Page 1

FortiGate Voice
™
Version 4.0 MR1
Administration Guide
Visit http://support.fortinet.com to register your FortiGate Voice product. By registering you
can receive product updates, technical support, and FortiGuard services.
Page 2

FortiGate Voice Administration Guide
Version 4.0 MR1
1 June 2010
01-410-112851-20100601
© Copyright 2010 Fortinet, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication including text, examples,
diagrams or illustrations may be reproduced, transmitted, or translated in any form or by any means,
electronic, mechanical, manual, optical or otherwise, for any purpose, without prior written permission of
Fortinet, Inc.
Trademarks
Dynamic Threat Prevention System (DTPS), APSecure, FortiASIC, FortiBIOS, FortiBridge, FortiClient,
FortiGate®, FortiGate Unified Threat Management System, FortiGuard®, FortiGuard-Antispam,
FortiGuard-Antivirus, FortiGuard-Intrusion, FortiGuard-Web, FortiLog, FortiAnalyzer, FortiManager,
Fortinet®, FortiOS, FortiPartner, FortiProtect, FortiReporter, FortiResponse, FortiShield, FortiVoIP, and
FortiWiFi are trademarks of Fortinet, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries. The names of actual
companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Introduction .............................................................................................. 5
Fortinet products ............................................................................................................ 6
Before you begin............................................................................................................. 6
How this guide is organized........................................................................................... 6
Document conventions .................................................................................................. 9
IP addresses............................................................................................................... 9
Example Network configuration ................................................................................ 11
Cautions, Notes and Tips ......................................................................................... 12
Typographical conventions ....................................................................................... 13
CLI command syntax conventions............................................................................ 13
Registering your Fortinet product............................................................................... 15
Fortinet products End User License Agreement ....................................................... 15
Training .......................................................................................................................... 15
Documentation ............................................................................................................. 15
Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD ..................................................................... 16
Fortinet Knowledge Base ......................................................................................... 16
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation ..................................................... 16
Customer service and technical support.................................................................... 16
Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration ....................... 17
General configuration steps ........................................................................................ 18
Connecting the FortiGate Voice unit........................................................................... 19
Configuring basic FortiGate Voice network and UTM settings ................................ 19
Configuring network settings for the devices on the Internal network ................... 22
Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings......................................... 22
Configuring the FortiFones on the internal network ................................................. 27
Adding extensions and configuring FortiFones for users behind a
NAT device..................................................................................................................... 28
FortiGate Voice IVR configuration............................................................................... 30
Providing access to the company directory............................................................... 30
Adding a shortcut for checking voicemail.................................................................. 31
Checking voicemail................................................................................................... 31
FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference.......... 33
Dashboard widgets ....................................................................................................... 33
Unit operation dashboard widget .............................................................................. 33
System resources dashboard widget........................................................................ 33
Configuring VoIP interface settings ............................................................................ 34
Configuring PSTN interfaces ....................................................................................... 34
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 3
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 4

Contents
PBX configuration......................................................................................................... 36
Configuring service providers ................................................................................... 36
Configuring extensions ............................................................................................. 37
Configuring extension groups (ring groups).............................................................. 39
Configuring dial plans ............................................................................................... 40
Configuring voice menu options ............................................................................... 43
Configuring direct inward dialing............................................................................... 44
Configuring PBX settings.......................................................................................... 45
Monitoring calls......................................................................................................... 46
Monitoring SIP Trunk status ..................................................................................... 46
Monitoring the status of PBX extensions.................................................................. 46
Logging of PBX activities............................................................................................. 47
Viewing log messages .............................................................................................. 47
FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference........................ 49
config pbx dialplan ....................................................................................................... 49
config pbx did................................................................................................................ 50
config pbx extension .................................................................................................... 51
config pbx global .......................................................................................................... 52
config pbx ringgrp ........................................................................................................ 53
config pbx smtp ............................................................................................................ 54
config pbx voice-menu ................................................................................................. 55
config pbx voip-provider .............................................................................................. 55
config system pstn ....................................................................................................... 57
config system interface ................................................................................................ 58
execute pbx ................................................................................................................... 58
diagnose pbx restart..................................................................................................... 60
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
4 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 5
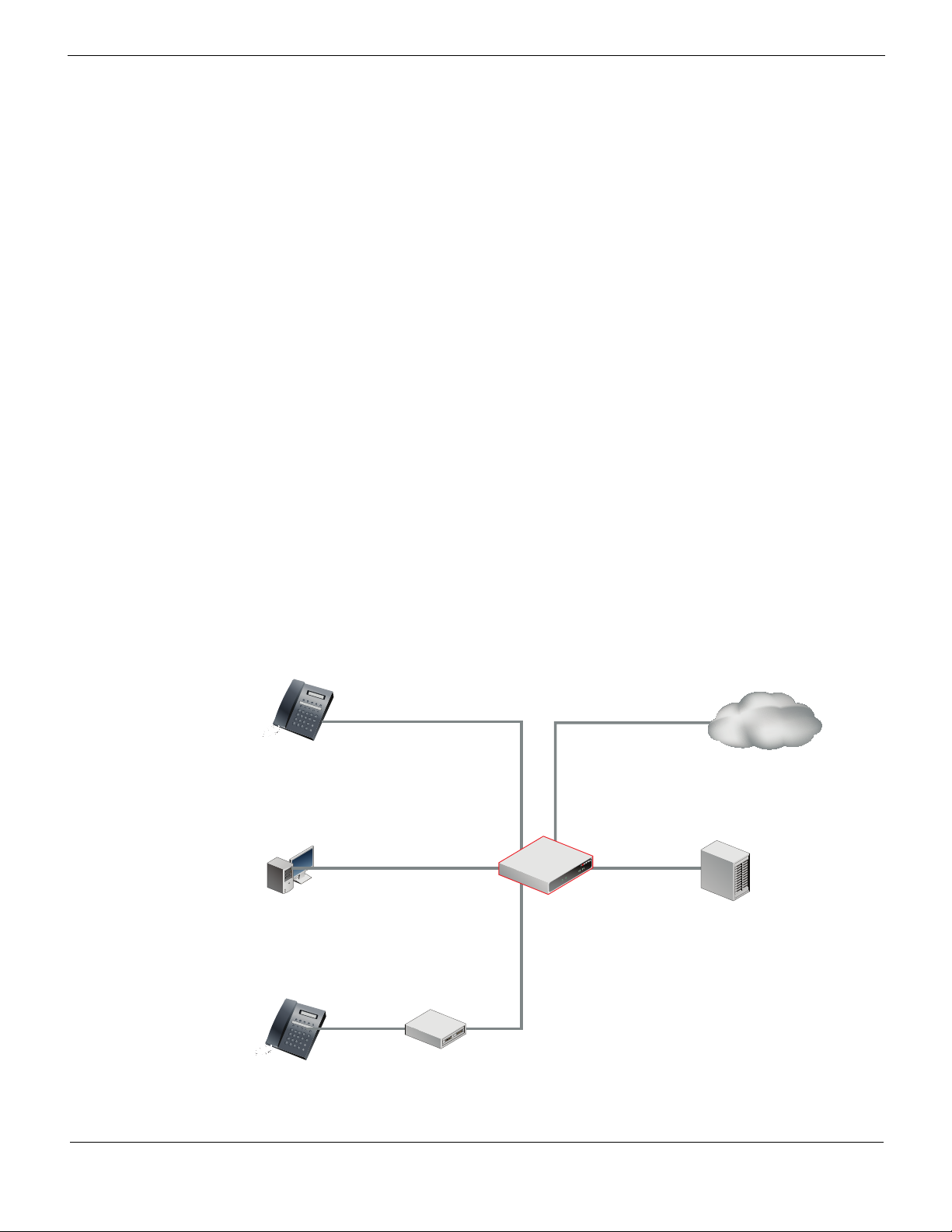
Introduction
FortiFones or
other
SIP Phones
SIP
LAN
WAN
FXO (x4)
(some models)
ISP
IMS
NGN
VPN
etc
Class 5
PSTN
(LEC)
SIP Trunking
LAN
LAN
SIP
SIP
PCs with
SIP Soft Phone
POTS/ISDN
Telephone
Adapters (ATA)
a/b - wire
BRI
a/b - wire
FortiGate Voice
unit
Service Provider
Network
Introduction
FortiGate Voice units integrate FortiGate UTM functionality with VoIP phone PBX
functionality. Some FortiGate Voice models also support connections to the public
switched telephone network (PSTN). A small office or an enterprise branch office can use
a FortiGate Voice unit to provide routing, Ethernet switching, Internet connectivity, UTM
security, VoIP gateway, and VoIP PBX features for the office.
FortiGate Voice PBX functionality includes:
• Four Foreign eXchange Office (FXO) interfaces for connected to up to 4 standard
public switch telephone network (PSTN) phone lines (some FortiGate Voice models)
• Flexible number dial plans
• Standard VoIP PBX feature set
• Integrated dial-back up modem and optional 3G wireless cards
•Voicemail
• Message notification
• Unified messaging
• Music on hold
• Automatic Call Distribution (ACD)
• Basic conferencing
• Statistics and logging
Figure 1: FortiGate Voice Network connections
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 5
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 6

Fortinet products Introduction
This document includes a configuration example that describes how to configure a
FortiGate Voice-80C to provide VoIP, networking, and UTM services for a branch office
network. Also included is a configuration reference to FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and
PSTN web-based manager and CLI functionality.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Fortinet products
• Before you begin
• How this guide is organized
• Document conventions
• Registering your Fortinet product
• Fortinet products End User License Agreement
• Training
• Documentation
• Customer service and technical support
Fortinet products
Fortinet's portfolio of security gateways and complementary products offers a powerful
blend of ASIC-accelerated performance, integrated multi-threat protection, and constantly
updated, in-depth threat intelligence. This unique combination delivers network, content,
and application security for enterprises of all sizes, managed service providers, and
telecommunications carriers, while providing a flexible, scalable path for expansion. For
more information on the Fortinet product family, go to www.fortinet.com/products.
Before you begin
This document is intended for administrators, not end users.
This FortiGate Voice Administration Guide is a supplement to the FortiGate Administration
Guide that provides detailed information about the PBX, and PSTN configuration for
system administrators of a FortiGate Voice unit. It is assumed that you have already
successfully installed a FortiGate unit by following the instructions in the FortiGate Voice-
80C QuickStart Guide. PSTN interfaces are supported on some FortiGate Voice models.
At this stage:
• You have administrative access to the web-based manager and/or CLI.
• The FortiGate Voice unit is integrated into your network.
• The operation mode has been configured.
• The system time, DNS settings, administrator password, and network interfaces have
been configured.
• Firmware, FortiGuard Antivirus and FortiGuard Antispam updates are completed.
Once that basic installation is complete, you can use this document.
How this guide is organized
This section of the guide provides a brief provides a chapter-by-chapter summary of this
guide.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
6 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 7

Introduction How this guide is organized
The most recent version of this document is available from the FortiGate page of the
Fortinet Technical Documentation web site.
You can also learn more about the FortiGate Voice product from the same FortiGate page,
as well as from the Fortinet Knowledge Base.
This administration guide contains the following chapters:
• Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration provides a configuration example
that describes how to configure a FortiGate Voice-80C unit to operate in NAT/Route
mode and provide basic UTM and SIP services for an example branch office network.
• FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference describes FortiGate
Voice web-based manager configuration settings.
• FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference describes upgrading and
managing firmware versions. You should review this section before upgrading your
FortiGate firmware because it contains important information about how to properly
back up your current configuration settings and what to do if the upgrade is
unsuccessful.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 7
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 8

