the connectors is clearly marked on the bottom site of the EVB. Care must be taken to
ensure correct connection.
Figure 3. 2-Level Power Connector
4.4 Power Switch (SW1)
Side switch SW1 can be used to isolate power supply input from the EVB voltage regulators if required:
• Position 1 will turn the EVB OFF
• Position 3 will turn the EVB ON
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor4
Configuration
4.5 Power Status—LEDs and Fuse
When Power is applied to the EVB, the Green Power LEDs adjacent to 5 V and 3.3 V of the voltage reg-
ulators show the presence of the supply voltage.
Green LED D9 = 3.3 V for EVB supply
Green LED D16 = 5 V for EVB supply
If there is no power to the MCU it is possible that either power switch SW1 is in the “OFF” position or
that the fuse F1 has blown. The fuse will blow if power is applied to the EVB in reverse-bias, where a
protection diode ensures that the main fuse blows rather than causing damage to the EVB circuitry. If the
fuse has blown, check the bias of your power supply connection then replace fuse F1 with a 20 mm 2 A
fast blow fuse.
4.6 MCU supply routing and Jumpers (J16, J18, J19, J20, J23)
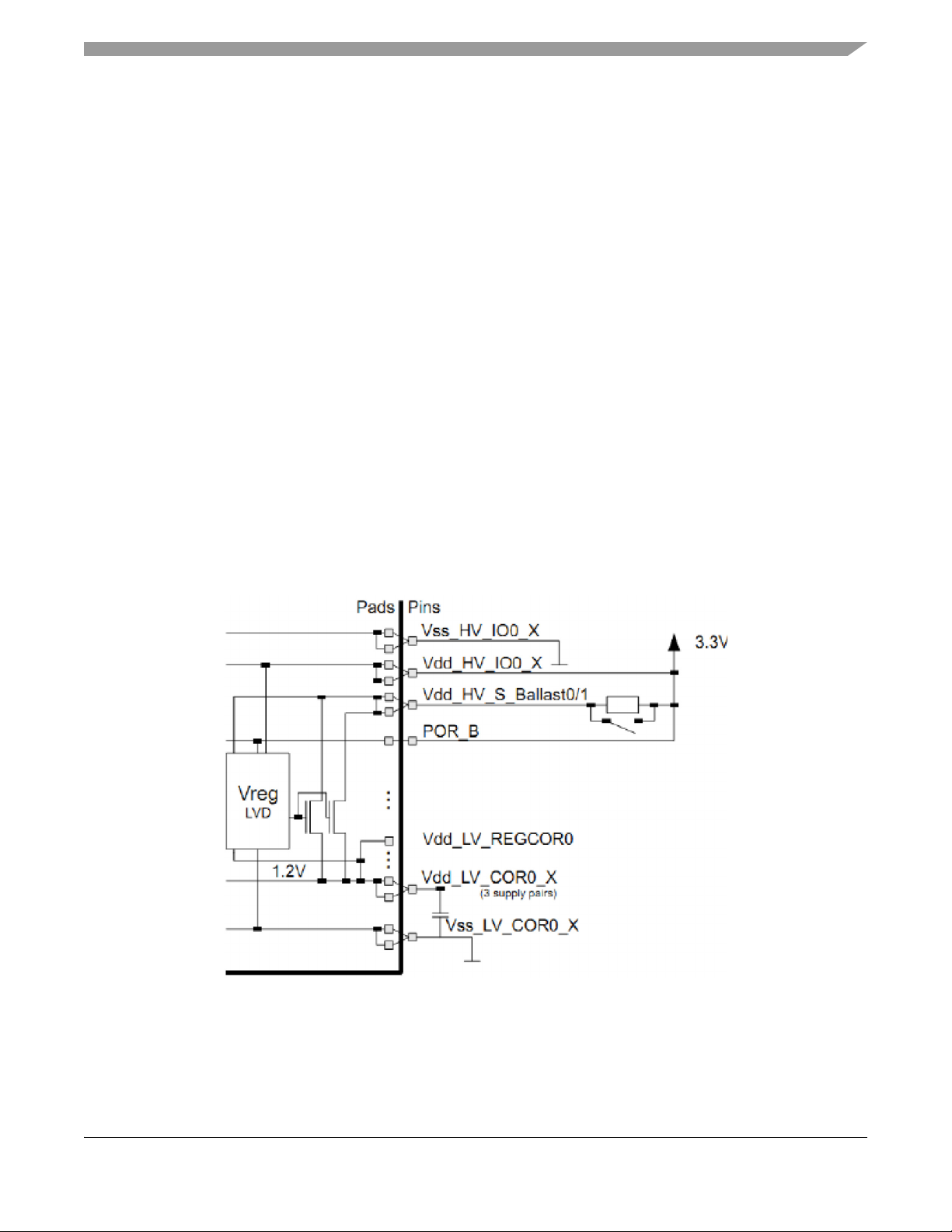
The EVB is designed to run the MCU at two supported regulation modes:
Internal regulation mode
In this mode the I/O supply, Ballast supply and ADC supply are at the same potential of typical 3.3 V
(+/- 10%). To reduce power dissipation on the chip, the possibilities of connecting the I/O supply with the
Ballast supply via a small resistor 2.5 is being explored. This will lead to the Ballast supply being lower
than the I/O supply.
Figure 4. Internal regulation mode
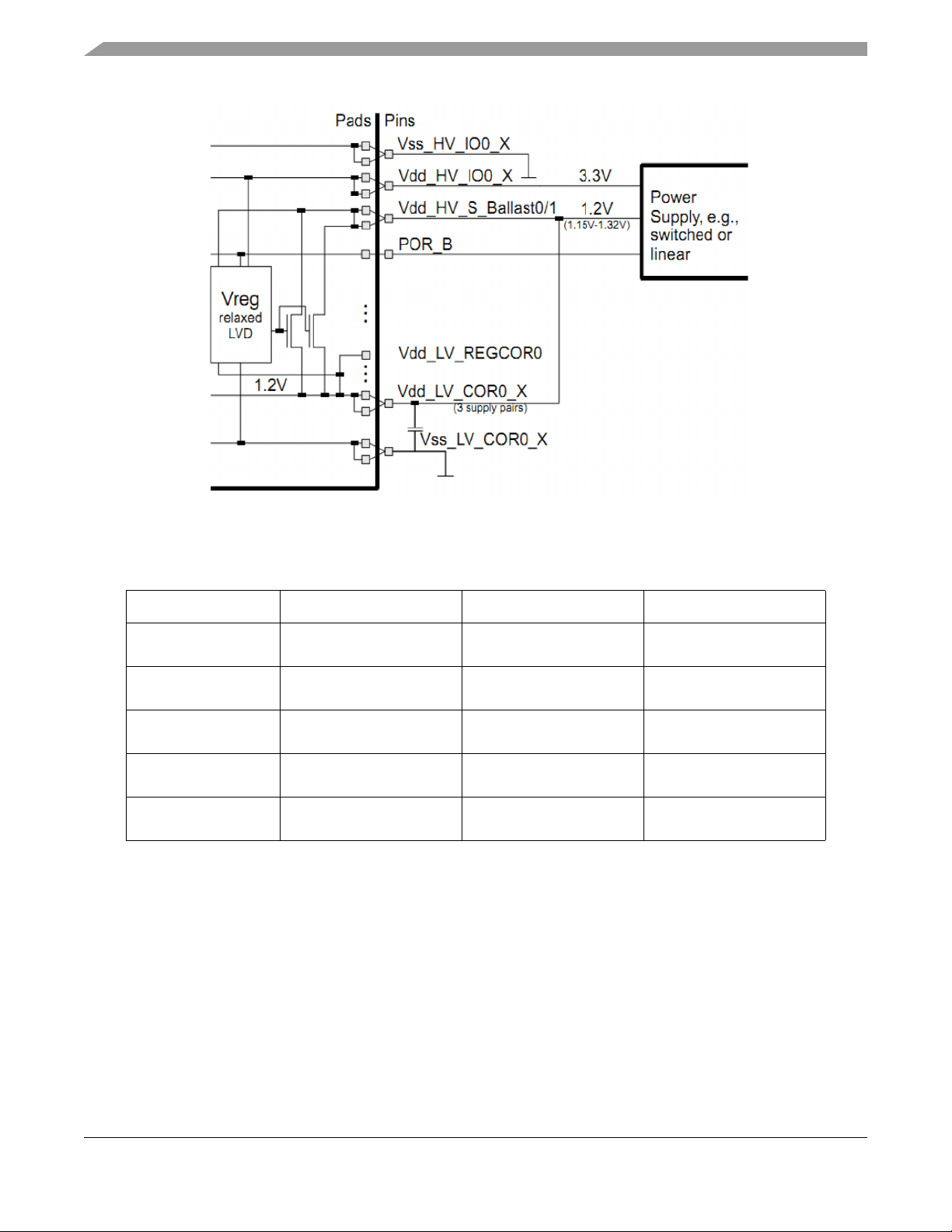
External regulation mode
In this mode, the Ballast supply is shorted to 1.2 V (+/-10%) generated from an external regulator. The I/O
supply and the MCU ADC supply continues to be at 3.3 V (+/-10%).
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 5
Configuration
Figure 5. External regulation mode
The FlexCAN circuity also has 5 V supplier to the transceiver.
Table 1. MCU Power Supply Jumpers – internal regulation mode
Power Domain Jumper Position Description
1.2 V J18
(VDD_LV)
3.3 V J19
(V_BALLAST_IN)
3.3 V J20
(V_BALLAST_IN_HDR)
3.3 V J16
(VDD_HV)
3.3 V J23
(VDD_HV_ADDR)
X This supplies VDD_LV
supply pins
1-2 This supplies
VDD_S_BALAST supply pin
2-3 (D) VDD_S_BALAST routed via
BALAST resistor
1-2 (D) This supplies VDD_HV
supply pins
1-2 (D) ADC reference voltage 3.3 V
The jumper configuration shown in Table 1, details the default state (D) of the EVB. In this configuration
all power is supplied from the regulators.
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor6
Table 2. MCU Power Supply Jumpers – external regulation mode
Power Domain Jumper Position Description
Configuration
1.2 V J18
(VDD_LV)
3.3 V J19
(V_BALLAST_IN)
3.3 V J20
(V_BALLAST_IN_HDR)
3.3 V J16
(VDD_HV)
3.3 V J23
(VDD_HV_ADR)
1-2 (D) This supplies VDD_LV
supply pins
2-3 (D) This supplies
VDD_S_BALAST supply
2-3 (D) VDD_S_BALAST routed via
BALAST resistor
1-2 (D) This supplies VDD_HV
supply pins
1-2 (D) ADC reference voltage 3.3 V
The jumper configuration shown in Table 2, details the default state (D) of the EVB. In this configuration
all power supplied from the regulators.
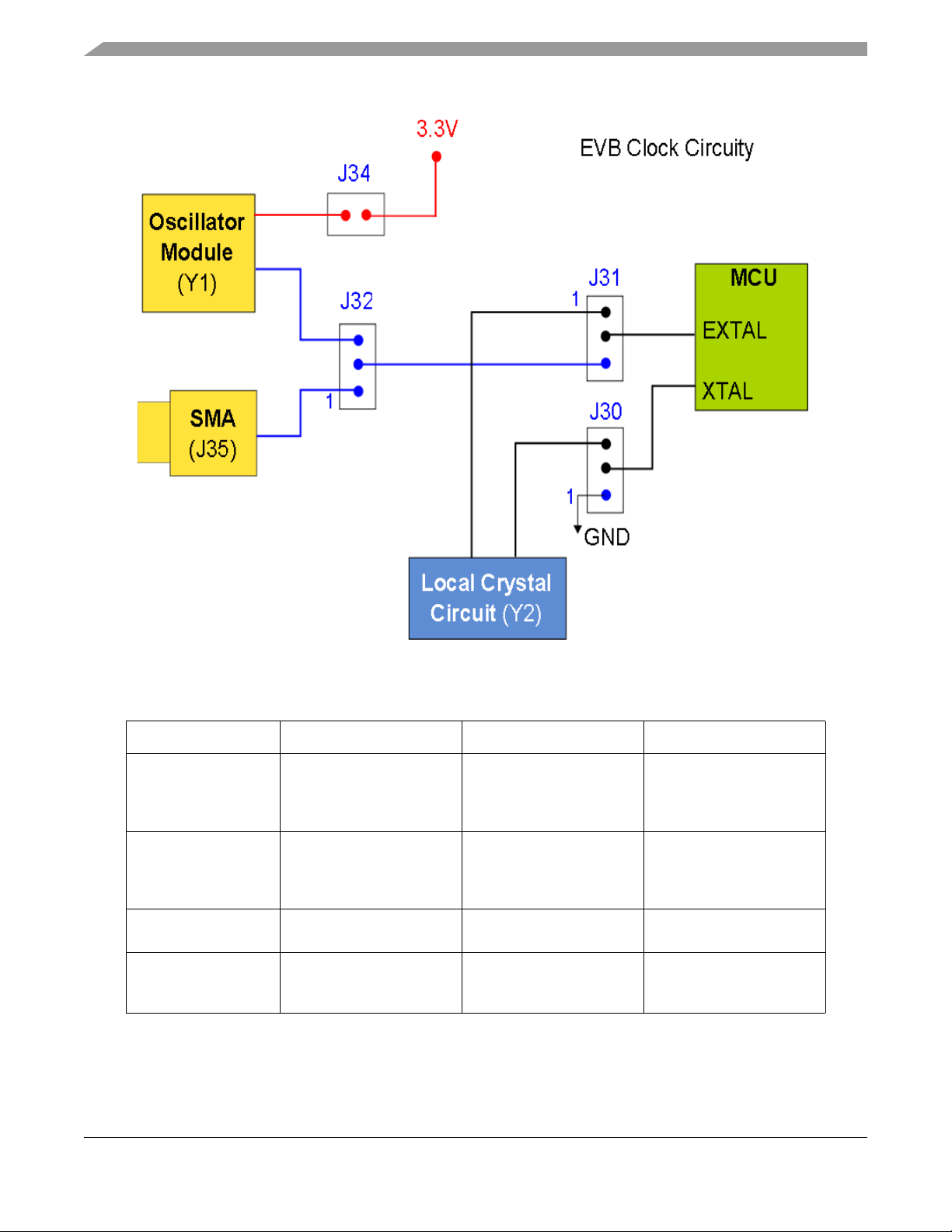
4.7 MCU clock control - Main Clock Selection (J30, J31, J32, J34)
EVB supports three possible MCU clock sources:
• The local 25 MHz oscillator circuit (Y2)
• An 8 MHz Oscillator module (Y1) on the EVB, driving the MCU EXTAL signal
• An external clock input to the EVB via the SMA connector, driving the MCU EXTAL signal
The clock circuity is shown in the diagram below. Please refer to the appropriate EVB schematic for
specific jumper numbers and circuity.
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Configuration
Table 3. Table Clock source jumper selection (J30, J31, J32, J34)
Jumper Position PCB Legend Description
J34 (Y1 PWR) FITTED (D)
REMOVED
J32 (OSC SEL) 1-2
2-3 (D)
J30
Must Match J31
J31
Must Match J30
1-2
2-3 (D)
1-2 (D)
2-3
Figure 6. EVB Clock Selection
EXTAL-SMA
OSC-MOD
Y2
GND
EVB-EXTAL
Y2
EVB oscillator module Y1 is
powered
EVB oscillator module Y1 is
not powered
SMA external square wave
input
8 MHz Oscillator is routed
from Y1
MCU clock is Y2 XTALIN
GND
MCU clock is selected by
J68
MCU clock is Y2 XTALOUT
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor8
Configuration
NOTE
The MPC5604E clock circuity is 3.3 V based. Any external clock signal
