
查询MC9S08QE128CFT供应商
Freescale Semiconductor
Data Sheet: Advance Information
MC9S08QE128 Series
Covers: MC9S08QE128, MC9S08QE96, MC9S08QE64
• 8-Bit HCS08 Central Processor Unit (CPU)
– Up to 50.33-MHz HCS08 CPU from 3.6V to 2.1V, and
20-MHz CPU at 2.1V to 1.8V across temperature range
– HC08 instruction set with added BGND instruction
– Support for up to 32 interrupt/reset sources
• On-Chip Memory
– Flash read/program/erase over fulloperatingvoltage and
temperature
– Random-access memory (RAM)
– Security circuitry to prevent unauthorized access to
RAM and flash contents
• Power-Saving Modes
– Two low power stop modes; reduced power wait mode
– Peripheral clock enable register can disable clocks to
unused modules, reducing currents; allows clocks to
remain enabled to specific peripherals in stop3 mode
– Very low power external oscillator can be used in stop3
mode to provide accurate clock to active peripherals
– Very low power real time counter for use in run, wait,
and stop modes with internal and external clock sources
–6μs typical wake up time from stop modes
• Clock Source Options
– Oscillator (XOSC) — Loop-control Pierce oscillator;
Crystal or ceramic resonator range of 31.25 kHz to
38.4 kHz or 1 MHz to 16 MHz
– Internal Clock Source (ICS) — FLL controlled by
internal or external reference; precision trimming of
internal reference allows 0.2% resolution and 2%
deviation; supports CPU freq. from 2 to 50.33 MHz
• System Protection
– Watchdog computer operating properly (COP) reset
with option to run from dedicated 1-kHz internal clock
source or bus clock
– Low-voltage detection with reset or interrupt; selectable
trip points
– Illegal opcode detection with reset
– Flash block protection
• Development Support
– Single-wire background debug interface
– Breakpoint capability to allow single breakpoint setting
during in-circuit debugging (plus two more breakpoints)
– On-chip in-circuit emulator (ICE) debug module
containing two comparators and nine trigger modes.
Document Number: MC9S08QE128
Rev. 3, 06/2007
MC9S08QE128
80-LQFP
Case 917A
2
14 mm
48-QFN
Case 1314
2
7 mm
32-LQFP
Case 873A
2
7 mm
Eight deep FIFO for storing change-of-flow addresses
and event-only data. Debug module supports both tag
and force breakpoints.
• ADC — 24-channel, 12-bit resolution; 2.5 μs conversion
time; automatic compare function; 1.7 mV/°C temperature
sensor; internal bandgap reference channel; operation in