How this guide is organized Introduction
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
8 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 9
Document conventions
Fortinet technical documentation uses the conventions described below.
IP addresses
To avoid publication of public IP addresses that belong to Fortinet or any other
organization, the IP addresses used in Fortinet technical documentation are fictional and
follow the documentation guidelines specific to Fortinet. The addresses used are from the
private IP address ranges defined in RFC 1918: Address Allocation for Private Internets,
available at http://ietf.org/rfc/rfc1918.txt?number-1918.
Most of the examples in this document use the following IP addressing:
• IP addresses are made up of A.B.C.D
• A - can be one of 192, 172, or 10 - the non-public addresses covered in RFC 1918.
• B - 168, or the branch / device / virtual device number.
• Branch number can be 0xx, 1xx, 2xx - 0 is Head office, 1 is remote, 2 is other.
• Device or virtual device - allows multiple FortiGate units in this address space
(VDOMs).
• Devices can be from x01 to x99.
• C - interface - FortiGate units can have up to 40 interfaces, potentially more than one
on the same subnet
• 001 - 099- physical address ports, and non -virtual interfaces
• 100-255 - VLANs, tunnels, aggregate links, redundant links, vdom-links, etc.
• D - usage based addresses, this part is determined by what device is doing
• The following gives 16 reserved, 140 users, and 100 servers in the subnet.
• 001 - 009 - reserved for networking hardware, like routers, gateways, etc.
• 010 - 099 - DHCP range - users
• 100 - 109 - FortiGate devices - typically only use 100
• 110 - 199 - servers in general (see later for details)
• 200 - 249 - static range - users
• 250 - 255 - reserved (255 is broadcast, 000 not used)
• The D segment servers can be farther broken down into:
• 110 - 119 - Email servers
• 120 - 129 - Web servers
• 130 - 139 - Syslog servers
• 140 - 149 - Authentication (RADIUS, LDAP, TACACS+, FSAE, etc)
• 150 - 159 - VoIP / SIP servers / managers
• 160 - 169 - FortiAnalyzers
• 170 - 179 - FortiManagers
• 180 - 189 - Other Fortinet products (FortiScan, FortiDB, etc.)
• 190 - 199 - Other non-Fortinet servers (NAS, SQL, DNS, DDNS, etc.)
• Fortinet products, non-FortiGate, are found from 160 - 189.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 9
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 10
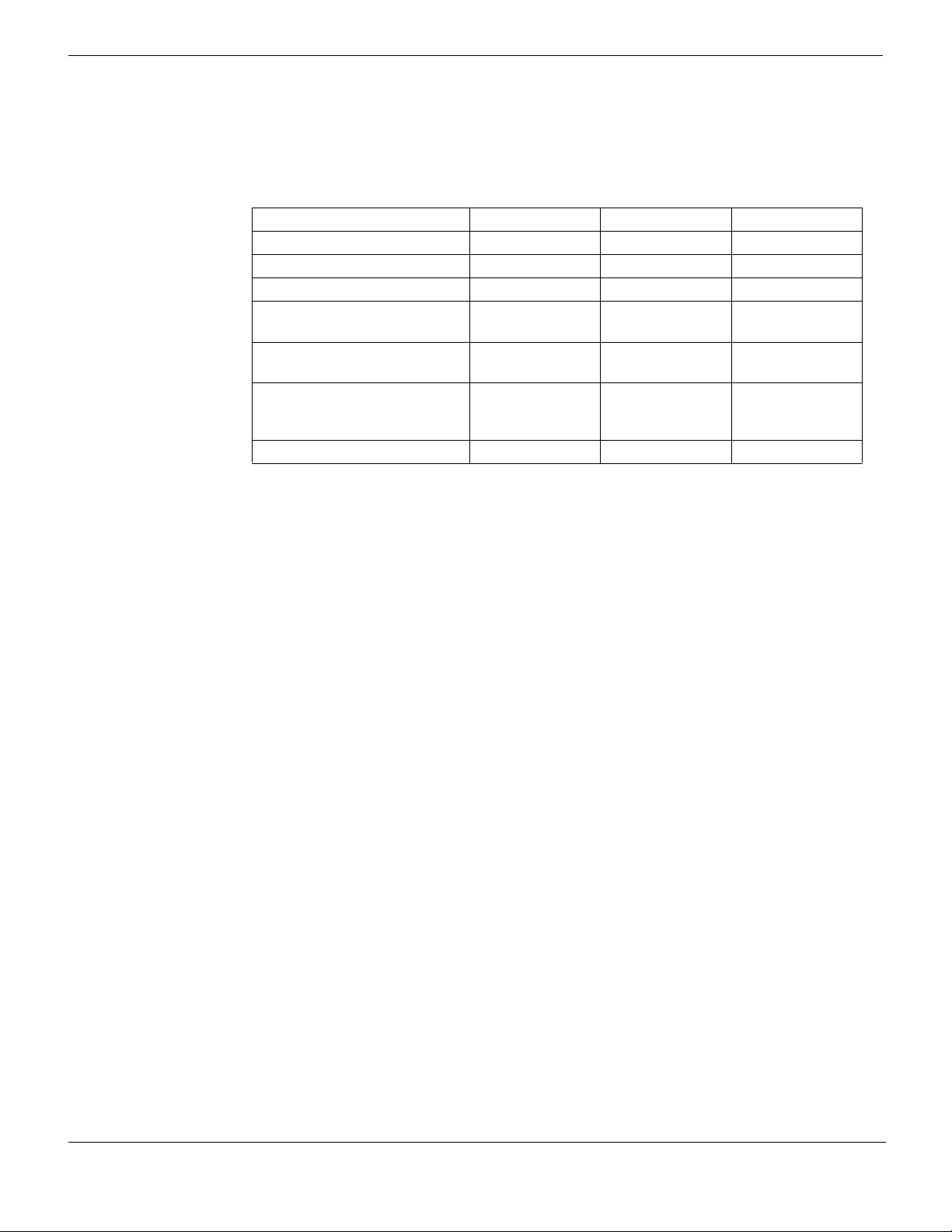
Document conventions
The following table shows some examples of how to choose an IP number for a device
based on the information given. For internal and dmz, it is assumed in this case there is
only one interface being used.
Table 1: Examples of the IP numbering
Location and device Internal Dmz External
Head Office, one FortiGate 10.011.101.100 10.011.201.100 172.20.120.191
Head Office, second FortiGate 10.012.101.100 10.012.201.100 172.20.120.192
Branch Office, one FortiGate 10.021.101.100 10.021.201.100 172.20.120.193
Office 7, one FortiGate with 9
VDOMs
Office 3, one FortiGate, web
server
Bob in accounting on the
corporate user network (dhcp)
at Head Office, one FortiGate
Router outside the FortiGate n/a n/a 172.20.120.195
10.079.101.100 10.079.101.100 172.20.120.194
n/a 10.031.201.110 n/a
10.0.11.101.200 n/a n/a
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
10 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 11
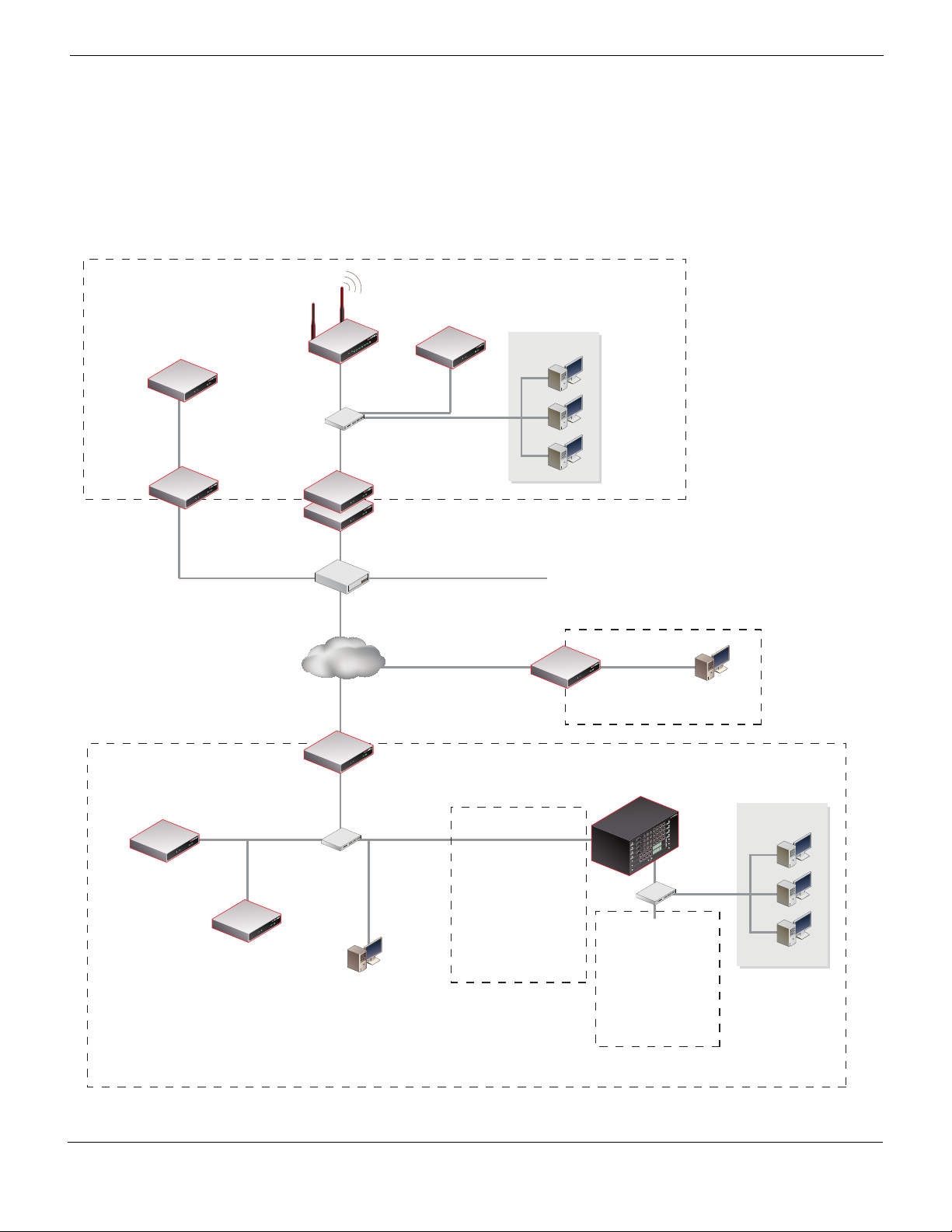
Port1
Port2 and Port3
Port1: 172.20.120.141
Port2: 10.11.101.100
FortiGate-620B
Cluster
FortiGate-51B
Linksys SRW2008
Windows PC
10.11.101.10
INT: 10.11.101.101
WLAN: 10.12.101.100
SSID: example.com
Password: supermarine
DHCP range: 10.12.101.200-249
FortiWiFi-80CM
FortiGate-82C
Port2: 10.11.101.102
Port1:
172.20.120.130
(sniffer mode)
Port8
(mirror of Port2 and Port3)
Port5
Old Lab
Head office
Linux PC
10.11.101.20
FortiAnalyzer-100B
Port2: 10.11.101.130
Switch: 10.21.101.100
Port4:
10.22.101.100
WAN1: 172.20.120.131
WAN1: 172.20.120.122
Internal: 10.31.101.100
FortiGate-111C
Linux PC
10.21.101.10
FortiGate-3810A
Port1:
10.21.101.101
FortiManager-3000B
Port1:
10.21.101.160
FortiSwitch-5003A
FortiGate-5050SM
Port1: 10.22.101.161
Port1: 10.22.101.104
FortiSwitch-5003A
FortiGate-5050SM
Port1: 10.21.101.161
Port1: 10.21.101.104
FortiGate-5005FA2
Cluster
FortiGate-5005FA2
Port1: 10.21.101.102
Port1: 10.21.101.102
Port1: 10.21.101.103
Branch office
Branch office
Internet
Internal
Network
Windows PC
10.31.101.10
Engineering
Network
10.22.101.0
FortiMail-100C
Port1: 10.11.101.110
Document conventions
Example Network configuration
The network configuration shown in Figure 2 or variations on it is used for many of the
examples in this document. In this example, the 172.20.120.0 network is equivalent to the
Internet. The network consists of a head office and two branch offices.
Figure 2: Example network configuration
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 11
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 12
Document conventions
Cautions, Notes and Tips
Fortinet technical documentation uses the following guidance and styles for cautions,
notes and tips.
Caution: Warns you about commands or procedures that could have unexpected or
undesirable results including loss of data or damage to equipment.
Note: Presents useful information, but usually focused on an alternative, optional method,
such as a shortcut, to perform a step.
Tip: Highlights useful additional information, often tailored to your workplace activity.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
12 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 13

