Page 1

FortiClient Endpoint
Security
Version 4.0 MR1
Administration Guide
™
Page 2

FortiClient Endpoint Security Administration Guide
Version 4.0 MR1
31 August 2009
04-40001-99556-20090626
© Copyright 2009 Fortinet, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication including text, examples,
diagrams or illustrations may be reproduced, transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or otherwise, for any purpose, without prior written permission of
Fortinet, Inc.
Trademarks
Dynamic Threat Prevention System (DTPS), APSecure, FortiASIC, FortiBIOS, FortiBridge, FortiClient,
FortiGate®, FortiGate Unified Threat Management System, FortiGuard®, FortiGuard-Antispam,
FortiGuard-Antivirus, FortiGuard-Intrusion, FortiGuard-Web, FortiLog, FortiAnalyzer, FortiManager,
Fortinet®, FortiOS, FortiPartner, FortiProtect, FortiReporter, FortiResponse, FortiShield, FortiVoIP, and
FortiWiFi are trademarks of Fortinet, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. The names of actual
companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
Regulatory compliance
FCC Class A Part 15 CSA/CUS
CAUTION: Risk of Explosion if Battery is replaced by an Incorrect Type.
Dispose of Used Batteries According to the Instructions.
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Introduction .............................................................................................. 1
About FortiClient Endpoint Security ............................................................................. 1
System requirements.................................................................................................. 1
Supported FortiGate models and FortiOS versions.................................................... 2
Language Support ...................................................................................................... 2
About this Guide ............................................................................................................. 2
Documentation ................................................................................................................ 3
Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD ....................................................................... 3
Fortinet Knowledge Center ........................................................................................ 3
Contact Fortinet technical documentation .................................................................. 3
Customer service and technical support...................................................................... 3
Installation ................................................................................................ 5
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 5
FortiClient software packages ....................................................................................... 5
Windows executable (.exe) installer ........................................................................... 5
MSI installer ................................................................................................................ 5
Installation notes......................................................................................................... 6
Standard FortiClient Installation.................................................................................... 6
Single-user installation................................................................................................ 6
Multiple-user installation ............................................................................................. 7
Custom Installer Packages ..................................................................... 9
Overview .......................................................................................................................... 9
Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager ................................................ 9
Creating the MST file with no command line parameters......................................... 10
Creating the sample installation................................................................................ 10
Performing additional customizations ....................................................................... 11
Creating the custom MSI installation file................................................................... 12
Customizing the FortiClient application for enterprise licensing ............................... 13
Deploying the customized FortiClient application ..................................................... 13
Transferring customizations to later versions of FortiClient...................................... 13
Customizing the installer using an MSI editor ........................................................... 14
Creating a FortiClient custom installation ................................................................. 15
Suppressing Features............................................................................................... 15
Sample command lines ............................................................................................ 15
Specifying install log file............................................................................................ 16
Language transforms................................................................................................ 16
Specifying multiple transforms on the command line ............................................... 16
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 i
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 4

Contents
Deploying the Customized Installation ....................................................................... 16
Endpoint NAC (FortiGate) distribution ...................................................................... 16
Active Directory installation....................................................................................... 17
Shared folder installation .......................................................................................... 17
Managing FortiClient with FortiManager .................................................................... 17
Enabling Remote Management with FortiManager .................................................. 18
Advanced Scenarios..................................................................................................... 20
Installing FortiClient as part of a cloned disk image ................................................. 20
Installing FortiClient on cloned computers................................................................ 20
Installing FortiClient on Citrix servers ....................................................................... 20
Configuring AntiLeak for FortiClient.......................................................................... 21
FortiClient Licensing ............................................................................. 23
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 23
Standard fixed licensing............................................................................................... 23
Enterprise licensing...................................................................................................... 24
Configuring enterprise licenses ................................................................................ 24
Creating enterprise client license keys ..................................................................... 25
Deploying enterprise client license keys................................................................... 25
Creating customized FortiClient installers ................................................................ 25
Corporate Security Policies .................................................................. 27
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 27
User view of security policy ...................................................................................... 27
Configuring a corporate security policy ..................................................................... 28
Endpoint Network Access Control ....................................................... 29
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 29
Enforcing use of FortiClient software ......................................................................... 29
Configuring FortiGuard Services ................................................................................ 30
Setting the FortiClient version..................................................................................... 30
Uploading the FortiClient installer to your FortiGate unit .......................................... 32
Enabling Endpoint Control........................................................................................... 32
Creating Endpoint Control profiles............................................................................ 32
Creating an Application Detection List...................................................................... 33
Applying an Endpoint Control profile to a firewall policy ........................................... 36
Monitoring Endpoints ................................................................................................ 37
Creating FortiClient VPNs ..................................................................... 39
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 39
Configuring VPN connections using FortiClient........................................................ 39
Configuring VPN connections on FortiGate units ..................................................... 39
About split tunneling ................................................................................................. 40
ii 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 5

Contents
Configuring VPN connections using FortiManager................................................... 40
Configuring VPN connections using custom installations....................................... 41
Configuring the FortiGate gateway as a policy server .............................................. 41
Per-User Web Filtering .......................................................................... 43
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 43
Web filtering on Windows networks.......................................................................... 43
Web filtering for remote users................................................................................... 43
Configuring web filtering.............................................................................................. 43
Managing FortiClient computers............................................................................... 44
Defining web filter profiles......................................................................................... 45
Configuring LDAP settings........................................................................................ 45
Assigning web filter profiles ...................................................................................... 45
Configuring VPNs without FortiClient Endpoint Security.................. 47
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 47
Using the FortiClient VPN Editor ................................................................................. 47
Importing VPN tunnel settings .................................................................................. 48
Configuring VPN tunnel settings............................................................................... 48
Configuring certificates for FortiClient VPN .............................................................. 50
Exporting configurations to the FortiClient VPN installer ........................................ 50
Using the FortiClient API....................................................................... 51
Overview ........................................................................................................................ 51
Controlling a VPN.......................................................................................................... 51
Linking to the COM library ........................................................................................ 51
Retrieving a list of VPN connection names............................................................... 52
Opening the VPN tunnel........................................................................................... 52
Responding to XAuth requests ................................................................................. 52
Monitoring the connection......................................................................................... 53
Setting and monitoring a security policy.................................................................... 53
Setting a security policy ............................................................................................ 54
Reading a security policy.......................................................................................... 54
Monitoring policy compliance.................................................................................... 54
Making the FortiClient application comply with the policy......................................... 55
API reference ................................................................................................................. 56
Appendix A: Installer Public Properties............................................... 57
Index .................................................................................61
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 iii
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 6

Contents
iv 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 7

Introduction About FortiClient Endpoint Security
Introduction
This chapter introduces you to FortiClient Endpoint Security software and the following
topics:
• About FortiClient Endpoint Security
• Documentation
• Customer service and technical support
About FortiClient Endpoint Security
FortiClient Endpoint Security is a unified security agent for Windows computers that
integrates personal firewall, IPSec VPN, antivirus, anti-spyware, anti-spam and web
content filtering into a single software package.
With the FortiClient application, you can:
• create VPN connections to remote networks including SSL VPN connections,
• scan your computer for viruses,
• configure real-time protection against viruses and unauthorized modification of the
Windows registry,
• restrict access to your system and applications by setting up firewall policies,
• apply Endpoint Network Application Control (NAC) to monitor and control applications
running on endpoints,
• use WAN Optimization to improve the efficiency of communication across the WAN,
• configure web filtering to process all web content against known malicious URLs to
block inappropriate material and malicious scripts including Java applets, cookies, and
ActiveX scripts entering the network,
• filter incoming email on your Microsoft Outlook® and Microsoft Outlook® Express to
collect spam automatically,
• use the remote management function provided by the FortiManager System.
System requirements
To install FortiClient 4.1 you need:
• A PC-compatible computer with Pentium processor or equivalent
• Compatible operating system and minimum RAM:
• Microsoft Windows 2000: 128 MB
• Microsoft Windows XP 32-bit and 64-bit: 256 MB
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003 32-bit and 64-bit: 384 MB
• Microsoft Windows Vista: 512 MB
• Microsoft Windows 7: 512 MB
• a compatible email application for the AntiSpam feature:
• Microsoft Outlook 2000 or later
• Microsoft Outlook Express 2000 or later
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 1
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 8

About this Guide Introduction
• a compatible email application for the AntiLeak feature:
• Microsoft Outlook 2000 or later
• 100 MB hard disk space
• Native Microsoft TCP/IP communications protocol
• Native Microsoft PPP dialer for dial-up connections
• an Ethernet connection
Note: The FortiClient software installs a virtual network adapter.
Supported FortiGate models and FortiOS versions
The FortiClient software supports all FortiGate models running FortiOS version 2.36, 2.5,
2.8, 3.0 and 4.0.
Language Support
The FortiClient Endpoint Security user interface and documentation is localized for:
• English
•French
• Simplified Chinese
• Japanese
• Korean
The FortiClient installation software detects which code page the computer is using and
installs the matching language version. For any languages other than the above are
detected, the English version of the software is installed.
About this Guide
This Administration Guide contains the following chapters:
• Installation describes several types of FortiClient installation beyond the simple end-
• Custom Installer Packages describes how to create a customized installation package
• Corporate Security Policies describes how you can require users to comply with a
• FortiClient Licensing describes how to manage enterprise licensing of FortiClient
• Enforcing use of FortiClient describes how to enforce use of FortiClient Endpoint
• Creating FortiClient VPNs describes how to configure VPNs on FortiGate units to work
• Configuring VPNs without FortiClient Endpoint Security describes how to configure
user installations described in the FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide.
to deploy to users in an organization. The customized installation can include enabling
centralized management by a FortiManager server.
security policy to use VPN tunnels. The policy can require users to enable firewall, realtime antivirus protection, web filtering or antispam.
computer, using either a volume license or a re-distributable license.
Security using a FortiGate unit that can check hosts for the presence FortiClient
Endpoint Security.
with the VPN client feature of FortiClient Endpoint Security.
FortiClient VPN, a light VPN client that you can distribute to users who do not have
FortiClient Endpoint Security.
2 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 9

Introduction Documentation
• Using the FortiClient API describes the COM-based FortiClient API.
• Per-User Web Filtering describes how to deploy the FortiClient application to perform
web filtering customized for each user on a Microsoft Windows network. For larger
deployments, a FortiManager system is used to manage web filter profiles.
Documentation
This manual, the FortiClient Endpoint Security Administration Guide, provides information
about deploying the FortiClient application in your organization.
The FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide and the FortiClient online help provide
information and procedures for using and configuring the FortiClient software.
Information about FortiGate Antivirus Firewalls is available from the FortiGate online help
and the FortiGate Administration Guide.
Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD
All Fortinet documentation is available on the Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD
shipped with your Fortinet product. (You do not receive this CD if you download the
FortiClient application.) The documents on this CD are current at shipping time. For up-todate versions of Fortinet documentation visit the Fortinet Technical Documentation web
site at http://docs.forticare.com.
Fortinet Knowledge Center
Additional Fortinet technical documentation is available from the Fortinet Knowledge
Center. The knowledge center contains troubleshooting and how-to articles, FAQs,
technical notes, a glossary, and more. Visit the Fortinet Knowledge Center at
http://kb.fortinet.com.
Contact Fortinet technical documentation
You can send information about errors or omissions in this document or any Fortinet
technical documentation to techdoc@fortinet.com.
Customer service and technical support
Fortinet Technical Support provides services designed to make sure that your Fortinet
systems install quickly, configure easily, and operate reliably in your network.
Please visit the Fortinet Technical Support web Site at http://support.fortinet.com to learn
about the technical support services that Fortinet provides.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 3
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 10

Customer service and technical support Introduction
4 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 11

Installation Overview
Installation
This chapter describes how to install FortiClient.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• FortiClient software packages
• Standard FortiClient Installation
Overview
You can install FortiClient directly from the Fortinet Web site or from a custom location,
such as your network.
FortiClient software packages
Fortinet provides different installation packages for FortiClient software. The two main
types of default installation packages for FortiClient software are:
• a Windows executable (.exe) file
• a .zip file (compressed archive) containing a Microsoft Installer (MSI) package,
language transform files and the FCRepackager tool
The 64-bit versions of these files have “_x64” in the name. If you are running 64-bit
Windows, you must use a 64-bit installation package.
Windows executable (.exe) installer
The Windows executable (.exe) installer provides easy installation on a single computer
by the end user. Any existing FortiClient installation on the computer is upgraded. The
FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide provides information about using these
installers.
To install the FortiClient software - Windows executable installer
1 Double-click the FortiClient installer program file.
2 Follow the instructions on the screen, selecting Next to proceed through the installation
options.
When the installation has completed, the FortiClient Configuration Wizard begins,
unless you are upgrading an existing installation.
MSI installer
The MSI installer in the .zip file package is customizable for a larger roll-out to many
computers in an organization. This customization procedures in this chapter use the .zip
file package exclusively. You can deploy the customized MSI installer to your users and
they can install it following the simple instructions in the FortiClient Endpoint Security User
Guide. You can preconfigure all application settings, including the configuration for
centralized management by a FortiManager system. For more information, see “Custom
Installer Packages” on page 9.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 5
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 12

Standard FortiClient Installation Installation
You can upgrade an existing FortiClient installation by installing a newer version of the
software. To upgrade using an MSI installer, you can double-click the MSI file or use the
following commend line:
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi
To install the FortiClient software - MSI installer
1 Extract the files from the FortiClient Setup .zip archive into a folder.
2 To perform a new installation or upgrade an existing installation, double-click the
FortiClient.msi file.
3 Follow the instructions on the screen, selecting Next to proceed through the installation
options.
When the installation has completed, the FortiClient Configuration Wizard begins,
unless you are upgrading an existing installation.
Installation notes
These notes describe special conditions that apply to specific types of installations.
• Installing on Windows Vista SP1 — Make sure that Windows is not installing updates
while you install the FortiClient application. If Windows Update has run and it
requested a reboot, be sure to reboot your computer before installing the FortiClient
application.
• Installing on servers — When installing FortiClient Endpoint Security on a server,
follow the antivirus guidelines for other products installed on the server. You might
need to exclude from antivirus scanning certain files and directories such as Exchange
Server, SQL Server and other software with database back-ends.
Note: If FortiClient is directly installed on SQL or Exchange server, the AntiVirus > Server
Protection window is disabled. To enable antivirus server protection, use the msi package
with the public property WITHEXCHANGE=1. For example: msiexec /i
forticlient.msi WITHEXCHANGE=1
Note: While Windows Server is supported, Fortinet does not recommend installing
FortiClient onto Domain Controllers.
• Installing from a drive created with subst — Installing from an MSI package does
not work if the MSI file is located on a drive created with the subst command. You can
do any of the following:
• specify the real path to the file
• move the MSI file to a location where this is not an issue
• use the .exe installer instead, if possible
Standard FortiClient Installation
Single-user installation
User can install the standard FortiClient application through such methods such as
downloading it from the FortiClient Web site or using a CD. For more information on
installing FortiClient, see the FortiClient User Guide or QuickStart Guide.
6 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 13