stop3; fully functional from 3.6V to 1.8V
• ACMPx — Two analog comparators with selectable
interrupt on rising, falling, or either edge of comparator
output; compare option to fixed internal bandgap reference
voltage; outputs can be optionally routed to TPM module;
operation in stop3
• SCIx — Two SCIs with full duplex non-return to zero
(NRZ); LIN master extended break generation; LIN slave
extended break detection; wake up on active edge
• SPIx— Two serial peripheral interfaces with Full-duplex or
single-wire bidirectional; Double-buffered transmit and
receive; MSB-first or LSB-first shifting
• IICx — Two IICs with; Up to 100 kbps with maximum bus
loading; Multi-master operation; Programmable slave
address; Interrupt driven byte-by-byte data transfer;
supports broadcast mode and 10 bit addressing
• TPMx — One 6-channel and two 3-channel; Selectable
input capture, output compare, or buffered edge- or
center-aligned PWMs on each channel
• RTC — 8-bit modulus counter with binary or decimal
based prescaler; External clock source for precise time
base, time-of-day, calendar or task scheduling functions;
Free running on-chip low power oscillator (1 kHz) for
cyclic wake-up without external components
• Input/Output
– 70 GPIOs and 1 input-only and 1 output-only pin
– 16 KBI interrupts with selectable polarity
– Hysteresis and configurable pull-up device on all input
pins; Configurable slew rate and drive strength on all
output pins.
– SET/CLR registers on 16 pins (PTC and PTE)
64-LQFP
Case 840F
2
10 mm
44-QFP
Case 824A
2
10 mm
This document contains information on a product under development. Freescale reserves the
right to change or discontinue this product without notice.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2007. All rights reserved.

Table of Contents
1 MC9S08QE128 Series Comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
2 Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
3 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.2 Parameter Classification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.3 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.4 Thermal Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.5 ESD Protection and Latch-Up Immunity . . . . . . . . . . . .14
3.6 DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
3.7 Supply Current Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3.8 External Oscillator (XOSC) Characteristics . . . . . . . . .21