Document conventions
Typographical conventions
Fortinet documentation uses the following typographical conventions:
Table 2: Typographical conventions in Fortinet technical documentation
Convention Example
Button, menu, text box,
field, or check box label
CLI input config system dns
CLI output FGT-602803030703 # get system settings
Emphasis HTTP connections are not secure and can be intercepted by a third
File content <HTML><HEAD><TITLE>Firewall
Hyperlink Visit the Fortinet Technical Support web site,
Keyboard entry Type a name for the remote VPN peer or client, such as
Navigation Go to VPN > IPSEC > Auto Key (IKE).
Publication For details, see the FortiOS Handbook.
From Minimum log level, select Notification.
set primary <address_ipv4>
end
comments : (null)
opmode : nat
party.
Authentication</TITLE></HEAD>
<BODY><H4>You must authenticate to use this
service.</H4>
https://support.fortinet.com.
Central_Office_1.
CLI command syntax conventions
This guide uses the following conventions to describe the syntax to use when entering
commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI).
Brackets, braces, and pipes are used to denote valid permutations of the syntax.
Constraint notations, such as <address_ipv4>, indicate which data types or string
patterns are acceptable value input.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 13
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 14
Document conventions
Table 3: Command syntax notation
Convention Description
Square brackets [] A non-required word or series of words. For example:
[verbose {1 | 2 | 3}]
indicates that you may either omit or type both the verbose word and
its accompanying option, such as:
verbose 3
Angle brackets <> A word constrained by data type.
To define acceptable input, the angled brackets contain a descriptive
name followed by an underscore ( _ ) and suffix that indicates the
valid data type. For example:
<retries_int>
indicates that you should enter a number of retries, such as 5.
Data types include:
• <xxx_name>: A name referring to another part of the
configuration, such as policy_A.
• <xxx_index>: An index number referring to another part of the
configuration, such as 0 for the first static route.
• <xxx_pattern>: A regular expression or word with wild cards
that matches possible variations, such as *@example.com to
match all email addresses ending in @example.com.
• <xxx_fqdn>: A fully qualified domain name (FQDN), such as
mail.example.com.
• <xxx_email>: An email address, such as
admin@mail.example.com.
• <xxx_url>: A uniform resource locator (URL) and its associated
protocol and host name prefix, which together form a uniform
resource identifier (URI), such as
http://www.fortinet./com/.
• <xxx_ipv4>: An IPv4 address, such as 192.168.1.99.
• <xxx_v4mask>: A dotted decimal IPv4 netmask, such as
255.255.255.0.
• <xxx_ipv4mask>: A dotted decimal IPv4 address and netmask
separated by a space, such as
192.168.1.99 255.255.255.0.
• <xxx_ipv4/mask>: A dotted decimal IPv4 address and
CIDR-notation netmask separated by a slash, such as such as
192.168.1.99/24.
• <xxx_ipv6>: A colon( : )-delimited hexadecimal IPv6 address,
such as 3f2e:6a8b:78a3:0d82:1725:6a2f:0370:6234.
• <xxx_v6mask>: An IPv6 netmask, such as /96.
• <xxx_ipv6mask>: An IPv6 address and netmask separated by a
space.
• <xxx_str>: A string of characters that is not another data type,
such as P@ssw0rd. Strings containing spaces or special
characters must be surrounded in quotes or use escape
sequences.
• <xxx_int>: An integer number that is not another data type,
such as 15 for the number of minutes.
Curly braces {} A word or series of words that is constrained to a set of options
delimited by either vertical bars or spaces.
You must enter at least one of the options, unless the set of options is
surrounded by square brackets [ ].
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
14 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 15
Registering your Fortinet product
Table 3: Command syntax notation (Continued)
Convention Description
Options
delimited by
vertical bars |
Options
delimited by
spaces
Mutually exclusive options. For example:
{enable | disable}
indicates that you must enter either enable or disable, but must
not enter both.
Non-mutually exclusive options. For example:
{http https ping snmp ssh telnet}
indicates that you may enter all or a subset of those options, in any
order, in a space-delimited list, such as:
ping https ssh
Note: To change the options, you must re-type the entire list. For
example, to add snmp to the previous example, you would type:
ping https snmp ssh
If the option adds to or subtracts from the existing list of options,
instead of replacing it, or if the list is comma-delimited, the exception
will be noted.
Registering your Fortinet product
Before you begin configuring and customizing features, take a moment to register your
Fortinet product at the Fortinet Technical Support web site, https://support.fortinet.com.
Many Fortinet customer services, such as firmware updates, technical support, and
FortiGuard Antivirus and other FortiGuard services, require product registration.
For more information, see the Fortinet Knowledge Center article Registration Frequently
Asked Questions.
Fortinet products End User License Agreement
See the Fortinet products End User License Agreement.
Training
Fortinet Training Services provides courses that orient you quickly to your new equipment,
and certifications to verify your knowledge level. Fortinet provides a variety of training
programs to serve the needs of our customers and partners world-wide.
To learn about the training services that Fortinet provides, visit the Fortinet Training
Services web site at http://campus.training.fortinet.com, or email training@fortinet.com.
Documentation
The Fortinet Technical Documentation web site, http://docs.fortinet.com, provides the
most up-to-date versions of Fortinet publications, as well as additional technical
documentation such as technical notes.
In addition to the Fortinet Technical Documentation web site, you can find Fortinet
technical documentation on the Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD, and on the Fortinet
Knowledge Center.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 15
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 16

Customer service and technical support
Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD
Many Fortinet publications are available on the Fortinet Tools and Documentation CD
shipped with your Fortinet product. The documents on this CD are current at shipping
time. For current versions of Fortinet documentation, visit the Fortinet Technical
Documentation web site, http://docs.fortinet.com.
Fortinet Knowledge Base
The Fortinet Knowledge Base provides additional Fortinet technical documentation, such
as troubleshooting and how-to-articles, examples, FAQs, technical notes, a glossary, and
more. Visit the Fortinet Knowledge Base at http://kb.fortinet.com.
Comments on Fortinet technical documentation
Please send information about any errors or omissions in this or any Fortinet technical
document to techdoc@fortinet.com.
Customer service and technical support
Fortinet Technical Support provides services designed to make sure that your Fortinet
products install quickly, configure easily, and operate reliably in your network.
To learn about the technical support services that Fortinet provides, visit the Fortinet
Technical Support web site at https://support.fortinet.com.
You can dramatically improve the time that it takes to resolve your technical support ticket
by providing your configuration file, a network diagram, and other specific information. For
a list of required information, see the Fortinet Knowledge Base article FortiGate
Troubleshooting Guide - Technical Support Requirements.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
16 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 17

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
Example FortiGate Voice branch office
configuration
This section describes how to configure a FortiGate Voice-80C unit to operate in
NAT/Route mode and provide basic UTM and SIP services for the example branch office
network shown in Figure 3 on page 18. The non-PSTN parts of this example configuration
also apply to FortiGate Voice models that do not include PSTN interfaces.
In this example the FortiGate Voice-80C unit provides:
• Internet connectivity, networking, and UTM features for the PCs on the branch office
internal network.
• An single line a/b wire connection between the FortiGate Voice-80C fxo1 interface and
a public switched telephone network (PSTN) line so that branch office phones can call
the PSTN or receive calls from the PSTN.
• VoIP PBX services for FortiFones and SIP soft phones connected to the branch office
internal network. PBX features include:
• Extensions to the FortiFones and SIP soft phones in the internal network. The
branch office phones use numeric extensions beginning with the number 6 and
including three more digits. Example valid extensions are 6123, 6456, and 6899.
• Extensions for phones behind NAT devices on the internal network.
• Extensions for phones behind NAT devices on a remote network.
• To collect voicemail the branch office phones dial *97.
• SIP trunking to a VoIP provider for calling the head office.
• To call a phone number on the PSTN, the branch office phones dial 9 followed by
the phone number. PSTN support will also include:
• Dialing 911 for emergencies
• Support for dialing international calls
• Support for dialing toll free calls
• Support for long distance calls
• The FortiGate Voice unit sends email notifications to users when they receive
voicemail.
• To call the head office, the branch office phones dial a head office extension
directly. The head office extension range is 2000-2999.
This configuration example describes configuring the FortiGate Voice-80C unit to support
these services and where required also provides configuration steps for other devices
such as the FortiFones and the remote FortiGate unit operating in NAT mode.
Details about the PSTN connection requirements, SIP trunking for the VoIP provider and
the Head Office SIP configuration are not described.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 17
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 18

General configuration steps Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
Figure 3: Example Branch Office network configuration
Branch Office
Internal network
PCs with SIP soft phones
and FortiFones
Subnet: 172.20.120.0
Extension Range 6000 - 6999
PC
FortiFone
PC
FortiFone
PC
FortiFone
behind a NAT
device
NAT device
SIP
LAN internal
172.20.120.10
a/b - wire
fxo1
192.168.10.10
FortiGate Voice-80C
PSTN
SIP Trunking SIP Trunking
WAN WAN
wan1
Internet
VoIP Provider
IP: 192.168.20.10
Remote Users
with FortiFones or
SIP soft phones
Extension range
6000 - 6999
Remote
FortiGate unit
in NAT mode
external
192.168.40.10
IP: 192.168.30.10
Extention Range
This section describes:
• General configuration steps
• Connecting the FortiGate Voice unit
• Configuring basic FortiGate Voice network and UTM settings
• Configuring network settings for the devices on the Internal network
• Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings
• Configuring the FortiFones on the internal network
• Adding extensions and configuring FortiFones for users behind a NAT device
Head Office
2000 - 2999
General configuration steps
1 Connect the FortiGate Voice unit to the Internet, the internal network and the PSTN.
2 Configure FortiGate Voice unit network and UTM settings.
The network configuration includes enabling the SIP Traffic option on the internal and
wan1 interfaces. You must enable SIP traffic on these interfaces to accept and process
SIP calls. No other special network configuration, firewall policies, or routing is required
for the FortiGate Voice to accept and process SIP calls.
Note: You do not have to add SIP firewall policies to enable SIP traffic for the FortiGate
Voice unit to function as a PBX. Also, with PBX functionality enabled, you cannot apply
FortiGate SIP application control features to SIP traffic received by FortiGate Voice
interfaces for which you have enabled the SIP Traffic option.
This example also describes how to configure the FortiGate Voice as a DHCP server
and DNS server for the branch office internal network. As a DHCP server the FortiGate
Voice can supply network configuration settings for the PCs and FortiFones on the
internal network.
3 Configure network settings for the PCs on the Internal network.
4 Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
18 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 19

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Connecting the FortiGate Voice unit
5 Configure the FortiFones on the internal network.
6 Configuring the FortiGate Voice unit to SIP phone users behind a remote NAT device.
Connecting the FortiGate Voice unit
The following procedure describes how to connect the FortiGate Voice unit to the Internet,
the branch office internal network, and the PSTN (supported by some FortiGate Voice
models).
To connect the FortiGate Voice unit
1 Use an Ethernet cable to connect the FortiGate Voice wan1 interface to the device that
connects the branch office to the Internet.
The device could be a cable or DSL modem or other device depending on how the
Branch Office connects to the Internet.
2 Use Ethernet cables to connect the PCs and FortiFones on the internal network to the
FortiGate Voice internal interface switch connectors.
You can connect up to 8 PCs and FortiFones directly to the FortiGate Voice Internal
interface switch connectors. To connect more devices, add Ethernet switches to your
network as required.
3 Use an RJ-45 telephone cable to connect the FortiGate Voice fxo1 port to the branch
office PSTN phone line supplied by your local telephone service provider.
Configuring basic FortiGate Voice network and UTM settings
The following procedures describe how to configure a FortiGate Voice to provide basic
Internet connectivity, network services, and UTM services for the branch office internal
network. Network services include configuring the FortiGate Voice to be the DHCP server
and DNS server for the internal network.
As part of the FortiGate Voice network interface configuration you must enable SIP Traffic
on the internal and wan1 interfaces so that the FortiGate Voice unit accepts SIP sessions
received by these interfaces. No other special network configuration, firewall policies, or
routing is required for the FortiGate Voice to accept SIP sessions from configured
extensions.
To configure basic network settings
1 Connect to the FortiGate Voice web-based manager.
2 Go to System > Network > Interface.
3 Edit the internal interface and configure the following settings:
Addressing Mode Manual
IP/Netmask 172.20.120.10/255.255.255.0
SIP Traffic Select Enable
Configure other network interface settings as required and select OK.
4 Edit the wan1 interface and configure the following settings:
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 19
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 20

Configuring basic FortiGate Voice network and UTM settings Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
Addressing Mode Manual
IP/Netmask 192.168.10.10/255.255.255.0
SIP Traffic Select Enable
Configure other network interface settings as required and select OK.
Note: You can also set the Addressing mode to DHCP or PPPoE for the wan1 interface
depending on the requirements of your ISP. In the example the wan1 interface has a static
IP address.
5 Go to System > Network > Options.
6 Add the IP addresses of the primary and secondary DNS servers used by the branch
office provided by your ISP.
7 Selected internal for Enable DNS forwarding from so that users on the internal network
can use the FortiGate Voice internal interface as their DNS server IP address.
The procedure “To configure the FortiGate Voice to be a DHCP server for the internal
network” on page 20 describes how to configure the FortiGate DHCP server to
configure PCs on the internal network to use the FortiGate Voice internal interface as a
DNS server.
8 Select Apply.
9 Go to Router > Static > Static Route.
10 Edit the default static route and configure the following settings:
Destination IP/Mask 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0
Device wan1
Gateway Enter the IP address of the default gateway provided by your ISP.
Distance 10
11 Select OK.
To configure the FortiGate Voice to be a DHCP server for the internal network
Use this procedure to add a new DHCP server for the internal network or to change the
configuration of the default FortiGateVoice DHCP server. The DHCP server will give PCs
on the Internal network IP addresses in the range 172.20.120.110 to 172.20.120.210 and
set their default gateway and DNS server to the IP address of the FortiGate Voice internal
interface.
1 Go to System > DHCP > Service and select the expand arrow for the internal interface.
2 Select the Add DHCP Server icon for the internal interface.
If a DHCP server has already been added for the internal interface, select the Edit icon
to change its configuration.
3 Configure the following settings.
Name Add a name for the DHCP server if you are adding a new one.
Enable Select
Type Regular
IP Range 172.20.120.110 - 172.20.120.210
Network Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway 172.20.120.10
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
20 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 21