Installation Standard FortiClient Installation
Multiple-user installation
You can use the FortiGate’s Web Config to manage the version of FortiClient (endpoint
control) running on multiple computers. See “Enforcing use of FortiClient software” on
page 29 for more information.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 7
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 14

Standard FortiClient Installation Installation
8 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 15

Custom Installer Packages Overview
Custom Installer Packages
This chapter describes how to create a custom MSI package for FortiClient Endpoint
Security that you can deploy to your users. The customized installation can include the
necessary configuration for central management by a FortiManager system.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager
• Customizing the installer using an MSI editor
• Deploying the Customized Installation
• Managing FortiClient with FortiManager
• Advanced Scenarios
Overview
This chapter describes two methods of producing a custom MSI installer: using
FCRepackager and using the MSI editor. The FCRepackager tool is included in the
FortiClientTools.zip file and is the recommended method to use.
With both types of customized installation, you can:
• set which features are installed
• include the FortiClient license key
• enable or disable the installation wizard
• enable or disable update scheduling
• set update schedule randomly on install
• enable or disable upgrade of existing installation
• enable management by a FortiManager system and set the FortiClient Manager
lockdown password
You can simply give your users the customized package to install. It works the same way
as the standard installer provided by Fortinet. There are several other ways to distribute
the customized installer, including a network installer image, Windows Active Directory
server or the FortiClient host check feature on some FortiGate units. These are described
in the “Installation” chapter.
Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager
FCRepackager is designed to speed up the creation of customized FortiClient installation
packages. This tool will create a Microsoft Transform (MST) file from the current
FortiClient installation settings. The current settings can be packed into an MST file by
running the FCRepackager with no command line parameters.
Optionally, you write the current installation settings into a FortiClient.msi file, so that endusers do not need to use the command line to incorporate MST files. To create a custom
msi file, see “Creating the custom MSI installation file” on page 12.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 9
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 16

Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager Custom Installer Packages
Using the FCRepackager tool, you can create a custom installation package in a few
steps:
1 Configure FortiClient. FortiClient must be installed and configured with the settings
that you want installed on the end-user computers.
2 Create a custom installation package using either FCRepackager or an MSI editor. The
FCRepackager application is easier to use.
3 Install the customized FortiClient application on your users’ computers. With the proper
administrative permissions, users can even do this themselves.
Creating the MST file with no command line parameters
In order to create an mst file, you need to use the FCRepackager tool. The FCRepackager
tool can be extracted from the FortiClientTools.zip file. The FortiClientTools.zip file can be
downloaded from the Fortinet Support Web site.
You also need to have FortiClient installed and configured with your desired settings to
create the custom mst file.
For more information and examples for creating a customized mst file using switches and
switch parameters, see the FCRepackager_Readme.txt file that comes in the
FortiClientTools.zip file.
To create the mst file with no command line parameters
1 Download the FortiClientTools.zip file from the Fortinet Support Web site and extract
the files into a folder.
2 Ensure FortiClient is installed and configured with the desired settings. The mst file is
created based on your current FortiClient settings.
3 Run the FCRepackager application. The FortiClient.mst file is automatically created in
the same directory.
Creating the sample installation
You must create a sample installation on a computer running one of the supported
operating systems. See “System requirements” on page 1. The computer should not
already have the FortiClient application installed.
The ADMINMODE=1 option used in the following procedure enables you to make registry
changes to your sample installation, which some customizations require. Also, this option
permits modification of files in the FortiClient program directory, which normally only the
FortiClient application can access. You should not use the ADMINMODE=1 option when
you install of the FortiClient application onto your users’ computers.
To perform the sample installation of the FortiClient software
1 Expand the FortiClient Endpoint Security installer .zip package into a new folder.
2 From the folder where you expanded the .zip package, install the FortiClient
application use the following command line:
• if FortiClient applications will not be centrally managed
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi ADMINMODE=1
The FortiClient application wizard starts. Follow the wizard to install the features you
require. Reboot the computer if the installer requests it. When the computer restarts,
the FortiClient installation wizard continues.
10 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 17

Custom Installer Packages Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager
3 Continue configuring the application. The wizard Advanced Setup option covers
security zones, proxy settings, update settings and AV scan settings. These can also
be configured later.
4 Configure the sample installation as you want the FortiClient application to be
configured on your user’s computers.
5 Optionally, perform additional customizations as described in “Performing additional
customizations” on page 11.
See the FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide for information about configuring
each of the FortiClient features.
Performing additional customizations
You can edit the registry to make additional customizations to your FortiClient installation.
Hiding the FortiTray
1 Using regedit or regedt32, edit the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Fortinet\FortiClient\FA_FORTITRAY
2 Set the key value to 0.
Permitting fallback to public FDS servers
Managed FortiClient computer receive push updates for antivirus definitions. Mobile users
might not always be able to connect to the FortiManager unit. Optionally, you can
configure FortiClient to use the default public FDS servers when necessary.
To permit fallback use of public FDS servers
1 Using regedit or regedt32, create the following DWORD value:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Fortinet\FortiClient\FA_UPDATE\
FallbackToDefault
2 Set the value to 1.
Disabling saving of VPN XAUTH passwords
This customization prevents users from saving their XAUTH passwords.
To disable saving of XAUTH passwords
1 Using regedit or regedt32, edit the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Fortinet\FortiClient\FA_IKE\
2 Add the value DontRememberPassword as a DWORD under the key.
3 Set the value of DontRememberPassword to 1.
Disabling web filter rating of IP addresses
The FortiClient web filter requests ratings from the FortiGuard web filtering service for both
the URL and the IP address. Optionally, you can disable the rating of IP addresses so that
web sites are rated only by URL.
To disable rating of IP addresses
1 Using regedit or regedt32, edit the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Fortinet\FortiClient\FA_WEBFILTER\
2 Add the value DontRateIP as a DWORD under the key.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 11
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 18
Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager Custom Installer Packages
3 Set the value of DontRateIP to 1.
Blocking all connections that have no firewall rule
By default, if there is no firewall rule for a particular network connection, the FortiClient
application asks the user whether to allow the connection. For an enterprise deployment,
you might prefer to block all connections except those that have a specific firewall rule to
permit them.
To block all connections by default
1 Using regedit or regedt32, edit the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Fortinet\FortiClient\FA_FCM\firewallbehavior
2 Set the key value to 0.
Changing the certificate key size
The default VPN certificate key size in FortiClient v4.0 is 2048 bits. You can change the
size.
To change the certificate key size
1 Using regedit or regedt32, edit the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Fortinet\FortiClient\FA_CERT\key_size
2 Set the key value to one of: 1 (1024 bits), 15 (1536 bits), 2 (2048 bits), 3 (3072 bits) or
4 (4096 bits).
Creating the custom MSI installation file
With the sample application configured as you want for your users, you can create a
custom MSI installer file for your customized FortiClient application.
1 Determine the command line options you need for your customized FortiClient installer
from the following table.
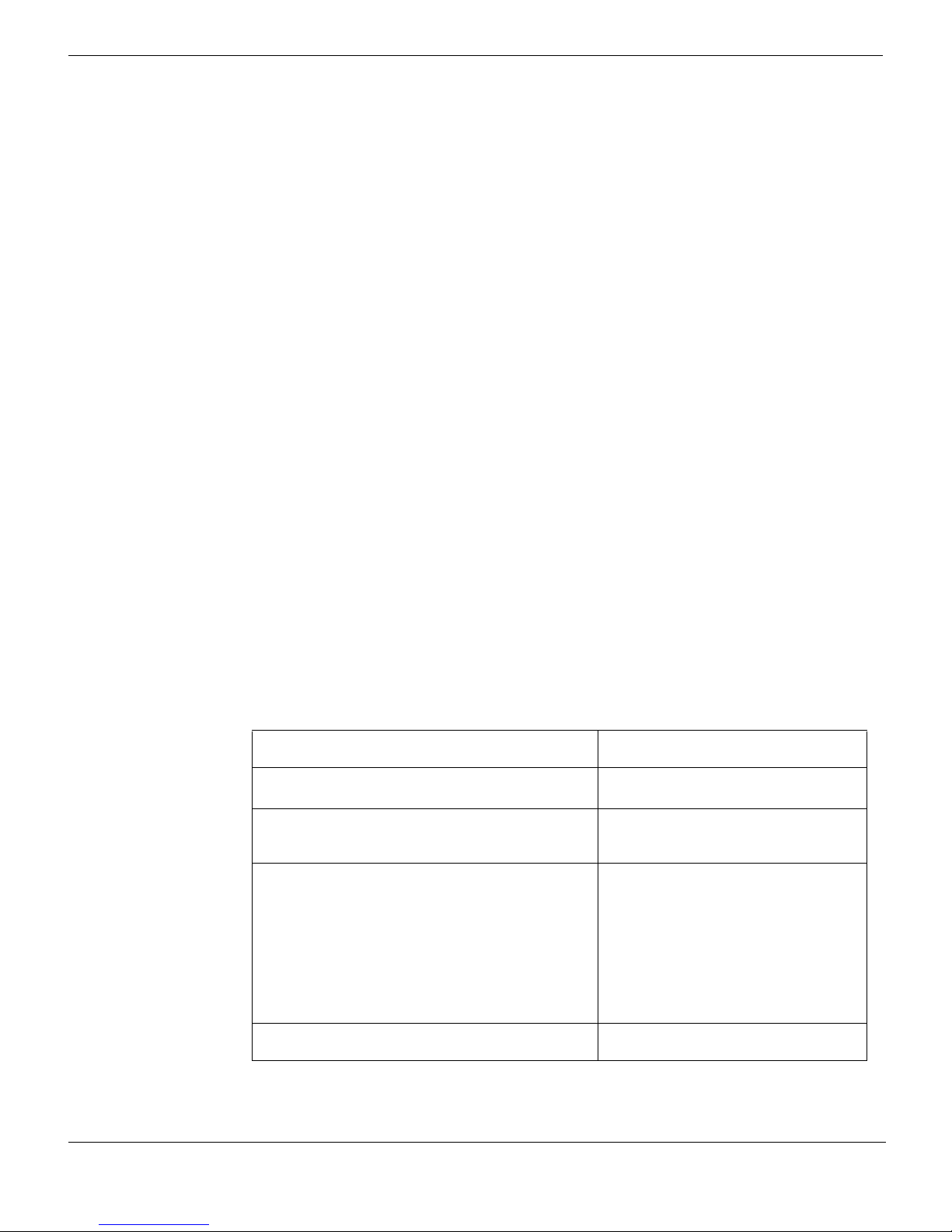
Table 1: FCRepackager options
Specify license key (for standard fixed license or
volume license from FDS, not for enterprise license)
Lock down program for FortiManager.
Specify the plain text password.
Set random AV update time between specified hours.
The sample installation must contain an update
schedule.
Specify which features can be installed.
The resulting .msi file cannot be used for upgrades,
only for new installations.
If the -i option is not specified, all features are available
for installation.
Shrink the .msi file by removing files for unused
features. Valid only when used with -m option.
-k <license_key>
-L <lockdown_password>
-s <start_hour>-<end_hour>
-i <feature1>[,<feature2>] ...
Features are:
AV Antivirus
VPN Virtual Private Network
FW Firewall
WF Web filter
AS Antispam
AL AntiLeak
Note: feature names are case-sensitive.
-z
Refer to the FCRepackager_Readme.txt file for more information about command line
options.
12 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 19

Custom Installer Packages Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager
2 In the folder where you expanded the installer .zip package, execute the following
command line:
FCRepackager -m FortiClient.msi <options from step 1>
A new subdirectory is created, named transformed. It contains the new FortiClient.msi
file.
Customizing the installer language
You can further modify your customized installer with one of the language .mst files
provided in the installer .zip file. This must be done as a separate step from the
customizations described previously. The language files are:
• 1033.mst = US English (default)
• 1036.mst = French
• 1041.mst = Japanese
• 2052.mst = Simplified Chinese
• 1028.mst = Traditional Chinese
For example, to change your customized installer language to French, execute the
following command in the folder where you expanded the installer .zip package:
FCRepackager -t 1036.mst -m transformed\FortiClient.msi
Customizing the FortiClient application for enterprise licensing
If you use enterprise licensing for your FortiClient computer, your FortiClient installer
needs specific additional customization. For more information, see “Enterprise licensing”
on page 24.
Deploying the customized FortiClient application
You can distribute your new FortiClient.msi file to users. Users simply double-click the file
to begin installation. On a Windows Advanced Server network, you can install the
application on end users’ computers remotely. See “Active Directory installation” on
page 17.
VPN certificates can be added to the customized installer.Use the FortiClientVPNEditor
file located in the FortiClientVPNTools .zip file. It can be used to embed VPN tunnels into
the FortiClient MSI file. See “Using the FortiClient VPN Editor” on page 47 for more
information.
Transferring customizations to later versions of FortiClient
When a newer version of FortiClient Endpoint Security is released, your existing users can
simply run the FortiClient installer and upgrade while keeping the customized settings. For
new users, you will need to create a customized version of the new installer.
To customize the newer FortiClient installer, you do not need to repeat all of the
customization steps described previously in this section. When you create your first
customized FortiClient installer, you can also save your customizations to a transform
(.mst) file. Simply run FCRepackager.exe again with no parameters. The output is a file
named FortiClient.mst.
To modify the new FortiClient .msi installer with your saved customizations, use the
following command:
FCRepackager -t FortiClient.mst -m FortiClient.msi
If the files are not in the current directory, you need to specify the path to them.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 13
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 20