3.9 Internal Clock Source (ICS) Characteristics . . . . . . . . .22
3.10 AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
3.10.1 Control Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
3.10.2 TPM Module Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
3.10.3 SPI Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.10.4 Analog Comparator (ACMP) Electricals . . . . . . 30
3.10.5 ADC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.10.6 Flash Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.11 EMC Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3.11.1 Radiated Emissions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.11.2 Conducted Transient Susceptibility . . . . . . . . . 34
4 Ordering Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
4.1 Device Numbering System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5 Package Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
5.1 Mechanical Drawings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6 Product Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
7 Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor2
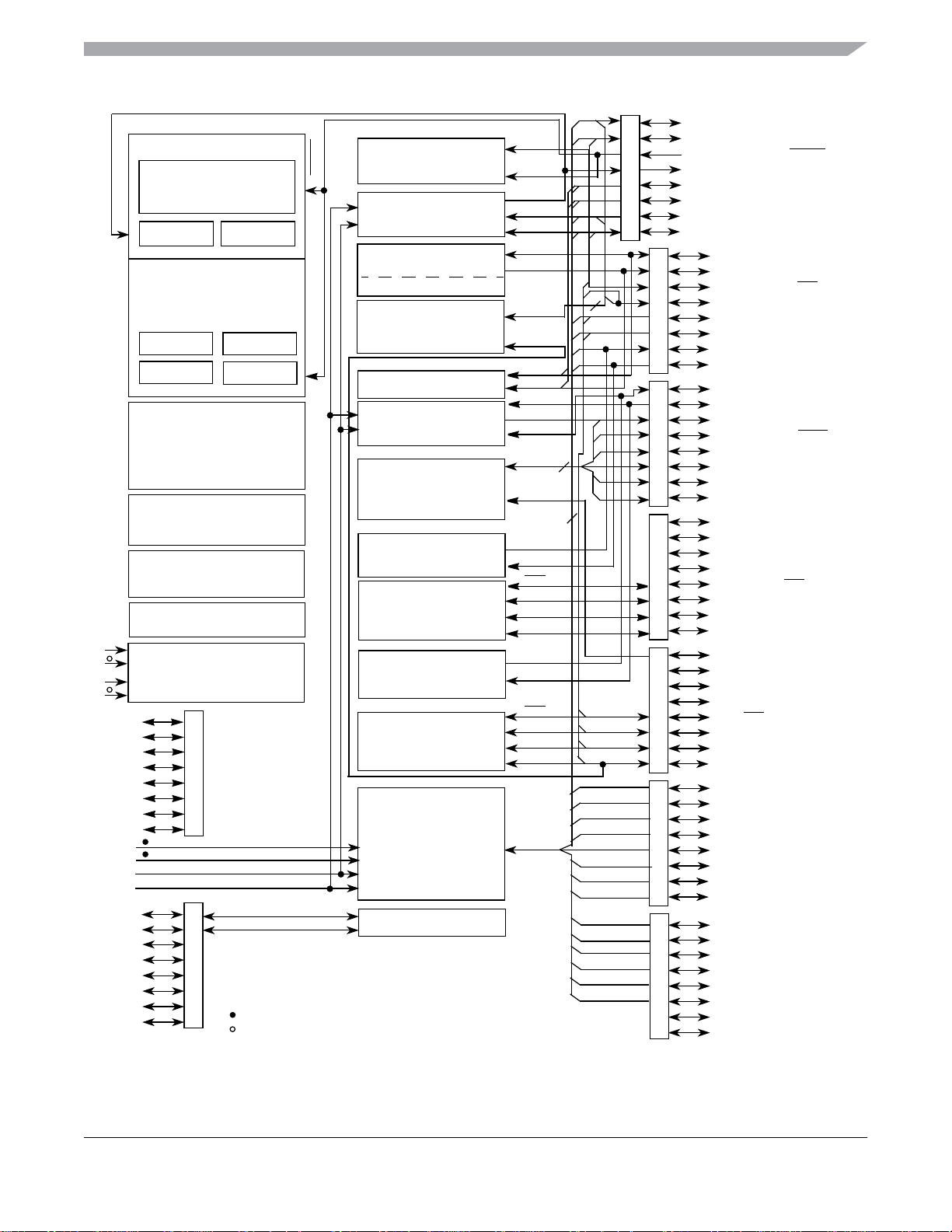
BKGD/MS
V
DD
V
DD
V
SS
V
SS
PTJ7
PTJ6
PTJ5
PTJ4
PTJ3
PTJ2
PTJ1
PTJ0
V
REFH
V
REFL
V
DDA
V
SSA
PTH7/SDA2
PTH6/SCL2
PTH5
PTH4
PTH3
PTH2
PTH1
PTH0
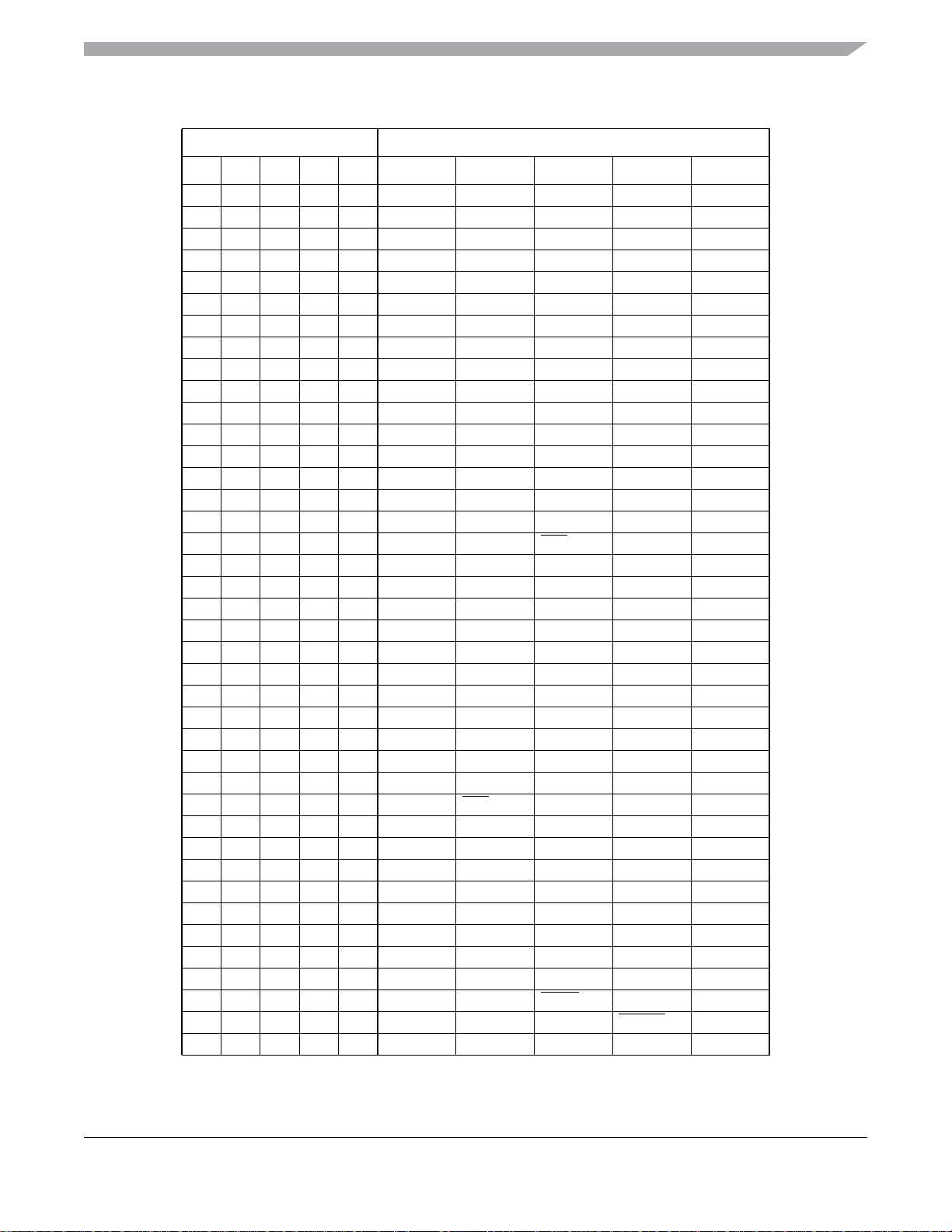
HCS08 CORE
CPU
BDC
BKP
HCS08 SYSTEM CONTROL
RESETS AND INTERRUPTS
MODES OF OPERATION
POWER MANAGEMENT
COP
INT
USER FLASH
128K / 96K / 64K
USER RAM
8K / 6K / 4K
DEBUG MODULE (DBG)
REAL TIME COUNTER (RTC)
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
LV D
IRQ
PORT J
PORT H
- V
REFH/VREFL
- VDD and VSS pins are each internally connected to two pads in 32-pin package
3-CHANNEL TIMER/PWM
RESET
IRQ
SDA2
SCL2
internally connected to V
MODULE (TPM1)
ANALOG COMPARATOR
(ACMP1)
INTERNAL CLOCK
SOURCE (ICS)
OSCILLATOR (XOSC)
3-CHANNEL TIMER/PWM
MODULE (TPM2)
IIC MODULE (IIC1)
ANALOG COMPARATOR
(ACMP2)
6-CHANNEL TIMER/PWM
MODULE (TPM3)
SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (SCI1)
SERIAL PERIPHERAL
INTERFACE MODULE (SPI2)
SERIAL COMMUNICATIONS
INTERFACE (SCI2)
SERIAL PERIPHERAL
INTERFACE MODULE (SPI1)
24-CHANNEL,12-BIT
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL
CONVERTER (ADC)
IIC MODULE (IIC2)
TPM1CH2-0
TPM1CLK
ACMP1O
ACMP1+
ACMP1-
EXTAL
XTAL
TPM2CH2-0
TPM2CLK
ACMP2+
ACMP2O
ACMP2-
TPM3CH5-0
TPM3CLK
in 48-pin and 32-pin packages
DDA/VSSA
SCL1
SDA1
TxD1
RxD1
SS2
MISO2
MOSI2