driven into the SMA connector must have a maximum voltage of 3.3 V.
4.8 Reset Boot Configuration (J44, J46, J47)
The MPC5604E has 3 boot configuration jumpers (BOOTCFG) that determine the boot location of the
MCU based at POR (Power On Reset). This is shown in the Table 4:
Table 4. BOOTCFG Control
J47 (FAB) J44 (ABS0) J46 (ABS2) Boot ID Boot Mode
1-2 2-3 2-3 — Serial Boot LinFlex
without autobaud
1-2 1-2 2-3 — Serial Boot FlexCAN
without autobaud
1-2 2-3 1-2 — Serial Boot via LinFlex
or FlexCAN in
autobaud
2-3 — — Valid SC (Single Chip)
2-3 — — Not Valid Safe Mode
4.9 NEXUS
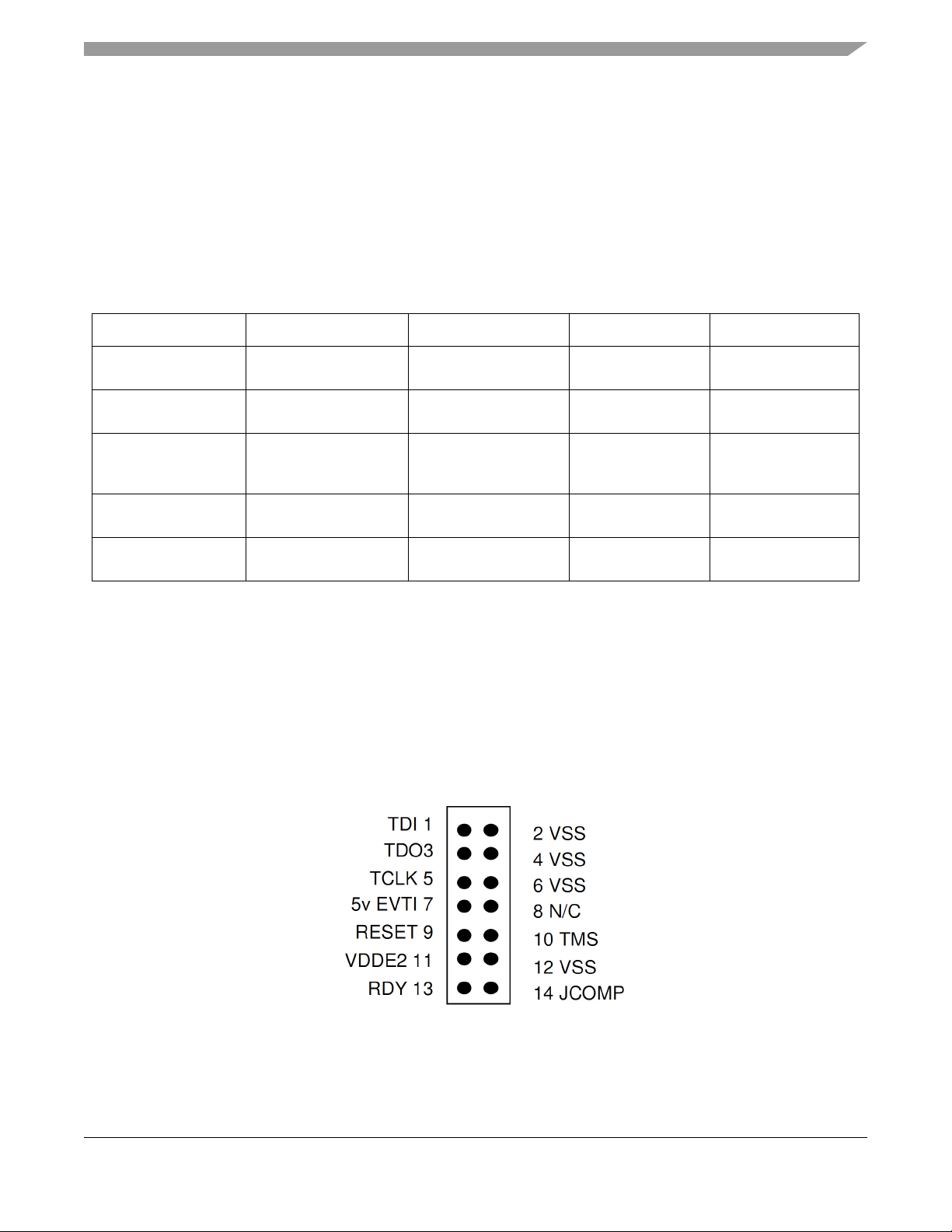
The EVB supports a standard JTAG cable with a 14-pin 0.1” walled header footprint.
4.9.1 Debug Connector Pinouts
The EVB is fitted with 14-pin JTAG connector. The following diagram shows the 14-pin JTAG connector
pin out (0.1” keyed header).
Figure 7. MPC5604E JTAG Connector
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Configuration
NOTE
In order to preserve the ability to accurately measure power consumption of
the MCU pins, the JTAG connector reference voltages will be sourced
directly from the 3.3 V regulator.
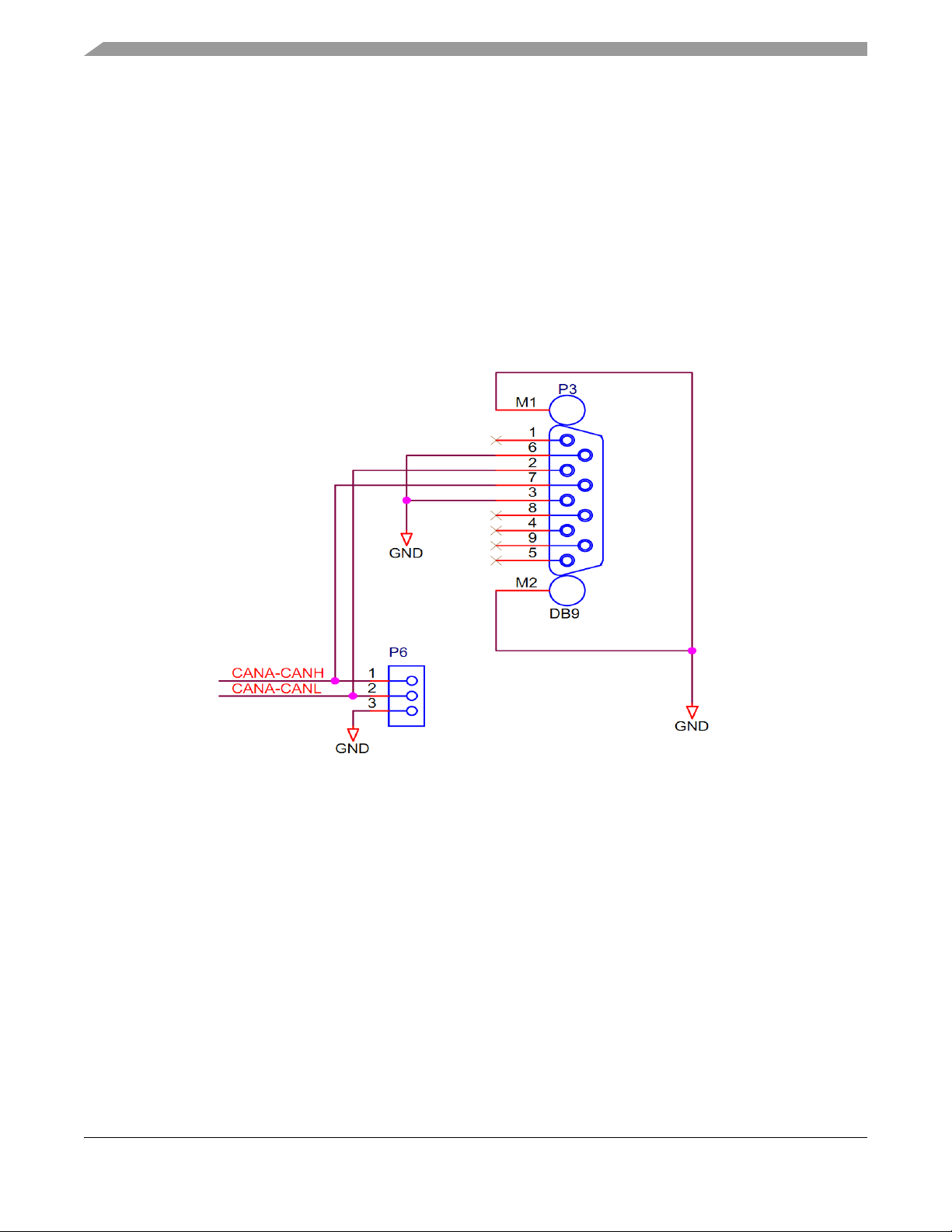
4.10 CAN Configuration (J10, J11, J12, J6, J9)
The EVB has one NXP TJA1041T high speed CAN transceiver on the MCU CAN channel. This can
operate with 3.3 V I/O from the MCU. For flexibility, the CAN transceiver I/O is connected to a standard
0.1” connector and DB9 connector at the top edge of the PCB. Connectors P6 and P3 provides the CAN
bus level signal interface for CAN-A. The pin out for these connectors is shown below.
Figure 8. CAN physical interface connector
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor10
Table 5. CAN Control Jumpers (J10, J11, J12, J6, J9)
Jumper Position PCB Legend Description
Configuration
J11 FITTED (D)
REMOVED
J12 FITTED (D)
REMOVED
J6 FITTED (D)
REMOVED
J10 FITTED (D)
REMOVED
J9
Position 1-2
J9
Position 3-4
J9
Position 5-6
FITTED (D)
REMOVED
FITTED (D)
REMOVED
FITTED (D)
REMOVED
• 5 V is applied to CAN
transceiver VCC
• No 5 V power is applied to
CAN transceiver
• 12 V Power is applied to
CAN transceiver VBAT
• No 12 V power is applied
to CAN transceiver
TX • MCU CAN_TXD is
connected to CAN
controller
• MCU CAN_TXD is NOT
routed to CAN controller.
RX • MCU CAN_RXD is
connected to CAN
controller
• MCU CAN_RXD is NOT
routed to CAN controller.
WAKE • CAN Transceiver WAKE
is connected to GND
• WAKE is not connected
and available on Pin 2
STB • CAN Transceiver STB is
connected to 5 V
• STB is not connected and
available on Pin 4
EN • CAN Transceiver is
Enabled
• EN is not connected and
available on Pin 6
Access to the Error and inhibit signals from the transceivers is provided on J14.
NOTE
You must do the fitting of the jumper headers carefully, as they can easily
be fitted in the incorrect orientation.
4.11 RS232 Configuration (J3, J7, J8)
The EVB has a single MAX3223 RS232 transceiver device, providing RS232 signal translation for the
MCU LINFlex channel.
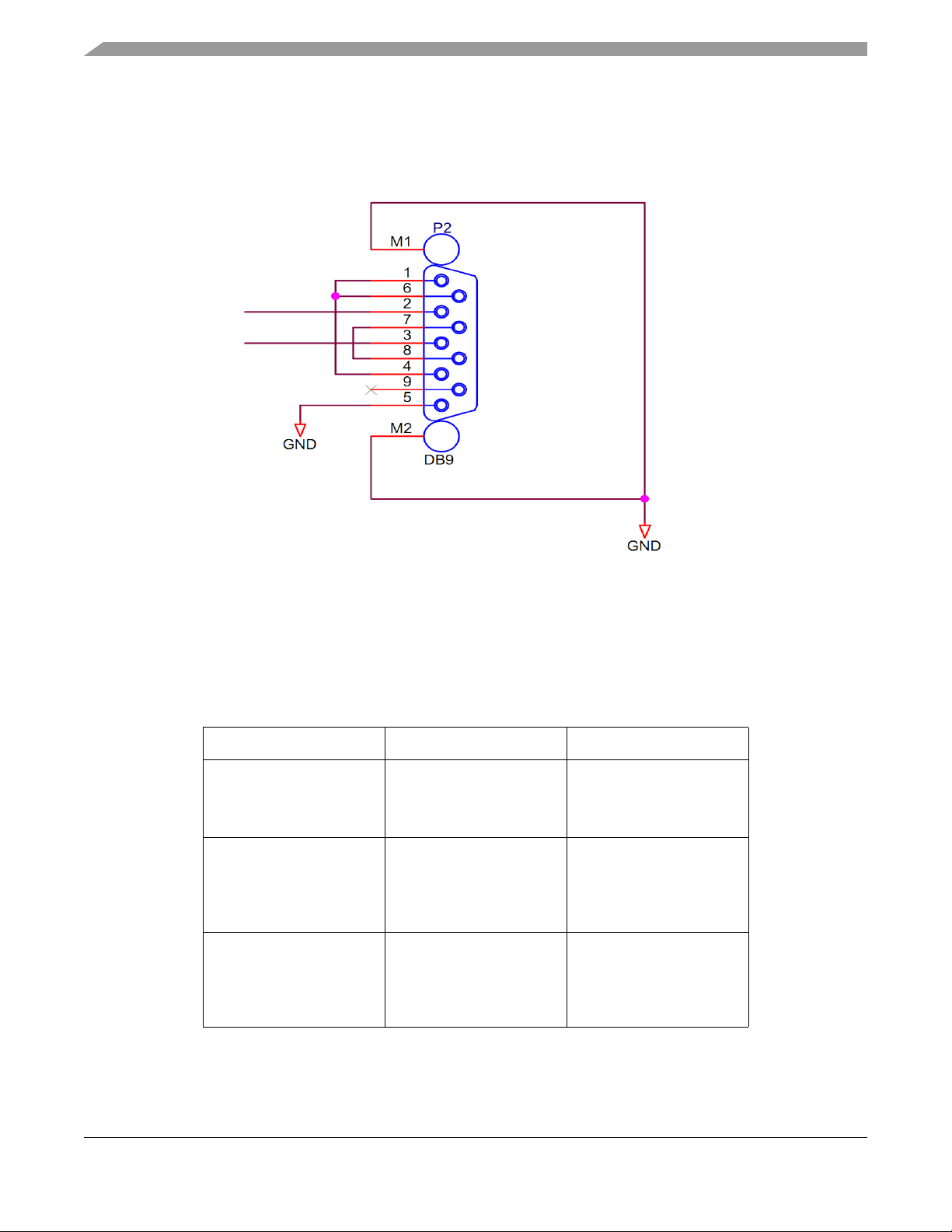
The RS232 output from the MAX3223 device is connected to a DB9 connector, allowing a direct RS232
connection to a PC or terminal. Connector P2 provides the RS232 level interface for MCU SCI (LINFlex).
The connector pinout is detailed below.
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 11
Configuration
NOTE
The hardware flow control is not supported on this implementation.
Figure 9. RS232 Physical Notifies Connector
The MPC5604E LINFlex also provides hardware LIN master capability which is supported on the EVB
via LIN transceiver. Jumpers J7 and J8 are provided to isolate the MCU LINFlex signals from the RS232
interface as described below. There is also a global power jumper (J3) controlling the power to the RS232
transceiver.
Table 6. RS232 Control Jumpers
Jumper Position Description
J3
(SCI-PWR)
J7 2-3 (D)
J8 2-3 (D)
FITTED (D)
REMOVED
REMOVED
REMOVED
• Power is applied to the
MAX3223 transceiver
• No power is applied to the
MAX3223 transceiver
• MCU TXD is routed to
MAX3223
• MCU TXD signal is
disconnected from
RS232/LIN
• MCU RXD is routed to
MAX3223
• MCU RXD signal is
disconnected from
RS232/LIN
The default configuration enables SCI. RS232 compliant interfaces (with no hardware flow control) are
available at DB9 connector P2. If the MCU is configured such that SCI is set as a normal I/O port, then
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor12