Customizing the installer using an MSI editor Custom Installer Packages
Caution: If you are using FortiClient version 4.0 or lower, the .mst files from those versions
are incompatible with FortiClient v4.0 MR1 and above. Therefore, you cannot use the
FCRepackager -t FortiClient.mst -m FortiClient.msi command.
Note: An MSI installation package can upgrade an existing installation only if it has the
same name as the original installation package. If necessary, rename the upgrade
installation package to match the file name of the previous customized FortiClient
installation package you provided to your users.
Customizing the installer using an MSI editor
Use an MSI editor to create a custom FortiClient installation package. For example, you
can use the MSI property LICENSE to include your license key. You can create and set
this property in the property table, or you can specify it on the command line using the
following command:
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi LICENSE=1234567890abc
Note that the installation will not abort if you specify an invalid license key. For a complete
list of installer public properties that can be specified when installing FortiClient, see
“Appendix A: Installer Public Properties” for more information. The installer public
properties can also be embedded into the MSI by using an MSI editing tool to make
changes to the MSI’s property table.
It is recommended that you use this method only if you are familiar with the MSI editor and
you only want to customize a few specific items. Do not edit the MSI file directly. Create a
transform file that contains the configuration changes you require. The transform file is
applied to the original MSI file at run time by the msiexec.exe executable file. Creating a
transform file takes a bit more time than editing the MSI file directly, however it will save
you time in the long run as you can apply the same transform file to future FortiClient
releases.
Caution: You must follow the editing rules described in this section. Ignoring these rules
may result in a custom installation that cannot be upgraded or patched by future releases of
FortiClient.
If possible, avoid modifying any other components. FortiClient sub-features do not support
“Advertised” installations.
The following rules MUST be followed:
• never delete a feature you do not need. If you do not need a feature, set the install level
to 0.
• never delete a component you do not need.
• never move a component from one feature to another.
• never modify the installation UI or installation execution order.
• never rename ANY existing component or feature.
• never change the component code of ANY existing component.
• never change the PRODUCTCODE.
• never change the UPGRADECODE.
• never add new features to the root of the feature tree. If you really need to add a
feature, add it as a sub-feature of an existing FortiClient feature. However, before you
add a feature, question why you are adding a feature and what you are trying to
accomplish.
14 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 21

Custom Installer Packages Customizing the installer using an MSI editor
Creating a FortiClient custom installation
Use an MSI editor and the original FortiClient MSI installation file for the following
procedure. These instructions assume you know how to:
• use an MSI editor
• use the command line msiexec commands
• roll out an MSI based installation to your network.
Note: You do not need to edit the MSI to disable the wizard. When you perform a silent or
reduced UI installation, the MSI automatically disables the FortiClient Wizard from
executing after rebooting the computer.
To create and test a custom FortiClient installation
1 Make a copy of the FortiClient.msi file and rename the copy (i.e. “target.msi”).
2 Open “target.msi” with an MSI editor and add your modifications to it.
3 Save the changes you made to the “target.msi” file and close the file.
4 With your MSI editor, make a transform file (*.mst)
• The base package must be FortiClient.msi.
• The target package must be target.msi.
• Give the .mst file a suitable name. We suggest you include the version of FortiClient
that was used to create the transform. For example, custom_4.0.mst.
5 Test the installation by installing the baseline package with the transform onto a single
computer. Use the following command:
msiexec /i <path to package>FortiClient.msi
TRANSFORMS=custom_4.0.mst /L*v c:\log.txt
where <path to package> is the path to your package if not in the current directory.
There are no spaces in TRANSFORMS=custom_4.0.mst. There is a space between
TRANSFORMS=custom_4.0.mst and /L*v c:\log.txt.
If there are any errors during installation, the log file is an invaluable source of
information.
6 Test FortiClient to make sure the modifications you made are present and correct. If
there are any mistakes, use your editor to make changes to the .mst file.
7 Test uninstalling the FortiClient software. It is critical that you do this before you roll out
FortiClient to your network. The uninstall must complete without an error or rollback
occurring.
8 Roll out your custom FortiClient installation specifying the transform file.
Suppressing Features
To suppress FortiClient features from installing, create a transform which sets the Install
Level of the feature to 0 (zero).
Sample command lines
• Install FortiClient
msiexec /i <folder of FortiClient.msi>\FortiClient.msi
FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=<FortiClientManager IP>
• Upgrade FortiClient
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 15
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 22

Deploying the Customized Installation Custom Installer Packages
msiexec /i <folder of FortiClient.msi>\FortiClient.msi
FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=<FortiClientManager IP>
REINSTALL=ALL REINSTALLMODE=vomus
• Install FortiClient on a computer which is behind a NAT device
msiexec /i <folder of FortiClient.msi>\FortiClient.msi
FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRIP=<FortiClientManager IP>
FMGRENABLEDISCOVER=1
• Upgrade FortiClient on a computer which is behind a NAT device
msiexec /i <folder of FortiClient.msi>\FortiClient.msi
FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRIP=<FortiClientManager IP> REINSTALL=ALL
REINSTALLMODE=vomus FMGRENABLEDISCOVER=1
Specifying install log file
When installing using the MSI file, the install does not create the install log automatically.
For an MSI installation to produce a log, add the following option to the command line:
/L*v <filepath>
For example:
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi /L*v %temp%\logfile.txt
Alternatively, you can install the appropriate logging active directory group policies.
Language transforms
The MST files that ship with the baseline FortiClient package are the English, Japanese
and Simplified Chinese language transforms for the installer user interface:
• 1033.mst = US English
• 1041.mst = Japanese
• 2052.mst = Simplified Chinese
• 1028.mst = Traditional Chinese
Specifying multiple transforms on the command line
You can specify multiple transforms on the command line. Separate each transform with a
semicolon. For example:
msiexec /i <path to package>FortiClient.msi
TRANSFORMS=custom4.0.mst;2052.mst
Deploying the Customized Installation
Endpoint NAC (FortiGate) distribution
You can use the FortiGate’s Web Config to manage the version of FortiClient (endpoint
control) running on multiple computers. See “Enforcing use of FortiClient software” on
page 29 for more information.
You can also update the FTP/HTTP replacement message on the FortiGate so that the
location of the custom installer on your network is shown in the message. Go to System >
Config to edit the replacement messages. See the FortiGate Administration Guide for
more information on replacement messages.
16 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 23

Custom Installer Packages Managing FortiClient with FortiManager
Active Directory installation
You can customize the FortiClient installation and use the Active Directory Server to install
different customized installations on different computers.
The following is a general description of how to deploy the FortiClient software to remote
computers using Active Directory Server. For more details, see the Active Directory
manuals or online help.
To complete this procedure, you must log on as a member of the Domain Administrators
security group, the Enterprise Administrators security group, or the Group Policy Creator
Owners security group.
To deploy FortiClient using Active Directory Server
1 Put the FortiClient MSI installation file into a shared folder.
2 Open the Group Policy Object Editor.
3 Select Computer Configuration.
4 Select Software Settings.
5 Right-click Software Installation, select New, and then select Package.
6 Select the FortiClient MSI installation file and select Open.
7 In Deploy Software, select Assigned.
Shared folder installation
You can place the FortiClient.msi file in a shared network folder from which users can
install the FortiClient application. The FortiClient.msi file is a compressed archive
containing all of the needed files. Creating an uncompressed set of installation files can
improve installation speed, especially if the customized FortiClient application does not
contain all features.
To create a network installer
1 Create or choose a shared network folder for the installation.
2 From the folder that contains the FortiClient.msi file, execute the following command:
msiexec /qb /a FortiClient.msi TARGETDIR=<location>
where <location> is the path to the shared network folder where you want to place
the uncompressed installation files, for example c:\fc_installer\.
The shared network folder contains a FortiClient.msi file that is smaller than the original
because the other files have been decompressed into a set of subfolders. To install the
customized FortiClient application on their own computer, users simply execute the
FortiClient.msi file.
Managing FortiClient with FortiManager
You can install the FortiClient Endpoint Security application from a .zip or .exe package
and configure it for central management. The installed FortiClient application can either
accept management from a FortiManager unit at a specific IP address, or discover
FortiManager units on its network.
For information about centrally managing FortiClient PCs with FortiManager, see the
FortiClient Manager chapter of the FortiManager Administration Guide.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 17
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 24

Managing FortiClient with FortiManager Custom Installer Packages
Enabling Remote Management with FortiManager
Network administrators can use FortiManager to manage FortiClient installations across a
network. This enables the administrator to apply a consistent FortiClient configuration for
all users. Managed FortiClient computer receive push updates for antivirus signatures.
To enable remote management using FortiManager, you must create a transform that
changes the values of specific properties within the installer.
To enable remote management
1 Create a new, or edit an existing, MSI transform file.
2 Open the Property table and change the value of FMGRENABLED from 0 to 1.
3 Change the property FMGTRUSTEDIPS to the IP address(es) of the FortiManager(s)
that FortiClient will accept commands from.
The addresses can be specified as individual IP address, IP address ranges, or
subnets. You can specify a mixed list of addresses, ranges and subnets by separating
each value with a comma. For example:
Property Name Property Value Meaning
TRUSTEDIPS
TRUSTEDIPS 172.18.2.0/255.255.255.0 (trust a subnet)
TRUSTEDIPS 172.16.3.1-172.16.3.50 (trust an IP address range)
TRUSTEDIPS 172.16.90.83,172.18.2.0/255.255.255.0,
172.16.90.83 (trust a single IP address only)
172.16.3.1-172.16.3.50 (all the above)
4 Optionally, you can specify the IP address of your FortiManager device at installation
time by setting the value of the property FMGRIP to the IP address of your
FortiManager device. The address specified in FMGRIP is automatically trusted and
does not need to be added to the FMGTRUSTEDIPS value.
Configuring central management by specified FortiManager units
Using installer command line options, you can specify the IP address of one or more
FortiManager units that will control the FortiClient configuration.
The command-line options are as follows:
FMGRENABLED=1 This enables FortiManager central management.
FMGRIP=<FM_IP_Primary> This specifies the primary (or only) FortiManager unit.
If there are multiple FortiManager units that could manage this FortiClient PC, add the
following option.
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=<FM_IP1>,<FM_IP2>,...
<FM_IP1>,<FM_IP2>, and so on can be individual IP addresses, IP address ranges or
subnets. You can omit the FMGRIP option if the primary FortiManager unit IP address is
included as a single IP address in the FMGTRUSTEDIPS option.
For a complete list of installer public properties that can be specified when installing
FortiClient, see “Appendix A: Installer Public Properties” for more information.
Example command lines for the .exe package
For a FortiClient PC centrally managed by a FortiManager unit on IP address
172.16.100.5, the installation command line is:
FortiClientSetup /v"FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRIP=172.16.100.5"
18 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 25

Custom Installer Packages Managing FortiClient with FortiManager
For a FortiClient PC centrally managed by either a primary FortiManager unit on IP
address 172.16.100.5 or a secondary FortiManager unit on 172.16.100.6, the installation
command line is:
FortiClientSetup /v"FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRIP=172.16.100.5
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=172.16.100.5,172.16.100.6"
Note: You must enter the entire command on a single line.
Example command lines for the .zip package
Expand the .zip package into a folder before you execute these commands.
For a FortiClient PC centrally managed by a FortiManager unit on IP address
172.16.100.5, the installation command line is:
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRIP=172.16.100.5
For a FortiClient PC centrally managed by either a primary FortiManager unit on IP
address 172.16.100.5 or a secondary FortiManager unit on 172.16.100.6, the installation
command line is:
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRIP=172.16.100.5
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=172.16.100.5,172.16.100.6
Note: You must enter the entire command on a single line.
Configuring central management by discovered FortiManager units
Using installer command line options, you can enable discovery of FortiManager units and
specify by IP address the FortiManager units from which the FortiClient application
accepts central management.
The command-line options are as follows:
FMGRENABLED=1 This enables FortiManager central management.
FMGRENABLEDISCOVER=1 This enables the FortiClient application to request central
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=<FM_IP1>,
<FM_IP2>,...
For a complete list of installer public properties that can be specified when installing
FortiClient, see “Appendix A: Installer Public Properties” for more information.
Example command lines for the .exe package
For a FortiClient PC that accepts central management by any FortiManager unit on subnet
172.16.100.0/24, the installation command line is:
FortiClientSetup /v"FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRENABLEDISCOVER=1
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=172.16.100.0/255.255.255.0"
Note: You must enter the entire command on a single line.
Example command lines for the .zip package
Expand the .zip package into a folder before you execute these commands.
For a FortiClient PC that accepts central management by any FortiManager unit on subnet
172.16.100.0/24, the installation command line is:
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRENABLEDISCOVER=1
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=172.16.100.0/255.255.255.0
Note: You must enter the entire command on a single line.
management.
Specify individual IP addresses, IP address ranges or subnets
from which the FortiClient application accepts central
management.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 19
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 26

Advanced Scenarios Custom Installer Packages
Changing the default firewall action
By default, the FortiClient firewall allows unknown applications to access the network, or
asks the user, depending on the selected firewall profile. (An unknown application is one
that is not on the firewall applications list.) To make the FortiClient firewall always block
unknown applications, add the DEFAULTAPPLICATION=1 command line option when you
run the FortiClient installer.
Advanced Scenarios
Installing FortiClient as part of a cloned disk image
If you configure computer using a cloned hard disk image, you need to remove the unique
identifier from the FortiClient application. You will encounter problems with FortiManager
Server if you deploy multiple FortiClient applications with the same identifier.
This section describes how to include a custom FortiClient installation in a cloned hard
disk image but remove its unique identifier. On each computer configured with the cloned
hard disk image, the FortiClient application will generate its own unique identifier the first
time the computer is started.
To include a FortiClient installation in a hard disk image
1 Using an MSI FortiClient installer, install and configure the FortiClient application to suit
your requirements.
You can use a standard or a customized installation package.
2 Right-click the FortiClient icon in the system tray and select Shutdown FortiClient.
3 From the folder where you expanded the FortiClient .zip package, run
RemoveFCTID.exe. The RemoveFCTID tool requires administrative rights.
Note: Do not make the RemoveFCTID tool part of a logon script.
4 Shut down the computer.
Note: Do not reboot the Windows operating system on the computer before you create the
hard disk image. The FortiClient identifier is created before you log on.
5 Create the hard disk image and deploy it as needed.
Installing FortiClient on cloned computers
If you intend to make an image of the hard drive for deployment to other computers, you
need to shut down FortiClient and use the RemoveFCTID tool to remove the FortiClient
identifier. For more information, see “Installing FortiClient as part of a cloned disk image”
on page 20.
Installing FortiClient on Citrix servers
You can install FortiClient Endpoint Security on Citrix Presentation Server 4.5 in a
Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2008 Beta 3 environment.
You can use a standard or a customized installation package, but you must select the
Custom installation option and make sure that you do not install the VPN feature. Citrix
uses the Windows IPsec service, which the FortiClient VPN would disable.
20 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 27