SPSCK2
TxD2
RxD2
SS1
MISO1
MOSI1
SPSCK1
PTA7/TPM2CH2/ADP9
PTA6/TPM1CH2/ADP8
PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/
PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS
PORT A
3
6
10
PTA3/KBI1P3/SCL1/ADP3
PTA2/KBI1P2/SDA1/ADP2
PTA1/KBI1P1/TPM2CH0/ADP1/ACMP1PTA0/KBI1P0/TPM1CH0/ADP0/ACMP1+
PTB7/SCL1/EXTAL
PTB6/SDA1/XTAL
PTB5/TPM1CH1/
PTB4/TPM2CH1/MISO1
PORT B
PORT C
PORT D
PORT E
PORT F
PORT G
PTB3/KBI1P7/MOSI1/ADP7
PTB2/KBI1P6/SPSCK1/ADP6
PTB1/KBI1P5/TxD1/ADP5
PTB0/KBI1P4/RxD1/ADP4
PTC7/TxD2/ACMP2PTC6/RxD2/ACMP2+
PTC5/TPM3CH5/ACMP2O
PTC4/TPM3CH4/
PTC3/TPM3CH3
PTC2/TPM3CH2
PTC1/TPM3CH1
PTC0/TPM3CH0
PTD7/KBI2P7
PTD6/KBI2P6
PTD5/KBI2P5
PTD4/KBI2P4
PTD3/KBI2P3/SS2
PTD2/KBI2P2/MISO2
PTD1/KBI2P1/MOSI2
PTD0/KBI2P0/SPSCK2
PTE7/TPM3CLK
PTE6
PTE5
PTE4
PTE3/SS1
PTE2/MISO1
PTE1/MOSI1
PTE0/TPM2CLK/SPSCK1
PTF7/ADP17
PTF6/ADP16
PTF5/ADP15
PTF4/ADP14
PTF3/ADP13
PTF2/ADP12
PTF1/ADP11
PTF0/ADP10
PTG7/ADP23
PTG6/ADP22
PTG5/ADP21
PTG4/ADP20
PTG3/ADP19
PTG2/ADP18
PTG1
PTG0
RESET
SS1
RSTO
Figure 1. MC9S08QE128 Series Block Diagram
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 3
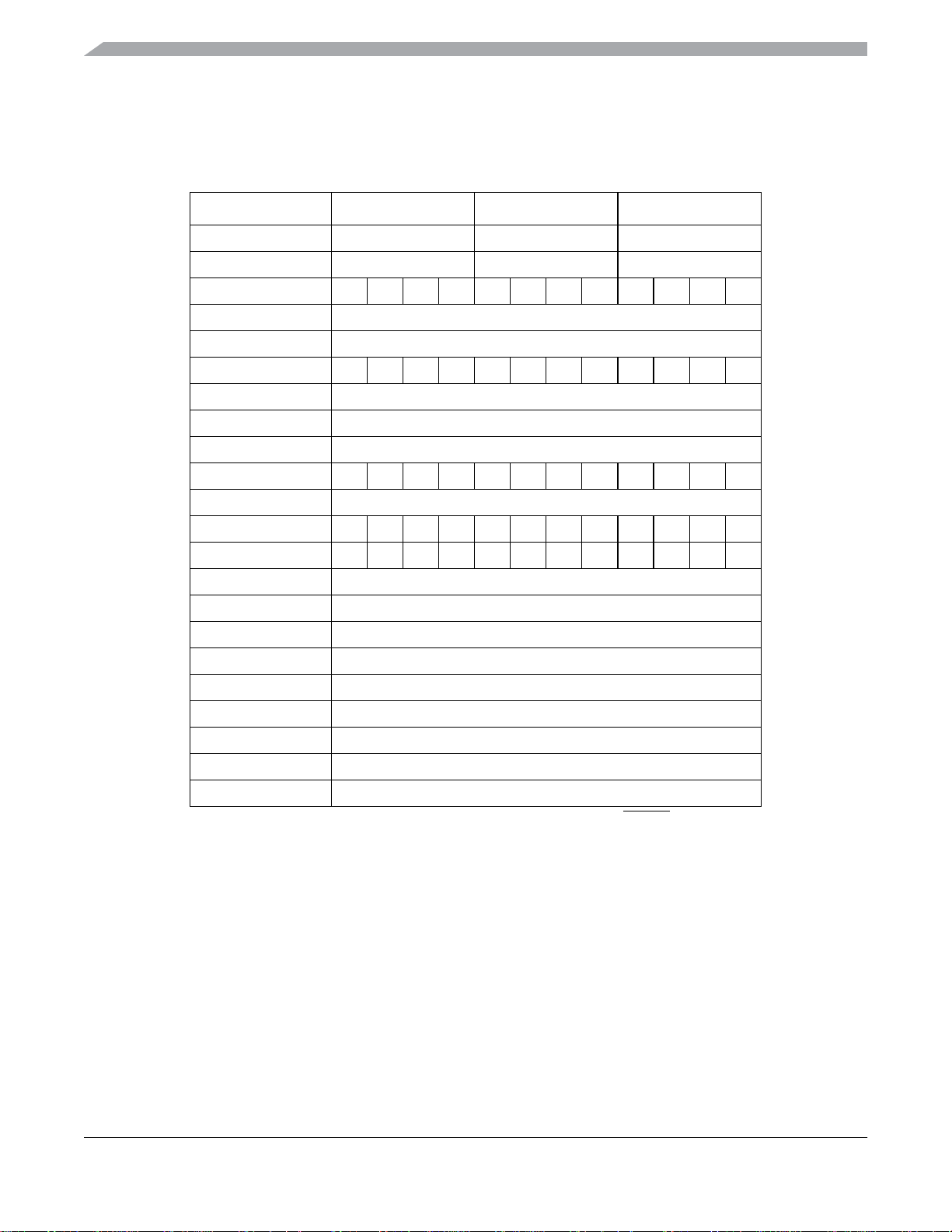
MC9S08QE128 Series Comparison
1 MC9S08QE128 Series Comparison
The following table compares the various device derivatives available within the MC9S08QE128 series.
Table 1. MC9S08QE128 Series Features by MCU and Package
Feature MC9S08QE128 MC9S08QE96 MC9S08QE64
Flash size (bytes) 131072 98304 65536
RAM size (bytes) 8064 6016 4096
Pin quantity 80 64 48 44 80 64 48 44 64 48 44 32
ACMP1 yes
ACMP2 yes
ADC channels 24 22 10 10 24 22 10 10 22 10 10 10
DBG yes
ICS yes
IIC1 yes
IIC2 yes yes no no yes yes no no yes no no no
IRQ yes
KBI 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 16 12
Port I/O
RTC yes
SCI1 yes
SCI2 yes
SPI1 yes
SPI2 yes
TPM1 channels 3
TPM2 channels 3
TPM3 channels 6
XOSC yes
1
1
Port I/O count does not include the input only PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/RESET or the output
only PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS.
70 54 38 34 70 54 38 34 54 38 34 26
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor4
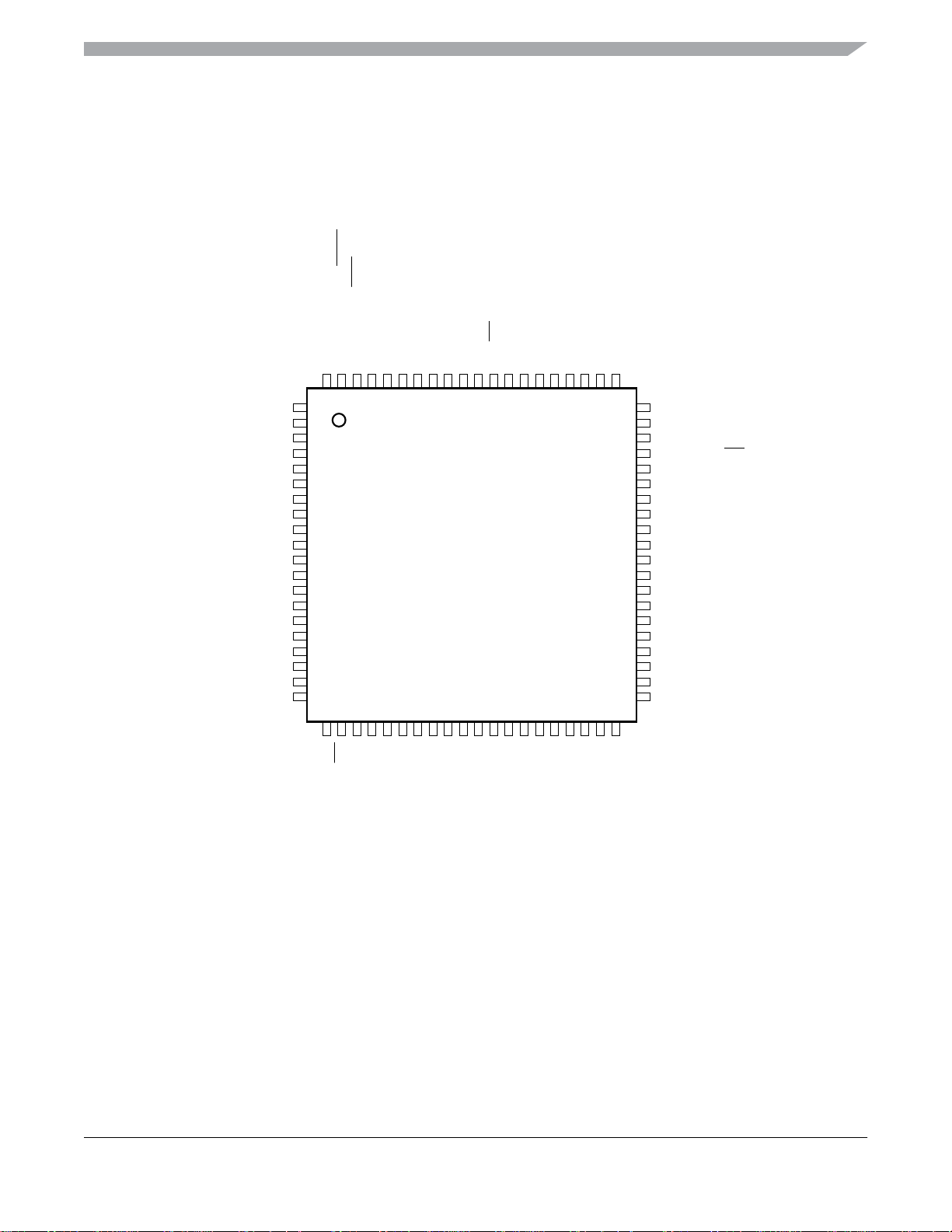
Pin Assignments
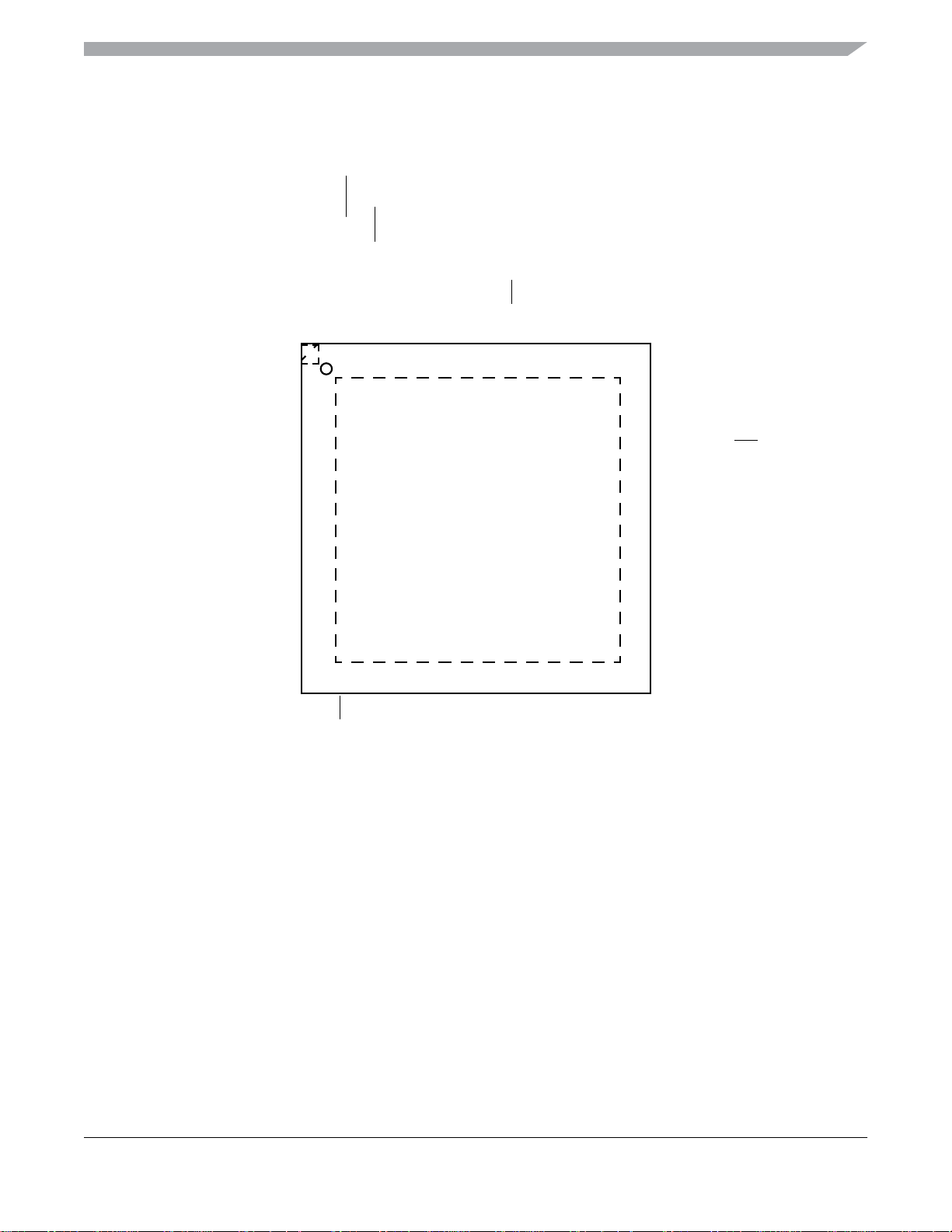
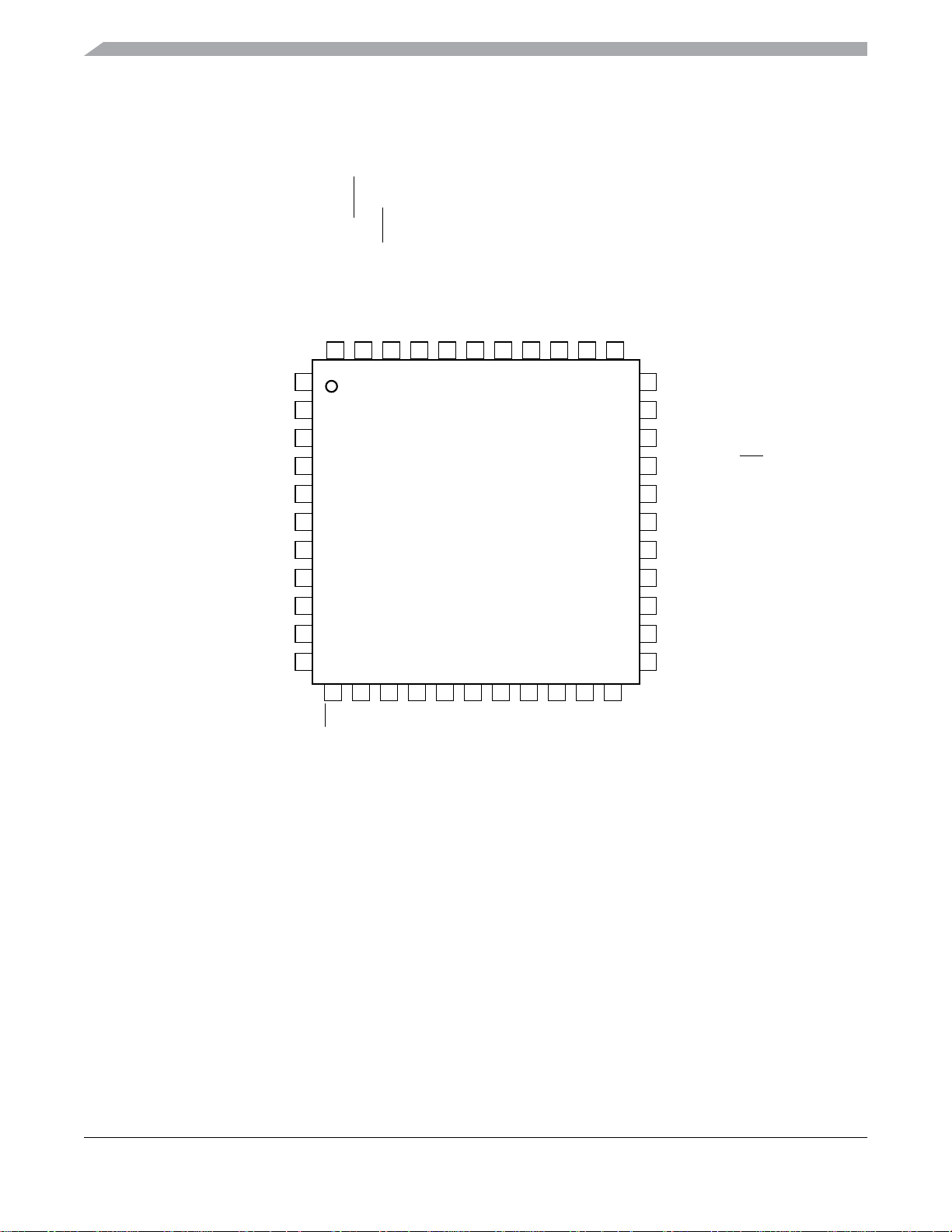
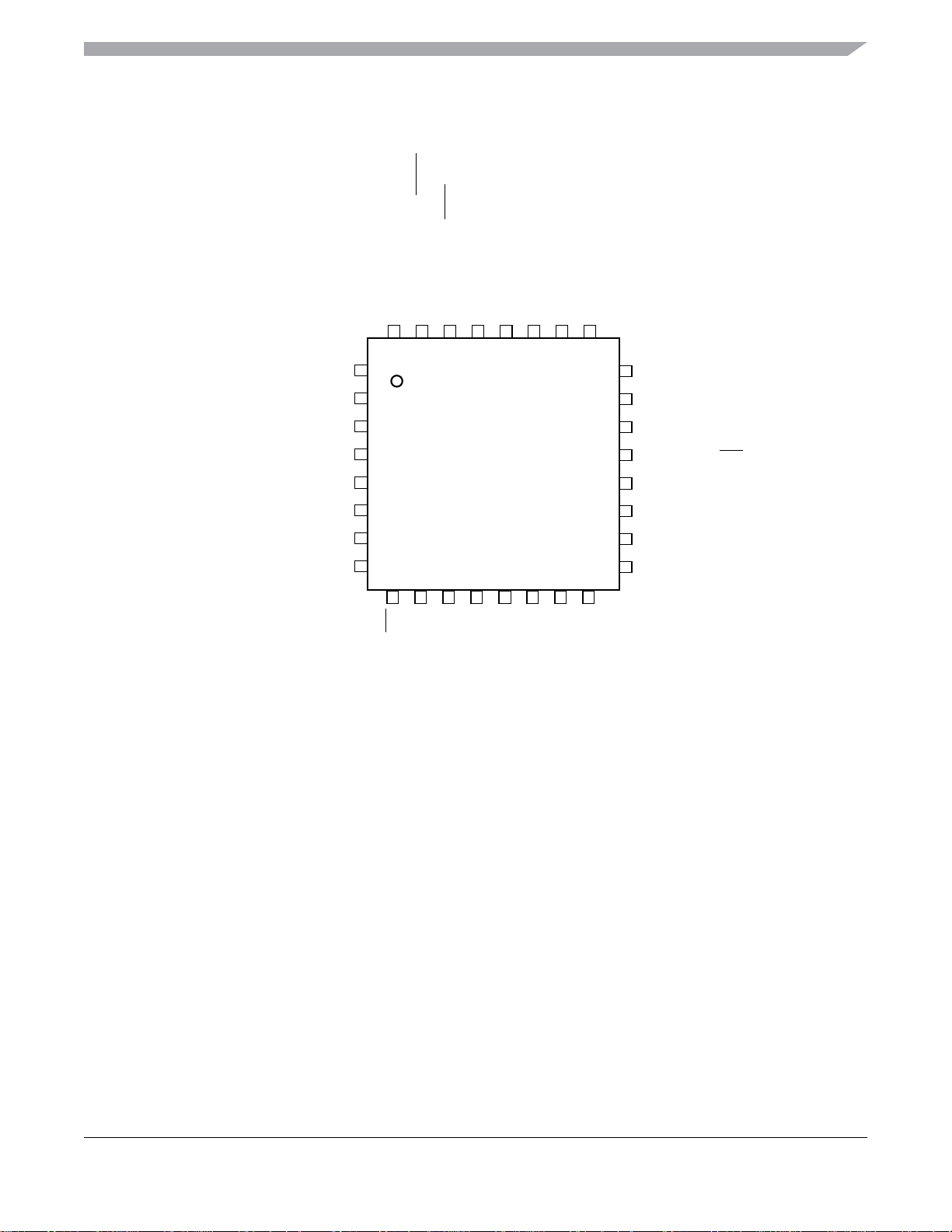
2 Pin Assignments
This section describes the pin assignments for the available packages. See Table 2 for pin availability by package pin-count.