Configuration
the relevant jumpers must be removed to avoid any conflicts occurring. If required, jumper J3 can be used
to completely disable the SCI transceiver.
4.12 LIN Configuration (J2, J5, J7, J8)
The EVB is fitted with one Freescale MCZ33661EF LIN transceiver. The LINFlex module incorporates a
UART mode, and as such, the LIN transceiver are connected to the TX and RX signals of SCI via UART.
For flexibility, the LIN transceiver is connected to a standard 0.1” connector (P7) and to one pin molex
connector (J1) at the top edge of the PCB as shown in the figure below.
For ease of use, the 12 V EVB supply is fed to pin1 of the P7 header and the LIN transceiver power input
to pin 2. This allows the LIN transceiver to be powered directly from the EVB supply by simply linking
pins 1 and 2 of header P7 using a 0.1” jumper shunt.
** Ensure P7 is added before running LIN as it is not the default on the EVB
Figure 10. LIN physical Interface Connector P7
Along with the MCU signal routing jumpers (J7 / J8), there is jumper (J5) to enable or disable the LIN
transceiver and jumper (J2) which determines if the LIN transceiver is operating in master or slave mode,
as defined in the table below.
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 13

Configuration
Table 7.
Jumper Position Description
J2 FITTED
REMOVED (D)
J5* FITTED (D)
REMOVED
J7 2-3 (D)
1-2
J8 2-3 (D)
1-2
• LIN transceiver is
configured for LIN Master
mode
• LIN transceiver is
configured for LIN Slave
mode
• The LIN transceiver is
enabled
• The LIN transceiver is
disabled
• MCU LIN_TXD is
connected to SCI TX
• MCU LIN0_TXD is
connected to LIN Physical
• MCU LIN_RXD is
connected to SCI TX
• MCU LIN_RXD is
connected to LIN Physical
NOTE
Jumper J5 do not route power to LIN transceivers, they only control an
enable line on the LIN device. Power to the LIN transceiver is supplied via
connector P7, Pin 2.
The Default LIN configuration is with the module enabled in master mode, LIN slave mode can be enabled
by removing jumper J2.
4.13 Ethernet
4.13.1 Ethernet Physical Interface (J22)
The EVB is fitted with a National Semiconductor DP83848C Ethernet physical interface (U10) and a RJ45
connector with integrated activity LEDs and magnetics (J24).
The National Semiconductor DP83848C physical interface is connected to the MII on the MPC5604E.
This is a fixed connection with no means of isolation. Pullups are also present on some of these signals.
These are detailed in the table below. Please be aware of this when using the related GPIOs.
Table 8. Pull up/Pull down resistors for Ethernet Physical
Port Pin Pull Direction Strength
FEC_CRS Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_RX_ER Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_RX_DV Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_RXD0 Down (GND) 2.2 k
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor14

