Page 1
© Copyright 2006 Fortinet Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Regulatory Compliance
FCC Class A Part 15 CSA/CUS
5 July 2006
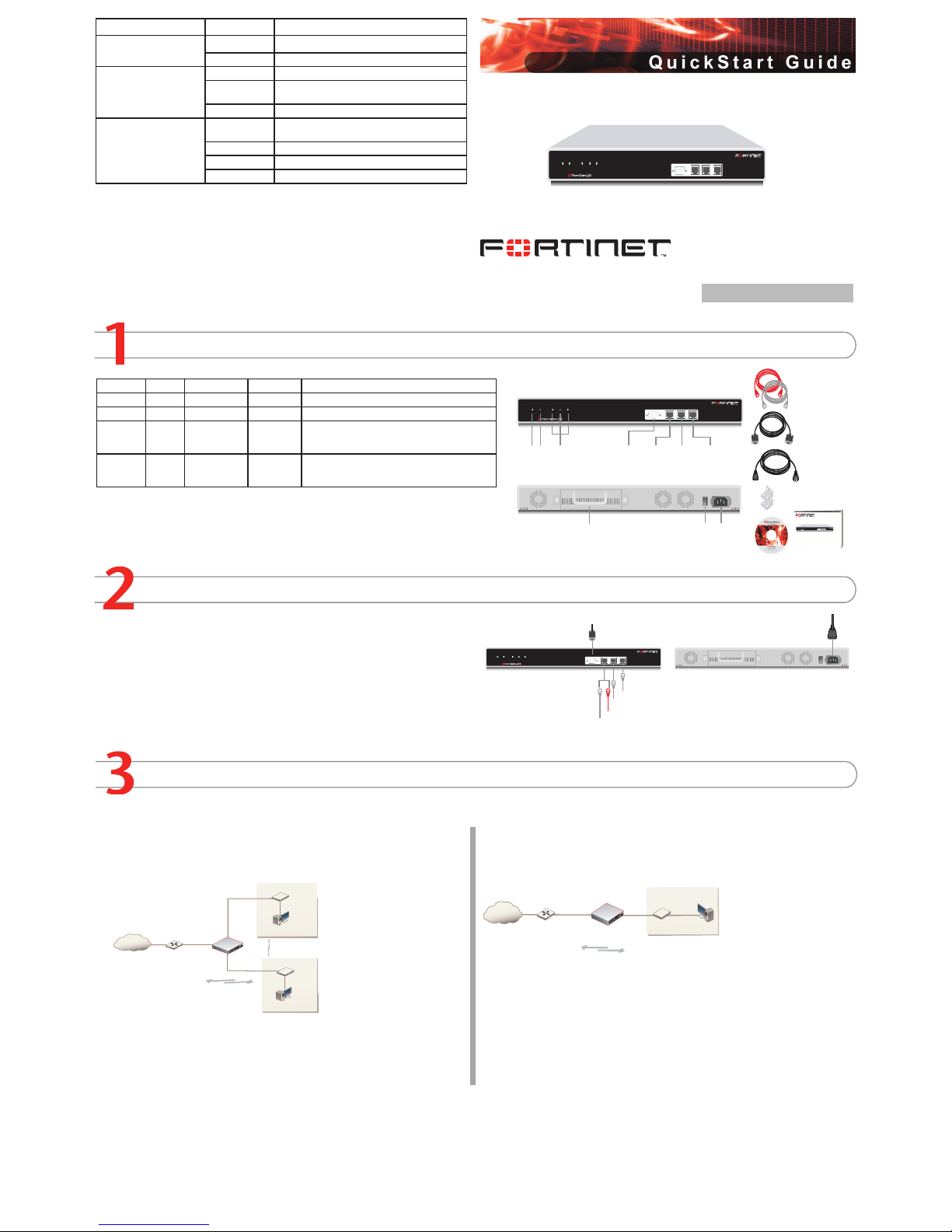
Checking the Package Contents
Connecting
Planning the Configuration
Connector Type Speed Protocol Description
Internal RJ-45 10/100 Base-T Ethernet Connection to the internal network.
External RJ-45 10/100 Base-T Ethernet Connection to the internet.
DMZ RJ-45 10/100 Base-T Ethernet Optional connection to a DMZ network, or to other
FortiGate-200 units for high availability. For details,
see the Documentation CD-ROM.
Console DB-9 9600 Bps RS-232 Optional connection to the management computer.
Provides access to the command line interface
(CLI).
Place the unit on a stable surface. It requires 1.5 inches (3.75 cm) clearance above and
on each side to allow for cooling.
Plug in power cable to unit before connecting power.
The Status light ashes while the unit is starting up and turns off when the system is up
and running.
•
•
•
Connect the FortiGate unit to a power outlet and to the internal and external networks.