PTD1/KBI2P1/MOSI2
PTD0/KBI2P0/SPSCK2
PTH7/SDA2
PTH6/SCL2
PTH5
PTE7/TPM3CLK
PTB7/SCL1/EXTAL
PTB6/SDA1/XTAL
PTH4
V
V
DDAD
V
REFH
V
REFL
V
SSAD
V
PTH3
PTH2
PTH1
PTH0
PTE6
DD
SS
PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS
80797877767574737271706968676665646362
1
PTC5/TPM3CH5/ACMP2O
PTC4/TPM3CH4/RSTO
PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/RESET
PTE0/TPM2CLK/SPSCK1
PTE1/MOSI1
PTG0
PTG3/ADP19
PTG2/ADP18
PTG1
PTE2/MISO1
PTE3/SS1
PTG5/ADP21
PTG4/ADP20
PTC7/TxD2/ACMP2-
PTC6/RxD2/ACMP2+
PTG7/ADP23
PTG6/ADP22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21222324252627282930313233343536373839
SS1
PTE5
PTC3/TPM3CH3
PTC2/TPM3CH2
PTB5/TPM1CH1/
PTB4/TPM2CH1/MISO1
PTD7/KBI2P7
PTD6/KBI2P6
PTD5/KBI2P5
PTJ7
PTJ6
PTJ5
PTJ4
PTF7/ADP17
PTC0/TPM3CH0
PTC1/TPM3CH1
PTF6/ADP16
PTF5/ADP15
PTF4/ADP14
Pins in bold are added from the next smaller package.
Figure 2. Pin Assignments in 80-Pin LQFP
PTA0/KBI1P0/TPM1CH0/ADP0/ACMP1+
PTA1/KBI1P1/TPM2CH0/ADP1/ACMP1-
61
60
PTA2/KBI1P2/SDA1/ADP2
59
PTA3/KBI1P3/SCL1/ADP3
58
PTD2/KBI2P2/MISO2
57
PTD3/KBI2P3/
56
PTD4/KBI2P4
55
PTJ0
54
PTJ1
53
PTF0/ADP10
52
PTF1/ADP11
51
V
SS
50
V
DD
49
PTE4
48
PTA6/TPM1CH2/ADP8
47
PTA7/TPM2CH2/ADP9
46
PTF2/ADP12
45
PTF3/ADP13
PTJ2
44
PTJ3
43
PTB0/KBI1P4/RxD1/ADP4
42
PTB1/KBI1P5/TxD1/ADP5
41
SS2
40
PTB3/KBI1P7/MOSI1/ADP7
PTB2/KBI1P6/SPSCK1/ADP6
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 5
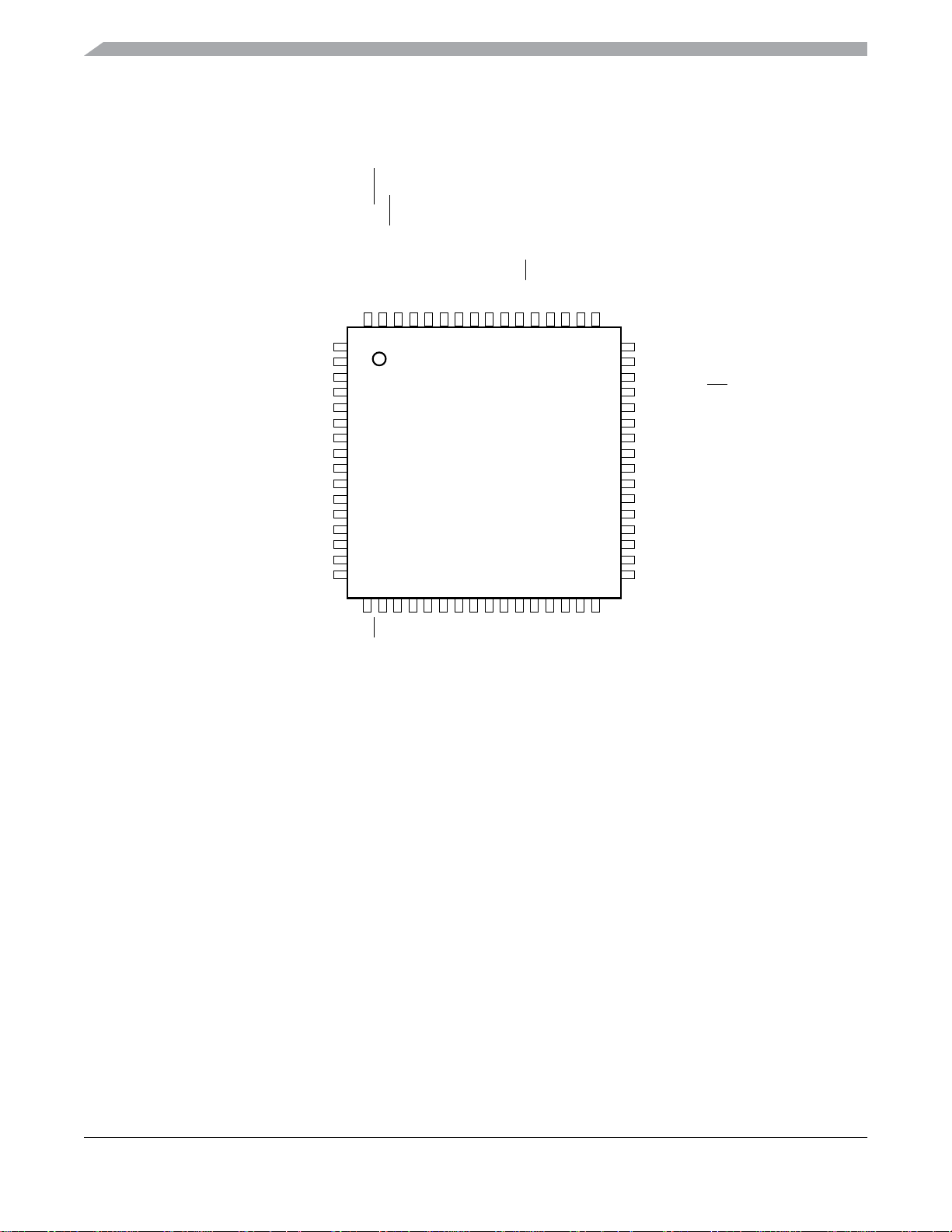
Pin Assignments
RESET
RSTO
SS1
PTD1/KBI2P1/MOSI2
PTD0/KBI2P0/SPSCK2
PTH7/SDA2
PTH6/SCL2
PTE7/TPM3CLK
PTB7/SCL1/EXTAL
PTB6/SDA1/XTAL
V
DDAD
V
REFH
V
V
SSAD
PTH1
PTH0
PTE6
V
DD
REFL
V
Figure 3. Pin Assignments in 64-Pin LQFP Package
PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS
646362616059585756555453525150
1
PTC5/TPM3CH5/ACMP2O
PTC4/TPM3CH4/
PTE0/TPM2CLK/SPSCK1
PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/
PTE1/MOSI1
PTG1
PTG0
PTE3/
PTE2/MISO1
PTG3/ADP19
PTG2/ADP18
PTA0/KBI1P0/TPM1CH0/ADP0/ACMP1+
PTC7/TxD2/ACMP2-
PTC6/RxD2/ACMP2+
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
SS
11
12
13
14
15
16
171819202122232425262728293031
SS1
PTE5
PTF7/ADP17
PTF6/ADP16
PTF5/ADP15
PTD7/KBI2P7
PTD6/KBI2P6
PTC3/TPM3CH3
PTC2/TPM3CH2
PTB5/TPM1CH1/
PTB4/TPM2CH1/MISO1
PTD5/KBI2P5
PTC0/TPM3CH0
PTC1/TPM3CH1
PTF4/ADP14
PTB3/KBI1P7/MOSI1/ADP7
Pins in bold are added from the next smaller package.