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Configuring basic FortiGate Voice network and UTM settings
Advanced Select
DNS Server 1 172.20.120.10
4 Change other settings if required and select OK.
To configure FortiGuard services for the FortiGate Voice unit
Use the following procedure to configure the FortiGate Voice unit to connect to the
FortiGuard Distribution Network (FDN) to update the antivirus, antispam and IPS attack
definitions. Before you can begin receiving updates, you must register the FortiGate Voice
unit from the Fortinet Support web site. For more information, see “Registering your
Fortinet product” on page 15.
1 Go to System > Maintenance > FortiGuard.
2 Select the expand arrow for AntiVirus and IPS Options to expand the options.
3 Select Update Now to update the FortiGuard services and definitions.
If the connection to the FDN is successful, the web-based manager displays a
message similar to the following:
Your update request has been sent. Your database will be updated
in a few minutes. Please check your update page for the status
of the update.
After a few minutes, if an update is available, the FortiGuard page lists new version
information for the FortiGate services and definitions. The system dashboard license
information widget also displays new dates and version numbers for the FortiGuard
definitions. Messages are recorded to the event log indicating whether the update was
successful or not.
To configure basic Internet access and UTM features
This procedure describes how to add a firewall policy that allows users on the internal
network to connect to the Internet. The firewall policy includes the scan protection profile
to apply UTM features, in this case virus scanning, to this traffic. This configuration is not
required for VoIP support. It just provides users on the internal network with UTMprotected access to the Internet.
1 Go to Firewall > Policy and select Create New to add a new firewall policy.
2 Configure the following settings.
Source Interface/Zone internal
Source Address all
Destination Interface/Zone want
Destination Address all
Schedule always
Service ANY
Action ACCEPT
3 Select Protection Profile and select the scan protection profile to apply UTM virus
scanning to the traffic accepted by the firewall policy.
4 Select OK to save the firewall policy.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 21
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 22

Configuring network settings for the devices on the Internal network Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
Configuring network settings for the devices on the Internal network
You can configure the PCs and other devices on the internal network to get their network
configuration automatically using DHCP. If required you can also configure devices on the
internal network with static IP addresses on the 172.20.120.0 subnet but outside the range
awarded by the FortiGate Voice DHCP server. Example static TCP/IP configuration:
IP Address 172.20.120.20
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway 172.20.120.10
DNS Server 172.20.120.10
You can also use the same network configuration for the SIP phones on the internal
network.
Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings
The procedures in this section describe how to configure the FortiGate Voice unit as the
PBX for SIP phones on the branch office internal network. These procedures describe
how to configure many of the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX features. PSTN features are
supported on some FortiGate Voice models. The following procedures are included:
• To configure the fxo1 PSTN interface
• To configure basic PBX system and voicemail notification settings
• To add a VoIP provider
• To add a dial plan for dialing the PSTN and the main office
• To add the extensions that are on the branch office internal network
To configure the fxo1 PSTN interface
This procedure describes how to configure the FortiGate Voice fxo1 PSTN interface to
connect the FortiGate Voice unit to one PSTN phone line. If you have more PSTN phone
lines you can connect and configure more fxo interfaces. Skip this procedure if your
FortiGate Voice unit does not include PSTN interfaces.
1 Go to System > Network > PSTN Interface and edit the fxo1 interface.
2 Configure the following settings.
Phone Number Enter the phone number of the PSTN phone line as provided by your
Display Name This name is used for caller ID for calls from the FortiGate Voice unit
Caller ID Options Configure the following options to support caller ID functions for calls
Catch Caller ID Select to enable the FortiGate Voice unit to receive caller ID
phone service provider.
The phone number is used for caller ID for calls from the FortiGate
Voice unit to the PSTN. It can be any number, but is usually the
actual phone number of the PSTN line connected to the fxo1
interface. Area code and country codes are optional.
to the PSTN. It can be any name, such as a company name, that
identifies the branch office.
from the internal network to the PSTN.
information from calls originating on the PSTN and send the caller ID
information to the extension that answers the call.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
22 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 23

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings
Caller ID Protocol Select the caller ID protocol required by PSTN line that the fxo
Caller ID Indicator Select the caller ID indicator required by the PSTN line. Contact your
Ring # Set the number of rings to wait before receiving caller ID information.
Hang-up Options Configure the following options to configure how the FortiGate Voice
Hang up on Polarity
Reversal
Hang up on Busy Tone Select if you want the FortiGate Voice unit to hang up automatically
Busy Tone Detection # The number of busy tones that the FortiGate Voice receives before
Busy Tone Duration Tune the FortiGate Voice unit to accurately detect busy tones on this
Busy Tone Interval
Administrative Status Set to Up if the fxo interface is connected to the PSTN and you want
interface is connected to. Contact your service provider for the name
of the protocol to use.
service provider for details.
In most cases, enter 1 to send caller ID information between the first
and second ring.Contact your service provider for details.
unit hangs up calls from the PSTN.
Select if the PSTN line uses polarity reversal to indicate a call has
been hung up. Contact your service provider for details.
when it receives a busy tone when attempting to dial a number on the
PSTN.
hanging up if Hang up on Busy Tone is selected.
PSTN line. You can change the default settings if busy tones are not
accurately detected.
to be able to receive and send calls on this PSTN interface.
3 Select OK.
To configure basic PBX system and voicemail notification settings
Use the following procedure to configure PBX system settings and voicemail notification
email settings that affect the overall performance of the PBX service and all of the users of
it. Usually you would configure these settings once and rarely thereafter.
1 Go to PBX > Calling Rules > Setting.
2 Configure the following settings.
Extension Range 6XXX
The example extension range means that every extension added
to the FortiGate Voice unit must have an extension that begins
with the number 6 and includes three more numbers.
Country Code Enter the international country calling code for the country or
Local Area Code Enter the local area code for the country or region in which you
Voicemail Access *97
Outgoing Prefix 9
Max Voicemail Duration 60 seconds
region in which you are installing the FortiGate Voice unit.
are installing the FortiGate Voice unit.
Phone users on the internal network can dial *97 to get their
voicemail.
Phone users must dial 9 to get an outside line. The outgoing
prefix should not be the same as the first number of the
extension range.
Limits a single voicemail message to 60 seconds.
3 Configure the voicemail notification email settings.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 23
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 24

Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
SMTP Server The name or IP address of an email server that the FortiGate
Authentication Select if the email server requires authentication.
User Name Enter a valid username for an account on the email server.
Password Enter the password for the account on the email sever.
Voice unit can send email notifications to when PBX users
receive a voicemail. For example: mail.example.com.
You can optionally create an email account on the email server
for the FortiGate Voice unit.
4 Select Apply to save the changes.
To add a VoIP provider
Use the following procedure to add the information required by the FortiGate Voice unit to
use a VoIP provider for routing SIP calls on the main office. In the example, the
organization uses a third-party VoIP provider to handle VoIP calls between the head office
and the branch office.
1 Go to PBX > Service Providers > SIP Trunk.
2 Configure the following settings.
Name VoIP_Provider_1
A name for the VoIP provider. This can be any name.
Domain 192.168.20.10
The VoIP provider’s IP address. This could also be the VoIP
providers domain name (for example, voip.example.com).
User Name Enter a valid user name for an account on the VoIP provider’s
Password Enter the password for the account on the VoIP provider’s SIP
Authorization User Name Enter a valid authorization user name for an account on the VoIP
Display User Name Enter a valid display user name for an account on the VoIP
Account Type Select Static or Dynamic depending on the account with the VoIP
Registration Interval If this is a dynamic account with the VoIP provider, enter the
DTMF Method Auto
server. This could also be a phone number including area code,
depending on the requirements of the VoIP provider.
sever.
provider’s server if required by the VoIP provider.
provider’s server if required by the VoIP provider.
provider.
registration interval as required by the VoIP provider. After each
registration interval the FortiGate Voice renews the registration of
the account with the VoIP provider.
Auto means the VoIP provider’s server and the FortiGate Voice
unit will negotiate to select a DTMF method. You could also
select a specific DTMF method if required.
3 Select OK to add the VoIP provider.
To add a dial plan for dialing the PSTN and the main office
Dial plans are used to route calls made from an extension to an external phone system.
The external phone system can be the PSTN or a VoIP provider. To route calls to an
external phone system you add dial plan rules that include a dial pattern and list of
outgoing destinations. When the FortiGate Voice unit receives a call from an extension
and the number dialed matches a pattern in a dial plan rule, the FortiGate Voice unit
routes the call to the outgoing destination added to the dial plan.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
24 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 25

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings
In addition to PSTN and head office support the dial plan must also support Emergency,
international, toll free and long distance dialing.
Use the following steps to add a dial plan with the following dial plan rules:
• Allows the branch office to call the PSTN
• Dialing 911 for emergencies
• Dialing 9 followed by a country code for international calls
• Dialing 9 followed by 18 for toll free calls
• Dialing 9 followed by 1 for long distance calls
• Dialing 9 for all other PSTN calls
• Allows the branch office to dial head office extensions directly. The dial plan rule sends
calls starting with 2 to the VoIP provider where they are routed to the head office. This
dial plan does not include any other settings because users dial the head office
extension number directly without a prefix.
1 Go to PBX > Calling Rules > Dial Plan and select Create New.
2 Add a name for the new dial plan, for example, Dial_Plan_1.
3 Select OK.
4 Select Create New to add the dial plan rule for dialing 911 for emergencies.
Name Emergency
Use Default Outgoing Prefix
(“9”)
Phone number Begin with 911
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo1
Not selected
5 Select Create New to add the dial plan rule for dialing 9 followed by a country code for
international calls.
Name International
Use Default Outgoing Prefix
(“9”)
Phone number Begin with o11
Action Block
Selected
6 Select Create New to add the dial plan rule for dialing 9 followed by 18 for toll free
calls.
Name Toll_Free
Use Default Outgoing Prefix
(“9”)
Phone number Begin with 18
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo1
Selected
7 Select Create New to add the dial plan rule for dialing 9 followed by 1 for long distance
calls.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 25
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 26

Configuring the FortiGate Voice PSTN and PBX settings Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
Name Long_Distance
Use Default Outgoing Prefix
(“9”)
Phone number Begin with 1
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo2
Selected
8 Select Create New to add the dial plan rule for dialing 9 for all other PSTN calls.
Name Other_PSTN_Numbers
Use Default Outgoing Prefix
(“9”)
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected Move PSTN - fxo1 to the Selected list to send calls to the PSTN
Selected
out the fxo1 interface.
9 Select Create New to add the dial plan rule for dialing the Head Office.
Name Head_Office_Dial_Rule
Use Default Outgoing Prefix
(“9”)
Phone number Begin with 2
Action Allow
Outgoing Move VoIP - VoIP_Provider_1 to the Selected list to send calls to
Deselect.
Indicates that outgoing calls to the Head Office must start with a
2.
the PSTN out the fxo1 interface.
10 Select OK.
To add the extensions that are on the branch office internal network
Use the following steps to add extensions to the FortiGate Voice unit for the IP phones that
are to be connected to the internal network. You add identifying information to each
extension entry. The IP phone must be configured with identifying information that
matches an entry in the extension list in order to get an extension from the FortiGate Voice
unit. Extension numbers are independent of the IP address of the IP phone.
1 Go to PBX > Extension > Extension and select Create New.
2 Configure the following settings to add extension 6001.
Extension 6001
Type SIP Phone
First Name The first name assigned to this extension. Usually a person’s first
Last Name The last name assigned to this extension. Usually a person’s last
Email The email address of the person assigned to this extension. The
name.
name.
When this extension calls another phone the caller ID displayed
on the called phone consists of the extension First Name
followed by the Last Name.
FortiGate Voice unit sends voicemail notifications for the
extension to this email address.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
26 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 27

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Configuring the FortiFones on the internal network
Password The SIP phone user password for the phone assigned to this
Dial Plan Dial_Plan_1
Voicemail Select
Voicemail Password Enter the numeric password that the SIP user must enter to get
Email Notification Select
Email Attachment Select to attach a recording of the user’s voicemail message to
Auto Delete Select to automatically delete voicemail messages.
Maximum Message # 50
extension.
For a FortiFone on the internal network to be able to register with
the FortiGate Voice unit to get this extension, the FortiFone
Register Name must consist of the extension First Name
followed by the Last Name separated by one space. The
FortiFone must also be configured with this Password and the IP
address of the FortiGate Voice internal interface.
voicemail. The password can contain numbers only.
the voicemail notification email.
The FortiGate Voice unit keeps up to 50 voicemail messages for
this extension.
3 Select OK to add the extension.
4 Repeat to add more extensions.
Configuring the FortiFones on the internal network
This section contains high-level instructions for installing and configuring FortiFones for
the example configuration. For more detailed information see the FortiFone
documentation.
To configure FortiFones on the internal network
The following steps describe how to configure a FortiFone on the internal network with
extension number 6001. This procedure would also apply to configuring a FortiFone for
most networks. See the documentation supplied with the FortiFone for details.
1 Connect and power on the FortiFone handset.
2 Connect to the handset web configuration interface.
The default web configuration interface address is http://192.168.0.1. To connect to this
address from a PC, your PC should have an IP address on the 192.168.0.0 subnet, for
example: 192.168.0.10/255.255.255.0.
The default Username is root. No password is required.
3 Go to Network > LAN Settings and set the IP Type to DHCP Client and select Submit.
4 Select Save & Reboot to save the IP addressing change.
5 Log into the FortiFone using the IP address it acquired from the DHCP server.
6 Go to SIP Settings > Service Domain and add the following configuration information:
Active On
Display Name The name to be displayed on the phone. This name is only
displayed on this phone. When this phone calls another phone
the name displayed is the First Name and Last Name added to
the FortiGate Voice Extension configuration.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 27
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 28