Before beginning to congure the FortiGate unit, you need to plan how to integrate the unit into your network. Your conguration plan depends on the operating mode you select: NAT/Route
mode (the default) or Transparent mode.
NAT/Route mode
In NAT/Route mode, each FortiGate unit is visible to the network that it is connected to. All of
its interfaces are on different subnets. Each interface that is connected to a network must be
congured with an IP
address that is valid for
that network.
You would typically use
NAT/Route mode when
the FortiGate unit is
deployed as a gateway
between private and
public networks. In its
default NAT/Route mode
conguration, the unit
functions as a rewall.
Firewall policies control
communications through
the FortiGate unit. No trafc can pass through the FortiGate unit until you add rewall policies. In NAT/Route mode, rewall policies can operate in NAT mode or in Route mode. In
NAT mode, the FortiGate unit performs network address translation before IP packets are
sent to the destination network. In Route mode, no translation takes place.
Transparent mode
In Transparent mode, the FortiGate unit is invisible to the network. All of its interfaces are on
the same subnet. You only have to congure a management IP address so that you can make
conguration changes.
You would typically use the
FortiGate unit in Transparent
mode on a private network
behind an existing rewall or
behind a router. In its default
Transparent mode conguration,
the unit functions as a rewall.
No trafc can pass through the
FortiGate unit until you add
rewall policies.
You can connect up to four network segments to the FortiGate unit to control trafc between
these network segments.
Router
Internet
Gateway to public network
204.23.1.5 10.10.10.2
Inter nal
netwo rk
Internal
External
Transparent mode policies
controlling traffic between
internal and external networks
10.10.10.1
Management IP
Refer to the Documentation CD-ROM for information on how to control trafc, and how to congure HA, antivirus protection, FortiGuard, Web content ltering, Spam ltering,
intrusion prevention (IPS), and virtual private networking (VPN).
FortiGate-200
01-30002-0034-20060705
LED State Description
Power
Green The FortiGate unit is on.
Off The FortiGate unit is off.
Status
Flashing Green The FortiGate unit is starting up.
Green The FortiGate unit is running normally.
Off The FortiGate unit is powered off.
Internal,
External
DMZ
Green The correct cable is in use and the connected
equipment has power.
Flashing Green Network activity at this interface.
Flashing Amber Network activity at this interface.
Off No link established.
Internet
DMZ
networ k
DMZ
10.10.10.1
10.10.10.2
Intern al
networ k
Internal
192.168.1.99
192.168.1.3
Route mode policies
controlling traffic between
Internal networks.
NAT policies controlling
traffic between internal
and external networks.
External
204.23.1.5
DMZ
CONSOLE
INTERNAL
EXTERNAL
INTERNALPOWER STATUS
EXTERNAL
DMZ
Straigh t-through E thernet cab le connects to Internet (public sw itch, route r or modem)
Straigh t-through E thernet cab le connects to LAN or s witch on in ternal netw ork
Crossov er Ethernet cable conn ects to man agement comp uter on int ernal netwo rk
or
Optiona l null mode m cable con nects to se rial port on management computer
Power c able connec ts to power outlet
Optiona l straight- through Eth ernet cable connects to DMZ networ k
DMZ
CONSOLE
INTERNAL
EXTERNAL
INTERNALPOWER STATUS
EXTERNAL
DMZ
Front
Back
DMZ
CONSOLE
INTERNAL
EXTERNAL
INTERNALPOWER STATUS
EXTERNAL
DMZ
DMZ
Interfa ce
Externa l
Interfa ce
Interna l
Interfa ce
Status
LED
Interna l, External ,
DMZ Int erface LEDs
Power
LED
RS-232 Serial
Connect ion
Removab le
Hard Dr ive
Power
Connect ion
Power
Switch
Power C able
Rack-Mo unt Bracket s
Null-Mo dem Cable
(RS-232 )
Documen tation
Etherne t Cables:
Orange - Crossover
Grey - Straight-th rough
USER MANUAL
FortiGate-200
QuickStart G uide
Copyright 2003 Fortinet Incorpora ted. All righ ts reserved .
Trademarks
Products mentioned in this docume nt are trad emarks.
DMZ
CONSOLE
INTERNAL
EXTERNAL
INTERNALPOWERSTATUS
EXTERNAL
DMZ
Page 2
Completing the Configuration
7
Congratulations!
You have nished conguring the basic settings. Your network is now protected from Internetbased threats. To explore the full range of conguration options, see the online help or the
Documentation CD-ROM.
Visit these links for more information and documentation for your Fortinet product.
Technical Documentation - http://docs.forticare.com
Fortinet Knowledge Center - http://kc.forticare.com
Fortinet Technical Support - http://support.fortinet.com
•
•
•
NAT/Route Mode
Internal Interface IP: ____.____.____.____
Netmask: ____.____.____.____
External Interface
IP: ____.____.____.____
Netmask: ____.____.____.____
DMZ IP: ____.____.____.____
Netmask: ____.____.____.____
The internal interface IP address and netmask must be valid for the internal
network.