PTA1/KBI1P1/TPM2CH0/ADP1/ACMP1-
49
48
PTA2/KBI1P2/SDA11/ADP2
PTA3/KBI1P3/SCL1/ADP3
47
PTD2/KBI2P2/MISO2
46
PTD3/KBI2P3/
45
PTD4/KBI2P4
44
PTF0/ADP10
43
PTF1/ADP11
42
V
41
SS
V
40
DD
PTE4
39
PTA6/TPM1CH2/ADP8
38
PTA7/TPM2CH2/ADP9
37
PTF2/ADP12
36
PTF3/ADP13
35
PTB0/KBI1P4/RxD1/ADP4
34
PTB1/KBI1P5/TxD1/ADP5
33
SS2
32
PTB2/KBI1P6/SPSCK1/ADP6
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor6
PTD1/KBI2P1/MOSI2
PTD0/KBI2P0/SPSCK2
PTE7/TPM3CLK
V
DD
V
DDAD
V
REFH
V
REFL
V
SSAD
V
SS
PTB7/SCL1/EXTAL
PTB6/SDA11/XTAL
PTE6
RESET
RSTO
PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/
PTC4/TPM3CH4/
PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS
48
47
PTC5/TPM3CH5/ACMP2O
46
45
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
14
15
13
16
PTE1/MOSI1
PTE0/TPM2CLK/SPSCK1
44
43
17
18
PTE2/MISO1
42
19
SS1
PTE3/
PTC6/RxD2/ACMP2+
PTC7/TxD2/ACMP2-
41
40
39
20
21
22
Pin Assignments
PTA0/KBI1P0/TPM1CH0/ADP0/ACMP1+
PTA1/KBI1P1/TPM2CH0/AD
PTA1/KBI1P1/TPM2CH0/ADP1/ACMP1-
37
38
23
PTA2/KBI1P2/SDA1/ADP2
36
PTA3/KBI1P3/SCL1/ADP3
35
PTD2/KBI2P2/MISO2
34
PTD3/KBI2P3/
33
PTD4/KBI2P4
32
V
31
SS
V
30
DD
PTE4
29
PTA6/TPM1CH2/ADP8
28
PTA7/TPM2CH2/ADP9
27
PTB0/KBI1P4/RxD1/ADP4
26
PTB1/KBI1P5/TxD1/ADP5
25
SS2
24
PTE5
PTD7/KBI2P7
PTD6/KBI2P6
PTC3/TPM3CH3
PTC2/TPM3CH2
PTD5/KBI2P5
PTC0/TPM3CH0
PTC1/TPM3CH1
PTB5/TPM1CH1/SS1
PTB4/TPM2CH1/MISO1
PTB3/KBI1P7/MOSI1/ADP7
PTB2/KBI1P6/SPSCK1/ADP6
Figure 4. Pin Assignments in 48-Pin QFN Package
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 7
Pin Assignments
PTD1/KBI2P1/MOSI2
PTD0/KBI2P0/SPSCK2
PTB7/SCL1/EXTAL
PTE7/TPM3CLK
V
DD
V
DDAD
V
REFH
V
REFL
V
SSAD
V
PTB6/SDA1/XTAL
SS
RESET
RSTO
PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/
PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS
44
1
PTC4/TPM3CH4/
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
12
14
PTE1
17
39
PTE2
38
18
PTE0/TPM2CLK
PTC5/TPM3CH5/ACMP2O
42
41
40
15
16
PTA0/KBI1P0/TPM1CH0/ADP0/ACMP1+
PTC6/RxD2/ACMP2+
PTC7/TxD2/ACMP2-
37
36
PTA1/KBI1P1/TPM2CH0/ADP1/ACMP1-
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
19
20
21
22
PTA2/KBI1P2/SDA1/ADP2
PTA3/KBI1P3/SCL1/ADP3
PTD2/KBI2P2/MISO2
PTD3/KBI2P3/SS2
PTD4/KBI2P4
V
SS
V
DD
PTA6/TPM1CH2/ADP8
PTA7/TPM2CH2/ADP9
PTB0/KBI1P4/RxD1/ADP4
PTB1/KBI1P5/TxD1/ADP5
PTD7/KBI2P7
PTD6/KBI2P6
PTC3/TPM3CH3
PTC2/TPM3CH2
PTD5/KBI2P5
PTC0/TPM3CH0
PTC1/TPM3CH1
PTB5/TPM1CH1/SS1
PTB4/TPM2CH1/MISO1
PTB3/KBI1P7/MOSI1/ADP7
PTB2/KBI1P6/SPSCK1/ADP6
Figure 5. Pin Assignments in 44-Pin QFP Package
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor8
1
1
RSTO
PTC4/TPM3CH4/
PTA5/IRQ/TPM1CLK/RESET
PTA4/ACMP1O/BKGD/MS
PTC6/RxD2/ACMP2+
PTC5/TPM3CH5/ACMP2O
PTA1/KBIP1/TPM2CH0/ADP1/ACMP
PTA0/KBIP0/TPM1CH0/ADP0/ACMP
PTC7/TxD2/ACMP2-
Pin Assignments
PTD1/KBI2P1/MOSI2
PTD0/KBI2P0/SPSCK2
V
DD
V
REFH/VDDAD
V
REFL/VSSAD
V
SS
PTB7/SCL1/EXTAL
PTB6/SDA1/XTAL
Figure 6. Pin Assignments 32-Pin LQFP Package
31 30 29 28
32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
PTB5/TPM1CH1/SS1
11
12 13 14
PTC3/TPM3CH3
PTC2/TPM3CH2
PTC1/TPM3CH1
PTC0/TPM3CH0
PTB4/TPM2CH1/MISO1
252627
PTA2/KBIP2/SDA1/ADP2
24
PTA3/KBIP3/SCL1/ADP3
23
22
PTD2/KBI2P2/MISO2
21
PTD3/KBI2P3/SS2
20
PTA6/TPM1CH2/ADP8
19
PTA7/TPM2CH2/ADP9
18
PTB0/KBI1P4/RxD1/ADP4
17
15
16
PTB3/KBI1P7/MOSI1/ADP7
PTB1/KBI1P5/TxD1/ADP5
PTB2/KBI1P6/SPSCK1/ADP6
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 9
Pin Assignments
Table 2. MC9S08QE128 Series Pin Assignment by Package and Pin Count
Pin Number Lowest ←⎯ Priority ⎯→ Highest
80 64 48 44 32 Port Pin Alt 1 Alt 2 Alt 3 Alt 4
11111PTD1 KBI2P1 MOSI2
22222PTD0 KBI2P0 SPSCK2
3 3 — — — PTH7 SDA2
4 4 — — — PTH6 SCL2
5 ————PTH5
6 ————PTH4
7533—PTE7 TPM3CLK
86443 V
97554 V
10866— V
11977— V
12 10 8 8 5 V
13 11 9 9 6 V
14 12 10 10 7 PTB7 SCL1 EXTAL
15 13 11 11 8 PTB6 SDA1 XTAL
16————PTH3
17————PTH2
18 14 — — — PTH1
19 15 — — — PTH0
20 16 12 — — PTE6
21 17 13 — — PTE5
22 18 14 12 9 PTB5 TPM1CH1
SS1
23 19 15 13 10 PTB4 TPM2CH1 MISO1
24 20 16 14 11 PTC3 TPM3CH3
25 21 17 15 12 PTC2 TPM3CH2
26 22 18 16 — PTD7 KBI2P7
27 23 19 17 — PTD6 KBI2P6
28 24 20 18 — PTD5 KBI2P5
29————PTJ7
30————PTJ6
31————PTJ5
32————PTJ4
33 25 21 19 13 PTC1 TPM3CH1
34 26 22 20 14 PTC0 TPM3CH0
35 27 — — — PTF7 ADP17
36 28 — — — PTF6 ADP16
37 29 — — — PTF5 ADP15
38 30 — — — PTF4 ADP14
39 31 23 21 15 PTB3 KBI1P7 MOSI1 ADP7
40 32 24 22 16 PTB2 KBI1P6 SPSCK1 ADP6
DD
DDA
REFH
REFL
SSA
SS
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor10
Pin Assignments
Table 2. MC9S08QE128 Series Pin Assignment by Package and Pin Count (continued)
Pin Number Lowest ←⎯ Priority ⎯→ Highest
80 64 48 44 32 Port Pin Alt 1 Alt 2 Alt 3 Alt 4
41 33 25 23 17 PTB1 KBI1P5 TxD1 ADP5
42 34 26 24 18 PTB0 KBI1P4 RxD1 ADP4
43————PTJ3
44————PTJ2
45 35 — — — PTF3 ADP13
46 36 — — — PTF2 ADP12
47 37 27 25 19 PTA7 TPM2CH2 ADP9
48 38 28 26 20 PTA6 TPM1CH2 ADP8
49 39 29 — — PTE4
50 40 30 27 — V
51 41 31 28 — V
52 42 — — — PTF1 ADP11
53 43 — — — PTF0 ADP10
54————PTJ1
55————PTJ0
56 44 32 29 — PTD4 KBI2P4
57 45 33 30 21 PTD3 KBI2P3
SS2
58 46 34 31 22 PTD2 KBI2P2 MISO2
59 47 35 32 23 PTA3 KBI1P3 SCL1 ADP3
60 48 36 33 24 PTA2 KBI1P2 SDA1 ADP2
61 49 37 34 25 PTA1 KBI1P1 TPM2CH0 ADP1 ACMP1-
62 50 38 35 26 PTA0 KBI1P0 TPM1CH0 ADP0 ACMP1+
63 51 39 36 27 PTC7 TxD2 ACMP2-
64 52 40 37 28 PTC6 RxD2 ACMP2+
65————PTG7 ADP23
66————PTG6 ADP22
67————PTG5 ADP21
68————PTG4 ADP20
69 53 41 — — PTE3
SS1
70 54 42 38 — PTE2 MISO1
71 55 — — — PTG3 ADP19
72 56 — — — PTG2 ADP18
73 57 — — — PTG1
74 58 — — — PTG0
75 59 43 39 — PTE1 MOSI1
76 60 44 40 — PTE0 TPM2CLK SPSCK1
77 61 45 41 29 PTC5 TPM3CH5 ACMP2O
78 62 46 42 30 PTC4 TPM3CH4
79 63 47 43 31 PTA5 IRQ TPM1CLK
RSTO
RESET
80 64 48 44 32 PTA4 ACMP1O BKGD MS
DD
SS
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 11
Electrical Characteristics
3 Electrical Characteristics
3.1 Introduction
This section contains electrical and timing specifications for the MC9S08QE128 series of microcontrollers available at the time
of publication.