Configuration
Table 8. Pull up/Pull down resistors for Ethernet Physical
Port Pin Pull Direction Strength
FEC_RXD1 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_RXD2 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_RXD3 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_TX_EN Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_TXD0 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_TXD1 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_TXD2 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_TXD3 Down (GND) 2.2 k
FEC_MDC_PHY Up (3.3 V) 1.5 k
FEC_MDIO_PHY Up (3.3 V) 1.5 k
The voltage domain that is used by the GPIO should be set to 3.3 V when power is applied to the physical
interface. Power can be removed from the physical interface via J22.
Table 9. Ethernet Physical Interface Power Supply Enabled (J22)
Jumper Position PCB legend Description
J22
(PHY PWR)
FITTED (D)
REMOVED
PHY PWR • The DP83848C Ethernet
Physical Interface is
powered from the 3.3 V
SR.
• The DP83848C Ethernet
Physical Interface is not
powered.
4.13.2 Ethernet MII connector (J49)
An universal 40-pin MII Connector is also provided on the board to provide possibility to connect
customer Ethernet Physical Interface to MPC5604E interface signals. Since this connector is normally
used by the Ethernet PHY daughter cards of standard PHY vendors, this provides a flexibility of
supporting validation with multiple PHY vendors.
Connector pin definition is located in the Section 6.1, “FEC (J33, J49) below.
Following resistors must be populated to enable connection between MPC5604E and MII connector on
board:
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 15

Configuration
Table 10. Resistor configuration for MPC5604E MII interface routed to MII connector
Resistor to be
populated
R62 0
R60 0
R58 0
R56 0
R54 0
R53 0
R82 0
R84 0
R86 0
R88 0
R90 0
R92 0
R94 0
FEC_TX_CLK routed to FEC_TX_CLK_CONN
FEC_TX_EN routed to FEC_TX_EN_CONN
FEC_TXD0 routed to FEC_TXD0_CONN
FEC_TXD1 routed to FEC_TXD1_CONN
FEC_TXD2 routed to FEC_TXD2_CONN
FEC_TXD3 routed to FEC_TXD3_CONN
FEC_RXD3 routed to FEC_RXD3_CONN
FEC_RXD2 routed to FEC_RXD2_CONN
FEC_RXD1 routed to FEC_RXD1_CONN
FEC_RXD0 routed to FEC_RXD0_CONN
FEC_RX_DV routed to FEC_RX_DV_CONN
FEC_RX_CLK routed to FEC_RX_CLK_CONN
FEC_MDIO routed to FEC_MDIO_CONN
Value Description
4.14 Video Connector (J45)
EVB has a possibility to connect Camera module to Video connector (J45). Camera signals are then routed
to the Video Encoder Wrapper module of MPC5604E. Video connector fits to standard connector used on
Omnivision camera evaluation boards.
Connector pin definition is located in the Section 6.4, “VIDEO (J45) below.
Following resistors and capacitors have to be populated to enable connection between MPC5604E and
Video connector on board:
Tab l e 11.
Resistor and
capacitor to be
populated
R33 10
R26 10
R35 10
R28 10
R37 10
L4 75
R39 10
R41 10
R43 10
PORT_A0 routed to CON_VID_DATA11
PORT_A1 routed to CON_VID_DATA10
PORT_A2 routed to CON_VID_DATA9
PORT_A3 routed to CON_VID_DATA8
PORT_A4 routed to CON_VID_DATA7
PORT_A5 routed to CON_VID_CLK
PORT_A6 routed to CON_VID_VSYNC
PORT_A7 routed to CON_VID_HSYNC
PORT_A8 routed to CON_VID_DATA6
Value Description
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor16

Tab l e 11.
Resistor and
capacitor to be
populated
R31 10 PORT_A9 routed to CON_VID_DATA5
R45 10
PORT_A10 routed to CON_VID_DATA4
Value Description
Configuration
R47 10
R49 10
R77 10
L6 75
PORT_A11 routed to CON_VID_DATA3
PORT_A12 routed to CON_VID_DATA2
PORT_A15 routed to VID_PWDN
PORT_C4 routed to MC_RGM_ABS0
Most of the Omnivision camera evaluation boards are configured via I2C interface. For this purpose J27,
J28, J39 and J37 should be connected correctly. For pin definitions see Section 6.8, “I2C clock selection
(J27, J28, J36, J37, J39, J40).
4.14.1 Audio Connector
EVB has a possibility to connect Sahara SGTL5000 daughter card to Audio connector J48. Audio signals
are routed to Serial Audio Interface module of MPC5604E.
Connector pin definition is located in the Section 6.3, “Audio (J48) below.
Following resistors and capacitors have to be populated to enable connection between MPC5604E and
Audio connector on board.
Table 12.
Resistor and
capacitor to be
populated
Value Description
R64 0 PORT_C3 routed to ETC1
R66 0
R32 0
R25 0
R34 0
R27 0
R36 0
R29 0
R38 0
R40 0
R42 0
R30 0
R44 0
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 17
PORT_C2 routed to ETC0
PORT_A0 routed to SAI0_DATA0
PORT_A1 routed to SAI0_DATA1
PORT_A2 routed to SAI0_DATA2
PORT_A3 routed to SAI0_DATA3
PORT_A4 routed to SAI0_SYNC
PORT_A5 routed to SAI1_SYNC
PORT_A6 routed to SAI2_SYNC
PORT_A7 routed to SAI0_BCLK
PORT_A8 routed to SAI2_DATA0
PORT_A9 routed to SAI2_BCLK
PORT_A10 routed to SAI2_MCLK

Default Jumper Summary Table
Resistor and
capacitor to be
populated
R70 0 PORT_B1 routed to SAI1_DATA0
R72 0
Table 12.
Value Description
PORT_B0 routed to SAI1_BCLK
R76 0
R78 0
PORT_A15 routed to SAI1_MCLK
PORT_C4 routed to SAI0_MCLK
Sahara SGTL5000 audio daughter card uses I2C interface for configuration. For this purpose J27, J28, J39
and J37 should be connected correctly. For pin definitions see Section 6.8, “I2C clock selection (J27, J28,
J36, J37, J39, J40).
5 Default Jumper Summary Table
Table 13. Default Jumper Positions
Jumper
Reference
J2 REMOVED 1 Master Mode Pullup disable
J3 1-2 1 Power on SCI is enabled
J4 1-2 1 Power for User switches is disabled
J5 1-2 1 Power on LIN is enabled
J6 1-2 1 CAN TXD is connected to MCU
J7 2-3 1 UART TXD is connected to MCU
J8 2-3 1 UART RXD is connected to MCU
Default Setting
Jump
Count
Description
J9 1-2
3-4
5-6
J10 1-2 1 CAN RXD is connected to MCU
J11 1-2 1 Power on CAN PHY is enabled
J12 1-2 1 Power on CAN PHY is enabled
J13 2-3 1 1.2 power supply switch is supplied from 12 V
J15 1-2 1 VPP_TEST should be grounded
J16 1-2 1 VDD_HV is enabled
J18 1-2 1 VDD_LV is enabled (external regulation
J19 2-3 1 VDD_BALAST is powered from 1.2 V
J20 2-3 1 VDD_BALAST_IN resistor is connected
J21 2-3 1 JTAG_RST is connected to Ethernet PHY
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
3 CAN control signals are on
mode)
(external regulation mode)
Freescale Semiconductor18

Table 13. Default Jumper Positions
User Connector Descriptions
Jumper
Reference
J22 1-2 1 Power on Ethernet PHY is enabled
J23 1-2 1 Power on VDD_HV_ADR is enabled
J30 2-3 1 Use on board 8.0 MHz crystal
J31 1-2 1 Use on board 8.0 MHz crystal
J32 2-3 1 Use on board 8.0 MHz crystal
J34 1-2 1 Use on board 8.0 MHz crystal
J41 1-2 1 3.3 V connected to FEC MII connector
J44 2-3 1 MC_RGM_ABS0 is tied to ground
J46 2-3 1 MC_RGM_ABS2 is tied to ground
J47 2-3 1 MC_RGM_FAB is tied to ground
Default Setting
Jump
Count
Description
6 User Connector Descriptions
This section details the pinout of the EVB user connectors. The connectors are 0.1 inch pitch turned pin
headers and are located at various locations on the EVB. They are grouped by port functionality and the
PCB legend shows the respective port number adjacent to each pin.
6.1 FEC (J33, J49)
Table 14. FEC Connector Pinout (J33)
Pin Function
1GND
2GND
3 FEC_TXD3
4 FEC_RXD2
5 FEC_TXD2
6 FEC_RXD3
7 FEC_TXD0
8 FEC_RXD1
9 FEC_TXD1
10 FEC_RXD0
11 FEC_TX_CLK
12 EC_RX_CLK
13 GND
14 GND
15 FEC_TX_EN
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 19