Transparent mode
Management IP IP: ____.____.____.____
Netmask: ____.____.____.____
The management IP address and netmask must be valid for the network you will be
managing the FortiGate unit from.
General settings
Administrator password:
Network Settings: Default Gateway:
____.____.____.____
Primary DNS Server: ____.____.____.____
Secondary DNS Server: ____.____.____.____
A default gateway is required for the FortiGate unit to route connections to the Internet.
Factory default settings
NAT/Route mode Transparent mode
Internal interface 192.168.1.99 Management IP 0.0.0.0
External interface 192.168.100.99 Administrative account settings
DMZ 10.10.10.1 User name admin
Password (none)
Configuring the FortiGate Unit
Web-based Manager
Connect the FortiGate internal interface to a management computer Ethernet interface.
Use a cross-over Ethernet cable to connect the devices directly. Use straight-through
Ethernet cables to connect the devices through a hub or switch.
Congure the management computer to be on the same subnet as the internal
interface of the FortiGate unit. To do this, change the IP address of the management
computer to 192.168.1.2 and the netmask to 255.255.255.0.
To access the FortiGate web-based manager, start Internet Explorer and browse to
https://192.168.1.99 (remember to include the “s” in https://).
Type admin in the Name eld and select Login.
NAT/Route mode
To change the administrator password
Go to System > Admin > Administrators.
Select Change Password for the admin administrator and enter a new password.
To congure interfaces
Go to System > Network > Interface.
Select the edit icon for each interface to congure.
Set the addressing mode for the interface. (See the online help for information.)
For manual addressing, enter the IP address and netmask for the interface.
For DHCP addressing, select DHCP and any required settings.
For PPPoE addressing, select PPPoE, and enter the username and password
and any other required settings.
To congure the Primary and Secondary DNS server IP addresses
Go to System > Network > Options, enter the Primary and Secondary DNS IP
addresses that you recorded above and select Apply.
To congure a Default Gateway
Go to Router > Static and select Edit icon for the static route.
Set Gateway to the Default Gateway IP address you recorded above and select OK.
Transparent mode
To switch from NAT/route mode to transparent mode
Go to System > Status, select Transparent.
Set the Management IP/Netmask to 192.168.1.99/24.
Set a default gateway and select apply.
To change the administrator password
Go to System > Admin > Administrators.
Select Change Password for the admin administrator and enter a new password.
To change the management interface
Go to System > Cong > Operation Mode.
Enter the Management IP address and netmask that you recorded above and select
Apply.
To congure the Primary and Secondary DNS server IP addresses
Go to System > Network > Options, enter the Primary and Secondary DNS IP
addresses that you recorded in step 5 and select Apply.
1.
2.
3.
4.
1.
2.
1.
2.
3.
•
•
•
1.
1.
2.
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
1.
2.
1.
Command Line Interface
Use the DB-9 serial cable and converter to connect the FortiGate Console port to the
management computer serial port.
Start a terminal emulation program (HyperTerminal) on the management computer.
Use these settings: Baud Rate (bps) 9600, Data bits 8, Parity None, Stop bits 1, and
Flow Control None.
At the Login: prompt, type admin and press Enter twice (no password required).
NAT/Rout mode
Congure the FortiGate internal interface.
config system interface
edit internal
set ip <intf_ip>/<netmask>
end
Congure the FortiGate external interface.
config system interface
edit external
set ip <intf_ip>/<netmask>
Congure the primary and secondary DNS server IP addresses.
config system dns
set primary <dns-server_ip>
set secondary <dns-server_ip>
end
Congure the default gateway.
config router static
edit 1
set gateway <gateway_ip>
end
Transparent Mode
Change from NAT/Route mode to Transparent mode and congure the Management IP
address.
config system settings
set opmode transparent
set manageip <mng_ip>/<netmask>
set gateway <gateway_ip>
end
Congure the DNS server IP address.
config system dns
set primary <dns-server_ip>
set secondary <dns-server_ip>
end
1.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
4.
1.
2.
Collecting Information
Choosing a Configuration Tool
Web-based manager
The FortiGate web-based manager is an easy to use management tool. Use it to congure
the administrator password, the interface and default gateway addresses, and the DNS
server addresses.
Requirements:
An Ethernet connection between the FortiGate unit and management computer.
Internet Explorer 6.0 or higher on the management computer.
•
•
Command Line Interface (CLI)
The CLI is a full-featured management tool. Use it to congure the administrator password,
the interface addresses, the default gateway address, and the DNS server addresses. To
congure advanced settings, see the Documentation CD-ROM.
Requirements:
The DB-9 serial connection between the FortiGate unit and management computer.
A terminal emulation application (HyperTerminal for Windows) on the management
computer.
•
•
 Loading...
Loading...