Adding extensions and configuring FortiFones for users behind a NAT device Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
User Name 6001
This is actually the Line Number or Extension Number and must
match the Extension Number added to the FortiGate Voice
Extension configuration for this phone.
Register Name 6001
The Register Name is used to authenticate the FortiFone and
must match the Extension Number added to the FortiGate Voice
Extension configuration for this phone. Both the User Name and
Register Name are required.
Register Password The Password added to the FortiGate Voice Extension
Domain Server Leave this field blank.
Proxy Server 172.20.120.10
Outbound Proxy Leave this field blank.
configuration for this phone. The Register Name and Register
Password are used to authenticate the phone with the FortiGate
Voice unit.
Not required since the configuration uses the FortiGate Voice
unit as a SIP proxy. This field is only used to add the phone to a
SIP service domain.
The IP address of the FortiGate Voice internal interface.
7 Select Submit.
8 Select Save & Reboot to save the service domain information.
9 If the FortiFone can successfully connect to and register with the FortiGate Voice unit
the Status of the FortiFone changes to Registered.
If Status does not change to Registered you should verify the Register Name or reenter the Password. You should also confirm that the Domain Server and Proxy Server
IP addresses are correct.
Adding extensions and configuring FortiFones for users behind a NAT device
When adding an extension for any SIP phone with a NAT device between the phone and
the FortiGate Voice unit you must enable NAT in the FortiGate Voice extension
configuration for the phone. You can enable NAT only from the CLI. This applies whether
the phone is on a remote network behind a NAT device or behind a NAT device on the
internal network.
To add an extension for a SIP phone behind a NAT device
The following procedure describes adding the extension from the FortiGate Voice CLI
because you must use the CLI to enable NAT. You could add the extension from the
web-based manager and then edit the extension from the CLI to enable NAT.
The following configuration is the same whether the phone is behind a NAT device on the
internal network or on a remote network,
1 Connect to the FortiGate CLI.
2 Enter the following command to add extension 6010.
The command includes setting nat to yes to enable NAT.
config pbx extension
edit 6010
set first-name <first_name_str>
set last-name <last_name_str>
set email <email_str>
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
28 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 29

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Adding extensions and configuring FortiFones for users behind a NAT device
set secret <password_str>
set dialplan Dial_Plan_1
set vm-secret <voicemail_password_str>
set email-notify enable
set attach enable
set nat yes
end
To configure FortiFones behind a NAT device on the internal network
The configuration for FortiFones behind a NAT device on the internal network is the same
as for FortiFones directly on the Internal network. See “To configure FortiFones on the
internal network” on page 27.
You may have to configure the NAT device to allow SIP sessions between the FortiFone
and the FortiGate Voice unit.
To configure FortiFones behind a NAT device on a remote network
The following steps describe how to configure a FortiFone on the remote network with
extension number 6010.
1 Connect and power on the FortiFone handset.
2 Connect to the handset web configuration interface.
The default web configuration interface address is http://192.168.0.1. To connect to this
address from a PC, your PC should have an IP address on the 192.168.0.0 subnet, for
example: 192.168.0.10/255.255.255.0.
The default Username is root. No password is required.
3 Go to Network > LAN Settings and set the IP Type to DHCP Client and select Submit.
4 Select Save & Reboot to save the IP addressing change.
5 Log into the FortiFone using the IP address it acquired from the DHCP server.
6 Go to SIP Settings > Service Domain and add the following configuration information:
Active On
Display Name The name to be displayed on the phone. This name is only
User Name 6010
Register Name 6010
Register Password The Password added to the FortiGate Voice Extension
Domain Server Leave this field blank.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 29
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
displayed on this phone. When this phone calls another phone
the name displayed is the First Name and Last Name added to
the FortiGate Voice Extension configuration.
This is actually the Line Number or Extension Number and must
match the Extension Number added to the FortiGate Voice
Extension configuration for this phone.
The Register Name is used to authenticate the FortiFone and
must match the Extension Number added to the FortiGate Voice
Extension configuration for this phone. Both the User Name and
Register Name are required.
configuration for this phone. The Register Name and Register
Password are used to authenticate the phone with the FortiGate
Voice unit.
Not required since the configuration uses the FortiGate Voice
unit as a SIP proxy. This field is only used to add the phone to a
SIP service domain.
Page 30

FortiGate Voice IVR configuration Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
Proxy Server 172.20.120.10
The IP address of the FortiGate Voice internal interface.
Outbound Proxy Leave this field blank.
7 If the FortiFone can successfully connect to and register with the FortiGate Voice unit
the Status of the FortiFone changes to Registered.
If Status does not change to Registered you should verify the Register Name or reenter the Password. You should also confirm that the Domain Server and Proxy Server
IP addresses are correct.
To configure the remote FortiGate unit in NAT mode
The remote FortiGate unit in NAT mode must be configured to allow SIP sessions
between the remote users on the remote network and the FortiGate Voice external
interface. To do this you need to:
• Add an internal to external firewall policy that allows SIP sessions so that the remote
users can start SIP sessions with the FortiGate Voice unit
• Add a virtual IP and an external to internal firewall policy that allows SIP sessions from
the FortiGate Voice wan1 interface to connect to the phones in the remote network
For higher security, you could configure IPSec tunneling between the branch office
network and the remote network and send SIP traffic over the IPSec tunnel.
FortiGate Voice IVR configuration
By default, when callers call into the FortiGate Voice PBX from a remote system such as
the PSTN the call is picked up by the PBX system which plays a default message asking
the caller to dial the extension number that they want to reach or to dial 0 for assistance. If
the caller dials 0 they can use the number keys on their phone to spell out the First Name
or Last Name of an extension to connect with that extension.
You can use the following procedure to add a custom welcome message.
To add a custom welcome message
1 Log into the FortiGate Voice web-based manager.
2 Go to PBX > Extension > Extension and select Create New.
3 Enter an Extension.
4 Set Type to IVR Recorder.
5 Enter a Password.
The password should include numbers only.
6 Select OK.
7 From a SIP phone that is registered with the FortiGate Voice unit, dial the Extension
added in step 3.
8 Follow the prompts to record a new welcome message.
Providing access to the company directory
Use the following procedure to allow phone users to dial 3 to access the FortiGate Voice
PBX directory. Phone users can use the directory to call an extension by using the number
keys on their phone to spell out the First Name or Last Name of an extension to connect
with that extension.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
30 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 31

Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration Adding a shortcut for checking voicemail
To provide access to the company directory from any extension
1 Log into the FortiGate Voice web-based manager.
2 Go to PBX > Calling Rules > Voice Menu.
3 Select the Edit icon for Key 3.
You can select any available key, but this example uses 3.
4 Set Action to Go to Company Directory and select OK.
Adding a shortcut for checking voicemail
Use the following procedure to allow phone users to dial 7 to access their voicemail.
To provide access to the company directory form any extension
1 Log into the FortiGate Voice web-based manager.
2 Go to PBX > Call > Voice Menu.
3 Select the Edit icon for Key 7.
You can select any available key, but this example uses 7.
4 Set Action to Check Voicemail and select OK.
Checking voicemail
Once users connect to their voicemail using the Voicemail Access number configured
from PBX > Calling Rules > Setting or by pressing the configured voicemail key they can
follow the prompts to listen to, store, and delete messages. Users can also change their
voicemail password.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 31
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 32

Adding a shortcut for checking voicemail Example FortiGate Voice branch office configuration
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
32 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 33

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference Dashboard widgets
FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
This section describes FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration settings. For
information about other FortiGate Voice web-based manager settings, see the FortiGate
Administration Guide or the FortiGate Voice online help.
This section describes:
• Dashboard widgets
• Configuring VoIP interface settings
• Configuring PSTN interfaces
• PBX configuration
• Logging of PBX activities
Dashboard widgets
There are two specific Dashboard widgets that contain valuable information at a glance
about the operation of your FortiGate Voice unit and PBX disk usage. The following
explain these widgets, the Unit Operation widget, and the System Resources widget.
Unit operation dashboard widget
Go to System > Status and view the Unit Operation widget to see the status of the
FortiGate Voice unit and its Ethernet and fxo interfaces. The fxo interfaces appear if your
FortiGate Voice unit includes PSTN interfaces.
Figure 4: FortiGate Voice-80C Unit operation widget
System resources dashboard widget
Go to System > Status and view the System Resources widget to see the status of the
amount of disk space left for the storage of PBX activities and events.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 33
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 34

Configuring VoIP interface settings FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
Figure 5: System Resources widget displaying PBX disk usage
Configuring VoIP interface settings
You can configure an interface to accept SIP traffic for the FortiGate Voice PBX.
To configure VoIP interface settings
1 Go to System > Network > Interface.
2 Select the interface that you want to configure VoIP settings for.
3 Select the SIP Traffic check box to enable SIP traffic.
4 Select OK.
Configuring PSTN interfaces
Some FortiGate Voice models include public switched telephone network (PSTN)
interfaces that you can use to connect the FortiGate Voice PBX to your local public
telephone network. Using these interfaces you can route calls from your FortiGate Voice
network to the public telephone network. The PSTN interfaces are named fxo1, fxo2, and
so on.
To configure the PSTN interfaces, go to System > Network > PSTN Interface, configure
settings for the fxo interface and then select OK.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
34 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 35

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference Configuring PSTN interfaces
Edit
Figure 6: Configuring PSTN interfaces
General PSTN interface settings
Column Settings Select to add or remove columns. This changes what information
Name The name of the PSTN interface.
Phone Number The phone number that is associated with that PSTN interface.
Display Name The name that displays on the phone’s LCD.
Administrative Status Status of the PSTN interface. A red down arrow indicates that the
Catch Caller ID If enabled, a green checkmark appears. If Catch Caller ID is disabled,
PSTN interface configuration settings
Basic Options The basic options for the interface.
Name The name of the PSTN interface.
Phone Number Enter the phone number of the PSTN phone line as provided by your
Display Name This name is used for caller ID for calls from the FortiGate Voice unit
Caller ID Options Configure the following options to support caller ID functions for calls
appears.
interface is down; a green up arrow indicates that the interface is up.
a gray X appears.
phone service provider.
The phone number is used for caller ID for calls from the FortiGate
Voice unit to the PSTN. It can be any number, but is usually the actual
phone number of the PSTN line connected to the fxo1 interface. Area
code and country codes are optional.
to the PSTN. It can be any name, such as a company name, that
identifies the branch office.
from the internal network to the PSTN.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 35
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 36

PBX configuration FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
Catch Caller ID Select to enable the FortiGate Voice unit to receive caller ID
Caller ID Protocol Select the caller ID protocol required by PSTN line that the fxo
Caller ID Indicator Select the caller ID indicator required by the PSTN line. Contact your
Ring # Set the number of rings to wait before receiving caller ID information.
Hang-up Options Configure the following options to configure how the FortiGate Voice
Hang up on Polarity
Reversal
Hang up on Busy Tone Select if you want the FortiGate Voice unit to hang up automatically
Busy Tone Detection The number of busy tones that the FortiGate Voice receives before
Busy Tone Duration Tune the FortiGate Voice unit to accurately detect busy tones on this
Busy Tone Interval
Administrative Status Set to Up if the fxo interface is connected to the PSTN and you want
information from calls originating on the PSTN and send the caller ID
information to the extension that answers the call.
interface is connected to. Contact your service provider for the name
of the protocol to use.
service provider for details.
In most cases, enter 1 to send caller ID information between the first
and second ring.Contact your service provider for details.
unit hangs up calls from the PSTN.
Select if the PSTN line uses polarity reversal to indicate a call has
been hung up. Contact your service provider for details.
when it receives a busy tone when attempting to dial a number on the
PSTN.
hanging up if Hang up on Busy Tone is selected.
PSTN line. You can change the default settings if busy tones are not
accurately detected.
to be able to receive and send calls on this PSTN interface.
PBX configuration
The following explains how to configure PBX settings for your network environment.
These settings include voicemail notification settings, configuring a VoIP provider as well
as system settings such as a voicemail access code and a maximum voicemail duration
time limit.
This section describes:
• Configuring service providers
• Configuring extensions
• Configuring extension groups (ring groups)
• Configuring dial plans
• Configuring voice menu options
• Configuring direct inward dialing
• Configuring PBX settings
• Monitoring calls
• Monitoring SIP Trunk status
• Monitoring the status of PBX extensions
Configuring service providers
You can configure multiple VoIP providers for your PBX configuration.
To configure VoIP providers, go to PBX > Service Providers > SIP Trunk, select Create
New, configure the settings and then select OK.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
36 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 37