Custom Installer Packages Advanced Scenarios
After installing the FortiClient application, restart the Citrix server. This resolves the
problem that the FortiClient installation can cause the Citrix console to lose
communication with the server.
To implement per-user web filtering, you need to define web filter profiles for your users.
For more information, see the FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide.
Configuring AntiLeak for FortiClient
The AntiLeak data loss prevention (DLP) feature prevents accidental leakage of sensitive
information through email messages. When you send an email message using Microsoft
Outlook (2000 or later), FortiClient searches the attachments for the words or patterns in
your sensitive words list. If any of the words or patterns are found, FortiClient logs the
message and can also block sending of the message.
Caution: Anti-Leak is available to those users upgrading from FortiClient 3.0 who were
previously using this feature. For a more comprehensive anti-leak solution, see data leak
prevention (DLP) in the FortiGate Administration Guide.
AntiLeak can examine the following file types:
• text (.txt)
• Microsoft Word (.doc)
• Microsoft Excel (.xls)
• Microsoft PowerPoint (.ppt)
• Adobe Portable Document Format (.pdf)
To use AntiLeak in FortiClient, you will have to create a custom installer package with
AntiLeak enabled.
To configure AntiLeak settings
1 Open the MSI in an MSI editor.
2 Navigate to the Feature table.
3 Find the record where the Feature field is Feature_AntiLeak.
4 In that record, change the Display field to 1.
5 Change the InstallLevel field to 1.
6 Save and close the MSI.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 21
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 28

Advanced Scenarios Custom Installer Packages
22 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 29

FortiClient Licensing Overview
FortiClient Licensing
Some features of FortiClient require a license in order to use the feature. This chapter
describes how to license FortiClient for a single user or in an enterprise environment.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• Standard fixed licensing
• Enterprise licensing
Overview
There are two modes of license management for your FortiClient computer.
Standard Fixed
License
Enterprise License The FortiManager unit controls licensing for FortiClient computer. There
Vol ume Instead of distributing a volume license key to your users, you install the
Redistributable You obtain a re-distributable license from FortiCare and subdivide that
Standard fixed licensing
There are several ways to apply standard fixed licensing:
• Provide the license key to your users to enter into the FortiClient application.
• Create a customized FortiClient installer that includes the license key. Distribute the
customized FortiClient installer to your users. The FCRepackager tool -k option
enables embedding of a standard fixed license key. For more information, see
“Creating a customized installer using FCRepackager” on page 9.
• If you manage FortiClient computer with a FortiManager unit, you can also manage
their licenses. See “To assign a standard fixed license with FortiManager”, next.
The FortiClient application is licensed by means of a license key entered
into the application. The license can be a single-user or a volume license.
FortiManager does not manage this method of licensing, but it can
distribute the license keys.
are two types of enterprise licensing:
license on your FortiManager unit. The license is applied to all of your
managed FortiClient computers that do not have a standard fixed license.
The volume license has a seat limit which the FortiManager unit enforces.
Volume license managed by FortiManager requires the forticlient msi
parameter set to 1.
license into client licenses for your users. You can set the expiry date and
seat count for each client license. The expiry date of your client licenses
cannot be later than that of the enterprise license. The total seat count limit
of your client licenses can exceed the seat count limit of the enterprise
license, but the total number of managed clients cannot.
The FortiClient application must be specifically customized for use with redistributable licensing. You can include the client license key in the
customized FortiClient installer or provide the license key to users to enter
manually.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 23
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 30

Enterprise licensing FortiClient Licensing
To assign a standard fixed license with FortiManager
1 Using FortiClient Manager, organize the managed FortiClient computer into client
groups where all members use the same license key.
For more information, see “Working with FortiClient groups” in the FortiClient chapter
of the FortiManager Administration Guide.
2 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Manage > FortiClient Key and select Add to add a
license key to the FortiManager database.
3 In the License Key field, enter the license key.
4 Optionally, enter a description.
5 In the Available Group(s) list, select the client groups that use this license key and then
select the green right arrow button to move the selected groups to the Assigned
Group(s) list.
6 Click OK.
7 In the FortiClient License Key Management list, select the Deploy to group icon for the
license key that you added. Click OK to confirm your request to deploy.
Enterprise licensing
To use enterprise licensing, you need to:
1 Obtain an Enterprise License from FortiCare and register it on your FortiManager unit.
For more information, see “Configuring enterprise licenses” on page 24.
2 Create at least one enterprise client license for your FortiClient computer. For more
information, see “Creating enterprise client license keys” on page 25.
3 Create a custom FortiClient installer that enables enterprise licensing. You can include
the client license key in the installer or provide the client license key to users to apply
after installation. For more information, see “Creating customized FortiClient installers”
on page 25.
4 Deploy the customized FortiClient installer to your users.
Configuring enterprise licenses
You need to register your enterprise license on your FortiManager unit.
To configure the enterprise license
1 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Settings > Enterprise License.
2 In the License Mode section, select Enterprise License.
3 In the Enterprise License Key field, enter the license key purchased from FortiCare.
4 Select Download to register the license. Information about the license displays below
the Enterprise License Key field.
5 In the Validation Type section, select Internal Validation.
6 Click Apply.
24 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 31

FortiClient Licensing Enterprise licensing
Creating enterprise client license keys
After you register your enterprise license (see “Configuring enterprise licenses” on
page 24), you can create enterprise client licenses for your FortiClient computer. For each
client license, you can set the seat limit. The total number of seats licensed through
enterprise client licenses cannot exceed the number of seats that the enterprise license
permits.
To create enterprise client license keys
1 Go to Setting > Enterprise License.
You must have an enterprise license registered on the FortiManager unit. For more
information, see “Configuring enterprise licenses” on page 24.
2 Select the Enterprise Client License Management link.
The list of enterprise client licenses is displayed.
3 Click Add.
The New Client License window opens, with an enterprise client license key value in
place.
4 In the Name field, enter a name to identify the license.
5 In the Seats Permitted field, enter a number seats that is no larger than the maximum
shown at the right.
6 In the Expiry Date field, enter a date that is no later than that of the enterprise license.
7 Optionally, enter a description.
8 Click OK.
Deploying enterprise client license keys
An enterprise client license key is effective only on FortiClient installations that are
customized to accept an enterprise license instead of a standard fixed license.
You need to create a customized FortiClient installer using the FCRepackager tool,
available in the FortiClient .zip installation package. Your customized installer can include
the license key, or you can distribute the license key separately to your users.
Creating customized FortiClient installers
To support enterprise licensing, you must make specific customizations of the installer.
1 Create a model FortiClient installation on a computer.
If you want to make other customizations in the FortiClient installer, you should make
them first, following the procedures in the Customization chapter. See “Creating a
customized installer using FCRepackager” on page 9. Then, install the result of those
customizations as your model installation.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 25
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 32

Enterprise licensing FortiClient Licensing
2 Customize licensing by using the FCRepackager tool with the following command line
options:
• -f <FortiManager_IP>, where <FortiManager_IP> is the IP address or
fully qualified domain name of the FortiManager unit that will license the FortiClient
computer,
• -a <license_model>, where <license_model> is 1 for enterprise client
license with FortiManager validation or 2 for enterprise client license with external
validation,
• -e <client license key>, where <client license key> is the enterprise
client license key created on the FortiManager unit. You can omit this command line
option if you prefer to distribute the license key in some other way,
• -m <installer_file>, where <installer_file> is the FortiClient .msi
installer file you used to create the model installation.
For example, to customize the FortiClient installer at c:\FortiClient to receive licensing
and validation from the FortiManager unit at 172.20.120.161, with client license key
116c2d1ae25f071cc53a013db36040836e, the command is (all on one line):
FCRepackager.exe -f 172.20.120.161 -a 1 -
e 116c2d1ae25f071cc53a013db36040836e -m
c:\FortiClient\forticlient.msi
The customized installer is created in a subdirectory called “transformed”,
c:\FortiClient\transformed, for example.
Distributing customized FortiClient installers
You can distribute the customized FortiClient installer in various ways, such as:
• Put the installer on a file share. Users simply double-click the file to begin installation.
• On a Windows Advanced Server network, install the application on end users’
computers remotely. For more information, see “Active Directory installation” on
page 17.
26 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 33

Corporate Security Policies Overview
Corporate Security Policies
Corporate Security Policies can be set up to enforce the use of certain FortiClient features.
This is commonly used to ensure that users of remote VPN connections are in compliance
with the established security policies.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• Configuring a corporate security policy
Overview
You can set a security policy for your managed FortiClient computer. Users cannot use a
VPN connection unless the FortiClient settings comply with the policy. The security policy
can require that any or all of the following features are enabled:
• Antivirus (real-time protection)
•Antispam
• Firewall (Normal mode)
• Web Filter
This provides security when users connect to your corporate network through a VPN.
User view of security policy
If a corporate security policy is set, the FortiClient Console General tab includes a
Corporate Policy Compliance section that displays the compliance status of the FortiClient
computer.
Figure 1: Corporate policy compliance status - in compliance
If the user disables any of the required features, the FortiClient computer is no longer in
compliance with the policy. If a VPN tunnel is in use, it is disconnected. The Corporate
Policy Compliance status changes to show the following.
Figure 2: Corporate policy compliance status - not in compliance
The user can bring FortiClient settings into compliance again by selecting the check box.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.1 Administration Guide
04-41-99556-20090626 27
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 34

Configuring a corporate security policy Corporate Security Policies
Configuring a corporate security policy
You configure your corporate security policy in the FortiClient Manager module of the
FortiManager unit. It is simplest to apply security policies to client groups. If you have
already created client groups, you can create security policies for those groups. If your
FortiClient computer are ungrouped, you can create a client group for the purpose of
applying security policies.
Tip: You can also configure corporate security policies using the installer public property
COMPLIANCE_POLICY. See “Appendix A: Installer Public Properties” on page 57 for more
information.
To configure a security policy
1 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Client/Group > Group.
2 Select the client group that you want to configure.
3 From the FortiClient menu, select VPN > Security Policy.
4 Select any of the following policies that you want to enforce:
• Firewall must be enabled
• Realtime AV must be enabled
• Webfiltering must be enabled
• Antispam must be enabled
5 Select Apply.
6 Repeat steps 2 through 5 if you want to create security policies for other client groups.
7 Go to Manage > Deploy Configuration.
8 Select the client group(s) where you created security policies and then select Deploy.
When the updated configuration is deployed to the FortiClient computer, their
configuration settings are made compliant with the policy. On the FortiClient Console
General tab, the Corporate Policy Compliance section shows the status message,
“FortiClient is compliant with corporate policy.”
28 04-41-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 35

Endpoint Network Access Control Overview
Endpoint Network Access Control
This chapter describes how to enforce the use of FortiClient by using a FortiGate unit’s
Endpoint NAC feature.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• Enforcing use of FortiClient software
• Configuring FortiGuard Services
• Setting the FortiClient version
• Enabling Endpoint Control
Overview
FortiGate units prevent viruses and other threats on the Internet from passing through the
firewall to your private network. However, a computer, especially a portable computer,
might become infected from media or unprotected connection to another network. This
infection could spread on your internal network. FortiClient Endpoint Control protects the
computer on which it is installed.
Endpoint NAC (Network Access Control) enforces the use of FortiClient endpoint security
in your network. The compliance check ensures that the endpoint is running the most
recent version of the FortiClient software, checks that the antivirus signatures are up-todate, and are not using any blocked applications (application detection).
You enable endpoint control in a FortiGate firewall policy. When traffic attempts to pass
through the firewall policy, the FortiGate unit runs compliance checks on the originating
host on the source interface. Non-compliant endpoints are blocked. If web browsing, they
receive a message telling them that they are non-compliant, or they are redirected to a
web portal where they can download the FortiClient application installer.
Enforcing use of FortiClient software
Endpoint control requires that all hosts using the firewall policy have FortiClient Endpoint
Security software installed. Make sure that all hosts affected by this policy are able to
install this software. Currently, FortiClient Endpoint Security is available for Microsoft
Windows 2000 and later only.
To set up endpoint control on your FortiGate unit, you need to
• Enable FortiGuard. This is required if you will use FortiGuard Services to update
FortiClient software or antivirus signatures. You do not need to enter account
information. See “Configuring FortiGuard Services” on page 30.
• Set the minimum required version of FortiClient and configure the source of FortiClient
installer downloads for non-compliant endpoints. See “Setting the FortiClient version”
on page 30.
• Enable endpoint control in the appropriate FortiGate firewall policies. See “Enabling
Endpoint Control” on page 32.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 29
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 36