User Connector Descriptions
Table 14. FEC Connector Pinout (J33)
Pin Function
16 NC
17 NC
18 NC
19 GND
20 GND
21 FEC_MDC
22 NC
23 FEC_MDIO
24 FEC_RX_DV
25 GND
26 GND
Table 15. MII Connector Pinout (J49)
Pin Function
1 POWER_MII_CONN
2MDIO
3MDC
4RXD3
5RXD2
6RXD1
7RXD0
8RXDV
9RXCLK
10 RXER
11 TXER
12 TXCLK
13 TXEN
14 TXD0
15 TXD1
16 TXD2
17 TXD3
18 COL
19 CRS
20 POWER_MII_CONN
21 POWER_MII_CONN
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor20

Table 15. MII Connector Pinout (J49) (continued)
Pin Function
22 GND
23 GND
24 GND
25 GND
26 GND
27 GND
28 GND
29 GND
30 GND
31 GND
32 GND
33 GND
34 GND
35 GND
36 GND
37 GND
User Connector Descriptions
38 GND
39 GND
40 POWER_MII_CONN
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 21

User Connector Descriptions
6.2 ADC(J38)
6.3 Audio (J48)
Table 16. ADC Connector Pinout (J38)
Pin Function
1GND
2GND
3 ADC0_AN[11]
4 ADC0_AN[13]
5GND
6GND
7 ADC0_AN[12]
8 ADC0_AN[14]
9GND
10 GND
Table 17. Audio Connector Pinout (J48)
Pin Function
1 3.3 V
2GND
3 SAI0_DATA3
4GND
5 SAI0_DATA2
6GND
7 SAI0_DATA1
8GND
9 SAI0_DATA0
10 GND
11 SAI0_BCLK
12 GND
13 SAI0_SYNC
14 GND
15 SAI0_MCLK
16 GND
17 ETC2/AN14 (ADC signal)
18 GND
19 AUD_IIC1_CLK
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor22

Table 17. Audio Connector Pinout (J48) (continued)
Pin Function
20 GND
21 AUD_IIC1_DATA
22 GND
23 SAI1_D0
24 GND
25 SAI1_BCLK
26 GND
27 ETC1
28 GND
29 SAI1_SYNC
30 GND
31 SAI1_MCLK
32 GND
33 AUD_IIC0_CLK
34 GND
35 AUD_IIC0_DATA
User Connector Descriptions
36 GND
37 SAI2_DATA0
38 GND
39 SAI2_BCLK
40 GND
41 SAI2_SYNC
42 GND
43 SAI2_MCLK
44 GND
45 ETC0
46 GND
47 AN13(ADC signal)
48 GND
49 5V
50 GND
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 23

User Connector Descriptions
6.4 VIDEO (J45)
Table 18. Video Connector Pinout (J45)
Pin Function
1 CON_VID_DATA4
2 CON_VID_DATA5
3 CON_VID_DATA6
4 CON_VID_DATA7
5 CON_VID_DATA8
6 CON_VID_DATA9
7 CON_VID_DATA10
8 CON_VID_DATA11
9VID_PWDN
10 NC
11 VID_IIC_DATA
12 NC
13 VID_IIC_CLK
14 CON_VID_HSYNC
15 GND
16 CON_VID_VSYNC
17 GND
18 CON_VID_CLK
19 MC_RGM_ABS0
20 5 V
21 GND
22 5 V
23 CON_VID_DATA2
24 CON_VID_DATA3
25 NC
26 NC
27 NC
28 NC
29 NC
30 NC
31 GND
32 GND
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor24

6.5 NMI (J29)
6.6 LINFLEX (P7)
User Connector Descriptions
Table 19. NMI Connector Pinout (J29)
Pin Function
1GND
2NMI
3 3.3 V
Table 20. LINFLEX Connector Pinout (P7)
Pin Function
112 V
2 LINC-VSUP
3LINC-LIN
4GND
6.7 FlexCAN (P6)
Table 21. FLEXCAN Connector Pinout (P6)
Pin Function
1CANH
2CANL
3GND
6.8 I2C clock selection (J27, J28, J36, J37, J39, J40)
Table 22. Routing IIC0 to Video Connector – video usecase
Signal description Jumper Reference Configuration Description
IIC 0 clock J25 2-3 Port_C5 routed to J39 as
IIC0_CLK signal
J39 1-2 IIC0_CLK signal routed to
J28
J28 2-3 IIC0_CLK is selected for
Video IIC clock
IIC 0 data J26 2-3 Port_C6 routed to J40 as
IIC0_DATA signal
J40 1-2 IIC0_DATA signal routed to
J37
J37 2-3 IIC0_DATA is selected for
Video IIC data
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 25

Known Bugs List
Table 23. Routing IIC1 to Video Connector – video usecase
Signal description Jumper Reference Configuration Description
IIC 1 clock J27 1-2 Port_A13 routed to J28
J28 1-2 IIC1_CLK signal is selected
for Video IIC clock
IIC 1 data J36 1-2 Port_A14 routed to J37
J37 1-2 IIC1_DATA signal is
selected for Video IIC data
Table 24. Routing IIC0 to Audio Connector – audio usecase
Signal description Jumper Reference Configuration Description
IIC 0 clock J25 2-3 Port_C5 routed to J39 as
IIC0_CLK signal
J39 2-3 IIC0_CLK signal selected for
Audio IIC clock
IIC 0 data J26 2-3 Port_C6 routed to J40 as
IIC0_DATA signal
J40 2-3 IIC0_DATA signal selected
for Audio IIC data
Table 25. Routing IIC1 to Video Connector – audio usecase
Signal description Jumper Reference Configuration Description
IIC 0 clock J27 2-3 IIC1_CLK signal is selected
for audio IIC clock
IIC 0 data J36 2-3 IIC1_DATA signal is
selected for audio IIC data
7 Known Bugs List
None
8 Schematic Diagrams
This section shows the schematic diagram of the MPC5604EEVB64.
Following are the topics covered in the schematic:
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor26

Table 26. Schematic sections
Power section Sheet 2
Resistor MUX Sheet 3
Video & Audio section Sheet 4
MII Connector section Sheet 5
Debug Interface section Sheet 6
Reset & Clock section Sheet 7
Ethernet Physical
Interface and RJ45
CAN Physical Interface Sheet 9
LIN & SCI Physical
Interface
MPC5604E SoC Sheet 11
LED & Switch section Sheet 12
User I/O connectors Sheet 13
Sheet 8
Sheet 10
Schematic Diagrams
MPC5604EEVB64 Evaluation board User Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 27

5
4
3
2
1
JP11
JP3
JP20
JP2
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
8
3
6
7
3.3V
1
1
1
1
JP21
JP5
JP6
JP18
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
Distribute Evenly over the board
D10
21
1N4148WS
C33
U12
2
BST
1
EPAD
0.1UF
SW
5
5VFB3V3_FB
FB
4
GND
2 1
IN
VCC
PG
EN/SYNC
9
MP2380
5.0V
1
1
1
1
L5
1 2
D15
B530C
4.7UH
HDR 1X1
1
JP4
HDR 1X1
1
JP24
HDR 1X1
1
JP1
HDR 1X1
1
JP19
GND
5.0V
R23
40.2K
TP7
C37
0.1UF
R22
7.68K
12
12
C39
C38
47UF
47UF
1.2V
HDR 1X1
1
C32
1.0 UF
JP7
JP10
JP8
JP9
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
1
1
1
R24 100K
R50
10.0K
Power supply input and filter
2.1mm Barrel
Connector
P4
1
P1
CON 2 TB
2
3
1
A
2
B
GND
D D
2 Lever
Connector
SW1
25136N
1 2 3
POWER SWITCH
F1
VSwitched VFused12V-IN
0.1UF
1 2
Fuse Holder
C509
C508
1000PF
D2 B130LB-13
2 1
Power Supply 3.3V
D7
1N4148WS
P12V
C C
C26
C28
C27
10UF
GND GND
10UF
0.1UF
C24
1.0 UF
R19 100K
10.0K
8
3
6
7
IN
VCC
PG
EN/SYNC
9
EPAD
MP2380
C25
U11
0.1UF
2
BST
1
3V3_L
SW
5
FB
4
GND
21
1 2
2 1
4.7UH
D8
B530C
+
L3
Main Power-In
L1
47UH
C3
68UF
TP6
P12V
+
C4
1000UF
GND
Power Supply 5.0 V
P12V
C34
10UF
GND GND
C36
C35
0.1UF
10UFR20
R18
40.2K
R17
13K
C29
0.1UF
3.3V
12
12
C31
C30
47UF
47UF
D9
LED GREEN
R21
100
5.0V
AC
4
D16
LED GREEN
R79
249
P12V
Power Supply 1.2V
J13
3
2
1
HDR TH 1X3
5.0V
VIN_VREG_1_2V
C12
10UF
C13
0.1UF
C11
10UF
GND GND
3
C9
1.0 UF
R7 100K
R8
10.0K
8
3
6
7
IN
VCC
PG
EN/SYNC
2
9
EPAD
MP2380
C10
U8
2
BST
1
SW
5
FB
4
GND
0.1UF
1 2
D6
B530C
2 1
4.7UH
L2
TP1
R6
162K
1.2VFB
C14
0.1UF
R5
324K
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
POWER SECTION
POWER SECTION
POWER SECTION
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
1.2V
12
12
C15
C16
47UF
47UF
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
___ ___
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
2 13
2 13
2 13
3.3V
AC
B B
GND GN D
A A
5

5
10
PORT_A0pg(11)
PORT_A1pg(11)
D D
PORT_A2pg(11)
PORT_A3pg(11)
PORT_A4pg(11)
C C
PORT_A5pg(11)
PORT_A6pg(11)
PORT_A7pg(11)
B B
A A
PORT_A8pg(11)
PORT_A9pg(11)
PORT_A10pg(11)
PORT_A11pg(11)
10
75 OHM
R32 0 DNP
R25 0 DNP
10
R34 0 DNP
10
R27 0 DNP
10
1 2
10
10
10
10
10
R33
R26
R35
R28
R37
R36 0 DNP
L4
R29 0 DNP
R39
R38 0 DNP
R41
R40 0 DNP
R43
R42 0 DNP
R31
R30 0 DNP
R45
R44 0 DNP
10
R47
R46 0 DNP
4
CON_VID_DATA11 pg(4)
SAI0_DATA0 pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA10 pg(4)
SAI0_DATA1 pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA9 pg(4)
SAI0_DATA2 pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA8 pg(4)
SAI0_DATA3 pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA7 pg(4)
SAI0_SYNC pg(4)
CON_VID_CLK pg(4)
SAI1_SYNC pg(4)
CON_VID_VSYNC pg(4)
SAI2_SYNC pg(4)
CON_VID_HSYNC pg(4)
SAI0_BCLK pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA6 pg(4)
SAI2_DATA0 pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA5 pg(4)
SAI2_BCLK pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA4 pg(4)
SAI2_MCLK pg(4)
CON_VID_DATA3 pg(4)
JP12
1
HDR 1X1
3
PORT_A15pg(11)
PORT_B0pg(11,13) CAN0_TXD pg(9)
PORT_B2pg(11,13)
PORT_C2pg(11)
PORT_C3pg(11)
2
R77 0
R76 0 DNP
R73 0
R72 0 DNP
R71 0
R70 0 DNP
R75 0
R74 0 DNP
R69 0
R68 0 DNP
R67 0
R66 0 DNP
R65 0
R64 0 DNP
75 OHM
1 2
L6
R78 0 DNP
VID_PWDN pg(4)
SAI1_MCLK pg(4)
SAI1_BCLK pg(4)
CAN0_RXD pg(9)PORT_B1pg(11,13)
SAI1_DATA0 pg(4)
LIN0_TXD pg(10)
AN13 pg(4)
LIN0_RXD pg(10)PORT_B3pg(11,13)
ETC2_AN14 pg(4)
JP25
1
HDR 1X1
ETC0 pg(4)
JP26
1
HDR 1X1
ETC1 pg(4)
MC_RGM_ABS0 pg(4,7)PORT_C4pg(11)
SAI0_MCLK pg(4)
1
10
R49
PORT_A12pg(11)
5
R48 0 DNP
4
CON_VID_DATA2 pg(4)
JP13
1
HDR 1X1
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
RESISTOR MUX
RESISTOR MUX
RESISTOR MUX
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
3 13
3 13
3 13