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference PBX configuration
Delete
Edit
Figure 7: VoIP Provider
Name Enter the name for the VoIP provider configuration. This can be any
Domain The VoIP provider’s domain name or IP address. For example,
User Name Enter a valid user name for an account on the VoIP provider’s server.
Password Enter the password for the account on the VoIP provider’s SIP sever.
Authorization User Name Enter a valid authorization user name for an account on the VoIP
Display User Name Enter a valid display user name for an account on the VoIP provider’s
Account Type Select Static or Dynamic depending on the account with the VoIP
Registration Interval If this is a dynamic account with the VoIP provider, enter the
DTMF Method Select the DTMF method used by the VoIP provider. Options are
Configuring extensions
name.
172.20.120.11 or voip.example.com.
This could also be a phone number including area code, depending
on the requirements of the VoIP provider.
provider’s server if required by the VoIP provider.
server if required by the VoIP provider.
provider.
registration interval as required by the VoIP provider. After each
registration interval the FortiGate Voice renews the registration of the
account with the VoIP provider.
RFC2833, Inband, Info, and Auto.
Auto means the VoIP provider’s server and the FortiGate Voice unit
will negotiate to select a DTMF method. You could also select a
specific DTMF method if required.
Extensions provide specific information for how to handle actions for that extension. You
can choose the type of extension, such as SIP Phone, IVR, or Conference.
To configure extensions, go to PBX > Extension > Extension, select Create New, enter the
information and then select OK.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 37
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 38

PBX configuration FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
Delete
Edit
Figure 8: Configuring extensions
General extension settings
Create New Select to create an extension.
Extension The extension number.
Type The type of extension the number is. Type can be:
• SIP Phone to configure a SIP phone extension
• IVR Recorder to configure the extension to call to leave a message for
the phone system operator. For IVR recorder you can add an extension
number and a password. From any PBX extension you can call this
extension and enter the password to get messages left by callers and
to program the IVR system and record a new voice mail message for
the system
• Conference to configure a conference bridge. For the Conference
extension you can add an extension number and a password. PBX
users can call this extension number and enter the password to join a
conference call.
Name The name of the extension.
Dial Plan The dial plan that will be used for that extension.
Extension configuration settings
Extension Enter the extension number.
Type Select the type of extension. You can choose from SIP Phone, IVR, or
First Name Enter the first name of the person that will be using this extension.
Last Name Enter the surname of the person that will be using this extension.
Email Enter the email address of the person that will be using this extension.
Password Enter the password of that accesses the email address.
Dial Plan Select the dial plan that will be used with this extension from the drop-
Voicemail Select if you want to have voicemail available for this extension.
Conference.
down list.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
38 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 39

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference PBX configuration
Delete
Edit
Voicemail Password Enter a voicemail password for accessing the voicemail.
Email Notification Select to have an email sent to the email address given in the Email field
Email Attachment Select to attach the actual voicemail message to the notification email.
Auto Delete Select to automatically delete the message.
Maximum Message # Enter a number for the maximum number of messages that can be stored
so that the person is notified when a voicemail message is in their
voicemail message inbox.
in the extension’s voicemail inbox before automatically deleting those
messages.
Configuring extension groups (ring groups)
Extension groups (also called ring groups) are a group of extensions that can be called
using one number. The extension group can be used to call all the extensions in the group
at the same time or to call the extensions one at a time until someone answers.
Note: The order in which the members are added to the ring group does not match the
order in which the FortiGate Voice unit calls them.
To configure an extension group, go to PBX > Extension > Group, select Create New,
enter the information, and then select OK.
Figure 9: Configuring extension groups
Extension Number The number to call to reach extension group. This number must be a valid
Description A description of the extension group.
# of Members The number of extensions in the extension group.
Ring Strategy Select a type from the drop-down list. You can choose either Sequential or
extension number for the FortiGate Voice configuration.
Ring All.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 39
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 40

PBX configuration FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
No Answer Action Select the action to take when there is no answer for the incoming caller. You
Voicemail
Extension
Member Select an extension in the Available column and then use the -> arrow to
Configuring dial plans
Dial plans route calls made from a FortiGate Voice extension to an external phone system.
The external phone system can be one or more PSTN lines if your FortiGate Voice unit
includes PSTN interfaces, or a VoIP service provider. To route calls to an external phone
system you add dial plan rules that define the extra digits that extension users must dial to
call out of the PBX. The rules also control how the FortiGate Voice unit handles these calls
including whether to block or allow the call, the destinations the calls are routed to and
whether to add digits to the beginning of the dialed number (called prepending).
For example, if PBX users should be able to dial 911 for emergencies you should include
a dial plan rule that sends all calls that begin with 911 to an external phone system. This
rule should also override the default outgoing prefix so that users can dial 911 without
having to dial 9 first.
You can also use dial plan rules to block some calls. For example, if you want to block
extensions from making international calls you can add dial plan rule that blocks calls that
start with the default outgoing prefix followed by 011.
When the FortiGate Voice unit receives a call from an extension that does not match the
FortiGate Voice unit’s extension range, the call is processed according to the dial plan
added to the extension. (If the extension does not have a dial plan the call is blocked). To
process the call, the FortiGate Voice unit selects the dial plan rule that best matches the
dialed numbers and processes the call using the settings in the dial plan rule. For
example, the emergency dial plan rule could route calls out a local PSTN line (if your
FortiGate Voice unit includes them) or to a remote VoIP provider.
can select Voicemail, which routes the caller to voicemail, IVR, or Hangup. If
you select Voicemail, the Voicemail Extension list appears and you need to
select the voicemail extension number.
Select the voicemail extension number from the drop-down list. This option
appears only when Voicemail is selected in No Answer Action.
move it to the Selected column.
To remove an extension from the Selected column, select the extension and
use the <- arrow to move it back to the Available column.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
40 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 41

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference PBX configuration
Figure 10: Configuring a dial plan
Go to PBX > Calling Rules > Dial Plan to add a dial plan.
General dial plan list settings
Create New Select to configure a dial plan. You can add multiple dial plans and assign them
Name The name of the dial plan.
# of Entries The number of entries in each dial plan.
Comments An optional description of the dial plan.
Dial plan rule configuration settings
Name Enter a descriptive name for the dial plan rule.
Use Default
Outgoing
Prefix("9")
Outgoing Prefix If you clear the Use Default Outgoing Prefix checkbox you can enter a different
Phone number
Begin with
to different extensions. For example, you might want to have a dial plan that
allows long distance calls and a dial plan that does not.
Select this checkbox if the dial plan rule should use the default outgoing prefix
(usually 9).
outgoing prefix for this dial plan.
Enter the leading digits of the phone number that this dial plan rule should match
with. For example, a dial plan rule for toll free numbers in North America should
begin with 18. The FortiGate Voice uses a best match to match a dialed number
with a dial plan. So each dial plan should have a different Phone number Begin
with setting. But you should plan your dial plan to make sure that unexpected
matches do not occur.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 41
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 42

PBX configuration FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
Prepend Add digits that should be prepended or added to the beginning of the dialed
Action Set the action to Allow if this dial plan rule should allow a call. Set the action to
Outgoing In the Available column, select one or more PSTN interfaces (if your FortiGate
number before the call is forwarded to its destination. You can prepend digits at
the beginning of a call of special dialing is required to reach and external phone
system.
Block if the dial plan should block a call. For example, if you want to block
international calls you could set the Phone Number begin with to 011 and set the
action to block.
Voice unit includes them) and/or VoIP service providers that the calls matching
this dial plan should be routed to and use the arrow to move to them to the
Selected column.
If you need to remove a PSTN interface or VoIP provider from the Selected list,
select the item and use the arrow to move it back to the Available column list.
The FortiGate Voice unit uses the PSTN interfaces and VoIP providers in the
Selected list in the order in which they are arranged in the list. You can arrange
the PSTN interfaces and VoIP providers in the Selected column using the up
and down arrows beside the Selected column. Select a PSTN interface or VoIP
provider and then use the arrows to arrange them in the list.
Example dial plan
This simplified example dial plan includes 5 dial plan rules that:
• Routes emergency calls (dialing 911) to the fxo1 PSTN interface
• Blocks international calls (the phone number begins with 011)
• Routes Toll Free calls (beginning with 18) to the fxo1 PSTN interface
• Routes non-international long distance calls (beginning with 1) to the fxo2 PSTN
interface
• Routes all other external calls to the fxo3 and fxo3 PSTN interfaces
In this example, all outgoing calls are routed to the PSTN and not to other VoIP service
providers.
Table 4: Rule 1: emergency calls using 911
Name Emergency
Use Default
Outgoing Prefix (“9”)
Phone number
Begin with
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo1
Table 5: Rule 2: international calls beginning with 011
Name International
Use Default
Outgoing Prefix (“9”)
Phone number
Begin with
Action Block
Table 6: Rule 3: Toll free calls starting with 18
Name To l l_ Fr ee
Use Default
Outgoing Prefix (“9”)
Not selected
911
Selected
o11
Selected
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
42 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 43

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference PBX configuration
Table 6: Rule 3: Toll free calls starting with 18
Phone number
Begin with
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo1
Table 7: Rule 4: Long Distance calls starting with 1
Name Long_Distance
Use Default
Outgoing Prefix (“9”)
Phone number
Begin with
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo2
Table 8: Rule 5: Other outgoing calls
Name Other_PSTN_Numbers
Use Default
Outgoing Prefix (“9”)
Phone number
Begin with
Action Allow
Outgoing Selected PSTN - fxo2, PSTN - fxo2
18
Selected
1
Selected
Configuring voice menu options
Configure voice menu options to provide PBX users with shortcuts to PBX functions such
as accessing their voice mail, finding numbers in the company directory, or dialing a ring
group.
To access voice menu functions PBX users dial a single number on their phones and wait
a few seconds for the PBX to respond. For example, you can use voice menu options to
allow PBX users to simply dial 3 to access their voice mail.
To configure voice menu options
1 Go to PBX > Calling Rules > Voice Menu.
2 In the row of the key that you want to configure voice menu options for, select the Edit
icon.
3 In the Action drop-down list, select one of the following:
None No action will be taken when a caller dial this number.
Ring Group The PBX user calls a ring group. Select the ring group to call. A
Check Voicemail Provides direct access to the PBX user’s voice mail inbox.
Go to Company Directory Provides direct access to the PBX company phone directory.
4 Select OK.
ring group is also called an extension group. To add ring groups,
see “Configuring extension groups (ring groups)” on page 39.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 43
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 44

PBX configuration FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
Delete
Edit
Configuring direct inward dialing
You can configure direct inward dialing (DID) for calls. DID allows the FortiGate Voice unit
to direct calls from external callers directly to PBX extensions. For example, you could set
up DID so that external users call 555-1234 and DID directs the call to extension 1234.
Using the FortiGate Voice unit direct inward dial settings you associate an incoming PSTN
interface (if supported by your FortiGate Voice unit) or VoIP service provider with a PBX
extension. When an incoming call is received from one of these sources, if the last digits of
the dialed number match the selected extension number the FortiGate Voice unit directs
the call directly to the extension. For this to work you must obtain an external phone
number with the last digits matching the selected extension.
To configure direct inward dialing, go to PBX > Calling Rules > Direct Inward Dial, enter
the information, and then select OK.
Figure 11: Direct inward dialing
General direct inward dialing settings
Name The name of the direct inward dialing configuration.
Incoming The incoming calls that received from the PSTN interface (if supported by your
Extension The extension that will be used.
Comments A description about the direct inward dial configuration.
Direct inward dialing configuration settings
Name Enter a name for the direct inward dialing configuration.
Incoming Select a PSTN interface or VoIP service provider from the drop-down list.
Extension Select an extension from the drop-down list.
Comments Enter a description, if applicable, for the direct inward dialing configuration.
FortiGate Voice unit) or from a VoIP service provider.
From the CLI you can use the cid-number option of the config pbx did command to
specify the number called from an external line that is re-directed to the selected
extension. Use this option if the extension number cannot be matched with the external
number. In the following example, DID sends calls received on the fxo1 PSTN interface
that end with 5555 to extension 1234.
config pbx did
edit did_example
set external-line fxo1
set cid-number 5555
set extension 1234
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
44 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 45