Configuring FortiGuard Services Endpoint Network Access Control
Note: You cannot enable Endpoint Compliance Check in firewall policies if the Redirect
HTTP Challenge to a Secure Channel (HTTPS) option is enabled in User > Options >
Authentication.
Optionally, you can configure software detection to monitor whether endpoints have
specific applications installed. For more information, see the Endpoint control chapter of
the FortiGate Administration Guide.
Configuring FortiGuard Services
The FortiGuard Distribution Network (FDN) and FortiGuard Services. The FDN provides
updates to antivirus definitions, IPS definitions, and the Antispam rule set. FortiGuard
Services include FortiGuard web filtering and the FortiGuard Analysis and Management
Service. You must be connected to the FortiGuard subscription service in order to receive
the services.
You can see if your FortiGate unit is connected to FortiGuard Services by going to
Endpoint NAC > Config and seeing a check mark next to FortiGuard Availability.
Figure 3: FortiGuard Availability
Go to System > Maintenance > FortiGuard to configure your FortiGate unit to use the
FortiGuard Distribution Network and FortiGuard Services.
Setting the FortiClient version
By default, FortiClient software is provided by FortiGuard Services and the latest version
is the required version. In your FortiGate unit’s web-based manager, go to Endpoint NAC
> Config to view the current settings as well as the latest available versions of FortiClient
software and antivirus signatures. There is a warning if FortiGuard service is not available.
If the version of FortiClient running on the endpoint does not meet the required version or
does not have up to date antivirus, firewall, and database, the non-compliant computer will
be blocked with the following exceptions:
• The user can download the required version of FortiClient.
• The user can update the antivirus definition files.
If the user attempts to access any web page, they will receive a message stating that they
can update or install FortiClient or update the antivirus definitions.
To set the required FortiClient version and the download location
1 In your FortiGate unit’s web-based manager, go to Endpoint NAC > Config and select
the FortiClient tab.
30 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 37

Endpoint Network Access Control Setting the FortiClient version
Figure 4: FortiClient Endpoint Security configuration
2 To download the latest FortiClient release, click Download. The latest version is
downloaded from FortiGuard.
3 To update the FortiClient endpoints, click Update Now. You will receive a message that
your update request is being sent and the FortiClient version will be updated in a few
moments.
4 In the FortiClient Installer Download Location section, select one of the following
options:
• FortiGuard Distribution Network — FortiGuard Services provides the FortiClient
software.
• This FortiGate — The FortiGate unit provides a FortiClient installer to download. Not
all FortiGate models support storage of FortiClient software. For information about
uploading a FortiClient installer to your FortiGate unit, see “Uploading the FortiClient
installer to your FortiGate unit” on page 32.
• Custom URL — Specify a URL for a server from which users can download the
FortiClient installer. You can use this option to provide a customized FortiClient
installer even if your FortiGate unit cannot store FortiClient software.
You need to use either the This FortiGate or Custom URL option if you want to provide
your users a customized version of the FortiClient application. This is required if a
FortiManager unit will centrally manage FortiClient applications. For information about
customizing the FortiClient application, see “Custom Installer Packages” on page 9.
5 In the FortiClient Version Required section, select one of the following:
• Latest Available — This is the default if the download location is FortiGuard.
• FortiClient Endpoint Security 4.n.n — This is available if the download location is
This FortiGate. It shows the version of the software stored on the FortiGate unit.
6 Click OK.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 31
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 38

Enabling Endpoint Control Endpoint Network Access Control
Uploading the FortiClient installer to your FortiGate unit
If you selected This FortiGate as the FortiClient Installer Download Location, you need to
upload the FortiClient installer to the FortiGate unit.
The FortiClient installer file name must begin with “FortiClientSetup_”, followed by the
version number, “4.0.2”, for example. You can upload either a .msi or .exe package.
To upload the FortiClient installer to the FortiGate unit
1 Place your installer file on a TFTP server that the FortiGate unit can access.
2 Connect to the FortiGate unit’s command line interface (CLI).
You can connect to the CLI through the FortiGate console, using SSH or Telnet (if
enabled), or by using the CLI Console window that is part of the web-based manager.
3 Enter the following CLI command
execute restore forticlient tftp <filename> <server_ip>
where <filename> is, for example, FortiClientSetup_4.0.2.msi
and <server_ip> is the IP address of the TFTP server.
The TFTP server uploads the file to the FortiGate unit.
For more information about using the CLI, refer to the FortiGate CLI Reference.
4 You can see the currently stored version of FortiClient software in the System
Information section of the FortiGate unit dashboard. To view the dashboard, go to
System > Status.
Enabling Endpoint Control
In order for a FortiGate unit to monitor applications, enforce antivirus and firewall use, and
ensure antivirus definitions are up to date on FortiClient, do the following:
• Create an Endpoint Control profile
• Create an application detection list
• Apply an Endpoint Control profile to a firewall policy
After these steps are completed, you can then monitor the endpoints.
Creating Endpoint Control profiles
Create endpoint control profiles so that you can apply them to firewall policies. This allows
the FortiGate unit to monitor which applications are running and installed through
FortiClient and enable the enforcement of FortiClient features such as antivirus and
firewall.
32 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 39

Endpoint Network Access Control Enabling Endpoint Control
Figure 5: New Endpoint NAC Profile window.
To create an Endpoint Control profile
1 Go to Endpoint NAC > Profile and click Create New.
2 Enter the name for the Endpoint NAC Profile.
3 Select the following options:
• Notify Hosts to Install FortiClient (warn only) — If a user attempts to access the
internet without FortiClient installed, a message to install FortiClient and a
“Continue to Website” link is displayed. The user can access the internet via the
link. This allows for a gradual rollout of FortiClient to all users without restricting
internet access.
• Quarantine Hosts to User Portal (enforce compliance) — If a user attempts to
access the internet without FortiClient installed, a message to install FortiClient is
shown. The user cannot access the internet until FortiClient is installed.
4 Select the Additional Client Options check box and select the following options:
• Antivirus enabled — Checks that the FortiClient Endpoint Security application
has the antivirus feature enabled.
• Antivirus up-to-date — Checks that the FortiClient Endpoint Security application
has the latest version of the antivirus signatures available from FortiGuard
Services.
• Firewall enabled — Checks that the FortiClient mode is set to Normal.
5 Select the Enable Application Detection check box and select the Application Detection
List to use the application detection feature. See “Creating an Application Detection
List”.
6 Click OK.
Creating an Application Detection List
You can create the list of applications to be monitored through the FortiGate unit. You can
determine which applications are allowed, monitored, or blocked from the FortiGate unit.
The application detection list is applied to the Endpoint Control Profile.
The list of available categories, vendors, and applications come from the FortiGuard
signature database and can be viewed in the Predefined tab.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 33
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 40

Enabling Endpoint Control Endpoint Network Access Control
To view the list of predefined applications
•Go to Endpoint NAC > Application Detection and select the Predefined tab. See
Table 2 on page 35 for the list of group and category definitions.
To create an Application Detection List
1 Go to Endpoint NAC > Application Detection > Detection List tab and click Create New.
Figure 6: New Detection List window
2 Enter a name for the list.
3 Enter any applicable comments about the list.
4 Click OK.
5 Click Create New.
6 In the New Application Detection Entry area, enter the following information. See
Table 2 on page 35 for the list of category definitions.
• Category — Select the applicable category.
• Vendor — Select the vendor that applies to the category.
• Application — Select the application.
• Action — Select one of the following:
• Allow — The FortiGate unit takes no action against applications.
• Monitor — The FortiGate unit records the application in the logs and in the
Endpoint NAC > Monitor list but will not take any action against the user.
• Block — The FortiGate unit quarantines the host and records the violating
applications in the logs and in the Endpoint NAC > Monitor list. A “quarantined”
message is shown to the user in the web browser.
7 Click OK.
8 Repeat steps 5 and 6 to create the application detection list.
Figure 7: Detection list
34 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 41

Endpoint Network Access Control Enabling Endpoint Control
9 For all other applications that are not specified in the list, select if you want to Allow,
Deny, or Monitor.
10 Click OK.
Table 2: Application groups and category definitions.
Category Description
Security
Anti-Malware
Software
Authentication
and
Authorization
Encryption, PKI Software that enables the encryption and decryption of data for security
Firewalls Software that protects the desktop from unauthorized remote access.
Hacking Software used to attack or evade access controls and privacy
Potentially
Unwanted
Software
Proxy
Avoidance
Remote Access Software that enables authorized access to and use of a desktop
System Audit Software used to monitor and log activity on a computer network,
Multimedia
Media Players Software that enables the creation and playback of audio or video files.
Communication
Groupware Software that enables the sharing of files and applications across work
Internet
Browsers
Email Software that enables the receiving, display, composing, and sending of
Instant
Messaging
P2P File
Sharing
Telephony,
Conferencing,
Fax
Critical Functions
Never Block Executables needed to enable the desktop machine to perform its basic
Entertainment
Adult Software that includes depictions of nudity or sexual activity or other
Software that detects, filters, and eliminates malicious content.
Software that restricts access to and use of the computer and its
contents to authorized users and authorized uses.
purposes.
measures on other computers.
Technologies that alter the operation of the user's hardware, software,
or network in ways that diminish control over the user experience,
privacy, or the collection and distribution of personal information.
Applications that enable or facilitate the avoidance or bypassing of
proxy server features.
computer or private network from a remote location.
including both legitimate use and attempts to access or use network
assets in unauthorized fashion, and to assess the status and security of
the network.
groups, networks, or enterprises and provides communication and
shared workspace for groups.
Software that interprets content and presents it on the desktop screen;
excludes browsers dedicated to a single or limited sources.
email from the desktop. Includes the client side of network applications
(e.g. Microsoft Outlook) and bulk email software, but not email
applications built into web browsers.
Software that enables the sending and receiving of synchronous, realtime messages on the desktop. (Also known as chat-room software.)
Software that enables file search and sharing across a network without
dependence on a central server.
Software that enables telephonic transmission of voice and other data,
including software for BBS, IP telephony, and dial-up internet access.
functions prior to the use of added applications.
elements that might be objectionable to non-consenting users.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 35
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 42

Enabling Endpoint Control Endpoint Network Access Control
Table 2: Application groups and category definitions.
Gambling Software that enables online wagering or pay-for-play activity.
Games Software that enables the playing of games, whether solo or jointly with
Screen Savers Software that creates a display on the desktop screen when no
Miscellaneous
Java Files Binary files containing code to be executed by a Java interpreter (i.e.
Other Executables not otherwise categorized.
Scripts Files containing non-malicious code to be executed by a scripting host
Temporary
Internet Files
Productivity
Management
Software
Database Software that enables the creation and utilization of structured sets of
Document
Viewers
Graphics Software packages that enable sophisticated graphics creation and
Generic
Productivity
Software
Microsoft Office Word processor, Spreadsheet, presentation, contacts, etc.
Proprietary Software developed within the firm for its own use and not as a product
Software
Development
Web and
Desktop
Publishing
System
Installers Executables that install applications.
System Utilities Other enabling tools not otherwise classified.
Operating
Systems
other players.
keystrokes or mouse movements have occurred for some specified
time.
files with .class or .jar extensions).
(i.e. as with .bat, .pl, .vbs extensions).
JavaScript files, which load onto the desktop chiefly in association with
HTML files.
Including CRM, ERP, SCM, etc.
information, the structure being provided by the definition of fields or
data objects, and the utilization consisting of analysis, synthesis, and
comparison across large quantities of such data.
Software other than that incorporated into document creation tools (e.g.
word processors) or other than web browsers that enable the creation
and viewing of documents and diagrams.
manipulation to engineering or studio standards. Includes CAD,
cartographic, rendering, and animation tools.
Software that provides a body of reference information and means for
accessing and displaying it. This also includes general desktop tools
such as calendars, clocks, and calculators.
or component of a product.
Tools used to create, debug, test, compile, and prepare for installation
and use new software programs.
Software that enables format conversion, manipulation, and integration
of text and image files for the purpose of publication on paper or on the
Web.
The fundamental programs that enable the computer to recognize and
accept input, to enable and organize the operation of devices and
application programs, to manage stored information, and to direct
output in designated modes.
Applying an Endpoint Control profile to a firewall policy
Once you have created an Endpoint profile, you can apply it to the firewall policy.
If FortiClient has a valid license, it periodically sends the list of application IDs to the
FortiGate unit. When the FortiGate unit receives an updated list, it compares the list of
applications against the Endpoint Profile that is assigned for that user and take the
following actions for each application:
36 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 43

Endpoint Network Access Control Enabling Endpoint Control
• Allow — The FortiGate unit takes no action against applications.
• Monitor — The FortiGate unit records the application in the logs and in the Endpoint
NAC > Monitor list but will not take any action against the user.
• Block — The FortiGate unit quarantines the host and records the violating applications
in the logs and in the Endpoint NAC > Monitor list. A “quarantined” message is shown
to the user in the web browser.
For more information about creating firewall policies, see the Firewall chapter of the
FortiGate Administration Guide.
To apply an Endpoint Control Profile to a firewall policy
1 Go to Firewall > Policy and select the Policy tab.
2 Select a firewall policy and click Edit.
Figure 8: Enabling Endpoint NAC in a firewall policy
3 Select Enable Endpoint NAC and do one of the following:
• Select the endpoint profile from the list.
•Select Create New and create an endpoint profile. See “To create an Endpoint
Control profile” on page 33.
4 Click OK.
Monitoring Endpoints
If you have the Application Detection List set to Monitor or Block and have applied it to an
Endpoint Control Profile and a firewall policy, you can view which applications have
attempted to pass through the Fortigate unit.
To monitor endpoints
1 Go to Endpoint NAC > Monitor.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 37
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 44

Enabling Endpoint Control Endpoint Network Access Control
Figure 9: Monitoring endpoints
2 To view endpoint details, click View on an entry.
3 In the Endpoint Details window, you can view details such as the status, FortiClient
version, detected applications, and so on.
4 Click Close.
5 To allow temporary access to the endpoint, select an entry and click Exempt
Temporarily .
6 In the Timeout Setting window, enter the number of minutes that the exemption will last
for and click OK.
The status of the endpoint changes to Non-compliant but temporarily exempted .
7 If an endpoint has been given an exemption, you can block the endpoint prior to the
exemption timeout by clicking Block Endpoint .
38 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 45