5
4
3
2
1
IIC1_CLK
PORT_A13pg(11)
IIC1_DATA
PORT_A14pg(11)
IIC0_CLK
IIC0_CLKpg(4)
IIC0_DATA
IIC0_DATApg(4)
3.3V
SAI0_DATA3pg(3)
SAI0_DATA2pg(3)
SAI0_DATA1pg(3)
SAI0_DATA0pg(3)
SAI0_BCLKpg(3)
SAI0_SYNCpg(3)
SAI0_MCLKpg(3)
ETC2_AN14pg(3)
AUD_IIC1_CLKpg(4)
AUD_IIC1_DATApg(4)
SAI1_DATA0pg(3)
SAI1_BCLKpg(3)
ETC1pg(3)
SAI1_SYNCpg(3)
SAI1_MCLKpg(3)
AUD_IIC0_CLKpg(4)
AUD_IIC0_DATApg(4)
SAI2_DATA0pg(3)
SAI2_BCLKpg(3)
SAI2_SYNCpg(3)
SAI2_MCLKpg(3)
ETC0pg(3)
5.0V
AN13pg(3)
3.3V
IIC0_CLK
3.3V
IIC0_DATA
AUD_IIC1_CLK
AUD_IIC0_CLK
AUD_IIC0_DATA
1
2
3
1
2
3
R540
4.7K
R539
4.7K
DNP
J45
CON_VID_DATA5pg(3) CON_VID_DATA4 pg(3)
CON_VID_DATA7pg(3)
CON_VID_DATA9pg(3)
5.0V
D D
Pin Numbering on this Omnivision mating connector
is mirror image of the numbering on the Omnivision
Daughter Card.
C C
B B
CON_VID_DATA11pg(3)
CON_VID_HSYNCpg(3)
CON_VID_VSYNCpg(3)
CON_VID_CLKpg(3)
CON_VID_DATA3pg(3)
6 5
HDR_2X16
GND
12
34
78
910
1112
VID_IIC_DATA
1314
VID_IIC_CLK AUD_IIC1_DATA
1516
1718
1920
2122
2324
2526
2728
2930
3132
OMNIVISION VIDEO INTERFACE
CON_VID_DATA6 pg(3)
CON_VID_DATA8 pg(3)
CON_VID_DATA10 pg(3)
VID_PWDN pg(3)
VID_IIC_DATA pg(4)
VID_IIC_CLK pg(4)
MC_RGM_ABS0 pg(3,7)
CON_VID_DATA2 pg(3)
VIDEO INTERFACE
DNP as female part required on EVB
J27
HDR TH 1X3
J36
HDR TH 1X3
J39
1
2
3
HDR TH 1X3
J40
1
2
3
HDR TH 1X3
J48
1 2
3 4
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
HDR_2X25
3.3V
R532
4.7K
3.3V
R537
4.7K
65
3.3V
R529
4.7K
AUD_IIC1_CLK
AUD_IIC1_DATA
AUD_IIC0_CLK
AUD_IIC0_DATA
GND
AUD_IIC1_CLK pg(4)
AUD_IIC1_DATA pg(4)
AUD_IIC0_CLK pg(4)
AUD_IIC0_DATA pg(4)
AUDIO INTERFACE
3.3V
R535
4.7K
HDR TH 1X3
J37
HDR TH 1X3
J28
1
2
VID_IIC_CLK
3
1
2
VID_IIC_DATA
3
VID_IIC_CLK pg(4)
VID_IIC_DATA pg(4)
MC_RGM_ABS2 pg(7)
HDR TH 1X3
1
IIC0_CLK
IIC0_DATA
2
3
HDR TH 1X3
1
2
3
J25
IIC0_CLK pg(4)
J26
IIC0_DATA pg(4)
MC_RGM_FAB pg(7)
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
VIDEO & AUDIO SECTION
VIDEO & AUDIO SECTION
VIDEO & AUDIO SECTION
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
4 13
4 13
4 13
PORT_C5pg(11)
A A
PORT_C6pg(11)
5
4
3

5
4
3
2
1
R52 0
FEC_TXD3pg(11)
R53 22
DNP
D D
FEC_TXD2pg(11)
FEC_TXD1pg(11)
FEC_TXD0pg(11)
C C
FEC_TX_ENpg(11)
FEC_TX_CLKpg(11)
FEC_MDCpg(11)
B B
5.0V
3
2
HDR TH 1X3
3.3V
A A
5
1
J41
R55 0
R54 22
DNP
R57 0
R56 22
DNP
R59 0
R58 22
DNP
R61 0
R60 22
DNP
R63 0
R62 22
DNP
R93 0
R80 22
DNP
FEC_MDIO_CONNpg(5)
FEC_MDC_CONNpg(5)
FEC_RXD3_CONNpg(5)
FEC_RXD2_CONNpg(5)
FEC_RXD1_CONNpg(5)
FEC_RXD0_CONNpg(5)
FEC_RX_DV_CONNpg(5)
FEC_RX_CLK_CONNpg(5)
FEC_TX_CLK_CONNpg(5)
FEC_TX_EN_CONNpg(5)
FEC_TXD0_CONNpg(5)
FEC_TXD1_CONNpg(5)
FEC_TXD2_CONNpg(5)
FEC_TXD3_CONNpg(5)
POWER_MII_CONN
4
GND
FEC_TXD2_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_TXD2_CONN pg(5)
FEC_TXD1_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_TXD1_CONN pg(5)
FEC_TXD0_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_TXD0_CONN pg(5)
FEC_TX_EN_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_TX_EN_CONN pg(5)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
RX_ER
11
TX_ER
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
COL
19
CRS
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
SH1
SH2
FEC_TXD3_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RXD3pg(11)
FEC_TXD3_CONN pg(5)
FEC_RXD2pg(11)
FEC_RXD1pg(11)
FEC_RXD0pg(11)
FEC_RX_DVpg(11)
FEC_TX_CLK_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RX_CLKpg(11)
FEC_TX_CLK_CONN pg(5)
FEC_MDC_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_MDIOpg(11)
FEC_MDC_CONN pg(5)
J49
5787170-4
3
R81 0
R82 0
DNP
R83 0
R84 0
DNP
R85 0
R86 0
DNP
R87 0
R88 0
DNP
R89 0
R90 0
DNP
R91 0
R92 0
DNP
R95 0
R94 22
DNP
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
FEC_RXD3_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RXD3_CONN pg(5)
FEC_RXD2_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RXD2_CONN pg(5)
FEC_RXD1_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RXD1_CONN pg(5)
FEC_RXD0_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RXD0_CONN pg(5)
FEC_RX_DV_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RX_DV_CONN pg(5)
FEC_RX_CLK_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_RX_CLK_CONN pg(5)
FEC_MDIO_PHY pg(8,13)
FEC_MDIO_CONN pg(5)
___ ___
___ ___
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MII CONNECTOR SECTION
MII CONNECTOR SECTION
MII CONNECTOR SECTION
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
X
X
5 13
5 13
5 13

5
D D
4
3
2
1
Place CAPS as close to
connector pins as
possible but do NOT fit
caps at board assembly.
C506
3.3V
R507
10.0K
R506
10.0K R505
JCOMPpg(7)
TMSpg(11)
TDI
TDO
TCK
JTAG-RST_B
TDIpg(11)
C C
B B
TDOpg(11)
TCKpg(11)
JTAG-RST_Bpg(7,8,11)
JCOMP
TMS
10.0K
3.3V
R503
10.0K
DNP
47PF
C504
DNP
47PF
GND
JTAG Connector
11 12
13 14
P5
1 2
3 4
7 8
9 10
CON_2X7
65
JTAG INTERFACE
3.3V
(VSS)
(VSS)
(VSS)
(N/C)
TMS
(VSS)
JCOMP
GND
R500
10.0K
R501
10.0K
DNP
A A
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
5
4
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
DEBUG INTERFACE
DEBUG INTERFACE
DEBUG INTERFACE
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
6 13
6 13
6 13