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference PBX configuration
end
end
Configuring PBX settings
Configure PBX system settings that affect the overall performance of the PBX service and
all of the users of it. Settings include the extension pattern for the PBX, the outgoing dial
prefix and the email server to use for sending voicemail notification email messages.
Usually you would configure these settings once and rarely thereafter.
To configure PBX settings group, go to PBX > Calling Rules > Setting, make configuration
changes as required and then select Apply.
Figure 12: Configuring PBX settings
PBX Global Settings
Extension Range Enter a pattern that defines the valid extensions that can be added to the
Country Code Enter the international country calling code for the country or region in which
Local Area Code Enter the local area code for the country or region in which you are installing
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 45
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
FortiGate Voice configuration. The pattern can include numbers that must be
in every extension and upper case Xs to indicate the number of digits. The
extension range can only contain numbers and the letter X.
• If you add numbers to the extension range, all extensions added to this
FortiGate Voice unit must include the same numbers in the same location
in the extension number. For example, if you include a 6 as the first digit,
all extensions added this FortiGate Voice unit must begin with the number
6.
• The Xs indicate the number of digits in addition to the required number
that each extension must have. For example, 6XXX indicates the
extensions must start with the number 6 and be followed by any three
numbers.
Usually you would add one or two numbers to the start of the extension range
to identify the extensions for this PBX and follow this with enough Xs to be
able to add the required number of extensions.
The extension range should not begin with the same number as the outgoing
prefix.
you are installing the FortiGate Voice unit.
the FortiGate Voice unit.
Page 46

PBX configuration FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
Voicemail Access Enter the exact pattern that PBX users dial to get their voicemail. For
Outgoing Prefix The number that PBX users must dial to get an outside line. For example, if
Max Voicemail
Duration
Voicemail Notification Email Settings
SMTP server Enter the email server IP address or domain name. The FortiGate Voice unit
Authentication Select if the email server requires authentication. If you enable authentication
User Name Enter a valid username for an account on the email server.
Password Enter the password for the account on the email sever.
Monitoring calls
You can monitor incoming and outgoing calls from PBX > Monitor > Active Call.
You can view information for all active calls including the originator of the call (From) the
destination of the call (To), how long the call has been active (Duration), the codec used
for transmitting voice packets, and the status of the call.
Monitoring SIP Trunk status
You can monitor status of the external SIP trunks or VoIP service providers that you have
added to the FortiGate Voice configuration. To monitor SIP trunk or VoIP service provider
status go to PBX > Monitor > SIP Trunk Status.
For each service provider you can see the name of the service provider, the host name of
the SIP server that the FortiGate Voice unit connects to, the account type, the username
for the account, and the state of the relationship between the FortiGate Voice unit and the
service provide. If status is Registered the FortiGate Voice unit is able to connect to and
register with the service provider.
example, for users to dial *99 to get their voice mail, enter *99.
users should dial 9 to get an outside line, add 9 to this field. The outgoing
prefix should not be the same as the first number of the extension range.
Select No Limit if you don’t want to limit the voice mail duration. Otherwise
enter a maximum time in seconds for voice mail recordings.
uses this email server for sending voicemail notification emails to PBX users.
you must also add a username and password.
Figure 13: Monitoring VoIP provider status
Monitoring the status of PBX extensions
You can monitor the status of the extensions added to the FortiGate Voice configuration.
Status information includes the extension number and the Host name or IP address of the
extension as registered with the FortiGate Voice unit. To monitor extension status go to
PBX > Monitor > Extension Status.
If the information displayed about an extension includes a host name or IP address the
extension is operating and can send or receive calls with the FortiGate Voice unit. If no
host name or IP address is displayed the extension cannot communicate with the
FortiGate Voice unit. For example, the extension could be shut down or not able to
connect to the FortiGate Voice because of network issues or configuration problems with
the configuration of the extension phone or softphone.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
46 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 47

FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference Logging of PBX activities
Figure 14: Monitoring extension status
Logging of PBX activities
After configuring PBX settings, you can configure logging of PBX activities and events. If
you are new to logging, see Logging and Reporting in FortiOS 4.0 User Guide before
proceeding.
To configure logging of PBX settings
1 Go to Log&Report > Log Config > Event Log.
2 Select the check box beside Enable to make the other event log options available.
3 Select the check box beside PBX event.
Viewing log messages
You can view the PBX activities and events from Log&Report > Log Access. The log
messages can be filtered so that you are viewing specific information, or you can display
them in Raw format. Raw format is the format of what a log message actually appears in
the log file.
To view PBX log messages, go to Log&Report > Log Access and then select the tab
associated with the logging device you chose to store logs on. For example, you want to
view PBX log messages from the FortiAnalyzer unit that they are on, so you select
Log&Report > Log Access > FortiAnalyzer.
For more information about log messages, see the FortiGate Log Message Reference and
also the Logging and Reporting in FortiOS 4.0 User Guide.
Example PBX log messages
The following log message indicates that the phone with FortiGate Voice extension
number 6005 called 914036085000 and the call was routed to the skype-088adb08
service provider. The call was answered and lasted for 1869 seconds.
2010-03-12 12:53:27 log_id=0162043782 type=event subtype=pbx pri=information
fwver=040000 vd=root action=PBX-call clid="6005", src="6005"
dst="914036085000"channel="SIP/6005-088a7c08" dstchannel="SIP/skype-088adb08"
duration=1869 start="Fri Mar 12 12:22:18 2010 " end="Fri Mar 12 12:53:27 2010 "
disposition="ANSWERED"msg="call from 6005=>914036085000, ANSWERED, for 1869
seconds"
The following log message indicates that the phone with FortiGate Voice extension
number 6012 with caller ID Example Caller called extension 6036. And that the call was
answered and lasted for 23 seconds.
2010-03-12 01:12:42 log_id=0162043782 type=event subtype=pbx pri=information
fwver=040000 vd=root action=PBX-call clid=""Example Caller" <6012>", src="6012"
dst="6036"channel="SIP/6012-084a9aa0" dstchannel="SIP/6036-08464150" duration=23
start="Fri Mar 12 01:12:19 2010 " end="Fri Mar 12 01:12:42 2010 "
disposition="ANSWERED"msg="call from 6012=>6036, ANSWERED, for 23 seconds"
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 47
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 48

Logging of PBX activities FortiGate Voice web-based manager configuration reference
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
48 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 49

FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference config pbx dialplan
FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
This section describes FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN configuration settings.
PSTN interfaces are not available on all FortiGate Voice models. For information about
other FortiGate Voice CLI commands see the FortiGate CLI Reference.
This section describes:
• config pbx dialplan
• config pbx did
• config pbx extension
• config pbx global
• config pbx ringgrp
• config pbx smtp
• config pbx voice-menu
• config pbx voip-provider
• config system pstn
• config system interface
• execute pbx
• diagnose pbx restart
config pbx dialplan
Use this command to add a dial plan and add rules to the dial plan. A dial plan rule
indicates an outgoing destination to send calls to. You can add multiple rules to a dial
plan. You add dial plans to extensions to control how to handle outgoing calls from the
extension.
Syntax
config pbx dialplan
edit <pbx_dialplan_name>
end
set comments <comment_string>
config rule
edit <rule_name_str>
set action {allow | block}
set callthrough {fxo1 | fxo2 | fxo3 | fx04 |
<voip_providers>}
set outgoing-prefix <pattern_str>
set phone-no-beginwith <patern_str>
set prepend <pattern_str>
set use-global-outgoing-prefix {no | yes}
end
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 49
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 50

config pbx did FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
Variables Description Default
edit
<pbx_dialplan_name>
comments
<comment_string>
config rule Configure a new dial plan rule. No
edit <rule_name_str> Enter the name of the dial plan rule to configure. No
action {allow |
block}
callthrough {fxo1 |
fxo2 | fxo3 | fx04 |
<voip_providers>}
outgoing-prefix
<pattern_str>
phone-no-beginwith
<patern_str>
prepend
<pattern_str>
use-globaloutgoing-prefix {no
| yes}
Enter the name for the dial plan. If you entering an existing
dial plan, select Tab to get to the dial plan that you want to
edit.
Optionally enter a description of the dial plan. No
Set the action to allow if this dial plan rule should allow a
call. Set the action to block if the dial plan should block a
call. For example, if you want to block international calls
you could set the Phone Number begin with to 011 and set
the action to block.
Select one or more destinations that the dial plan rule
sends outgoing calls to. fxo1, fxo2, fxo3, and fx04 are
the 4 PSTN interfaces. <voip_providers> are the VoIP
providers added to the FortiGate Voice. A dial plan rule
can send calls to one or more destinations.
If you set use-global-outgoing-prefix to no you
can enter a different outgoing prefix for this dial plan.
Enter the leading digits of the phone number that this dial
plan rule should match with. For example, a dial plan rule
for toll free numbers in North America should begin with
18. The FortiGate Voice uses a best match to match a
dialed number with a dial plan. So each dial plan should
have a different Phone number Begin with setting. But you
should plan your dial plan to make sure that unexpected
matches do not occur.
Add digits that should be prepended or added to the
beginning of the dialed number before the call is
forwarded to its destination. You can prepend digits at the
beginning of a call of special dialing is required to reach
and external phone system.
Select yes if the dial plan rule should use the default
outgoing prefix (usually 9). Select no to add a different
outgoing-prefix.
No
default
default
default
default
No
default
No
default
null
null
null
yes
config pbx did
Use this command to configure Direct Inward Dialing (DID). DID allows calls from external
phone systems to dial directly to extensions added to the FortiGate Voice unit.
Syntax
config pbx did
edit <pbx_did_name>
set external-line {fxo1 | fxo2 | fxo3 | fx04 |
<voip_providers>}
set cid-number <phone_number>
set extension <extension_number>
set comment <comment_string>
end
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
50 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 51

FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference config pbx extension
Variables Description Default
edit <pbx_did_name> Enter the name for the Direct Inward Dial. No
external-line {fxo1
| fxo2 | fxo3 | fx04
| <voip_providers>}
cid-number
<phone_number>
extension
<extension_number>
comment
<comment_string>
Select one external system that can dial directly to an
extension. fxo1, fxo2, fxo3, and fx04 are the 4 PSTN
interfaces. <voip_providers> are the VoIP providers
added to the FortiGate Voice.
Enter the phone number dialed by a caller on the external
system.
Enter the FortiGate Voice extension number the call is
directed to.
Enter a description, if applicable, about the direct inward
dial configuration.
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
config pbx extension
Use this command to add SIP phone extensions to the FortiGate Voice unit.
Syntax
config pbx extension
edit <extension_number>
set attach {enable | disable}
set auto-delete {enable | disable}
set dialplan <dialplan_name>
set email <user_email>
set email-notify <user_email_address>
set first-name <first_name>
set last-name <surname_name>
set nat {no | yes}
set secret <user_password>
set type {conference | ivr | sip-phone}
set vm-secret <user_password>
set voicemail {enable | disable}
set max-msg <max_messages_ allowed>
end
Variables Description Default
edit
<extension_number>
attach
{enable | disable}
auto-delete
{enable | disable}
dialplan
<dialplan_name>
email <user_email> Enter the user’s email address. No
email-notify
<user_email_address>
Enter the extension number. The extension number has to
match the config pbx global extension pattern.
Enable the voicemail message as an attachment in an
email.
Enable to automatically delete voice mail. No
Enter the dial plan that you want to use for the extension. No
Enter the email address of the user that will be used when
notifying them that they have a voicemail message.
No
default
No
default
default
default
default
No
default
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 51
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 52

config pbx global FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
Variables Description Default
first-name
<first_name>
last-name
<surname_name>
nat {no | yes} Enter to indicate that the phone is behind a NAT device. No
secret
<user_password>
type {conference |
ivr | sip-phone}
vm-secret
<user_password>
voicemail
{enable | disable}
max-msg
<max_messages_
allowed>
Enter the person’s first name. No
Enter the surname of the person. No
Enter the user’s password for voicemail. No
Enter the type of extension to configure.
• sip-phone to configure a SIP phone extension
• ivr to add an interactive voice response (IVR)
configuration. Use this setting to customize the
welcome message when a external caller calls the
system. Create the IVR and then call the extension
number to customize the welcome message. An ivr
extension only requires an extension number and a
secret.
• conference to add a conference bridge. Multiple
users can call the conference bridge extension number
enter the secret and have a conference call. A
conference bridge only requires an extension
number and a secret.
Enter the user’s password for accessing their voicemail
inbox.
Enable the extension to have voicemail. No
Enter the maximum number of voicemail messages that
are allowed in a user’s voicemail inbox.
default
default
default
default
sipphone
No
default
default
No
default
config pbx global
Use this command to configure voicemail settings such as using music while the incoming
caller is put on hold, as well as the country and the extension pattern of the user.
Syntax
config pbx global
end
set country-area <country_name>
set extension-pattern <extension_pattern>
set local-area-code <code_string>
set max-voicemail <max_length_seconds>
set outgoing-prefix <pattern_str>
set ring-timeout <time_int>
set rtp-hold-timeout <time_int>
set rtp-timeout <time_int>
set voicemail-extension <access_number>
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
52 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 53

FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference config pbx ringgrp
Variables Description Default
country-area
<country_name>
extension-pattern
<extension_pattern>
local-area-code
<code_string>
max-voicemail
<max_length_seconds>
outgoing-prefix
<pattern_str>
ring-timeout
<time_int>
rtp-hold-timeout
<time_int>
rtp-timeout
<time_int>
voicemail-extension
<access_number>
Enter the name of the country in which the FortiGate Voice
unit is installed.
Enter a pattern that defines the valid extensions that can
be added to the FortiGate Voice configuration. The pattern
can include numbers that must be in every extension and
upper case Xs to indicate the number of digits. The
extension range can only contain numbers and the letter
X.
• If you add numbers to the extension range, all
extensions added to this FortiGate Voice unit must
include the same numbers in the same location in the
extension number. For example, if you include a 6 as
the first digit, all extensions added this FortiGate Voice
unit must begin with the number 6.
•The Xs indicate the number of digits in addition to the
required number that each extension must have. For
example, 6XXX indicates the extensions must start with
the number 6 and be followed by any three numbers.
Usually you would add one or two numbers to the start of
the extension range to identify the extensions for this PBX
and follow this with enough Xs to be able to add the
required number of extensions.
The extension range should not begin with the same
number as the outgoing prefix.
Enter the local area code for the country or region in which
you are installing the FortiGate Voice unit.
Limit the length of voicemail messages in seconds. Set to
0 for no limit.
The number that PBX users must dial to get an outside
line. For example, if users should dial 9 to get an outside
line, add 9 to this field. The outgoing prefix should not be
the same as the first number of the extension range.
The number of seconds that an extension should be
allowed to ring before going to voicemail.
The amount of time in seconds that the extension will wait
on hold for RTP packets before hanging up the call. 0
means no time limit.
The amount of time in seconds during an active call that
the extension will wait for RTP packets before hanging up
the call. 0 means no time limit.
Enter the voicemail extension number that a user will use
to access their voicemail inbox.
USA
null
408
60
9
20
0
60
No
default
config pbx ringgrp
Use this command to add and configure the extension groups. An extension group here is
referred to a ring group and is a group of extensions that can be called using one number.
You can configure the ring group to call all of the extensions in the group at the same time
or to call the extensions one at a time until someone answers.
Note: The order in which the members are added to the ring group does not match the
order in which the FortiGate Voice unit calls them.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 53
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 54

config pbx smtp FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
Syntax
config pbx ringgrp
edit <ring_group_name>
set description <description_str>
set member <acd_group_member>
set no-answer-action {hangup | ivr | voicemail}
set strategy {ring-all | sequential}
set voicemail-of-extension <extension_number>
end
Variables Description Default
edit
<ring_group_name>
description
<description_str>
member
<acd_group_member>
no-answer-action
{hangup | ivr |
voicemail}
strategy {ring-all |
sequential}
voicemail-ofextension
<extension_number>
Enter the name for the group. No
A description of the extension group.
Enter the ACD member for the group. No
Enter the action that will be taken when none of the
extensions in the ring group answers.
• hangup hand up and end the call.
• ivr return the caller to the attendant where they can
try another extension.
• voicemail the caller is directed to the voicemail
system where they can leave a message.
Control how the extensions in the group are called by the
ring group.
• ring-all calls all of the extensions in the group at
the same time.
• sequential calls the extensions in the group one at a
time in the order in which they have been added to the
group.
Enter the extension number to use for voicemail if no one
answers the call and no-answer-action is set to
voicemail.
default.
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
config pbx smtp
Use this command to configure the FortiGate Voice unit to send voicemail notification
email messages. Using this command you configure the email server that the FortiGate
Voice unit sends email notifications to.
Syntax
config pbx smtp
set port <smtp_server_port>
set server <smtp_server_ip_ address>
set authenticate {enable | disable}
set password <password_str>
set username <username_str>
end
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
54 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 55

FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference config pbx voice-menu
Variables Description Default
port
<smtp_server_port>
server
<smtp_server_ip_
address>
authenticate
{enable | disable}
password
<password_str>
username
<username_str>
Enter the port number that the email server uses for
SMTP.
Enter the email server IP address or domain name. No
Select enable if the email server requires authentication.
If you enable authentication you must also add a
username and password.
Enter the password for the account on the email sever.
Enter a valid username for an account on the email server. No
25
default
disable
default
config pbx voice-menu
Use this command to configure the menu that callers will access when they call. The
variable config press-<number> configures the settings for the type of ring group and
the type of group associated with that number.
Syntax
config pbx voice-menu
set comment <comment_string>
config [press-0 | press-1 | press-2 | press-3 | press-4 |
press-5 | press-6 | press-7 | press-8 | press-9]
set type {directory | none | ring-group | voicemail}
set ring-group
end
end
Variables Description Default
comment
<comment_string>
config [press-0 |
press-1 | press-2 |
press-3 | press-4 |
press-5 | press-6 |
press-7 | press-8 |
press-9]
type {directory |
none | ring-group |
voicemail}
ring-group Enter to include a specific ring-group if you have select
Enter a description of the voice-menu settings, if
applicable.
Use this command when configuring what action each
number on the phone’s keypad will take.
For example, you want the personnel directory to come up
every time someone presses 1; config press-1
variable would have the type directory selected in
type.
Enter the type of action that is associated with the specific
number on the phone’s keypad. For example, the office
phone directory is heard when a caller presses 0 because
config press-0 has directory as its type.
ring-group in type. This variable appears only when
ring-group is selected in type.
No
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
config pbx voip-provider
Use this command to configure the VoIP provider for the PBX.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 55
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 56

config pbx voip-provider FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
Syntax
config pbx voip-provider
edit <provider_name>
set user <user_name>
set domain {<VoIP_provider_address_ipv4> |
<VoIP_provider_domain>
set secret <password>
set authuser <authuser>
set display-name <display_name>
set reigstration-interval <refresh_interval>
set account-type {static | dynamic}
set port <port_provider>
set dtmf-method {auto | inband | info | rfc2833}
set codec {alaw | g729 |none | ulaw}
set codec1 {alaw | g729 |none | ulaw}
set codec2 {alaw | g729 |none | ulaw}
end
Variables Description Default
edit <provider_name> Enter the VoIP provider’s name. No
user <user_name> Enter the user name for the provider. You can enter
secret <password> Enter the password associated with the provider. No
domain
{<VoIP_provider_address
_ipv4> |
<VoIP_provider_domain>
authuser <authuser> Enter the authentication user for the account. No
display-name
<display_name>
reigstration-interval
<refresh_interval>
account-type
{static | dynamic}
port <port_provider> Enter the port that the provider will be using. No
dtmf-method {auto |
inband | info |
rfc2833}
codec {alaw | g729
|none | ulaw}
codec1 {alaw | g729
|none | ulaw}
codec2 {alaw | g729
|none | ulaw}
the phone number registered with this provider
instead.
The VoIP provider’s domain name or IP address. For
example, 172.20.120.11 or voip.example.com.
Enter the name that will be used as the caller ID name
if the provider supports this feature.
Enter a number for the refresh interval. No
Enter to define the type of account. No
Enter the DTMF method that will be used. No
Enter the most preferred Codec for the VoIP provider. ulaw
Enter the second most preferred Codec for the VoIP
provider.
Enter the third most preferred Codec for the VoIP
provider.
default
No
default
default
No
default
default
No
default
default
default.
default
default
none
none
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
56 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 57

FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference config system pstn
config system pstn
Use this command to configure the PSTN interfaces. PSTN interfaces are available on
some FortiGate Voice models.
Syntax
config system pstn
edit <fxo_name>
set cid-name <caller_name>
set cid-number <caller_name>
set status {enable | disable}
set user-callerid {enable | disable}
set cid-signalling {bell | dtmf | v23 | v23-jp}
set cid-start {polarity | ring}
set send-callerid-after <integer>
set hangup-on-polarity-reversal
set hangup-on-zero-voltage
set hangup-on-busy-tone
set busycount <integer>
set busy-tone-length <integer>
set busy-quiet-length <integer>
set codec {alaw | ulaw}
end
Variables Description Default
edit <fxo_name> Enter the name of the FXO. No
cid-name
<caller_name>
cid-number
<caller_name>
status
{enable | disable}
user-callerid
{enable | disable}
cid-signalling {bell
| dtmf | v23 |
v23-jp}
cid-start
{polarity | ring}
send-callerid-after
<integer>
hangup-on-polarityreversal
hangup-on-zerovoltage
hangup-on-busy-tone Enter to have the phone hang up when a busy tone is
busycount <integer> Enter a number for the accurate number of busy tones that
This name is used for caller ID for calls from the FortiGate
Voice unit to the PSTN. It can be any name, such as a
company name, that identifies the branch office.
Enter the phone number of the PSTN phone line as
provided by your phone service provider.
Enable the status of the port. No
Enable to catch the caller ID. No
Enter the caller ID protocol. The protocol v23-jp is the v23
protocol for Japan.
Enter to start transmitting the caller ID. No
Enter a number for the number of rings after that the caller
ID began to transmit.
Enter to have the phone hang up when there is polarity
reversal.
Enter to have the phone hang up when there is zero
voltage.
detected.
are detected.
default
No
default
No
default
default
default
No
default
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
No
default
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 57
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 58

config system interface FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
Variables Description Default
busy-tone-length
<integer>
busy-quiet-length
<integer>
codec {alaw | ulaw} Enter the Codec preference type based on the country. No
Enter a number that determines how logn the busy tone is
on.
Enter a number that determines how long the busy tone is
off.
No
default
No
default
default
config system interface
Use this command to allow traffic for the VoIP protocol, SIP, to flow on a specific interface.
Syntax
config system interface
edit <interface_name>
set voip {enable | disable}
end
Variables Description Default
edit
<interface_name>
voip
{enable | disable}
Enter the interface that you want to allow SIP traffic on. No
Enable the VoIP SIP protocol for allowing SIP traffic on the
interface.
default
disable
execute pbx
Use this command to view active channels and to delete, list or upload music files for
when music is playing while a caller is on hold.
Syntax
execute pbx active-call <list>
execute pbx extension <list>
execute pbx music-on-hold {delete | list | upload}
execute pbx prompt upload ftp <file.tgz>
<ftp_server_address>[:port] [<username>] [password>]
execute pbx prompt upload tftp <file.tgz>
<ftp_server_address>[:port] [<username>] [password>]
execute pbx prompt upload usb <file.tgz>
<ftp_server_address>[:port] [<username>] [password>]
execute pbx restore-default-prompts
execute pbx sip-trunk list
Variables Description
active-call <list> Enter to display a list of the active calls being processed by the
FortiGate Voice unit.
extension <list> Enter to display the status of all extensions with SIP phones that have
connected to the FortiGate Voice unit.
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
58 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 59

FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference execute pbx
Variables Description
music-on-hold
{delete | list |
upload}
prompt upload ftp
<file.tgz>
<ftp_server_address>
[:port] [<username>]
[password>]
prompt upload tftp
<file.tgz>
<ftp_server_address>
[:port] [<username>]
[password>]
prompt upload usb
<file.tgz>
<ftp_server_address>
[:port] [<username>]
[password>]
restore-defaultprompts
sip-trunk list Enter to display the status of all SIP trunks that have been added to
Enter to either delete, list or upload music on hold files. You can
upload music on hold files using FTP, TFTP, or from a USB drive
plugged into the FortiGate Voice unit.
Upload new pbx voice prompt files using FTP. The voice prompt files
should be added to a tar file and zipped. This file would usually have
the extension tgz. You must include the filename, FTP server address
(domain name of IPv4 address) and if required the username and
password for the server.
Upload new pbx voice prompt files using TFTP. The voice prompt files
should be added to a tar file and zipped. This file would usually have
the extension tgz. You must include the filename and TFTP server IP
address.
Upload new pbx voice prompt files from a USB drive plugged into the
FortiGate Voice unit. The voice prompt files should be added to a tar
file and zipped. This file would usually have the extension tgz. You
must include the filename.
Restore default English voicemail and other PBX system prompts.
Use this command if you have changed the default prompts and want
to restore the default settings.
the FortiGate Voice configuration.
Example command output
Enter the following command to view active calls:
execute pbx active-call
Call-From Call-To Duration
6016 6006 00:00:46
Enter the following command to display the status of all extensions
execute pbx extension list
Extension Host Dialplan
6052 Unregister company-default
6051 Unregister company-default
6050 Unregister company-default
6022 Unregister company-default
6021/6021 172.30.63.34 company-default
6020 Unregister company-default
Enter the following command to display the status of all SIP trunks
execute pbx sip-trunk list
Name Host Username Account-Type State
Provider_1 192.169.20.1 +5555555 Static N/A
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
01-410-112851-20100601 59
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
Page 60

diagnose pbx restart FortiGate Voice VoIP, PBX, and PSTN CLI Reference
diagnose pbx restart
Use this diagnose command to restart the FortiGate Voice PBX daemon.
diagnose pbx restart
FortiGate Voice Version 4.0 MR1 Administration Guide
60 01-410-112851-20100601
http://docs.fortinet.com/ • Feedback
 Loading...
Loading...