Creating FortiClient VPNs Overview
Creating FortiClient VPNs
This chapter describes how create policy-based, route-based, and SSL VPNs using
FortiClient, FortiGate, or FortiClient Manager.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Configuring VPN connections using FortiClient
• Configuring VPN connections on FortiGate units
• Configuring VPN connections using FortiManager
• Configuring VPN connections using custom installations
• Configuring the FortiGate gateway as a policy server
Overview
There are several ways to create VPN connections for remote users:
• FortiClient
• FortiGate
• FortiManager
• Custom installation
Configuring VPN connections using FortiClient
FortiClient Endpoint Security can establish a VPN tunnel between your computer and a
FortiGate unit or other VPN gateway. You can set up a VPN using one of the following
types in VPN > Connections:
• Automatic IPsec
• Manual IPsec
• SSL VPN
See the FortiClient Endpoint Security Guide for more information on how to configure
VPNs in FortiClient.
Configuring VPN connections on FortiGate units
There are several ways to configure FortiGate units to accept VPN connections from
FortiClient users.
• A policy-based VPN.
• A route-based VPN.
• SSL VPN.
For information on how to set up VPN connections using a FortiGate unit, see the
FortiGate Administration Guide.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 39
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 46

Configuring VPN connections using FortiManager Creating FortiClient VPNs
About split tunneling
Split tunneling allows the remote access VPN client to connect to the corporate network
via the VPN link, and connect to the Internet via the interface the VPN connection was
established over (not the VPN channel itself).
For example, suppose you have a remote access VPN client connecting to the corporate
network over a wireless network. The user with split tunneling enabled is able to connect
to file servers, database servers, mail servers and other servers on the corporate network
through the VPN connection. In contrast, when the user connects to Internet resources
(web sites, FTP sites, etc), the connection request doesn’t go through the VPN link, it goes
through the wireless connection and out the gateway provided by the hotel network.
When using FortiClient:
• If split tunneling is enabled, then when the user connects to the FortiGate unit, it will tell
the VPN client that split tunneling is allowed and will send back the lists of routes. The
routes are then installed on the user’s computer at the top of its routing table.
• If split tunneling is disabled, the FortiGate unit will tell the VPN client to direct all traffic
through the FortiGate. This will have the same effect as installing a default route on the
client to send all traffic over the VPN. Note that the local network routes take
priority over the default route so the remote user can still send traffic on the
local network outside the tunnel.
For example, a FortiGate unit is allowing users to access two networks via SSL VPN:
• 10.0.0.0/24
• 11.0.0.0/24
The client has two interfaces: Wireless1 and VPN1 where VPN1 is the SSL VPN tunnel.
Table 3: Original Routing Table
Destination Gateway
1.1.1.0/24 Wireless1
0.0.0.0/0 Wireless1 (default)
Table 4: Routing table when split tunneling is disabled
Destination Gateway
0.0.0.0/24 VPN1 (default)
1.1.1.0/24 Wireless1
Table 5: Routing table when split tunneling is enabled
Destination Gateway
10.0.0.0/24 VPN1
11.0.0.0/24 VPN1
1.1.1.0/24 Wireless1
0.0.0.0/0 Wireless1 (default)
Configuring VPN connections using FortiManager
You can create an automatic VPN connection or the FortiClient Manager can
automatically download a VPN setting from the FortiGate unit to which your FortiClient
computer connects.
For more information, see the FortiManager System Administration Guide.
40 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 47

Creating FortiClient VPNs Configuring VPN connections using custom installations
Configuring VPN connections using custom installations
To create VPN connections using custom installations, use the VPN Editor tool to embed
the VPN tunnels into the MSI package. For more information on the VPN Editor tool, see
“Using the FortiClient VPN Editor” on page 47.
Configuring the FortiGate gateway as a policy server
You can configure a FortiGate gateway to work as a VPN policy server for FortiClient
automatic configuration. When FortiClient users connect to the FortiGate gateway to
download VPN policies, they are challenged for a user name and password. Configure the
FortiGate unit as follows:
1 Create a user account for each FortiClient user.
2 Create a user group and add the FortiClient users to it.
For more information about creating users and groups, see the FortiGate
Administration Guide.
3 Create a dialup VPN. See the FortiGate Administration Guide for more details.
4 Connect to the FortiGate unit CLI and configure VPN policy distribution as follows:
config vpn ipsec forticlient
edit <policy_name>
set phase2name <phase2_name>
set usergroupname <group_name>
set status enable
end
<phase2_name> must be the name of the VPN phase 2 configuration. <group_name>
must be the name of the user group you created for FortiClient users.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 41
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 48

Configuring the FortiGate gateway as a policy server Creating FortiClient VPNs
42 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 49

Per-User Web Filtering Overview
Per-User Web Filtering
This chapter describes how to deploy the FortiClient application to perform web filtering
customized for each user on a Microsoft Windows network. For larger deployments, a
FortiManager system simplifies management of user web filter profiles.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• Configuring web filtering
Overview
FortiClient Endpoint Security web filtering controls access to web sites based on
FortiGuard Service web site rating categories and black/white URL lists. The web filter
profile selects which FortiGuard categories the user is permitted to access. Additionally,
URLs in the black list are always blocked and URLs in the white list are always permitted.
You select a web filter profile for each user or user group. Users with no assigned profile
are assigned to a global profile. You can create as many profiles as you need, one per
user if necessary.
You can define web filter profiles and users locally in the FortiClient application. This is
most suitable for a computer with a limited number of users, or if you decide to assign
occasional users to a default web filter profile. For information about configuring
FortiClient web filtering, see the Web Filter chapter of the FortiClient Endpoint Security
User Guide.
If you have many FortiClient installations, you can manage their configurations with a
FortiManager unit. This eliminates the need to configure all of the profiles and users on
every FortiClient application you install.
Web filtering on Windows networks
On a Microsoft Windows network, any user can log on at any computer. If you want to
perform web filtering configurable to the group or user level, you can use a FortiManager
unit to provide web filter profile information to each FortiClient application as needed.
Web filtering for remote users
You can install FortiClient on a Windows Terminal Server or a Citrix Presentation Server to
provide web filtering for remote users on a Windows network. The user’s computer does
not need to have the FortiClient application installed. See “Installing FortiClient on Citrix
servers” on page 20.
Configuring web filtering
To manage FortiClient web-filtering with a FortiManager unit, you need to:
• add each FortiClient computer as a managed client
• define the web filter profiles you will assign to users
• configure LDAP settings to obtain Windows group/user information
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 43
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 50

Configuring web filtering Per-User Web Filtering
• assign web filter profiles to groups and users
Managing FortiClient computers
FortiClient Manager can search for FortiClient computer on your network. FortiClient
applications must be configured at installation with the IP addresses or subnets on which
they accept remote management.
Optionally, you can lock the FortiClient application settings so that users, even those with
administrative privileges, cannot change the application’s settings unless they know the
password configured on the FortiManager unit.
To set FortiClient Manager options
1 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Settings > System > System Setting.
2 In the FortiClient Lockdown section, if you want to lock the configuration on the
FortiClient computer that you add, select Enable Lockdown and then enter a password.
If you want to apply lockdown to existing clients, select Apply Lockdown Setting to All.
3 In the Client Discovery section, check that the ports that connect to your network are
enabled to listen for broadcast and unicast requests from FortiClient computer.
4 To add new FortiClient computer directly to the Managed clients list, select Auto-
populate managed client list. Otherwise, select Add to temporary client list.
5 Click Apply.
To search for FortiClient computer
1 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Client/Group > Client and select Search/Add New.
2 Do one of the following:
•Select Lookup single client and enter the IP address of the FortiClient computer.
•Select Scan attached networks, select the interface that connects to the network
and enter the IP address and subnet mask of the network to scan.
3 Click Search.
4 If you selected the Add to temporary clients option (see “To set FortiClient Manager
options”), discovered FortiClient computer are listed in the Temporary Client list.
Otherwise, discovered FortiClient computer are added to the Managed Client list.
Configuring FortiClient installations to request registration
You can configure the FortiClient application to request management from a particular
FortiManager unit. Depending on the FortiClient Manager settings, the FortiClient
computer appears on the Temporary clients list or is added automatically to the Managed
clients list.
Install the FortiClient application using the Microsoft Installer (the .msi file in the .zip
package). Start the installer from the command line as follows to enable central
management by a FortiManager server. Type the command on a single line.
msiexec /i FortiClient.msi FMGRENABLED=1 FMGRTRUSTEDIPS=<IP>
FMGRENABLEDISCOVER=1
<IP> is the address of the FortiManager unit
44 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 51

Per-User Web Filtering Configuring web filtering
Defining web filter profiles
In the FortiClient Manager, go to Global Configuration > Web Filter Profile. Click Create
New. Enter the following information and click OK.
Name Enter a name for the profile.
Comments Optionally, enter descriptive information about the profile.
Bypass URLs
Block URLs
Select category to
block
Select classification
to block
Bypass URLs are allowed even if they are in a blocked category.
Block URLs are always blocked.
To add a URL, enter it in the field below the list and select Add.
To remove a URL, select it in the list and then select Delete.
Either select Select All or select individual categories to block. You can
expand the categories to select specific sub-categories.
Either select Select All or select individual classifications to block.
Configuring LDAP settings
FortiClient Manager uses LDAP protocol to retrieve information about Windows AD users
and groups from the domain controller.
Go to Settings > LDAP Group/User > LDAP Settings and click Create New. Enter the
following information and select OK.
Name Enter a name for this LDAP server.
Server Name/IP Enter the fully-qualified domain name or IP address of the Windows AD
Server Port Enter the port used to communicate with the LDAP server. The default is
BaseDN Enter the Base Distinguished Name for the server. You can get this
BindDN Enter the Bind Distinguished Name for the server. You can get this
Password Enter the password required for logon to make queries.
Test Connection Select this button to attempt a connection to the domain controller using the
Assigning web filter profiles
You can assign web filter profiles to Windows groups and users.
To assign web filter profiles to groups
1 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Settings > LDAP Group/User > LDAP Group/User.
2 From the LDAP Server list, select the Windows AD domain controller.
3 Select Synchronize.
4 Expand domains as needed to show groups.
5 From the Web Filter Profile list, select the profile you want to assign.
6 Select group(s) (each one has a check box) and then select Assign Profile.
For each selected group, the Web Filter Profile column lists the assigned profile.
7 Repeat Step 4 through Step 6 for each web filter profile you want to assign.
domain controller.
port 389. If needed, change the port to match the server.
information from the server’s administrator.
information from the server’s administrator.
settings you have entered. The results of the connection test display below
the button.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 45
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 52

Configuring web filtering Per-User Web Filtering
To assign web filter profiles to users
1 In the FortiClient Manager, go to Setting > LDAP Group/User > LDAP Group/User.
2 From the LDAP Server list, select the Windows AD domain controller.
3 Select Synchronize.
4 Select LDAP Users at the top left of the page.
5 From the Domain list, select the required domain.
6 From the Web Filter Profile list, select the profile you want to assign.
7 Select the user(s) you want to assign.
Optionally, to find a user, type the name in the User Name box at the top right of the
page and select Go.
8 Click Assign Profile.
For each selected user, the Web Filter Profile column lists the assigned profile.
9 Repeat Step 6 through Step 8 for each web filter profile you want to assign.
46 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 53

Configuring VPNs without FortiClient Endpoint Security Overview
Configuring VPNs without FortiClient
Endpoint Security
FortiClient VPN is a light-weight VPN client designed for enterprise deployment. Users
cannot install the FortiClient VPN application if they have FortiClient Endpoint Security
installed as FortiClient Endpoint Security is an upgrade to FortiClient VPN.
FortiClient VPN provides a connection to the corporate VPN for employees working from
home or traveling. You pre-configure the VPN settings before providing the installer file to
your users. The user needs only to start the application and select the Connect button.
The FortiClient VPN Editor can be installed on a computer that has FortiClient Endpoint
Security installed. The editor automatically imports your VPN settings.
The following topics are included in this section:
• Overview
• Using the FortiClient VPN Editor
• Exporting configurations to the FortiClient VPN installer
Overview
Fortinet customers can obtain the FortiClient VPN package from the Fortinet Support web
site at http://support.fortinet.com. The FortiClient VPN package contains:
• the FortiClient VPN installer file (32-bit and 64-bit) for several locales:
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_en-US.msi 32-bit English
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_x64_en-US.msi 64-bit English
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_fr-FR.msi 32-bit French
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_x64_fr-FR.msi 64-bit French
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_zh-CN.msi 32-bit Simplified Chinese
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_x64_zh-CN.msi 64-bit Simplified Chinese
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_zh-TW.msi 32-bit Traditional Chinese
FortiClientVPN_4.0.2.nnnn_x64_zh-TW.msi 64-bit Traditional Chinese
• a tools folder containing the configuration tool, FortiClientVPNEditor.
Users cannot install the FortiClient VPN application if they have FortiClient Endpoint
Security installed. FortiClient Endpoint Security is an upgrade to FortiClient VPN.
The FortiClient VPN Editor can be installed on a computer that has FortiClient Endpoint
Security installed. The editor automatically imports your VPN settings.
Using the FortiClient VPN Editor
The FortiClient VPN Editor can configure or import configurations for VPN tunnels,
certificates and revocation lists and then save them to one of the FortiClient VPN installer
files or to a configuration file.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 47
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 54

Using the FortiClient VPN Editor Configuring VPNs without FortiClient Endpoint Security
To start the FortiClient VPN editor
1 Expand the FortiClient VPN package into a folder.
2 Go to the tools subfolder.
3 Double-click FortiClientVPNEditor.exe.
To provide VPN tunnel definitions to your users, you will need to import or configure the
VPN settings in the FortiClient VPN editor.
Importing VPN tunnel settings
If the computer you use to run the FortiClient VPN editor also has the FortiClient
application installed on it, the FortiClient tunnel configurations are available in the
FortiClient VPN editor. This is convenient if your FortiClient application has the same
tunnel configuration that you want to provide to your users.
You can also import tunnel definitions into the FortiClient VPN editor from .vpl or .vpz
export files, or from customized FortiClient installer files (.msi).
Note: The .vpz export file contains both the tunnel settings and any certificates the tunnel
requires. If possible, import a .vpz file instead of a .vpl file for tunnels that use certificates.
To import VPN tunnel settings
1 In the FortiClient VPN editor, select the Tunnels tab.
2 Select Import.
3 In the Open window, select one of the following file types:
• a VPN policy package (.vpz)
• a VPN policy files (.vpl)
• a customized FortiClient installer file (.msi)
4 Select Open.
The imported tunnels are listed.
Configuring VPN tunnel settings
If you do not have a source from which to import VPN settings, you can configure a VPN
tunnel just as you would in the FortiClient application. Both automatic configuration and
manual configuration are supported. Automatic configuration is compatible with a
FortiGate remote gateway configured as a VPN policy server. For more information, see
the FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide.
To configure a VPN tunnel - automatic configuration
1 In the FortiClient VPN editor, select the Tunnels tab.
2 Select New.
3 In the New Connection window, enter a connection name.
4 For Configuration, select Automatic.
5 For Policy Server, enter the IP address or FQDN of the FortiGate gateway.
6 Select OK.
To configure a VPN tunnel - basic configuration
1 In the FortiClient VPN editor, select the Tunnels tab.
48 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 55