5
4
3
2
REMOVE XTAL jumper when driving EXTAL from
Oscillator Module or External Source
1
Power On Reset
D D
KS11R23CQD
1.2V
5.0V
R511
12K
R510
2K
C C
GND
Boot Config
B B
HDR TH 1X3
GND
J47
123
R544
4.7K
C8
0.1UF
SW2
3.3V
1
3
4 2
GND
C7
0.1UF
GND
3.3V
R543
4.7K
MC_RGM_FAB pg(4)
4
3
C5
0.1UF
SW3
KS11R23CQD
9 8
U4
VCC
MR
STM6315RDW13F
1
3
4 2
U6D
74LVC14AD
2
RST
1
VSS
3.3V
R3 10.0K
2
U7
STM6904TGEDS6F
3
V2IN
5
V3IN
VCC
6
V4IN
TRSEL
MR
VSS
4
U6E
11 10
74LVC14AD
3.3V
J44
123
R548
4.7K
RST
JCOMPpg(6)
R547
4.7K
MC_RGM_ABS0 pg(3,4)
7
1
C6
0.1UF
GND
HDR TH 1X3
GND
1
2
U2
3
BAS70
8
U3
2
BAS70
PW_ON_RESET_Bpg(8,11)
3
1
13 12
U6F
74LVC14AD
HDR TH 1X3
GND
3 4
JTAG-RST_B pg(6,8,11)
3.3V
J46
123
R546
4.7K
U6B
74LVC14AD
3.3V
147
U6A
VCC
1 2
GND
74LVC14AD
GND
J4
1
2
3
HDR TH 1X3
GND
U6C
5 6
74LVC14AD
R545
4.7K
MC_RGM_ABS2 pg(4)
R2
1.5K J31
AC
LED RED
D4
GND
R4
AC
1.5K
LED RED
D5
GND
R1
AC
1.5K
LED RED
D3
GND
Clock Circuit
C555
18pF
GND
Note - Internal
Pull-Up on Pin 1
SMA style
Connector
STRAIGHT SMA CONNECTOR ,PLACE NEAR TO SOC
Y2
25MHZ
1 2
C556
18pF
R536 0
GND
HDR TH 1X3
1
2
HDR TH 1X3
Y1
8MHz
4
R538 100
3
J30
1
2
3
GND
J34
OSC-MOD
EXTAL-SMA
EXTAL_J
R534
1.0M
XTAL_J
C554
0.01UF
1
E/D
GND2VCC
OUT
3
CON_1_SMA
2
3
1
4
5
J35
GND
EVB-EXTAL
(MCU Crystal Output)
(MCU Crystal Input)
HDR 1X2 TH
3.3V
1
2
HDR TH 1X3
EXTAL pg(11)
XTAL pg(11)
J32
123
EVB-EXTAL
A A
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
5
4
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
RESET & CLOCK SECTION
RESET & CLOCK SECTION
RESET & CLOCK SECTION
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
7 13
7 13
7 13

5
D D
4
3
2
1
Ethernet Section
3.3V
C C
TX Resistors: Place Cose to PI
RX Resistors: Place Close to MCU
FEC_TXD3_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_TXD2_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_TXD1_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_TXD0_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_TX_EN_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_TX_CLK_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_RXD3_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_RXD2_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_RXD1_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_RXD0_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_RX_DV_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_RX_ER
FEC_COL
FEC_CRS
B B
PW_ON_RESET_Bpg(7,11)
TP4
TP5
TP3
FEC_RX_CLK_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_MDC_PHYpg(5,13)
FEC_MDIO_PHYpg(5,13)
JTAG-RST_Bpg(6,7,11)
HDR TH 1X3
J21
3
2
1
1 8
RN3A
3 6
22
RN3C
4 5
RN3D
22
R521 22
R515 22
1 8
22
R16 22
RN2A
22
2 7
RN3B
GND GND
2 7
RN2B
22
1 8
RN4A
22
R527
R526
2.2K
2.2K
J22
C17
33PF
3 6
2 7
RN4B
22
R528
2.2K
HDR 1X2 TH
1
2
QZ1
25MHZ
RN2C
22
3 6
RN4C
22
R525
2.2K
C19
33PF
21
4 5
RN2D
R14 22
4 5
RN4D
22
R524
2.2K
EP_3.3V
C532
R517
1.5K
22
22
R522
R523
2.2K
R13
2.2K
2.2K
0.1UF
R519
1.5K
GND
QZ1_X1
QZ1_X2
R520
R518
2.2K
R516
2.2K
2.2K
C536
+
C23
10UF
0.1UF
U10 10/100 single phy
32
22
34
X1
33
AVDD33
X2
6
TXD3_SNIMODE
5
TXD2
4
TXD1
3
TXD0
2
TXEN
1
TXCLK
46
RXD3_PHYAD3
45
RXD2_PHYAD2
44
RXD1_PHYAD1
43
RXD0_PHYAD1
39
RXDV_MIIMODE
41
RXER_MDIXEN
42
COL_PHYAD0
40
CRS_LEDCFG
38
RXCLK
31
MDC
30
MDIO
29
RESET
7
PWRDN_INT
R514
2.2K
GND GND
AGND_215AGND_1
36
19
R11
R10
2.2K
2.2K
20
RSVDPU221RSVDPU1
IOVDD33_248IOVDD33_1
25MHZ_OUT
dp83848c
LEDACTCOL_ANEN
LEDLINK_AN0
LEDSPEED_AN1
IOGND_247IOGND_135DGND
8
These are 100MHz all lines must be matched and as short as possible
18
RN1A
49.9
PFBOUT
PFBIN1
PFBIN2
RBIAS
TP2
25
17
TDP
16
TDN
14
RDP
13
RDN
28
26
27
23
18
37
24
RSVD512RSVD411RSVD310RSVD29RSVD1
GND
C531
R9
0.1UF
4.7K
GND
C533
0.1UF
EP_PF
C21
0.1UF
C22
+
10UF
RN1B
49.9
2 7
36
RN1C
49.9
RN1D
49.9
4 5
C520
0.1UF
GND
C18
C529
0.1UF
0.1UF
GND
GND GND
ETDP
ETDN
ERDP
ERDN
C20
0.1UF
3.3V
R12
249
3.3V
R15
249
J24
1
TD+
2
TD-
3
CT-T
6
CT-R
7
RD+
8
RD-
9
RLEDA
10
RLEDK
11
LLEDK
12
LLEDA
RJ45-8
SHIELD1
SHIELD2
4
GND
CG1
CG2
GND
To RJ45 Port
CHSGND25CHSGND1
A A
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
ETHERNET PHYSICAL INTERFACE AND RJ45
ETHERNET PHYSICAL INTERFACE AND RJ45
ETHERNET PHYSICAL INTERFACE AND RJ45
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
5
4
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
8 13
8 13
8 13

5
D D
CAN interface
C C
4
J11
1
2
J12
3.3V
1
2
GND
HDR 1X2 TH
GND
HDR 1X2 TH
CAN-5V
C516
0.1UF
HDR 1X2 TH
J6
1
1
2
J10
CAN-12V
2
1 2
3 4
GND
C515
1000PF
J14 HDR 1X2 TH
J9
5.0V
P12V
HDR 1X2 TH
CAN0_RXDpg(3)
3.3V
C513
0.1UF
2
1
CANA-TX
CANA-RX
65
3
C511
C512
0.1UF
1000PF
GND
C514
1000PF
5
10
3
U5
7
VI/O
VCC
INH
8
VBAT
14
9
1
4
6
ERR
WAKE
TXD
RXD
STB
EN
TJA1041T
13
CANH
12
CANL
11
R508
SPLIT
GND
2
GND
60.4
CANA-CANH
CANA-CANL
R509
60.4
C510
0.01UF
GND
2
P3
M1
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
GND
P6
1
2
3
GND
5
M2
DB9
GNDCAN0_TXDpg(3)
1
B B
A A
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
5
4
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
CAN PHYSICAL INTERFACE
CAN PHYSICAL INTERFACE
CAN PHYSICAL INTERFACE
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
9 13
9 13
9 13

5
4
3
2
1
LIN Interface
J7
D D
C C
HDR TH 1X3
3
2
1
J8
HDR TH 1X3
3
2
1
UART_A_TX
UART_A_RX
LIN0_TXD pg(3)
LIN0_RXD pg(3)
J5
1
2
R504 10.0K
HDR 1X2 TH
LINC-RX
LINC-TX
3.3V
U500
1
RXD
2
EN
3
WAKE
TXD4GND
MCZ33661EF
VSUP
INH
LIN
J2
1
C500
1000PF
2
GND
8
7
6
5
GNDGNDGND
Master Mode Pullup Enable
HDR 1X2 TH
D1
2 1
N16966294
GF1A
C501
0.1UF
R502 1.0K
LINC-VSUP
LINC-LIN
P12V
P7
1
4Pin Header
2
3
4
HDR_1X4
GND
J1
1
2
3
LIN Molex Connector
4
CON PLUG 4
GND
SCI Interface
J3
3.3V
B B
UART_A_TX
UART_A_RX
1
C2
0.1UF
C1
0.1UF
2
HDR 1X2 TH
C505
0.1UF
P2
C507
1000PF
GND
U1
19
2
VCC
C1+
4
C1-
5
C2+
6
C2-
13
T1IN
12
T2IN
15
R1OUT
10
R2OUT
1
EN
14
FORCEON
GND
GND
18
INVALID
FORCEOFF
MAX3223
T1OUT
T2OUT
C503
3
V+
0.1UF
17
GND
8
16
R1IN
9
R2IN
3.3V
11
20
7
V-
C502
0.1UF
GND
M1
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
M2
GND
DB9
GND
GND
A A
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
5
4
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
LIN & SCI PHYSICAL INTERFACE
LIN & SCI PHYSICAL INTERFACE
LIN & SCI PHYSICAL INTERFACE
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
10 13
10 13
10 13