3.2 Parameter Classification
The electrical parameters shown in this supplement are guaranteed by various methods. To give the customer a better
understanding the following classification is used and the parameters are tagged accordingly in the tables where appropriate:
Table 3. Parameter Classifications
Those parameters are guaranteed during production testing on each individual device.
P
Those parameters are achieved by the design characterization by measuring a statistically relevant sample
C
size across process variations.
Those parameters are achieved by design characterization on a small sample size from typical devices
under typical conditions unless otherwise noted. All values shown in the typical column are within this
T
category.
Those parameters are derived mainly from simulations.
D
NOTE
The classification is shown in the column labeled “C” in the parameter tables where
appropriate.
3.3 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings are stress ratings only, and functional operation at the maxima is not guaranteed. Stress beyond the
limits specified in Table 4 may affect device reliability or cause permanent damage to the device. For functional operating
conditions, refer to the remaining tables in this section.
This device contains circuitry protecting against damage due to high static voltage or electrical fields; however, it is advised that
normal precautions be taken to avoid application of any voltages higher than maximum-rated voltages to this high-impedance
circuit. Reliability of operation is enhanced if unused inputs are tied to an appropriate logic voltage level (for instance, either
VSS or VDD) or the programmable pull-up resistor associated with the pin is enabled.
Table 4. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Supply voltage V
Maximum current into V
Digital input voltage V
Instantaneous maximum current
Single pin limit (applies to all port pins)
Storage temperature range T
1
Input must be current limited to the value specified. To determine the value of the required
current-limiting resistor, calculate resistance values for positive (V
voltages, then use the larger of the two resistance values.
2
All functional non-supply pins are internally clamped to VSS and VDD.
DD
1, 2, 3
DD
I
DD
In
I
D
stg
–0.3 to +3.8 V
120 mA
–0.3 to VDD+ 0.3 V
± 25 mA
–55 to 150 °C
) and negative (VSS) clamp
DD
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor12
Electrical Characteristics
3
Power supply must maintain regulation within operating VDDrange during instantaneous and
operating maximum current conditions. If positive injection current (V
I
, the injection current may flow out of VDD and could result in external power supply going
DD
out of regulation. Ensure external V
load will shunt current greater than maximum injection
DD
> VDD) is greater than
In
current. This will be the greatest risk when the MCU is not consuming power. Examples are: if
no system clock is present, or if the clock rate is very low (which would reduce overall power
consumption).
3.4 Thermal Characteristics
This section provides information about operating temperature range, power dissipation, and package thermal resistance. Power
dissipation on I/O pins is usually small compared to the power dissipation in on-chip logic and voltage regulator circuits, and it
is user-determined rather than being controlled by the MCU design. To take P
the difference between actual pin voltage and VSSor VDDand multiply by the pin current for each I/O pin. Except in cases of
unusually high pin current (heavy loads), the difference between pin voltage and VSS or VDD will be very small.
Table 5. Thermal Characteristics
Rating Symbol Value Unit
into account in power calculations, determine
I/O
Operating temperature range
(packaged)
Maximum junction temperature T
T
A
JM
Thermal resistance
Single-layer board
32-pin LQFP
θ
JA
48-pin QFN 81
64-pin LQFP
θ
80-pin LQFP 60
JA
Thermal resistance
Four-layer board
32-pin LQFP
θ
JA
48-pin QFN 26
64-pin LQFP
θ
80-pin LQFP 47
JA
The average chip-junction temperature (TJ) in °C can be obtained from:
TL to T
H
–40 to 85
95 °C
82
69
54
50
°C
°C/W44-pin LQFP 69
°C/W
°C/W44-pin LQFP 47
°C/W
TJ = TA + (PD×θJA) Eqn. 1
where:
TA= Ambient temperature, °C
θJA = Package thermal resistance, junction-to-ambient, °C/W
PD = P
P
int
P
I/O
Freescale Semiconductor 13
+ P
int
I/O
= IDD× VDD, Watts — chip internal power
= Power dissipation on input and output pins — user determined
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Electrical Characteristics
For most applications, P
I/O
<< P
and can be neglected. An approximate relationship between PDand TJ(if P
int
is neglected)
I/O
is:
PD = K ÷ (TJ + 273°C) Eqn. 2
Solving Equation 1 and Equation 2 for K gives:
K = PD× (TA + 273°C) + θJA× (PD)
2
Eqn. 3
where K is a constant pertaining to the particular part. K can be determined from equation 3 by measuring PD(at equilibrium)
for a known TA. Using this value of K, the values of PDand TJcan be obtained by solving Equation 1 and Equation 2 iteratively
for any value of TA.
3.5 ESD Protection and Latch-Up Immunity
Although damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD) is much less common on these devices than on early CMOS circuits,
normal handling precautions should be used to avoid exposure to static discharge. Qualification tests are performed to ensure
that these devices can withstand exposure to reasonable levels of static without suffering any permanent damage.
All ESD testing is in conformity with AEC-Q100 Stress Test Qualification for Automotive Grade Integrated Circuits. During
the device qualification ESD stresses were performed for the human body model (HBM), the machine model (MM) and the
charge device model (CDM).
A device is defined as a failure if after exposure to ESD pulses the device no longer meets the device specification. Complete
DC parametric and functional testing is performed per the applicable device specification at room temperature followed by hot
temperature, unless specified otherwise in the device specification.
Table 6. ESD and Latch-up Test Conditions
Model Description Symbol Value Unit
Series resistance R1 1500 Ω
Human
Body
Machine
Latch-up
Storage capacitance C 100 pF
Number of pulses per pin — 3
Series resistance R1 0 Ω
Storage capacitance C 200 pF
Number of pulses per pin — 3
Minimum input voltage limit – 2.5 V
Maximum input voltage limit 7.5 V
Table 7. ESD and Latch-Up Protection Characteristics
No. Rating
1 Human body model (HBM) V
2 Machine model (MM) V
3 Charge device model (CDM) V
4 Latch-up current at T
1
Parameter is achieved by design characterization on a small sample size from typical devices
under typical conditions unless otherwise noted.
1
= 85°CI
A
Symbol Min Max Unit
HBM
MM
CDM
LAT
± 2000 — V
± 200 — V
± 500 — V
± 100 — mA
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor14
3.6 DC Characteristics
This section includes information about power supply requirements and I/O pin characteristics.