Configuring VPNs without FortiClient Endpoint Security Using the FortiClient VPN Editor
2 Select New.
3 Enter the following information:
Connection Name Enter a descriptive name for the connection.
Configuration Select Manual
Remote Gateway Enter the IP address or the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of
Remote Network Enter the IP address and netmask of the network behind the
Authentication Method Select Pre-shared Key or X509 Certificate.
Pre-shared Key Enter the pre-shared key. This is available if Authentication
X509 Certificate Select the X509 Certificate. The certificate must already be
the remote gateway.
FortiGate unit.
Method is Pre-shared Key.
configured. This field is available if Authentication Method is
X509 Certificate.
4 Select Advanced if you need to:
• modify IKE or IPSec settings (see “Configuring IKE and IPSec policies” in the
FortiClient Endpoint Security User Guide)
• configure the FortiClient VPN to use a virtual IP address
• add the IP addresses of additional networks behind the remote gateway
• configure Internet browsing over IPSec
• configure extended authentication (XAUTH)
The Advanced Settings window opens. This is the starting point for the rest of the
procedures in this section.
To configure the virtual IP address
In the Advanced Settings window, do the following:
1 Select Acquire virtual IP address and then select Config.
2 In the Virtual IP Acquisition window, do one of the following:
•Select Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) over IPSec.
•Select Manually Set and enter the IP address, Subnet Mask, DNS Server and WINS
Server addresses as required.
3 Select OK.
To add additional remote networks to a connection
In the Advanced Settings window, do the following:
1 In the Remote Network section, select Add.
2 In the Network Editor window, enter the IP Address and Subnet mask of the remote
network and then select OK.
3 Repeat Steps 1 and 2 for each additional network that you want to add.
You can specify up to 16 remote networks.
4 Select OK.
To enable Internet browsing over IPSec
In the Advanced Settings window, do the following:
1 In the Remote Network section, select Add.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 49
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 56

Exporting configurations to the FortiClient VPN installer Configuring VPNs without FortiClient Endpoint Security
2 Enter 0.0.0.0./0.0.0.0 and select OK.
3 Select OK.
To configure XAuth
In the Advanced Settings window, do the following:
1 Select the Config button for eXtended Authentication.
2 In the Extended Authentication window, select the maximum number of attempts the
the user can make to enter the correct user name and password.
Automatic XAUTH login is not available for the FortiClient VPN application.
3 Select OK.
Configuring certificates for FortiClient VPN
Configuring certificates is optional. Many VPN configurations do not use certificates.
If the computer you use to run the FortiClient VPN editor also has the FortiClient
application installed on it, FortiClient certificates are available in the FortiClient VPN editor.
You can also import certificates.
The FortiClient VPN Editor configures certificates in exactly the same way as the
FortiClient application. Only the page names differ.
FortiClient VPN Editor page FortiClient Endpoint Security page
Certificates VPN > My Certificates
Certificate Authorities VPN > CA Certificates
Revocation Lists VPN > CRL
Refer to the “Managing digital certificates” section in the VPN chapter of the FortiClient
Endpoint Security User Guide for detailed information about working with certificates.
Exporting configurations to the FortiClient VPN installer
When you have finished creating configurations in the FortiClient VPN Editor, you can
easily export them to a FortiClient VPN installer. If you configured any certificates, these
are also exported.
To export the tunnel configurations
1 On the Tunnels page, select the Export check box for each tunnel configuration that
you want to export.
2 Select the Export button.
The Save As window opens.
3 In the Save as type list, select Installer Package File (*.msi).
4 Locate the FortiClient VPN installer file to update with VPN tunnel configurations.
5 Select Save.
You can also save configurations to a VPN policy file (.vpl) or policy package (.vpz) for
distribution to FortiClient Endpoint Security users. The policy package is the preferred
format because the file is password protected and it includes any certificates that the
tunnel requires.
50 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 57

Using the FortiClient API Overview
Using the FortiClient API
You can operate FortiClient VPNs using the COM-based FortiClient API.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Overview
• Controlling a VPN
• Setting and monitoring a security policy
• API reference
Overview
The FortiClient COM library provides functionality to:
• Retrieve a list of the VPN tunnels configured in the FortiClient application.
• Start and stop any of the configured VPN tunnels.
• Send XAuth credentials.
• Set the security policy for the FortiClient VPN.
• Retrieve status information:
• configured tunnel list
• active tunnel name
• connected or not
• idle or not
• remaining key life
• current security policy
• Respond to FortiClient-related events:
• VPN connect
• VPN disconnect
• VPN is idle
• no longer in compliance with security policy
• XAuth authentication requested
Controlling a VPN
This section uses example code snippets in Visual Basic to show how to operate a VPN
tunnel programmatically.
Linking to the COM library
The COM library for FortiClient is fccomintdll.dll, located in the FortiClient installation
directory, by default c:\Program Files\Fortinet\FortiClient. Using your development
environment, create a reference to this library.
Begin FCCOMINTDLLLibCtl.VPN VPN1
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 51
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 58

Controlling a VPN Using the FortiClient API
This creates VPN1 as the FortiClient object.
Depending on your development environment, you might also need a type library file. You
can find the file FCCOMIntDLL.tlb in the FortiClient .zip installation package.
Retrieving a list of VPN connection names
If needed, you can obtain a list of the VPN connections configured in the FortiClient
application. The GetTunnelList function returns an array of the names.
tunnelList = VPN1.GetTunnelList
Typically, an application might put the tunnel names into a list from which the user
chooses the required tunnel name. In this example, the list control List1 is populated with
the tunnel names:
List1.Clear
For i = LBound(tunnelList) To UBound(tunnelList)
List1.AddItem (tunnelList(i))
Next
Opening the VPN tunnel
Use the Connect method to establish the tunnel. The only parameter is the tunnel name,
as configured in the FortiClient application. In this example, the tunnel name is “Office”:
VPN1.Connect “Office”
Responding to XAuth requests
If the VPN peer requires you to supply XAuth credentials, you can easily provide for this
by writing code that responds to the On XAuthRequest event. In this example, a small
window opens in which the user enters the user name and password.
Private Sub VPN1_OnXAuthRequest(ByVal bstrTunnelName As String)
Dialog.Show 1
outUserName = ""
outPassword = ""
outSavePassword = False
If Not Dialog.Cancelled Then
outUserName = Dialog.UserName
outPassword = Dialog.Password
outSavePassword = Dialog.SavePassword
End If
VPN1.SendXAuthResponse bstrTunnelName, outUserName,
outPassword, outSavePassword
End Sub
52 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 59

Using the FortiClient API Setting and monitoring a security policy
Monitoring the connection
There are both function-based and event-based ways to monitor the VPN connection.
Events
The FortiClient API includes event calls for which you write appropriate code. Using
events, you can provide live status information for users. This example shows how an
application could respond to the OnConnect and OnDisconnect events by updating a user
interface display. A check box, ConnectCheck, is selected when the VPN connects and
cleared when the VPN disconnects.
Private Sub VPN1_OnConnect(ByVal bstrTunnelName As String)
ConnectCheck.Value = 1
textName = bstrTunnelName
End Sub
Private Sub VPN1_OnDisconnect(ByVal bstrTunnelName As String)
ConnectCheck.Value = 0
textName = bstrTunnelName
End Sub
There is also an OnIdle event.
Functions
At any time, you can programmatically determine which VPN connection is active using
the GetActiveTunnel function, like this:
TunnelName = VPN1.GetActiveTunnel
The returned string is empty if no VPN tunnel is up.
The boolean function IsConnected returns True if the named connection is up, like this:
If IsConnected("Office") Then
Rem perform functions requiring Office VPN
....
End If
There is also an IsIdle function.
Setting and monitoring a security policy
The FortiClient application can enforce a security policy. Users cannot use a VPN
connection unless the FortiClient settings comply with the policy. The security policy can
require that any or all of the following features are enabled:
• Antivirus (real-time protection)
•Antispam
• Firewall (Normal mode)
• Web Filter
This is usually applied in an enterprise environment to provide security when users
connect to the corporate network through a VPN. A FortiManager unit can deploy the
security policy to FortiClient computer.
The FortiClient API can also create a security policy. This section uses example code
snippets in Visual Basic to show how to set and monitor a corporate security policy
programmatically.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 53
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 60

Setting and monitoring a security policy Using the FortiClient API
Setting a security policy
The SetPolicy method passes four boolean values, one for each feature: antivirus,
antispam, firewall, and web filter. If the value is True, the policy requires that the feature is
enabled. It is quite easy to create a check box for each of the boolean values and call
SetPolicy in response to the user selecting a “Set Policy” button.
In this example, check boxes are named for the features (AVcheck for the antivirus check
box, for example) and the “Set Policy” button is named SetSecPolicy.
Private Sub SetSecPolicy_Click()
VPN1.SetPolicy AVcheck.Value, AScheck.Value, FWcheck.Value,
WFcheck.Value
The FortiClient application receives the policy but does not change any settings. The
FortiClient General tab and system tray menu show the option “Make compliant with
corporate policy”.
If you want to programmatically make the FortiClient settings comply with the policy you
set, you must use the MakeSystemPolicyCompliant method.
Reading a security policy
You can retrieve the security policy from the FortiClient application with the GetPolicy
method. This returns four boolean values, one for each feature: antivirus, antispam,
firewall, and web filter. If the value is True, the policy requires that the feature is enabled. If
all four values are False, there is no security policy.
This example uses the returned boolean values to set check boxes named for the features
(AVcheck for the antivirus check box, for example).
VPN1.GetPolicy a, b, c, d
AVcheck.Value = Int(a)
If b Then
AScheck.Value = 1
Else
AScheck.Value = 0
End If
If c Then
FWcheck.Value = 1
Else
FWcheck.Value = 0
End If
If d Then
WFcheck.Value = 1
Else
WFcheck.Value = 0
End If
The check boxes show the state of each feature in the policy. You could then make
changes to the policy and set them using the SetPolicy method, as shown in “Setting a
security policy” on page 54.
Monitoring policy compliance
The FortiClient API includes event calls for which you write appropriate code. Using
events, you can provide live status information for users. The OnOutOfCompliance event
returns four boolean values, one for each feature. A value of True indicates that the
feature is not in compliance with the policy.
54 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 61

Using the FortiClient API Setting and monitoring a security policy
This example shows how an application could respond to the OnOutOfCompliance event.
A window opens that lists the out-of-compliance features.
Private Sub VPN1_OnOutOfCompliance(ByVal bAV As Boolean, ByVal
bAS As Boolean, ByVal bFW As Boolean, ByVal bWF As Boolean)
OOCDialog.Show 1
OOCDialog.Text = ""
If bAV Then
OOCDialog.Text = OOCDialog.Text + "Antivirus\n"
End If
If bAS Then
OOCDialog.Text = OOCDialog.Text + "Antispam\n"
End If
If bFW Then
OOCDialog.Text = OOCDialog.Text + "Firewall\n"
End If
If bWF Then
OOCDialog.Text = OOCDialog.Text + "Web Filter"
End If
End Sub
Making the FortiClient application comply with the policy
The FortiClient API includes a method that enables the features required by the security
policy, bringing the application back into compliance. In this example, there is a “Make
Compliant” button.
Private Sub MakeCompliantBtn_Click()
VPN1.MakeSystemPolicyCompliant
End Sub
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 55
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 62

API reference Using the FortiClient API
API reference
Table 6: Methods
Connect(bstrTunnelName As String) Open the named VPN tunnel. This connection
Disconnect(bstrTunnelName As String) Close the named VPN tunnel.
GetPolicy
(pbAV As Boolean,
pbAS As Boolean,
pbFW As Boolean,
pbWF As Boolean)
GetRemainingKeyLife
(bstrTunnelName As String,
pSecs As Long,
pKBytes As Long)
MakeSystemPolicyCompliant() Apply the security policy defined by SetPolicy.
SendXAuthResponse
(tunnelName As String,
userName As String,
password As String,
savePassword As Boolean)
SetPolicy
(bAV As Boolean,
bAS As Boolean,
bFW As Boolean,
bWF As Boolean)
Table 7: Functions
must already be configured in your FortiClient
application.
Retrieve security policy settings for
Antivirus
AntiSpam
Firewall
Web Filter
True means feature must be enabled.
Retrieve the remaining key life for the named
connection. Whether keylife time (pSecs) or data
(pKBytes) are significant depends on the detailed
settings in the FortiClient application.
Send XAuth credentials for the named connection:
User name
Password
True if password should be saved.
Set security policy settings for
Antivirus
AntiSpam
Firewall
Web Filter
True means feature must be enabled.
GetActiveTunnel() As String Retrieve the name of the active connection.
GetTunnelList() Retrieve the list of all connections configured in the
IsConnected
(bstrTunnelName As String)
As Boolean
IsIdle(bstrTunnelName As String)
As Boolean
Table 8: Events
OnConnect(bstrTunnelName As String) Connection established.
OnDisconnect(bstrTunnelName As String) Connection disconnected.
OnIdle(bstrTunnelName As String) Connection idle.
OnOutOfCompliance(bAV As Boolean, bAS
As Boolean, bFW As Boolean, bWF As
Boolean)
OnXAuthRequest(bstrTunnelName As String) The VPN peer on the named connection requests
FortiClient application.
Return True if the named connection is up.
Return True if the named connection is idle.
FortiClient has gone out of compliance with
security policy. Arguments correspond to features.
True indicates the feature is out of compliance with
security policy.
XAuth authentication.
56 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 63