5
D D
4
3
C551
C550
0.1UF
C553
0.01UF
C552
1000PF
1000PF
GND GND GND
VDD_HV_ADR
C546
0.1UF
C549
0.01UF
C542
0.1UF
C548
1000PF
0.01UF
C547
C543
1000PF
C545
1000PF
2
VDD_HV
C544
1000PF
C517
0.1UF
C521
0.01UF
C519
1000PF
C518
1000PF
1
J16
HDR 1X2 TH
1
2
VDD_ADR
1
2
HDR 1X2 TH
J23
3.3V
VSSA
HDR 1X2 TH
1.2V
C C
B B
3.3V
R512 10.0K
PW_ON_RESET_Bpg(7,8)
J18
C534
C539
1000PF
C535
0.1UF
1000PF
JTAG-RST_B
PW_ON_RESET_B
NMI_B
0.1UF
C528
0.01UF
C537
C541
C538
1
2
0.1UF
0.1UF
3.3V
C540
0.01UF
GND GND GND
PORT_A0pg(3)
PORT_A1pg(3)
PORT_A2pg(3)
PORT_A3pg(3)
PORT_A4pg(3)
PORT_A5pg(3)
PORT_A6pg(3)
PORT_A7pg(3)
PORT_A8pg(3)
PORT_A9pg(3)
PORT_A10pg(3)
PORT_A11pg(3)
PORT_A12pg(3)
PORT_A13pg(4)
PORT_A14pg(4)
PORT_A15pg(3)
FEC_RXD3pg(5)
FEC_RX_CLKpg(5)
PORT_C2pg(3)
PORT_C3pg(3)
PORT_C4pg(3)
PORT_C5pg(4)
PORT_C6pg(4)
R531 10.0K
JTAG-RST_Bpg(6,7,8)
EXTALpg(7)
XTALpg(7)
TDOpg(6)
TCKpg(6)
TMSpg(6)
TDIpg(6)
NMI_Bpg(13)
C530
C522
1000PF
1000PF
U9
2
A[0]/VID_D[11]/DSPI1_SIN/EIRQ[0]/GPIO[0]/SAI0_D[0]
3
A[1]/VID_D[10]/EIRQ[1]/GPIO[1]/SAI0_D[1]/DSPI1_SOUT
4
A[2]/VID_D[9]/ETIMER0_ETC[5]/EIRQ[2]/GPIO[2]/SAI0_D[2]/DSPI1_SCK/SAI1_D[0]
5
A[3]/VID_D[8]/DSPI2_SIN/EIRQ[3]/GPIO[3]/SAI0_D[3]/SAI2_D[0]
8
A[4]/VID_D[7]/ETIMER0_ETC[3]/EIRQ[4]/GPIO[4]/SAI0_SYNC/DSPI2_SOUT
9
A[5]/VID_CLK/ETIMER0_ETC[4]/EIRQ[5]/GPIO[5]/SAI1_SYNC/DSPI2_SCK/SAI1_D[0]
10
A[6]/VID_D[0]/ETIMER0_ETC[1]/EIRQ[6]/GPIO[6]/SAI2_SYNC/DSPI2_CS0/VID_VSYNC
16
A[7]/VID_D[1]/ETIMER0_ETC[2]/EIRQ[7]/GPIO[7]/SAI0_BCLK/DSPI2_CS1/VID_HREF
24
A[8]/VID_D[6]/LIN1_RX/EIRQ[8]/GPIO[8]/SAI1_BCLK/DSPI1_CS0/SAI2_D[0]
25
A[9]/VID_D[5]/EIRQ[9]/GPIO[9]/SAI2_BCLK/DSPI1_CS1/LIN1_TX
26
A[10]/VID_D[4]/DSPI0_SIN/EIRQ[10]/GPIO[10]/SAI2_MCLK/ETIMER0_ETC[5]
27
A[11]/VID_D[3]/LIN0_RX/RX/GPIO[11]/CAN0_TX/DSPI0_CS1/DSPI1_CS0
28
A[12]/VID_D[2]/CAN0_RX/EIRQ[11]/GPIO[12]/LIN0_TX/DSPI0_CS0/LIN1_TX
29
A[13]/EIRQ[12]/GPIO[13]/IIC1_CLK/FCU0_F[0]/DSPI0_CS0
30
A[14]/DSPI0_SIN/EIRQ[13]/GPIO[14]/IIC1_DATA/FCU0_F[1]/DSPI0_CS1
61
A[15]/DSPI1_SCK/ETIMER0_ETC[0]/EIRQ[18]/GPIO[15]/DSPI0_SCK/CE_RTC_PPS3/SAI1_MCLK
53
C[0]/FEC_RX_D3/GPIO[32]
54
C[1]/FEC_RX_CLK/EIRQ[15]/GPIO[33]
57
C[2]/VID_D[0]/LIN0_RX/EIRQ[16]/GPIO[34]/ETIMER0_ETC[0]/CAN0_TX/CE_RTC_PPS1
60
C[3]/VID_D[1]/CAN0_RX/EIRQ[17]/GPIO[35]/ETIMER0_ETC[1]/LIN0_TX/SAI1_SYNC
62
C[4]/CE_RTC_TRIGGER1/MC_RGM_ABS[0]/EIRQ[19]/GPIO[36]/MC_CGL_MC_CGL/ETIME0_ETC[4]/SAI0_MCLK
63
C[5]/MC_RGM_ABS[2]/EIRQ[20]/GPIO[37]/IIC0_CLK/ETIMER0_ETC[3]/DSPI2_CS2
64
C[6]/MC_RGM_FAB/EIRQ[21]/GPIO[38]/IIC0_DATA/DSPI1_CS0/DSPI2_CS3
15
RESET
14
EXTAL
13
XTAL
43
TDO
42
TCK
41
TMS
40
TDI
31
POR
1
NMI
0.1UF
C523
C526
0.01UF
0.1UF
C525
C524
C527
1000PF
1000PF
VDD_LV
V_BALLAST_IN
7
21
35
58
VDD_LV_PLL0/VDD_LV_COR0_0
VDD_LV_COR0_1/VDD_LV_FLA1
VDD_LV_COR0_2/VDD_LV_FLA0
VSS_LV_PLL0/VSS_LV_COR0_0
6
23
38
47
55
11
VDD_HV_FLA0
VDD_HV_OSC0_REG0
B[2]/ADC0_AN[13]/CE_RTC_TRIGGER1/GPIO[18]/LIN0_TX/CE_RTC_PPS2/CE_RTC_ALARM1
B[3]/ADC0_AN[14]/LIN0_RX/EIRQ[14]/GPIO[19]/ETIMER0_ETC[2]/DSPI0_SOUT/CE_RTC_PPS1
VSS_LV_COR0_2
VSS_LV_COR0_1/VSS_LV_FLA1
59
36
VPP_TEST/TEST
VDD_HV_IO0_2/VDD_HV_FLA1
VDD_HV_ADR0/VDD_HV_ADV0
VDD_HV_S_BALLAST0/VDD_HV_S_BALLAST1
B[0]/ADC0_AN[11]/GPIO[16]/CAN0_TX/CE_RTC_ALARM2/SAI1_BCLK
B[1]/ADC0_AN[12]/CAN0_RX/TRIGGER2/GPIO[17]/SAI1_D[0]
VSS_HV_OSC0_REG0/VSS_HV_IO0_012VSS_HV_ADR0/VSS_HV_ADV022VSS_HV_IO0_2/VSS_HV_FLA1
VSS_HV_FLA0
37
56
V_BALLAST_IN_HDR
J19
1
2
3
HDR TH 1X3
1.2V
B[4]/FEC_RX_DV/GPIO[20]
B[5]/GPIO[21]/FEC_TX_D0/SSCM_DEBUG[0]
B[6]/GPIO[22]/FEC_TX_D1/SSCM_DEBUG[1]
B[7]/GPIO[23]/FEC_TX_D2/SSCM_DEBUG[2]
B[8]/GPIO[24]/FEC_TX_D3/SSCM_DEBUG[3]
B[9]/GPIO[25]/FEC_TX_EN/SSCM_DEBUG[4]
B[10]/GPIO[26]/FEC_MDC/SSCM_DEBUG[5]
B[11]/GPIO[27]/FEC_MDIO/SSCM_DEBUG[6]
B[12]/FEC_TX_CLK/GPIO[28]/SSCM_DEBUG[7]
B[13]/FEC_RX_D0/GPIO[29]
B[14]/FEC_RX_D1/GPIO[30]
B[15]/FEC_RX_D2/GPIO[31]
HDR TH 1X3
GND
17
18
19
20
32
33
34
39
44
45
46
48
49
50
51
52
J20
1
2
3
V_BALLAST_IN_RES
J15
123
HDR TH 1X3
3.3V
R513
2.55
PORT_B0 pg(3,13)
PORT_B1 pg(3,13)
PORT_B2 pg(3,13)
PORT_B3 pg(3,13)
FEC_RX_DV pg(5)
FEC_TXD0 pg(5)
FEC_TXD1 pg(5)
FEC_TXD2 pg(5)
FEC_TXD3 pg(5)
FEC_TX_EN pg(5)
FEC_MDC pg(5)
FEC_MDIO pg(5)
FEC_TX_CLK pg(5)
FEC_RXD0 pg(5)
FEC_RXD1 pg(5)
FEC_RXD2 pg(5)
3.3V
L501
600OHM
A A
5
GND VSSA
3.3V
VDD_ADR
L500600OHM
4
VSSA
GND
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
SOC
SOC
SOC
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
11 13
11 13
11 13

5
4
3
2
1
HDR TH 1X3
J42
GND
3.3V
User switches
GND
123
R542
10.0K
SW4
1 3
SPST PB NO
42
3.3V
J43
3
2
1
HDR TH 1X3
GND
User LED's
HDR 1X1
JP14
D D
C C
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
HDR 1X1
JP15
JP16
JP17
YELLOW LED
1
1
1
1
AC
D11
YELLOW LED
AC
D12
YELLOW LED
AC
D13
YELLOW LED
AC
D14
LED's are SMD (1206) Yellow
RN5A
1 8
49.9
RN5C
3 6
49.9
1 8
RN6A 49.9
3 6
RN6C 49.9
3.3V
RN5B
2 7
49.9
RN5D
4 5
49.9
2 7
RN6B 49.9
4 5
RN6D 49.9
HDR 1X1
JP22
1
C557
0.1UF
B B
HDR 1X1
A A
5
4
R541
10.0K
1
JP23
C558
0.1UF
GND
SW5
1 3
SPST PB NO
42
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
LED & SWITCH SECTION
LED & SWITCH SECTION
LED & SWITCH SECTION
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
12 13
12 13
12 13

5
4
3
2
1
1 x FEC
D D
GND GND
FEC_TXD3_PHYpg(5,8)
FEC_TXD2_PHYpg(5,8)
FEC_TXD0_PHYpg(5,8)
FEC_TXD1_PHYpg(5,8)
FEC_TX_CLK_PHYpg(5,8) FEC_RX_CLK_PHY pg(5,8)
FEC_TX_EN_PHYpg(5,8)
FEC_MDC_PHYpg(5,8)
FEC_MDIO_PHYpg(5,8)
J33
1 2
3 4
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
HDR_2X13
65
FEC_RXD2_PHY pg(5,8)
FEC_RXD3_PHY pg(5,8)
FEC_RXD1_PHY pg(5,8)
FEC_RXD0_PHY pg(5,8)
FEC_RX_DV_PHY pg(5,8)
ADC0
J38
1 2
PORT_B0pg(3,11)
PORT_B1pg(3,11)
C C
GND
3 4
65
7 8
9 10
HDR 2X5
R533
4.7K
J29
3
NMI_Bpg(11)
2
1
HDR TH 1X3
PORT_B2 pg(3,11)
PORT_B3 pg(3,11)
3.3V
GND
R530
4.7K
B B
A A
5
4
GND
X
X
___ ___
___ ___
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
ICAP Classification: FCP: FIUO: PU BI:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Drawing Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Page Title:
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
Size Document Number Rev
C
C
C
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
Date: Sheet of
3
2
Wednesday, October 12, 2011
___ ___
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
MPC5604-EVB
USER I/O CONNECTORS
USER I/O CONNECTORS
USER I/O CONNECTORS
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
SCH-27073 PDF: SPF-27073 A1
1
X
13 13
13 13
13 13

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
Web Support:
http://www.freescale.com/support
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
Technical Information Center, EL516
2100 East Elliot Road
Tempe, Arizona 85284
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
www.freescale.com/support
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
www.freescale.com/support
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064
Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or
implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated
circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to
any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be
provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary
in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer application by
customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor products are
not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for
surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life,
or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor and
its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of,
directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale
Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
RoHS-compliant and/or Pb-free versions of Freescale products have the functionality
and electrical characteristics as their non-RoHS-compliant and/or non-Pb-free
counterparts. For further information, see http://www.freescale.com or contact your
Freescale sales representative.
For information on Freescale’s Environmental Products program, go to
http://www.freescale.com/epp.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2011. All rights reserved.
Document Number: MPC5604EEVB64UM
Rev. 0
10/2011
 Loading...
Loading...