Table 8. DC Characteristics
Electrical Characteristics
Num C Characteristic Symbol Condition Min Typ
1
Max Unit
1 Operating Voltage 1.8 3.6 V
Output high
C
voltage
P All I/O pins,
2
T 2.3 V, I
C 1.8V, I
3D
4
Output high
current
Output low
C
voltage
P All I/O pins,
Max total I
T 2.3 V, I
C 1.8 V, I
Output low
D
current
P Input high
6
voltage
CV
P Input low voltage all digital inputs
7
CV
8 C Input hysteresis all digital inputs V
9P
Input leakage
current
All I/O pins,
low-drive strength
high-drive strength
for all
OH
ports
All I/O pins,
low-drive strength
high-drive strength
Max total I
OL
for all
ports
all digital inputs
all input only pins
(Per pin)
V
I
OHT
V
I
V
V
|I
OH
OL
OLT
IH
IL
hys
In|
1.8 V, I
2.7 V, I
= –2 mA VDD – 0.5 — —
Load
= –10 mA VDD – 0.5 — —
Load
= –6 mA VDD – 0.5 — —
Load
= –3 mA VDD – 0.5 — —
Load
— — 100 mA
1.8 V, I
2.7 V, I
= 2 mA — — 0.5
Load
= 10 mA — — 0.5
Load
= 6 mA — — 0.5
Load
= 3 mA — — 0.5
Load
— — 100 mA5
VDD> 2.7 V 0.70 x V
> 1.8 V 0.85 x V
DD
——
DD
——
DD
VDD> 2.7 V — — 0.35 x V
>1.8 V — — 0.30 x V
DD
VIn = VDD or V
SS
0.06 x V
— 0.1 1 μA
——mV
DD
DD
DD
V
V
V
10 P
Hi-Z (off-state)
leakage current
all input/output
(per pin)
|I
OZ|
VIn= VDDor V
SS
— 0.1 1 μA
Pull-up resistors all digital inputs, when
11 P
12 D
DC injection
2, 3, 4
current
Total MCU limit, includes
enabled
Single pin limit
sum of all stressed pins
13 C Input Capacitance, all pins C
14 C RAM retention voltage V
15 C POR re-arm voltage
5
16 D POR re-arm time t
Low-voltage detection threshold —
P
17
high range
R
V
V
PU
I
IC
In
RAM
POR
POR
LVDH
VIN< VSS, VIN> V
VDD falling
V
rising
DD
17.5 — 52.5 kΩ
–0.2 — 0.2 mA
DD
–5 — 5 mA
—— 8pF
— 0.6 1.0 V
0.9 1.4 2.0 V
10 — — μs
2.08
2.16
2.1
2.19
2.2
2.27
V
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor 15
Electrical Characteristics
Table 8. DC Characteristics (continued)
1.82
1.90
2.46
2.46
2.1
2.19
1
Max Unit
1.91
1.99
2.56
2.56
2.2
2.27
Num C Characteristic Symbol Condition Min Typ
18 P
19 P
20 P
21 P Low-voltage inhibit reset/recover hysteresis V
22 P Bandgap Voltage Reference
1
Typical values are measured at 25°C. Characterized, not tested
2
All functional non-supply pins are internally clamped to VSS and VDD.
3
Input must be current limited to the value specified. To determine the value of the required current-limiting resistor, calculate
Low-voltage detection threshold —
low range
Low-voltage warning threshold —
high range
Low-voltage warning threshold —
low range
6
V
V
V
V
LVDL
LVWH
LVWL
hys
BG
VDD falling
V
rising
DD
VDD falling
V
rising
DD
VDD falling
V
rising
DD
1.80
1.88
2.36
2.36
2.08
2.16
—80—mV
1.19 1.20 1.21 V
resistance values for positive and negative clamp voltages, then use the larger of the two values.
4
Power supply must maintain regulation within operating VDDrange during instantaneous and operating maximum current
conditions. If positive injection current (V
In>VDD
in external power supply going out of regulation. Ensure external V
) is greater than IDD, the injection current may flow out of VDDand could result
load will shunt current greater than maximum injection
DD
current. This will be the greatest risk when the MCU is not consuming power. Examples are: if no system clock is present, or if
clock rate is very low (which would reduce overall power consumption).
5
Maximum is highest voltage that POR is guaranteed.
6
Factory trimmed at VDD = 3.0 V, Temp = 25°C
40
35
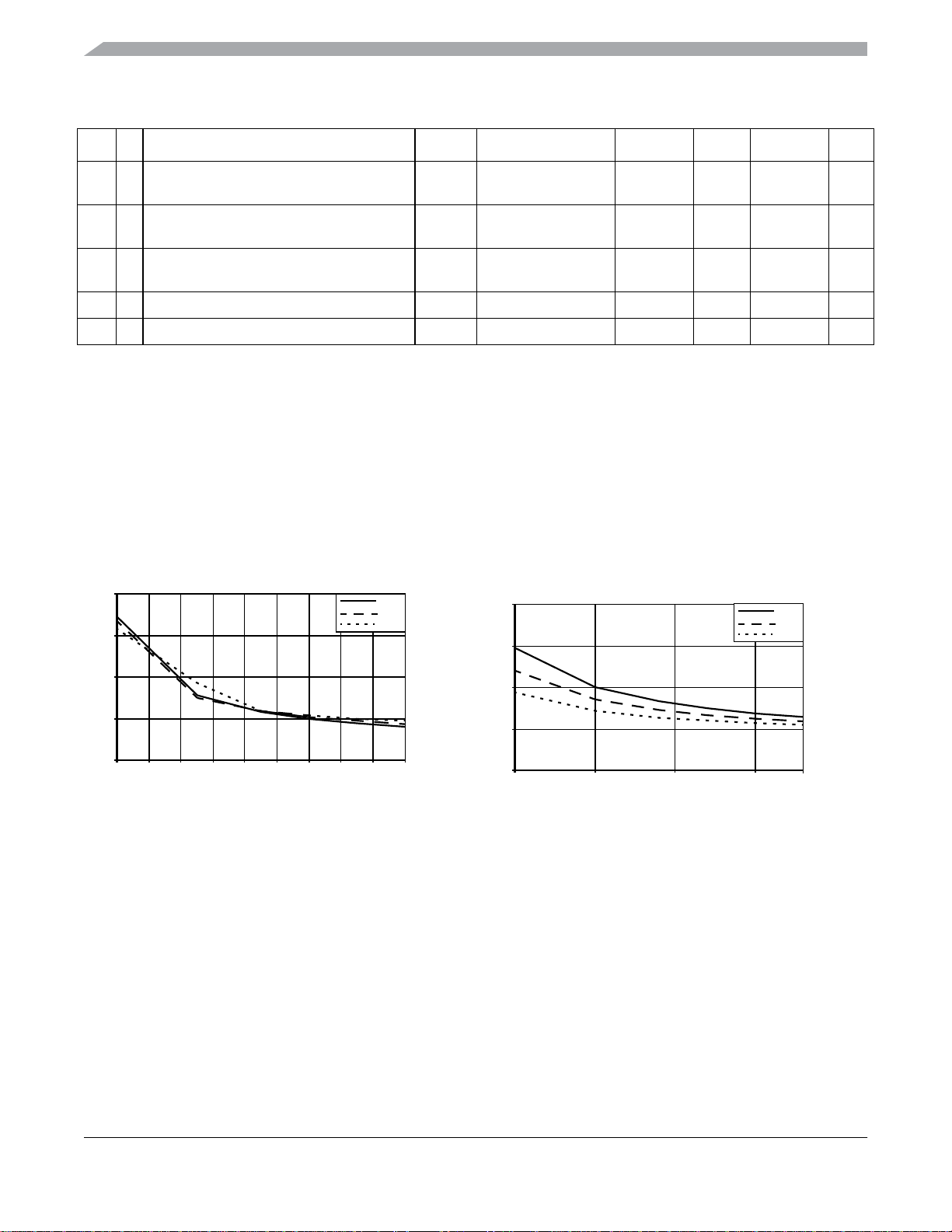
PULL-UP RESISTOR TYPICALS
85°C
25°C
–40°C
40
35
PULL-DOWN RESISTOR TYPICALS
85°C
25°C
–40°C
V
V
V
30
25
PULL-UP RESISTOR (kΩ)
20
1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.4 3.6
VDD (V)
Figure 7. Pull-up and Pull-down Typical Resistor Values
MC9S08QE128 Series Advance Information Data Sheet, Rev. 3
30
25
PULL-DOWN RESISTANCE (kΩ)
20
1.8 2.3 2.8 3.3
(V)
V
DD
3.6
Freescale Semiconductor16
 Loading...
Loading...