Appendix A: Installer Public Properties
Appendix A: Installer Public
Properties
Ta bl e 9 shows a list of installer public properties that can be specified when installing
FortiClient. The public properties can also be embedded into the MSI by using an MSI
editing tool to make changes to the MSI’s property table.
Caution: Public properties are case-sensitive.
Table 9: Installer public properties when installing FortiClient (Part 1 of 4).
Public property Range Default Description Comment
ADMINMODE [0..1] 0 Disables FortiShield. Typically used for troubleshooting.
ADMINPWD md5 of the
AV_BEFORE_VPN [0..1] 0 0=AV update should be forced
COMPLIANCE_POLICY [OR together:
DISABLEPROXYSELF
TEST
DISABLESWUPDATES [0..1] 0 0=no
ENABLE_FORTIPROXY [0..1] 1 0=no
ENABLE_REGMON [0..1] 0 If set to 1, regmon will be enabled
FMGRAVALERTINT 300000+ 300000 The reporting window (in
FMGRDISCOVERATT
EMPTS
admin password
0 Sets the default “corporate
FW=0x1h,
AV=0x2h,
WF=0x4h,
AS=0x8h,
AL=0x10h]
[0..1] 0 0=disable
0+ 0 The number of times to try to
FortiClient is locked down from
the moment it is installed with this
password.
before a VPN connection is
attempted.
1=An AV update is attempted
before VPN connection is
established.
compliance policy”.
1=enable
1=yes
1=yes
by default.
milliseconds).
FortiClient will avoid sending the
same antivirus alert to FortiClient
Manager if it occurs in the this
window.
locate FortiClient Manager before
giving up.
If the user cancels the AV update
before it is complete, FortiClient
will refuse to connect the VPN
tunnel.
When > 0, FortiClient will show
whether it is currently compliant
with corporate policy.
VPN connections cannot be
established if Forticlient is noncompliant.
FortiClient uses a proxy for some
functions. The self-test sends a
packet to 1.1.1.1 to determine
whether network connectivity can
be established.
When set to 1, FortiClient will not
seek to obtain SW updates from
FortiProtect Distribution Server.
When managed by FortiManager,
FortiClient will ONLY get software
updates from FortiClient Manager.
Used for troubleshooting.
0=infinite
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 57
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 64

Appendix A: Installer Public Properties
Table 9: Installer public properties when installing FortiClient (Part 2 of 4).
Public property Range Default Description Comment
FMGRDISCOVERINTE
RVAL
30000+ 30000 The interval (in milliseconds)
between attempts to discover
FortiClient Manager.
FMGRENABLED [0..1] 0 When set to 1, FortiClient will be
manageable by FortiClient
Manager
FMGRENABLEDISCO
VER
[0..1] 0 FortiClient will use a DHCP-like
protocol to try to discover
FortiClient Manager.
Requires FMGRIP and/or
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS to be
specified
Requires FMGRENABLED=1 and
FMGRIP and/or
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS to be
specified
FMGRFWALERTINT 3600000+ 3600000 The reporting window (in
milliseconds).
FortiClient will avoid sending the
same firewall alert to FortiClient
Manager if it occurs in the this
window.
FMGRFWBEHAVIOR [0..1] 1 0=Firewall runs in 'paranoid
mode': all network traffic is
blocked. To allow traffic,
advanced firewall rules must be
specified
1=The firewall behaves normally
FMGRHEARTBEAT 60000+ 60000 This is the time between
heartbeats sent to FortiClient
Manager (in milliseconds)
FMGRHEARTBEATCO
UNT
1+ 3 If this many consecutive
heartbeats are not returned from
FortiClient Manager, FortiClient
will assume the FortiClient
Manager is not online.
FMGRIP a single ip
address or a
fqdn
This is the preferred address
FortiClient should use to register
for remote management
FMGRIP is automatically added to
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS
FMGRRAISEALERT [0..1] 1 0=FortiClient does not inform
FortiClient Manager of
firewall/antivirus alerts.
0=FortiClient informs FortiClient
Manager of firewall/antivirus
alerts.
FMGRTIMEOUT 30000+ 30000 This is the network timeout
interval (in milliseconds) that
FortiClient uses to determine if
FortiClient Manager is not
accessible.
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS csv list of ip
addresses/fqdns
/subnets
These are addresses that
FortiClient will accept
management requests from.
FWDEFAULTAPPACTION[0..1] 0 If set to 1, FortiClient's firewall will
permit 'unknown' applications to
access the network without
prompting the user.
If 0, the FW will ask the user if the
application should be permitted
access to the network.
HIDETRAY [0..1] 0 When set to 0, the tray icon is
hidden from users.
It is not possible to shutdown
FortiClient if the tray icon is
hidden.
58 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 65

Appendix A: Installer Public Properties
Table 9: Installer public properties when installing FortiClient (Part 3 of 4).
Public property Range Default Description Comment
LICENSE a valid license
key
LICENSE_VALIDATIO
[0..2] 0 0=Licenses are validated by
N_TYPE
FortiClient is installed with this
license.
FortiProtect Distribution Server
Validity depends on the
LICENSE_VALIDATION_TYPE
1=Licenses are validated by
FortiClient Manager
2=Licenses are validated by a
2nd or 3rd party system
NOREMEMBER_VPN_
PWD
[0..1] 0 If set to 1, the user’s username
and password will not be stored.
NOTRAYFLASH [0..1] 0 If set to 1, the tray icon will not
flash to notify the user that it
wants attention.
OPTIMIZE [0..1] 1 If this is set to 1, and antivirus
and/or firewall are being installed,
these features will be optimized
for the computer FortiClient is
being installed on. This can take
seconds to minutes depending on
the performance of the computer.
To disable optimization during
installation, set this value to 0.
REORDERVNIC [0..1] 1 0=Does not push FortiClient's
virtual adapter to the bottom of
the adapter list.
After installation, the features will
self-optimize in the background
with no assistance required from
the end-user. However, the
optimization is spread over a much
longer period (hours/days).
Allowing FortiClient to optimize
during installation gives maximum
performance benefit up front.
0 is required in some
circumstances, such as if Cisco's
VPN is currently installed.
1=Pushes FortiClient's virtual
adapter to the bottom of the
adapter list so that is enumerated
last by windows.
SWUPDATEREQUIRE
SADMIN
UPDATEFAILOVERPORT[any valid port
[0..1] 0 0=no
1=yes
8000 If the initial update connection
number]
fails, FortiClient will try again
When set to 1, only admin users
will be able to perform software
updates from FortiClient.
using this prot number.
UPDATEFALLBACK [0..1] 1 If this setting is set to 1 and
FortiClient is configured to use a
custom update server and if that
connection fails then FortiClient
will attempt to update from
FortiProtect Distribution Server.
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 59
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 66

Appendix A: Installer Public Properties
Table 9: Installer public properties when installing FortiClient (Part 4 of 4).
Public property Range Default Description Comment
USESWUID [0..1] 1 0=FortiClient will use a unique
identifier derived from the
computer that FortiClient is
running on.
1=FortiClient will use a software
1 is the preferred option, 0 can
lead to unique identifier collisions.
Note: If making hard disk images,
the “RemoveFortiClientID” tool
before creating the image.
unique identifier generator
WFLOGALLURLS [0..1] 0 If this is set to 1 and WF is
installed, all URLs visited will be
logged
WANACCDBDIR [any valid
directory]
WANACCPROTOCOLS [csv list of one or
more of:
installatio
n
directory
The directory that the WAN
acceleration database should be
located
The protocols that should be
accelerated
http,cif,ftp,mapi]
WFDONTRATEIP [0..1] 0 If set to 1 and if an IP address is
browsed to (instead of a FQDN),
FortiClient will not request a rating
for that IP address from the
FortiGuard network.
60 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 67

Index
Index
Symbols
.exe, 5
.msi, 5
A
ADMINMODE, 57
antileak, 21
API, 51
controlling VPN
monitoring connections
monitoring security policies
policy compliance
reading security policies
security policies
VPN connection names
VPN tunnel
XAuth requests
application detection list
creating
application groups
AV update schedule randomizing, 12
AV_BEFORE_VPN, 57
, 51
, 53
, 54
, 55
, 54
, 53, 54
, 52
, 52
, 52
, 37
, 33
, 35
B
block access unless firewall rule permits
installation option
, 12
C
category definitions, 35
certificate key size
changing for installation
Citrix servers
installing
cloned disk image
including FortiClient
cloned PC hardware
install with USESWUID option
code page, 2
COM library
comments on Fortinet technical documentation
COMPLIANCE_POLICY, 57
corporate security policy
FortiClient, setting
viewing
creating
application detection list
custom installer packages
endpoint control profiles
custom installer packages
customer service, 3
, 20
, 51
, 27
, 12
, 20
, 20
, 28
, 33
, 9
, 32
, 9
, 3
customization of FortiClient installer
changing installer language, 13
creating
deploying
Endpoint NAC distribution
for enterprise licensing
language transforms
licensing
log file
sample command lines
specifying multiple transforms on the command line
supressing features
transferrring to later versions
using FCRepackager
using MSI editor
, 15
, 13
, 16
, 25
, 16
, 13
, 16
, 15
, 15
, 13
, 9
, 14
D
disable XAUTH password saving
installation option
DISABLEPROXYSELFTEST
DISABLESWUPDATES, 57
disabling web filter rating by IP addresses
installation option
documentation, 3
, 11
, 57
, 11
E
ENABLE_FORTIPROXY, 57
ENABLE_REGMON, 57
enabling
endpoint control
endpoint control
enabling
endpoint control profile
apply to firewall policy
endpoint control profiles
creating
Endpoint NAC distribution
deploying customized installation
endpoints
monitoring
, 32
, 32
, 32
, 36
, 16
, 37
F
FCRepackager
using to create customized installer
FCRepackager tool
FCRepackager_Readme.txt
FDS servers, fallback to public servers, 11
firewall
changing default firewall action
firewall policy
applying endpoint control profile
FMGRAVALERTINT
FMGRDISCOVERATTEMPTS, 57
FMGRDISCOVERINTERVAL
FMGRENABLED
FMGRENABLEDISCOVER, 58
, 10
, 10
, 57
, 58
, 58
, 9
, 20
, 36
, 16
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 61
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 68

Index
FMGRFWALERTINT, 58
FMGRFWBEHAVIOR, 58
FMGRHEARTBEAT, 58
FMGRHEARTBEATCOUNT
FMGRIP, 58
FMGRRAISEALERT, 58
FMGRTIMEOUT
FMGRTRUSTEDIPS
FortiClient
custom installation
enforcing use
installing, standard installation
software packages
VPN
, 39
FortiClient COM library, 51
FortiClient packages
uploading to FortiGate unit
FortiClient PCs
adding to FortiManager database
FortiClient version
setting
FortiClientTools.zip
FortiGate
VPN connections
FortiGate models
supported by FortiClient
FortiGuard Distribution Network (FDN), 30
FortiGuard Services, 30
FortiManager
configuring central management
configuring for FortiClient web filtering
configuring web filter profiles
FortiClient Manager options
remote management
VPN
, 40
Fortinet customer service, 3
Fortinet Knowledge Center, 3
FortiOS versions
supported by FortiClient
FortiTray
installation option to hide
FWDEFAULTAPPACTION
, 58
, 29
, 30
, 10
, 58
, 58
, 9
, 6
, 5
, 32
, 44
, 39
, 2
, 18, 19
, 45
, 44
, 17
, 2
, 11
, 58
H
hide FortiTray
installation option
HIDETRAY
, 58
, 11
I
installation options
block access unless firewall rule permits
disable web filter rating by IP address
disable XAUTH password saving
hide FortiTray
permit fallback to public FDS
, 11
, 11
, 11
, 43
, 11
, 12
installing
introduction
, 5
, 5
.exe
.msi
, 5
as part of a cloned disk image
Citrix servers
custom installer packages
distributing customized installers
FortiClient
multiple-user
notes
, 6
on cloned PC hardware
setting to request FortiManager registration
shared folder installation
single-user
using Active Directory server
, 20
, 5
, 7
, 6
, 20
, 9
, 26
, 20
, 17
, 17
, 1
L
language support, 2
LDAP
for Windows user and group information
LICENSE, 59
license
creating a client license key
deploying client license key
enterprise license
enterprise license, applying
enterprise license, registering
redistributable enterprise license
standard fixed license
standard fixed license, applying
volume license
license key
specifying in FCRepackager customization
LICENSE_VALIDATION_TYPE, 59
lockdown
enabling in FCRepackager customization
, 23
, 23
, 25
, 25
, 24
, 24
, 23
, 23
, 23
M
monitoring
endpoints
MSI installation file
creating
shrinking
mst file, 10
, 37
, 12
, 12
N
NOREMEMBER_VPN_PWD, 59
NOTRAYFLASH
, 59
O
OPTIMIZE, 59
, 44
, 45
, 12
, 12
62 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 69

Index
P
per-user web filtering
assigning profiles
configuring FortiManager for
overview
remote users
Windows network
policy server
configuring FortiGate unit as
public installer properties
, 43
, 45
, 43
, 43
, 57
R
remote management
enabling in MSI customization
FortiManager
RemoveFCTID.exe
removing identifier, 20
REORDERVNIC, 59
, 17
, 20
S
sample installation
for customization
SWUPDATEREQUIRESADMIN
system requirements, 1
, 10
T
technical support, 3
U
UPDATEFAILOVERPORT, 59
, 43
, 41
, 18
, 59
UPDATEFALLBACK
USESWUID, 60
USESWUID installation option, 20
, 59
V
viewing
corporate security policy
VPN
custom installation, 41
FortiClient
FortiGate
FortiManager
VPN Editor, 41
VPN XAUTH passwords
installation option to disable saving
, 39
, 39
, 40
, 27
W
WANACCDBDIR, 60
WANACCPROTOCOLS
web filter
disabling rating of IP addresses
web filter profiles
assigning to groups and users
defining in FortiClient Manager
web filtering
assigning profiles
configuring FortiManager for
on Citrix server
on Windows Terminal server
overview
remote users
Windows network
WFDONTRATEIP
, 43
, 60
, 45
, 43
, 43
, 43
, 43
, 60
, 11
, 11
, 45
, 45
, 43
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
04-40001-99556-20090626 63
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 70

Index
64 04-40001-99556-20090626
FortiClient Endpoint Security Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 71

www.fortinet.com
Page 72

www.fortinet.com
 Loading...
Loading...